DATA BULLETIN
MX806A
Audio Processor
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
Features
Half-Duplex Audio Processor
Dynamic Control of Signal Levels
Performs Signal Conditioning and
Filtering requirements for both
Transmit and Receive
Three separate signal sections:
Input process
Main Process
Mixing and Output Drives
Low Power Operation
Member of DBS800 Family (C-BUS
Compatible)
C-BUS INTERFA CE
MIC. AMP
VOGAD AMP
HIGHPASS
FILTER
GAIN
SET
PRE-EMPHASIS
LIMITING
FILTERING
GAIN SETTING
MODULATION
MIXER AMP
VOGAD
SENSE
VOGAD
SENSE
OR
MAIN PROCESS
CLOCK
GENERAT OR
BUFFER
ATTENUAT OR
ATTENUAT OR
ATTENUAT OR
INPUT
PROCESS
DE-EMPHASIS
FILTER
OUTPUT DRIVES
#
#
#
#
#
## #
#
#
#
#
LOUDSPEAKER
AUDIO
MODULATION 2
OUT
MODULATION 1
OUT
TRANSMITTER
MODULATION
DRIVES
MOD
OUT
MOD
IN
MAIN
PROCESS
OUT
PRIMARY
AND
SECONDARY
AUDIO
INPUTS
Voice
Sub-Audio
Tone
MSK,etc.
COMMAND
DATA
SERIAL
CLOCK
CHIP
SELECT
VOGAD SENSE
CALIBRATION INPUT
TX
MIC IN
RX
AUDIO IN
XTAL/CLOCK
XTAL
TO EXTERNAL
AUDIO PROCESSES
EXTERNAL AUDIO
PROCESS IN
POWER
SUPPL Y
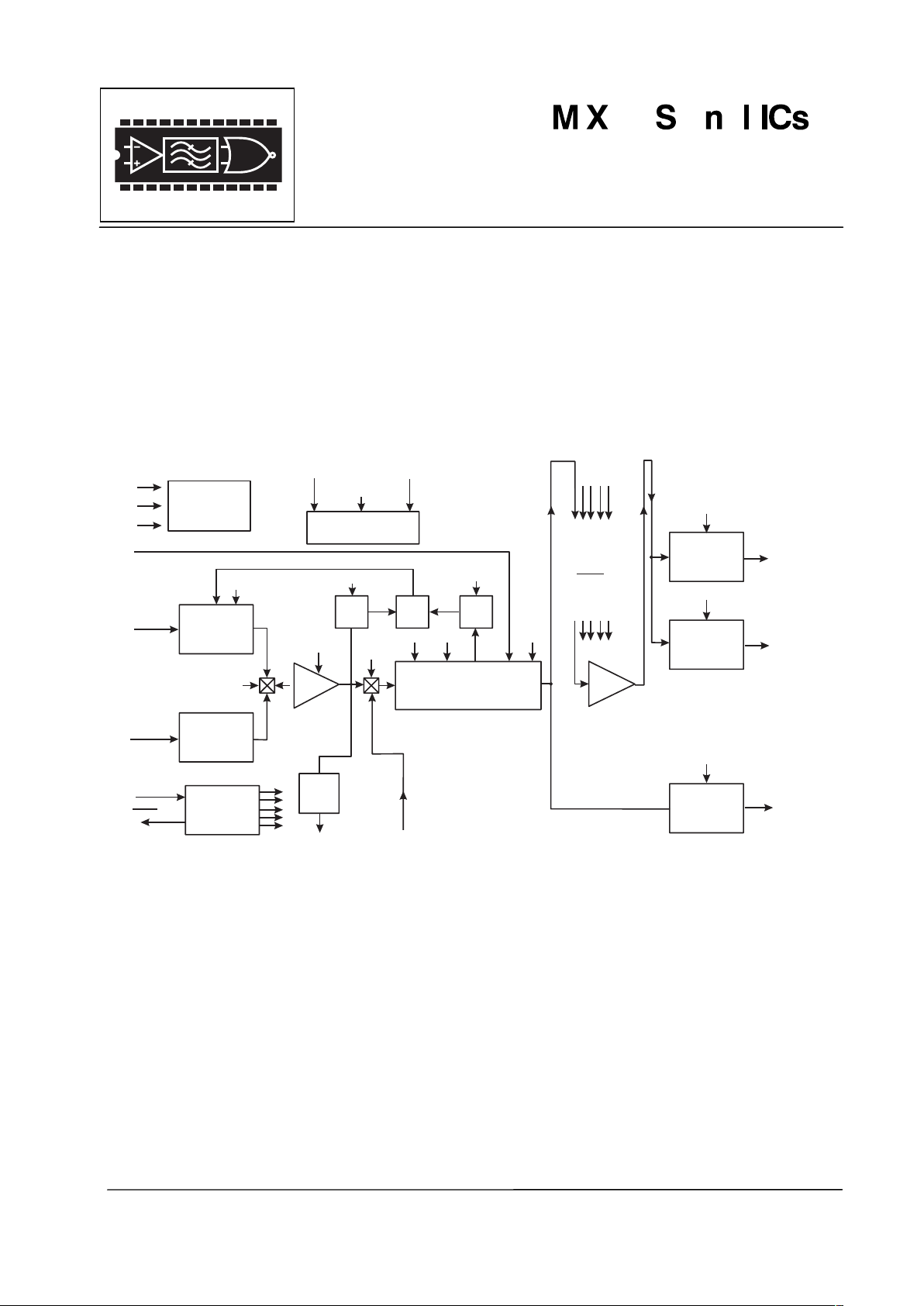
The MX806A LMR audio processor is intended too primarily to operate as the “Audio Terminal” or radio
systems using the DBS800 Digitally Integrated Baseband Subsystem.
The MX806A half-duplex device has signal paths and level setting elements that are configured and adjusted
by digital information sent from the radio microcontroller using C-BUS protocol. (C-BUS is the serial interface
for all DBS 800 ICs.)
The Signal Path is divided into three sections: Input Process, Main process, and Mixing and Output Drives.
If selected, signal level stability and output accuracy of the MX806A is maintained by a voltage-controlled gain
system using selectable signal-level detectors. Signal levels can be dynamically controlled to provide
“dynamic compensation” for factors such as temperature drift, VCO non-linearity, etc.
The MX806A audio stages can be completely disabled – or the whole IC can be placed into powersave mode,
leaving only clock and C-BUS circuitry active.
The MX806A may be used with a 5.0V power supply and is available in the following packages:
24-pin SOIC (MX806ADW), 24-pin PLCC (MX806ALH), and 24-pin PDIP (MX806AP).

Audio Processor 2 MX806A
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
Contents
Section Page
1 Block Diagram................................................................................................................3
2 Signal List.......................................................................................................................4
3 External Components....................................................................................................6
4 General Description.......................................................................................................7
4.1 Signal Path .......................................................................................................................... 7
4.2 VOGAD................................................................................................................................ 7
4.2.1 VOGAD Components Calculations – Figure 2 and Figure 5.....................................................8
4.3 Calibration Methods............................................................................................................. 8
4.3.1 TX Calibration: From Mic. In to Modulator Drives Out.............................................................8
4.3.2 RX Calibration: From RX Audio In to Audio Out......................................................................8
5 Controlling Protocol....................................................................................................10
5.1.1 Control Command – (Preceded by A/C 10H)..........................................................................11
5.1.2 Mode Command – (Preceded by A/C 11H)............................................................................12
5.1.3 Modulator Levels – (Preceded by A/C 12H) ........................................................................... 13
5.1.4 Volume Set – (Preceded by A/C 13H)....................................................................................15
6 Application Notes ........................................................................................................16
7 Performance Specifications........................................................................................17
7.1 Electrical Specifications..................................................................................................... 17
7.1.1 Absolute Maximum Limits.......................................................................................................17
7.1.2 Operating Limits......................................................................................................................17
7.1.3 Operating Characteristics .......................................................................................................18
7.1.4 Timing..................................................................................................................................... 21
7.2 Packages........................................................................................................................... 22
MXCOM, Inc. reserves the right to change specifications at any time without notice.
Audio Processor 3 MX806A
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
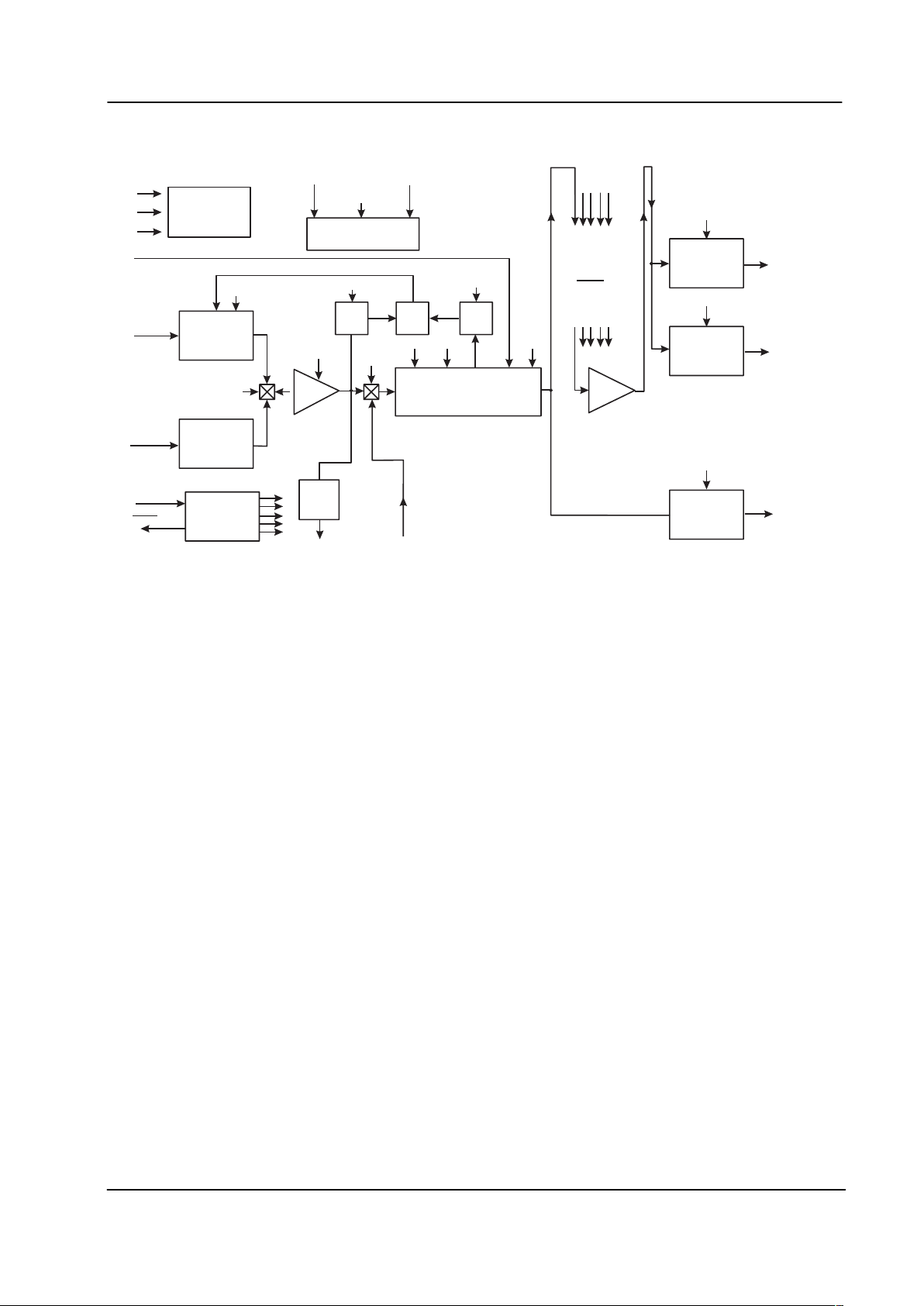
1 Block Diagram
C-BUS INTERFACE
MIC. AMP
VOGAD AMP
HIGHPASS
FILTER
GAIN
SET
PRE-EMPHASIS
LIMITING
FILTERING
GAIN SETTING
MODULATION
MIXER AMP
VOGAD
SENSE
VOGAD
SENSE
OR
MAIN PROCESS
CLOCK
GENERATOR
BUFFER
ATTENUATOR
ATTENUATOR
ATTENUATOR
INPUT
PROCESS
DE-EMPHASIS
FILTER
OUTPUT DRIVES
#
#
#
#
#
## #
#
#
#
#
LOUDSPEAKER
AUDIO
MODULATION 2
OUT
MODULATION 1
OUT
TRANSMITTER
MODULATION
DRIVES
MOD
OUT
MOD
IN
MAIN
PROCESS
OUT
PRIMARY
AND
SECONDARY
AUDIO
INPUTS
Voice
Sub-Audio
Tone
MSK,etc.
COMMAND
DATA
SERIAL
CLOCK
CHIP
SELECT
VOGAD SENSE
CALIBRATION INPUT
TX
MIC IN
RX
AUDIO IN
XTAL/CLOCK
XTAL
TO EXTERNAL
AUDIO PROCESSES
EXTERNAL AUDIO
PROCESS IN
POWER
SUPPL Y
Figure 1: Block Diagram
Audio Processor 4 MX806A
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
2 Signal List
Pin Signal Description
1
Xtal
The output of the 4.032MHz on-chip clock oscillator. External components are
required at this output when a Xtal is used. See Figure 2.
2 Xtal/Clock
The input to the on-chip 4.032MHz clock oscillator inverter. A 4.032MHz Xtal or
externally derived clock should be connected here. See Figure 2. This clock
provides timing for on-chip elements, filters, etc.
3 Serial Clock This is the ‘C-BUS’ serial Clock input. This clock, produced by the
microcontroller, is used for transfer timing of commands and data to and from the
MX805A. See Section 6 and Section 7.1.4.
4 Command Data This is the ‘C-BUS’ serial data input from the microcontroller. Command Data is
loaded to this device in 8-bit bytes, MSB (bit 7) first and LSB (bit 0) last,
synchronized to the Serial Clock. The Command/Data instruction is acted upon
at the end of loading the whole instruction. Command information is detailed in
Table 3 through Table 7. See Section 6 and Section 7.1.4.
5
CS
Select Chip . This is the ‘C-BUS’ data loading control function. This input is
provided by the microcontroller. Command Data transfer sequences are initiated,
completed or aborted by the
CS signal. See Section 6 and Section 7.1.4.
6 VOGAD OUT The error-voltage output of the selected VOGAD sensor. This output, with
external attack and decay setting components, should be connected as in Figure
2 and Figure 3, to the VOGAD In pin.
7 RX Audio In
The audio input to the MX806A from the radio receiver’s demodulator circuits.
This input, which requires AC coupling with capacitor C12, is selected via a
Control Command bit.
8 VOGAD In The gain control signal from the selected VOGAD sensor (VOGAD Out) to the
Input Process voltage-controlled amplifier. The required sensor is selected via a
Mode Command. The choice of two sensors enables gain control from either the
Input Process or an External Process. External attack and decay setting
components should be applied as recommended. See Figure 2 and Figure 3.
9V
BIAS
The output of the on-chip analog circuitry bias system, held internally at VDD/2.
This pin should be decoupled to V
SS
by capacitor C10. See Figure 2.
10 Mic In (+) The non-inverting input to the microphone Op-Amp. This input requires external
components for Op-Amp gain/attenuation setting as shown in Figure 2.
11 Mic In (-) The inverting input to the microphone Op-Amp. This input requires external
components for Op-Amp gain/attenuation setting as shown in Figure 2.
12 V
SS
Negative Supply (GND)
13 Mic Out The output of the Microphone Op-Amp, used with the Mic In (-) input to provide
the required gain/attenuation using external components as shown in Figure 2.
The external components shown are to assist in the use of this amplifier with
wither inverting or non-inverting inputs. During Powersave (Volume Command
this output is placed at V
SS
.)
14 Processed Audio In The input to the device from such external audio processed as Voice Store and
Retrieve or Frequency Domain Scrambling. This input, which requires AC
Coupling with capacitor C13, is selected by a Mode Command bit.
15
External Audio
Process
The buffered output of the Input Processing Stage. Its purpose is to further
external audio processing stages prior to re-introduction at the Processed Audio
In Pin.
16 Calibration Input A unique audio input to be used for dynamic balancing of the modulator drives for
measuring Deviation Limiter levels. A CUE (beep) input from the MX803 Audio
Tone Processor can be entered on this line. This audio input must be externally
biased. It is selected via a Mode Command bit.
17 Main Process Out The output of the Main Process stage. This output should be mixed with any
additional system audio inputs (Audio, Sub-Audio Signaling, MSK) in the on-chip
Modulation Summing Amplifier. External components shown in Figure 2 should
be used as required.
Audio Processor 5 MX806A
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
Pin Signal Description
18 Sum In
19 Sum Out
The input and output terminals of the on-chip Modulation Summing Amplifier.
External components are required for input signals and gain/attenuation setting as
shown in Figure 2. For single-signal, no gain requirements, Main Process Out
may be linked directly to Modulation In.
20 Modulation In The final, composite modulating signal to VCO (Mod 1) and Reference (Mod 2)
Output Drives
21 Audio Output The processed audio signal output intended as a received audio (volume) output.
Though normally used in the RX mode, operation in TX is permitted. The output
level of this attenuator is controlled via a Volume Set command. During
Powersave this output is placed at V
SS
.
22 Modulation 1 Drive The drive to the radio modulator Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) from the
composite audio summing stage.
23 Modulation 2 Drive The drive to the radio modulator Reference Oscillator from the composite audio
summing stage.
Note: These VCO output attenuators are individually adjustable using the
Modulator Level command. During Powersave these outputs are placed at V
SS
.
24 V
DD
Positive Supply. A single 5.0V regulated supply is required. Levels and voltages
within this Audio Processor are dependent upon this supply.
Table 1: Signal List
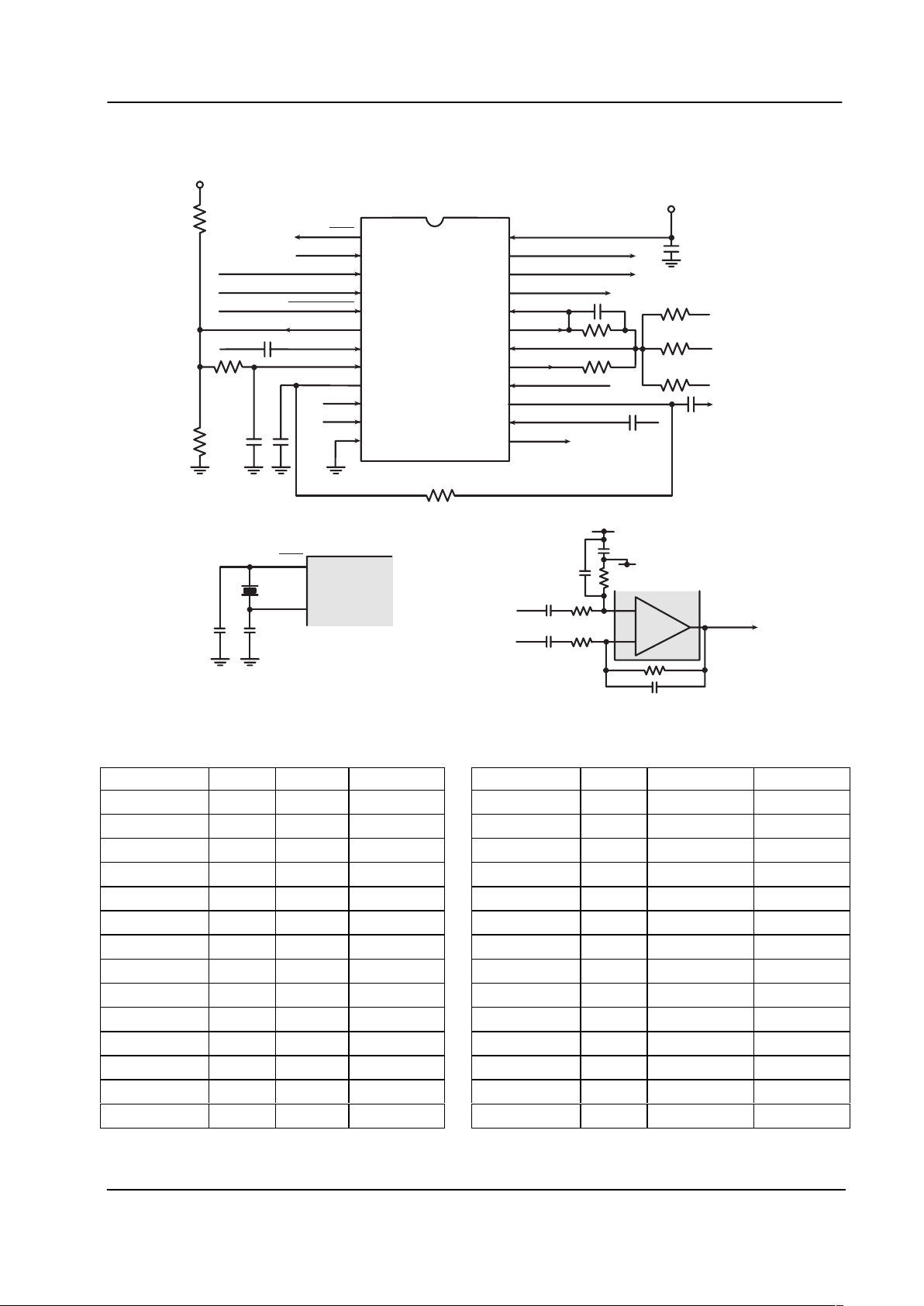
Audio Processor 6 MX806A
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
3 External Components
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
MX806AJ
XTAL
XTAL/CLOCK
SERIAL CLOCK
COMMAND DA TA
CHIP SELECT
VOGAD OUT
RX AUDIO IN
VOGAD IN
MIC. IN (+)
MIC. IN (-)
V
BIAS
V
V
V
V
V
V
SS
SS
BIAS
DD
DD
DD
MODULATION 2 DRIVE
MODULATION 1 DRIVE
AUDIO OUT
MOD. IN
MIX OUT
MIX IN
CALIBRATION IN
EXTERNAL AUDIO PROCESS
PROCESSED AUDIO IN
MIC. OUT
MAIN PROCESS
OUT
EXTERNAL SIGNAL
AND
DATA INPUTS
SEE INSET 2
SEE INSET 1
C11
C13
C14
R8
R7
R9
R10
R11
R6
C12
R5
R12
R13
C8
C10
C9
MIC. OUT
C5
R4
C4
+
-
C2
R2
C1
R1
MIC. IN (+)
MIC. IN (-)
R3
C3
MX806AJ
MX806AJ
10
11
13
INSET 2
INSET 1
1
2
XTAL
XTAL/CLOCK
X1
C7
C6
Figure 2: Recommended External Components
Component Notes Value Tolerance Component Notes Value Tolerance
R1
10k
±10% C2
.47F
±20%
R2
10k
±10% C3 270pF ±20%
R3
20k
±10% C4 270pF ±20%
R4
20k
±10% C5
0.1F
±20%
R5
10k
±10% C6 33pF ±20%
R6
2.2M
±10% C7 5-65pF ±20%
R7
100k
±10% C8
1.0F
±20%
R8
100k
±10% C9
1.0F
±20%
R9
100k
±10% C10
1.0F
±20%
R10
100k
±10% C11 22pF ±20%
R11
100k
±10% C12
0.1F
±20%
R12
2.2M
±10% C13
0.01F
±20%
R13
470k
±10% C14
0.01F
±20%
C1
.47F
±20% X1 4.00MHz
Table 2: Recommended External Components

Audio Processor 7 MX806A
1998 MX-COM, Inc. www.mxcom.com Tel: 800 638 5577 336 744 5050 Fax: 336 744 5054 Doc. # 20480064.006
4800 Bethania Station Road, Winston-Salem, NC 27105-1201 USA All trademarks and service marks are held by their respective companies.
Recommended External Component Notes:
1. Input Op-Amp gain/attenuation components (voltage gain = 6.0dB) are shown in Inset 1 is a differential
configuration to demonstrate the versatility of this input. Components for a single (+ or -) input may be
used.
2. Resistor values R7 to R11 (summation components) are dependent upon application and configuration
requirements.
3. Xtal circuit capacitors C6 (CD) and C7 (CG) shown in Inset 2 are recommended in accordance with MXCOM’s Crystal Oscillator Application Note. Circuit drive and drain resistors are incorporated on-chip.
Operation of any MX-COM IC without a Xtal clock input may cause device damage. To minimize damage
in the event of a Xtal/drive failure, you should install a current limiting device (resistor or fast-reaction
fuse) on the power-input (V
DD
).
4 General Description
The MX806A LMR audio processor is intended too primarily to operate as the “Audio Terminal” or radio
systems using the DBS800 Digitally Integrated Baseband Subsystem.
The MX806A half-duplex device has signal paths and level setting elements that are configured and adjusted
by digital information sent from the radio microcontroller using C-BUS protocol. (C-BUS is the serial interface
for all DBS 800 ICs.)
4.1 Signal Path
The Signal path is divided into three sections:
Input Process:
This stage has selectable TX/RX paths. Transmits voice signals pass through microphone
pre-amplifier, voltage controlled gain (VOGAD) and highpass filter stages. Received audio is de-emphasized.
This initial audio, after line-in gain adjustment, may be switched to external audio processes (such as
scrambling) or to the internal Main Process stages.
Main Process
: Conditioning for the input or external process signals is completed in this stage. It is
comprised of pre-emphasis, high and lowpass switched capacitor filters and a deviation limiter.
Mixing and Output Drives
: Main audio for transmission is mix with signaling and data from external sources
(other DBS 800 ICs) to provide the composite signal for the digitally adjustable transmitter modulation drives.
Received audio level is adjusted for output to loudspeaker circuitry.
If selected, signal level stability and output accuracy of the MX806A is maintained by a voltage-controlled gain
system using selectable signal-level detectors. Signal levels can be dynamically controlled to provide
“dynamic compensation” for factors such as temperature drift, VCO non-linearity, etc.
The MX806A audio stages can be completely disabled – or the whole IC can be placed into powersave mode,
leaving only clock and C-BUS circuitry active.
4.2 VOGAD
The overall Gain Control system of the MX806A consists of 2 selectable signal peak detectors whose output
is fed via external integrating components to adjust the gain of the Voltage Controlled Amplifier positioned in
the TX Input Process Path. The transmit input signals is presented to Peak Detector 1 or 2. The Peak
Detectors are enabled individually by a Mode Command. When the input signal exceeds the peak - to - peak
threshold of the detector, a 5-volt level is produced at the VOGAD Out pin. This level remains for as long as
the signal exceeds the threshold. The integrated level to the VOGAD In pin causes the Voltage Controlled
Amplifier gain to be reduced. As can be seen from Figure 3 and Figure 5, Peak Detector 1 allows control of
the audio level to the external audio process and Peak Detector 2 allows control of transmit deviation levels.
 Loading...
Loading...