MTZ 952.5 User Manual

BELARUS
952.5
952.5-0000010B OM
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
2013

The operator's manual was composed by an engineer of the first Department of
Constructive and Experimental Works (DCEW-1), A.V. Runov, with participation of key
specialists of DCEW-1 of RUE “Minsk Tractor Works”
Publication responsible person – Y.M. Korotky, head of engineering office of design documentation of the DCEW-1.
Executive editor – A.G. Stasilevich, design manager of tractor production of PA “MTW”.
Editor-in-chief – I.N. Uss, PA “MTW” chief designer.
Operator's manual contains brief description and specifications of tractors Belarus 952.5
produced by Minsk Tractor Works. The main tractors operating rules are set forth, the information about their adjustments and maintenance is provided.
Operator's manual is meant for tractor study, operation rules and servicing of tractors
“BELARUS-952.5”.
In view of P/A “MTW” policy directed to constant upgrading of produced goods, the construction of some units and parts of Belarus tractor may undergo changes which are not
reflected in present edition. The detailed information may be obtained from “BELARUS”
dealer.
© RUE ”Minsk Tractor Works”, 2013
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced in any form without written
permission of RUE “MTW”.

952.5-0000010 OM
CONTENT
1 TRACTOR DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ..................................................................11
1.1 Tractor assignment............................................................................................................... 11
1.2 Technical specifications.......................................................................................................12
1.3 Tractor composition..............................................................................................................15
1.4 Vibration level at the operator's working place of the tractor “BELARUS-952.5”..................... 18
1.5 Noise level at the operator's working place of the tractor “BELARUS-952.5”..................18
1.6 Tractor and its component marking ................................................................................... 18
2 CONTROLS AND INSTRUMENTS ......................................................................................20
2.1 Layout of controls and instruments of the tractor ............................................................20
2.2 Switches of instrument board .............................................................................................21
2.3 Upper shield unit of button switches and rear wiper switch...........................................23
2.4 Cab heater and fan control.................................................................................................. 24
2.5 Conditioner control ............................................................................................................... 25
2.5.1 Conditioner control in conditioning mode ......................................................................25
2.5.2 Conditioner control in a heating mode ........................................................................... 25
2.5.3 Cab ventilation ................................................................................................................... 26
2.6 Instrument board................................................................................................................... 27
2.7 Pilot lamps unit......................................................................................................................28
2.7.1 General information ..........................................................................................................28
2.7.2 Functioning algorithm of pilot lamp to indicate operation of heating plugs....................29
2.8 Integrated indicator...............................................................................................................30
2.8.1 General information ..........................................................................................................30
2.8.2 Assignment and operation principle of integrated indicator gauges .........................30
2.8.3 Pilot lamps of the integrated indicator............................................................................ 33
2.8.4 Description of testing the indicator performance..........................................................34
2.8.5 Programming panel of integrated indicator ................................................................... 34
2.9 Engine control panel .............................................................................................................36
2.9.1 General information ..........................................................................................................36
2.9.2 Information display ............................................................................................................ 36
2.9.2.1 General information ....................................................................................................... 36
2.9.2.2 Adjustment of brightness and sharpness of the information display .....................37
2.9.2.3 Call up of changeable images and parameters on the screen of the information
display ........................................................................................................................................... 37
2.10 Steering................................................................................................................................ 40
2.10.1 General information ........................................................................................................40
2.10.2 Steering wheel adjustments ..........................................................................................40
2.11 Parking brake control......................................................................................................... 40
2.12 Handle for fuel feed manual control ................................................................................40
2.13 Tractor pedals ..................................................................................................................... 41
2.14 Gear shifting ........................................................................................................................ 41
2.14.1 General information ........................................................................................................41
2.14.2 Gears shifting in the transmission with a double-lever GB control and speed-
increase gear unit........................................................................................................................ 41
2.14.3 Gear shifting in transmission with a single-lever GB control and speed-increase
gear unit ........................................................................................................................................ 42
2.14.4 Gears shifting in transmission with double-lever GB control and reverse gear unit
........................................................................................................................................................44
2.14.5 Gears shifting in the transmission with a single-lever GB control and reverse gear
unit ................................................................................................................................................. 45
2.15 Control panel for rear axle DL and rear PTO. .......................................................................47
3

952.5-0000010 OM
2.16 FDA drive control................................................................................................................ 48
2.17 Rear power take-off shaft control .......................................................................................... 49
2.17.1 Lever shifting rear PTO from continuous drive to ground-speed drive............................... 49
2.17.2 Rear power take-off shaft engagement ....................................................................... 49
2.17.3 Two-speed continuous drive of rear PTO switch ....................................................... 50
2.17.4 Tractor operation without use of rear PTO.................................................................. 50
2.18 Rear lift linkage control with hydraulic lift........................................................................50
2.18.1 RLL control elements with hydraulic lift ....................................................................... 50
2.18.2 General information about control rules for RLL with hydraulic lift..........................51
2.19 HLL pump control ............................................................................................................... 52
2.20 Hydraulic lift linkage distribution valve sections (remote cylinders) control .................52
2.20.1 Remote hydraulic cylinders with distribution valve RP70-1221 (RP70-1221 C) or
RP70-1221.1 (RP70-1221.1 C) or RS213Mita (RS213Belarus) installed control by
means of levers. ..........................................................................................................................52
2.20.2 Remote hydraulic cylinders with distribution valve RP70-622 or (RP70-1221TC)
installed control by means of joystick and lever....................................................................... 54
2.21 Cutout fuses ........................................................................................................................55
2.21.1 General information ........................................................................................................55
2.21.2 Fuses for electrical equipment system ........................................................................55
2.21.3 Fuse for engine electronic control system ..................................................................56
2.22 Cab locks and handles ......................................................................................................60
2.22.1 Cab door locks................................................................................................................. 60
2.22.2 Left-side window opening ..............................................................................................60
2.22.3 Rear window opening..................................................................................................... 61
2.22.4 Cab roof opening............................................................................................................. 61
2.22.5 Cab emergency exits...................................................................................................... 61
2.23 Seat and its adjustments................................................................................................... 61
2.23.1 General information ........................................................................................................61
2.23.2 Adjustments of BELARUS seat ....................................................................................62
2.23.3 Adjustments of Grammer seat ......................................................................................63
2.24 Controlling pneumatic system compressor ....................................................................63
2.25 Connector elements of the electrical equipment ........................................................... 64
2.25.1 Socket to connect coupled agricultural equipment ..........................................................64
2.25.2 Connection of additional electrical equipment of coupled machines................................64
2.26 Creeper control ................................................................................................................... 65
2.27 Controls of tractor equipped with RLL control system with draft control unit,
mechanical control of rear axle differential lock and rear PTO. ............................................. 66
2.27.1 General information ........................................................................................................66
2.27.2 Mechanical control of rear axle differential lock. ....................................................66
2.27.3 Rear PTO mechanical control...................................................................................... 67
2.27.4 RLL fixing mechanism control in transport position.................................................67
2.27.5 Adjustable implement lifting limiter. ...........................................................................67
2.27.6 Rear PTO control with draft control unit. ....................................................................67
2.27.6.1 General information..................................................................................................... 67
2.27.6.2 Draft control unit operation providing draft, positional and depth control of
agricultural implements position. ..............................................................................................68
2.27.6.3 Draft control unit operation providing draft, positional, mixed and depth control
of agricultural implements position. .......................................................................................... 71
2.27.7 Hydraulic hook or lowered link grippers control. ......................................................72
4

952.5-0000010 OM
3 INTENDED USE OF TRACTOR ........................................................................................... 73
3.1 Safety measures to be taken preparing tractor for operation ........................................73
3.2 Tractor use............................................................................................................................. 74
3.2.1 Boarding the tractor ..........................................................................................................74
3.2.2 Preparing for start and starting the engine....................................................................74
3.2.3 Tractor motion start, GB shifting ..................................................................................... 75
3.2.4 Tractor stop ........................................................................................................................78
3.2.5 Engine stop ........................................................................................................................78
3.2.6 Leaving the tractor ............................................................................................................78
3.2.7 PTO use.............................................................................................................................. 78
3.2.8 Selection of optimal inner pressure in tires depending on operational conditions
and load on tractor axles............................................................................................................ 80
3.2.8.1 Selection of optimal inner pressure in tires depending on operational conditions
and load on tractor axles............................................................................................................ 80
3.2.8.2 Tire inflation ....................................................................................................................81
3.2.9 Rear wheel track formation.............................................................................................. 82
3.2.9.1 Track formation of rear wheels, mounted on terminal hubs....................................82
3.2.9.2 Track formation of rear wheels, mounted on taper hubs ...............................................83
3.2.10 Rear wheel twinning ....................................................................................................... 84
3.2.11 Front wheel track formation........................................................................................... 85
3.2.11.1 General information..................................................................................................... 85
3.2.11.2 Front wheels track formation of the tractors equipped with FDA with planetary
cylindrical wheel-hub drives.......................................................................................................85
3.2.11.3 Possible variants of front wheels track installation of the tractors, equipped with
FDA with taper wheel hubs and information on tires, mounted on tractors with FDA 72-
2300020-А-04. ............................................................................................................................. 87
3.3 Safety measures to be taken when operating the tractor ..............................................89
3.3.1 General safety measures to be taken when operating the tractor ............................89
3.3.2 Fire safety measures ........................................................................................................92
3.4 Tractor final assembly and run-in....................................................................................... 93
3.4.1 Tractor final assembly ......................................................................................................93
3.4.2 Technical maintenance before tractor run-in ................................................................93
3.4.3 Tractor run-in...................................................................................................................... 93
3.4.4 Technical maintenance during tractor run-in ................................................................94
3.4.5 Technical maintenance after tractor run-in.................................................................... 94
3.5 Emergency actions............................................................................................................... 95
4 COUPLING OF IMPLEMENTS.............................................................................................. 96
4.1 General information.............................................................................................................. 96
4.2 Types of implements coupled with tractor “BELARUS-952.5” ......................................97
4.3 Rear lift linkage ....................................................................................................................98
4.3.1 General information ..........................................................................................................98
4.3.2 Three-point rear lift linkage ..............................................................................................98
4.3.3 RLL components adjustment rules............................................................................... 101
4.3.3.1 Buckles ..........................................................................................................................101
4.3.3.1.1 General information.................................................................................................. 101
4.3.3.1.2 Telescopic buckles ................................................................................................... 101
4.3.3.1.3 Outer turnbuckles ..................................................................................................... 103
4.3.3.1.4 Inner buckles ............................................................................................................. 104
4.3.3.2 Lifting rod....................................................................................................................... 105
4.3.3.3 Upper link ......................................................................................................................106
4.3.3.4 Lower links ....................................................................................................................106
4.3.3.4.1 General information.................................................................................................. 106
5

952.5-0000010 OM
4.3.3.4.2 Installation of crossbar and rear ends of split lower links in operation
position........................................................................................................................................ 107
4.3.4 Attachment of implements to a tractor ......................................................................... 108
4.4 Drawbar hitches ..................................................................................................................109
4.4.1 General information ........................................................................................................109
4.4.2 Drawbar hitch DH-2V (short towing yoke)................................................................... 110
4.4.3 Drawbar hitch DH-ЗV (long towing yoke) .................................................................... 111
4.4.4 Drawbar hitch DH-2R (python)...................................................................................... 112
4.4.5 Drawbar hitch DH-1М-01 (draw bar) ............................................................................ 113
4.4.6 Drawbar hitch DH -1 (crossbar) ....................................................................................114
4.4.7 Drawbar hitch DH-2 (hydraulic hook) and combined drawbar DH-2М-02 (with
hydraulic hook in operation position and floating drawbar in additional position)........... 115
4.4.8 Combined drawbar DH-1M-02 (combined drawbar with floating drawbar in operating
position and hydraulic hook in additional position). ...................................................................116
4.4.9 Drawbar hitch DH-1М (floating drawbar/pendulum) ..................................................116
4.4.10 Lowering link .................................................................................................................. 116
4.4.11 Basic parameters and coupling dimensions of DH-1M-02 (combined drawbar
with floating drawbar (pendulum) in operating position, of DH-1M (floating drawbar) and
of lowering link).......................................................................................................................... 117
4.4.12 Drawbar hitch DH-1ZH (crossbar) .............................................................................. 118
4.4.13 Drawbar hitch DH-1ZH-01 (twin crossbar) ................................................................ 118
4.4.14 Repositioning of floating drawbar and hydraulic hook in combined drawbar ...........119
4.5 Usage patterns of tractor hydraulic system for driving of operated parts and other
elements of unitized hydraulically operated machines and aggregates........................... 123
4.6 Front ballast weight installation .........................................................................................124
4.7 Trailer brake actuator......................................................................................................... 125
4.7.1 General information ........................................................................................................125
4.7.2 Double-line pneumatic drive of trailer brakes .............................................................125
4.7.3 Hydraulic drive of trailer brakes ....................................................................................126
4.7.3.1 General information ..................................................................................................... 126
4.7.3.2 Adjustment of hydraulic actuator of trailer brakes ..................................................127
4.8 Determination of PTO shaft and cardan shaft applicability..........................................128
4.9 Features of application of PTO shafts and cardan shafts............................................128
4.10 Ways of changing of drawbar features and passing ability of the tractors .....................132
4.11 Features of the tractor application in special conditions ............................................133
4.11.1 Tractor operation in areas with rugged topography.................................................133
Possibility of the tractor application for haulage allocation for reserve.............................133
4.11.2 Application of substances for the purpose of chemical treatment......................... 133
4.11.3 Operation in a forest ..................................................................................................... 133
4.12 Finding of total weight, loads on the front and rear axles, tires holding capacity and
required minimum ballast......................................................................................................... 134
4.13 Possibility of front loader installation ............................................................................. 136
4.13.1 General information ......................................................................................................136
4.13.2 Safety measures at tractor “BELARUS-952.5” operation with loader installed... 138
6

952.5-0000010 OM
5 MAINTENANCE .....................................................................................................................142
5.1 General instructions ........................................................................................................... 142
5.2 Providing access to the components for maintenance services........................................... 144
5.3 Maintenance procedure..................................................................................................... 145
5.4 Scheduled maintenance servicing operations ............................................................... 148
5.4.1 Maintenance on a shift basis (SBMS) in every 8 – 10 hours of operation or
per shift ....................................................................................................................................... 148
5.4.2 Maintenance services in every 125 hours of operation............................................. 154
5.4.3 Maintenance services in every 250 hours of operation (2MS-1), in every 500 hours
of operation (MS-2), in every 1000 hours of operation (MS-3), in every 2000 hours of
operation (special maintenance) and maintenance service that is inconsistent with
intervals of MS-1, 2MS-1, MS-2, MS-3 and special MS......................................................159
5.4.3.1 General instructions..................................................................................................... 159
5.4.3.2 Operation 30. Check/adjustment of clearances in steering joints........................ 159
5.4.3.3 Operation 31. Check and adjustment of wheels toe-in......................................... 160
5.4.4 General maintenance services...................................................................................... 161
5.4.4.1 General guidelines....................................................................................................... 161
5.4.4.2 Operation 72. Adjustment of oil pressure in the engine lubrication system .... 161
5.4.4.3 Operation 73. Maintenance of engine air cleaner................................................... 162
5.5 Seasonal maintenance services ......................................................................................163
5.6 Safety measures during maintenance and repair operations......................................164
5.6.1 General safety requirements ......................................................................................... 164
5.6.2 Safety precautions for exclusion of hazardous situations, related to an accumulator
battery and a fuel tank ..............................................................................................................164
5.6.3 Guidelines for safe use of leveling jacks and statement of places where they shall
be installed ................................................................................................................................. 165
5.7 Filling and lubrication of the tractor with fuel and lubrication materials...................... 167
6. POSSIBLE MALFUNCTIONS AND GUIDELINES FOR
TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................................. 172
7 TRACTOR STORAGE ..........................................................................................................184
7.1 General instructions ........................................................................................................... 184
7.2 Requirements for inter-shift storage of machines.......................................................... 184
7.3 Requirements for short-term tractors storage ................................................................ 184
7.4 Requirements for outdoors long-term storage ............................................................... 185
7.5 Preservation ........................................................................................................................186
7.6 Depreservation and represervation ................................................................................. 186
7.7 Putting tractor into operation after long-term storage ................................................... 186
7.8 Safety requirements for preservation ..............................................................................187
8. TRACTOR TOWING ............................................................................................................187
Service bulletins ........................................................................................................................188
7

952.5-0000010 OM
Introduction
The present manual is designed for studying the structure, operation rules and mainte-
nance of tractors “BELARUS-952.5”.
Scrutinize this manual. It will help you to study the rules of correct operation and main-
tenance.
Failure to follow this instruction can lead to operator's injury or a breakdown of a tractor.
Operation of a tractor, its maintenance and repair shall be carried out only by employees, familiar with all of its parameters and characteristics and informed about necessary safety
requirements to prevent casualties.
In connection with constant development of the tractor some changes, which are not
depicted in the present manual, can be introduced in the structure of certain units and parts.
Any arbitrary changes made by a consumer release the manufacturer from responsibility for possible further injuries to the operator and tractor breakdown.
Adopted abbreviations and conventional notations:
ADL – automatic differential lock;
AB – accumulator battery;
DL – differential lock;
RADL – rear axle differential lock;
PLU – pilot lamps unit;
FB – fuse block;
FC – fast coupling;
PTO – power takeoff shaft;
PRS – power reception shaft;
HSC – hydrostatic steering control;
HLL – hydraulic lift linkage;
HS – hydraulic system;
HRC – hydraulic creeper
FFVS – frequency fuel volume sensor;
STM – shift-time maintenance;
SPTA – spare parts, tools and accessories;
RA – rear axle;
RLL – rear lift linkage;
II – integrated indicator;
GB – gearbox;
MTU – machine and tractor unit;
CC – coupling clutch;
MCR – mechanical creeper;
LL – lift linkage;
IAH – inlet air heater;
FDA – front driving axle;
VC – voltage converter;
FDAD – front driving axle drive;
CM – control module;
IICP – integrated indicator control module;
HPH – high pressure hoses;
HP – heating plugs;
SM – seasonal maintenance;
MS – maintenance service;
MS1 – maintenance service No1;
MS2 – maintenance service No2;
MS3 – maintenance service No3;
DH –drawbar hitch;
ECS – electronic control system;
EECS – engine electronic control system;
EE – electrical equipment.
8

The manufacturer uses standard international symbols, regarding application of instruments and control units.
Given below are the symbols with indication of their meanings.
— see the manual ;
952.5-0000010 OM
— control manipulations;
— brake;
— manual brake;
— audible beep;
— alarm signaling;
— fuel;
— coolant;
— heating plugs;
— fast;
— slowly;
— forward;
— reverse;
— accumulator charging;
— cab roof light;
— parking lights;
— engine speed;
— oil pressure in the engine;
— temperature of engine cool-
ant;
— off / stop;
— on / start;
— gradual adjustment;
— tractor turn indicator;
— trailer turn indicator;
— upper beam;
— low beam;
— working lights;
— differential lock;
— PTO engaged;
9

952.5-0000010 OM
— front screen wiper;
— rear screen wiper and washer;
— brake fluid level in main cylin-
der tanks;
— oil pressure in HSC
— beacon
— oil pressure in gearbox
— braking of gearbox
— front driving axle drive;
— fan;
— air filter clogged;
— engine start;
— road-train
— external cylinder – retracting
— external cylinder – protracting
— air pressure in pneumatic system
— swivel lever – up
— swivel lever – down
— external cylinder – floating
— engine stop
10
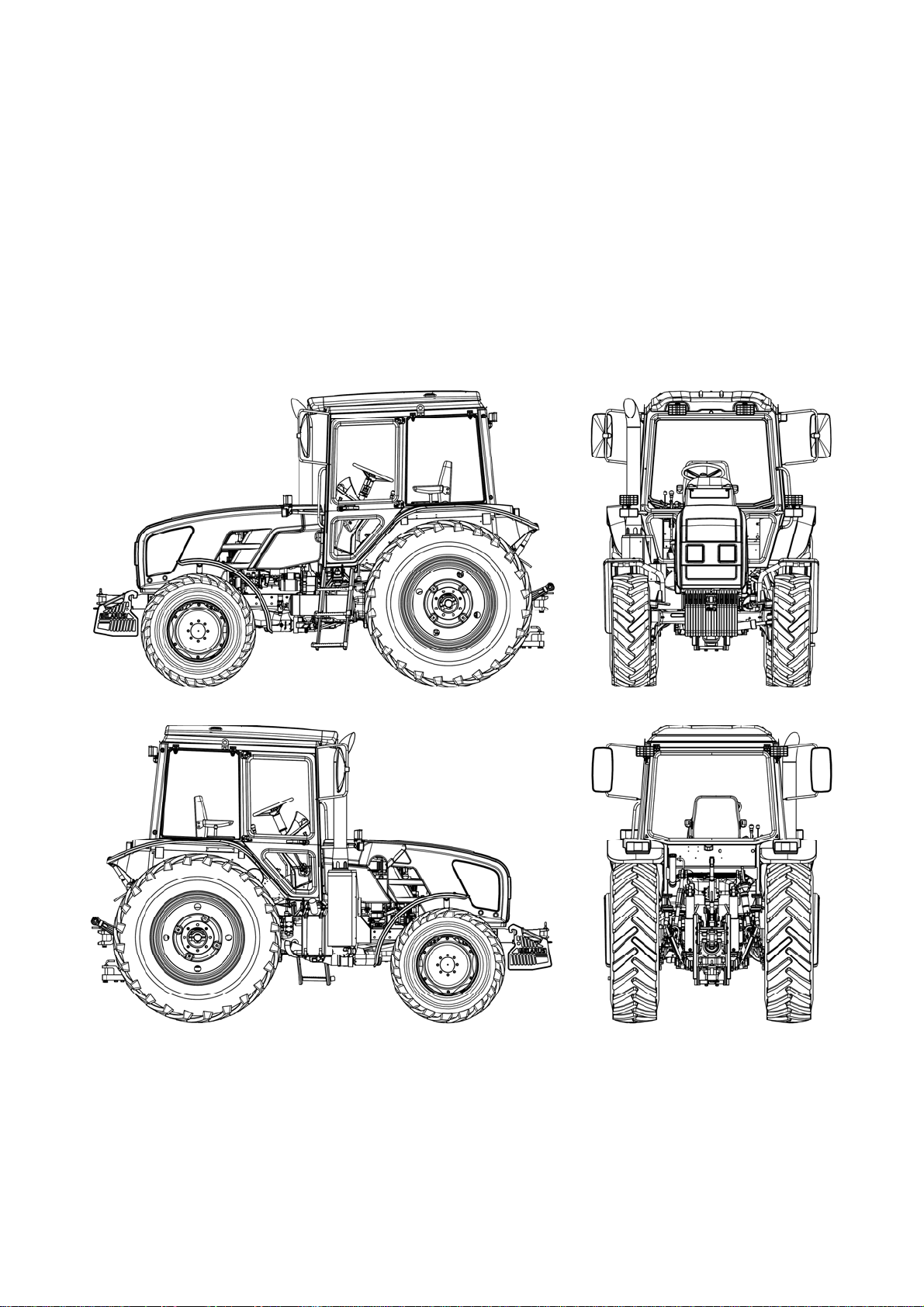
952.5-0000010 OM
1 TRACTOR DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
1.1 Tractor assignment
The tractor “BELARUS-952.5” is intended for performance of various general –
purpose agricultural operations with mounted, semi-mounted and trailed machines and
implements, for loading-unloading works and transportation works.
The tractor “BELARUS-952.5” is a general-purpose wheeled tractor of traction class
1,4 with the wheel formula 4X4.
Appearance of the tractor “BELARUS-952.5” is presented in figures 1.1.1.
Figure 1.1.1 – Basic configuration of tractor “BELARUS-952.5”
11
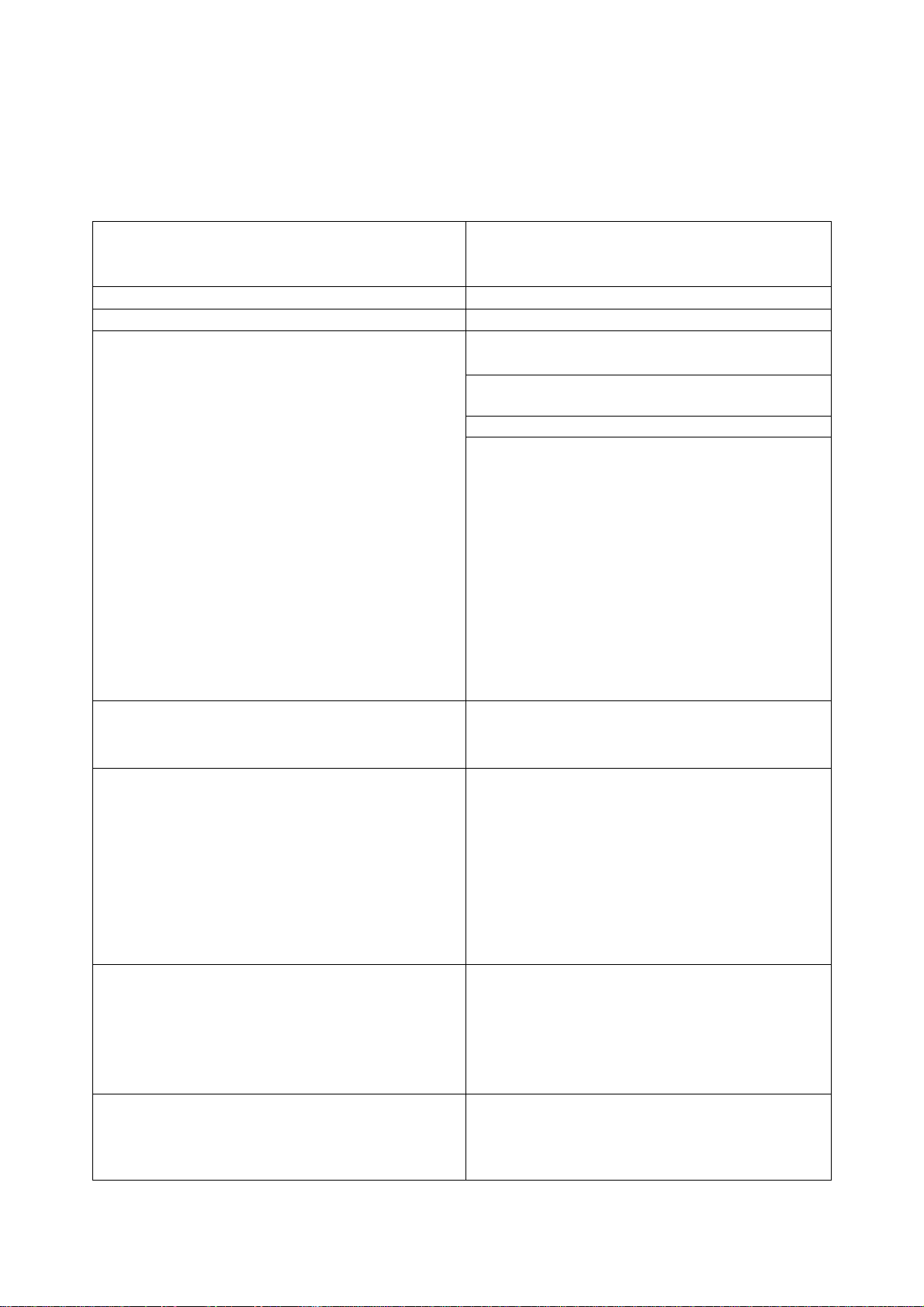
952.5-0000010 OM
Main parameters and technical specifications of tractor BELARUS-952.5 are given in
table 1.1.
Table 1.1.
1.2 Technical specifications
Parameter
(characteristics) title
Parameter value for the tractor
“BELARUS-952.5”
1 Traction class as per GOST 27021
2 Rated traction force, kN
3 Engine
а) model
b) engine type
1)
2)
D-245.5S3В
turbocharged with intercooling of the
charged air
c) number and position of cylinders 2) four, in-line, vertical
d) displacement, l 2)
4,75
e) engine power, kW:
1) rated 2)
2) normal
70,0±2,0
67,4±2,0
f) crankshaft rated speed, rpm 2)
1800
g) specific fuel consumption at normal
power, g/(kW·h)
2)
(223+7)
h) turning torque rated factor, % 2)
i) max turning torque, N·m 2)
464±18
4 Number of gears:
а) for forward travel
14 3)
b) for reverse travel
5 Tractor travel speed (design) at crankshaft rated speed, and with tires 18.4R34
km/h:
а) for forward motion:
1) least
2) highest
2,7 3)
38,1
b) for backward motion:
1) least
2) highest
5,6 3)
12,6
6 Tractor weight, kg:
а) structural
b) operating with ballast
c) operating without ballast
d) max. operating
e) ex-works 4)
4405±100
5095±100
4655±100
7000
4505
7 Distribution of operating weight on axles, kg:
а) on front 2310±40
b) on rear 2785±60
5)
(1730±40
5)
(2925±40
1,4
14
25
4 3)
6)
6)
)
)
12
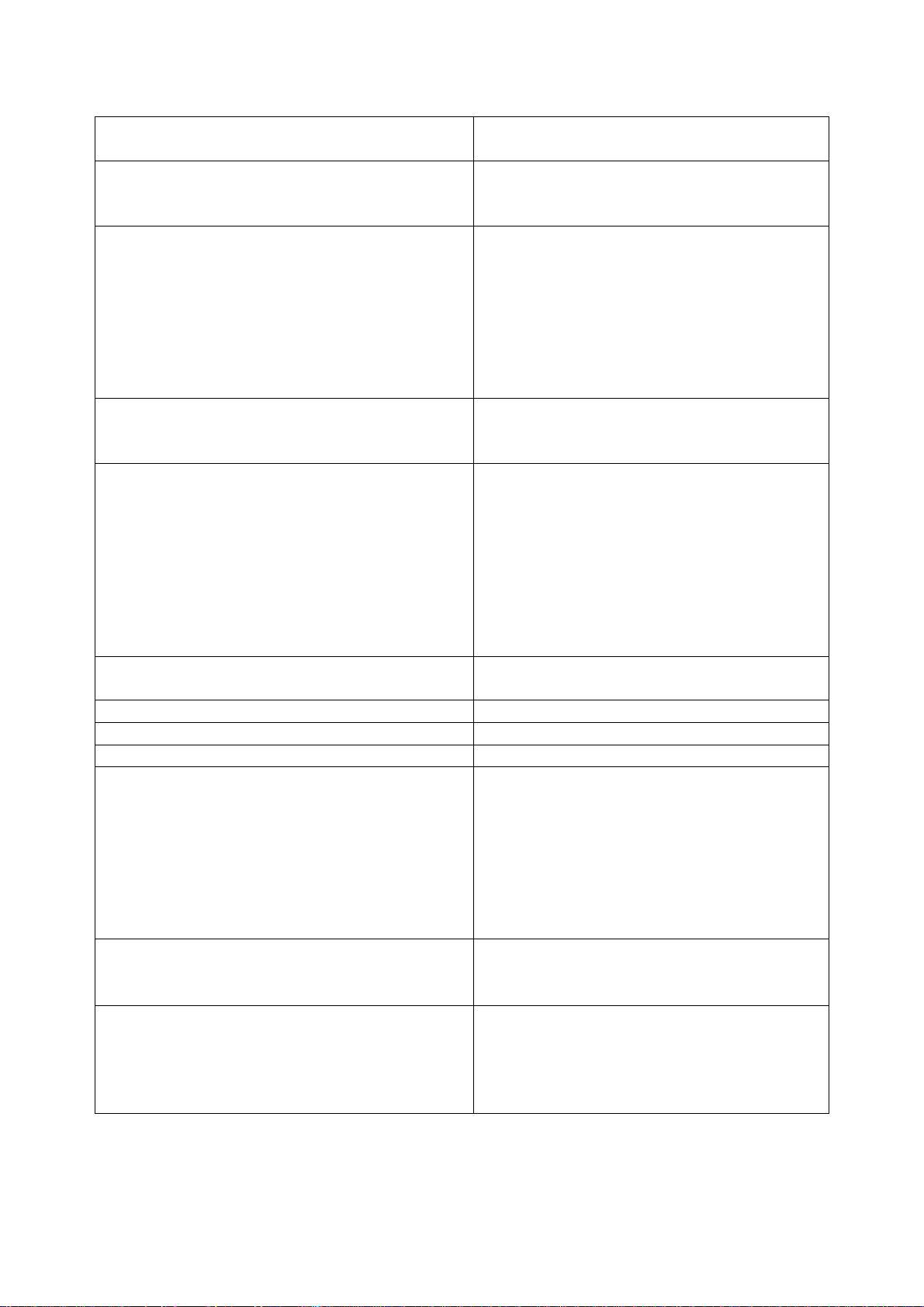
Table 1.1 continued
Parameter
(characteristics) title
Parameter value for the tractor
“BELARUS-952.5”
8 Permitted load on axles, kN:
а) on front 37
b) on rear 53
9 Max weight of the trailer, kg
а) without brakes 2100
b) with independent brake 3500
c) with overrunning brake 3500
d) equipped with a brake system (trailer
brakes are interconnected with tractor
brakes)
10 Agrotechnical clearance, mm (under
the axle tubes of rear wheels and on tyres
of basic configuration) not less than:
11 Track dimensions (on tyres of basic
configuration), mm:
а) on front wheels for short beam
FDA 822-2300020-02/04
b) on front wheels for long beam
FDA 822-2300020-02/04
c) for rear wheels
d) for front wheels with mounted
FDA 72-2300020-А-04
1415±20, 1515±20, 1585±20, 1685±20,
1735±20, 1835±20, 1900±20, 2000±20
1535±20, 1635±20, 1705±20, 1805±20,
1855±20, 1955±20, 2020±20, 2120 ±20
from 1500±20 to 1600±20 and from 1800±20 to 2100 ±20
1420±20, 1530±20, 1640±20,
1720±20, 1830±20, 1940±20
12 Least radius of turning circle (with
braking), m
13 Tractor base, mm 2450±20
14 Maximum fordable depth, m 0,85
15 Service life, years 12
16 Overall dimensions, mm:
а) length with weights and rear lift linkage
in transport position
b) length over external diameters of
wheels
4440±50
3850±50
c) width on rear wheel axle shaft ends
1970±20
d) height to the top of cab 2850±30
17 Tyres (basic configuration):
а) front wheels 360/70R24
b) rear wheels 18.4R34
18 Electrical equipment as per GOST
3940:
а) rated supply voltage in on-board
power system, V
b) rated ignition voltage, V 12
952.5-0000010 OM
18000
510
4,5
12
13
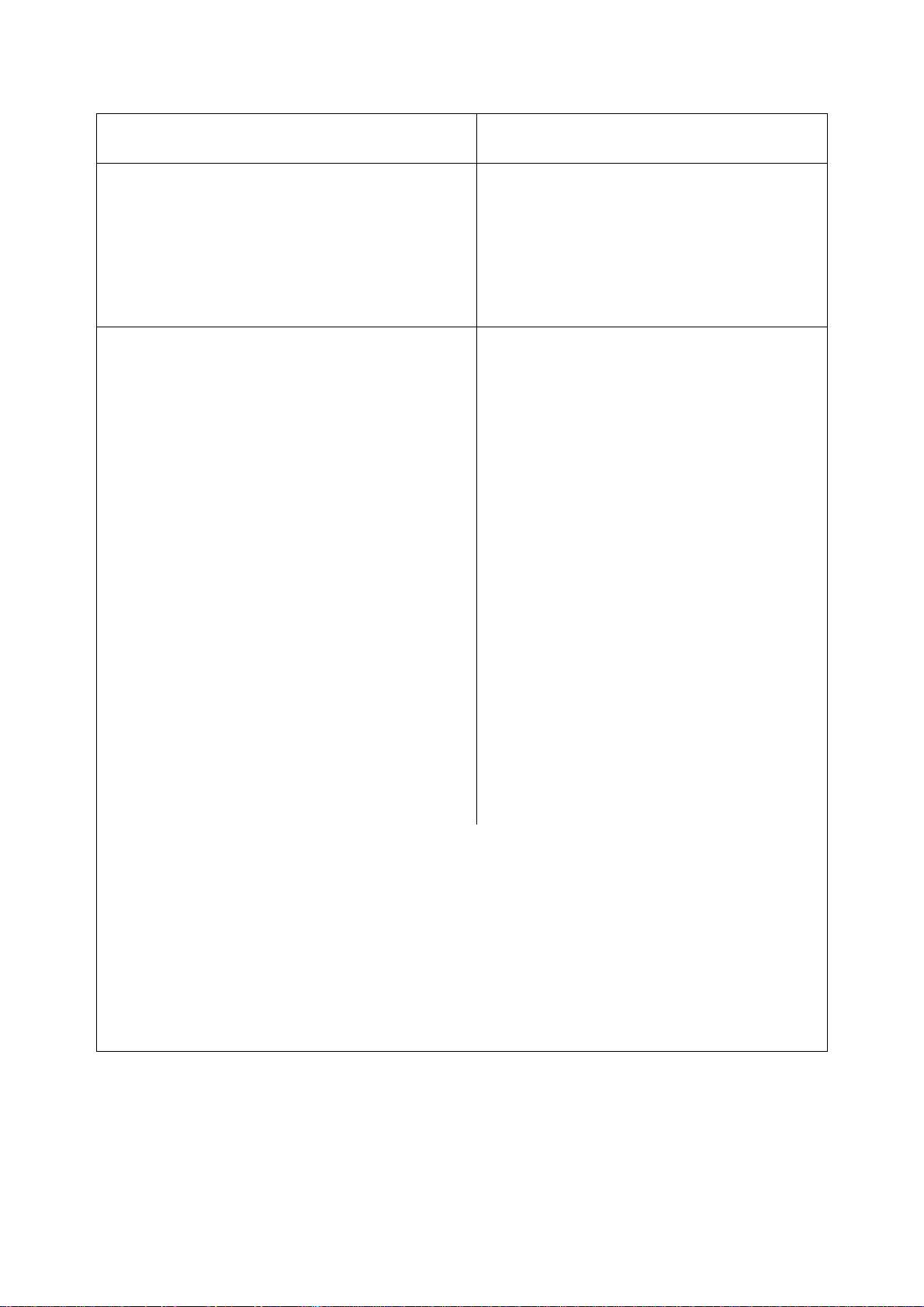
952.5-0000010 OM
Table 1.1 finished
Parameter
(characteristics) title
19 Hydraulic system:
а) pump displacement under crankshaft
rated speed, l/min, not less than
Parameter value for the tractor
“BELARUS-952.5”
46
b) safety valve operation pressure, MPa
20-2
c) conventional volume factor, not less
than
20 Working equipment:
а) rear power take-off shaft:
1) rated speed of PTO shaft end with
the ground-speed drive on, rpm:
- position I (under the engine crankshaft
speed of 1632 rpm)
- position II (under the engine crankshaft
speed of 1673 rpm)
2) rated speed of PTO shaft end with
the continuous drive on, rev/meter of
travel:
b) rear lift linkage:
540 (596 7))
1000 (1076 7))
(on rear tires of standard configuration
(18.4R34))
0,65
3,36
1) loading capacity of rear lift linkage on
suspension axis on tractors with hydraulic lift,
4200
kg, not less than
2) loading capacity of rear lift linkage on
suspension axis on tractors with draft control
unit, kg, not less than
3000
3) time for raising rear lift linkage from
lowermost position into uppermost position
with test load on suspension axis, sec., not
3
more than
c) drawbar hitch: In section 4 “Coupling of implements”
__________________________________ ________________________________________________ ___________________________
1)
Engine parameters, not specified in the table 1.1, shall meet 245 S3В – 0000100
OM document.
2)
For referential use.
3)
Without a creeper. Installation of a creeper against order provides additional sixteen forward travel speeds and sixteen reverse travel speeds (on tractors with speed
increase unit).
4)
Specified depending on the configuration.
5)
With ballast weights mounted.
6)
Without ballast weights.
7)
At 1800 rpm of engine crankshaft speed
-1)
..
Note – Number of gears and travel speeds of the tractor at crankshaft rated speed
are given in table 1.1 for tractor “BELARUS-952.5” with speed increase unit mounted in
tractor transmission (basic configuration). Number of gears and travel speed of the tractor
“BELARUS-952.5 with reverse gear unit (optional configuration) are given in clauses
2.14.4 and 2.14.5 of the subsection 2.14 “Gear shifting”.
14

952.5-0000010 OM
1.3 Tractor composition
Tractor framework – semi-frame.
Undercarriage: front and rear driving wheels, with pneumatic tyres of low pressure.
Steering wheels are front wheels. The wheels can be twinned by means of spacers.
The tractor is equipped with 4-stroke piston four-cylinder inner combustion engine
with in-line vertical arrangement of cylinders, with direct injection of diesel fuel and compression ignition, corresponding to environmental requirements of Stage 3B.
System of engine lubrication is combined, some parts are lubricated under pressure, some – by spattering. The lubrication system consists of an oil sump, oil pump, liquid-oil heat exchanger, oil filter and oil filter with paper filtering element.
The engine fuel supply system consists of the following parts:
- accumulator system of fuel supply Common RAIL, including a high-pressure fuel
pump, injectors, fuel accumulator under high pressure, sensors of engine working environment condition (pressure and temperature of fuel and air), electromagnetic actuating
mechanisms (fuel governor, electromagnetic injection valves), electronic unit of control and
communication check circuits, low-pressure pipelines, high-pressure pipelines;
- fuel fine filters;
- fuel coarse filters.
System of engine start-up is electric starter. A means of start-up facilitation under
low environmental temperatures are the heating plugs.
System of air delivery consists of a turbocharger, an air pipeline and a system of
charged air cooling.
The turbocharger is executed as follows: radial centripetal turbine and centrifugal
single-stage compressor with cantilever arrangement of wheels in relation to supports.
The system of air purification consists of a dry-type air cleaner of “Donaldson” com-
pany with two paper filtering elements. This air cleaner has two stages of purification.
Cooling system for charged air is of a radiator type. The CAC radiator is intended for
cooling the air, charged into the inlet collector.
System of engine cooling is closed-type with coolant compulsory circulation executed by a centrifugal pump. The water pump is driven by a V-belt from the crankshaft pulley. For acceleration of engine warming up after start-up and for automatic control of a
temperature mode at various loadings and ambient temperatures there is an thermostat.
To provide for a required chemical composition of exhaust gases under Tier-IIIB
stage the system of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is additionally installed in the exhaust system.
The coupling clutch is frictional, dry, single-disk, spring-loaded. The CC overlays are
asbestos free. The coupling control drive is mechanical.
The gearbox is synchromesh with double-lever or single-lever control, with
synchronized speed increase unit, 14F + 4R
Option – synchromesh GB with double-lever or single lever control with
synchronized reverse gear unit, GB 7F+6R.
The rear axle is with the main drive, differential and final drives.
Brakes: service brakes are multidisk, oil-lubricated, located on final drive pinion
shafts; the parking brake is independent, manually controlled. It is possible to mount the
dry-friction brakes. The trailer brake control drive can be either double-line pneumatic, or
hydraulic, interlocked with tractor service brakes control. Against order the tractor may not
be equipped with the trailer brake pneumatic drive – tires are inflated through a valve of
the pneumatic compressor.
15

952.5-0000010 OM
The rear power takeoff shaft is continuous dual-speed (540 and 1000 min-1) and synchronous, the direction of rotation is clockwise when viewed from the shaft end face. There are
PTO shaft end extensions: PTO shaft end extension 1 (6 splines, 540 min-1), PTO shaft
end extension 1c (8 splines, 540 min-1), PTO shaft end extension 2 (21 splines, 1000 min-
1).
Steering is hydrostatic. The feed pump is gear-type, the direction of rotation is left. The
dosing pump is gerotor-type. The type of the rotation mechanism - one hydraulic cylinder
(TS63x200) of bidirectional operation and a steering linkage.
The front driving axle – with main gear, a self-locked differential, final gears (planetary
gear groups). The FDA drive is a transfer gearbox with automatic FDA engagement, two
cardan shafts and intermediate bearing with overload clutch. The FDA drive control is mechanical.
The hydraulic system is remote cylinder hydraulic system with hydraulic lift (which provides
draft control, position control, depth and mixed control of the agricultural implements), or
with draft control unit (which provides draft, position and depth control of agricultural implements), with left and right side outputs. Optional can be mounted rear right outputs, interconnected with left side outputs. For operation with constant supply hydraulic units, for
example hydraulic engines, optional on the rear can be mounted free drain.
The rear lift linkage is a three-point linkage of category 2 under ISO 730 and a linkage 2
under GOST 10677 with outer or inner lock of lower links. There are two cylinders
TS80x220.
On tractors with hydraulic lift are mounted two cylinders TS80x220.
On tractors with draft control unit is mounted one cylinder TS100x200 (optional can be installed cylinder TS110x200).
Drawbar hitches on tractors equipped with hydraulic lift:
- short towing yoke DH 2V – for coupling with semi-trailers and semi-trailed imple-
ments;
- long towing yoke DH 3V – for coupling with trailers and trailed implements;
- pin DH-2R (“Pithon”) – for coupling with semi-trailers and semi-trailed machines
(option);
- towing bar DH-1M-01 –for coupling with semi-trailed and trailed agricultural ma-
chines (option);
- crossbar DH-1 – for coupling with trailed and semi-trailed machines (option).
- twin cross member DH-1ZH-01 – for coupling with trailed and semi-trailed ma-
chines (against order).
Drawbar hitches on tractors equipped with rear lift linkage with draft control unit:
- hydraulic hook DH-2 – for coupling with semitrailers and semitrailed agricultural
machines;
- floating drawbar DH-1M for coupling with semitrailed and trailed agricultural ma-
chines (optional);
- combined drawbar DH-1M-02 (with variable functions of DH-2 and DH-1M) – for
coupling with semitrailed and trailed agricultural machines; with semitrailers and semitrailed agricultural machines depending on mounted coupling element (optional);
-lowering link – for coupling with semitrailed and trailed agricultural machines
(optional);
- crossbar DH-1ZH – for coupling with trailed and semitrailed machines (optional);
- twin crossbar DH-1ZH-01 for coupling with trailed and semi-trailed machines
(option).
16

952.5-0000010 OM
The cabin is a one-seated with a protective rigid framework, having thermal, noise
and vibration insulation, equipped with a sprung seat adjustable for operator's height and
weight, with rear-view mirrors, with a sun visor, with electrical wipers for front and rear
screens, with front and rear screen washers, with a roof lamp and a place to install a radio
set, with a system of heating and ventilation (upon request – additional air-conditioning).
Upon request the tractor can be equipped with an additional seat. The cab doors have got
locks, there are keys for the left door. Right door is for emergency exit. The cab complies
with category 2 under EN 15695-1:2009.
The electrical equipment complies with GOST 3940. The rated power supply voltage for on-board network is 12V. The rated voltage for the start-up is 12V.
Instruments are a combination of devices; these are an integrated indicator; informational display; pilot lamps (glow lamps and light emitting diodes), located on the block of
pilot lamps, on the control panel of the rear axle differential lock and rear PTO, on the engine control system board.
17
952.5-0000010 OM
The vibration level at the operator's seat complies with the Council Directive
78/764/ЕEС. Values for the vibration level are given in the EU type approval on each type
of a seat.
1.5 Noise level at the operator's working place of the tractor “BELARUS-952.5”
Noise level at the operator's workplace conforms to Directive 2009/76/ЕС, Appendix
2, and does not exceed the value 86 dB (A). External noise level conforms to Directive
2009/63/ЕС and does not exceed the value 89 dB (A).
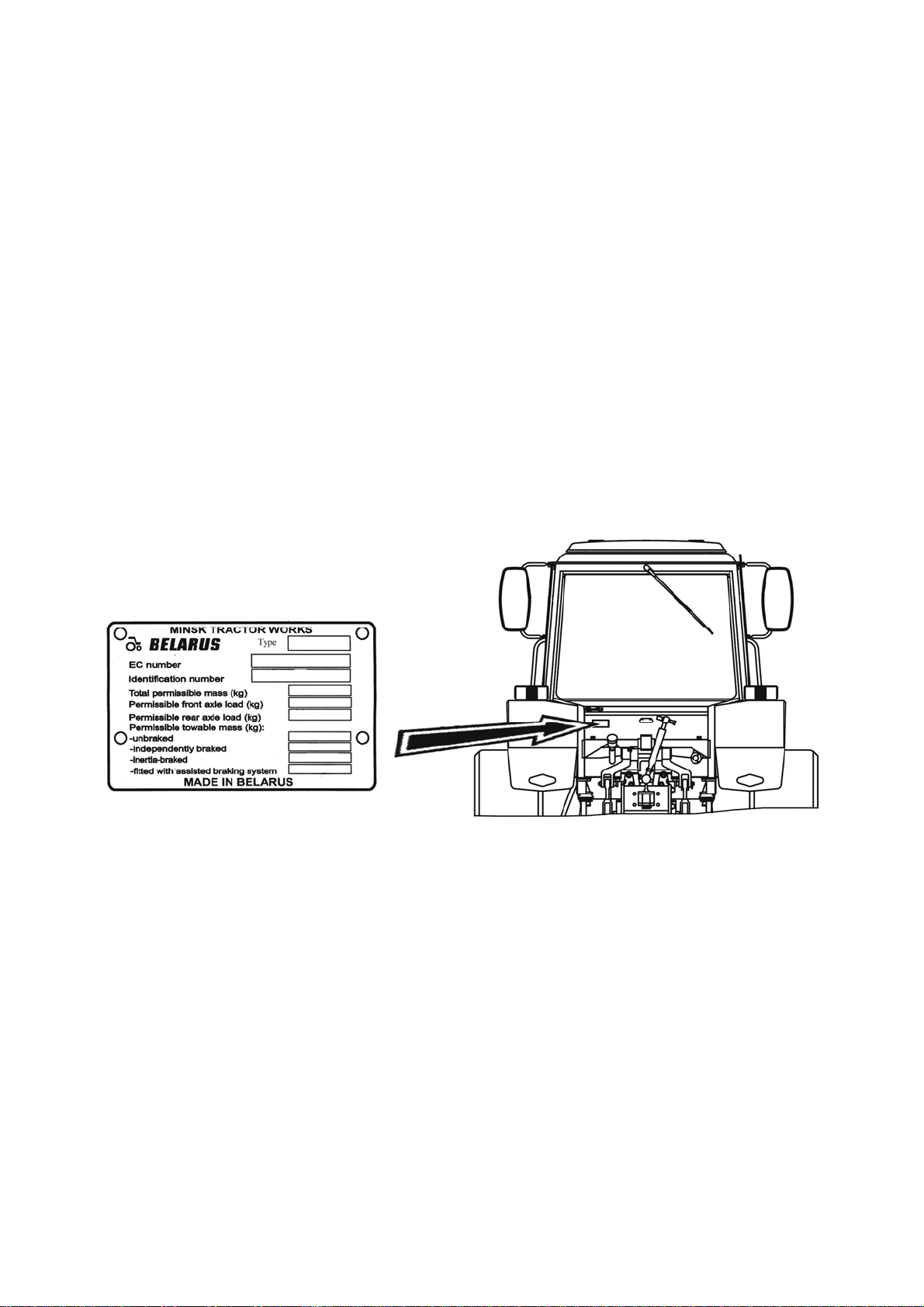
1.6 Tractor and its component marking
Metal nameplate is fixed at the rear of the cab on the left side, as shown in fig.
1.6.1.
Additionally the tractor serial number is applied by means of percussion on the right
side member and duplicated on the right plate of the front ballast weight.
1.4 Vibration level at the operator's working place of the tractor “BELARUS-952.5”
Figure 1.6.1 – Place of application the tractor nameplate
Engine number and numbers of its components are given in engine operation manual.
Numbers of tractor components are given in table 1.2
18
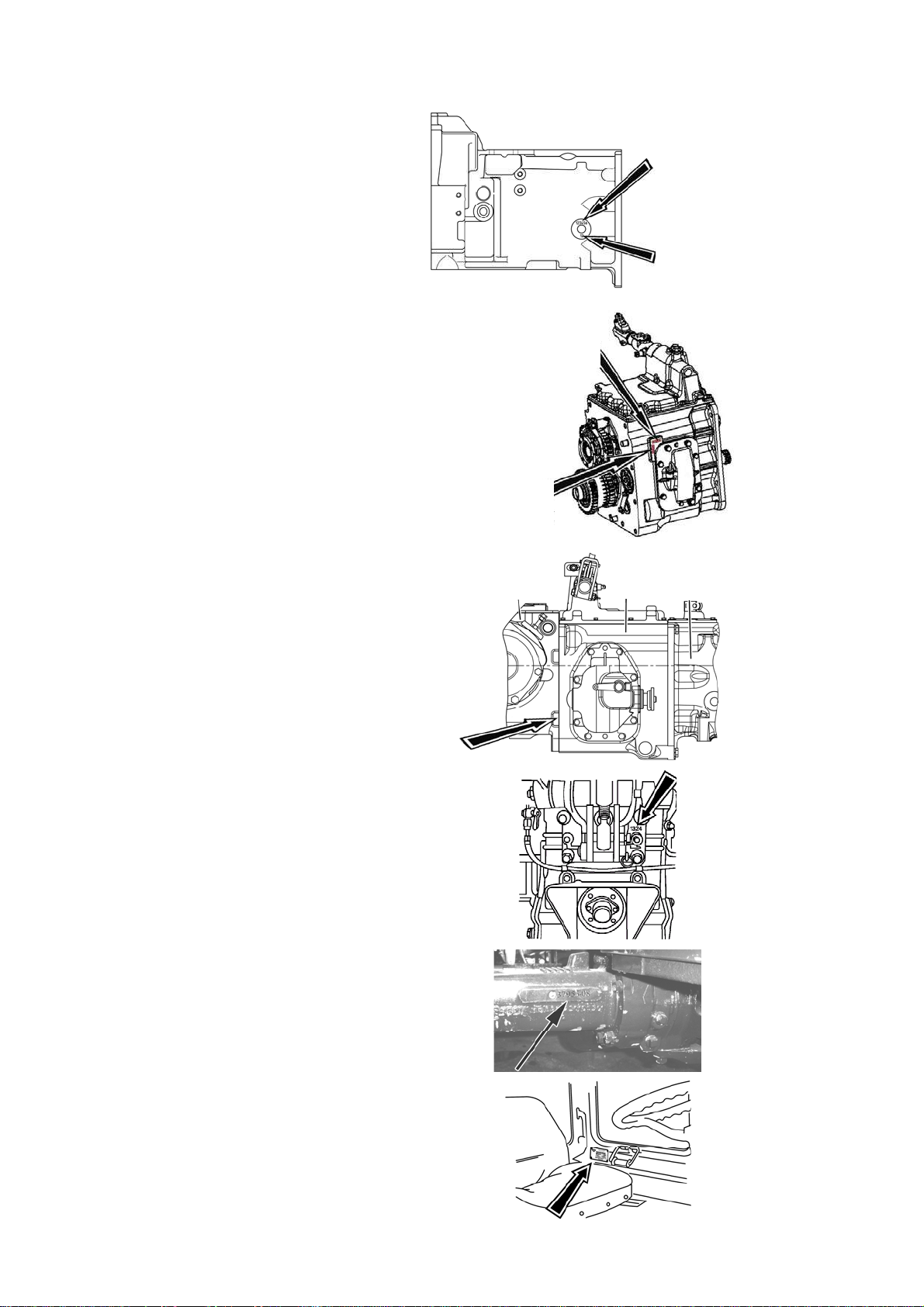
Table 1.2 – Numbers of tractor components
Number of clutch casing
(to the left along the tractor
movement)
Serial number
Number of gear box
(to the left along the tractor
movement)
Clutch
configuration
number
952.5-0000010 OM
Serial number
Clutch case
configuration
number
Transmission and rear axle
serial number on tractors with
hydraulic lift (to the right along
the tractor movement)
Transmission and rear axle
serial number on tractors with
draft control unit (on rear axle
body from behind)
FDA number
RA
GB
Clutch case
Cab serial number
19
952.5-0000010 OM
2 CONTROLS AND INSTRUMENTS
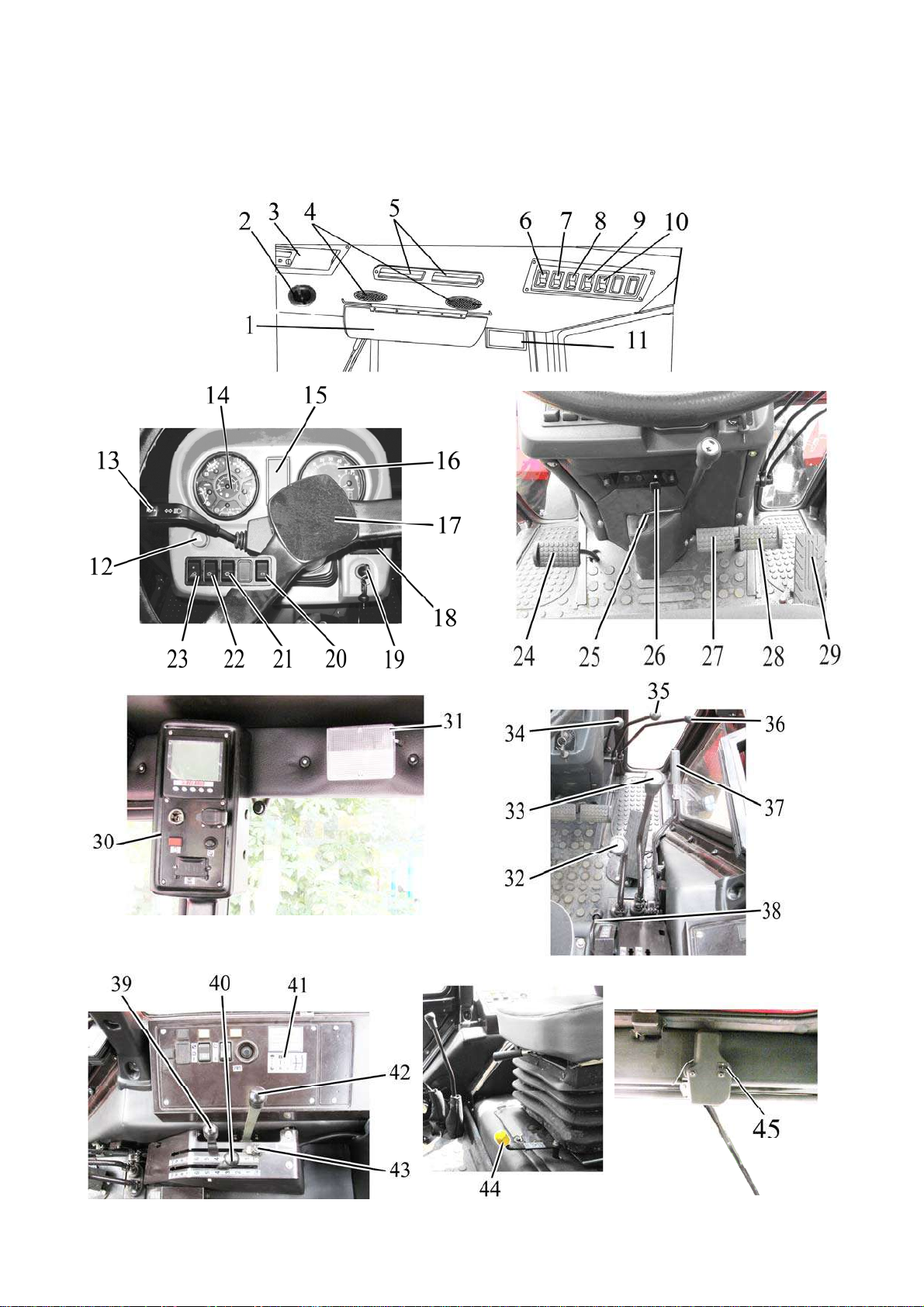
2.1 Layout of controls and instruments of the tractor
Controls and instruments, located in the tractor cab, are presented in fig. 2.1.1.
Figure 2.1.1 – Tractor controls and instruments
20
952.5-0000010 OM
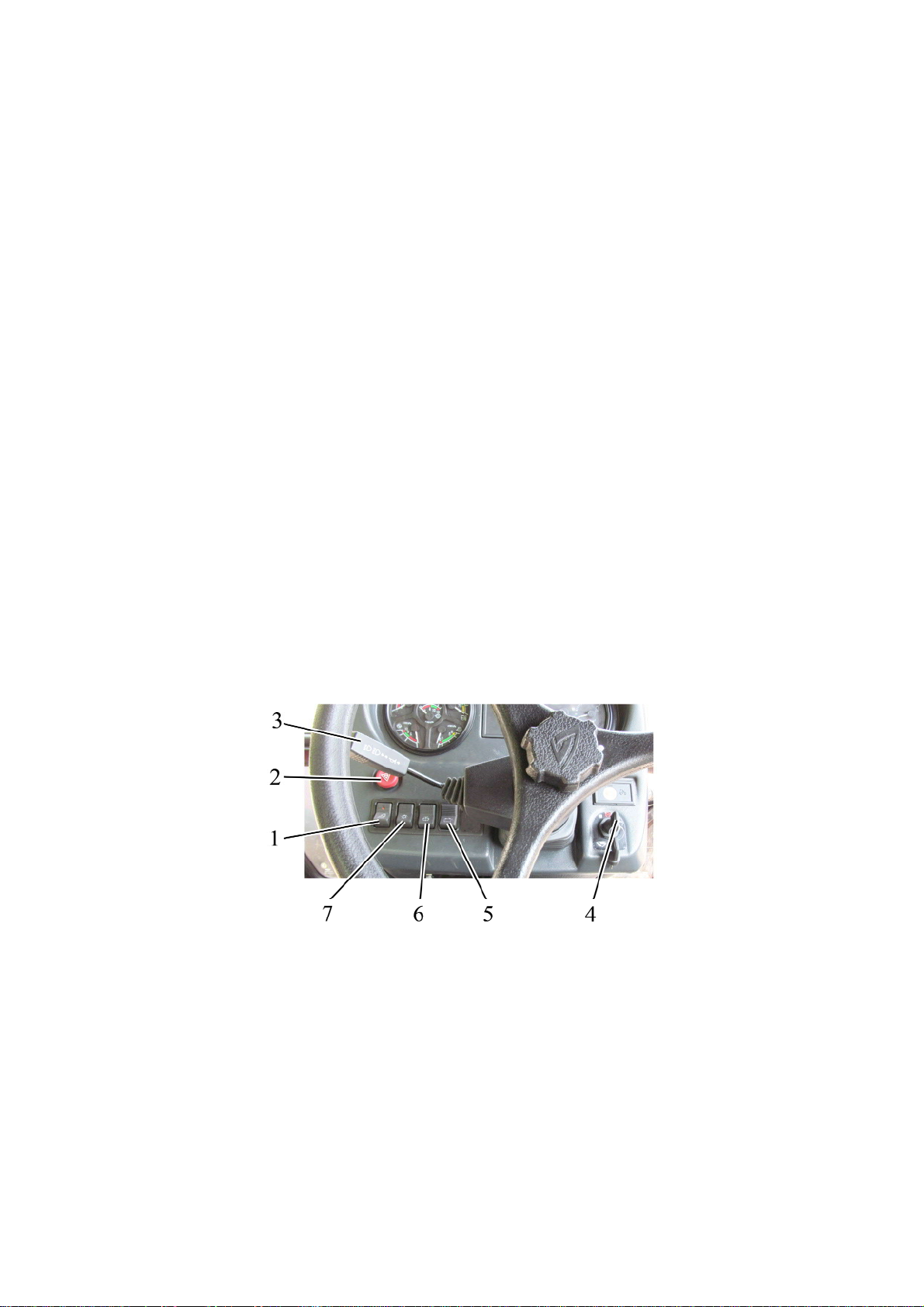
To the figure 2.1.1 – Layout of controls and instruments of the tractor:
1 – sun visor; 2 – handle to control the cab heater valve; 3 – place for radio receiver (car
stereo) installation; 4 – deflectors; 5 –recirculation shutters; 6 – windscreen wiper switch; 7 – cab
heater fan switch; 8 – rear lights switch; 9 – switch of front lights on the cab roof; 10 – „Road-train“
light switch (design variant); 11 – rear view mirror; 12 – emergency flashing switch; 13 – multifunctional underwheel switch; 14 – instrument board; 15 – pilot lamps unit; 16 – integrated indicator; 17
– steering wheel; 18 – integrated indicator control panel; 19 – starter and instruments switch; 20 –
accumulator battery remote disconnect switch; 21 – windscreen washer switch; 22 – central light
switch; 23 – switch of front lights mounted on handgrips switch; 24 – clutch control pedal; 25 –
control lever of speed increase unit; 26 – handle for steering rake tilt fixation; 27 – left brake control pedal; 28 – right brake control pedal; 29 – accelerator pedal; 30 – engine control board; 31 –
cab lamp with switch; 32 – range shifting lever of gearbox; 33 – gear shifting lever of gearbox;
34,35,36 – levers to control hydrosystem outlets; 37 – parking brake control lever; 38 – FDA drive
control lever; 39, 40 – RLL hydrohoist control levers; 41 – console to control rear axle DL and rear
PTO; 42 – handle to control fuel supply.. 43 – limiter for the position control lever; 44 – handle to
switch between the ground-speed and continuous drives of PTO; 45 – rear screen wiper switch;
Instead of electrohydraulic control of rear axle DL and rear PTO, control system of rear
lift linkage with hydraulic lift your tractor can be optional equipped with mechanical control of
rear axle DL and rear PTO, with control system of RLL with draft control unit.
Also your tractor can be additional equipped with the following:
- instead of fan-heater an air-conditioner can be mouted;
- instead of double-lever GB control an single-lever GB control can be mounted;
- instead of speed increase unit an reverse gear unit can be mounted;
- instead of HLL outputs control with a help of levers optional can be mounted HLL
outputs control with joystick and lever;
- creeper installation is possible.
2.2 Switches of instrument board
1 – switch of front working lights, mounted on handgrips; 2 – emergency flashing
switch; 3 – multifunctional underwheel switch; 4 – starter and instruments switch; 5 – accumulator battery remote switch; 6 – windscreen washer switch; 7 – central light switch.
Figure 2.2.1 – Switches of instrument board
The starter and instruments switch 4 (see fig. 2.2.1) has four positions:
- «0» – off;
- «I» – instruments; pilot lamps unit, heating plugs are on;
- «II» – starter is on (non-fixed position);
- «III» – radio set is on.
21

The layout of positions of starter and instruments disconnect switch is given in fig.
2.2.2 and in informational plate of the switch.
952.5-0000010 OM
Figure 2.2.2 – Layout of positions of starter and instruments disconnect switch
ATTENTION: THE REPEATED SWITCH-ON OF THE STARTER IS POSSIBLE
ONLY AFTER RETURN OF THE KEY INTO POSITION “0” OF THE SWITCH. TO TURN
THE STARTER AND INSTRUMENTS SWITCH INTO POSITION “III” IT IS NECESSARY
TO PRESS IN THE KEY WHEN IN “0” POSITION AND TURN IT CONTRACLOCKWISE!
The multifunctional underwheel switch 3 (fig 2.2.1) provides for activation of turn
blinkers, switching between upper and lower beam of headlights, upper beam blinking, audible beep:
- as you move the lever of the underwheel switch 3 from or to yourself the right and
the left flashers are turned on accordingly. As the tractor has made a turn the lever automatically returns to the initial position.
- the audible beep is activated by pressing the lever in axial direction. The beep can be
activated in any position of the underwheel switch 3.
- as the road headlights are turned on (the button 7 is set to position “III”) and the
lever of the underwheel switch 3 is moved down, the upper beam gets activated, and as
the road headlights are on and the lever of the underwheel switch is moved up – the lower
beam gets activated.
- as you move the lever of the switch 3 from the lower beam position up against the
stop, the upper beam turns on for a short time (“upper beam blinking, non-fixed position) irrespective of irrespective of the position of the central light switch. As you release the lever it
will automatically return to the lower beam position.
Pressing the emergency flashing button 2 (fig. 2.2.1) activates the emergency flashing. A pilot lamp, built in the button, flashes simultaneously with the emergency flashing
lights. Repeated pressing the button 2 deactivates the emergency flashing.
The central light switch 7 (fig.2.2.1) has three positions:
- position “I” – “off” (the upper part of the button is pressed as in fig 2.2.1);
- position ”II” – “front and rear parking lights, license plate lights, lighting of instruments on
the dashboard and also parking lights on a trailed machine are on” (middle position);
- position “III” – “all consumers of “II” position and road headlights are on” (lower part of
the button is pressed against the stop as in fig. 2.2.1).
When pressing the button of front working lights switch 1 (fig. 2.2.1) two front working lights, located on light brackets, are actuated together with a light indicator, built in the
button.
Pressing the button 6 ((Figure 2.2.1) (non-fixed position) turns the windscreen
washer on. Releasing the button 6 turns the windscreen washer off.
Pressing the button (non-fixed position) of the accumulator battery remote disconnect switch 5 (fig. 2.2.1) the accumulator batteries are powered, the repeated pressing deactivates the accumulator batteries.
22
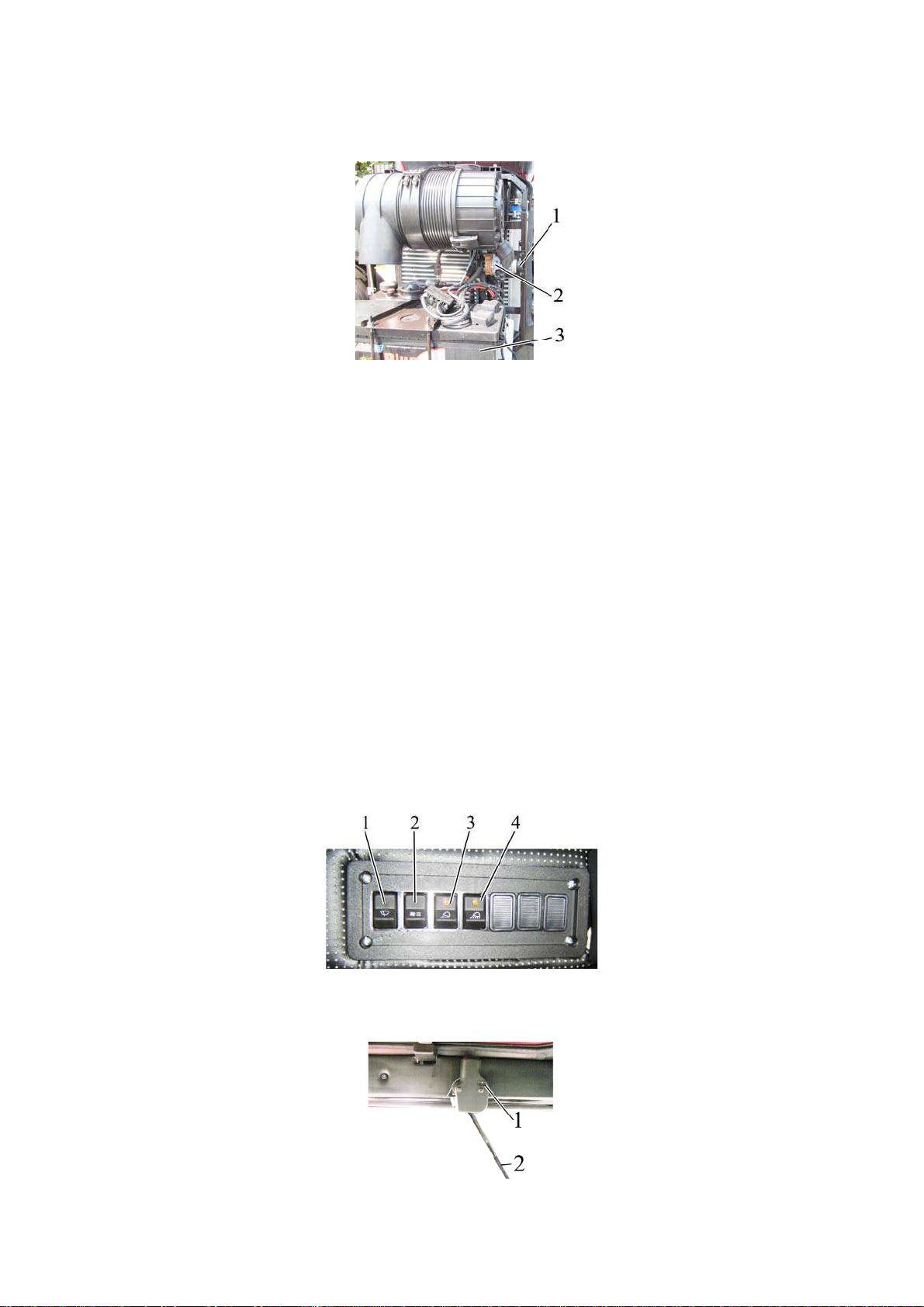
952.5-0000010 OM
It is possible to activate and deactivate the accumulator battery by means of the accumulator battery manual switch 2 (figure 2.2.3) located in the area of the accumulator battery installation. To activate and deactivate the accumulator battery it is necessary to press
the button 1.
1 – button; 2 – AB manual disconnect switch; 3 – accumulator battery.
Figure 2.2.3 – Installation of the accumulator battery manual disconnect switch
2.3 Upper shield unit of button switches and rear wiper switch
Pressing the switch button 1 ((Figure 2.3.1) turns on the windscreen wiper.
The switch has got three positions:
“Off”;
“On with low speed”;
“On with high speed”.
Pressing the switch button 2 (Figure 2.3.1) turns on air ventilation in the cab.
The switch has three positions:
“Off”;
“On in the mode of low feed of air”;
“On in the mode of large feed of air”.
More detailed information on controlling the heater fan is given below.
Pressing the switch button 3 (Figure 2.3.1) turns two rear working lights on as well
as the light indicator, built into the button.
Pressing the switch button 4 (Figure 2.3.1) turns two front working lights on the cab
roof on as well as the light indicator, built into the button.
1 – windscreen wiper switch; 2 – cab heater switch; 3 – rear working lights switch; 4 – switch of front
working lights on cab roof.
Figure 2.3.1 – Upper shield unit of button switches
The rear window wiper is turned on and off with a switch 1 (Figure 2.3.2).
1 – switch; 2 – rear window wiper arm.
Figure 2.3.2 – Activation and deactivation of rear window wiper
23
952.5-0000010 OM
2.4 Cab heater and fan control
Cab heater and fan controls are shown in Figure 2.4.1.
1 - heater valve handle; 2- cab heater hose; 3- T-piece; 4- clamp;
5-deflector; 6 - recirculating screen; 7- cab fan switch.
Figure 2.4.1 – Cab heater and fan controls
Cab heater and fan can operate in two modes: heating and ventilation.
In order to actuate heater and fan in heating mode it is necessary to perform the follow-
ing:
- after filling of cooling system start the engine and let it operate at medium rpm for
warming-up of water up to the temperature from + 500C to 700C, then open heater valve.
To do this turn the valve handle 1 (Fig. 2.4.1) counterclockwise up to the stop. Increase
engine rpm and in 1…2 minutes ensure that coolant is circulated through heating radiator.
The heating radiator should start warming-up. In course of this level of coolant in the engine cooling system should come down.
- refill coolant in the expansion chamber in half of the expansion chamber capacity.
- switch the heater fan on by means of switch 7 and direct the air flow by means of deflectors 5;
- the volume of air ventilated into the cab can be controlled by opening of recirculating
screens 6;
In order to drain coolant from heating system disconnect cab heater hoses 2 (are situated to the left and to the right of tractor cab) from T-pieces 3 by loosening the clamps 4
and drain cooling liquid into special reservoir. After coolant has been drained blow off the
system with compressed air. After blowing off connect cab heater hoses 2 with T-pieces 3
and tighten the clamps 4.
ATTENTION: WHEN HEATING AND VENTILATING SYSTEM IS OPERATED IN
HEATING MODE CAB VENTILATION IS PERFORMED SIMULTANEOUSLY. TO OPERATE
HEATING AND VENTILATING SYSTEM IN VENTILATING ONLY (DURING WARM SEASON) THE HEATER’S VALVE SHOULD BE CLOSED!
You tractor can be equipped with conditioning system instead of heating and ventilating
system. Guidelines on conditioner control are presented below.
24
2.5 Conditioner control
2.5.1 Conditioner control in conditioning mode
The conditioner control unit has switches 1 and 2 (figure 2.5.1).
952.5-0000010 OM
1 – Switch for air flow adjustment;
2 – Conditioner cut-out switch and cooling capacity adjustment;
Figure 2.5.1 Conditioner control unit
With the help of the switch 1 you can change air flow by changing fan speed. The
switch 2 allows to change temperature of cold and dry air coming out from deflectors 4
(fig. 2.1.1) in the conditioning mode.
ATTENTION: THE AIR CONDITIONER CAN BE SWITCHED ON AND OPERATE
ONLY WITH THE ENGINE ON!
To switch on the conditioner it is required to do the following:
- turn the cut-out switch 2 (figure 2.5.1) clockwise by 180° until a blue scale be-
gins;
- then turn the switch 1 to one of three marked positions (the fan rotor has three
kinds of rotation speed). After 3-5 minutes adjust a required temperature in the
cab with the switch 2;
- it is possible to adjust a mixture of outer air and recirculation air with recirculation
shutters 5 (figure 2.1.1) located on the upper panel;
To switch off the conditioner it is required to turn both switches 1 and 2 (figure 2.5.1)
counterclockwise into “0” position.
ATTENTION: MAKE SURE THE CONDITIONER IS SWITCHED OFF BEFORE
STOPPING THE ENGINE!
ATTENTION: WHEN THE CONDITIONER OPERATES IN THE COOLING MODE
MAKE SURE THAT THE HEATER CONTROL VALVE IS SHUT OFF IN ORDER TO
PREVENT THE SYSTEMS OF HEATING AND COOLING FROM SIMULTANEOUS
OPERATION!
2.5.2 Conditioner control in a heating mode
ATTENTION: REFILLING THE ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM SHALL BE CARRIED
OUT ONLY WITH LOW-FREEZING LIQUID SPECIFIED IN SUBSECTION "REFILLING
AND LUBRICATION OF A TRACTOR WITH LUBRICANTS”!
25

952.5-0000010 OM
To set the conditioner into the heating mode do the following:
- after refilling the cooling system with the cooling fluid start the engine and let the engine
run at medium idle without opening the heater control valve to reach 70-80°C of cooling
system temperature;
- then open the control valve with a handle 2 (figure 2.5.2), to do this turn the handle 2
counterclockwise against the stop;
- increase engine speed and let it run for one-two minutes until the heater radiator is filled
up with the fluid. Make sure the fluid circulates through the heater. The heater radiator
must warm up. Herewith the cooling fluid level in the cooling system radiator will decrease;
- refill the cooling fluid in expansion tank till the cooling fluid level in the expansion tank
reaches the half of the expansion tank;
- to warm up the cab quickly switch on the heater fan and open recirculation shutters;
ATTENTION: WHEN OPERATING IN THE HEATING MODE THE SWITCH 2 (FIGURE
2.5.1) SHALL BE COMPLETELY OFF TO PREVENT THE COOLING SYSTEM AND THE
HEATING SYSTEM FROM SIMULTANEOUS OPERATION!
1 – deflectors, 2 – handle of heater control valve
Figure 2.5.2 – Installation of heater control valve
Note – Rules of draining the cooling fluid from the air heating and conditioning system are
given in subsection 2.4 “Cab heater and fan control”.
2.5.3 Cab ventilation
During the conditioner operation in the cooling and heating modes the cab ventilation is executed simultaneously. To make the conditioner operate only in the ventilation
mode it is necessary to close the heater control valve, set the switch 2 (figure 2.5.1.) in position “0” and the switch 1 in any of three marked positions.
26
952.5-0000010 OM
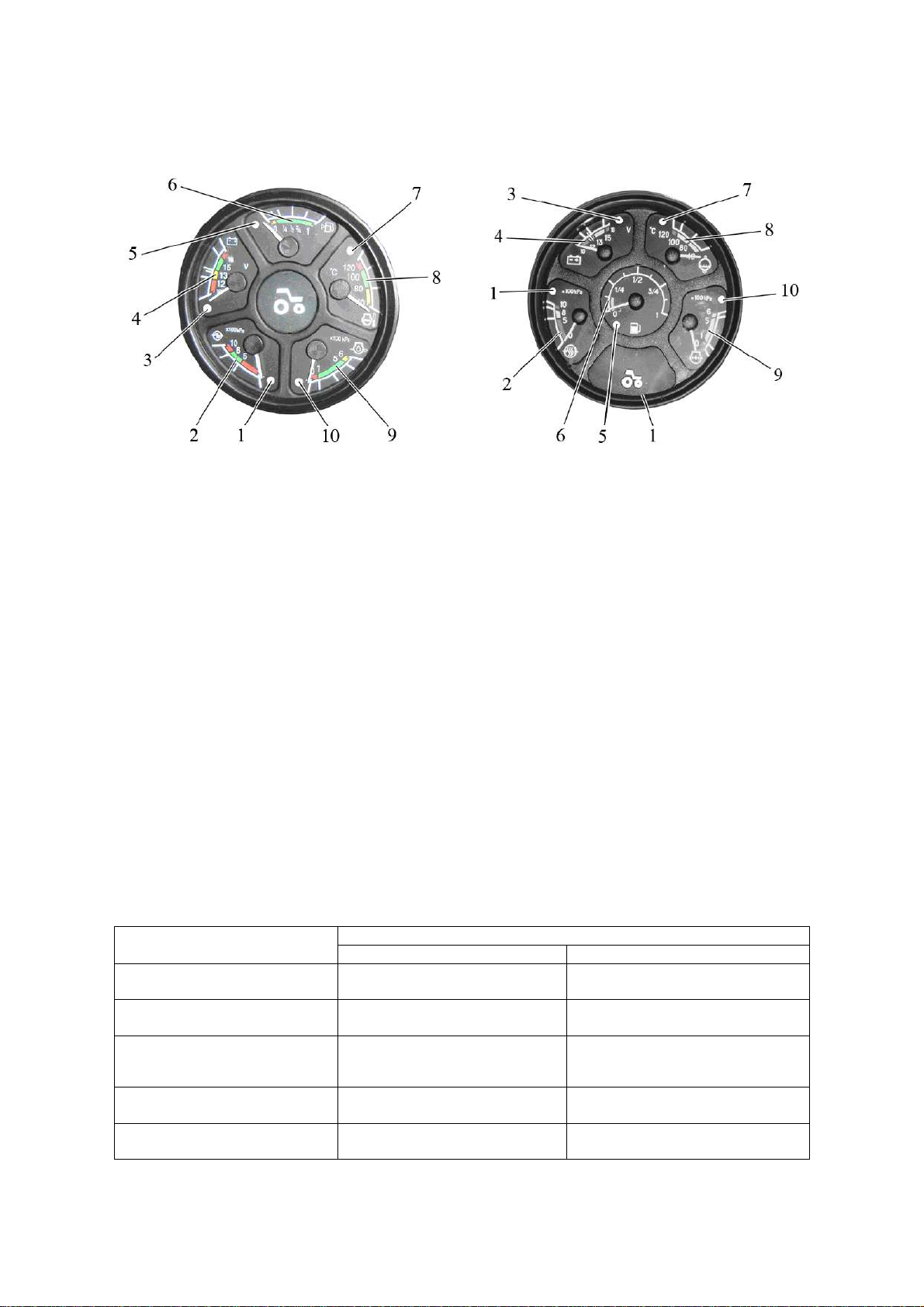
2.6 Instrument board
The instrument board 14 (figure 2.1.1) includes five gauges with five signal lamps
as shown in figure 2.6.1.
Variant 1 Variant 2
1 – signal lamp of emergency air pressure in the pneumatic system; 2 – gauge to
indicate air pressure in the pneumatic system; 3 – pilot lamp of additional accumulator battery (not used); 4 – voltage gauge; 5 – signal lamp of reserve fuel volume in the tank;
6 – gauge to indicate fuel volume in the tank; 7 – signal lamp of emergency temperature of
engine coolant; 8 – gauge to indicate temperature of engine coolant; 9 – gauge to indicate
oil pressure in the engine lubrication system; 10 – signal lamp of emergency oil pressure in
the engine lubrication system;
Figure 2.6.1 – Instrument board
2.6.1 The scale of the gauge of oil pressure in the pneumatic system 2 has three zones:
- working – from 500 to 800 kPa (green color);
- emergency (two) — from 0 to 500 kPa and from 800 to 1000 kPa (red color).
A signal lamp 1 (red color) is built in the gauge scale which lights up when the pressure in
the pneumatic system drops below 500 kPa.
2.6.2 The voltage gauge 4 (figure 2.6.1) indicates accumulator batteries voltage with the
engine stopped when the key of starter and instruments switch (figure 2.2.2) is set in position “I”. With the engine running the voltage gauge indicates voltage on generator terminals.
The states of the power supply system depending on the position of the
gauge pointer on the scale are given in table 2.1.
Table 2.1 – The states of the power supply system
States of power supply system Zone on the voltage gauge
scale 4 (figure 2.5.1), color
13,0 – 15,0 V
green
10,0 – 12,0 V
red
12,0 – 13,0 V
yellow
15,0 – 16,0 V
red
white line in the yellow zone -
with the engine running with the engine stopped
normal mode of charge –
the generator is out of order
No AB charge
(low charging voltage)
accumulator battery
discharged
AB has a normal charge
AB recharge –
Rated AB electromotive force
is 12,7 V
ATTENTION: IF THE VOLTAGE GAUGE INDICATES ABSENCE OF AB CHARGE,
CHECK THE STATE AND TENSION OF THE GENERATOR DRIVE BELT!
27
952.5-0000010 OM
2.6.3 The scale of the gauge indicating fuel volume in the tank 6 (figure 2.6.1) has the
divisions “0-1/4-1/2-3/4-1”. A signal lamp 5 (orange color) is built in the gauge scale, which
lights up when fuel volume in the tank drops below 1/8 of the total tank volume.
ATTENTION: DO NOT LET THE TANK BECOME EMPTY (THE GAUGE POINTER IS IN
THE ZONE OF ORANGE COLOR)!
2.6.4 The gauge scale of engine coolant temperature 8 has three zones:
- working – from 80 to 105 °С (green color);
- informational – from 40 to 80 °С (yellow color);
- emergency – from 105 to 120 °С (red color);
An emergency temperature lamp (red color) 7 is built in the scale, which operates in
two modes:
- lights up and operates in a flashing mode with coolant values from 109 up to and in-
cluding 112 °С.
- glows in a continuous mode with coolant temperature values from 113 °С and higher.
2.6.5 The oil pressure gauge scale in the engine lubricating system 9 has three zones:
- working – from 100 to 500 kPa (green color);
- emergency (two) – 0 to 100 kPa and from 500 to 600 kPa (red color).
A signal lamp of emergency oil pressure drop 10 (red color) is built in the gauge scale,
which lights up when the pressure drops below 100 kPa.
ATTENTION: WHEN THE COLD ENGINE IS STARTED THE PRESSURE CAN BE 600 kPa
and HIGHER!
ATTENTION: IF THE EMERGENCY PRESSURE LAMP IS ON WITH THE ENGINE RUNNING,
IMMEDIATELY STOP THE ENGINE AND ELIMINATE THE FAILURE!
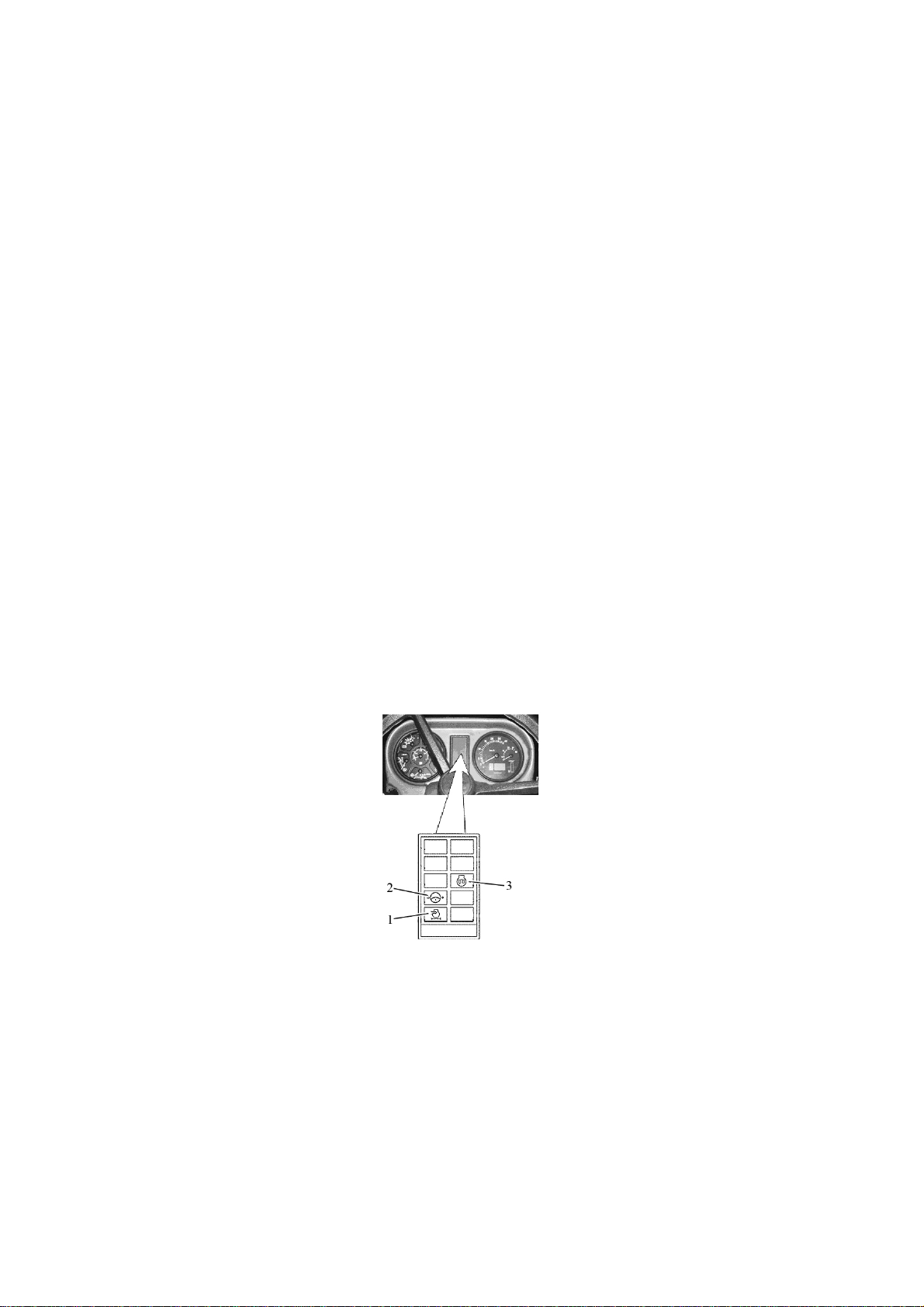
2.7 Pilot lamps unit
2.7.1 General information
The pilot lamps unit 15 (figure 2.1.1) includes three lamps. The allocation scheme is
presented in figure 2. 7.1.
1 – pilot lamp to indicate that the air cleaner filter is clogged to the max. (orange color);
2 – pilot lamp to indicate emergency oil pressure drop in the system of hydrostatic power
steering (red color); 3 – pilot lamp to indicate operation of heating plugs (orange color)
Figure 2.7.1 – Pilot lamps unit
The operating principle of the pilot lamps of CLU is the following:
- pilot lamp 1 to indicate that the air filter is clogged to the max. (figure 2.7.1) lights up
when the max. permissible level of filter dirtiness is exceeded and the filter requires cleaning;
- pilot lamp 2 to indicate emergency oil pressure drop in the system of hydrostatic
power steering lights up when the oil pressure in the system of hydrostatic power steering
drops below 0,08 MPa (periodic lighting up of the lamp 2 with engine minimal speed is assumed – when revolutions are increased the lamp 2 shall go out);
- pilot lamp to indicate operation of heating plugs 3 indicates heating plugs operation
(functioning algorithm of the pilot lamp indicating heating plugs operation is provided below).
28
952.5-0000010 OM
As a means of start facilitation heating plugs (HP) are used in tractors “BELARUS –
952.5”, they are mounted in the cylinder head. For individual control of heating plug opera-
tion modes, indication of their operation a heating plug control unit is used.
The heating plugs are activated, if the engine temperature exceeds +5°C. Hereby a
heating plug pilot lamp 3 (figure 2.7.1) lights up for 2 sec., or doesn’t light up at all.
If engine temperature is below +5°C, the heating plugs are activated automatically
as the key of starter and instrument switch is turned from position “0” (off) into position “I”
(Instruments on). Hereby the heating plug pilot lamp 3 lights up in the pilot lamp unit of the
dashboard. The heating plug operation time depends on engine temperature as per table
2.2. The engine is to be started as the lamp 3 goes out after the time, specified in table
2.2. After the engine start-up, the heating plugs remain on for some time, then they go out.
The heating plug operation time after the engine start-up depends on the engine temperature at the moment of the heating plug activation. (see table 2.2).
If during (10±1) sec. after the lamp 3 goes out the engine will not be started, heating plugs
become switched off.
The heating plug operation algorithm has the following emergency modes:
- as the key of starter and instrument switch is turned from position “0” (Off) into
position “I” (Instruments on) the heating plug pilot lamp starts to flash continuously with
2 Hz frequency. This means that there is a failure in the heating plug operation – all heating plugs are closed-circuit or their connection is disturbed (disconnected from the heating
plug control unit), the heating plug control unit is not powered or the power supply wire is
damaged. Herewith, in case of short circuit the heating plug control unit cuts power supply
(12V) to the heating plugs.
- after the engine start-up the heating plug pilot lamp 3 starts flashing for one minute
with 3 sec. of cycle duration and 0,25 sec. of flash duration. The number of flashes can be
different. The start-up procedure runs in an ordinary way. This means that one or mote
(but not all) heating plugs are faulty. The number of flashes within one cycle equals to the
number of faulty heating plugs;
If the specified trouble is not eliminated, it might be difficult to start the engine at low
temperature.
- during the pre-start heating before engine start-up the pilot lamp 3 flashes with
1 Hz frequency. This points at short-circuit of the heating plug temperature sensor,
or breakage in the heating plug temperature sensor circuit, or sensor failure. Time
of engine pre-start heating as well as plug heating after engine start-up is set forth
in the table 2.2
IT IS FORBIDDEN TO OPERATE THE TRACTOR UNTIL FAILURES OF THE
HEATING PLUG SYSTEM ARE FOUND OUT AND ELIMINATED, AS IT MAY LEAD TO
DISCHARGE OF ACCUMULATOR BATTERIES!
Table 2.2 – Heating plug operation time depending on engine temperature
2.7.2 Functioning algorithm of pilot lamp to indicate operation of heating plugs
Engine
temperature, °С
more than 5
from plus 5 to 0
from 0 to minus 10
from minus 10 to minus 15
from minus 15 to minus 20
from minus 20 to minus 25
more than minus 25
short circuit or sensor
breakout, sensor failure
Time of engine pre-start
heating, sec.
0 0
15 25
20 50
25 75
35 100
42 125
50 150
50 150
Time of heating after en-
gine start-up, sec.
29
952.5-0000010 OM
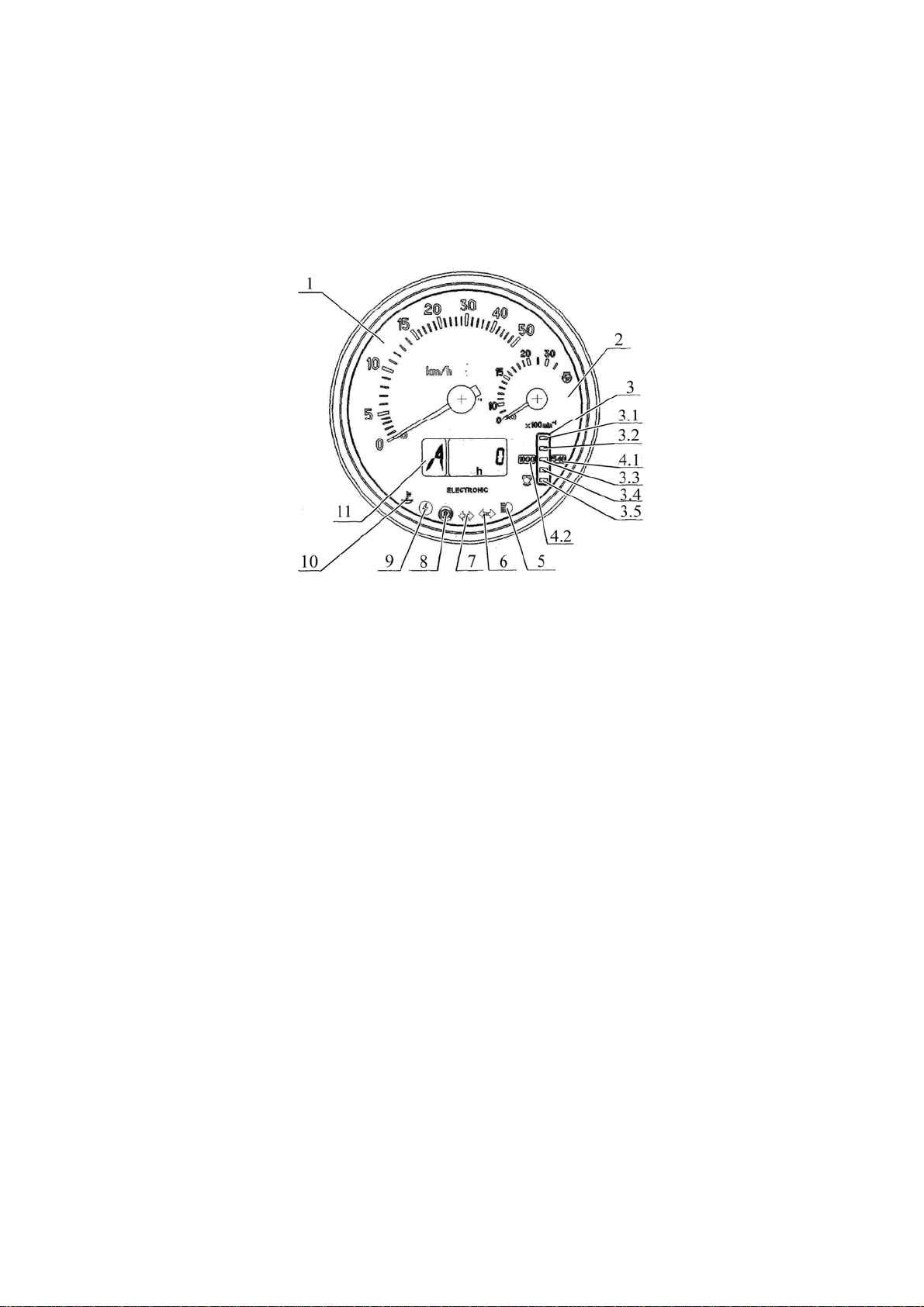
2.8 Integrated indicator
2.8.1 General information
The integrated indicator 16 (figure 2.1.1) (hereinafter II) and the integrated indicator control
panel 18 (figure 2.1.1) (hereinafter IICP) display information on operational parameters of
systems and units of the tractor and provide operator with data on violation of work or
breakdown of any system.
The II includes gauges and signal lamps as per figure 2.8.1.
1 – velocity gauge (needle indicator);
2 – engine speed gauge (needle indicator);
3 –PTO speed gauge (light indicator);
3.1, 3.5 – segments of PTO speed scale (yellow color);
3.2, 3.3, 3.4 – segments of PTO speed scale (green color);
4.1, 4.2– annunciator of PTO speed scale range (yellow color);
5 – pilot lamp to indicate headlights upper beam switching (blue color);
6 – pilot lamp to indicate switching of trailer turn blinkers (green color);
7 – pilot lamp to indicate switching of tractor turn blinkers (green color);
8 – pilot lamp to indicate parking brake engagement (red color);
9 – pilot lamp to indicate enhanced voltage in on-board system (red color);
10 – pilot lamp to indicate low level of coolant (yellow color);
11 – multifunction display.
Figure 2.8.1– Integrated indicator
2.8.2 Assignment and operation principle of integrated indicator gauges
а) Velocity gauge 1 (figure 2.8.1) indicates a design speed of the tractor on a needle indicator. The design speed exceeds the actual one, as tractor skidding is not taken into account.
The gauge is actuated by signals coming from pulse sensors of rotation frequency of
toothed gears of final drives of right and left rear wheels. The speed is indicated in accordance
with the signal from the sensor installed on the final drive gear of the wheel, turning with a less
speed.
In case one of the speed sensors is faulty the integrated indicator shows speed readings in accordance with the signal coming from the correct sensor. Specific faults of circuits or
speed sensors when the signals from them are missing are displayed in liquid crystal display
as “0” digit, characterizing the fault location – to the right or to the left (see below).
b) The engine speed gauge 2 (figure 2.8.1) indicates rotation frequency of the engine
crankshaft on a needle indicator.
Information on engine speed on tractor BELARUS-952.5 comes from the electronic
control unit. The range of speed readings is from 0 to 3500 (rpm).
30
 Loading...
Loading...