Page 1

Model RF500S
DSL/Cable Router
with Built-in 4-port 10/100 Switch
User Guide
Page 2

User Guide
DSL/Cable Router
with Built-in 4-port 10/100 Switch
P/N S0000093 Revision A
This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior expressed written permission
from Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 2000 by Multi Tech Systems, Inc.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with respect to the content hereof and
specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Furthermore, Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes
from time to time in the content hereof without obligation of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. to notify any person
or organization of such revisions or changes.
Record of Revisions
Revision Description
A
(8/21/2000) Manual Released at Software Version 7.1
Patents
This product is covered by one or more of the following U.S. Patent Numbers: 5.301.274; 5.309.562;
5.355.365; 5.452.289; 5.453.986. Other patents pending.
TRADEMARKS
Trademark of Multi-Tech Systems, is the Multi-T ech logo. Windows, Windows 95, 98, NT and 2000
are trademarks of Microsoft. All other trademarks are owned by their respective companies.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View, Minnesota 55112 U.S.A.
(763) 785-3500 or (800) 328-9717
U. S. FAX (763) 785-9874
Technical Support (800) 972-2439
Internet Address: http://www.multitech.com
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................ 7
Front Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 8
Front Panel Description......................................................................................................................... 8
Back Panel ................................................................................................................................................. 8
Back Panel Description ........................................................................................................................ 8
Typical Applications .................................................................................................................................... 9
Connecting a Remote Site via Cable Modem ....................................................................................... 9
Connecting a Local Site by Segmenting the LAN ................................................................................1 0
Connecting a Local Site to the Internet ...............................................................................................11
Specifications ............................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
Hardware Installation .................................................................................................................................14
Safety..................................................................................................................................................14
Unpacking the RF500S........................................................................................................................14
Cabling ................................................................................................................................................15
Chapter 3 - Software Installation
and Configuration
Software Installation and Configuration......................................................................................................17
Software Installation............................................................................................................................17
Using RouteFinder Setup Wizard ...............................................................................................................18
T esting your Connection ......................................................................................................................30
Chapter 4 - Telnet
Using T elnet to Configure your RouteFinder ...............................................................................................32
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
RouteFinder Manager.................................................................................................................................39
General Settings ........................................................................................................................................40
WAN Ethernet Segment ......................................................................................................................41
Async Port ..........................................................................................................................................42
Remote Access - Remote Access Settings ........................................................................................46
Enable IP Mapping - Virtual Server .....................................................................................................47
Port Settings..............................................................................................................................................48
Edit Login Script for Remote Access ..................................................................................................49
Writing a login script for IP Routing .....................................................................................................50
Modem String Settings........................................................................................................................52
LAN DHCP Server .....................................................................................................................................53
Routing Settings ........................................................................................................................................55
Routing T able.......................................................................................................................................56
Filter Settings ............................................................................................................................................57
Refresh Device List ...................................................................................................................................61
Device Name and Password ......................................................................................................................62
Save Settings to File .................................................................................................................................63
Load Settings ............................................................................................................................................64
Upgrade Firmware......................................................................................................................................65
General Diagnostic ....................................................................................................................................66
iii
Page 4

Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
RouteFinder Monitor...................................................................................................................................68
Running RouteFinder Monitor ..............................................................................................................68
Refresh Device List ...................................................................................................................................69
T est Connection.........................................................................................................................................70
T erminate Connection ................................................................................................................................71
Save to File ...............................................................................................................................................72
Save Now ............................................................................................................................................72
Autosave .............................................................................................................................................72
IP Address/Name ......................................................................................................................................73
Event Messages........................................................................................................................................74
TCP/IP T ab ................................................................................................................................................75
Time T ab ....................................................................................................................................................76
Status T ab..................................................................................................................................................77
Statistics Tab .............................................................................................................................................78
Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
LAN Client Settings ...................................................................................................................................80
Setting up Remote Access Clients ............................................................................................................81
Accessing a Windows NT Server ........................................................................................................81
Accessing a Novell Server ..................................................................................................................88
Accessing a Windows NT Server and a Novell NetWare Server..........................................................94
Accessing a Unix Server...................................................................................................................103
Make New Connection (Windows 2000 only) ..................................................................................... 10 7
Chapter 8 - LAN -to- LAN Settings
LAN -to- LAN Settings .............................................................................................................................109
Setting up LAN -to- LAN Routing.......................................................................................................109
Using the Find Computer command ..................................................................................................110
Using LMHosts..................................................................................................................................111
Chapter 9 - Troubleshooting ..................................................................... 112
Troubleshooting........................................................................................................................................113
Common Problems............................................................................................................................113
Chapter 10 - Service, Warranty
and Technical Support
Introduction..............................................................................................................................................117
Limited Warranty................................................................................................................................ 117
Addendum for North American Products...........................................................................................117
Addendum for International Products ................................................................................................118
Out of Warranty Repair Costs............................................................................................................118
Software User License Agreement...........................................................................................................119
T echnical Support....................................................................................................................................121
Contacting T echnical Support ............................................................................................................121
Recording RouteFinder Information ...................................................................................................121
On-line Warranty Registration ............................................................................................................121
About the Internet ....................................................................................................................................121
Ordering Accessories ..............................................................................................................................122
Appendix
Appendix A - Regulatory Compliance Information....................................................................................124
Class B Statement - FCC Part 15 .....................................................................................................124
Page 5

Appendix B - T ools for your RF500S ........................................................................................................125
RouteFinder Monitor ..........................................................................................................................125
PING .................................................................................................................................................125
WINIPCFG and IPCONFIG ...............................................................................................................125
TRACERT .........................................................................................................................................126
Appendix C - Cabling Diagrams ...............................................................................................................127
Glossary ..................................................................................................................................................128
Index........................................................................................................................................................133
Page 6

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Page 7

Introduction
Congratulations on the purchase of the Multi-T ech System’s RouteFinder model RF500S, one
of the finest broadband routers available today .
The RouteFinder connects a cable or DSL modem to an Ethernet LAN to provide high-speed
broadband access to the Internet for multiple users. The RouteFinder router features a built-in
4-port 10/100 switch, one asynchronous port for backup Internet access or dial-in remote
access, and firewall services. This solution is ideal for any business looking for cost-effective
broadband access to the Internet for every use on the LAN or for the home user looking to
share their DSL cable modem.
Connects up to 253 internal IP addresses to the Internet with broadband speed. The
RouteFinder can be configured as a DHCP server to handle requests for Internet services and
route to and from the ISP. Up to 253 internal IP addresses are connected to the Internet with
only one IP account. The W AN Ethernet port has a bandwidth of 10M bs which is 179 times
faster than a 56k modem and can support DSL or cable speeds of up to 2.5M bs.
Built-in 10/100 Switch. The integrated 4-port 10/100 switch eliminates the need for an
additional hub or switch to connect users not on a LAN. It ensures high-speed transmission
and can serve as a completely dedicated full duplex backbone.
Network Security . The RouteFinder uses the NA T protocol to provide security from hackers
attempting to access the office LAN without the extra cost of a firewall. It implements firewall
and gateway security for LAN-based resources. Additionally , the RouteFinder supports
Internet access restriction by IP address, client protocols or a list of forbidden sites.
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Dial Backup or Dial-in RAS Port. The RouteFinder also provides an additional asynchronous
port that, when connected to a dial-up modem or ISDN terminal adapter, serves as a backup
resource for Internet access if your cable or DSL service goes down. It can also serve as
dial-in remote access for your telecommuters or mobile users.
Virtual Server Support. In addition to providing shared Internet access, the RouteFinder can
support Web, FTP or other Internet servers. Once configured, the RouteFinder accepts only
unsolicited IP packets addressed to the Web or FTP server.
LAN Segmentation. For added LAN security , the RouteFinder can be used to segment the
LAN by connecting the corporate servers to one RouteFinder Ethernet port and the Internet
Servers to the other Ethernet port. This configuration puts the corporate servers behind a
firewall and the Internet servers outside the firewall. To continue to provide Internet access,
connect a modem or ISDN terminal adapter to the RouteFinder’s asynchronous port.
The RouteFinder RF500S
7
Page 8

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Front Panel
Front Panel Description
LAN
Link/ACT Lights when the LAN client is correctly connected to the 10 BaseT Ethernet LAN.
100 Lights when the LAN client correctly establishes a 100M bs connection.
FDX/COL A constant light indicates a successful LAN connection. A frequently flickering light
indicates a potential network connection problem.
Serial
Data Blinks when the Serial async port is receiving or transmitting data.
D CD Lights when the Serial async port is properly connected to a remote site.
RF500S Front Panel
WAN
Link Lights when a successful connection to the 10BaseT WAN is established.
RX D Lights when the LAN port is receiving data.
TXD Lights when the LAN port is transmitting data.
Power Lights when power is being supplied to the router.
Back Panel
Back Panel Description
Power 5VDC The 5V DC Power socket is used to connect the device to the AC power
10 BT WAN The WAN port is used to connect the router to a DSL or Cable modem.
ASYNC The Serial async port connects the router to a standard modem (optional).
Reset The Reset button is used to reset the router to factory defaults.
10/100 BT LAN The 4-10/100 ports are used to connect the router to LAN client workstations.
Uplink/Normal Slide the switch to the Uplink position to use the number 1 LAN 10/100 port
5VDC
WAN
Serial
Reset
1234
Uplink/Normal
RF500S Back Panel
adapter.
If the RF500S is set to use the Uplink feature, the number 1 LAN port is
inactive as a LAN port.
to expand your network by connecting a network cable to another router,
switch or hub. To connect the number 1 port to a LAN client workstation,
slide the switch to the Normal position.
8
Page 9
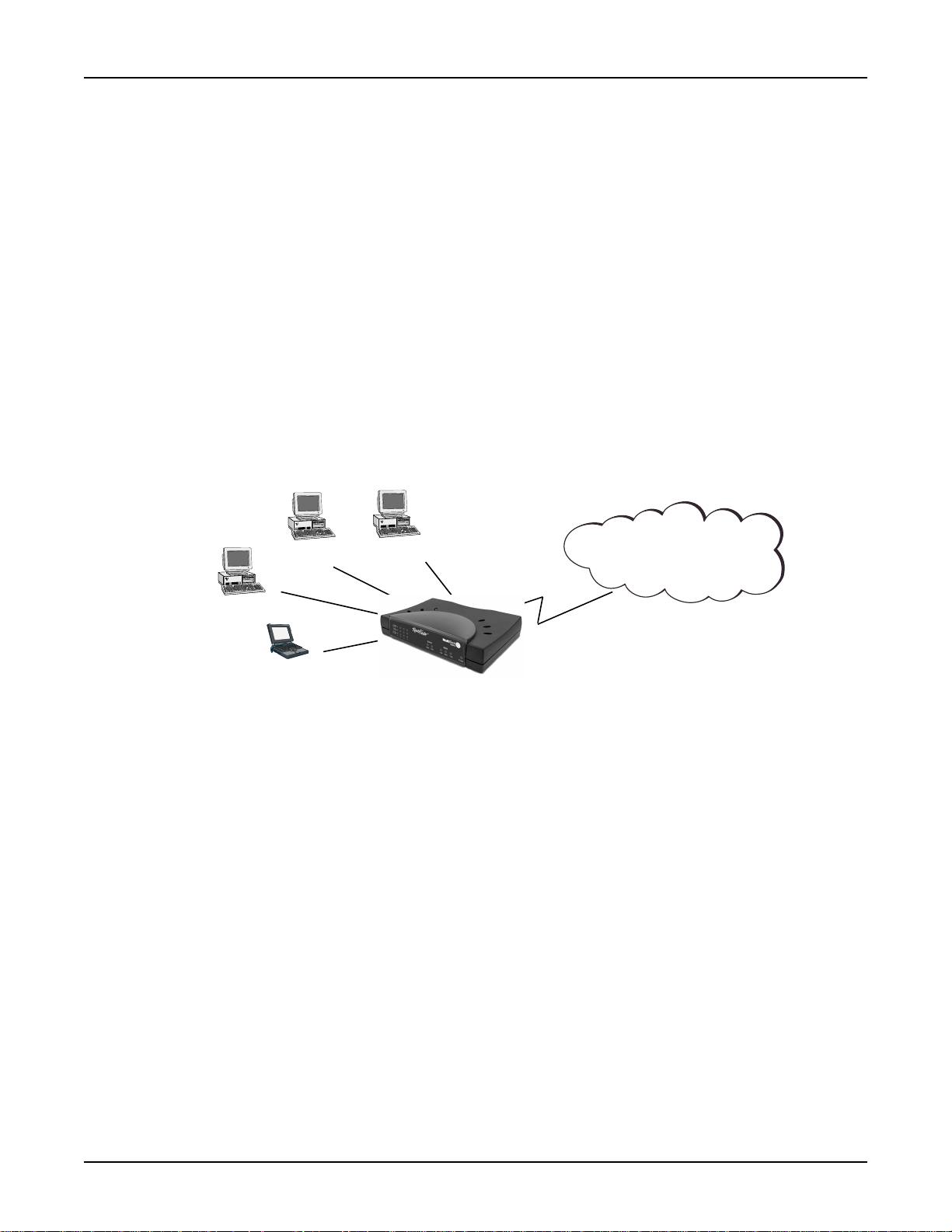
Typical Applications
The following examples provide information about typical applications using the RF500S. They
describe using the RF500S to connect a remote site via a cable modem, using the RF500S to
segment a local area network, and using the RF500S to connect a LAN to the Internet using one
shared IP address.
Connecting a Remote Site via Cable Modem
In the following example the RF500S is used to connect a LAN to the Internet via DSL or a cable
modem.
Kernal: NA T (outgoing TCP/IP connection sharing a single Internet IP address or
using multiple IP mapping)
• Virtual Server (allowing incoming specific TCP/IP service request redirect to
an internal server)
• Static Routing (Routing table setting to Internal Local Gateways)
• Firewall
External: Fixed External Port IP or DHCP client (Dynamic IP assigned)
Internal: Device Fixed IP
DHCP Server
Chapter 1 - Introduction
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.104
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.103
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.105
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.106
Cable Modem
RouteFinder
RF500S
IP Address
192.168.0.1
Connect Remote Site via Cable Modem
Internet
9
Page 10

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Connecting a Local Site by Segmenting the LAN
In this application, the RF500S is used to connect LAN segments within a local site.
Kernal: IP Routing Static Routing (Routing table to External or Internal Gateways)
External: Fixed External IP or DHCP client (Dynamic IP only)
Internal: Device Fixed IP
• Firewall
DHCP Server
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.105
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.104
Department
Segment
(Ethernet)
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.106
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.1.100
RouteFinder
RF500S
IP Address
Server
IP Address
192.168.0.103
192.168.0.1
IP Address
192.168.1.102
Connect Local Site (Segmenting the LAN)
Server
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.1.101
Major
Segment
(Ethernet)
10
Page 11

Chapter 1 - Introduction
Connecting a Local Site to the Internet
In this application, the RF500S is used to connect up to 253 Internal IP addresses to the Internet
using a single shared external IP address.
Kernal: NA T
(outgoing TCP/IP connection sharing single External Port IP or using
multiple IP Mapping)
• Virtual Server (allow incoming specific TCP/IP service request redirect to
internal server)
• Firewall
External: Fixed External Port IP and mask DNS IP, Gateway IP or DHCP client
(Dynamic IP for the device, DNS and Gateway assigned.)
Internal: Device Fixed IP
DHCP Server
Internet
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.106
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.105
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.0.104
NAT
Server
IP Address
192.168.0.103
Hidden Clients and Servers
RouteFinder
RF500S
IP Address
192.168.0.1
Gateway
Server
IP Address
192.168.1.102
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.1.100
Workstation
IP Address
192.168.1.101
Major
Segment
Connect Local Site (I External IP address = 253 Internal IP addresses)
11
Page 12

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Specifications
Hardware ARM RISC CPU
LAN Ports Number of Ports: 4
WAN Ports 1 x 10BaseT
Protocols Security: PAP/CHAP, MSCHAP, NA T Firewall, RADIUS and Callback for
LED Indicators 1 indicator for Power On
32 bit, 40MHZ
4MB DRAM and 512k Flash ROM
UART Serial port controller
Interface: 10Base T/100BaseTX, - One port can be used for uplink
Standard: 802.3
1 x RS232 (V .24)
DTE Speed: Up to 460K asynchronous
remote access.
Network: TCP/IP, IPX, DHCP , PPP, PPPoE
Filtering: Protocol, port number, URL address and IP address
3 indicators for WAN function (LINK, TxD, RxD)
2 indicators for Serial Async function (DA TA, DCD)
3 indicators for each of 4 LAN ports functions (LINK/ACT , 100, FDX/COL)
Power Output 5VDC, 1000mA
Dimensions 7.1 in. (w) x 4.9 in. (h) x 1.4 in. (d)
18.1 cm x 12.5 cm x 3.5 cm
Weight 380g
13 oz.
Memory RAM: 4MB
Flash ROM: 512k
Operating
Environment: T emperature Range: 32 - 120 degrees F (0 - 50 degrees C)
Humidity: 25-85% non-condensing
Approvals: FCC Part 15 & CE Mark
Warranty 2 - year warranty
12
Page 13

Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
Page 14

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Hardware Installation
Safety
1. Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
2. Never install telephone jacks in a wet location unless the jack is specifically designed for wet
locations.
3. This product is to be used with UL and cUL listed computers.
4. Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been
disconnected at the network interface.
5. Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be
a remote risk of electrical shock from lightening.
7. Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
8. T o reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 A WG or larger Telecommunications line Cord.
Unpacking the RF500S
The RF500S shipping box contains the following items:
• System CD
• Tucows CD
• Power Supply
• The RouteFinder RF500S
• The RF500S RouteFinder Quick Start Guide
• A serial cable
If any of the items is missing or damaged, please contact Multi-Tech Systems.
14
Page 15
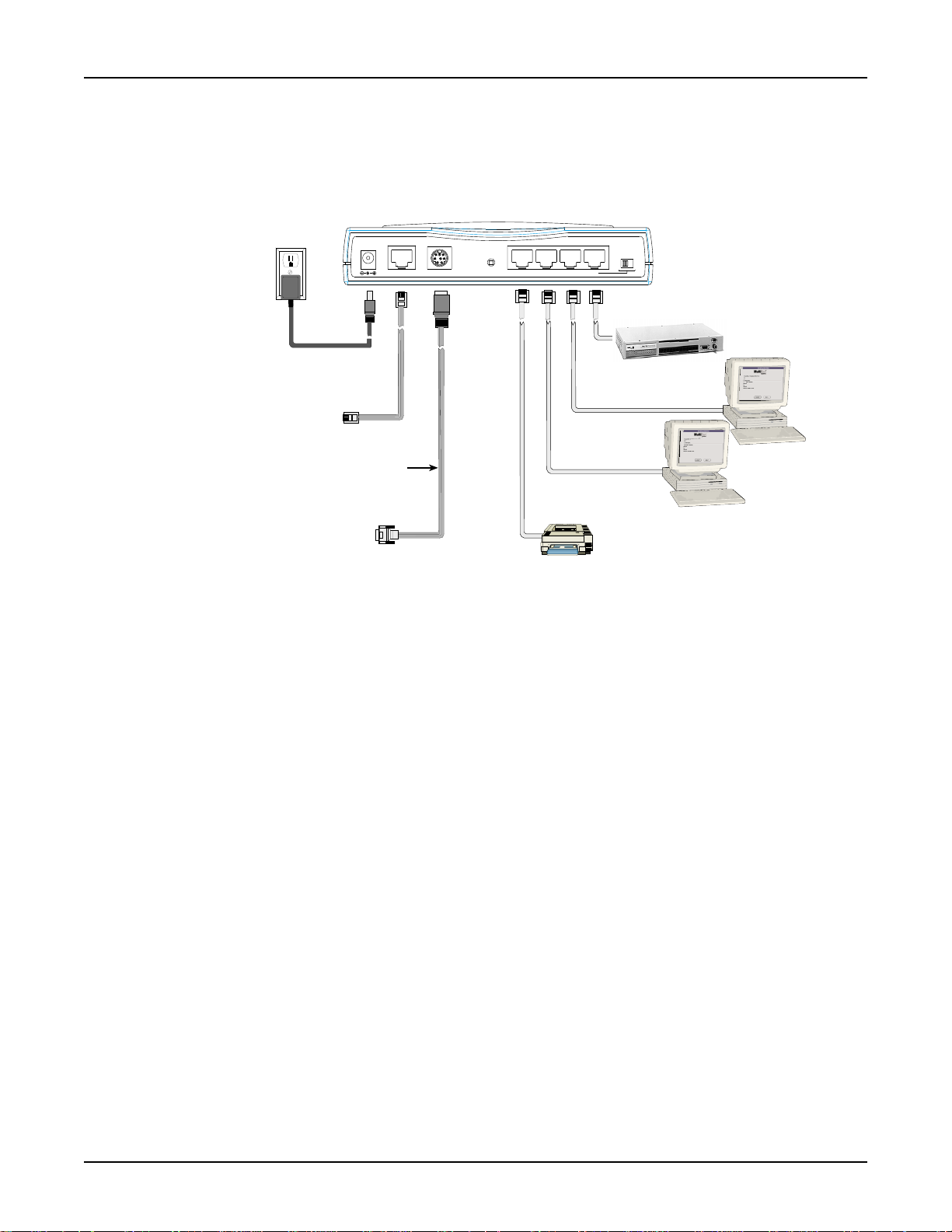
Chapter 2 - Hardware Installation
Cabling
Cabling your RouteFinder requires making the appropriate connections to PCs, Cable or DSL
modem, analog modem or ISDN T A (optional), AC power and the router . Because this device also
acts as a DHCP server , after your device is properly cabled, you will need to follow the
configuration instructions provided in the Software Installation and Configuration chapter.
Power Connection
To Cable Modem
or DSL Modem
To optional
Modem or
ISDN TA
5VDC
Serial Cable
Serial
WAN
Reset
Uplink/Normal
1234
Optional
Uplink
Network Printer
Hub
PC
PC
Cabling the RouteFinder RF500S
1. Before beginning, turn the power off on all network devices (PCs, Cable, DSL modems, analog
modems, ISDN T As and the router).
2. Connect the Ethernet port of each PC or network device to one of the 4 LAN ports (if you are
using the Uplink option, port number 1 cannot be used as a LAN port).
3. If you are using an analog modem, connect it to the Serial Async port.
4. If you are using the Uplink option to connect to another network segment, slide the
Normal
switch into the Uplink position. Connect the LAN cable to LAN port #1. Plug the other
Uplink/
end of the LAN cable into another hub, router or switch.
Note: If you are not using the Uplink feature, place the switch in the Normal position.
5. Connect a network cable from the cable or DSL modem to the 10 BT W AN port.
6. Connect the provided power supply cable to the 5VDC power port on the back of the router.
Plug the power supply into an AC power outlet as shown above.
7. Power on your DSL modem or Cable.
8. If you are using an analog modem or ISDN T A, power on the device.
9. Press and hold the RouteFinder’s Reset button for 3 seconds to restore the default settings.
10. Y ou are ready to configure software for your RouteFinder and network PCs.
15
Page 16

Chapter 3 - Software Installation
and Configuration
Page 17

Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
Software Installation and Configuration
Before beginning the installation process, ensure that your system meets all hardware and
software requirements:
• Intel 486 or higher processor.
• 10/100 BaseT cable to connect the RF500S to the network.
• One DSL or Cable Modem.
• A networked computer with Windows 95/98/2000, Windows NT 3.5 or higher and TCP/IP
protocol installed (or, a non-Windows system with TCP/IP properly installed to enable Telnet
configuration).
• Any Windows communication application for Dial-Out operation.
• Any PPP supported communication application for Dial-In operation.
• TCP/IP installed and configured on each workstation accessing the Internet.
Software Installation
The software installation process involves installing the RouteFinder Utilities, including
RouteFinder Setup Wizard, RouteFinder Manager and RouteFinder Monitor. A description of each
component follows:
RouteFinder Setup Wizard
The RouteFinder Setup Wizard provides a step-by-step process to assist you in entering all the
basic settings needed to configure your RF500S for general use. All settings that are entered in
the Setup Wizard can be found in their respective menus in the RouteFinder Manager.
RouteFinder Manager
RouteFinder Manager is the main program used to configure all settings for your RF500S.
Complete information about options within the RouteFinder Manager can be found in the
RouteFinder Manager chapter in this User Guide.
RouteFinder Monitor
RouteFinder Monitor is a multi-purpose utility designed to let you know the status of your RF500S
connection. The monitor offers the ability to point and click on an event to access troubleshooting
procedures. Refer to the RouteFinder Monitor chapter in this User Guide for more information.
17
Page 18
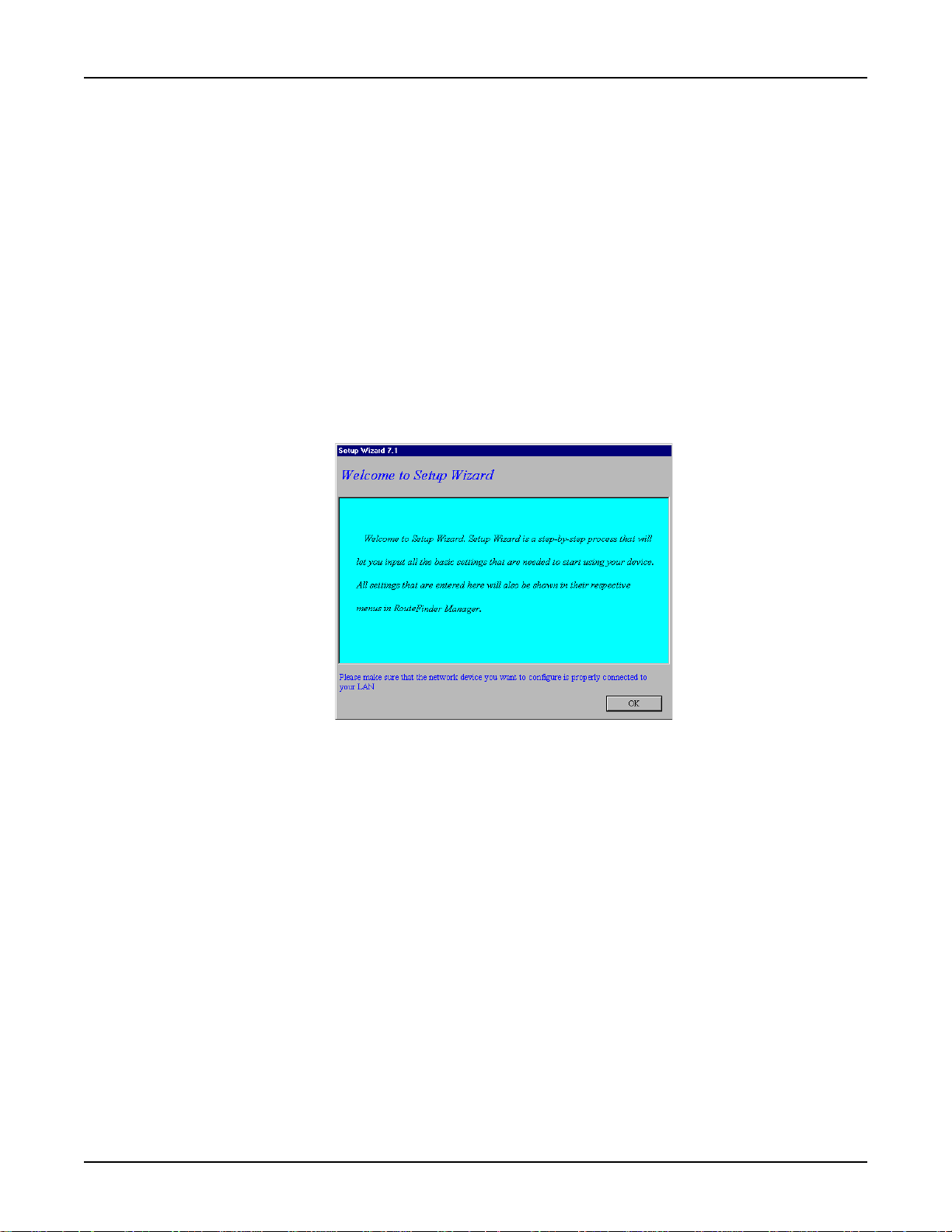
RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Using RouteFinder Setup Wizard
Note: Before beginning this procedure, ensure that your RF500S is properly connected to the
network and is powered on.
After installing the software, you may return to the RouteFinder Setup Wizard at any time, by
clicking Start | Programs | RouteFinder Manager | RouteFinder Wizard.
Before running the Setup Wizard, it is strongly recommended that you exit all Windows programs.
1 . Insert the RF500S System CD into your computer’s CD-ROM drive. The RF500S System CD
screen appears.
Note: If Autorun is disabled on your computer , use Windows Explorer to view the contents of
the CD. Double-click the CD icon to display the RF500S System CD main screen.
2. Click Install Software.
3 . Follow the on-screen instructions to install the software.
4 . When the software installation completes, the Setup Wizard dialog box displays.
18
Click OK.
Page 19
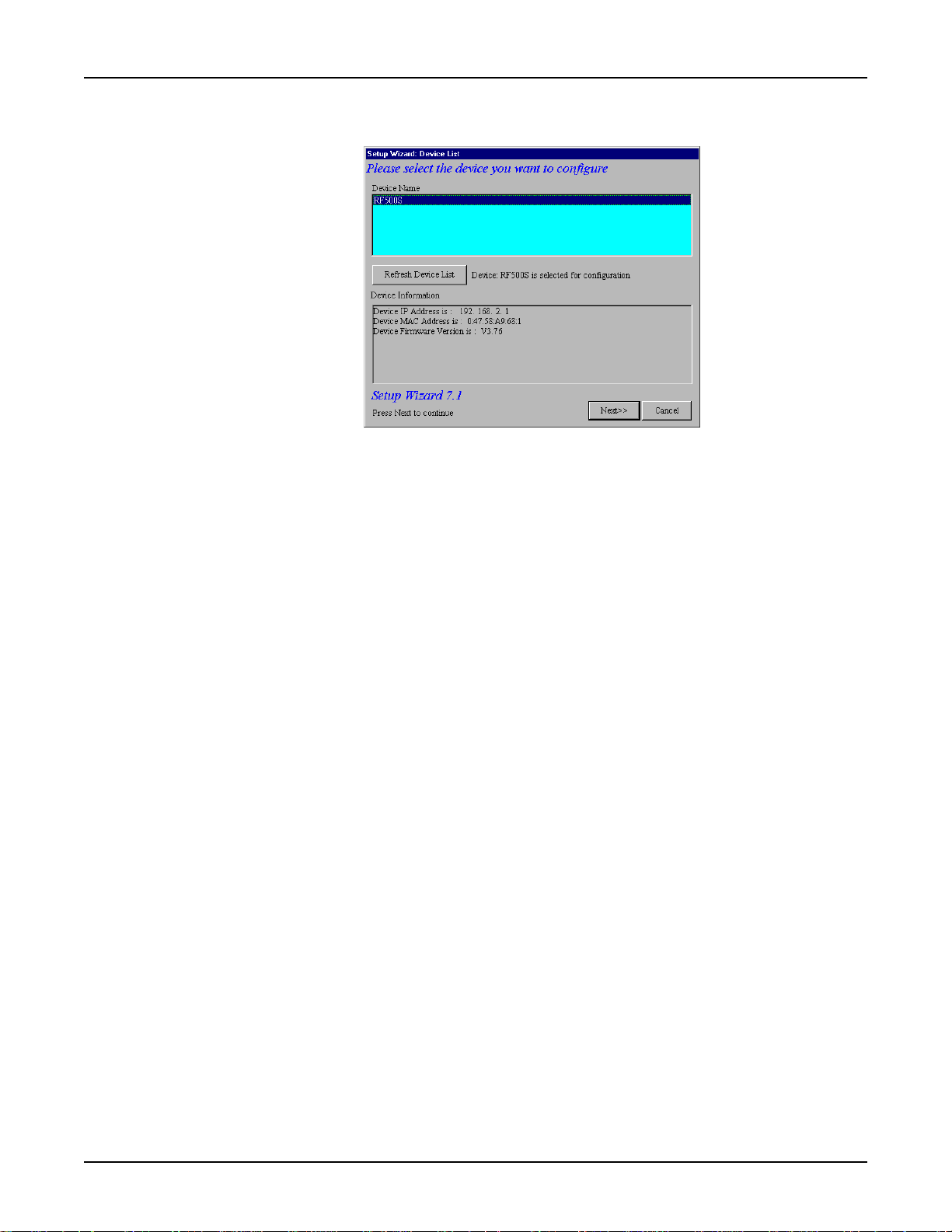
Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
5. The Setup Wizard: Device List dialog box displays. The Setup Wizard automatically checks
your network for available network devices and displays them on the screen.
Select the device you wish to configure from the Device Name list.
Record the values presented in the Device Information panel for later reference.
Device IP Address
Device MAC Address
Device Firmware Version
Click Next>>.
______________________
____________________
_________________
Note: If a message appears indicating the device is not found, or you do not see the device
you are attempting to configure listed, click the Refresh Device List button.
19
Page 20
RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
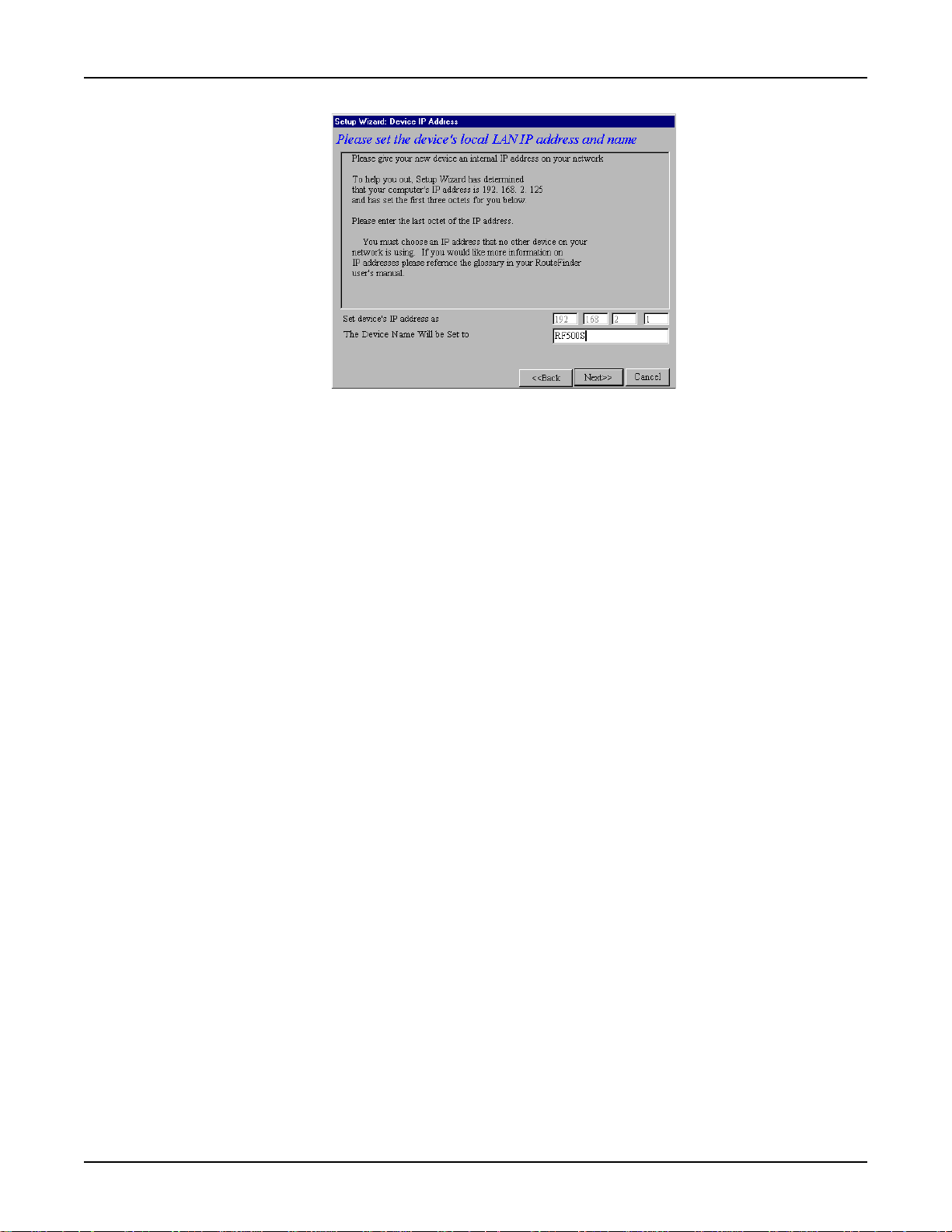
6. The Setup Wizard: Device IP Address dialog box displays.
• Enter your local internal network’s IP address for this device.
The Setup Wizard will automatically detect the first three octets of your local IP address. You
must enter the last octet only .
• If you wish, you can change the network name of your RouteFinder. If your ISP requires your
device to have a name, you may use the value entered in this field.
• Click Next>> to continue. The device will search the network to ensure that the IP address is
valid. This may take several seconds.
Note: If your ISP provided you with an IP address, do not enter that address in this field.
Enter the IP address for this device on your local network. Refer to the Glossary in this User
Guide for additional information on IP addressing.
20
Page 21
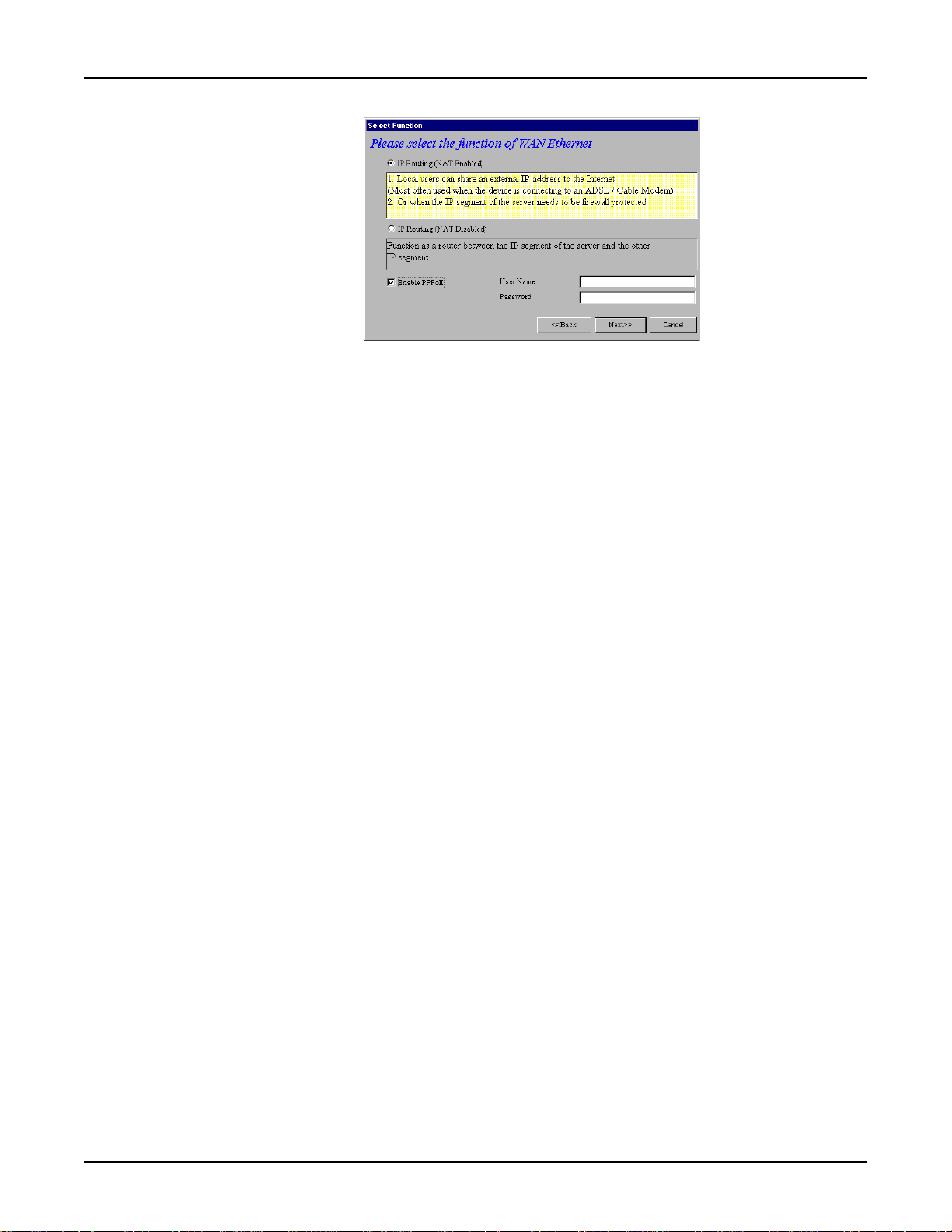
7. The Select Function dialog box displays.
Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
Select the function of the WAN Ethernet port by choosing
Routing (NAT Disabled)
PPPoE
• Select
address for accessing the Internet. This option is most often used when the RF500S is
connected to a DSL or cable modem, or when the IP segment of the server needs firewall
protection.
• Select
segments. This option is ideal for organizations needing to segment workgroups.
• Select
modem connection. Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP. This option
is most often used when connecting via DSL to the Internet.
Note: Enable PPPoE is valid only when IP Routing (NAT Enabled) is selected.
Click Next>>.
. If you are using NAT Enabled, you may also select
.
IP Routing (NAT Enabled)
IP Routing (NAT Disabled)
Enable PPPoE
to use the RF500S with a time-base, rather than fixed-cost DSL
IP Routing (NAT Enabled) or IP
Enable
to allow local LAN clients to share one external IP
to allow the RF500S to function as a router between IP
21
Page 22
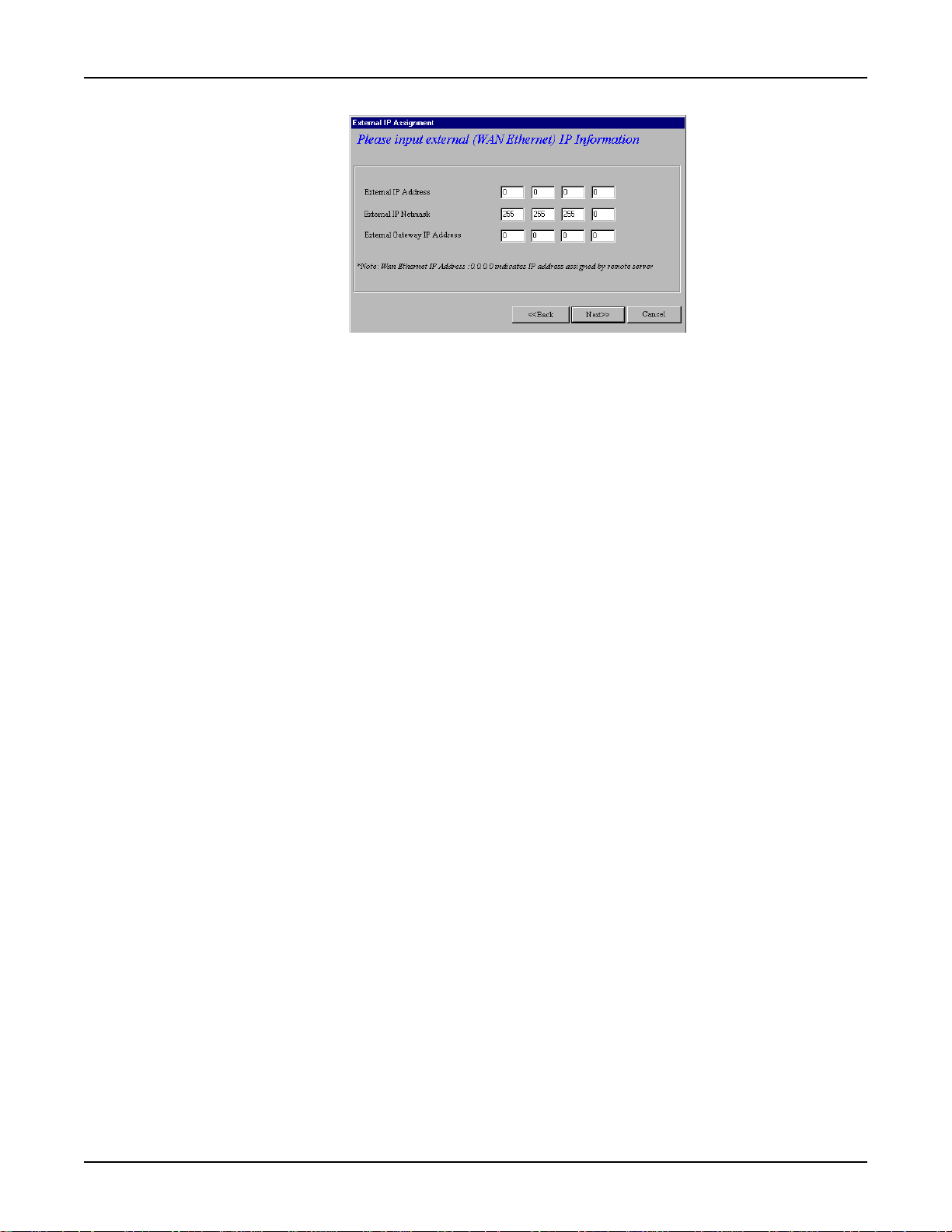
RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
8. The External IP Assignment dialog box displays.
Enter the WAN Ethernet IP address information
administrator.
• In the
• In the
• In the
External IP Address
External IP Netmask
networks, the Netmask is generally set to 255.255.255.0).
External Gateway IP Address
network.
box, enter the WAN Ethernet IP Address.
box, enter the Netmask of the WAN Ethernet IP Segment (for Class C
box, enter the IP address of the Gateway to the destination
provided by your ISP
or other external network
Note: If your ISP uses dynamic IP addressing (DHCP), leave the External IP address and the
External Gateway IP address at the default values of 0.0.0.0. Set the External IP Netmask to the
default value of 255.255.255.0.
Click Next>>.
22
Page 23

Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
9. The Asynchronous port function dialog box displays. Select 1) Remote Access, 2) IP Routing
(NA T Enabled) or 3) IP Routing (NA T Disabled).
• Select
the remote user is connected to the network locally . Remote Access instructions continue on
page 24.
• Select
Ethernet) to share one IP address to the Internet. You may also select this option to use the serial
async port for dial backup in the event the DSL or cable modem becomes unavailable.
• Select
IP Routing instructions continue on page 26.
Remote Access
to allow remote users to dial-in to the network to access resources as if
IP Routing (NA T Enabled)
IP Routing (NAT Disabled)
to allow all users in the two IP segments (LAN and WAN
to connect other IP segments through the serial async port.
Note: The IP Routing (NAT Enabled) feature of the serial async port is valid only if the WAN port is
configured as NA T Disabled.
Click Next>>.
23
Page 24
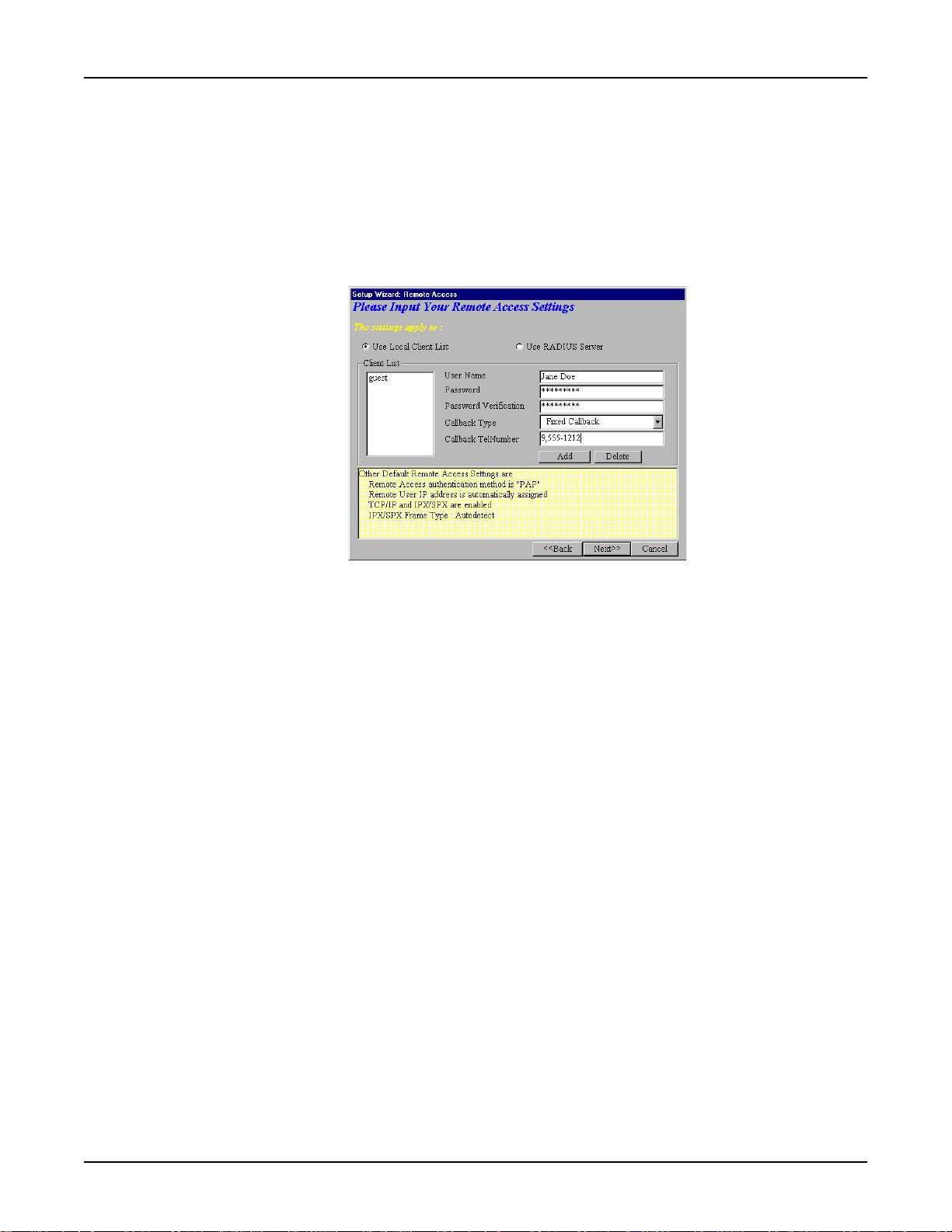
RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
1.) Remote Access
Y ou must define the location of your remote user account database by selecting a)
List
or b)
Use RADIUS Server
.
Use Local Client
Note: The Local Client List allows you to add a maximum of 64 users.
a.) Use Local Client List
Use Local Client List allows you to create an authentication database consisting of user names,
passwords and dial-in options for each remote user. Y ou must provide the following information for
each client:
User Name:
Enter the User Name to authenticate the remote dial-in user.
Password:
Enter the Password to authenticate the remote dial-in user. Passwords are limited to 16 characters.
Password Verification:
Re-enter the remote dial-in user’s password.
Callback Type:
Select one of the following three callback options for each remote client:
•
No Callback:
being authenticated.
•
Fixed Callback:
After the PPP negotiation, the device will disconnect, then callback the telephone number you enter in
the callback telephone number field. This option is best used for clients requiring callback security
while dialing-in from the same location each time.
•
Variable Callback:
locations and need callback security . This option allows clients to specify the callback telephone
number each time they connect to the network.
Click Add after entering information for each Local Client.
Click Next>> and continue with Step 10 when all users have been added to the database.
Select this option to allow the remote user to immediately connect to the network after
No Callback
This option allows you to specify a fixed callback telephone number for the user.
Select
Variable Callback
is the default setting.
for remote users that travel or dial-in from various
24
Page 25
Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
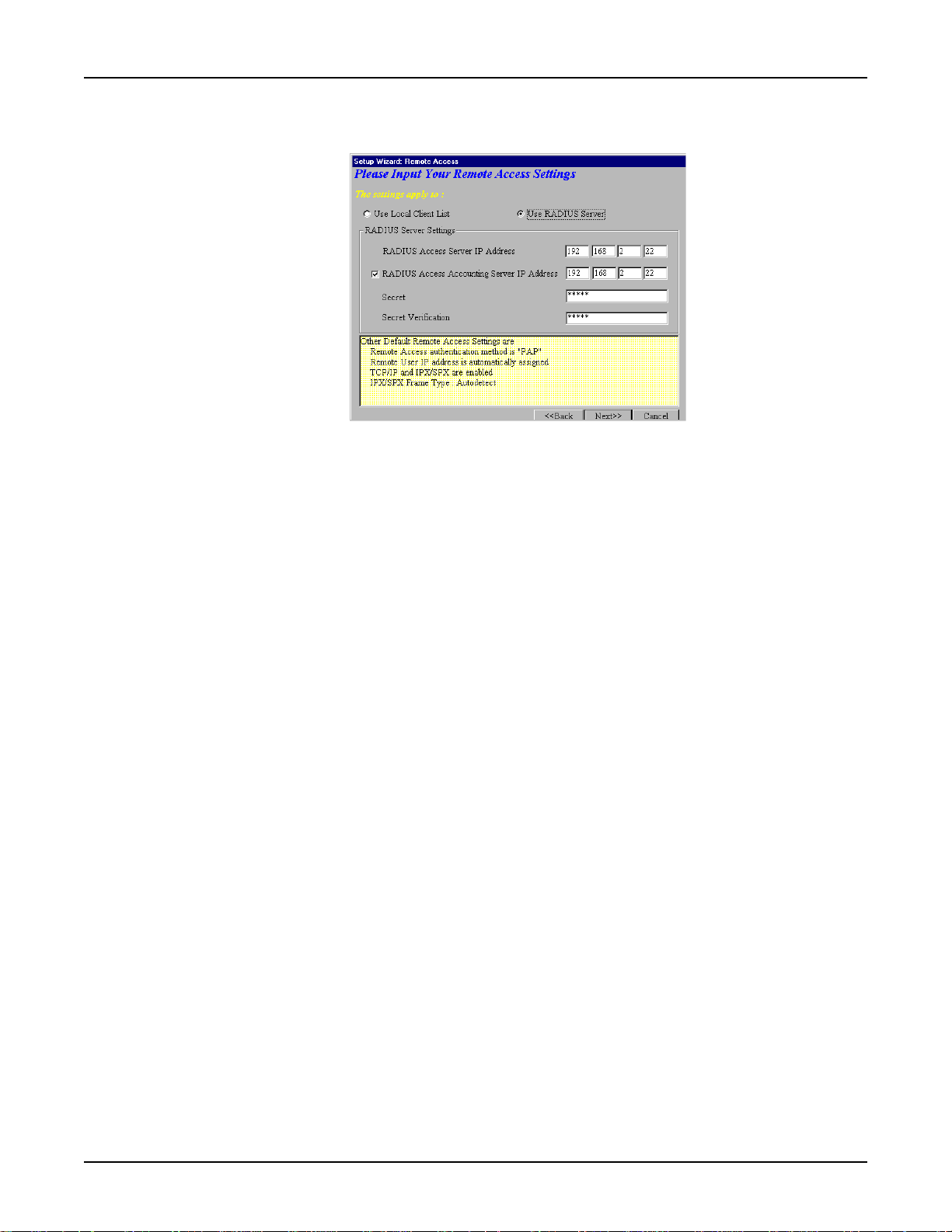
b.) Use RADIUS Server
Select this option if you would like your remote clients to be authenticated on a RADIUS server.
Y ou must enter the following RADIUS Server Settings:
RADIUS Access Server IP Address:
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Access Server.
RADIUS Accounting Server IP Address:
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Accounting Server.
Secret:
Enter your Secret RADIUS code or password.
Secret Verification:
T o confirm your Secret code, re-enter your code or password.
Note: In most cases, the RADIUS Access Server and the RADIUS Accounting Server are the
same server, so the IP addresses will also be the same.
Click Next>> and continue with Step 10.
25
Page 26

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
2.) IP Routing (NAT Enabled) and
3.) IP Routing (NAT Disabled)
If you select
displays.
Enter the information required to dial-up and login to your ISP’s remote server:
T elephone Number:
Enter the phone number used to dial your remote server (ISP).
Note: If you must dial a number to get an outside line (e.g., “9”, or “0”), enter the required number
plus a “w”(wait) or a comma in the T elephone box. (e.g., 9w555-2323 or 9,,5552323) Each comma
provides a 3-4 second delay.
IP Routing
for the asynchronous port, the Setup Wizard: IP Routing dialog box
User Name:
Enter the User Name for your remote server or ISP account.
Password:
Enter the Password for your remote server or ISP account.
Password Verification:
Re-enter the password for your remote account.
Click Next>>.
26
Page 27

Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
10. The Setup Wizard: DNS IP Address dialog box displays.
Enter your ISP’s DNS Server IP address. If you are not sure of the IP address, contact your ISP.
Refer to the Glossary in the User Guide for more information about the DNS Server.
Click Next>>.
11. The Setup Wizard: Modem Settings dialog box displays.
The final step in configuring your RF500S for basic operations is to define your modem
Manufacturer, Model and the DTE baudrate or speed of communication between the RF500S’s
serial async port and your modem or ISDN T A.
Select your modem and baudrate as described on the following pages.
Note: If you do not have a device attached to the serial async port, use the default modem
values, and click Next>>.
12. T o select your modem, in the
click
The system loads modem information.
Asynchronous port settings
box,
27
Page 28
RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
13. The Modem Initial Command dialog box displays.
Select your modem manufacturer, then select the model from the list provided. Click OK (if your
modem is not listed and you have a driver disk, click Have Disk... to install your modem).
Note: This setting configures the initial string of the asynchronous port on the RF500S so that it
will know how to communicate with your modem. If you are using an analog modem and your
modem is not included in the selection list, in most cases, Standard Modem will work. If you are
using an ISDN T A, refer to the ISDN T A ’s User Guide for information on the initialization and hang
up strings. Use RouteFinder Manager to enter modem strings.
14. The Setup Wizard: Modem Setting dialog box re-displays.
Use the
speed of communication between the asynchronous port of the RF500S and the modem). For
DCE speed compression modems, this value can normally be set to about 4 times the speed of
your modem. Keep in mind that if you set the baudrate too high, the dial-up connection may fail.
Asynchronous port settings
list to select the baudrate. Select the DTE speed (i.e., the
Note: Y ou may need to set a lower baudrate since the theoretical maximum connection speed may
not be attainable due to variations in quality of phone line and ISP connections.
Click Next>> to complete the basic configuration.
15. The Check List dialog box displays summarizing your configuration selections. Ensure that all
values have been correctly entered. If you find an incorrect setting, click <<Back to return to the
screen containing the error and correct it. When complete, use the Next>> button to return to the
Check List dialog box.
28
Click Finish to complete the configuration.
Page 29

Chapter 3 - Software Installation and Configuration
16. The Note dialog box displays indicating that you have completed the Setup Wizard.
Read the “IMPORTANT!” information contained in the dialog box. Choose Run Monitor
(recommended), Run Manager or Exit.
29
Page 30

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Testing your Connection
When you select Run Monitor, the RouteFinder Monitor program loads.
1. To test your current settings, select Test Connection. Select Connect Port 1 to test the W AN
port. Select Connect Port 2 to test the serial async port. The monitor activity will appear in the
display window. Refer to the RouteFinder Monitor chapter in this User Guide for additional
information about the monitoring capabilities of the RF500S.
2. After successfully using the Test Connection option in Run Monitor, refer to the LAN Client
Settings chapter of this User Guide to continue with your installation by configuring your LAN
workstations.
Note: If a problem occurs while testing your connection, or you need to configure more advanced
options for your RouteFinder, use RouteFinder Manager by selecting Programs | RouteFinder
Manager | RouteFinder Manager.
30
Page 31

Chapter 4 - Telnet
Page 32

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Using Telnet to Configure your RouteFinder
Telnet is a telecommunications software utility which allows you to access a remote device. The
RouteFinder RF500S has a built-in T elnet Server that enables a T elnet client to remotely configure the
device using a menu system.
Important: Non-Windows operating system users must use the T elnet menu system to define the
function of the WAN and async ports, to define how IP addresses are administered, to configure IP
addresses on your local and remote systems and to set up any necessary virtual server, routing table
and packet filtering options.
Note: T o successfully configure your router using T elnet, TCP/IP must be correctly configured on your
computer. The router and computer must also be located on the same subnet.
1. Start your telnet session and connect to the RouteFinder RF500S using the router’s default IP
address of
192.168.2.1
and vt100 terminal emulation.
If you are using a graphical interface such as the one shown above, click Connect.
2. When prompted to input the Router Password, press Enter.
3. The RF500S T elnet Server Menu displays.
T o use the menu, type the letter corresponding to the parameter you’d like to change.
Depending on the parameter you are changing, you are presented with an open field into which you
may type new information, or you are presented with a list of options from which you may select a
value. Each menu item is described in the following pages.
32
Note: After entering parameters for all settings that you want to change, continue to type “q“ to
return to the previous menu until you reach the main T elnet Server menu. Select Save and
Restart Server to save your new configuration.
Page 33

Chapter 4 - T elnet
Router IP Address
Enter the IP address assigned to the RF500S on your local network. The new address will take effect
after you have selected
Save and Restart Server
.
Router Subnet Mask
Enter the subnet mask for your local network.
Router Name
Enter a network name for the RF500S. If your ISP requires your device to have a name, you may use
the value entered in this field.
Router Password
The default is no password. If you choose to use a password, ensure that you write the password
down and keep it in a safe place. If you forget the password, contact the Multi-Tech System’s
Technical Support group for assistance. Refer to Chapter 10 in this User Guide for contact
information.
WAN Ethernet MAC addr.
This field displays the current MAC address of your router. Edit this field only if required by your
remote system or ISP.
WAN Ethernet Settings
Define the function of the WAN port by selecting Internet Access (IP Routing - NAT Enabled) or LAN to- LAN access (IP Routing - NA T Disabled). Refer to the W AN Ethernet Segment section of the
RouteFinder Manager chapter for more information.
Internet Access
If you use the WAN port for Internet Access, you must configure the following options:
Enter the IP port information provided by your ISP or other external network administrator .
Note: If your ISP uses dynamic IP addressing, leave the External Port IP address and External
Gateway IP address at the default values of 0.0.0.0. Set the External IP Netmask to the default
value of 255.255.255.0.
LAN -to- LAN Access
To use the WAN port to connect to another LAN, you must configure the following:
Enter the IP and Netmask address of the network to which you are connecting.
33
Page 34

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Async Port Settings
The async port may be used for
Port section of the RouteFinder Manager chapter.
IP Routing
or
Remote access
. For more information, see the Async
IP Routing
If you will use the async port for IP Routing, enter the following information as described:
T elephone number:
Enter the phone number the async device must dial to connect to the remote system.
User Name:
Enter the User Name that will be used for authentication on the remote system.
Password:
Enter the Password associated with the User Name for the remote system.
Idle Timeout:
Enter the amount of idle time allowed to pass before the connection times out. The default value is 5
minutes.
Serial Baudrate:
Use the list to select the appropriate baudrate of the modem attached to your async port. You may
need to select a lower speed to ensure a quality connection.
Modem Pre-Initial string:
Consult your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for this information. The default value will work for most
analog modems.
Modem Initial string:
Consult your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for this information.
Modem dialup string:
Consult your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for this information.
Modem hangup string:
Consult your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for this information.
Login script:
Select Enable or Disable.
Edit login script:
Refer to the RouteFinder Manager chapter of this User Guide for information on editing scripts.
External IP address:
Enter the IP addresss of the remote device to which you are connecting.
34
NA T Function:
Select Enable or Disable. Refer to the Glossary in this User Guide for additional information on NA T.
Page 35

Chapter 4 - T elnet
Assign Remote IP:
Select Enable or Disable. If you select Enable, you will be prompted to enter an address to be
assigned to the remote system.
Remote Access:
To configure the async port for Remote Access, enter values for each of the following fields:
Remote Access Port Settings
IP Assigned Method:
Select the method the client will use to have their IP address assigned.
Protocols:
Default value is
connecting to a Netware server, you must have IPX enabled.
Both IP and IPX enabled
. You may select to use only one protocol, however if you are
IPX/SPX Frame T ype:
The default value is
Ethernet_II, Ethernet_802.3, Ethernet 802.2 or Ethernet_snap.
Authentication Method:
Select either None, P AP or CHAP. Refer to the RouteFinder Manager chapter of this User Guide for
additional information.
Edit User Database:
T o add users to the database, select the next available letter. Enter the User Name, Password and
Callback type for each user that you add to the database. You may enter up to 64 remote clients.
Idle Timeout:
The default value is 5 minutes.
Serial Baudrate:
Select one of the available options. Y ou may need to use a slower speed to ensure a quality
connection.
Modem Pre-initial string:
Refer to your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for information. The default value will work for most
analog modems.
Modem Initial string:
Refer to your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for information.
Modem Dialup string:
Refer to your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for information.
Autodetect
. If you have problems with your network connection, you may select
Modem Hangup string:
Refer to your modem or ISDN T A User Guide for information.
Edit login script:
Select this option to edit the login script executed when the client connects to the network. Refer to
the RouteFinder Manager chapter of this User Guide for additional information about creating and
editing scripts.
35
Page 36

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
RADIUS Server:
Select
RADIUS Access Server IP:
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Access server.
RADIUS Accounting Server IP:
Enter the IP address of the RADIUS Accounting server. In most configurations, the Access and
Accounting server are located on the same machine, so the IP address is the same for both fields.
RADIUS Secret:
Enter the secret code or password for the RADIUS Server.
Enable
to configure remote users to authenticate on a RADIUS Server.
Router DNS IP Address
Enter the IP address of your Internet Service Provider’s DNS server.
DHCP Server
Y ou may select
information to workstations as they connect to the network, select Enable. When you enable DHCP,
you will be prompted to provide the beginning and ending IP addresses in the range of addresses
administered by your RouteFinder. Refer to the LAN DHCP section of the RouteFinder Manager
chapter of this User Guide for additional information.
Disable
or
Enable
. If you would like the RF500S DHCP server function to provide IP
Virtual Server
Select
necessary to allow remote clients to access specific devices on your network via the Internet. Refer
to the General Settings section of the RouteManager chapter in this User Guide for more information
about Enabling IP Mapping.
Disable
or
Enable
. If you select Enable, you may enter the external and internal IP Addresses
Routing Table
The Routing Table option lets you create a routing table so your RouteFinder will route IP packets to
the proper network. For more information, refer to the Routing T able section of the RouteFinder
Manager chapter of this User Guide.
Client Filter Settings
The Filter Settings option allows you to define which packets are allowed to either pass through, or be
blocked from passing through the RF500S ports. You may filter packets for network services including
Mail, WWW, FTP, Telnet and News. See the Filter Settings section of the RouteFinder Manager
chapter for more information about filtering options.
36
Load Default Settings
Use this option to return the router to the factory default settings.
Save and Restart Server
This option saves your RouteFinder configuration into Flash memory and restarts the device to enable
the settings to take effect. The system will pause while settings are being saved.
Note: After completing your configuration, you must select Save and Restart Server or your settings
will be lost when the device is powered off.
Page 37

Chapter 4 - T elnet
Diagnostic
The Diagnostic option performs basic testing of the RouteFinder, displays information about your
firmware and offers options for assigning the LAN and WAN MAC addresses as may be required by
your ISP.
Type any key to return to the main menu.
37
Page 38

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
Page 39

RouteFinder Manager
RouteFinder manager is the main program used to configure all the settings of your RF500S.
1. T o run RouteFinder Manager , click on the RouteFinder Manager icon on your desktop, or click
Start | Programs | RouteFinder Manager | RouteFinder Manager.
2. The Manager dialog box displays.
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
3. The RF500S automatically searches your network for devices available for configuration and
displays them in the Available Devices list box.
Note: Before using any of the Manager options, you must select the device you are attempting to
configure from the A vailable Devices list. If you need to update the list, click Refresh Device
List. You must exit RouteFinder Manager before using the device.
After you have selected a device from the
information about the name, IP address, MAC address and Firmware version of your RouteFinder .
The buttons in the left column of the screen offer the ability to change the device’s name and
password, save and load settings, upgrade the firmware or run general diagnostics on the device.
The buttons in the right column provide access to advanced configuration options for General
Settings, Port Settings, LAN DHCP Server Options, Router Settings and Filter Settings.
Additional information about all of these options is included in this chapter.
Note: If the IP address of the device you are attempting to configure is not within the same
subnet, the “Please Set the Device IP” dialog box displays, requesting you to input an IP
address in the same subnet.
Should an error message appear, refer to the Troubleshooting chapter of this User Guide.
Available Devices
list, the Status field provides
39
Page 40

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
General Settings
After selecting your device from the
all of the major network settings for the RF500S including LAN and WAN Ethernet segment settings,
DNS information, IP Routing and Remote Access settings. Most of the settings on these screens
were entered in Setup Wizard; however, some important settings can be entered only in RouteFinder
Manager.
Available Devices
list, select General Settings to view or change
LAN Ethernet Segment
Server IP address:
This IP address is the internal LAN IP address of the RF500S. The address entered into the
Setup Wizard is displayed here (e.g., 192.168.2.1).
Server IP Netmask:
The RF500S subnet mask generally can be left at the default value of 255.255.255.0.
40
Page 41

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
WAN Ethernet Segment
Select NA T (Network Address T ranslation) to provide firewall protection and enable all local LAN
users to share one IP address to access the Internet. If the NAT box is
Ethernet is configured as a router to route network traffic between the LAN Ethernet segment and
the WAN Ethernet segment. The External Port IP Addresses are provided by your ISP or remote
system administrator.
PPPoE:
If your ISP uses Point -to- Point Protocol over Ethernet for authentication purposes, select the
PPPoE box and enter your ISP account User Name and Password in the fields provided.
External Port IP Address:
Enter the IP address provided by your ISP or remote system administrator.
External Port IP Netmask:
Enter the subnet mask of the port as provided by your ISP or remote system administrator .
Gateway IP Address:
Enter your ISP or remote network’s Gateway IP address.
Note: If your ISP uses a DHCP server to automatically assign a login IP address, subnet mask,
gateway IP address or DNS IP address, enter 0.0.0.0 as your External Port IP Address and the
Gateway IP Address.
not
checked, the WAN
41
Page 42

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Async Port
The Async Port can be configured to provide either
to connect your network to another router through the Serial async port. Remote Access allows remote
users to dial-in to the device to access and share network resources as if they were logged on to the
network locally .
1. To configure the RF500S for IP Routing, select IP Routing in the
General Settings dialog box.
2. Click PPP Settings.
3. The IP Routing Settings dialog box displays.
IP Routing
or
Remote Access
Async Port
. IP Routing is used
section of the
IP Routing (NAT Enabled):
If NA T is enabled, all local users will be firewall protected and will share one IP address through
the Async port. Enter values in the fields as described:
T el Number:
Enter the phone number required to access your ISP.
User Name:
Enter the account user name to be authenticated by your ISP.
Password:
Enter the user account password to be authenticated by your ISP.
Password Verification:
Re-enter the user account password for verification.
External (Port) IP:
Enter the fixed IP address provided by the remote site System Administrator. If this address is
automatically assigned by the remote site DHCP server , enter 0.0.0.0
Assign Remote Site an IP Address:
Check the box if you will specify the IP Address of the remote site.
Remote IP address:
Enter the IP address the remote site will use.
42
Page 43

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
Allow Remote Dial-In
This option allows a remote site to dial-in to this network.
1. From the IP Routing Settings dialog box, select Allow Remote Dial-In.
2. Click Remote Authentication Settings.
3. The Remote Connection Authentication dialog box displays.
4. Y ou must select one of three methods to define the authentication protocol to be used when a
remote site is dialing in to your site. You may select:
• None - No authentication needed.
• P AP - User Name and unencrypted Password are transmitted over the network.
• CHAP - DHCP sends a key which is used to encrypt the user name and password. Encryption
provides added protection from potential interception of authentication information.
Note: If you select PAP or CHAP, you must indicate where the authentication process should
occur, by selecting Use Local Settings, Use Local Client List or Use RADIUS Authentication.
Refer to Remote Connection Authentication Settings following this section.
5. Click OK when complete.
Callback Settings
From a remote site, you can trigger your RF500S to establish a connection with your ISP.
1. Click
Callback Settings
a.
No Callback
b.
T rigger (ISP) Server Connection
server after a remote user dials into the asynchronous port. The device can be triggered
to automatically establish a connection with the ISP in one of two ways:
•The ISP server is dialed after the RF500S receives a PPP (modem) connection from a
remote user.
•The RF500S makes the connection to the ISP server after receiving a regular telephone
call. The remote user calls the RF500S async port to trigger the connection to the ISP
server.
c.
Remote Callback -
callback. Y ou must enter the callback telephone number (the telephone number the
device should call) in the T el Number field.
and select one of three call back options:
- The RouteFinder will establish a connection with the ISP
After dialing, the RF500S hangs up and waits for the remote site to
2. Click OK to complete.
43
Page 44

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Remote Connection Authentication Settings
When you select Allow Remote Dial-in, you must determine the method that remote users must use to
be authenticated on your system. If you choose the
select
Use Local Settings, Use Local Client List
Use Local Setting
Y ou may create a
must type the same user name and password that you specify .
Use Local Client List
The Local Client list is a list of all User Names and Passwords that can access your network from
a remote site. When a remote user dials in to the RF500S, the user’s access profile information
(user name, password, callback status, etc.) is validated by checking the user information in this
list. The RF500S can include up to 64 users in the Local Client list. Click Local Client List to add
your remote users.
Important: The RF500S is set up with a default user of guest which requires no password. For
security reasons, either delete the guest user id guest or provide it with a password.
Remote User Name
PAP
or
Use RADIUS Server
and
Remote Password
or
CHAP
authentication protocol, you must
authentication.
to log in to the system. All users
Client Information
For each new remote user added to the system, enter the following information:
User Name:
Specify a user name with a maximum of 16 characters.
Password:
Specify the password corresponding to the user name. Passwords are limited to 16 characters.
Password Verification:
Verify the password by re-entering the user password in the box provided.
Callback Type:
The callback feature provides an added level of security to your dial in system. A remote client
dials in to the network and then disconnects. The RF500S then calls the client back. The feature
can be implemented using
No Callback:
The RouteFinder does not perform a callback function. This is the default setting.
Fixed Callback:
The RouteFinder will connect to the client by dialing the number specified in the
T elNumber
V ariable Callback:
This option allows the remote client to specify the phone number the RouteFinder should callback
each time a dial up connection is established.
field.
no callback, fixed callback
or
variable callback
.
Your
44
Page 45

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
Assign a specific IP address for this user:
Select this option if you would like to have a specific IP address assigned to this user . Enter the
IP address in the field provided. This IP address will be used each time the client logs in and will
override the
box,
Async
Click Add to complete adding this client to the Local Client List.
Assign Remote Site an IP Address
tab.
option as shown in the IP Router Setting dialog
Use Radius Authentication
Choosing RADIUS Authentication allows you to use the user information (user name, password, IP
address, etc.) stored on a separate RADIUS server on the network.
Note: A RADIUS Server (Remote Authentication Dial-In Service) is an accounting and
authentication system used by many large companies and Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
After a client dials in to the network and enters their username and password, the information is
passed to a RADIUS server. The RADIUS server checks that the information is correct, and then
allows access to the system.
1. From the Remote Access Settings dialog box, in the
Use RADIUS Authentication, then click RADIUS Setup.
2. The RADIUS Configuration dialog box displays.
3. Use the List box to select the
authenticated.
4. Complete the provided fields for the Access and Accounting Server fields:
RADIUS Access Server IP Address:
Enter the IP Address of the RADIUS Access Server.
RADIUS Accounting Server IP Address:
Enter the RADIUS Accounting Server IP Address
Main
or
Backup RADIUS Server
Remote Users Authentication
from which the device will be
section, click
Note: In most cases, the RADIUS Accounting Server and the Access server are the same device.
If this is true for your configuration, enter the same IP address in both fields.
Secret:
Enter your Secret RADIUS code or password.
Secret Confirmed:
Re-enter your Secret RADIUS code.
5. Click OK when complete.
45
Page 46

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Remote Access - Remote Access Settings
1. From the General Settings dialog box,
Remote Access Settings.
2. The Remote Access Settings dialog box displays.
Complete the fields as follows:
Async Port
section, select Remote Access and click
IP Assigned Method for Remote Clients:
A remote client must have an IP address to connect to the network. IP addresses may be
assigned
manually
automatically
assigned.
from a designated IP address pool using DHCP, or the IP address may be
Assign an IP Address Automatically:
The RS500S DHCP feature will issue the remote site user an IP address automatically if the
DHCP function is enabled. If DHCP is disabled, the device will automatically search for a DHCP
server and request an IP address for the remote client.
Assign an IP address manually:
Enter an IP address for the remote client.
Network Protocols:
Y ou must select the network protocols you would like to enable for the dial-in service. The default
enables both TCP/IP and IPS/SPX. If you do not need both protocols, you may disable one of
them. If you are connecting to a Netware Server, IPX/SPX must be enabled.
IPX/SPX Frame T ype:
The RouteFinder RF500S can automatically detect what kind of IPX/SPX frame type you are
using. You may manually select a frame type by using the list box.
Remote Client Authentication:
Remote authentication settings allow you to specify how you would like to authenticate remote
users. Y ou may select
Connection Authentication Settings in this chapter for more information). Choosing RADIUS
configuration allows you to use the user information (user name, password, IP address, etc.)
stored on a separate RADIUS server on the network.
Use Local Client List
or
Use RADIUS Authentication
(refer to Remote
46
3. Click OK when complete.
Page 47

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
Enable IP Mapping - Virtual Server
IP Mapping is available only when NAT is enabled. If NAT is enabled for a particular port, that port is
firewall protected. The
access to your LAN via the Internet. For example, you can use the IP mapping function to access an
FTP server on your LAN via the Internet. IP Mapping is most suitable to fixed or static IP addressing.
1. To enable IP Mapping, from the General Settings dialog box, select Enable IP Mapping, then
click IP Mapping (Virtual Server).
2. The Virtual Server Mapping dialog box displays.
Enable IP Mapping
function allows you to open a “hole” in your firewall to allow
For each service you’d like to set up:
1. Use the
2. Enter the IP address supplied by your ISP in the External IP field. If your ISP uses dynamic IP
addressing, set this field to 0.0.0.0. Your device will use the dynamically assigned address when
connecting to your ISP.
3. Enter the TCP/IP port number for the service that you will be using for IP mapping. Common
TCP/IP port numbers are listed below:
For more information on port numbers, visit http://www.metadigm.co.uk/
If you would like to map all services for this external IP address to a computer on your LAN, you
can enter port number 0. This means that whenever anyone accesses your external IP address,
they will automatically be “mapped” to the internal computer that you specify, regardless of what
port number they are using.
4. Enter the Internal IP address of the server to which you want to map the External IP address.
5. Enter the port number for the service that you will be using for this IP mapping.
Click Insert to include the mapping.
6. Click OK when you have completed mapping addresses.
Port No.
WW W Port 80
FTP Port 20 or 21
SMTP Port 25
POP3 Port 110
field to select either the WAN or Async (Serial) port.
Note: IP Mapping function allows you to have only one port service on your LAN. For example, if
you map an external IP (16.895.1.3) to an internal IP address (192.168.2.22 - a www server), only
the internal IP address in your local network can serve as the www .server for the external IP
address.
47
Page 48

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Port Settings
The Modem Settings options are used to configure the communication between your modem or ISDN
T A and your RouteFinder serial port. You must specify the baudrate, modem and modem string
settings for your device.
1. To view or change the port settings, from the main Manager dialog box, click Port Settings. The
Port Settings dialog box displays.
2. Complete the fields as follows:
Baudrate:
Use the list to select the Remote Access DTE speed for your device.
The absolute maximum setting for a given port on the network device is 4 x the speed of your
modem. If the baudrate is set too high, your network device may fail to establish a dial-up
connection. For example, if you have a 14.4Kbps modem, the highest speed selected is 57.6Kbs.
If your modem does not appear in the list provided, the Standard Modem selection will work in
most cases.
Important: If you are using an ISDN Terminal Adapter, refer to the Async to Sync PPP string in
the User Manual provided with the device to determine the correct initialization, dialup and hang up
strings.
Note: Due to variations in ISP connections and phone line quality, this theoretical maximum
speed is not attainable. Y ou may need to set the baudrate at a lower speed.
48
Page 49

Edit Login Script for Remote Access
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
1. From the Port Settings,
2. The login Script dialog box displays.
A sample remote access login script is shown below. If a remote access client is configured to
“bring up a terminal window after dialing”, this remote access login script initiates.
For Remote Access, the device will act as the server side...
Send ‘Welcome’ displays “Welcome” to remote site.
Send sends an Enter (Carriage return + line feed) to the remote site.
“Send Username” prompts the remote site for a user name.
“Retrieve 1” will wait for the remote site to enter the user name that will be used for PPP
authentication.
“Send Password” prompts the user for a password.
“Retrieve 2” will wait for the remote site to enter a password.
“Verify 3” instructs the device move to login script line 3 if PPP authentication fails.
“Go” means start PPP protocol.
Async
tab, click Edit Login Script.
49
Page 50

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Writing a login script for IP Routing
To write an effective login script, you must obtain the correct login script information from your ISP
and become familiar with using the login script commands.
Every ISP has a unique login interface screen. Check with your ISP to determine how your ISP
requests information from you when using a PPP connection.
Note: Y ou can create a simple dial-up connection to view your ISP interface log-in screen using DialUp Networking in Windows 95, 98, NT or 2000.
Some common commands are:
Send and SH FUNCTION
Send ‘ATZ’ Resets the Modem
Send ‘A TDT 888-1234’ Dials the phone number “888-1234”
Send ‘JaneDoe’ Types “JaneDoe” at the ISP interface
SH ‘1234’ Types “1234” at the ISP interface but displays **** on the RouteFinder
Send ‘’ Sends Enter (carriage return plus line feed) to the ISP
Wai t FUNCTION
Wait 5 The Modem will wait for 5 seconds before moving the next line in the
Wait ‘CONNECT’ The Modem will wait for CONNECT to display before moving to the next
Wait ‘CONNECT 6’ Modem will wait for “CONNECT” to display before moving to the next
monitor to hide the password.
login script.
command.
command. If CONNECT does not display , the modem will go to line 6 of
the login script.
Other FUNCTION
Go Begins PPP
Jum p4 Goes back to line 4 of the login script.
Hangup Hangs up the modem.
Example 1:
# Login Script Meaning of Each Login Script Command
1 Send‘ATZ‘ Rests Modem
2 Send‘ATS0 =1‘ Sends initial string ‘A TS0 =1‘ to modem
3 Send‘ATDT888-1234‘ Dial phone number 888-1234
4 Wait‘CONNECT‘ Waits for ISP to send reply ‘CONNECT‘
5 Wait‘username:‘ W aits for ISP to send reply ‘username‘
6 Send‘JaneDoe‘ Sends the user name ‘JaneDoe‘ to the ISP
7 Wait‘password‘ Waits for ISP to send reply ‘password‘
8SH‘1234‘ Sends password ‘1234‘ to the ISP
9 Wait‘===>‘ Waits for ISP to send reply ‘===>‘
10 Send‘1‘ Selects option 1(PPP) for this ISP
11 Go Starts PPP mode
Script for Normal Reliable ISP
50
Page 51

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
Example 2 :
# Login Script Meaning of Each Login Script Command
1 Send‘ATZ‘ Resets modem
2 Send‘ATS0 =1‘ Sends initial string ‘A TS0 =1‘ to modem
3 Send‘ATDT8881234 Dials phone number 888-1234
4 Wait‘CONNECT‘2 Wait for ISP to send reply ‘CONNECT‘. If no CONNECT , returns
5 Wait‘username:‘12 Waits for ISP to send reply ‘username‘. If no response, goes to
6 Send‘JaneDoe‘ Sends the username ‘JaneDoe‘ to the ISP
7 Wait‘password‘ Waits for ISP to send reply‘ password‘
8SH‘1234‘ Sends password ‘1234‘ to ISP
9 Wait‘====>‘ Waits for ISP to send reply ‘===>‘
10 Send‘1‘ Selects option 1 (PPP) for this ISP
11 Go Starts PPP mode
12 Hangup Hangs up Modem
Example 3 :
# Login Script Meaning of Each Login Script Command
1 Send‘ATZ‘ Resets modem
2 Send‘ATS0 =1‘ Sends initial string ‘A TS0 =1‘ to modem
3 Send‘ATDT8881234 Dials phone number 888-1234
4Wait‘CONNECT’ 1 2 W aits for ISP to send reply ‘CONNECT’. If no reply, goes to line
5 Wait ‘username:’ 12 Waits for ISP to send reply ‘username’. If no response, goes to
6 Send‘JaneDoe‘ Sends the username ‘JaneDoe‘ to ISP
7 Wait‘password‘ Waits for ISP to send reply‘ password‘
8SH‘1234‘ Sends password ‘1234‘ to ISP
9 Wait‘====>‘ Waits for ISP to send reply ‘===>‘
10 Send‘1‘ Selects option 1 (PPP) for this ISP
1 1 Go Starts PPP mode (Rest of script ignored)
12 Hangup Hangs up Modem
13 Send ‘A T S0=1’ Sends initial string ‘A T SO=1’ to modem
14 Send ‘A TDT 8885678’ Dials phone number 888-5678 (ISP #2)
15 Wait ‘Connect’ 23 Waits for ISP to send reply ‘CONNECT’. If no CONNECT, goes
16 Wait ‘username:’ 23 Waits for ISP to send reply ‘username’. If no response, goes to
17 Send ‘Stephen’ Sends the username ‘Stephen’ to ISP
18 Wait ‘password:’ Waits for the ISP to send ‘password:’
19 SH ‘5678’ Sends password ‘5678’ to ISP
20 Wait‘====>‘ Waits for ISP to send reply ‘===>‘
21 Send‘1‘ Selects option 1 (PPP) for this ISP
22 Go Starts PPP mode
23 Hangup Hangs up Modem
2 4 Jump 2 Goes back to line 2 to re-dial ISP#1
Script for Unreliable ISP (Redial until connected)
to line 2 to re-dial.
line 12.
Script for Unreliable ISP (2nd ISP backup)
12 for ISP #2.
line 12 for ISP #2.
to line 23.
line 23.
51
Page 52

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Modem String Settings
The most important modem string is the initialization string because your network device uses it to
establish communications with your modem or ISDN T A. The modem initialization string displayed is
the modem or ISDN T A initialization string entered in the Setup Wizard. For most analog modems, the
Standard Modem selection will work. For additional information, refer to the Modem Settings
information presented in the Software Installation and Configuration Chapter of this User Guide.
Important: There is no standard ISDN TA initialization string. If your ISDN T A is not included in the
modem list, check your ISDN T A User’s Guide for information for the initialization string for an
Asynchronous to Synchronous PPP connection. If you are using only one channel of your ISDN
connection, you can enter the Async to Sync PPP initialization string. If you are bundling your
connection channels, you’ll need to use a Multilink-PPP initialization string. You must also enter the
two phone numbers in the T elephone Number field of the General Settings dialog box. Also verify that
your ISDN TA supports the dial-up string A TDT. Most ISDN T As support ATDT , but some support ATD
or A TDI.
Dial-up/Hang-up Settings
The Dial-up/Hang-up settings allow you to specify your connection time (idle timeout or auto
reconnect) and the number of times to attempt to connect (if connection cannot be established).
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click Port Settings.
2. From the
Async
tab, click Dial-up/Hang-up Settings.
Individual Port Options
Individual Port Options lets you set the idle-timeout function for each serial port of the RouteFinder.
Y ou can set the number of minutes you wish to allow a connection to stay idle before disconnection.
Note: Default idle timeout for IP Routing is 5 minutes. Default idle timeout for Remote Access is 30
minutes.
If you un-check the idle-timeout, once a client establishes a connection, the connection will be
maintained until you turn off your modem, unplug your network device or use the
function in the RouteFinder monitor program.
The Automatic Reconnect (Always connect) essentially maintains your connection (e.g., idle time out
= infinite). If the connection is disconnected for any reason, it will automatically attempt to reconnect.
T erminate Connection
Dial-up Retry Options
The Dial-Up Retry option allows you to specify the number of times the RouteFinder should attempt to
establish a connection.
If the retry count is 0, the device will not dial-out to connect to the remote site.
Note: Automatic Reconnect will override the Retry count setting if retry count is set to 0.
52
Page 53

LAN DHCP Server
Note: Refer to the Glossary at the back of this User Guide for more information about the DHCP
function.
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click LAN DHCP Server.
Note: The LAN DHCP Server option indicates if DHCP is Enabled or Disabled. By default the
DHCP function is Enabled. To Disable the function, you must open the DHCP Configuration dialog
box, select Disabled and click OK.
2. The DHCP Configuration dialog box displays.
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
3. Complete the following information:
DNS IP Address:
Enter the ISP’s DNS IP address. You may enter up to 4 ISP DNS IP addresses. Click Insert.
IP Address Pool:
The IP Address Pool contains the range of IP addresses that will be automatically assigned to the
clients of your network as they connect to the network.
Note: By default, the IP address pool range is from 100 to 200. Ranges are listed in the IP
Address Pool table.
To
change
1. Select the existing range of addresses.
2. Enter a new range.
3. Press Insert.
To
delete
1. Select the range of addresses.
2. Press Delete.
IP Address Mapping Reservation:
You can use the IP Address Mapping Reservation option to give a
computers on your network. Each time a computer is powered on and connects to the network, it
will receive the same IP address. Static IP addresses are frequently assigned to network
resources such as printers, servers, hubs and routers that are consistently shared by network
clients.
the range:
an IP Address range:
static
IP address to particular
53
Page 54

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
To assign a static IP Address:
Enter the MAC address manually or use the MAC address search tool.
To use the MAC address search tool:
1. Enter the IP address of the computer .
2. Click Search to find the MAC address.
3. Once the address has been located, click Add to reserve the address.
To delete a static IP Address:
1. Select the static address you would like to delete.
2. Click Delete.
Note: Refer to the User Guide Glossary for information about determining a computer’s netmask
address.
54
Page 55

Routing Settings
Routing is the process of moving a packet of data from source to destination. The RF500S acts as a
router to enable messages to pass from one computer to another and eventually reach the target
machine. Part of this process involves analyzing a
information below to create a routing table to connect your network to another network, or to connect
subnets within your network.
Note: A routing table is required to use the LAN -to- LAN routing function of the RF500S.
1. From the main Manager dialog box, select Routing Settings.
2. The Routing Settings dialog box displays.
routing table
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
to determine the best path. Use the
Static Routing
For each different subnet on your LAN, enter:
IP: Enter the (network/subnet) IP address to which you want to route.
Netmask: Enter the subnet mask of your Network IP address.
Gateway: Enter the IP address of the gateway device linking your network to the
other network/subnet. The IP address should be in the same subnet as
your RF500S. If you are using this device with the LAN -to- LAN
function, the gateway IP should be set as the IP address of the
RouteFinder.
Interface: Select the port (LAN or W AN, etc.) that the routed packet should pass
through. Select
are using the RF500S with the LAN -to- LAN function, the Interface
should be set as the WAN port that connects you to the other subnet.
Click Insert to save the information to the routing table.
To delete this information, select it from the routing table and click
Delete.
Default Gateway: Default gateway is an IP address that all packets are routed to, when
the device is unable to find a route match (the destination IP address of
the packet in the routing table).
Click Add Default Gateway to save the IP address of the default
gateway .
Local Network
if you are using a separate router. If you
Interface: Select the port (LAN or W AN, etc.) interface where the gateway is
located.
55
Page 56

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Routing Table
The routing table stores the routing information so that the RF500S knows how to route the IP packets
to the proper network.
WAN Ethernet 192.168.5.254
RF500S - 2
PC 1
192.168.3.9
RF500S - 1
WAN Ethernet 192.168.3.1
LAN Ethernet 192.168.5.1
LAN Ethernet 172.168.2.254
PC 2
172.168.2.1
What is the purpose of the routing table?
In the diagram above, the RF500S-1 has the routing information to route between 192.168.3.x and
192.168.5.x. The device does not have the information about how to route to the 172.168.2.x
network. If you want the RF500S-1 to route to 172.168.2.x, you must add the following information
to the routing table:
IP: 172.168.2.0
Network: 255.255.255.0
Gateway IP: 192.168.5.254
Interface: Ethernet (Local Network)
If you would like the RF500S-2. to route to 192.168.3.x, enter the following routing table
information into the RF500S Routing settings:
IP: 192.168.3.0
Network: 255.255.255.0
Gateway IP: 192.168.5.1
Interface: WAN Ethernet
56
Page 57

Filter Settings
Y ou can use Filter Settings to choose which packets are allowed to enter the network and which
packets will be blocked. Filter Settings can be used to filter network services such as Mail, WWW,
FTP , Telnet and News.
1. From the main Manager dialog box, select your RF500S, then Filter Settings.
2. The Filter Settings dialog box displays.
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
3. Select the
• The Block function filters by blocking packets from going
the LAN port. To enable the Block IP filter function, select Enable Block IP Filter Function.
• The Pass function filters by defining which packets can go
your LAN. To enable the Pass IP filter function, click the
Filter Function.
4. To filter packets to be passed or blocked, use the Packets Defined by list to select
User
Packets Defined by TCP/IP:
If you choose to define by TCP/IP, you must enter the IP information of the packet(s), then select
either
IP Address:
Enter the IP address of the packet to be blocked or allowed to Pass. Keep in mind the option that
you’ve checked, either
going) or
Netmask:
Enter the subnet mask for the packet.
TCP/IP Service Port:
Enter the Socket Port you would like to block or allow to pass (e.g., HTTP= 80)
Block
.
By Destination
By Source,
tab or the
Pass
tab to define your filtering.
out
the WAN port or coming in through
into
your WAN port or come on to
Pass
tab and select Enable Pass IP
or
By Source
By Destination,
(enter the IP address of the device to which the packet is coming from).
.
(enter the IP address of the device to which the packet is
TCP/IP
or
57
Page 58

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Privilege Level
Use the Privilege list box to select an appropriate level for this filter.
It is common to set many filter rules for a particular client. At times, the rules you have set may
conflict with one another. When a conflict occurs, the filter with the higher privilege level will
override the other filter(s).
Note: Level one is the highest level, level sixteen is the lowest privilege level.
Example:
Let’s say you configure a filter rule for Source IP address 192.168.100.72 with a privilege level of
16 to Pass using socket number 80. At the same time, you set the same filter rule to block IP
Address 192.168.100.72 with a privilege level of one. The RF500S will implement the filter to
block the IP address 192.168.100.72 because the privilege level is higher .
Note: If conflicting rules have the same privilege level, then the RF500S will block the packet.
Click Insert to add each IP address to the list.
To remove a defined packet, select the packet you’d like to delete from the table and click Delete.
Packets defined by User:
If you choose to define by User, you must define the byte pattern of the packet(s). The RF500S
uses the defined byte patterns to block or pass packets from the WAN or from the LAN.
1. In the
2. In the
Starting from which byte number:
In this field, indicate the first byte in the packet the RF500S should read to determine if the byte
pattern (in Hex) is one that should be filtered. Exclude the PPP header . Start from byte 0 of the
network protocol.
Byte Pattern (in Hex):
Enter the packet byte pattern that you would like the RF500S to recognize as a packet to be
filtered. (Block/Pass from the WAN to the LAN). The maximum pattern size is 12 bytes.
Click Insert to add each byte pattern to the table.
To delete a defined packet, select the packet in the table and click Delete.
Block
dialog box, select Enable Block User Defined Pattern Function.
Packets defined by User
field, select From LAN or From WAN.
58
Page 59

Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
Enable Client Filter Settings
The
Client Filter
are authorized to access them.
1. From the Filter Settings dialog box, select Enable Client Filter Setting.
2. Click Client Filter Settings.
3. The Filter Settings dialog box displays.
allows you to decide which services are allowed into your network and which clients
The filter works by filtering TCP/IP port numbers. The 5 most commonly used port numbers are
listed for you. They include the port numbers for Mail, WWW , FTP, Telnet and News. If you would
like to filter other services, you must know the port number for the service.
4. Click Edit to enter new service port numbers.
5. Enter the TCP/UDP Port Number and click Add.
Note: Refer to the Glossary of the User Guide for a definition of Port.
6. Click Privileged Clients.
59
Page 60

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
7. The Privileged Client Table dialog box displays.
LAN Local Client List
In the Privileged Client Table, enter the clients you wish to have privileged access to the services
that you have selected in the Filter Settings dialog box. The filter uses MAC addresses to
identify the privileged clients. You can enter the MAC address directly or you can use the MAC
address search tool by entering the IP address of the computer, then using the Search button to
find the MAC address.
After completing the IP Address and MAC (Node) address, click Add to include the information in
the Node (MAC) address list.
Remote Clients
(Applies to Remote Access Port(s))
Select Include WAN Async Clients as Privileged Clients or Include W AN Ethernet Clients as
privileged clients to filter Remote Clients by the port they are coming in through.
8. Click OK when complete.
60
Page 61

Refresh Device List
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click Refresh Device List to search the LAN for available
network devices and display them in the Available Devices list.
Note: If a device does not appear in the list, click Refresh Device List again to determine if the
device will appear on the list. If the device still does not appear, ensure that all cables are
correctly connected and that the RF500S is powered on. If the device still does not appear in the
list, refer to the T roubleshooing chapter of this User Guide.
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
61
Page 62

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Device Name and Password
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click Device Name and Password. Y ou may use the default
device name or use this dialog box to change the name or add a password for your device.
Device Name:
This field displays the name of your network device. To change the name, simply enter a new
name in the field. If you are connecting to an ISP via cable modem or DSL, and your ISP requires
you to enter a computer name, you may use the device name that you’ve entered on this screen.
Device Password:
The RouteFinder manager does not come with a password enabled. If you choose to provide the
device with a password, you will be prompted to enter the password each time you want to
configure your network device. T o enter a Password, type your password in the Device Password
field, then re-enter your password in the Password Verification field.
Note: If you choose to use a password, ensure you have selected something that will be easy to
remember or write it down and store it in a safe location. If you have completely forgotten your
password, contact the Multi-T ech T echnical Support group for assistance. Refer to Chapter 10 in
this User Guide for more information about our T echnical Support services.
2. Click OK.
62
Page 63

Save Settings to File
The Save Settings to File option allows you to save your settings to a file. This option provides a
method for backing up your system configuration so that it can be used in the event your settings
become accidently deleted. This option can also be used if you would like to have more than one set
of settings for your RouteFinder.
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click Save Settings to File.
2. The Save Settings to File dialog box displays.
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
T o save your settings to a file:
1. In the File Name field, enter a name for your file.
Note: Do not change the file type extension. If you try to use the Load Settings function, the
manager program will look for the specific file extension compatible with your device. For
example, *.co1 is used only for 1 WAN port units, *.co2 is used only for 2 WAN port units.
2. The File Directory field displays the default path to the configuration files. You may save a copy
of the file to a different location by changing the path in the File Directory field.
3. Press OK to save the settings to the file name specified in step 1.
63
Page 64

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Load Settings
The Load Settings option allows you to load either the default settings of your network device or to
load settings previously saved to a file.
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click Load Settings.
2. The Load Settings dialog box displays.
3. T o return the RouteFinder to factory default settings, select Load Default Setting.
4. To load a configuration from a file, select Load Settings From File.
• In the File Name field, enter the name of the file containing the settings you would like to use .
• Indicate the location of the file by entering the full path to the file in the File Directory field.
• Select the file from the
5. Press OK to load and apply the settings to the RouteFinder .
Available Files
table.
64
Page 65

Upgrade Firmware
Warning: Upgrade the firmware of your RouteFinder RF500S only under the advice and direction of the
Multi-T ech T echnical Support Group. Improperly upgrading the RF500S may disable the device!
The Upgrade Firmware options allow you to upgrade your RF500S firmware. The Upgrade Firmware
option upgrades the firmware of your RF500S, not the RouteFinder Manager or Monitor software.
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click Upgrade Firmware.
2. The Upgrade Firmware dialog box displays.
Chapter 5 - RouteFinder Manager
T o Upgrade your firmware:
1. Download the latest firmware from the Multi-Tech System’s web site at www.multitech.com.
2. Copy the firmware to the directory containing the RouteFinder Manager program files. Refer to the
default Firmware File Directory field to determine the location of the files on your system.
3. Enter the location of the new firmware file in the Firmware File Directory field. RouteFinder
Manager will automatically detect the new firmware file name and display it in the
Name
field. The version number of your firmware will display in the
4. Click Upgrade to upgrade your firmware.
5. A message appears stating the upgrade has started.
6. After several minutes, an informational dialog box displays indicating the upgrade was successful.
7. Click OK.
8. From the main Manager dialog box, click Save and Exit.
9. Click Yes to restart the RouteFinder using the new firmware version.
Firmware File Version
Firmware File
field.
65
Page 66

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
General Diagnostic
The General Diagnostic option on the main RouteFinder Manager dialog box displays network device
information and allows you to determine if the RF500S is functioning properly .
1. From the main Manager dialog box, click General Diagnostic.
2. The General Diagnostic dialog box displays information about the RF500S.
3. Record the information if necessary and click OK to exit.
66
Page 67

Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
Page 68

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
RouteFinder Monitor
RouteFinder Monitor is a utility that provides both monitoring and troubleshooting functions.
Running RouteFinder Monitor
1. Click on the RouteFinder Monitor icon, or select Start | Programs | RouteFinder Manager |
RouteFinder Monitor.
2. The RouteFinder Monitor dialog box displays.
Note: If you receive a message stating “Device is not found”, refer to the Troubleshooting chapter
in this User Guide.
68
Page 69

Refresh Device List
Click Refresh Device List from the main RouteFinder Monitor dialog box to display a list of network
devices in the Available Devices window .
Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
69
Page 70

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Test Connection
The Test Connection option tests your connection settings and assist you in determining if problems
are due to the modem, the RouteFinder, or an incorrect setting. Test Connection uses the attached
modem(s) to dial-up the remote server (ISP) and establish a connection.
1. From the main RouteMonitor dialog box, click T est Connection to begin testing.
2. The T est Connection dialog box displays.
3. Select
connection.
4. The monitor display window displays the actions of the test.
5. T o terminate the connection, refer to the T erminate Connection instructions which follow .
6. Click Exit to close the Test Connection dialog box.
Connect Port 1
to test the WAN connection, or
Connect Port 2
to test the Async
70
Page 71

Terminate Connection
The T erminate Connection option is designed to allow the Network Administrator to terminate an
RF500S connection instantly.
1. From the main RouteFinder Monitor dialog box, select T erminate Connection.
2. The T erminate Connection dialog box displays.
Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
3. Select
4. Click Terminate Connection.
5. Click Exit to return to the RouteFinder Monitor dialog box.
Disconnect Port 1
or
Disconnect Port 2
.
71
Page 72

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Save to File
Click Save to a File to save a monitoring session to a file. This feature can be used to create an event
log to send to our Technical Support group for evaluation.
1. From the main RouteFinder Monitor dialog box, select Save to File.
2. The Save Log Files dialog box displays.
Save Now
If you want to save the monitor display at any point in time, select the monitor you’d like to save
to a file (TCP/IP, Event Message, etc.). Select the
like to save the file and click Save.
File Name
and
File Directory
to which you’d
Autosave
If you wish to automatically save the information displayed on the monitor to a database file,
enable the AutoSave function. Options for this function include:
Overwrite database file
This option saves the information collected by the monitor to a database file based on the time
interval that you specify, overwriting the last saved database file.
Append Database file
This option saves the information collected by the monitor to a database file based on the time
interval that you specify , updating and appending to the file.
Note: The Append Database file option will reset the monitor and clear the screens after the
autosave has appended the information to the file.
Warning: The database size limit is equal to the amount of available disk space. Use this option
with caution!
3. Click OK when complete.
72
Page 73

IP Address/Name
The IP Address/Name function allows you to associate a name with a particular IP address and name
on your network. This information will appear in the relevant monitor displays. The IP Address/Name
option is used to assist the Network Administrator in determining which users are transmitting and
receiving data without having to remember their specific IP addresses.
Each computer listed must have a fixed IP address for your network. You may configure a fixed IP
address on the individual computer or use the RF500S’s DHCP server IP reservation system (refer to
the LAN DHCP section of RouteFinder Manager chapter of this User Guide).
1. From the main RouteFinder Monitor dialog box, click IP Address/Name.
2. The IP User Mapping dialog box displays.
Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
3. Enter each computer’s IP Address and associated User Name in the provided fields.
4. Click Add after each IP address and name have been added to the list.
5 . When all addresses have been added, click OK.
73
Page 74

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Event Messages
Event Messages are displayed in the lower half of the RouteFinder Monitor display. Event
Messages provide information about the communication occurring between your network device, ISDN
T A/modem and the remote server (ISP).
To assist you in troubleshooting, you may point and click on any event message to bring up a help
screen.
74
Page 75

TCP/IP Tab
The TCP/IP tab displays all TCP/IP requests made by your network device. You may select to view
TCP/IP sessions for the
WAN Ethernet
or the
Async Port
Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
.
1. The
displayed, click the
TCP/IP
Note: The TCP/IP sessions displays the history of the TCP/IP session through the selected port.
The TCP/IP information presented does not represent the current status of the TCP/IP session.
The TCP/IP tab displays the following information:
Date/Time: Indicates the date the request was made.
Port: Indicates the port you are viewing.
Type: Displays the type of request being made.
Local IP: Indicates which IP address you have requested information from.
Remote IP: Indicates which IP address was requested.
Port Number: Indicates which TCP/IP port was requested.
tab is the default tab displayed in the RouteFinder Monitor dialog box. If it is not
TCP/IP
tab.
2. To Exit RouteFinder Monitor, close the window .
75
Page 76

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Time T ab
The Time Tab provides information about the amount of time the device has been powered on, the total
connection time, the current connection time and the amount of data transferred and received.
1. From the main RouteFinder Monitor dialog box, click the
2. The
Time
tab displays information for each port.
Device Power Turned On:
This field displays the time/date that your RF500S was powered on.
Power -On- Time:
This field displays the total time that has elapsed since your RouteFinder was powered on.
T otal Connection T ime:
This field displays the total connection time for each port that has been logged on since the
RouteFinder was powered on.
Time
tab.
Current Connection:
This field displays the time that has elapsed since the current connection was established for the
port.
TX Bytes:
This field displays the total number of bytes transmitted for each port since your RouteFinder was
last powered on.
RX Bytes:
This field displays the total number of bytes received for each port since your RouteFinder was
last powered on.
3. To Exit RouteFinder Monitor, close the window .
76
Page 77

Status T ab
The
Status
tab provides information about the status of the
Chapter 6 - RouteFinder Monitor
WAN Ethernet
and
Async
ports.
1. From the RouteFinder Monitor dialog box, click the
2. The
Status
tab information displays:
WAN Ethernet:
This indicator light shows that either the IP Routing or the Remote Access function is in use.
Async Port
Modem Power:
The indicator light is lit when the modem power is turned on.
Modem Ready:
The Network Device sends a pre-initialization and initialization command to the modem or ISDN
T A. If this communication is successful, the indicator light will be lit, indicating your modem is
ready to make a connection.
Status
tab.
Modem Connected:
If the Network Device has detected that your modem has successfully dialed up a connection to a
remote site, the indicator light will be lit.
PPP Connected:
After a connection is established, if the RouteFinder has detected that the PPP connection is
successful, this indicator light will be lit.
3. To Exit RouteFinder Monitor, close the window .
77
Page 78

RouteFinder RF500S User Guide
Statistics T ab
The Statistics tab indicates, by port, how many bytes of data have come in and out through the
RouteFinder..
1. From the RouteFinder Monitor dialog box, click the
2. The
3. Y ou may view the following information:
Statistics
IP Address:
The IP address of the network device.
Name:
The Name as entered in the IP/Address name option of the Main RouteFinder Monitor dialog box.
tab dialog box displays:
Statistics
tab.
Tx Bytes:
Displays the number of bytes transmitted from the computer with this IP address.
Rx Bytes:
Displays the number of bytes received from the computer with this IP address.
Total Bytes:
Displays the total number of bytes received and transmitted from the computer with this IP
address.
4. Use the Reset button to set the IP statistics to zero.
5. To Exit RouteFinder Monitor, close the window .
78
Page 79

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Page 80

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
LAN Client Settings
In order for a computer to access the Internet, the TCP/IP protocol must be installed on the computer .
Computers on your local LAN as well as computers dialing in to your network may use dynamic or
static IP addresses. Dynamic IP addresses may be automatically assigned by the DHCP function of
the RF500S or another DHCP server . Static IP addresses can either be reserved from the DHCP
server or manually configured on the individual workstation.
To install or verify that TCP/IP is installed on your workstations, click Start | Settings | Control
Panel, click Network, then view the Protocol information. If the TCP/IP protocol is not installed on
your workstations, you must add it. Refer to the
Windows documentation for assistance in adding the protocol.
The default setting in Windows is to have IP information (IP Address, DNS Server IP address and
Gateway IP address) automatically assigned by a DHCP server such as the one built-in to your
RouteFinder.
If you’d like to manually configure the IP addresses on your workstation, you will need to provide an IP
address and subnet mask (the local LAN IP address and subnet you want to assign to the individual
computer), a Gateway address (the local LAN IP address of your RouteFinder) and a DNS Server
address (the DNS IP address provided by your ISP).
Warning: As a general rule, you should have only one DHCP server working on your network. If you
decide to use a DHCP server other than that provided with your RouteFinder , you should use
RouteFinder Manager to disable the DHCP LAN Server function. Y ou should also set your
RouteFinder’s IP address as the gateway to the other DHCP server .
Adding TCP/IP
section in the following pages, or your
80
Page 81

Setting up Remote Access Clients
Dial-in connections to Windows NT , Novell and Unix servers require slightly dif ferent configurations.
This section discusses the settings necessary to connect a Windows 95/98/NT/2000 workstation to
these various servers.
Note: the Windows 2000 operating system has a Network Connection Wizard for making new
connections, shown on the last page of this section.
The basic process consists of installing a dial-up adapter and a network protocol. Then, depending on
the server to which you are connecting, you will likely need to install client software and specify the
particular services you would like to use.
Accessing a Windows NT Server
Windows NT Server combines the best aspects of an application server , a file and printer server , a
communications server, and a W eb server , and its interoperability and management features make it
an excellent network operating system (NOS) for organizations, whether they have mixed computing
environments or operate entirely on Windows NT Server . Perform the following procedures when you
need to connect your PC workstation to a remote Windows NT Server .
Adding the dial-up adapter (NT Server Connection):
Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Windows 95/98:
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel.
2. Double-click the
Win95 Win98
Network
icon to open the Network dialog box.
81
Page 82

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
3. Click Add; the Select Network Component T ype dialog box opens.
4 . Select (i.e., highlight) Adapter, then click Add. The Select Network adapters dialog box opens.
Win95/98
5 . In the
6. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Windows NT:
Dial-up Networking adds PPP and SLIP protocol support, enabling your workstation to gain access to
a remote computer or network, even if your computer is not on a network.
1. Double-click My Computer , then double-click Dial-Up Networking. The following screen is
2. Click Install, then follow the onscreen instructions to configure your connection.
Manufacturer
Dial-up adapter.
displayed:
s option box, select Microsoft. In the
Network Adapter
s option box select
82
Page 83

Adding TCP/IP (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98/NT:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Protocol and click Add.
Configuration
tab, click Add.
Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
3. The Select Network Protocol dialog box is displayed. In the
only], select Microsoft. In the Network Protocols option box, select TCP/IP [Win95/98] or TCP/
IP Protocol [WinNT only].
[Note: Windows NT workstation has no
Win95/98 WinNT
4. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Manufacturers
Manufacturers
option box.]
option box [Win95
Adding Client for Microsoft Networks (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
Configuration
tab, click Add.
2. Select Network Client and click Add.
3. The Select Network Client dialog box displays. In the Manufacturer’s option box, select
Microsoft. In the Network Clients option box, select Client for Microsoft Networks.
4. Click OK to add this Client and return to the Network dialog box.
83
Page 84

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
Adding File and Print Sharing for Microsoft Networks (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Services and click Add.
Configuration
tab, click Add.
3. The Select Network Service dialog box displays. In the
Microsoft. Select File and Printer sharing for Microsoft Networks.
[Note: Windows 98 has no
Win95 Win98
4. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Manufacturers
option box.]
Manufacturers
Set Your Primary Network Logon (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the
Primary Network Logon
select (the previously installed) Client for Microsoft Networks.
option box on the Configuration tab of the Network dialog box,
option box, select
84
2. Click OK to close the Network dialog box.
Page 85

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Set up Properties of Components (NT Server Connection):
Dial-up Adapter:
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
Configuration
tab, select the TCP/IP - Dial-up adapter.
2. Click Properties. The TCP/IP Properties dialog box opens with the
selected.
3 . Ensure that Obtain an IP Address Automatically is selected. (It’s the default.)
4. Click OK to close the TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
IP Address
Network Client:
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
Configuration
tab, select Client for Microsoft Networks.
tab
2. Click Properties. The Client for Microsoft Networks Properties dialog box opens.
3. On the
4. Click the Windows NT domain field, then enter the name of your Windows NT domain, as
provided by your Network Administrator .
5. Click OK to return to the Network dialog box.
General
tab, select (check)
“Log on to Windows NT domain.”
85
Page 86

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
Identification:
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box, select the
Identification
tab.
2 . In the
3 . Enter a name and description for your computer in the fields provided.
4. Click OK.
Workgroup
provided by your Network Administrator .
field, enter the name of your NT domain or the name of your workgroup as
Access:
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box, select the
2. In the
Control Access to Shared resources using
Access Control
group, select Share-Level access control.
tab.
86
3. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Note: Y ou must restart your system for the new settings to take effect.
Once your machine has restarted, you may continue the configuration process.
Page 87

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Make Your New Connection (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. Double-click My Computer .
2 . Double-click the Dial-Up Networking folder.
3. Double-click Make New Connection (or Add New Connection, Win98).
4 . Follow the onscreen instructions to configure your connection.
Windows NT:
1. Double-click My Computer .
2. Double-click Dial-Up Networking.
3. When the Dial-Up Networking dialog box opens, click Install.
4. Follow the onscreen instructions to configure your connection.
Set Dial-up type (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. Right-click the newly created connection icon, then click Properties; the My Connection dialog
box opens.
2 . On the General tab, click
95, Windows NT 3.5, Internet.
3 . Click (to check or enable) only the following items: Log on to network, Enable software
compression, and TCP/IP. [Note: do not disturb any other items that are already checked.]
Server Type;
the Server Types dialog box opens. Select PPP: Windows
Dial in to your network (NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1 . You are ready to dial in to your network.
2 . Double-click the
3 . Enter the user name (if necessary) and password configured for you on the RF500S.
Note: If your particular situation permits, click (to check) Save password.
4. Click Connect.
5. After connecting to the RF500S, you can access the same services and resources as if you were
connected to the network locally.
new connection
icon; the Connect T o dialog box opens.
87
Page 88

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
Accessing a Novell Server
Novell NetWare products are used on up to 70 percent of PC-based local area networks (LANs).
Perform the following procedures when you need to connect your PC workstation to a remote Novell
Server.
Adding the dial-up adapter (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel.
2 . Double-click the
Win95 Win98
Network
icon to open the Network dialog box.
88
3. Click Add. The Select Network Component T ype dialog box opens.
Page 89

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
4. Select (i.e., highlight) Adapter, then click Add. The Select Network adapters dialog box opens.
Win95/98
5 . In the
6. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Windows NT :
Dial-up Networking adds PPP and SLIP protocol support, enabling your workstation to gain access to
a remote computer or network, even if your computer is not on a network.
1. Double-click My Computer, then double-click Dial-Up Networking. The following screen is
2. Click Install, then follow the onscreen instructions to configure your connection.
Manufacturer
Dial-up adapter.
displayed:
s option box, select Microsoft. In the
Network Adapter
s option box select
Adding IPX/SPX (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
dialog box opens.
2. Select Protocol and click Add. The Select Network Protocol dialog box opens.
Configuration
tab, click Add. The Select Network Component Type
89
Page 90

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
3. In the
4. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Windows NT :
Manufacturers
IPX/SPX-compatible Protocol.
option box, select Microsoft. In the Network Protocols option box, select
Note: NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible T ransport is probably already installed, along with NWLink
NetBIOS and TCP/IP Protocol; however , if NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible T ransport does not
appear on
1. In the Network dialog box,
opens.
the
Protocols
tab of the Network dialog box, perform the following steps:
Protocol
tab, click Add. The Select Network Protocol dialog box
2. Select NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible T ransport , then click OK to return to the Network dialog
box.
3. Click Close to close the Network dialog box and return to the Desktop.
Adding Client for NetWare Networks (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Network Client and click Add.
3. The Select Network Client dialog box displays. In the Manufacturer’s option box, select
Microsoft. In the Network Clients option box, select Client for NetWare Networks.
Configuration
tab, click Add.
90
4. Click OK to add this Client and return to the Network dialog box.
Page 91

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Set Up Properties of Components (Novell Server Connection):
Network Client:
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
2. Click Properties. The Client for Microsoft Networks Properties dialog box opens.
Configuration
tab, select Client for Microsoft Networks.
3. On the
4. Click the Windows NT domain field, then enter the name of your Windows NT domain, as
provided by your Network Administrator .
General
tab, select (check)
“Log on to Windows NT domain.”
5. Click OK to return to the Network dialog box.
6. In the Network dialog box,
Configuration
tab, select Client for NetWare Networks.
91
Page 92

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
7. Click Properties.
8. On the
necessary , select the First Network Drive, then ensure that Enable logon script processing is
checked (enabled). (It’s the default.)
9. Click OK to return to the Network dialog box.
General
tab, in the Preferred server field, enter the name of your Novell Server Domain. If
Set Your Primary Network Logon:
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
as the Primary Network Logon.
Configuration
tab, select Client for NetWare Networks
92
2. Click OK. Y ou are returned to the Desktop.
Page 93

Set Your Access Control (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box, select the
Access Control
tab.
Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
2. In the
Control Access to shared resources using
option box, select Share-Level Access Control.
Note: Y ou must restart your system for the new settings to take effect.
Make Your New Connection (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. Double-click My Computer .
2 . Double-click the Dial-Up Networking folder.
3. Double-click Make New Connection (or Add New Connection, Win98).
4 . Follow the onscreen instructions to configure your connection.
Windows NT :
1. Double-click My Computer .
2. Double-click Dial-Up Networking.
3 . When the Dial-Up Networking dialog box opens, click Install.
4 . Follow the onscreen instructions to configure your connection.
Set Dial-up type (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. Right-click the newly created connection icon, then click Properties; the My Connection dialog
box opens.
2. On the General tab, click
95, Windows NT 3.5, Internet.
3. Click (to check or enable) only the following items: Log on to network, Enable software
compression, and TCP/IP. [Note: do not disturb any other items that are already checked.]
Server Type;
the Server Types dialog box opens. Select PPP: Windows
Dial in to your network (Novell Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. Y ou are ready to dial in to your network.
2. Double-click the
3. Enter the user name (if necessary) and password configured for you on the RF500S.
Note: If your particular situation permits, click (to check) Save password.
4. Click Connect.
5. After connecting to the RF500S, you can access the same services and resources as if you were
connected to the network locally.
new connection
icon; the Connect T o dialog box opens.
93
Page 94

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
Accessing a Windows NT Server and a Novell NetWare Server
Note: Before configuring your remote site, ensure TCP/IP has been installed on your NT Server.
Perform the following procedures if your PC workstation needs to access both a Windows NT Server
and a Novel NetWare Server .
Adding the dial-up adapter (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98/NT:
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel.
2 . Double-click the
Win95 Win98
Network
icon to open the Network dialog box.
94
3. Click Add; the Select Network Component Type dialog box opens.
Page 95

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
4. Select (i.e., highlight) Adapter, then click Add. The Select Network adapters dialog box opens.
Win95/98 WinNT
5. (Win95/98 only) In the
box select Dial-up adapter.
[Note: In Windows NT workstation there is no
6. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Manufacturer
s option box, select Microsoft. In the
Manufacturers
option box.]
Network Adapter
Adding TCP/IP (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98/NT:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Protocol and click Add.
3. The Select Network Protocol dialog box is displayed. In the
only], select Microsoft. In the Network Protocols option box, select TCP/IP [Win95/98] or TCP/
IP Protocol [WinNT only].
[Note: Windows NT workstation has no
Win95/98 WinNT
Configuration
tab, click Add.
Manufacturers
Manufacturers
option box.]
option box [Win95
s option
4. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
95
Page 96

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
Adding Client for Microsoft Networks (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Network Client and click Add.
3. The Select Network Client dialog box displays. In the Manufacturer’s option box, select
Microsoft. In the Network Clients option box, select Client for Microsoft Networks.
4. Click OK to add this Client and return to the Network dialog box.
Configuration
tab, click Add.
Adding File and Print Sharing for Microsoft Networks
(Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Services and click Add.
3. The Select Network Service dialog box displays. In the
Microsoft. Select File and Printer sharing for Microsoft Networks.
[Note: Windows 98 has no
Win95 Win98
Configuration
Manufacturers
tab, click Add.
Manufacturers
option box.]
option box, select
96
4. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Page 97

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Adding IPX/SPX (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
dialog box opens.
2. Select Protocol and click Add. The Select Network Protocol dialog box opens.
Configuration
tab, click Add. The Select Network Component Type
3. In the
4. Click OK (twice) to return to, and then close, the Network dialog box.
Windows NT:
Manufacturers
IPX/SPX-compatible Protocol.
option box, select Microsoft. In the Network Protocols option box, select
Note: NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible T ransport is probably already installed, along with NWLink
NetBIOS and TCP/IP Protocol; however , if NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible T ransport does not
appear on the Protocols
1. In the Network dialog box,
opens.
tab of the Network dialog box, perform the following steps:
Protocol
tab, click Add. The Select Network Protocol dialog box
2. Select NWLink IPX/SPX Compatible T ransport , then click OK to return to the Network dialog
box.
3. Click Close to close the Network dialog box and return to the Desktop.
Adding Client for NetWare Networks (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1. In the Network dialog box,
2. Select Network Client and click Add.
Configuration
tab, click Add.
97
Page 98

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
3. The Select Network Client dialog box displays. In the Manufacturer’s option box, select
Microsoft. In the Network Clients option box, select Client for NetWare Networks.
4. Click OK to add this Client and return to the Network dialog box.
Set Your Primary Network Logon (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the
Primary Network Logon
(the previously installed) Client for Microsoft Networks.
option box on Configuration tab of the Network dialog box, select
98
2. Click OK to close the Network dialog box.
Page 99

Chapter 7 - LAN Client Settings
Set Up Properties of Components (Novell/NT Server Connection):
Dial-up Adapter:
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
Configuration
tab, select the TCP/IP - Dial-up adapter.
2. Click Properties. The TCP/IP Properties dialog box opens with the
3 . Ensure that Obtain an IP Address Automatically is selected. (It’s the default.)
4. Click OK to close the TCP/IP Properties dialog box.
IP Address
Network Client:
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
Configuration
tab, select Client for Microsoft Networks.
tab selected.
2. Click Properties. The Client for Microsoft Networks Properties dialog box opens.
3. On the
4. Click the Windows NT domain field, then enter the name of your Windows NT domain, as
provided by your Network Administrator .
5. Click OK to return to the Network dialog box.
6 . In the Network dialog box,
General
tab, select (check)
Configuration
“Log on to Windows NT domain.”
tab, select Client for NetWare Networks.
99
Page 100

Route Finder RF500S User Guide
7. Click Properties.
8 . On the
Select the First Network Drive and Enable Logon Script processing.
9. Click OK.
Network Protocol:
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box,
2. Click Properties.
3. Disable Client for Microsoft Networks and File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks.
This will ensure that when you log into your NT server , Windows will use the TCP/IP protocol.
Next, you must
Set Your Identification:
Windows 95/98:
1 . In the Network dialog box, select the
General
tab, in the preferred Server field, enter the name of your Novell Server Domain.
enable
Configuration
Client for Microsoft Networks.
tab, select IPX/SPX Compatible Protocol.
Identification
tab.
100
2 . In the
3 . Enter a name and description for your computer in the fields provided.
4. Click OK.
Workgroup
provided by your Network Administrator .
field, enter the name of your NT domain or the name of your workgroup as
 Loading...
Loading...