MXIC MX27C4100MC-15, MX27C4100MI-10, MX27C4100MI-12, MX27C4100MI-15, MX27C4100PC-10 Datasheet
...
FEATURES
• 256K x 16 organization(MX27C4096, JEDEC pin
out)
• 512K x 8 or 256K x 16 organization(MX27C4100,
ROM pin out compatible)
• +12.5V programming voltage
• Fast access time: 100/120/150 ns
• Totally static operation
• Completely TTL compatible
• Operating current: 60mA
• Standby current: 100uA
• Package type:
- 40 pin plastic DIP
- 44 pin PLCC
- 40 pin SOP
REV. 3.4, AUG. 22, 2001
P/N: PM0197
1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MX27C4100/4096 is a 5V only, 4M-bit, One Time
Programmable Read Only Memory. It is organized as
256K words by 16 bits per word(MX27C4096), 512K x 8
or 256K x 16(MX27C4100), operates from a single + 5
volt supply, has a static standby mode, and features fast
single address location programming. All programming
signals are TTL levels, requiring a single pulse. For
programming outside from the system, existing EPROM
programmers may be used. The MX27C4100/4096
supports a intelligent fast programming algorithm which
can result in programming time of less than two minutes.
This EPROM is packaged in industry standard 40 pin
dual-in-line packages, 40 lead SOP, and 44 lead PLCC
packages.
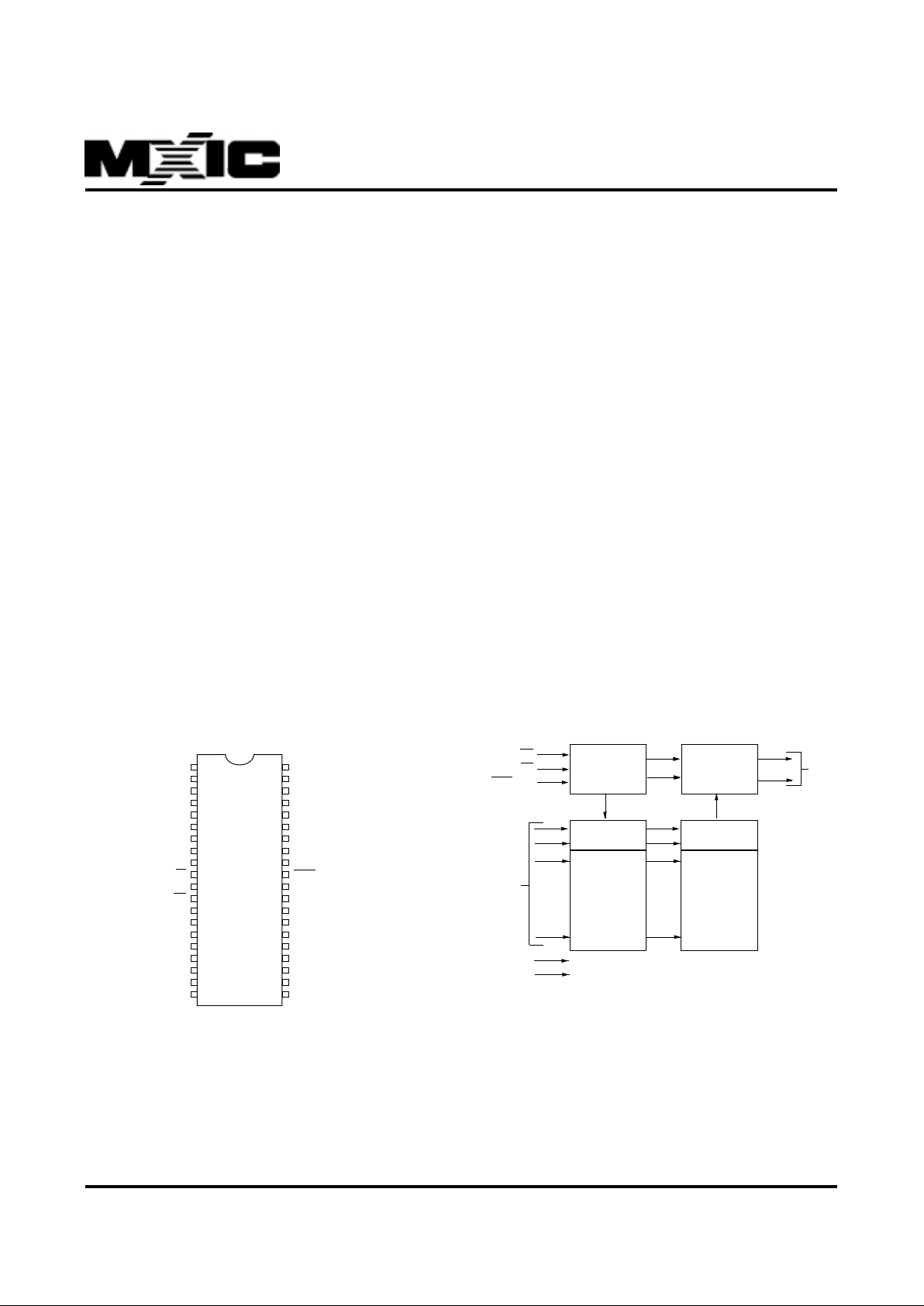
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
SOP/PDIP(MX27C4100)
BLOCK DIAGRAM (MX27C4100)
MX27C4100/27C4096
4M-BIT [512K x 8/256K x 16] CMOS EPROM
MX27C4100
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
BYTE/VPP
GND
Q15/A-1
Q7
Q14
Q6
Q13
Q5
Q12
Q4
VCC
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
CE
GND
OE
Q0
Q8
Q1
Q9
Q2
Q10
Q3
Q11
CONTROL
LOGIC
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
Q0~Q14
Q15/A-1
CE
OE
BYTE/VPP
A0~A17
ADDRESS
INPUTS
Y-DECODER
X-DECODER
Y-SELECT
4M BIT
CELL
MAXTRIX
VCC
GND
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
2
REV. 3.4, AUG. 22, 2001
P/N: PM0197
MX27C4100/27C4096
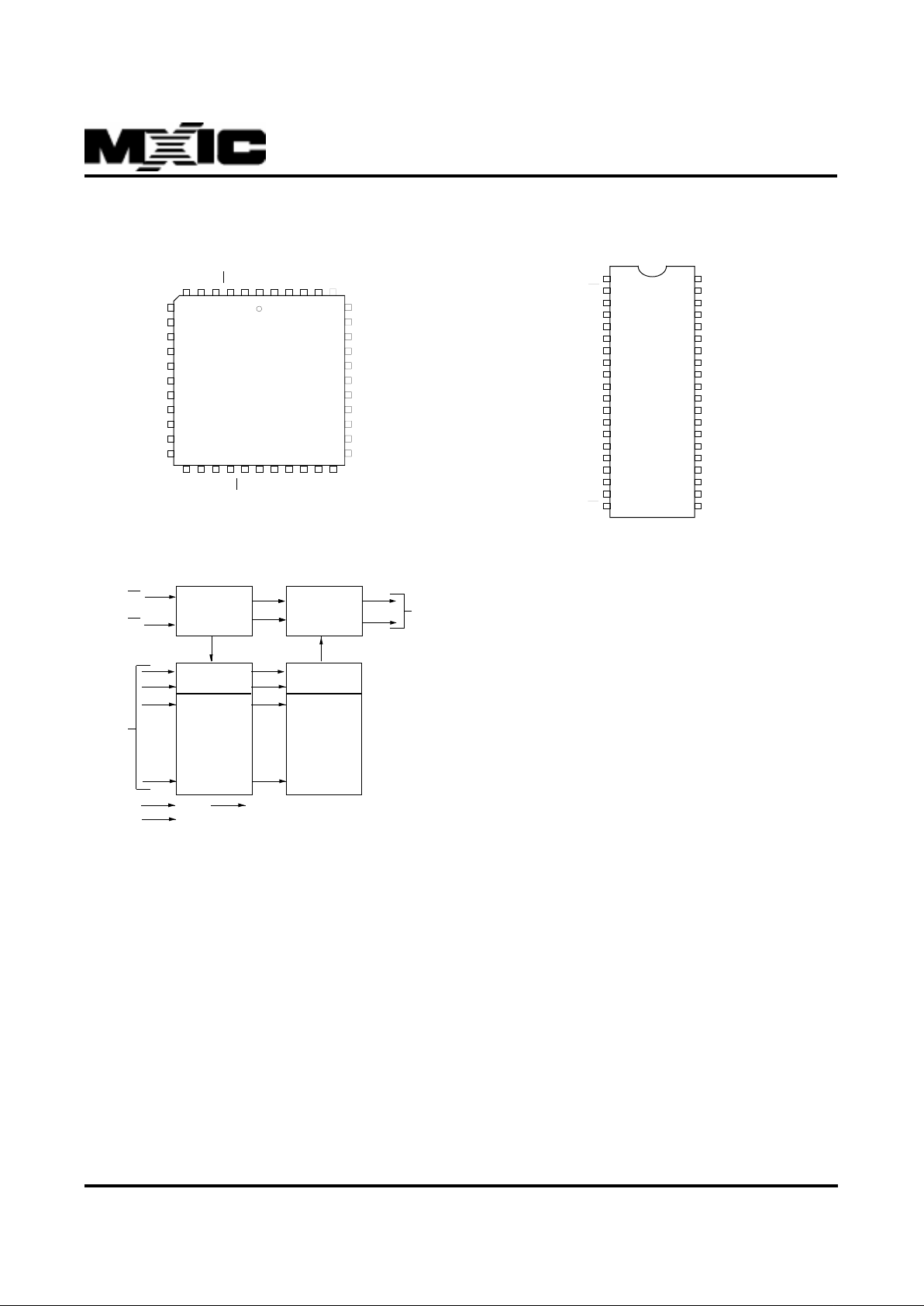
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
PLCC(MX27C4096)
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
PDIP(MX27C4096)
BLOCK DIAGRAM (MX27C4096)
MX27C4096
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
VCC
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
GND
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
VPP
CE
Q15
Q14
Q13
Q12
Q11
Q10
Q9
Q8
GND
Q7
Q6
Q5
Q4
Q3
Q2
Q1
Q0
OE
MX27C4096
Q12
Q11
Q10
Q9
Q8
GND
NC
Q7
Q6
Q5
Q4
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
GND
NC
A8
A7
A6
A5
Q13
Q14
Q15CEVPPNCVCC
A17
A16
A15
A14
Q3Q2Q1
Q0
OE
NC
A0A1A2A3A4
64440
39
34
29
7
12
17
18 23 28
1
CONTROL
LOGIC
OUTPUT
BUFFERS
Q0~Q15
CE
OE
A0~A17
ADDRESS
INPUTS
Y-DECODER
X-DECODER
Y-SELECT
4M BIT
CELL
MAXTRIX
VCC
GND
VPP
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.

3
REV. 3.4, AUG. 22, 2001
P/N: PM0197
MX27C4100/27C4096
WORD MODE(BYTE = VCC)
CE OE Q15/A-1 MODE Q0-Q14 SUPPLY CURRENT
H X High Z Non selected High Z Standby(ICC2)
L H High Z Non selected High Z Operating(ICC1)
L L DOUT Selected DOUT Operating(ICC1)
NOTE : X = H or L
TRUTH TABLE OF BYTE FUNCTION(MX27C4100)
BYTE MODE(BYTE = GND)
CE OE Q15/A-1 MODE Q0-Q7 SUPPLY CURRENT
H X X Non selected High Z Standby(ICC2)
L H X Non selected High Z Operating(ICC1)
L L A-1 input Selected DOUT Operating(ICC1)
SYMBOL PIN NAME
A0~A17 Address Input
Q0~Q14 Data Input/Output
CE Chip Enable Input
OE Output Enable Input
BYTE/VPP Word/Byte Selection/Program Supply Voltage
Q15/A-1 Q15(Word mode)/LSB addr. (Byte mode)
VCC Power Supply Pin (+5V)
GND Ground Pin
PIN DESCRIPTION(MX27C4100)
PIN DESCRIPTION(MX27C4096)
SYMBOL PIN NAME
A0~A17 Address Input
Q0~Q15 Data Input/Output
CE Chip Enable Input
OE Output Enable Input
VPP Program Supply Voltage
VCC Power Supply Pin (+5V)
GND Ground Pin
4
REV. 3.4, AUG. 22, 2001
P/N: PM0197
MX27C4100/27C4096
The verification should be performed with OE and CE at
VIL(for MX27C4096), OE at VIL and CE at VIH(for
MX27C4100) and VPP at its programming voltage.
AUTO IDENTIFY MODE
The auto identify mode allows the reading out of a binary
code from an EPROM that will identify its manufacturer
and device type. This mode is intended for use by
programming equipment for the purpose of
automatically matching the device to be programmed
with its corresponding programming algorithm. This
mode is functional in the 25°C± 5°C ambient
temperature range that is required when programming
the MX27C4100/4096.
To activate this mode, the programming equipment
must force 12.0 ± 0.5 V on address line A9 of the device.
Two identifier bytes may then be sequenced from the
device outputs by toggling address line A0 from VIL to
VIH. All other address lines must be held at VIL during
auto identify mode.
Byte 0 ( A0 = VIL) represents the manufacturer code,
and byte 1 (A0 = VIH), the device identifier code. For the
MX27C4100/4096, these two identifier bytes are given
in the Mode Select Table. All identifiers for manufacturer
and device codes will possess odd parity, with the MSB
(Q15) defined as the parity bit.
READ MODE
The MX27C4100/4096 has two control functions, both of
which must be logically satisfied in order to obtain data
at the outputs. Chip Enable (CE) is the power control
and should be used for device selection. Output Enable
(OE) is the output control and should be used to gate
data to the output pins, independent of device selection.
Assuming that addresses are stable, address access
time (tACC) is equal to the delay from CE to output (tCE).
Data is available at the outputs tOE after the falling edge
of OE's, assuming that CE has been LOW and
addresses have been stable for at least tACC - t OE.
WORD-WIDE MODE
With BYTE/VPP at VCC ± 0.2V outputs Q0-7 present
data Q0-7 and outputs Q8-15 present data Q8-15, after
CE and OE are appropriately enabled.
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
THE PROGRAMMING OF THE MX27C4100/4096
When the MX27C4100/4096 is delivered, or it is
erased, the chip has all 4M bits in the "ONE" or HIGH
state. "ZEROs" are loaded into the MX27C4100/4096
through the procedure of programming.
For programming, the data to be programmed is applied
with 16 bits in parallel to the data pins.
VCC must be applied simultaneously or before VPP,
and removed simultaneously or after VPP. When
programming an MXIC EPROM, a 0.1uF capacitor is
required across VPP and ground to suppress spurious
voltage transients which may damage the device.
FAST PROGRAMMING
The device is set up in the fast programming mode when
the programming voltage VPP = 12.75V is applied, with
VCC = 6.25 V and OE = VIH (Algorithm is shown in
Figure 1). The programming is achieved by applying a
single TTL low level 100us pulse to the CE input after
addresses and data line are stable. If the data is not
verified, an additional pulse is applied for a maximum of
25 pulses. This process is repeated while sequencing
through each address of the device. When the
programming mode is completed, the data in all address
is verified at VCC = VPP = 5V ± 10%.
PROGRAM INHIBIT MODE
Programming of multiple MX27C4100/4096's in parallel
with different data is also easily accomplished by using
the Program Inhibit Mode. Except for CE and OE, all like
inputs of the parallel MX27C4100/4096 may be
common. A TTL low-level program pulse applied to an
MX27C4100/4096 CE input with VPP = 12.5 ± 0.5 V will
program the MX27C4100/4096. A high-level CE input
inhibits the other MX27C4100/4096s from being
programmed.
PROGRAM VERIFY MODE
Verification should be performed on the programmed
bits to determine that they were correctly programmed.

5
REV. 3.4, AUG. 22, 2001
P/N: PM0197
MX27C4100/27C4096
BYTE-WIDE MODE
With BYTE/VPP at GND ± 0.2V, outputs Q8-15 are tristated. If Q15/A-1 = VIH, outputs Q0-7 present data bits
Q8-15. If Q15/A-1 = VIL, outputs Q0-7 present data bits
Q0-7.
STANDBY MODE
The MX27C4100/4096 has a CMOS standby mode
which reduces the maximum VCC current to 100 uA. It
is placed in CMOS standby when CE is at VCC ± 0.3 V.
The MX27C4100/4096 also has a TTL-standby mode
which reduces the maximum VCC current to 1.5 mA. It
is placed in TTL-standby when CE is at VIH. When in
standby mode, the outputs are in a high-impedance
state, independent of the OE input.
TWO-LINE OUTPUT CONTROL FUNCTION
To accommodate multiple memory connections, a twoline control function is provided to allow for:
1. Low memory power dissipation,
2. Assurance that output bus contention will not
occur.
It is recommended that CE be decoded and used as the
primary device-selecting function, while OE be made a
common connection to all devices in the array and
connected to the READ line from the system control bus.
This assures that all deselected memory devices are in
their low-power standby mode and that the output pins
are only active when data is desired from a particular
memory device.
SYSTEM CONSIDERATIONS
During the switch between active and standby
conditions, transient current peaks are produced on the
rising and falling edges of Chip Enable. The magnitude
of these transient current peaks is dependent on the
output capacitance loading of the device. At a minimum,
a 0.1 uF ceramic capacitor (high frequency, low inherent
inductance) should be used on each device between
Vcc and GND to minimize transient effects. In addition,
to overcome the voltage drop caused by the inductive
effects of the printed circuit board traces on EPROM
arrays, a 4.7 uF bulk electrolytic capacitor should be
used between VCC and GND for each eight devices.
The location of the capacitor should be close to where
the power supply is connected to the array.

6
REV. 3.4, AUG. 22, 2001
P/N: PM0197
MX27C4100/27C4096
MODE SELECT TABLE (MX27C4100)
BYTE/
MODE CE OE A9 A0 Q15/A-1 VPP(5) Q8-14 Q0-7
Read (Word) VIL VIL X X Q15 Out VCC Q8-14 Out Q0-7 Out
Read (Upper Byte) VIL VIL X X VIH GND High Z Q8-15 Out
Read (Lower Byte) VIL VIL X X VIL GND High Z Q0-7 Out
Output Disable VIL VIH X X High Z X High Z High Z
Standby VIH X X X High Z X High Z High Z
Program VIL VIH X X Q15 In VPP Q8-14 In Q0-7 In
Program Verify VIH VIL X X Q15 Out VPP Q8-14 Out Q0-7 Out
Program Inhibit VIH VIH X X High Z VPP High Z High Z
Manufacturer Code(3) VIL VIL VH VIL 0B VCC 00H C2H
Device Code(3) VIL VIL VH VIH 1B VCC 38H 00H
NOTES: 1. VH = 12.0 V ± 0.5 V
2. X = Either VIH or VIL
3. A1 - A8 = A10 - A17 = VIL(For auto select)
4. See DC Programming Characteristics for VPP voltage during
programming.
NOTES: 1. VH = 12.0V ± 0.5V
2. X = Either VIH or VIL
3. A1 - A8, A10 - A17 = VIL(for auto select)
4. See DC Programming Characteristics for VPP voltages.
5. BYTE/VPP is intended for operation under DC Voltage conditions
only.
6. Manufacture code = 00C2H
Device code = B800H
MODE SELECT TABLE (MX27C4096)
PINS
MODE CE OE A0 A9 VPP OUTPUTS
Read VIL VIL X X VCC DOUT
Output Disable VIL VIH X X VCC High Z
Standby (TTL) VIH X X X VCC High Z
Standby (CMOS) VCC±0.3V X X X VCC High Z
Program VIL VIH X X VPP DIN
Program Verify VIH VIL X X VPP DOUT
Program Inhibit VIH VIH X X VPP High Z
Manufacturer Code(3) VIL VIL VIL VH VCC 00C2H
Device Code(3) VIL VIL VIH VH VCC 0151H
 Loading...
Loading...