MX COM Inc MX826DW, MX826J, MX828DS, MX828DW, MX828P Datasheet
DATA BULLETIN
PRELIMINARY INFORMATION
MX826
AMPS/NAMPS SYSTEM
AUDIO PROCESSOR
© 1997 MX•COM Inc. www.mxcom.com Tele: 800 638-5577 910 744-5050 Fax: 910 744-5054 Doc. # 20480070.004
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
Features
• Full-Duplex Audio Processing for AMPS/
NAMPS Cellular Systems
• On-Chip Speech and SAT Capabilities
– TX/RX Filtering & Gain – SAT Channel
Pre-/De-Emphasis – Deviation Limiter
• Serial
µµ
µµ
µProcessor Interface
• “Sidetone” Output Available
• Access to External Processes
– Companding – Signaling –
VSR Codec (Store/Play)
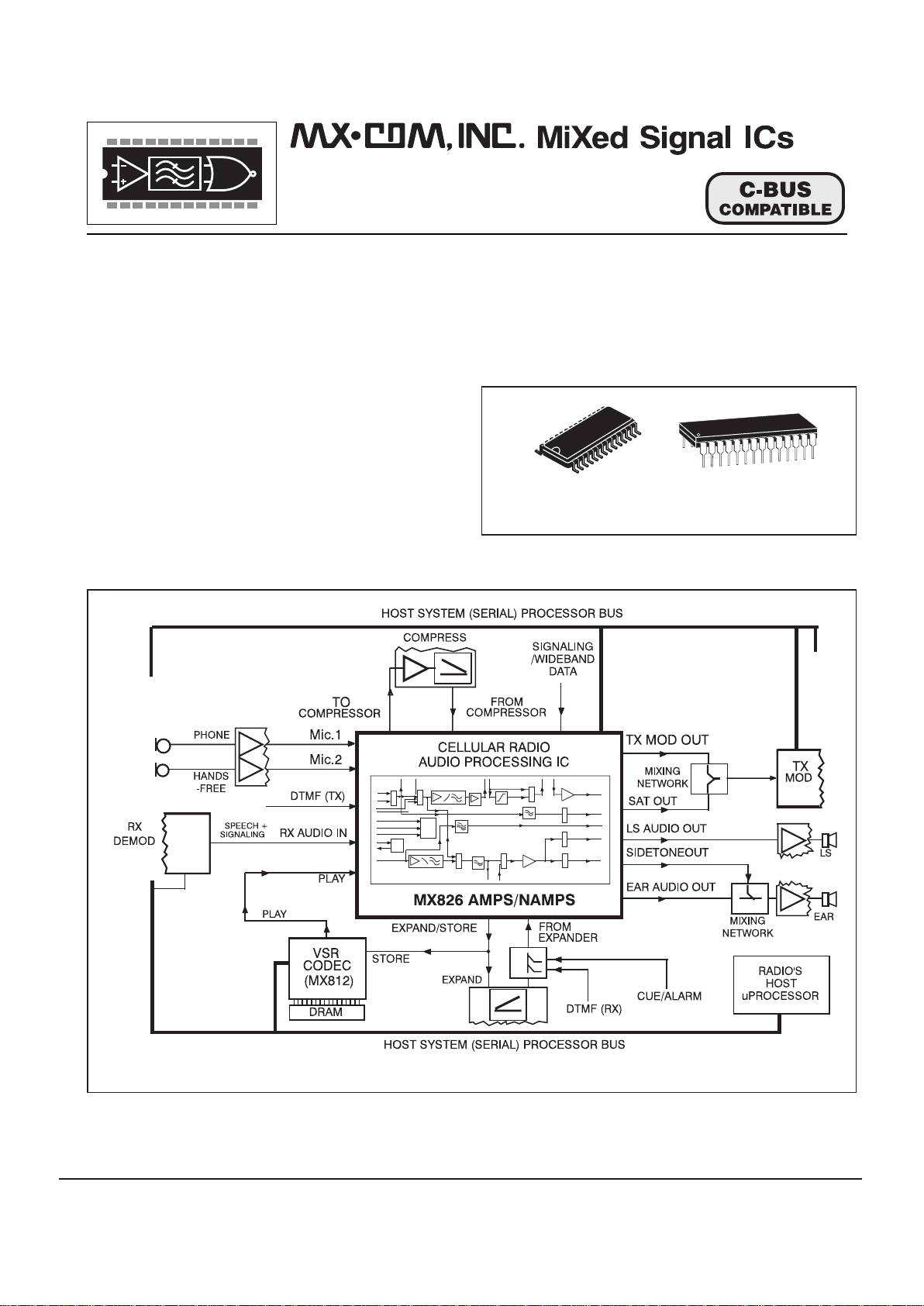
Figure1 - The MX826 AMPS/NAMPS Audio Processor Installed in a Cellular System
• HandsFree Compatibility
• Powersave (Low-Current) Settings
MX826DW MX826J
28-pin SOIC 28-pin CDIP
AMPS/NAMPS System Audio Processor. MX826 Preliminary Information
© 1997 MX•COM Inc. www.mxcom.com Tele: 800 638-5577 910 744-5050 Fax: 910 744-5054 Doc. # 20480070.004
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
Description
The MX826 is a µProcessor controlled full-duplex
audio processor on a single-chip with separate TX and
RX paths to provide all the filter/gain/limiting functions
necessary to pre-process audio, wideband-data and SAT
cellular communications systems using the AMPS/NAMPS
or TACS/ETACS/JTACS specifications.
Selectable inputs available to the transmit path are: a
choice of two microphones and DTMF/signaling, with
access, in this path, to external compression circuitry.
Operationally the TX path provides input gain/filtering, a
deviation limiter and TX Modulation Drive controls.
In the RX path the SAT signal is separated from the
incoming audio via a filter block and made available at a
separate pin for mixing externally with the TX Modulation
Drive.
The RX path consists of an input gain/filter block for
voice, inputs from an external audio expansion system
and an output gain control driving either a loudspeaker
system or earpiece.
Unique to the MX816/826/836 cellular audio
processors is the ability to route audio (TX or RX) to an
external Voice Store and Retrieve (VSR) device such as
the MX802 or MX812 thus providing the radio system with
a voice answering and announcement facility using
external DRAM.
As a member of the DBS800 family, the MX826
follows C-BUS protocol. (C-BUS is the serial interface
used by all DBS800 integrated circuits.)
The MX826, a low-power CMOS device which reduces
the amount of microcircuits and components required in
a cellular audio system by providing more functions on a
single chip, is available in 28-pin SOIC and CDIP packages.
1 Xtal: The output of the on-chip clock oscillator.
2 Xtal/Clock: The input to the on-chip clock oscillator. A Xtal or externally derived clock (f
XTAL
) should be
connected here. Note that operation of the MX826 without a suitable Xtal or clock input may cause device
damage. See Figure 2 (notes).
3 Serial Clock: The “C-BUS” serial data clock input. This clock, produced by the µController, is used for
transfer timing of commands and data to the MX826. See Timing Diagrams.
4 Command Data: The “C-BUS” serial data input from the µController. Data is loaded to the MX826 in 8-
bit bytes, MSB (B7) first, and LSB (B0) last, synchronized to the Serial Clock. See Timing Diagrams.
5 Chip Select (CS): The “C-BUS” data loading control function. This input is provided by the µController.
Data transfer sequences are initiated, completed or aborted by this signal. See Timing Diagrams.
6V
BIAS
: The internal circuitry bias line, held at VDD/2 this pin must be decoupled to VSS. See Figure 2.
7 Rx Audio In: Normally taken from the radio's discriminator output, this input has a 1MΩ internal resistor
to V
BIAS
and requires to be connected via a capacitor.
8 Expand/Store: A common output that can be used as either an input to an external audio expander or
the input to a voice storage medium such as the MX812. Components relevant to the external device
requirements should be used at this output. See Figures 2 and 3.
9 (Expanded) Audio In: The audio input, via SW5, from an external expander or audio mixing function. This
input has a 1MΩ internal resistor to V
BIAS
and requires to be connected via a capacitor. See Figures 2 and
3.
10 TX Mod Out: The composite TX audio output to the transmitter modulator from a variable attenuation
stage (11H). This output is set to V
BIAS
via an internal 1MΩ resistor when set to Powersave or OFF.
11 LS Audio Out: An audio output of the Rx path (or selected audios, see Figure 3) for a loudspeaker system.
This is available for handsfree operation. This output can be connected to V
BIAS
when not required, by SW6
(Configuration Command (10H)). A driver amplifier may be required.
Notes on Inputs: To minimize aliasing effects, lowpass filtering may be required at the inputs to this device
(especially those supplied from switched-capacitor-type devices) to ensure the input spectrum is kept
below 63kHz.
Pin Function

AMPS/NAMPS System Audio Processor. MX826 Preliminary Information
© 1997 MX•COM Inc. www.mxcom.com Tele: 800 638-5577 910 744-5050 Fax: 910 744-5054 Doc. # 20480070.004
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
12 Ear Audio Out: An audio output of the Rx path (or selected audios), available as an output for a handset
earpiece. This output, in parallel with the LS Audio Out function, can be connected to V
BIAS
when not
required, by SW7 (Configuration Command (10H)). A driver amplifier may be required.
13 Sidetone: A switched “sidetone” from the microphone inputs made available for mixing externally with
the “Ear” audio. See Figure 3.
14 VSS: Negative supply rail. Signal ground.
15 TX Mix: The output of the TX Mix Amplifier. Used with external components, it allows the TX Filter
Out output to mix with externally generated signalling tones prior to the final level adjustment.
16 SAT Out: The output of the SAT Bandpass filter. This level is recovered from the input RX audio and
is available for mixing externally with the transmitter modulation. See Figure 3.
17 TX Mix In: The input to the TX Mix Amplifier. Used with external components, it allows the TX Filter
Out output to mix with externally generated signalling tones prior to the final level adjustment. The
recovered SAT signal may be introduced at this point. See Figures 2 and 3.
18 TX Filter Out: The output of the Deviation Limiter/Lowpass Filter stage. This stage can be by-passed
using SW3 (Configuration Command). See Figure 3.
19 No internal connection – Leave open circuit.
20 Deviation Limiter In: Input to the on-chip deviation limiter. This input should be a.c. coupled to the
Pre-Emphasis Out pin. The a.c. coupling will achieve maximum possible symmetry of limiting as this
input has a 1MΩ internal resistor to V
BIAS
. See Figure 2.
21 Pre-Emphasis Out: Audio output from the TX Gain/Pre-Emphasis function. This output should be
a.c. coupled to the Deviation Limiter In pin. See Figures 2 & 3.
22 DTMF In: To introduce DTMF type audio, at a suitable level for transmission, to the TX Path,
controlled by SW2 (Configuration Command (10H)). This input has an internal 1MΩ resistor to V
BIAS
and should be connected via a capacitor.
23 Compression In: The audio input from an external compression system. This input has an internal
1MΩ resistor to V
BIAS
and should be connected via a capacitor.
24 Compression: The output to an external audio compression system. Currently available compressor/
expanders have Op-Amps incorporated. The compressor can be by-passed by SW2.
25 Mic.2 In:
26 Mic.1 In:
27 Play In: The input via SW2 from a voice storage device such as the MX812. This “replayed” audio
can be sent to RX or TX paths allowing a Messaging/Voice Notepad/Answering facility. This input has
an internal 1MΩ resistor to V
BIAS
and should be connected via a capacitor.
28 VDD: Positive supply rail. A single +5-volt power supply is required. Levels and voltages within this
Audio Processor are dependent upon this supply.
C-BUS is MX-COM’s proprietary standard for the transmission of commands and data between a
µController and the relevant Cellular microcircuits. It may be used with any µController, and can, if
desired, take advantage of the hardware serial I/O functions embodied into many types of µController .
The “C-BUS” data rate is determined solely by the µController.
Pin Function
TX voice (Mic.) inputs, selectable by SW1 available for handsfree mic./handset mic. or
any TX audio input. Pre-amplification may be required at these inputs. These inputs
each have an internal 1MΩ resistor to V
BIAS
and should be connected via a capacitor.
AMPS/NAMPS System Audio Processor. MX826 Preliminary Information
© 1997 MX•COM Inc. www.mxcom.com Tele: 800 638-5577 910 744-5050 Fax: 910 744-5054 Doc. # 20480070.004
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
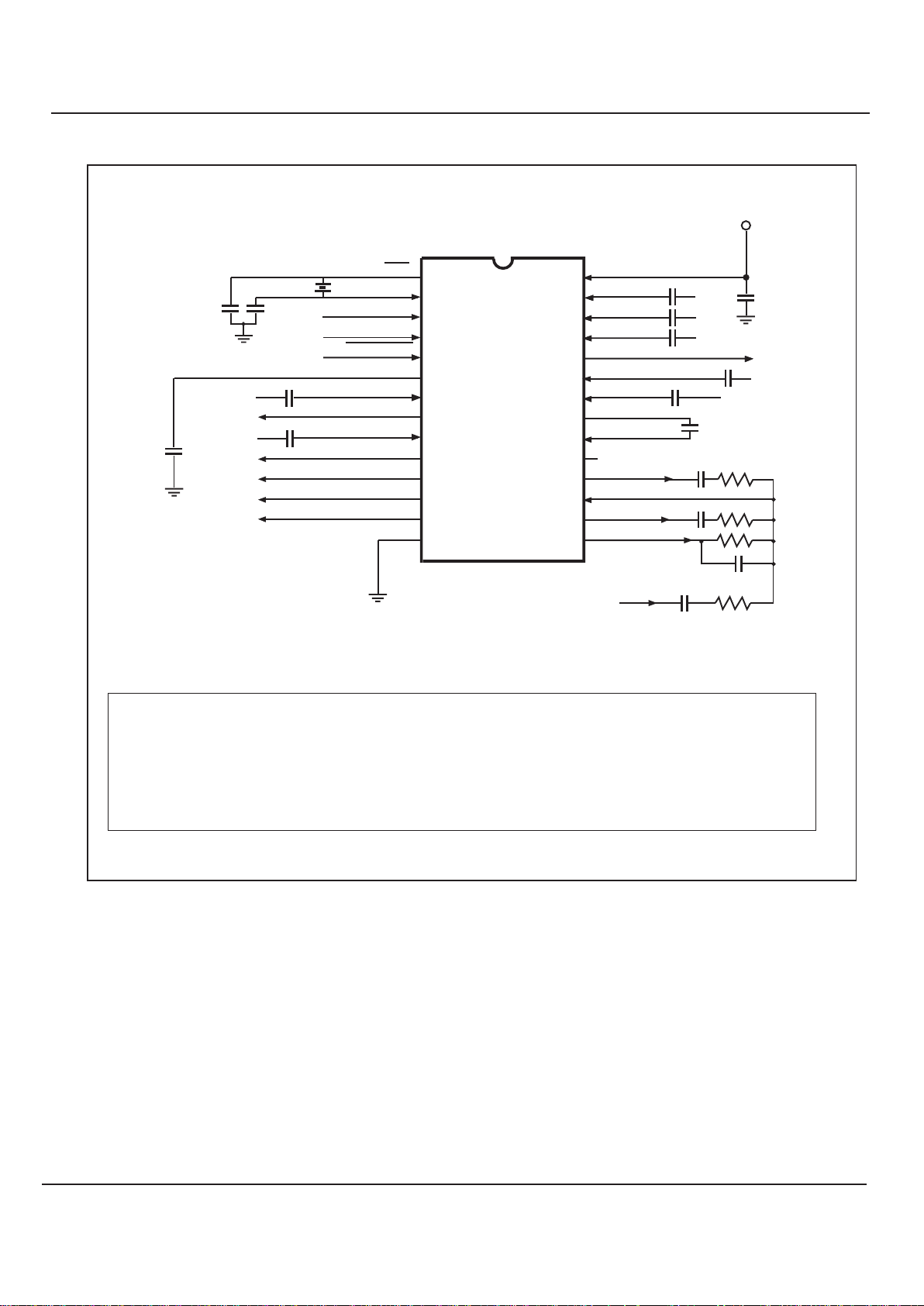
Application Information
Notes
1. Xtal/clock operation
Operation of any MX-COM IC without a Xtal or
clock input may cause device damage. To minimize
damage in the event of a Xtal/drive failure, you
should install a current limiting device (resistor or
fast-reaction fuse) on the power input (VDD).
Figure 2 - Recommended External Components
Tolerances – Capacitors ±20%
C3= 100nF
C
4
100nF
C
5
100nF
C
6
100nF
C
7
100nF
C13= 100nF
C
14
100nF
C
15
100pF
C
16
100nF
X
1
4.000MHz
R1= 100kΩ
R
2
as required
R
3
100kΩ
R
4
as required
C
1
100nF
C
2
100nF
C8= 100nF
C
9
33pF
C
10
100nF
C
11
33pF
C
12
1.0µF
2. SAT Output
It is possible, due to the impedance of this output,
that an external buffer amplifier will be required
when interfacing or mixing with other cellular system
sections.
3. TX Mix Gain
The value of R4 should be chosen with R3/C15 in
order to provide the required gain.
XTAL/CLOCK
SERIAL CLOCK
COMMAND DATA
V
BIAS
RX AUDIO IN
EXPAND/STORE
(EXPANDED) AUDIO IN
TX MOD OUT
LS AUDIO OUT
EAR AUDIO OUT
SIDETONE OUT
V
SS
SAT OUT
TX MIX IN
TX FILTER OUT
DEV LIM IN
PRE-EMP OUT
DTMF IN
(COMPRESSED) AUDIO IN
COMPRESS
MIC.2 IN
MIC.1 IN
PLAY IN
V
DD
CHIP SELECT
V
DD
XTAL
C
11
C
9
X
1
C
4
C
8
C
12
C
7
C
6
C
5
C
1
C
3
C
10
MX826J
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
TX MIX
C
13
C
2
Signaling and
Wideband Data
C
14
C
15
C
16
R
1
R
3
R
4
R
2
 Loading...
Loading...