Multitech CF220-DID, CallFinder CF220 Quick Start Manual

CallFinder™
Model CF220
DID Adapter
Quick Start Guide
CallFinder Model CF220 DID Enabler
Quick Start Guide
P/N 82000160, Revision A
Copyright © 2004 by Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved. This publication may not be reproduced, in whole or in part,
without prior expressed written permission from Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. makes no representation or warranties with respect to the
contents hereof and specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or
fitness for any particular purpose. Furthermore, Multi-Tech Systems, Inc. reserves the
right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time in the content
hereof without obligation of Multi-Tech Systems, Inc., to notify any person or or-
ganization of such revisions or changes.
Record of Revisions
Revision Date Description
A 12/23/04 Initial Release, Rev A.
Trademarks
CallFinder, Multi-Tech, and the Multi-Tech logo are trademarks of Multi-Tech
Systems, Inc. All other brand and product names mentioned in this publication are
trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Technical Support
Country By Email By Phone
France: support @multitech.fr +(33) 1-64 61 09 81
India: support @multitechindia.com +91 (124) 6340778
U.K.: support @multitech.co.uk +(44) 118 959 7774
U.S. and Canada: support @multitech.com (800) 972-2439
Rest of World: support @multitech.com +(763) 717-5863
World Headquarters
Multi-Tech Systems, Inc.
2205 Woodale Drive
Mounds View, Minnesota 55112 U.S.A.
Fax (763) 785-9874, http://www.multitech.com, ftp://ftp.multitech.com
2
Contents
GETTING STARTED ............................................................................... 5
RONT PANEL LEDS................................................................................. 5
F
E SUPPLY............................................................................................... 5
W
OU SUPPLY............................................................................................. 6
Y
REREQUISITE: ORDERING THE DID LINES ............................................. 7
P
INSTALLATION PROCESS ................................................................... 8
P
ART A: CONNECTING THE CALLFINDER TO POWER OUTLETS, PHONE
LINES, AND ETHERNET ............................................................................. 8
1. Connect CallFinder 5Vdc Power Supply to AC Outlet.................... 8
2. Connect CallFinder 48Vdc Power Supply to AC Outlet.................. 8
3. Connect CallFinder to DID Lines.................................................... 9
4. Connect CallFinder to Ethernet Network. ....................................... 9
4. Identify CallFinder’s Extension Ports (FXS/FXO)
for Later Hookup ........................................................................... 10
5. Do Power-On Test ......................................................................... 10
ART B: CONFIGURING THE CALLFINDER SOFTWARE ............................ 11
P
1. Setting Admin PC to Startup IP Address ....................................... 11
2. Logging In (I)................................................................................. 12
3. Setting CallFinder IP Addresses.................................................... 12
4. Resetting Admin PC to Its Regular IP Address.............................. 13
5. Logging In (II) ............................................................................... 13
6. Setting Administrative Functions................................................... 14
7. Setting Up the Mail Server............................................................. 15
8. Configuring the CallFinder’s Channels ........................................ 17
9. Changing Administrator’s Password for CallFinder SW .............. 21
10. Assigning DID Numbers to PBX Users (Extensions)................... 22
ART C: TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................. 23
P
1. What if I can't see the web page for my CallFinder ?.................... 23
2. What if I don't get an email when I set the mail server address ? . 23
3. What if the CallFinder channel doesn't answer a call
on the DID line? ............................................................................ 26
3
FFCF MANAGER SOFTWARE FUNCTIONS....................................28
NSTALLING FFCF MANAGER SOFTWARE ...............................................28
I
DDING CALLFINDER UNITS TO THE SYSTEM .........................................30
A
UPLICATING CALLFINDER PHONEBOOK IN OTHER CF UNITS
D
(SYNCHRONIZATION)...............................................................................31
TECH SUPPORT .....................................................................................33
4
Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start Getting Started
Getting Started
This guide shows you how to set up your Multi-Tech Model CF220
CallFinder.
The CallFinder is a DID-to-analog telephony adapter. It brings
analog DID services to a key telephone system or PBX that is not
DID-enabled. When equipped with the CallFinder, the phone
system can route incoming DID calls directly to end-user extensions.
The CallFinder has two DID channels. Each channel is connected
to the telco DID line on one side and to the PBX/key system on the
other side. A CallFinder extension port can be connected either to a
trunk port or to a station port on a PBX. The choice between trunk
port or station port connections depends on port availability, logging
requirements, and/or on whether it is necessary for incoming DID
calls to be treated like outside calls instead of intra-PBX calls.
Front Panel LEDs
We Supply
• A CF220 CallFinder with factory-installed software
• Two power supplies – one 5Vdc and one 48Vdc
• Two common telephone cables (RJ11 at both ends)
• Two DID telephone cables (RJ11 at one end; RJ12 at other end)
• A utility software program for updating CallFinder firmware
• This printed Quick Start Guide
5
Getting Started Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start
You Supply
• Two nearby AC power outlets
• Two nearby connections to a PBX
• A connection to your Ethernet LAN
• One or two nearby analog DID trunk lines each with a block of
associated DID telephone numbers
• A PC with an Ethernet connection and a web browser from which
to configure the CallFinder unit. (Windows or Linux can be used
to access the CallFinder software. Windows NT, Windows 2000,
or Windows XP are required to access the FaxFinder/CallFinder
Manager software.)
6
Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start Getting Started
Prerequisite: Ordering the DID Lines
To operate the CallFinder system, you will need one or two DID
(Direct Inward Dial) lines in your office. You must order the DID
lines from your local telephone operating company (telco). A DID
line allows one phone line to be associated with multiple directory
numbers. However, only one call can occur on this line at any given
time.
DID lines are sold in groups. For example, a telco in New York City
might offer a DID line with a set of 10 directory numbers in the range
of 212-555-4100 through 212-555-4109.
When ordering your DID line, ask the telco representative for these
details about the DID service. These details will be important when
setting up your CF220 unit.
Parameter Value Required by
Telco
Number of digits used
to designate the DID extension
(usually 3, 4, 6, or 7)
Type of “DID Start” used
(wink, immediate, or delay dial)
You will need this information to configure your CallFinder unit (see
step 8 on page 17).
7
Server Installation Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start
Installation Process
Part A: Connecting the CallFinder to Power Outlets,
Phone Lines, and Ethernet
Summary: Place the CallFinder in a convenient location, and then
connect it to your AC power outlets and Ethernet. Before connecting
the extension lines, you need to know whether the CallFinder's ports
will function as FXO or FXS. The CallFinder’s default extension
interface setting is FXO to prevent damage from a mistaken
connection. Be aware that an incorrect connection could damage
the CallFinder unit or the PBX. Do not connect FXS to FXS.
1. Connect CallFinder 5Vdc Power Supply to AC Outlet
Make sure the power switch is OFF. Plug the DC power transformer
for the 5 Vdc power supply into a power outlet or power strip. Plug
the other end into the “Power 5Vdc” jack on your CallFinder. The DC
power transformer is included with your CallFinder.
Caution: Use only the 5 Vdc power transformer supplied
with the CallFinder. Use of any other transformer
voids the warranty and can damage the
CallFinder. The CallFinder’s 5Vdc and 48 Vdc
power supplies have different connector types to
prevent mix-ups.
2. Connect CallFinder 48Vdc Power Supply to AC Outlet
Make sure the power switch is OFF. Plug the DC power transformer
for the 48 Vdc power supply into a power outlet or power strip. Plug
the other end into the “Power 48 Vdc” jack on your CallFinder. The
DC power transformer is included with your CallFinder.
Caution: Use only the 48 Vdc power transformer supplied
with the CallFinder. Use of any other transformer
voids the warranty and can damage the
CallFinder. The CallFinder’s 5Vdc and 48 Vdc
power supplies have different connector types to
prevent mix-ups.
8
Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start Server Installation
3. Connect CallFinder to DID Lines
Plug one end of the phone cable into the CallFinder’s Channel 1 DID
jack and the other end into an analog DID trunk line jack. The DID
Line cable is included with your CallFinder.
Caution: The DID Line cable has an RJ11 connector on
one end (this is the larger of the two connectors; it
goes to the telephone wall receptacle). The DID
Line cable has an RJ12 connector on the other
end (this is the smaller connector; it goes to the
DID Port on the CallFinder unit).
Never plug the DID connector into a standard
POTS Line. This may damage the CallFinder or
the central office equipment. Use only an analog
DID Line.
Repeat for the CallFinder’s Channel 2 DID port.
4. Connect CallFinder to Ethernet Network.
Plug one end of your RJ45 ethernet cable into the CallFinder’s
ethernet jack and the other end into your network ethernet hub. This
ethernet cable is not included with your CallFinder unit.
Caution: Before connecting to the Ethernet Network, make
sure that the network to which you are connecting
the CallFinder is not a 192.168.2.x subnet.
If it is a 192.168.2.x subnet, it will clash with the
CallFinder because the CallFinder’s default IP
address is 192.168.2.1. To remedy such a
situation, connect from the Admin PC to the
CallFinder using an RJ45 crossover cable until the
CallFinder’s IP address has been configured.
Thereafter, connect the CallFinder into the
network with an ordinary RJ45 cable.
9
Server Installation Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start
4. Identify CallFinder’s Extension Ports (FXS/FXO) for Later
Hookup
CAUTION: You must wait until after the CallFinder software
has been configured before connecting the cables
between the CallFinder’s Extension (FXS/FXO)
Ports and the PBX. Because the CallFinder and
the PBX can both supply battery power, the cable
connections must be done properly. Otherwise
equipment damage could occur.
Before making connections to the CallFinder Extension (FXS/FXO)
channels, you must know the type of PBX port to which each
CallFinder port will be connected and set the “Extension Port” field in
the CallFinder Channel Configuration screen appropriately.
When connecting to a PBX Station Port,
set the CallFinder channel to FXO.
When connecting to a PBX Trunk Port,
set the CallFinder channel to FXS.
When the Channel Configuration | Extension Port software field
has been set properly for both CallFinder channels, you can proceed
to connect the cable between each of the CallFinder’s FXS/FXO
ports and the corresponding PBX port.
5. Do Power-On Test
Test your CallFinder by turning it on (an on-off switch is located on
the back panel). When you apply power, the CallFinder performs a
diagnostic self-test. The Status indicator flashes when the test is
complete and the unit is ready. If this does not happen, check that
the power switch is on, the power supply is solidly connected, and
the AC outlet is live.
10
Multi-Tech CallFinder Quick Start Server Installation
Part B: Configuring the CallFinder Software
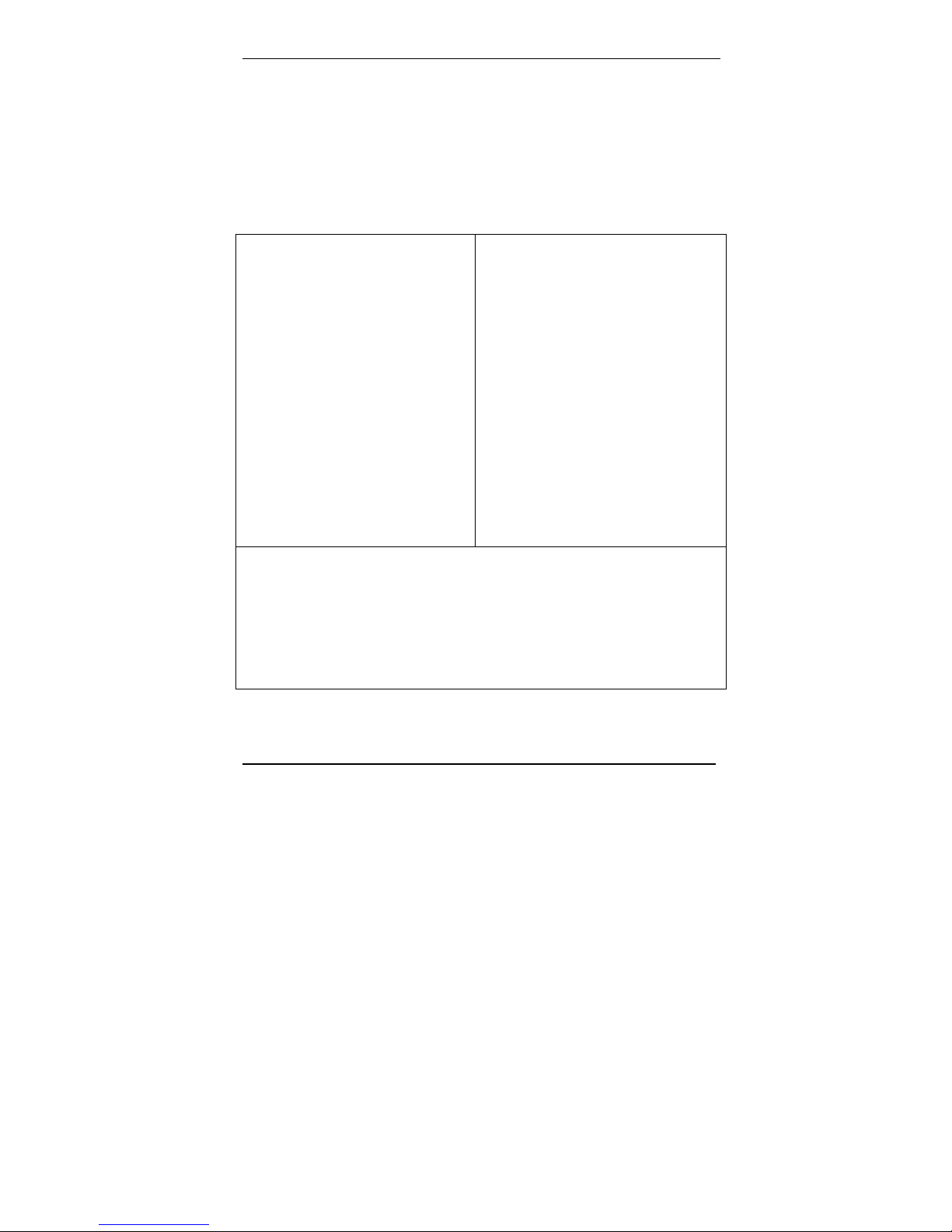
1. Setting Admin PC to Startup IP Address
a. Connect a pc to your network.
b. Set the pc IP address to 192.168.2.x subnet (using any address
excluding 192.168.2.1).
Windows XP
a. From the Windows desktop,
right-click on “My Network Places,”
and select “Properties.”
b. In the Network Connection
screen, right-click on “Local Area
Connection.”
c. In the Local Area Connection
Properties screen, on the
“General” tab, scroll to the “Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP)” entry and select
it. Click “Properties.”
d. In the Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) Properties screen, record
the existing IP address. Then reset
the IP address to 192.168.2.2.
Windows NT
a. From the Windows desktop, right-click on “Network Neighborhood,” and
select “Properties.”
b. In the Network screen, on the “Protocols” tab, select “TCP/IP Protocol” in
the list of Network Protocols. Click “Properties.”
c. In the Microsoft Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties screen, record
the existing IP address. Then reset the IP address to 192.168.2.2.
Windows 2000
a. From the Windows desktop, rightclick on “My Network Places,” and
select “Properties.”
b. In the Network and Dialup
Connections screen, right-click on
“Local Area Connection” and select
“Properties.”
c. In the Local Area Connection
Properties screen, select the
“Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” entry.
Click “Properties.”
d. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties screen, record the
existing IP address. Then reset the
IP address to 192.168.2.2.
11
 Loading...
Loading...