Multitech MultiVOIP MVP210, MultiVOIP MVP410, MultiVOIP MVP810, MultiVOIP MVP810-FX, MultiVOIP MVP810-SS User Manual
Page 1

MultiVOIP®
Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
MVP210/410/810
MVP210/410/810-SS
MVP210/410/810-FX
User Guide
Page 2

User Guide
S000383E
Analog MultiVOIP Units (Models MVP210, MVP410, MVP810)
(Models MVP210-SS, MVP410-SS, MVP810-SS)
(Models MVP210-FX, MVP410-FX, MVP810-FX)
Upgrade Unit (Model MVP428)
This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior expressed written permission from Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. All
rights reserved.
Copyright © 2011, by Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. makes no representations or warranty with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied
warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Furthermore, Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. reserves the right to revise this
publication and to make changes from time to time in the content hereof without obligation of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. to notify any
person or organization of such revisions or changes. Check Multi-Tech’s Web site for current versions of our product documentation.
Record of Revisions
Revision Date Description
A 09/26/05 Doc re-organization. Follows S000249K. Describes 6.08 software release.
B 04/25/07 Update tech support contact list & revise warranty.
C 02/18/08 Format revision and software version x.11 update. Add SS & FX series.
D 04/21/09 Temperature change, remove outdated sections.
E 09/14/2011 Removed references to product CD
Patents
This Product is covered by one or more of the following U.S. Patent Numbers: 6151333, 5757801, 5682386, 5.301.274; 5.309.562;
5.355.365; 5.355.653; 5.452.289; 5.453.986. Other Patents Pending.
Trademark
Registered trademarks of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. are MultiVOIP, Multi-Tech, and the Multi-Tech logo. Windows is a registered
trademark of Microsoft.
World Headquarters
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View, Minnesota 55112
Phone: 763-785-3500 or 800-328-9717
Fax: 763-785-9874
http://www.multitech.com
Technical Support
Country By Email By Phone
Europe, Middle East, Africa: support@multitech.co.uk
U.S., Canada, all others: support@multitech.com (800) 972-2439 or (763) 717-5863
(44) 118 959 7774
Warranty
Please visit www.multitech.com for warranty information for your product.
2 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 – Product Overview .......................................................................................................................... 6
Feature Comparison Table ............................................................................................................................................ 6
Interfaces to Help You Use the MultiVOIP .................................................................................................................... 7
Overview of Front Panel LEDs ....................................................................................................................................... 7
Computer Requirements ........................................................................................................................................... 8
Specifications ............................................................................................................................................................ 9
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP ........................................................................................... 10
Safety Warnings ...................................................................................................................................................... 10
Lithium Battery Caution .............................................................................................................................................. 10
Safety Warnings Telecom ............................................................................................................................................ 10
Unpacking Your MultiVOIP ...................................................................................................................................... 10
MVP210 models content list ....................................................................................................................................... 10
MVP410/810 models content list ................................................................................................................................ 11
Mounting MVP410 and MVP810 in Racks ................................................................................................................ 11
Safety Recommendations for Rack Installations ......................................................................................................... 11
Installing into 19-Inch Rack.......................................................................................................................................... 11
Connecting the MVP210 to LAN and Telephone Equipment ..................................................................................... 12
Connecting MultiVOIP to LAN and Telephone Equipment (MVP-410/810) ................................................................ 15
Chapter 3 – Installing Software ...................................................................................................................... 18
Installing MultiVOIP Software ................................................................................................................................. 18
Configuring for VOIP Communications ..................................................................................................................... 21
Setting IP Address ........................................................................................................................................................ 22
Setting Voice/Fax Parameters ..................................................................................................................................... 24
Setting Interface Parameters ....................................................................................................................................... 26
Setting Call Signaling ................................................................................................................................................... 29
Setting the Region or Country ..................................................................................................................................... 31
Defining the Phone Book ............................................................................................................................................. 32
Saving Your Settings and Rebooting ............................................................................................................................ 33
Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP ........................................................................................................ 34
Software Categories Covered in This Chapter .......................................................................................................... 34
Navigating the Software .......................................................................................................................................... 35
Using the Web Browser Interface ............................................................................................................................ 35
Setting up the Web Browser interface (Optional) ....................................................................................................... 35
Configuration Information Checklist ........................................................................................................................ 36
Setting Ethernet/IP ...................................................................................................................................................... 37
Setting Voice/Fax Parameters ..................................................................................................................................... 40
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 3
Page 4

Contents
Configuring Interface Parameters ............................................................................................................................... 45
Call Signaling ................................................................................................................................................................ 58
Configuring SNMP ....................................................................................................................................................... 67
Configuring Regional Parameters ................................................................................................................................ 68
Configuring SMTP Parameters ..................................................................................................................................... 72
RADIUS ......................................................................................................................................................................... 75
Logs/Traces .................................................................................................................................................................. 77
NAT Traversal .............................................................................................................................................................. 78
Supplementary Services .............................................................................................................................................. 79
Save Settings ................................................................................................................................................................ 82
Connection .................................................................................................................................................................. 82
Troubleshooting Software Issues ................................................................................................................................ 83
Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book ........................................................................................................ 84
Identify Remote VOIP Site to Call ............................................................................................................................ 84
Identify VOIP Protocol to be Used ........................................................................................................................... 84
Initially Configuring the Phonebook ........................................................................................................................ 85
Before You Begin ......................................................................................................................................................... 85
Configuring the Outbound Phonebook ....................................................................................................................... 85
Configuring the Inbound Phonebook .......................................................................................................................... 87
Phone Book Descriptions ........................................................................................................................................ 88
Outbound Phone Book/List Entries ............................................................................................................................. 88
Inbound Phone Book/List Entries ................................................................................................................................ 93
Phone Book Save and Reboot ..................................................................................................................................... 96
Phonebook Examples .............................................................................................................................................. 97
North America ............................................................................................................................................................. 97
Europe ....................................................................................................................................................................... 100
Variations of Caller ID ........................................................................................................................................... 106
Chapter 6 – Using the Software .................................................................................................................... 109
Statistics Section ................................................................................................................................................... 111
Call Progress .............................................................................................................................................................. 111
Logs ............................................................................................................................................................................ 113
IP Statistics ................................................................................................................................................................. 116
Link Management ...................................................................................................................................................... 118
Registered Gateway Details ....................................................................................................................................... 119
Servers ....................................................................................................................................................................... 120
Advanced ................................................................................................................................................................... 123
MultiVOIP Program Menu Items ........................................................................................................................... 124
Updating Firmware .................................................................................................................................................... 125
4 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 5

Contents
Implementing a Software Upgrade ........................................................................................................................... 126
Downloading IFM Firmware ...................................................................................................................................... 129
Setting and Downloading User Defaults .................................................................................................................... 131
Setting a Password .................................................................................................................................................... 132
Upgrading Software ................................................................................................................................................... 134
FTP Server File Transfers (“Downloads”) ................................................................................................................ 135
Web Browser Interface ......................................................................................................................................... 140
Setting Up SysLog Server Functions ....................................................................................................................... 142
Appendix A – Cable Pin-Outs ........................................................................................................................ 143
Command Cable .................................................................................................................................................... 143
Ethernet Connector ............................................................................................................................................... 143
Voice/Fax Channel Connectors .............................................................................................................................. 144
Appendix B – TCP/UDP Port Assignments ..................................................................................................... 145
Well Known Port Numbers .................................................................................................................................... 145
Port Number Assignment List ................................................................................................................................ 145
Appendix C – Installing an MVP428 Upgrade Card ........................................................................................ 146
Procedure Overview .................................................................................................................................................. 146
Installing the Card ...................................................................................................................................................... 146
Appendix D – Regulatory Information .......................................................................................................... 149
EMC, Safety, and R&TTE Directive Compliance ...................................................................................................... 149
FCC Part 15 Class A Statement ............................................................................................................................... 149
Industry Canada .................................................................................................................................................... 149
Canadian Limitations Notice .................................................................................................................................. 149
Appendix E – Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Statement ................................................ 151
Appendix F – C-ROHS
HT/TS Substance Concentration ................................................................................. 152
Index ............................................................................................................................................................ 153
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 5
Page 6
Chapter 1 – Product Overview
The MultiVOIP gateways, MVP210, MVP410, and MVP810 provide toll-free voice and fax communications over
the Internet or an Intranet. By integrating voice and fax into your existing data network, you can substantially
save on inter-office long distance toll charges. MultiVOIP gateways connect directly to phones, fax machines, key
systems, PSTN lines, or a PBX to provide real-time, toll-quality voice connections to any office on your VOIP
network. The –SS series models only support the SIP protocol through the FXS/FXO interface with SIP
survivability as well.
An illustration of the MVP410/810 chassis follows.
An illustration of the MVP210 chassis follows
The MultiVOIP model MVP210 is a two-channel unit, the model MVP410 is a four-channel, and the MVP810 is an
eight-channel unit. All of these units have a 10/100Mbps Ethernet interface and a command port for
configuration. The MVP428 is an expansion circuit card for the four-channel MVP410 that turns it into an eightchannel MVP810.
These MultiVOIPs inter-operate with a telephone switch or PBX, acting as a switching device that directs voice
and fax calls over an IP network. The MultiVOIPs have “phonebooks,” directories that determine to who calls
may be made and the sequences that must be used to complete calls through the MultiVOIP. The phonebooks
allow the phone user to interact with the VOIP system just as they would with an ordinary PBX or telco switch.
When the phonebooks are set, special dialing sequences are minimized or eliminated altogether. Once the call
destination is determined, the phonebook settings determine whether the destination VOIP unit must strip off
or add dialing digits to make the call appear at its destination to be a local call.
Feature Comparison Table
The table that follows describes differences between the models.
MultiVOIP
H.323
SPP
SIP
SIP Survivability
®
●
●
● ● ●
MultiVOIP®-SS MultiVOIP® -FX
●
●
DID
E&M
FXS/FXO
6 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
●
●
● ● ●
Page 7

Chapter 1 – Product Overview
Interfaces to Help You Use the MultiVOIP
Two interfaces help you use your MultiVOIP:
● A web interface
● Windows software interface
The web interface and the Windows interface share content and organizational attributes. However, each
interface has different logging capabilities.
Overview of Front Panel LEDs
Eight sets of channel-operation LEDs appear on both the MVP410 and MVP810 models. However, on the
MVP410, only the lower four sets of channel-operation LEDs are functional. On the MVP810, all eight sets are
functional.
An illustration of the MVP410/810 LEDs follows.
The MVP210 models have the general-operation indicator LEDs and two sets of channel-operation LEDs. An
illustration of the MVP210 LEDs follows.
Front Panel LED Definitions
LED Description
General Operation LEDs (one set on each MultiVOIP model)
Power Indicates presence of power
Boot
Ethernet
XMT
RCV
XSG
RSG
After power up, the Boot LED is on briefly while the MultiVOIP is booting. It lights whenever the MultiVOIP is
booting or downloading a setup configuration data set
FDX. LED indicates whether Ethernet connection is half-duplex or full-duplex (FDX) and, in half-duplex mode,
indicates occurrence of data collisions. LED is on constantly for full-duplex mode; LED is off constantly for halfduplex mode. When operating in half-duplex mode, the LED flashes during data collisions.
LNK. Link/Activity LED. This LED is lit if Ethernet connection has been made. It is off when the link is down (i.e.,
when no Ethernet connection exists). While link is up, this LED flashes off to indicate data activity.
Channel-Operation LEDs (one set for each channel)
Transmit. This indicator blinks when voice packets are being transmitted to the local area network.
Receive. This indicator blinks when voice packets are being received from the local area network.
Transmit Signal. This indicator lights when the FXS-configured channel is off-hook, the FXO-configured channel
is receiving a ring from the Telco, or the M lead is active on the E&M configured channel. That is, it lights when
the MultiVOIP is receiving a ring from the PBX.
Receive Signal. This indicator lights when the FXS-configured channel is ringing, the FXO-configured channel
has taken the line off-hook, or the E lead is active on the E&M-configured channel.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 7
Page 8

Chapter 1 – Product Overview
Computer Requirements
The computer on which the MultiVOIP’s configuration program is installed must meet these requirements:
● IBM-compatible PC with MS Windows operating system
● Have an available COM port for connection to the MultiVOIP
The computer does not need to be connected to the MultiVOIP permanently. It only needs to be connected
when local configuration and monitoring are done. You can perform configuration and monitoring remotely
through the IP network.
8 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 9
Chapter 1 – Product Overview
Specifications
MVP210 models MVP410 models MVP810 or MVP410 + 428
Operating Voltage/Current
Mains Frequencies 50/60 Hz 50/60 Hz 50/60 Hz
Power Consumption 19 watts 29 watts 46 watts
Mechanical Dimensions
Weight
Ambient temperature range
External transformer: 3A
@5V
1.4” H
6.2” W x
9” D x
----------------
3.6cm H
15.8cm W x
22.9cm D x
1.8lbs (.82kg)
2.6lbs (1.17kg)
with transformer
Maximum
condensing relative humidity.
Minimum
: 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit) @ 20-90% non-
: 0 degrees Celsius (32 degrees Fahrenheit).
100-240 VAC
1.2 - 0.6 A
1.75” H x
17.4” W x
8.5” D
-----------------
4.5cm H x
44.2 cm W x
21.6 cm D
7.1 lbs
(3.2 kg)
100-240 VAC
1.2 - 0.6 A
1.75” H x
17.4” W x
8.5” D
-----------------
4.5cm H x
44.2 cm W x
21.6 cm D
7.7 lbs.
(3.5 kg)
Warranty 2 years
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 9
Page 10

Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the
MultiVOIP
The MVP210 MultiVOIP models are tabletop units. The MVP410 and MVP810 MultiVOIPs are heavier units. As
such two or more people need to install these units into racks. Read the safety notices before beginning
installation.
Safety Warnings
Lithium Battery Caution
A lithium battery on the voice/fax channel board provides backup power for the timekeeping capability. The
battery has an estimated life expectancy of ten years. When the battery starts to weaken, the date and time
may be incorrect. If the battery fails, the board must be sent back to Multi-Tech Systems for replacement.
Warning:
There is danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced.
Safety Warnings Telecom
1. Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
2. Never install a telephone jack in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet locations.
3. This product is to be used with UL and UL listed computers.
4. Never touch un-insulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been disconnected at
the network interface.
5. Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
6. Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote risk
of electrical shock from lightning.
7. Do not use a telephone in the vicinity of a gas leak.
8. To reduce the risk of fire, use only a UL-listed 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
Unpacking Your MultiVOIP
When unpacking your MultiVOIP, check the package’s contents. The contents can differ according to model. If
any items are missing, contact Multi-Tech Technical Support.
MVP210 models content list
● MVP210
● DB9 to RJ45 cable
● Power transformer
● Power cord
● Printed cabling guide
10 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 11
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
MVP410/810 models content list
● MVP410 or MVP810
● DB9 to DB25 cable
● Mounting brackets and screws
● Power cord
● Printed Cabling Guide
Mounting MVP410 and MVP810 in Racks
You can mount the MultiVOIPs in an industry-standard EIA 19-inch rack enclosure.
Safety Recommendations for Rack Installations
Ensure proper installation of the unit in a closed or multi-unit enclosure by following the recommended
installation as defined by the enclosure manufacturer. Do not place the unit directly on top of other equipment
or place other equipment directly on top of the unit. If installing the unit in a closed or multi-unit enclosure,
ensure adequate airflow within the rack so that the maximum recommended ambient temperature is not
exceeded. Ensure that the unit is properly connected to earth ground by verifying that it is reliably grounded
when mounted within a rack. If a power strip is used, ensure that the power strip provides adequate grounding
of the attached apparatus.
When mounting the equipment in the rack, make sure mechanical loading is even to avoid a hazardous
condition. The rack used should safely support the combined weight of all the equipment it supports.
Ensure that the mains supply circuit is capable of handling the load of the equipment. See the power label on the
equipment for load requirements (full specifications for MultiVOIP models are presented in chapter 1 of this manual).
This equipment should only be installed by properly qualified service personnel. Only connect like circuits - connect SELV
(Secondary Extra Low Voltage) circuits to SELV circuits and TN (Telecommunications Network) circuits to TN circuits.
Installing into 19-Inch Rack
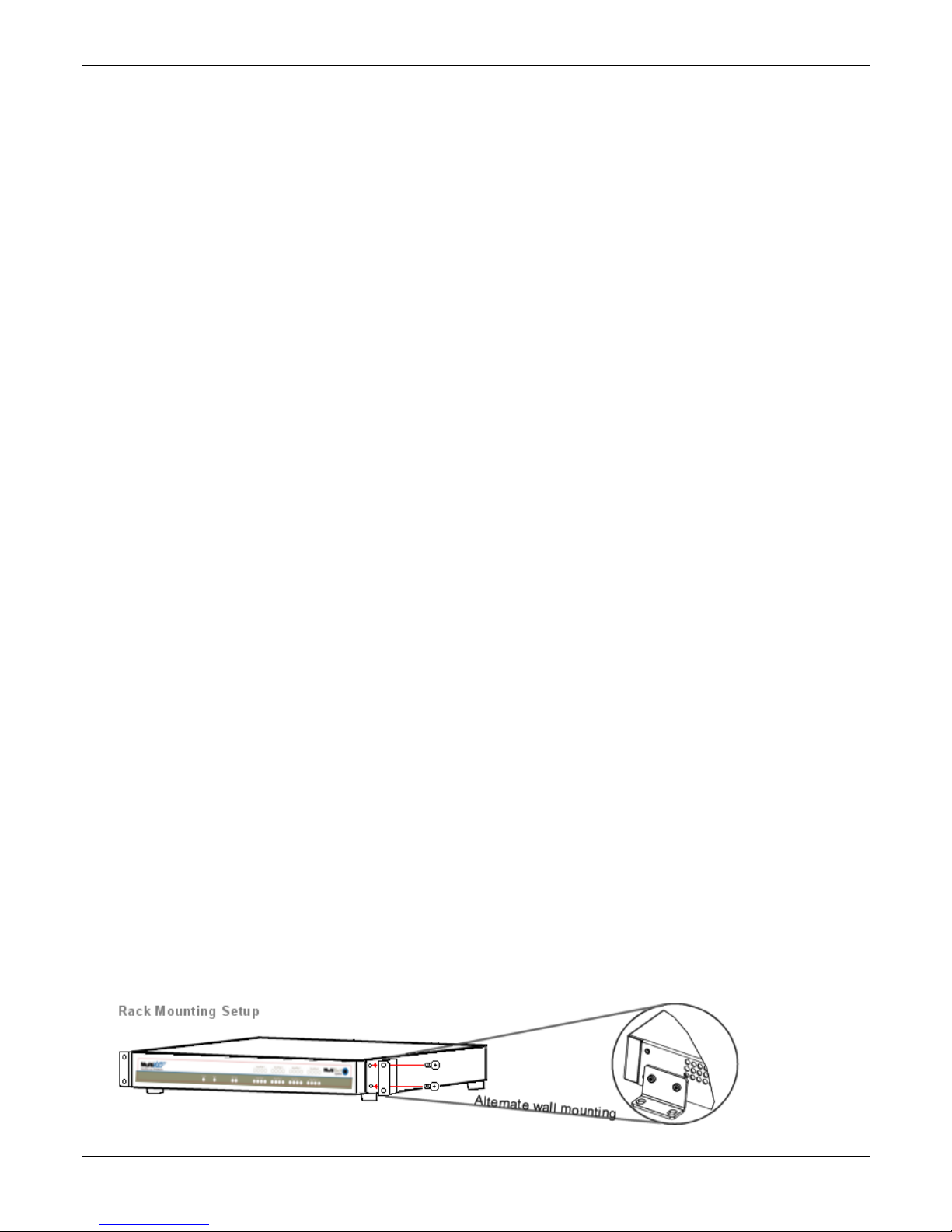
Attaching the MultiVOIP to a rack-rail of an EIA 19-inch rack enclosure requires two people.
You must attach the brackets to the MultiVOIP chassis with the screws provided, as shown the first figure that
follows, and then secure unit to rack rails by the brackets, as shown in the second figure that follows. Because
equipment racks vary, screws for rack-rail mounting are not provided. Follow the instructions of the rack
manufacturer and use screws that fit.
1. Position the right rack-mounting bracket on the MultiVOIP using the two vertical mounting screw holes.
2. Secure the bracket to the MultiVOIP using the two screws provided.
3. Position the left rack-mounting bracket on the MultiVOIP using the two vertical mounting screw holes.
4. Secure the bracket to the MultiVOIP using the two screws provided.
5. Remove feet (4) from the MultiVOIP unit.
6. Mount the MultiVOIP in the rack enclosure. Use the rack manufacture’s mounting procedure to do so.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 11
Page 12
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
Connecting the MVP210 to LAN and Telephone Equipment
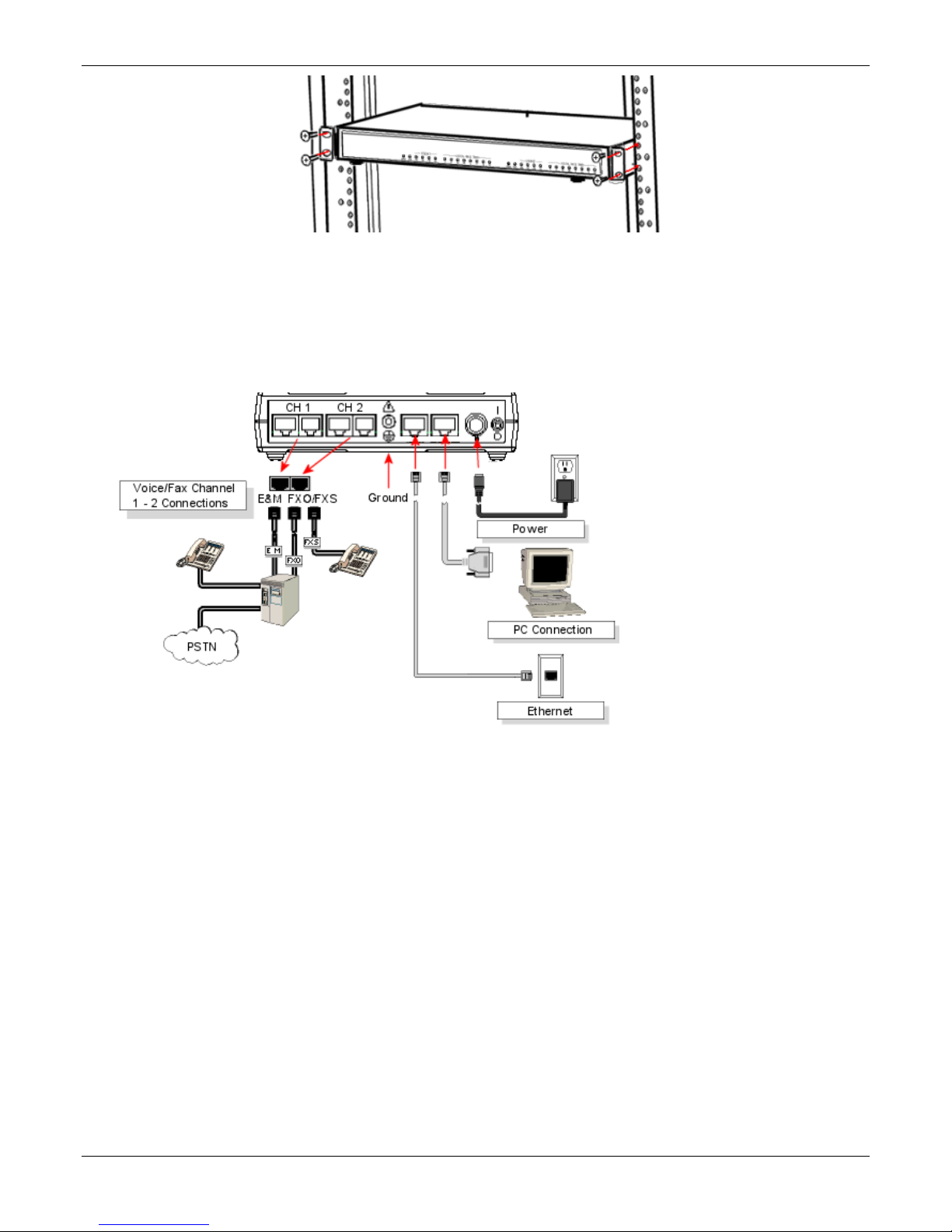
To connect the MultiVOIP unit to your LAN and telephone equipment:
1. Connect the power cord supplied with your MultiVOIP to the power connector on the back of the MultiVOIP
and to a live AC outlet as shown in the figure that follows.
Note: The –SS and –FX models do not have the E&M jacks as shown.
2. Connect the MultiVOIP to a PC by using a RJ-45 (male) to DB-9 (female) cable. Plug the RJ-45 end of the
cable into the Command port of the MultiVOIP and the other end into the PC serial port.
3. Connect a network cable to the ETHERNET 10/100 connector on the back of the MultiVOIP. Connect the
other end of the cable to your network.
a. For an FXS or FXO connection (-SS and -FX series).
(FXS Examples: analog phone, fax machine |
FXO Examples: PBX extension, POTS line from telco central office)
Connect one end of an RJ-11 phone cord to the Channel 1 FXS/FXO connector on the back of the
MultiVOIP. Connect the other end to the device or phone jack.
b. For an E&M connection.
(E&M Example: trunk line from telephone switch)
Connect one end of an RJ-45 phone cord to the Channel 1 E&M connector on the back of the MultiVOIP.
Connect the other end to the trunk line.
Verify that the E&M Type in the E&M Options group of the Interface dialog box is the same as the E&M
trunk type supported by the telephone switch. See Appendix B for an E&M cabling pin-out.
12 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 13

Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
c. For a DID connection.
(DID Example: DID fax system or DID voice phone lines)
Connect one end of an RJ-11 phone cord to the Channel 1 FXS/FXO connector on the back of the
MultiVOIP. Connect the other end to the DID jack.
Note: DID lines are polarity sensitive. If the DID line rings busy consistently during testing, you need to
reverse the polarity of one end of the connector (swap the wires to the two middle pins of one RJ-11
connector).
4. Repeat the above step to connect the remaining telephone equipment to the second channel on your
MultiVOIP.
5. Ensure that the unit is properly connected to earth ground by verifying that it is reliably grounded when
mounted within a rack. This can be accomplished by connecting a grounding wire between the chassis and a
metallic object that provides an electrical ground.
6. Turn on power to the MultiVOIP by placing the ON/OFF switch on the back panel to the ON position. Wait
for the BOOT LED on the MultiVOIP to go off before proceeding. This may take a few minutes.
7. Install the MultiVOIP software, as described in a later chapter in this guide.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 13
Page 14
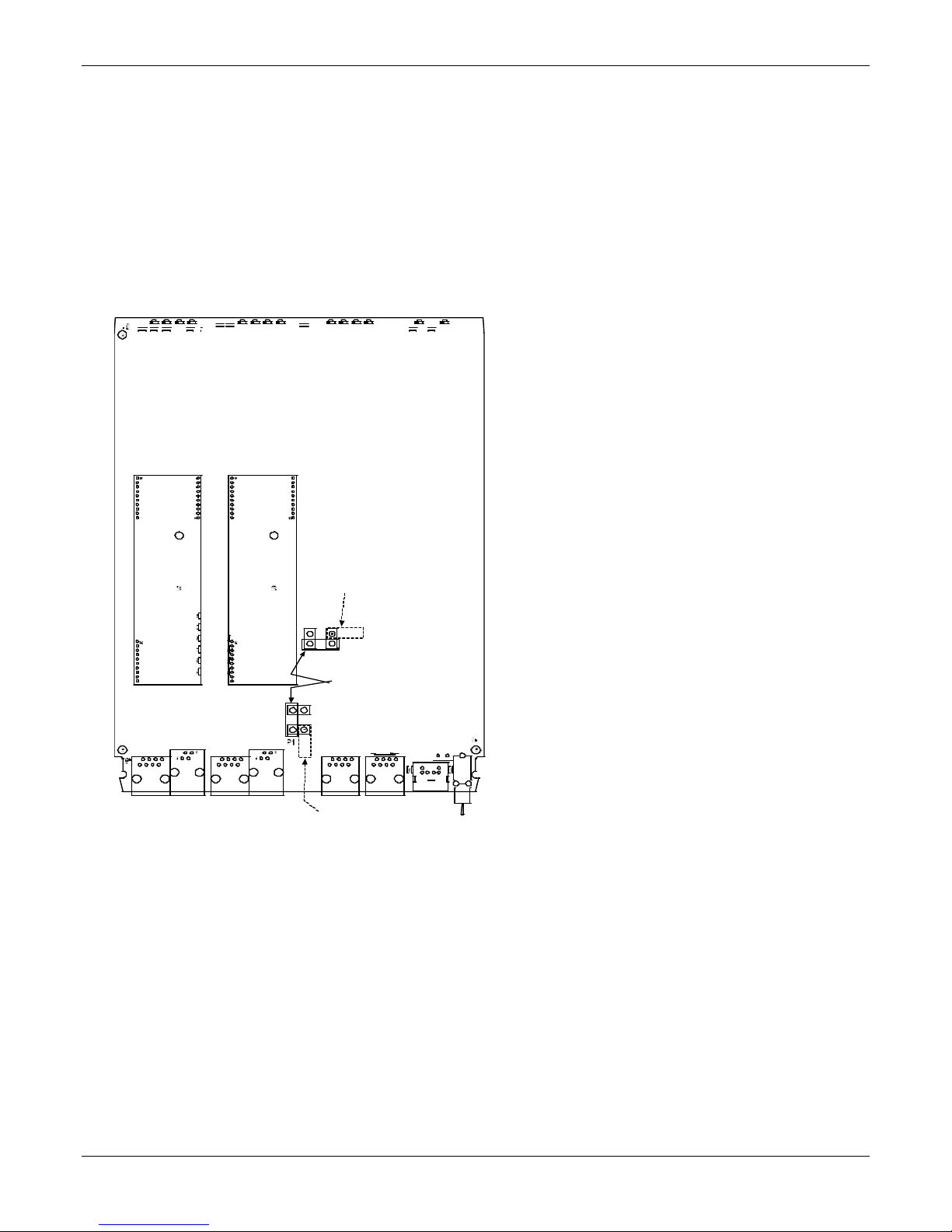
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
For DID channels only
For any channel on which you are using the DID interface type, you must change the jumper on the MultiVOIP
circuit card. DID is not supported on the –SS or –FX models.
1. Disconnect power. Unplug the AC power cord from the wall outlet or from the receptacle on the MultiVOIP
unit.
2. Using a #1 Phillips driver, remove the screw (at bottom of unit, near the back-cover end) that attaches the
main circuit card to the chassis of the MVP210.
3. Pull the main circuit card out about half way.
4. Identify the channels on which the DID interface is used.
LED12
LED14
LED11 LED10
LED13
R114
R58 R2R57
R72
R113
R56
R55
LED7
LE D 8
LE D 5 LE D 3 LED1
LED6 LE D4LE D 9
R74
LED2
R205
MVP210 Circuit Board
Ch1
J3
Ch2
J9J5
JP1
J7
as configured
for DID Interface
JP4
JP8
Ch 1 Jumper
P7
JP7
as shipped,
for non-DID interfaces
Ch 2 Jumper
Block
J11
J1
as configured
for DID Interface
Block
FB3
S10
J15
5. Position the jumper for each DID channel so that it does not connect the two jumper posts. For DID
operation of a VOIP channel, the MultiVOIP works properly if you simply remove the jumper altogether, but
that is inadvisable because the jumper might be needed later if a different telephony interface is used for
that VOIP channel.
6. Slide the main circuit card back into the MultiVOIP chassis and replace the screw at the bottom of the unit.
14 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 15
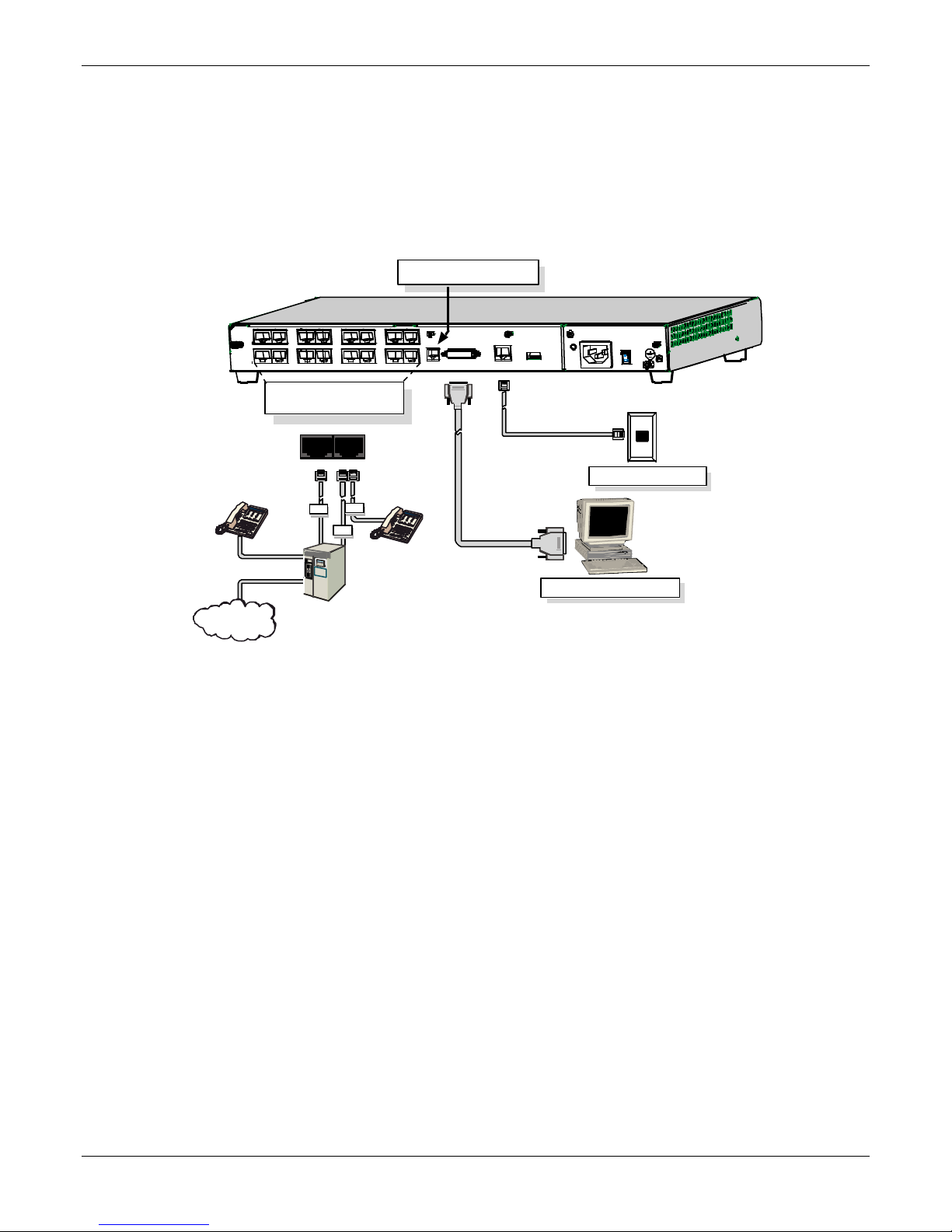
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
Connecting MultiVOIP to LAN and Telephone Equipment
(MVP-410/810)
To connect the MultiVOIP to your LAN and telephone equipment.:
1. Connect the power cord supplied with your MultiVOIP to a live AC outlet and to the power connector on the
back of the MultiVOIP as shown at top right in the figure that follows. The E&M jacks are not present on the
–SS and –FX models.
Command Modem connector
for remote configuration
E&M FXS/FXO E&M FXS /FXO E&M FXS/FX O E&M FXS/FXO
E&M FXS/F XO E&M FXS/FXO
Voice/Fax Chann e l Connect ions
Chan nel s 1-4 Bo tt o m MV P 410 /8 10
Chan nel s 5-8 To p MVP8 10 O nl y
E&M FXS/FXO
E&M
FXO
PSTN
E&M FXS/FXO E&M FXS/FXO
FXS
COMMAND
MODEM
COMMAND
ETHERNET
10 BASET
Ethernet Connection
C om m an d P or t Con n ec ti on
2. Connect the MultiVOIP to a PC by using a DB-25 (male) to DB-9 (female) cable. Plug the DB-25 end of the
cable into the Command port of the MultiVOIP and the other end into the PC serial port.
3. Connect a network cable to the ETHERNET 10BASET connector on the back of the MultiVOIP. Connect the
other end of the cable to your network.
a. For an FXS or FXO connection (-SS and -FX series).
(FXS Examples: analog phone, fax machine |
FXO Examples: PBX extension, POTS line from central office.)
Connect one end of an RJ-11 phone cord to the Channel 1 FXS/FXO connector on the back of the
MultiVOIP. Connect the other end to the device or phone jack.
b. For an E&M connection.
(E&M Example: trunk line from telephone switch.)
Connect one end of an RJ-45 phone cord to the Channel 1 E&M connector on the back of the MultiVOIP.
Connect the other end to the trunk line.
Verify that the E&M Type in the E&M Options group of the Interface dialog box is the same as the E&M
trunk type supported by the telephone switch. See Appendix B for an E&M cabling pin-out.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 15
Page 16
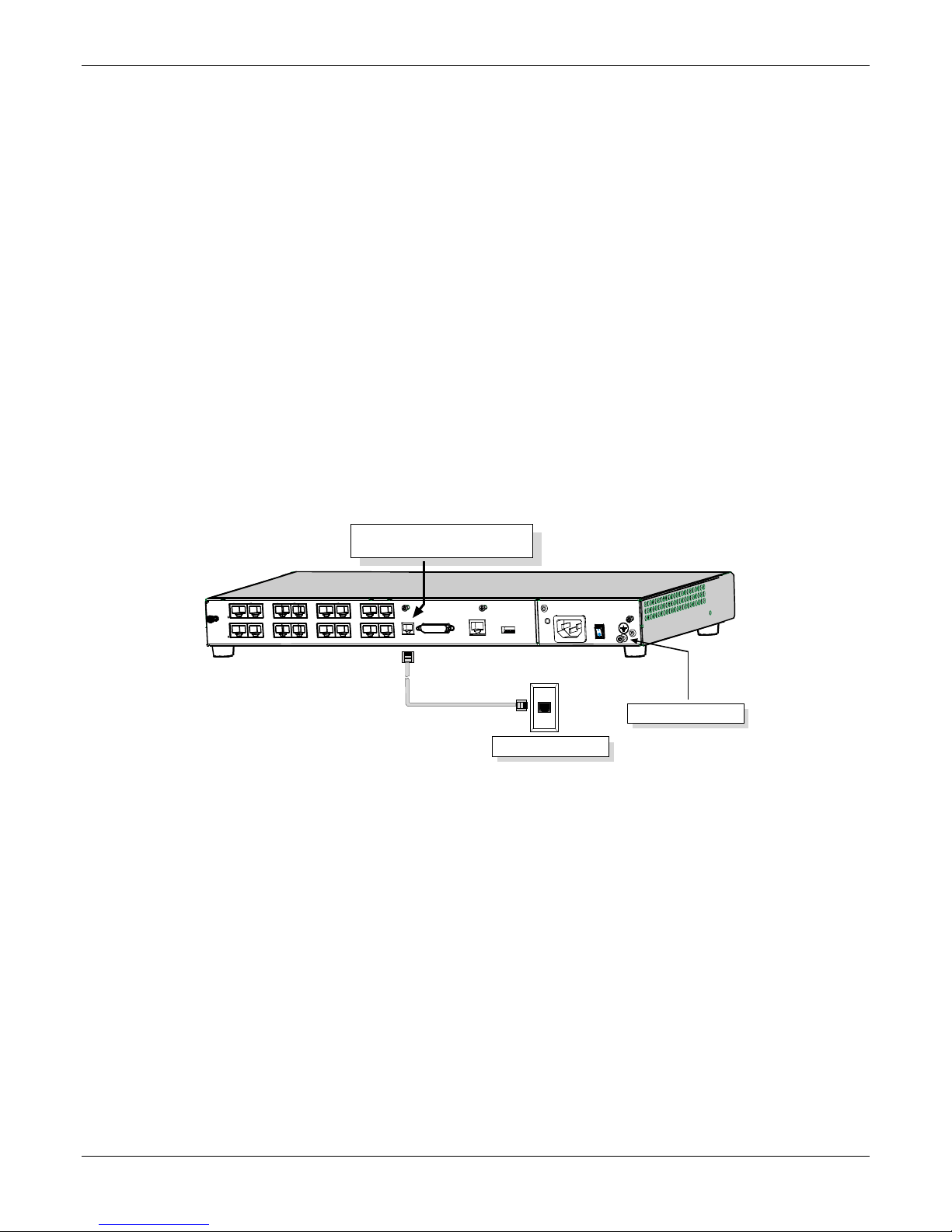
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
c. For a DID connection.
(DID Examples: DID fax system or DID voice phone lines.)
Connect one end of an RJ-11 phone cord to the Channel 1 FXS/FXO connector on the back of the
MultiVOIP. Connect the other end to the DID jack.
Note: DID lines are polarity sensitive. If, during testing, the DID line rings busy consistently, you need to
reverse the polarity of one end of the connector (swap the connections of the wires to the two middle
pins of one RJ-11 connector).
4. Repeat step 3 to connect the remaining telephone equipment to each channel on your MultiVOIP. Although
a MultiVOIP’s channels are often all configured identically, each channel is individually configurable. So, for
example, some channels of a MultiVOIP might use the FXO interface and others the FXS; some might use the
DID interface and others E&M, etc.
5. If you intend to configure the MultiVOIP remotely using the MultiVOIP Windows interface, connect an
RJ-11 phone cable between the Command Modem connector (not available on the –SS or –FX series) and a
receptacle served by a telco POTS line. See the first figure that follows.
6. The Command Modem is built into the MVP410 and 810 units only. To configure the MultiVOIP remotely
using its Windows interface, you must call into the MultiVOIP’s Command Modem. Once a connection is
made, the configuration process is identical to local configuration with the Windows interface.
Command Modem connector
for remote configuration
E&M FXS/FX O
E&M FXS/FXO
E&M FXS/FXO
E&M FXS/FXO
E&M FXS/FXO E&M FXS/FXO
E&M FXS/FXO E&M FXS/FXO
COMMAND
MODEM
COMMAND
ETHERNET
10 BASET
MVP-410/810
Rear Panel
Grounding Screw
Telco POTS Line
7. Ensure that the unit is properly connected to earth ground by verifying that it is reliably grounded when
mounted within a rack. You can do this by connecting a grounding wire between the chassis grounding
screw and a metallic object that provides an electrical ground.
8. Turn on power to the MultiVOIP by placing the ON/OFF switch on the back panel to the ON position. Wait
for the Boot LED on the MultiVOIP to go off before proceeding. This may take a few minutes.
9. Go to Chapter 3 to load the MultiVOIP software.
For DID channels only
For any channel on which you are using the DID interface type, you must change the jumper on the MultiVOIP
circuit card. DID is not supported on the –SS or –FX models.
1. Disconnect power. Unplug the AC power cord from the wall outlet or from the receptacle on the MultiVOIP
unit.
2. Using a #1 Phillips driver, remove the three screws (at back of unit) that attach the main circuit card to the
chassis of the MultiVOIP.
16 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 17
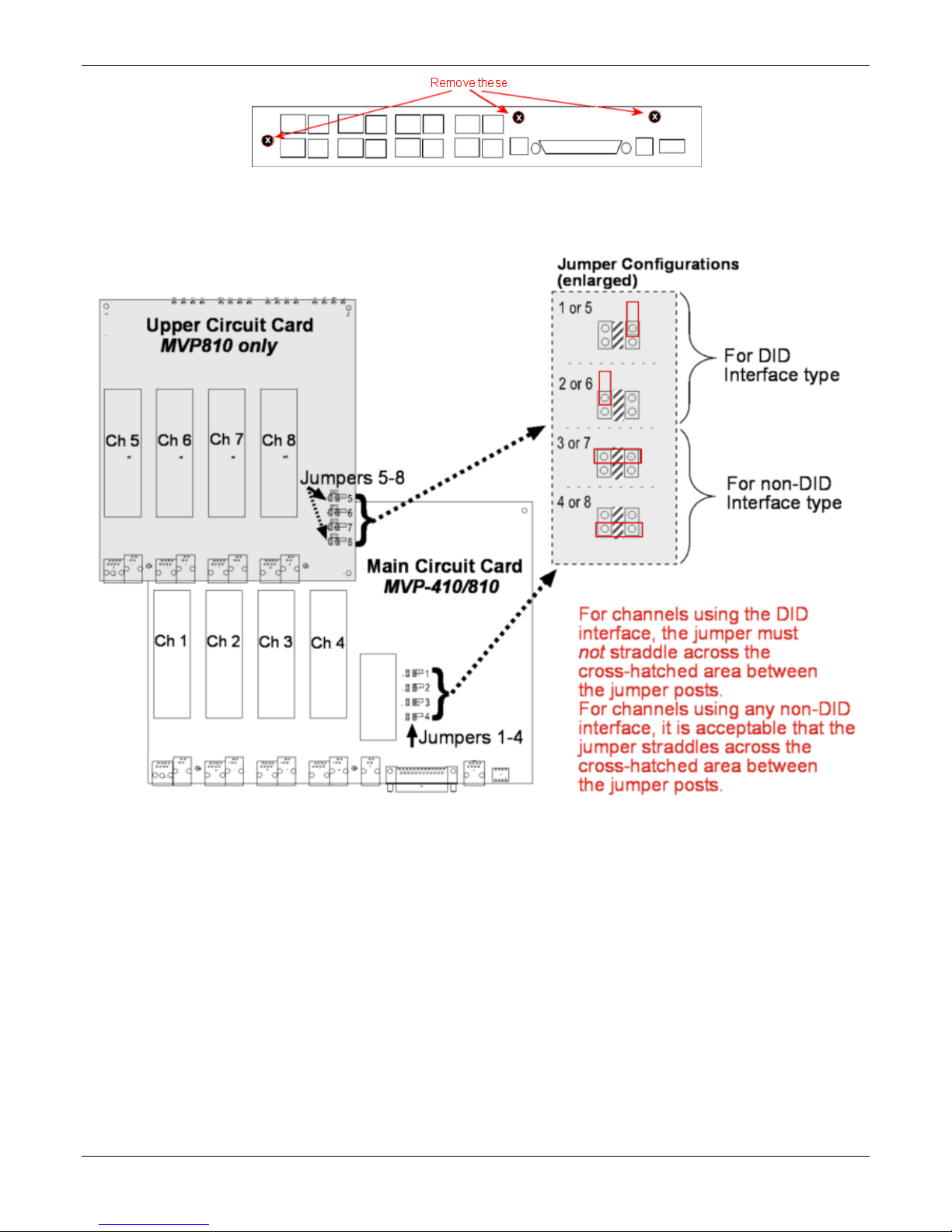
Chapter 2 – Installing and Cabling the MultiVOIP
3. Pull the main circuit card out about 5 inches (the power connection to the board prevents it from being
removed entirely from the chassis).
4. Identify the channels on which the DID interface is used.
5. Position the jumper for each DID channel so that it does not connect the two jumper posts. For DID
operation of a VOIP channel, the MultiVOIP works properly if you simply remove the jumper altogether, but
that is inadvisable because the jumper might be needed later if a different telephony interface is used for
that VOIP channel.
6. Slide the main circuit card back into the MultiVOIP chassis and replace the three screws.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 17
Page 18
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Setting up your MultiVOIP involves the following tasks:
1. Install the software onto the PC. This step is described in further detail in this chapter.
2. Set values for telephony and IP parameters appropriate for your system. This step is described in detail in
Chapter 4.
3. Define phone books that contain the dialing patterns for VOIP calls made to different locations. This step is
described in greater detail in Chapter 5.
Installing MultiVOIP Software
These installation steps do not present every screen or option in the installation. It is recommended that
someone familiar with Windows installs the software.
1. Download the firmware from the Multi-Tech website.
2. Ensure that your MultiVOIP is properly connected and that the power is turned on.
3. After you extract the downloaded firmware zip file, a setup.exe file appears. To start the installation
program, double-click this setup file.
4. The installation wizard starts. Click Next to continue.
5. The wizard steps you through the installation. The first pane asks you to select the destination for the
MultiVOIP software. Specify a location and click Next.
18 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 19
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
6. Select a program folder location for the MultiVOIP software program icon. Click Next. Progress screens
appear while files are being copied.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 19
Page 20

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
7. In the next wizard panel, select the COM port that the command PC uses when communicating with the
MultiVOIP unit.
After you install the software, you can re-set the COM port using the MultiVOIP Software. To do so, from the
sidebar menu, select Connection | Settings. Or use keyboard shortcut Ctrl + G.
Note: If the COM port setting made here conflicts with the actual COM port resources available in the
command PC, the “Error in Opencomm handle” message appears when the MultiVOIP program is launched.
If this occurs, you must reset the COM port.
8. A completion wizard panel appears.
Click Finish.
9. After you install the software, you are prompted to run the MultiVOIP software to configure the VOIP.
Software installation is now complete.
20 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 21
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Configuring for VOIP Communications
This section describes the basic configuration needed to start VOIP communications.
● Ethernet/IP
● Voice/Fax
● Interface
● Call Signaling
● Regional
● Phone Book
This setup process is followed by an important Save & Reboot step.
Other chapters in this guide describe configuration in detail.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 21
Page 22
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Setting IP Address
For basic functioning of the unit, you must set a unique LAN IP address as well as a subnet mask and Gateway IP.
Other settings here control specific features and protocols. These setting are not necessary for basic operation.
Chapter 4 describes all settings.
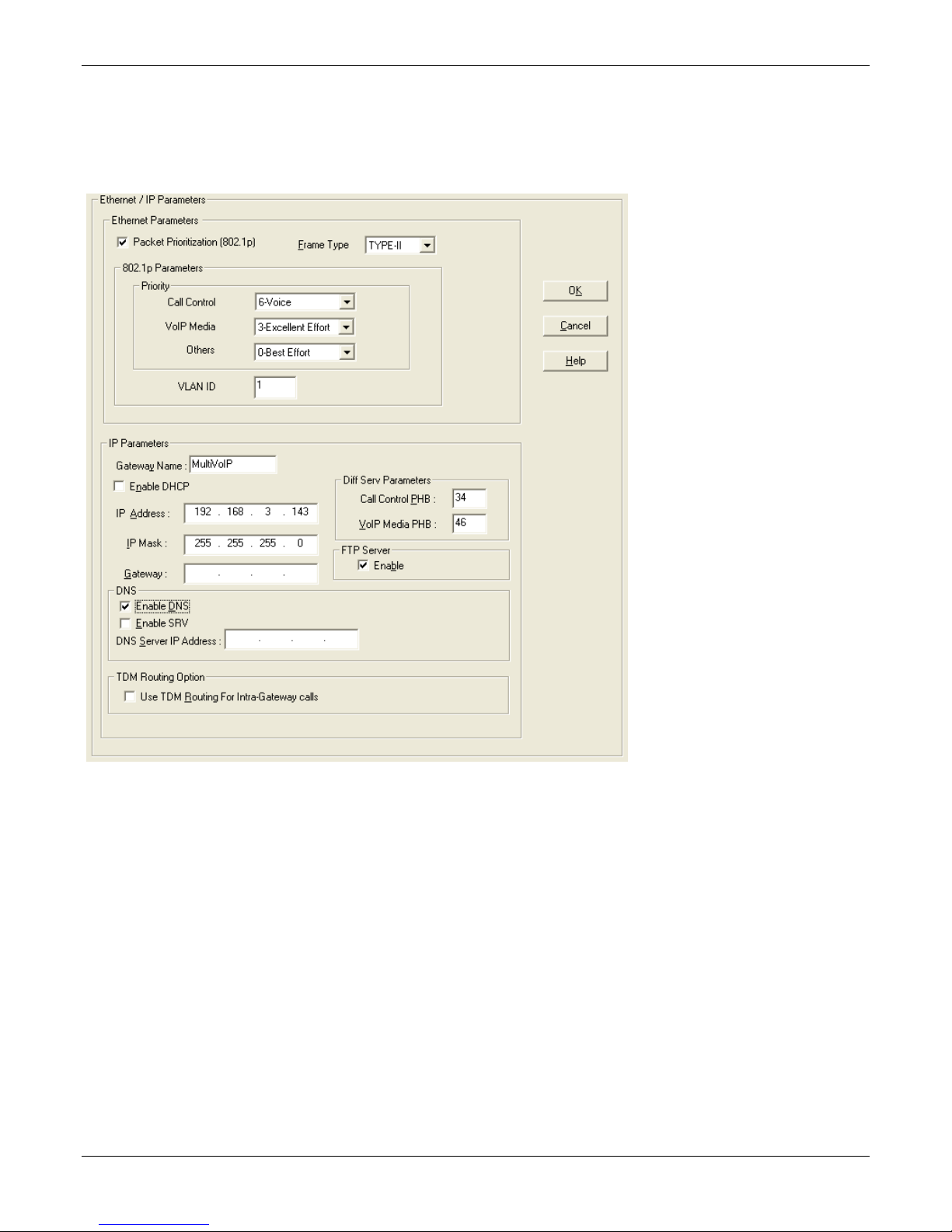
To configure IP settings:
1. If you are using packet prioritization:
a. Check Packet Prioritization.
b. Set 802.1p Priority Parameters as needed. The Priority levels can be from 0 – 7, where 0 is lowest
priority. VLAN ID identifies a virtual LAN by a number (1 to 4094)
2. From the Frame Type drop-down list, select the Frame Type that matches the network to which the
MultiVOIP is attached: TYPE II or SNAP
3. Enter Gateway Name.
4. If DHCP is used, check Enable DHCP.
5. Enter IP Address for the MultiVOIP unit.
6. Enter Subnet IP Mask for the MultiVOIP unit.
7. Enter Gateway IP.
8. If desired, check the Enable DNS checkbox.
22 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 23

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
9. Enter DNS Server IP Address
10. If desired, check the Enable SRV checkbox.
11. The Diff Serv Parameters group helps you specify settings for routers that are Diff Serv compatible
Setting both values to 0 effectively disables Diff Serv.
12. FTP Server Enable is only needed for firmware and software updates to the MultiVOIP.
13. If desired, check the TDM Routing checkbox.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 23
Page 24
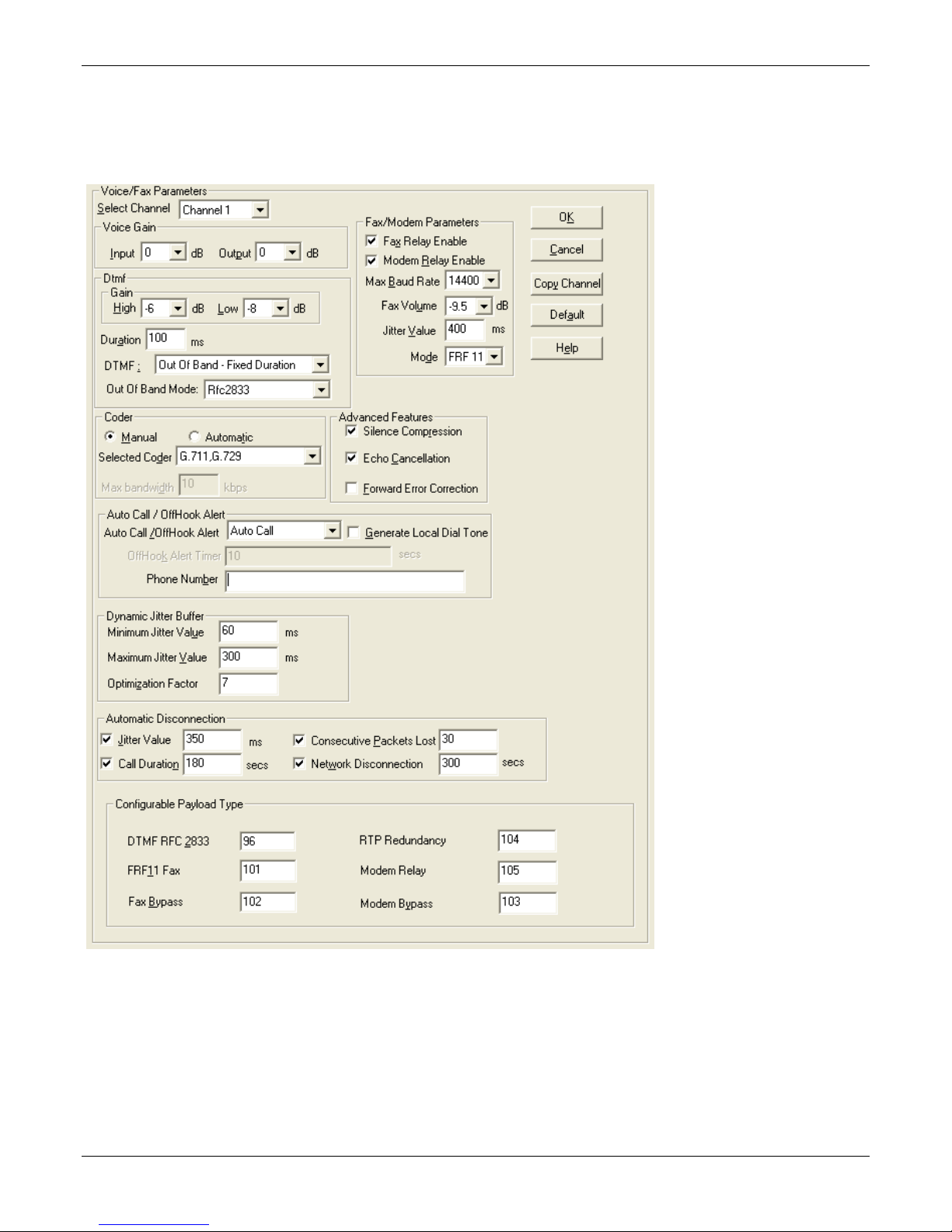
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Setting Voice/Fax Parameters
You must configure the individual channels before using your unit. If channels have the same parameters, you
can use the Copy Channel button to save time. You can note some options for future changes if necessary, but
default settings likely work, without adjustment.
24 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 25

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
To configure channels:
1. From the Select Channel drop-down list, select the channel you want to configure.
2. In the Fax/Modem Parameters group:
a. From the Set Max Baud Rate drop-down list, select a rate that matches a fax machine (2400 to 14400
bps).
b. Do not change the setting in the Fax Volume drop-down menu. Such changes can adversely impact the
modem’s operation.
c. From the Jitter Value drop-down list, select the desired time for packet reassembly.
d. From the Mode drop-down list, select T.38 or FRF 11.
e. To allow modem traffic through the VOIP system, check the Modem Relay Enable checkbox.
3. Do not change settings in the Dtmf group. Adjusting Voice Gain and DTMF may adversely affect quality.
4. In the Selected Coder drop-down list, select a coder or allow automatic negotiation
5. In the Advance Features group:
● To not send silence packets, check Silence Compression.
● To remove echo and improve voice quality, select Echo Cancellation.
● To recover some bad packets, check Forward Error Correction.
6. Use the Auto Call / OffHook Alert group to allow automatically calling of a remote VOIP without dialing. This
is described in greater detail in Chapter 4.
7. In the Dynamic Jitter group, change values if necessary (details in Chapter 4)
● Select any Automatic Disconnection options needed to ensure lines are not left “open”
● Configurable Payload Types are best left at their defaults. Not in the –SS models
8. Configure each channel as described in the preceding steps. You can use the Copy Channel button to quickly
transfer the settings from one channel to another.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 25
Page 26
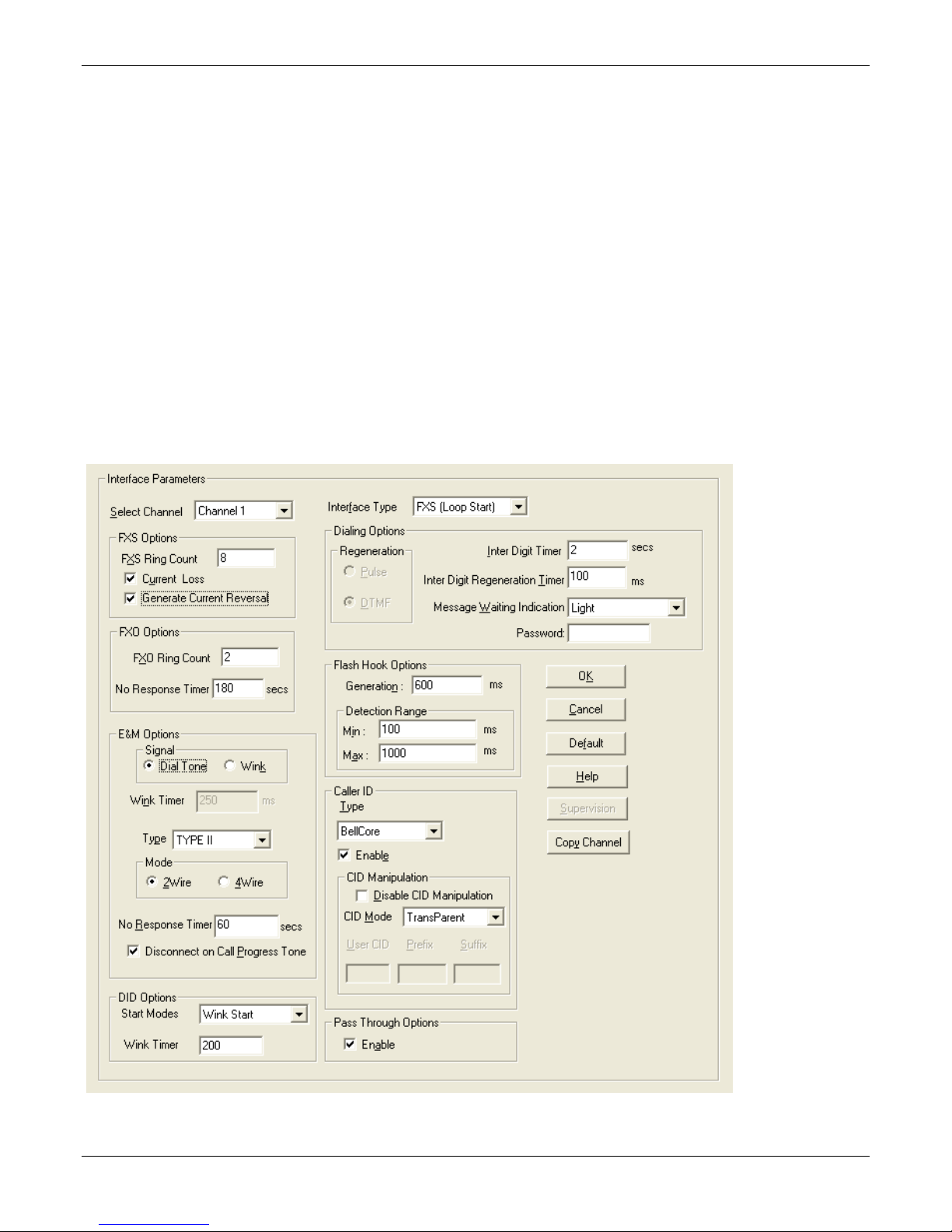
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Setting Interface Parameters
The Interface parameters control the telephony settings that are applied to the individual MultiVOIP channels.
Configure each channel for the type of interface you are using. Channel 1 is selected by default.
Note: Features are available or unavailable depending on the selected interface type. The one option available
for all interface types is the inter digit timer option. This option defines the maximum time that the unit waits
before mapping the dialed digits to an entry in the phone book database. If too much time elapses between
digits, and the wrong numbers are mapped, you hear a rapid busy signal. If this happens, hang up and dial again.
If the Interface Type is FXS (Loop Start), a station device such as an analog telephone, fax machine or KTS (Key
Telephone System) is connected to an analog channel. The FXS options group is active.
If the Interface Type is FXO, the Dialing Options Regeneration, Flash Hook Timer and Ring Count groups are
enabled. The FXO Ring Count allows you to set the number of rings before the unit answers the incoming call.
Check with your local in-house phone personnel to verify whether your local PBX dial signaling is pulse or tone
(DTMF). The Flash Hook Options Generation setting allows you to enter the time, in milliseconds, for the
duration of the flash hook signal.
If the Interface Type is E & M, you are connecting to an analog E & M trunk on your PBX. Check with your inhouse phone personnel to determine the signaling type (Dial Tone or Wink) and if it is 2-wire or 4-wire. The –SS
and –FX series do not support E&M or DID operation.
26 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 27

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
To set Interface Parameters:
1. From the Channel drop down list, select Channel whose parameters you want to configure.
2. From the Interface Type drop down list, select FXS, FXO, E&M or DID (FXS/FXO only for –SS and –FX series)
3. From the Regeneration group, select how signal is regenerated; as Pulse or DTMF
4. In the Inter Digit Timer field, type time the MultiVOIP waits between digits.
5. From the Message Waiting Indication drop-down list, for E&M only select Light or None.
6. In the Inter Digit Regeneration Timer field, type time between sent DTMF digits.
7. In the Flash Hook Options group:
● Generation (used in conjunction with FXO/E&M)
● Detection Range (used in conjunction with FXS/E&M)
8. In the Caller ID group:
● Bellcore is the only option available
● CallerID Manipulation is available if needed
● CID Manipulation is not available in the –SS models
9. In the FXS Options group:
● In the Ring Count field, type the number of rings allowed before call abandoned; default is 8.
● Check Use Current Loss if you want the MultiVOIP to interrupt current to disconnect.
● Check Generate Current Reversal if you want to activates Answer/Disconnect Supervision to FXO.
10. In the FXO Options group:
● In the Ring Count field type the number of rings before MultiVOIP answers.
● In the No Response Timer field, type the time to attempt call before abandoning.
11. Click Supervision to set call answering and disconnection settings.
a. Complete Answer fields:
• Current Reversal (use current reversal to answer)
• Answer Delay
• Answer Delay Timer (in seconds)
• Tone Detection (allow tone sequence to disconnect)
• Available Tones
• Answer Tones (shows current selection from Available Tones)
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 27
Page 28

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
b. Complete Disconnect fields:
• Current Reversal (use current reversal to disconnect)
• Current Loss (loss of current triggers disconnect)
• Current Loss Timer (time after current loss to disconnect; in milliseconds)
• Silence Detection Enable (use silence detection to disconnect)
• Silence Detection Type (one-way or two-way)
• Silence Timer (time of silence needed to trigger disconnect; in seconds)
• DTMF Tone (use tones to disconnect)
• Disconnect Tone Sequence (select tone pairs to use for disconnecting)
• Tone Detection (disconnect from termination of tone)
• Available Tones
• Disconnect Tones (shows current selection from Available Tones)
12. In the E&M Options group (not supported by –SS and –FX series):
● In the Signal group, select Dial Tone or Wink.
● In Wink Timer field, type a type, whose range can be 100 to 350 milliseconds; default is 250.
● From the Type drop-down list, select TYPE 1 or TYPE 11.
● In the Mode group select 2-wire or 4-wire.
● In the No Response Timer field type the time, in seconds, after which an FXO call is disconnected.
● Check Disconnect on Call Progress Tone if you want to disconnect when PBX issues call progress tone.
13. In the Pass Through Options group select Enable to create an open audio patch; not for use with Wink
signaling.
14. In the DID Options group: (not supported by –SS and –FX series)
● From Start Modes drop-down list, select Immediate, Wink or Delay Dial.
● In the Wink Timer field type time, in milliseconds.
28 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 29
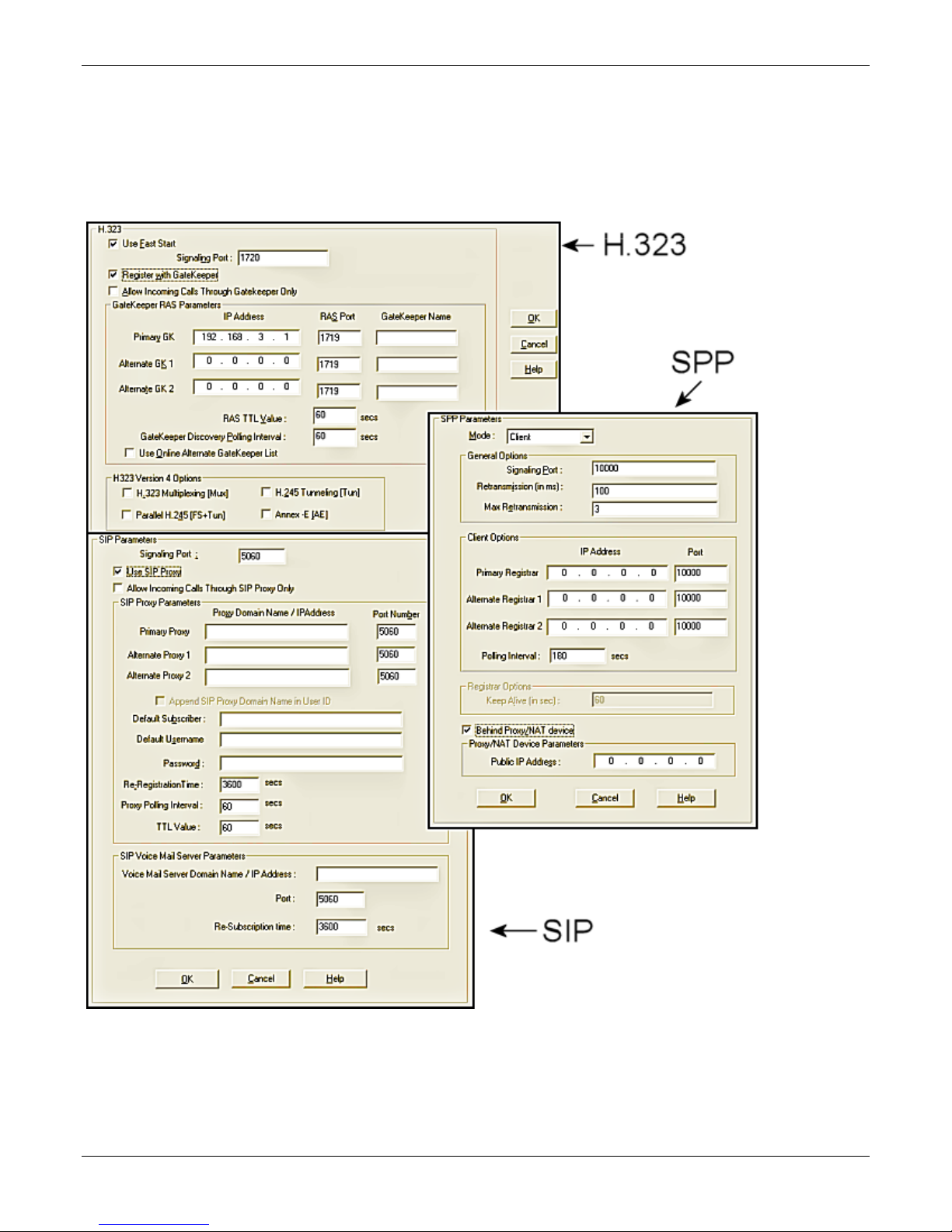
Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Setting Call Signaling
There are three choices for Call Signaling: H.323, SIP and SPP, the –SS models only support SIP and the –FX
models support SIP and SPP, but not H.323. It is best to select one of these as the protocol to be used, rather
than mixing them. Single Port Protocol (SPP) is a non-standard protocol created by Multi-Tech that allows
dynamic IP allocation. Generally, the default settings do not work for most users. If necessary you can change
individual parameters. Chapter 4 provides details for all settings.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 29
Page 30

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Configuring H.323 Call Signal
This feature is not supported by –SS and –FX series.
1. Check Fast Start, as this may be needed for third-party vendor compatibility.
2. In the Signaling Port field, type a port number. The default is 1720.
3. If a gatekeeper is to control VOIP check Register with Gatekeeper.
4. Check Allow Incoming Calls Through Gatekeeper Only.
5. In the Gatekeeper RAS Parameters group, set the following:
a. Enter parameters for Primary and any Alternate Gatekeepers
b. RAS TTL Value (“Time To Live” in seconds)
c. Gatekeeper Discovery Polling Interval (time between attempts connecting to gatekeepers)
d. Use Online Alternate Gatekeeper List
6. For details about the parameters in the H.323 Version 4 Options group, see Chapter 4.
Configuring SIP Call Signal
1. In the Signaling Port field, type a port number. The default is 5060.
2. Check SIP Proxy if operating with a proxy server.
3. Check Allow Incoming Calls Through SIP Proxy Only.
4. In the SIP Proxy Parameters group, set the following:
a. Enter information for Primary and any Alternate Proxy servers
b. Append SIP Proxy Domain Name in User ID
c. Enter User Name and Password
d. Re-Registration Time (in seconds)
e. Proxy Polling Interval (time between proxy server connect attempts)
f. TTL Value (in seconds)
Configuring SPP Call Signal
This feature is not supported by –SS series.
1. From the Mode drop-down list, select Direct, Client or Registrar.
2. In the Signaling Port field, type a port number which must be unique for any VOIP unit behind same firewall.
3. Retransmission field, (time before retransmission of lost packets)
4. Max Retransmission field (number of retransmission attempts)
5. In the Client Options group:
a. Enter information for the Primary and Alternate Registrars
b. In the Polling Interval field, type the time between connect attempts.
6. In Registrar Options group, in the Keep Alive field, type the time out for client un-registering.
7. If appropriate check Behind Proxy/NAT device, then type the address of the Public IP of Proxy/NAT server.
30 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 31

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Setting the Region or Country
Select the country or region in which the MultiVOIP unit operates. Use the custom option if the available
settings are not adequate.
1. From the Country/Region drop-down list, select the location of the MultiVOIP.
2. If no location fits your needs, select Custom and set the tones manually.
To create user-defined tones to be used with FXO Supervision, click Add.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 31
Page 32

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Defining the Phone Book
A populated phone book helps the VOIP unit translate call traffic. You need the information for both a local site
and any remote sites. Chapter 5 provides detailed descriptions and examples.
32 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 33

Chapter 3 – Installing Software
Configuring the Outbound Phone Book
1. Select Add Entry.
2. To allow unmatched destinations an alternative, check Accept Any Number.
3. In the Destination Pattern field, type the number necessary to get out from the PBX system followed by the
calling code of the destination
4. In the Remove Prefix field, type the PBX access digit. This is the same number as needed to get out of the
PBX system.
5. In the Add Prefix field, type other needed digits.
6. In the IP Address field, type the IP address of the call destination. If desired, in the Description field, add a
description.
7. In the Protocol Type group, select the protocol used.
–SS models use SIP only. -FX models do not support H.323.
a. For H.323, Enter Gateway settings.
b. For SIP: Select Transport Protocol, Proxy and URL if needed.
c. For SPP: Enter Registrar settings if needed.
8. To enter an Alternate IP Address for outbound traffic, click Advanced.
Configuring the Inbound Phone Book
1. Select Add Entry
2. Accept Any Number for inbound traffic does not work when external routing devices are used
3. Enter any access digits followed by the local calling code in the Remove Prefix field
4. Enter any digits needed to access an outside line in the Add Prefix field
5. Select Hunting in the Channel Number field to have the VOIP use the next available channel
6. Add a description if you like
7. Call Forward may be set up (details available in Chapter 5)
8. Select Registration Option
Saving Your Settings and Rebooting
After you change settings on the VOIP unit, you must select the Save & Reboot option. If you do not, all changes
are lost when you reset or shut down the MultiVOIP.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 33
Page 34

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your
MultiVOIP
Two interfaces help you use your MultiVOIP:
● A web interface
● Windows software interface
You must set eight parameters for proper MultiVOIP operation. You must know the IP address used, the IP mask,
the Gateway IP, the Domain Name Server information, and the telephone interface type.
Initially, you must configure the MultiVOIP locally. To do so, use a connection between the command port of the
MultiVOIP and the COM port of the computer. Use the MultiVOIP configuration software to configure the
MultiVOIP.
You can later make changes to the configuration locally or remotely.
Alternatively, MultiVoipManager is a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent program that
extends the capabilities of the MultiVOIP configuration software. MultiVoipManager allows the user to manage
any number of VOIPs on a network, whereas the MultiVOIP configuration software manages only one. The
MultiVoipManager can configure multiple VOIPs simultaneously. MultiVoipManager may reside on the same PC
as the MultiVOIP configuration software.
This chapter explains the setup portion of the software described in the following section.
Chapter 5 describes the Phone Book setup.
Chapter 6 discusses the Statistics options and overall maintenance of the MultiVOIP.
Software Categories Covered in This Chapter
● Ethernet/IP
● Voice/Fax
● Interface
● Call Signaling
● H.323/SIP/SPP
● SNMP
● Regional
● SMTP
● RADIUS
● Logs/Traces
● NAT Traversal
● Supplementary services
● Save Setup
● Connection
● Settings
34 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 35

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Navigating the Software
To launch the MultiVOIP software:
1. From the Start button, select All Programs, MultiVOIP x.xx, where x represents version number.
2. Select Configuration.
The software offers several ways to access the parameter that you want to use:
● Through the left-hand panel
● From the drop-down menu
● Clicking a taskbar icon, if available
● Keyboard shortcut, if available
After you enter initial settings, you can configure the MultiVOIP through a Web browser rather than the
Windows interface.
Using the Web Browser Interface
The MultiVOIP web browser interface provides the same commands and configuration parameters as the
MultiVOIP Windows interface, except for logging functions. When using the web browser interface, logging can
be done by email (the SMTP option).
Setting up the Web Browser interface (Optional)
After you set an IP address for the MultiVOIP unit, you can configure the unit by using the MultiVOIP web
browser interface. Before using the web browser interface to configure the unit, set it up:
1. Set IP address of MultiVOIP unit using the MultiVOIP Configuration program (the Windows interface).
2. Save Setup in Windows interface.
3. Close Windows interface.
4. Install Java program (on first use only).
5. Open web browser.
6. Browse to IP address of MultiVOIP unit.
7. If username and password are established, enter them when prompted.
8. Set browser to allow pop-ups. The MultiVOIP Web interface makes use of pop-up windows.
9. The configuration panes in the web browser have the same content as their counterparts in the software;
only the presentation differs.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 35
Page 36

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuration Information Checklist
The following chart helps you organize the configuration information needed. The –SS and –FX models do not
support E&M or DID.
Info
Type of Configuration Info Gathered: Configuration screen where info is entered:
IP info for VOIP unit
• IP address
• Gateway
• DNS IP (if used)
• 802.1p Prioritization (if used)
Interface Type
• E&M
• FXS/FXO*
• DID-DPO
E&M info (only if E&M used)
• Type (1-5)
• 2 or 4 wires
• Dial Tone or Wink
Country code Regional parameters
Ethernet/IP parameters
Interface parameters
(*In FXS/FXO systems, channels used for phone, fax, or key
system are FXS; channels used for analog PBX extensions
or analog telco lines are FXO
Interface parameters
).
Obtained?
D
Info
Entered?
D
Email address for VOIP (optional) SMTP parameters
Reminder: Be sure to Save Setup after entering configuration values.
36 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 37

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Setting Ethernet/IP
This section describes the Ethernet settings needed for the MultiVOIP unit. In each field, enter the values that fit
the network to which the MultiVOIP is connected. For many settings, the default values work best. Try these
settings first unless you are certain that you need to change a parameter.
The Ethernet/IP Parameters fields are described in the tables that follow. Note that both Diff Serv parameters
(Call Control PHB and VOIP Media PHB) must be set to zero if you enable Packet Prioritization (802.1p). Nonzero
Diff Serv values negate the prioritization scheme.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 37
Page 38

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Ethernet/IP Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Ethernet Parameters
Packet Prioritization
(802.1p)
Frame Type Type II, SNAP Must be set to match network’s frame type. Default is Type II.
802.1p A draft standard of the IEEE about data traffic prioritization on Ethernet networks. The 802.1p draft is an
Call Control Priority 0-7, where 0 is
VOIP Media Priority 0-7, where 0 is
Others (Priorities) 0-7, where 0 is
VLAN ID 1 - 4094 The 802.1Q IEEE standard allows virtual LANs to be defined within a network. This
IP Parameter fields
Gateway Name alphanumeric Descriptor of current VOIP unit to distinguish it from other units in system.
Enable DHCP Y/N
IP Address n.n.n.n The unique LAN IP address assigned to the MultiVOIP.
IP Mask n.n.n.n Subnetwork address that allows for sharing of IP addresses within a LAN.
Gateway n.n.n.n The IP address of the device that connects your MultiVOIP to the Internet.
Table is continued on next page…
Y/N Select to activate prioritization under 802.1p protocol (described below).
extension of the 802.1D bridging standard. 802.1D determines how prioritization operates within a MAClayer bridge for any kind of media. The 802.1Q draft for virtual local-area-networks (VLANs) addresses
the issue of prioritization for Ethernet networks in particular.
802.1p enacts this Quality-of-Service feature using 3 bits. This 3-bit code allows data switches to reorder
packets based on priority level. The descriptors for the 8 priority levels are given below.
802.1p PRIORITY LEVELS
LOWEST PRIORITY
1 – Background: Bulk transfers and other activities permitted on the network, but should not affect the
use of network by other users and applications.
2 – Spare: An unused (spare) value of the user priority.
0 – Best Effort (default): Normal priority for ordinary LAN traffic.
3 – Excellent Effort: The best effort type of service that an information services organization would
deliver to its most important customers.
4 – Controlled Load: Important business applications subject to some form of “Admission Control”, such
as preplanning of Network requirement, characterized by bandwidth reservation per flow.
5 – Video: Traffic characterized by delay < 100 ms.
6 – Voice: Traffic characterized by delay < 10 ms.
7 - Network Control: Traffic urgently needed to maintain and support network infrastructure.
HIGHEST PRIORITY
lowest priority
lowest priority
lowest priority
disabled by
default
:
Sets the priority for signaling packets.
Sets the priority for media packets.
Sets the priority for SMTP, DNS, DHCP, and other packet types.
field identifies each virtual LAN by number.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a method for assigning IP address and other
IP parameters to computers on the IP network in a single message with great
flexibility. IP addresses can be static or temporary depending on the needs of the
computer.
38 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 39

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Ethernet/IP Parameter Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
Diff Serv
Parameter
fields
Call Control PHB 0 – 63
VOIP Media PHB 0 – 63
FTP Parameter fields
FTP Server
Enable
DNS Parameter fields
Enable DNS Y/N
Enable SRV Y/N Enables ‘service record’ function. Service record is a category of data in the Internet Domain
DNS Server IP
Address
Diff Serv PHB (Per Hop Behavior) values pertain to a differential prioritizing system for IP packets as handled by
Diff Serv-compatible routers. There are 64 values, each with an elaborate technical description. These
descriptions are found in TCP/IP standards RFC2474, RFC2597, and, for present purposes, in RFC3246, which
describes the value 34 (34 decimal; 22 hex) for Assured Forwarding behavior (default for Call Control PHB) and
the value 46 (46 decimal; 2E hexadecimal) for Expedited Forwarding behavior (default for VOIP Media PHB).
Before using values other than these default values of 34 and 46, consult these standards documents and/or a
qualified IP telecommunications engineer.
To disable Diff Serv, configure both fields to 0 decimal.
Value is used to prioritize call setup IP packets.
default = 34
default = 46
Y/N
Default =
disabled
See “FTP Server
File Transfers”
in Chapter 6
Default =
disabled
n.n.n.n IP address of specific DNS server to be used to resolve Internet computer names.
Setting this parameter to 0, along with VOIP Media PHB below disables Diff Serv.
Value is used to prioritize the RTP/RTCP audio IP packets.
Setting this parameter to 0, along with Call Control PHB above disables Diff Serv.
MultiVOIP unit has an FTP Server function so that firmware and other important operating
software files can be transferred to the VOIP via the network.
Enables Domain Name Space/System function where computer names are resolved using a
worldwide distributed database.
Name System specifying information on available servers for a specific protocol and domain,
as defined in RFC 2782. Newer internet protocols like SIP, STUN, H.323, POP3, and XMPP
may require SRV support from clients. Client implementations of older protocols, like LDAP
and SMTP, may have been enhanced in some settings to support SRV.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 39
Page 40

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Setting Voice/Fax Parameters
Configure the Voice/Fax section for each channel used. However, once you have established a set of Voice/FAX
parameters for a particular channel, you can apply this entire set of Voice/FAX parameters to another channel
by using the Copy Channel button and its dialog box. To copy a set of Voice/FAX parameters to all channels,
select “Copy to All” and click Copy.
The majority of the settings should be left at their default settings as changes often introduce problems with
signal quality. In each field, enter the values that fit your particular setup. The –SS models do not have
Configurable Payload Type available.
The Voice/FAX Parameters settings are described in the tables that follow.
40 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 41

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Voice/Fax Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Default -- When this button is clicked, all Voice/FAX parameters are set to their default values.
Select Channel
Copy Channel --
Voice Gain -- Signal amplification (or attenuation) in dB.
Input Gain
Output Gain
DTMF Gain --
DTMF Gain,
High Tones
DTMF Gain, Low
Tones
DTMF Parameters
Duration (DTMF)
DTMF
In/Out of Band
Out of Band Mode
FAX Parameters
1-2 (210)
1-4 (410)
1-8 (810)
+31dB to
–31dB
+31dB to
–31dB
+3dB to
-31dB &
“mute”
+3dB to
-31dB &
“mute”
60 – 3000
ms
Out of
Band, or
Inband
RFC 2833,
SIP Info
Channel to be configured is selected here.
Copies the Voice/FAX attributes of one channel to another channel. Attributes can be copied
to multiple channels or all channels at once.
Modifies audio level entering voice channel before it is sent over the network to the remote
VOIP. The default & recommended value is 0 dB.
Modifies audio level being output to the device attached to the voice channel. The default
and recommended value is 0 dB.
The DTMF Gain (Dual Tone Multi-Frequency) controls the volume level of the DTMF tones
sent out for Touch-Tone dialing.
Default value: -4 dB. Not to be changed except under supervision of Multi-Tech Technical
Support.
Default value: -7 dB. Not to be changed except under supervision of Multi-Tech Technical
Support.
When DTMF: Out of Band is selected, this setting determines how long each DTMF digit
‘sounds’ or is held. Default = 100 ms.
When DTMF Out of Band is selected, the MultiVOIP detects DTMF tones at its input and
regenerates them at its output. When DTMF Inband is selected, the DTMF digits are passed
through the MultiVOIP unit as they are received.
RFC2833 method. Uses an RTP mode defined in RFC 2833 to transmit the DTMF digits.
SIP Info method. Generates dual tone multi frequency (DTMF) tones on the telephony call
leg. The SIP INFO message is sent along the signaling path of the call.
You must set this parameter per the capabilities of the remote endpoint with which the VOIP
communicates. The RFC2833 method is the more common of the two methods.
Fax Enable Y/N Enables or disables fax capability for a particular channel.
Modem Relay
Enable
Max Baud Rate
(Fax)
Fax Volume
(Default =
-9.5 dB)
Jitter Value (Fax) Default =
Mode (Fax) FRF 11;
Table is continued on next page…
Y/N When enabled, modem traffic can be carried on VOIP system. When disabled, modem traffic
bypasses the VOIP system (Modem Bypass mode).
2400, 4800,
7200, 9600,
12000,
14400 bps
-18.5 dB
to –3.5 dB
400 ms
T.38
Set to match baud rate of fax machine connected to channel (see Fax machine’s user
manual).
Default = 14400 bps.
Controls output level of fax tones. To be changed only under the direction of Multi-Tech’s
Technical Support.
Defines the inter-arrival packet deviation (in milliseconds) for the fax transmission. A higher
value increases the delay, allowing a higher percentage of packets to be reassembled. A
lower value decreases the delay allowing fewer packets to be reassembled.
FRF11 is frame-relay FAX standard using these coders: G.711, G.728, G.729, G.723.1.
T.38 is an ITU-T standard for real time faxing of Group 3 faxes over IP networks. It uses T.30
fax standards and includes special provisions to preclude FAX timeouts during IP
transmissions.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 41
Page 42

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Voice/Fax Parameter Definitions (continued)
Coder Parameters
Coder Manual or
Automatic
Selected Coder
(SS models only)
Selected Coder
Max bandwidth
(coder)
Silence
Compression
Echo Cancellation Y/N Determines whether echo cancellation is enabled (checked) for this
Forward Error
Correction
Table is continued on next page…
G.711 a/u law 64 kbps;
G.726, @ 16/24/32/40 kbps;
G.727, @ nine bps rates;
G.723.1 @ 5.3 kbps, 6.3 kbps;
G.729, 8kbps;
Net Coder @
6.4, 7.2, 8, 8.8, 9.6 kbps
G.711, G.729
-or-
G.729, G.711
11 – 128 kbps
Advanced Features
Y/N Determines whether silence compression is enabled (checked) for this
Y/N Determines whether forward error correction is enabled (checked) for
Determines whether selection of coder is manual or automatic. When
Automatic is selected, the local and remote voice channels negotiate
the voice coder to be used by selecting the highest bandwidth coder
supported by both sides without exceeding the Max Bandwidth
setting. G.723, G.729, or G.711 are negotiated.
Select from a range of coders with specific bandwidths. The higher the
bps rate, the more bandwidth is used. The channel that you are calling
must have the same voice coder selected.
Default = G.723.1 @ 6.3 kbps, as required for H.323. Here 64K of digital
voice is compressed to 6.3K, allowing several simultaneous
conversations over the same bandwidth that would otherwise carry
only one.
To make selections from the Selected Coder drop-down list, the
Manual option must be enabled.
Coder Priority has two options (G.711,G.729 or G.729, G711) on the
Selected Coder listing of the Coder group on the Voice/Fax screen. If
G.711 is the higher priority, i.e., G.711 is preferred to G729 on the
sending side, then G.711, G.729 option is selected. Similarly, if G.729
has the higher priority, then G.729, G.711 option is selected.
It is used whenever a user wants to advertise both G.711 and G.729
coders with higher preference to a particular coder.
It is useful when the calls are made from a particular channel on the
VOIP to two different destinations where one supports G.711 and the
other supports G.729.
This drop-down list enables you to select the maximum bandwidth
allowed for this channel. The Max Bandwidth drop-down list is enabled
only if the Coder is set to Automatic.
If coder is to be selected automatically (“Auto” setting), then enter a
value for maximum bandwidth.
voice channel.
With Silence Compression enabled, the MultiVOIP does not transmit
voice packets when silence is detected, thereby reducing the amount
of network bandwidth that is being used by the voice channel (default
= on).
voice channel.
Echo Cancellation removes echo and improves sound quality (default =
on).
this voice channel.
Forward Error Correction enables some of the voice packets that were
corrupted or lost to be recovered. FEC adds an additional 50%
overhead to the total network bandwidth consumed by the voice
channel (default = Off).
42 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 43

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Voice/Fax Parameter Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
AutoCall/Offhook Alert Parameters
Auto Call / Offhook
Alert
Generate Local Dial
Tone
Offhook Alert Timer 0 – 3000
AutoCall,
Offhook
Alert
Y/N Used for AutoCall only. If selected, dial tone is generated locally while the call is being
seconds
The AutoCall option enables the local MultiVOIP to call a remote MultiVOIP without
the user having to dial a Phone Directory Database number. As soon as you access the
local MultiVOIP voice/fax channel, the MultiVOIP immediately connects to the remote
MultiVOIP identified in the Phone Number box of this option.
If the “Pass Through Enable” field is checked in the Interface Parameters screen,
AutoCall must be used.
The Offhook Alert option applies only to FXS channels.
The Offhook Alert option works like this: if a phone goes off hook and yet no number
is dialed within a specific period of time (as set in the Offhook Alert Timer field), then
that phone automatically dials the Alert phone number for the VOIP channel. (The
Alert phone number must be set in the Voice/Fax Parameters | Phone Number field;
if the VOIP system is working without a gatekeeper unit, there must also be a matching
phone number entry in the Outbound Phonebook.). One use of this feature would be
for emergency use where a user goes off hook but does not dial, possibly indicating a
crisis situation. The Offhook Alert feature uses the Intercept Tone, as listed in the
Regional Parameters screen. This tone is outputted on the phone that was taken off
hook but that did not dial. The other end of the connection hears audio from the
“crisis” end, as during a normal phone call.
Both functions apply on a channel-by-channel basis. It would not be appropriate for
either of these functions to be applied to a channel that serves in a pool of available
channels for general phone traffic. Either function requires an entry in the Outgoing
phonebook of the local MultiVOIP and a matched setting in the Inbound Phonebook of
the remote VOIP.
established between gateways. The capability to generate dial tone locally would be
particularly useful when there is a lengthy network delay.
The length of time that must elapse before the off hook alert is triggered and a call is
automatically made to the phone number listed in the Phone Number field.
Phone Number -- Phone number used for Auto Call function or Offhook Alert Timer function. This phone
number must correspond to an entry in the Outbound Phonebook of the local
MultiVOIP and in the Inbound Phonebook of the remote MultiVOIP (unless a
gatekeeper unit is used in the VOIP system).
Table is continued on next page…
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 43
Page 44

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Voice/Fax Parameter Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
Dynamic Jitter
Dynamic Jitter Buffer Dynamic Jitter defines a minimum and a maximum jitter value for voice
communications. When receiving voice packets from a remote MultiVOIP, varying
delays between packets may occur due to network traffic problems. This is called
Jitter. To compensate, the MultiVOIP uses a Dynamic Jitter Buffer. The Jitter Buffer
enables the MultiVOIP to wait for delayed voice packets by automatically adjusting
the length of the Jitter Buffer between configurable minimum and maximum values.
An Optimization Factor adjustment controls how quickly the length of the Jitter
Buffer is increased when jitter increases on the network. The length of the jitter
buffer directly affects the voice delay between MultiVOIP gateways.
Minimum Jitter Value 60 to 400
ms
Maximum Jitter Value 60 to 400
ms
Optimization Factor 0 to 12 The Optimization Factor determines how quickly the length of the Dynamic Jitter
The minimum dynamic jitter buffer of 60 milliseconds is the minimum delay that
would be acceptable over a low jitter network.
Default = 150 ms
The maximum dynamic jitter buffer of 400 milliseconds is the maximum delay
tolerable over a high jitter network.
Default = 300 ms
Buffer is changed based on actual jitter encountered on the network. Selecting the
minimum value of 0 means low voice delay is desired, but increases the possibility of
jitter-induced voice quality problems. Selecting the maximum value of 12 means
highest voice quality under jitter conditions is desired at the cost of increased voice
delay.
Default = 7.
Auto Disconnect
Automatic
Disconnection
Jitter Value 1-65535 The Jitter Value defines the average inter-arrival packet deviation (in milliseconds)
Call Duration 1-65535 Call Duration defines the maximum length of time (in seconds) that a call remains
Consecutive Packets
Lost
Network Disconnection 1 to 65535;
-- The Automatic Disconnection group provides four options which can be used singly
or in any combination.
before the call is automatically disconnected. The default is 300 milliseconds. A
higher value means voice transmission is more accepting of jitter. A lower value is
less tolerant of jitter.
Inactive by default. When active, default = 300 ms. However, value must equal or
exceed Dynamic Minimum Jitter Value.
connected before the call is automatically disconnected.
Inactive by default.
When active, default = 180 sec.
This may be too short for some configurations, requiring upward adjustment.
1-65535 Consecutive Packets Lost defines the number of consecutive packets that are lost
after which the call is automatically disconnected.
Inactive by default.
When active, default = 30
Specifies how long to wait before disconnecting the call when IP network connectivity
Default =
30 sec.
with the remote site has been lost.
Configurable Payload Type
(Not available on the –SS series)
The Configurable Payload Type is located on the bottom of the Voice/Fax screen. The Configurable Payload Type
is used when the remote side uses a different payload type for the associated features. In previous firmware
versions, MultiVOIP’s used 101 for DTMF RFC2833. If the remote side uses some other dynamic payload type
such as 110, it fails. To avoid these failures, the payload types are configurable.
DTMF RFC2833 Configurable Payload Type is supported only for SIP & SPP and not for H.323.
44 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 45

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
When interoperating with older MultiVOIP products (i.e., earlier than release x.11), for backward compatibility,
configure the payload type values to default ones, which match the values of older MultiVOIP’s.
Configuring Interface Parameters
The Telephony Interface parameters are set individually for each channel and include the line types as well as
some specific situational settings for those that need them. The kinds of parameters for which values must be
chosen depend on the type of telephony supervisory signaling or interface used (FXO, E&M, etc.). Here you find
the various parameters grouped and organized by interface type. Note that the SS and FX models only support
FXS/FXO. In each field, enter the values that fit your particular setup. Once you have established a set of
Interface parameters for a particular channel, you can apply this entire set of Voice/FAX parameters to another
channel by using the Copy Channel button and its dialog box. To copy a set of Interface parameters to all
channels, select “Copy to All” and click Copy. The screen below shows more options available than are actually
used for clarity. Your settings determine what fields are available. The –SS series of MultiVOIPs do not support
Caller ID Manipulation.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 45
Page 46

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuring FXS Loop Start Parameters
The figure and table that follow describe the parameters applicable to FXS Loop Start.
FXS Loop Start Interface: Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Dialing Options fields
FXS (Loop Start) Y/N Enables FXS Loop Start interface type.
Inter Digit Timer 1 - 10 seconds This is the length of time that the MultiVOIP waits between digits. When the
time expires, the MultiVOIP looks in the outbound phonebook for the number
entered and place the call accordingly.
Default = 2.
Message Waiting Indication -- Not applicable to –SS series MultiVOIPs.
Inter Digit Regeneration
Time
FXS Options fields
FXS Ring Count, FXS 1-10 Maximum number of rings that the MultiVOIP issues before giving up the
Current Loss Y/N When enabled, the MultiVOIP interrupts loop current in the FXS circuit to
Generate Current Reversal Y/N When selected, this option implements Answer Supervision and Disconnect
Table is continued on next page…
in milliseconds
The length of time between the outputting of DTMF digits.
Default = 100 ms.
attempted call.
initiate a disconnection. This tells the device connected to the FXS port to hang
up. The Multi-VOIP cannot drop the call; the FXS device must go on hook.
Supervision to the FXO interface using current reversal to indicate events.
Applicable only when FXS and FXO interfaces are connected back to back.
46 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 47

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
FXS Loop Start Interface: Parameter Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
Flash Hook Options fields
Generation -- Not applicable to FXS interface
Detection Range for Min. and Max.,
50 - 1500
milliseconds
Pass Through Enable Y/N When enabled, this parameter creates an open audio path through the
Caller ID fields
Type Bellcore The MultiVOIP currently supports only one implementation of Caller ID. That
Enable Y/N Caller ID information is a description of the remote calling party received by
CID Manipulation Enabled by default
with Caller ID
enable above
Disable
For a received flash hook to be regarded as such by the MultiVOIP, its
duration must fall between the minimum and maximum values given here
MultiVOIP.
If the Pass-Through feature is enabled, the AutoCall feature must be enabled
for this VOIP channel in the Voice/Fax Parameters screen
implementation is Bellcore type 1 with Caller ID placed between the first and
second rings of the call.
the called party. The description has three parts: name of caller, phone
number of caller, and time of call. The ‘time-of-call’ portion is always
generated by the receiving MultiVOIP unit (on FXS channel) based on its date
and time setup.
The forms of the ‘Caller Name’ and ‘Caller Phone Number’ differ depending
on the IP transmission protocol used (H.323, SIP, or SPP) and upon entries in
the phonebook screens of the remote (CID generating) VOIP unit. The CID
Name and Number appearing on the phone at the terminating FXS end
comes either from a central office switch (showing a PSTN phone number),
or the phonebook of the remote (CID sending) VOIP unit.
This is not implemented in the –SS series VOIPs.
Caller ID Manipulation is used whenever the user wants to manipulate the
Caller ID before sending it to the remote end. Caller ID Manipulation is
activated on the Interface Screen. By enabling Caller ID option, you can set
manipulation to Transparent, User CID, Prefix, Suffix, or Prefix and Suffix.
Caller ID Manipulation is a feature, where the Caller ID detected from the
PSTN line can be changed and then sent to the remote side over IP.
CID Mode Transparent,
User CID,
Prefix,
Suffix
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 47
The MultiVOIP is not allowed to modify the caller ID info and then send it
to the PSTN side. It only allows it to detect the caller ID from the PSTN line,
modify it and then send them via IP to the remote end point.
Transparent
manipulation.
User CID
Prefix
Suffix
: the CID received from PSTN is sent out as such, without any
: the CID received from PSTN is replaced by this User CID value.
: the CID received from PSTN is prefixed with this value.
: the CID received from PSTN is suffixed with this value.
Page 48

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuring Message Waiting
The Message Waiting Indication feature provides an audible or visible indication that a message is available. A
type of message waiting is sounding a special dial tone (called stutter dial tone), lighting a light, or indicator on
the phone.
When a user enables a subscription for message waiting indication, a subscription is made with the Voice Mail
Server (VMS) for that particular event. When the Voice Mail Server finds a change in the state of a
corresponding mailbox or some event happens (e.g., when a new voice message is recorded or a message is
deleted, then the VMS server sends a notification to the gateway. Its indication to the user is a flashing LED or
sounding a stutter dial tone.
The message waiting feature is active when:
● You enable the Use SIP Proxy option on the Call Signaling SIP screen.
● You enter a Primary Proxy IP address in the SIP Proxy Parameters Primary Proxy field.
● You enter the Voice Mail Server Domain Name or IP Address in the SIP Voice Mail Server Parameters Group.
● You set the Interface Type to FXS (Loop start).
Then, the FXS Options Group becomes active. The Message Waiting Indication options are None, Light, or
Stutter Dial Tone.
To receive messages from the VMS (Voice Mail Server/System):
● The subscription is enabled.
● You must enter the voice mail server address in the SIP Voice Mail Server Parameters Group.
You configure the Voice Mail server IP Address, Port and Re-subscription time on the SIP Call Signaling screen.
When configured, the “Subscribe with Voice Mail Server” option is activated in the inbound phone book. Only
when this option is enabled, the subscribe message is sent to the VMS.
To enable the Message Waiting features, all of the following must occur:
1. The "Use SIP Proxy" must be enabled, and the SIP Proxy Parameters and Voice Mail Server Parameters in the
SIP Call Signaling Menu must be set, and the Interface Type option must be set to FXS (Loop Start) on the
Interface menu's "Message Waiting Indication" options become active.
2. Then the "Message Waiting Indication" options must be set to light or stutter tone for the "Subscribe to
Voice Mail Server" option to become available in the Inbound phone book entry with that channel selected.
3. To send Subscriptions for Inbound Phone Book entries, all the following four conditions have to be satisfied:
● You enter a valid voice mail server domain name or IP address in the Voice Mail Server Domain Name/IP
Address field on the Call Signaling screen.
● For an Inbound Phone Book entry, a subscription with Voice Mail Server checkbox is enabled on the Add
or Edit Inbound Phone Book entries screen.
48 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 49

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
● The Channel type corresponding to that Inbound phone book entry has to be FXS on the Interface
screen.
● The Message Waiting Indication has to be either Light or Stutter Dial Tone on the Interface Parameters
screen.
The password on the Interface screen is used for that particular channel when a “SUBSCRIBE” request is sent;
that is, if the MultiVOIP gets a 401/407 response from a subscribe request. It then uses the configured
password, calculates the response, and resends the “SUBSCRIBE” request.
FXO Parameters
The parameters that apply to the FXO telephony interface type are shown in the figure and described in the
table that follows.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 49
Page 50

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Field Name Values Description
Interface Type FXO Enables FXO functionality
Dialing Options
Regeneration Pulse, DTMF Determines whether digits generated and sent out are pulse tones or DTMF.
Inter Digit Timer 1 to 10 seconds This is the length of time that the MultiVOIP waits between digits. When the
Message Waiting
Indication
Inter Digit
Regeneration Time
FXO Options
FXO Ring Count 1-99 Number of rings required before the MultiVOIP answers the incoming call.
50 to 20,000
milliseconds
FXO Interface: Parameter Definitions
time expires, the MultiVOIP looks in the phonebook for the number entered.
Default = 2.
-- Not applicable to FXO interface
The length of time between the outputting of DTMF digits.
Default = 100 ms.
No Response Timer 1 – 65535
(in seconds)
Flash Hook Options fields
Generation 50 - 1500
milliseconds
Detection Range -- Not applicable to FXO.
Caller ID fields
Caller ID Type Bellcore The MultiVOIP currently supports only one implementation of Caller ID. That
Caller ID enable Y/N Caller ID information is a description of the remote calling party received by
CID Manipulation Enabled by default
with Caller ID
enable above
Disable
Length of time before call connection attempt is abandoned.
Length of flash hook that is generated and sent out when the remote end
initiates a flash hook and it is regenerated locally. Default = 600 ms.
implementation is Bellcore type 1 with caller ID placed between the first and
second rings of the call.
the called party. The description has three parts: name of caller, phone
number of caller, and time of call. The ‘time-of-call’ portion is always
generated by the receiving MultiVOIP unit (on FXS channel) based on its date
and time setup. The forms of the ‘Caller Name’ and ‘Caller Phone Number’
differ depending on the IP transmission protocol used (H.323, SIP, or SPP)
and upon entries in the phonebook screens of the remote (CID generating)
VOIP unit. The CID Name and Number appearing on the phone at the
terminating FXS end comes either from a central office switch (showing a
PSTN phone number), or the phonebook of the remote (CID sending) VOIP
unit.
This is not implemented in the –SS series VOIPs.
Caller ID Manipulation is used whenever the user wants to manipulate the
Caller ID before sending it to the remote end. Caller ID Manipulation is
activated on the Interface Screen. By enabling Caller ID option, you can set
manipulation to Transparent, User CID, Prefix, Suffix, or Prefix and Suffix.
Caller ID Manipulation is a feature, where the Caller ID detected from the
PSTN line can be changed and then sent to the remote side over IP.
CID Mode Transparent,
User CID,
Prefix,
Suffix
50 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
The MultiVOIP is not allowed to modify the caller ID info and then send it
to the PSTN side. It only allows it to detect the caller ID from the PSTN line,
modify it and then send them via IP to the remote end point.
Transparent
manipulation.
User CID
Prefix:
Suffix
: the CID received from PSTN is sent out as such, without any
: the CID received from PSTN is replaced by this User CID value.
the CID received from PSTN is prefixed with this value.
: the CID received from PSTN is suffixed with this value.
Page 51

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
FXO Supervision
When the selected Interface type is FXO, the Supervision button is active. Click Supervision to access call
answering supervision parameters and call disconnection parameters that relate to the FXO interface type.
The table that follows describes the settings for FXO Supervision.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 51
Page 52

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Field Name Values Description
Answer Supervision fields
Current Reversal Y/N When this option is selected, the FXO interface sends notice to make
Answer Delay Y/N When this option is selected, the FXO interface sends the connection notice
Answer Delay
Timer
Tone Detection Y/N When selected, call disconnection is triggered by a tone sequence
1 – 65535
(in seconds)
FXO Supervision Parameter Definitions
connection upon detecting current reversal from the PBX (which occurs
when the called extension goes off hook).
to the calling party only when the Answer Delay Timer expires. The
connection notice is sent regardless of whether or not the called extension
has gone off hook.
When Answer Delay is enabled, this value determines when the FXO
interface sends the connection notice.
Available Tones dial tone,
ring tone,
busy tone,
unobtainable tone
(fast busy),
survivability tone,
re-order tone
Answer Tones any tone from
Available Tones list
Disconnect Supervision fields There are four possible criteria for disconnection under FXO: current
Current Reversal Y/N Disconnection to be triggered by reversal of current from the PBX.
Current Loss Y/N Disconnection to be triggered by loss of current. That is, when Current Loss
Current Loss Timer 200 to 2000
(in milliseconds)
Silence Detection
Enable
Silence Detection
Type
Silence Timer in
seconds
Table is continued on next page…
Y/N Enables/disables silence-detection method of supervising call disconnection.
One-Way or
Two-Way
integer value Duration of silence required to trigger disconnection.
List from which tones can be chosen to signal call answer.
Currently chosen call-answer supervision tone.
reversal, current loss, tone detection, and silence detection. Disconnection
can be triggered by more than one of the three criteria.
is enabled (“Y”), the MultiVOIP hangs up the call at a specified interval after
it detects a loss of current initiated by the attached device.
Determines the interval after detection of current loss at which the call is
disconnected.
Disconnection to be triggered by silence in one direction only or in both
directions simultaneously
52 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 53

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
FXO Supervision Parameter Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
Disconnect Supervision fields
DTMF Tone Enables supervision of call disconnection using DTMF tones.
DTMF Tone Pairs
Low Tones
1 2 3 A 697Hz
4 5 6 B 770Hz
7 8 9 C 852Hz
* 0 # D 941Hz
High Tones
1209Hz 1336Hz 1447Hz 1633Hz
Disconnect Tone
Sequence
1st tone pair
+
nd
tone pair
2
These are DTMF tone pairs.
Values for first tone pair are: *, #, 0, 1-9, and A-D.
Values for second tone pair are: none, 0, 1-9, A-D, *, and #.
The tone pairs 1-9, 0, *, and # are the standard DTMF pairs found on phone
sets. The tone pairs A-D are “extended DTMF” tones, which are used for
various PBX functions.
Tone Detection Y/N Enables supervision of call disconnection by detecting cessation of a pre-
specified tone from the PBX.
Available Tones dial tone,
List from which tones can be chosen to signal call disconnection.
ring tone,
busy tone,
unobtainable tone (fast
busy),
survivability tone,
re-order tone
Disconnect
Tones
any tone from Available
Tones list
Currently chosen disconnection supervision tone.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 53
Page 54

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
E&M Parameters
The parameters applicable to the E&M telephony interface type are shown in the figure and described in the
table that follows.
Analog MVP210/410/810 models support the E&M interface. -SS and -FX models do not.
54 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 55

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
E&M Interface Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Interface E&M Enables E&M functionality
Type I – V Type of E&M interface being used – the individual types are detailed below.
Default = Type II.
Mode 2-wire or 4-wire Each E&M interface type can be either 2-wire or 4-wire audio.
Signal Dial Tone or
Wink
Wink Timer 100 - 350
milliseconds
No Response Timer 1 – 65535
(in seconds)
Disconnect on Call
Progress Tone
Pass Through Enable Y/N When enabled (“Y”), this feature is used to create an open audio path for 2-
Dialing Options
Inter Digit Timer 1 - 10 seconds This is the length of time that the MultiVOIP waits between digits. When the
Message Waiting
Indication
Y/N Allows call on FXO port to be disconnected when a PBX issues a call-progress
Light or None Allows MultiVOIP to pass mode-code sequences between Avaya Magix PBXs
When Dial Tone is selected, no wink is required on the E lead or M lead in
the call initiation or setup.
When Wink is selected, a wink is required during call setup.
This is the length of the wink for wink signaling. Applicable only when Signal
parameter is set to “Wink.”
The value here denotes the time (in seconds) after which the call attempt
would be disconnected by the FXO Interface because there was no answer.
tone denoting that the phone station on the PBX that has been involved in
the call has been hung up
or 4-wire. The E&M leads are passed through the VOIP transparently.
Applicable only for E&M Signaling with Dial Tone (not applicable for Wink
signaling).
time expires, the MultiVOIP looks in the phonebook for the number entered.
Default = 2.
to turn on and off the message-waiting light on a PBX extension phone.
Mode codes:
*53 + PBX extension
Î turns message light on.
#53 + PBX extension
Î turns message light off.
Signals to turn message-waiting lights on/off are not sent to phones
connected directly to the MultiVOIP on FXS channels, not to other nonAvaya Magix PBX phone stations on the VOIP network
Inter Digit
Regeneration Timer
Flash Hook Options fields
Generation 50 - 1500
Detection Range for Min. and Max.,
50 – 20000
milliseconds
milliseconds
50 - 1500
milliseconds
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 55
The length of time between the outputting of DTMF digits.
Default = 100 ms.
Length of flash hook that is generated and sent out when the remote end
initiates a flash hook and it is regenerated locally. Default = 600 ms.
For a received flash hook to be regarded as such by the MultiVOIP, its
duration must fall between the minimum and maximum values given here.
Page 56

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
E&M Interface Types
There are five different types of the E&M interface and the MVP210/410/810 models support them all; but Type
IV is largely unused and is not described in this section. The figures that follow show the pin assignments for the
MVP RJ48 connector when used in the E&M jacks on the back of the unit as well as how the signals are used for
types one, two, three and five. Common ground between the MultiVOIP and PBX is required for all E&M Types
except Type II. Two and four wire audio is available for all E&M types
The illustration that follows shows MultiVOIP E&M Pin assignments and RJ48 Jack.
The illustration that follows shows E&M line types.
The illustration that follows shows audio wiring.
56 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 57

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
DID Parameters
The parameters applicable to the Direct Inward Dial (DID) telephony interface type are shown in the figure that
follows and described in the table that follows. The –SS and –FX models do not support DID.
The DID interface allows one phone line to direct incoming calls to any one of several extensions without a
switchboard operator. Of course, one DID line can handle only one call at a time. The parameters apply to the
customer-premises side of the DID connection (DID-DPO, dial-pulse originating). The network side of the DID
connection (DID-DPT, dial-pulse terminating) is not supported.
DID Interface Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Interface DID-DPO Enables the customer-premises side of DID functionality
DID Options MultiVOIP’s use of DID applies only for incoming DID calls. The Start Mode
used by the MultiVOIP must match that used by the originating telephony
equipment; else DID calls cannot be completed.
Start Modes Immediate Start,
Wink Start,
Delay Dial
Wink Timer
(in ms)
Dialing Options
Inter Digit Timer Integer values,
Message Waiting
Indication
Inter-Digit
Regeneration Timer
Integer values,
in milliseconds
in seconds
-- Not applicable to DID-DPO interface.
Integer values,
in milliseconds
For Immediate Start, the VOIP detects the off-hook condition initiated by
the telco central-office call and becomes ready to receive dial digits
immediately.
For Wink Start, the VOIP detects the off-hook condition. Then the VOIP
reverses battery polarity for a specified time (140-290 ms; a “wink”) and
then becomes ready to receive dial digits.
For Delay Dial, the VOIP detects the off-hook condition. Then the VOIP
reverses battery polarity for a specified time (reverse polarity duration has
wider acceptable range than for Wink Start) and then becomes ready to
receive dial digits.
This is the length of the wink for Wink Start and Delay Dial signaling modes.
Applicable only when Start Mode parameter is set to “Wink Start” or “Delay
Dial.”
This is the length of time that the MultiVOIP waits between digits. When the
time expires, the MultiVOIP looks in the phonebook for the number entered.
Default = 2.
This parameter is applicable when digits are dialed onto a DID-DPO channel
after the connection has been made. The length of time between the
outputting of DTMF digits.
Default = 100 ms.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 57
Page 58

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Call Signaling
Three types of Call Signaling are available: H.323, SIP and SPP. Each type has features that may make it more
appealing to use than the others, depending on your needs. The –SS and –FX models do not support H.323
signaling.
H.323
H.323 is an ITU-T recommended set of standards for audio and video communications. The fields for this screen
are defined in the table below.
58 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 59

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
H.323 Call Signaling Parameter Definitions.
Field Name Values Description
Use Fast Start Y/N Enables the H.323 Fast Start procedure. May need to be enabled/disabled for
compatibility with third-party VOIP gateways.
Signaling Port port Default: 1720 (H.323)
Register with Gatekeeper Y/N Check this field to have traffic on current VOIP gateway controlled by a gatekeeper.
Allow Incoming Calls
Through Gatekeeper Only
GateKeeper RAS Parameters
Primary GK -- This is the preferred gatekeeper for controlling the traffic of the current VOIP.
Y/N When selected, incoming calls are accepted only if those calls come through the
gatekeeper.
Alternate GK
1 and 2
IP Address n.n.n.n IP address of the GateKeeper.
RAS Port 1719 Well-known port number for GateKeepers. Must match port number (1719).
Gatekeeper Name alpha-
RAS TTL Value seconds The H.323 Gatekeeper “Time to Live” value. As soon as a MultiVOIP gateway registers
Gatekeeper Discovery
Polling Interval
Use Online Alternate
Gatekeeper List
H.323 Version 4 Options
H.323 Multiplexing Y/N Signaling for multiple phone calls can be carried on a single port rather than opening a
H.245 Tunneling (Tun) Y/N H.245 messages are encapsulated within the Q.931 call-signaling channel. Among other
Parallel H.245
(FS + Tun)
-- A first and a second alternate gatekeeper can be specified for use by the current VOIP for
situations where the Primary GK is busy or otherwise unavailable.
Optional. The name of the GateKeeper with which this MultiVOIP is trying to register. A
numeric
integer
60 - 300
When selected, VOIP seeks an alternate gatekeeper (when none of the 3 gatekeepers shown on this
screen are available) from a list. The list resides on the Primary gatekeeper or one of the Alternate
gatekeepers. The gatekeeper holding the list would download that list onto the VOIP gateways within
the system.
Y/N FS (Fast Start) is a Q.931 feature of H.323v2 to hasten call setup as well as ‘pre-opening’
primary gatekeeper and two alternate units are listed.
with a gatekeeper a countdown timer begins. The RAS TTL Value is the interval of the
countdown timer. Before the TTL countdown expires, the MultiVOIP gateway needs to
register with the gatekeeper in order to maintain the connection. If the MultiVOIP does
not register before the TTL interval expires, the MultiVOIP gateway’s registration with
the gatekeeper expires and the gatekeeper no longer permits call traffic to or from that
gateway. Calls in progress continue to function even if the gateway becomes deregistered
The interval between the VOIP gateway’s successive attempts to connect to and be
governed by a higher level gatekeeper. The Primary GK is the highest level gatekeeper.
Alternate GK1 is second; Alternate GK2 is the lowest.
separate signaling port for each. This conserves bandwidth resources.
things, the H.245 messages let the two endpoints tell each other what their technical
capabilities are and determine who, during the call, is the client and who is the server.
Tunneling is the process of transmitting these H.245 messages through the Q.931
channel. The same TCP/IP socket (or logical port) already being used for the Call Signaling
Channel is then also used by the H.245 Control Channel. This encapsulation reduces the
number of logical ports (sockets) needed and reduces call setup time.
the media channel before the CONNECT message is sent. This pre-opening is a
requirement for certain billing activities. Under Parallel H.245 FS + Tun, this Fast Connect
feature can operate simultaneously with H.245 Tunneling.
Annex –E (AE) Y/N Multiplexed UDP call signaling transport. Annex E is helpful for high-volume VOIP system
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 59
endpoints. Gateways with lesser volume can afford to use TCP to establish calls.
However, for larger volume endpoints, the call setup times and system resource usage
under TCP can become problematic. Annex E allows endpoints to perform call-signaling
functions under the UDP protocol, which involves substantially streamlined overhead
(this feature should not be used on the public Internet due to potential problems with
security and bandwidth usage).
Page 60

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol is available for application layer control of the MultiVOIP. The fields are detailed in
the table that follows.
60 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 61

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
SIP Call Signaling Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
SIP Proxy Parameters
Signaling Port port Port number on which the MultiVOIP UserAgent software module is waiting for any
incoming SIP requests. Default = 5060
Use SIP Proxy Y/N Allows the MultiVOIP to work in conjunction with a proxy server.
Allow Incoming Calls
Through SIP Proxy Only
Primary Proxy -- This is the preferred SIP proxy server for controlling the traffic of the current VOIP.
Alternate Proxy 1 and 2 -- A first and a second alternate SIP proxy server can be specified for use by the VOIP for
Y/N When selected, incoming calls are accepted only if those calls come through the proxy.
situations where the Primary proxy server is otherwise unavailable.
Proxy Domain Name / IP
Address
Append SIP Proxy Domain
Name in User ID
Port Number port Logical port number for proxy communications. Default = 5060
Default Subscriber This is not implemented in the –SS series VOIPs.
Default Username name If the Username is not populated in the Phone Book, this is the Username that is used.
Password password Password for proxy server function. See “Default Username” description above.
Re-Registration Time 10–65535
Proxy Polling Interval 60 - 300 The interval between the VOIP gateway’s successive attempts to connect to and be
TTL Value SIP proxy
n.n.n.n Network address of the proxy server that the VOIP is using.
Y/N When checked, the domain name of the SIP Proxy serving the MultiVOIP gateway is
included as part of the User ID for that gateway. If unchecked, the SIP Proxy’s IP address is
included as part of the User ID instead of the SIP Proxy’s domain name.
This is used as the default end point register with a Proxy.
This works the same for the password as well.
This is the timeout interval for registration of the MultiVOIP with a SIP proxy server. The
seconds
“Time to
Live”
value.
(in
seconds)
time interval begins the moment the MultiVOIP gateway registers with the SIP proxy
server and ends at the time specified by the user in the Re-Registration Time field (this
field). When/if registration lapses, call traffic routed to/from the MultiVOIP through the
SIP proxy server ceases. However, calls in progress continue to function until they end.
governed by a higher level SIP proxy server. The Primary Proxy is the highest level
gatekeeper. Alternate Proxy 1 is second; Alternate Proxy 2 is the lowest order SIP proxy
server.
As soon as a MultiVOIP gateway registers with a SIP proxy server (allowing the proxy
server to control its call traffic) a countdown timer begins. The TTL Value is the interval of
the countdown timer. Before the TTL countdown expires, the MultiVOIP gateway needs to
register with the gatekeeper in order to maintain the connection. If the MultiVOIP does
not register before the TTL interval expires, the MultiVOIP gateway’s registration with the
proxy server expire and the proxy server no longer permits call traffic to or from that
gateway. Calls in progress continue to function even if the gateway becomes deregistered.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 61
Page 62

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuring SIP Server
The MultiVOIP 210/410/810-SS models have the additional capability of SIP survivability. This section describes
the settings for SIP server mode.
SIP Server Configuration Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Operating Mode Survivability
-orstand-alone
Survivability Status
Check
Registrar Options
Allow Undefined
Registrations
Accept Registrations
for:
Domain Names name Endpoints (separated by semicolon) from which the MVP-SS accepts registrations.
Accept Registrations
for:
IP Addresses n.n.n.n List of IP addresses (separated by semicolon) of endpoints from which the MVP-SS accepts
Re-Registration
Time
Register,
Options
Y/N If undefined registrations are allowed, then gateways other than those listed in the
any/specific
domains
n.n.n.n
-orany IP
addresses
in seconds;
(default is
3600)
In “Survivability” mode, the MVP-SS unit can function as a SIP server for other gateways in its
network in case that network loses contact with the network’s main SIP server (typically a
PBX). When in “Survivability” mode the unit is a backup SIP server.
In “Stand-Alone” mode, the MVP-SS functions as a primary SIP server for other gateways. In
this mode, the MVP-SS operate to technical advantage with ‘smart’ SIP phones. Such smart SIP
phones can choose the SIP server under which they operate and, consequently, can be
controlled by either the SIP-based PBX or by the MVP-SS
One of two status-check packets is sent to the main SIP Proxy servers to which the MVP-SS
serves as a backup. This packet determines if the MVP-SS takes over SIP server functions or
stays in normal backup mode. “Options” and “Register” are two SIP request “methods.” The
Options method solicits information but does not set up a connection. The Register method
conveys information about a user’s location to the SIP server. The “Register” method may
entail more data overhead than the “Options” method. If your SIP server supports these
methods, you can use either one. If only one is supported, use the supported method.
Predefined Endpoints list can register with the MVP-SS unit as it functions in its SIP server
mode. If undefined registrations are not allowed, then incoming registrations are allowed if
they originate from endpoints at accepted domains or IP addresses.
Defines if registrations to the MVP-SS SIP server are accepted from any domain or only from
specified domains. Multiple domains can be listed, separated by semicolons. The “any
domains” option is intended for private networks not accessible via Internet.
Determines if registrations to the MVP-SS SIP server are accepted from any IP address or only
from specified IP addresses. Multiple IP addresses can be listed (separated by semicolon). The
“any IP addresses” option is intended for private networks not accessible via Internet or PSTN.
registrations.
The time after which the UserAgent Client registers with the proxy server. Expired registration
indicates the gateway lost contact with the main SIP server and that the MVP-SS unit enters
‘survivability’ mode. In this mode, the MVP-SS unit completes calls acting as a backup to the
main SIP server. Normally, the MVP-SS initiates re-registration before the interval lapses.
62 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 63

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
SIP Server: Predefined Endpoint Parameters.
Use the SIP Server Endpoints screen to specify the VOIP gateways that depend on the MVP-SS unit:
● As their primary SIP server (if the MVP-SS is used in “Stand-Alone” mode, as set in the SIP Server |
Configuration screen) or
● As their backup SIP server (if the MVP-SS is used in “Survivability” mode, as set in the SIP Server
|Configuration screen).
The main screen for Predefined Endpoints is a list. If you click Add or Edit for entries in this list, a secondary
screen appears where you can add new endpoints or edit existing ones.
When your work with the list is complete, click Save.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 63
Page 64

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
SIP Server Predefined Endpoints Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Endpoint Name name Identifier for gateway within SIP VOIP system. Maximum length is 33 characters.
Password password This password is for authentication of gateway to SIP server.
Registration Type Static,
Dynamic
Re-Registration
Interval
Contact Information
Address n.n.n.n The IP address at which this endpoint can be reached.
Port 0 – 64000 Digital time slot on which SIP calls are made. Default is 5060
Re-Registration Time See “Re-Registration Interval” entry above.
integer
values; in
seconds;
default is
3600
Static registrations are fixed and the contact information for them is configured by the
user and not subject to removal from the registration list due to timeouts.
Dynamic registrations are registered from an external endpoint with the contact
information. Dynamic entries must re-register before the re-registration interval expires
else they are removed from the list. Endpoints removed from this list can neither make
nor receive calls.
The time after which the MultiVOIP UserAgent Client is supposed to register with the
proxy server.
Expiration of the registration interval means that the gateway has lost contact with the
main SIP server and that the MVP-SS unit enters its ‘survivability’ mode. In survivability
mode, the MVP-SS unit completes calls acting as a backup to the main SIP server.
Normally, however, the MVP-SS initiates re-registration with some small margin of time
before the interval lapses.
64 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 65

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
SPP
Multi-Tech developed Single Port Protocol for dynamic IP addressing when the feature is set to Registrar/Client
mode. The other setting, Direct mode, has IP addresses assigned to the gateways. The table below describes
fields in the general SPP Call Signaling screen. The –SS models do not support SPP.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 65
Page 66

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Field Name Values Description
Mode Direct,
Client, or
Registrar
General Options
Port port The UDP port on which data transmission occurs. Each client VOIP has its own port. If two
Re-transmission 50 - 5000ms If packets are lost (as indicated by absence of an acknowledgment) then the endpoint
SPP Call Signaling Parameter Definitions
In direct mode, all VOIP gateways have static IP addresses assigned to them.
In registrar/client mode, one VOIP gateway serves as registrar and all other gateways,
being its clients, point to that registrar. The registrar assigns IP addresses dynamically.
client VOIPs are both behind the same firewall, then they must have different ports
assigned to them.
If there are two clients and each is behind a different firewall, then the clients could have
different port numbers or the same port number.
(Default port number = 10000.)
retransmits the lost packets after this designated time duration has elapsed. (Default
value = 2000 milliseconds.)
Max Retransmission
Client Options Client Option fields are active only in registrar/client mode and only for client VOIP units.
Primary Registrar -- This is the preferred SPP registrar gateway for controlling the traffic of the current VOIP.
Alternate Registrar
1 and 2
Registrar IP
Address
Registrar Port 10000 or
Polling Interval integer
Registrar Options
Keep Alive 30 – 300
Proxy/NAT Device Parameters
0 - 20 Number of times the VOIP re-transmits a lost packet (if no acknowledgment has been
received). (Default value = 3)
-- A first and a second alternate SPP Registrar gateway can be specified for use by the
current VOIP for situations where the Primary Registrar gateway is busy or otherwise
unavailable.
n.n.n.n This is the IP address of the registrar VOIP to which this client is assigned. (Default value
= 0.0.0.0; effectively, there is no useful default value.)
This is the port number of the registrar VOIP to which this client is assigned. (Default port
other
60 - 300
(seconds)
number = 10000.)
The interval between the VOIP gateway’s successive attempts to connect to and be
governed by a higher level SPP registrar gateway. The Primary Registrar is the highest
level registrar gateway. Alternate Registrar 1 is second; Alternate Registrar 2 is the
lowest order SPP registrar gateway.
Registrar Option fields are active only in registrar/client mode and only for registrar VOIP
units.
Time-out duration before a registrar un-registers a client that does not send its “I’m
here” signal. Client normally sends its “I’m here” signal every 20 seconds. Timeout
default = 60 seconds.
Behind Proxy/NAT
device
Proxy/NAT Device
Parameters –
Public IP Address
Y/N Enables MultiVOIP (running in SPP Registrar mode) to operate ‘behind’ a proxy/NAT
n.n.n.n The public IP address of the proxy/NAT device which the MultiVOIP is behind.
66 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
device (NAT = Network Address Translation).
Page 67

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuring SNMP
If you want to manage your MultiVOIP remotely using the MultiVoipManager software, set the Simple Network
Management Protocol parameters. To make the MultiVOIP controllable by a remote PC running the
MultiVoipManager software, check the Enable SNMP Agent checkbox on the SNMP Parameters screen.
The –SS and –FX series MultiVOIPs have limited SNMP functionality available. If this is something you want to
use on those models, contact Multi-Tech support for assistance.
The table that follows describes the SNMP Parameter fields.
SNMP Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Enable SNMP Agent Y/N Enables the SNMP code in the firmware of the MultiVOIP. This must be
enabled for the MultiVOIP to communicate with and be controllable by the
MultiVoipManager software.
Default: disabled
Trap Manager Parameters
Address n.n.n.n IP address of MultiVoipManager PC.
Community
Name
Port Number 162 The default port number of the SNMP manager receiving the traps is the
Community
Name 1
Permissions Read-Only,
-- A “community” is a group of VOIP endpoints that can communicate with each
other. Often “public” is used to designate a grouping where all end users have
access to entire VOIP network. However, calling permissions can be
configured to restrict access as needed.
standard port 162.
Length = 19 characters (max.)
Case sensitive.
Read/Write
First community grouping.
If this community needs to change MultiVOIP settings, select Read/Write.
Otherwise, select Read-Only to view settings.
Community
Name 2
Permissions Read-Only,
Length = 19 characters (max.)
Case sensitive.
Read/Write
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 67
Second community grouping
If this community needs to change MultiVOIP settings, select Read/Write.
Otherwise, select Read-Only to view settings.
Page 68

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuring Regional Parameters
Use the Regional Parameters to set the phone signaling tones and cadences. For the country selected, the
standard set of frequency pairs is listed for dial tone, busy tone, ‘unobtainable’ tone (fast busy or trunk busy),
ring tone, and other, more specialized tones. If desired settings are not available, use the Custom selection to
set the tones as needed.
The table that follows describes the Regional Parameters fields.
68 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 69

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
“Regional Parameter” Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Country/Region
Advisory screen
Standard Tones fields
Type column
Frequency 1 freq. in Hertz Lower frequency of pair.
Frequency 2 freq. in Hertz Higher frequency of pair.
Gain 1
Gain 2
Cadence
(ms) On/Off
Custom (button) -- Click Custom to open the Custom Tone Pair Settings screen. (The “Custom”
Table is continued on next page…
USA,
Japan, UK,
Custom
dial tone,
ring tone,
busy tone,
unobtainable tone
(fast busy),
survivability tone,
re-order tone
gain in dB
+3dB to –31dB
and “mute” setting
gain in dB
+3dB to –31dB
and “mute” setting
n/n/n/n
four integer time
values in
milliseconds; zero
value for dial-tone
indicates continuous
tone
Name of a country or region that uses a certain set of tone pairs for dial tone, ring tone,
busy tone, unobtainable tone (fast busy tone), survivability tone (tone heard briefly, 2
seconds, after going off hook denoting survivable mode of VOIP unit), re-order tone (a tone
pattern indicating the need for the user to hang up the phone), and intercept tone (a tone
that warns an a party that has gone off hook but has not begun dialing, within a prescribed
time, that an automatic emergency or attendant number is called; the automatic call can be
used to direct an attendant’s attention to a disabled or distressed caller, allowing an
appropriate response to be made).
In some cases, the tone-pair scheme denoted by a country name may also be used outside
of that country. The “Custom” option (button) assures that any tone-pairing scheme
worldwide can be accommodated.
Note 1: Intercept tone is applicable only when the FXS telephony interface has been chosen
in the Interface screen and when the AutoCall / OffHook Alert field is set to OffHook Alert in
the Voice/Fax Parameters screen. The time allowed for dialing before the automatic calling
process begins is set in the OffHook Alert Timer field of the Voice/Fax Parameters screen.
Note 2:
to MultiVantage VOIP units only
“Survivability” tone indicates a special type of call-routing redundancy and applies
This message appears when the Country field is
changed. It informs the operator that, when the
Country field changes, user defined tones are deleted.
Type of telephony tone-pair for which frequency, gain, and cadence are being
presented.
Amplification factor of lower frequency of pair.
This applies to the dial, ring, busy and ‘unobtainable’ tones that the MultiVOIP
outputs as audio to the FXS, FXS, or E&M port.
Default: -16dB
Amplification factor of higher frequency of pair.
This applies to the dial, ring, busy, and ‘unobtainable’ (fast busy) tones that the
MultiVOIP outputs as audio to the FXS, FXO, or E&M port. Default: -16dB
On/off pattern of tone durations used to denote phone ringing, phone busy,
connection unobtainable (fast busy), dial tone (“0” indicates continuous tone),
survivability, and re-order. Default values differ for different countries/regions.
Although most cadences have only two parts (an “on” duration and an “off”
duration), some telephony cadences have four parts. Most cadences, then, are
expressed as two iterations of a two-part sequence. Although this is
redundant, it is necessary to allow for expression of 4-part cadences.
button is active only when “Custom” is selected in the Country/Region field.)
This screen lets you specify tone pair attributes that are not found in any of the
standard national/regional telephony toning schemes.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 69
Page 70

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
“Regional Parameter” Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
Country Selection for
Built-In Modem
(not applicable to
MVP210)
User Defined Tones fields
Type column alphanumeric
Frequency 1 Freq. in Hertz Lower frequency of pair.
Frequency 2 Freq. in Hertz Higher frequency of pair.
Gain 1
Gain 2
Cadence
(ms) On/Off
country name MultiVOIP units operating with the X.06 software release (and above) include a
built-in modem. The administrator can dial into this modem to configure the
MultiVOIP unit remotely. The country name values in this field set telephony
parameters that allow the modem to work in the listed country. This value may
be different than the Country/Region value. For example, a user may need to
choose “Europe” as the Country/Region value but “Denmark” as the CountrySelection-for-Built-In-Modem value.
Name of supervisory tone pair. Cannot be same as name of any standard tone
name
+3dB to –31dB
and “mute” setting
+3dB to –31dB
and “mute” setting
n/n/n/n
four integer time
values in
milliseconds; (zero
value indicates
continuous tone)
pair.
Amplification factor of lower frequency of pair.
This applies to any supervisory tones that the MultiVOIP outputs as audio to
the FXS, FXS, or E&M port. Default: “Mute”
Amplification factor of higher frequency of pair.
This applies to any supervisory tones that the MultiVOIP outputs as audio to
the FXS, FXO, or E&M port. Default: “Mute”
On/off pattern of tone durations used to denote supervisory tones specified by
user. Supervisory tones relate to answering and disconnection of calls.
Although most cadences have only two parts (an “on” duration and an “off”
duration), some telephony cadences have four parts. Most cadences, then, are
expressed as two iterations of a two-part sequence. Although this is redundant,
it is necessary to allow for expression of 4-part cadences.
70 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 71

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Setting Custom Tones and Cadences (optional). A secondary dialog box allows you to customize DTMF tone
pairs to create unique ring-tones, dial-tones, busy-tones or “unobtainable” tones or “re-order” tones or
“survivability” tones. This helps the user to specify tone-pair attributes that are not found in any of the standard
national/regional telephony toning schemes. To customize DTMF tone pairs, click Custom. The Custom button is
active only when Custom is selected in the Country/Region field.
Custom Tone-Pair Settings Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Tone Pair
Frequency 1 Frequency in Hertz Frequency of lower tone of pair.
Frequency 2 Frequency in Hertz Frequency of higher tone of pair.
Gain 1 +3dB to –31dB
Gain 2 +3dB to –31dB
Cadence 1 integer time value in
Cadence 2 duration in milliseconds Cadence 2 is duration of first “off” period in signaling cadence.
Cadence 3 duration in milliseconds Cadence 3 is duration of second “on” period in signaling cadence.
Cadence 4 duration in milliseconds Cadence 4 is duration of second “off” period in the signaling cadence.
dial tone, busy tone
ring tone, ‘unobtainable’ tone,
survivability tone,
re-order tone
Tone Pair Values About Defaults: US telephony values are used as defaults on this screen.
and “mute” setting
and “mute” setting
milliseconds; zero value for dialtone indicates continuous tone
Identifies the type of telephony signaling tone for which frequencies are being
specified.
This outbound tone pair enters the MultiVOIP at the input port.
This outbound tone pair enters the MultiVOIP at the input port.
Amplification factor of lower frequency of pair. This figure describes amplification
that the MultiVOIP applies to outbound tones entering the MultiVOIP at the input
port. Default: -16dB
Amplification factor of higher frequency of pair. This figure describes
amplification that the MultiVOIP applies to outbound tones entering the
MultiVOIP at the input port. Default: -16dB
On/off pattern of tone durations used to denote phone ringing, phone busy, dial
tone (“0” indicates continuous tone) survivability and re-order. Cadence 1 is
duration of first period of tone being “on” in the cadence of the telephony signal.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 71
Page 72

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Configuring SMTP Parameters
Setting the SMTP Parameters (Log Reports by Email). Use the SMTP Parameters screen for configuring how log
reports are handled by email.
Email Address for VOIP (for email call log reporting)
This is needed only if log reports of VOIP call traffic are sent by email.
● Ask Mail Server administrator to set up email account (with password) for the MultiVOIP unit.
● Supply a unique identifier to each MultiVOIP unit.
● Obtain the IP address of the mail server computer.
MultiVOIP as Email Sender. When SMTP is used, the MultiVOIP has an email account (with Login Name and
Password) on a mail server connected to the IP network.
Using this account, the MultiVOIP sends out email messages containing log report information. The “Recipient”
of the log report email is ordinarily the VOIP administrator.
Because the MultiVOIP cannot receive email, you must set up a “Reply-To” address. The “Reply-To” address
usually belongs to a technician with access to the mail server or MultiVOIP or both,
You can also set up the VOIP administrator the “Reply-To” party.
The main function of the Reply-To address is to receive error or failure messages regarding the emailed reports.
The figure that follows shows the SMTP Parameters window.
72 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 73

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
“SMTP Parameters” Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Enable SMTP Y/N To send log reports by email, enable this checkbox. To enable the SMTP feature,
you must also select “SMTP” in the Logs screen.
Requires
Authentication
Login Name alpha-numeric User Name for the MultiVOIP unit’s email account.
Password alpha-numeric Login password for MultiVOIP unit’s email account.
Mail Server IP
Address
Port Number 25 25 is a standard port number for SMTP.
Mail Type text or html The type of mail in which log reports are sent.
Subject text User specified. Subject line that appears for all emailed log reports for this
Reply-To Address email address User specified. This email address functions as a source email identifier for the
Recipient Address email address Email address where VOIP administrator receives log reports.
Mail Criteria
Number of Records integer This is the number of log records that must accumulate to trigger the sending of a
Y/N If checked, the MultiVOIP sends Authentication information to the SMTP server.
The authentication information indicates if the email sender has permission to use
the SMTP server.
n.n.n.n Mail server’s IP address. This mail server must be accessible on the IP network to
which the MultiVOIP is connected.
MultiVOIP unit.
MultiVOIP, which, of course, cannot usefully receive email messages. The Reply-To
address provides a destination for returned messages indicating the status of
messages sent by the MultiVOIP (esp. to indicate when log report email was
undeliverable or when an error has occurred).
Criteria for sending log summary by email. The log summary email is sent out
either when the user-specified number of log messages has accumulated, or once
every day or multiple days, whichever comes first.
log-summary email.
Number of Days integer This is the number of days that must pass before triggering the sending of a log-
summary email.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 73
Page 74

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Click Select Fields to open the SMTP Parameters dialog box. This secondary dialog box helps you customize
email logging. The MultiVOIP software logs data about aspects of the call traffic going through the MultiVOIP.
The Custom Fields screen lets you pick which items are included in the email log reports.
“Custom Fields” Definitions
Field Description Field Description
Select All Log report to
include all fields shown.
Start Date,
Time
Date and time the phone call began.
Channel
Number
Duration Length of call. Packets
Packets Sent Total packets sent in call. Bytes Received Total bytes received in call.
Bytes Sent Total bytes sent in call. Coder Voice Coder /Compression Rate used for
Packets Lost Packets lost in call. Prefix Matched When selected, the phonebook prefix
Outbound
Digits
Received
Call Status Successful or unsuccessful. DTMF
Call Direction Indicates call’s originating party.
Server Details The IP address of the traffic control server
Data channel carrying call. Call Mode Voice or fax.
Total packets received in call.
Received
call is listed in log.
matched in processing the call is listed in
log.
The DTMF dialing digits received by this
gateway from the remote gateway
presuming that DTMF is set to "Out of
Band."
(if any) being used (whether an H.323
gatekeeper, a SIP proxy, or an SPP registrar
gateway) is displayed here if the call is
handled through that server.
Call Type Indicates the Call Signaling protocol used
for the call (H.323, SIP, or SPP).
Indicates whether the DTMF dialing digits
Capability
are carried "Inband" or "Out of Band." The
corresponding field values differ for the 3
different VOIP protocols.
For H.323, this field can display "Out of
Band" or "Inband". For SIP it can display
either "Out of Band RFC2833" or "Out of
Band SIP INFO" to indicate the out-ofband condition or "Inband" to indicate the
in-band condition. For SPP it can display
"Out of Band RFC2833" or "Inband".
Disconnect
Reason
Gateway
Number
IP Address IP address where call originated. IP Address IP address where call was completed or
Descript Identifier of site where call originated. Descript Identifier of site where call was completed
Options When selected, log does not Silence
Indicates whether the call was
disconnected simply because the desired
conversation was done or some other
irregular cause occasioned disconnection
(e.g., a technical error or failure). Values are
"Normal" and "Local" disconnection.
From Details To Details
Originating gateway Gateway Name Completing or answering gateway
Compression and Forward Error Correction
by call originator.
Outbound
Digits Sent
Options When selected, log does not use Silence
The dialing digits sent by this gateway to
the remote gateway presuming that
DTMF is set to "Out of Band."
answered.
or answered.
Compression and Forward Error
Correction by party answering call.
74 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 75

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
RADIUS
In general, RADIUS is concerned with authentication, authorization, and accounting. The MultiVOIP supports the
accounting and authentication functions. The accounting function is well suited for billing of VOIP telephony
services. In the Select Attributes secondary screen (accessed by clicking on Select Attributes button), you can
select the parameters that the RADIUS server tallies.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 75
Page 76

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
The table that follows describes the fields of the RADIUS screen.
RADIUS Screen Field Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Enable Accounting Y/N When checked, the MultiVOIP accesses the accounting functions of the RADIUS
server.
Server Address n.n.n.n IP address of the RADIUS server that handles accounting (billing) for the current
MultiVOIP unit.
Accounting Port 1 - 65535 TDM time slot at which RADIUS accounting information is transmitted and received.
Retransmission
Interval
Number of
Retransmissions
Shared Secret alpha-numeric Client encryption key for the current VOIP unit.
Select Attributes
(button)
If the MultiVOIP sends out a packet to the RADIUS server and doesn't receive a
response in the retransmit interval, it retransmits that packet again and waits the
0 - 255
-- Gives access to RADIUS Attributes screen. On Attributes screen, one can specify the
retransmit interval again for a response. How many times it does this is determined
by the setting in the Number of Retransmissions field.
parameters to be tallied by the RADIUS server for accounting (usually billing)
purposes.
A secondary RADIUS dialog box, RADIUS Attributes, helps you customize accounting information that the
MultiVOIP sends to the RADIUS server. The MultiVOIP software logs data about many aspects of the call traffic
going through the MultiVOIP. The RADIUS Attributes screen lets you select the items to include in the
accounting reports sent to the RADIUS server.
“RADIUS Attributes” Definitions
Field Description Field Description
Select All Log report to include all fields
shown.
Channel
Number
Duration Length of call. Packets Received Total packets received in call.
Packets Sent Total packets sent in call. Bytes Received Total bytes received in call.
Bytes Sent Total bytes sent in call. Coder Voice Coder /Compression Rate used for call is
Packets Lost Packets lost in call. Prefix Matched When selected, the phonebook prefix matched
Outbound
Digits Sent
Server Details The IP address of the traffic control server being used is displayed here if the call is handled through that
Gateway
Number
Data channel carrying call. Call Mode Voice or fax.
DTMF digits received by this
gateway from remote gateway (if
that DTMF set to "Out of Band").
server. The Options field refers to non-mandatory server features that might be activated. For example, with
H.323, various H.323 Version 4 options might be listed.
From Details To Details
Originating gateway Gateway
Start Date, Time Date and time the phone call began.
listed in log.
in processing the call is listed in log.
Call Status Successful or unsuccessful.
Completing or answering gateway
Name
IP Address IP address where call originated. IP Address IP address where call was completed/answered.
Descript Identifier of where call originated. Descript Identifier of where call was completed/answered.
Options When selected, log does not use Silence
Compression and Forward Error
Correction by call originator.
76 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Options When selected, log does not use Silence Compression
and Forward Error Correction by party answering call.
Page 77

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Logs/Traces
The Logs/Traces window lets you choose how the VOIP administrator receives log reports about the MultiVOIP’s
performance and the phone call traffic that is passing through it. The VOIP administrator receives log reports in
one of three ways:
● In the MultiVOIP program (interface)
● Through email (SMTP)
● At the MultiVoipManager remote VOIP system management program (SNMP).
If you enable console messages, you can customize the messages included in and excluded from log reports. To
do so, click Filters and use the Console Messages Filter Settings screen.
If you use the logging function, select the logging option that applies to your VOIP system design.
To use a SysLog Server program for logging, in the SysLog Server group, check the Enable checkbox. The
common SysLog logical port number is 514.
If using the MultiVOIP web browser interface for configuration and control of MultiVOIP units, be aware that the
web browser interface does not support logs directly. However, when the web browser interface is used, log
files can still be e-mailed to the VOIP administrator. This requires using the SMTP logging option.
“Logs” Screen Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Enable Console
Messages
Filters (button) Click to access secondary screen on where console messages can be included/excluded by
Turn Off Logs Y/N Check to disable log-reporting function.
Logs Buttons Only one of these three log reporting methods, GUI, SMTP, or SNMP, may be chosen.
GUI
SNMP
SMTP
SysLog Server Enable Y/N Check this item if logging is done with a SysLog Server program.
IP Address n.n.n.n IP address of computer, in VOIP network, on which SysLog Server program is running.
Port 514 Logical port for SysLog Server. 514 is commonly used.
Online Statistics
Updation Interval
Y/N Allows MultiVOIP debugging messages to be read by using a basic terminal program like
HyperTerminal ™ or equivalent. In most cases, disabled this option because it uses MultiVOIP
processing resources. Console messages are meant for IT support personnel.
category and on a per-channel basis.
User must view logs at the MultiVOIP configuration program.
•
Log messages are delivered to the MultiVoipManager application program.
•
Log messages are sent to user-specified email address.
•
integer Set the interval (in seconds) at which logging information is updated.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 77
Page 78

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
NAT Traversal
Setting the NAT Traversal parameters. NAT (Network Address Translation) parameters are applicable only when
the MultiVOIP is operating in SIP mode. STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (Network Address
Translation)) is a protocol for assisting devices behind a NAT firewall or router with their packet routing. This is
not available on the –SS models.
The following table describes NAT Traversal fields.
Field Name Values Description
Enable (STUN) Y/N Enables STUN client functionality in the MultiVOIP.
STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP through NATs (Network Address Translation)) is a
protocol that allows a server to assist client gateways behind a NAT firewall or router
with their packet routing.
Name/IP (Server) n.n.n.n IP address of the STUN server.
Port (Server; NAT/STUN) port;
default=
3478
Keep Alive (Timers;
NAT/STUN)
60 – 3600
(seconds)
The data port (TDM time slot) at which STUN info is transmitted and received.
The interval at which the STUN client sends indicator (“Keep Alive”) packets to the
STUN server to determine whether or not the STUN server is available.
NAT Traversal Definitions
78 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 79

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Supplementary Services
Supplementary Services features derive from the H.450 standard, which brings to the VOIP telephony
functionality once only available with PSTN or PBX telephony. Even though the H.450 standard refers only to
H.323, Supplementary Services are still applicable to the SIP and SPP VOIP protocols.
Three of the features implemented under Supplementary Services are closely related.
● Call Transfer. Call Transfer allows one party to re-connect the party with whom they have been speaking to
a third party. The first party is disconnected when the third party becomes connected. A programmable
phone keypad sequence—for example, #7—allows the feature to be used.
● Call Hold. Call Hold allows one party to maintain an idle (non-talking) connection with another party while
receiving another call (Call Waiting), while initiating another call (Call Transfer), or while performing some
other call management function. A programmable phone keypad sequence—for example, #7—allows the
feature to be used.
● Call Waiting. Call Waiting notifies an engaged caller of an incoming call and allows them to receive a call
from a third party while the party with whom they have been speaking is put on hold. Feature is used by a
programmable phone keypad sequence (for example, #7).
Call Name Identification is similar but not identical to the premium PSTN feature commonly known as Caller ID.
Call Name Identification. When enabled for a given VOIP unit (the ‘home’ VOIP), this feature gives notice to
remote VOIPs involved in calls. Notification goes to the remote VOIP administrator, not to individual phone
stations. When the home VOIP is the caller, a plain English descriptor is sent to the remote VOIP identifying the
channel over which the call is being originated (for example, “Calling Party - Omaha Sales Office Line 2”). If that
VOIP channel is dedicated to a certain individual, the descriptor could say that, as well (for example “Calling
Party - Harold Smith in Omaha”). When the home VOIP receives a call from any remote VOIP, the home VOIP
sends a status message back to that caller. This message confirms that the home VOIP’s phone channel is either
busy or ringing or that a connection has been made (for example, “Busy Party - Omaha Sales Office Line 2”).
These messages appear in the Statistics – Call Progress screen of the remote VOIP.
Copying Parameters to Other Channels
Supplementary services parameters are applied on a channel-by-channel basis. However, after you establish a
set of supplementary parameters for a particular channel, you can apply this entire set of parameters to another
channel. To do so:
1. Click Copy Channel.
2. In the dialog box that opens, to copy a set of parameters to all channels, select Copy to All.
3. Click Copy.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 79
Page 80

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
The table that follows describes the Supplementary Services fields.
Supplementary Services Parameter Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Select Channel 1-2 (210);
1-4 (410);
1-8 (810)
Call Transfer Enable Y/N Select to enable the Call Transfer function in the VOIP unit.
Transfer Sequence Any phone keypad
character
Call Hold Enable Y/N Select to enable Call Hold function in VOIP unit.
Hold Sequence phone keypad
characters
Call Waiting Enable Y/N Select to enable Call Waiting function in VOIP unit.
Retrieve Sequence Phone keypad
characters, two
characters in length
Call Name Identification
Enable
Table is continued on next page…
Enables CNI function. Call Name Identification is not the same as Caller ID. When enabled on a given
VOIP unit currently being controlled by the MultiVOIP interface (the ‘home VOIP’), Call Name
Identification sends an identifier and status information to the administrator of the remote VOIP
involved in the call. The feature operates on a channel-by-channel basis (each channel can have a
separate identifier).
If the home VOIP is originating the call, only the Calling Party field is applicable. If the home VOIP
is receiving the call, then the Alerting Party, Busy Party, and Connected Party fields are the only
applicable fields (and any or all of these could be enabled for a given VOIP channel). The status
information confirms back to the originator that the home VOIP, is either busy, or ringing, or that the
intended call has been completed and is currently connected.
The identifier and status information are made available to the remote VOIP unit and appear in
the Caller ID field of its Statistics – Call Progress screen. (This is how MultiVOIP units handle CNI
messages; in other VOIP brands, H.450 may be implemented differently and then the message
presentation may vary.)
The channel to be configured is selected here.
This is a “blind” transfer and the sequence of events is as follows:
Callers A and B are having a conversation.
Caller A wants to put B into contact with C.
Caller A dials call transfer sequence.
Caller A hears dial tone and dials number for caller C.
Caller A gets disconnected while Caller B gets connected to caller C.
A brief musical jingle is played for the caller on hold.
The numbers and/or symbols that the caller must press on the phone
keypad to initiate a call transfer.
The call-transfer sequence can be 1 to 4 characters in length using any
combination of digits or characters (* or #).
The sequences for call transfer, call hold, and call waiting can be from 1 to 4
digits in length consisting of any combination of digits 1234567890*#.
Call Hold allows one party to maintain an idle (non-talking) connection with
another party while receiving another call (Call Waiting), while initiating
another call (Call Transfer), or while performing some other call
management function.
The numbers and/or symbols that the caller must press on the phone
keypad to initiate a call hold.
The call-hold sequence can be 1 to 4 characters in length using any
combination of digits or characters (* or #).
The numbers and/or symbols that the caller must press on the phone
keypad to initiate retrieval of a waiting call.34-29
The call-waiting retrieval sequence can be 1 to 4 characters in length using
any combination of digits or characters (* or #).
This is the phone keypad sequence that a user must press to retrieve a
waiting call. Customize-able. Sequence should be distinct from sequence
that might be used to retrieve a waiting call via the PBX or PSTN.
80 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 81

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Supplementary Services Definitions (continued)
Field Name Description
Calling Party,
Allowed Name
Type (CNI)
Alerting Party,
Allowed Name
Type (CNI)
Busy Party,
Allowed Name
Type (CNI)
Connected Party,
Allowed Name
Type (CNI)
Caller ID This is the identifier of a specific channel of the ‘home’ VOIP unit. The Caller Id field typically describes a
Default When this button is clicked, all Supplementary Service parameters are set to their default values.
Copy Channel Copies the Supplementary Service attributes of one channel to another channel. Attributes can be copied to
If the ‘home’ VOIP unit is originating the call and Calling Party is selected, then the identifier (from the
Caller Id field) is sent to the remote VOIP unit being called. The Caller Id field gives the remote VOIP
administrator a plain-language identifier of the party that is originating the call occurring on a specific
channel.
This field is applicable only when the ‘home’ VOIP unit is originating the call.
Example. Suppose a VOIP system has offices in both Denver and Omaha. In the Omaha VOIP unit (the
‘home’ VOIP in this example), Call Name Identification has been enabled, Calling Party has been enabled as
an Allowed Name Type, and “Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” has been entered in the Caller Id field.
When channel 2 of the Omaha VOIP is used to make a call to any other VOIP phone station (for example,
the Denver office), the message “Calling Party - Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” appears in the “Caller
Id” field of the Statistics - Call Progress screen of the Denver VOIP.
If the ‘home’ VOIP unit is receiving the call and Alerting Party is selected, then the identifier (from the
Caller Id field) tells the originating remote VOIP unit that the call is ringing.
This field is applicable only when the ‘home’ VOIP unit is receiving the call.
Example. Suppose a VOIP system has offices in both Denver and Omaha. In the Omaha VOIP unit (the
‘home’ VOIP unit in this example), Call Name Identification has been enabled, Alerting Party has been
enabled as an Allowed Name Type, and “Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” has been entered in the Caller
Id field of the Supplementary Services screen.
When channel 2 of the Omaha VOIP receives a call from any other VOIP phone station (for example, the
Denver office), the message “Alerting Party - Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” is sent back and appears in
the Caller Id field of the Statistics – Call Progress screen of the Denver VOIP. This confirms to the Denver
VOIP that the phone is ringing in Omaha.
If the ‘home’ VOIP unit is receiving a call directed toward an already engaged channel or phone station and
Busy Party is selected, then the identifier (from the Caller Id field) tells the originating remote VOIP unit
that the channel or called party is busy.
This field is applicable only when the ‘home’ VOIP unit is receiving the call.
Example. Suppose a VOIP system has offices in both Denver and Omaha. In the Omaha VOIP unit (the
‘home’ VOIP unit in this example), Call Name Identification has been enabled, Busy Party has been enabled
as an Allowed Name Type, and “Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” has been entered in the Caller Id field
of the Supplementary Services screen.
When channel 2 of the Omaha VOIP is busy but still receives a call attempt from any other VOIP phone
station (for example, the Denver office), the message “Busy Party - Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” is
sent back and appears in the Caller Id field of the Statistics – Call Progress screen of the Denver VOIP. This
confirms to the Denver VOIP that the channel or phone station is busy in Omaha.
If the ‘home’ VOIP unit is receiving a call and Connected Party is selected, then the identifier (from the
Caller Id field) tells the originating remote VOIP unit that the attempted call has been completed and the
connection is made.
This field is applicable only when the ‘home’ VOIP unit is receiving the call.
Example. Suppose a VOIP system has offices in both Denver and Omaha. In the Omaha VOIP unit (the
‘home’ VOIP unit in this example), Call Name Identification has been enabled, Connected Party has been
enabled as an Allowed Name Type, and “Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” has been entered in the Caller
Id field of the Supplementary Services screen.
When channel 2 of the Omaha VOIP completes an attempted call from any other VOIP phone station (for
example, the Denver office), the message “Connect Party - Omaha Sales Office Voipchannel 2” is sent back
and appears in the Caller Id field of the Statistics – Call Progress screen of the Denver VOIP. This confirms
to the Denver VOIP that the call has been completed to Omaha.
person, office, or location, for example, “Harry Smith,” or “Bursar’s Office,” or “Barnesville Factory.”
multiple channels or all channels at once.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 81
Page 82

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Save Settings
Save & Reboot
Saving the MultiVOIP Configuration. When values have been set for all of the MultiVOIP’s various operating
parameters, click Save Setup in the sidebar, then Save & Reboot.
Creating a User Default Configuration. When a “Setup” (complete grouping of parameters) is being saved, you
are prompted about designating that setup as a “User Default” setup. A User Default setup may be useful as a
baseline of site-specific values to which you can easily revert. Establishing a User Default Setup is optional.
Connection
Settings
This is also accessible from the Start menu in the MultiVOIP software folder.
Set Baud Rate. The Connection option in the sidebar menu has a “Settings” item that includes the baud-rate
setting for the COM port of the computer running the MultiVOIP software.
The default COM port established by the MultiVOIP program is COM1. Do not accept the default value until you
have checked the COM port allocation on your PC. To do this, check for COM port assignments in the system
resource manager of your Windows operating system. If COM1 is not available, you must change the COM port
setting to a COM port that you have confirmed as being available on your PC.
82 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 83

Chapter 4 – Configuring Your MultiVOIP
Troubleshooting Software Issues
In the lower left corner of the screen, the connection status of the MultiVOIP appear. The messages in the lower
left corner change as detection occurs. The message “MultiVOIP Found” confirms that the MultiVOIP is in
contact with the MultiVOIP configuration program. If the message displayed is “MultiVOIP Not Found!” please
try the resolutions that follow.
Fixing a COM Port Problem
If the MultiVOIP main screen appears but is grayed out and seems inaccessible, the COM port that was specified
for its communication with the PC is unavailable and must be changed. An error message appears.
To change the COM port setting:
1. From the COM Port Setup dialog box, perform one of the following:
● Go to the Connection pull-down menu. Select and choosing Settings.
● Use the left side control panel. In the Select Port field, select a COM port that is available on the PC. If
no COM ports are currently available, re-allocate COM port resources in the computer’s MS Windows
operating system to make one available.
Fixing Cabling Problems
If the computer cannot locate the MultiVOIP device, three error messages appear.
These messages indicate that MultiVOIP is disconnected from the network. For instructions on MultiVOIP cable
connections, see Chapter 3.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 83
Page 84

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone
Book
When a VOIP serves a PBX system, ensure that the VOIP’s operation is transparent to the telephone end user.
Make sure the VOIP does not dial extra digits to reach users elsewhere on the network that the VOIP serves.
VOIP service commonly reduces dialed digits. This allows users (served by PBXs in facilities in distant cities) to
dial their co-workers with 3-, 4-, or 5-digit extensions as if they were in the same facility.
Also, ensure the VOIP setup allows users to make calls on a non-toll basis to any numbers accessible without toll
by users at all other locations on the VOIP system. Consider, for example, a company with VOIP-equipped offices
in New York, Miami, and Los Angeles, each served by its own PBX. When the VOIP phone books are set correctly,
personnel in the Miami office should be able to make calls without toll not only to the company’s offices in New
York and Los Angeles, but also to any number that’s local in those two cities.
To achieve transparency of the VOIP telephony system and to give full access to all types of non-toll calls made
possible by the VOIP system, the VOIP administrator must properly configure the “Outbound” and “Inbound”
phone-books of each VOIP in the system.
The “Outbound” phonebook for a particular VOIP unit describes the dialing sequences required for a call to
originate locally (typically in a PBX in a particular facility) and reach any of its possible destinations at remote
VOIP sites, including non-toll calls completed in the PSTN at the remote site.
The “Inbound” phonebook for a particular VOIP unit describes the dialing sequences required for a call to
originate remotely from any other VOIP sites in the system, and to terminate on that particular VOIP.
The MultiVOIP’s Outbound phonebook lists the phone stations it can call; its Inbound phonebook describes the
dialing sequences that can be used to call that MultiVOIP and how those calls are directed. The phone numbers
are not listed individually, but are, instead, described by rule.
Identify Remote VOIP Site to Call
After installing the MultiVOIP, confirm that it is configured and operating properly by checking end-to-end
connectivity. To do so, discover another VOIP that you can call for testing. Obtain the remote site’s IP and
telephone information.
If this is the very first VOIP in the system, coordinate the installation of this MultiVOIP with an installation of
another unit at a remote site.
Identify VOIP Protocol to be Used
Determine if you want to use H.323, SIP, or SPP. Although you can mix protocols in a single VOIP system, it is
better to use the same VOIP protocol for all VOIP units in the system.
SPP is a non-standard protocol developed by Multi-Tech. SPP is not compatible with the “Proprietary” protocol
used in Multi-Tech’s earlier generation of VOIP gateways.
The –SS series of MultiVOIPs only support the SIP protocol.
The –FX models do not support H.323.
84 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 85

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Initially Configuring the Phonebook
This section describes setting up the phone book. It provides examples that help you enter the correct numbers
for proper MultiVOIP operation.
Initially, you set up two VOIP locations and establish VOIP communication. Once this is accomplished, you can
easily add other VOIP sites to the network.
Before You Begin
Before you configure the phone book:
● Obtain access to another VOIP that you can call for testing.
● Make sure the VOIP is at a remote location, typically somewhere outside of your building.
● Obtain the phone number and IP address for the remote site. It is assumed that the MultiVOIP is operating
with a PBX.
Configuring the Outbound Phonebook
1. Open the MultiVOIP program. (Start | MultiVOIP xxx | Configuration)
2. Go to Phone Book | Outbound Phonebook | Add Entry.
3. Record the calling code of the remote VOIP (area code, country code, city code, etc.) to be called.
Follow the example that best fits your situation:
North America,
Long-Distance Example
Technician in Seattle (area 206)
must set up one VOIP there,
another in Chicago (area 312,
downtown).
Answer: Write down 312.
4. Suppose you want to call a phone number outside of your building using a phone station that is an extension
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
Technician in central London (area
0207) to set up VOIP there, another
in Birmingham (area 0121).
Answer: write down 0121.
Technician in Rotterdam (country
31; city 010) to set up one VOIP
there, another in Bordeaux (country
33; area 05).
Answer: write down 3305.
from your PBX system (if present). What digits must you dial? Often a “9” or “8” must be dialed to “get an
outside line” through the PBX (i.e., to connect to the PSTN). Generally, “1 “or “11” or “0” must be dialed as a
prefix for calls outside of the calling code area (long-distance calls, national calls, or international calls).
Write down the digits you must dial before you can dial a remote area code.
North America,
Long-Distance Example
Seattle/Chicago system.
Seattle VOIP works with PBX that
uses “8” for all VOIP calls. “1” must
immediately precede area code of
dialed number.
Answer: write down 81.
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
London/Birmingham system.
London VOIP works with PBX that
uses “9” for all out-of-building calls
whether by VOIP or by PSTN. “0”
must immediately precede area
code of dialed number.
Answer: write down 90.
Rotterdam/Bordeaux system.
Rotterdam VOIP works with PBX
where “9” is used for all out-ofbuilding calls. “0” must precede all
international calls.
Answer: write down 90.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 85
Page 86

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
5. In the Destination Pattern field of the Add/Edit Outbound Phonebook screen, enter the digits from step 4
followed by the digits from step 3.
North America,
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
Long-Distance Example
Seattle/Chicago system.
Answer: enter 81312 as Destination
Pat-tern in Outbound Phone-book
of Seattle VOIP.
London/Birmingham system.
Leading zero of Birmingham area
code is dropped when combined
with national-dialing access code.
Rotterdam/Bordeaux system.
Answer: enter 903305 as
Destination Pattern in Outbound
Phonebook of Rotterdam VOIP.
(Such practices vary by country.)
Answer: enter 90121 as Destination
Pattern in Outbound Phonebook of
London VOIP.
Not 900121.
6. In the Remove Prefix field, enter the initial PBX access digit—8 or 9.
North America,
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
Long-Distance Example
Seattle/Chicago system.
Answer: enter 8 in “Remove Prefix”
field of Seattle Outbound
Phonebook.
London/Birmingham system.
Answer: enter 9 in “Remove Prefix”
field of London Outbound
Phonebook.
Rotterdam/Bordeaux system.
Answer: enter 9 in “Remove Prefix”
field of Outbound Phonebook for
Rotterdam VOIP.
Note: Some PBXs do not hand off the 8 or 9 to the VOIP. But for those PBX units that do, it’s important to
enter the “8” or “9” in the “Remove Prefix” field in the Outbound Phonebook. Doing so precludes the need
to make two inbound phonebook entries at remote VOIPs: one for situations when 8 is used as the PBX
access digit and another for when 9 is used.
7. In the Protocol Type field group, select the VOIP protocol used—H.323, SIP, or SPP. Use the appropriate
screen under Configuration | Call Signaling to configure the VOIP protocol in detail.
8. Click OK to exit from the Add/Edit Outbound Phonebook screen.
86 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 87

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Configuring the Inbound Phonebook
1. Open the MultiVOIP program. (Start | MultiVOIP xxx | Configuration)
2. Go to Phone Book | Inbound Phonebook | Add Entry.
3. In the Remove Prefix field, type the local calling code (area code, country code, city code, etc.) preceded by
any other access digits that are required to reach your local site from the remote VOIP location. Think of it
as though the call were being made through the PSTN – even though it is not.
North America,
Long-Distance Example
Seattle/Chicago system.
Seattle is area 206. Chicago
employees must dial 81 before
dialing any Seattle number on the
VOIP system.
Answer: 1206 is prefix to be
removed by local (Seattle) VOIP.
4. In the Add Prefix field, type digits that must be dialed from your local VOIP to access the PSTN.
North America,
Long-Distance Example
Seattle/Chicago system.
On Seattle PBX, “9” is used to get an
outside line.
Answer: Local (Seattle) VOIP adds 9
as prefix.
5. In the Channel Number field, enter Hunting. The hunting value means the VOIP unit assigns the call to the
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
London/Birmingham system.
Inner London is 0207 area.
Birmingham employees must dial 9
before dialing any London number
on the VOIP system.
Answer: 0207 is prefix to be
removed by local (London) VOIP.
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
London/Birmingham system.
On London PBX, “9” is used to get
an outside line.
Answer: Local (London) VOIP add 9
as prefix.
Rotterdam/Bordeaux system.
Rotterdam is country code 31, city
code 010. Bordeaux employees
must dial 903110 before dialing any
Rotterdam number on the VOIP
system.
Answer: 03110 is prefix to be
removed by local (Rotterdam) VOIP.
Rotterdam/Bordeaux system.
On Rotterdam PBX, “9” is used to
get an outside line.
Answer: Local (Rotterdam) VOIP
adds 9 as prefix.
first available channel. If desired, you can assign specific channels to specific incoming calls, that is, to any
set of calls received with a particular incoming dialing pattern.
6. In the Description field, type the ultimate destination of the calls. For example, in a New York City VOIP
system, “incoming calls to Manhattan office,” might describe a phonebook entry, as might the descriptor
“incoming calls to NYC local calling area.” Ensure the description makes the routing of calls easy to
understand. The field is limited to 40 characters.
North America,
Long-Distance Example
Seattle/Chicago system.
Possible Description:
Free Seattle access, all employees
7. Repeat steps 2-6 for each inbound phonebook entry. When all entries are complete, go to step 8.
8. To exit the inbound phonebook, click OK.
9. Click Save Setup. Select Save and Reboot. Click OK.
The initial inbound phonebook configuration is complete.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 87
Euro, National Call Example Euro, International Call Example
London/Birmingham system.
Possible Description:
Local-rate London access, all
employees
Rotterdam/Bordeaux system.
Possible Description:
Local-rate Rotterdam access, all
employees
Page 88

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Phone Book Descriptions
Outbound Phone Book/List Entries
Fields in the Details group differ depending on the protocol (H.323, SIP, or SPP) associated with the selected list
entry.
88 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 89

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book
Enter Outbound Phone Book data for your MultiVOIP unit. Note that the Advanced button gives access to the
Alternate IP Routing feature, if needed. Alternate IP Routing can be implemented in a secondary screen (as
described after the primary screen field definitions below). The –SS only allows SIP settings and the –FX models
do not allow H.323.
The table that follows describes the fields of the Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book window.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 89
Page 90

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book: Field Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Accept Any
Number
Destination
Pattern
Total Digits as needed Number of digits the phone user must dial to reach specified destination. This field
Remove Prefix dialed digits Portion of dialed number to be removed before completing call to destination.
Add Prefix dialed digits Digits to be added before completing call to destination.
IP Address n.n.n.n The IP address to which the call is directed if it begins with the destination pattern
Description alpha-numeric Describes the facility or geographical location at which the call is completed.
Protocol Type SIP or H.323
Y/N When checked, “Any Number” appears as the value in the Destination Pattern field.
The Any Number feature works differently depending on whether or not an
external routing device is used (Gatekeeper for H323 protocol, Proxy for SIP
protocol, Registrar for SPP protocol).
When no external routing device is used. If Any Number is selected, calls to phone
numbers not matching a listed Destination Pattern are directed to the IP Address in
the Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book screen. “Any Number” can be used in addition
to one or more Destination Patterns.
When external routing device is used. If Any Number is selected, calls to phone
numbers not matching a listed Destination Pattern are directed to the external
routing device used (Gatekeeper for H323 protocol, Proxy for SIP protocol, Registrar
for SPP protocol). The IP Address of the external routing device must be set in the
Phone Book Configuration screen.
prefixes,
area codes,
exchanges,
line numbers,
extensions
or SPP
Defines the beginning of dialing sequences for calls that are connected to another
VOIP in the system. Numbers beginning with these sequences are diverted from the
PSTN and carried on Internet or other IP network.
not used in North America
given.
Indicates protocol to be used in outbound transmission. Single Port Protocol (SPP) is
a non-standard protocol designed by Multi-Tech. The –SS models only support SIP
and the –FX models do not support H.323.
H.323 fields The –SS and –FX models do not support H.323
Use Gatekeeper Y/N Indicates whether or not gatekeeper is used.
Gateway H.323 ID alpha-numeric The H.323 ID assigned to the destination MultiVOIP. Only valid if “Use Gatekeeper”
is enabled for this entry.
Gateway Prefix numeric This number becomes registered with the GateKeeper. Call requests sent to the
gatekeeper and preceded by this prefix are routed to the VOIP gateway.
H.323 Port
Number
Table is continued on next page…
1720 This parameter pertains to Q.931, which is the H.323 call signaling protocol for
setup and termination of calls (aka ITU-T Recommendation I.451). H.323 employs
only one “well-known” port (1720) for Q.931 signaling. If Q.931 message-oriented
signaling protocol is used, 1720 must be chosen as the H.323 Port Number.
90 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 91

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Add/Edit Outbound Phone Book: Field Definitions (continued)
Field Name Values Description
SIP Fields
Use Proxy Y/N Select if proxy server is used.
Transport
Protocol
SIP Port
Number
SIP URL sip.userphone@hostserver,
TCP or
UDP
5060 or other
*See RFC 3087 (“Control of
Service Context using SIP
Request-URI,” by the Network
Working Group).
where “userphone” is the
telephone number and
“hostserver” is the domain
name or an address on the
network
SPP Fields The –SS series of MultiVOIPs do not support SPP
VOIP administrator must choose between UDP and TCP transmission protocols.
UDP is a high-speed, low-overhead connectionless protocol where data is
transmitted without acknowledgment, guaranteed delivery, or guaranteed
packet sequence integrity. TCP is slower connection-oriented protocol with
greater overhead, but having acknowledgment and guarantees delivery and
packet sequence integrity.
The SIP Port Number is a UDP logical port number. The VOIP “listens” for SIP
messages at this logical port. If SIP is used, 5060 is the default, standard or “well
known” port number used. If 5060 is not used, then the port number is the one
specified in the SIP Request URI (Universal Resource Identifier).
Looking similar to an email address, a SIP URL identifies a user's address.
In SIP communications, each caller or callee is identified by a SIP URL:
sip:user_name@host_name. The format of a sip URL is very similar to an email
address, except that the “sip:“ prefix is used.
Use Registrar Y/N
Port Number numeric When operating in “Registrar/Client” mode, this is the port by which the
Alternate
Phone
Number
Remote
Device is
[legacy VOIP]
Advanced
button
Gives access to secondary screen where an Alternate IP Route can be specified for backup or redundancy of signal
paths. For SIP & H.323 operation only.
numeric Phone number associated with alternate IP routing.
Y/N When checked, this MultiVOIP can operate with ‘first-generation’ MultiVOIP
Select this checkbox to use registrar when VOIP system is operating in the
“Registrar/Client” SPP mode. In this mode, one VOIP (the registrar, as set in
Phonebook Configuration screen) has a static IP address and all other VOIPs
(clients) point to the registrar’s IP address as functionally their own. However, if
your VOIP system overall is operating in “Registrar/Client” mode but you want
to make an exception and use Direct mode for the destination pattern of this
particular Add/Edit Phonebook entry, leave this checkbox unselected. Also do
not select this if your overall VOIP system is operating in the Direct SPP mode –
in this mode all VOIPs are peers with unique static IP addresses.
gateway receives all SPP data and control messages from the registrar gateway.
(This ability to receive all data and messages via one port allows the VOIP to
operate behind a firewall with only one port open.)
When operating in “Direct” mode, this is the Port by which peer VOIPs receive
data and messages.
units in the same IP network. These include MVP-110/120/200/400/800.
This is not available for the –SS series of MultiVOIPs.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 91
Page 92

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Configuring Alternate Routing
Alternate routing provides an alternate path for calls if the primary IP network cannot carry the traffic.
Sometimes during failure, call traffic is temporarily diverted into the PSTN. However, you also use alternate
routing to divert traffic to a redundant (backup) unit in case one VOIP unit fails.
Alternate routing facilitates PSTN Failover protection. It allows you to re-route VOIP calls automatically over the
PSTN if the VOIP system fails. You can program the MultiVOIP to respond to excessive delays in the transmission
of voice packets, which the MultiVOIP interprets as a failure of the IP network. Upon detecting an excessive
delay in transmission of voice packets (overly high “latency” in the network) the MultiVOIP diverts the call to
another IP address, which itself is connected to the PSTN (for example, via an FXO port on the self-same
MultiVOIP is connected to the PSTN).
To set up alternate routing:
1. Click Advanced. The Alternate Routing window opens.
2. Specify the IP address of the alternate route for each destination pattern entry in the Outbound Phonebook.
The following table describes alternate routing fields.
Field Name Values Description
Alternate IP
Address
Round Trip
Delay
n.n.n.n Alternate destination for outbound data traffic if excessive delay in data transmission.
Default is 300
milliseconds
The Round Trip Delay determines when a data pathway is considered blocked. When the
delay exceeds the threshold specified here, the data stream is diverted to the alternate
destination specified as the Alternate IP Address.
92 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Alternate Routing Field Definitions
Page 93

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
PSTN Failover Feature. You can program the MultiVOIP to divert calls to the PSTN temporarily if the IP network
fails. The following figure provides an example.
3. Call diverts to
Alt IP address in voip
accessing PSTN line.
FXS
1. Call originates.
FXO
VOIP
PSTN Line
IP
NETWOR K
2. IP network fails.
VOIP
4. Call completed
via PSTN.
PBX
Inbound Phone Book/List Entries
The Details group and the Registration Options group display information about selected setup options and
protocols. The Subscription Options group is used with a Voice Mail Server.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 93
Page 94

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Add/Edit Inbound Phone Book
94 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 95

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Enter Inbound Phone Book data for your MultiVOIP. The table that follows describes the Add/Edit Inbound
Phone Book window.
Add/Edit Inbound Phone Book: Field Definitions
Field Name Values Description
Accept Any
Number
Remove Prefix dialed digits portion of dialed number to be removed before completing call to destination
Add Prefix dialed digits digits to be added before completing call to destination
Y/N When checked, “Any Number” appears as the value in the Remove Prefix field.
The Any Number feature of the Inbound Phone Book does not work when an external
routing device is used (Gatekeeper for H.323 protocol, Proxy for SIP protocol, Registrar
for SPP protocol).
When no external routing device is used. If Any Number is selected, calls received from
phone numbers not matching a listed Prefix (shown in the Remove Prefix column of the
Inbound Phone Book) are admitted into the VOIP on the channel listed in the Channel
Number field. “Any Number” can be used in addition to one or more Prefixes.
(often a local PBX)
(often a local PBX)
Channel
Number
Description -- Describes the facility or geographical location at which the call originated.
Call Forward Parameters
Enable Y/N Check the checkbox to enable the call forwarding.
Forward
Condition
Forward
Destination
Ring Count integer When “No Response” is condition for forwarding calls, this determines how many
Registration
Option
Parameters
channel, or
“Hunting”
Unconditional,
Busy,
No Response
IP address,
phone number,
port number,
etc
In an H.323 VOIP system, gateways can register with the system using one of these identifiers: an E.164
identifier, a Tech Prefix identifier, or an H.323 ID identifier. This section not available for the –FX and –SS
series models.
In a SIP VOIP system, gateways can register with the SIP Proxy. This is the only area available to the –SS
series.
In an SPP VOIP system, gateways can register with the SPP Registrar VOIP unit.
Channel number to which the call is assigned as it enters the local telephony equipment
(often a local PBX). “Hunting” directs the call to any available channel.
Unconditional. When selected, all calls received are forwarded.
Busy. When selected, calls are forwarded when station is busy.
No Response. When selected, calls are forwarded if called party does not answer after a
specified number of rings, as specified in Ring Count field.
Forwarding can be conditioned on both “Busy” and “No Response
Phone number or IP address to which calls are directed.
For H.323 calls, the Forward Destination can be either a Phone Number or an IP Address.
For SIP calls, the Forward Destination can be one of the following:
(a) phone number,
(b) IP address,
(c) IP address: port number,
(d) phone number: IP address: port number,
(e) SIP URL, or
(f) phone #: IP address.
For SPP calls, the Forward Destination can be one of the following:
(a) phone number,
(b) IP address: port, or
(c) phone number: IP address: port.
unanswered rings are needed to trigger the forwarding.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 95
Page 96

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Authorized User Name and Password for SIP
To enable the Registration Options on the Add/Edit Inbound Phone Book, activate Use SIP Proxy Option on the
Call Signaling, SIP Parameters Screen. Then add the IP address for the Primary Proxy in the SIP Proxy Parameters.
This allows you to add a Username and Password to the Inbound Phone Book entry. The –SS models only have a
password option available.
This feature is used when the MultiVOIP registers with the proxies that support authorization and need the
username, password and the endpoint name to be unique.
The VOIP sends Register request to Registrar for each entry with its configured Username and Password. When
Authentication is enabled for the endpoint, then the registrar/proxy sends “401 Unauthorized/407 Proxy
Authentication Required” response when it receives a REGISTER/INVITE request. Now, the endpoint has to send
the authentication details in the Authorization header. In this header one of the fields is “username”.
Generally proxies accept requests even if both Endpoint Name and Username are same. But some proxies
expect that the Endpoint Name and Username should be different.
To support these proxies, we have the username and password configuration for every inbound phone book
entry which gets registered with a proxy.
If the username and password are not configured in the inbound phone book, then the registration happens
with the default username and password that are configured in the SIP Call Signaling Page.
Phone Book Save and Reboot
After you complete Outbound and Inbound Phonebook entries, click Save Setup to save your configuration. You
can change the configuration later, if desired.
You must complete the initial MultiVOIP setup locally or by using the built-in Remote Configuration/Command
Modem using the MultiVOIP program. After initial configuration, you can configure, re-configure and update all
the MultiVOIP units in the VOIP system from one location. To do so, use the MultiVOIP web interface software
program or the MultiVOIP program with the built-in modem.
96 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 97

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Phonebook Examples
North America
This section describes how Outbound and Inbound Phonebook entries work with multiple area codes. This
example uses a company with offices in Minneapolis and Baltimore.
The local calling area of Minneapolis consists of multiple adjacent area codes. Baltimore’s local calling area
consists of a base area code plus an overlay area code.
Company
VOIP/PBX
5
SIte
NW
Suburbs
763
SW Suburbs
Mpls
612
952
St. Paul
& Suburbs
651
...
5
The illustration that follows shows an outline of the equipment setup in both offices.
Outstat e MD
Company
VOIP/PBX
SIte
Baltimore
410
Baltimore/
Overlay
443
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 97
Page 98

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
The figure that follows shows Outbound Phonebook entries for the VOIP located in the company’s Baltimore
facility.
The entries in the Minneapolis VOIP’s Inbound Phonebook match the Outbound Phonebook entries of the
Baltimore VOIP, as shown below.
To call the Minneapolis/St. Paul area, a Baltimore employee must dial eleven digits. This assumes that the
Baltimore PBX does not require an 8 or 9 to seize an outside phone line.
If a Baltimore employee dials any phone number in the 612 area code, the company’s VOIP system automatically
handles the call. When receiving the call, the Minneapolis VOIP removes the digits 1612. But before the
suburban-Minneapolis VOIP can complete the call to the PSTN of the Minneapolis local calling area, it must dial
“9” (to get an outside line from the PBX) and then a comma (which denotes a pause to get a PSTN dial tone) and
then the 10-digit phone number which includes the area code (612 for the city of Minneapolis; which is different
than the area code of the suburb where the PBX is actually located -- 763).
Similar events occur when the Baltimore employee calls numbers in the 651 and 952 area codes because
numbers in these area codes are local calls in the Minneapolis/St. Paul area.
98 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Page 99

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
The simplest case is a call from Baltimore to a phone within the Minneapolis/St. Paul area code where the
company’s VOIP and PBX are located, namely 763. Here, the local VOIP removes 1763 and dials 9 to direct the
call to its local 7-digit PSTN.
Finally, consider the longest entry in the Minneapolis Inbound Phonebook, “17637175. Note that the main
phone number of the Minneapolis PBX is 763-717-5170. The destination pattern 17637175 means that all calls
to Minneapolis employees stay within the suburban Minneapolis PBX and do not reach or are not carried on the
local PSTN. Similarly, the Inbound Phone Book for the Baltimore VOIP (shown first below) generally matches the
Outbound Phone Book of the Minneapolis VOIP (shown second below).
Notice the extended prefix to be removed: 14103257. This entry allows Minneapolis users to contact Baltimore
co-workers as though they were in the Minneapolis facility, using numbers in the range 7000 to 7999.
Note also that a comma (as in the entry 9,443) denotes a delay in dialing. A one-second delay is commonly used
to allow a second dial tone to be generated for calls going outside of the facility’s PBX system.
The Outbound Phone Book for the Minneapolis VOIP is shown below. The third destination pattern, “7”
facilitates reception of co-worker calls using local-appearing-extensions only. In this case, the “Add Prefix” field
value for this phonebook entry would be “1410325”.
MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways 99
Page 100

Chapter 5 – Configuring the Phone Book
Europe
The most direct use of the VOIP system is making calls between the offices where the VOIPs are located.
Consider, for example, the Wren Clothing Company. This company has VOIP-equipped offices in London, Paris,
and Amsterdam, each served by its own PBX. VOIP calls between the three offices completely avoid
international long-distance charges. These calls are free. The phonebooks can be set up to allow all Wren
Clothing employees to contact each other using 3-, 4-, or 5-digit numbers, as though they were all in the same
building.
United Kingdom
Wren Clothing Co.
VOIP/PBX Site
London
5
Wren Clothing Co.
VOIP/PBX Site
5
Amsterdam
The
Netherlands
Wren Clothing Co.
VOIP/PBX Site
Paris
5
Free VOIP Calls
France
In another use of the VOIP system, the local calling area of each VOIP location becomes accessible to all of the
VOIP system’s users. As a result, international calls can be made at local calling rates.
For example, suppose that Wren Clothing buys its zippers from The Bluebird Zipper Company in the western part
of metropolitan London. In that case, Wren Clothing personnel in both Paris and Amsterdam could call the
Bluebird Zipper Company without paying international long-distance rates. Only London local phone rates would
be charged. This applies to calls completed anywhere in London’s local calling area.
Generally, local calling rates apply only within a single area code, and, for all calls outside that area code,
national rates apply. There are, however, some European cases where local calling rates extend beyond a single
area code. Local rates between Inner and Outer London are one example of this. It is also possible, in some
locations, that calls within an area code may be national calls - but this is rare.
United Kingdom
Wren Clothing Co.
Paris
VOIP/PBX Site
London
5
5
Bluebird Zipper Co.
London
Wren Clothing Co.
VOIP/PBX Site
France
100 MultiVOIP® Voice/Fax over IP Gateways
Wren Clothing Co.
VOIP/PBX Site
5
Amsterdam
The
Netherlands
Calls at London local rates
Local Calling Area
 Loading...
Loading...