Page 1

MultiMobile™ USB V.92 Portable
USB Modem
MT9234MU User Guide
Page 2

MultiMobile USB User Guide
Revision
Date
Description
D
10/01/09
Update EMC and add Support Portal link.
E
12/14/09
Added Brazil cable requirement to Appendix A, Windows 7 install procedure.
F
07/07/11
Removed references to product CD.
G
09/18/12
Updated RoHS statement.
H/I
3/13/14
4/12/17
Added Russian statement.
Updated Russian statement.
51BCountry
By Email
By Phone
Europe, Middle East, Africa:
support@multitech.co.uk
+(44) 118 959 7774
U.S., Canada, all others:
support@multitech.com
(800) 972-2439 or (763) 717-5863
V.92 Portable USB Modem
MT9234MU
S000409 Rev. I
Copyright
This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior expressed written permission from Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. All rights
reserved. Copyright © 2017 Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. makes no representations or warranty with respect to the contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied
warranty of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Furthermore, Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. reserves the right to revise this
publication and to make changes from time to time in the content hereof without obligation of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. to notify any person or
organization of such revisions or changes.
Patents
This device is covered by one or more of the following patents: 6,031,867; 6,012,113; 6,009,082; 5,905,794; 5,864,560; 5,815,567; 5,815,503;
5,812,534; 5,809,068; 5,790,532; 5,764,628; 5,764,627; 5,754,589; 5,724,356; 5,673,268; 5,673,257; 5,644,594; 5,628,030; 5,619,508; 5,617,423;
5,600,649; 5,592,586; 5,577,041; 5,574,725; 5,559,793; 5,546,448; 5,546,395; 5,535,204; 5,500,859; 5,471,470; 5,463,616; 5,453,986; 5,452,289;
5,450,425; D353,598; 5,355,365; 5,309,562; 5,301,274. Other patents pending.
Trademarks
MultiTech and the MultiTech logo are registered trademarks of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. MultiMobile is a trademark of Multi-Tech. All other brand
and product names mentioned in this publication are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
World Headquarters
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View, Minnesota 55112
Phone: 763-785-3500 or 800-328-9717
Fax: 763-785-9874
Internet Address: HUhttp://www.multitech.com
Contacting MultiTech Support
To better serve our customers, manage support requests and shorten resolution times, we have created the online web portal that lets you
submit questions regarding products directly to our technical support team. Get answers to your most complex questions, ranging from
implementation, troubleshooting, product configuration, firmware upgrades and much more.
To create an account and submit a Support Case on the Portal, visit support.multitech.com
Online Web Portal https://support.multitech.com/
The Knowledge Base provides immediate answers to your questions and gives you access to support resolutions for all MultiTech products. Visit
our support area on the website for other support services.
Knowledge Base and Support Services www.multitech.com/en_US/SUPPORT
Technical Support
Business Hours: M-F, 9am to 5pm CST
Warranty
To read the warranty statement for your product, please visit: HUhttp://www.multitech.com/support/warranty-registrationUH
2 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 3
Contents
0BChapter 1 – Product Description .....................................................................................................................5
11BFeatures ..................................................................................................................................................................... 5
12BTelecom Safety Warnings .......................................................................................................................................... 6
13BShipping Package Contents ....................................................................................................................................... 6
15BTechnical Specifications ............................................................................................................................................. 7
16B ................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
AT Commands ............................................................................................................................................................ 7
1BChapter 2 – Installing the Modem ...................................................................................................................8
29B
Connecting the Modem to Your System ................................................................................................................... 8
18BInstalling the Modem Driver ...................................................................................................................................... 9
Installing Windows Drivers ........................................................................................................................................ 9
74BInstalling the Modem .............................................................................................................................................. 10
Installing the MT9234MU in Windows 7 ................................................................................................................. 14
Configuring the Modem for Your Country .............................................................................................................. 17
2BChapter 3 – Operating the Modem ............................................................................................................... 18
20BFront Panel .............................................................................................................................................................. 18
21BConnecting to the Internet ...................................................................................................................................... 18
Internet Connection ................................................................................................................................................ 19
Chapter 4 – Remotely Configuring Modems .................................................................................................. 20
24BChanging the Setup Password ................................................................................................................................. 20
Changing the Remote Escape Character ................................................................................................................. 21
4BAppendix A – Regulatory Compliance ........................................................................................................... 22
35B
FCC Part 15 Class B Statements ............................................................................................................................... 22
Industry Canada ....................................................................................................................................................... 22
36B
FCC Part 68 Telecom ................................................................................................................................................ 22
37B
Canadian Limitations Notice .................................................................................................................................... 23
38B
EMC, Safety, and R&TTE Directive Compliance ....................................................................................................... 24
39B
International Modem Restrictions .......................................................................................................................... 24
40B
New Zealand Telecom Warning Notice ................................................................................................................... 24
41
Russian Statement ................................................................................................................................................... 25
South African Notice ................................................................................................................................................ 25
Thailand Approval .................................................................................................................................................... 26
Brazil Regulatory Special Cable Requirement ......................................................................................................... 26
5BAppendix B – Installing on Linux ................................................................................................................... 27
26BInstalling the Modem on Computers Using the Linux 2.4 Kernel ............................................................................ 27
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 3
Page 4

Installing the Modem on Computers Using the Linux 2.6 Kernel ............................................................................ 32
Installing the Modem on Computers Using the Linux 2.6.20 Kernel and Above .................................................... 36
6BAppendix C – Environmental Information ..................................................................................................... 38
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment............................................................................................................. 38
REACH Statement .................................................................................................................................................... 38
Restriction of the Use of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) ......................................................................................... 39
Information on HS/TS Substances According to Chinese Standards ....................................................................... 40
Information on HS/TS Substances According to Chinese Standards (in Chinese) ................................................... 41
Appendix D – ASCII Conversion ..................................................................................................................... 42
ASCII Conversion Chart ............................................................................................................................................ 42
9BIndex ........................................................................................................................................................... 43
4 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 5

0BChapter 1 – Product Description
Command
Buffer
40 characters
Diagnostics
Power-on self test, local analog & local digital loop, remote digital loop.
LED
Indicators
LEDs for Data, Carrier Detect, Off Hook, Terminal Ready
Intelligent
Features
Fully AT command compatible; autodial, redial, repeat dial; pulse or tone
dial; dial pauses; auto answer; caller ID; EIA extended automode; adaptive
line probing; automatic symbol and carrier frequency during start-up,
retrain, and rate renegotiation; call status display, auto-parity and data rate
selections; keyboard-controlled modem options; non-volatile memory; onscreen displays for modem option parameters; command lines of up to 40
characters each; help menus; remote configuration.
The MultiMobile USB V.92 Portable USB modem MT9234MU provides V.92/56K data rates, fax and file
transfer capabilities and a hot-swappable USB interface. This modem, weighing only 2 ounces, is ideal for
mobile users who want email and Internet access on the road. The MT9234MU modem can also serve as
the mobile user’s home office desktop modem.
11BFeatures
5 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 6

12BTelecom Safety Warnings
Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
Never install a telephone jack in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet
locations.
Use this product with UL and cUL listed computers.
Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been
disconnected at the network interface.
Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a
remote risk of electrical shock from lightning.
Do not use a telephone in the vicinity of a gas leak.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
This product must be disconnected from the telephone network interface when servicing.
13BShipping Package Contents
CHAPTER 1 – PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
MT9234MU modem
One RJ-11 cable
Inspect the contents for signs of any shipping damage. If damage is observed, do not power up the unit.
Contact Multi-Tech’s Technical Support for advice.
To use the modem, you must have a computer with an unused USB post and a nearby telephone line jack.
6 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 7

CHAPTER 1 – PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Trade Name
MultiMobile™ USB
Model Number
MT9234MU
Data Rates
56K download speeds from digital V.92/V.90 servers;
33.6K upload and download speeds from non-V.92/V.90 servers and other client
modems
Fax Rates
33.6K and below
Standards:
Data
V.92, V.90 enhanced, V.34 and below
Error Correction
V.42
Data Compression
V.44, V.42bis, MNP Class 5
Fax
V.34, Class 2.1 & 1.0, V.17, Group 3; Class 1 & 2, Error Correction Mode
Cables
1 USB series A
1 RJ-11
Operation
USB Port: 12M bps
Line Type: Dial-up
Operating System
Support
Windows Vista, XP, 2003, 2000
Linux 2.4 kernel versions 2.4.28 and above
Linux 2.6 kernel versions 2.6.8 through 2.6.10
Linux 2.6 kernel versions 2.6.11 and above (with a kernel patch for 2.6.20.4, which
may be applicable to earlier 2.6 kernel versions, as well)
Physical Description
1.3” w x 1.0” h x 3.1” d; 2 oz
3.0 cm w x 2.5 cm h x 8.0 cm d; 62 g
Operating
Environment
Operating Temperature: +32° to +120° F (0° to 50° C)
Humidity Range: 25–85% non-condensing
Approvals
CE Mark
EMC: FCC Part 15 Class B
EN 55024
Safety: UL/cUL 60950-1
EN 60950-1
Telecom: 47CFR Part 68
CS03
TBR21
Limited Warranty
2 years
15BTechnical Specifications
16B
AT Commands
AT Commands for this product are published in a separate document. You can download this document from
the MultiTech website.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 7
Page 8
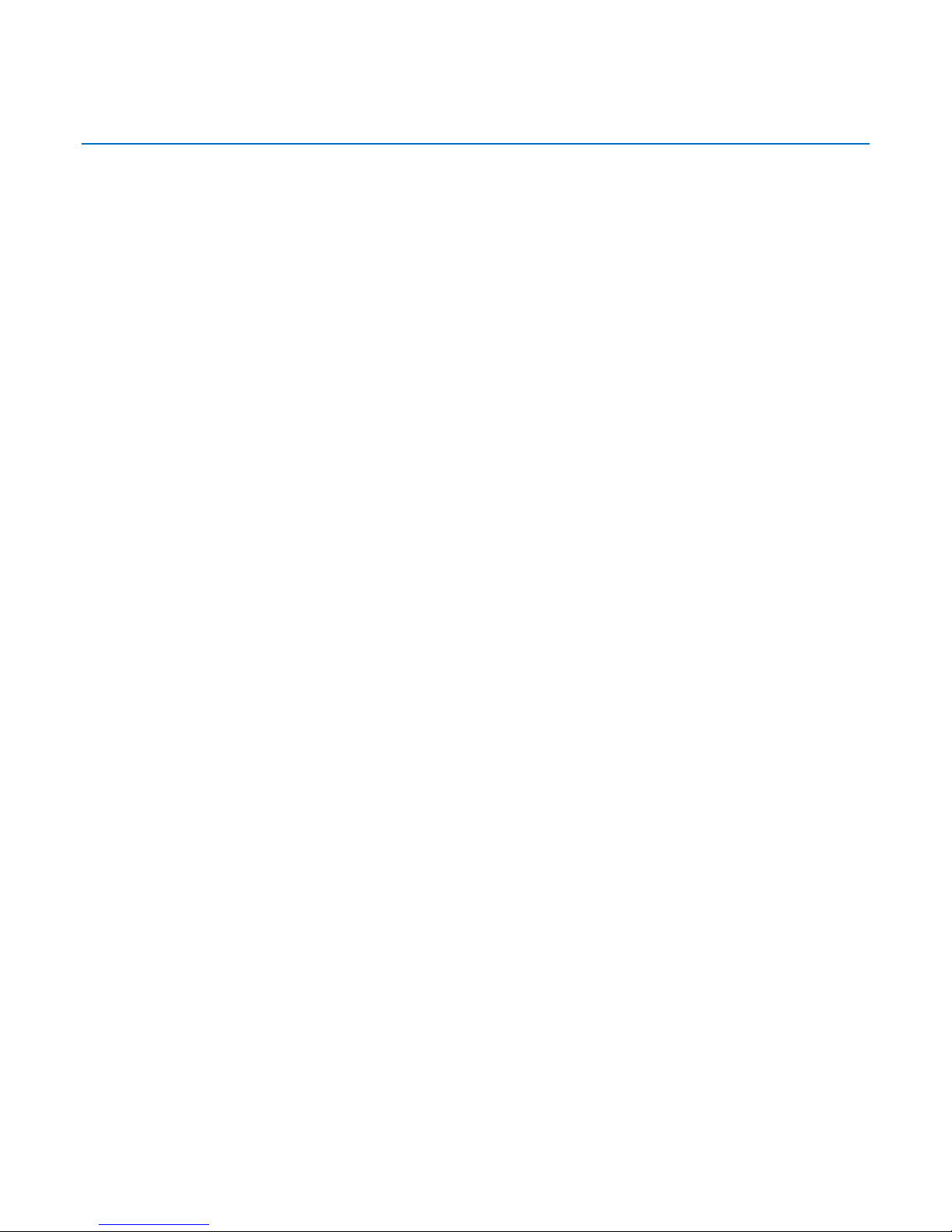
1BChapter 2 – Installing the Modem
This chapter explains how to install your modem. To use your modem, you must connect the
MT9234MU’s USB cable connector to your computer (“USB”) and to a telephone line (“LINE”).
29B
Connecting the Modem to Your System
Connect the MT9234MU to your computer’s USB port and connect the telephone line to your MT9234MU
and a telephone wall jack.
Connecting the USB Cable
Plug the USB cable connector on the modem into a USB port connector on your computer.
Connecting the Phone Line
Plug one end of the phone cable into the modem’s LINE jack, and the other end into a phone line wall jack.
Note: The Federal Communications Commission (FCC), and Industry Canada impose certain restrictions on
equipment connected to public telephone systems. See Appendix A for more information.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 8
Page 9

CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
18BInstalling the Modem Driver
30B
Before You Begin
Before you install the driver:
Download the driver from the MultiTech website and store the driver in a known location on your
computer.
Compatibility: This MultiMobile MT9234MU MultiModem is compatible with Windows Operating
Systems Vista, XP, 2003, Server 2008, and Linux.
Windows Drivers: The MultiMobile MT9234MU driver must be installed in your computer’s
program directory. You can download the desired driver from the MultiTech website.
A complete set of drivers for each operating system is organized into Vista and XP with either 32-bit
or 64-bit processor. Most users select either the 32-bit Vista or 32-bit XP drivers. Windows 2003
also uses the XP drivers.
Server users can select either 32-bit or 64-bit depending on their application. For server users to
determine whether they have a 32-bit or 64-bit operating system, go to Start I All Programs I
Accessories I System Tools I Computer and click System Properties. Under System, System Type:
64-bit Operating System appears.
Linux Drivers: You can also download Linux Operating System drivers from the MultiTech website.
Refer to the Readme file for the correct driver file and installation guide for your distribution and
version of Linux.
Installing Windows Drivers
Wizards guide you through the software Installation in this order:
Installing the Serial Port.
Installing the modem driver.
Installing the MT9234MU in Windows Vista
1. Power up your computer.
2. If you have not already done so, connect the modem’s USB cable to a USB port on the computer
and connect the phone line between the modem and a telephone wall jack.
3. Windows detects that the new modem is present.
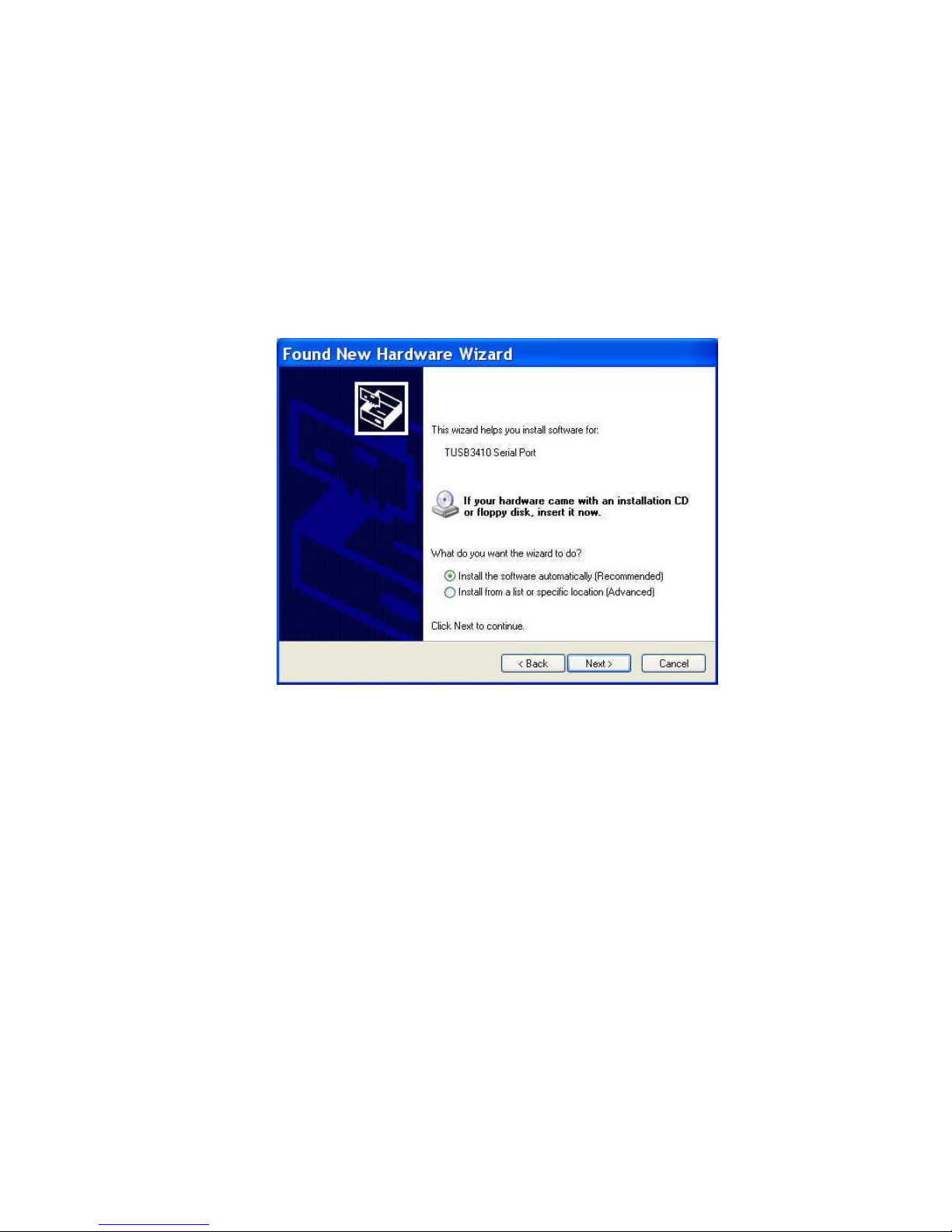
Installing the TUSB3410 Serial Port Driver
To install the TUSB3410 serial port:
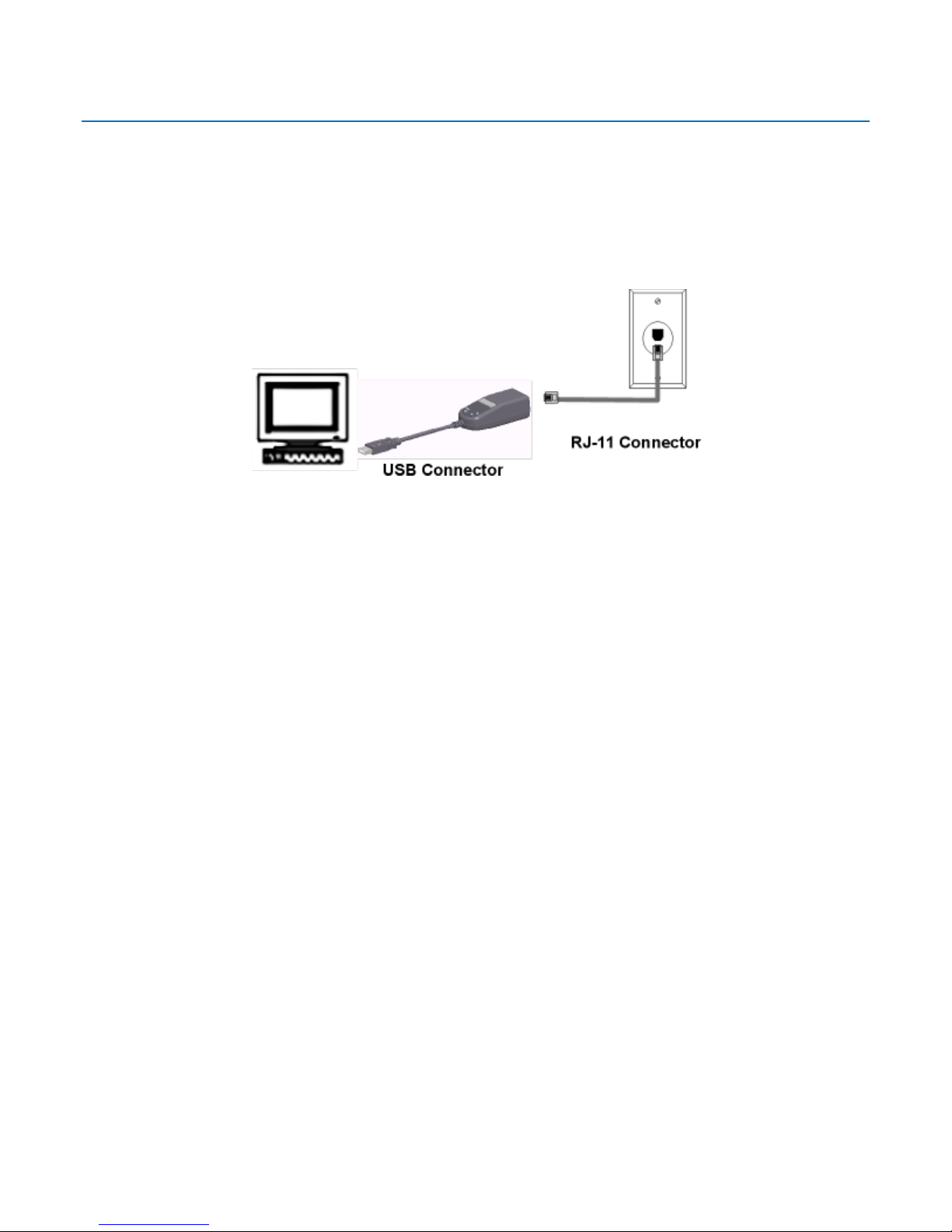
1. The Found New Hardware wizard opens. Click Locate and install driver software
(recommended). Windows guides you through the process of installing driver software for your
device.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 9
Page 10
CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
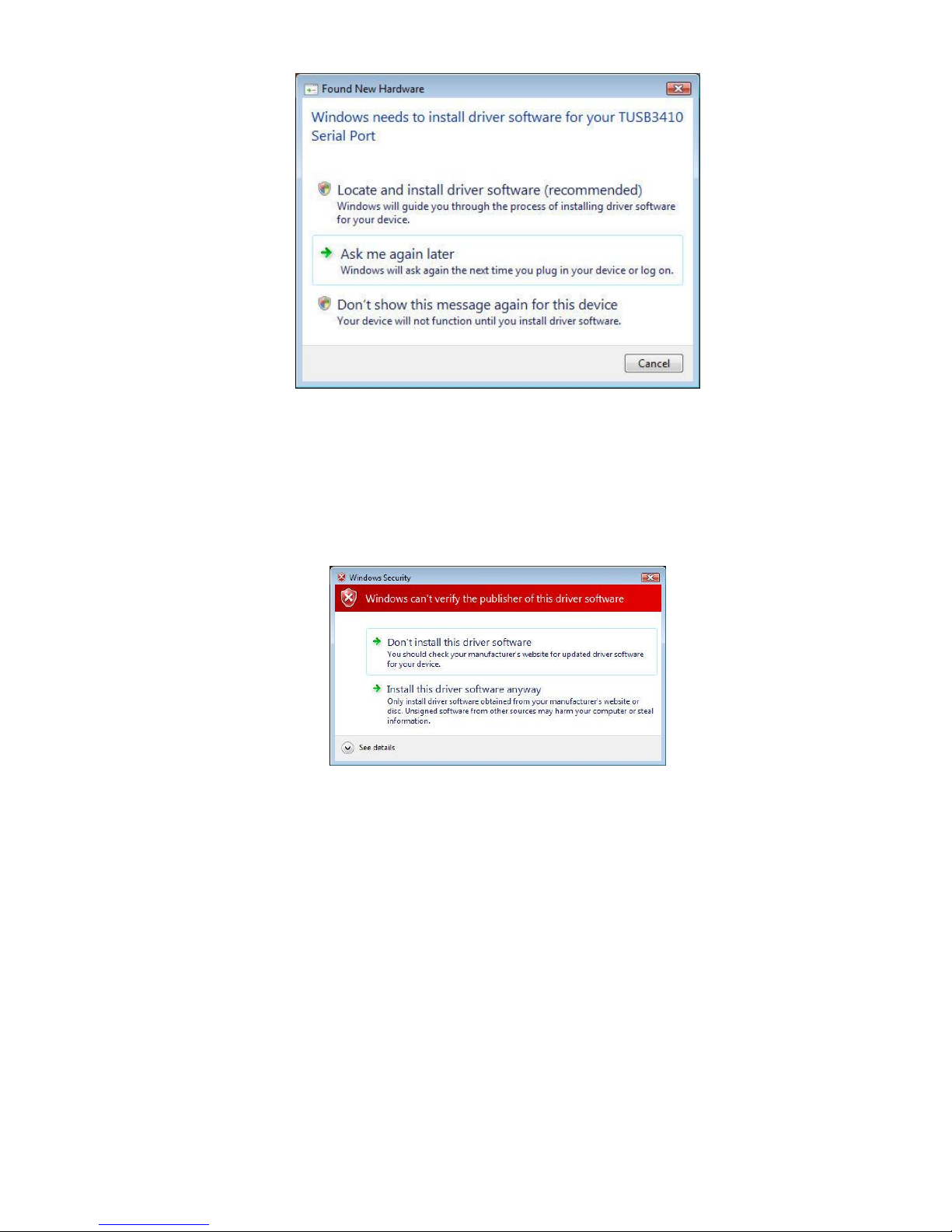
2. In the next wizard pane, click I don’t have the disc. Show me other options. Windows may
prompt you to search online, but this is not necessary.
3. In the next wizard pane, select Browse my computer for driver software (advanced).
4. At the Browse for driver software on your computer pane, click Browse.
5. Navigate to the location where downloaded the drivers and click Next. The dialog box, Windows
can’t verify the publisher of this driver software, appears.
6. Select Install this driver software anyway. When the software is successfully installed, a wizard
pane appears to tell you so.
7. Click Close.
74BInstalling the Modem
1. The Found New Hardware – MultiTech Systems MT9234MU wizard pane appears. Select I don’t
have the disc. Show me other options. Click Next.
2. In the next wizard pane, select Browse my computer for driver software (advanced).
3. To install the software, in the next wizard pane, click Install.
10 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 11
CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
4. The wizard pane The software for this device has been successfully installed appears, to
indicate that Windows has finished installing the driver software.
5. Click Close.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 11
Page 12
CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
Installing the MT9234MU in Windows Server 2008, XP, 2003
This section describes how to install the modem with a computer running Windows 2008, XP or 2003. This
section presents Windows XP illustrations. For all the operating systems noted, the installation procedure is the
same, but some illustrations may vary from those shown in this section.
Installing the Serial Port for Windows Server 2008, XP, 2003
1. Connect the USB cable between the MultiModem and the PC.
2. If prompted, Can Windows connect to Windows Update to search for software? Select No, not
this time. Then click Next.
3. Click Install from a list or specific location (Advanced), and then click Next.
4. Select only Search removable media (floppy, CD-ROM…) Include this location in the search.
5. Click Browse and browse to the location where you stored the drivers downloaded from the
MultiTech website.
6. Select the Windows_Drivers folder and then the WinXP32 folder. Or, if you are installing drivers
on an XP 64-bit Operating System, select the WinXP64 driver.
7. Click Next.
12 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 13
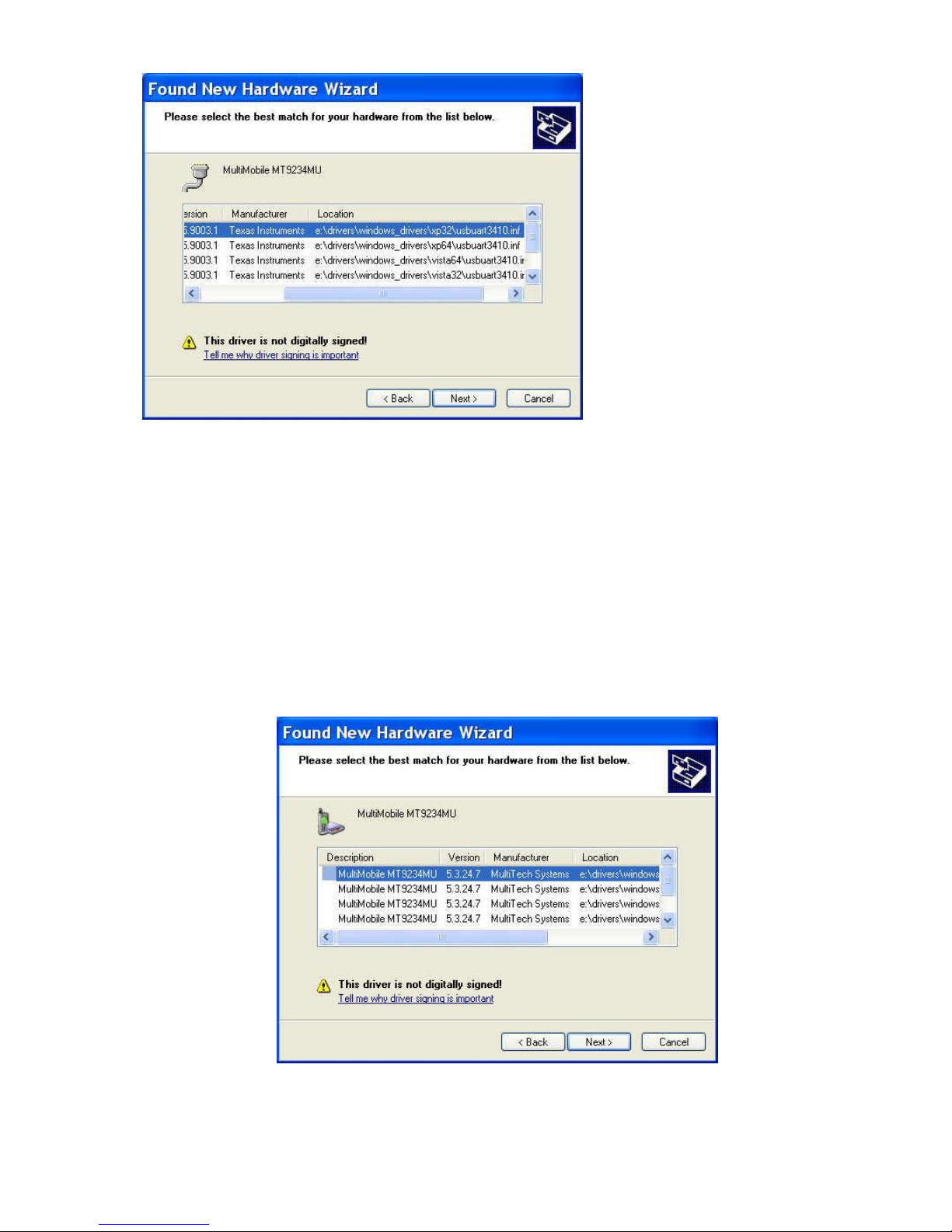
CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
8. Select either MultiMobile MT9234MU xp32 or xp64 depending on your operating system.
9. Click Finish when prompted.
Installing the Modem for Windows Server 2008, XP, 2003
1. If the Welcome to the Found New Hardware Wizard pane asking – Can Windows connect to
Windows update to search for software? Select No, not this time. Then click Next.
2. Select Install from a list or specific location (Advanced). Then click Next.
3. Select Include this location in the search. Click Browse.
4. Browse to the location where you stored the drivers that you downloaded from the MultiTech
website. Select the WinXP32 driver, or if you are installing drivers on an XP 64-bit operating
system, select the WinXP64 folder.
5. Click Next. A Windows Logo Testing pane may appear. Click Continue Anyway.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 13
Page 14

CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
6. Click Finish when prompted.
Installing the MT9234MU in Windows 7
After inserting your MT9234MU into an available USB port, Windows 7 reports that the driver software was not
successfully installed. To point Windows 7 to the drivers:
1. From the Windows Start button select Control Panel. Left-click Hardware and Sound.
2. In the Devices and Printers group, click Device Manger.
3. Right-click on TUSB3410 Serial Port and select Update Driver Software.
14 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 15

CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
4. Click Browse my computer for driver software.
5. Click Browse and navigate to the location where you stored the drivers downloaded from the
MultiTech website.
6. Select the appropriate driver (either 34-bit or 64-bit) and click OK.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 15
Page 16

CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
7. Click Next. If a Windows Security window appears, click Install this driver software anyway.
8. Click Close to complete the first portion of the install. Repeat the procedure to finalize the
installation.
9. In the Device Manager window, open Other devices and right-click the MultiTech Systems
MT9234MU.
10. Select Upgrade Driver Software.
11. Left-click Browse my computer for driver software. The location window is still populated with
the drive you selected earlier. Click Next.
12. If a Windows Security window appears, click Install this driver software anyway.
13. Click Close to complete the installation. Your modem is installed and ready to use.
16 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 17

CHAPTER 2 – INSTALLING THE MODEM
Configuring the Modem for Your Country
Different countries have different requirements for how modems must function. Therefore, before you
use the modem, you must configure it to match the defaults of the country in which you are using it. You
can configure the MT9234MU either manually using AT commands or with the Global Wizard. Both
methods are described below.
54BUsing the Global Wizard Utility to Configure Country Code
The Global Wizard configuration utility is recommended for computers running Windows Vista, Windows
Server 2008, XP, and 2003. The Global Wizard can configure your modem for a specific country with just a
few mouse clicks.
1. Insert the MT9234MU Installation CD into the CD-ROM drive. The Autorun dialog box appears.
2. Click Initial Setup and Country Selection. The Global Wizard dialog box appears. Click Next.
3. View the Global Wizard as it searches for your modem and identifies it. Click Next.
4. Select the country in which the modem is to be used, and then click Next.
5. Review your choice of country. If it is correct, click Next to configure the modem.
6. When Global Wizard announces that the parameters have been set, click Finish to exit.
55BUsing AT Commands to Configure Country Code
If you are comfortable using AT commands, you can configure your modem using AT commands. You must
enter these commands in your communication program’s terminal window.
To configure the modem for a specific country, execute the following AT commands:
1. Type AT%T19,0,nn (where nn represents the country code). Press Enter.
2. The modem responds “OK.”
3. Type AT&F&W (this saves changes). Press Enter.
4. The modem responds “OK.”
5. Type ATI9 (this verifies that country code has been chosen). Press Enter.
6. The modem displays the country code in decimal format followed by an “OK.”
7. Check to be sure the code for your country is displayed. If not, repeat procedure to correct.
Here are two examples of country, command, and result codes.
Example Country/Region AT Command Country Code
(Hexidecimal) (Decimal)
Euro/NAM* AT%T19,0,34 (default) 52
You can find the complete list of country/region codes on the Multi-Tech Web site at
http://www.multitech.com/products/analog-modems/global-modems/global-modem-approvals
The Global Modem Country Approvals page displays. On this page you can view approvals, configuration
strings and responses by country and product.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 17
Page 18

2BChapter 3 – Operating the Modem
20BFront Panel
The MT9234MU has 4 LEDs on the front panel indicating status, configuration, and activity:
Data. The Data LED flashes when the modem is transmitting/receiving data to/from another
modem.
Carrier Detect. The CD LED lights when the modem detects a valid carrier signal from another
modem. It is on when the modem is communicating with the other modem and off when the link is
broken.
Off-Hook. The OH LED lights when the modem is off-hook, which occurs when the modem is dialing,
online, or answering a call. The LED flashes when the modem pulse-dials.
Terminal Ready. The TR LED lights when Windows detects and initializes the modem.
21BConnecting to the Internet
To access the Internet and Web through your modem, establish a dial-up account with an Internet service
provider (ISP). To locate an ISP near you, look in a local directory or computer publication. To help you
establish an account, your ISP provides you with the following information:
User name (also called user ID)
Password
Access number (the number you call to connect to the server)
Host name and/or domain name
Domain Name Server (DNS) server address
If, besides the Web, you use the Internet for e-mail and newsgroups, your ISP can also provide you with
the following information:
E-mail or POP mail address
POP server address
Mail or SMTP address
News or NNT server address
18 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 19

CHAPTER 3 – OPERATING THE MODEM
Internet Connection
Before you can connect to the Internet, you must set up a remote-node client program on your computer.
Windows uses HyperTerminal to establish your connection to the ISP’s server, which is the shared
computer that manages calls from clients (your computer) to the Internet. Most, if not all, Windows
browsers can automatically open this connection. For instructions on how to set up this connection,
consult your ISP or your operating system’s online help or printed documentation. Many ISPs provide a
program that installs and configures this connection automatically for you.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 19
Page 20

Chapter 4 – Remotely Configuring Modems
Remote configuration is a network management tool that allows you to configure modems anywhere in
your network from one location. With password protected remote configuration, you can issue AT
commands to a remote MT9324MU modem for maintenance or troubleshooting as if you were on site.
The following steps are valid regardless of whether the connection is established by the local or the
remote MultiTech modem.
To configure modems:
1. Establish a data connection with a remote MT9324MU modem.
2. Send three remote configuration escape characters followed by AT and the setup password, and
press ENTER. Example: %%%ATMTSMODEM. You have four tries to enter the correct password
before being disconnected. If the password is correct, the remote modem responds with OK.
3. You can now send AT commands to configure the remote modem.
4. When you have finished configuring the remote modem, save the new configuration by typing
AT&W0, and pressing Enter.
5. Type ATO and press Enter to exit remote configuration. You can then break the connection in
the normal way.
Caution: If you hang up while you are in remote configuration mode, it may lock up the remote modem.
24BChanging the Setup Password
MultiTech modems are shipped with a default setup password (MTSMODEM). Because anyone who has
an owner’s manual knows the default setup password, for security you should change the password and
possibly also the remote configuration escape character.
1. Open a data communications program such as HyperTerminal. .
2. To change the password, type AT#S=xxxxxxxx, where xxxxxxxx stands for the password, and
press ENTER. The password can include any keyboard character, and must be one to eight
characters long. The modem responds with OK.
3. The new password is saved automatically. You can now either enter more AT commands or exit
the data communications program. The next time you remotely configure the modem you must
use the new setup password.
Note: You can only change the setup password locally; you cannot do it remotely. Also, passwords are
case sensitive. The next time you enter the password, it must be in the same case as you set it up.
20 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 21

CHAPTER 4 – REMOTELY CONFIGURING MODEMS
Changing the Remote Escape Character
To increase security, you can change a remote modem’s remote configuration escape character. The
remote configuration escape character is stored in register S9. The factory default is 37, which is the ASCII
code for the percent character (%). For ASCII code characters, refer to Appendix E. Setting S9 to 0 (zero)
disables remote configuration entirely—but if you do this remotely, you won’t be able to change it back
remotely.
1. Establish a remote configuration link with the remote modem as described in “Basic Procedure.”
2. Type ATS9=n, where n is the ASCII code for the new remote configuration escape character,
then press Enter.
3. To save the new value, type AT&W and press Enter.
4. Type ATO<CR> to exit remote configuration.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 21
Page 22

4BAppendix A – Regulatory Compliance
35B
FCC Part 15 Class B Statements
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to 47 CFR Part 15 regulations. The stated limits in this regulation are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Plug the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the CFR 47 rules. Operation of this device is subject to the following
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference that may cause undesired operation.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Industry Canada
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment
Regulations.
Cet appareil numerique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du Reglement sur le material
brouilleur du Canada.
36B
FCC Part 68 Telecom
1. This equipment complies with part 68 of the Federal Communications Commission Rules. On the outside
surface of this equipment is a label that contains, among other information, the FCC registration number.
This information must be provided to the telephone company.
2. The suitable USOC jack (Universal Service Order Code connecting arrangement) for this equipment is
shown below. If applicable, the facility interface codes (FIC) and service order codes (SOC) are shown.
3. An FCC-compliant telephone cord and modular plug is provided with this equipment. This equipment is
designed to be connected to the telephone network or premises wiring using a compatible modular jack
that is Part 68 compliant. See installation instructions for details.
4. The ringer equivalence number (REN) is used to determine the number of devices that may be connected
to the telephone line. Excessive RENs on the telephone line may result in the device not ringing in response
to an incoming call. In most, but not all, areas the sum of the RENs should not exceed 5.0. To be certain of
the number of devices that may be connected to the line, as determined by the total RENs, contact the
local telephone company.
5. If this equipment causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone company will notify you in
advance that temporary discontinuance of service may be required. But if advance notice is not practical,
22 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 23

APPENDIX A – REGULATORY COMPLIANCE
the telephone company will notify you as soon as possible. Also, you will be advised of your right to file a
complaint with the FCC if you believe it is necessary.
6. The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment, operations, or procedures that
could affect the operation of the equipment. If this happens, the telephone company will provide advance
notice in order for you to make necessary modifications in order to maintain uninterrupted service.
7. If trouble is experienced with this equipment (the model of which is indicated below) please contact MultiTech Systems, Inc. at the address shown below for details of how to have repairs made. If the trouble is
causing harm to the telephone network, the telephone company may request you remove the equipment
from the network until the problem is resolved.
8. No repairs are to be made by you. Repairs are to be made only by Multi-Tech Systems or its licensees.
Unauthorized repairs void registration and warranty.
9. This equipment should not be used on party lines or coin lines.
10. If so required, this equipment is hearing-aid compatible.
11. Manufacturing Information:
Manufacturer: Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Trade Name MultiMobile USB
Model Number: MT9234MU
Registration Number: AU7MM04B9234MU
Service Center in USA: Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View, MN 55112
U.S.A.
(763) 785-3500
(763) 785-9874 Fax
37B
Canadian Limitations Notice
Notice: The ringer equivalence number (REN) assigned to each terminal device provides an indication of the
maximum number of terminals allowed to be connected to a telephone interface. The termination on an
interface may consist of any combination of devices subject only to the requirement that the sum of the ringer
equivalence numbers of all the devices does not exceed 5.
Notice: The Industry Canada label identifies certificated equipment. This certification means that the
equipment meets certain telecommunications network protective, operational and safety requirements.
The Industry Canada label does not guarantee the equipment will operate to the user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure that it is permissible to be connected to the facilities
of the local telecommunications company. The equipment must also be installed using an acceptable
method of connection. The customer should be aware that compliance with the above conditions may not
prevent degradation of service in some situations. Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an
authorized Canadian maintenance facility designated by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by
the user to this equipment or equipment malfunctions may give the telecommunications company cause
to request the user to disconnect the equipment.
Users should ensure for their own protection that the electrical ground connections of the power utility,
telephone lines and internal metallic water pipe system, if present, are connected together. This
precaution may be particularly important in rural areas.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 23
Page 24

APPENDIX A – REGULATORY COMPLIANCE
Caution: Users should not attempt to make such connections themselves, but should contact the appropriate
electric inspection authority, or electrician, as appropriate.
38B
EMC, Safety, and R&TTE Directive Compliance
The CE mark is affixed to this product to confirm compliance with the following European Community
Directives:
Council Directive 2004/108/EC of 15 December 2004 on the approximation of the laws of Member States
relating to electromagnetic compatibility;
and
Council Directive 2006/95/EC of 12 December 2006 on the harmonization of the laws of Member States
relating to electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits;
and
Council Directive 1999/5/EC of 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunications terminal
equipment and the mutual recognition of their conformity.
39B
International Modem Restrictions
Some dialing and answering defaults and restrictions may vary for international modems. Changing
settings may cause a modem to become non-compliant with national telecom requirements in specific
countries. Also note that some software packages may have features or lack restrictions that may cause
the modem to become non-compliant.
40B
New Zealand Telecom Warning Notice
1. The grant of a Telepermit for any item of terminal equipment indicates only that Telecom has
accepted that the item complies with minimum conditions for connection to its network. It
indicates no endorsement of the product by Telecom, nor does it provide any sort of warranty.
Above all, it provides no assurance that any item will work correctly in all respects with another
item of Telepermitted equipment of a different make or model, nor does it imply that any
product is compatible with all of Telecom’s network services. .
This equipment is not capable under all operating conditions of correct operation at the higher
speed which it is designated. 33.6 kbps and 56 kbps connections are likely to be restricted to
lower bit rates when connected to some PSTN implementations. Telecom will accept no
responsibility should difficulties arise in such circumstances.
2. Immediately disconnect this equipment should it become physically damaged, and arrange for
its disposal or repair.
3. This modem shall not be used in any manner which could constitute a nuisance to other
Telecom customers.
24 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 25

APPENDIX A – REGULATORY COMPLIANCE
4. This device is equipped with pulse dialing, while the Telecom standard is DTMF tone dialing.
There is no guarantee that Telecom lines will always continue to support pulse dialing.
Use of pulse dialing, when this equipment is connected to the same line as other equipment,
may give rise to ‘bell tinkle’ or noise and may also cause a false answer condition. Should such
problems occur, the user should not contact the Telecom Faults Service.
The preferred method of dialing is to use DTMF tones, as this is faster than pulse (decadic)
dialing and is readily available on almost all New Zealand telephone exchanges.
5. Warning Notice: No ‘111’ or other calls can be made from this device during a mains power
failure.
6. This equipment may not provide for the effective hand-over of a call to another device
connected to the same line.
7. Some parameters required for compliance with Telecom’s Telepermit requirements are
dependent on the equipment (PC) associated with this device. The associated equipment shall
be set to operate within the following limits for compliance with Telecom’s Specifications:
For repeat calls to the same number:
There shall be no more than 10 call attempts to the same number within any 30-minute
period for any single manual call initiation, and
The equipment shall go on-hook for a period of not less than 30 seconds between the end of
one attempt and the beginning of the next attempt.
For automatic calls to different numbers:
The equipment shall be set to ensure that automatic calls to different numbers are spaced
such that there is no less than 5 seconds between the end of one call attempt and the
beginning of another.
For automatically answered incoming calls:
The equipment shall be set to ensure that calls are answered between 3 and 30 seconds of
receipt of ringing.
8. For correct operation, total of the RNs of all devices connected to a single line at any time
should not exceed 5.
41
Russian Statement
MT9234MU is Russia approved, Declaration of Conformity # Д-МДФТ-0827 through 02/20/2020 (for
MT9234MU).
South African Notice
This modem must be used in conjunction with an approved surge protection device.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 25
Page 26

APPENDIX A – REGULATORY COMPLIANCE
Thailand Approval
Translation in Thai
“This telecom device and equipment is conform to technical standard no….”
or
“This telecom device and equipment is conform to requirement to NTC”
“ .........”
or
“ .”
Brazil Regulatory Special Cable Requirement
Model: MT9234MU – special cable needed.
Attention:
A special phone cable is required for regulatory compliance.
Um cabo especial para telefone é requerido para a conformidade regulatória.
26 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 27

5BAppendix B – Installing on Linux
The MT9234MU supports Linux 2.4 kernel versions (2.4.28 and above), 2.6 kernel versions 2.6.8 through
2.6.10, and, with a special patch, Linux kernel versions 2.6.11 through 2.6.20.4 and above. There are three
separate installation procedures for these ranges of kernel versions. When installation is complete, you
must use AT commands to configure the modem for the country in which it is operating.
26BInstalling the Modem on Computers Using the Linux 2.4 Kernel
This procedure applies to Linux 2.4 kernel versions 2.4.28 and above.
These tgz and source RPM packages (ti_usb-1.2.tgz and ti_usb-1.2-1.src.rpm) contain a device driver for
the MT9234MU’s TI USB 3410 processor in the Linux 2.4 kernels.
This package is designed for these hardware platforms: a standard PC with i486, Pentium, or compatible
CPUs (32 bit x86).
This package has been tested on these Linux distributions:
Red Hat 8.0
Red Hat 9.0
SUSE Linux Standard Server 8.0
Most likely this package will work on many other Linux distributions based on the 2.4 kernels, but this has
not yet been tested. Note that different distributions can make custom changes to the Linux kernel, and
there is a small chance that these changes might be incompatible with this package.
This package will not work in the Linux 2.6 kernels. Separate packages of the TI USB 3410/5052 driver are
available for the Linux 2.6 kernels.
These packages are available from http://www.brimson.com/downloads
The tgz package will be named ti_usb-X.Y.tgz, and the source RPM package will be named ti_usb-X.YZ.src.rpm, where X.Y-Z is the version number. See www.brimson.com/downloads/README for a
description of the packages available.
If you have questions or problems with this package please contact Texas Instruments technical support or
Brimson technical support.
27 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 28

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
1. cd /usr/src/linux-<version>
Change to the source directory.
2. make mrproper
Clean up any old files.
3. Use either of these commands:
make oldconfig
-OR-
make cloneconfig
Make a configuration file to match your
running kernel.
for Red Hat
for SUSE
For other distributions these same
commands might work, or you might
need to find a config file in /boot or in a
configs directory, copy it to .config, and
run "make oldconfig".
4. make dep
Create the dependency and version files.
57BInstalling the Kernel Sources
To build the TI USB driver you must have the matching kernel sources for your kernel.
To verify that you have matching kernel sources, run "uname -r" to get the version of the running kernel.
Then check for the directory /usr/src/linux-<version>, /lib/modules/<version>/source,
/lib/modules/<version>/build, or /usr/src/linux-<stripped_version>, where stripped_version has the extra
version information removed. In these directories look for the files include/linux/autoconf.h and .config.
If you do not find the correct kernel source directory, you must find and install the kernel sources from
your distribution CDs or other media.
58BPreparing the Kernel Sources
This step may or may not be necessary, depending on how your Linux distribution installs the kernel
sources.
Log in as root and do the following:
If you have built your own kernel, the kernel sources are already installed and prepared. If you are using a
kernel that came with a Linux distribution, it can sometimes be difficult to get the kernel sources correctly
installed and prepared, since each Linux distribution handles kernel sources slightly differently.
For example, if you get errors about the wrong kernel version, you may have installed the wrong kernel
sources, or you may need to edit the kernel version in the top level Makefile of the kernel sources. If you
get compilation errors, perhaps you forgot to run "make oldconfig" and "make dep".
If you have difficulties, look carefully at the error messages when installing the TGZ or RPM packages-those messages should give you an indication of just what the error is.
28 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 29

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
1.
rpmbuild --rebuild ti_usb-X.Y-Z.src.rpm
-- OR --
rpm --rebuild ti_usb-X.Y-Z.src.rpm
This command builds the driver package
for your kernel.
For Red Hat.
For SUSE.
2.
cd /usr/src/redhat/RPMS/i386
-- OR --
cd /usr/src/packages/RPMS/i386
For Red Hat.
For SUSE.
Or use the appropriate path for your
Linux distribution.
3. rpm -Uvh ti_usb-X.Y-Z.i386.rpm
This command installs the driver package.
59BBuilding and Installing the TI USB Driver from the Source RPM Package
Follow this step if your distribution supports RPM packages; otherwise, follow the next step on installing
from a TGZ package.
You need the TI USB source RPM package for this step. The Introduction section above describes where to
find the latest TI USB source RPM.
Log in as root and do the following:
If there are problems in this process, you may need to go back to install and prepare the kernel sources as
described above. You may need to remove the RPM package with "rpm -e ti_usb-X.Y-Z" or remove RPM
temporary files. Red Hat stores RPM temporary files in /var/tmp and /usr/src/redhat/BUILD; other
distributions may store them in other places.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 29
Page 30

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
1. tar xvzf ti_usb-X.Y.tgz
Un-package the files.
2. cd ti_usb-X.Y
3. ./configure
Configure the package for your
distribution and kernel.
4. make
Build the driver.
5. make install
Install the ti_usb driver.
60BBuilding and Installing the TI USB Driver from the TGZ Package
Use the TI USB tgz package for this step. The Introduction section above describes where to find the latest
TI USB tgz package.
Log in as root and do the following:
If there are problems in this process, you may need to go back to install and prepare the kernel sources as
described above.
Loading the TI USB Driver
The ti_usb driver is automatically loaded when you plug in the TI USB 3410 device, provided your device
uses the default vendor and product ids. If it does not, see the section entitled "VENDOR and PRODUCT
IDS" in the Release Notes file for Linux 2.4 kernel installations (on the product CD as file name
ti_usb_release_notes-1 2.txt).
The first TI USB 3410 device plugged in appears as /dev/ttyTIUSB0, the next as /dev/ttyTIUSB1, and so on.
Note that these device names are different from the device names used by the Linux usbserial driver. See
the section below entitled "DEVICE FILES" for more information.
If TI USB devices were in use before installing the new TI USB driver, old versions of the drivers are still
loaded. You must unload these old versions before the newly installed driver is used.
The simplest way to unload the old drivers and load the new is to reboot.
Alternatively, you can close all open TI USB serial ports, disconnect the TI USB serial devices, and then
unload the old TI USB serial driver with the command
rmmod ti_usb
Completion. Then reconnect the TI USB serial devices and the new driver is loaded.
30 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 31

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Device Files
Because the TI USB driver does not use usbserial (to avoid known problems with usbserial) it uses its own
device file names, /dev/ttyTIUSB0, /dev/ttyTIUSB1, and so on.
The device files are created automatically when the ti_usb driver is loaded. This is done by the module
post-install command in /etc/modules.conf, which runs the script /etc/ti_usb/make_devices.
You can change the device names that ti_usb uses. First you should remove the old device files by running
/etc/ti_usb/make_devices remove
Then edit /etc/ti_usb/make_devices. At the top of this file you find these parameters:
DEVICE_NAME which determines the basename of the TI USB device files.
DEVICE_COUNT which determines the number of device files created, DEVICE_GROUP which
determines the group owner of the device files.
DEVICE_PERMISSIONS which determines the device file permissions.
For example, to create 8 TI USB device files named /dev/ttyusb0 through /dev/ttyusb7, owned by the
uucp group, and having permissions 0660, change the parameters like this
DEVICE_NAME=/dev/ttyusb
DEVICE_COUNT=8
DEVICE_GROUP=uucp
DEVICE_PERMISSIONS=0660
After editing make_devices, run the script to create the new device files, like this
/etc/ti_usb/make_devices
If you use devfs, the ti_usb devices are /dev/usb/ti/0, /dev/usb/ti/1, and so on in the order they are
plugged in. The ti_usb driver has not been tested with devfs.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 31
Page 32

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
cd ti_usb-X.Y
Give a full or relative path to the
unpacked source file directory.
make uninstall
44B
Uninstalling the TI USB Driver (for 2.4 kernel versions)
If you installed the TI USB RPM package, you can uninstall it by logging in as root and running the
command
rpm -e ti_usb-X.Y-Z
If you installed the TI USB TGZ package, you can uninstall it by logging in as root and running the following
commands:
Installing the Modem on Computers Using the Linux 2.6 Kernel
26BThis procedure applies to Linux 2.6 kernel versions 2.6.8 through 2.6.10.
These tgz and source RPM packages (ti_usb_2.6-1.2.tgz and ti_usb_2.6-1.2-1.src.rpm) contain a device
driver for the MT9234MU’s TI USB 3410 processor in the Linux 2.6 kernels.
These packages have been tested on the Fedora Core 2 Linux distribution.
Most likely these packages work on many other Linux distributions based on the 2.6 kernels, but this has
not yet been tested. Note that different distributions can make custom changes to the Linux kernel, and
there is a small chance that these changes might be incompatible with this package.
The TI USB 3410/5052 driver has been tested in the kernel.org kernels 2.6.5 through a pre-release version
of 2.6.10, and in the Fedora Core 2 kernels 2.6.5-1.358 and 2.6.9-1.6. There are limitations in kernels
before 2.6.8; see the section on Known Limitations in the Release Notes file for kernel 2.6 (the file name is
ti_usb_2 6_release_notes-1 2.txt).
These packages do not work in the Linux 2.4 kernels (however, installation in the 2.4 kernels is covered
earlier in this chapter).
These packages are available from http://www.brimson.com/downloads
The tgz package is named ti_usb_2.6-X.Y.tgz, and the source RPM package is named ti_usb_2.6-X.YZ.src.rpm, where X.Y-Z is the version number. See www.brimson.com/downloads/README for a
description of the packages available.
If you have questions or problems with this package, please contact Texas Instruments technical support
or Brimson technical support.
Installing the Kernel Sources
To build the TI USB driver you must have the matching kernel sources for your kernel.
In particular, you must have the file usb-serial.h for your kernel sources. Sometimes Linux distributions
include the kernel headers but not the complete kernel sources, and usb-serial.h is missing. However, the
complete kernel sources should still be available as a separate add-on package.
32 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 33

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
1. cd /usr/src/linux-<version>
Change to the source directory.
2. make mrproper
Clean up any old files.
3. Use either of these commands:
make oldconfig
-OR-
make cloneconfig
Make a configuration file to match your
running kernel.
for Red Hat
for SUSE
For other distributions these same
commands might work, or you might
need to find a config file in /boot or in a
configs directory, copy it to .config, and
run "make oldconfig".
4. make prepare
To prepare the kernel sources for your
machine.
To verify that you have matching kernel sources, run "uname -r" to get the version of the running kernel.
Then check for the directory /usr/src/linux-<version>, /lib/modules/<version>/source,
/lib/modules/<version>/build, or /usr/src/linux-<stripped_version>, where stripped_version has the extra
version information removed. In these directories look for the files include/linux/autoconf.h, .config, and
drivers/usb/serial/usb-serial.h.
If you do not find the correct kernel source directory, you must find and install the kernel sources from
other media.
Preparing the Kernel Sources
This step may or may not be necessary, depending on how your Linux distribution installs the kernel
sources.
Log in as root and do the following:
If you built your own kernel, the kernel sources are already installed and prepared. If you are using a
kernel that came with a Linux distribution, it can sometimes be difficult to get the kernel sources correctly
installed and prepared, since each Linux distribution handles kernel sources slightly differently.
For example, if you get errors about the wrong kernel version, you may have installed the wrong kernel
sources, or you may need to edit the kernel version in the top level Makefile of the kernel sources. If you
get errors about a missing usb-serial.h, you may only have the kernel headers installed. If you have
trouble getting the full kernel sources installed and prepared, you can copy the correct version of usbserial.h to drivers/usb/serial in the kernel headers directory and then the other kernel sources are not
needed.
If you have difficulties, look carefully at the error messages when installing the TGZ or RPM packages.
Those messages should give you an indication of just what the error is.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 33
Page 34

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
1.
rpmbuild --rebuild ti_usb_2.6-X.Y-Z.src.rpm
-- OR --
rpm --rebuild ti_usb_2.6-X.Y-Z.src.rpm
This command builds the driver package
for your kernel.
For Red Hat.
For SUSE.
2.
cd /usr/src/redhat/RPMS/i386
-- OR --
cd /usr/src/packages/RPMS/i386
For Red Hat.
For SUSE.
Or use the appropriate path for your
Linux distribution.
3. rpm -Uvh ti_usb_2.6-X.Y-Z.i386.rpm
This command installs the driver package.
Building and Installing the TI USB Driver from the Source RPM Package
Follow this step if your distribution supports RPM packages; otherwise, follow the next step on installing
from a TGZ package.
You need the TI USB 3410/5052 source RPM package for this step. The Introduction section above
describes where to find the latest TI USB 3410/5052 source RPM.
Log in as root and do the following:
If there are problems in this process, you may need to go back to install and prepare the kernel sources as
described above. You may need to remove the RPM package with "rpm -e ti_usb_2.6-X.Y-Z" or remove
RPM temporary files. Red Hat stores RPM temporary files in /var/tmp and /usr/src/redhat/BUILD; other
distributions may store them in other places.
34 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 35

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
1. tar xvzf ti_usb_2.6-X.Y.tgz
Un-package the files.
2. cd ti_usb_2.6-X.Y
3. ./configure
Configure the package for your
distribution and kernel.
4. make install
Build and install the ti_usb_3410_5052
driver.
Building and Installing the TI USB Driver from the TGZ Package
Follow this step if your distribution does not support RPM packages; otherwise, follow the previous step
on installing from an RPM package.
You need the TI USB 3410/5052 tgz package for this step. The Introduction section above describes where
to find the latest TI USB 3410/5052 tgz package.
Log in as root and do the following:
If there are problems in this process, you may need to go back to install and prepare the kernel sources as
described above.
Loading the TI USB 3410/5052 Driver
The ti_usb_3410_5052 driver should be automatically loaded when you plug in the TI USB 3410/5052
devices, provided your device uses the default vendor and product ids. If it does not, see the section of
the Release Notes file "VENDOR and PRODUCT IDS" (on the product CD as file name
ti_usb_2.6_release_notes-1.2.txt ).
The first TI USB 3410/5052 device plugged in appears as /dev/ttyUSB0, then next as /dev/ttyUSB1, and so
on. These device names are shared with other USB serial devices.
If TI USB devices had been in use before installing the new TI USB driver, old versions of the drivers are still
loaded. These old versions must be unloaded before the newly installed driver is used.
The simplest way to unload the old drivers and load the new is to reboot.
Alternatively, you can close all open TI USB serial ports, disconnect the TI USB serial devices, and then
unload the old TI USB serial driver with the command
rmmod ti_usb_3410_5052
Completion. Then reconnect the TI USB serial devices and the new driver is loaded.
47B
Uninstalling the TI USB Driver (for 2.6 kernel versions)
If you installed the TI USB RPM package, you can uninstall it by logging in as root and running the
command
rpm -e ti_usb_2.6-X.Y-Z
If you installed the TI USB TGZ package, you can uninstall it by logging in as root and running the following
commands:
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 35
Page 36

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
cd ti_usb_2.6-X.Y
Give a full or relative path to the
unpacked source file directory.
make uninstall
Installing the Modem on Computers Using the Linux 2.6.20
Kernel and Above
48B
This procedure applies to Linux 2.6 kernel versions 2.6.11 through 2.6.20 and higher.
This tgz package contains a patch for the Linux kernel version 2.6.20 and later to add support for
MultiTech modems. The patch was generated from the 2.6.20.4 kernel source. Additional support files like
hotplug scripts, udev rules and firmware images are also included.
The TI USB 3410/5052 driver should be included in the official Linux kernel in version 2.6.20 or later. The
official Linux kernel does not yet have support for the Multitech modems, however; to add that support
you need this package.
This package has been tested on these Linux distributions: (a) Fedora Core 6, and (b) CentOS 5.
Most likely this package works on many other Linux distributions based on the 2.6 kernels, but this has not
yet been tested. Note that different distributions can make custom changes to the Linux kernel, and there
is a small chance that these changes might be incompatible with this package.
These packages are available from http://www.brimson.com/downloads
If you have questions or problems with this package, please contact Texas Instruments technical support
or Brimson technical support.
68BPatching and Rebuilding the Kernel
Apply the patch ti_usb_multitech_2.6.20.4.patch. This patch should apply to 2.6.20.4 and later kernels.
Then rebuild and reinstall your kernel and/or kernel modules. Be sure the TI USB driver is configured on.
Detailed instructions on patching and building a kernel can be found elsewhere.
69BInstalling the Hotplug Scripts
The ti_usb_3410_5052 driver needs a hotplug script to work correctly. This hotplug script is used to
change the device configuration.
Copy ti_usb_3410_5052 to /etc/hotplug/usb/ti_usb_3410_5052. Be sure the script is owned by root:root
and has permissions r-xr-xr-x.
If the device configuration is not being set properly, you might need a slightly different hotplug script,
depending on your Linux distribution. If this does not work, remove /etc/hotplug/usb/ti_usb_3410_5052
and instead copy /etc/ti_usb/ti_usb_3410_5052.hotplug into /etc/hotplug.d/usb.
Some distribution have deprecated hotplug scripts. If this is the case, you most likely need a udev rule to
perform this function.
36 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 37

APPENDIX B – INSTALLING ON LINUX
Command
Explanation
cd ti_usb_2.6-X.Y
Give a full or relative path to the
unpacked source file directory.
make uninstall
70BInstalling udev Rules
The ti_usb_3410_5052 driver needs a udev rule to work correctly. This udev rule is used to change the
device configuration.
Copy 25_ti_usb_3410_5052.rule to /etc/udev/rules.d. Be sure the rule is owned by root:root and has
permissions r-xr-xr-x.
If the device configuration is not being set properly, you might need a slightly different udev rule, depending
on your Linux distribution.
Note: This is only needed if firmware is not built into the driver.
71BInstalling the Firmware Images
Copy ti_mts_fw_cdma, ti_mts_fw_edge, ti_mts_fw_gsm, ti_mts_fw_mt9234mu and
ti_mts_fw_mt9234zbausb to /usr/lib/hotplug/firmware/ or /lib/firmware depending on your distribution.
Be sure the files are owned by root:root and have permissions r--r--r--.
72BLoading the TI USB 3410/5052 Driver
The ti_usb_3410_5052 driver should be automatically loaded when you plug in the TI USB 3410/5052
devices, provided your device uses the default vendor and product ids. If it does not, see the section
below titled "VENDOR and PRODUCT IDS".
The first TI USB 3410/5052 device plugged in appears as /dev/ttyUSB0, then next as /dev/ttyUSB1, and so
on. These device names are shared with other USB serial devices.
If TI USB devices had been in use before installing the new TI USB driver, old versions of the drivers are still
loaded. You must unload these old versions before the newly installed driver is used.
The simplest way to unload the old drivers and load the new is to reboot.
Alternatively, you can close all open TI USB serial ports, disconnect the TI USB serial devices, and then
unload the old TI USB serial driver with the command
rmmod ti_usb_3410_5052
Then reconnect the TI USB serial devices and the new driver is loaded.
50B
Uninstalling the TI USB Driver (for 2.6 kernel versions)
If you installed the TI USB RPM package, you can uninstall it by logging in as root and running the
command
rpm -e ti_usb_2.6-X.Y-Z
If you installed the TI USB TGZ package, you can uninstall it by logging in as root and running the following
commands:
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 37
Page 38

6BAppendix C – Environmental Information
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment
WEEE Directive
The WEEE Directive places an obligation on EU-based manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and importers
to take-back electronics products at the end of their useful life. A sister directive, ROHS (Restriction of
Hazardous Substances) complements the WEEE Directive by banning the presence of specific hazardous
substances in the products at the design phase. The WEEE Directive covers all MultiTech products
imported into the EU as of August 13, 2005. EU-based manufacturers, distributors, retailers and importers
are obliged to finance the costs of recovery from municipal collection points, reuse, and recycling of
specified percentages per the WEEE requirements.
Instructions for Disposal of WEEE by Users in the European Union
The symbol shown below is on the product or on its packaging, which indicates that this product must not
be disposed of with other waste. Instead, it is the user’s responsibility to dispose of their waste equipment
by handing it over to a designated collection point for the recycling of waste electrical and electronic
equipment. The separate collection and recycling of your waste equipment at the time of disposal will
help to conserve natural resources and ensure that it is recycled in a manner that protects human health
and the environment. For more information about where you can drop off your waste equipment for
recycling, please contact your local city office, your household waste disposal service or where you
purchased the product.
July, 2005
REACH Statement
Registration of Substances
After careful review of the legislation and specifically the definition of an “article” as defined in EC
Regulation 1907/2006, Title II, Chapter 1, Article 7.1(a)(b), it is our current view Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
products would be considered as “articles”. In light of the definition in § 7.1(b) which requires registration
of an article only if it contains a regulated substance that “is intended to be released under normal or
reasonably foreseeable conditions of use,” Our analysis is that Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. products
constitute nonregisterable articles for their intended and anticipated use.
Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC)
Per the candidate list of Substances of Very High Concern (SVHC) published October 28, 2008 we have
reviewed these substances and certify the Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. products are compliant per the EU
“REACH” requirements of less than 0.1% (w/w) for each substance. If new SVHC candidates are published
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. MT9234MU User Guide 38
Page 39

APPENDIX C – ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATION
by the European Chemicals Agency, and relevant substances have been confirmed, that exceeds greater
than 0.1% (w/w), Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. will provide updated compliance status.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. also declares it has been duly diligent in ensuring that the products supplied are
compliant through a formalized process which includes collection and validation of materials declarations
and selective materials analysis where appropriate. This data is controlled as part of a formal quality
system and will be made available upon request.
Restriction of the Use of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Certificate of Compliance
2011/65/EU
MultiTech Systems confirms that its embedded products comply with the chemical concentration
limitations set forth in the directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament (Restriction of the use of
certain Hazardous Substances in electrical and electronic equipment - RoHS)
These MultiTech products do not contain the following banned chemicals1:
● Lead, [Pb] < 1000 PPM
● Mercury, [Hg] < 1000 PPM
● Hexavalent Chromium, [Cr+6] < 1000 PPM
● Cadmium, [Cd] < 100 PPM
● Polybrominated Biphenyl, [PBB] < 1000 PPM
● Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether, [PBDE] < 1000 PPM
Environmental considerations:
● Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) =1
● Maximum Soldering temperature = 260C (in SMT reflow oven)
1
Lead usage in some components is exempted by the following RoHS annex, therefore higher lead
concentration would be found in some modules (>1000 PPM);
–Resistors containing lead in a glass or ceramic matrix compound.
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 39
Page 40

APPENDIX C – ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATION
Name of the
Component
Hazardous/Toxic Substance/Elements
Lead
(PB)
Mercury
(Hg)
Cadmium
(CD)
Hexavalent
Chromium
(CR6+)
Polybrominated
Biphenyl
(PBB)
Polybrominated
Diphenyl Ether
(PBDE)
Printed Circuit Boards
O O O O O
O
Resistors
X O O O O
O
Capacitors
X O O O O
O
Ferrite Beads
O O O O O
O
Relays/Opticals
O O O O O
O
ICs
O O O O O
O
Diodes/ Transistors
O O O O O
O
Oscillators and Crystals
X O O O O
O
Regulator
O O O O O
O
Voltage Sensor
O O O O O
O
Transformer
O O O O O
O
Speaker
O O O O O
O
Connectors
O O O O O
O
LEDs
O O O O O
O
Screws, Nuts, and other
Hardware
X O O O O
O
AC-DC Power Supplies
O O O O O
O
Software /
Documentation CDs
O O O O O
O
Booklets and
Paperwork
O O O O O
O
Chassis
O O O O O
O
Information on HS/TS Substances According to Chinese
Standards
In accordance with China’s Administrative Measures on the Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic
Information Products (EIP) # 39, also known as China RoHS, the following information is provided
regarding the names and concentration levels of Toxic Substances (TS) or Hazardous Substances (HS)
which may be contained in Multi-Tech Systems Inc. products relative to the EIP standards set by China’s
Ministry of Information Industry (MII).
X Represents that the concentration of such hazardous/toxic substance in all the units of
homogeneous material of such component is higher than the SJ/Txxx-2006 Requirements for
Concentration Limits.
O Represents that no such substances are used or that the concentration is within the
aforementioned limits.
40 MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide
Page 41

APPENDIX C – ENVIRONMENTAL INFORMATION
成分名称
有害/有毒物质/元素
铅 (PB)
汞
(Hg)
镉
(CD)
六价铬
(CR6+)
多溴联苯
(PBB)
多溴二苯醚
(PBDE)
印刷电路板
O O O O O
O
电阻器
X O O O O
O
电容器
X O O O O
O
铁氧体磁环
O O O O O
O
继电器/光学部件
O O O O O
O
IC
O O O O O
O
二极管/晶体管
O O O O O
O
振荡器和晶振
X O O O O
O
调节器
O O O O O
O
电压传感器
O O O O O
O
变压器
O O O O O
O
扬声器
O O O O O
O
连接器
O O O O O
O
LED
O O O O O
O
螺丝、螺母以及其它五金件
X O O O O
O
交流-直流电源
O O O O O
O
软件/文档 CD
O O O O O
O
手册和纸页
O O O O O
O
底盘
O O O O O
O
Information on HS/TS Substances According to Chinese
Standards (in Chinese)
依照中国标准的有毒有害物质信息
根据中华人民共和国信息产业部 (MII) 制定的电子信息产品 (EIP) 标准-中华人民共和国《电子信息
产品污染控制管理办法》(第 39 号),也称作中国 RoHS,下表列出了 Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. 产
品中可能含有的有毒物质 (TS) 或有害物质 (HS) 的名称及含量水平方面的信息。
X 表示所有使用类似材料的设备中有害/有毒物质的含量水平高于 SJ/Txxx-2006 限量要求。
O 表示不含该物质或者该物质的含量水平在上述限量要求之内。
MultiMobile USB User Guide MT9234MU User Guide 41
Page 42

Appendix D – ASCII Conversion
ASCII Conversion Chart
CTRL CODE HEX DEC CODE HEX DEC CODE HEX DEC CODE HEX DEC
@ NUL 00 0 SP 20 32 @ 40 64 ` 60 96
A SOH 01 1 ! 21 33 A 41 65 a 61 97
B STX 02 2 " 22 34 B 42 66 b 62 98
C ETX 03 3 # 23 35 C 43 67 c 63 99
D EOT 04 4 $ 24 36 D 44 68 d 64 100
E ENQ 05 5 % 25 37 E 45 69 e 65 101
F ACK 06 6 & 26 38 F 46 70 f 66 102
G BEL 07 7 ' 27 39 G 47 71 g 67 103
H BS 08 8 ( 28 40 H 48 72 h 68 104
I HT 09 9 ) 29 41 I 49 73 i 69 105
J LF 0A 10 * 2A 42 J 4A 74 j 6A 106
K VT 0B 11 + 2B 43 K 4B 75 k 6B 107
L FF 0C 12 , 2C 44 L 4C 76 l 6C 108
M CR 0D 13 - 2D 45 M 4D 77 m 6D 109
N SO 0E 14 . 2E 46 N 4E 78 n 6E 110
O SI 0F 15 / 2F 47 O 4F 79 o 6F 111
P DLE 10 16 0 30 48 P 50 80 p 70 112
Q DC1 11 17 1 31 49 Q 51 81 q 71 113
R DC2 12 18 2 32 50 R 52 82 r 72 114
S DC3 13 19 3 33 51 S 53 83 s 73 115
T DC4 14 20 4 34 52 T 54 84 t 74 116
U NAK 15 21 5 35 53 U 55 85 u 75 117
V SYN 16 22 6 36 54 V 56 86 v 76 118
W ETB 17 23 7 37 55 W 57 87 w 77 119
X CAN 18 24 8 38 56 X 58 88 x 78 120
Y EM 19 25 9 39 57 Y 59 89 y 79 121
Z SUB 1A 26 : 3A 58 Z 5A 90 z 7A 122
[ ESC 1B 27 ; 3B 59 [ 5B 91 { 7B 123
\ FS 1C 28 < 3C 60 \ 5C 92 | 7C 124
] GS 1D 29 = 3D 61 ] 5D 93 } 7D 125
^ RS 1E 30 > 3E 62 ^ 5E 94 ~ 7E 126
_ US 1F 31 ? 3F 63 _ 5F 95 DEL 7F 127
NUL Null, or all zeros VT Vertical Tab SYN Sync.
SOH Start of Header FF Form Feed ETB End Transmission Block
STX Start of Text CR Carriage Return CAN Cancel
ETX End of Text SO Shift Out EM End of Medium
EOT End of Transmission SI Shift In SUB Substitute
ENQ Enquiry DLE Data Link Escape ESC Escape
ACK Acknowledge DC1 Device Control 1 FS File Separator
BEL Bell or Alarm DC2 Device Control 2 GS Group Separator
BS Backspace DC3 Device Control 3 RS Record Separator
HT Horizontal Tab DC4 Device Control 4 US Unit Separator
LF Line Feed NAK Negative Acknowledge DEL Delete
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. MT9234MU User Guide 42
Page 43

9BIndex
INDEX
A
AT Commands ........................................................... 7
C
Carrier detect LED ................................................... 18
China’s Administrative Measures on the Control of
Pollution ............................................................. 40
Connecting the modem ............................................ 8
D
Data LED ................................................................. 18
F
Front panel .............................................................. 18
L
LED indicators ....................................................... 18
Line connection ........................................................ 8
Linux 2.4 installation
2.4.28 and above ................................................ 27
Linux 2.6 installation
2.6.11 through 2.6.20 and higher ....................... 36
2.6.8 through 2.6.10 ........................................... 32
Linux Drivers ............................................................. 9
Shipping Package Contents ...................................6
O
Off-Hook LED ......................................................... 18
R
remote configuration............................................. 20
escape character ................................................ 21
remote node operation ......................................... 19
Required equipment .................................................6
RoHS Compliance ................................................... 39
S
Safety Warning Telecom ...........................................6
servicing your modem ........................................... 23
S-registers
S9 21
T
Terminal ready LED .............................................. 18
V
Vista Operating System and Driver Installation ........9
W
M
MT9234MU
Connecting the modem ........................................ 8
Product description .............................................. 5
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. MT9234MU User Guide 43
warranty ................................................................ 23
WEEE Directive ...................................................... 38
 Loading...
Loading...