Page 1

Scanner
USER GUIDE
Appendices
The TWAIN Dialog Box
Page 2

2
Copyright Information
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form by any means, mechanical, optical, electronic, recording, or otherwise, without our written permission.
We reserve the right to revise this manual and to make changes to any
or all parts at any time, without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions and changes.
All other brand or product names mentioned in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
FCC Statement
This digital equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if it is not installed and used according to the instruction manual, it may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur
in a particular installation. If this equipment causes harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off or on, you are encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient the receiving antenna
• Increase the distance between the equipment and the receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
NOTE:
1. The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate
the equipment.
2. Shielded interface cables and AC power cord, if any, must be used
in order to comply with the emission limits.
Page 3
3
The TWAIN Dialog Box ............................................. 4
To Acquire the TWAIN Dialog Box ...................... 5
Performing a Simple Scan ...................................... 6
(1) Place the Document/Image ......................... 6
(2) Preview the Image ....................................... 6
(3) Select the Scan Size .................................... 7
(4) Set the Scan Mode ..................................... 7
(5) Set the Resolution ...................................... 7
(6) Execute the Scan ......................................... 7
The TWAIN Dialog Box (Details)..............................8
The Preview Window and Buttons........................ 9
The Image Setting Buttons.................................. 10
Scan Settings ....................................................... 11
The Main Tab ................................................ 11
The Enhance Tab ........................................... 14
The Filters Tab ............................................... 18
About Tab ..................................................... 19
Using Batch Scan ................................................ 20
Batch Scan Controls ...................................... 20
To Perform a Batch Scan ................................ 21
Appendices
A: Scanning Tips................................................. 22
B: Troubleshooting ............................................. 23
Table of Contents
Page 4
4
The TWAIN Dialog Box
The TWAIN dialog box is a scanning option provided
with your scanner. TWAIN is an industry standard that
allows scanning directly into any TWAIN-compliant
software. It eliminates most compatibility problems
associated with software and input devices supplied by
different vendors.
You can access the TWAIN dialog box from within most
image editing software such as the application software
bundled with the scanner (e.g., PhotoShop®).
Page 5

5
To Acquire the TWAIN Dialog Box
You can acquire the TWAIN dialog box from within any
TWAIN-compliant software (i.e., Photo Express™). To
acquire the TWAIN dialog box, using Photo Express™ as an
example, the steps are:
1. Launch Windows®.
2. Launch Photo Express™ (TWAIN-compliant program).
3. Under the File menu, open the Acquire command and
choose Scanner. The Select Data Source dialog box
appears.
4. Choose your scanner model from the list.
5. Click the Acquire button. The Select Data Source dialog
box closes. The TWAIN Dialog box appears.
To acquire the TWAIN dialog box in other TWAINcompliant image editing software, please refer to the Online Help System, Software Reference.
Page 6
6
Performing a Simple Scan
You’re using this scanner for the first time. We suggest you
to test drive it by scanning the whole area. To scan the whole
area, please take the following steps:
(1) Place the image or document to be scanned.
(2) Click Preview to see the image in the Preview Window.
(3) Select the scan size.
(4) Select the desired scan mode.
(5) Select the desired resolution.
(6) Click the Scan button.
(1) Place the Document/Image
To scan a document, place your original face down on the
scanner’s glass plate and then please follow these steps:
a. Lift the document cover.
b. Place the document face down on the glass.
c. Slowly lower the document cover, making sure the
document remains in place.
NOTE: Remove the document after scanning is complete
(2) Preview the Image
A Preview is a quick scan of the original. From this
rough scan you can learn how the image will look like
after it is scanned.
Page 7

7
(6) Execute the Scan
The scan button is used once you have
completed the preview, determined the
scan regio and selected the final scan
settings to be used for the scan.
Congratulations! You’ve scanned your first image. In
the following sections. We’ll show you how to modify
settings so this scanner meets your needs better.
(3) Select the Scan Size
From the list of available paper sizes, select the size of
the document you wish to scan. If you want to scan the
whole area, select A4. Custom will automatically be
selected when you use the Crop Frame to change the
image area to be scanned.
(4) Set the Scan Mode
The Scan Mode determines how the
scanner will view the image. Select
Color to capture images in color. Select
Gray to capture images in shades of
gray. When you wish to scan line art or
text for OCR (Optical Character
Recognition), select Line Art.
(5) Set the Resolution
The Resolution, which is measured in dots per inch (dpi),
determines the effect of the image as it is displayed or
printed. Images scanned at a high resolution capture more
information. However, high-resolution images require
more memory.
See Scan Tips on Appendix A.
Page 8

8
The TWAIN Dialog Box (Details)
The TWAIN dialog box consists of two
sections- the left section where most of the
TWAIN control settings are found and the
right section, which is the Preview window.
For more detailed or additional
information regarding the features and
functions of your scanner software,
please refer to the on-line help system
by clicking on the Help icon.
Cropping Tool
Cropping Tool
Allows you to selectively
scan a portion..
Zoom
Magnifies or shrinks
the image in the
Preview Window.
Batch Scan
Allows up to 10 scan
regions for multiple
scanning.
Preview Window
Exit
Exits the program.
Language Box
Selects the language.
Help
Preview Button
Scan Button
Scan
Settings
Page 9

9
• Preview
Preview (a quick low-resolution scan of the
entire original image) the image in order
to get a clearer idea of the image area you
want to include in your final scan. To preview, the
steps are:
1. Place the document face down on the scan window
glass;
2. Click on the Preview button. After the scanner has
scanned the document, the scanned image will appear
in the Preview Window.
• Cropping Tool
You can select an area, if you don’t want to scan the
whole document. This is optional.
• Zoom Tools
The Zoom In tool increases the magnification (multiple
levels) of the image area. In magnified view, you can
drag the Crop Frame to the exact area you want to
scan. Use the Zoom Out tool to shrink the image.
The Preview Window & Buttons
The Preview window is where the preview image appears.
It is recommended that you preview each document/image
before scanning. Using the preview image, you can specify
the final image area to be included in the scan and/or apply
the enhance and filters features.
Page 10

10
• Batch Scan Button
Clicking this button allows you to create multiple scan
areas using different scan settings on the image shown
in the Preview Window. For more details, please refer
to the topic Using Batch Scan.
• Scan
After determining the exact image area you wish
to scan and selecting your desired scan settings,
click the Scan button to perform the scan. When
scanning is complete, the image will be displayed on
the main screen of the host software behind the TWAIN
dialog box.
• Help
Provides on-line help for the scanner and software
functions.
• Language Icon
Selects the language you would like to view the
TWAIN interface in.
• Exit Icon
Exits the program.
The Image Setting Buttons
The Image Setting buttons allow you to create your own
convenient scan settings. Saving image settings allows you
to use the same settings again and again without resetting the
image options.
• Load Button
Stores selected settings.
• Save Button
Savesthe actual image settings in a folder.
• Previous Button
Reloads the last saved image settings.
• Reset Button
Returns the image settings to their default values.
• Information Button
Displays all the current control settings of the TWAIN
dialog box.
Page 11

11
Scan Settings
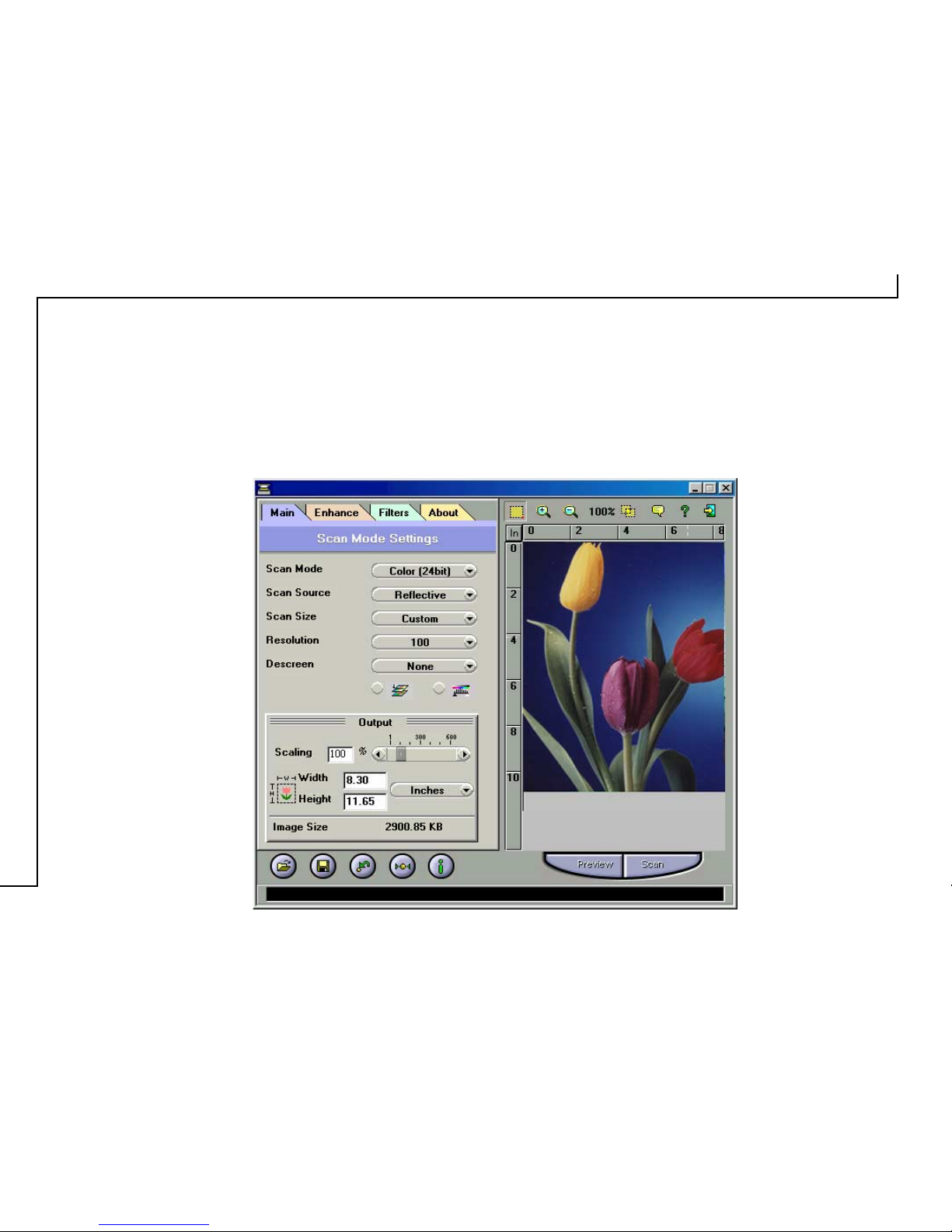
The Main Tab
The Main tab allows you to control the scanning
parameters, such as scan mode, scan source, resolution,
etc. These parameters determine how the original image
or document will be scanned.
Scan Mode
The Scan Mode determines how the scanner reads the original image
or document. When choosing a scan mode, it is recommended to
consider what purpose the resulting scanned image will be used for.
•LineArt
Use this mode to scan text documents for use in
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) or when
you wish to scan black-and-white drawings.
• Gray
Select Gray to capture images in shades of gray.
• Color
Select Color to capture images in color.
Page 12

12
Scan Source
The Scan Source setting is used to select the type of
document you will be scanning.
• Reflective
Use Reflective when scanning paperbased documents such as photographs
or text.
With the optional Transparency Adapter, you can also scan
Positive and Negative transparencies.
• Positive
Select Positive when scanning slides or transparencies.
• Negative
Select Negative when scanning film negatives or
similar negative transparencies.
Scan Size
From the list of available sizes, select the size of the
document you wish to scan. Custom will automatically
be selected when you use the Crop Frame to change the
image area to be scanned.
Resolution
The Resolution, which is measured in dots per inch (dpi),
determines the appearance of the image as it is displayed
or printed. Images scanned at a higher resolution capture
more information and therefore require more disk space
for storage. You can select from a wide range of preset
resolutions.
Descreen
A tool for reducing moiré patterns in
scanned images of originals that were
created by a halftone process. Moiré
patterns appear as unpleasant
interference patterns.
• None
Choose None if you want to scan images of
photographic quality.
• Newspaper
Choose Newspaper when the image is made up of
coarse dot patterns commonly found in newspaper
photos.
75 dpi (400%) 300 dpi (400%)
Page 13

13
• Magazine
Choose Magazine when scanning images whose
quality is similar to images found in glossy or waxcoated magazines.
• Art Print
Choose Art Print when scanning images from very
high quality art prints that show only very fine dots.
Color Match
This is an effective tool for ensuring that the colors
captured by the scanner more accurately reflect the actual
colors of the original image. Without color matching,
the scanner captures a wider range of colors but these
colors may not accurately match the true colors of the
original image, making the scan appear different from
the original.
Color Balance
This tool balances the lightest and darkest areas of an
image so that they are evenly distributed.
Output Scaling
Output scaling allows you to enlarge/shrink the size of
the final output image. Adjust the scaling by using the
slide bar or typing the desired setting in the Output Scaling
box. For example, setting the Output Scaling to 200%
will double the amount of pixels contained in the image.
Width and Height
The Width and Height values show the dimensions of the
image area inside the Crop Frame. You can change the
measurement unit to centimeters or inches.
Image Size
Image Size displays the amount of disk space needed to
display or save the image outlined by the Crop Frame.
The Image Size information is automatically updated
anytime you change any of the scan settings or resize the
Crop Frame.
Without Color Balance With Color Balance
Page 14

14
If you wish to see the effects of your changes in the
Preview Window, click on the Preview button.
Channel Selector
Channel refers to the red, green, and blue
colors that make up a color image. You can
choose to change the channels individually
or choose Master to change all channels
equally and simultaneously. An image in
Gray Mode has one channel.
Brightness Control
Using 255 steps, this tool allows you to adjust the overall
amount of light in the image. A value of –127 will make
the image appear very dark, whereas, a value of +127
will make the image appear very bright.
Brightness –50 Brightness 0 Brightness 50
The Enhance Tab
The Enhance tab contains preprocessing controls that
can be applied to the image before making the final scan.
To access the Enhance tab, click Enhance.
The Enhance tab contains two picture thumbnails (Original
and Sample) of the preview image, several control settings,
and a histogram of the image. Alterations made to the
enhance settings appear in the sample thumbnail.
The image that appears in the thumbnails will
automatically be replaced with the Preview image.
Thumbnails
Page 15

15
Contrast Control
Using 255 steps, this tool controls the disparity in tone
between the dark and light areas of an image. Positive values
create greater differences between dark and light areas of the
image, whereas, negative values create greater similarities
between the dark and light areas of the image.
Contrast –50 Contrast 0 Contrast 50
Preview Button
Click the Preview button to see any changes made to the
image. The changes will appear in the Preview window.
Level
You can easily use the level slider to adjust an image’s contrast
and brightness. You can drag the little white triangle to control
the amount of hightlights, and the black triangle to the
shadows, if you haven’t set the two values using the
eyedroppers. The gray triangle in the middle controls the
image’s midtone. After the highlight and shadow values are
determined, use the gray triangle to roughly control an image’s
contrast.
You can control each channel’s levels if you scan in RGB.
Eyedropper tools
Eyedroppers are used to identify an image’s hightlights and
shadows. Click on the darkest area that still contains detail
with the black eyedropper to set the shadow value. Any
darker parts will be regarded as black. And then the lightest
area with the white eyedropper to set the hightlight. This is
the first step to control an image’s overall tonal range.
Eyedroppers
Page 16

16
Curve
If your original is too dark or too light, you lose vital detail
after scanning. You can fix this problem by using curves.
The curve function is applicable to grayscale and 24/48-bit
color images. Simply put, if you knew how to use Adobe®
Photoshop® or any other equivalent softwares’ curve
function, you can safely skip this section.
Applying a curve to an image is to enhance favored
brightness ranges at cost of others, like enhancing the
shadow at cost of the highlight and midtone. If done
properly, you can energize a dull image using curves without
sacrificing the overall image quality. To write a curve, simply
place an anchor on the diagonal line and adjust its position.
Add more anchors if you have to write a more complex curve.
You can also remove anchors.
To emphasize shadow, raise the anchor; to emphasize
highlight, lower the anchor; to emphasize midtone, write an
S-shaped curve; to decrease contrast, write an inverted Scurve.
Experts apply curves to individual channels to color-correct
an image. Usually this is done to a CMYK image to be
printed.
add/remove
anchors
Page 17

17
Hue/Saturation
If you knew HSB colorspace, you can also skip this section.
In plain English, hue roughly means color: red, yellow, green,
blue, purple; and saturation means a color’s purity. When a
maple leaf turns red, it changes hue. If you place a bright blue
cardboard outdoors, its color will fade, it will be less and less
saturated.
The Hue Slider is composed of two color bars. The upper one
is static and the lower one movable. Slide the latter, and
you will see the image shift its overall coloring. This
function mostly affects loud colors, less on mute colors. It
does not change black, whte and gray.
The Saturation Slider lets you to adjust an image’s color
purity. Slide it to the left and the image becomes dull, like a
black and white photo. Slide it to the right and the image
becomes more colorful.
These two functions are disabled when scanning in
grayscale or 48-bit color.
Page 18

18
The Filters Tab
The Filters tab contains special effect controls that allow
you to alter the image before making your final scan. To
access the Filters tab, click Filters.
The Filters tab also contains two thumbnails of the
previewed image. Any filter you choose will immediately
show its effect in the sample thumbnail.
None
No filter is applied if None (default setting) is selected.
Blur
The Blur filter smoothes the image by lightening the pixels
that are in sharp contrast to their neighboring pixels. The
amount of blur applied is controlled with the plus and
minus buttons.
Sharpen
The Sharpen filter enhances the detail in blurry images by
improving the focus and increasing the contrast in the
image. The amount of sharpness applied is controlled with
the plus and minus buttons.
Page 19

19
Invert
The Invert filter transforms an image to its negative by
converting all color values to their opposites: whites
become black, blues become yellow, etc.
Flip
The Flip filter creates a mirror image of the original by
flipping the image horizontally.
Unsharp Mask
The Unsharp Mask filter detects sharp edges and color
boundaries and then emphasizes them.
Emboss
The Emboss filter makes the elements in an image
appear raised or sunken by reducing the color within
the image and tracing its edges with black.
About Tab
The About tab contains the current driver version
number, information about the interface device, and
the copyright notice. To access the About tab, click
About.
Page 20

20
Using Batch Scan
Batch scanning is an easy way to multi-scan any part of your
document using a variety of scan settings (Certain application
programs do not support this function). Using Batch Scan
you can specify up to 10 scan regions or scan a single region
several times using different scan modes, resolutions, filters,
and more.
Batch Scan Controls
Create Batch Scan: allows the user to create a new
batch scan.
Duplicate Batch Scan: duplicates the selected batch
scan settings.
Delete Batch Scan: deletes a batch scan.
Exit Batch Scan: exits the batch scan box.
Batch Ahead/Back: These arrows allow you to
scroll through your batch job list.
The Batch Box contains the thumbnail image, DPI,
scan mode and image size of each batch scan. The
batch number (e.g., 1/3, number 1 out of three) is always
displayed at the top of the batch box along with the
Batch Scan Status.
Page 21

21
NOTE: You can assign different scan sizes (A4, A5 or
custom) to each image separately.
NOTE: Using the Batch Scan arrows allows you to view
different batch jobs.
To Perform a Batch Scan
1. Click on the Batch Scan button. The Batch
Scan dialog box appears.
2. In the TWAIN dialog box, set the desired
scan mode and resolution for the current
scan region.
3. Repeat steps 2 if you wish to create additional scan
regions.
4. Click Scan. The scanner will begin to scan the batch jobs
one after the other.
Page 22

22
Appendices
Space requirements for different scan modes:
Appendix A: Scanning Tips
The following tables provide helpful information you can
use when setting the scan mode and/or resolution.
Recommended scanning resolutions for various output
devices are listed as follows:
Certain newer functions are supported by our bundled software
only. Other scanner-compatible softwares are supported via the
standard software interface (TWAIN). They are compatible with
this scanner, but do not support our latest functions. Fully
compatible softwares are listed below:
SCAN – PhotoShop
®
FAX – only compatible with our provided fax utility software
when you install the software drivers
OCR – FineReader™ OCR
EMAIL – Microsoft® Internet Explorer 4.0, Netscape®
Communicator 4.5, Lotus cc:Mail 8.2 or higher.
Make sure to set up your email client properly. Refer to the
documentation that came with your email client or consult
your system administrator if any problem exists.
Page 23

23
Appendix B: Troubleshooting
NOTES:
• It is not possible to print and scan at the same time.
• Do not disassemble the device to fix problems!
• When not using the scanner for long periods of time,
you should unplug the power adapter from the
wall socket.
1. The computer fails to recognize the scanner.
Check to ensure the scanner is correctly connected to
the computer. Power off your computer and the
scanner, and reconnect them by carefully following
our hardware installation instructions.
2. The scan command is not executed.
The scanner cable may be connected loosely. Check
to ensure the scanner is correctly connected to the
computer.
3. Why do my images look blotchy or blurry?
If your scans are looking bad on screen, but printing
out satisfactorily, it could be your video driver that is
causing the problem. Try changing the resolution and
color settings in the “Display” portion of your
Windows® control panel (after first making sure that
you have the proper driver disks to restore your
system to the original settings). You should be using
a driver that provides 16+million colors, and a resolution
of at least 800 x 600.
4. What resolution should I scan at?
a. You should scan at the resolution of your output device.
b. If you plan to display your scans on a computer monitor
(Internet), which has a resolution of 72DPI, we
recommend scanning at 72 DPI.
c. If your output device is an inkjet printer:
• For color images,
scan at 1/3 the allowable resolution of the printer.
• For Gray Mode or Line Art images,
scan at the full resolution of the printer.
5. The scanned picture is not clear.
We recommend that you keep the scan window glass and
the document cover clean. They should be cleaned on a
regular basis. The cleaning steps are:
a. Turn off the scanner and unplug the power cord.
b. Open the document cover and use a cloth dampened with
alcohol to clean the scan window glass and the cover
separately.
c. Use a lint-free dry cloth to dry the glass and cover.
 Loading...
Loading...