Page 1

RF760/660/600VPN
Internet Security Appliance
User Guide
Page 2

User Guide
RouteFinder RF760/660/600VPN
S000323D Revision D
This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior expressed written permission from Multi-Tech
Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 2005 by Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. makes no representations or warranty with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims
any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Furthermore, Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the content hereof without obligation of
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. to notify any person or organization of such revisions or changes.
The links we have provided in this manual to other company Web sites cannot be not guaranteed. They are active at the
time of publication, but cannot be guaranteed for any extended period of time.
Record of Revisions
Revision Date Description
A 01/30/04 First release for the RF760VPN. The guide combines the RF600VPN and the
RF660VPN user information.
B 11/01/04 & New software – version 3.20 and
01/25/05 New software – version 3.21. POP3 Proxy new. New Rescue Kernel section.
C 04/19/05 New software – Version 3.23 (one new field on the SMTP SPAM screen and one new
field on the Packet Filters > Advanced screen).
D 11/22/05 New software – Version 3.25. A System Scheduler was added to Administration. A User
Authentication section was added to the Proxy > HTTP Proxy screen. A Remote SMTP
Virus Quarantine section was added to Proxy > SMTP Proxy. Maximum Mail Size
Allowed and Message Filtering added to Proxy >SMTP Proxy > SMTP SPAM Filtering.
Remote POP3 Virus Protection section was added to Proxy > POP3 Proxy. A Message
Filtering section was added to Proxy > POP3 Proxy > POP3SPAM Filtering. Adaptive
Message Database Backup was added to the Tracking > Backup screen. The screen
for Statistics & Logs > HTTP Access has been enhanced.
Hardware change: new compact flash.
Patents
This device is covered by one or more of the following U.S. Patent Numbers: 6,219,708; 5,301,274; 5,309,562; 5,355,365;
5,355,653; 5,452,289; 5,453.986.
The modem is covered by one or more of the following U.S. Patent Numbers: 6,031,867; 6,012,113; 6,009,082; 5,905,794;
5,864,560; 5,815,567; 5,815,503; 5,812,534; 5,809,068; 5,790,532; 5,764,628; 5,764,627; 5,754,589; D394,250; 5,724,356;
5,673,268; 5,673,257; 5,644,594; 5,628,030; 5,619,508; 5,617,423; 5,600,649; 5,592,586; 5,577,041; 5,574,725; D374,222;
5,559,793; 5,546,448; 5,546,395; 5,535,204; 5,500,859; 5,471,470; 5,463,616; 5,453,986; 5,452,289; 5,450,425; D361,764;
D355,658; D355,653; D353,598; D353,144; 5,355,365; 5,309,562; 5,301,274 Other Patents Pending
Trademarks
Trademarks of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.: Multi-Tech, the Multi-Tech logo, and RouteFinder.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries.
Kaspersky Anti-Virus engine copyright by Kaspersky Labs. Surfcontrol is the registered product of Surfcontrol PLC.
All products or technologies are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Technical Support
Country By Email By Phone
France: support@multitech.fr (33) 1-64 61 09 81
India: support@multitechindia.com 91 (124) 6340778
U.K.: support@multitech.co.uk (44) 118 959 7774
U.S. and Canada: support@multitech.com (800) 972-2439
Rest of the World: support@multitech.com (763) 717-5863
World Headquarters
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View, Minnesota 55112
(763) 785-3500 or (800) 328-9717
Fax 763-785-9874
Internet Address: http://www.multitech.com
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Contents
Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview............................................................................... 7
Product Description ........................................................................................................................................................... 7
Features ............................................................................................................................................................................ 7
Feature Highlights.............................................................................................................................................................. 8
Ship Kit Contents............................................................................................................................................................... 9
License Keys ................................................................................................................................................................... 10
Additional RouteFinder Documentation ........................................................................................................................... 10
Safety Warnings .............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Safety Recommendations for Rack Installations ............................................................................................................. 11
RouteFinder Front Panels................................................................................................................................................ 12
RF760/660VPN Front Panel ...................................................................................................................................12
RF600VPN .............................................................................................................................................................13
RouteFinder Back Panels ................................................................................................................................................ 14
RF760VPN Back Panel ..........................................................................................................................................14
RF660VPN Back Panel ..........................................................................................................................................14
RF600VPN Back Panel ..........................................................................................................................................14
Specifications .................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Overview of RouteFinder VPN Technology ..................................................................................................................... 17
Networks.................................................................................................................................................................17
The Firewall ............................................................................................................................................................17
Network Components That Work with the Firewall .................................................................................................17
Typical Applications ......................................................................................................................................................... 20
Chapter 2 – Installation....................................................................................................................................... 21
Pre-Installation Planning.................................................................................................................................................. 21
Planning and Establishing the Corporate Security Policy .......................................................................................21
Planning the Network..............................................................................................................................................22
Establishing an Address Table ...............................................................................................................................22
System Administrator Required Planning ........................................................................................................................ 22
Installation Overview........................................................................................................................................................ 23
Hardware Installation Procedure.............................................................................................................................23
Cabling Overview....................................................................................................................................................23
Setting up a Workstation and Starting the RouteFinder VPN .......................................................................................... 24
Navigating Through the Screens ..................................................................................................................................... 26
Menus and Sub-Menus...........................................................................................................................................27
Chapter 3 – Configuration .................................................................................................................................. 28
Initial Configuration Step.................................................................................................................................................. 28
Second Configuration Step.............................................................................................................................................. 29
The Wizard Setup Screen................................................................................................................................................ 30
Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples ................................................................................................................ 31
Example 1 – LAN-to-LAN VPN (Branch Office) ............................................................................................................... 31
Example 2 – Remote Client-to-LAN VPN Configuration .................................................................................................. 36
Example 3 – Remote Client-to-LAN Configuration Using DNAT and Aliasing ................................................................. 37
Example 4 – Client-to-LAN Configuration Using PPTP Tunneling ................................................................................... 38
Chapter 5 – URL Categorization ........................................................................................................................ 39
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 3
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software .................................................................................................................... 42
Menu Bar ......................................................................................................................................................................... 42
Administration.................................................................................................................................................................. 43
Administration > System Setup...............................................................................................................................43
Adminstration > SSH ..............................................................................................................................................45
Administration > SNTP Client ................................................................................................................................46
Administration > Administrative Access..................................................................................................................47
Administration > Site Certificate..............................................................................................................................49
Administration > License Key .................................................................................................................................50
Administration > Intrusion Detection .......................................................................................................................51
Administration > Tools ............................................................................................................................................52
Administration > System Scheduler........................................................................................................................54
Administration > Factory Defaults...........................................................................................................................54
Administration > User Authentication > Local Users...............................................................................................55
Administration > User Authentication > RADIUS & SAM ........................................................................................56
Administration > Restart .........................................................................................................................................58
Administration > Shutdown .....................................................................................................................................58
Networks & Services........................................................................................................................................................ 59
Networks & Services > Networks............................................................................................................................59
Networks & Services > Services.............................................................................................................................61
Networks & Services > Network Groups.................................................................................................................63
Networks & Services > Service Groups..................................................................................................................64
Proxy ............................................................................................................................................................................... 65
General Information About Proxies.........................................................................................................................65
Proxy > HTTP Proxy...............................................................................................................................................66
Proxy > HTTP Proxy > Custom Filters..................................................................................................................69
Proxy > SMTP Proxy ..............................................................................................................................................71
Proxy > SMTP Proxy > SMTP SPAM Filtering .......................................................................................................74
Proxy > POP3 Proxy...............................................................................................................................................77
Proxy > POP3 Proxy > POP3 SPAM Filtering ........................................................................................................78
Proxy > SOCKS Proxy............................................................................................................................................80
Proxy > DNS Proxy.................................................................................................................................................82
Network Setup ................................................................................................................................................................. 83
Network Setup > Interface ......................................................................................................................................84
Network Setup > PPP.............................................................................................................................................86
Change Your Country/Region Code .......................................................................................................................86
Network Setup > PPPoE ........................................................................................................................................87
Network Setup > DHCP Client................................................................................................................................88
Network Setup > Dynamic DNS..............................................................................................................................89
Network Setup > Routes.........................................................................................................................................90
Network Setup > Masquerading .............................................................................................................................91
Network Setup > SNAT ..........................................................................................................................................92
Network Setup > DNAT ..........................................................................................................................................93
DHCP Server................................................................................................................................................................... 94
DHCP Server > Subnet Settings.............................................................................................................................94
DHCP Server > Fixed Addresses ...........................................................................................................................94
Tracking........................................................................................................................................................................... 95
Tracking > Accounting ............................................................................................................................................95
Tracking > Update Services....................................................................................................................................96
Tracking > Backup..................................................................................................................................................98
Tracking > Version Control ...................................................................................................................................100
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Packet Filters................................................................................................................................................................. 101
Packet Filters > Packet Filter Rules......................................................................................................................101
Packet Filters > ICMP...........................................................................................................................................103
Packet Filters > Advanced....................................................................................................................................104
Packet Filters > Enable/Disable Log.....................................................................................................................105
VPN (Virtual Private Networks)...................................................................................................................................... 106
VPN > IPSec.........................................................................................................................................................106
Introduction to Virtual Private Networks................................................................................................................106
VPN > x.509 Certificates.......................................................................................................................................111
VPN > IPSec Bridging ..........................................................................................................................................111
VPN > PPTP.........................................................................................................................................................112
Wizard Setup ................................................................................................................................................................. 114
Statistics & Logs ............................................................................................................................................................ 116
Statistics & Logs > Uptime....................................................................................................................................117
Statistics and Logs > Hardware ............................................................................................................................117
Statistics and Logs > Networks.............................................................................................................................118
Statistics & Logs > Interfaces ...............................................................................................................................120
Statistics & Logs > SMTP Proxy...........................................................................................................................121
Statistics & Logs > Accounting .............................................................................................................................122
Statistics & Logs > Self Monitor ............................................................................................................................123
Statistics & Logs > IPSec......................................................................................................................................124
Statistics & Logs > PPTP......................................................................................................................................124
Statistics & Logs > Packet Filter ...........................................................................................................................125
Statistics & Logs > Port Scans..............................................................................................................................126
Statistics & Logs > View Logs...............................................................................................................................126
Statistics & Logs > HTTP Access .........................................................................................................................127
Statistics & Logs > DHCP.....................................................................................................................................128
Statistics & Logs > SMTP & POP3 Virus Quarantines..........................................................................................129
Statistics & Logs > SMTP SPAM Quarantines......................................................................................................129
Statistics & Logs > Administrative Authentication Log ..........................................................................................129
Chapter 7 – User Authentication Methods...................................................................................................... 130
Proxy Services and Authentication Methods ........................................................................................................130
Which Method Should You Choose? ....................................................................................................................130
Authentication Setup...................................................................................................................................................... 131
Setting Up RADIUS Authentication.......................................................................................................................131
Setting Up A Microsoft IAS RADIUS Server .........................................................................................................131
Setting Up NT/2000 SAM (SMB) Authentication...................................................................................................132
Chapter 8 – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs).......................................................................................... 133
Chapter 9 – Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................................... 139
Appendix A – Disposition of Events for the RouteFinder v3.2x................................................................... 141
1. Abstract ..................................................................................................................................................................... 142
II. Inbound Access Log .................................................................................................................................................. 143
III. Outbound Access Log .............................................................................................................................................. 145
IV. Access Requests through Firewall Dropped ............................................................................................................ 146
V. Access Requests to Firewall Dropped....................................................................................................................... 146
VI. Administrative Authentication Logs .......................................................................................................................... 147
VII. Admin Port Access Log ........................................................................................................................................... 147
VIII. Startup History Log................................................................................................................................................. 147
IX. User Log................................................................................................................................................................... 147
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 5
Page 6

Table of Contents
X. Fragmented Dropped Log ......................................................................................................................................... 147
XI. ICMP Information ..................................................................................................................................................... 148
Appendix B – The RouteFinder Rescue Kernel.............................................................................................. 149
Method 1 – How to Perform the Install Using No External Server ................................................................................. 150
Method 2 – How to Perform the Install Using an External FTP Server .......................................................................... 151
Method 3 – How to Perform the Install If the Other Methods Fail or If the File Systems Are Corrupted ........................ 152
Appendix C – Board Components, Hardware Upgrades & Add-ons, Software Add-ons, Overnight
Replacement ...................................................................................................................................................... 153
Board Components........................................................................................................................................................ 153
Hardware Upgrades and Add-ons ................................................................................................................................. 154
Software Add-ons .......................................................................................................................................................... 156
Overnight Replacement Service .................................................................................................................................... 156
Appendix D – CD-ROM Drive Adapter and Pin Out ....................................................................................... 157
CD-ROM Drive Adapter Pin Out ...........................................................................................................................157
Appendix E – RouteFinder Maintenance ........................................................................................................158
Appendix F – Ordering Accessories ............................................................................................................... 160
SupplyNet Online Ordering Instructions................................................................................................................160
Appendix G – Technical Support..................................................................................................................... 161
Technical Support Contacts........................................................................................................................................... 161
Recording RouteFinder Information............................................................................................................................... 161
Appendix H – Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. Warranty and Repairs Policies .....................................................162
Appendix I – Regulatory Compliance.............................................................................................................. 164
Appendix J – License Agreements.................................................................................................................. 166
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. End User License Agreement (EULA) ..........................................................................166
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE .....................................................................................................................168
SurfControl URL Filtering End-User Terms ..........................................................................................................170
Kaspersky Standard End User License Agreement..............................................................................................173
Appendix K – Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE)............................................. 175
Glossary ............................................................................................................................................................. 176
Index ................................................................................................................................................................... 186
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 6
Page 7

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Chapter 1 – Product Description,
Features, and Overview
Your Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinder Internet security appliance is an integrated VPN gateway/firewall designed to
maximize network security without compromising network performance. It uses data encryption, user authentication, and the
Internet to securely connect telecommuters, remote offices, customers, and suppliers to the corporate office while avoiding
the cost of private leased lines or dial-up charges.
Product Description
All three RouteFinder models provide advanced network firewall (Stateful Packet Inspection and NAT), application firewall
(DMZ, proxies, filter, optional email anti-virus protection), VPN gateway (IPSec, PPTP, 3DES, authentication), and full router
capabilities. Their Ethernet ports provide connectivity to your network, to the Internet access via router, DSL, cable or
dedicated line, and to the DMZ.
The RouteFinder’s DMZ port permits connecting of Voice over IP gateways, like MultiVOIPs, and public servers such as
email and Web to be safely connected. And its full-featured router hardware allows the entire network to share an Internet
link by connecting to an existing cable modem, DSL modem, or router.
An optional email anti-virus update product offered by Multi-Tech with your RouteFinder purchase includes protection against
new virus types and security gaps with automatically transferred updates.
The browser-based interface eases VPN configuration and management. The VPN functionality is based on the IPSec and
PPTP protocols and uses Triple DES 168-bit encryption to ensure that your information remains private. In addition, the
RF760/660VPN includes firewall security utilizing Stateful Packet Inspection and optional email anti-virus protection.
The RouteFinder VPNs can be used on the desktop or mounted in racks.
Features
• Supports IPSec and PPTP VPN tunneling
• Utilizes 168-bit Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES)
• Built-in Stateful Packet Inspection firewall with Network Address Translation (NAT)
• Encapsulating Security Protocol (ESP)
• Authentication Header (AH)
• Internet Key Exchange (IKE), with support of Diffie-Hellman Group 2
• Authentication Algorithm: HMAC-MD5 and HMAC-SHA1
• Authentication using shared secrets, RSA digital signatures, and X.509 certificates
• Perfect Forward Secrecy
• Key exchanges using Internet PKIs (Public Key Infrastructure)
• Free one-year content filtering subscription
• Automatic dial-backup with built-in modem (RF760VPN and RF660VPN)
• Automatic system updates to protect your network against the latest threats
• Application layer security using SMTP, POP3, HTTP, DNS and SOCKS proxies
• Secure local or remote management using HTTP, HTTPS or SSH
• Reporting function provides valuable troubleshooting information
• Three built-in 10/100 Ethernet ports (LAN, WAN, DMZ) for the RF600VPN and the RF660VPN.
Three built-in 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports (LAN, WAN, DMZ) for the RF760VPN
• Shared broadband or dedicated Internet access for LAN users with one IP address
• Internet access Control Tools provide client and site filtering and traffic monitoring and reporting
• IP address mapping/port forwarding and DMZ port
• Two-year warranty
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 7
Page 8

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Feature Highlights
RouteFinder Applications. The RouteFinder combines Virtual Private Networking (VPN), firewall, e-mail anti-virus
protection, and content filtering in one box. It is a cost-effective, easy to manage solution that is ideal for the small to medium
business looking to add one or all of the following applications to their network:
Remote User VPN. The client-to-LAN VPN application replaces traditional dial-in remote access by allowing a remote user
to connect to the corporate LAN through a secure tunnel over the Internet. The advantage is that a remote user can make a
local call to an Internet Service Provider, without sacrificing the company’s security, as opposed to a long distance call to the
corporate remote access server.
Branch Office VPN. The LAN-to-LAN VPN application sends network traffic over the branch office Internet connection
instead of relying on dedicated leased line connections. This can save thousands of dollars in line costs and reduce overall
hardware and management expenses.
Firewall Security. As businesses move toward always-on broadband Internet connections, the network becomes more
vulnerable to Internet hackers. The RouteFinder provides a full-featured Stateful Packet Inspection firewall to provide
security from intruders attempting to access the office LAN.
Email Anti-Virus Protection. An optional email virus protection subscription ensures the network is protected against the
latest virus outbreaks.
Content Filtering. A free, one-year URL content filtering subscription allows you to automatically manage what Web content
is available.
Plug-and-Play Security Appliance. The RouteFinder plugs in at the Internet connection of each office. It provides three
independent network interfaces (LAN, WAN and DMZ) that separate the protected office network from the Internet while
offering an optional public network for hosting Web, e-mail, or ftp servers. Each network interface is independently monitored
and visually displayed on the front of the RouteFinder.
Secure VPN Connections. The RouteFinder uses IPSec and PPTP industry standard protocols, data encryption, user
authentication, and the Internet to provide high-performance, secure VPN connections. For LAN-to-LAN connectivity, the
RouteFinder utilizes the IPSec protocol with strong 168-bit 3DES encryption using IKE and PSK key management. In
addition, it provides very high performance with 15M bps (RF660VPN) of 3DES encryption throughput. The RF600VPN = 3M
bps and the RF760VPN = 50M bps. For client-to-LAN connectivity, Multi-Tech provides optional IPSec client software. The
RouteFinder also supports remote users that want to use the PPTP VPN client built into the Windows operating system. This
provides 40-bit or 128-bit encryption, user name and password authentication.
State-of-the-Art Firewall Security. The RouteFinder provides network layer security utilizing Stateful Packet Inspection, the
sophisticated firewall technology found in large enterprise firewalls, to protect the network against intruders and Denial of
Service (DoS) attacks. It also uses Network Address Translation (NAT) to hide internal, non-routable IP addresses and
allows internal hosts with unregistered IP addresses to function as Internet-reachable servers. In addition to network layer
security, it provides application level security using SMTP, HTTP, DNS, and SOCKS proxies. The RouteFinder also utilizes
filters to block specific Internet content to protect against viruses, dangerous ActiveX controls, Java, Javascript, and Cookies.
An automatic update feature provides the highest level of security by automatically downloading and installing the latest
system software and security patches protecting against any newly discovered hacker attacks with a single click.
Content Filtering. The RouteFinder includes a one-year URL content filtering subscription. It utilizes SurfControl® content
categorization list, the world's largest database of Internet content, which includes 5 million Web sites covering over 900
million Web pages. Daily updates of categorized sites are available for download. In addition, it includes URL Access and
Deny Reporting. The subscription can easily be renewed on an annual basis.
Automatic Dial Backup. The RouteFinder provides a serial port that, when connected to a dial-up modem or ISDN terminal
adapter, can serve as a backup resource for Internet access and VPN tunneling if your cable or DSL service goes down. In
addition to the serial port, the RouteFinder RF660VPN and RF760VPN models include a built-in modem.
Optional VPN Client Software. Multi-Tech provides an easy-to-use IPSec VPN client software that transparently secures
Internet communications anytime, anywhere. VPN client software is ideal for business users who travel frequently or work
from home. It provides secure remote access through the RouteFinder VPN gateway for applications such as remote
access, file transfer, e-mail, Web browsing, messaging or IP telephony. Encryption and authentication operations are
completely transparent to the end user. In general, IPSec provides stronger encryption than PPTP resulting in better overall
security.
Comprehensive Service and Support. The Multi-Tech commitment to service means we provide a two-year product
warranty and service that includes telephone technical support, 24-hour web site and FTP support.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 8
Page 9

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
E-mail Anti-Virus Protection. Computer viruses are one of the leading security threats to Internet-connected networks.
Users can unknowingly download and launch dangerous viruses that can damage data or cause computer crashes. Viruses
can also be used as delivery mechanisms for hacking tools, compromising the security of the network, even if a firewall is
installed. An optional e-mail virus protection subscription utilizes a high-performance, ICSA-tested, anti-virus engine which
checks both incoming and outgoing e-mail for viruses in real-time. Automatic anti-virus updates are downloaded at userdefined intervals to ensure protection is current. The e-mail anti-virus protection can be easily renewed on an annual basis.
Ask about our free 30-day evaluation.
User Authentication. To increase the level of security, user identity can be verified before access to Internet services is
permitted. The RouteFinder supports authentication at a local user database as well as at external user databases, like
Windows 2000 or Radius server.
Robust, Easy-to-Use Management. The RouteFinder includes robust management support allowing a network
administrator to securely manage the devices either through a web browser or at the command line. The browser-based
option uses the HTTP or HTTPS protocol, also known as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to provide 128-bit encryption to
secure the management session. The command line interface is accessible via SSH (Secure Shell) and supports SCP
(Secure Copy).
Reporting. The RouteFinder also includes a suite of integrated monitoring and reporting tools that help administrators
troubleshoot the Internet security system and report to management the usage of the Internet. This includes reporting on
system uptime, hardware, and network utilization. HTTP and SMTP proxy reports provide information about any actions
needed to handle virus-infected e-mails. The RouteFinder also disables and logs attempted port scans. In addition, it
provides accounting reports and a self-monitor that sends an e-mail notification of system-level issues.
Ship Kit Contents
The RouteFinder VPN is shipped with the following:
• One Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinder VPN
• One Power Cord
• One printed Quick Start Guide
• One external power supply for the RF600VPN
Note: The power supply for the RF660VPN and RF760VPN is internal
• Two Rack Mounting Brackets and four mounting screws
• One RouteFinder VPN documentation CD which contains documentation, license agreements, Adobe Acrobat
Reader, and License keys
• One RouteFinder VPN Software Recovery CD
Note
If any of these items are missing, contact Multi-Tech Systems or your dealer or distributor. Inspect the contents for signs of
any shipping damage. If damage is observed, do not power up the RouteFinder VPN; contact Technical Support at MultiTech Systems, Inc. for advice.
Software Recovery CD Warning
Do not use the Software Recovery CD for any purpose except for re-installing software onto the RouteFinder VPN hard
drive.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 9
Page 10

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
License Keys
System License Key
Each RouteFinder VPN ships with a unique individual system License Key, a 20-digit alphanumeric number.
You can enter and view License Key information from the RouteFinder's Web Management software at Administration
> License Key > Open System License Key. This screen shows the entered License Key number and indicates
whether it is a valid License Key number.
The License Key number is tied to and tracked with your RouteFinder's serial number. Whenever you require additional
licenses, you must first provide Multi-Tech with your current License Key and serial number information in order for us to
update your RouteFinder. With a valid License Key, you are entitled to use Multi-Tech’s Update service and support.
What to Do if a Trial License Key Expires
If the license key is a trial key, after expiry of the license period, the WAN interface of the RouteFinder will shut down. If
the DHCP client or PPPoE is enabled, they will be disabled. The user can connect to the RouteFinder through the LAN
interface and enter another valid license key to proceed further. The user has to manually enable the DHCP client /
PPPoE after entering another valid license key.
URL Categorization License Key
An 11-digit numeric key Universal Resource Locator (URL) Categorization License Key is also shipped with your
RouteFinder. This Key allows you to set up a URL database that limits clients’ access to places on the Internet by
blocking sites you do not want accessed. In other words, you can deny users access to various categories of Web sites
you select.
AntiVirus License Key
AntiVirus software with its corresponding License Key is available as a special purchase from Multi-Tech.
Where to Find the License Key Number Label
License Key numbers are printed on labels and are located:
• On the bottom of the RouteFinder chassis
• On the hard drive inside the chassis
• On the front cover of the Quick Start Guide.
Additional RouteFinder Documentation
These additional RouteFinder reference documents are included on the system CD and are also posted on the Multi-Tech
Web site.
1. The RouteFinder configured with DNAT and aliases.
2. Setting up a PPTP server and a PPTP remote client.
3. The VPN tunnel configured for manual mode example and IPSec pass-through in manual mode example.
4. A quick start guide for the add-on product IPSec SSH client.
5. Hard-Disk Drive Recovery.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 10
Page 11

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Safety Warnings
Lithium Battery Caution
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. A lithium battery on the RouteFinder VPN PC board provides
backup power for the time-keeping capability. The battery has an estimated life expectancy of ten years. When it starts
to weaken, the date and time may be incorrect. If the battery fails, send the board back to Multi-Tech for battery
replacement.
Ethernet Ports Caution
The Ethernet ports are not designed to be connected to a Public Telecommunication Network.
Software Recovery CD Warning
Do not use the Software Recovery CD for any purpose except for re-installing software onto the RouteFinder VPN hard
drive.
Telecom Warnings for Modem
• Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
• Never install telephone jacks in a wet location unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations.
• This product is to be used with UL and cUL listed computers.
• Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at the
network interface.
• Avoid using a telephone during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk of electrical shock from
lightening.
• Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
• To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger Telecommunications line cord.
Safety Recommendations for Rack Installations
Ensure proper installation of the ROUTEFINDER in a closed or multi-unit enclosure by following the recommended
installation as defined by the enclosure manufacturer. Do not place the ROUTEFINDER directly on top of other equipment
or place other equipment directly on top of the ROUTEFINDER.
If installing the ROUTEFINDER in a closed or multi-unit enclosure, ensure adequate airflow within the rack so that the
maximum recommended ambient temperature is not exceeded.
Ensure that the ROUTEFINDER is properly connected to earth ground via a grounded power cord. If a power strip is used,
ensure that the power strip provides adequate grounding of the attached apparatus.
Ensure that the main supply circuit is capable of handling the load of the ROUTEFINDER. Refer to the power label on the
equipment for load requirements.
Maximum ambient temperature for the ROUTEFINDER is 50 degrees Celsius (120° F).
This equipment should only be installed by properly qualified service personnel.
Connect like circuits. In other words, connect SELV (Secondary Extra Low Voltage) circuits to SELV circuits and TN
(Telecommunications Network) circuits to TN circuits.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 11
Page 12

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
RouteFinder Front Panels
RF760/660VPN Front Panel
The R760VPN and the RF660VPN have 16 LEDs that show device and network operating status.
For the RF760VPN, these LEDs are labeled 10/100/1G.
• When 10, the LED is Off.
• When 100, the LED is Green.
• When 1G, the LED is Orange.
RF760 / 660VPN LED Descriptions
LAN LEDs Description
LINK
ACT
100MB or
10/100/1G
WAN LEDs Description
LINK
ACT
100MB or
10/100/1G
DMZ LEDs Description
LINK
ACT
100MB or
10/100/1G
Modem Description of Modem LEDs
DCD
RD
DTR
TD
System Description of System LEDs
HDD ACT
ALERT
POWER
LAN LINK LED - Indicates link integrity for the LAN Ethernet port. If the Ethernet link is valid at 10 Mbps,
100 Mbps, or 1G (RF760VPN) the LINK LED is lit. If the Ethernet link is invalid, the LINK LED is off.
ACT (Activity) LED - Indicates transmit and receive activity on the LAN Ethernet port. When activity is
present on the LAN Ethernet port, the ACT LED is lit. When no activity is present on the LAN Ethernet
port, the ACT LED is off.
For the RF760VPN: If the Ethernet link is valid at 10 Mbps, the LAN LED is off. If the Ethernet link is
valid at 100 Mbps, the LED is green. If the Ethernet link is valid at 1G, the LED is orange.
For the RF660VPN: The LAN 100MB LED is lit if the LAN Ethernet port is linked at 100 Mbps. The
LAN 100 MB LED is off at 10 Mbps.
WAN LINK LED - Indicates link integrity for the WAN Ethernet port. If the link is valid in either 10 Mbps,
100 Mbps, or 1G (760VPN), the LINK LED is on; if the WAN Ethernet link is invalid, the LINK LED is off.
WAN ACT (Activity) LED - Indicates either transmit or receive activity on the WAN Ethernet port. When
activity is present, the ACT LED is on; when no activity is present, the ACT LED is off.
For the RF760VPN: If the Ethernet link is valid at 10 Mbps, the LED is off. If the Ethernet link is valid at
100 Mbps, the LED is green. If the Ethernet link is valid at 1G, the LED is orange.
For the RF660VPN: The 100MB LED is lit if the LAN Ethernet port is linked at 100 Mbps. The 100 MB
LED is off at 10 Mbps.
DMZ LINK LED - Indicates link integrity for the DMZ Ethernet port. If the link is valid in either 10 Mbps,
100 Mbps, or 1G (760VPN) the LINK LED is on; if the DMZ Ethernet link is invalid, the LINK LED is off.
ACT (Activity) LED - Indicates either transmit or receive activity on the DMZ Ethernet port. When activity
is present, the ACT LED is lit. When no DMZ Ethernet port activity is present, the ACT LED is off.
For the RF760VPN: If the Ethernet link is valid at 10 Mbps, the LED is off. If the Ethernet link is valid at
100 Mbps, the LED is green. If the Ethernet link is valid at 1G, the LED is orange.
For the RF660VPN: The 100MB LED is lit if the LAN Ethernet port is linked at 100 Mbps. The 100 MB
LED is off at 10 Mbps.
DCD (Data Carrier Detect) LED - Lights when the modem detects a valid carrier signal from another
modem; on when the modem is communicating with the other modem and off when the link is broken.
RD (Read Data) LED - Flashes when the modem is receiving data from another modem.
DTR (Data Terminal Ready) LED - Lights when the operating system detects and initializes the modem.
TD (Transmit Data) LED - Flashes when the modem is transmitting data to another modem.
HDD ACT (Hard Disk Drive Activity) LED - Lights when the hard disk drive is accessed.
ALERT LED - Not used.
POWER LED - Off when the RouteFinder is in a reset state. When lit, the RouteFinder is not in a reset
state.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 12
Page 13

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
RF600VPN
The RF600VPN has 12 front panel LEDs that show the network operating status.
General LED Descriptions
POWER
STATUS
HDD ACT
LAN, WAN, DMZ LED Descriptions
10MB
ACT
100MB
POWER LED - Off when the RF600VPN is in a reset state. When the POWER LED is lit, the
RF600VPN is not in a reset state.
STATUS LED - Off when the RF600VPN is booting up.
HDD ACT (Hard Disk Drive Activity) LED - Lights when the RF600VPN hard disk drive is accessed.
10MB LED - Lights when the LAN client has a valid link at 10MB.
ACT (Activity) LED - Indicates either transmit or receive activity on the LAN Ethernet port. When
activity is present on the LAN Ethernet port, the ACT LED is lit. When no activity is present on the
LAN Ethernet port, the ACT LED is off.
100MB LED - Lights when the LAN client has a valid link at 100MB.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 13
Page 14
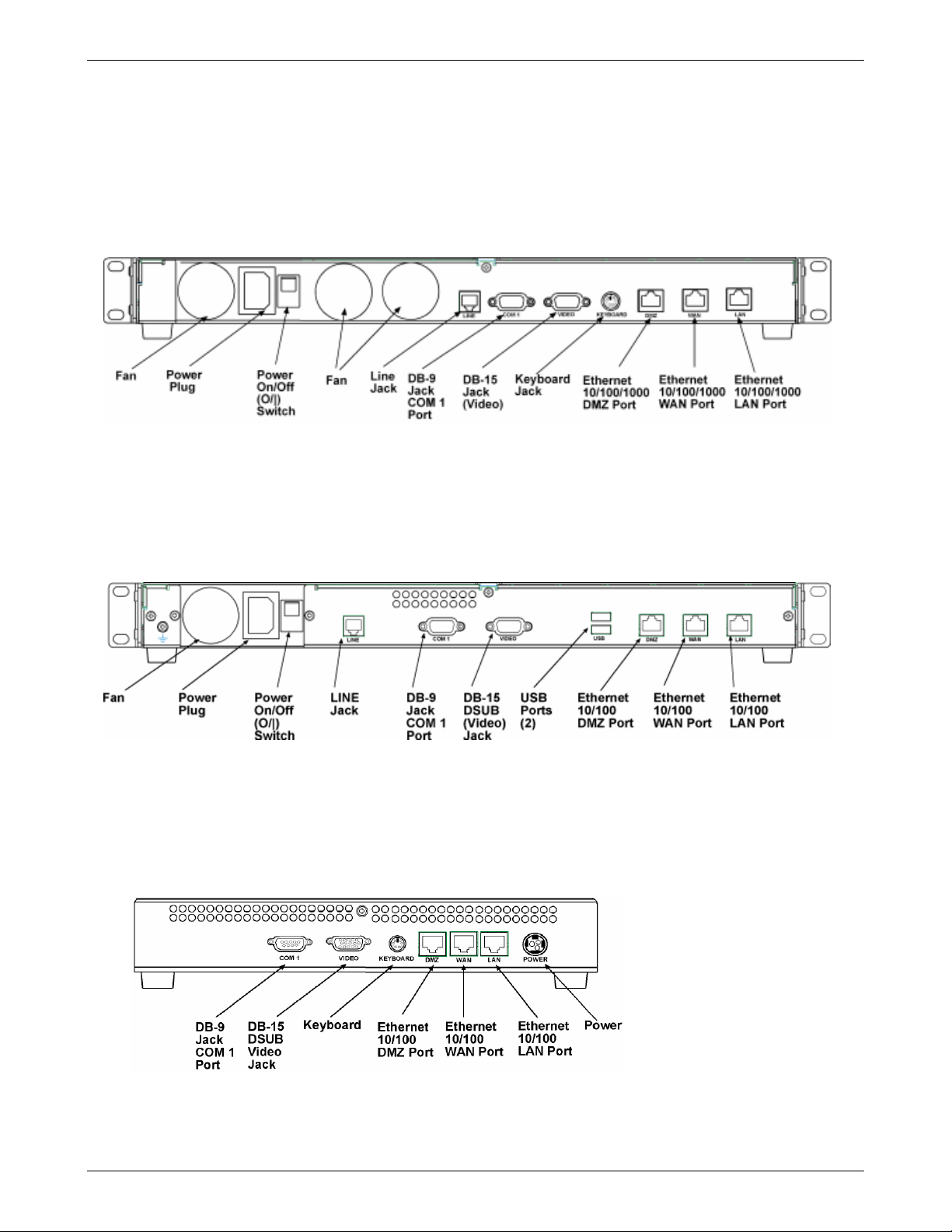
Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
RouteFinder Back Panels
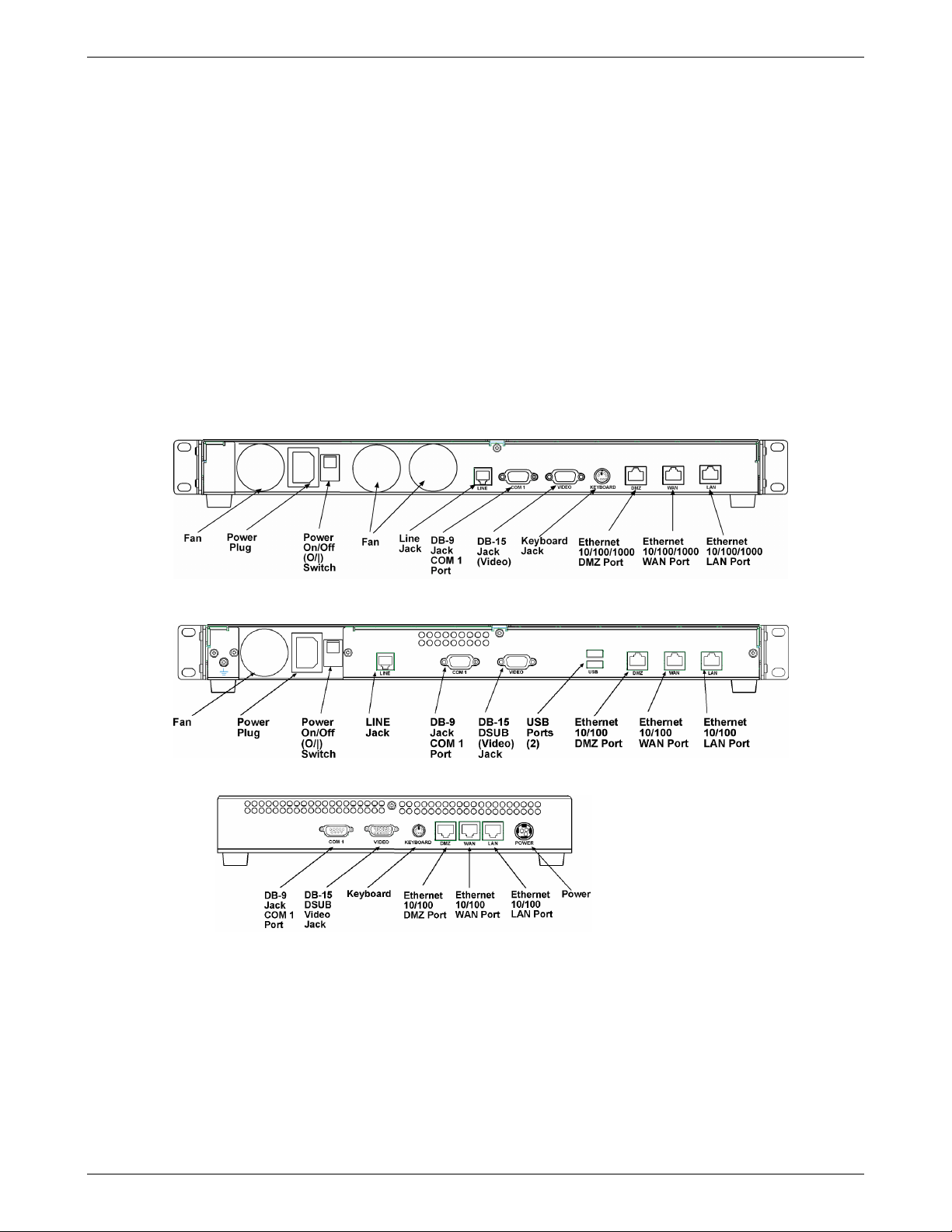
RF760VPN Back Panel
The RF760VPN back panel has three fans, a power plug, a POWER Switch (| / O), an RJ-11 LINE jack, a DB-9 COM1 jack,
a DB-15 High-density DSUB (VIDEO) jack, a keyboard jack, an Ethernet 10/100/1000 DMZ Port, and an Ethernet
10/100/1000 WAN Port, and an Ethernet 10/100/1000 LAN Port.
RF660VPN Back Panel
The RF660VPN back panel has a fan, a power plug, the POWER Switch (| / O), an RJ-11 LINE jack, a DB-9 COM1 jack, a
DB-15 High-density DSUB (VIDEO) jack, two USB (Revision 1.1 compliant) jacks, an RJ-45 DMZ jack, an RJ-45 (WAN)
jack, and an RJ-45 (LAN) jack.
RF600VPN Back Panel
The RF600VPN back panel has a DB-9 COM1 jack, a DB-15 High-density DSUB (VIDEO) jack, a keyboard jack, an RJ-45
DMZ jack, an RJ-45 WAN jack, an RJ-45 LAN jack, and a POWER jack.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 14
Page 15
Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Specifications
Appliance Features RF760VPN RF660VPN RF600VPN
Ethernet Ports
Number of Network Users
Rackmount or Standalone
VPN Features RF760VPN RF660VPN RF600VPN
Remote User (Client-to-LAN)
Branch Office (LAN-to-LAN)
3DES Encryption
3DES Throughput
Protocols Security: IPSec, IKE, NAT,
Recommended Number of
Tunnels (IPSec)
Recommended Number of
Tunnels (PPTP)
Firewall Features RF760VPN RF660VPN RF600VPN
Throughput
Anti-Virus Option
Content Filtering
Application Proxies
Port and IP Filtering
Denial of Service Protection
(DoS)
Stateful Packet Inspection
Network Address Translation
(NAT)
Virtual Server
Port Scan
Intrusion Detection/Notification
H.323 Pass Through
Management Features RF760VPN RF660VPN RF600VPN
Email Alert
Local & Remote Management
Logging
Reporting
Web Based (HTTP, HTTPS/SSL)
Secure Shell (SSH)
Syslog
Other Features RF760VPN RF660VPN RF600VPN
Shared Internet Access
Automatic Dial-Backup
Integrated Modem
PPPoE
DHCP Client/Server
User Authentication
Automatic Firmware Downloads
Warranty
3x10/100/1000BaseT
(LAN,WAN, DMZ)
Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited
Both Both Both
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
50M bps 15M bps 3M bps
PPTP, HTTPS, SSH, SCP
Authentication: Shared
secret and built-in
authentication server
Network: TCP/IP, DNS
Filtering: Protocol, port
number, and IP address
Proxies: HTTP, SMTP,
DNS, SOCKS
100 50 25
100 50 25
300M bps 80M bps 20M bps
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes No
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
2 Years 2 Years 2 Years
3x10/100BaseT
(LAN,WAN, DMZ)
Security: IPSec, IKE, NAT,
PPTP, HTTPS, SSH, SCP
Authentication: Shared
secret and built-in
authentication server
Network: TCP/IP, DNS
Filtering: Protocol, port
number, and IP address
Proxies: HTTP, SMTP,
DNS, SOCKS
3x10/100BaseT
(LAN,WAN, DMZ)
Security: IPSec, IKE, NAT,
PPTP, HTTPS, SSH, SCP
Authentication: Shared
secret and built-in
authentication server
Network: TCP/IP, DNS
Filtering: Protocol, port
number, and IP address
Proxies: HTTP, SMTP,
DNS, SOCKS
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 15
Page 16
Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Power & Physical
RF760VPN RF660VPN RF600VPN
Description
Power - Voltage & Frequency
Power Consumption
Physical Description Dimensions:
Operating Environment Temperature Range:
Approvals
100-240v AC, 50-60 Hz 100-240v AC, 50-60 Hz 100-240v AC, 50-60 Hz
50 Watts 30 Watts 15 Watts
17" w × 1.75" h × 10.5" d;
(43.18cm × 4.45cm ×
26.67cm)
Weight: 10 lbs. (4.54 kg)
32° to 120° F (0-50°C)
Humidity: 25-85%
noncondensing
FCC Part 68
FCC Part 15 (Class A)
CE Mark
UL60950
ICSA Firewall Certified
Dimensions:
17" w × 1.75" h × 10.5" d;
(43.18cm × 4.45cm ×
26.67cm)
Weight: 10 lbs. (4.54 kg)
Temperature Range:
32° to 120° F (0-50°C)
Humidity: 25-85%
noncondensing
FCC Part 68
FCC Part 15 (Class A)
CE Mark
UL60950
ICSA Firewall Certified
Dimensions:
12" w × 1.7" h × 8" d;
(30.4cm × 4.4cm ×
20.3cm)
Weight: 5.8 lbs. (2.6 kg)
Temperature Range:
32° to 120° F (0-50°C)
Humidity: 25-85%
noncondensing
FCC Part 68
FCC Part 15 (Class A)
CE Mark
UL60950
ICSA Firewall Certified
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 16
Page 17
Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Overview of RouteFinder VPN Technology
Before we look at how the RouteFinder works and how to use it, we will illustrate why the RouteFinder is necessary for the
protection of networks, as well as show which problems and risks exist without an appropriate security system.
Networks
The systems in the global network communicate via the Internet Protocol Family (IP), including TCP, UDP, or ICMP. The IP
addresses are the basis of this communication. They identify all available units within the network.
The Internet itself is actually just a collection of computer networks around the world of varying shape, size, and speed.
Where two or more networks join, a whole host of tasks arise, which are dealt with by routers, bridges, or gateways. A
special type of connection between two networks is called a firewall.
Generally speaking, three types of networks meet at the firewall:
1. External network/Wide Area Network (WAN)
2. Internal Network/Local Area Network (LAN)
3. De-Militarized Zone (DMZ)
The Firewall
The characteristic tasks of a firewall as a connection between WAN, LAN and DMZ are:
• Protection from unauthorized access
• Access control
• Ensure information integrity
• Perform analysis of protocols
• Alert the administrator of relevant network events
• Conceal internal network structure
• Decoupling of servers and clients via proxies
• Ensure confidentiality
There are several generic network components that, brought together under the heading Firewall, are responsible
for these tasks. The following sections provide a brief look at some of the forms and their derivatives.
Network Components That Work with the Firewall
Network Layer Firewalls: Packet Filter
As the name suggests, the Packet Filter is where IP packets (consisting of address information, some flags, and the
payload) are filtered. With this kind of firewall you can grant or deny access to services, according to different
variables. Some of these variables are:
• The source address
• The target address
• The protocol (e.g. TCP, UDP, ICMP)
• The port number
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 17
Page 18

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
The great advantage of a network layer firewall is its independence of both the operating system and the
applications running on the machine.
In more complex network layer firewall implementations, the packet filtering process includes the interpretation of
the packet payload. The status of every current connection is analyzed and recorded. This process is called stateful
inspection.
The packet filter records the state of every connection and lets only those packets pass that meet the current
connection criteria. This is especially useful for establishing connections from a protected network to an unprotected
network.
If a system establishes a connection to a protected network, the Stateful Inspection Packet Filter lets a host’s
answer packet pass back into the protected network. If the original connection is closed, no system from the
unprotected network can send packets into the protected network any longer – unless you explicitly allow it.
Well Known Ports are controlled and assigned by the IANA, and on most systems, can only be used by system (or
root) processes or by programs run by privileged users. Ports are used in TCP (RFC793) to name the ends of
logical connections which carry long term conversations; and, typically, these same port assignments are used with
UDP (RFC768). The assigned ports are in the range 0-1023. IETF RFC 1700 provides a list of the well-known port
number assignments. IETF RFCs are available on the Internet from a number of sources.
Application Layer Gateways: Proxies
A second significant type of firewall is the application layer gateway. It is responsible for buffering connections
between exterior systems and your system. Here, the packets aren’t directly passed on, but a sort of translation
takes place, with the gateway acting as an intermediary stop and translator.
The application gateway buffering processes are called proxy servers, or, for short‚ proxies. Every proxy can offer
further security features for its designed task. Proxies generally offer a wide range of security and protocol options.
Each proxy serves only one or a few application protocols, allowing high-level security and extensive logging and
analysis of the protocol’s usage.
Examples of existing proxies are:
• The SMTP proxy - Responsible for email distribution and virus checking.
• The HTTP proxy - Supporting Java, JavaScript, ActiveX-Filter, and ad banner filtering.
• The SOCKS proxy (the generic circuit-level proxy) - Supporting applications such as FTP clients, ICQ,
IRC, or streaming media.
Application level gateways offer the advantage of physical and logical separation of the protected and unprotected
networks. They make sure that no packet is allowed to flow directly between networks, resulting in higher security.
Protection Mechanisms
Further mechanisms ensure added security. Specifically, the use of private IP addresses in combination with
Network Address Translation (NAT) in the form of:
• Masquerading
• Source NAT (SNAT)
• Destination NAT (DNAT)
These allow a whole network to hide behind one or a few IP addresses, preventing the identification of your network
topology from the outside.
With these protection mechanisms in place, Internet connectivity remains available, but it is no longer possible to
identify individual machines from the outside.
By using Destination NAT (DNAT), it is still possible to place servers within the protected network/DMZ and make
them available for an assigned service.
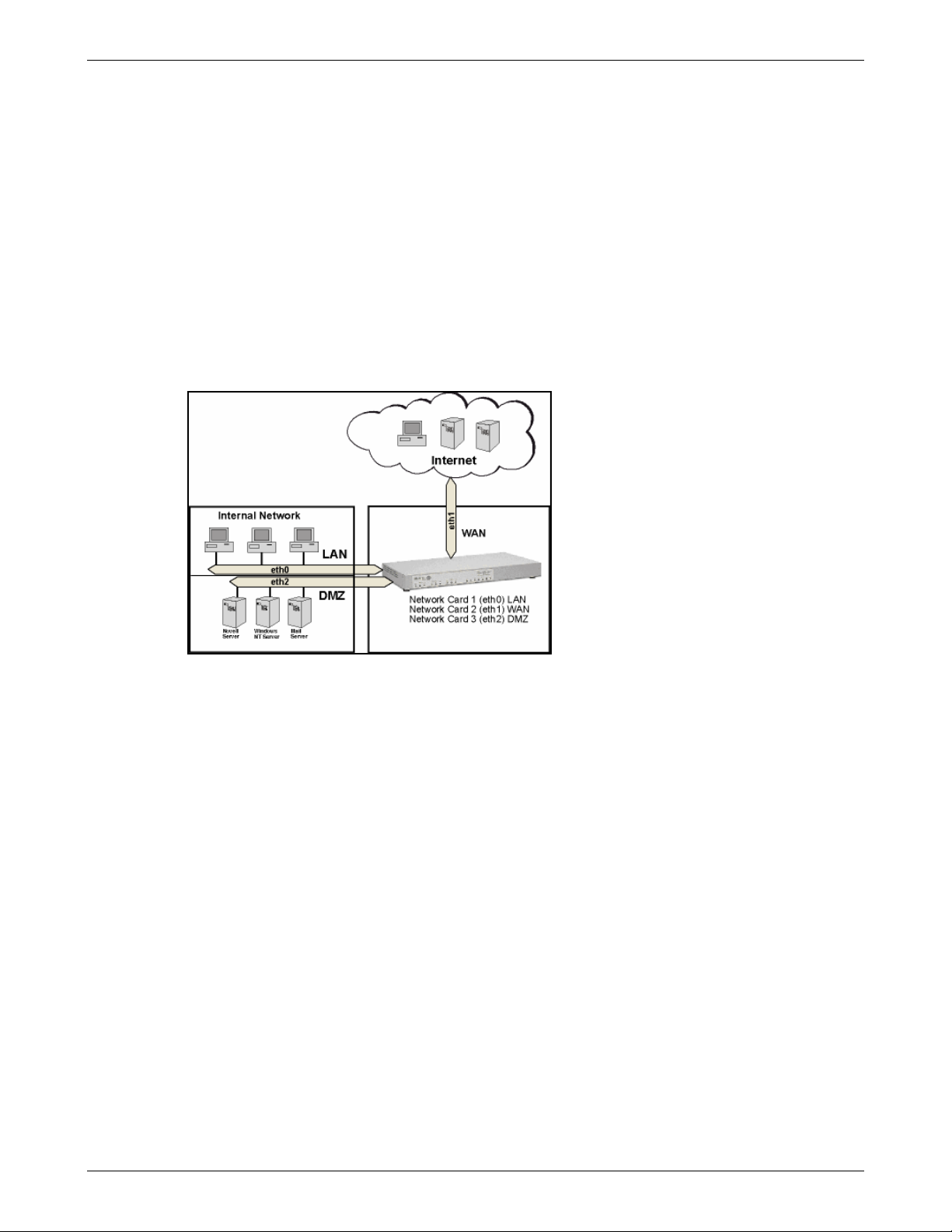
In the sample graphic above, a user with the IP 5.4.3.2, port 1111 sends a request to the Web server in the DMZ.
Of course, the user knows only the external IP (1.1.1.1, port 80). Using DNAT, the RouteFinder now changes the
external IP address to 10.10.10.99, port 80 and sends the request to the Web server. The Web server then sends
the answer with its IP address (10.10.10.99, port 80) and the user’s IP. The RouteFinder recognizes the packet by
the user address, and it then changes the internal IP (10.10.10.99, port 80) into the external IP address (1.1.1.1,
port 80).
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 18
Page 19

Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
To satisfy today’s business world needs, the IT infrastructure must offer real-time communication and co-operate
closely with business partners, consultants, and branches. Increasingly, the demand for real-time capability is
leading to the creation of extranets that operate either:
• via dedicated lines, or
• unencrypted lines via the Internet
Each of these methods has advantages and disadvantages, as there is a conflict between the resulting costs and
the security requirements.
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) establishes secure (i.e., encrypted) connections via the Internet, an important
function especially if your organization operates at several locations that have Internet connections. These secure
connections use the IPSec standard derived from the IP protocol IPv6.
ISO Layers and TCP/IP
Once set up, this encrypted connection is used automatically (i.e., without extra configurations or passwords at the client
systems) regardless of the type of data that is to be transferred. This protects the content during the transport. At the
other end of the connection, the transferred data is transparently decoded and is available for the recipient in its original
form.
The RouteFinder VPN uses a hybrid of the above listed basic forms of firewalls and combines the advantages of both
variations: the stateful inspection packet. Stateful inspection packet filter functionality offers platform-independent
flexibility, and the ability to define, enable or disable all necessary services. Existing proxies make the RouteFinder an
application gateway that secures vital client system services, such as HTTP, Mail, and DNS by using a proxy. The
ROUTEFINDER also enables generic circuit-level proxy via SOCKS.
VPN, Source NAT, Destination NAT, masquerading, and the ability to define static routes make the dedicated firewall an
efficient distribution and checkpoint in your network.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 19
Page 20
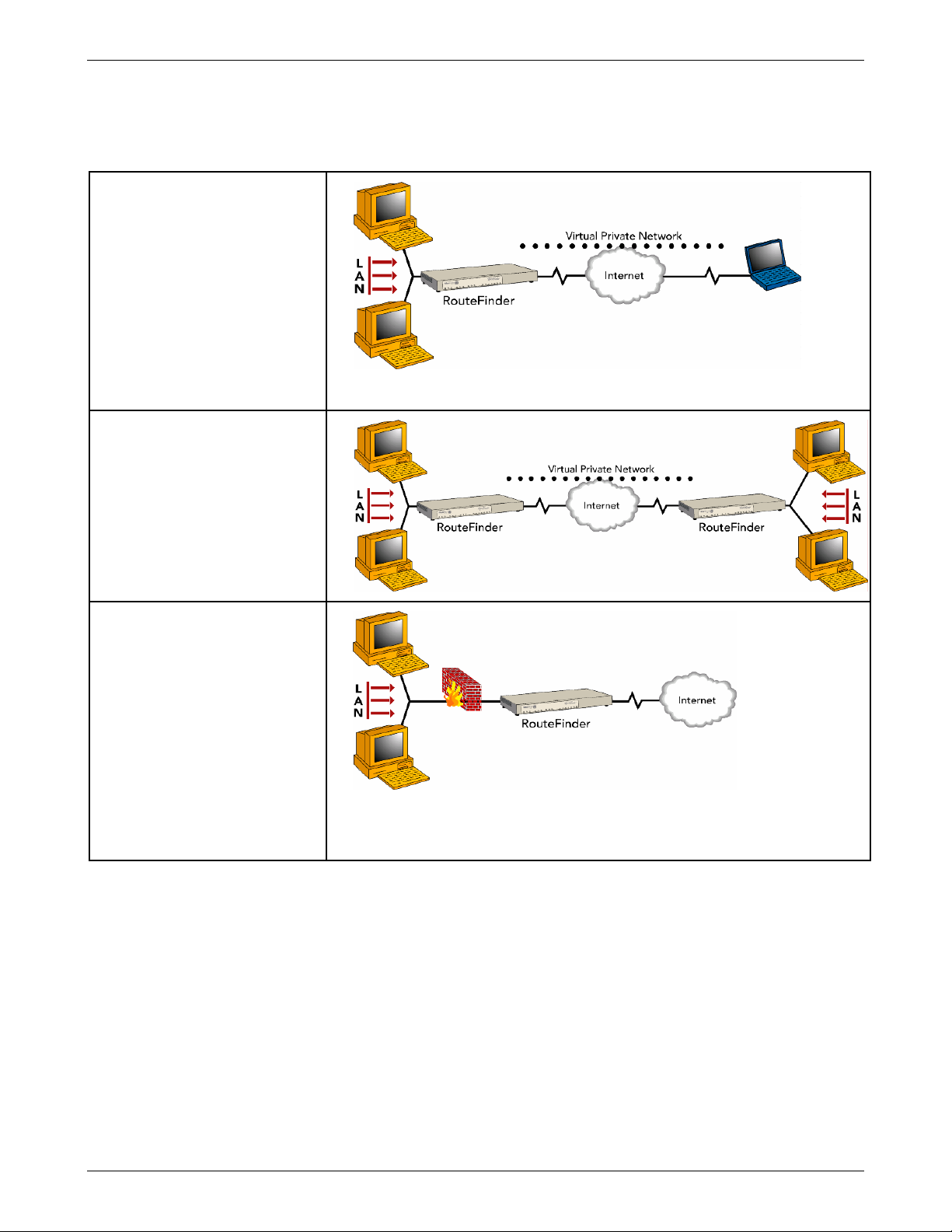
Typical Applications
Remote User VPN
The client-to-LAN VPN application
replaces traditional dial-in remote
access by allowing a remote user
to connect to the corporate LAN
through a secure tunnel over the
Internet. The advantage is that a
remote user can make a local call
to an Internet Service Provider,
without sacrificing the company’s
security, as opposed to a long
distance call to the corporate
remote access server.
Branch Office VPN
The LAN-to-LAN VPN application
sends network traffic over the
branch office Internet connection
instead of relying on dedicated
leased line connections. This can
save thousands of dollars in line
costs and reduce overall hardware
and management expenses.
Chapter 1 – Product Description, Features, and Overview
Firewall Security
As businesses shift from dial-up
or leased line connections to
always-on broadband Internet
connections, the network
becomes more vulnerable to
Internet hackers.
The RouteFinder VPN provides a
full-featured firewall based on
Stateful Packet Inspection
technology and NAT protocol to
provide security from intruders
attempting to access the office
LAN.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 20
Page 21

Chapter 2 – Installation
Pre-Installation Planning
Chapter 2 – Installation
Planning and Establishing the Corporate Security Policy
Having an organization-wide security policy is the first, and perhaps most, important step in general security planning.
Organizations without a well-devised top-level security policy will not have ready answers to questions such as:
• Who is allowed access to which servers?
• Where are the backups stored?
• What is the recovery procedure for a security breach?
These questions must be answered in terms of security costs, usability, compatibility with internal "culture", and
alignment with your site's legal requirements.
Putting a security policy in place and keeping abreast of new security issues as they arise are paramount to securing
your network.
Contents of a Corporate Internet Security Policy
The policy statements should be clear, easy to understand, and supported by management.
All enterprises should have a carefully planned security policy that protects their network. Your security policy
should define both what should be protected as well as how it should be protected. A comprehensive, clear, and
well-communicated security policy is an important first step in protecting any network from the many threats
associated with the power of the Internet.
A corporate Internet security policy should cover at least 6 major areas, including:
1. Acceptable Use – Define the appropriate use of the network and other computing resources by any and all
users. This should include policy statements like: “password sharing is not permitted"; "users may not share
accounts"; and "users may not make copies of copyrighted software.”
2. Remote Access – Outline acceptable (and unacceptable) means of remotely connecting to the internal
network. Cover all
DSL, cable modem, Telnet, and others. Specify who
may obtain remote access. The security policy must also address who is allowed high-speed remote access
and any extra requirements associated with that privilege (e.g., all remote access via DSL requires that a
firewall be installed). You will also want to define users' email security here (e.g., in MS Outlook at Tools >
Options > Security > Zone Settings > Security Settings).
3. Information Protection – Provide guidelines to users that define the use and transmission of sensitive
information to ensure the protection of your enterprise’s key elements of information (e.g., set a standard for
encryption level (such as 3DES) for information sent over the Internet).
4. Firewall Management – Define how firewall hardware and software are managed. This includes change
requests and approval, periodic review of firewall configurations, and firewall access privilege settings.
5. Special Access – Provide guidelines for any special, non-standard needs for access to specialized networks
or systems.
6. Network Connection – Establish policies for adding new devices and new users to the network, with an
approval process, along with the associated security requirements.
of the possible ways that users remotely access the internal network, such as dial-in, ISDN,
is allowed to have remote access as well as how users
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 21
Page 22
Chapter 2 – Installation
Planning the Network
Before installing, you should plan your network and decide which computer is to have access to which services. This
simplifies configuration and saves you a lot of time that you would otherwise need for corrections and adjustments.
Establishing an Address Table
Enter the configuration information (e.g., the IP addresses used, Net Mask addresses, and the Default Gateway) into the
appropriate field of the Address Table below. Please print this page and use it to fill in your specific ROUTEFINDER and
network information (e.g., the IP address used, email lists, etc.), and keep it for future reference.
Network Card connected
to the internal network
(LAN on eth0)
Network Card connected
to the external network
(WAN on eth1)
Network Card connected
to the DMZ
(eth2)
IP Address Net Mask Default Gateway
___.___.___.___
___.___.___.___
___.___.___.___
___.___.___.___
___.___.___.___
___.___.___.___
___.___.___.___
System Administrator Required Planning
The system administrator must complete these setup requirements before installing the ROUTEFINDER software:
• Set the correct configuration of the Default Gateway
• Install an HTTPS-capable browser (e.g., the latest version of Microsoft Internet Explorer or Netscape
Navigator)
• Activate JavaScript and Cascading Style Sheets
• Make sure that no proxies are entered in the browser
• If Secure Shell (SSH) is to be used, you must install an SSH client program (e.g., PuTTY in Windows 2000
or the bundled SSH client in most Linux packages).
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 22
Page 23
Chapter 2 – Installation
Installation Overview
RouteFinder VPN installation is divided into four steps:
1. Hardware installation
2. Cabling
3. Software initial configuration
4. RouteFinder configuration
Hardware Installation Procedure
The RouteFinder VPN is designed to install either on a desktop or in a standard EIA 19" rack and is shipped with the
mounting hardware to install the RouteFinder VPN in the standard EIA 19" rack. If installing in a rack, use the provided
mounting hardware and follow the rack enclosure manufacturer’s instructions to safely and securely mount the
RouteFinder the rack enclosure. Proceed to the cabling procedure.
Cabling Overview
Cabling your RouteFinder VPN involves making the proper Power, DMZ, WAN and LAN connections as illustrated and
described below.
RF760VPN
RF660VPN
RF600VPN
1. Using an RJ-45 Ethernet cable, connect the DMZ RJ-45 jack to the DMZ device or network (Optional – for example,
a Voice over IP gateway).
2. Using an RJ-45 Ethernet cable, connect the WAN RJ-45 jack to the device for the external network.
3. Using an RJ-45 Ethernet cable, connect the LAN RJ-45 jack to the internal network switch or hub.
Note: Use a cross-over Ethernet cable if connecting to a single device.
4. With the RF760 or RF660 RouteFinder VPN Power switch in the off (Ο) position and using the supplied power cord,
plug one end into the RouteFinder VPN connect power plug and the other end into a live power outlet.
Note: The status LED blinks continuously after power-up.
5. Wait for the RouteFinder VPN to beep five times, indicating that it is ready to be configured with a Web browser.
Shutdown Caution: Never switch off the RouteFinder VPN Power until after you have performed the Shutdown
process. If the RouteFinder VPN is not properly shut down before switching off Power, the next startup may take a little
longer, or in the worst case, data could be lost.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 23
Page 24
Chapter 2 – Installation
Setting up a Workstation and Starting the
RouteFinder VPN
This section of the Quick Start Guide covers the steps for setting up a workstation that is connected to the RouteFinder VPN,
starting up the RouteFinder VPN, opening the RouteFinder VPN Web Management program, performing the time zone
setup, and using the Menu bar to navigate through the Web Management software screens.
Connections
1. Connect a workstation to the RouteFinder's LAN port via Ethernet. Connections are described on the previous
page.
Note: If not using a hub, use a cross-over cable to connect a PC NIC to the RouteFinder's Ethernet 10/100
LAN Port.
2. Set the workstation IP address to 192.168.2.x subnet.
3. Obtain an Internet Public IP address so it can be assigned to the WAN port.
4. Connect to the Internet at the RouteFinder WAN port.
Power Up
5. Turn on power to the RouteFinder VPN. After several minutes, you will hear 5 beeps signifying the software
has fully booted.
Note: If you hear a continuous beep or no beep, cycle RouteFinder VPN power, connect an external monitor
and check the hard drive.
Open a Web Browser
6. Bring up a Web browser on the workstation. Type the default Gateway address: https://192.168.2.1 and press
the Enter key.
IMPORTANT: Be sure to type https (http will not work).
Note: Make sure your PC’s IP address is in the same network as the router’s IP address. WINIPCFG and
IPCONFIG are tools for finding a computer’s default gateway and MAC addresses. In Windows 98/ME you can
type WINIPCFG. In Windows 2000/NT/ME/XP, you can type IPCONFIG.
7. In some environments, one or more Security Alert screen(s) may display. At the initial Security Alert screen,
click Yes and follow any additional on-screen prompts.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 24
Page 25
Chapter 2 – Installation
Login
8. The Login screen is displayed.
• Type the default User name: admin (all lower-case).
• Tab to the Password field and type the default password: admin (all lower-case).
• Click the Login button.
Note: The User name and Password entries are case-sensitive (both must be
typed in lower-case). The password can be up to 12 characters. Later, you will want
to change the password from the default (admin) to something else. If Windows
displays the AutoComplete screen, you may want to click No to tell Windows OS to
not remember the password for security reasons.
Password Caution: Use a safe password! Your first name spelled backwards is
not a sufficiently safe password; a password such as xfT35$4 is better.
It is recommended that you change the default password. Do not keep this default
password; create your own password.
9. If someone else is already logged onto the RouteFinder VPN or you were logged in recently, the following
message displays.
Do you want to log the user out?
Click Yes.
If you click No, you are returned to the Login screen.
Web Management Software Opens
The Web Management Home screen is displayed. Web Management software is factory-installed on your RouteFinder.
(This is a view of the top part of the Home screen.)
(This is a view of the Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. informational part of the Home screen.)
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 25
Page 26

Chapter 2 – Installation
t
Navigating Through the Screens
Before using the software, you may find the following information about navigating the screens and the structuring of the
menus helpful.
The Web Management Screen
Menu Bar
Sub Menu
Screen
Buttons
Screen
Name
Work/Inpu
Area
RouteFinder Menu Bar
Menu Selections
Administration Set up system parameters, Administrative Access, User Authentication; enter licenses
Networks & Services Define networks, services, and groups to make them available to be used by other
Proxy Set up proxies.
Network Setup Set up the LAN, WAN, and DMZ Ethernet ports; PPP modem link, etc.
DHCP Server Configure the DHCP server settings.
Tracking Set up tracking of all packets through the network ports in the RouteFinder VPN, set up
Packet Filters Define filter rules and ICMP rules.
VPN Virtual Private Network. Set up a secure communication tunnel to specific Internet
Statistics & Logs View and download all the statistics and log files maintained by your system.
and certificates, etc. See entire list of functions on next page.
functions such as allowed networks, packet filters, VPN, and proxies.
automatic download and upgrade of packages from a specified Update server, set up
import/export backup configurations.
systems.
Screen Buttons
Home The main screen.
Wizard Setup Change passwords and quickly set up your RouteFinder VPN with the basic
configuration that will set it up as a firewall.
Help Describes what to do on each screen.
Logout Logout and return to the login screen.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 26
Page 27
Chapter 2 – Installation
Sub-Menu
Each item on the Menu Bar has its own sub-menu which displays on the left side of the screen.
When you click one of the Menu Bar buttons, the screen that displays is the first sub-menu option. You can choose
other sub-menu screens by clicking the screen name in the sub-menu.
This is an example of the Administration sub-menu. It displays when Administration is clicked on the Menu Bar.
Menus and Sub-Menus
Administration
System Setup
SSH
SNTP Client
Administrative Access
Site Certificate
License Key
Intrusion Detection
Tools
System Scheduler
Factory Defaults
User Authentication
Local Users
Radius & SAM
Restart
Shutdown
Tracking Packet Filters VPN Statistics & Logs
Accounting
Update Services
Backup
Version Control
Networks & Services Proxy Network Setup DHCP Server
Network
Services
Network Groups
Service Groups
Packet Filter Rules
ICMP
Advanced
Enable/Disable Log
HTTP Proxy
Custom Filters
SMTP Proxy
SMTP SPAM Filtering
POP3 Proxy
POP3 SPAM Filtering
SOCKS Proxy
DNS Proxy
IPSec
X.509 Certificates
IPSec Bridging
PPTP
Interface
PPP
PPPoE
DHCP Client
Dynamic DNS
Routes
Masquerading
SNAT
DNAT
Uptime
Hardware
Networks
Interfaces
SMTP Proxy
Accounting
Self Monitor
IPSec
PPTP
Packet Filter
Port Scans
View Logs
HTTP Access
DHCP
SMTP Virus Quarantine
POP3 Virus Quarantine
SMTP SPAM Quarantine
Administrative Authentication Log
Subnet Settings
Fixed Addresses
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 27
Page 28
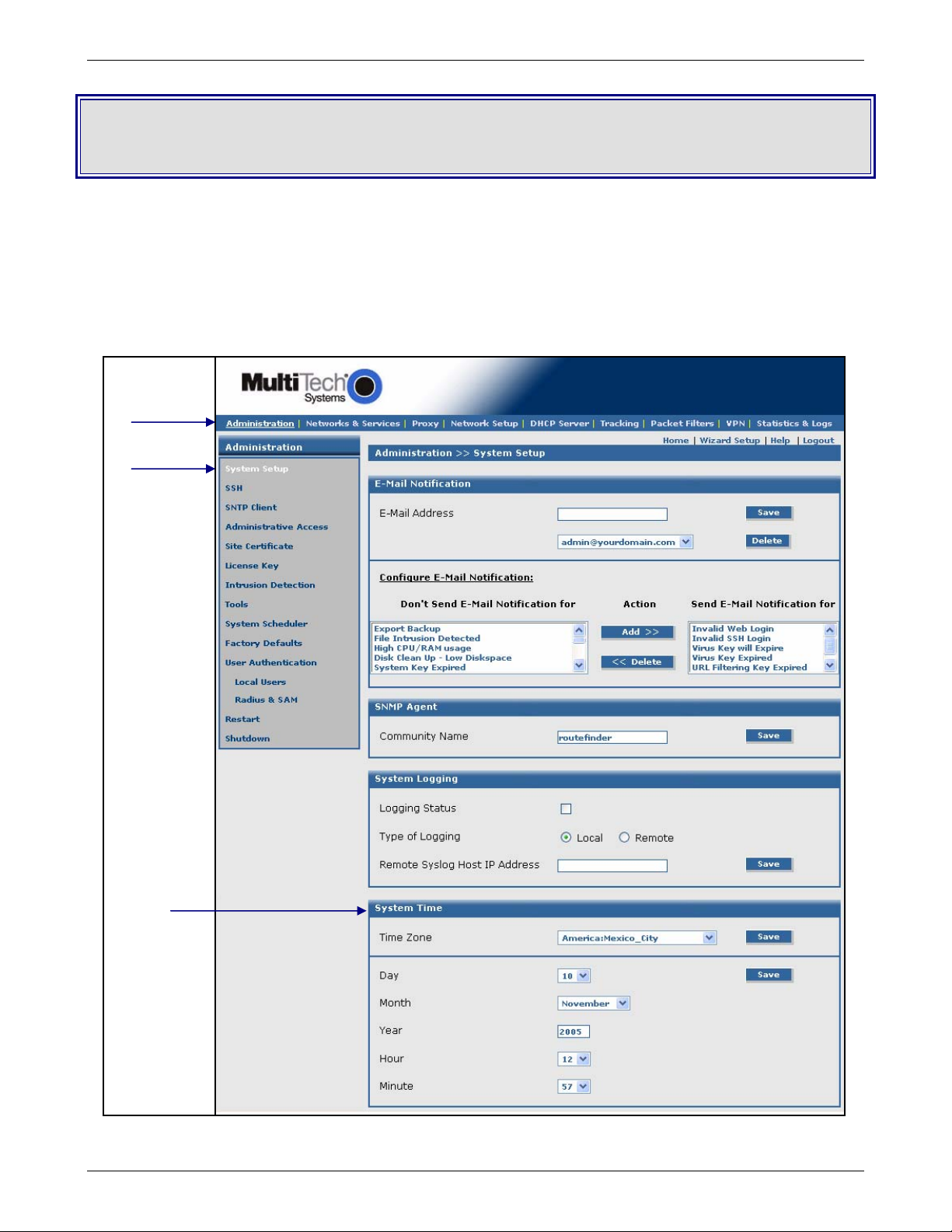
Chapter 3 – Configuration
Initial Configuration Step
Set Up Your Time Zone
Click Administration on the menu bar. The System Setup screen displays.
Set the following:
• Set System Time by selecting your Time Zone
• Set the current Day, Month, Year, Hour, and Minute
Administration
System Setup
Chapter 3 – Configuration
System Time
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 28
Page 29
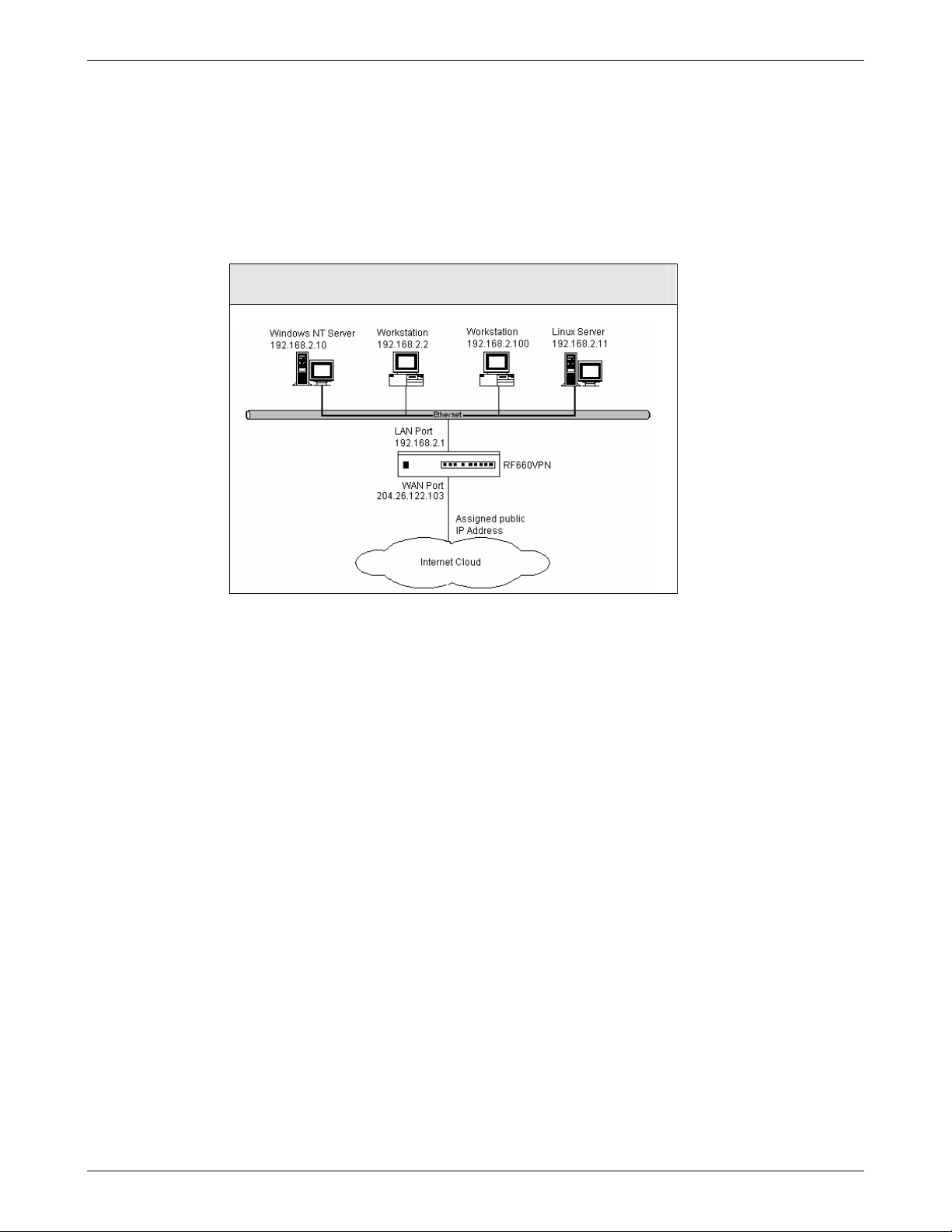
Chapter 3 – Configuration
Second Configuration Step
Using the Wizard Setup is a quick way to enter the basic configuration parameters to allow communication between the
LAN’s workstation(s) and the Internet as shown in the example below.
Important Note: An initial configuration must be completed for each type of RouteFinder functions: firewall configuration,
LAN-to-LAN configuration, a LAN-to-Remote Client configuration.
Note About License Agreements: It is suggested that you read the legal information and license agreement before
beginning the configuration. This information can be found in the Appendix.
RouteFinder VPN Initial Configuration
The addresses used in this example are entered through the Wizard Setup. See the screen example on the next page.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 29
Page 30

The Wizard Setup Screen
Click on the Wizard Setup button. The following screen displays.
Chapter 3 – Configuration
1. Enter your Administrator Email Address (can be anything).
Example: admin@yourdomain.com
2. Enter your Hostname for the RouteFinder (can be anything).
Example: routefinder.domainname.com
3. LAN IP Address and Subnet Mask default into the fields. This should be acceptable for your site.
4. Enter the WAN IP Address. This is the PUBLIC STATIC IP address.
Set this option based on information provided by your ISP. Example: 204.26.122.103
5. Change the Gateway IP address; this is the IP address of the router that connects to the Internet.
Example: 204.26.122.1
6. Place a checkmark in the Packet Filter Rule LAN-ANY-ANY-ALLOW box. This will enable the rule.
7. Change Password Settings as appropriate for your network. It is highly recommended that you change all default
passwords. Do not leave them at the defaults.
8. Click Save to save the settings you just entered.
9. The following message displays. Click OK to close the message box and save your changes.
Click OK to save the changes. Please be patient. Wizard
Setup will take a few minutes to implement the changes. Do not
close the Browser.
10. One more message displays. Note that saving your settings will take 1-2 minutes.
Please do not close the browser. Server is saving the values.
After a few minutes you will be redirected to the new IP address.
If you are not redirected, change the address in the location bar
to 192.168.2.1.
11. Test your workstation to see that it can access the Internet. If a connection is established, then the settings have
been entered correctly.
Your Basic Configuration Is Now Complete
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 30
Page 31

Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
r
Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
Example 1 – LAN-to-LAN VPN (Branch Office)
The setup for a LAN-to-LAN VPN (branch office) requires two RF660VPNs - one in the home office and one in the remote
branch office. It requires additional parameters beyond the Wizard Setup to be entered; these are listed in the table below.
For the RouteFinder VPN in remote branch office follow the same procedures as the home office procedures; just use
different IP addresses. The addresses and parameters in this example are used throughout this section as a point of
reference for you.
For details about this and other setups, see the RouteFinder Setup Examples Reference Guide, which is available on the
RouteFinder CD and on the Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. Web site at http://www.multitech.com
Site A - Static IP Addresses (Input these parameters
using the RF660VPN in the home office).
1. Domain name = site-A.com
2. Public Class C = 204.26.122.x
3. Networks & Services > Networks
LAN: 192.168.2.0 – 255.255.255.0
RemoteLAN: 192.168.10.0 – 255.255.255.0
RemoteWAN_IP: 204.26.122.3 – 255.255.255.255
4. Network Setup > Interface
Default gateway = 204.26.122.1
Host name = RF660VPN.site-A.com
Eth0 = LAN, 192,168.2.1, 255.255.255.0
Eth1 = WAN, 204.26.122.103, 255.255.255.0
Eth2 = DMZ (don’t care)
5. Packet Filters > Packet Filter Rules
LAN – Any – Any – Accept
RemoteLAN – Any – Any – Accept
6. VPN > IPSec
Check and Save VPN Status
Add an IKE connection:
Connection name = SiteA
Check Perfect Forward Secrecy
Authentication Method = Secret
Enter secret key (must be same on both sides)
Select Encryption = 3DES
Local WAN IP = WAN
Local LAN = LAN
Remote Gateway IP = RemoteWAN_IP
Remote LAN = RemoteLAN
Disable UID
Site B - StaticIP Addresses (Input these parameters
using the RF660VPN in the branch office).
1. Domain name = site-B.com
2. Public Class C = 204.26.122.x
3. Networks & Services > Netwo
LAN: 192.168.10.0 – 255.255.255.0
RemoteLAN: 192.168.2.0 – 255.255.255.0
RemoteWAN_IP: 204.26.122.103 – 255.255.255.255
4. Network Setup > Interface
Default gateway = 204.26.122.1
Host name = RF660VPN.site-B.com
Eth0 = LAN, 192.168.10.1, 255.255.255.0
Eth1 = WAN, 204.26.122.3, 255.255.255.0
Eth2 = DMZ (don’t care)
5. Packet Filters > Packet Filter Rules
LAN – Any – Any – Accept
RemoteLAN – Any – Any – Accept
ks
Site B - Static IP Addresses (continued)
6. VPN > IPSec
Check and Save VPN Status
Add an IKE connection:
Connection name = SiteB
Check Perfect Forward Secrecy
Authentication Method = Secret
Enter secret key (must be the same on both sides)
Select Encryption = 3DES
Local WAN IP = WAN
Local LAN = LAN
Remote Gateway IP = RemoteWAN_IP
Remote LAN = RemoteLAN
Disable UID
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 31
Page 32
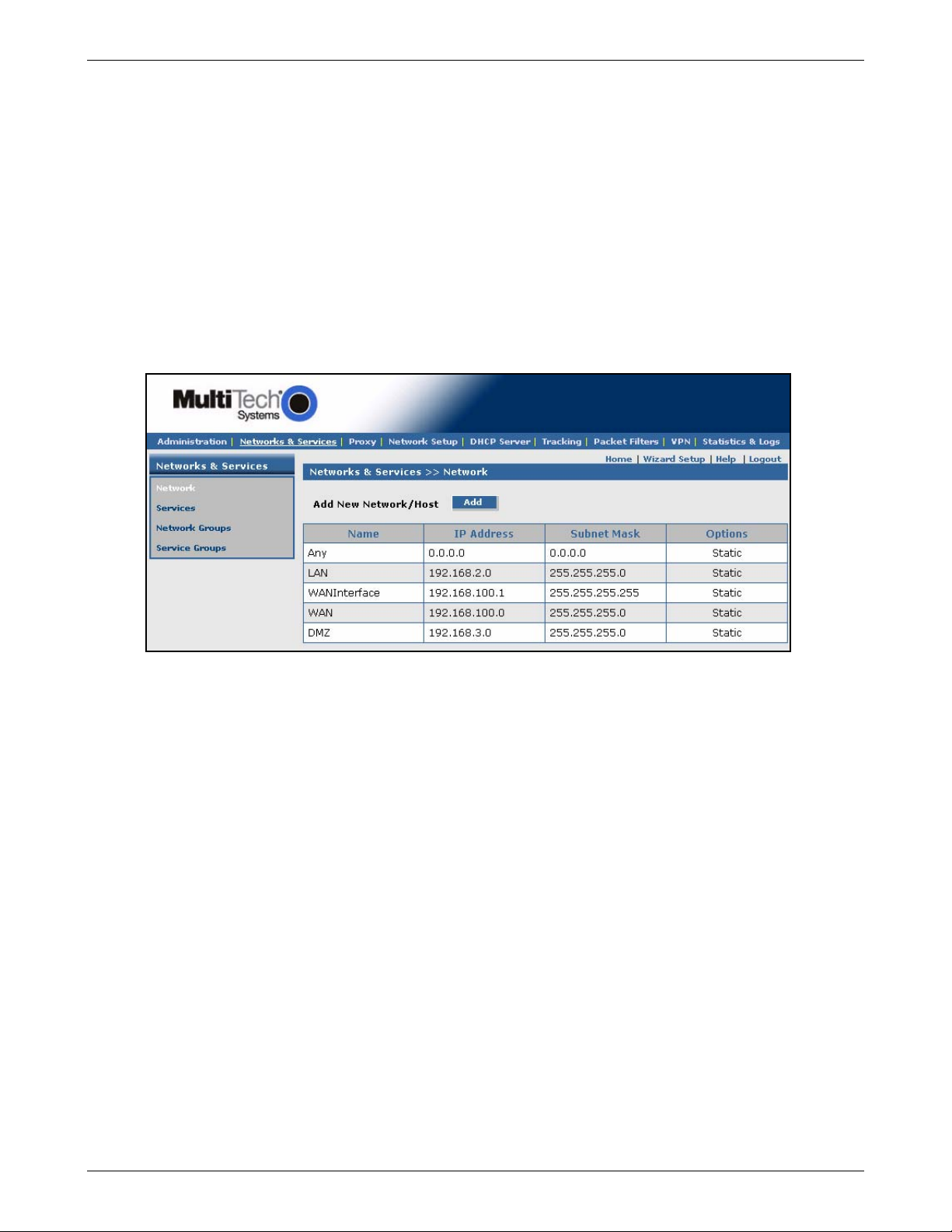
Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
Setup Networks & Services
Site A Configuration on the RouteFinder VPN in the Home Office
To configure your RouteFinder VPN in the home office in preparation for connection to a remote branch office, click the
Networks & Services button on the Menu bar, and then select Networks. Set the following:
1. Add a network for the remote LAN port (private LAN on eth0 at the branch office). Enter the following:
• Name = RemoteLAN
• IP address = 192.168.10.0
• Subnet mask = 255.255.255.0
2. Add a network for the remote WAN port (public WAN on eth1 at the branch office). Enter the following:
• Name = RemoteWAN_IP
• IP address = 204.26.122.3
• Subnet mask = 255.255.255.255
Example 1 will add two network entries to the table on this screen:
RemoteLAN 192.168.10.0 255.255.255.0 Edit | Delete
RemoteWAN_IP 204.26.122.3 255.255.255.255 Edit | Delete
Name IP Address Subnet Mask Options
Notes:
• Default Entries
The first four entries on this screen are default entries and cannot be changed.
• Network Data Displays on Other Screens
Networks added using the Add Network/Host on this screen will display in the Remote Gateway IP and Remote
LAN dropdown boxes on the VPN > IPSec > IKE screen.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 32
Page 33

Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
Set Packet Filters
Site A Configuration: RouteFinder VPN in the Home Office
Establish remote access filtering: click on Packet Filters > Packet Filter Rules.
1. For the Remote LAN at the branch office to access the RouteFinder’s LAN, select the following parameters for the
Remote LAN rule:
RemoteLAN – Any – Any – Accept
Note: The rule LAN – Any – Any – Accept, which displays at the bottom of the screen, was created when you
performed your initial setup using the Setup Wizard.
View
Rules by
clicking
the Show
button.
Set
Parameters
here
The rule entered in the 1 lan ANY ANY ACCEPT Edit|Delete|Move
Setup Wizard displays in
this table as shown here
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 33
Page 34

Set VPN IPSec Protocol
Site A Configuration: RouteFinder VPN in the Home Office
Establish an IPSec Protocol for your remote branch office access: click on VPN > IPSec.
1. Check the VPN Status box, and then click Save.
2. Click the Add button for Add IKE Connection.
Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
The VPN IPSec > IKE screen displays.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 34
Page 35

Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
3. Enter the following information in order to establish an IPSec IKE connection.
• Enter a Connection name. (Example: SiteA)
• Place a checkmark in the box to enable Perfect Forward Secrecy.
• Select Secret for the Authentication Method.
• Enter a shared Secret string using alphanumeric characters. (Example: 1o2t3t4f)
• Select 3DES for Select Encryption.
• Accept the defaults for IKE Life Time and Key Life.
• Enter the number of retries you want the device to make in order to establish the connection. Use zero for
unlimited retries.
• Select the Local WAN IP and Local LAN. The Local WAN IP is the Public Static IP address of the WAN port
(Example: WAN). The Local LAN is the private IP Network on the LAN port. (Example: LAN).
• Select the Remote Gateway IP and Remote LAN. The Remote Gateway IP is the Public Static IP address of
the WAN port at the Remote site (Example: RemoteWAN_IP). The Remote LAN is the private IP network on
the LAN Port of the remote site (Example: RemoteLAN). Leave the Remote LAN blank.
Note: FQDN is a DNS resolvable fully qualified domain name with which the right peer can be identified. When
FQDN is selected, the Remote Gateway IP should be blank.
• Disable UID.
4. Click Add.
5. The newly created IPSec IKE configuration displays at the bottom of the VPN > IPSec screen.
To enable the connection, check the connection’s Status box at the bottom of the screen.
Note: Be sure that the checkmark is still in the VPN Status box at the top of the screen. Both status boxes must be
checked in order for the tunnel to start.
New IKE configuration: ; SiteA WAN lan RemoteWAN_IP RemoteLAN Edit | Delete
This completes the configuration for Site A (the RouteFinder in your home office) to support a tunnel through the
Internet to remote branch office.
Configuring Site B
For Site B (RouteFinder in the branch office), input the parameters listed in the table at the beginning of this section.
Then follow the steps for Site A, except that now you will use the parameters for Site B listed in the example on the first page
of this chapter.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 35
Page 36

Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
Example 2 – Remote Client-to-LAN VPN Configuration
The VPN function to setup your RouteFinder so that your network allows a remote client to have access to the LAN through
a secure tunnel on the Internet. Your RouteFinder includes an easy-to-use IPSec VPN client connection that transparently
secures your Internet communications anytime, anywhere. This example shows the setup to allow a remote client to see a
LAN, where the remote client is using SSH Sentinel.
The example shows how to configure a Remote Client-to-LAN setup. For details about this and other setups, refer to the
RF660VPN Setup Examples Reference Guide, which is available on the CD included with your RouteFinder and on the
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. Web site at http://www.multitech.com/DOCUMENTS
This setup requires:
• one RF660VPN at the home office and
• a remote client with SSH Sentinel software.
For the SSH Sentinel Client Setup at the remote site, see the separate SSH Sentinel Guide.
SSH Sentinel Client Accessing LAN Through
RF660VPN RouteFinder (Input these
parameters on the RF660VPN in the home
office).
1. Domain name = Sentinel
2. Public Class C = 204.26.122.x
3. Networks & Services > Network
LAN: 192.168.2.0 – 255.255.255.0
Sentinel_Client: 204.26.122.50 –
255.255.255.255
4. Network Setup > Interface
Default gateway = 204.26.122.1
Host name = RF660VPN.Site-A.com
Eth0 = LAN, 192,168.2.1, 255.255.255.0
Eth1 = WAN, 204.26.122.103, 255.255.255.0
Eth2 = DMZ (don’t care)
5a. Packet Filters > Packet Filter Rules (remote
client static IP)
LAN – ANY – ANY – Accept
Sentinel – ANY – ANY – Accept
5b. Packet Filter > Packet Filter Rules (remote
client dynamic IP)
ANY – ANY – ANY – Accept
6. VPN > IPSec
Check and Save VPN Status
Add an IKE connection:
Connection name = Sentinel
Check Perfect Forward Secrecy
Authentication Method = Secret
Enter secret key (must be same both sides)
Select Encryption = 3DES
Local Interface = WAN
Local LAN Subnet = LAN
Remote IP = Sentinel_Client (remote client
static IP)
Remote IP = Any (remote client dynamic IP)
Remote Subnet = None
UID = Disable
.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 36
Page 37

Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
Example 3 – Remote Client-to-LAN Configuration
Using DNAT and Aliasing
Use this procedure to configure the RF660VPN with DNAT and Aliasing. This configuration allows a Windows 2000 Remote
Client to Telnet through the RF660VPN to several Windows 2000 Systems located on the LAN.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 37
Page 38

Chapter 4 – Configuration Examples
Example 4 – Client-to-LAN Configuration Using PPTP
Tunneling
Use this procedure to configure the RF660VPN as a PPTP server for VPN Remote Client Access (aka, PPTP Roadwarrior
configuration). (Note: IPX and Netbeui not supported when using PPTP tunneling.)
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 38
Page 39

Chapter 5 – URL Categorization
Chapter 5 – URL Categorization
The Universal Resource Locator (URL) Categorization License Key allows you to set up a URL database that limits clients’
access to places on the Internet by blocking sites you do not want accessed. In other words, you can deny users access to
various categories of Web sites you select.
Important Settings
• Client access to the Internet works in conjunction with the HTTP proxy running in transparent mode.
• The RouteFinder must be connected to the Internet for the URL License to be activated.
Setting Up HTTP Proxy and URL Filtering
• Click Proxy from the Menu bar. The HTTP Proxy screen displays.
• Check Status box and click Save.
Important: The Status box must be checked before you can enter and activate your URL Categorization
License Key.
Note About URL License Key: The URL License number must be entered on the Administration > License Key
screen before the URL Categorization section of this screen displays. The key number is located on the bottom of
the RouteFinder chassis and on the front of the Quick Start Guide.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 39
Page 40

Chapter 5 – URL Categorization
• Go to the Administration > License Key screen to enter your URL License Key. This is a required in order to
use this feature.
• Click the Open button across from URL Categorization License Key.
The Administration > License Key > URL Categorization screen displays:
• Using upper case letters, enter the 11-digit serial number of the URL License Key and click the
Save button. IMPORTANT: It is important that the serial number be entered in upper case.
• Click the Activate button. The categorization engine's expiration date and time display.
• Return to the Proxy > HTTP Proxy screen to set your URL filtering categories. See the screen on
the previous page.
• Check the Transparent box and click Save.
• Check the URL Filter box and click Save. Once you click Save, two additional fields display: URL
Categories and Networks / Hosts to bypass URL Filtering.
• Click Edit for URL Categories (Allowed/Filtered). Not shown on the screen example above.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 40
Page 41

Chapter 5 – URL Categorization
• The URL Categories screen displays. You can use this screen to allow or block Web sites from users.
• Use the Allow and Filter buttons to move a URL Category from the URL Categories Allowed list to
the URL Categories Filtered or from Filtered to Allowed.
• When you have established your filtered and allowed categories, click the Backup button to create a
backup of your URL category database files.
• When you are finished organizing the categories, click the Back button to exit the screen.
How to Test Web Sites for Blocking
You can test specific Web sites to see if the URL has been blocked (use Get URL Category to perform this
test) or submit a site to be blocked or unblocked by the SurfControl software, which sets up the categories
stored in this software.
How to Test the Filtering
Type a URL in the http:// box and click the Go button. This will test the URL to see if it is allowed or
blocked.
Note: You can also test a site through your browser by entering a Web address that you feel should
be blocked by the filter through one of the categories you had chosen or a category preset by the URL
software. For instance, if you selected the Finance and Investment category to be filtered, try to
access www.etrade.com
stating the status of this Web site.
Important: The sites listed in the Favorites box of the browser will not be blocked unless the cache is
emptied in the browser.
. This site should be blocked. A message displays under the URL address
Establishing Filtering Rules for Networks and Hosts
Return to the Proxy > HTTP Proxy screen by clicking the Back button on the Proxy > HTTP Proxy >
URL Categorization screen.
• Click the Edit button for Networks / Hosts to bypass URL Filtering. The Networks / Hosts to
bypass URL Filtering screen displays. You can use this screen to allow or block Web sites from
Networks / Hosts.
• Click the Add button to move a network/host name into the Network/Hosts to Bypass URL Filtering
box.
• If you decide that you do not want one or more of the networks/hosts bypassing the filter, select the
name and click the Delete button. The name moves back into the Available Networks/Host box.
Submitting a Site to SurfControl for Reconsideration
Filtered categories are setup and controlled by the SurfControl software that is built into your RouteFinder
VPN. There may be a category you would like to see added or deleted. You can submit sites to be blocked
or unblocked. Click the words Click Here to open a proposal screen and send it to SurfControl.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 41
Page 42

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
This chapter describes each screen and its function in the RouteFinder VPN software. The aim of the administrator in
setting the options in the software should be to let as little as possible and as much as necessary through the RouteFinder
VPN, for both incoming as well as outgoing connections.
Note: If you have not done so already, plan your network and decide which computers are to have access to which services.
This simplifies the configuration and saves you a lot of time that you would otherwise need for corrections and adjustments.
Menu Bar
The Menu bar will provide the organization of this chapter.
Important Note About Logout
Logout Closes the Software Program and Saves Settings
The best way to exit WebAdmin is to choose Logout. This will save all your current settings. The browser connection is
terminated and you are returned to the Login screen. Note that clicking the browser’s Back button will not effectively
return you to the previous menu or directory at this point.
If you close the browser while configuring the RouteFinder, the last session stays active until the end of the time-out,
and no new administrator can log in. The timeout period is set at Administration > Administrative Access > Time
Before Automatic Disconnect.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 42
Page 43

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > System Setup
Administration
Administration > System Setup
In the Administration part of the software, you can set the RouteFinder general system-based parameters.
System Setup includes general system parameters such as the Administrator's email address, SNMP Agent, System
Logging, Remote Syslog Host, and the System Time.
Email Notification
Email Address: Enter the Email Address of the administrator who will receive the email notifications. Click
Save. You can delete the entry and change it at any time, if desired.
At least one email address must be entered in this field.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 43
Page 44

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > System Setup
Configure Email Notifications the RouteFinder VPN Will Send
Select the types of notifications that you want sent. Click the Add button. The name will then appear in the Send
Email Notification For box. You can remove a type by clicking the Delete button. The name will than move back
to the Don't Send Email Notification For box.
1. Export Backup (the backup file will be attached)
2. File Intrusion Detection (File Integrity Checks and Network Intrusions)
3. High CPU/RAM Usage (Hard disk usage exceeding 70%)
4. Disk Clean Up – Low Diskspace
5. System Key Expired (10 days before expiry)
6. Invalid Web Login
7. Invalid SSH Login
8. Port Intrusion Detected
9. PPP backup link down
10. PPP backup link up
11. URL Filtering Server Error
12. Auto System Update
13. Virus Key Will Expire
14. Virus Key Has Expired
15. Virus Database Updated
16. URL Filtering Key Expired
17. URL Filtering Key Will Expire (10 days, 2 days, and 1 day before expiry)
18. URL Filtering Categories Updated
19. URL Categories Update Failed
20. Bayesian Database Has Reached Maximum
21. POP3 Virus Mail
22. HTTP Access Deny Reports
The mail settings are saved in the server configuration. The first email ID in the list should be the Administrator's
ID, so that when the first ID is added or deleted, the session is terminated and the Web server restarted.
SNMP Agent – Community Name
Type the community name for the SNMP Agent.
System Logging
Check the Logging Status box to activate and enable the host to receive log messages from other machines.
Select the type of logging, either Local or Remote.
Then type the IP address of the Remote Syslog Host to which all log messages from the RouteFinder will be
forwarded. Click Save. The IP address is a required parameter.
On the remote host, syslog should be invoked with the "-r" option to enable the host to receive log messages
from other machines. This is especially recommended if you want to collect the log files of several systems on
one host. The default setting is ’off’.
System Time
Select the system time, time zone, and current date.
Note: It is not recommended that you change from summertime to wintertime and back. We suggest entering
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), regardless of your global position, especially if you plan to operate Virtual Private
Networks across different time zones. Changing the system time can lead to the following time-warp effects:
Forward time adjustment (winter to summertime)
• The time-out for the Web Admin has expired and your session is not valid anymore.
• Log information for some time periods may be missing in the time-based reports.
• Most diagrams show this time period as a straight line at the height of the old value.
• All the values for Accounting in this time period are 0.
Backward time adjustment (summer to wintertime)
• The time-based reports already contain log information for the corresponding time period which, as far
as the system is concerned, comes from the future: this information is not overwritten, but is retained.
• The writing of the log files is continued from the point of time before the setback time is reached.
• Most diagrams show the values of this time period as compressed.
• The already-recorded data (from the future) retain their validity for the Accounting function.
• The accounting files are continued when the setback time is reached again. Therefore, it is
recommended that the time should only be set once during initial configuration and later should only
be slightly adjusted. No adjustments from wintertime to summertime should be made, especially if the
collected reporting and accounting information is to be further processed.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 44
Page 45

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > SSH
Administration > SSH
What Is SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is a program to log into another computer over a network to execute commands in a remote machine
and to move files from one machine to another. It provides strong authentication and secure communications over an
insecure network. It is intended as a replacement for rlogin, rsh, and rcp. The SSH configuration provides access to the
firewall using SSH channel. SSH is a text-oriented interface suitable only for the experienced administrators. Access via SSH
is encrypted and, therefore, impossible for outside users to tap into it.
Prerequisites
• For access via SSH, you need an SSH Client, which most Linux systems already include. For MS Windows, the
program PuTTY is recommended as an SSH client.
• To log into the RouteFinder with Secure Shell (SSH, Port 22), use the login user account and the appropriate
password that was set up during installation. Remember to change your password regularly!
• Networks allowed to access the RouteFinder using SSH are added on this screen; other networks can be defined
on the Networks & Services > Networks screen.
Status and SSH Port
Initially, this screen displays with Status as the only prompt. Once Status is checked and you click Save, SSH
is enabled and the other options display. The TCP port number for the SSH session is specified in the SSH
Port Number field; the default is Port 22.
SSH requires name resolution for the access protocol; otherwise, a time-out occurs with the SSH registration.
This time-out takes about one minute. During this time it seems as if the connection is frozen or that it can’t be
established. After that, the connection returns to normal without any further delay.
Allowed Networks
Networks allowed to access the RouteFinder through SSH can be added and deleted here. The default Any in
Allowed Networks ensures a smooth installation and allows everyone to access SSH service.
Caution: While the default setting (Any) allows everyone to access the SSH service, we recommend that you
restrict access to the SSH service for security reasons. You should delete access from all other networks!
When deleting a network, the program checks whether you are still able to access Administration >
Administrative Access from your active IP address after the deleting procedure. If this is no longer possible,
the process is not carried out. This check is carried out for the security of the administrator and will ensure that
the administrator cannot become locked out accidentally. After completing the adjustments, it is a good idea to
disable SSH access again for security reasons.
Allowed Users
Users allowed to access the RouteFinder through SSH can be added and deleted here. Highlight the Users
you want to have access to SSH service and click the Add button. Users can be deleted from this list at any
time.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 45
Page 46

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > SNTP Client
Administration > SNTP Client
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) is an internet protocol used to synchronize the clocks of computers on the network.
Clicking the SNTP Client check box enables the firewall to act as a SNTP client.
SNTP Client
Check the SNTP Client box to activate SNTP Client.
SNTP Server Address
Enter the IP address of the SNTP Server for which the firewall will contact to synchronize its clock. Then click
the Save button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 46
Page 47

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Administrative Access
Administration > Administrative Access
The networks and hosts that are allowed to have administrative access are selected on this screen. This is a good way to
regulate access to the configuration tools.
Administrative Access - Available Networks and Allowed Network
Select the networks/hosts that will be allowed administrative access. Note that the selection box list will include
those networks you enter under Networks & Services > Networks.
You can change access by moving network/hosts names from the Available list to/from the Allowed list. The
RouteFinder will display an ERROR message if you try to delete access to a network that would cause you to lock
yourself out.
Allowed Networks
The default Any has been entered here for ease of installation. ANY allows administrative access from
everywhere once a valid password is provided.
Caution: As soon as you can limit the location from which the RouteFinder is to be administered (e.g., your IP
address in the internal network), replace the entry ANY in the selection menu with a smaller network. The
safest approach is to have only one administrative PC given access to the RouteFinder. You can do this by
defining a network with the address of a single computer from the Networks and Services > Networks
screen.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 47
Page 48

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Administrative Access
Change Password
You should change the password immediately after initial installation and configuration, and also change it
regularly thereafter. To change the password, enter the existing password in the Old Password field, enter the
new password into the New Password field, and confirm your new password by re-entering it into the
Confirmation entry field.
Caution: Use secure passwords! For example, your name spelled backwards is not secure enough;
something like xfT35$4 is better.
Time Before Automatic Disconnect
An automatic inactivity disconnection interval is implemented for security purposes. In the Time Before
Automatic Disconnect entry field, enter the desired time span (in seconds) after which you will be
automatically disconnected from the software program if no operations take place.
After the initial installation, the default setting is 3000 seconds. The smallest possible setting is 60 seconds. If
you close the browser in the middle of an open configuration session without closing via Exit, the last session
stays active until the end of the time-out and no new administrator can log in.
If using SSH, you can manually remove the active session if you log into the RouteFinder as login user via
SSH. With the command SU, you become a root user and can then interrupt the current connection with rm -f
/tmp/wfelock.
Administrative Access HTTPS Port
This field is used for setting the HTTPS port for Web administration. After setting the HTTPS port, the
connection is terminated. The browser settings have to be changed for the new port number before starting the
next session.
By default, port 443 is configured for HTTPS sessions. The value of the port number should lie between 1 and
65535. Well known ports and ports already used by the firewall are not allowed.
If you want to use the HTTPS service for other purposes (e.g., a diversion with DNAT), you must enter a
different TCP port for the interface here. Possible values are 1-65535, but remember that certain ports are
reserved for other services. We suggest you use ports 440-450. To have Administrative Access after the
change, you must append the port to the IP address of the ROUTEFINDER separated by a colon (e.g.,
https://192.168.0.1:445)
.
Administrative Access HTTP Port
Check this box if you want to use HTTP to access the RouteFinder’s software. This is less secure, but it is
faster when performing administrative tasks. Click Save.
Logo and Version on Logon Page
Check this box if you want the logo and version number to display on the logon page. Click Save.
Administrative Authentication Log
Log Successful Attempts
If you check this box, the successful login attempts at the RouteFinder's administrative access interface will be
recorded and displayed on the Statistics & Logs > Administrative Authentication screen.
Log Failed Attempts
If you check this box, the failed login attempts at the RouteFinder's administrative access interface will be
recorded and displayed on the Statistics & Logs > Administrative Authentication screen.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 48
Page 49

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Site Certificate
Administration > Site Certificate
Public keys are used as the encryption algorithm for security systems. For the validity of public keys, certificates are issued
by a Certificate Authority. The Certificate Authority certifies that the person or the entity is authenticated and that the present
public key belongs to that same person or entity. As the certificate contains values such as the name of the owner, the
validity period, the issuing authority, and a stamp with a signature of the authority, it is seen as a digital pass. On this screen,
you enter server certificate information, which the firewall needs to authenticate itself to your browser. After saving the
settings, the browser’s security information settings have to be cleared.
Enter the Certificate Information
Country Code – Use the default (United States) or change to the country of operation.
State or Region – Type the state, province, region, etc. of operation.
City – Type the city name.
Company – Type the company name.
Organization Unit – Type the organizational unit (e.g., Sales & Marketing).
Contact Email – Type the email address of the contact for RouteFinder certificate data (e.g., the RouteFinder
administrator) over the default (myname@mydomain.com).
Firewall Host Address – Enter the RouteFinder‘s host address. Use the same address that you will use to
open the Administration Access interface. It can be one of the RouteFinder IP addresses.
• Example: If you access Administration Access with https://192.168.10.1
be 192.168.10.1. If you access Administration Access with a DNS host name (e.g., https://MultiAccess
Communications Server.mydomain.com), then use this name instead.
• Note: The Host Address field MUST
browser to open Administration Access.
match the host Address or IP Address that you use in your
, the Host Address must also
Click Save
The browser will reconnect to the VPN. At the security Alert screen, click View Certificate. Then click Install
Certificate if you have not previously installed it:
Install the Certificate into the Trusted Root Certification Authorities Store
1. When the first screen displays, click the Install Certificate button.
2. On the Welcome to Certificate Import Wizard screen, click the Next button.
3. On the Certificate Manager Import Wizard screen, click Next. You can elect to have the certificate
automatically placed into a directory or you can Browse and choose your own directory. If you elect to
place all certificates into a selected location, follow the on-screen prompts for Select Certificate Store,
Physical Stores, and Root Stores.
4. When the certificate has been added to the Root Store, the Completing the Certificate Manager Import
Wizard displays. Click Finish.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 49
Page 50
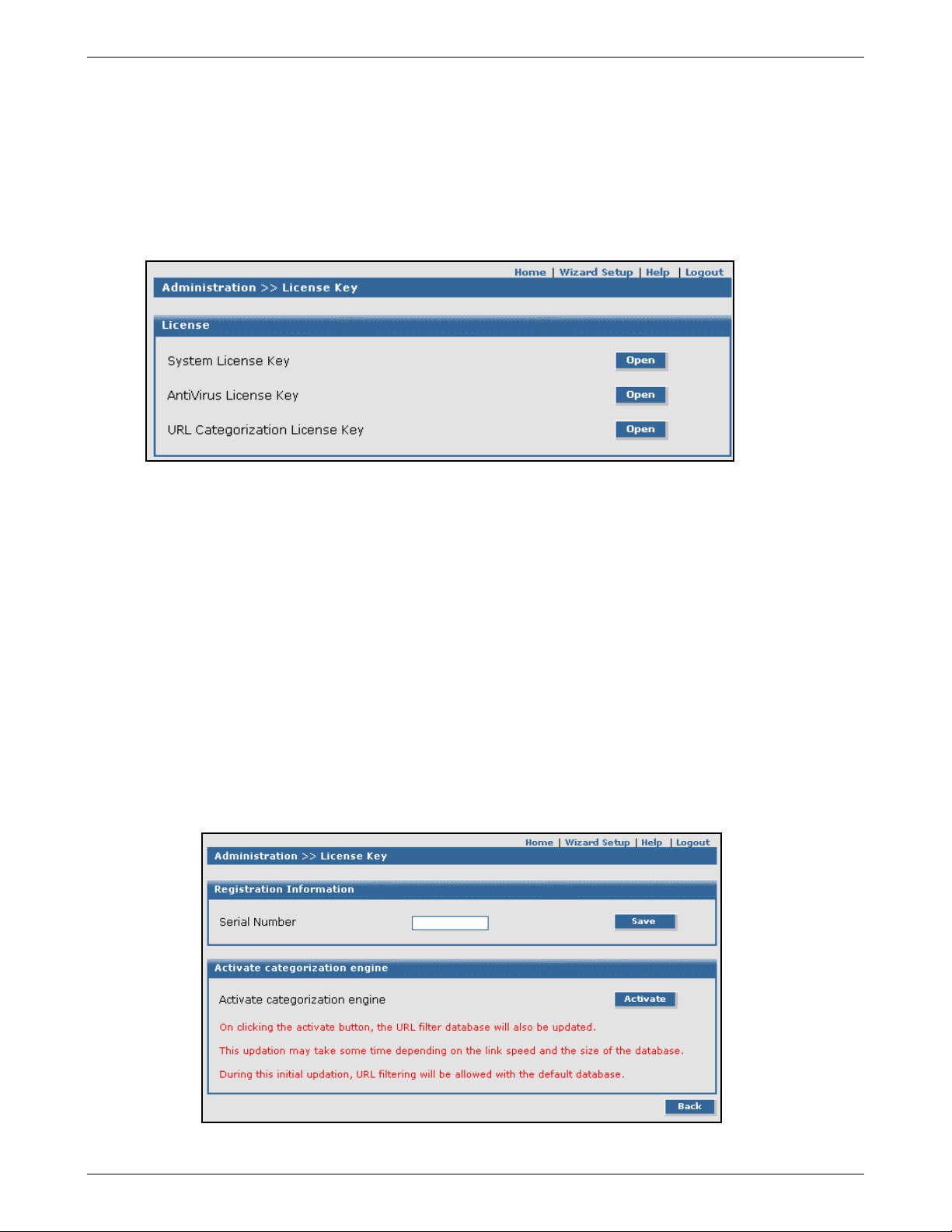
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > License Key
Administration > License Key
The system license key, virus scanner license key, and the URL Categorization engine license key can be configured from
this screen.
Notes:
• Each RouteFinder ships with a unique individual system license key. It is a 20-digit code that is provided on the
RouteFinder CD.
• Each RouteFinder ships with a URL Categorization License Key. It is provided on the RouteFinder CD.
• The AntiVirus key can be purchased from Multi-Tech Sales Support.
License
Click the Open button for the desired license key. The Enter License Key screen displays.
System License Key
Enter the license key number assigned to your RouteFinder and click Save. When you have entered the
License Key accurately, the Enter System License Key screen is re-displayed.
Important:
• The license key number is a 20-digit alphanumeric entry; the letters must all be in upper case.
• If you enter your license key number incorrectly, the message Error: License is invalid is
displayed. Check the license key number and re-enter it. One common entry error is mistaking a 0
(zero) for an o (the letter O). Another entry error is entering lower case letters or symbols.
• The License Key number is tied to and tracked with your RouteFinder‘s serial number.
• Whenever you require additional licenses, you must first provide Multi-Tech with your current
License Key and serial number information in order for us to update your RouteFinder.
• With a valid License Key, you are entitled to use Multi-Tech’s Update service and support.
AntiVirus License Key
The AntiVirus license key can be purchased from Multi-Tech sales support.
URL Categorization Key
This license key is included with your RouteFinder when it ships, but you must enter the license key to
activate the feature. The key number is included on the RouteFinder CD.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 50
Page 51

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Intruder Detection
Administration > Intrusion Detection
The Intrusion Detection mechanism notifies the administrator if there has been any tampering with the files on the server.
Intrusion Detection
Enable File Integrity Check – Check the box to enable File Integrity Checking.
Time Interval – Select the amount of time you would like the system to conduct this check. Options are every 5
Minutes, Hourly, or Daily. Then click the Save button.
Network Intrusion Detection
This allows the user to detect attacks on the network. In the event that port scans are carried out by hackers
who look for a secure network with weak spots. When this feature is enabled, it informs the administrator by
email as soon as the attack has been logged. The administrator can decide what actions are to be taken. By
default, DOS attack, minimum fragmentation checks, port scans, DNS attacks, bad packets, overflows, chat
accesses, Web attacks will be detected; and then the administrator is informed. Apart from the above, the user
can configure user-defined rules for intrusion detection.
Enable Network Intrusion Detection for LAN – Check the box to enable Network Intrusion Detection for the
LAN. Then click the Save button.
Enable Network Intrusion Detection for WAN – Check the box to enable Network Intrusion Detection for the
WAN. Then click the Save button.
Enable Network Intrusion Detection for DMZ – Check the box to enable Network Intrusion Detection for the
DMZ. Then click the Save button.
User-Defined Network Intrusion Detection Rules
SRC IP Address
This selection allows you to choose the network from which the information packet must be sent for the rule to
match. Network groups can also be selected. The ANY option matches all IP addresses; it does not matter
whether they are officially assigned addresses or private addresses. These Networks or groups must be
predefined in the Networks menu.
Destination IP Address
This selection allows you to choose the network to which the information packet must be sent for the rule to
match. Network groups can also be selected. These network clients or groups must have been previously
defined in the Networks menu.
Protocol
This selection allows you to choose the corresponding service. The service must have been previously defined
in the Services menu. Select intrusion detection rules from the following dropdown list boxes:
Add
After the rules are defined/selected, click the Add button. The commands can be deleted by clicking Delete
under the Command option.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 51
Page 52

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Tools
Administration > Tools
There are three tools that can help you test the network connections and RouteFinder functionality. Ping and Trace Route
test the network connections on the IP level. TCP Connect tests TCP services for availability.
Notes:
1. For these tools to function, the ICMP on firewall function in Packet Filter > ICMP must be enabled.
2. For the Name Resolution function, enable the DNS proxy function in Proxy > DNS. To use the Name Resolution
function, enable a name server in the menu (item) Proxy > Name Server. When the Name Server is enabled, the IP
addresses of the reply packets will be converted into valid names.
PING
Ping is an acronym for Packet Internet Groper. The PING utility is used as a diagnostic tool to determine if a
communication path exists between two devices on the network. The utility sends a packet to the specified
address and then waits for a reply. PING is used primarily to troubleshoot Internet connections, but it can be
used to test the connection between any devices using the TCP/IP protocol.
If you PING an IP address, the PING utility will send four packets and stop.
If you add a -t to the end of the command, the PING utility will send packets continuously.
Host – Specify the IP address or name of the other computer for which connectivity is to be checked.
Number of PINGS – Select the number of pings. You can choose 3 (the default), 10 or 100 pings. Enter
the IP address or the name into the Host entry field (e.g., port 25 for SMTP).
Timeout – Specify the time that packets can exist.
Packet Size – Specify the number of data bytes to be sent.
Start – After clicking the Start button, a new browser window opens with the PING statistics accumulating.
"Close the PING Statistics Window to A Sample" PING log is shown below.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 52
Page 53

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Tools
Trace Route
Trace Route is a tool for finding errors in the network routing. It lists each router’s addresses on the way to
remote systems. If the path for the data packets is temporarily unavailable, the interruption is indicated by
asterisks (*). After a number of tries, the attempt is aborted. The interrupted connection can have many causes,
including the packet filter on the RouteFinder not allowing the operation of Trace Route.
Trace Route lists the path of the data packets all the way to the desired IP address. The path ends when the
destination address has been reached. Should the data packets' path momentarily not be traceable, stars (*)
appear to indicate a time-out. After a fixed number of time-outs, the attempt is aborted. This can have various
reasons (e.g., a packet filter doesn‘t allow Trace Route). If it is not possible to locate a name despite activated
name resolution, the IP address is shown after several attempts instead.
Host – Specify the IP address or the name of the other computer to test this tool.
Start – Click the corresponding Start button to start the test.
TCP Connect
This tool tests the TCP services for availability. At the IP level, only the source and target addresses are used.
TCP, however, additionally requires the use of port numbers. A connection on the TCP level is identified by the
source address and port as well as the target address and port.
Host - Enter the IP address or the name of the Host.
Port - Enter the port number into the TCP port entry field. Example: Port number 80 for the HTTP service.
Start - Start the test connection by clicking the Start button.
A Sample Trace Route Log
A Sample TCP Connect Log
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 53
Page 54

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > System Scheduler
Administration > Factory Defaults
Administration > System Scheduler
The System Scheduler is a module built into the RouteFinder that schedules the tracking or checking of the following:
• Tracking bounced emails on the SMTP Proxy
• Tracking bounced RouteFinder emails
• Tracking SMTP Report Logs
• Checking disk usage of quarantined emails
1. Click Change Schedule Period for the Event Name that you would like to change. Once clicked, the
Event Name and a drop down list box displays.
2. From the drop down list box, select a new amount of time.
Each Event offers the following time choices:
minutely (every minute)
twomins (every two minutes)
threemins (every three minutes)
fivemins (every five minutes)
sevenmins (every seven minutes)
elevenmins (every eleven minutes
thirtymins (every thirty minutes)
hourly (every hour)
daily – 1 (once a day)
daily – 2 (twice a day)
daily – 3 (three times a day)
midnight (each day at midnight)
weekly (once a week)
fortnightly (once every two weeks)
monthly (once a month)
3. Click the Change button. The new time selection is scheduled and displays in Scheduled Period.
Administration > Factory Defaults
Click the Factory Defaults button on this screen to return all RouteFinder settings to the original factory defaults. This will
change all the settings you have modified. You may want to record current settings for referencing later on.
You have the option to Clear All Logs before resetting the factory defaults.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 54
Page 55

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > User Authentication > Local Users
Administration > User Authentication > Local Users
In this part of the software enter local users and define their access to various proxies.
External user databases can also be accessed (e.g., RADIUS servers, Windows NT servers, or Windows 2000 servers).
User Authentication is useful if a user database already exists on such a server, in which case the user need not be created
on the RouteFinder again.
At the IP level, you can limit the access to the proxy services of your RouteFinder by setting Packet Filter rules on your
internal clients. This poses certain problems, however, if you are using a dynamic configuration protocol internally, such as
DHCP or BOOTP. In this case, user authentication becomes irrelevant. When requests are made to a proxy service, the
client must authenticate himself with his user name and password. This makes the authentication person-based (i.e., userbased) and not IP-based, thus making a person-based Accounting in the HTTP proxy access protocol possible.
Prerequisite
Before you can use Local Authentication, you must activate User Authentication for the respective proxy services. In
Proxy (e.g., Proxy > HTTP or Proxy > SOCKS) check the Local in the Authentication Types menu; then click Add.
User Definition
User Name Enter the name of the user. This is a required field.
Password Enter the user’s password. The password should be a minimum of 8 characters.
Confirmation Confirm the password entered above by entering it again.
Description Enter a short comment that will identify the user to you.
HTTP User Check this checkbox if you want the user to have access to the HTTP proxy.
SOCKS User Check this checkbox if you want the user to have access to the SOCKS proxy.
SSH User Check this checkbox if you want the user to have SSH access.
Add Button Click Add after all the parameters are entered. After a successful definition, the new user
displays in the user table.
Edit or Delete You can edit or delete entries in the table by highlighting the desired entries and clicking Edit
or Delete under Command.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 55
Page 56

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > User Authentication > RADIUS & SAM
Administration > User Authentication > RADIUS & SAM
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a protocol with which equipment such as an ISDN router can
access information from a central server for user authentication. It also manages technical information needed for the
communication of the router with the equipment of the caller. This includes, for example, the protocols used, IP addresses,
telephone numbers, timeouts, routes, etc. Together they create a user profile that is stored in a file or a database on the
RADIUS server. RADIUS is also used as a generic authentication protocol.
The RADIUS protocol is very flexible and is available for most operating systems, including Microsoft Windows NT/2000.
RouteFinder RADIUS implementation lets you configure access rights on the basis of proxies and users.
A RADIUS server should not be visible to the world at large, but should be contained behind the firewall. If the RADIUS
server is visible from the Internet, a number of attacks become possible.
Note: In order to use any of these authentication methods, you must activate user authentication and the type of
authentication for the services. Mark the option (Local, SAM, RADIUS) in the select menu of the respective services. SSH by
default authenticates users using the local system, and you cannot disable local authentication for SSH; whereas, for
SOCKS and HTTP, any type of authentication can be enabled or disabled.
RADIUS Prerequisite
Before you can activate RADIUS authentication, you need a RADIUS server on your network. The server could also
be somewhere in the external network (Internet). But, since the passwords are transferred in plain text, we strongly
recommend that the RADIUS server be located close to the RouteFinder and that they are connected via a
switching hub. In case of transfer via a public network, we recommend the use of an encrypted tunnel.
RADIUS Settings
RADIUS Server Address
Set the IP address of the RADIUS server.
RADIUS Server Secret
Enter the password for the RADIUS server.
Save
After entering the above parameters, click the Save button.
A Note About Microsoft IAS
For information about Microsoft’s IAS (RADIUS server for MS Windows NT and 2000), see Multi-Tech’s
RASExpress RADIUS Setup Reference Guide. The guide also gives you step-by-step setup examples and
links to Microsoft’s ISA site.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 56
Page 57

SAM Prerequisite
In order to be able to use this authentication method, your network requires a Microsoft Windows NT or 2000
computer that contains the user information. This can be a Primary Domain Controller (PDC) or an independent
server.
This server has a NETBIOS name (the NT/2000 server name) and an IP address.
1. Under the Administration menu, open User Authentication > RADUIS & SAM.
2. Confirm your entries by clicking the Save button.
Important Note: If you are using SAM authentication, you should deactivate the guest account of your Windows
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > User Authentication > RADIUS & SAM
Domain Enter the name of your MS Windows NT/2000 domain into this field.
Accepted characters are: the alphabet, the numbers 0 to 9, the minus sign, and underscore.
Caution: This is not an Internet domain (e.g., Company.com) but a simple denominator (e.g.,
Intranet). If, instead of using the Microsoft domain concept, you only have a simple server,
then enter the NetBIOS name. This corresponds to the entry in the PDC name entry field.
PDC Name Enter the NETBIOS name of the primary domain controller into this field. As of Microsoft
Windows 2000, these names are also official DNS names. The RouteFinder only supports
names consisting of alphanumeric and minus and full-stop characters. Special characters
such as % ! # _ { } are not
PDC IP Enter the IP address of the primary domain controller into this field.
BDC Name If you are using a backup domain controller, enter the name into this field. If you do not have
a backup domain controller, enter the PDC name again.
BDC IP Enter the IP address of the backup domain controller into this field. If you do not have a
backup domain controller, enter the PDC IP address again.
domain. Otherwise all user/password combinations are counted as valid.
permitted.
SAM
This authentication method uses an MS Windows NT/2000 domain controller or a standalone server to evaluate the
requests. Many businesses are already using MS Windows NT/2000 networks that are based on the MS Windows
NT/2000 active directory domain concept.
The advantage of SAM is that it is very easy to configure if there is already a PDC (Primary Domain Controller) or a
simple server with a user database running in the network.
The disadvantage is that this model cannot discern between different user groups and proxies. This means that you
can grant only all users or none of the users access to a particular proxy.
SAM Settings
Domain
Enter the domain name of the PDC/DC Domain.
Primary Domain Controller Name
Enter the NETBIOS name of the Domain Controller.
Primary Domain Controller Address
Enter the address of the Domain Controller.
Backup Domain Controller Name
Enter the NETBIOS name of the Backup Domain Controller (if present). If you are not using a backup
domain controller, then you can enter Primary Domain Controller name in this field.
Backup Domain Controller Address
Enter the address of the Backup Domain Controller.
Save
After entering the above parameters, click the Save button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 57
Page 58

Administration > Restart
1. Click the Restart button to shut down and restart the RouteFinder.
The message Are you sure you want to restart the system? is displayed.
2. Click the OK button to confirm that you want to restart the RouteFinder WebAdmin software. The complete
restart can take 4 to 5 minutes. When the restart process is complete, the RouteFinder will generate 5
consecutive beeps; you can now continue RouteFinder operation.
If you do not want to restart the RouteFinder software, click Cancel.
Administration > Shutdown
1. Click the Shutdown button to shut down the RouteFinder. This is the correct way to shut down the
RouteFinder. It ensures that all the services are shut down correctly.
Are you sure you want to shutdown the system? message displays.
• If you do not want to shut down the RouteFinder, click the Cancel button to return to the
Administration > Shutdown menu.
• If you want to shut down the RouteFinder, click the OK button to confirm.
The Login screen displays while the shut down process takes place (2 to 5 minutes). A continuous beep occurs
when shutdown is complete. At this point you can power off the RouteFinder.
Caution: You should switch off the RouteFinder power only after you have performed this Shutdown process. If
the RouteFinder is not properly shut down before switching off Power, the next start may take a little longer. In the
worst case, data could be lost. Since the RouteFinder is now also checking the consistency of the file system, it
may have to restart up to three times.
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Administration > Restart
Administration > Shutdown
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 58
Page 59

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Networks & Services > Networks
Networks & Services
Networks & Services > Networks
A network always consists of a Name, an IP address, and a Subnet Mask address. Once you add a network, the information
displays at the bottom of the screen. This network table contains some generic networks by default, which cannot be deleted
or edited.
Important Notes:
• LAN and WAN interfaces will change if changes are made to LAN/WAN IP addresses in Network Setup.
• To define a single host, enter its IP address and use a netmask of 255.255.255.255. Technically, single hosts are
treated in the same way as networks.
• You can also use the bit "spelling" for the Subnet mask (e.g., write 30 instead of 255.255.255.252).
• A network or host can be deleted only if it is not used for any route or by any other module.
• If a network is being used by a routing section, that network cannot be edited. Similarly, if a host address is edited
and changed to a network address, and if that host was used by SNAT or DNAT, the changed will not be
performed.
Add Network
Name
Enter a straightforward name into the Name entry field. This name is later used to set packet filter rules,
etc. Accepted characters: alphabetic, numerical 0 to 9, the minus sign, underscore. Maximum characters
are 39.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the network.
Subnet Mask
Enter the Net Mask.
How to Confirm Your Entries
Confirm your entries by clicking the Add button.
After a successful definition, the new network is entered into the network table. This network will now be
referenced in other menus under this name. You can edit and delete networks by clicking Edit or Delete in the
Options column for the network you want to change. The Edit Network Publications (in this example) is
displayed. The name of the network cannot be changed, but the IP Address and Subnet Mask can be edited.
You can delete a newly created network by clicking on Delete in the Options column for a desired network.
Example 1: IP address 192.168.2.1 Subnet mask 255.255.255.0 Define a private Class-C net.
Example 2: IP address 216.200.241.66 Subnet mask 255.255.255.255 Define a host in the Internet.
Note About Entries: Entries can be made in the dot notation style (e.g. 255.255.255.0 for a class C network).
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 59
Page 60

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Networks & Services > Networks
After clicking the Add button, the Networks you have setup display on the lower part of the screen.
Example 1 – After the networks in the example are added, you will see the following entries added to the
table on this screen:
RemoteLAN 192.168.100 255.255.255.0 Edit | Delete
RemoteWAN_IP 204.26.122.3 255.255.255.255 Edit | Delete
Name IP Address Subnet Mask Options
Notes:
• The first four networks on this screen are default entries and cannot be changed.
• Networks added using the Add Network/Host function on this screen will also display in the Remote Gateway IP
and Remote LAN dropdown boxes on the VPN > IPSec > IKE screen.
Entries on This Screen Affect Other Screens
Networks added on this screen will display on the following screens:
Administration Access
Network Groups
SSH
Packet Filter Rules
Network Intrusion Detection
Routing
Masquerading
SNAT
DNAT
HTTP Proxy
SMTP Proxy
DNS Proxy
IPSec
PPTP
Network Names added on this screen will be made available to:
Add Allowed Networks on Administration Access screen
Add packet filter rules
Add source for Destination Networks on the Network Intrusion Detection screen
Add Routes on the Routing screen
SNAT
Masquerading
Port scan detection and DNAT sections
Add allowed networks on SSH, HTTP Proxy, and DNS Proxy screens
Add relay networks on SMTP Proxy screen
Add subnets on IPSec screen
Add local and remote IP addresses on PPTP screen
Mac address filtering (destination IP address) on the Packet Filters > Advanced screen
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 60
Page 61

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Networks & Services > Services
Networks & Services > Services
On this screen you can set the RouteFinder protocol services. Protocols make ongoing administration easier and enable the
configuration of user-defined services. These services are used in many of the other configuration settings on the system. A
service protocol setting consists of a Name, the Protocol, the S-Port/Client (source port), and the D-Port/Server
(destination port).
Add Services
Name Enter a unique name in Name entry field. You will need this later (e.g., to set packet filter
rules). The name should not be present in the service or service group list. Using a space
in the name is not allowed. After you have entered the name, click the Add button.
Protocol Select from the following protocols: TCP, UDP, TCP & UDP, ICMP, AH, and ESP. When
you select a protocol, the corresponding protocol fields will display.
Source Port Enter the source port for the service. The entry options are a single port (e.g. 80), a list of
port numbers separated by commas (e.g. 25, 80, 110), or a port range (e.g. 1024:64000)
separated by a colon (:). It will be displayed if the type of the protocol is TCP, UDP, or
TCP+UDP.
Destination Port Enter the destination port for the protocol. It is displayed if the type of protocol is TCP,
UDP, or TCP+UDP.
ICMP Code Specifies the ICMP type. It is displayed if the type of protocol is ICMP and the ICMP Type
is Redirect Network, Network Unreachable, or Time to Live Exceeded.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 61
Page 62

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Networks & Services > Services
Editing and Deleting User-Added Services
There are options for editing or deleting the user added services. However, there are some standard services which
cannot be edited or deleted. If the service is used by the Packet Filter rules, SNAT, or DNAT, it cannot be deleted.
For editing any user-defined service, the Edit button has to be clicked to get the fields corresponding to the service
entry.
Edit By clicking Edit in the Options column, the information is loaded into the entry menu of the Edit
Service screen. You can then edit the entry. You can edit user-added services only. The entries
can be saved using the Save button.
Delete By clicking Delete in the Options column, the service is deleted from the Services table. Changes
can be saved using the Save button.
Notes About Protocols
• TCP & UDP allow both protocols to be active at the same time.
• The ICMP protocol is necessary to test network connections and RouteFinder functionality, as well as for
diagnostic purposes. In the Packet Filter > ICMP menu you can enable ICMP Forwarding between
networks, as well as RouteFinder ICMP reception (e.g., to allow ping support).
• The ESP protocol is required for Virtual Private Network (VPN).
• The AH protocol is required for Virtual Private Network (VPN).
• For AH and ESP, the SPI is a whole number between 256 and 65536, which has been mutually agreed upon
by the communication partners. Values below 256 are reserved by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA).
Entries on This Screen Affect Other Screens
Service Names added on this screen will display on the following screens
Screen Fields
Packet Filter Rules Add packet filter rules
Packet Filters > Advanced MAC Address Based Filtering
Network Intrusion Detection Add specific services for Network Intrusion Detection
SNAT Add rule
DNAT Add rule
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 62
Page 63

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Networks & Services > Network Groups
Networks & Services > Network Groups
On this screen you can combine various networks into groups. The networks added in the screen Network & Services >
Networks can be placed into groups.
Rules and Suggestions for Establishing a Network Group
• A network that is already a part of a group cannot be added to any other group.
• It is suggested that you start a group name with a G- or Group-. This will identify group network names in
contrast to network names.
• When editing Network Groups, note that by pressing the Shift key, several entries can be selected together
allowing them to be added or deleted together.
• Every change in Network Groups is effective immediately.
About the Screen
Initially, the screen opens with only the Add Network Group field showing. Once a name is entered, the Select
Group section displays. When the View/Edit button is clicked, the Edit xxxxxx section of the screen displays.
Add Network Group
Enter a unique name for the Network Group. This name is used later if you want to perform operations such
as setting packet filter rules. Click the Add button.
Select Group [Group Names Entered Above Now Display Here]
Select the group from the drop-down list box you would like to Edit or Delete.
View/Edit Group
Click the View/Edit Group button. This allows you to view and edit the networks which are not part of
any group and the list of networks which fall under that group. These networks are available to be part
of your newly named network group. The Edit Support section of the screen displays.
Delete Group
Click the Delete button to delete the group selected.
Edit xxxxx (Networks to Add and Networks in the Group)
Networks to Add
Use the Networks to Add button to add networks into the newly named group.
Deleting Networks from a Group
Networks can be deleted from the newly created group by clicking the Delete Network button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 63
Page 64

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Networks & Service > Service Groups
Networks & Services > Service Groups
On this screen you can combine multiple Services (see Services section) into groups, called Service Groups. Service
Groups are treated like single services.
Rules and Suggestions for Establishing Service Groups
• A service that is already a part of a group cannot be added to any other group.
• A service can also be deleted from a group.
• Every change made to Service Groups is effective immediately.
About the Screen
Initially, the screen opens with only the Add Service Group field showing. Once a name is entered, the Select
Group section displays. When the View/Edit button is clicked, the Edit xxxx section of the screen displays.
Add Service Group
Enter a unique name for the Service Group. This name is required for later operations such as creating a
higher-level service group or to set packet filter rules. Click Add.
All names will be added to Select Group drop-down list box from which you can Edit or Delete a Service
Group.
Select Group [Group Names Entered Above Now Display Here]
Select the group from the drop-down list box you would like to Edit or Delete.
View/Edit Group
Click the View/Edit Group button. This allows you to view and edit the services for that group. The
Edit Support section of the screen displays.
Delete Group
Click the Delete button to delete the group selected.
Edit xxxx (Networks to Add and Networks in the Group)
Services to Add
Use the Services to Add button to add services into the newly named group. Available services are:
ANY H323 IMAP NEWS SNMP SSH
DNS HTTP netbios-dgm PPTP SNTP Telnet
FTP HTTPS netbios-ns POP3 SOCKS TRACE ROUTE
FTP-CONTROL IDENT netbios-ssn SMTP SQUID
Deleting Services from a Group
Services can be deleted from the newly created group by clicking the Delete Service button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 64
Page 65

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy
Proxy
While the packet filter filters the data traffic on a network level, the use of a Proxy (also called an Application Gateway)
increases the security of the RouteFinder on the application level, as there is no direct connection between client and server.
Every proxy can offer further security for its application protocols. Since each proxy is intended to serve only one or a few
application protocols, it usually offers more sophisticated features for logging and real-time analysis of transferred content.
General Information About Proxies
Proxy Services and Authentication Methods
The SOCKSv5 and HTTP proxy services support user authentication. Both proxies can be configured so that they either
accept all clients (based on IP addresses), or only those clients with a valid user name and password. If you activate
user authentication, you must determine which method your RouteFinder will use to evaluate the requested credentials,
otherwise the proxy service cannot be used.
The RouteFinder supports user authentication against:
• RADIUS server
• Windows NT SAM user base
• Defined user database in Administration Access
The three user databases can also be interrogated one after the other.
To Switch Off Proxy Using Netscape Navigator
1. Open the menu Edit/Settings/Extended/Proxies.
2. At Manual Proxies Configuration, click the View button.
3. At No Proxy For, enter the IP address of your RouteFinder.
4. Click the OK button to save the entries.
To Switch Off Proxy Using Microsoft Internet Explorer
1. Open the menu Extras/Internet options.
2. Choose the register card Connections.
3. Open the menu LAN Settings/Extended.
4. Under Exceptions, enter the IP address of your RouteFinder.
5. Click the OK button to save your settings.
Rules and Suggestions for Using HTTP Proxy
• A valid name server is required for using an HTTP proxy.
• Administration Access should not
browser in such a way that the IP address of the RouteFinder is not reached via a proxy.
• The HTTP proxy is an application gateway that converts the HTTP protocol (TCP/IP-port 80) for the
transmission of Web pages. To use an active HTTP proxy, you need matching browser settings (TCP/IP
address of your RouteFinder and port 3128); otherwise, the proxy must be run in transparent mode. Requests
to HTTPS (TCP/IP port 443) are forwarded unchanged.
• Parts of a Web page such as streaming audio and video are not loaded via port 80 (HTTP), but via a different
TCP port. These must be dealt with via an appropriate rule in the Packet Filter Rules.
be called up via one of its own proxies. You should configure your Web
Using Transparent Mode with HTTP Proxy
• While using transparent mode, all networks that should be forwarded transparently to the Proxy must be
assigned. All unassigned networks that you want to connect to the Internet without the proxy must be inserted
with a corresponding rule in Packet Filter. There is no access to the HTTP proxy using predefined settings in
the browser in transparent mode.
• If you choose Non-Transparent mode, consider the following:
• You must assign the networks that are to be allowed to use the proxy.
• No unassigned networks can use the HTTP proxy if the proxy is configured in the browser.
• You must set up the RouteFinder internal IP and port 3128
• User Authentication is possible only in non-transparent mode.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 65
Page 66

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > HTTP Proxy
Proxy > HTTP Proxy
The HTTP Proxy is capable of transferring www requests. HTTP use can be viewed in the Statistics & Logs menu.
HTTP Proxy Section
Status
To enable HTTP, check the Status box and click Save.
Transparent
To enable Transparent mode, place a check mark in the Transparent box and click the Save button. This mode
matches for HTTP requests only via port 80 from the internal network and forwards them to the proxy. This
process is invisible to the user. No further administration is required because no changes to the browser setting
of the end user are necessary. See the previous page for notes about using Transparent mode.
Networks (Allowed or Denied)
To select the networks you want to be available for the HTTP proxy, click the Edit button. The HTTP Transparent
Networks screen displays. By clicking the desired Change Status button, you change that network's status to
Allowed, Denied, as well as Available.
Banner Filter, Java Script Filter, and Cookie Filter
To enable any one or any combination of these filters, check the box. Click the corresponding Save button each
time you enable a filter.
Banner Filter – If this is enabled, then the Web page banners will be filtered out before the page is
forwarded to the Web client.
Java Script Filter – If this is enabled, then all the Java Script components in the Web pages will be filtered
out before the page is forwarded to the Web client.
Cookie Filter – When this is enabled, then cookies in the Web pages will be filtered out before the page is
forwarded to the Web client.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 66
Page 67

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > HTTP Proxy > URL Categorization
URL Categorization Section of the Main Proxy HTTP Screen
1. Enable URL Categorization by checking the URL Filter box on the main Proxy HTTP screen. The URL
Categorization section expands as shown here (a cutout section of the main screen with the URL
Categorization section expanded is shown here).
2. Click the URL Categories (allowed/filtered) Edit button. The URL Categories screens displays. URL
Categories can be configured to be filtered/forwarded by the firewall.
URL Categories (allowed/filtered)
On this screen you can change URL categories from Allowed to Filtered and vice versa). The Allow
and Filter buttons will move a URL Category from Allowed to Filtered box and back again.
The categories are setup and controlled by SurfControl software, which is built into your RouteFinder.
See URL Categorization in Chapter 2 for a detailed discussion of this screen.
3. Networks / Hosts to bypass URL Filtering
Click the Edit button for Networks / Hosts to bypass URL Filtering. Use the Add button to move a
network/host name into the Bypass URL Filtering box. If you decide that you do not want one or more of
the networks/hosts bypassing the filter, select the name and click the Delete button. The name moves back
into the Available list.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 67
Page 68

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > HTTP Proxy > User Authentication
User Authentication Section of the Main Proxy HTTP Screen
To enable User Authentication, check the User Authentication box and click Save (a cutout section of the main
screen with the User Authentication section expanded is shown here).
Note: If User Authentication is disabled, then the HTTP Proxy can be configured to function in transparent mode.
Authentication Types
1. Select the desired Authentication Type from the drop down list box.
Available Authentication Types are:
• Local
• RADIUS
• SAM
2. Click the Save button.
Available Users
1. Select the User you want to have access to HTTP Proxy server from the Available Users list.
2. Click the Add button. The user now displays in the Allowed Users box.
You can remove an allowed user by highlighting the name and clicking the Delete button. The name
goes back to the Available Users list.
Notes:
Adding New Users: New users can be added to the Available Users list on the Administration >
User Authentication screen.
Non-Transparent Mode: If the HTTP proxy functions in a non-transparent mode, then the authentication
mechanism through which the user can be authentication can be configured.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 68
Page 69

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > HTTP Proxy > Custom Filters
Proxy > HTTP Proxy > Custom Filters
The URL Categories in the HTTP Proxy page allows URLs to be filtered or forwarded by the firewall. On this screen, you can
configure Custom Filters. Custom filters will take preference over URL categories. You can use custom filters to build groups
of filters or lists that can be filtered by networks. The set of rules for the forwarding and filtered of URLs for a particular
network can be configured here.
Default Action for Custom URL Lists
Default Action
Select either Allow or Deny for your Custom Filter. Click the Save button.
Add Custom URL List
URL List Name
A Custom URL Group or List has to be named before defining a rule. Enter a name for the URL to include in
the list here. Click the Add button to save the name. On this screen List1 has been added as a URL group.
After clicking the Add button, the Access Rules section of the screen displays.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 69
Page 70

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > HTTP Proxy > Custom Filters
Access Rules
The Access Rules function enables you to define custom rules. With these custom rules, networks or network
groups can be allowed or denied access to certain URLs. URLs can be added or deleted from this list. Click the
Edit button to open a screen for entering URLs into the list. A text box and a list box for the URL will be shown.
The list box will contain the list of URLs that are already part of this list. URLs can be added to the list by
entering it into the text box and clicking the Add button.
URLs can be deleted from the list by selecting it and clicking the Delete button. Then click the Save button.
After making any changes, click the Save button to save these changes.
An access rule consists of three parts:
1. Network or Network Group
2. URL Group or List
3. Set either Allow or Deny
Example Using a Group Name
List Name: URL List named List1 contains google.com
Networks: There are two networks Net1 and Net2
Rules: Two rules have been configured:
Net1 – List1 – allow and
Net2 – List1 – deny
What Does This Mean:
• Users from Net1 trying to access google.com will be allowed to access the site.
• Users from Net2 trying to access google.com will not be allowed to access the site.
• Users from any other network will be allowed/denied access based on the URL Categorization
rules.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 70
Page 71

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SMTP Proxy
Proxy > SMTP Proxy
On this screen (the full screen displays once the Status box is checked), you can configure the SMTP proxy and the Virus
Protection function. The SMTP proxy acts as an email relay. It accepts email for your Internet domains and passes them on
to your internal email distribution system. This can be accomplished via a Microsoft Exchange Server, for example. Emails
are transparently scanned for known viruses and other harmful content.
The SMTP proxy also acts as a gateway for outgoing mail, thus taking over the job of email distribution from your internal
email system.
Rules and Suggestions for Using SMTP Proxy
• For SMTP, a valid name server (DNS) must be enabled. The RouteFinder sends notifications to the administrator
even if SMTP is disabled. The RouteFinder processes up to 25 incoming SMTP connections simultaneously
preventing Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The 26th incoming connection is not accepted.
SMTP Proxy
Status
To enable SMTP, check the Status box and click the Save button. When enabled, the SMTP Proxy starts
functioning and listens on port 25.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 71
Page 72

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SMTP Proxy
When Status is checked, the screen expands to display the following fields:
Accepted Incoming Domains
All the domains for which the SMTP Proxy can accept emails must be listed here. The domain for which
emails are accepted must be registered with the DNS server. Thus, the SMTP Proxy accepts only emails
which are addressed to the domains listed here.
Domains will be listed in the drop-down box from which they can be deleted, if desired.
Mail Relay
All the networks that can use the SMTP Proxy as a relay agent are configured here. A list of the various
networks configured using this software is displayed. You can add networks that can use the SMTP proxy
as a relay agent by using the Add button. All other networks not included in this list can send emails to
only those domains in the Accepted Incoming Domains list. The IP address of the mail server needs to be
added in the list of relay networks.
Add SMTP Routes
The SMTP Proxy decides on the path or the route to be taken for any domains based on the SMTP
Routes configuration. Thus, the domain name and the IP address of the MTA (Mail Transfer Agent) to
which mails are destined to this domain are to be forwarded are listed here.
Example: xyz.com:192.168.1.34. Any email to domain xyz.com is forwarded to 192.168.1.34, which is the
IP address of an MTA. If the SMTP route is not mentioned for a domain, then a DNS-lookup decides
where this email is to be forwarded or else a default route can be specified so that email to any domain is
forwarded to the default gateway. Example: 192.168.1.10.
Domain and Host
The fully qualified Domain Name and Host of the SMTP Proxy must be entered here.
Main SMTP Screen Continued
Queue Cleanup
Click the Clean button to delete emails held in the relay agent's mail queue. All mails waiting to be
delivered will be cleaned up. This option is to be used with extreme care.
Virus Protection – SMTP Virus Protection
Enables/disables virus scanning for SMTP traffic that passes through the RouteFinder. Both incoming and
outgoing emails are scanned, if they are sent via the SMTP proxy. If a valid virus license scanner license
key is not entered, this option will not be displayed.
An anti-virus license must be purchased from Multi-Tech in order to use virus protection, and the license
can be uploaded to the RouteFinder from the Administration > License Keys screen.
Remote SMTP Virus Quarantine – Remote SMTP Virus Quarantine Status
Check the Remote SMTP Virus Quarantine Status box to activate the remote quarantining of SMTP
virus emails. If activated, then local quarantining no longer exists.
Action Taken on Virus Emails
Change Action on Infected Mails: Select the action to be taken on infected emails for SMTP traffic.
If the action selected is Notify, options to send the information to the administrator / sender / recipient will
be displayed. Notification regarding infected mails will be send based on these settings.
If the action is Block, the mail will be silently dropped.
In both cases, the infected emails will be stored in the virus quarantine folder of the RouteFinder. The
administrator can view the emails, delete them, or forward them to a specified email ID.
Click the Save button after a Change Action.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 72
Page 73

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SMTP Proxy
SMTP Proxy Example
An entry Company.com covers all further sub-domains; for example, subsidiary1.Company.com and
subsidiary2.Company.com. The RouteFinder must be the MX (Mail Exchanger) for Company.com.
Incoming emails to non-registered domains are rejected (except for senders listed in Mail relay for below).
Confirm every registered domain by clicking the Add button. The domains are entered into a window from
which the entered domains can be deleted again at any time.
Mail relay for
Select all the networks from the select menu that are allowed to use the SMTP proxy on the
RouteFinder. Networks not entered here can only use the SMTP proxy to send emails to the above
listed domains. Confirm every selected network by clicking the Add button.
Note: If you assign Any, then everybody connected to the Internet can use your SMTP proxy for
SPAM purposes.
SMTP Routes
Determine the MTA (Mail Transfer Agent) to which each incoming domain is forwarded. The MTA is
determined by its IP address. You can also configure the forwarding of email into your internal
messaging system here. If you want to use the SMTP proxy as the SMTP relay (also often called
"SmartHost“) for your internal email server, configure it to use the internal address of your
RouteFinder system as a relay. However, for this to work, the IP address of your internal email server
must have been entered in the Mail relay for select menu. (Remember to insert the forwarding of the
domains to your internal email server.)
All outgoing mail is then forwarded via the SMTP proxy of the RouteFinder.
All settings are immediately active and are preserved after leaving the Proxies > SMTP menu.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 73
Page 74

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SMTP Proxy > SMTP SPAM Filtering
Proxy
On this screen the SPAM filtering parameters can be set so that all incoming and outgoing emails sent to the internal mail
server(s) will go through the SPAM filtering process.
>
SMTP Proxy
>
SMTP SPAM Filtering
RBL (Real Time Black List) Check
Real Time Black List (RBL) – Check this box to block emails from the IP addresses listed in RBL sites. If
emails are to be blocked, the IP address or URL of an RBL server must be entered. If you check RBL, then you
will be provided with the list Authentic List. Here you can configure IP addresses for which the RBL check can
be bypassed.
RBL Server URL – Enter the IP address of the sites to be blocked. Then click Save.
Spam Filtering
Authentic List – Enter any sender’s email ID that you wish to bypass the spam filtering process.
Authentic Networks – Enter any sender’s network name that you wish to bypass the spam filtering process.
Example: testuser@routefinder.yourdomain.com
If you want to add email IDs from the domain routerfinder.yourdomain.com, then add it as:
@routefinder.yourdomain.com
Blocked Networks – Enter the name(s) of any network(s) from which email cannot be sent. If any user tries to
send an email from a blocked network, the email connection is rejected.
Sender Black List – Enter a sender email addresses to be blocked. Then, if the sender’s email address
matches any entry in the list, the email will not be forwarded.
If all emails from a domain are to be blocked, add this @ symbol before the domain name:
testuser@routefinder.yourdomain.com
If you want to block all email from the domain routefinder. yourdomain.com, then add it as
@routefinder.yourdomain.com
If you want to block all email from the domain routefinder. yourdomain.com, then add it as
@routefinder.yourdomain.com
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 74
Page 75

Recipient Black List
Enter a recipient’s email address to be blocked. Then, if the recipient’s email address matches any entry in
the list, the email will not be forwarded.
If all email from a domain is to be blocked, add this @ symbol before the domain name:
testuser@routefinder.yourdomain.com
If you want to block all email from the domain routefinder. yourdomain.com, then add it as
@routefinder.yourdomain.com
Check for NULL Sender
If you check this option, email with an empty sender address sent to more than one recipient will not be
relayed.
Note: If the email contains only one recipient ID, even if this option is checked, the email will be relayed to
the recipient, since it is legitimate to have NULL sender address in error.
Reverse DNS Test
If you check this option, the SMTP Proxy will try to resolve the domain name part of a sender’s email ID. If
it is resolved to an IP address, then the email will be relayed. If the sender’s name is in the Authentic List,
then the reverse DNS test will not be performed for the domain.
Bad Patterns in Sender/Recipient Address
Enter any pattern in an email address that you would like to block. Then both the sender and recipient
email addresses will be checked for these patterns. If the patterns match, the email will not be relayed.
Control Characters:
1. Exclamation mark (!): Bypass the SPAM check for this entry alone.
Example: All email from or to the domain abc.com will be stopped except for test@abc.com:
*@abc.com
!test@abc.com
2. Asterisk (*): Stop all email from or to this domain.
Example: All email from or to the domain abc.com will be stopped.
*@abc.com
3. Set ([…]): Stop all email from a set such as @abc[0-9]*.com.
Example: All email from or to the domains that include numbers in the first part of their
names such as 0, 234, or 789023 will be stopped.
0.com
234.com
789023.com
4. Question mark (?): Stop all email with a match zero or one occurrence of the preceding
character or set of characters.
Example: All email from or to the domains abc.com, abc0.com, abc1.com, …abc9.com.
*abc[0-9]?.com
5. Backslash (\): Literal expression of the following character (the following character is a
metacharacter):
@\[[0-9]{1-3}\[0-9]{1-3}\[0-9]{1-3}\]
The first two characters after the @ character \[ means take the literal value of the [
character.
Example: All email addresses with IP addresses like username@[1.1.1.1] will not be
allowed.
Note: SPAM emails with percent-hack can be eliminated by adding *%* to the Bad Patterns
list.
Maximum Mail Size Allowed
The size of each email will be compared with the Maximum Size entered here, and if the mail size is more
than the Maximum Size, then that mail will not be relayed. This check will be bypassed for users added to
the SPAM Filtering Authentic List (on this same screen).
Message Filtering
When Message Filtering is checked, the screen expands to display the following fields:
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SMTP Proxy > SMTP SPAM Filtering
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 75
Page 76

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SMTP Proxy > SMTP SPAM Filtering
Message Filtering. If you check this option, then the email message or body will be searched for the
extensions and expressions added here. If there is a match, the email will be quarantined so that the
administrator can decide whether to forward or delete the email.
Note About Extensions: Examples of extensions are bmp, exe, gif. Also, double extensions such as
tar.gz cannot be used.
Note About Expression Format: If you want to search for the expression as is in the email, then add
it just as it is. If you want to use the entry as a regular expression, then enclose the entry with these
brackets: < >
Note About Wild Card: The wild card ‘*’ cannot be used to filter all attachments.
Adaptive Message Filtering.
If this operation is enabled, then the mail message or body will be searched for auto-learned
expressions by the Adaptive Message Filtering function. Click the Help button for this screen to read
more about Adaptive Message Filtering.
Remote SMTP SPAM Quarantine. This screen displays when Message Filtering is checked.
Check the Status box to enable Remote SMTP SPAM Quarantining, which will send all SMTP SPAM
emails to the configured email address entered into the E-Mail Address of Spam Account field.
Click the Save button.
Note: If remote quarantine is enabled, then local quarantine no longer exists.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 76
Page 77

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > POP3 Proxy
Proxy > POP3 Proxy
In order to use this function, you must have a valid Antivirus Scanner license key installed. To install one, go to the
Administration > License > Virus Scanner page.
Use this screen to configure POP3 virus filtering-related settings. All outgoing email will go through this POP3 virus filtering
process.
Note About This Screen: Initially, only the POP3 Virus Protection prompt and the Remote POP3 Virus Quarantine
Status prompts display. The other two prompts display after checking the initial check boxes and clicking the Save button.
POP3 Virus Protection
POP3 Virus Protection – Check the box to enable POP3 virus scanning of the traffic that goes through the
RouteFinder. Click the Save button.
Inform Admin for Virus Mails – Check this box to have information sent to the administrator. The
administrator will receive notification regarding infected emails.
Save – Click the Save button to activate this function.
Remote POP3 Virus Protection
Remote POP3 Virus Quarantine – Check the Status box to enable POP3 virus scanning of the traffic that
goes through the RouteFinder. Click the Save button.
Email Address of Virus Account – Enter the address of the POP3 Virus Email Account. All POP3 virus
quarantined emails will be forwarded to this account. Click the Save button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 77
Page 78

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > POP3 Proxy > POP3 SPAM Filtering
Proxy > POP3 Proxy > POP3 SPAM Filtering
The administrator can configure POP3 SPAM filtering and related settings on this screen. All outgoing email retrieved from
the internal mail server(s) will go through this POP3 virus filtering.
POP3 SPAM Protection
POP3 SPAM Protection
Check the box to enable POP3 SPAM Protection.
Subject of SPAM Mails
Enter a word that you would like to add to the subject line of any email identified by the virus scanner as
SPAM. The word SPAM is a good choice.
POP3 SPAM Filtering
Sender White List
Enter the sender email IDs that will not be checked for SPAM. For example, if all the emails from the
specific domain abc.com are not to be checked for SPAM, then the entry should be @abc.com.
Once you enter the ID and click the Add button, the ID displays in a list below the entry field. You may
enter more than one email ID, and each ID can be deleted.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 78
Page 79

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > POP3 Proxy > POP3 SPAM Filtering
Recipient White List
Enter the recipient email IDs that will not be checked for SPAM. For example, if all the emails from the
specific domain cde.com are not to be checked for SPAM, then the entry should be @cde.com.
Once you enter the ID and click the Add button, the ID displays in a list below the entry field. You may
enter more than one email ID, and each ID can be deleted.
Authentic Networks
Select the network from which a user may retrieve unfiltered email. In other words, the email on this
network is not checked for SPAM. Select from Any, LAN, WANInterface, DMZ.
Once you select a network and click Add, the network displays in a box below this entry field. You may
select more than one network, and a network can be deleted whenever you want to make a change.
Blocked Networks
If the user tries to retrieve email from the network entered in the list, then that connection of retrieving
emails is rejected.
Check for NULL Sender
If this option is enabled, email with an empty sender address is marked as SPAM.
Bad Pattern in Sender Address
The sender email address will be checked to see if matches any of the patterns added the list. If there is a
match, then the email will be marked as SPAM.
Control Character: Asterisk (*) is a general pattern-matching character. For example, if the entry is
xyz*@ abc.com, then all email from the domain abc.com with user names starting with
xyz will be marked as SPAM.
Message Filtering
If you check Message Filtering, two additional prompts display. File attachments and specified expressions will
be filtered.
Attachment Filtering
Enter the file extensions to be filtered. Email will be searched for these extensions. If there is a match, the
email will be quarantined so that the administrator can decide whether to forward or delete the email.
Note About Extensions: Examples of extensions are bmp, exe, gif. Also, double extensions such as
tar.gz cannot be used. The wild card ‘*’ cannot be used to filter all attachments.
Expression
The email message and body will be searched for the expressions added here. If the expression is "as is"
is to be searched for in the email, it is added with quotation marks. If the entry is to be used as a regular
expression, the entry should be enclosed in < >.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 79
Page 80

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SOCKS Proxy
Proxy > SOCKS Proxy
SOCKS is a universal proxy supported by many client applications. SOCKS5 is an IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force)
approved standard, proxy protocol for TCP/IP-based networking applications. The basic purpose of the protocol is to enable
hosts on one side of a SOCKS server to gain access to hosts on the other side of a SOCKS Server without requiring direct
IP access. When an application client needs to connect to an application server, the client connects to a SOCKS proxy
server. The proxy server connects to the application server on behalf of the client and then relays data between client and
the application server. For the application server, the proxy server is the client.
Differences Between SOCKS and NAT:
SOCKS allows BIND requests (listening on a port on behalf of a client; however, very few clients support this function)
•
• SOCKS5 allows user authentication.
• The SOCKS proxy is used for point-to-point connections.
The RouteFinder‘s SOCKS implementation supports the SOCKS v4 and the SOCKS v5 protocol versions. However,
when using SOCKS v4, User Authentication is not possible.
Socks Default Port – 1080. Almost all clients will default to this port setting, so it normally does not need to be configured.
Notes: All changes in Proxy become effective immediately without additional notice.
SOCKS Proxy
Status
To enable SOCKS, check the Status box. Click the Save button.
External Interface
The SOCKS Proxy uses an external interface to send outgoing requests. Select the interface that you want
to use. The options are LAN, WAN, and DMZ. This is the external interface to the Internet.
Internal Interface
Select one or two interfaces on which SOCKS is to accept connections from clients. The options are LAN,
WAN, and DMZ. The interfaces listed here can be used by clients with port 1080 to access the SOCKS
proxy.
User Authentication
To enable User Authentication, check the User Authentication box. If this function is enabled, SOCKS
proxy users must log in with their user names and passwords. User Authentication is available with
SOCKSv5 only. If you are using SOCKSv4, User Authentication is not available.
Authentication Types
Select the method of user authentication. Options are Local, RADIUS, and Sam. If you choose the Local
method, you can choose whether or not local users may use the SOCKS proxy.
If you disable User Authentication, then client applications must be configured with empty user name and
password fields!
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 80
Page 81

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > SOCKS Proxy
Allowed Users and Available Users
Enter a straightforward name that will identify a user group in the Allowed Users text box. Click the Add
button. The name will display in the Available Users box. Once the name has been accepted, you can
delete it at any time.
Add Users
A list of all users who are allowed to access the SOCKS Proxy can also be configured by selecting the
users from the right selection box and clicking the Add button. These users can also be added by checking
the checkbox against SOCKS users in the User Authentication > Users section. The left box contains
SOCKS users and the right box consists of all the local users who are not allowed to access SOCKS.
Delete Users
The users who are now allowed to access the SOCKS Proxy can be changed by selecting the users from
the left box and clicking the Delete button. These users can also be deleted by unchecking the checkbox
against SOCKS users in the User Authentication > Users section. The left box contains SOCKS users
and the right box consists of all the local users who are not allowed to access SOCKS.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 81
Page 82

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Proxy > DNS Proxy
Proxy > DNS Proxy
DNS Proxy is a module used to redirect DNS requests to name servers. This module supports a caching-only name server
which will store the DNS entries for a specified item. So, when there is a query next time, the values will be taken from the
cache and the response will be sent from the module itself. This will shorten the waiting time significantly, especially if it is a
slow connection.
On this screen you can enter the DNS (Domain Name Server) Proxy for your RouteFinder and configure it.
Note: If you configure several name servers, the servers are queried in the listed order.
DNS Proxy
Status
To enable the DNS proxy, check the DNS Status box. Click the Save button.
Interface to Listen To
Select the Interface option from the drop down list box. Options include LAN, WAN, and DMZ. Click the
Add button. Your choice will display in the box under the selection list. It you want to change or delete and
interface, highlight the name and click the Delete button.
Available Networks
This lists all the networks which are defined under Networks & Services > Networks. Select the one you
want to be available for the DNS proxy. Click the Add button after highlighting your choice.
Allowed Networks
This is a list of all the networks which are allowed to access the DNS proxy. Any other requests are not
forwarded to the DNS proxy.
Note: You can delete these networks at any time.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 82
Page 83

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > Interfaces
Network Setup
The Network Setup menus consist of Interface, PPP, PPPoE, DHCP Client, Dynamic DNS, Routes, Masquerading, SNAT,
and DNAT screens. With the help of DNAT and SNAT, the destination and source address of the IP packets are converted.
With Masquerading you can hide private networks from the outside world behind one official IP address.
About Interfaces
During initial installation, the RouteFinder automatically recognizes the installed network card and adds them to the
configuration.
Important: To change to an earlier configuration that you had saved, the RouteFinder must be re-installed. Use the
Tracking > Backup function to read in the configuration you had set for the RouteFinder after the new installation.
The RouteFinder must be the interface between the LAN and the Internet. All information packets must pass through the
RouteFinder.
We strongly recommend that you NOT put the interfaces of the RouteFinder physically together on one network
segment via a hub or a switch, unless the segment is configured as a VLAN switch. To do so can lead to faulty ARP
(Address Resolution Protocol) resolutions (ARP clash). Some operating systems (e.g., Microsoft Windows) cannot cope
with this. That is why one network interface should be used per physical segment.
About the Interfaces Screen
The first network card (eth0) is always the interface to the internal network (LAN). It is called the trusted network.
The second network card (eth1) is the interface to the external network (Internet). It is the untrusted network.
The RouteFinder must have at least these two networks active to protect separate networks or network segments from
each other.
Example: The network cards could be connected in the following way:
Network card 1: INTERNAL (to the local network)
Network card 2: EXTERNAL (to the Internet)
Network card 3: DMZ1 (DMZ for server)
The host name and the default gateway must only be defined once. The host name is, for example,
FIREWALL.yourdomain.com; the gateway could be your Internet router.
A suitable IP address must be entered for each network card. Let‘s assume that you are using a Class-C network for
your internal network, in this case the entry for network card 1 could look like the following:
Description: INTERNAL
IP address: 192.168.2.1 (Default)
Net mask: 255.255.255.0 (Default)
The description is for clarity purposes and is used in all further configurations. Make sure that the RouteFinder IP
address is entered as the default gateway in the protected networks.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 83
Page 84

Network Setup > Interface
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > Interface
Local Host
Default Gateway and Host Name
The Default Gateway and the Host Name must be defined for your RouteFinder. The Default Gateway was
already set during initial installation. Click the Save button after entering the Host Name.
Notes:
• If the gateway address and DNS addresses are assigned by a PPPoE server or a DHCP server or
through a backup link, the value cannot be changed.
• The same IP Address cannot be entered for two different interfaces.
Domain Name Server
External Name Server
Enter a name for the Domain Server. Click the Add button. The name displays in the box just under this
field. Once the name is in this box, you can highlight it and delete it or move it
WINS Server
WINS Server
Enter a name for the WINS Server. Click the Add button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 84
Page 85

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > Interface
Network Cards
About Network Card 1 (LAN eth0)
Network Card 1 is the interface to the internal network (LAN). The information was entered during initial
installation. This can be changed.
About Network Card 2 (WAN eth1)
Network Card 2 is the interface to the external network (Internet). This network card (eth1)
About Network Card 3 (DMZ eth2)
This network card (eth2) is the interface to the optional DMZ network. A DMZ (De-militarized Zone) is a
special LAN on the public network side of a firewall to allow a single WAN router to support both private
(VPN) and public access to resources. Using a DMZ allows one IP Address (computer) to be exposed to
the Internet. Some applications require multiple TCP/IP ports to be open. A DMZ allows just one computer
to be exposed for that purpose. It is recommended that you set your computer with a static IP to use DMZ.
Effect of Changes
When you make a change that affects other administration functions and configurations, an informational
screen displays. It tells you that the network interface you have just changed is used in several other
configurations, and then the configurations affected by this change are listed for you. If the automatic
changes are acceptable, continue editing. If the automatic changes are not
Back button and continue.
Name
Enter a definition of the network card into the Name entry field.
IP Address and Subnet Mask
Enter the IP address and the corresponding Subnet Mask into the appropriate entry fields. For example:
Network Card 1 (LAN eth0) Network Card 2 (WAN eth1) Network Card 3 (DMZ eth2)
Name (Description): LAN
IP Address: 192.168.2.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Caution: When entering a new IP address for Network Card 1, it is possible to “lock yourself out“. If you
do, in most cases you will need to reinstall the RouteFinder to re-establish access.
Proxy ARP on This Interface
If you check the Proxy ARP on This Interface checkbox, the RouteFinder will automatically announce
itself as responsible for all packets to destinations for which it has an Interface Route. You can use this
function to "half-bridge" a network into another LAN segment.
Note: All packet filtering rules still apply when Proxy ARP is enabled. This is not a full bridging function!
If the Proxy ARP on This Interface function is activated, the RouteFinder will relay the ARP protocol on this
network card for all the networks known to it. This means that the RouteFinder will accept and forward
packets on the Proxy ARP interface for all other directly connected networks.
This function is necessary in some special cases; e.g., when the correct routes for a network cannot be set
and the network has to be passed on through the firewall. This can be the case if you have no access to
the router of your Internet provider.
A Possible Error: The Interfaces menu doesn’t contain entry fields for all the network cards.
Possible Cause of Error: The missing network card was added after the installation of the RouteFinder,
or it wasn’t recognized during installation.
Solution: Reinstall the RouteFinder software. You can use the backup feature (described earlier in this
chapter) to transfer your configuration between the installations.
NIC Type, MAC Address, IRQ, and IO Port Info
This information defaults into the corresponding fields.
Save
Confirm your settings by clicking the Save button.
Name (Description): WAN
IP Address: 192.168.100.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
acceptable, click your browser‘s
Name (Description): DMZ
IP Address: 192.168.3.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
IP Aliases
From this part of the Interfaces screen you can add RouteFinder network interface IP Aliases. IP aliases can be
used to assign additional IP addresses to a network card. The RouteFinder will treat the additional addresses
as equals to the primary network card addresses. IP aliases are required to administer several logical networks
on one network card. They can also be necessary in connection with the SNAT function to assign additional
addresses to the firewall. Up to 100 additional addresses can be configured on each network card.
Interface
From the drop down list box, select the network name to which you want to assign an alias.
IP Address
Enter the network IP address for the network named.
Netmask
Enter the Netmask to be used for this network.
Save
Click the Save button.
Delete IP Alias
An IP alias is deleted by highlighting it in the table and then clicking the Delete button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 85
Page 86
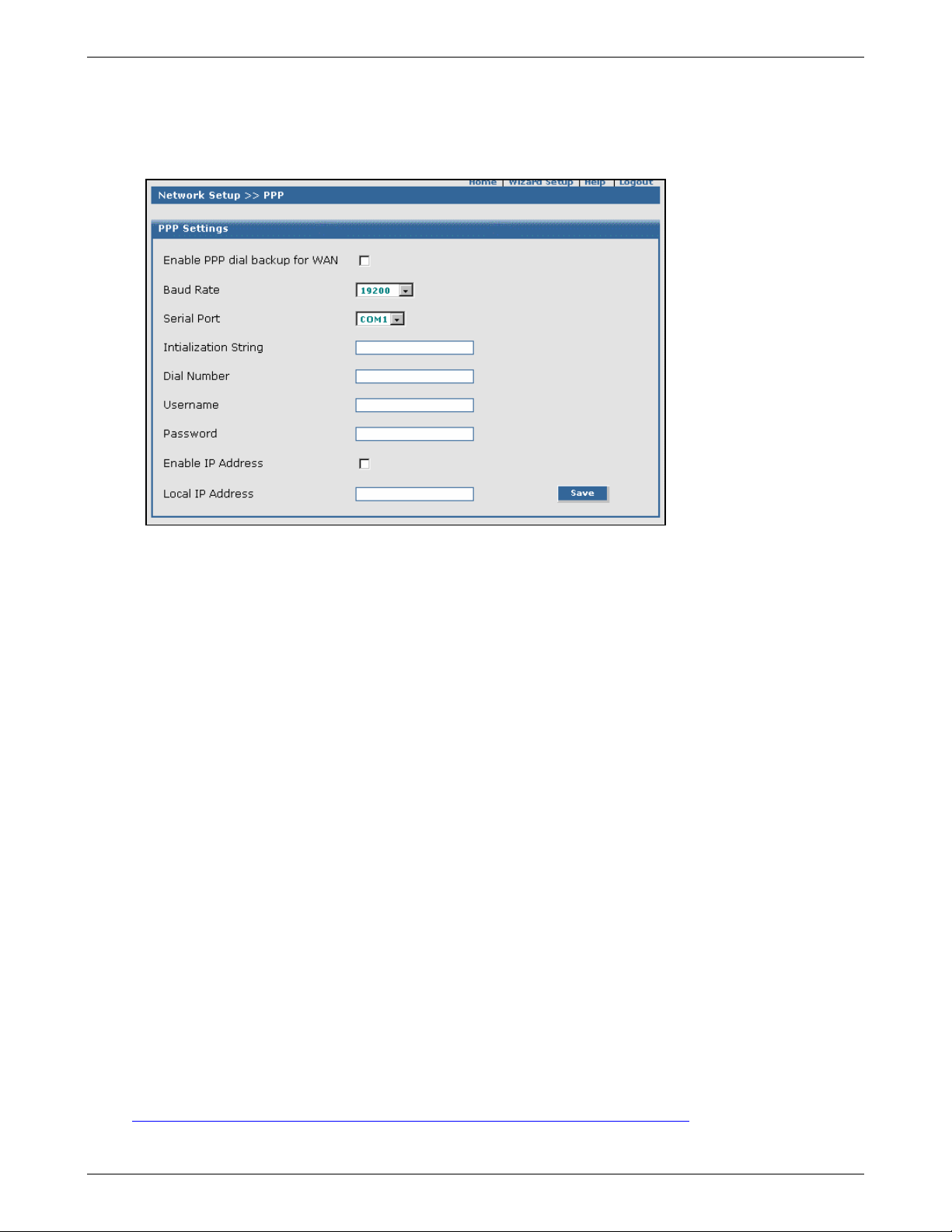
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > PPP
Network Setup > PPP
The PPP link is used as a backup link to the WAN interface. If the PPPoE or static link goes down, the backup link will
automatically come up and the system will be again connected to the ISP. On this screen you can set up PPP dial up backup
for your WAN interface.
PPP Settings
Enable PPP Dial Backup for WAN – To enable PPP Dial Backup for WAN, check the corresponding checkbox.
Baud Rate – Select the baud rate from the drop down list box. Options: 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, and 115200.
Serial Port – Select the Serial Port from the drop down list box. Options: COM1 and COM2; use COM2.
Initialization String – Enter the set of commands you want sent to the modem at startup. The initialization string
sets speed, error correction, compression, various timeout values, and how to display results to the user. You can
also change your country or region code by including the country/region code AT command in the initialization
string (see directions below).
Dial Number – Enter the phone number that the modem will use to connect to the PSTN.
User Name – Enter the ISP User Name designated for dialup access.
Password – Enter the ISP Password designated for dialup access; the password is optional.
Enable IP Setting – Check this box to enable the IP setting. This option can be set to make the firewall negotiate
for a particular IP address from the ISP.
Local IP Address – If the checkbox Enable IP is checked, the IP address has to be entered in this field.
Save – Click Save to activate these settings.
Change Your Country/Region Code
To change the country/region code, the initialization string must contain the AT command for your specific country
or region.
1. Type AT%T19,0,nn, where nn is the country/region code in hexadecimal notation.
Click Enter.
OK displays.
2. To verify that the correct country/region has been configured, type:
ATI9 and click Enter.
3. The country/region code displays:
Example: Country/Region AT Command (hexadecimal) Result code (decimal)
Euro/NAM AT%T19,0,34 (default) 52
A list of country/region codes can be found on the Multi-Tech Web site at
http://www.multitech.com/PRODUCTS/Categories/Modems/global/configuration.asp#chart
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 86
Page 87

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > PPPoE
Network Setup > PPPoE
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) is a specification for connecting multiple computer users on an Ethernet local
area network to a remote site through DSL or cable modems or similar devices. PPPoE can be used to have an office or
building-full of users share a common Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable modem, or wireless connection to the internet.
PPPoE combines the Point-to-Point (PPP), commonly used in dialup connections, with the Ethernet protocol which support
multiple users in a local area network.
Important: If DHCP client is enabled, the PPPoE cannot be used. The internet connection can be either PPPoE or DHCP
client at any given time.
PPPoE on WAN
Enable PPPoE on WAN
To Enable PPPoE on WAN, check the corresponding box. This will enable the interface connected to the
ADSL modem (this will be the interface to the internet).
User Name
This field defines the ADSL User Name given by the ISP.
Password
The user’s password must be entered in this field.
DNS Address from Peer
Check this box if you want to obtain DNS server addresses from the peer (i.e., the ISP).
Save
Click Save to activate these settings.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 87
Page 88

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > DHCP Client
Network Setup > DHCP Client
On this screen you can enable DHCP Client (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), which is a TCP/IP protocol that enables
PCs and workstations to get temporary or permanent IP addresses out of a pool from centrally-administered servers. This
screen will provide user messages such as the one shown is red. Later, it will display the Current DHCP Client Status. For
example: DHCP Client has not yet obtained an IP address from the DHCP server.
Important: If PPPoE is enabled, then DHCP client cannot be enabled. The interface to the internet can be either through
PPPoE or DHCP client at any time.
If DHCP client is enabled and if the IP address has been assigned, then the following values will be displayed on this screen:
• Assigned IP Address
• Mask
• DHCP
• DNS Address
• Gateway Address
• Renew Time (time at which the DHCP client should begin trying to contact its server to renew the lease it has
obtained).
• Expiry Time (time at which the DHCP client must stop using the lease if it has not been able to contact a server in
order to renew it).
DHCP Settings
DHCP Client on WAN
To Enable DHCP Client on WAN, check the corresponding checkbox.
Save
Click the Save button after enabling this function.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 88
Page 89

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > Dynamic DNS
Network Setup > Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS allows a user to connect his PC to the Internet with a dynamic IP address, so that he will be able to use
applications that require a static IP address.
Dynamic DNS Settings
Dynamic DNS Client
Check the box to enable Dynamic DNS Client for this machine.
User Name
Enter the name or the email ID you have specified while registering with the Dynamic DNS server.
Password
Enter the password you had specified while registering with the Dynamic DNS server.
Dynamic DNS Server
Enter the server to which you have registered for dynamic DNS service.
At present, only the following servers are supported for this function:
1. dyndns.org
2. zoneedit.com
3. easydns.com
4. hn.org
5. dslreports.com
6. dnspark.com
Domain Name
Enter the domain name which you have registered with the Dynamic DNS server.
Use Wildcard
If you enable this option, subdomains of the domain you have registered will also be resolved to the same
IP address.
For example, if you have registered test.dyndns.org, and the IP address assigned to it is resolved to
a.b.c.d, all the subdomains (e.g., dns.test.dyndns.org) will also be resolved to a.b.c.d.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 89
Page 90
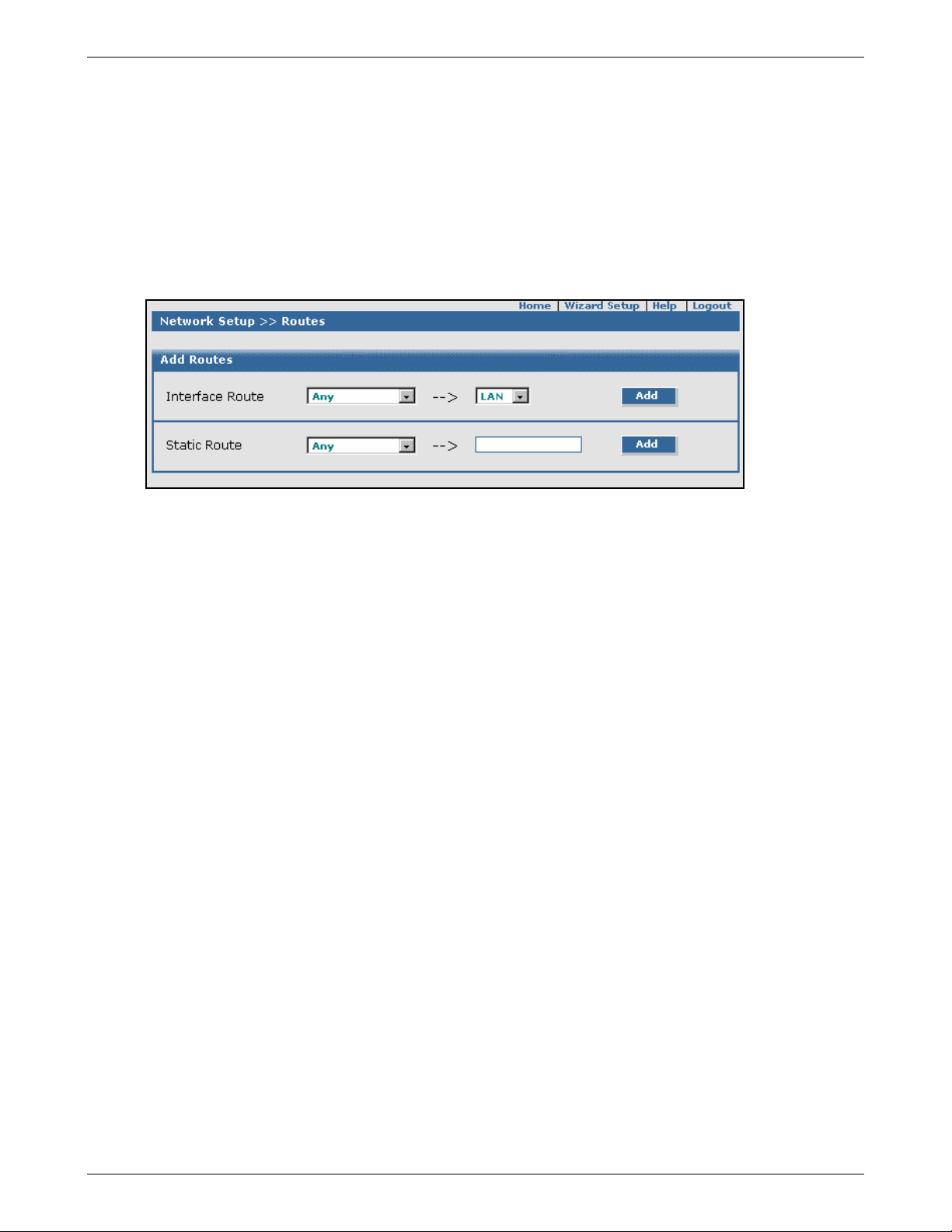
Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > Routes
Network Setup > Routes
Routing information is used by every computer connected to a network to identify whether it is sending a data packet directly
to the Firewall or passing it on to another network. There are two types of routes used by the firewall, interface routes that
describe routing entries for directly connected networks and static routes that describe routes which are to be routed using a
secondary router. You can add and delete entries in both these type of routes.
The RouteFinder itself adds routing entries for directly connected networks. These routes are called Interface Routes.
Further entries for networks in which the RouteFinder itself is NOT a member must be made manually (e.g., if there is a
second router on the network and a particular network is to be routed to it, for example if the second router is to be
responsible for this network).
Add Routes - Interface Route
Interface Route
Select an already defined network and a network card. The entries are confirmed by clicking the Add
button. Also, existing entries can be deleted by highlighting the entry and clicking the Delete button.
Note: While adding a route, if the network cannot be reached through that interface, the route will not be
added.
Add Routes - Static Route
This selection defines networks that are not directly connected, but are connected through a secondary
router or gateway. Select an already defined network for the drop-down list. Enter the external IP address
which will act as a gateway for this network. Confirm your entry by clicking the Add button. Existing
entries can be deleted by highlighting the entry and clicking the Delete button.
Note: The specified gateway should be reachable first. This means that a static route should already be
configured for the gateway.
Delete a Route
Select a Route from the table and click the Delete button. When deleting a Route, the interface adapts
accordingly.
Note: You can view the Routing Table in Statistics & Logs > Networks > Routing Table.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 90
Page 91

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > Masquerading
Network Setup > Masquerading
Masquerading is a process which allows a whole network to hide behind one or several addresses preventing the
identification of your network topology from the outside. Masquerading enables the user to enter only one source network. All
services are automatically included in the transition. The translation takes place only if the packet is sent via the indicated
network interface. The address of this interface is used as the new source of the data packets.
On this screen you can select networks or network groups to be masked to selected network cards. Masquerading is
especially useful for connecting private networks to the Internet. It allows you to hide internal IP addresses and network
information from the outside network.
Masquerading
Masquerading
Select one of the networks already defined in the Networks menu. Select a network from each box (from
and to networks).
Add
Click the Add button. The Masqueraded network route displays below.
Edit or Delete a Route
Select Masqueraded network route from the lower box and click the Edit or Delete button. When deleting
a Masqueraded network route, the interface adapts accordingly.
Example
In this example, the sent packet does not contain any internal information. The reply to the request is
recognized by the RouteFinder and is passed on to the requesting computer.
Computer A with the address XY is inside a masked network within the RouteFinder.
It starts an HTTP request into the Internet. Computer A - and all computers in this network - use the only
official IP address. For all data packets that are to go into the Internet, the IP address of the sender is
exchanged for the IP address of the external network card.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 91
Page 92

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > SNAT
Network Setup > SNAT
The SNAT (Source Network Address Translation) process allows attaching private networks to public networks. SNAT is
used when you want to have a LAN using a private IP network to be connected to the internet via a firewall. Since the private
IP addresses are not routed on the internet, you have to apply SNAT on the firewall’s external interface.
The firewall’s internal interface serves as the default gateway for the LAN. Hence, a rule is added to the firewall to replace
the source address of all packets crossing the firewall’s external interface from inside to outside with the firewall’s own IP
address. Once the request gets answered from the Internet host, the firewall will receive the reply packets and will forward
them to the client on the LAN.
On this screen you can set up the RouteFinder‘s ability to rewrite the source address of in-transit data packages using
SNAT. This functionality is equivalent to DNAT, except that the source addresses of the IP packets are converted instead of
the target addresses being converted. This can be helpful in more complex situations (e.g., diverting reply packets of
connections to other networks or hosts).
Important
For SNAT support, the TCP and/or UDP settings must be enabled at Networks & Services > Services > Protocol.
Important
As the translation takes place after the filtering by packet filter rules, you must allow connections that concern your SNAT
rules in Packet Filters > Packet Filter Rules with the original source address. Packet filter rules are covered later in this
chapter.
Note: To create simple connections from private networks to the Internet, you should use the Network Setup >
Masquerading function instead of SNAT. In contrast to Masquerading, SNAT is a static address conversion, and the
rewritten source address does not have to be one of the RouteFinder‘s IP addresses.
Add SNAT Definition
From the drop down list boxes, select IP packet characteristics to be translated. The options are:
Pre SNAT Source
Select the original source network of the packet. The network must be predefined in the Networks
menu. The entry is confirmed by clicking the Add button. Existing entries can be deleted or edited by
clicking the Edit or the Delete buttons.
Service
Allows the corresponding service for the Pre SNAT Source entry field to be chosen from the select
menus. The service must have already been defined in the Services menu.
Destination
Select the target network of the packet. The network must have been defined in the Network menu.
The entry is confirmed by clicking the Add button. Existing entries can be deleted or edited by clicking
the Edit or the Delete buttons.
Post SNAT Source
Selects the source addresses of all the packets after the translation. Only one host can be specified
here. The entry is confirmed by clicking the Add button. Existing entries can be deleted or edited by
clicking the Edit or the Delete buttons.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 92
Page 93

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Network Setup > DNAT
Network Setup > DNAT
On this screen you can set up DNAT re-routing. DNAT (Destination Network Address Translation) describes the target
addresses of the IP packets. Use DNAT if you want to operate a private network behind your RouteFinder firewall and
provide network services that run only behind this private network available to the Internet. Note that for DNAT support, the
TCP and/or UDP settings must be enabled (at Networks & Services > Services > Protocol).
Important Notes:
You cannot add a DNAT rule with the Pre DNAT Network as ANY, with Service as ANY, and a Destination
•
Service as ANY. All the packets will be routed to the system with Post SNAT network, and then the services in
the firewall will not function properly.
• As the address conversion takes place BEFORE the filtering by the packet filter rules, you must set the
appropriate rules in the Packet Filter > Rules menu to let the already-translated packets pass. You can find
more about setting packet filter rules earlier in this chapter.
Add DNAT Definition
The DNAT screen contains four drop down list boxes. The first two define the original target of the IP packets
that are to be re-routed. The last two define the new target to which the packets are forwarded. From the drop
down list boxes, select IP packet characteristics to be translated.
Pre DNAT Destination
Select the target host or target network (e.g., PPTP-Pool) and the corresponding Service (e.g., DNS,
FTP, FTP-CONTROL) to be redirected. Note that a network can consist of one single address with net
mask 255.255.255.255.
Post DNAT Destination
Select a host to which the IP packets are to be diverted. Only one host can be defined as the Post
DNAT destination.
Important: If you are using a port range as the Post DNAT Service, you must enter the same Service
definition as you entered in the Pre DNAT Service. In other words, you can only map one port range
to the same port range. Select a corresponding Service (e.g., DNS, FTP, FTP-CONTROL) to be
redirected.
Add, Edit, Delete
Click the Add button to save your choices. After saving the settings, a table is created. You can edit or
delete entries by highlighting the desired entries and clicking either the Edit or Delete button listed
under Command.
DNAT Example
Your Internet/private network has the address range 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0. You now want to make a Web
server that is running on port 80 of the server with the IP address 192.168.0.20 accessible to clients outside your
LAN. These clients cannot contact its address directly, as the IP address is not routed in the Internet. It is, however,
possible to contact an external address of your RouteFinder from the Internet. With DNAT, you can re-route port 80
on the RouteFinder’s external interface onto the Web server.
Note: To divert port 443 (HTTPS), you must change the value of the TCP port on the Administration >
Administrative Access screen in the field Administrative Access HTTPS Port (e.g., port 444).
Examples of DNAT Network Combinations
You can map:
IP/Port ⇒ IP/Port
IP/Port-Range ⇒ IP/Port
IP/Port-Range ⇒ IP/Port-Range (only if the Port-Range is the same for PRE and POST)
IP-Range/Port ⇒ IP/Port
IP-Range/Port-Range ⇒ IP/Port
You cannot
The “way back" (return) translation is done automatically; you do not need a rule for it.
map:
IP ⇒ IP
IP-Range ⇒ IP
IP-Range ⇒ IP-Range
IP ⇒ IP-Range (load balancing)
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 93
Page 94

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
DHCP Server > Subnet Settings
DHCP Server > Fixed Addresses
DHCP Server
DHCP Server > Subnet Settings
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol which allows individual devices on an IP network to get their own
network configuration information (IP address, subnetmask, broadcast address, etc.) from a DHCP server. The overall
purpose of the DHCP is to make it easier to administer a large network. The DHCP package includes the DHCP server and
a DHCP relay agent.
DHCP Server on LAN
DHCP Server on LAN
The DHCP Server is enabled by default. If you would like to disable it, uncheck the DHCP Server on LAN
checkbox. If you change the check mark, click the Save button to activate the change.
Add
Click the Add Subnet button which will open the table for entering the Subnet IP Address and Mask.
Edit or Delete
You can edit or delete entries by selecting the desired entries and clicking either the Edit button or Delete
button listed under Options.
DHCP Server > Fixed Addresses
The DHCP server can be made to assign a fixed IP address for a particular user by identifying the MAC address. This
binding can be made permanent by configuring the same using this screen. The same IP address would not be used for any
DHCP client with a different MAC address, even if there is no active DHCP connection with that IP address.
DHCP Server Fixed Addresses
Add Fixed Address
Enter both a MAC address and an IP address.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 94
Page 95

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Tracking > Accounting
Tracking
Tracking > Accounting
The Accounting function records all the IP packets on the external network cards and sums up their size. The traffic sum for
each day is calculated once a day. Additionally, the traffic sum for the current month is calculated and displayed. This is the
amount that your ISP (Internet Service Provider) will charge to you if your payment plan is based on the amount of data you
transfer.
On this screen you can specify which local devices will have their network traffic counted and recorded. You can also
exclude hosts or networks from the accounting process.
After this accounting is in place, you can view the Accounting of your RouteFinder in the Statistics & Logs > Accounting
menu.
You can also exclude Hosts or Networks from Accounting. After installing your RouteFinder, all networks are included in the
accounting function. Excluding a network from Accounting could be useful if the interface to the DMZ is entered in the
Accounting while one particular computer in the DMZ is not to be accounted. If this one computer is only to be used for
internal purposes, it does not make sense to include its information traffic in the accounting balance.
Note: The traffic will be displayed as graphs in Statistics & Logs > Accounting.
Accounting Device
Accounting Device
From the Accounting Device drop down box, select the network to have its traffic counted. The options are
LAN, WAN, and DMZ. Click the Add button to confirm your entry. After the entry is completed, a table for
this network is created.
IP-Based Accounting
IP Address
Enter the IP addresses for which traffic is to be monitored. The traffic to and from the particular IP address
destined to one of the firewall’s interfaces and the traffic to and from the particular IP address and
forwarded by the firewall will be considered for accounting. Click the Add button.
VPN Accounting
VPN-Based Accounting
Check the VPN Accounting Status box to have the VPN status monitored by the accounting function. Click
the Save button.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 95
Page 96

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Tracking > Update Services
Tracking > Update Services
On this screen you can define RouteFinder update parameters. If you use the Update Service, your RouteFinder can be
continually updated with new virus protection patterns, system patches, security features, and new features. The Updates
are signed and encrypted and read in via an encrypted connection.
System Update Server
Server Name and Directory
Enter the name or IP address of the server you want to specify as the system update server and enter the
path to this server. Click the Save button.
Virus Update Server
Server Name and Directory
Enter the name or IP address of the server you want to specify as the virus database update server and
enter the path to this server. This process downloads and installs new virus detection patterns for the
firewall‘s virus scanner. To ensure that patterns stay up-to-date at all times, the process can be automated
by setting a time interval after which the system automatically checks for virus pattern updates at the
specified update server.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 96
Page 97

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Tracking > Update Services
Update Services
Update System, Update Virus Patterns, Update URL Categories Database
This section of the screen allows you to start the update processes of these services. Click the Start
button to start the Update System, Update Virus Patterns, and/or Update URL Categories Database
processes.
Note that the Current Version and Updates displays automatically.
Time Interval for Automatic Update of Virus Patterns
Your RouteFinder can be continually updated with new virus patterns (with optional email virus scan
subscription), system patches, and security features that can be automatically read into your running system.
The updates are signed and encrypted and read in via an encrypted connection. To setup an automatic virus
update function, check the Enable Update checkbox. Then select the time interval after which the system
automatically checks for the virus pattern updates at the specified update server. The time intervals are hourly,
daily, weekly, and monthly.
Time Interval for Automatic Update of URL Categories
Your RouteFinder can be continually updated with new URL categories. To setup an automatic URL category
update function, check the Enable Update checkbox. Then select the time interval after which the system
automatically checks for URL category database updates from its server. The time intervals are daily, weekly,
fortnight, and monthly.
System Update - Livelog
After clicking the System Update - Livelog button, a list of all downloaded packages along with the download
time will be displayed.
Virus Update - Livelog
After clicking the Virus - Livelog button, a log file of the virus pattern updates will be displayed.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 97
Page 98

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Tracking > Backup
Tracking > Backup
The Backup function lets you save the RouteFinder settings on a local hard disk. With a backup file, you can set a recently
installed RouteFinder to the identical configuration level as an existing RouteFinder. This is useful in case there is a problem
with your new settings. Also, a new RouteFinder can be installed and the backup read in minutes. This means a replacement
system can be running in a very short time. The backup file contains all configuration settings except the VPN RSA Key.
The Backup function is responsible for the following:
1. Saves your firewall settings as a zip file.
2. Sends the backup as an attachment to an email to the administrator.
3. Allows you to import the backup either from the firewall or the browser machine. In this case, the settings will revert
back to the settings saved in the corresponding zip file.
4. Allows you to download the backup from the firewall directly to your browser machine.
Important Notes About Backups:
• You will probably want to keep routine backups of all aspects of your RouteFinder to let you re-build it in case of an
emergency, as well as to use as evidence if and when you discover a successful attack (letting you compare the
before and after states of the RouteFinder).
• You may want to store all alerts and notifications.
• Passwords are saved, but the RSA key is not saved.
Backup
Comments for Export Backup
This field is a required field. Enter an explanation of the backup file for future reference. Click Save. This
starts the backup and includes the comment as part of the backup file. The file name generated by the
RouteFinder is made up of backup’s date and time in the format yyyy-mm-dd.hh-mm.zip. The file is saved
to your hard drive and can be emailed.
Caution: When reading in the backup file, the RouteFinder automatically configures itself as recorded in
the backup file. For example, if IP addresses or passwords have since changed or have been forgotten,
you might not be able to access the RouteFinder anymore.
Import Backup from Firewall/VPN
This function is used for restoring the configuration files from a backup file present in the firewall itself.
After clicking the Import button, a list of all the backup files maintained in the firewall will be displayed.
Select the file you want to import and click the Get Comments button to read the comments for this file
and verify that this is the file you want. Once you are sure of the file you want, click the Import button.
Passwords will be saved.
Note: Backups taken from a previous version cannot be imported.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 98
Page 99

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Tracking > Backup
Import Backup from Remote Client
When a backup is taken, the backup file is sent to the administrator through email. This function is used for
restoring the configuration files from a remote client. After clicking the Import button, a list of all the
backup files maintained on the remote client’s PC display. Select the file you want to import and click the
Get Comments button to read the comments for this file to verify that this is the file you want. Once you
are sure of the file you want, click the Import button.
Download Backup
Click the Download button to backup files saved in the firewall to the local machine.
Status
Enable Periodic Backup
Place a checkmark in this box to set up an automatic performance of the periodic backups. Click the Save
button.
Interval for Periodic Backup
Select how often you would like automatic periodic backups to be performed. Options are daily, weekly,
and monthly. Then click the Save button.
Maximum Backup to Store
Set the maximum number of backups that you want to be retained in the server. Enter a number between
1-20.
Adaptive Database Backup
Enables Adaptive Database Backup.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 99
Page 100

Chapter 6 – RouteFinder Software
Tracking > Version Control
Tracking > Version Control
These settings are the configuration management system settings. All configuration files can be saved in a repository in a
CVS server. There are fields for setting the IP address of CVS server, user name, password, and the repository path. The
corresponding user account and the directory structure should be created on the CVS server.
CVS Settings
User Name
Enter the name of the user for whom the account will be created.
Password
Enter the password for this user.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of the server where the account for the user will be created.
Repository
Enter the repository path in the server where the files can be checked in.
Examples
How to Create the CVS Server
1. Use a repository name of TEST (the repository name should always be in capital letters).
2. Let the path to the repository be: /usr/local/cvs
3. Create a repository in the server using the command: cvs -d/usr/local/TEST init
Note: A new directory cvsroot will be created under /usr/local/cvs.
Configuring the CVS Server
1. Add a group “CVS” to the system. Any user who needs to access the repository should be in this
group.
2. Change the directory to /usr/local/cvs and set the repository’s ownership and permissions as you want
them to be for this group.
3. Then change the permissions of the CVSROOT directory to ug+rwx.
4. Now create the directory TEST under usr/local/cvs.
Setting Up a CVS Password Authentication Server
1. Make sure the lines “cvspserver 2401/tcp” and “cvspserver 2401/udp” are present in:
/etc/xinetd.d
2. Add a file named “cvspserver” containing the following information:
service cvspserver
{
disable = no
flags = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/bin/cvs
server_args = -f --allow-root=/usr/local/cvs pserver
log_on_failure += USERID
log_type = FILE /root/bin/temp
}
Restart xinetd
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. RouteFinderVPN RF760/660/600VPN User Guide (PN S000323D) 100
 Loading...
Loading...