Page 1

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Models FR3060/3100
User Guide
Page 2

User Guide
88302200 Revision A
MultiFRAD 3000-Series (Model Numbers FR3060 and FR3100)
This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior expressed written permission from
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Copyright © 1998, by Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and
specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Furthermore, Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from
time to time in the content hereof without obligation of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. to notify any person or
organization of such revisions or changes.
Record of Revisions
Revision Description
A Manual released. All pages at revision A.
(3/26/98)
P ATENTS
This Product is covered by one or more of the following U.S. Patent Numbers:
5.355.365; 5.355.653; 5.452.289; 5.453.986
Trademark of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. are MultiFRAD and the Multi-Tech logo.
Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft.
. Other Patents Pending.
TRADEMARK
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View , Minnesota 55112
(612) 785-3500 or (800) 328-9717
Fax 612-785-9874
Tech Support (800) 972-2439
Fax-Back (612) 717-5888
Internet: http://www.multitech.com
Tech Writer: brian@multitech.com
5.301.274; 5.309.562
;
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 - Introduction and Description
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................ 6
Preview of this Guide ................................................................................................................................. 6
Front Panel Description.............................................................................................................................. 8
Back Panel Description ............................................................................................................................ 10
Power Connector ............................................................................................................................... 10
Frame Ground (GND) Connector ...................................................................................................... 10
Internal Composite Link (T1 DSU) Connector ................................................................................... 10
Monitor (XMT/RCV) Connector.......................................................................................................... 10
Command Port Connector ................................................................................................................. 10
External Composite Link (RS232/V .35) Connector............................................................................ 10
Ethernet 10Base-T Connector ........................................................................................................... 10
Channels 1 & 2 (RS232/V.35) Connectors ........................................................................................ 10
Channels 3 - 10 Connectors ...............................................................................................................11
Voice/Fax Channels 1 - 8 Connectors ................................................................................................11
T echnical Specifications........................................................................................................................... 12
Ethernet Port...................................................................................................................................... 12
Command Port................................................................................................................................... 12
Composite Link (external).................................................................................................................. 12
Channel Connectors ............................................................................................................. ............. 12
Electrical/Physical............................................................................................................ .................. 12
Requirement .................................................................................................................... .................. 12
Chapter 2 - Installation
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 14
Unpacking your MultiFRAD 3000 ............................................................................................................. 14
Safety Warnings....................................................................................................................................... 14
Cabling your MultiFRAD 3000.................................................................................................................. 15
Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 18
Loading your Software ............................................................................................................................ 18
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 28
Before Y ou Begin............................................................................................................................... 28
Setup Menu.............................................................................................................................................. 29
IP Setup ................................................................................................................................................... 30
IPX Setup ................................................................................................................................................. 32
Spanning Tree Setup................................................................................................................................ 34
Statistics................................................................................................................................................... 35
IP Statistics ........................................................................................................................................ 36
IPX Port Statistics.............................................................................................................................. 37
STP (Spanning T ree) Port Statistics.................................................................................................. 38
SNMP Statistics ................................................................................................................................. 39
WAN Statistics................................................................................................................................... 40
PPP Statistics .................................................................................................................................... 41
iii
Page 4

Data Port Statistics................................................................................................................................... 42
Frame Relay Statistics....................................................................................................................... 43
WAN Port Setup....................................................................................................................................... 45
Point to Point Setup ................................................................................................................................. 46
Frame Relay Setup .................................................................................................................................. 47
Data Port Configuration............................................................................................................................ 52
Chapter 5 - Remote Configuration
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 54
Modem-Based Remote Configuration Procedure..................................................................................... 54
LAN-Based Remote Configuration ........................................................................................................... 56
Windows Sockets Compliant TCP/IP Stack....................................................................................... 56
Chapter 6 - Router Management
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 60
MultiFRAD Telnet Server Menu................................................................................................................ 60
MultiFRAD Configuration.......................................................................................................................... 61
Remote User Database............................................................................................................................ 61
WEB Browser Management..................................................................................................................... 62
Chapter 7 - Warranty, Service and Tech Support
Introduction .............................................................................................................................................. 66
Limited Warranty ...................................................................................................................................... 66
On-line Warranty Registration............................................................................................................ 66
Tech Support ............................................................................................................................................ 67
Recording MultiFRAD Information ..................................................................................................... 67
Contacting Tech Support via E-mail................................................................................................... 67
Service ..................................................................................................................................................... 68
The Multi-Tech BBS ................................................................................................................................. 68
To log on to the Multi-Tech BBS......................................................................................................... 68
To Download a file.............................................................................................................................. 69
About CompuServe.................................................................................................................................. 70
About the Internet..................................................................................................................................... 70
About the Multi-Tech Fax-Back Service ................................................................................................... 70
Appendices
Appendix A - Cabling Diagrams................................................................................................................ 72
Appendix B - Regulatory Information ....................................................................................................... 75
Appendix C - Network Overview .............................................................................................................. 76
Glossary
Index
iv
Page 5

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 1 - Introduction and Description
Page 6

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
Welcome to Multi-Tech's new MultiFRAD 3000 series, model numbers 3060 and 3100, a Frame
Relay Access Device (FRAD) that encapsulates non-packetized data streams from serial and LAN
devices into frame relay frames. The MultiFRAD 3000-Series features six or ten synchronous or
asynchronous data channels, an IP/IPX router, and a composite link that connects to a common
carrier frame relay network service or private frame relay network. A FRAD is designed to handle
non-packetized data streams from its data channels and local area networks and frame that data with
header and trailer information prior to transmission to a frame relay network. On the receiving end of
the communication, the FRAD strips away the frame relay control information in order that the target
device is presented with the data packaged in its original form.
The MultiFRAD 3060 allows up to six non-frame relay devices such as LANs or Multiplexers to be
connected to its RS232 data channels, an Ethernet LAN connection for IP or IPX routing or
transparent bridging, an RS232 command port, and a trunk line interface for access to a Frame
Relay Network. The MultiFRAD 3100 allows up to ten non-frame relay devices to be connected,
along with the Ethernet port, command port, and trunk line interface connections.
Note: for the purposes of this manual, all future references to
both model MultiFRAD 3060 and MultiFRAD 3100, unless otherwise noted.
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Composite Link
CD
RCV
XMT
PWR
BTG
Preview of this Guide
This User Guide describes the MultiFRAD and details how to install and configure it. The information
contained in each chapter is as follows:
Chapter 1 - Introduction and Description
Chapter 1 describes the MultiFRAD including front panel descriptions, back panel connectors, and
relevant technical specifications.
Chapter 2 - Installation
This chapter provides information on unpacking and cabling your MultiFRAD. Safety Warnings are
detailed, followed by the installation procedure in which each of the cables are connected to the
MultiFRAD and the unit is powered on.
MultiFRAD
Voice/Fax Channel 8
FXS
E&M
FXO
3000-Series
CTS
RCV
EXT
V35
LNK
Voice/Fax Channel 4 Voice/Fax Channel 3 Voice/Fax Channel 2
FXS
E&M
FXO
Ethernet
Channel 1
V35
V35
LNK
COL
XMT
XMT
RCV
FAX
FAX
Channel 2
Voice/Fax Channel 7
FXS
XMT
E&M
FXO
RCV
XSG
RSG
XMT
RCV
XSG
RSG
FXS
E&M
FXO
Channel 3
Channel 4
RCV
XMT
XMT
XMT
RCV
RCV
Voice/Fax Channel 6
XMT
RCV
XSG
FAX
RSG
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
XSG
FXO
FAX
Channel 6
RSG
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
XSG
FXO
FAX
RSG
Channel 7
Channel 8
XMT
RCV
RCV
XMT
RCV
XSG
FAX
RSG
Channel 5
XMT
RCV
Figure 1. MultiFRAD 3000-Series
XMT
FXS
FXO
FXS
FXO
RCVXMT
Voice/Fax Channel 5
XMT
E&M
RCV
FAX
Voice/Fax Channel 1
XMT
E&M
RCV
FAX
Channel 9 Channel 10
XMT
RCV
should be taken to include
XSG
RSG
XSG
RSG
XMT
RCV
Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
Chapter 3 details the software loading and configuration procedures. The MultiFRAD software
diskettes are windows based, and configuration options are available, and described in this chapter.
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
Chapter 4 describes the MultiFRAD software from an applications approach, and includes examples
of possible uses.
6
Page 7

Chapter 1 - Introduction and Description
Chapter 5 - Remote Configuration
This chapter provides procedures for changing the configuration of a remote MultiFRAD. Remote
configuration allows you to change the configuration of a unit by simply connecting a PC with
communications software to a remote MultiFRAD that has communications software and a modem
connected to the command port. You can then configure the unit.
Chapter 6 - Router Management
Chapter 6 describes a typical Telnet Client application.
Chapter 7 - Warranty, Service and Tech Support
Chapter 7 provides instructions on getting service for your MultiFRAD at the factory , a statement of
the limited warranty , information about our user bulletin board service, and space for recording
information about your MultiFRAD prior to calling Multi-Tech’s Technical Support personnel.
7
Page 8

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Front Panel Description
The front panel of the MultiFRAD contains three main groups of LEDs that provide the information on
the LAN connections, Voice/Fax channel activity (not currently available), and the general status of
the MultiFRAD.
FXS
FXS
Composite Link Ethernet Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 4 Channel 5 Channel 6 Channel 7 Channel 8 Channel 9 Channel 10
RCV
BTG
PWR
The LED’s are as follows:
PWR Power. This indicator lights when the ON/OFF switch is in the ON position.
BTG Booting. This indicator lights when the MultiFRAD is booting.
Composite Link
RCV Receive. This indicator blinks when the composite link is receiving data.
XMT Transmit. This indicator blinks when the composite link is transmitting data.
CD Carrier Detect. This indicator lights when the MultiFRAD detects a carrier signal.
CTS Clear To Send. This indicator lights when the composite link device is ready to transmit
data.
V35 V.35 Interface. This indicator lights when the composite link is configured for a V.35
interface.
EXT External Link. This indicator lights when the MultiFRAD is configured for an external
composite device.
LNK Link. This indicator lights indicating that the MultiFRAD is connected to the local area
network. It will blink slowly when management frames are detected, quickly when at least
one, but not all, pvc’s are active, and will light solidly when all pvc’s are active.
V35 EXT LNK
CD CTS
XMT
RCV
XMT COL LNK
Voice/Fax Channel 8 Voice/Fax Channel 7 Voice/Fax Channel 6 Voice/Fax Channel 5
XMT RCV XSG
E&M FAX
FXD
Voice/Fax Channel 4 Voice/Fax Channel 3 Voice/Fax Channel 2 Voice/Fax Channel 1
E&M FAX
FXD
V35
XMT RCV XSG
XMT
RSG
RSG
RCV
XMT
V35
XMT RCV XSG
FXS
E&M FAX
FXD
FXS
E&M FAX
FXD
RCV
RSG
XMT RCV XSG
RSG
RCVXMT RCVXMT RCVXMT RCVXMT RCVXMT RCVXMTRCVXMT RCVXMT
XMT RCV XSG
FXS
E&M FAX
FXD
XMT RCV XSG
FXS
E&M FAX
FXD
FXS
E&M FAX
FXD
RSG
FXS
E&M FAX
FXD
RSG
XMT RCV XSG
XMT RCV XSG
RSG
RSG
Ethernet
RCV Receive. This indicator blinks when packets are being received from the local area network.
XMT Transmit. This indicator blinks when packets are being transmitted to the local area
network.
COL Collision. This indicator lights when a collision is in progress; that is, when two nodes are
transmitting packets at the same time.
LNK Link. This indicator lights indicating that the MultiFRAD is connected to the local area
network.
Channels 1 and 2
V35 V.35 Interface. This indicator lights when the channel is configured for a V.35 interface.
XMT Transmit. This indicator blinks when the channel is transmitting data.
RCV Receive. This indicator blinks when the channel is receiving data.
Channels 3 through 10
XMT Transmit. This indicator blinks when the channel is transmitting data.
RCV Receive. This indicator blinks when the channel is receiving data.
8
Page 9

Chapter 1 - Introduction and Description
Voice/Fax Channels 1 - 8
Note: the Voice/Fax Channels are not currently supported.
FXS Foreign Exchange Station. This indicator lights when the voice/fax channel is configured
for FXS operation.
FXO Foreign Exchange Office. This indicator lights when the voice/fax channel is configured for
FXO operation.
E&M Ear & Mouth Operation. This indicator lights when the voice/fax channel is configured for
E&M operation.
FAX Fax. This indicator lights when there is fax traffic on the voice/fax channel.
XMT Transmit. This indicator lights when voice or fax data is being transmitted.
RCV Receive. This indicator lights when voice or fax data is being received.
XSG Transmit Signal. This indicator lights when the FXS-configured channel is of f-hook, the
FXO-configured channel is receiving a ring from the telco, or the M lead is active when the
voice/fax channel is configured for E&M operation (i.e., the MultiFRAD is receiving a ring
from the PBX).
RSG Receive Signal. This indicator lights when the FXS-configured channel is ringing, the FXO-
configured channel is off-hook, or the E lead is active on the E&M-configured channel.
9
Page 10

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Back Panel Description
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
8
E&M FXO FXS E&M FXO FXS E&M FXO FXS E&M FXO FXS
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
4
CHANNEL 10
CHANNEL 9
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
7
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
3
CHANNEL 8
CHANNEL 7
CHANNEL 6
CHANNEL 5
The connectors are as follows:
Power Connector
The POWER connector is used to connect the external power supply to the MultiFRAD. The
connector is a 6-pin circular DIN connector.
Frame Ground (GND) Connector
Use the GND connector to connect the MultiFRAD’s frame ground to the PBX’s frame ground when
the MultiFRAD is configured for E&M operation.
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
6
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
2
CHANNEL 4
CHANNEL 3
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
5
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
1
CHANNEL 2 (RS232/V.35)
CHANNEL 1 (RS232/V.35)
10BASET
ETHERNET
COMMAND PORT
EXT. COMPOSITE LINK (RS232/V.35)
INTERNAL
COMPOSITE
LINK
T1 DSU
POWER
MONITOR
XMT RCV
GND
I
O
Internal Composite Link (T1 DSU) Connector
This connector is not currently supported.
Monitor (XMT/RCV) Connector
This connector is not currently supported.
Command Port Connector
Use this DB-25 female connector to connect the MultiFRAD to a PC running Windows in order to
configure the MultiFRAD.
External Composite Link (RS232/V.35) Connector
Use this DB-25 male connector to connect the MultiFRAD to an external modem, DSU, ISDN
terminal adapter, or any device that is synchronous, full duplex, and supplies clocking signals on pins
15 and 17. The connection interface can be either RS232 or V.35.
Ethernet 10Base-T Connector
Use the Ethernet 10Base-T (UTP) connector to connect the MultiFRAD router port to a LAN. The
connector is an RJ-45 jack.
10
Channels 1 & 2 (RS232/V.35) Connectors
The connectors for Channels 1 and 2 are used to connect the MultiFRAD to data devices. A data
device can be a HDLC synchronous device such as a multiplexer or an asynchronous device such as
a PC. These two data channels can be either RS232 or V.35. The connectors are DB-25 female
connectors.
Page 11

Chapter 1 - Introduction and Description
Channels 3 - 10 Connectors
These DB-25 female connectors are used to connect the MultiFRAD to channel devices. These
connections can be to either asynchronous or HDLC synchronous RS232 data equipment such as
multiplexers.
Voice/Fax Channels 1 - 8 Connectors
Note: the Voice/Fax connectors are not currently supported.
E&M
Use the E&M connector to connect the MultiFRAD Voice/Fax channel to the E&M connector on an
analog PBX (Private Branch eXchange) trunk when linking two PBX’s together. The E&M connector
is an RJ-48 jack.
FXO
Use the FXO (Foreign eXchange Office) connector to connect the MultiFRAD V oice/Fax channel to
an analog station card on the local PBX. This connection is also commonly referred to as an OPX
(Off Premises eXtension). The FXO connector is an RJ-11 jack.
FXS
Use the FXS (Foreign eXchange Station) connector to connect the MultiFRAD Voice/Fax channel to
an analog station instrument (telephone, fax machine, or key telephone system). The FXS connector
is an RJ-11 jack.
11
Page 12

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Technical Specifications
• Provides access to frame relay networks for SLIP, PPP, async and HDLC sync devices.
• Trunk and Data ports may be configured as EIA-232 or V.35
• Trunk Speeds up to T1/E1 synchronous
• 4MB DRAM
• 1MB of flash memory
Ethernet Port
• One Ethernet Interface - 10Base-T (twisted Pair) RJ-45 connector
Command Port
• Single 19.2Kbps asynchronous Command Port with a DB-25 female connector
Composite Link (external)
• Access Rate: 1.544M bps (T1) or 2.048M bps (E1) sync on DTE-type RS232 or V.35 interface.
Channel Connectors
• 6 on the FR3060; 10 on the FR3100
• Data Rate: synchronous to 128K bps on RS232/V.35 interface;
asynchronous to 115.2K bps on RS232/V.35 interface.
Electrical/Physical
• Operating Environment: 32-104o F (0-40o C); 95% non-condensing humidity
• Power Requirements: 100-250V AC at 50/60 Hz
• Dimensions: 17.4” wide x 3.75” high x 8” deep
44.2 cm wide x 8.9 cm high x 20.3 cm deep
• Weight: 7.4 lbs.
3.4 kg
Requirement
• PC with Windows 3.1x/95/NT, Terminal/Dumb Terminal @19200 for menu driven local
configuration, or Remote Configuration via web browser or Telnet.
12
Page 13

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 2 - Installation
Page 14
MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
This chapter will guide you through the unpacking and installation of your MultiFRAD. The installation
procedure, which is preceded by important safety instructions, will provide step by step instruction on
cabling and powering-on the MultiFRAD. Chapter 3 will provide instruction on loading and
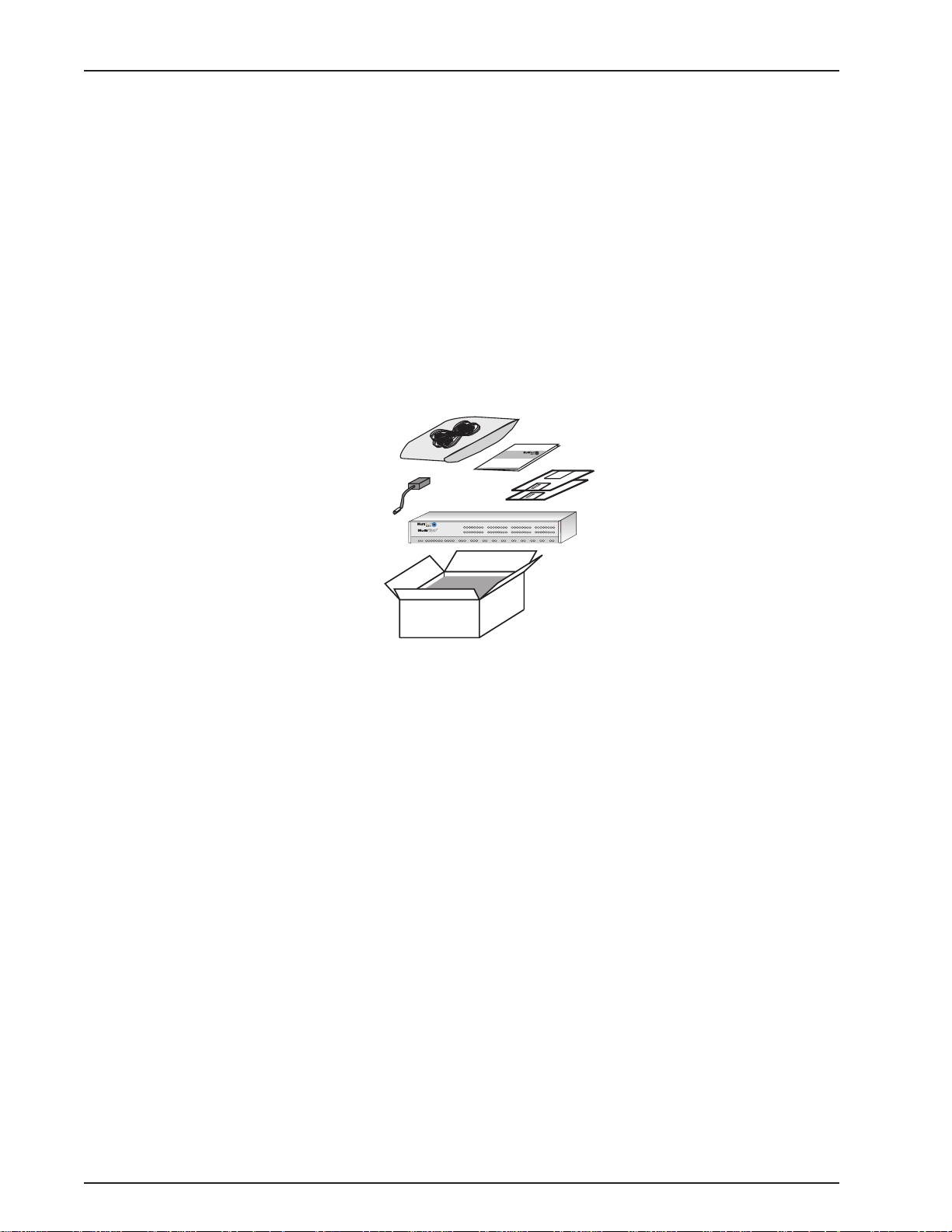
configuring the MultiFRAD software.
Unpacking your MultiFRAD 3000
Remove all items from the box. Your shipping box should contain the MultiFRAD, a power supply ,
various cables, software and manual diskettes, and a MultiFRAD 3000-Series Quick Start Guide.
Please inspect all items before proceeding with the installation. If any of the items appears to be
damaged in any way , do not power up the unit; contact Multi-Tech’ s Technical Support personnel for
advice (See Chapter 7). If no damage is observed, configure the MultiFRAD using the information in
this chapter.
Safety Warnings
1. Never install telephone wiring during a lightning storm.
2. Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for wet
locations.
3. Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been
disconnected at the network interface.
4. Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
5. Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a
remote risk of electrical shock from lightning.
6. Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
Quick Start Guide
Voice/Fax Channel 8
Voice/Fax Channel 7
Voice/Fax Channel 6
Voice/Fax Channel 5
XMT
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
RCV
PWR
BTG
Composite Link
CD
CTS
XMT
3000-Series
Ethernet
RCV
XMT
EXT
V35
LNK
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
FXO
FAX
Voice/Fax Channel 4 Voice/Fax Channel 3 Voice/Fax Channel 2
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
FXO
FAX
Channel 2
Channel 1
RCV
V35
V35
LNK
XMT
COL
XMT
RCV
FXS
E&M
FXO
XSG
FAX
RSG
XSG
XMT
RSG
FXS
E&M
FXO
FAX
Channel 3
Channel 4
XMT
XMT
RCV
RCV
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
XSG
RCV
XSG
FXO
FAX
RSG
RCV
XSG
RSG
Channel 5
XMT
RCV
RSG
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
XSG
FXO
FAX
RSG
Voice/Fax Channel 1
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
XSG
FXO
FAX
RSG
XMT
FXS
E&M
RCV
XSG
FXO
FAX
RSG
Channel 7
Channel 6
Channel 9 Channel 10
Channel 8
XMT
XMT
XMT
RCV
XMT
RCVXMT
RCV
RCV
RCV
Figure 2. Unpacking
MultiExpress
14
Page 15
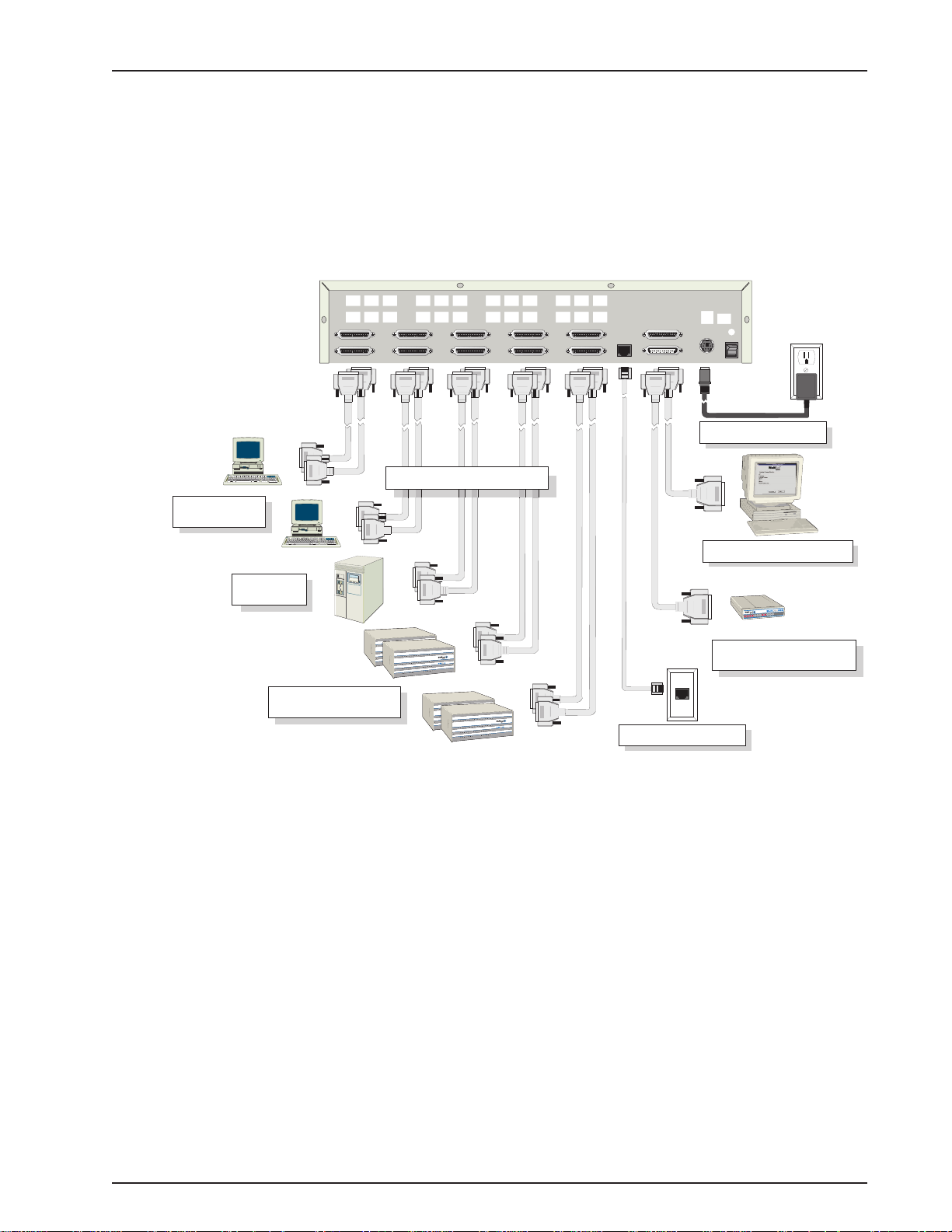
Cabling your MultiFRAD 3000
Cabling your MultiFRAD involves making the proper Power, Command Port, Ethernet, and Channel
connections. Figure 3 shows the back panel connectors and the associated cable connections. The
MF3060 supports up to 6 data channels and the MF3100 supports up to 10 data channels. The MF
3060 cannot be upgraded to support 10 channels. Table 1 details the procedures for connecting the
cables to your MultiFRAD.
Chapter 2 - Installation
PC or
Terminal Units
AS400
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
8
E&M FXO FXS E&M FXO FXS E&M FXO FXS E&M FXO FXS
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
4
CHANNEL 10
CHANNEL 9
TM
Statistical Multiplexers
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
7
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
3
CHANNEL 8
CHANNEL 7
CHANNEL 6
CHANNEL 5
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
6
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
2
Channel Connections
CHANNEL 4
CHANNEL 3
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
5
VOICE/
FAX
CHANNEL
1
10BASET
ETHERNET
COMMAND PORT
EXT. COMPOSITE LINK (RS232/V.35)
CHANNEL 2 (RS232/V.35)
CHANNEL 1 (RS232/V.35)
INTERNAL
COMPOSITE
LINK
MONITOR
XMT RCV
T1 DSU
GND
I
POWER
O
Power Connection
Command Port Connection
T1 CSU/DSU or Comparable
Link Device
Ethernet Connection
Figure 3. Cable Connections
T able 1. Cabling Procedure
Step Procedure
1 Connect one end of an DB-25 cable to each of the data channel connectors on the back of
your MultiFRAD (labeled CHANNEL 1-6 for the MF3060, CHANNEL 1-10 for the MF3100).
See Figure 3. Connect the other end of each cable to the channel devices. Repeat for each
of the up to 6 or 10 channels you are connecting.
NOTE: only Channels 1 and 2 support the RS232/V.35 protocol, and all channels support
either asynchronous or HDLC synchronous RS232 data equipment such as multiplexers.
2 Connect one end of an DB-25 (female) cable to the Ext. Composite Link Connector on the
back of the MultiFRAD (as shown in Figure 3). Connect the other cable end to your T1 CSU/
DSU or compatible link device.
3 If you have a LAN, make the network connection by connecting a RJ-45 (UTP) cable to the
10 BASE-T Ethernet connector (shown in Figure 3) on the back of the MultiFRAD. Connect
the other end of the cable to your LAN.
15
Page 16

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
4 Connect the MultiFRAD to a PC using an appropriate RS232 cable. Plug the male end of the
cable into the Command Port on the back of the MultiFRAD and the other end into the pc’s
serial port. See Figure 3.
5 Connect one end of the power supply to a live AC outlet and connect the other end to the
MultiFRAD as shown in Figure 3. The power connector is a 7-pin circular DIN connector.
6 Turn on power to the MultiFRAD by placing the ON/OFF switch on the back panel to the ON
position.
At this time your MultiFRAD is completely cabled. Proceed to the next section to load your software.
16
Page 17

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
Page 18
MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
This chapter will guide you through the installation and initial configuration of the MultiFRAD software
included in your shipping box. Chapter 4 will provide a more detailed description of the software and
it’s features.
Loading your Software
The following loading procedure does not provide every screen or option in the process of installing
the MultiFRAD software. The assumption is that a technical person is doing the installation and that
a thorough knowledge of Windows and the software loading process is understood. Additional
information on the MultiFRAD software is provided in the following chapter.
1. Run Windows on the pc connected to the Command Port.
2. Insert the MultiFRAD 3000 diskette into the disk drive on the pc connected to the Command
Port.
3. Win3.1 users - access Run by clicking on the File menu in Program Manager and then click
on Run. In the Run dialog box, type a:\setup or b:\setup (depending on the location of your
floppy disk drive) in the Command Line field and then click on OK.
Win95 users - click on the Start box and then click on Run. In the Run dialog box click on
the down arrow and choose a:\setup or b:\setup (depending on the location of your floppy
disk drive) in the Command Line field and then click on OK.
18
4. Follow the on-screen instructions to install your MultiFRAD 3000 software.
The On-Line Helps for the MultiFRAD software provide a detailed explanation of each dialog
box and each option. To access the On-Line Help, click on the ? button in the dialog box
about which you would like additional information.
Page 19
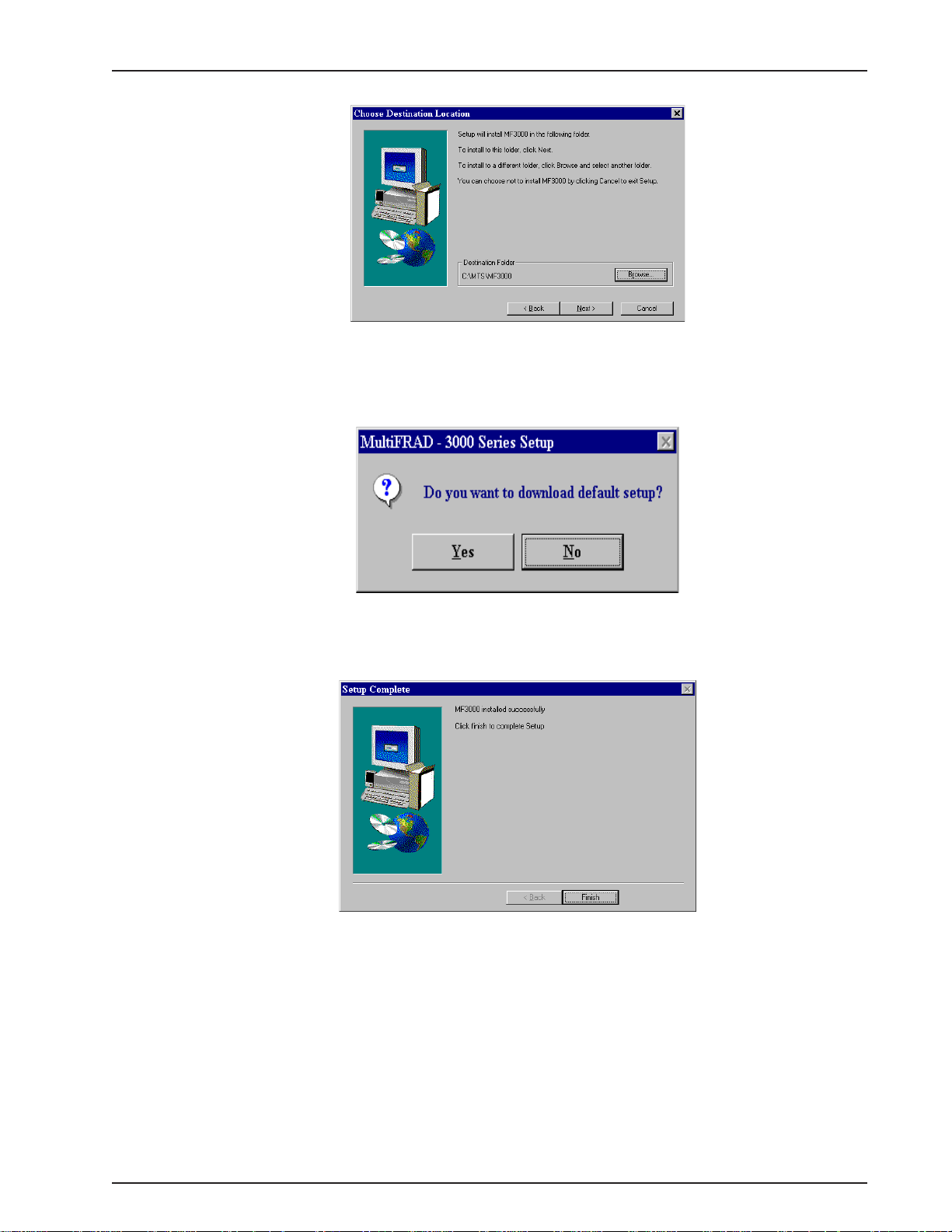
Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
5. You may choose the Destination Location of your MF3000 software or you can choose the
default destination by clicking on the Next button. If you click on the Browse button you can
choose from several. It is recommended to choose the default destination.
6. Do you want to download default setup? dialog box is displayed. Click on the Yes button to
continue.
7. The MultiFRAD 3000 software has been successfully installed, click on Finish to continue
configuring your MultiFRAD.
8. To configure your MultiFRAD, a series of five default dialog boxes, MultiFRAD - Novell IPX
Protocol Default Setup, MultiFRAD - IP Protocol Default Setup, MultiFRAD - WAN Port
Default Setup, MultiFRAD - Data Port Default Setup, and MultiFRAD - Frame Relay DLCI
Default Setup will be displayed.
19
Page 20
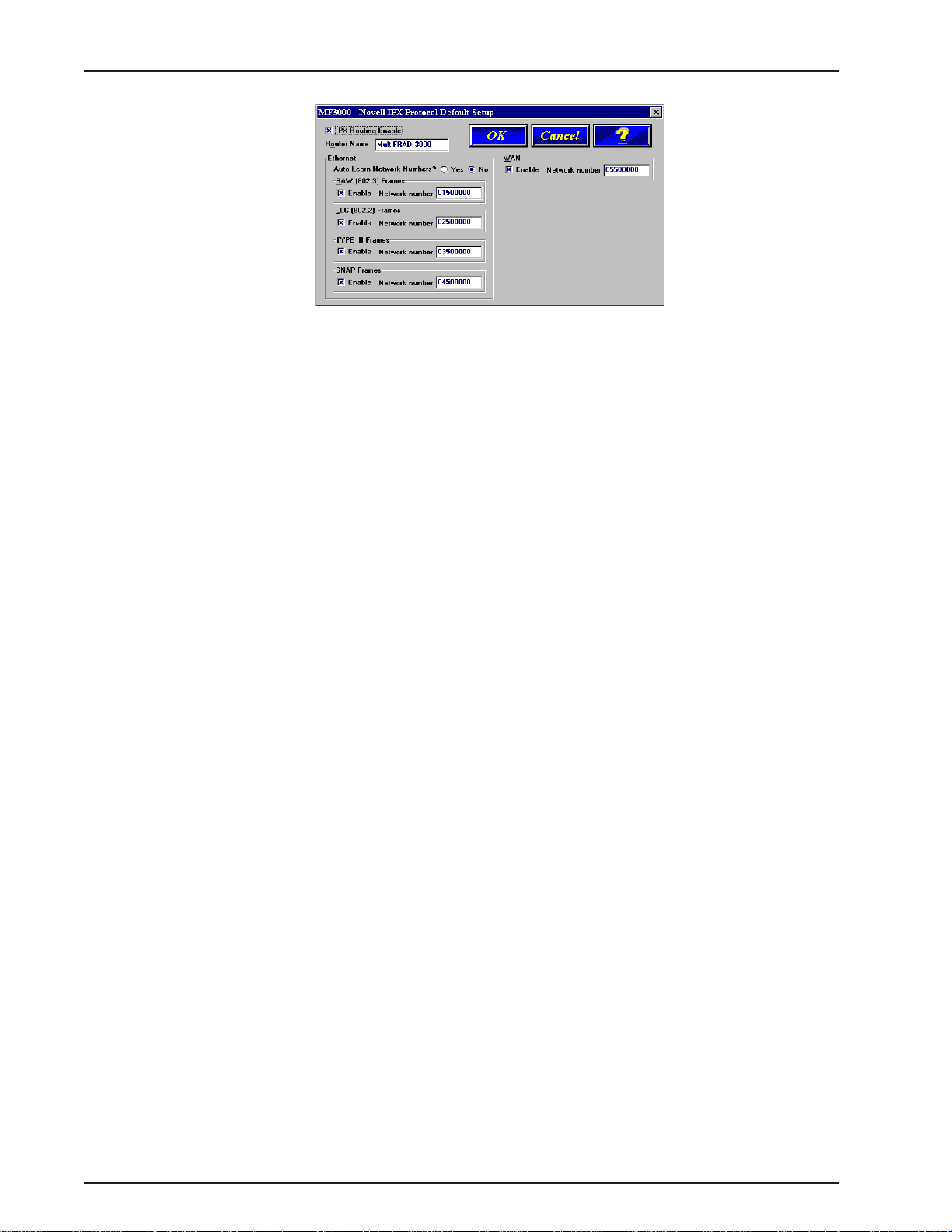
MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
If your network protocol is IPX, continue with the following steps. If you are not using IPX
routing, click on IPX Routing Enable check box to disable IPX, then click on the OK
button, and proceed to step 13.
9. Router Name: You can use the default Router Name or you can assign a new Router Name
in this field. If you assign a new Router Name, it must be a printable ASCII string of a
maximum of 47 characters. The router name is used by the MultiFRAD to advertise its
service in the IPX inter-network.
10. Ethernet: You can enable Auto Learn Network Numbers by leaving the default Yes or you
can manually assign the network numbers by clicking on No in the Auto Learn Network
Numbers field.
If no file server is connected to the Ethernet segment, then this field should be No
(recommended).
If you enable Auto Learn (Yes), the MultiFRAD will learn the IPX network numbers from the
file server.
If you select No for Auto Learn, record the network numbers assigned by the network file
server for each of the four frame types (Raw (802.3), LLC (802.2), EthernetII (Type II),
SNAP) in the space provided below.
RAW (802.3) Frames Network Number _____________
LCC (802.2) Frames Network Number ______________
TYPE_II Frames Network Number _________________
SNAP Frames Network Number ___________________
WAN Network Number __________________________
When you manually assigning network numbers, you must make sure they match the
network numbers assigned to your local file server (if any).
11. WAN: Enter the WAN network number for the Frame Relay WAN Port by clicking on the
Network Number box and back spacing through the default number and entering your new
WAN Number. Make sure the WAN network number is the same as the MultiFRAD on the
other end of the link.
The WAN network number has to be assigned by the Network Administrator and must be
unique throughout the entire inter-network.
Note: The WAN port does not have the capability of learning the network number, unlike the
LAN port (i.e., the WAN port does not have a file server).
12. Click on OK when you are satisfied with your selections.
13. If you clicked OK from the IPX Protocol Default Setup dialog box (step 8), the IP Protocol
Default Setup dialog box is displayed.
20
Page 21

Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
14. To change the IP parameters, proceed to the next step. If you are not using IP routing, click
on the IP Routing Enable check box to disable IP routing and proceed to step 20 (the WAN
Ports Default Setup).
15. The default Ethernet IP Address has to be changed to your unique LAN address. Assign an
acceptable unique IP address to the Ethernet port.
16. Change the default Subnet Mask and Frame Type to the values you have assigned to your
LAN port.
17. The default WAN Address has to be changed to your unique W AN address. Assign an
acceptable unique WAN Address to the WAN port.
18. Change the default Subnet Mask and Remote Address for WAN to the values you have
assigned to your WAN.
19. Click on OK when you are satisfied with your selections.
20. The WAN Port Default Setup dialog box is displayed. The WAN Port is enabled in this dialog
box. Frame Relay is also enabled. If your WAN port is going to be used in Point-to-point
protocol, click on the Enable PPP. If PPP is enabled, then the Modem Command Setup field
is active and either Asynchronous or Direct Connect needs to be enabled.
The WAN port can be further configured once the installation of the software is completed, by
clicking on the MultiFRAD Configuration icon and clicking on the WAN button.
21. Click on the OK button in the WAN Port Default Setup dialog box.
22. The Data Port Configuration dialog box allows you to individually configure each of the ten
data channels. After configuring a given channel, you may copy that channel’ s configuration
to any of the other channels by selecting the desired channels in the “Duplicate To” group
and clicking on the “Copy” button.
If your data device is a synchronous device, ensure that the clocking and, if an internal clock
is used, the Speed is correct. Also, check the Encoding Scheme, Between Frames, and
InterFrame Timer are correct for your channel device. Refer to user documentation for the
parameters of the channel device.
21
Page 22
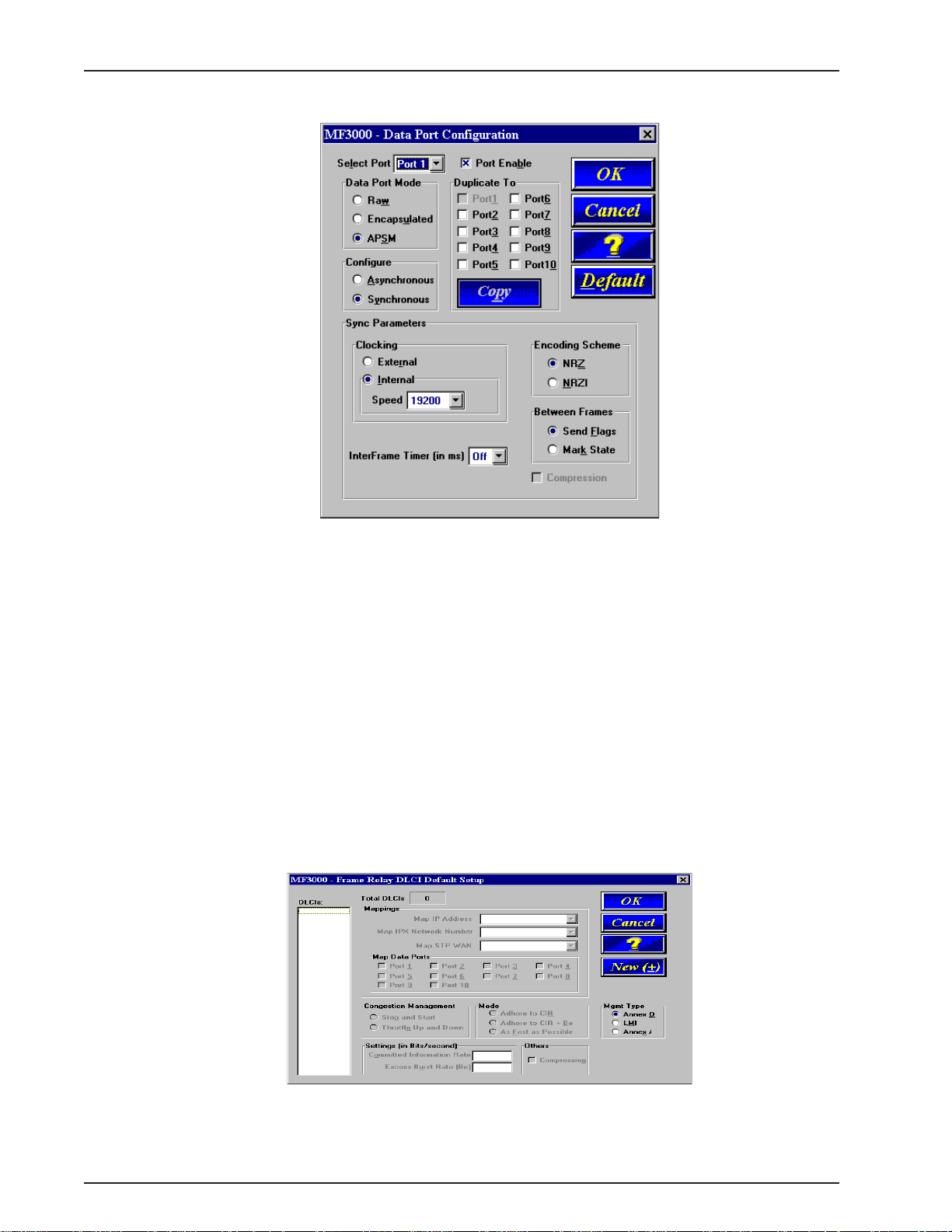
MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
If your data device is an Asynchronous device, then click on Asynchronous check box, and
set the Baud Rate by clicking on the Baud Rate down arrow and the drop down list box
displays the baud rate. Also, select the W ord Length, Parity, Stop Bits, etc. for your device.
Refer to the user documentation for the parameters of the data device.
23. Click on OK when you are satisfied with your data port configurations.
24. If you enabled PPP in the WAN Ports Default Setup dialog box, proceed to step 36.
If you enabled Frame Relay in the WAN Ports Default Setup dialog box, the Frame Relay
DLCI Default Setup dialog box is displayed with all the groups inactive.
Your MultiFRAD can detect DLCIs and the frame relay management type when the unit is
connected to an active frame relay network service. At this point your MultiFRAD is not
communicating with the frame relay network. But if you know your DLCIs and want to add
them at this point, you can continue with the next step. If you wish to wait until your
MultiFRAD is communicating with the frame relay network, proceed to step 36 to finish
installing your software.
22
25. Click on the New (+/-) button and the Frame Relay New DLCI dialog box is displayed with
Enter DLCI Number field active. Enter a DLCI number that was provided by your service
provider at subscription time.
Page 23

Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
26. Click on the OK button, the Frame Relay DLCI Default Setup dialog box is displayed with the
all the groups active and your DLCI displayed in the DLCIs field.
You can map a protocol stack and/or data port to a DLCI.
27. To map this DLCI to a protocol stack, click on a protocol stack’s down arrow for each protocol
that your LAN is using. When you click on the down arrow for a protocol, the listing displays
None and your logical IP WAN addresses and/or logical IPX network numbers.
28. To map this DLCI to a data port, click on Data Port Mappings and choose the Port
number(s) that you want to associate with this DLCI.
29. Ensure that Throttle Up and Down in the Congestion Management category is selected.
30. Ensure that Adhere to CIR + Be check box in the Mode category is selected. Multi-Tech
recommends this setting initially .
31. Click on the Committed Information Rate numeric box in the Settings (in Bits/second)
category and enter the CIR value provided by your service provider at subscription time for
this DLCI.
32. Click on the Excess Burst Rate (Be) numeric box in the Settings (in Bits/second) category
and enter the Be value provided by your service provider at subscription time for this DLCI.
33. The Compression option in the Others group may be desirable at low link speeds. With a
high speed link, Multi-Tech recommends not using this feature.
34. Click on the Management type supported by the Frame Relay network. The network
management type is supplied by your service provider at subscription time.
35. Repeat steps 25 through 34 for each new DLCI.
36. The Checking MultiFRAD dialog box is displayed.
23
Page 24
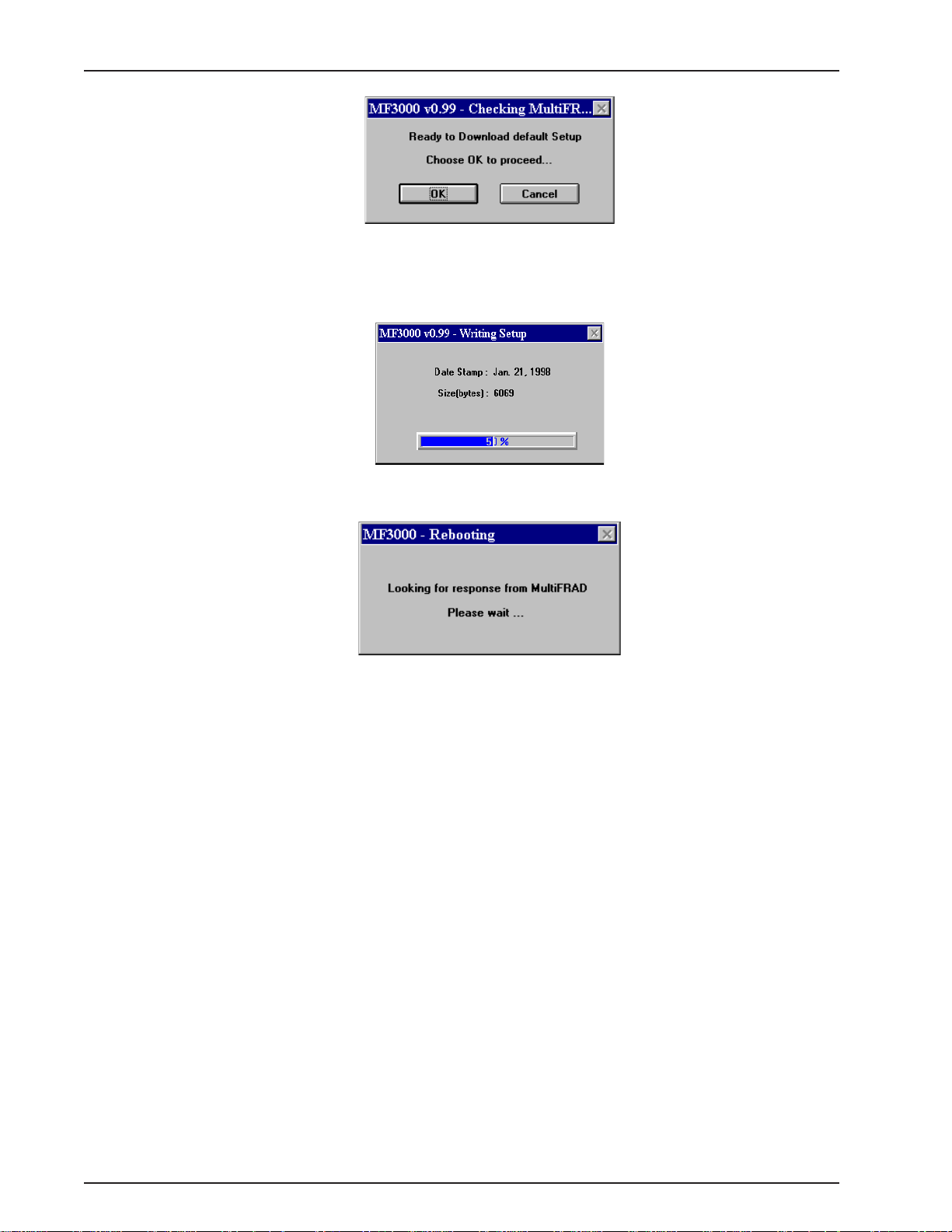
MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
The Setup utility is "Ready to Download default setup Choose OK to proceed." Click on OK
to proceed.
37. Writing Setup dialog box is displayed as the setup configuration is written to the MultiFRAD.
38. After the setup is written to the MultiFRAD, the unit is rebooted.
39. Check to ensure that the BTG LED on the MultiFRAD is Off after the download is complete
and the MultiFRAD is rebooted.
40. Win3.1 users - you are returned to your Program Manager where the MultiFRAD Program
Group and Program Item (Windows icons) have been created.
Win95 users - you are returned to your MultiFRAD 3000 folder which will be visible on your
desktop.
Your MultiFRAD is operational at this time.
41. If you need to further configure your MultiFRAD once the software is installed, proceed with
the following:
Win3.1 users - from the Program Manager, click on the MultiFRAD Configuration icon in
the MultiFRAD 3000 Program Group. The main Setup dialog box is displayed.
Win95 users - from your desktop, highlight Programs, MultiFRAD 3000 folder, and then click
on MultiFRAD Configuration. The main Setup dialog box is displayed.
24
Page 25
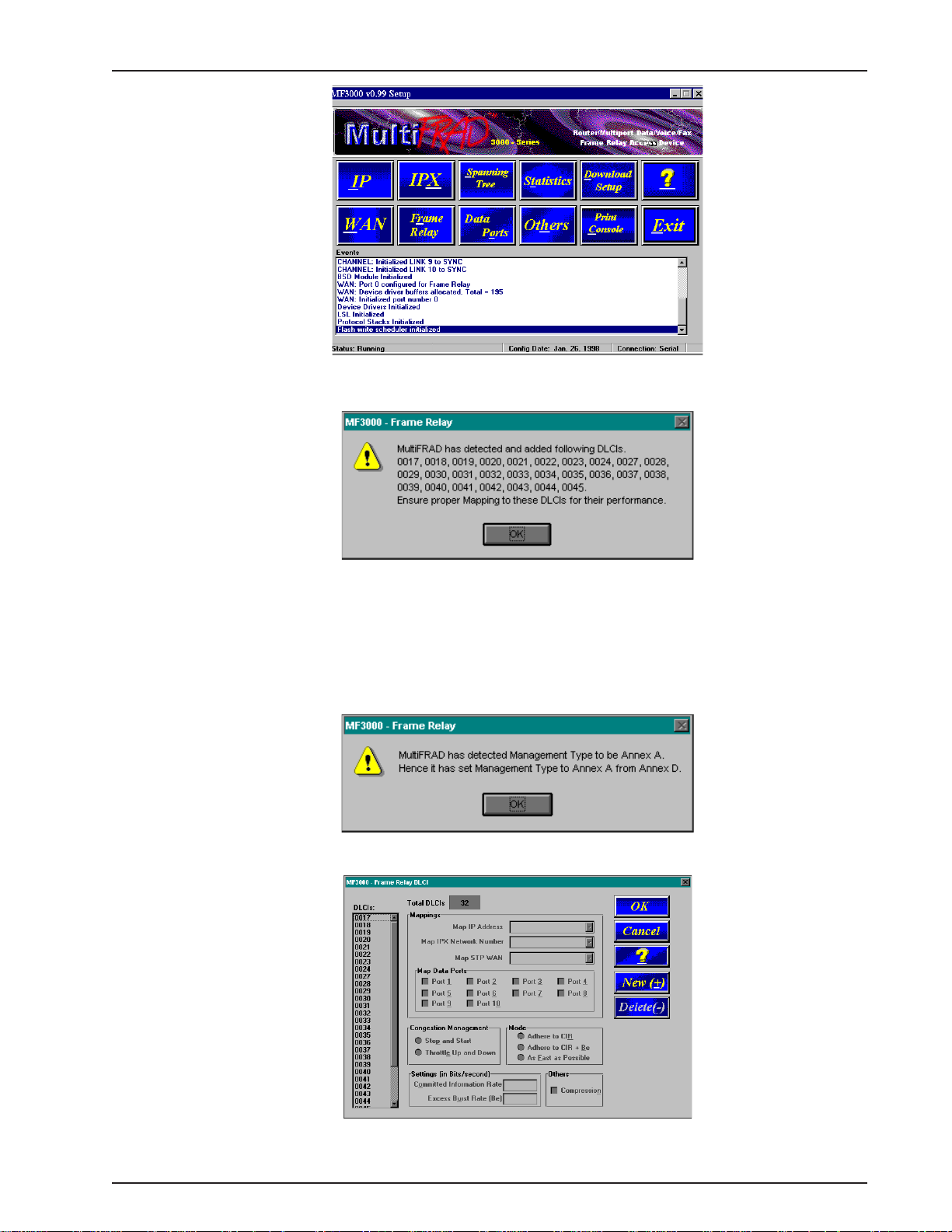
Chapter 3 - Software Loading and Configuration
42. From the main Setup dialog box, click on the Frame Relay button.
43. A Frame Relay dialog box stating “MultiFRAD has detected and added following DLCIs” is
displayed. Click on the OK button.
44. A second Frame Relay dialog box is displayed, stating “MultiFRAD has detected
Management T ype to be Annex A. Hence it has set Management type to Annex A from
Annex D”. The Management Types are Annex A, Annex D, or LMI. Any one could appear in
this dialog box.
Click on the OK button and the Frame Relay , DLCI dialog box is displayed.
25
Page 26

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
45. Click on a DLCI that you want to map. The Mappings, Map Data Ports, and all the other
groups become active.
46. To map this DLCI to a protocol stack, click on a protocol stack’s down arrow for each protocol
that your LAN is using. When you click on the down arrow for a protocol, the listing displays
None and your logical IP WAN addresses and/or logical IPX network numbers.
47. To map this DLCI to a data port, click on Data Port Mappings and choose the Port
number(s) that you want to associate with this DLCI.
48. Ensure that Throttle Up and Down in the Congestion Management category is selected.
49. Ensure that Adhere to CIR + Be check box in the Mode category is selected. Multi-Tech
recommends this setting initially .
50. Click on the Committed Information Rate numeric box in the Settings (in Bits/second)
category and enter the CIR value provided by your service provider at subscription time for
this DLCI.
51. Click on the Excess Burst Rate (Be) numeric box in the Settings (in Bits/second) category
and enter the Be value provided by your service provider at subscription time for this DLCI.
52. The Compression option in the Others group may be desirable at low link speeds. With a
high speed link, Multi-Tech recommends not using this feature.
53. Repeat steps 45 through 52 for each new DLCI.
54. Click on the OK button when you are satisfied with your selections.
56. Writing Setup dialog box is displayed as the setup configuration is written to the MultiFRAD.
57. After the setup is written to the MultiFRAD, the unit reboots.
58. Check to ensure that the BTG LED on the MultiFRAD is Off after the download is complete
and the MultiFRAD is rebooted.
59. Win3.1 users - you are returned to your Program Manager where the MultiFRAD Program
Group and Program Item (Windows icons) have been created.
Win95 users - you are returned to your MultiFRAD 3000 folder which will be visible on your
desktop.
Your MultiFRAD is operational at this time.
26
Page 27

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
Page 28

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
This chapter describes the MultiFRAD 3000 software from an applications approach in how the
configuration can be changed with recommendations on the impact of that change. The major
configuration parameters were set during your loading of the software and downloading of your
configuration at the end of the software installation. The MultiFRAD 3000 software is designed for the
Microsoft ® Windows ® environment.
Recommendations are provided in some case that if you change this parameter or that parameter, it
may affect your unit in this way. The approach in this chapter is not to cover every dialog box and
describe every option, your new Help menu system provides that information. The Help menus
define each button, option, field, and recommend values where applicable. The Help menus are a
dynamic help system in that information is presented corresponding to the active dialog box. You do
not have to scan through unrelated information in order to find the Help menu you are looking for.
Before You Begin
Before you begin, lets cover a few procedural matters so that they are out of the way.
To view or change your MultiFRAD configuration in Windows95, click on the Start button, point to
Programs, then MultiFRAD 3000, and click on MultiFRAD Configuration. You may also start the
MultiFRAD Configuration from My Computer by selecting the MF3000 directory and double clicking
on the fradcon Application in the file list.
28
Page 29
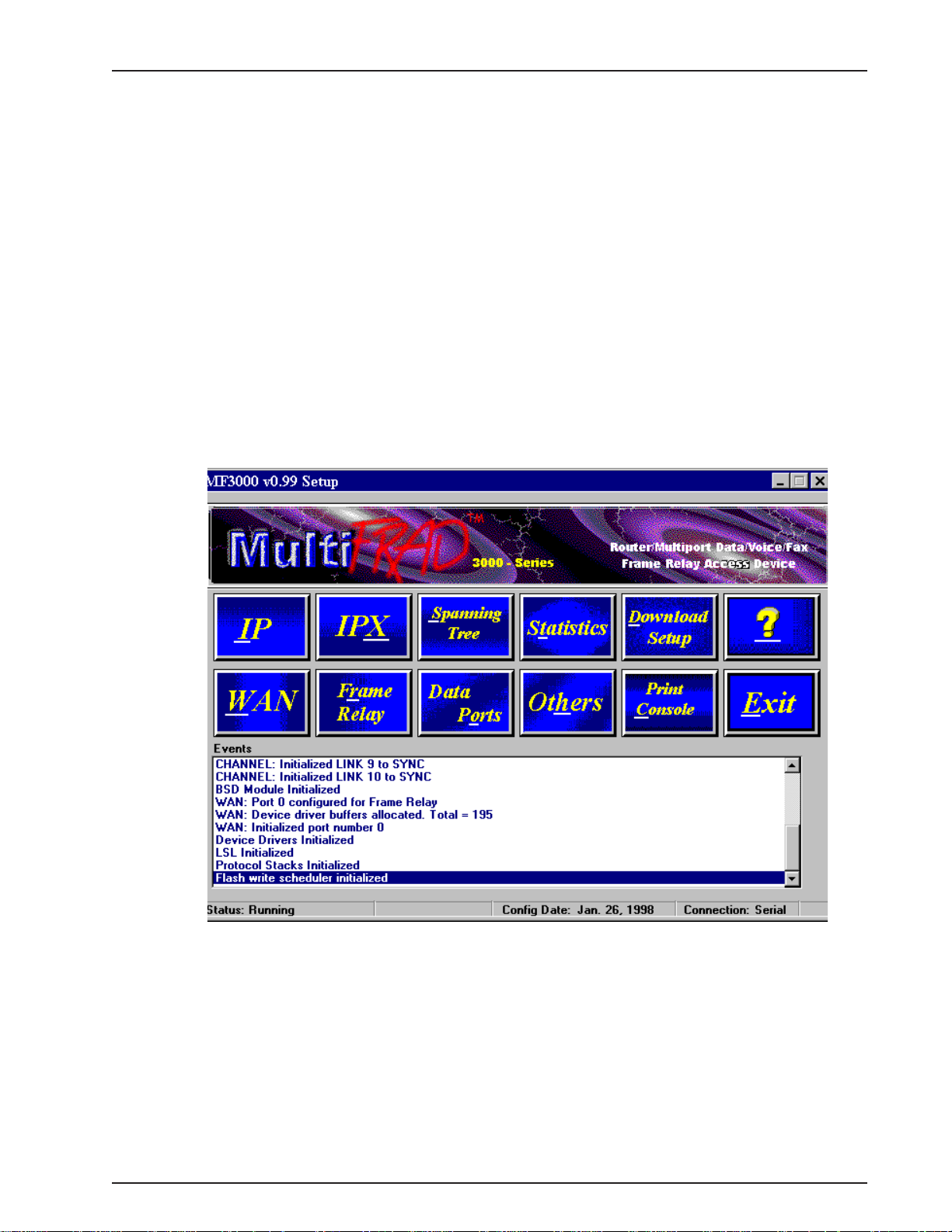
Setup Menu
The MultiFRAD 3000-Series Setup menu consists of 12 buttons in which you can point and click, an
Events window in the middle of the menu, and a status bar at the bottom of the menu. The 12
buttons allow you to display and change the protocol stacks, statistics, WAN port setup, Frame Relay
parameters, data port configuration, enable applications such as SNMP Agent, T elnet Server, WEB
Server, and assign a MultiFRAD password.
The Events window, in the center of the window, is a smaller version of the print console. It can be a
useful tool in times of troubleshooting. Its purpose is to provide information about the boot process
and ongoing information regarding the status of “events” such as the type of frame relay
management selected and which PVCs become active.
The status bar at the bottom of the Setup menu displays the status of the unit, e.g., Running, the date
that the unit was configured, the type of connection on the command port, e.g., if the pc connected to
the command port is using its serial port to communicate with the MultiFRAD or if the pc is
communicating with the MultiFRAD via an Ethernet connection. The last field on the status bar is the
Rights field which displays either Read/Write or Read only rights. The first user to communicate with
the MultiFRAD has Read/Write rights. This enables the first user to change the configuration of the
MultiFRAD. A second user has read only rights which means they can only display the configuration
of the MultiFRAD.
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
If your WAN port is configured for frame relay, then the button to the right is Frame Relay. If your
WAN port is configured for Point-to-Point, then the button to the right is PPP.
29
Page 30
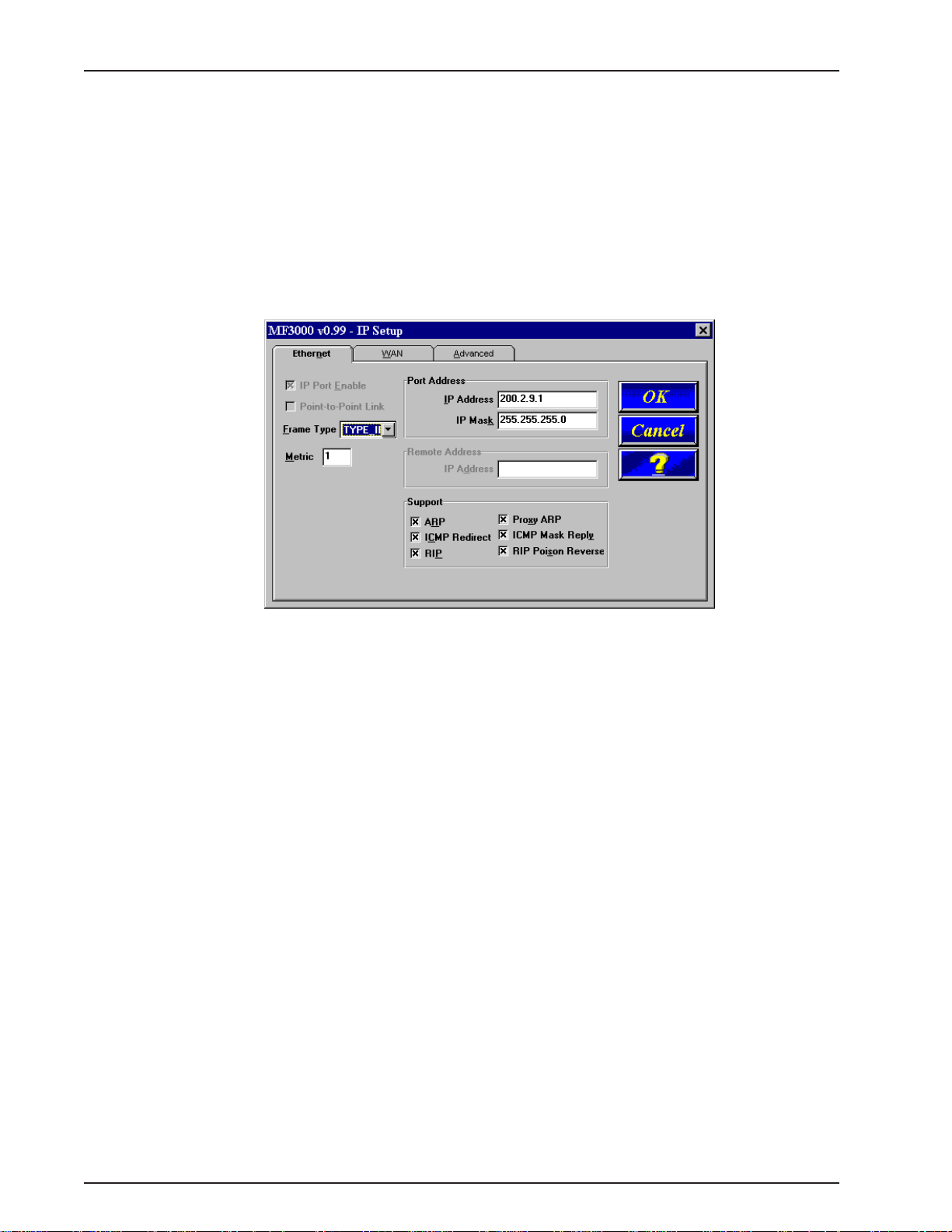
MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
IP Setup
The IP Setup dialog box allows you change the IP routing capabilities, add or delete logical W ANs,
enable the DHCP relay agent, assign DNS address, and define default and static routes. The initial
routing capabilities were established during the software installation. You can change IP routing
parameters by clicking on the Advanced tab and changing, for example, the RIP Response Time or
RIP Route Aging Time. The WAN tab allows you to change the WAN port IP address, the remote
address, and if logical WAN ports are being added for frame relay, you can add them by clicking on
the Add button.
The Ethernet IP Setup dialog box displays the parameters for your Ethernet port with the IP Address
established during the initial loading of the software.
An IP address is a combination of a network number and a host number or ID. IP address masks are
used to specify the network or subnet portion of the IP address. IP addresses and masks are 32-bit
values. These are usually provided in what is known as the dotted decimal notation. In this notation,
each 8-bit portion of the address is given a decimal quantity separated by a dot. For example,
192.2.10.1. The MultiFRAD expects all IP addresses to be provided in dotted decimal notation.
Among IP addresses, address 0.0.0.0 and 127.?.?.? cannot be specified as they are special case
addresses not used on the internetwork for addressing. For Class A, B, and C addresses, you will
usually specify address masks of 255.0.0.0, 255.255.0.0 and 255.255.255.0 respectively unless other
subnets have been set up.
The net mask specifies the network or subnet portion of an IP address. The net mask is a 32-bit
value presented in a dotted decimal notation.
From the Ethernet IP Setup dialog box you can switch to the WAN IP Setup dialog box or the
Advanced IP Setup dialog box.
The WAN IP Setup dialog box allows you to disable or enable IP routing on the WAN port, change the
port IP Address, mask, and remote IP address. If the WAN port is configured for frame relay, this
dialog box allows you to add logical WANs. How the logical IP WAN ports are configured is controlled
by the WAN Port Setup dialog box.
30
Page 31

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
To add logical WAN in a frame relay configuration, click on the Add(+) button and the next WAN
number is displayed in the List of Logical WANs window on the left side of the W AN dialog box. To
delete the last logical WAN assigned, click on the Delete (-) button.
The Advanced IP Setup dialog box controls the timers, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
and Domain Name System (DNS) options, the default route, filters, and Static Routes.
In most cases, you should not have to change any of the timers (i.e., default TTL, reassembly
timeout, RIP response time and RIP route aging time). The DNS Resolver is supplied for remote
Telnet clients when the router is configured for remote access and the terminal server application is
enabled.
31
Page 32

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
IPX Setup
The IPX Setup dialog box controls the four frame types, the WAN ports setup, and the advanced tab
enables IPX routing, auto learn of Ethernet network numbers, and the distributed name of the
MultiFRAD.
The RIP and SAP default timers should not have to be changed for most applications. Disabling IPX
and SPX Watchdog Spoofing in the Bandwidth Optimization group has proven effective under certain
circumstances with Citrix clients.
The IPX WAN Setup dialog box allows you to enable or disable IPX routing on the W AN port, change
the network number for the WAN port, enable or disable NetBIOS, change the default RIP and SAP
timers, and optimize the bandwidth. If the WAN port is configured for frame relay, this dialog box
allows you to add logical WAN. How the logical IPX W AN ports are configured is controlled by the
WAN Port Setup dialog box.
32
Page 33

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
The IPX WAN network number has to be the same on both ends of the link and must be unique
throughout the internetwork. If the WAN port is configured in a point to point configuration, both W AN
network numbers have to be the same and unique. If the WAN port is configured in a frame relay
configuration, both virtual WAN numbers have to be the same and unique. In a frame relay
configuration, the logical WAN network number has to be the same and unique at both ends of the
Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC).
The Advanced IPX Setup dialog box controls the routing of the protocol and auto learn of Ethernet
network numbers, defines the broadcast name of the MultiFRAD, and IPX filtering.
If bridging of IPX packets is desired, IPX routing must be disabled and frame type support for the
frame type must be enabled.
If there is a server on the local segment, then IPX network number auto learn should be enabled. If
there is no server, or if for some reason the router comes up before the server, the router will default
to some random network numbers after a short period of time.
33
Page 34

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Spanning Tree Setup
The Spanning Tree Setup dialog box controls transparent bridging when the Bridging option is
enabled or if there are any loops or redundant links in the internetwork, then Spanning Tree Algorithm
option must be used. Spanning Tree is a method of transparent bridging, as opposed to source route
bridging which the MultiFRAD does not support.
The MultiFRAD defaults with one logical WAN port mapped to a DLCI. It is not necessary to map this
port to a DLCI, however, care should be taken if additional logical WANs are created. Additional
WAN will default to a disabled state. If they are to be used, they must be mapped to a DLCI. In most
applications, the forwarding state should be enabled on the first logical WAN and blocking should be
set on any additional WANs. The MultiFRAD will make the transition from blocking to forwarding
automatically when it is required.
34
Page 35

Statistics
The Statistics dialog box allows you to view statistics on the major events of the MultiFRAD. The
Statistic dialog box changes depending on the way the WAN port is configured. If the MultiFRAD is
configured in a point-to-point configuration, the button to the right of the WAN changes to PPP and
the DLCI button will be grayed out. If the WAN port is configured for a frame relay configuration, then
the button to the right of the WAN changes to Frame Relay and the DLCI button is active.
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
Statistics can be a helpful troubleshooting tool. For example, viewing the WAN Statistics you can
see if the MultiFRAD is sending or receiving on its composite link or WAN port. When the MultiFRAD
is configured in a frame relay mode, it will transmit management frames approximately every ten
seconds, trying to establish communication with the provider’s switch. If the unit is sending frames
but not receiving any , this may be an indication of a problem with the link device or the frame relay
network. Statistics in the frame relay dialog box actually show the number of management frames
being sent and received, and can also indicate a link or frame relay network problem. (One way to
determine if a problem is local would be to set your DSU to internal clocking and put it in loopback by
means of a DSU loopback cable (RJ-45). If the MultiFRAD, the cable and the DSU are all functioning
properly , the WAN statistics will reflect that fact by showing the same amount of bytes received as
transmitted.)
Another helpful statistic screen is DLCI. It reflects the status of the PVC, i.e., active or inactive and
whether or not the MultiFRAD is experiencing network congestion (reflected by FECNs or BECNs
received).
35
Page 36

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
IP Statistics
IP is a connection-less network protocol that resides in the network layer of a conventional OSI
layered model (for more information on this model, refer to Appendix C). Depending on what is going
on at the application layer, IP will typically use one of two transport layer protocols. User Datagram
Protocol (UDP), a connection-less transport layer protocol used with TFTP or SNMP; and Transport
Control Protocol (TCP) is a connection-oriented transport layer protocol used with FTP, Telnet, and
SMTP.
UDP makes use of the port concept and has no measures for flow control, reliability, or error
recovery. It is used when the full services of TCP are not required, and the reliability measures must
be assumed by another layer.
TCP works well in environments where the reliability measures are not assumed by other layers. It is
connection-oriented and has a full range of services.
For the most part these statistics are informational, and their use as a troubleshooting tool will be
contingent on the applications running in the upper layers. For instance, if you were having problems
connecting to MultiFRAD’s web server , you would look under the TCP section to see if any
connections are being established. If not, that may indicate the web server is not enabled. Or, if you
were having problems establishing a remote connection through TFTP, you could look in the UDP
section to see if any packets are being received. If not, you may need to review your network
addressing.
The Port Tab allows you to view generic IP statistics for a given Ethernet IP Port. Either the Ethernet
(LAN) port, or any logical IP WAN port statistics can be viewed in this window. The practicality of
statistical use in troubleshooting will depend on the application running in the upper layers.
36
Page 37

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
IPX Port Statistics
The IPX Port Statistics dialog box displays information pertaining to the IPX Port, for example, the
frame type used or the number of packets transmitted/received.
IPX is a network layer protocol that is usually associated with Novell NetwareTM networks. It allows
for encapsulation of four different frame types over a single physical LAN connection (provided each
frame type has a unique network address): RAW (802.3), LLC (802.2), Ethernet II, and SNAP.
These statistics are mostly informational but could be useful for troubleshooting. For instance, if
there was a question as to which frame type your workstation was using, you could view the statistics
for each frame type and determine which one is being used by the amount of packets transmitted and
received.
37
Page 38

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
STP (Spanning Tree) Port Statistics
The STP (Spanning T ree) Port Statistics dialog box displays information regarding the selected STP
port, for example, the number of frames discarded or forwarded.
Spanning Tree transParent (STP) bridging is the method of bridging used by the MultiFRAD as
specified in IEEE 802.1d standard. Enabling the spanning tree algorithm in addition to spanning tree
bridging provides for a loop-free environment with redundant paths (if present) that will transition from
blocking to forwarding automatically in case of a root bridge failure.
The STP Port statistics are mostly informative but may be helpful in troubleshooting. For example,
viewing the number of forward transitions could indicate if the port has ever become active (in which
case forward transitions will be greater than zero).
38
Page 39

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
SNMP Statistics
The SNMP Statistics dialog box provides statistical information on Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP).
SNMP is an application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange of management information
between network devices. There are three key components in SNMP: the devices that are to be
managed, agents, and the network management systems. The managed device is the network
device, like a router. The agent is the software module residing in the managed device pertaining to
network management. The network management system runs the SNMP application that controls
the managed devices and monitors their status. There are four primary operations performed using
SNMP. They are Set, Get, Get Next, and Trap.
You can use these statistics to help troubleshoot in the event you have a problem communicating
with the MultiFRAD from your SNMP manager .
39
Page 40

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
WAN Statistics
The WAN Statistics dialog box provides statistical information regarding the MultiFRAD’s WAN port,
including the number of packets transmitted/received, and total bytes transmitted/received.
The WAN Port Statistics dialog box pertains to the traffic on the MultiFRAD’s composite link (WAN)
port. The Statistics that fall into “Others” category relate to the physical layer between the MultiFRAD
and the link device, i.e. the CSU/DSU. These statistics can be helpful in troubleshooting suspected
problems at the physical layer, i.e., the WAN port itself, the link device (CSU/DSU), and any
associated cabling.
40
Page 41

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
PPP Statistics
The PPP Statistics dialog box provides statistical information related to Point-to-Pint Protocol (PPP).
For example, this dialog box displays the current protocol and compression methods enabled.
The statistics in this dialog box will only apply when you are accessing your network remotely with a
PPP client. The Network Control Protocol (NCP) is the means by which PPP clients negotiate the
network-layer protocols. IP and IPX network-layer protocols are supported on the MultiFRAD.
The Link Control Protocol (LCP) is the means by which PPP clients negotiate and configure the data
link for a given PPP connection.
41
Page 42

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Data Port Statistics
The Data Port Statistics dialog box displays statistical information, such as bytes or blocks received/
transmitted, for the various data ports.
This window shows the statistics for all data channels. By highlighting and double clicking on a
particualr port, you can view the individual channel statistics, as well as various hardware signals
(CTS, RTS, DSR, DCD, DTR) and XON/XOFF status. It also gives an indication of buffer utilization
and receive flow time.
These may be indicators that either the data channels, or more likely the devices attached to them,
are being driven harder than they should be. Excessive buffer utilization and/or receive flow control
time can usually be reduced or eliminated by slowing the speed at which the channel is operating.
42
Page 43

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
Frame Relay Statistics
The Frame Relay Management Statistics dialog box can be a useful tool for troubleshooting
MultiFRAD installations and monitoring the performance of active links, and determining if the
MultiFRAD is talking to the provider’s switch.
The Polling Details section lists the various management frames sent and received. For every
Status Enquiry Sent, a Status Response should be received from the network. Likewise, for every
Full Status Enquiry Sent, there should be one Full Status Response received. The two status
enquiry types are used by the FRAD to verify that the frame relay network is operational, and to
determine which DLCIs are active. Under default settings a status enquiry is sent every ten seconds,
and every sixth enquiry will be a Full Status Enquiry .
The Enquiries Sent and the Responses Received should increment together, and should be equal
under normal circumstances. Any gap between them reflects a breakdown in communication with
the provider’s switch, and will be reflected as Missed Status Responses.
The Status Errors section lists the number of errors that have occurred. A Missed Status Response
means that the frame relay network did not respond to a status enquiry from the MultiFRAD before
the next status enquiry was sent (by default there are 10 seconds between status enquiries).
A Sequence Error means that the sequence numbers in a received status response do not match
what the MultiFRAD expected based on its Status Enquiry . Basically, the Status Enquiry has two
numbers (or counts), and one should be incremented by the network and then both numbers should
be returned to the FRAD in the Status Response. Sequence Number Errors also reflect missing
packets between the MultiFRAD and the switch, but should not be a cause for alarm unless they are
incrementing rapidly and steadily .
The Link Details section records the number of times the frame relay link between the MultiFRAD
and the network has gone up (become active) or gone down (become inactive). The Link Details
provide a more general picture of the status of communication between the MultiFRAD and the frame
relay network.
43
Page 44

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
The DLCI Statistics dialog box shows the individual DLCI status and statistics. This information can
be helpful in determining if the DLCI is active, if it is going up and down, and if the MultiFRAD is
experiencing frame relay network congestion (FECN/BECN). It also gives an indication of the
momentary throughput on individual DLCIs.
When trying to troubleshoot a frame relay circuit, once it has been established that management
frames are being sent and received, the next step is to determine whether the DLCIs are becoming
active. This is dialog box that will give that indication. A FRAD needs to be present at both ends for
the DLCI to be active. Keep in mind that the frame relay network tells the FRAD the status of the
PVC with one of its status responses. But the network will not say the PVC is active until it has
established management communication at both ends of the PVC. If the FRADs at both ends of the
PVC show that they are communicating with the frame relay network and the DLCI still shows active,
and there is a communication problem over that PVC, there may be a problem with your service
provider. If all DLCIs show active at both (or all) locations and there is still an end-to-end
communication problem, it is likely that it is in the configuration of the MultiFRAD. At that point you
should review your protocol stack/data port parameters and DLCI mappings.
44
Page 45

WAN Port Setup
The WAN Port Setup dialog box controls how the port is configured (i.e., frame relay or point-topoint). If the WAN port is configured for frame relay, then the mode of the port is synchronous. If the
port is configured for point-to-point, then the mode can be either synchronous or asynchronous. If
the mode is asynchronous, then the connection method can be either answering or dialing. If the
connection method is dialing, then a number to be dialed has to be entered in the dial number field
and the modem type chosen in this field.
If the Frame Relay Device Driver is chosen, the MultiFRAD encapsulates data on its composite link
for transmission over a frame relay network. Enabling this device driver requires additional frame
relay configuration by choosing the Frame Relay button in the Main Menu.
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
If the PPP/SLIP mode is chosen, the MultiFRAD is configured for a point-to-point configuration which
allows for the transferring of packets between two end points. Enabling this device driver allows for
either an asynchronous or synchronous device to be connected between the end points. If an
asynchronous device is used, the MultiFRAD can be used as a single port remote access server.
When the PPP/SLIP mode is used, further configuration is required using the PPP button in the Main
Menu.
45
Page 46

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Point to Point Setup
The Point to Point Setup dialog box controls the WAN port protocol, dial on demand, and remote port
setup. The WAN port protocol can be either Point to Point Protocol (PPP) or Serial Line Internet
Protocol (SLIP). PPP is the more robust of the two protocols in that it allows the end-points to
negotiate use of the link and protocol parameters in a standardized way and also allows for
standardized encapsulation of the packets. SLIP is an older protocol and requires manual
authentication using a script.
In order to display the PPP dialog box, the WAN Port Setup dialog box has to be configured for PPP/
SLIP.
46
PPP is the default protocol. If SLIP is being used, click on the PPP Enable option to disable PPP.
Click on the SLIP Enable option. Determine if the TCP header is going to be compressed using VJC
compression. If VJC compression is used, click on the CSLIP (Van Jacobson Compression) option.
Page 47

Frame Relay Setup
The Frame Relay dialog box displays the CIR Measurement Interval in milliseconds, the
Management T ype and details of that management type, and the number of DLCI’ s that are active.
The MultiFRAD can detect DLCIs and the Management T ype when you are connected to an active
frame relay service. So it is important that if you change any frame relay parameters, that the new
parameters agree with the way your frame relay service is provisioned.
In the Frame Relay Setup dialog box, you can change the Management T ype by choosing one of the
three options and then the detail parameters for that option are displayed to the right of the
Management T ype. For example, in the above dialog box, Annex D is the chosen management type
with the Full Status Enquiry Interval [N391] set to 6 down thru Polling Verification Timer [T392] set to
15.
Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
Usually , you will have no need to change the management type because the MultiFRAD will
automatically detect the network’s management type at power-up, or when the network becomes
active. This auto-detection feature takes about 1 to 2 minutes to detect the management type and
get a list of the DLCI’s.
Occasionally the Management T ype parameters can be changed to correct a problem. In these
cases making the following changes could alleviate the problem:
1. Change the Link Integrity Verification Timer. This feature sets how often the MultiFRAD verifies
that the link is good. Changing the setting from the default value of 10 seconds, to a lower value, i.e.,
5 seconds, will increase the frequency of those verifications.
2. Change the Full Status Enquiry Interval to affect how often DCLI Status is updated. This
parameter defines how often the MultiFRAD will send a request for DLCI status information along
with the Link Integrity Verification request. The default value is to include such a request every sixth
time the link integrity is checked. A value less than every sixth request will allow faster detection of
active/inactive DLCIs, but will also produce a slight increase in management overhead.
3. Change the Monitored Events Count and the Error Threshold to affect the MultiFRAD’s
sensitivity to errors on the link. Every management frame received by the MultiFRAD is considered
an event, and if the link integrity sequence numbers are wrong, for example, it is considered an
“errored” event. With the default settings, if Error Threshold is 3 and Monitored Events Count is 4,
and 3 out of 4 events are “errored”, then the link is considered to be bad, and the FRAD stops
sending on all DLCIs and restarts the initial procedures to activate the link.
4. Change the CIR Measurement Interval to change the time frame in which the FRAD calculates
throughput for each DLCI. By default, every 1000 milliseconds (1 second), the MultiFRAD calculates
how much information has been sent on each DLCI, and depending on the congestion management
option for a DLCI the MultiFRAD may stop sending on that DLCI because it has exceeded its CIR or
CIR+Be rating. By changing the CIR Measurement interval, the throughput calculations can be made
more or less often.
Note: performance could be compromised if the MultiFRAD is set to calculate throughput too often.
47
Page 48

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
If you click on the DLCI button on the right side of the dialog box, the Frame Relay DLCI dialog box is
displayed.
If you have connected to a frame relay service, this dialog box should display your current DLCI
numbers automatically . It also shows the protocol mapping of the high lighted DLCI, which data port
it is mapped to, and how you set up your Congestion Management, Mode, CIR, and Be values. To
change the mapping of a DLCI, high light the DLCI number in the DLCIs: window on the left side of
the dialog box. The dialog box will then change to the mapping of that DLCI. To add a new DLCI that
has not been auto detected, click on the New (+) button and the Frame Relay New DLCI dialog box is
displayed.
To add a new DLCI Number, enter the number in the Enter DLCI Number window. You do not have
to enter the leading zeros.
When you click on the OK button, the new DLCI appears in the DLCI’s window in the Frame Relay
DLCI dialog box.
48
Page 49

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
When a DLCI has just been detected, or if you have just made a new DLCI, it has not yet been
mapped to a protocol address or a data port. The default Congestion Management, mode, CIR, and
Be are displayed. You should verify these default setting with how your new DLCI is provisioned by
you service provider.
Congestion Management, Mode, and CIR/Be settings are used to avoid congestion and possible loss
of data. The Committed Information Rate (CIR) and Excess Burst rate (Be) settings are throughput
amounts determined by the network and user when each DLCI is ordered. The CIR is the basic
throughput which the network will try to set aside for that DLCI. It will always be equal to or less than
the actual access rate of the physical line (i.e., if the frame relay physical link is a 56K DDS line, the
sum of the CIRs of all DLCIs on that link should not exceed 56K bps). The Be is the excess burst
throughput rate (added to CIR) that the network should accept for that DLCI before significant loss of
data occurs due to the discarding of frames during times of congestion. Note, however, that in frame
relay there is no absolute guarantee of a congestion-free link, regardless of CIR and Be settings.
The CIR and Be settings on the MultiFRAD should match the settings that the network has
provisioned.
The Congestion Management and Mode settings determine how the MultiFRAD handles congestion.
The Mode selects whether the MultiFRAD should use its own throughput calculations to avoid
congestion, or simply send data to the network as fast as possible. The MultiFRAD calculates
throughput after every CIR Measurement Interval, and can limit throughput to either the CIR (Adhere
to CIR) or the CIR plus the Be (Adhere to CIR+Be). The Congestion Management setting selects
whether the MultiFRAD should stop sending data when congestion is indicated (Stop and Start), or
gradually reduce throughput during times of congestion (Throttle Up and Down).
Compression can be enabled on a per-DLCI basis by clicking on the Others-Compression box. If
compression is required, it must be enabled on both the local and remote ends of the PVC.
49
Page 50

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
To map a new DLCI (e.g., 17) to a protocol, return to the Main Menu and then click on the protocol
stack that you are using. In the lower left part of the protocol stack dialog box a list of Logical WANs
is displayed. To add a new logical WAN, click on the Add (+) button and the next logical W AN
number will appear in the list on the left hand side of the dialog box.
For example lets map our new DLCI 17 to the IP protocol as a WAN 2 with an IP Port Address of
200.2.11.1, an IP Mask of 255.255.255.0, and a remote IP Address of 200.2.11.2. From the Main
Menu, click on the IP button. The IP Setup dialog box is displayed. Click on the WAN tab at the top
of the dialog box. The WAN parameters are displayed. Click on the Add (+) button and WAN 2 is
added to the List of Logical WANs. Default IP addresses will be displayed for the Port Address and
Remote Address and a default IP Mask will appear in its window. If either address or mask needs to
be changed, click on the appropriate window and the change the numbers.
50
When you click on the OK button in the IP WAN dialog box, you now have an IP address for a
second logical WAN. Now we have to tie that IP address to a DLCI which in our example is DLCI 17.
Now, return to the Frame Relay DLCI dialog box and high light DLCI 17. Click on the Protocol
Mappings Map IP Address down arrow and the IP address 200.2.11.1 appears. Click on this address
and now IP address 200.2.11.1 is mapped to DLCI 17.
Page 51

Chapter 4 - MultiFRAD Software
We now have WAN IP address 200.2.11.1 from the IP protocol stack mapped to DLCI 17. Let’s say
we also want to map a data channel to DLCI 17. The data ports that are already mapped to other
DLCIs are grayed out. In our example, lets map data port 3to DLCI 17. Simply click on Port 3 in the
Data Port Mappings group and an X appears in the box at the left of Port 3. Now we have both data
port 3 and IP WAN address 200.2.11.1 mapped to DLCI 17. The MultiFRAD allows multiple sources
of data to be mapped to the same DLCI because the MultiFRAD multiplexes all the data onto the
DLCI. In other words, bandwidth for that DLCI is shared by all the data sources mapped to the DLCI.
Of course this means that all the data sources must go to the same remote site, since the frame relay
network will send all data on DLCI 17 to the same place.
An example of a typical application taking advantage of this “Multiplexed DLCI” configuration follows:
(Terminals)
MMH900
LAN
MultiFRAD 3000-Series
Frame Relay
Composite
Link
(PCs)
File
Server
LAN
MultiFRAD 3000-Series
Frame Relay
Composite
Link
Unix
etc.
MMH900
DLCI17
Frame Relay Network
AB
(In this example, the MultiFRAD is introduced to allow significant cost savings over traditional leased
lines or point-to-point routers.)
Because the MultiFRAD can map both data ports and LAN traffic onto one DLCI, multiple DLCIs from
point A to point B are not needed.
51
Page 52

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Data Port Configuration
The Data Port Configuration dialog box allows you to change the parameters of the data transferred
between the data device and the MultiFRAD. The MultiFRAD can transfer data between the data
device and MultiFRAD in either a synchronous or asynchronous mode. If your data device is an
asynchronous device, choose the Configure Asynchronous option and configure the MultiFRAD to
match your device. If the data device is a synchronous device, choose the Configure Synchronous
option and configure the MultiFRAD to match your synchronous device. The Data Port Configuration
dialog box also allows you to configure each channel independently .
For example, port 1 could be connected to a Multi-Tech MultiMux MMH904. In this situation, port 1
could be configured with the following options:
´ Data Port Mode set to APSM (Advanced Priority Statistical Multiplexer),
´ Synchronous Configuration,
´ Internal Clocking with Speed set to 19200,
´ Encoding Scheme set to NRZ for all Multi-Tech Muxes,
´ Between Frames set to Send Flags, and
´ InterFrame Timer (in ms) has to be off.
The MMH904 would have to be configured for an external composite link device. This means that
the 8-position DIP Switch on the MMH904 would have to be toggled to the closed position and an
external composite link cable connected between the MMH904 and the MultiFRAD Channel
connector.
In most applications, the encoding scheme, interframe timer, and between frames will be used at their
default settings. If you are unsure of your devices configuration, start with the defaults or refer to
your device’s documentation.
52
Page 53

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 5 - Remote Configuration
Page 54

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
This chapter provides procedures for changing the configuration of a remote unit. Remote
configuration allows a PC at one site (local site) to dial a remote MultiFRAD and change the
configuration of that remote unit. Remote configuration can be accomplished either directly through
the LAN or remotely using modems. To remotely configure a MultiFRAD, a local PC needs to be
connected to a dial-up line and the MultiFRAD software configured to call the remote MultiFRAD. The
remote MultiFRAD needs to have a modem connected to a dial-up line and the Command Port. Once
the connection to the remote unit is made, you can change the configuration as you see fit. Once the
configuration is changed, you can down load the new configuration to the remote MultiFRAD. Refer
to the Modem-Based Remote Configuration Procedure in this chapter to remotely configure a
MultiFRAD.
To configure the remote MultiFRAD through the LAN, change the communication type to the IP based
Trivial File T ransfer Protocol (known as TFTP) and change the configuration as you see fit. Refer to
the LAN-Based Remote Configuration Procedure in this chapter to configure a remote MultiFRAD.
Modem-Based Remote Configuration Procedure
1 At the remote site, remove the serial cable from the PC to the Command Port connector on the
back panel of the MultiFRAD.
2 At the remote site, connect a special cable (Remote Configuration Cable) to the Command Port
connector on the back panel of the MultiFRAD and the RS232 connector on the modem. The
special cable is a serial cable with male connectors on both ends. Refer to Appendix A for cable
details.
Connect the modem to your local telephone line.
Provide your telephone number to the person verifying your configuration.
Configure the remote modem for 19200 baud and turn on Force DTR.
3 At the main site, connect your local PC to a modem that is connected to a dial-up line.
4 Install the MultiFRAD software on the local PC and start the Configuration Port Setup program:
Windows 3.1x
Windows 95
5 The MultiFRAD Setup dialog box is displayed.
: double click on the Configuration Port Setup Icon in the MultiFRAD program group.
: Click on Start >> Programs >> MultiFRAD 3000 >> Configuration Port Setup.
54
Verify that the Communication Type field is set for Com port and the Select Port field is set for
the Com port of your local PC.
Page 55

Chapter 5 - Remote Configuration
In the Dial String field, enter the AT command for dialing (ATDT) plus the phone number of the
remote MultiFRAD.
If your Modem Initialization String, Initialization Response, or Connect Response values are
different than the defaults in the dialog box, refer to your modem user documentation and change
the default values to match your modem.
Click on OK when you are satisfied with your selections.
6 You are returned to the Windows program. Start the MultiFRAD Configuration program.
Windows 3.1x
Windows 95
: Double click on the MultiFRAD Configuration icon in the Program Manager.
: Click on Start >> Programs >> MultiFRAD 3000 >> MultiFRAD Configuration.
7 The Dialing Router Dialog Box is displayed while software is dialing the remote MultiFRAD.
8 The Reading Setup Dialog Box is displayed.
9 The MultiFRAD Setup dialog box is displayed. This is the dialog box of the remote MultiFRAD.
Refer to Chapter 4 for a description of each dialog box. For a detailed description of each field
within a dialog box, refer to the on-line helps provided within your MultiFRAD software.
10 After you have changed the configuration of the remote MultiFRAD, click on the Download
Setup button to update the configuration. The remote MultiFRAD will be brought down, the new
configuration written to the unit, and the unit will reboot.
1 1 Click on the Exit button when the downloading is complete.
12 The Hangup connection with Router? dialog box is displayed
Click on the Yes button to disconnect the phone connection to the remote site.
13 If the same telephone number is not going to be used again in the immediate future, you may
want to remove it from the Port Setup dialog box.
14 At the remote site, reconnect the MultiFRAD to the serial port of the PC and from the Program
Manager screen click on the MultiFRAD Configuration Icon to verify that the MultiFRAD is
running.
55
Page 56

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
LAN-Based Remote Configuration
Windows Sockets Compliant TCP/IP Stack
The configuration program requires a Windows Sockets compliant TCP/IP stack. Microsoft provides a
TCP/IP stack free for Windows for Workgroups 3.11. TCP/IP protocol software must be installed and
functional before the configuration program can be used.
1 You must assign an internet (IP) address for the PC and for each node that will be managed by
the configuration program. Refer to the protocol software documentation for instructions on how
to set the IP addresses.
Once you have completed this step, you should be able to use the protocol Ping command for
the PC host name. You should also test the network interface configuration by Pinging another
TCP/IP device that is connected to the network.
2 Install the MultiFRAD software on the local PC and at the Windows Program Manager screen,
and run the Configuration Port Setup program:
Windows 3.1x
Windows 95: Click on Start >> Programs >> MultiFRAD 3000 >> Configuration Port Setup.
3 The MultiFRAD Setup dialog box is displayed.
Verify that the Communication Type field is set IP.
In the Router IP Address field, enter the IP Address of the remote MultiFRAD.
4 Click on OK when you are satisfied with your selections.
The windows Program Manager menu is displayed.
: double click on the Configuration Port Setup Icon in the MultiFRAD program group.
56
5 Double click on the MultiFRAD Configuration icon.
The Reading Setup dialog box is displayed.
Page 57

Chapter 5 - Remote Configuration
6 The MultiFRAD Setup dialog box is then displayed. This is the dialog box of the remote
MultiFRAD. You can select any of the Protocol Stacks, Device drivers, or other buttons and
change the configuration of the remote MultiFRAD. Refer Chapter 4 for a description of the
MultiFRAD software. For definitions of each dialog box or fields within a dialog box, refer to the
on-line helps provided in the MultiFRAD software.
7 After you have changed the configuration of the remote MultiFRAD, click on the Download
Setup button to update the configuration. The remote MultiFRAD will be brought down, the new
configuration written to the unit, and the unit will reboot.
8 Click on the Exit button when the downloading is complete.
9 Click on the MultiFRAD Configuration icon in the Program Manager screen to verify that the
MultiFRAD is running.
57
Page 58

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
58
Page 59

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 6 - Router Management
Page 60

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
A typical Telnet client application, and typical WEB-browser management of the MultiFRAD are
described in this chapter. The MultiFRAD has a built-in Telnet Server for access through Telnet
clients. A typical Telnet client is allowed to configure the MultiFRAD and its data ports. In addition,
the MultiFRAD can be remotely accessed and configured from anywhere on the internet through its
WEB interface.
For a detailed description of the MultiFRAD software, refer to Chapter 4 in this User Guide. For a
detailed description of each parameter, refer to the on-line helps provided within your MultiFRAD
software.
The TCP/IP stack has to be loaded before the Telnet client can run and the Telnet Server option in
the MultiFRAD software has to be enabled. To access the T elnet Client, double click on the Telnet
icon. A blank Telnet screen is displayed. Click on Connect and then Remote System.
When the Connect to remote host dialog box is displayed, a Host Name has to be entered. In this
example, the IP Host Name is 200.2.9.1.
Enter you MultiFRAD IP Address in the Host Name field. Click on the Connect button and the
MultiFRAD Telnet Server dialog box is displayed.
MultiFRAD Telnet Server Menu
The MultiFRAD management menu provides two options; MultiFRAD Configuration and Remote User
Database. The MultiFRAD Configuration options allow you to select the protocol stack, high or low
level device drivers, applications, Mux data ports, filtering, priority , or system information. The
Remote User Database option allows you to build and maintain a user database for remote access.
60
When you enter a password in the Applications Setup dialog box in the MultiFRAD Software, once
you choose an option from the MultiFRAD Telnet Server dialog box, you must enter your password
before your choice is accepted.
Page 61

MultiFRAD Configuration
The MultiFRAD Configuration option allows you to view and change parameters on the protocol
stacks, high and low level device drivers, enable or disable the supported servers, configure MUX
data ports, set up filtering and priority , or view system information.
To select an option, enter the number of the option and hit the Enter key . For example, to select the
Protocol Stacks option, type 1 <Enter>. For details on a parameter, refer to the on-line helps.
Chapter 6 - Router Management
Remote User Database
The Remote User Database option from the MultiFRAD management menu allows you add and
configure a list of users who will access the MultiFRAD remotely. After selecting Remote User
Database (type 2 <Enter>) from the main menu, type A <Enter> to add a new user to the database.
The following list of options is displayed:
By selecting and configuring the various options and entering the desired information, you can
construct a database of remote users for the MultiFRAD. For a detailed description of each option,
refer to the on-line help provided in your MultiFRAD software.
61
Page 62

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
WEB Browser Management
The MultiFRAD can be accessed from anywhere on the connected internet via the built-in WEB
Browser interface. You must check this option in Other setup to enable the function. Depending on
the rights of the user (read/write, or read only), it is possible to view the current parameters and
statistics of the MultiFRAD as well as configure and download setup changes to the MultiFRAD.
You can access MultiFRAD configuration by typing the IP Address of the unit into the address line of
your web browser. In this example, the IP address is 200.2.9.1.
Click on the word Login to gain access to the MultiFRAD. The following screen appears:
Enter the proper User Name and Password, and then click OK. You are brought to the MultiFRAD
3000 Configuration menu page.
62
Page 63

Chapter 6 - Router Management
Note: the first user to access the MultiFRAD will have
users will have
read only
rights, and therefore, some of the options within the WEB interface will be
read/write
rights over the unit. All subsequent
inactive (i.e., will not be linked).
From the MultiFRAD 3000 Configuration menu, you can access current settings and view statistics,
as well as configure and download a new setup to the MultiFRAD.
63
Page 64

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
64
Page 65

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Chapter 7 - Warranty, Service and Tech Support
Page 66

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Introduction
This chapter will provide you the resources for receiving service or support for your MultiFRAD. The
chapter starts with a description of the warranty, and continues with instructions for contacting the
Service department, Technical Support group, and various Multi-Tech internet resources.
Limited Warranty
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. (“MTS”) warrants that its products will be free from defects in material or
workmanship for a period of two years from the date of purchase, or if proof of purchase is not
provided, two years from date of shipment. MTS MAKES NO OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, AND ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE HEREBY DISCLAIMED. This warranty does not apply to any
products which have been damaged by lightning storms, water, or power surges or which have been
neglected, altered, abused, used for a purpose other than the one for which they were manufactured,
repaired by the customer or any party without MTS’s written authorization, or used in any manner
inconsistent with MTS’s instructions.
MTS’s entire obligation under this warranty shall be limited (at MTS’s option) to repair or replacement
of any products which prove to be defective within the warranty period, or, at MTS’ s option, issuance
of a refund of the purchase price. Defective products must be returned by Customer to MTS’s factory
transportation prepaid.
MTS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES AND UNDER NO
CIRCUMSTANCES WILL ITS LIABILITY EXCEED THE PURCHASE PRICE FOR DEFECTIVE
PRODUCTS.
On-line Warranty Registration
If you would like to register your MultiFRAD electronically, you can do so at the following address:
http://www.multitech.com/support/register.htm
66
Page 67

Tech Support
Multi-Tech has an excellent staff of technical support personnel available to help you get the most out
of your Multi-Tech product. If you have any questions about the operation of this unit, call 1-800-972-
2439. Please fill out the MultiFRAD information (below), and have it available when you call. If your
MultiFRAD requires service, the tech support specialist will guide you on how to send in your
equipment (refer to the next section).
Recording MultiFRAD Information
Please fill in the following information on your MultiFRAD. This will help tech support in answering
your questions. (The same information is requested on the Warranty Registration Card.)
Model No.: _________________________
Serial No.: _________________________
Software Version: ____________________
The model and serial numbers are on the bottom of your MultiFRAD.
Please note the type of external link device that is connected to your MultiFRAD before calling tech
support. Also, note the status of your MultiFRAD including LED indicators, screen messages,
diagnostic test results, DIP-Switch settings, problems with a specific application, etc. Use the space
below to note the status:
Chapter 7 - Warranty, Service and Tech Support
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Contacting Tech Support via E-mail
If you prefer to receive service on-line, via the internet, you can contact Tech Support via e-mail at
the following address:
http://www.multitech.com/_forms/email_tech_support.htm
67
Page 68

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Service
If your tech support specialist decides that service is required, your MultiFRAD may be sent (freight
prepaid) to our factory . Return shipping charges will be paid by Multi-Tech Systems.
Include the following with your MultiFRAD:
• a description of the problem.
• return billing and return shipping addresses.
• contact name and phone number .
• check or purchase order number for payment if the MultiFRAD is out of warranty. (Check with
your technical support specialist for the standard repair charge for your MultiFRAD).
• if possible, note the name of the technical support specialist with whom you spoke.
If you need to inquire about the status of the returned product, be prepared to provide the serial
number of the product sent.
Send your MultiFRAD to this address:
You should also check with the supplier of your MultiFRAD on the availability of local service and/or
loaner units in your part of the country .
MULTI-TECH SYSTEMS, INC.
2205 WOODALE DRIVE
MOUNDS VIEW, MINNESOTA 55112
ATTN: SERVICE OR REPAIRS
The Multi-Tech BBS
For customers who do not have Internet access, Multi-Tech maintains a bulletin board system (BBS)
that mirrors its FTP site. Information available from the BBS includes new product information,
product upgrade files, and problem-solving tips. The phone number for the Multi-Tech BBS is (800)
392-2432 (USA and Canada) or (612) 785-3702 (international and local).
The BBS can be accessed by any asynchronous modem operating at 1200 bps to 33,600 bps at a
setting of 8 bits, no parity , and 1 stop bit (8-N-1).
To log on to the Multi-Tech BBS
1. Set your communications program to 8-N-1.
2. Dial our BBS at (800) 392-2432 (USA and Canada) or (612) 785-3702 (international and
local).
3. At the prompts, type your first name, last name, and password; then press ENTER. If you are
a first time caller, the BBS asks if your name is spelled correctly. If you answer yes, a
questionnaire appears. You must complete the questionnaire to use the BBS on your first
call.
4. Press ENTER until the Main Menu appears. From the Main Menu you have access to two
areas: the Files Menu and News. For help on menu commands, type ?.
68
Page 69

Chapter 7 - Warranty, Service and Tech Support
To Download a file
If you know the file name
1. From the Main Menu, type F to access the Files Menu, then type D.
2. Enter the name of the file you wish to download from the BBS.
3. If a password is required, enter the password.
4. Answer Y or N to the automatic logoff question.
5. Select a file transfer protocol by typing the indicated letter, such as Z for Zmodem (the
recommended protocol).
6. If you select Zmodem, the transfer will begin automatically . If you select another protocol, you
may have to initiate the transfer yourself. (In most datacomm programs, the P AGE DOWN
key initiates the download.)
7. When the download is complete, press ENTER to return to the File Menu.
8. To exit the BBS, type G and press ENTER.
If you don’t know the file name
1. From the Main Menu, type F to access the Files Menu. For a list of file areas, type L, press
ENTER, then type L and press ENTER again. (If you do not type the second L, you will list all
of the files on the BBS.)
2. Mark each file area you would like to examine by typing its list number and pressing ENTER.
3. Enter L to list all the files in the selected file areas. Enter C to go forward in the file list and P
to go back.
4. To mark one or more files for download, type M, press ENTER, type the list numbers of the
files, and press ENTER again.
5. Enter D. You will see a list of the files you have marked. Enter E if you would like to edit the
list; otherwise enter D again to start the download process.
6. Select a file transfer protocol by typing the indicated letter, such as Z for Zmodem (the
recommended protocol).
7. If you select Zmodem, the file will transfer automatically . If you select another protocol, you
may have to initiate the transfer yourself. (In most data communications programs, the P AGE
DOWN key initiates the download.)
8. When the download is complete, press ENTER to return to the File Menu.
9. To exit the BBS, type G and press ENTER.
69
Page 70

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
About CompuServe
In addition to the BBS, Multi-Tech provides support through CompuServe’s Modem V endor Forum
(GO MODEMVEN). Refer to your CompuServe documentation for special operating procedures.
About the Internet
Multi-Tech is a commercial user on the Internet, and we retrieve messages from our customers on a
periodic basis. Multi-Tech’s presence includes a Web site at:
http://www.multitech.com
and an ftp site at:
ftp://ftp.multitech.com
About the Multi-Tech Fax-Back Service
Multi-Tech’s fax-back system provides 24-hour access to sales, marketing, and technical literature.
Dial 612-717-5888, follow the voice prompts, and request document number 10 for a catalog of
available documents. For convenience, have your fax number handy:
_________________________. From the catalog of available documents, you can order newsletters,
white papers, press releases, etc. from the sales and marketing index (pages 1-4), or order basic
modem operation and troubleshooting guides from the technical support and engineering index. Just
enter the applicable FB Doc. # from the left column of the catalog.
70
Page 71

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Appendices
Page 72

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Appendix A - Cabling Diagrams
Command Port Cable
13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14
To COMMAND PORT
Connector
LAN Cables
PIN NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
22
25
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
PIN NO.
10BASE-T
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
22
25
TRANSMIT DATA (BA)
RECEIVE DATA (BB)
SIGNAL GROUND (AB)
To
DTE
Device
(Terminal
Device
i.e. ASCII
Terminal)
72
10Base-T (RJ-45)
Pin Circuit Signal Name
1 TD+ Data T ransmit Positive
2 TD- Data Transmit Negative
3 RD+ Data Receive Positive
4 RD- Data Receive Negative
Page 73

Trunk Cable
To
External
Synchronous
Modem/DSU
Connector
13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14
RS232C/V.24 * Link Cable
PIN NO.
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
15
17
20
25
PIN NO.
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
15
17
20
25
CHASSIS GROUND (AA)
TRANSMIT DATA (BA)
RECEIVE DATA (BB)
REQUEST TO SEND (CA)
CLEAR TO SEND (CB)
SIGNAL GROUND (AB)
CARRIER DETECT (CF)
TRANSMIT CLOCK (DB)
RECEIVE CLOCK (DD)
DATA TERMINAL READY (CD)
Appendix A - Cabling Diagrams
To MultiRouter
Link 1,2 or 3
RS232C/V.35
Connector
V.35 Adapter Cable Configured on a RS232C/V.35**
Link Cable
V.35 34-PIN CONNECTOR
Chassis Ground
Request To Send
Data Set Ready
Data Terminal Ready
Send Data (A)
Send Data (B)
Terminal Timing (A)
Terminal Timing (B)
Send Timing (A)
Send Timing (B)
V.35 34-PIN
CONNECTOR (MALE)
A
B
C
D
E
F
H
P
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
a
A
D
C
E
J
H
K
N
M
P
T
S
U
X
W
Y
BB
AA
CC
FF
EE
HH
KK
LL
MM
As viewed from the connector side
CONNECTOR (FEMALE)
B
F
L
R
V
Z
DD
JJ
NN
Data Carrier Detect
Receive Data (A)
Receive Data (B)
Receive Timing (A)
Receive Timing (B)
25-PIN
1
7
4
5
6
8
20
2
3
12
22
23
17
25
18
15
21
Signal Ground
Clear To Send
PROTECTIVE GROUND
SIGNAL GROUND
REQUEST TO SEND
CLEAR TO SEND
DATA SET READY
DATA CARRIER DETECT
DAT A TERMINAL READY
TRANSMIT DATA A
RECEIVE DATA A
TRANSMIT DATA B
RECEIVE DATA B
EXTERNAL TX CLOCK A
RECEIVE CLOCK A
EXTERNAL TX CLOCK B
RECEIVE CLOCK B
TRANSMIT CLOCK A
TRANSMIT CLOCK B
* The MultiFRAD RS232C interface circuits have been designed to meet the
electrical specificaitons given in EIA (Electronic Industries Association) RS232C
and CCITT (Consultative Committee International Telegraph and Telephone) V.24
Standards.
** When configured for V.35 interface operation on the link, the V.35 adapter
cable should be used. This cable uses a 25-pin female connector at one end and
a 34-pin winchester male connector at the other end.
73
Page 74

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Remote Configuration Cable
To
COMMAND PORT
Connector
PIN NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
22
25
Male
PIN NO.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
22
25
Male
FRAME GROUND
TRANSMIT DATA (TX)
RECEIVE DATA (RX)
REQUEST TO SEND (RTS)
CLEAR TO SEND (CTS)
SIGNAL GROUND
To
DCE
Device
(Communication
Device
i.e. Modem)
74
Page 75

Appendix B - Regulatory Information
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy , and if not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case
the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Warning: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for
compliance could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Appendix B - Regulatory Information
75
Page 76

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Appendix C - Network Overview
Network architecture defines how computer equipment and other devices are linked together to form
a communications system that allows users to share information and resources. There are
proprietary network architectures and open architectures like the Open Systems Interconnection
(OSI) model defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). The OSI model
defines a layered model for an open systems environment in which a process running in one
computer communicates with a similar process on another computer if they implement the same OSI
layer communications protocol. The OSI protocol stack shown in Figure B-1 is commonly used as a
reference. During a communications session, processes running in each layer on each computer
communicate with one another. The bottom layer defines the actual physical components such as
connectors and cable and the electrical transmission of data bits between systems. The layers
immediately above define data packaging and addressing methods. Still further up are methods for
keeping communication sessions alive. Finally , the uppermost layers describe how applications use
the underlying communication systems to interact with applications on other systems.
Application Layer 7
Presentation Layer 6
Session Layer 5
Transport Layer 4
Network Layer 3
Data-Link Layer 2
Physical Layer 1
Figure B-1. OSI Protocol Stack
Protocols are loaded into a computer as software drivers. Each layer of the protocol stack defines a
specific set of functions. An application at the uppermost layer interacts with the layer below when it
needs to send information to another system on the network. The request is packaged in one layer
and passed down to the next layer, which adds information related to functions handled at that layer,
creating a new packet within a packet. This package is then passed down to the next layer and the
process continues. Each layer adds information to the message packet and this information is read
by the corresponding layer in the receiving system's protocol stack. In this way , each protocol layer
communicates with its corresponding protocol layer to facilitate communication.
The physical layer defines the physical characteristics of the interface, such as mechanical
components and connectors, electrical aspects such as voltage levels representing binary values,
and functional aspects such as setting up, maintaining, and taking down the physical link. Well
known physical layer interfaces for data communication include RS-232 and RS-449, the successor
to RS-232.
The data-link layer defines the rules for sending and receiving information across the physical
connection between two systems. This layer encodes and frames data for transmission, in addition to
providing error detection and control. Because the data-link layer can provide error control, higher
layers may not need to handle such services. However, when reliable media is used, there is a
performance advantage by not handling error control in this layer, but in higher layers.
76
The Network layer defines protocols for opening and maintaining a path on the network between
systems. It is concerned with data transmission and switching procedures, and hides such
procedures from upper layers. The network layer can look at packet addresses to determine routing
methods. If a packet is addressed to a workstation on the local network, it is sent directly there. If it's
addressed to a network on another segment, the packet is sent to a routing device, which forwards it
on the network. Some common protocols occupying the network layer are Internet Protocol (IP),
X.25, Novell's Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), Banyan's VINES Internet Protocol (VIP).
Page 77

Appendix C - Network Overview
The transport layer provides a high level of control for moving information between systems,
including more sophisticated error handling, prioritization, and security features. It provides quality
service and accurate delivery by providing connection-oriented services between two end systems.
The transport layer controls the sequence of packets, regulates traffic flow , and recognizes duplicate
packets. It assigns packetized information which is a tracking number that is checked at the
destination. If data is missing from the packet, the transport layer at the receiving end arranges with
the transport layer of the sending system to have packets retransmitted. This layer ensures that all
data is received and in the proper order.
The session layer coordinates the exchange of information between systems by using conversational
techniques, or dialogues. Dialogues are not always required, but some applications may require a
way of knowing where to restart the transmission of data if a connection is temporarily lost, or may
require a periodic dialog to indicate the end of one data set and the start of a new one.
Presentation layer protocols are part of the operating system and the application the user runs on a
workstation. Information is formatted for display or printing in this layer. Codes within the data, such
as tabs or special graphics sequences, are interpreted. Data encryption and translation of other
character sets are also handled in this layer.
Applications access the underlying network services using defined procedures in this layer. The
application layer is used to define a range of applications that handle file transfers, terminal sessions,
and message exchanges. Data starts at the application and presentation layers, where a user works
with a network application, such as an electronic mail program. Requests for services are passed
through the presentation layer to the session layer which begins the process of packetizing the
information. A connection-oriented communication session may be opened between the two systems
to provide reliable transmissions. Once the session is established, protocol layers begin exchanging
information as appropriate.
Packet
A packet is a package of data that is exchanged between devices over a data communications link.
Data exchanged between devices may include messages and commands, control codes for
managing the session, and data. Information is placed in packets by various communications
subsystems of the transmitting system, then framed into a serial bit-stream and sent across the
communications link. One of the main reasons for packetizing and framing information is that errors
on the communication link only affect a small, discernible part of the transmission, which is easily
retransmitted.
The process starts at the application layer. An application in one computer has some information to
send to another computer. The information is sent down through the protocol stack, across the wire,
and up through the protocol stack of the other computer. This information takes the form of a
protocol data unit (PDU). As the PDU moves through the layers of the sending computer, each layer
attaches specific information to the PDU that is relevant to the protocols in that layer. This attached
information is destined for the peer layer in the receiving computer. For example, the transport layer
in the sending computer adds a sequence number to the PDU. This sequence number is read by the
transport layer in the receiving computer to resequence the packets.
The communication protocol defines the packet structure and the networking system in use and
defines the frame structure for bit-stream transmission. Each protocol layer attaches information
destined for its peer layer in the other computer. When the PDU reaches the physical layer, it is
transmitted as a stream of bits. On copper wire, the bit-streams take the form of voltage level
changes that represent binary ones and zeros. The data-link layer places the PDU in one or more
frames and uses a media access method (such as CSMA/CD or token) to gain access to the
transmission media. The PDU might be subdivided into a number of separately addressed frames.
The frame format is defined by the network in use. For example, Ethernet defines frames that can
hold up to 1,500 bytes of packet data.
77
Page 78

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
In general, a packet is a collection of information that contains data (payload) and headers (pilot).
Headers include the source and destination address as well as control information to handle errors
and keep packets flowing properly . Each packet is a separate block of information that can have a
different destination address, and in some cases, different sizes. A typical packet holds 512 bytes of
information, so it takes many packets to transfer a large file over a network.
As packets traverse a network, the addressing information contained in them is used by bridges and
routers to direct packets to their destination, or keep them off of networks where they don't belong.
Routers direct packets along a specific path that has been predetermined as the best route to the
packets' destination. Routers use algorithms to determine efficient paths in conjunction with other
routers on the network. Administrators can also manually configure routers, based on the cost or
speed of routes. Information can be transmitted to another system using either connection-oriented
or connection-less methods. A connection-less session is more efficient for short, bursty
transmissions since a session setup is not required, but the end system may need to perform more
work to resequence packets that arrive out of order and check for lost packets.
Network Address
Every node on a network has an assigned address that other nodes use when communicating with it.
For Ethernet and token ring network adapters, unique addresses are assigned at the factory .
ARCNET networks have user-definable addresses. For example, the address of an Ethernet and
token ring network adapter consists of a 6-byte address, half of which is a special number identifying
the board's manufacturer. The last half of the address is a unique number for the board assigned at
the factory . This strategy virtually guarantees that no two Ethernet or token ring network interface
cards will ever have the same address and prevents conflicts.
When separate networks are connected into an internetwork, a new addressing scheme is required.
On interconnected NetWare networks, each network segment has its own address, which is used for
routing purposes and differentiate each segment from the others.
In TCP/IP networks such as the Internet, every node has a numeric address that identifies both a
network and a local host or node on the network. This address is written as four numbers separated
by dots, for example 148.1.9.1. The assignment of addresses is arbitrary within a company or
organization, but if the company plans to connect with the Internet, it is important to obtain registered
addresses from an outside agency to conform with international addressing standards. Applications
running in computers also have addresses that other applications, either local or remote, use to
communicate with the application. On TCP/IP networks, a socket is a combination of an Internet
address plus an application address.
Internet Protocol (IP)
Internet Protocol is a connection-less communication protocol that by itself provides a datagram
service. Datagrams are self-contained packets of information that are forwarded by routers based on
their address and the routing table information contained in the routers. Datagrams can be
addressed to a single node or to multiple nodes. There is no flow control, acknowledgment of
receipt, error checking, and sequencing. Datagrams may traverse different paths to the destination
and thus arrive out of sequence. The receiving station is responsible for resequencing and
determining if packets are lost. IP handles congestion by simple discarding packets. Resequencing
and error handling are taken care of by upper layer protocols.
IP works on a number of local and wide area networks. When IP runs in the LAN environment on an
Ethernet network, for example, the data field in the Ethernet frame holds the IP packet and a specific
field in the frame indicates that IP information is enclosed. IP uses an addressing scheme that works
independently of the network addressing scheme. For example, every Ethernet adapter has a
factory-assigned address for each node.
78
Page 79

Appendix C - Network Overview
IP Addressing
Every node on an IP network requires a 4-byte numeric address that identifies both a network and a
local host or node on the network. This address is written as four numbers separated by dots, for
example, 148.1.9.1. In most cases, the network administrator sets up these addresses when
installing a device.
The assignment of addresses is arbitrary within a company or organization, but if a company plans to
connect with the Internet anytime in the near future, a registered addresses should be obtained from
the Defense Data Network (DDN) Network Information Center (NIC), which is managed by Network
Solutions in Chantilly , V irginia. With the growing popularity of the Internet, it is recommended that all
organizations obtain registered addresses to avoid address conflicts in the future.
There are three classes of Internet addresses; Class A, B and C. Class A networks use the first byte
of the IP address for the network number and the remaining three bytes for the host number. The
first byte may have any value from one to 127.
Class B networks use the first two bytes of the IP address for the network number and the last two
bytes for the host number. The first byte must have a value from 128 to 191.
Class C networks use the first three bytes of the IP address for the network number and the last byte
for the host number. This scheme provides for a very large number of dif ferent networks, each with
up to 255 addressable devices. The first byte must have a value from 192 to 223.
The part of the IP address that refers to the network is called the network address. A network mask
is the bit pattern which yields the network address in a Boolean AND operation with the IP address.
For example, in Class C networks, network addresses take the form X.X.X.0. The network mask for
Class C networks is 255.255.255.0. In all of the IP addresses on a given network, the network
address will remain the same while the host portion will be different for each host or workstation.
79
Page 80

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
80
Page 81

3000-Series
Router/Multiport Data/Voice/Fax
Frame Relay Access Device
Glossary
Page 82

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
A
Access: The T1 line element made up of two pairs of wire that the telephone company brings to the customer premises. The Access
portion ends with a connection at the local telco (LEC or RBOC).
Accunet Spectrum of Digital Services (ASDS): The AT&T 56K bps leased (private) line service. Similar to services of MCI and
Sprint. ASDS is available in nx56/64K bps, where n=1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12.
ACK (ACKnowledgement code) (pronounced "ack"): A communications code sent from a receiving modem to a transmitting modem
to indicate that it is ready to accept data. It is also used to acknowledge the error-free receipt of transmitted data. Contrast with NAK.
Adaptive Differential Pulse Code (ADCPM): In multimedia applications, a technique in which pulse code modulation samples are
compressed before they are stored on a disk. ADCPM, an extension of the PCM format, is a standard encoding format for storing audio
information in a digital format. It reduced storage requirements by storing differences between successive digital samples rather than full
values.
Address: A numbered location inside a computer. It's how the computer accesses its resources, like a video card, serial ports,
memory, etc.
AMI line coding: One of two common methods of T1 line coding (with B8ZS). AMI line coding places restrictions on user data (B8ZS
does not).
Analog signal: A waveform which has amplitude, frequency and phase, and which takes on a range of values between its maximum
and minimum points.
Analog Transmission: One of two types of telecommunications which uses an analog signal as a carrier of voice, data, video, etc. An
analog signal becomes a carrier when it is modulated by altering its phase, amplitude and frequency to correspond with the source
signal. Compare with digital transmission.
Application Program Interface (API): A software module created to allow dissimilar, or incompatible applications programs to transfer
information over a communications link. APIs may be simple or complex; they are commonly required to link PC applications with
mainframe programs.
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) (pronounced "askey"): A binary code for data that is used in
communications and in many computers and terminals. The code is used to represent numbers, letters, punctuation and control
characters. The basic ASCII code is a 7-bit character set which defines 128 possible characters. The extended ASCII file provides 255
characters.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM): A very high-spped method of transmission that uses fixed-size cells of 53 bytes to transfer
information over fiber; also known as cell relay.
AT Commands: A standard set of commands used to configure various modem parameters, establish connections and disconnect.
The "AT" is used to get the "attention" of the modem before the actual command is issued.
Availability: The measure of the time during which a circuit is ready for use; the complement of circuit "outage" (100% minus %
outage = % available).
B
B7ZS (Bipolar 7 Zero Suppression) line coding: One method of T1 line coding (see also "B8ZS" and "AMI"). B7ZS line coding does
not place restrictions on user data (AMI does).
B8ZS (Bipolar 8 Zero Suppression) line coding: One of two common methods of T1 line coding (with AMI). B8ZS line coding does
not place restrictions on user data (AMI does). A coding method used to produce 64K bps "clear" transmission. (See also "B7ZS" and
"AMI" line coding)
Backbone: 1. A set of nodes and their interconnecting links providing the primary data path across a network. 2. In a local area
network multiple-bridge ring configuration, a high-speed link to which the rings are connected by means of bridges. A backbone may be
configured as a bus or as a ring. 3. In a wide area network, a high-speed link to which nodes or data switching exchanges (DSEs) are
connected. 4. A common distibution core that provides all electrical power, gases, chemicals, and other services to the sectors of an
automated wager processing system.
Background: An activity that takes place in the PC while you are running another application. In other words, the active user interface
does not correspond to the 'background' task.
Bandwidth: The transmission capacity of a computer channel, communications line or bus. It is expressed in cycles per second (hertz),
the bandwidth being the difference between the lowest and highest frequencies transmitted. The range of usable frequencies that a
transmission medium will pass without unacceptable attenuation or distortion. Bandwidth is a factor in determining the amount of
information and the speed at which a medium can transmit data or other information.
82
Page 83

Glossary
Backward Explicit Congestion Notification (BECN): A bit that tells you that a certain frame on a particular logical connection has
encountered heavy traffic. The bit provides notification that congestion-avoidance procedures should be initiated in the opposite
direction of the received frame. See also FECN (Forward Explicit Congestion Notification).
Basic Rate Interface (BRI): An ISDN access interface type comprised of two B-channels each at 64K bps and one D-channel at 64K
bps (2B+D).
Bell Operating Companies (BOC): The family of corporations created during the divestiture of AT&T. BOCs are independent companies which service a specific region of the US. Also called Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs).
Bell Pub 41450: The Bell publication defining requirements for data format conversion, line conditioning, and termination for direct DDS
connection.
Bell Pub 62310: The Bell publication defining requirements for data format conversion, line conditioning, and termination for direct DDS
connection.
Binary Synchronous Communication (BSC): A form of telecommunication line control that uses a standard set of transmission
control characters and control character sequences, for binary synchronous transmission of binary-coded data between stations.
Bit (Binary digIT): A bit is the basis of the binary number system. It can take the value of 1 or 0. Bits are generally recognized as the
electrical charge generated or stored by a computer that represent some portion of usable information.
Bit Error Rate Test (BERT): A device or routine that measures the quality of data transmission. A known bit pattern is transmitted, and
the errors received are counted and a BER (bit error rate) is calculated. The BER is the ratio of received bits in error relative to the total
number of bits received, expressed in a power of 10.
Bit robbing: The use of the least significant bit per channel in every sixth frame for signaling. The line signal bits "robbed" from the
speech pat conveys sufficient pre-ISDN telephony signaling information with the remaining line signal bits providing sufficient line
signaling bits for recreating the original sound. See "robbed bit signaling".
Blue Alarm: An error indication signal consisting of all 1s indicating disconnection or attached device failure. Contrast "Red Alarm" and
"Yellow Alarm".
Bps (bits per second): A unit to measure the speed at which data bits can be transmitted or received. Bps differs from baud when
more than one bit is represented by a single cycle of the carrier.
Bridges: 1. A functional unit that interconnects two local area networks that use the same logical link protocol but may use different
medium access control protocols. 2. A functional unit that interconnects multiple LANs (locally or remotely) that use the same logical link
control protocol but that can use different medium access control protocols. A bridge forwards a frame to another bridge based on the
medium access control (MAC) address. 3. In the connection of local loops, channels, or rings, the equipment and techniques used to
match circuits and to facilitate accurate data transmission.
Buffer: A temporary storage register or Random Access Memory (RAM) used in all aspects of data communications which prevents
data from being lost due to differences in transmission speed. Keyboards, serial ports, muxes and printers are a few examples of the
devices that contain buffers.
Bus: A common channel between hardware devices either internally between components in a computer, or externally between stations
in a communications network.
Byte: The unit of information a computer can handle at one time. The most common understanding is that a byte consists of 8 binary
digits (bits), because that's what computers can handle. A byte holds the equivalent of a single character (such as the letter A).
C
Call Setup Time: The time to establish a circuit-switched call between two points. Includes dialing, wait time, and CO/long distance
service movement time.
Carrier Group Alarm (CGA): A T1 service alarm generated by a channel bank when an OOF condition occurs for a predefined length
of time (usually 300mS to 2.5 seconds). The CGA causes the calls using a trunk to be dropped and for trunk conditioning to be applied.
Carrier signal: An analog signal with known frequency, amplitude and phase characteristics used as a transport facility for useful
information. By knowing the original characteristics, a receiver can interpret any changes as modulations, and thereby recover the
information.
CCITT (Consultative Committee for International Telephone and Telegraph): An advisory committee created and controlled by the
United Nations and headquartered in Geneva whose purpose is to develop and to publish recommendations for worldwide standardization of telecommunications devices. CCITT has developed modem standards that are adapted primarily by PTT (post, telephone and
telegraph) organizations that operate telephone networks of countries outside of the U.S. See also ITU.
Central Office (CO): The lowest, or most basic level of switching in the PSTN (public switched telephone network). A business PABX
or any residential telephone connects to the PSTN at a central office.
83
Page 84

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Centrex: A multi-line service offered by operating telcos which provides, from the telco CO, functions and features comparable to those
of a PBX for large business users. See also "Private Branch Exchange", "Exchange".
Channel: A data communications path between two computer devices. Can refer to a physical medium (e.g., UTP or coax), or to a
specific carrier frequency.
Channel bank: A device that acts as a converter, taking the digital signal from the T1 line into a phone system and converting it to the
analog signals used by the phone system. A channel bank acts as a multiplexer, placing many slow-speed voice or data transactions on
a single high-speed link.
Circuit-switched Network: A technology used by the PSTN that allocates a pair of conductors for the exclusive use of one communication path. Circuit switching allows multiple conversations on one talk path only if the end-users multiplex the signals prior to transmission.
Circuit switching: The temporary connection of two or more communications channels using a fixed, non-shareable path through the
network. Users have full use of the circuit until the connection is terminated.
Clear Channel: A transmission path where the full bandwidth is used (i.e., no bandwidth needed for signaling, carrier framing or control
bits). A 64K bps digital circuit usually has 8K bps used for signaling. ISDN has two 64K bps circuits, and a 16K bps packet service of
which part is used for signaling on the 64K channels.
Client-Server: In TCP/IP, the model of interaction in distributed data processing in which a program at one site sends a request to a
program at another site and awaits a response. The requesting program is called a client; the answering program is called a server.
Cluster Controller: A device that can control the input/output operations of more than one device connected to it. A cluster controller
may be controlled by a program stored and executed in the unit, or it may be entirely controlled by hardware.
Committed Burst Size: the maximum number of bits that the frame relay network agrees to transfer during any measurement interval
Committed Information Rate (CIR): An agreement a customer makes to use a certain minimum data transmission rate (in bps). The
CIR is part of the frame relay service monthly billing, along with actual usage, that users pay to their frame relay service provider.
Compression: 1. The process of eliminating gaps, empty fields, redundancies, and unnecessary data to shorten the length of records or
blocks. 2. In SNA, the replacement of a string of up to 64-repeated characters by an encoded control byte to reduce the length of the
data stream to the LU-LU session partner. The encoded control byte is followed by the character that was repeated (unless that
character is the prime compression character). 3. In Data Facility Hierarchical Storage Manager, the process of moving data instead of
allocated space during migration and recall in order to release unused space. 4. Contrast with decompression.
COMx Port: A serial communications port on a PC.
congestion: A network condition where there is too much data traffic. The ITU I.233 standard defines congestion management in
terms of speed and burstiness.
congestion notification: The function in frame relay that ensures that userdata transmitted at a rate higher than the CIR are allowed
to slow down to the rate of the available network bandwidth.
Consecutive Severely Errored Seconds (CSES): An error condition that occurs when from 3 to 9 SES (Severely Errored Seconds) are
logged consecutively.
Customer Premise Equipment (CPE): The generic term for data comm and/or terminal equipment that resides at the user site and is
owned by the user with the following exclusions: Over voltage protection equipment, inside wiring, coin operated or pay telephones,
"company-official" equipment, mobile telephone equipment, "911" equipment, equipment necessary for the provision of communications
for national defense, or multiplexing equipment used to deliver multiple channels to the customer.
D
D4: the T1 4th generation channel bank.
D4 channelization: Refers to the compliance with AT&T TR 62411 for DS1 frame layout.
D4 framing: The T1 format for framing in AT&T D-Series channel banks, in which there are 12 separate 193-bit frames in a super-
frame. A D4 framing bit is used to identify the channel and the signaling frame. Signalling for voice channels is carried in-band for every
channel, along with the encoded voice. See "robbed-bit signaling".
Data Communications Equipment (DCE): Any device which serves as the portal of entry from the user equipment to a telecommunications facility. A modem is a DCE for the telephone network (PSTN) that is commonly on site at the user’s premises. Packet Switched
Networks have another level of DCE which is most often located at a central office.
Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI): One of the six components of a frame relay frame. Its purpose is to distinguish separate
virtual circuits across each access connection. Data coming into a frame relay node is thus allowed to be sent across the interface to the
specified "address". The DLCI is confirmed and relayed to its destination, or if the specification is in error, the frame is discarded.
Dataphone Digital Service (DDS): A private line digital service that offers 2400, 4800, 9600 and 56K bps data rates on an inter-LATA
basis by AT&T and on an intra-LATA basis by the BOCs.
84
Page 85

Glossary
Data Service Unit (DSU): A device that provides a digital data service interface directly to the data terminal equipment. The DSU
provides loop equalization, remote and local testing capabilities, and a standard EIA/CCITT interface.
Dedicated Line: A communication line that is not switched. The term leased line is more common.
Default: This is a preset value or option in software packages, or in hardware configuration, that is used unless you specify otherwise.
Device driver: Software that controls how a computer communicates with a device, such as a printer or mouse.
Digital Cross-connect System (DCS): The CO device which splits and redistributes the T1 bandwidth. the DCS takes time slots from
various T1 lines and alters them to provide the needed connectivity. DCS connections are made with software at an administrator's
workstation.
Digital Data: Information represented by discrete values or conditions (contrast "Analog Data").
Digital Loopback: A technique used for testing the circuitry of a communications device. Can be initiated locally, or remotely (via a
telecommunications device). The tested device decodes and encodes a received test message, then echoes the message back. The
results are compared with the original message to determine if corruption occurred en route.
Digital PBX: A Private Branch Exchange that operates internally on digital signals. See also "Exchange".
Digital Service, level 0 (DS0): The world-wide standard speed (64K bps) for digital voice conversation using PCM (pulse coded
modulation).
Digital Service, level 1 (DS1): The 1.544M bps voice standard (derived from an older Bell System standard) for digitized voice
transmission in North America. The 1.544M bps consists of 24 digitally-encoded 64K bps voice channels (north America) and 2.048M
bps (30 channels) elsewhere.
Digital Signal: A discrete or discontinuous signal (e.g., a sequence of voltage pulses). Digital devices, such as terminals and computers, transmit data as a series of electrical pulses which have discrete jumps rather than gradual changes.
Digital Signaling Rates (DSn): A hierarchical system for transmission rates, where "DS0" is 64K bps (equivalent to ISDN B channel),
and DS1 is 1.5 Mbps (equivalent to ISDN PRI).
Digital Transmission: A method of electronic information transmission common between computers and other digital devices. Analog
signals are waveforms: a combination of many possible voltages. A computer's digital signal may be only "high" or "low" at any given
time. Therefore, digital signals may be "cleaned up" (noise and distortion removed) and amplified during transmission.
Digitize: To convert an analog signal to a digital signal.
DIP switch (pronounced "dip switch"): A set of tiny toggle switches, built into a DIP (dual in-line package), used for setting
configurable parameters on a PCB (printed circuit board).
Driver: A software module that interfaces between the Operating System and a specific hardware device (i.e. color monitors, printers,
hard disks, etc.). Also known as a device driver.
Drop and Insert: The process where a portion of information carried in a transmission system is demodulated ("Dropped") at an
intermediate point and different information is included ("Inserted") for subsequent transmission.
DTE (Data Terminating Equipment): A term used to include any device in a network which generates, stores or displays user
information. DTE is a telecommunications term which usually refers to PCs, terminals, printers, etc.
DTMF (Dual-Tone MultiFrequency): A generic push-button concept made popular by AT&T TouchTone.
E
E&M: A telephony trunking system used for either switch-to-switch, or switch-to-network, or computer/telephone system-to-switch
connection.
EIA: The Electronics Industries Association is a trade organization in Washington, DC that sets standard for use of its member
companies. (See RS-232, RS-422, RS530.)
Encapsulation: A technique used by network-layer protocols in which a layer adds header information to the protocol data unit from the
preceding layer. Also used in "enveloping" one protocol inside another for transmission. For example, IP inside IPX.
Errored Seconds (ES): Any second of operation that all 1.544M bits are not received exactly as transmitted. Contrast "Error Free
Seconds".
Error Free Seconds (EFS): Any second of operation that all 1.544M bits are received exactly as transmitted. Contrast "Errored
Seconds".
ESF Error Event: A T1 error condition that is logged when a CRC-6 error or an OOF error occurs.
Ethernet: A 10-megabit baseband local area network that allows multiple stations to access the transmission medium at will without
prior coordination, avoids contention by using carrier sense and deference, and resolves contention by using collision detection and
transmission. Ethernet uses carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD).
85
Page 86

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Excess Zeros: A T1 error condition that is logged when more than 15 consecutive 0s or less than one 1 bit in 16 bits occurs.
Exchange: A unit (public or private) that can consist of one or more central offices established to serve a specified area. An exchange
typically has a single rate of charges (tariffs) that has previously been approved by a regulatory group.
Exchange Area: A geographical area with a single uniform set of charges (tariffs), approved by a regulatory group, for telephone
services. Calls between any two points within an exchange area are local calls. See also "Digital PBX", "PBX".
Exchange Termination (ET): The carrier's local exchange switch. Contrast with "Loop Termination - LT".
Explicit Congestion Management: The method used in frame relay to notify the terminal equipment that the network is overly busy.
The use of FECN and BECN is called explicit congestion management. Some end-to-end protocols use FECN or BECN, but usually not
both options together. With this method, a congestion condition is identified and fixed before it becomes critical. Contrast with "implicit
congesion".
Extended Super Frame (ESF): One of two popular formats for framing bits on a T1 line. ESF framing has a 24-frame super-frame,
where robbed bit signaling is inserted in the LSB (bit 8 of the DS-0 byte) of frames 6, 12, 18 and 24. ESF has more T1 error measurement capabilities than D4 framing. ESF and B8ZS are typically both offered to provide clear channel service.
F
Failed Seconds: A test parameter where the circuit is unavailable for one full second.
Failed Signal: A T1 test parameter logged when there are more than 9 SES (Severely Errored Seconds).
Fax (facsimile): Refers to the bit-mapped rendition of a graphics-oriented document (fax) or to the electronic transmission of the image
over telephone lines (faxing). Fax transmission differs from data transmission in that the former is a bit-mapped approximation of a
graphical document and, therefore, cannot be accurately interpreted according to any character code.
Firmware: A category of memory chips that hold their content without electrical power, they include ROM, PROM, EPROM and
EEPROM technologies. Firmware becomes "hard software" when holding program code.
Foreground: The application program currently running on and in control of the PC screen and keyboard. The area of the screen that
occupies the active window. Compare with "background".
Fractional T1 (FT1): A digital data transmission rate between 56K bps (DS0 rate) and 1.544M bps (the full T1 rate - in North America).
FT1 is typically provided on 4-wire (two copper pairs) UTP. Often used for video conferencing, imaging and LAN interconnection due to
its low cost and relatively high speed. FT1 rates are offered in 64K bps multiples, usually up to 768K bps.
Frequency: A characteristic of an electrical or electronic signal which describes the periodic recurrence of cycles. Frequency is
inversely proportional to the wavelength or pulse width of the signal (i.e., long wavelength signals have low frequencies and short
wavelength signals yield high frequencies).
Foreign Exchange (FX): A CO trunk with access to a distant CO, allowing ease of access and flat-rate calls anywhere in the foreign
exchange area.
Foreign Exchange Office (FXO): provides local telephone service from a CO outside of ("foreign" to) the subscriber's exchange
area. In simple form, a user can pick up the phone in one city and receive a tone in the foreign city.
Connecting a POTS telephone to a computer telephony system via a T1 link requires a channel bank configured for the FX connection.
To generate a call from the POTS set to the computer telephony system, a FXO connection must be configured.
Foreign Exchange Station (FXS): See FX, FXO. To generate a call from the computer telephony system to the POTS set, a FXS
connection must be configured.
Forward Explicit Congestion Notification (FECN): A bit that tells you that a certain frame on a particular logical connection has
encountered heavy traffic. The bit provides notification that congestion-avoidance procedures should be initiated in the same direction of
the received frame. See also BECN (Backward Explicit Congestion Notification).
Frame: A group of data bits in a specific format to help network equipment recognize what the bits mean and how to process them. The
bits are sent serially, with a flag at each end signifying the start and end of the frame.
Frame Relay: A form of packet switching that uses small packets and that requires less error checking than other forms of packet
switching. Frame relay is effective for sending "bursty" data at high speeds (56/64K, 256K, and 1024K bps) over wide area networks.
Frame Relay specifications are defined by ANSI documents ANSI T1.602, T1.606, T1S1/90-175, T1S1/90-213, and T1S1/90-214. In
using frame relay, blocks of information (frames) are passed across a digital network interface using a "connection number" that is
applied to each frame to distinguish between individual frames.
86
Page 87

Glossary
Frame Relay Forum: A non-profit organization of 300+ vendors and service providers, based in Foster City, CA, that are developing
and deploying frame relay equipment.
Frame Relay Implementors Forum: A group of companies supporting a common specification for frame relay connection to link
customer premises equipment to telco network equipment. Their specification supports ANSI frame relay specs and defines extensions
such as local management.
Frame Relay Access Device (FRAD): A piece of equipment that acts as a concentrator or frame assembler/dissassember that can
support multiple protocols and provide basic "routing" functions.
G
Gateway: 1. Afunctional unit that interconnects two computer networks with different network architectures. A gateway connects
networks or systems of different architectures. A bridge interconnects networks or systems with the same or similar architectures. 2. A
network that connects hosts.
Graphical User Interface (GUI): A type of computer interface consisting of a visual metaphor of a real-world scene, often of a desktop.
Within that scene are icons, representing actual objects, that the user can access and manipulate with a pointing device.
H
Handshaking: A process that two modems go through at the time of call setup to establish synchronization over the data communica-
tions link. It is a synchronization and negotiation process accomplished by the exchange of predefined, mutually recognized control
codes.
High-level Data Link Control (HDLC): An ISO standard, bit-oriented data communications protocol that provides nearly error-free data
transfers.
I
Hexadecimal: A base 16 numbering system used to represent binary values. Hex uses the numbers 0-9 and the letters A-F: usually
notated by an "h" (e.g., "4CF h", read "four charley fox, hex"). The result is that one hex digit represents a 4-bit value.
Implicit congestion management: A method of informing the terminal that the network is busy. This method relies on the end-system
protocol to detect and fix the congestion problem. (TCP/IP is an example of a protocol using only implicit congestion management.)
See also "explicit congestion management".
In-band: Refers to the type of signalling over the conversion path on an ISDN call. Contrast "out-of-band".
Insufficient Ones: A T1 error condition that is logged when less than one 1 in 16 0s or less than 12.5 % average 1s density is
received.
Inter Exchange Carrier (IEC): The long distance company (LE) who's central office provides the point of reference for T1 access. Any
common carrier authorized by the FCC to carry customer transmissions between LATAs.
Internet: Refers to the computer network of many millions of university, government and private users around the world. Each user has
a unique Internet Address.
Internet Address (IP Address): A unique 32-bit address for a specific TCP/IP host on a network. Normally printed in dotted decimal
format (e.g., 129.128.44.227).
Internet Protocol (IP): A protocol used to route data from its source to its destination in an Internet environment. The Internet Protocol
was designed to connect to local area networks. Although there are many protocols that do this, IP refers to the global system of
interconnecting computers. It is a highly distributed protocol (each machine only worries about sending data to the next step in the
route).
Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX): A NetWare communications protocol used to route messages from one node to another. IPX
packets include network addresses and can be routed from one network to another. An IPX packet can occasionally get lost when
crossing networks, thus IPX does not guarantee delivery of a complete message. Either the application has to provide that control, or
NetWare's SPX protocol must be used.
Interoperable: Devices from different vendors that can exchange information using a standard's base protocol.
I/O Addresses: Locations within the I/O address space of your computer used by a device, such as an expansion card, a serial port, or
an internal modem. The address is used for communication between software and a device.
IRQ Level (Interrupt Request Level): The notification a processor receives when another portion of the computer's hardware requires
its attention. IRQs are numbered so that the device issuing the IRQ can be identified, and so IRQs can be prioritized.
87
Page 88

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
ISA (Industry Standards Architecture) (pronounced "ice a"): The classic 8 or 16-bit architecture introduced with IBM's PC-AT
computer.
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network): An International telecommunications standard for transmitting voice, video and data
over a digital communications line. ISDN is a world-wide telecommunications service that uses digital transmission and switching
technology to support voice and digital data communications. Frame relay was partially based on ISDN's data link layer protocol
(LAPD). Frame relay can be used to transmit across ISDN services offering circuit-switched connection at 64K bps and higher speeds.
Contrast Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).
ITU-TSS (formerly CCITT): International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunications Sector; the United Nations organization that
prepares standards ("Recommendations") for resolving communications issues and problems.
K
Key Telephone System (KTS): Phone devices with multiple buttons that let you select incoming or outgoing CO phone lines directly.
Similar in operation to a PBX, except a KTS you don't have to dial a "9" for a call outside the building.
Key Service Unit (KSU): A small device containing the switching electronics for a business key telephone system (KTS).
Key Set: A telephone set with several buttons for call holding, line pickup, intercom, autodialing, etc. Also called a touchtone phone
(Ericsson) and a KTS (Key Telephone Set).
L
LAPB: Link Access Procedure Balanced; based on the X.25 Layer 2 specification. A full-duplex point-to-point bit-synchronous protocol
commonly used as a data link control protocol to interface X.25 DTEs. LAPB is the link initialization procedure that establishes and
maintains communications between the DTE and the DCE.
LAPD: Link Access Protocol for the D-Channel; based on the ISDN Q.921 specification. A full-duplex point-to-point bit-synchronous
link-level protocol for ISDN connections; different from LAPB in its framing sequence. Transmission is in units called "frames", and a
frame may contain one or more X.25 packets.
Line Coding: The representation of 1s and 0s on a T1 line. The two methods of line coding commonly used, B8ZS and AMI, differ in
the restrictions placed on user data. T1 line coding ensures that sufficient timing information is sent with the digital signal to ensure
recovery of all the bits at the far end. Timing information on the T1 line is included in the form of 1s in the data stream; a long string of
0s in the data stream could cause problems recovering the data.
Line Termination (LT): The electronics at the ISDN network side of the user/network interface that complements the NT1 at the user
side. The LT and the NT1 together provide the high-speed digital line signals required for BRI access.
Listed Directory Number (LDN): The main number assigned by the telco; the number listed in the telephone directory and also
provided by Directory Assistance. Some devices can have more than one LDN, such as ISDN devices that have one LDN for voice and
another LDN for data.
Local Area Network (LAN): 1. A computer network located on a user's premises within a limited geographical area. Communication
within a local area network is not subject to external regulations; however, communication across the LAN boundary may be subject to
some form of regulation. 2. A LAN does not use store and forward techniques. 3. A network in which a set of devices are connected to
one another for a communication and that can be connected to a larger network.
Local Access and Transport Area (LATA): A post-divestiture geographical area generally equivalent to a Standard Metropolitan
Statistical Area. At divestiture, the territory served by the Bell system was divided into approximately 161 LATAs. The Bell Operating
Companies (BOCs) provide Intra-LATA services.
Local Exchange Carrier (LEC): The local phone company which provides local (i.e., not long distance) transmission services. AKA
"telco". LECs provide T1 or FT1 access to LDCs (unless the T1 circuit is completely intra-LATA). Inter-LATA T1 circuits are made up of
a combination of Access and Long Haul facilities.
Local Management Interface (LMI): A specification for frame relay equipment that defines status information exchange.
Local Loop: A transmission path, typically twisted-pair wire, between an individual subscriber and the nearest public telecommunica-
tions network switching center. The wires provide ISDN service, but require an NT1 at the user end and an LT at the network end.
(AKA, "loop" or "subscriber loop".)
Logical Link Control (LLC2): In a local area network, the protocol that governs the exchange of transmission frames between data
stations independently of how the transmission medium is shared. The LLC2 protocol was developed by the IEEE 802 commitee and is
common to all LAN standards.
Logical Unit (LU): A type of network accessible unit that enables end users to gain access to network resources and communicate with
each other.
88
Page 89

Glossary
Long Haul: The T1 element that connects to the Access portion of the long distance company's (LDC's) central office. The LDC is
commonly called the point of presence (POP). Each LDC has a number of POPs, located throughout the country. The LDC is also
called an IEC (Inter Exchange Carrier).
Long Haul Communications: The type of phone call reaching outside of a local exchange (LE).
M
Management Information Base (MIB): A database of network management information used by the Common Management Informa-
tion Protocol (CMIP) and the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Megacom: An AT&T service with a normal WATS line (typically T1) between the customer premise and the AT&T serving class 4 CO
are the customer's responsibility.
MegaLink: BellSouth's leased T1 service.
Message: Associated with such terms as packet, frame, and segment. 1. In information theory, an ordered series of characters
intended to convey information. 2. An assembly of characters and sometimes control codes that is transferred as an entry from an
originator to one or more recipients.
Modem: A communications device that enables a computer to transmit information over a telephone line. It converts the computer's
digital signals into analog signals to send over a telephone line and converts them back to digital signals at the receiving end. Modems
can be internal and fit into an expansion slot, or external and connect to a serial port.
Multiplexer (Mux): 1. A device that takes several input signals and combines them into a single output signal in such a manner that
each of the input signals can be recovered. 2. A device capable of interleaving the events of two or more activities or capable of
distributing the events of an interleaved sequence to the respective activities. 3. Putting multiple signals on a single channel.
Multiprotocol: A device that can interoperate with devices utilizing different network protocols.
Multithreading: The ability of a software system to be able to handle more than one transaction concurrently. This is contrasted to the
case where a single transaction is accepted and completely processed before the next transaction processing is started.
N
Nailed Connection: A permanent or dedicated circuit of a previously switched circuit or circuits.
Nailed-up Circuit: A semipermanent circuit established through a circuit-switching facility for point-to-point connectivity.
NAK (Negative Acknowledgment): Communications code used to indicate that a message was not properly received, or that a
terminal does not wish to transmit. Contrast with ACK.
Network: A group of computers connected by cables or other means and using software that enables them to share equipment, such
as printers and disk drives to exchange information.
Node: Any point within a network which has been assigned an address.
O
Object-Orientated: A method for structuring programs as hierarchically organized classes describing the data and operations of objects
that may interact with other objects.
Office Channel Unit - Data Port (OCU-DP): The CO channel bank used as the interface between the customer's DSU and the
channel bank.
Off-hook: The condition of a device which has accessed a phone line (with or without using the line). In modem use, this is equivalent
to a telephone handset being picked up. Dialing and transmission are allowed, but incoming calls are not answered. Contrast "onhook".
Off Premise Extension (OPX): An extension or phone that terminates in a location other than that of the PBX. Commonly used to
provide a corporate member with an extension of the PBX at home.
Ones Density: the measure of the number of logical 1s on a T1 line compared to a given total number of bits on that line; used for
timing information in data recovery in AMI and B8ZS.
On-Hook: The condition of a device which has not accessed a phone line. In modem use, this is equivalent to a telephone handset that
has not been picked up. In other words, it can receive an incoming call. Contrast "off-hook".
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF): A hierarchical Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) routing algorithm for IP that is a proposed standard
for Internet. OSPF incorporates least-cost routing, equal-cost routing, and load balancing.
89
Page 90

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Outage: The measure of the time during which a circuit is not available for use due to service interrupt. Outage is the complement of
circuit "availability" (100% minus % available = % outage).
Out-of-band: Signaling that is separated from the channel carrying the information (i.e., the voice/data/video signal is separate from the
carrier signal). Dialing and various other "supervisory" signals are included in the signaling element. Contrast "In-band" signaling.
Out of Frame (OOF): A T1 alarm condition that is logged on the loss of 2, 3 or 4 of 5 consecutive FT framing bits.
P
Packet: 1. In data communication, a sequence of binary digits, including data and control signals, that is transmitted and switched as a
composite whole. The data, control signals and, possibly, error control information are arranged in a specific format. 2. Synonymous
with data frame. 3. In TCP/IP, the unit of data passed across the interface between the Internet layer and the link layer. A packet
includes an IP header and data. A packet can be a complete IP datagram or a fragment of an IP diagram. 4. In X.25, a data transmission information unit. A group of data and control characters, transferred as a unit, determined by the process of transmission. Commonly used data field lengths in packets are 128 or 256 bytes. 5. The field structure and format defined in the CCITT X.25 recommendation.
Packet Assembler/Dissembler (PAD): Used by devices to communicate over X.25 networks by building or stripping X.25 information
on or from a packet.
Packet Data: The information format ("packetized") used for packet-mode calls.
Packet Mode: Refers to the switching of chunks of information for different users using statistical multiplexing to send them over the
same transmission facility.
Parity bit: An extra bit attached to each byte of synchronous data used to detect errors in transmission.
Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC): A connection between two endpoints dedicated to a single user. IN ISDN, PVCs are established by
network administration and are held for as long as the user subscribes to the service.
Physical Unit (PU): The component that manages and monitors the resources (such as attached links and adjacent link stations)
associated with a node, as requested by an SSCP via an SSCP-PU session. An SSCP activates a session with the physical unit in order
to indirectly manage, through the PU, resources of the node such as attached links. This term applies to type 2.0, type 4, and type 5
nodes only.
Point of Presence (POP): The central office's end points of the long distance carriers.
Point to Point Protocol (PPP): A protocol that lets a PC user access TCP/IP (Internet member) using an ISDN terminal adapter or a
high-speed modem over a standard telephone line.
Port: A location for input or output data exchange. Computers, muxes, etc. have ports for various purposes.
Primary Rate Interface (PRI): Used on ISDN. In North America, and Japan, PRI is one 64Kbps D channel and 23 B channels.
Elsewhere, it is one D channel and 30 B channels.
Primitive: An abstract representation of interaction across the access points indicating that information is being passed between the
service user and the service provider. The OSI Reference Model defines four types of primitives: Request, Indication, Response and
Confirm.
Private Branch Exchange (PBX): A telephone exchange located on the customer's premises. The PBX provides a circuit switching
facility for telephone extension lines within the building, and access to the public telephone network. See also "Exchange".
PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory - pronounced "prom"): A permanent memory chip that can be programmed or filled by
the customer after by the manufacturer has set initial values. Contrast with ROM.
Protocol: 1. A set of semantic and syntactic rules that determines the behavior of functional units in achieving communication. 2. In
Open Systems Interconnection architecture, a set of semantic and syntactic rules that determine the behavior of entities in the same
layer in performing communication functions. 3. In SNA, the meanings of and the sequencing rules for requests and responses used for
managing the network, transferring data, and synchronizing the states of network components. 4. Synonymous with line control
discipline.
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network): A worldwide public voice telephone network that is used as a telecommunications
medium for the transmission of voice, data and other information.
Public Data Network (PDN): A packet-switched network that is available to the public for individual ("subscriber") use. Typically,
controlled by a government or a national monopoly.
Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN): The group of circuit-switching voice carriers, which are commonly used as analog data
communications services.
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM): 1. In data communication, variation of a digital signal to represent information; for example, by means
of pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), pulse duration modulation (PDM), or pulse position modulation (PPM). 2. Transmissions of
analog information in digital form through sampling and encoding the samples with a fixed number of bits.
90
Page 91

Glossary
Pulse dialing: One of two methods of dialing a telephone, usually associated with rotary-dial phones. Compare with "tone dialing".
Q
Quantizing: The process of analog-to- digital conversion by assigning a range, from the contiguous analog values, to a discrete
number.
R
Random Access Memory (RAM): A computer's primary workspace. All data must be stored in RAM (even for a short while), before
software can use the processor to manipulate the data. Before a PC can do anything useful it must move programs from disk to RAM.
When you turn it off, all information in RAM is lost.
Rate Enforcement: The concept in frame relay where frames sent faster than the CIR are to be carried only if the bandwidth is
available, otherwise they are to be discarded. (The frame relay network assumes that anything exceeding the CIR is of low priority.)
Rate enforcement makes sure that the network will not get so congested that it isn't able to meet the agreed on CIR
Recognized Private Operating Agency (RPOA): A corporation, private or government-controlled, that provides telecommunications services. RPOAs, such as AT&T, participate as non-voting members in the CCITT.
Red Alarm: A T1 error condition generated when a local failure (e.g., loss of synchronization) iexists for 2.5 seconds, causing a Carrier
Group Alarm (CGA). See also "Blue Alarm" and "Yellow Alarm".
Request for Comment (RFC): A set of papers in which Internet standards (published and proposed), along with generally-accepted
ideas, proposals, research results, etc. are published.
Ring Down Box: A device that emulates a CO by generating POTS calls for testing and product demos.
Ring Down Circuit: A tie line connecting phones where picking up one phone automatically rings another phone. A feature used for
emergencies to alert the person at the other phone of the incoming call.
RJ-11: An industry standard interface used for connecting a telephone to a modular wall outlet; comes in 4-and 6-wire packages.
RJ-45: An 8-wire modular connector for voice and data circuits.
Robbed Bit Signaling: The popular T1 signaling mechanism where the A and B bits are sent by each side of the T1 termination and are
"buried" in the voice data of each voice channel in the T1 circuit. Since the bits are "robbed" infrequently, voice quality is remains
relatively uncompromised. See "bit robbing".
The robbed-bit signaling technique is used in D4 channel banks to convey signaling information. The eighth (least significant) bit of each
of the 24 8-bit time slots is "robbed" every sixth frame to convey voice-related signaling information such as on-hook, off-hook, etc., for
each channel.
Router: A device that connects two networks using the same networking protocol. It operates at the Network Layer (Layer 3) of the OSI
model for forwarding decisions.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP): A distance vector-based protocol that provides a measure of distance, or hops, from a transmitting workstation to a receiving workstation.
RS232-C: An EIA standard for a serial interface between computers and peripheral devices (modem, mouse, etc.). It uses a 25-pin DB25, or a 9-pin DB-9 connector. The RS-232 standard defines the purposes, electrical characteristics and timing of the signals for each of
the 25 lines.
RS-422: The EIA standard for a balanced interface with no accompanying physical connector. RS-422 products can use screw
terminals, DB-9, various DB-25, and DB-37 connectors.
RS-530: The EIA standard for the mechanical/electrical interface between DCEs and DTEs transmitting synchronous or asynchronous
serial binary data. RS-530 provides for high data rates with the same connector used for RS-232; however, it is incompatible with RS-
232.
S
Serial Port: The connector on a PC used to attach serial devices (those that need to receive data one bit after another), such as a
mouse, a printer or a modem. This consists of a 9- or 25-pin connector that sends data in sequence (bit by bit). Serial ports are referred
to as "COMx" ports, where x is 1 to 4 (i.e., COM1 through COM4). A serial port contains a conversion chip called a "UART" which
translates between internal parallel and external serial formats.
Service: The requirements offered by an RPOA to its customers to satisfy specific telecommunications needs.
Severely Errored Seconds (SES): Refers to a typical T1 error event where an error burst occurs (a short term, high bit-error rate that
is self-clearing). Per the ITU-T (CCITT) G.821: any second in which the BER is less than 1x10-3.
91
Page 92

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Signaling: The process of establishing, maintaining, accounting for, and terminating a connection between two endpoints (e.g., the
user premises and the telco CO). Central office signals to the user premises can include ringing, dial tone, speech signals, etc. Signals
from the user's telephone can include off-hook, dialing, speech to far-end party, and on-hook signals.
In-band signaling techniques include pulse and tone dialing. With common channel signaling, information is carried out-of-band.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): TCP/IP protocol that allows network management.
Simultaneous Voice Data (SVD): A technology for letting a user send data via a modem, and use a handset to talk to another user at
the same time over the same connection. The alternative, making a second call, can be expensive or even impossible. The uses for
SVD are telecommuting, videoconferencing, distant learning, tech support, etc.
Stop Bit: One of the variables used for timing in asynchronous data transmission. Depending on the devices, each character may be
trailed by 1, 1.5, or 2 stop bits.
Superframe (D4): A T1 transmission format that consists of 12 DS1 frames, or 2316 bits. A DS1 frame consists of 193 bit positions. A
frame overhead bit is in the first position, and it is used for frame and signaling phase alignment only.
Subscriber Loop: See "Local loop".
Switched 56: A circuit-switched (full duplex digital synchronous data transmission) service that lets you dial a number and transmit data
to it at 56K bps. It is a relatively low cost service, widely used in North America for telecommuting, videoconferencing and high speed
data transfers. Many phone companies are (or will be) phasing out Switched 56 in favor of ISDN service.
Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC): A type of data transmission where the connection is maintained only until the call is cleared.
Switched Line: In communications, a physical channel established by dynamically connecting one or more discreet segments. This
connection lasts for the duration of the call after which each segment may be used as part of a different channel. Contrast with leased
line.
Switched Network: A network in which a temporary connection is established from one point via one or more segments.
Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC): A discipline conforming to subsets of the Advanced Data Communications Control Proce-
dures (ADCCP) of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and High-level Data Link Control (HDLC) of the International
Organization for Standardization, for managing synchronous, code-transparent, serial-by-bit information transfer over a link connection.
Transmission exchanges may be duplex, or half-duplex over switched or nonswitched links. The configuration of the link connection may
be point-to-point, multipoint, or loop.
Synchronous Transmission: The transmission of data which involves sending a group of characters in a packet. This is a common
method of transmission between computers on a network or between modems. One or more synchronous characters are transmitted to
confirm clocking before each packet of data is transmitted. Compare to Asynchronous Transmission.
Systems Network Architecture (SNA): The description of the logical structure, formats, protocols, and operational sequences for
transmitting information units through, and controlling the configuration and operation of of, networks.
T
Tariff: The rate/availability schedule for telephone and ISDN services from a regulated service provider.
TCP/IP: A set of communication protocols that support peer-to-peer connectivity functions for both local and wide area networks.
T Carrier: The generic name for a digitally multiplexed carrier system. In the North American digital hierarchy, a T is used to designate
a DS (digital signal) level hierarchy. Examples: T1 (DS1) is a 1.544 M bps 24-channel designation. In Europe, T1 is called E1. The T
Carrier system was originally designed for transmitting digitized voice signals, but has since been adapted for digital data applications.
T1: A digital transmission link capable of 1.544M bps. T1 uses two pairs of normal UTP, and can handle 24 voice conversations, each
digitized at 64K bps. T1 is a standard for digital transmission in the U.S., Canada, Japan and Hong Kong. T1 is the access method for
high-speed services such as ATM, frame relay, and SMDS. See also T Carrier, T1 line and FT1.
T1 Channel Tests: A set of diagnostics that vary by carrier, used to verify a T1 channel operation. Can include Tone, Noise Level,
Impulse Noise Level, Echo Cancellors, Gain, and Crosstalk testing.
T1 Framing: To digitize and encode analog voice signals requires 8000 samples per second (twice the highest voice frequency of 4000
Hz). Encoding in an 8-bit word provides the basic T1 block of 64K bps for voice transmission. This "Level 0 Signal, as its called, is
represented by "DS-0", or Digital Signal at Level 0. 24 of these voice channels are combined into a serial bit stream (using TDM), on a
frame-by-frame basis. A frame is a sample of all 24 channels; so adding in a framing bit gives a block of 193 bits (24x8+1=193).
Frames are transmitted at 8000 per second (the required sample rate), creating a 1.544M (8000x193=1.544M) transmission rate.
T1 Line: A digital communications facility that functions as a 24-channel pathway for data or voice. A T1 line is composed of two
separate elements: the Access element and the Long Haul element.
92
Page 93

Glossary
T1 Mux: A device used to carry many sources of data on a T1 line. The T1 mux assigns each data source to distinct DS0 time slots
within the T1 signal. Wide bandwidth signals take more than one time slot. Normal voice traffic or 56/64K bps data channels take one
time slot. The T1 mux may use an internal or external T1 DSU; a "channel bank" device typically uses an external T1 CSU.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Program (TCP/IP): A multilayer set of protocols developed by the US Department of
Defense to link dissimilar computers across dissimilar and unreliable LANs.
Terminal: The screen and keyboard device used in a mainframe environment for interactive data entry. Terminals have no "box", which
is to say they have no file storage or processing capabilities.
Terminal Adapter (TA): An ISDN DTE device for connecting a non-ISDN terminal device to the ISDN network. Similar to a protocol
converter or an interface converter, a TA connects a non-ISDN device between the R and S interfaces. Typically a PC card.
Tie line: A dedicated circuit linking two points without having to dial a phone number (i.e., the line may be accessed by lifting the
telephone handset or by pushing a button).
Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM): Division of a transmission facility into two or more channels by allotting the common channel to
several different information channels, one at a time.
Time Slot: One of 24 channels within a T1 line. Each channel has a 64K bps maximum bandwidth. "Time slot" implies the time
division multiplexing organization of the T1 signal.
Toll Call: A call to a location outside of your local service area (i.e., a long distance call).
Tone dialing: One of two methods of dialing a telephone, usually associated with Touch-Tone® (push button) phones. Compare with
pulse dialing.
Topology: Physical layout of network components (cables, stations, gateways, and hubs). Three basic interconnection topologies are
star, ring, and bus networks.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): A communications protocol used in Internet and in any network that follows the US Department
of Defense standards for internetwork protocol. TCP provides a reliable host-to-host protocol between hosts in packet-switched
communications networks and in interconnected systems of such networks. It assumes that the Internet protocol is the underlying
protocol.
Transport Layer: Layer 4 of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model; provides reliable, end-to-end delivery of data, and detects
transmission sequential errors.
Transport Protocol Data Unit (TPDU): A transport header, which is added to every message, contains destination and source
addressing information that allows the end-to-end routing of messages in multi-layer NAC networks of high complexity. They are
automatically added to messages as they enter the network and can be stripped off before being passed to the host or another device
that does not support TPDU's.
Trunk: Transmission links that interconnect switching offices.
TSR (terminate and stay resident): A software program that remains active and in memory after its user interface is closed. Similar to
a daemon in UNIX environments.
Tunneling: Encapsulation data in an IP packet for transport across the internet.
Twisted pair wiring: A type of cabling with one or more pairs of insulated wires wrapped around each other. An inexpensive wiring
method used for LAN and telephone applications, also called UTP wiring.
U
UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) (pronounced "you art"): A chip that transmits and receives data on the
serial port. It converts bytes into serial bits for transmission, and vice versa, and generates and strips the start and stop bits appended
to each character.
UNIX: An operating system developed by Bell Laboratories that features multiprogramming in a multi-user environment.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): Telephone-type wiring. Transmission media for 10Base-T.
V
V.25bis: An ITU-T standard for synchronous communications between a mainframe or host and a modem using HDLC or other
character-oriented protocol.
V.54: The ITU-T standard for local and remote loopback tests in modems, DCEs and DTEs. The four basic tests are:
• local digital loopback (tests DTE send and receive circuits),
• local analog loopback (tests local modem operation),
• remote analog loopback (tests comm link to the remote modem), and
• remote digital loopback (tests remote modem operation).
Virtual Circuit: A logical connection. Used in packet switching wherein a logical connection is established between two devices at the
start of transmission. All information packets follow the same route and arrive in sequence (but do not necessarily carry a complete
address).
93
Page 94

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
94
Page 95

Index
Index
A
About CompuServe ......................................................................................................................................70
About the Internet .........................................................................................................................................70
About the Multi-Tech Fax-Back Service ........................................................................................................70
B
Back Panel Description ................................................................................................................................10
BBS68
C
Cable Connections .......................................................................................................................................15
Cabling Diagrams .........................................................................................................................................72
Cabling Procedure........................................................................................................................................15
CompuServe ..................................................................................................................... ...........................70
Connectors
Channels 1 & 2 (RS232/V.35) ...................................................................................................................10
Channels 3 - 10.........................................................................................................................................11
Command Port..........................................................................................................................................10
Ethernet 10Base-T....................................................................................................................................10
External Composite Link (RS232/V .35).....................................................................................................10
Frame Ground (GND) ...............................................................................................................................10
Internal Composite Link (T1 DSU) ............................................................................................................10
Monitor (XMT/RCV) ..................................................................................................................................10
Power .......................................................................................................................................................10
Voice/Fax Channels 1 - 8..........................................................................................................................1 1
E&M ...................................................................................................................................................... 11
FXO....................................................................................................................................................... 11
FXS .......................................................................................................................................................11
Contacting Tech Support via E-mail ..............................................................................................................67
D
Data Port Configuration ................................................................................................................................52
Data Port Statistics .......................................................................................................................................42
F
Fax-Back Service .........................................................................................................................................70
Frame Relay Access Device...........................................................................................................................6
Frame Relay Setup.......................................................................................................................................47
Frame Relay Statistics..................................................................................................................................43
Front Panel
Description..................................................................................................................................................8
G
Glossary .......................................................................................................................................................81
I
Internet .........................................................................................................................................................70
Internet Protocol (IP) ....................................................................................................................................78
95
Page 96

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
IP Addressing ...............................................................................................................................................79
IP Setup........................................................................................................................................................30
IP Statistics...................................................................................................................................................36
IPX Port Statistics.........................................................................................................................................37
IPX Setup .....................................................................................................................................................32
L
LED's
BTG ............................................................................................................................................................8
Channels 1 and 2........................................................................................................................................8
RCV ........................................................................................................................................................8
V35..........................................................................................................................................................8
XMT ........................................................................................................................................................8
Channels 3 through 10................................................................................................................................8
RCV ........................................................................................................................................................8
XMT ........................................................................................................................................................8
Composite Link ...........................................................................................................................................8
CD...........................................................................................................................................................8
CTS.........................................................................................................................................................8
EXT .........................................................................................................................................................8
LNK .........................................................................................................................................................8
RCV ........................................................................................................................................................8
V35..........................................................................................................................................................8
XMT ........................................................................................................................................................8
Ethernet ......................................................................................................................................................8
COL.........................................................................................................................................................8
LNK .........................................................................................................................................................8
RCV ........................................................................................................................................................8
XMT ........................................................................................................................................................8
PWR ...........................................................................................................................................................8
Voice/Fax Channels 1 - 8............................................................................................................................9
E&M ........................................................................................................................................................9
FAX .........................................................................................................................................................9
FXO.........................................................................................................................................................9
FXS .........................................................................................................................................................9
RSG ........................................................................................................................................................9
XMT ........................................................................................................................................................9
XSG ........................................................................................................................................................9
Limited Warranty ............................................................................................................... ...........................66
On-line Warranty Registration...................................................................................................................66
Loading Software.........................................................................................................................................18
M
Multi-Tech BBS.............................................................................................................................................68
MultiFRAD ......................................................................................................................................................6
MultiFRAD Configuration ..............................................................................................................................61
N
Network Address ..........................................................................................................................................78
Network Overview ........................................................................................................................................76
O
On-line Warranty Registration.......................................................................................................................66
OSI Protocol Stack .......................................................................................................................................76
96
Page 97

Index
P
Packet ..........................................................................................................................................................77
Point to Point Setup......................................................................................................................................46
PPP Statistics...............................................................................................................................................41
R
Recording MultiFRAD Information ................................................................................................................67
Regulatory Information .................................................................................................................................75
Remote Configuration...................................................................................................................................54
LAN-Based ...............................................................................................................................................56
Modem-Based ..........................................................................................................................................54
Remote User Database ................................................................................................................................61
S
Safety Warnings ...........................................................................................................................................14
Service .........................................................................................................................................................68
Setup Menu ..................................................................................................................................................29
Data Port Configuration.............................................................................................................................52
Frame Relay Setup ...................................................................................................................................47
IP Setup ....................................................................................................................................................30
IPX Setup..................................................................................................................................................32
Point to Point Setup ........................................................................................................... .......................46
Spanning Tree Setup ................................................................................................................................34
Statistics ..................................................................................................................... ..............................35
Data Port Statistics................................................................................................................................42
Frame Relay Statistics ..........................................................................................................................43
IP Statistics ...........................................................................................................................................36
IPX Port Statistics .................................................................................................................................37
PPP Statistics........................................................................................................................................41
SNMP Statistics.....................................................................................................................................39
STP (Spanning Tree) Port Statistics ......................................................................................................38
WAN Statistics.......................................................................................................................................40
WAN Port Setup........................................................................................................................................45
SNMP Statistics............................................................................................................................................39
Software .......................................................................................................................................................18
Spanning Tree Setup....................................................................................................................................34
Statistics .......................................................................................................................................................35
Data Port Statistics ...................................................................................................................................42
Frame Relay Statistics ..............................................................................................................................43
IP Statistics ...............................................................................................................................................36
IPX Port Statistics .....................................................................................................................................37
PPP Statistics ...........................................................................................................................................41
SNMP Statistics ........................................................................................................................................39
STP (Spanning Tree) Port Statistics..........................................................................................................38
WAN Statistics ..........................................................................................................................................40
STP (Spanning Tree) Port Statistics .............................................................................................................38
T
Tech Support ................................................................................................................................................67
Contacting Tech Support via E-mail ..........................................................................................................67
Recording MultiFRAD Information.............................................................................................................67
T echnical Specifications ...............................................................................................................................12
Channel Connectors .................................................................................................................................12
Command Port..........................................................................................................................................12
Composite Link (external) .........................................................................................................................12
97
Page 98

MultiFRAD 3000-Series User Guide
Electrical/Physical .....................................................................................................................................12
EtherNet Port ............................................................................................................................................12
Requirement .............................................................................................................................................12
Telnet
Cient .......................................................................................................................... ...............................60
MultiFRAD Configuration ..........................................................................................................................61
Remote User Database ............................................................................................................................61
Server Menu .............................................................................................................................................60
U
Unpacking your MultiFRAD 3000 .................................................................................................................14
W
WAN Port Setup ...........................................................................................................................................45
WAN Statistics..............................................................................................................................................40
WEB Browser Management .........................................................................................................................62
98
 Loading...
Loading...