Page 1
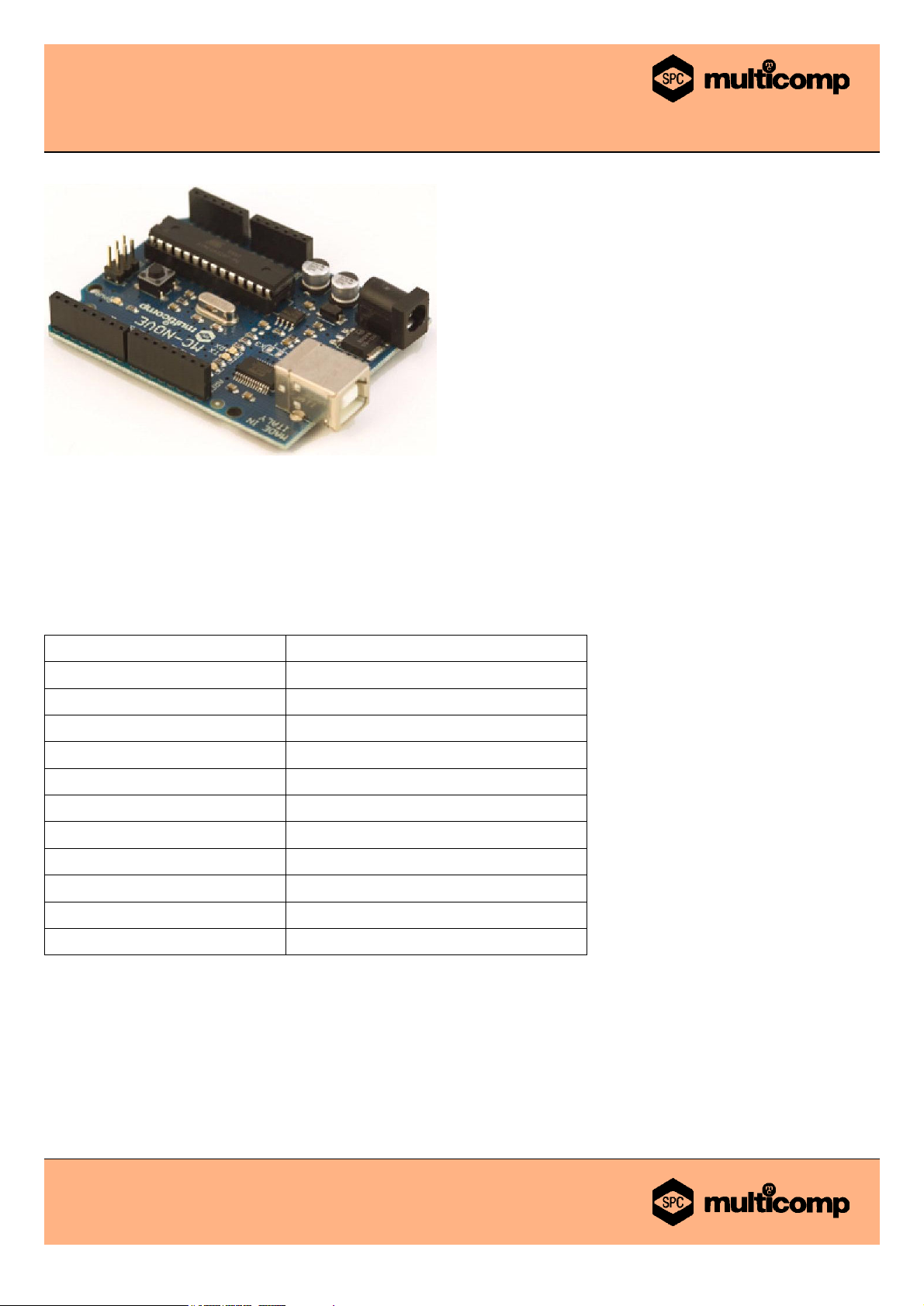
MC-NOVE
Arduino™ Duemilanove Compatible Development Board
Page <1> 28/05/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Overview
The MC-NOVE is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (datasheet). It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can
be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a
reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or
power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
Microcontroller ATmega328
Operating Voltage 5V
Input Voltage (recommended) 7 to 12V
Input Voltage (limits) 6 to 20V
Digital I/O Pins 14 (of which 6 provide PWM output)
Analog Input Pins 6
DC Current per I/O Pin 40mA
DC Current for 3.3V Pin 50mA
Flash Memory 32KB of which 2KB used by bootloader
SRAM 2KB
EEPROM 1KB
Clock Speed 16MHz
Summary
Power
The MC-NOVE can be powered via the USB connection or with an external power supply.
The power source is selected automatically.
External (non-USB) power can come either from an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be connected by
plugging a 2.1mm centre-positive plug into the board's power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in the Gnd and Vin pin
headers of the POWER connector.
The board can operate on an external supply of 6 to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may supply less
than five volts and the board may be unstable. If using more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the board.
The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
Page 2

MC-NOVE
Arduino™ Duemilanove Compatible Development Board
Page <2> 28/05/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
The power pins are as follows:
• VIN. The input voltage to the board when it's using an external power source (as opposed to 5 volts from the USB
connection or other regulated power source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying voltage via
the power jack, access it through this pin.
• 5V. The regulated power supply used to power the microcontroller and other components on the board. This can
come either from VIN via an on-board regulator, or be supplied by USB or another regulated 5V supply
• 3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board FTDI chip. Maximum current draw is 50mA.
• GND. Ground pins.
Memory
The ATmega328 has 32 KB of flash memory for storing code (of which 2 KB is used for the bootloader) The ATmega328 has 2 KB
of SRAM and 1 KB of EEPROM (which can be read and written with the EEPROM library).
Input and Output
Each of the 14 digital pins on the MC-NOVE can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead()
functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive a maximum of 40 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor
(disconnected by default) of 20-50 kOhms. In addition, some pins have specialized functions:
• Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. These pins are connected to the
corresponding pins of the FTDI USB-to-TTL Serial chip.
• External Interrupts: 2 and 3. These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or
a change in value. See the attachInterrupt() function for details.
• PWM: 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function.
• SPI: 10 (SS), 11 (MOSI), 12 (MISO), 13 (SCK). These pins support SPI communication, which, although provided by the
underlying hardware, is not currently included in the Arduino™ language.
• LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the
pin is low, it's off.
The MC-NOVE has 6 analog inputs, each of which provides 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different values). By default they
measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and the
analogReference() function. Additionally, some pins have specialized functionality:
• I
2
C: 4 (SDA) and 5 (SCL). Support I2C (TWI) communication using the Wire library.
There are a couple of other pins on the board:
• AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference().
• Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one
on the board.
Communication
The MC-NOVE has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer, another Arduino™, or other microcontrollers. The
ATmega328 provide UART TTL (5V) serial communication, which is available on digital pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). An FTDI FT232RL
on the board channels this serial communication over USB and the FTDI drivers (included with the Arduino™ software) provide a
virtual com port to software on the computer. The Arduino™ software includes a serial monitor which allows simple textual data to
be sent to and from the board. The RX and TX LEDs on the board will flash when data is being transmitted via the FTDI chip and
USB connection to the computer (but not for serial communication on pins 0 and 1).
A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the MC-NOVEs digital pins.
The ATmega328 also support I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino™ software includes a Wire library to simplify use of
the I2C bus; see the documentation for details. To use the SPI communication, please see the ATmega328 datasheet.
Page 3

MC-NOVE
Arduino™ Duemilanove Compatible Development Board
Page <3> 28/05/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Programming
The MC-NOVE can be programmed with the Arduino™ software (download). Select "Arduino™ Duemilanove w/ ATmega328" from
the Tools > Board menu. For details, see the reference and tutorials.
The ATmega328 on the MC-NOVE comes pre-burned with a bootloader that allows you to upload new code to it without the use of
an external hardware programmer. It communicates using the original STK500 protocol (reference, C header files).
You can also bypass the bootloader and program the microcontroller through the ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming) header; see
these instructions for details.
Automatic (Software) Reset
Rather than requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the MC-NOVE is designed in a way that allows it to be
reset by software running on a connected computer. One of the hardware flow control lines (DTR) of the FT232RL is connected to
the reset line of the ATmega328 via a 100 nanofarad capacitor. When this line is asserted (taken low), the reset line drops long
enough to reset the chip. The Arduino™ software uses this capability to allow you to upload code by simply pressing the upload
button in the Arduino™ environment. This means that the bootloader can have a shorter timeout, as the lowering of DTR can be
well-coordinated with the start of the upload.
This setup has other implications. When the MC-NOVE is connected to either a computer running Mac OS X or Linux, it resets each
time a connection is made to it from software (via USB). For the following half-second or so, the bootloader is running on the MCNOVE. While it is programmed to ignore malformed data (i.e. anything besides an upload of new code), it will intercept the first few
bytes of data sent to the board after a connection is opened. If a sketch running on the board receives one-time configuration or
other data when it first starts, make sure that the software with which it communicates waits a second after opening the connection
and before sending this data.
The MC-NOVE contains a trace that can be cut to disable the auto-reset. The pads on either side of the trace can be soldered
together to re-enable it. It's labelled "RESET-EN". You may also be able to disable the auto-reset by connecting a 110 ohm resistor
from 5V to the reset line; see this forum thread for details.
USB Overcurrent Protection
The MC-NOVE has a resettable polyfuse that protects your computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent. Although most
computers provide their own internal protection, the fuse provides an extra layer of protection. If more than 500 mA is applied to the
USB port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short or overload is removed.
Physical Characteristics
The maximum length and width of the MC-NOVE PCB are 2.7 and 2.1 inches respectively, with the USB connector and power jack
extending beyond the former dimension. Three screw holes allow the board to be attached to a surface or case. Note that the
distance between digital pins 7 and 8 is 160 mil (0.16"), not an even multiple of the 100 mil spacing of the other pins.
Schematic & Reference Design
EAGLE files: arduino-duemilanove-reference-design.zip
Schematic: arduino-duemilanove-schematic.pdf
Page 4

MC-NOVE
Arduino™ Duemilanove Compatible Development Board
Page <4> 28/05/10 V1.1
http://www.farnell.com
http://www.newark.com
http://www.cpc.co.uk
Disclaimer This data sheet and its contents (the "Information") belong to the Premier Farnell Group (the "Group") or are licensed to it. No licence is granted for the use of it other than for information purposes
in connection with the products to which it relates. No licence of any intellectual property rights is granted. The Information is subject to change without notice and replaces all data sheets previously supplied.
The Information supplied is believed to be accurate but the Group assumes no responsibility for its accuracy or completeness, any error in or omission from it or for any use made of it. Users of this data
sheet should check for themselves the Information and the suitability of the products for their purpose and not make any assumptions based on information included or omitted. Liability for loss or damage
resulting from any reliance on the Information or use of it (including liability resulting from negligence or where the Group was aware of the possibility of such loss or damage arising) is excluded.
This will not operate to limit or restrict the Group's liability for death or personal injury resulting from its negligence. SPC Multicomp is the registered trademark of the Group. © Premier Farnell plc 2010.
Description Part Number
BOARD, ATMEGA328, DUEMILANOVE-CLONE MC-NOVE
Part Number Table
 Loading...
Loading...