MYSON MTL005 Datasheet

MYSON
This datasheet contains new product information. Myson Technology reserves the rights to modify the product specification without
Double scan capability for interlaced input.
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
XGA Flat Panel Controller
FEATURES
General
• Auto configuration of sampling clock frequency, phase, H/V center, as well as white ba lance.
• Auto detection of present or non-present or over range sync signals and their polarities.
• Composite sync separation and odd/even field detection of interlaced video.
• No external memory required.
• On-chip output PLL provide clock frequency fine-tune (inverse, duty cycle and delay).
• Serial 2-wire I
• 3.3V supplier, 5V I/O tolerance in 128-pin PQFP package.
Input Processor
• Single RGB (24-bit) input rates up to 100MHz.
• Support both non-interlaced and interlaced RGB graphic input signals.
• YUV 4:2:2 or YUV 4:1:1 (CCIR601/CCIR656) interlaced video input.
• Glue-free connection to Philips SAA711x digital video decoder.
• Built-in YUV to RGB color space converter.
• Compliant with digital LVDS/PanelLink TMDS input interface.
• PC input resolution up to XGA 1024x768 @85Hz.
2
C host interface.
Rev 0.9
Video Processo r
• Independent programmable Horizontal and Vertical scaling up ratios from 1 to 32
• Flexible de-interlacing unit for digital YUV video input data.
• Zoom to full screen resolution of de-interlaced YUV video data stream.
• Built-in programmable gain control for white balance alignments.
• Built-in programmable 8-bit gamma correction table.
• Built-in programmable temporal color dithering.
• Built-in programmable interpolation look-up table.
• Support smooth panning under viewing window change.
Output Processo r
• Single pixel (18/24-bit) or Dual pixel (36/48-bit) per clock digital RGB output.
• Built-in output timing generator with programmable clock and H/V sync.
• Support VGA/SVGA/XGA display resolution.
• Overlay input interface with external OSD controller.
•
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MTL005 Flat Panel Display (FPD) Controller is a low-cost input format converter for TFT-LCD Monitor or
LCD TV application which accepts 15-pin D-sub RGB graphic signals (through ADC), YUV signals from
digital video decoder or digital RGB graphic signals from PanelLink TMDS receiver. It comprises a RGB/YUV
input processor, video scaling up processor, OSD input interface and output display processor in 128-pin
PQFP.
notice. No liability is assumed as a result of the use of this product. No rights under any patent accompany the sale of the product.
Revision 0.9 - 1 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
MTV212
MTV130
OSD
Decoder
S-Video
video
RGB
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
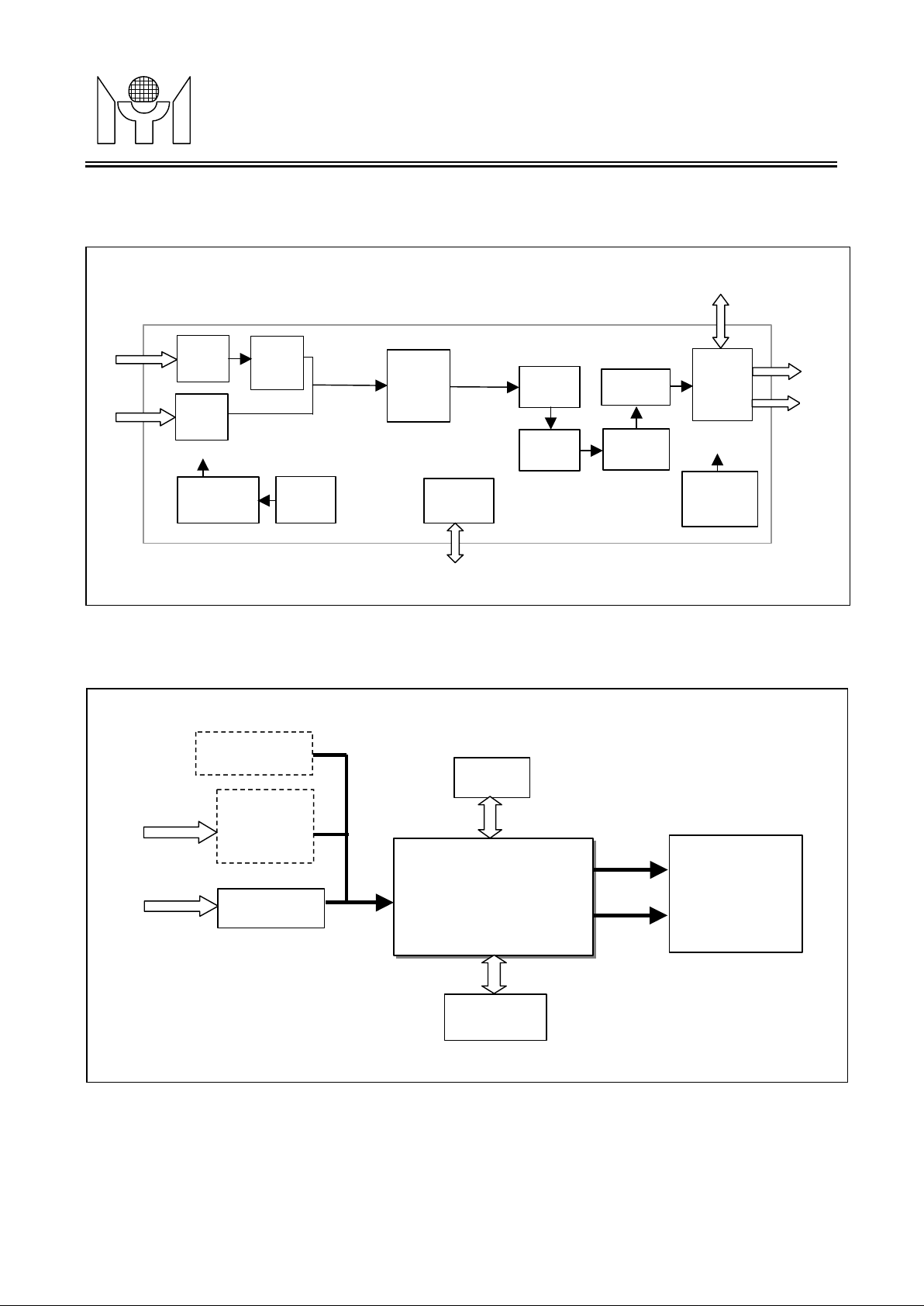
BL OCK DIAGRAM
Digital
PC
YUV
Input
RGB
Input
Auto
Calibration
YUV
to
RGB
Mode
Detect
Zoom
Buffer
Host
Interface
To I2C Bus
Scale
Up
Gain
Control
Dithering
Gamma
Correct
Rev 0.9
To external OSD
OSD
&
Output
MUX
Display
Timing
Generator
RGB
output
APPLICA TIONS
LVDS/PanelLink
TMDS Receiver
Composite/
D-sub RGB
graphic signals
Digital
Video
ADC
MTL005
FPD Monitor
Controller
8-bit MCU
TFT-LCD
Flat Panel
Revision 0.9 - 2 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
038* NC
037* R1OUT1
* R1OUT0
* DVDD
* G1OUT7
DVSS *065
TDIE *066
VSYNC
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
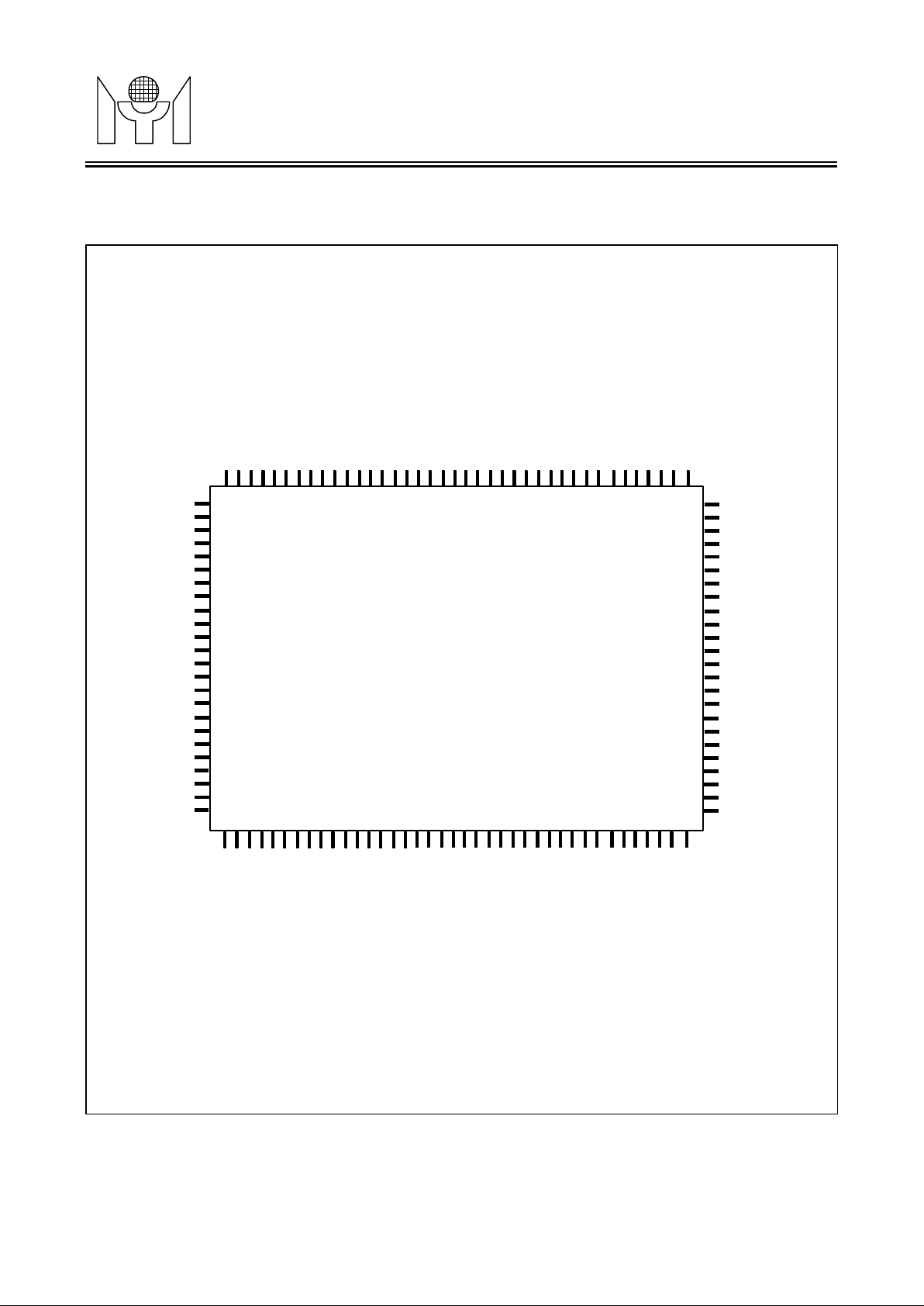
1. PIN CONNECTION
DVSS *102
PVSS *103
SCL *104
SDA *105
TESTMODE *106
EXTDCLK2 *107
PVDD *108
EXTDCLK1 *109
DVSS *110
B2OUT0 *111
B2OUT1 *112
B2OUT2 *113
B2OUT3 *114
B2OUT4 *115
B2OUT5 *116
B2OUT6 *117
B2OUT7 *118
DVDD *119
G2OUT0 *120
G2OUT1 *121
G2OUT2 *122
G2OUT3 *123
G2OUT4 *124
G2OUT5 *125
G2OUT6 *126
G2OUT7 *127
DVSS *128
AVSS *101
XO *100
XI *099
AVDD *098
GIN2 *085
GIN1 *086
GIN0 *087
DVDD *088
BIN7 *089
BIN6 *090
BIN5 *091
BIN4 *092
BIN3 *093
BIN2 *094
BIN1 *095
BIN0 *096
DVDD *097
MTL005
(128-pin PQFP)
GIN3 *084
GIN4 *083
GIN5 *082
GIN6 *081
GIN7 *080
DVSS *079
RIN0 *078
RIN1 *077
RIN2 *076
RIN3 *075
RIN4 *074
RIN5 *073
RIN6 *072
RIN7 *071
DVDD *070
HSYNC *069
IPCLK *068
*067
Rev 0.9
064* DVSS
063* RAWHS
062* RGBSEL
061* ADHS
060* ADVS
059* CLAMP
058* TMDSSEL
057* DVDD
056* OHSYNC
055* OCLK
054* OVSYNC
053* IRQ
052* PVDD
051* OSDEN
050* OSDBLU
049* OSDGRN
048* OSDRED
047* RSTZ
046* DVSS
045* R1OUT7
044* R1OUT6
043* R1OUT5
042* R1OUT4
041* R1OUT3
040* R1OUT2
039* PVSS
036
035
034
033* G1OUT6
032* G1OUT5
031* G1OUT4
030* G1OUT3
029* G1OUT2
028* G1OUT1
027* G1OUT0
026* DVSS
025* B1OUT7
024* B1OUT6
023* B1OUT5
022* B1OUT4
021* B1OUT3
020* B1OUT2
019* B1OUT1
018* B1OUT0
017* DVDD
016* DHSYNC
015* DVSYNC
014* DVSS
013* DDCLK1
012* DDEN
011* DDCLK2
010* PVDD
009* R2OUT7
008* R2OUT6
007* R2OUT5
006* R2OUT4
005* R2OUT3
004* R2OUT2
003* R2OUT1
002* R2OUT0
001* PVSS
Revision 0.9 - 3 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
Vertical sync for external OSD
Horizontal sync for external OSD
OSD overlay enable
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Rev 0.9
2. PIN DESCRIPTION
ADC Input Int er face (RGB or YUV or TMDS Inpu t Data)
Name Type Pin# Description
IPCLK I 68 Input pixel clock
VSYNC I 67 Input Vertical sync
HSYNC/CS I 69 Input Horizontal or Composite sync
RIN[7:0]/YIN[7:0] I 71-78 Red or Y channel or TMDS input data
GIN[7:0]/UVIN[7:0] I 80-87 Green or UV channel or TMDS input data
BIN[7:0] I 89-96 Blue or TMDS input data, or Control bit for YUV video input
Bit 4: VPHREF, Video input Horizontal reference signal
Bit 3: VPVS, Video input VSYNC signal
Bit 2: VPODD, Video input ODD/EVEN field signal
Bit 1: VPHS, Video input HSYNC signal
Bit 0: VPCLK, Video input clock signal
RAWHS I 63 Input source HSYNC for measurement
TDIE I 66 TMDS digital input enable
RGBSEL O 62 Input select. 1:RGB input, 0:YUV input
TMDSSEL O 58 TMDS input select, active high
CLAMP O 59 Clamp pulse output for ADC
Displ ay Outp ut Interface
Name Type Pin# Description
DDEN O 12 Display data output enable
DVSYNC O 15 Display Vertical sync output
DHSYNC O 16 Display Horizontal sync output
DDCLK1 O 13 Display output clock 1
DDCLK2 O 11 Display output clock 2
R1OUT[7:0] O 45-40,
37-36
G1OUT[7:0] O 34-27 Green output even data , bit[7:2] for 6-bit panel
B1OUT[7:0] O 25-18 Blue output even da ta , bit[7:2] for 6-bit panel
R2OUT[7:0] O 9-2 Red output odd data , bit[7:2] for 6-bit panel
G2OUT[7:0] O 127-120 Green output odd data , bit[7:2] for 6-bit panel
B2OUT[7:0] O 118-111 Blue output odd data , bit[7:2] for 6-bit panel
Red output even data , bit[7:2] for 6-bit panel
Host Interface
Name Type Pin# Descrip tio n
RST# I 47 System reset input, active low.
SCL I 104 Serial bus clock
SDA I/O 105 Serial bus data
TESTMODE I 106 Test Mode, Normally grounded.
IRQ O 53 Interrupt request output
OSD Interf ac e
Name Type Pin# Description
OCLK O 55 Clock for external OSD
OVSYNC O 54
OHSYNC O 56
OSDRED I 48 OSD red input
OSDGRN I 49 OSD green input
OSDBLU I 50 OSD blue input
OSDEN I 51
Revision 0.9 - 4 - 2000/12/29

MYSON
Oscillator frequency input
Oscillator frequency output
Vertical sync for A/D converter
Horizontal sync for A/D converter
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Other Interface
Name Type Pin# Description
XI I 99
XO O 100
EXTDCLK1 I 109 External display clock input 1
EXTDCLK2 I 107 External display clock input 2
ADVS O 60
ADHS O 61
NC - 38 No connection
3.3V Power and Grou n d
Name Pin# Description
DVDD 17, 35, 57, 70, 88, 97, 119 Digital power 3.3V
DVSS 14, 26, 46, 64, 65, 79, 102, 110, 128 Digital ground
PVDD 10, 52, 108 Pad power 3.3V
PVSS 1, 39, 103 Pad ground
AVDD 98 Analog power 3.3V
AVSS 101 Analog ground
Rev 0.9
Revision 0.9 - 5 - 2000/12/29

MYSON
depending on the type of input images.
In this mode, only one field is displayed at the time. First field and second field is toggled displayed. The
inputs presence check, frequency counting, polarity detection and control. It contains
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Rev 0.9
3. FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
3.1 Input Process or
General Descrip t io n
The function of Input Interface is to provide the interface between MTL005 and external in put devices. It can
process both non-interlaced and interlaced RGB graphic input, YUV video input, and digita l RGB input
compliant with digital LVDS/PanelLink TMDS interface. It also contains the built-in YUV to RGB color space
converter.
3.1.1 RGB Inpu t Format
Since MTL005 is a low cost solution, the RGB input port can only work in Single Pixel mode (24 bits). The
R/G/BIN ports are sampled at the rising edge of the RGB input clock.
3.1.2 TMDS Input Form at
The Digital RGB input port works likewise as described in Sec 3.1.1 except one more input pin is needed:
Digital Input Enable DIEN.
With a single pixel input interface, the supported format is up to true color, including 18 bit/pixel or 24 bit/pixel.
3.1.3 YUV Inpu t Format
The YUV input port supports interlaced video data from the most common video decoder ICs like SAA711x.
The 16 bit data bus is shared with the ports RIN[7:0] and GIN[7:0]. The 16 bit data is sampled at the rising
edge of the shared video clock VPCLK when the shared data enable HREF is active. The supported formats
are YUV4:1:1 and YUV4:2:2 with CCIR601/CCIR656 standard.
3.1.4 Inp ut HSYNC Path
Besides the pin HSYNC, MTL005 provides another pin RAWHS to support Sync Processor in MTL005.
Generally, the HSYNC generated by an ADC may have a very narro w pulse width an d a dif ferent polarity
from the original HSYNC provided by the source. The RAWHS input provides the path of original HSYNC
connection to MTL005, which makes Sync Processor in MTL005 work correctly.
3.1.5 YUV to RGB Convert er
It is used to convert YCbCr format into RGB format. The basic equations are as follows:
R = Y + 1.371(Cr - 128)
G = Y - 0.698(Cr - 128) - 0.336(Cb - 128)
B = Y + 1.732(Cb - 128)
3.1.6 De-interlace mod e
For interlace input, MTL005 features several de-interlacing algorithms for processing interlaced video data
¨ Tog gl e Mode
missing lines are calculated from duplicating the neighbor lines.
¨ Spatial Mod e
In this mode, two fields are toggled displayed, just like Toggle mode. The missing lines are calculated from
interpolating the neighbor lines. An average good quality for still and moving pictures is achieve d i n th is mode.
3.1.7 Sync Processor
The V/H SYNC processing block performs the functions of Composite signal separation/insertion, SYNC
a de-glitch circuit to
filter out any pulse shorter than one OSC period treated as noises on V/H SYNC pulses.
Revision 0.9 - 6 - 2000/12/29

MYSON
MTL005 can measure VSYNC/HSYNC frequency counted in proper clocks and save the information in
registers. Users can read it out to calculate VSYNC/HSYNC frequency as
input sample registers to aid in centering the screen automatically.
s phase and frequency. MTL005
colors. This advanced function helps firmware to analyze ADC performance. Usually Firmware can use this
s phase and frequency.
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
¨ V/H SYNC Frequency Counter
f
= f
= f
osc
osc
/ N
/ N
vsync
f
hsync
,Where f
f
f
N
N
¨ V/H SYNC Presenc e Chec k
vsync
hsync
osc
vsync
hsync
51/256
vsync
58
hsync
: VSYNC frequency
: HSYNC frequency
: oscillator clock with 14.31818 MHz
: counted number of VSYNC
: counted number of HSYNC
in the following formulas:
Rev 0.9
This function checks the input VSYNC, where Vpre flag is set when VSYNC is over 40Hz or cleared when
VSYNC is under 10Hz ,and the input HSYNC, where Hpre flag is set when HSYNC is over 10Khz or cleared
when HSYNC is under 10Hz.
¨ V/H Polari ty Detect
This function detects the input VSYNC/HSYNC high and low pulse duty cycle. If the high pulse duration is
longer than that of the low pulse, the negative polarity is asserted; otherwise, positive polarity is asserted.
¨ Comp os it e SYNC separatio n/ins erti on
MTL005 continuously monitors the input HSYNC. If the input VSYNC can be extracted from it, a CVpre flag is
set. MTL005 can insert HSYNC pulse during Composite VSYNC’s active time and the insertion frequency
can adapt to original HSYNC’s.
3.1.8 Aut o Tune
Auto Tune function consists of Auto Position automatically centering the screen and Auto Calibration
containing Phase Calibration, Histogram, Min/Max Value, and Pixel Grab described as below. W ith this auto
adjustment support it is possible to measure the correct phase, frequency, gain, and offset of ADC. The
horizontal and vertical back porches of input image and the horizontal and vertical active reg ions can also be
measured. Firmware can adjust input image registers automatically by reading Auto Tune’s registers in single
or burst mode.
¨ Auto Position
MTL005 provides Horizontal/Vertical back porch and active region values. Users can use these values to set
¨ Phase Calibrati on
MTL005 provides Auto Calibration registers to measure the quality of current ADC’s phase and frequency.
The biggest Auto Calibration registers value means the right value of ADC’
has two kinds of algorithms to calculate Auto Calibration’s value. One is traditional Difference method,
another is MYSON’s proprietary method. It is suggested to use the latter one for better performance
¨ Histogr am
Histogram means the total number of input pixels below/above one threshold value, for individual R, G, B
information to measure ADC’s noise margin, adjust its offset and gain, or even aid in the mode detection.
¨ Mi n /Max Value
Min/Max value means minimum or maximum pixel value within the specified input act ive image region for
each RGB channel. This information is usually used to adjust ADC’s offset and gain.
¨ Pixel Grab
Pixel Grab means users can grab a single input pixel at any one point. The position of the point can be
programmed by users. This is another traditional method to measure ADC’
Revision 0.9 - 7 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
: Image will be scaled up based on scaling factor. Every point of output image comes
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Rev 0.9
3.2 Video Proc ess o r
General Descrip t io n
MTL005 possesses a powerful and programmable video processor b y providing the following functions:
Scaling Up/Down, Gain Control, Brightness Control, Gamma Correction, Dithering Control, and Flip & Mirror.
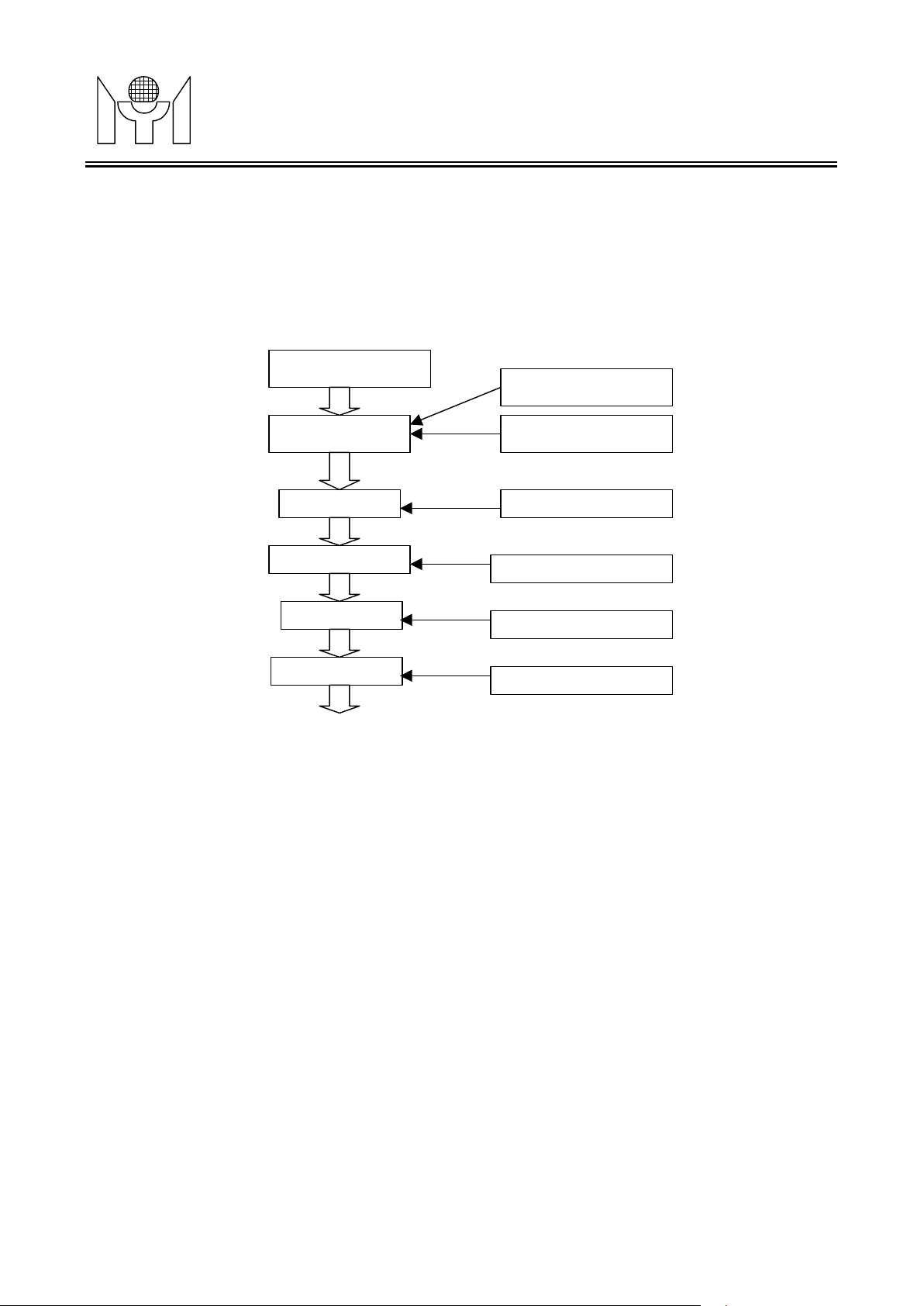
The block diagram of Video Processor is as follows:
FLIP/MIRROR
Scaling Factor
SCALING
GAIN
BRIGHTNESS
Transition Table
Gain Factor
Brightness Factor
GAMMA
DITHERING
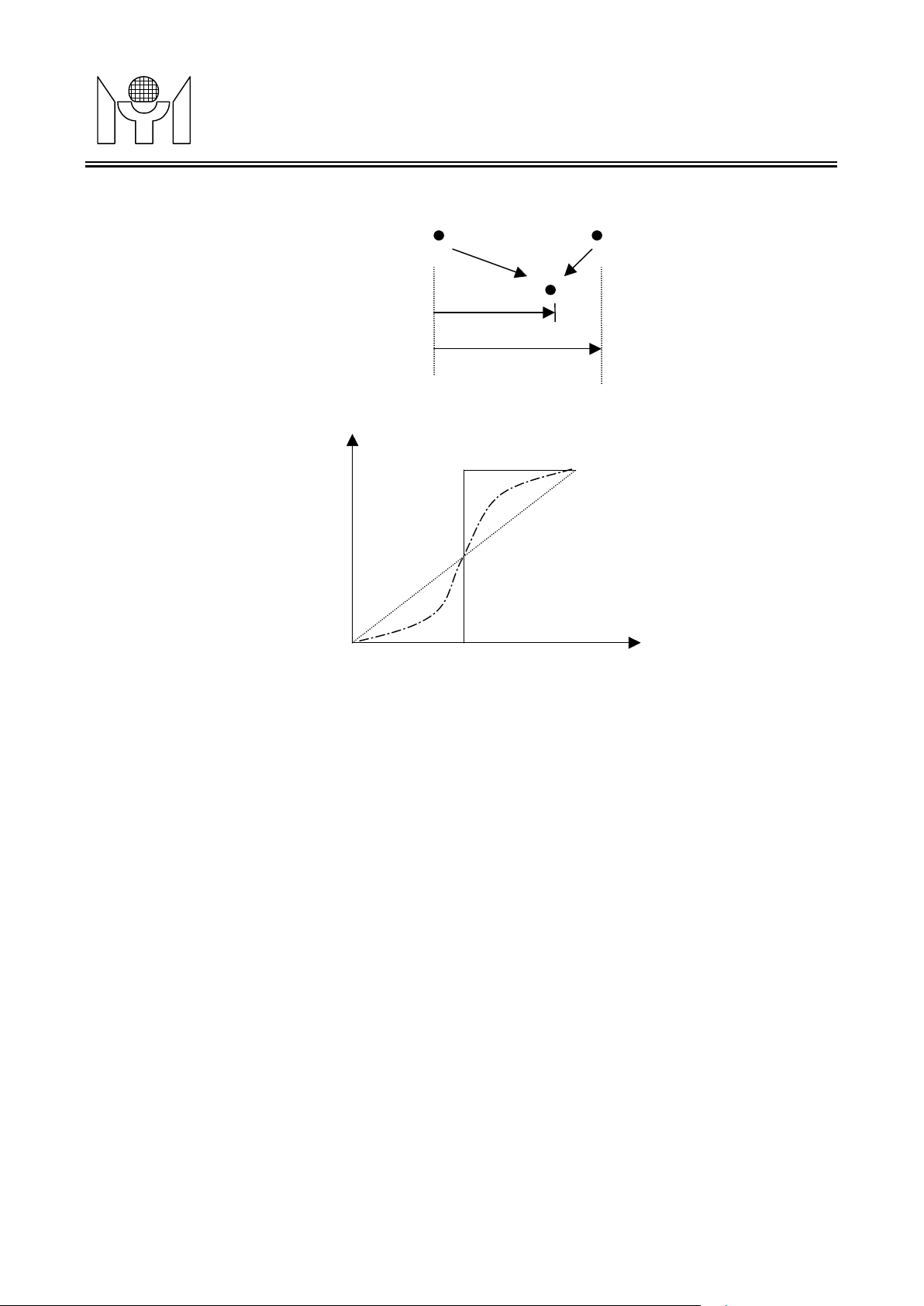
Fig. 3.2.1 Video Processor Block Diagram
3.2.1 Scaling
MTL005 provides scaling function up ranging from 1 to 32, and for both horizontal and vertical processing.
For scaling up, both horizontal and vertical processing, MTL005 provides four methods:
¨ Pass Mod e: Image will be passed through without considering any scaling factor.
¨ Dupl ic ate Mode
from the input. In this method, Output image will have the good contrast but may be non-uniformed.
¨ Bi linear Mode: Image will be scaled up based on scaling factor. Every point of output image data will be
filtered by bilinear filter. In this method, output image will have the good scaling quality but may be
blurred.
¨ Interpo l atio n Table Mode: Image will be scaled up based on scaling factor. Every point of output image
data will be filtered by user defined filter.
Gamma Table
Dithering Table
Revision 0.9 - 8 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
white balance is possible by using this function.
true color (8 bits per color) or high color (6 bits per color) display.
Dithering coefficient will change by time.
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Input pixel A B
Interpolation pixel
SC
64
SC’
[a]
63
32
[b]
O
Rev 0.9
[a]: duplicate filter
[b]: bilinear filter
[c]: user defined filter
[c]
32 63
Fig. 3.2.2 Scaling filter
3.2.2 Gain/Brightness Control
MTL005 provides Gain and Brightness control to adjust the contrast and brightness of output color by
programming gain and brightness coefficients. This adjustment is applied to RGB colors individually. Auto-
3.2.3 Gamma Correcti on
Gamma Correction is used to compensate the non-linearity of LCD display panel. MTL005 contains a 8-bit
Gamma table to fix this phenomenon.
3.2.4 Color Dithering
MTL005 supports
In the latter case, users can turn on dithering function to avoid artificial contour due to truncation. For
dithering, it supports two methods:
¨ Static dithering: Dithering coefficient is fixed.
¨ Temporal dithering :
O = [(64-SC’)*A + SC’*B]/64
SC
Revision 0.9 - 9 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
output frame rate m ust be
equal to input frame rate and output display time must be equal to input display time, because of no frame
3.3.1 Display Timing modes
is equal to internal display clock.
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Rev 0.9
3.3 Outpu t Process or
General Descrip t io n
Output processor provides the interface for both LCD panel and OSD controller.
buffer.
3.3.1 Displ ay Timing Generation
Output frame rate is equal to input frame and external frame buffer is not needed.
Input Frame
X
X: lock position
Output
Fig.
3.3.2 OSD Overlay
MTL005 allows the integration of overlay data with the scaled output pixel stream. It provides a fully
compatible OSD interface. Individual OSD clock, OSD HSYNC and OSD VSYNC are sent to external OSD
device. MTL005 receives OSD Enable, OSD Red, OSD Green, and OSD Blue from external OSD device.
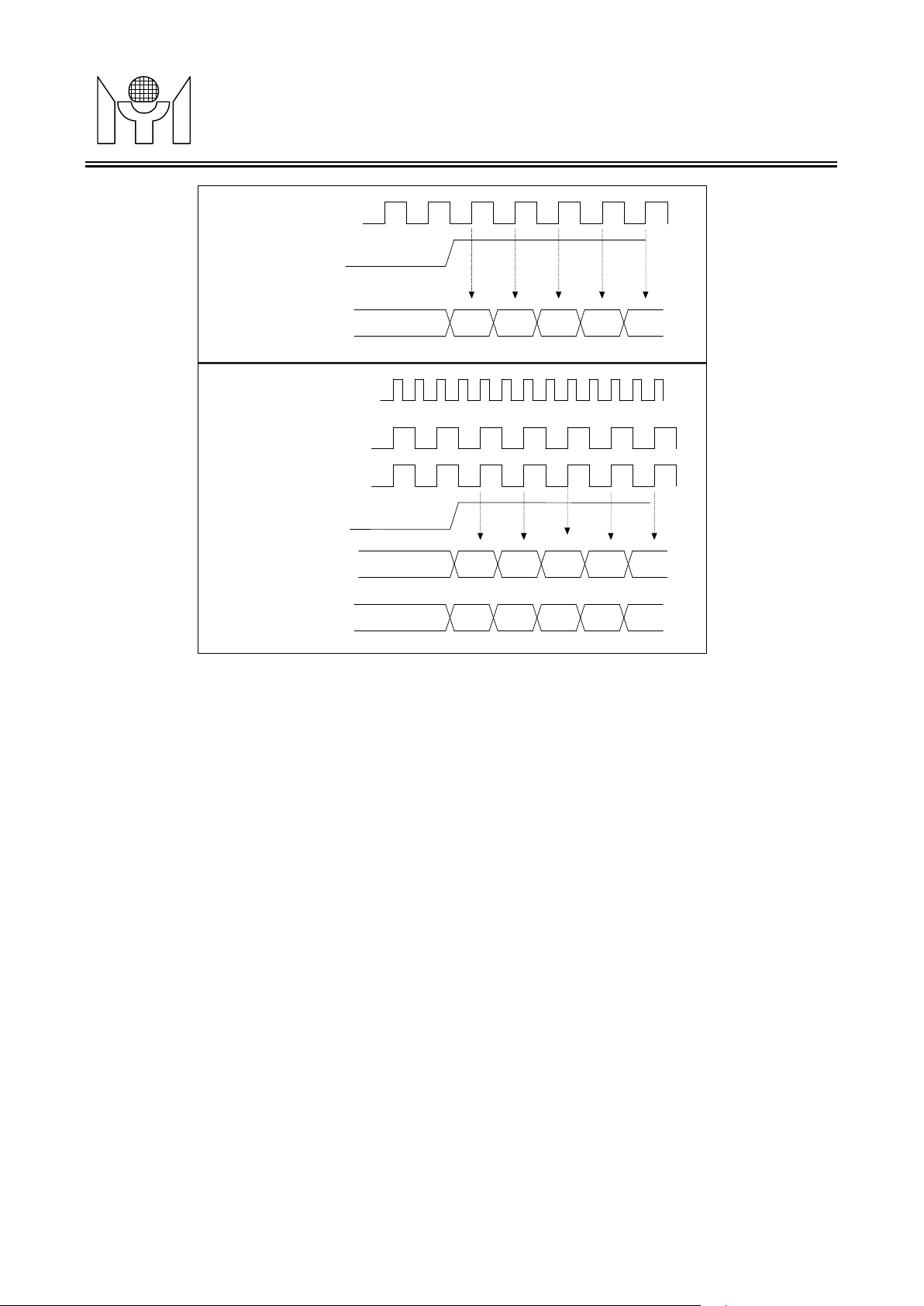
3.3.3 RGB Outp u t Format
MTL005 output interface consists of two pixel ports, each containing Red, Green, and Blue color information
with a resolution of 6/8 bits per color. These two ports are mapped to PORT1 and PORT2.
The control signals for output port are display horizontal sync signal (DHSYNC), display vertical sync signal
(DVSYNC) and display data enable signal (DDEN).
All the signals mentioned above are synchronous to the output clock. The output timing relative to the active
edge of the output clock is programmable.
There are two RGB output formats:
¨ Sing l e Pixel Mode
It is designed to support TFT panels with single pixel input. Only PORT1 is active. The f requency of DCLK1
¨ Dual Pixel Mod e
It is designed to support TFT panels with dual pixel input. PORT1 and PORT2 are use d. The first pixel is at
PORT1, and the second at PORT2.
Revision 0.9 - 10 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
R1OUT/G1OUT
R1OUT/G1OUT
R2OUT/G2OUT
SINGLE PORT
3.3.2 Display Data Timing
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
DCLK
DDEN
000 rgb0 rgb1 rgb2 rgb3 rgb4
000 rgb0 rgb2 rgb4 rgb6 rgb8
DUA L PORT
/B1OUT
DCLK
DCLK1
DCLK2
DDEN
/B1OUT
Rev 0.9
/B2OUT
Fig.
000 rgb1 rgb3 rgb5 rgb7 rgb9
Revision 0.9 - 11 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
means a LOW to HIGH transition of SDA when SCK is high. And data of SDA only can change during SCK is
The I2C interface supports Random Write, Sequential Write, Current Address Read, Random Read and
For Random Write operation, it contains the slave address with R/W bit set to 0 and the word address which
is comprised of eight bits and provides to access any one of 256 bytes in the selected memory range. Upon
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Rev 0.9
3.4 Host Inter fac e
General Descrip t io n
The main function of Host Interface is to provide the interface between MTL005 and externa l CPU by 2-wire
I2C Bus. It can generate all the I/O decoded control timing to control all the registers in MTL005.
3.4.1 I2C Serial Bu s
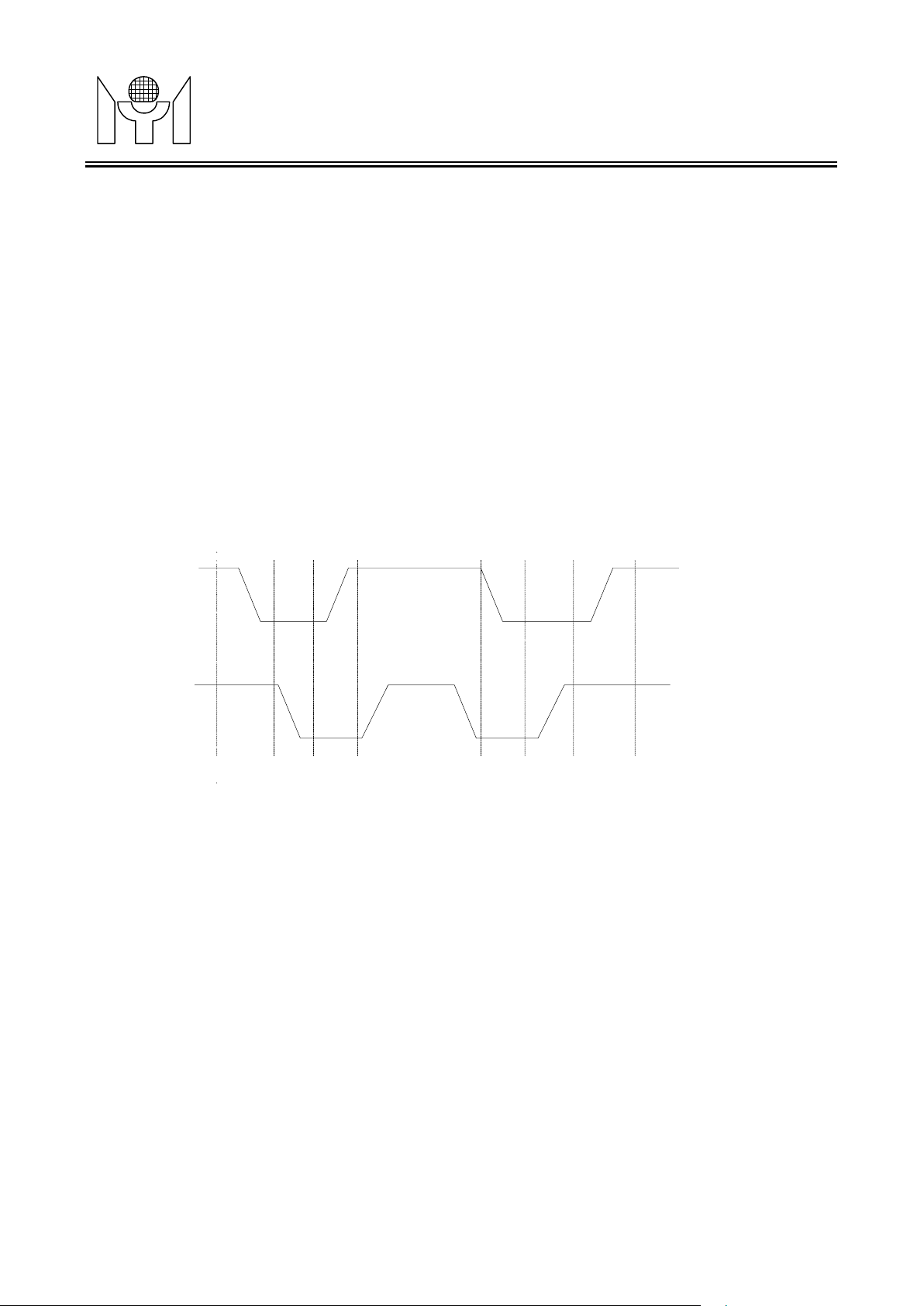
The I2C serial interface use 2 wires, SCK (clock) and SDA(data I/O). The SCK is used as the sampling clock
and SDA is a bi-directional signal for data. The communication must be started with a valid START condition,
concluded with STOP condition and acknowledged with ACK condition by receiver.
The I2C bus device address of MTL005 is 0111010x.
SCK, serial bus clock.
SDA, bi-directional serial bus data.
The START condition means a HIGH to LOW transition of SDA when SCK is high, the STOP condition
low. Ref. Fig.3.5.1.
SDA
SCK
START
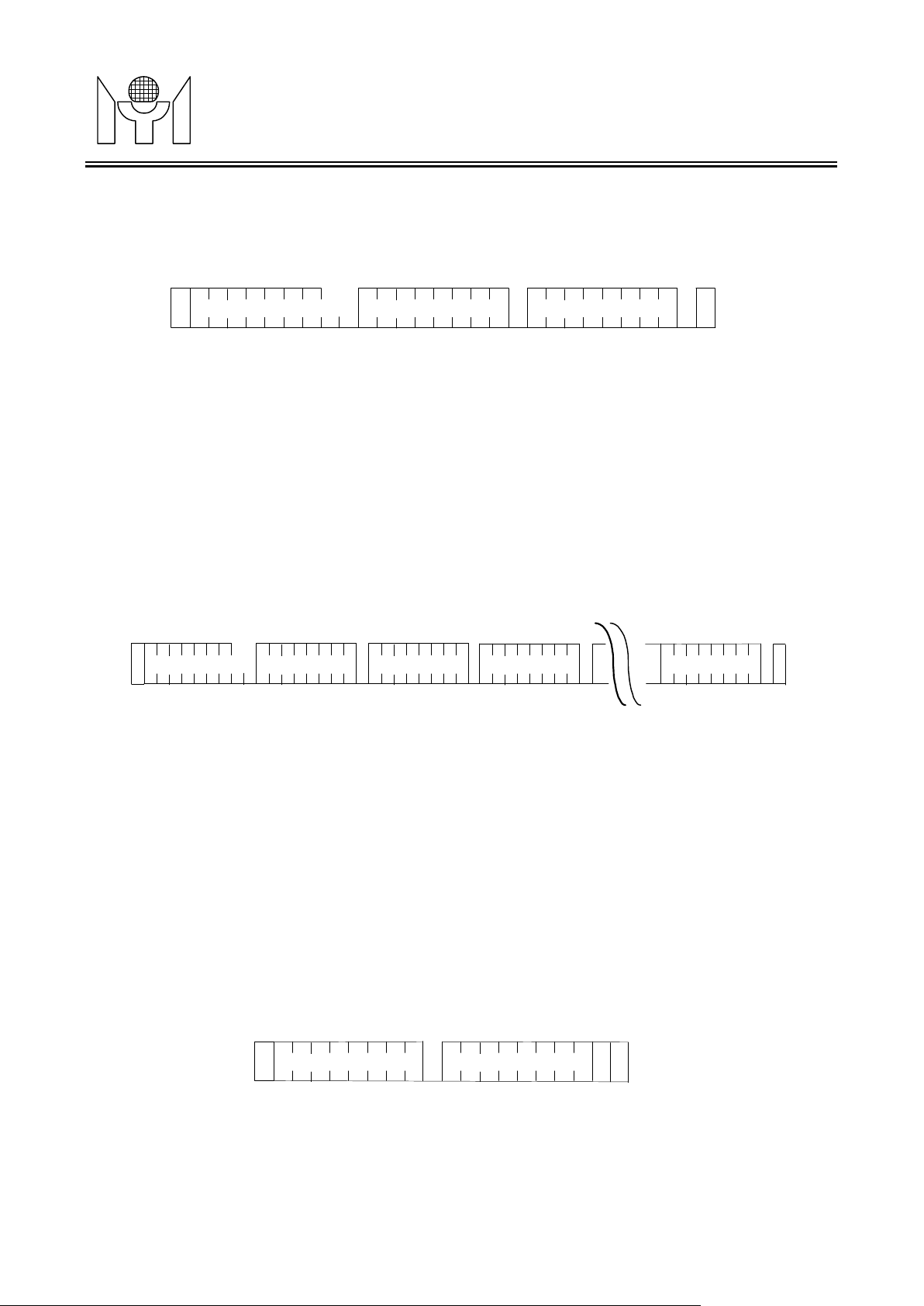
Fig. 3.4.1 START, STOP ,and DATA definition
Sequential Read operations.
¨ Random Write
receipt of the word address, MTL005 responds with an Acknowledge, waits the data bits again responding an
Acknowledge, and then the master generates a stop condition. Ref. Fig.3.5.2.
DATA
CHANGE
DATA
CHANGE
STOP
Revision 0.9 - 12 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
3.4.2 Random Write
Current Add ress Read
access address is n, the read data should access from address n+1. Upon receipt of the slave address with
R/W bit set to 1, MTL005 generates an Acknowledge and transmits eight bits data. After receiving data the
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
S
T
A
R
T
SDA
¨ Sequential Writ e
The initial step of Sequential Write is the same as Random Write, after the receipt of each word data,
MTL005 will respond with an Acknowledge and then internal address counter will increment by one for next
data write. If the master would stop writing data, it generates stop condition. Ref. Fig. 3.5.3.
S
T
A
SLAVE
R
ADDRESS
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
ADDRESS
A
W
C
K
Fig.
WORD
WORD
ADDRESS
DATA n
A
C
K
DATA n+1
DATA
A
C
K
DATA n+x
Rev 0.9
S
T
O
P
S
T
O
P
SDA
A
W
C
K
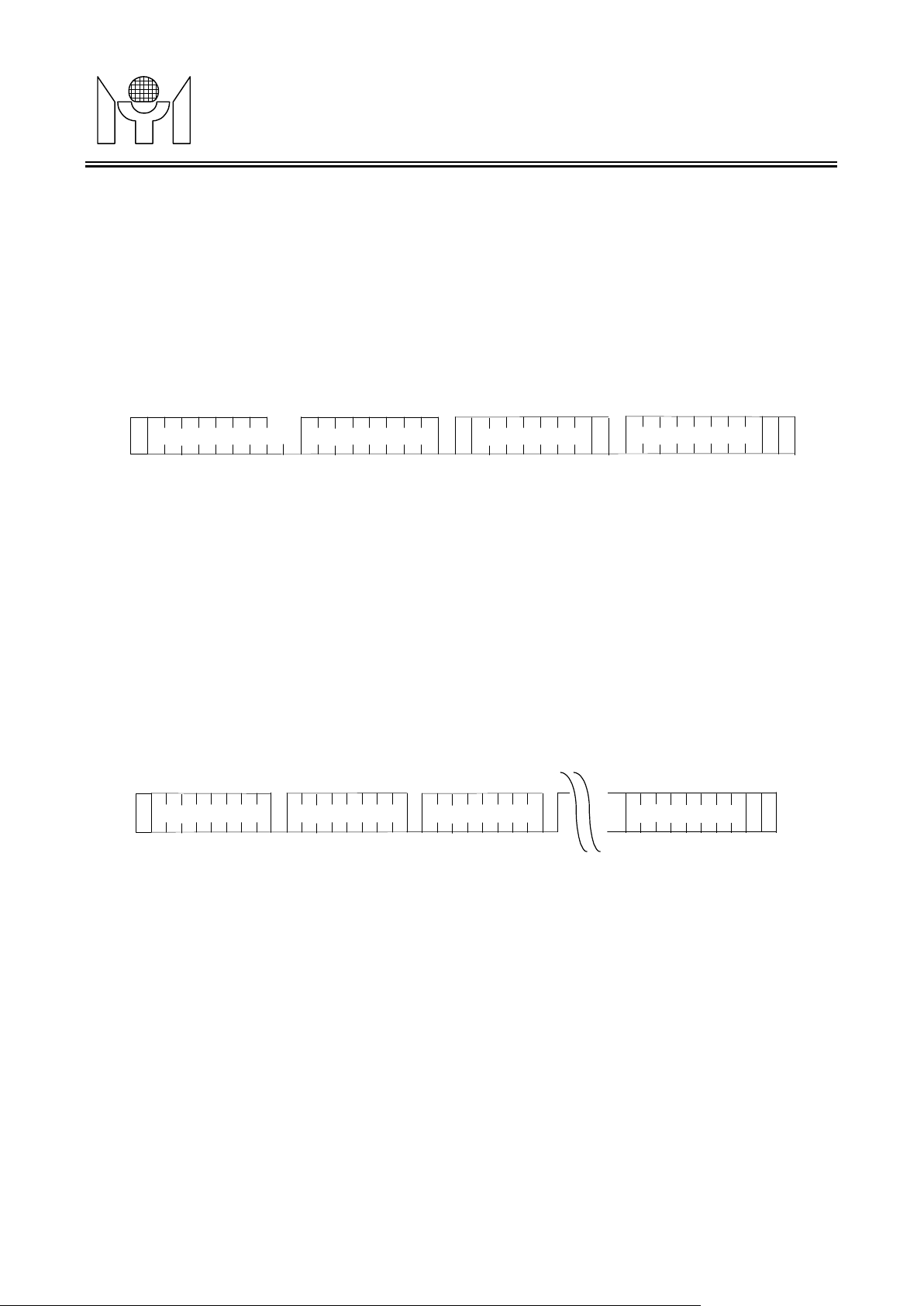
Fig. 3.4.3 Sequential Write
¨
MTL005 contains an address counter which maintains the last access address incremented by one. If the last
master will generate a stop condition instead of an Acknowledge. Ref. Fig. 3.5.4.
S
T
A
R
ADDRESS
T
SDA
SLAVE
A
C
K
R
A
C
K
DATA
A
C
K
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
A
C
K
Fig. 3.5.4 Current Address Read
Revision 0.9 - 13 - 2000/12/29
MYSON
0, and word address for read.
After responding an Acknowledge, MTL005 then transmits eight bits data right after the master generating
the start condition and slave address with R/W bit set to 1. After completion of receiving data, the master will
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
¨ Rando m Read
The operation of Random Read allows accessing any address. Before reading data operation, it must issue a
“dummy write” operation—a start condition, a slave address with R/W bit set to
generate a stop condition instead of an Acknowledge. Ref. Fig 3.5.5.
S
T
A
R
T
A
C
K
SLAVE
ADDRESS
DATA
A
R
C
K
SDA
S
T
A
R
T
SLAVE
ADDRESS
WORD
ADDRESS
A
W
C
K
Fig. 3.4.5 Random Read
Rev 0.9
S
T
O
P
¨ Sequent i al Read
The initial step can be as either Current Address Read or Random Read. The first read data is transmitted
the same manner as other read methods. However, the master generates an Acknowledge indicating that it
requires more data to read. MTL005 continues to output data for each Acknowledge received. The output
data is sequential and the internal address counter increments by one for next read data. Ref. Fig. 3.5.6.
S
T
A
SLAVE
R
ADDRESS
T
SDA
A
R
C
K
Fig. 3.4.6 Sequential Read
3.4.2 Interrupt
MTL005 supports one interrupt output signal (IRQ) which can be programmed to provide SYNC related or
function status related interrupts to the system. Upon receiving the interrupt request, Firmware needs to first
check the interrupt event by reading the Interrupt Flag Control registers (Reg. E8h and E9h) to decide what
events are happening. After the operation is finished, Firmware needs to clear interrupt status by writing the
same registers Reg. E8h and E9h. Furthermore, by using the Interrupt Flag Enable registers (Reg. EAh and
EBh), each interrupt event can be masked.
DATA n
A
C
K
DATA n+1
DATA n+x
A
C
K
S
T
O
P
3.4.3 Update Regist er Contents
I/O write operation to some consecutive register set can have the “Double Buffer” effect by setting the
Reg. C1h/D4. Written data is first stored in an intermediate bank of latches and then transf erred to the active
register set by setting Reg. C1h/D1-0.
Revision 0.9 - 14 - 2000/12/29

MYSON
XI and XO by an external quartz crystal at 14.31818 MHz. First one is the same as to the oscillator clock at
: the desired display clock
MTL005
TECHNOLOGY
Rev 0.9
3.5 On-Chip PLL
General Descrip t io n
The MTL005 needs two clock sources to drive synchronous circuits on chip. These clocks are generated
from the internal Phase Lock Loop (PLL) circuits with reference to the oscillator clock which is applied to pin
frequency (14.31818 MHz) to detect and measure graphic vertical and horizontal SYNC Frequency, Polarity
as well as Presence. The second is the display clock for display controller on chip and output signals to LCD
panel.
3.5.1 Reference Cloc k
It is the counting basis of counter values in SYNC Processor such as VS and HS period count registers; that
is, the read back values from these registers must multiply the period of this clock to estimate VS and HS
frequency. Incorporating with polarity and frequency information of VS and HS, it can show the input graphic
image mode and pixel clock frequency.
3.5.2 Display Clock
This clock is the synchronous clock for LCD panel. According to the LCD panel resolution of applications, the
display clock range is from 50 MHz to 200 MHz by means of choosing a set of appropriate values for M, N as
well as R. The formula to calculate desired frequency of display clock is as f ollows:
f
= f
mclk
5(M+2)/(N+2)51/R
osc
Where f
mclk
f
osc
M : post-divider ratio
N : pre-divider ratio
R : optional divider ratio
: oscillator clock with 14.31818 MHz
Revision 0.9 - 15 - 2000/12/29
 Loading...
Loading...