

CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1-1
The MS-6117 is a high-performance personal computer mainboard based on
the Pentium® II processor .
The mainboard uses the highly integrated Intel® 82440LX AGPset which
optimize the system bandwidth and concurrency with the implementation of
Quad Port Acceleration (QPA). QPA provides 4-port concurrent arbitration
of the processor bus, graphics, PCI bus and SDRAM.
The Intel® 82371AB chipset integrates all system control functions such as
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface). The ACPI provides
more Energy Saving Features for the OSPM(OS Direct Power Management)
function. The Intel® 82371AB chipset also improves the IDE transfer rate by
supporting Ultra DMA/33 IDE that transfers data at the rate of 33MB/s.
The mainboard also supports the LM78 System Hardware Monitor
Controller as optional function. The LM78 function includes: CPU /power
supply/chassis fan revolution detect, CPU/system voltage monitor, system
temperature monitor , and chassis intrusion detect(optional).
Chapter 1
INTRODUCTION

CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Mainboard Features
CPU
l Slot 1 for Pentium
®
II processor .
l Supports 200MHz, 233MHz, 266MHz, 300MHz, and 333MHz.
l Core/Bus ratios are x2, x2.5, x3, x3.5, x4, x4.5, x5, x5.5, x6 and higher.
Switching V oltage Regulator
l On-board switching mode DC-DC Step Down Regulator .
l Conforms to Intel
®
VRM ver 8.1 specifications.
l Over-Voltage and Over-Current protection.
Chip Set
l Intel
®
82440LX PCI Chipset.
Clock Generator
l 66.6MHz clocks are supported.
Main Memory
l Supports six memory banks using three 168-pin unbuffered DIMM
sockets.
l Supports a maximum memory size of 512MB with SDRAM, or 1GB with
EDO.
l Supports ECC(Error Check Correct) and EC(Multiple-Bit Error Correction)
function.
l Supports 3.3v Extended Data Output (EDO) and SDRAM DIMM.
Slots
l One AGP(Accelerated Graphics Port) slot.
- AGP specification compliant
- AGP 66/133MHz 3.3v device support
l Five 32-bit Master PCI Bus slots and two 16-bit ISA bus slots wherein
one shared slot that can be used as ISA or PCI.
l Supports 3.3v/5v PCI bus Interface.
1-2

CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1-3
On-Board IDE
l An IDE controller on the Intel
®
82371AB PCI Chipset provides IDE HDD/
CD-ROM with PIO, Bus Master and Ultra DMA/33 operation modes.
l Can connect up to four IDE devices.
On-Board Peripherals
l On-Board Peripherals include:
- 1 floppy port supports 2 FDD with 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M and
2.88Mbytes.
- 2 serial ports (COMA + COMB)
- 1 parallel port supports SPP/EPP/ECP mode
- 2 USB ports
- 1 IrDA connector for SIR.
BIOS
l The mainboard BIOS provides “Plug & Play” BIOS which detects the
peripheral devices and expansion cards of the board automatically .
l The mainboard provides a Desktop Management Interface(DMI) function
which records your mainboard specifications.
On-Board System Hardware Monitor(LM78)
l CPU/Power Supply/Chassis Fan Revolution Detect
l CPU Fan Control (the fan will automatically stop when the system enters
suspend mode)
l System Voltage Detect
l Chassis Intrusion Detect(reserved)
l Display Actual Current Voltage
RTC
l Non-Volatile R TC.
Keyboard Connector
l PS/2
®
keyboard interface and PS/2® mouse interface.

CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1-4
Dimension
l A TX Form Factor: 30.5cm(L) x 18.6cm(W) x 4 layers PCB.
l Double deck I/O connectors, compatible with Intel
®
Venus Mainboard.
Mounting
l 6 mounting holes.
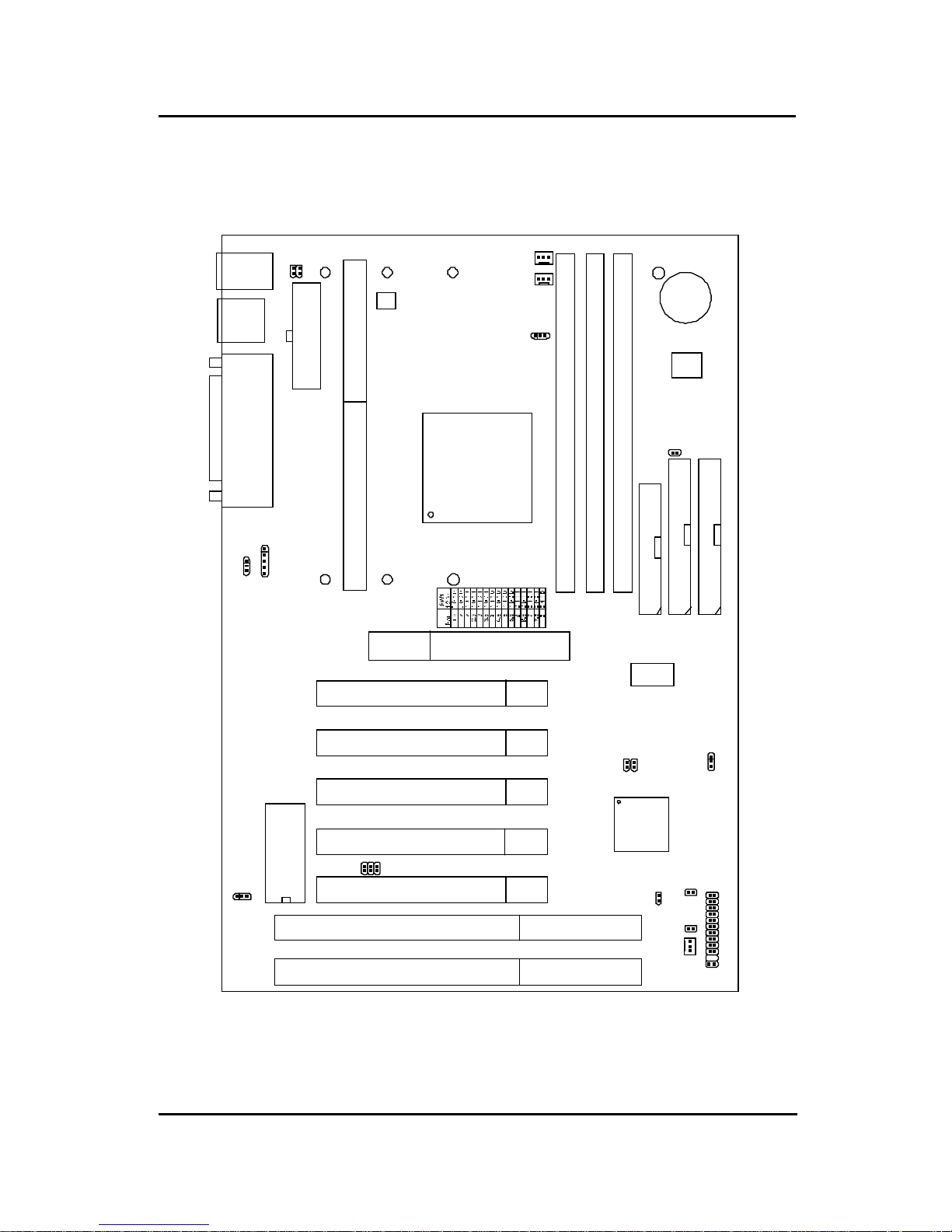
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 Mainboard Layout
MS-61 17
FDC
IDE2
IDE1
DIMM 3
DIMM 2
DIMM 1
Top: mouse
Bottom:
keyboard
Top: Port 1
USB
Bottom:
Port 2
Top: LPT
Bottom:
COM A
COM B
ATX
Power Supply
CFAN1
PSFAN1
LM78
(optional)
PCI SLOT 3
PCI SLOT 2
PCI SLOT 1
SLOT 1
AGP
PCI SLOT 5
PCI SLOT 4
JGS1
JGL1
ISA SLOT 1
ISA SLOT 2
BATT
+
LM75
(optional)
BIOS
JMODE1
SFAN1
IR1
JFAN
JSW2
SW1
Clock
Generator
J10 J9
JFP1
FW82371AB
JBAT1
Chassis Intrusion
Sensor (optional)
1-5
J7 J8
FW82443LX
J11
J1

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Chapter 2
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.1 Central Processing Unit: CPU
The mainboard operates with Intel® Pentium® II processor . The mainboard
uses a CPU Slot called Slot 1 for easy CPU installation and a DIP switch
(SW1) to set the proper speed for the CPU. The CPU should always have a
Heat Sink and a cooling fan attached to prevent overheating.
2-1

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.1-1 CPU Installation Procedures
2-2
A. OEM Pentium® II Processor Installation Procedures
There are two kinds of Pentium® II processor that is currently used: the
OEM version and the Boxed version. OEM Pentium® II Processor has no
Heat Sink, Fan and Heat Sink Support, while the Boxed Pentium® II
Processor is provided with Heat Sink w/ fan and Heat Sink Support.
Required Things:
Pentium® II processor - Processor .
*Retention Mechanism(RM) - Plastic Guide that holds the S.E.C. Catridge
in the Slot 1 connector .
*Retention Mechanism Attach Mount(RMAM) - Bolt/Bridge assemblies
inserted up through the bottom of the
motherboard. RM secures to RMAM ( 2
RMAM required per RM ).
*Heat Sink Support Base (HSSBASE) - Plastic support bar mounted to
the mainboard under the ATX heatsink.
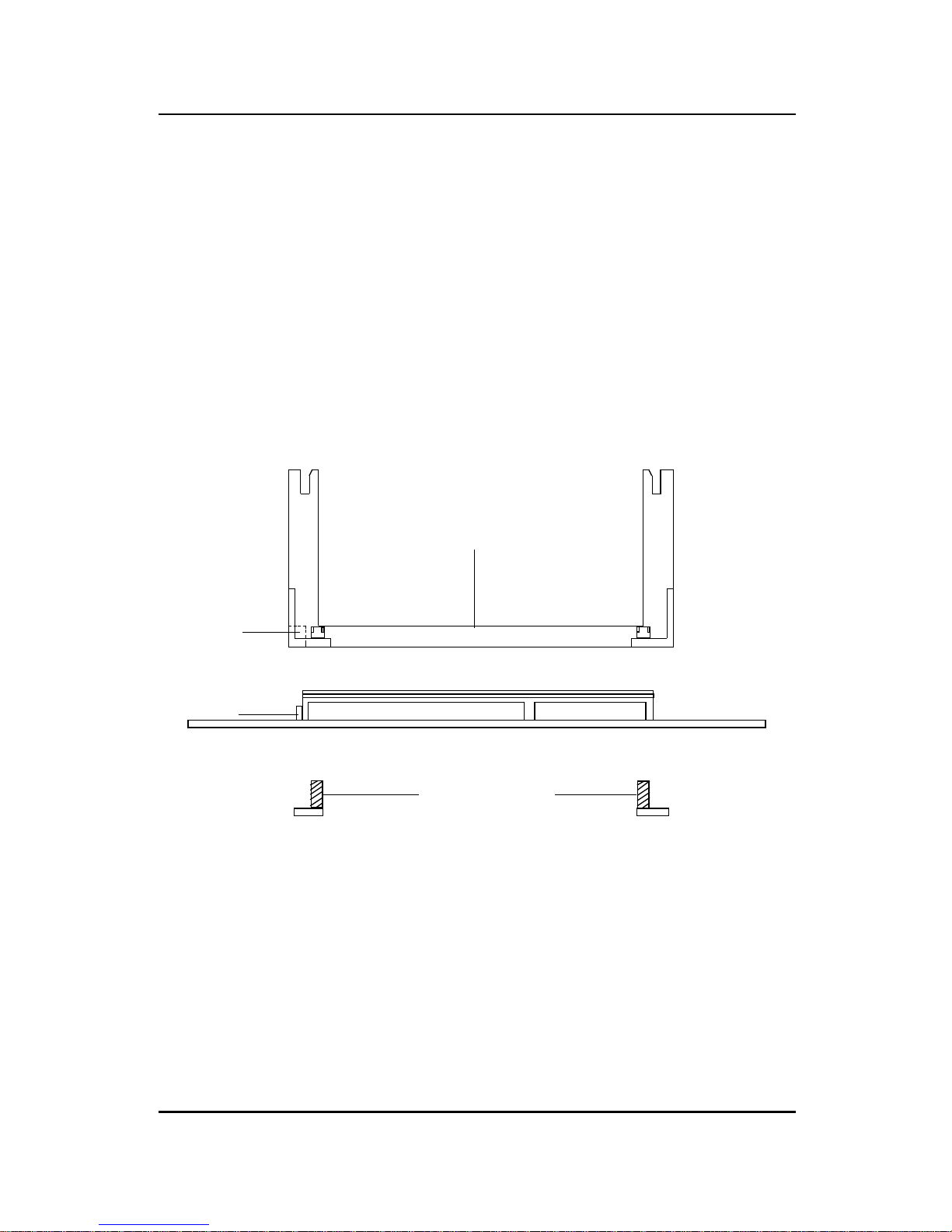
(One leg is always bigger than the other one)
Processor
Lock
Retention
Mechanism
Pentium
®
II
Processor
Heat Sink
W/Fan
Notch Hole
Heat Sink
Support Base
Heat Sink
Support Pin
Heat Sink
Support
Top Bar

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
*Heat Sink Support Pin (HSSPIN) - Plastic pins inserted through the
HSSBASE to secure it to the mainboard (2
required per Assembly).
*Heat Sink Support T op Bar (HSSTOP) - Plastic bar that clips onto the
HSSBASE through the fins on the ATX
heatsink.
**Heat Sink w/ fan - Heat Sink that can be attached to the Pentium® II
processor with metal clip.
Note: * Provided by MSI mainboard.
** Provided by Special request.
RM
HSSPIN
HSSTOP
HSSBASE
2-3
RMAM
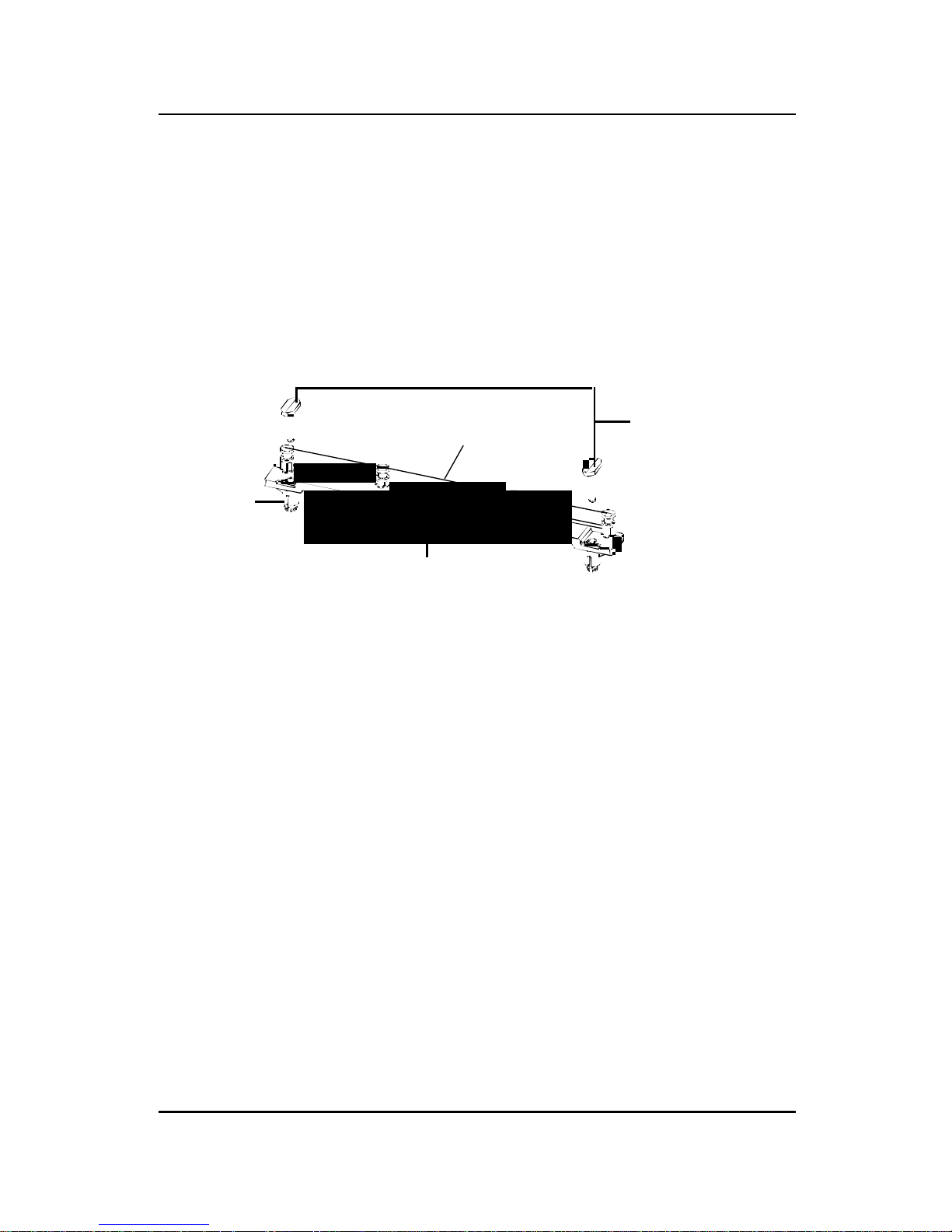
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-4
SLOT1
Retention
Mechanism
ê
ê
Key
êê
Retention
Mechanism
Attach Mount
Notch
Key
Step 1: Insert the Retention Mechanism Attach Mount at the bottom
of the mainboard.
Step 2: Install the Retention Mechanism.
Look for the key on Slot 1, and match it with the Notch Key on the
Retention Mechanism for proper direction. Then, attach the
Retention Mechanism to the Retention Mechanism Attach Mount.
Use a Screwdriver to secure the Retention Mechanism.
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Step 3: Install the Heat Sink Support Base.
Look for the T wo holes across Slot 1, and match it with the T wo legs
of the Heat Sink Support Base for the proper direction. T ake note
that one hole/leg is bigger than the other. The Four top pins of the
Heat Sink Support Base should also be oriented towards Slot 1.
Push the Heat Sink Support Base onto the mainboard, until you hear
a click sound. Check for a perfect fit.
Step 4: Install the Heat Sink Support Pin.
Push the Heat Sink Support Pins onto the two holes of the Heat Sink
Support Base. Check for a perfect fit. These pins are used to secure
the Heat Sink Support Base.
Heat Sink
Support Base
Heat Sink
Support Pin
Leg
pins
2-5
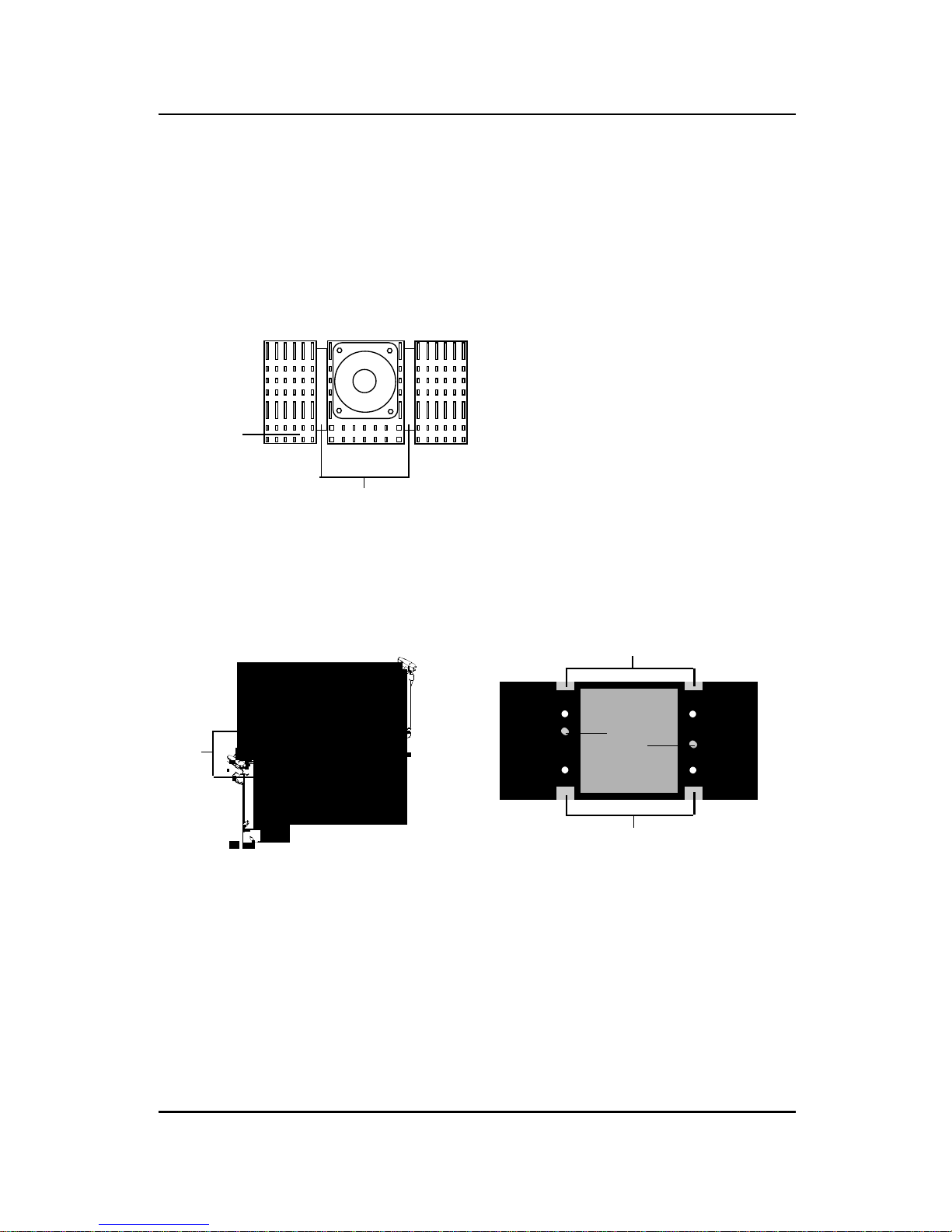
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
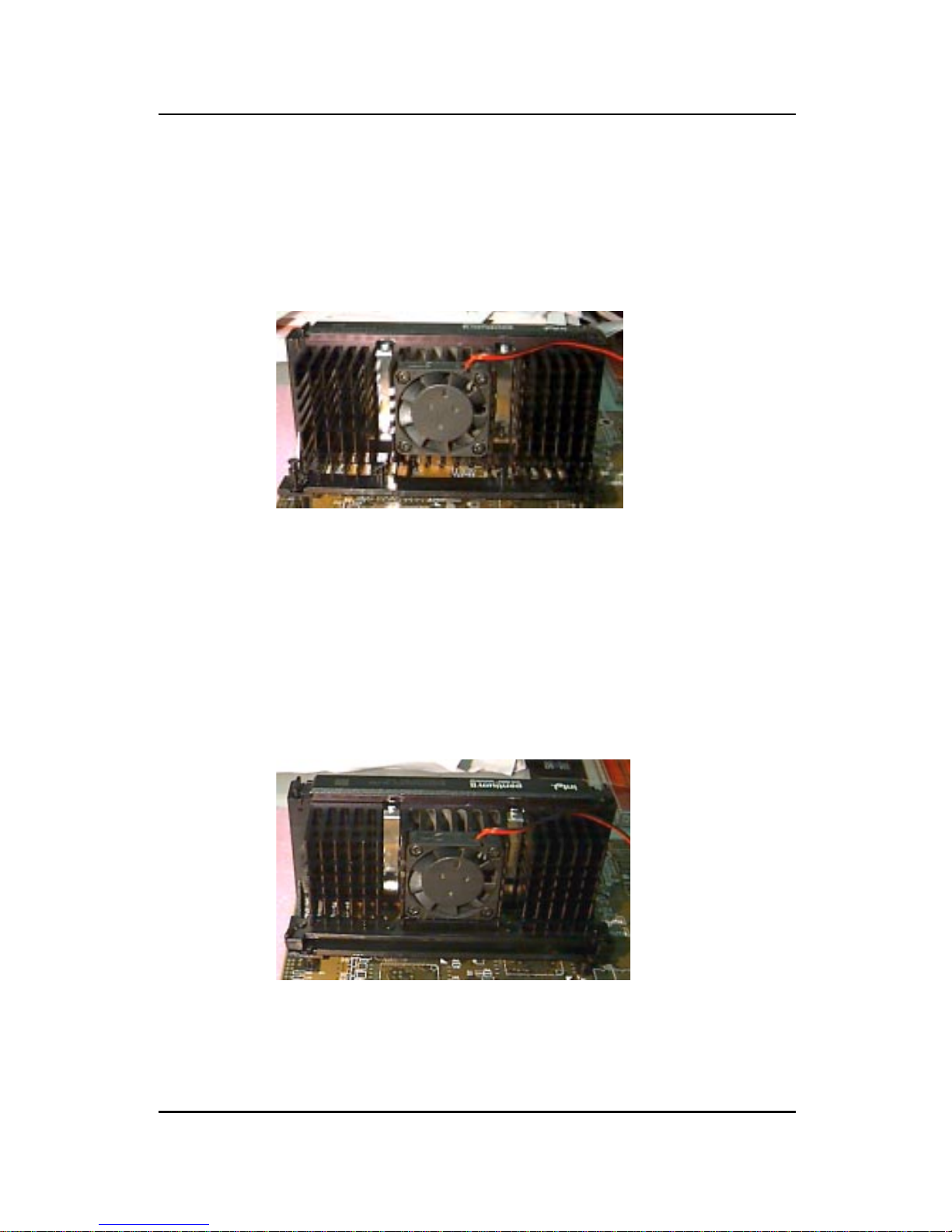
S. E.C. Car trid ge - Th erma l
P
Isometric View
Step 5: Install the Heat Sink with Fan to the Processor .
Push down the metal clips, so that they are in line with the back of
the Heat Sink. Be careful, so as not detach the metal clips from the
Heat Sink.
In case the metal clips are detached from the Heat Sink, re-attach
them. Look for the arrow on the metal clip. This arrow should be
pointing down and aligned with the Heat Sink Support Base Holder.
Attach the Heat Sink to the processor.
- Look at the back of the Heat Sink and take note of the 2 secure
posts. Insert these 2 Secure posts to the 2 secure holes on the
back of the processor.
- Align the ears of the metal clips with the clip holders on the back of
the processor. Use a screw driver to push the metal clips onto the
clip holders. Check for a perfect fit.
2-6
Pentium® II Processor (Back)
â
The arrow
should be
pointing
down.
Metal Clips
Heat Sink w/ Fan
Metal Clips Ear
Metal Clips Ear
Secure
Posts
Heat Sink w/ Fan(Back)
Heat Sink
Base Holder
Secure
holes
Clip Holder
Clip Holder
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-7
Step 6: Install the Processor .
Unlock the Processor by pushing in the Processor Locks.
Insert the Processor like inserting a PCI or an ISA card.
Step 7: Lock the Processor Locks.
Secure the CPU by pulling the Processor Locks out.
è
ç
ç
è

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-8
Step 8: Install the Heat Sink Support Top Bar .
Push the Heat Sink Support T op Bar to the Heat Sink Support Base,
Until you hear a “click” sound. Check for a perfect fit.
The installation is now complete.
Heatsink
Support Top
Bar
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
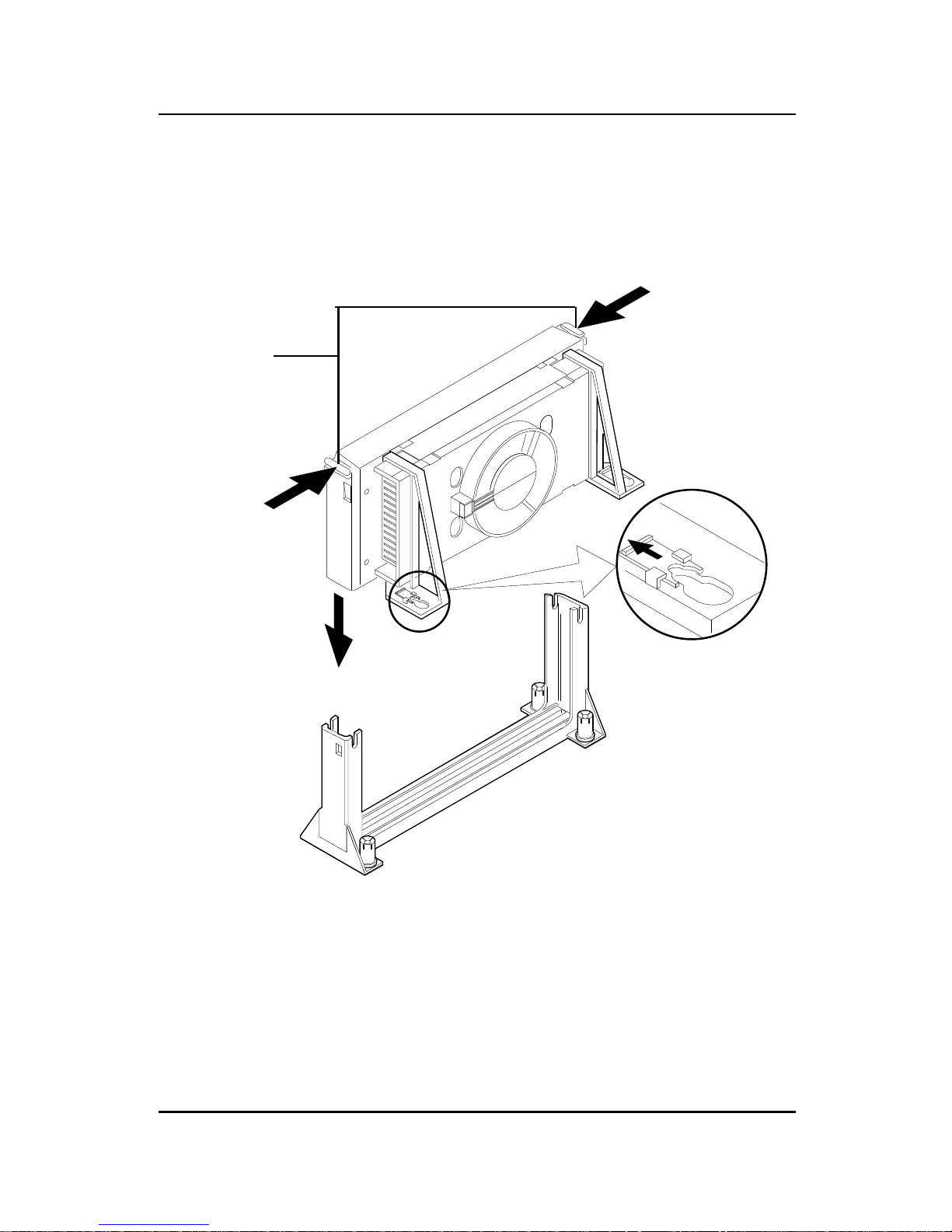
B. Boxed Pentium® II Processor Installation Procedures
The Boxed Pentium® II Processor has a built- in Fan and Heat Sink. It also
has a Heat Sink Support. So if you’re going to use a Boxed PentiumTM II
Processor , all you need is the Retention Mechanism.
2-9
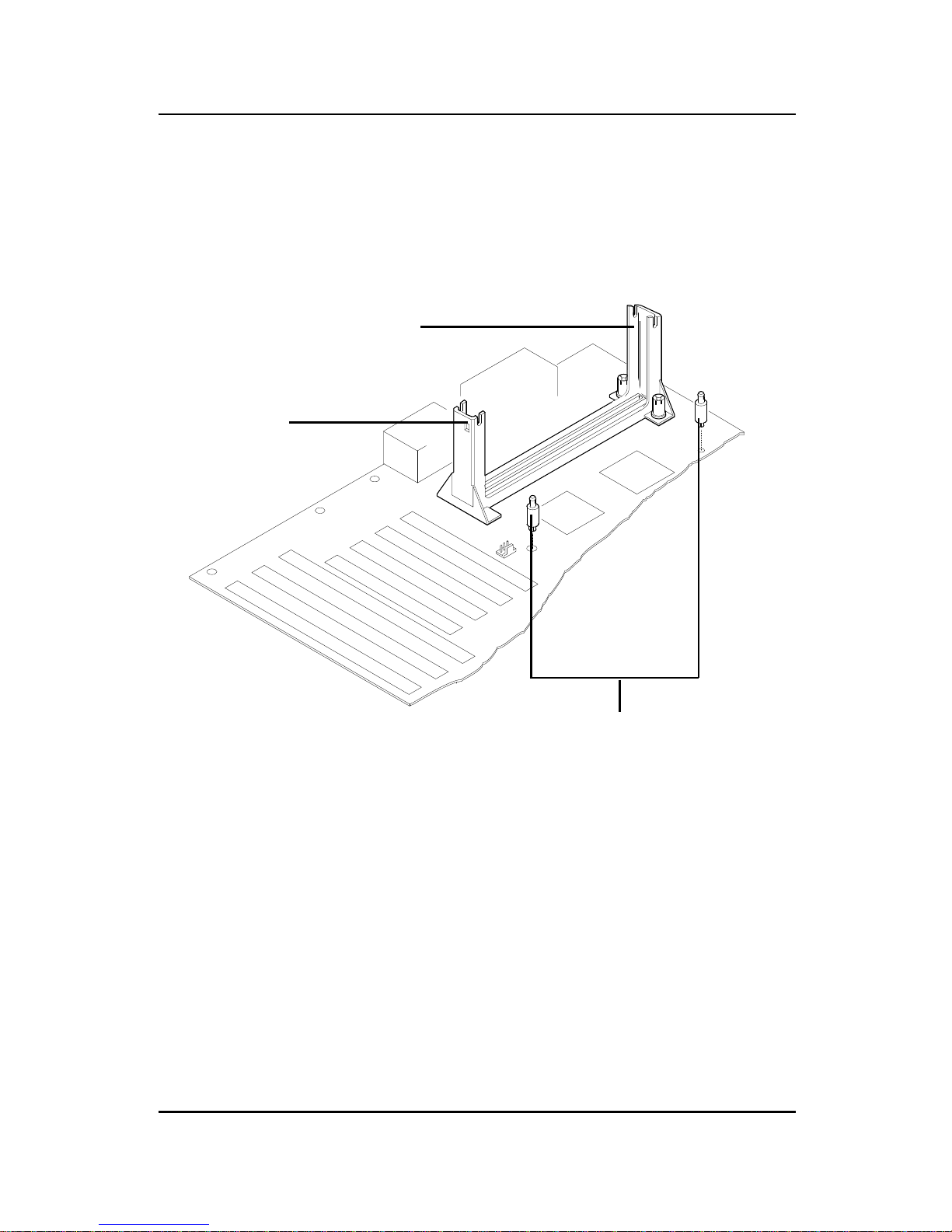
SLOT1
Retention
Mechanism
ê
ê
Key
êê
Retention
Mechanism
Attach Mount
Notch
Key
Step 1: Insert the Retention Mechanism Attach Mount at the bottom
of the mainboard.
Step 2: Install the Retention Mechanism.
Look for the key on Slot 1, and match it with the Notch Key on the
Retention Mechanism for proper direction. Then, attach the
Retention Mechanism to the Retention Mechanism Attach Mount.
Use a Screwdriver to secure the Retention Mechanism.
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
Step 3: Install the Heat Sink Support Base.
Look for the 2 holes across Slot 1, and match it with the 2 Heat Sink
Support Base. Take note that one hole/base is bigger than the other.
Push the Heat Sink Support Base onto the mainboard, until you hear
a click sound. Check for a perfect fit.
2-10
PC-3742
Retention
Mechanism
Notch
Hole
Heat Sink
Support Base
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
PC-3743
Heat Sink
Support Lock
Intel
®
Boxed
Pentium® II
Processor
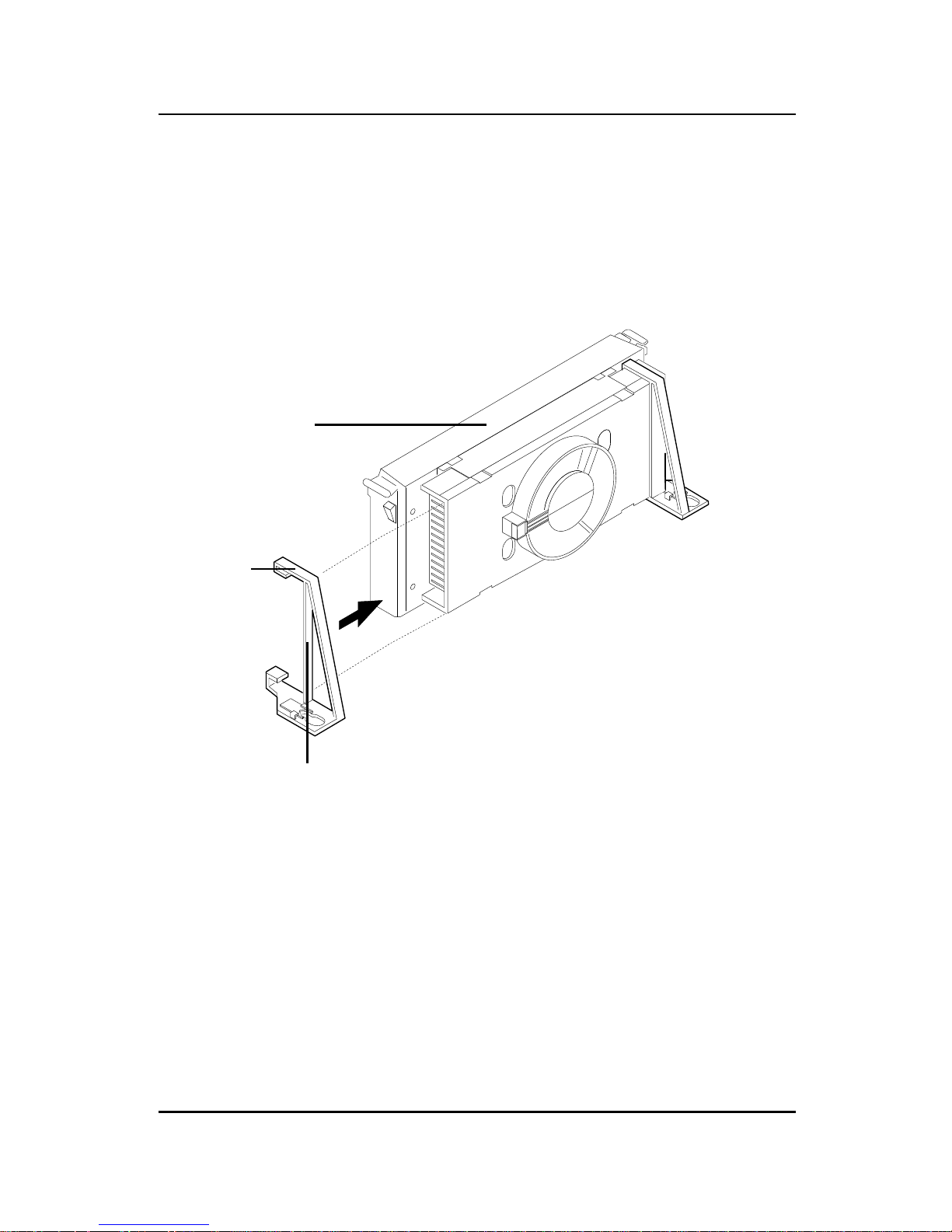
Step 4: Install the Heat Sink Support.
Attach the 2 Heat Sink Supports to the sides of the Processor. These
Heat Sink Supports will fit in any direction, so be sure that the Heat
Sink Support Locks are oriented outwards for the proper direction.
2-11
Heat Sink
Support
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
PC-3744
Processor
Lock
Heatsink
Support
Lock
2-12
Step 5: Unlock the Processor Locks and Heat Sink Support Locks.
Push in the Processor Locks. Open the Heat Sink Support Locks.
Step 6: Insert the Processor like inserting a PCI or an ISA card.
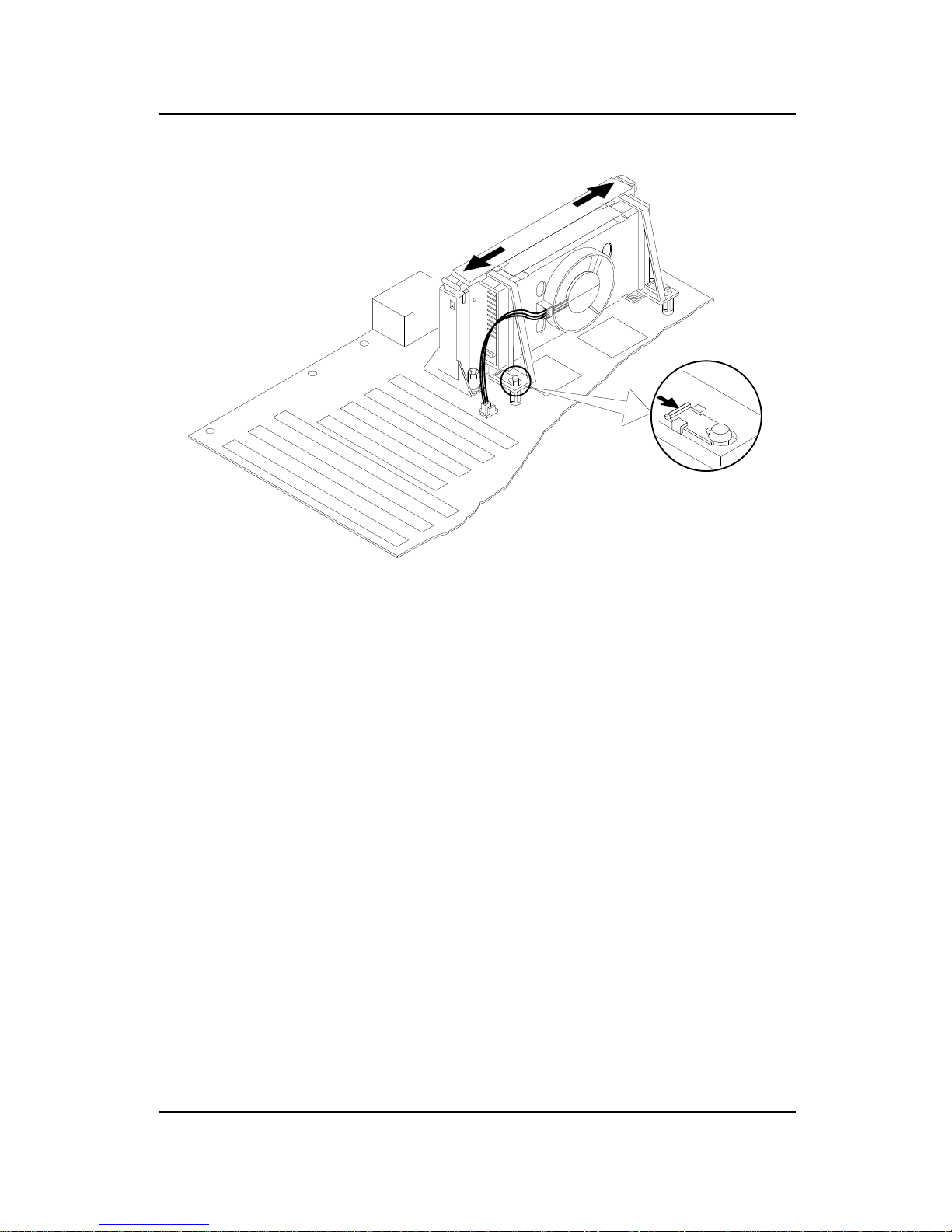
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
PC-3745
2-13
Step 7: Lock the Processor Locks and Heat Sink Support Locks
Secure the CPU by pushing out the Processor Locks. Close the Heat
Sink Support Locks.
The installation is now complete.
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.1-2 CPU Speed Setting: SW1
To adjust the speed of the CPU, you must know the specification of your
CPU (always ask the vendor for CPU specification). Then look at Table 2.1
(200 ~ 333MHz Pentium® II processor ) for proper setting.
2-14
Table 2.1 200 ~ 333MHz Intel® Pentium® II processor
233MHz
266MHz
300MHz
333MHz
200MHz
CPU
Type
SW1
1 1 0 1
1 0 0 1
1 1 1 0
1 0 1 0
1 1 0 0
1 = ON
0 = OFF

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-15
2.1-3 CPU Clock Generator Setting: J10/J9
These jumper is used to set the CPU Clock.
J10 J9
CPU Clock J10 J9
66 MHz
68 MHz
75 MHz
Note: 68/75 MHz CPU clock are both
reserved function.
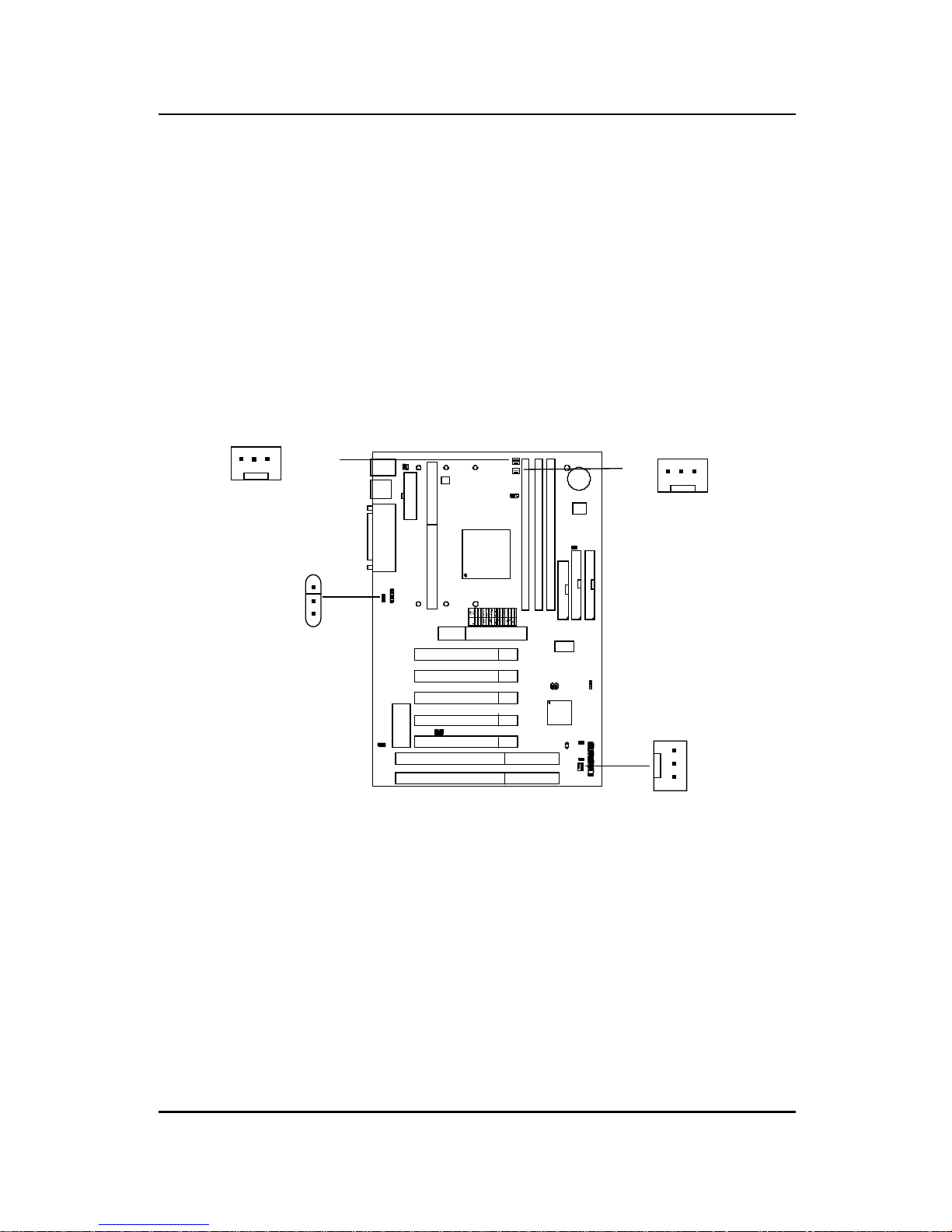
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
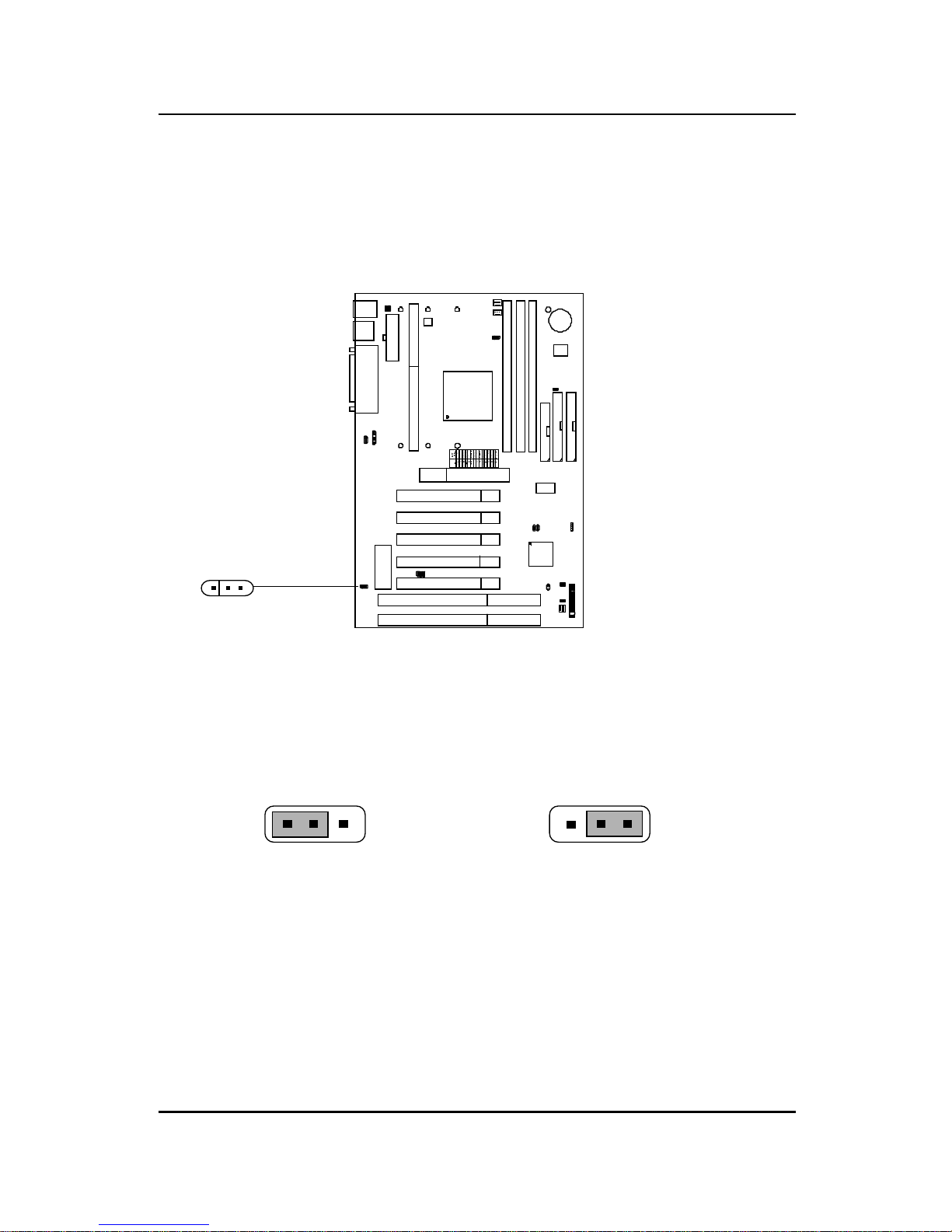
2.1-4 CPU Fan Power Connectors: JFAN/CFAN1/SFAN1/
PSFAN1
These connectors support system cooling fan with +12V. It supports three
pin head connector. When connecting the wire to the connector, always
take note that the red wire is the positive and should be connected to the
+12V, the black wire is Ground and should be connected to GND. If your
mainboard has LM78 chipset on-board, you must use a specially designed
fan with speed sensor to take advantage of LM78’ s CPU fan control.
2-16
SENSOR
+12V
GND
SF AN1
CFAN1
PSFAN1
Note: 1. CFAN1/SFAN1/PSF AN1 are the CPU, Power and Chassis
Cooling Fan Speed Connector (reserved for LM78 System Hardware
Monitor Option.)
2. Always consult vendor for proper CPU cooling fan.
For fans with fan speed sensor , every rotation of the fan will send out 2
pulses. LM78 will count and report the fan rotation speed.
SENSOR
+12V
GND
SENSOR
+12V
GND
PSFAN1 : Power Supply Fan
CFAN1 : CPU Fan
SFAN1 : System(Chassis) Fan
JFA N
+12V
GND
GND
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-17
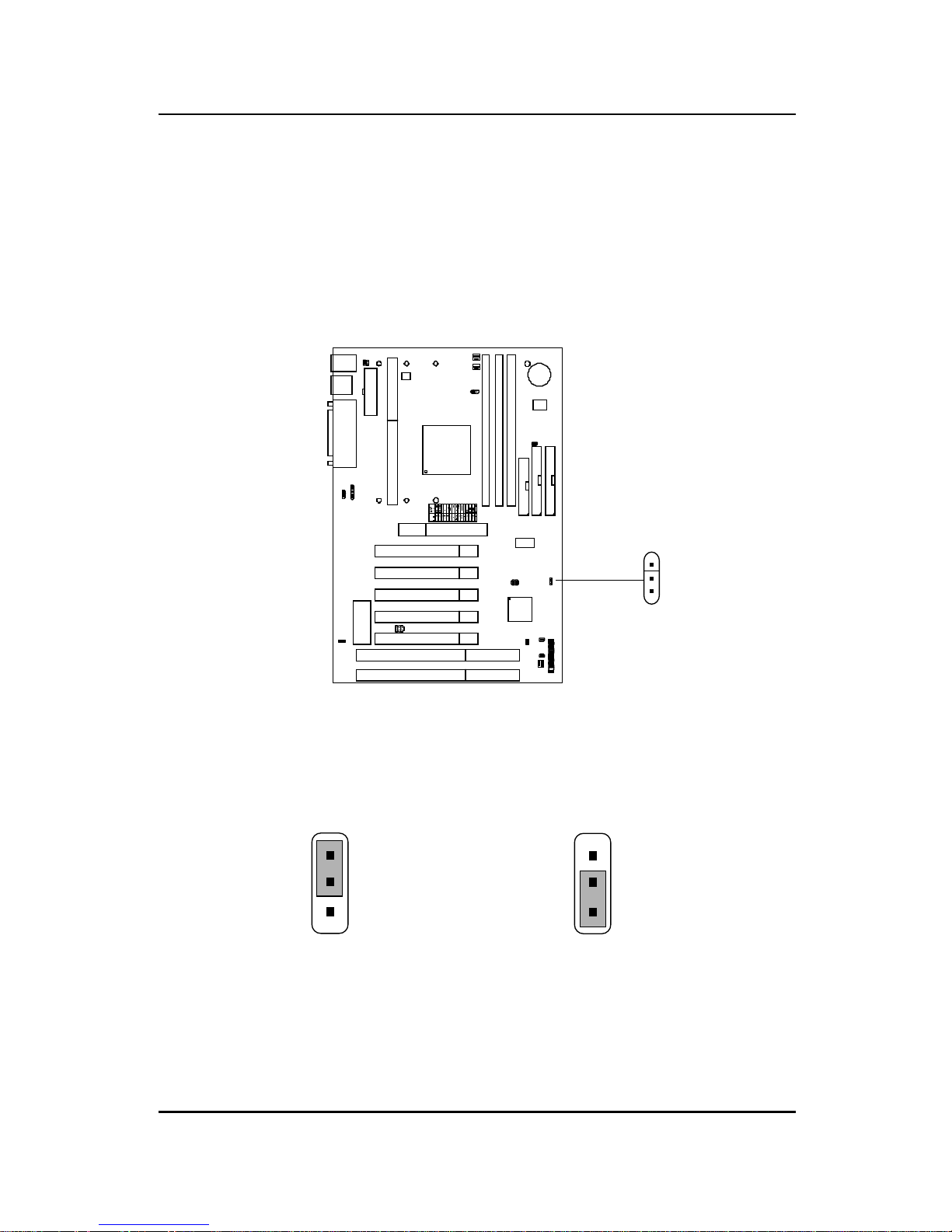
2.2 Flash ROM Programming Voltage: JMODE1
This jumper is for setting the V oltage of the Flash ROM BIOS.
Voltage Setting
JMODE1
3
JMODE1
+12V
(default)
13
1
JMODE1
+12V PWD VC C
Note: Short 1-2 pin, if you’re using Intel® or flash memory and you want to
flash the ROM data.
13
+12V PWD VCC
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-18
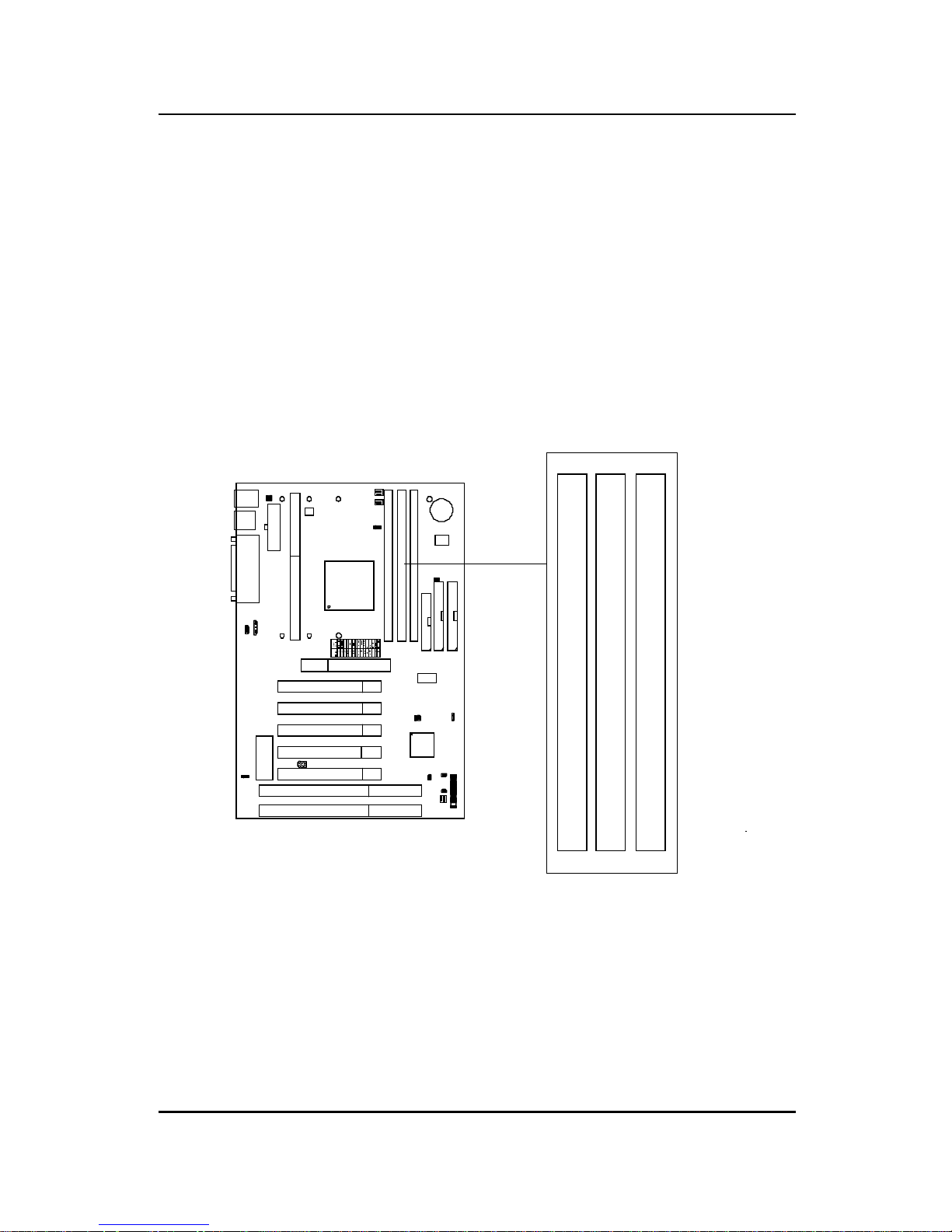
2.3 External Battery Connector: JBAT1
A battery must be used to retain the mainboard configuration in CMOS
RAM. If you use the on-board battery , you must short 1-2 pins of JBAT1
to keep the CMOS data.
Keep Data
Clear Data
1
1
3
3
Note: You can clear CMOS by shorting 2-3 pin, while the system is off.
Then, return to 1-2 pin position. Avoid clearing the CMOS while
the system is on; it will damage the mainboard.
JBA T1
1
3
2
2
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
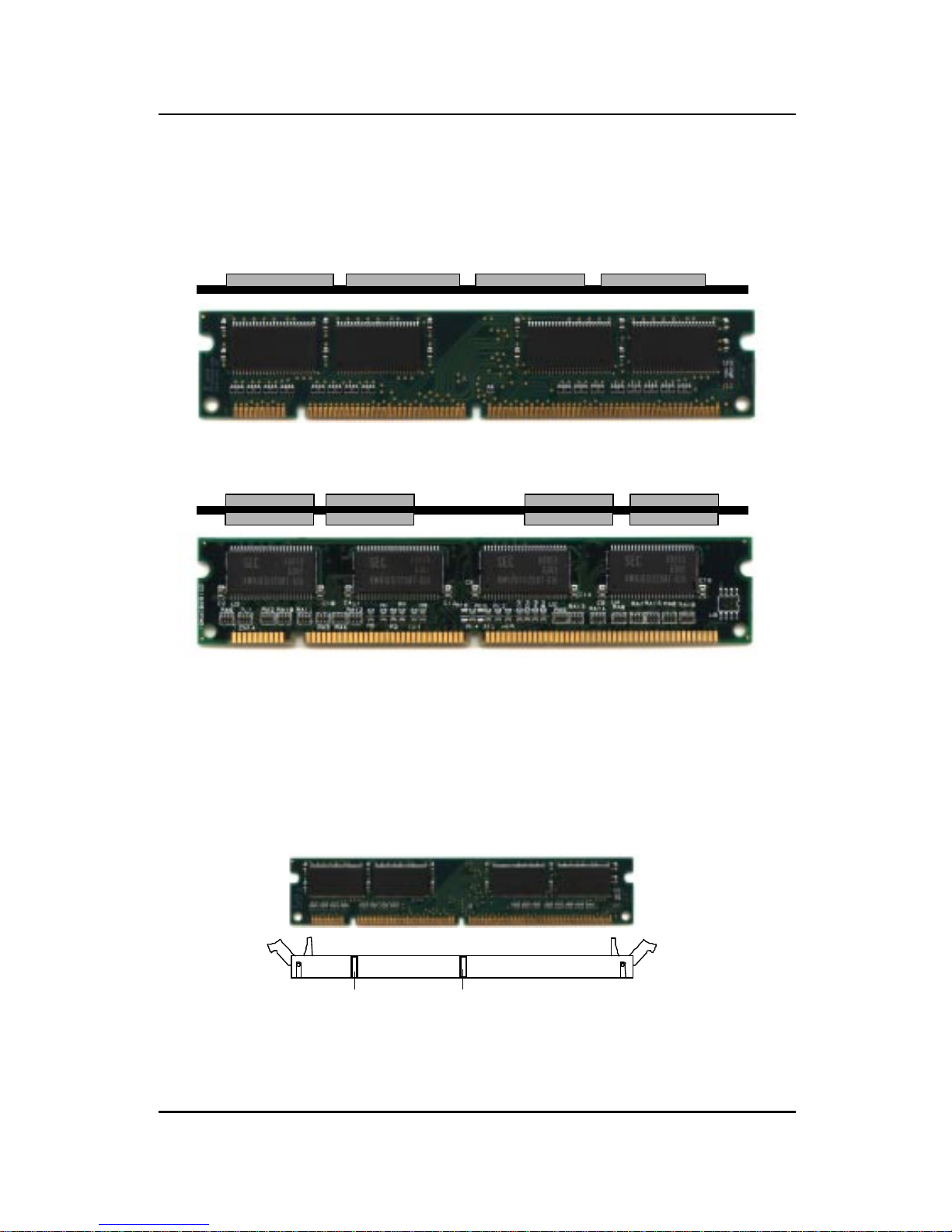
2.4 Memory Installation
2.4-1 Memory Bank Configuration
The mainboard supports a maximum of 1 GB of memory for EDO and 512MB
for SDRAM: It provides three 168-pin unbuffered DIMMs (Double In-Line
Memory Module) sockets. It supports 8 MB to 256 Mbytes DIMM memory
module. The memory module can be either SDRAM or EDO (Extended Data
Output) Mode DRAM. A DIMM consists of two Banks and may have a
maximum of 256 MB of memory .
DIMM1(Bank0 + Bank1)
DIMM2(Bank2 + Bank3)
DIMM3(Bank4 + Bank5)
2-19
Note: FP(Fast Page) & BEDO(Burst EDO) are not supported.
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-20
A. How to install a DIMM Module
1. The DIMM slot has a two Notch Key “VOLT and DRAM”, so the
DIMM memory module can only fit in one direction.
2. Insert the DIMM memory module vertically into the DIMM slot.
Then push it in.
3. Close the plastic clip at the side of the DIMM slot.
Single Sided DIMM
Double Sided DIMM
Note: Y ou can only use a 3.3 volt DIMM module (EDO or SDRAM).
VOLTDRAM
2.4-2 Memory Installation Procedures

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
1. Supports EDO and SDRAM.
2. Supports unbuffered DIMM.
3 . To operate properly , at least one 168-pin DIMM module must be
installed.
4. This mainboard supports Table Free memory, so memory can be installed
on DIMM1, DIMM2, or DIMM 3 in any order.
5. Supports 3.3 volt DIMM.
6. The DRAM addressing and the size supported by the mainboard is
shown next page.
2.4-1 Memory Population Rules
2-21

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
4M 1Mx4 SYMM 10 10 4MBx8 8MBx16
16 M 1Mx16 SYMM 10 10 4MBx2 8MBx4
1Mx16 ASYM 12 8 4MBx2 8MBx4
2M x 8 ASYM 11 1 0 8MBx4 16MBx8
2M x 8 ASYM 12 9 8MBx4 16MBx8
4Mx4 SYMM 11 11 16MBx8 32MBx16
4M x 4 ASYM 12 1 0 16MBx8 32MBx16
64 M 2Mx32 ASYM 11 10 8MBx1 16MBx2
2Mx32 ASYM 12 9 8MBx1 16MBx2
2Mx32 ASYM 13 8 8MBx1 16MBx2
4Mx16 SYMM 11 11 16MBx2 32MBx4
4Mx16 ASYM 12 10 16MBx2 32MBx4
8M x 8 ASYM 12 1 1 32MBx4 64MBx8
16Mx4 SYMM 12 12 64MBx8128MBx16
16 M 1Mx16 ASYM 11 8 8MBx4 16MBx8
2M x 8 ASYM 11 9 16MBx8 32MBx16
4M x 4 ASYM 11 1 0 32MB 64MB
64 M 2Mx32 ASYM 11 9 32MBx2 64MBx4
2Mx32 ASYM 12 8 16MBx2 32MBx4
4Mx16 ASYM 11 10 32MB 64MB
4Mx16 ASYM 13 8 32MB 64MB
8M x 8 ASYM 13 9 64MB 128MB
16Mx4 ASYM 13 10 128MB 256MB
64 M 2Mx32 ASYM 11 8
4Mx16 ASYM 12 8
8M x 8 ASYM 12 9
16Mx4 ASYM 12 10
DRAM
Tech.
DRAM
Density &
Width
DRAM
Addressing
Address Size
MB/SIMM
Row
Column
Single
Side(S)
Double
Side(D)
DRAM
Tech.
DRAM
Density &
Width
DRAM
Addressing
Address Size
MB/DIMM
Row
Column
Single
Side(S)
Double
Side(D)
T able 2.4-1 EDO DRAM Memory Addressing
no.
pcs.
no.
pcs.
no.
pcs.
no.
pcs.
Table 2.4-2 SDRAM Memory Addressing
2-22

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-23
2.5 Case Connector: JFP1
The Turbo LED, Reset Switch, Key Lock, Power LED, Speaker and HDD
LED are all connected to the JFP1 connector block.
JFP1
Keylock
Power
LED
+
T urbo
LED
+
Reset
Switch
Speaker
HDD LED
+

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-24
2.5-1 Turbo LED
The Turbo LED is always ON. You can connect the Turbo LED from the
system case to this pin.
2.5-2 Reset Switch
Reset switch is used to reboot the system rather than turning the power ON/
OFF . A void rebooting while the HDD LED is lit. You can connect the Reset
switch from the system case to this pin.
2.5-3 Keylock
Keylock allows you to disable the keyboard for security purposes. Y ou can
connect the keylock to this pin.
2.5-4 Power LED
The Power LED is always lit while the system power is on. Y ou can connect
the Power LED from the system case to this pin.
2.5-5 Speaker
Speaker from the system case is connected to this pin.
2.5-6 HDD LED
HDD LED shows the activity of a hard disk drive. A void turning the power
off while the HDD led is lit. Y ou can connect the HDD LED from the system
case to this pin.

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-25
2.6 Floppy Disk Connector: FDC
The mainboard also provides a standard floppy disk connector FDC that
supports 360K, 720K, 1.2M, 1.44M and 2.88M floppy disk types. This
connector support the provided floppy drive ribbon cables.
FDC
1

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-26
2.7 Hard Disk Connectors: IDE1 & IDE2
The mainboard has a 32-bit Enhanced PCI IDE Controller that provides PIO
mode 0~4, Bus Master , and Ultra DMA/33 function. It has two HDD
connectors IDE1 (primary) and IDE2 (secondary). You can connect up to
four hard disk drives, CD-ROM, 120MB Floppy (reserved for future BIOS)
and other devices to IDE1 and IDE2. These connectors support the
provided IDE hard disk cable.
IDE1(Primary IDE Connector)
The first hard drive should always be connected to IDE1. IDE1 can
connect a Master and a Slave drive. You must configure second hard
drive to Slave mode by setting the jumper accordingly .
IDE2(Secondary IDE Connector)
IDE2 can also connect a Master and a Slave drive.
Primary IDE Connector
Secondary IDE Connector
1
1

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-27
2.8 Power Supply
2.8-1 ATX 20-pin Power Connector: JPWR1
This connector supports the power button on-board. Using the ATX power
supply , functions such as Modem Ring Wake-Up and Soft Power Off are
supported by this mainboard. This power connector supports instant power
on function which means that system will boot up instantly when the power
connector is inserted on the board.
ATX
Power Connector
11
20
10
1
PIN SIGNAL
11 3.3V
12 -12V
1 3 GND
1 4 PS_ON
1 5 GND
1 6 GND
1 7 GND
18 -5V
19 5V
20 5V
PIN SIGNAL
1 3.3V
2 3.3V
3 GND
45V
5 GND
65V
7 GND
8 PW_OK
9 5V_SB
10 12V
PIN DEFINITION
W arning: Since the mainboard has the instant power on function, make sure
that all components are installed properly before inserting the power
connector to ensure that no damage will be done.

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.8-2 Remote Power On/Off Switches: JSW1/JSW2
Connect to a 2-pin push button switch. During OFF state, press once and
the system turns on. During ON stage, push once and the system goes to
sleep mode: pushing it more than 4 seconds will change its status from ON
to OFF. If you want to change the setup, you could go to the BIOS Power
Management Setup. This is only used for ATX type power supply.
2-28
JSW2
JSW1
Note: The two switches are provided by the mainboard for your
convenience, so you can use any of them. The two switches have
the same feature.

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-29
2.9 IrDA Infrared Module Connector: IR1
The mainboard provides one 5-pin infrared (IR) connector for IR modules.
This connector is for optional wireless transmitting and receiving infrared
module. You must configure the setting through the BIOS setup to use the
IR function. FIR and Consumer IR are reserved functions.
VCC
NC
IRRX
GND
IRTX
1
IR1

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.10 Serial Port Connectors: COM A & COM B
The mainboard has two 9-pin male DIN connectors for serial ports COM A
and COM B. These two ports are 16550A high speed communication ports
that send/receive 16 bytes FIFOs. You can attach a mouse or a modem cable
directly into these connectors.
2-30
PIN SIGNAL
1 DCD(Data Carry Detect)
2 SIN(Serial In or Receive Data)
3 SOUT(Serial Out or Transmit Data)
4 DTR(Data Terminal Ready)
5 GND
6 DSR(Data Set Ready)
7 RTS(Request T o Send)
8 CTS(Clear To Send)
9 RI(Ring Indicate)
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
COM A
COM B
PIN DEFINITION

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.11 Parallel Port Connector: LPT
The mainboard provides a 25 pin female centronic connector for LPT . A
parallel port is a standard printer port that also supports Enhanced Parallel
Port(EPP) and Extended capabilities Parallel Port(ECP). See connector and
pin definition below:
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
1 STROBE 14 AUTO FEED#
2 DA TA0 15 ERR#
3 DA TA1 16 INIT#
4 DA T A2 17 SLIN#
5 DA TA3 18 GND
6 DA TA4 19 GND
7 DA TA5 20 GND
8 DA TA6 21 GND
9 DA TA7 22 GND
10 ACK# 23 G ND
11 BUSY 2 4 GN D
12 PE 25 GND
13 SELECT
PIN DEFINITION
2-31
13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14
LPT

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.12 Mouse Connector: JKBMS1
The mainboard provides a standard PS/2® mouse mini DIN connector for
attaching a PS/2® mouse. You can plug a PS/2® mouse directly into this
connector . The connector location and pin definition are shown below:
2-32
PS/2 Mouse (6-pin Female)
2.13 Keyboard Connector: JKBMS1
The mainboard provides a standard PS/2® keyboard mini DIN connector for
attaching a keyboard. You can plug a keyboard cable directly to this
connector.
PS/2 Keyboard (6-pin Female)
Pin1
Mouse DATA
Pin6
NC
Pin2
NC
Pin4
VCC
Pin3
GND
Pin5
Mouse Clock
Pin1
KBD DATA
Pin6
NC
Pin2
NC
Pin3
GND
Pin5
KBD Clock
Pin4
VCC

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.14 USB Connector: USB
The mainboard provides a UHCI(Universal Host Controller Interface)
Universal Serial Bus root for attaching USB devices like: keyboard, mouse
and other USB devices. You can plug the USB device directly to this
connector .
USB Port 1
USB Port 2
2-33
1 2 3 4
PIN SIGNAL
1VCC
2 -Data0
3 GND
4 +Data0

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.15 Power Saving Switch Connector: JGS
Attach a power saving switch to JGS. When the switch is pressed, the
system immediately goes into suspend mode. Press any key and the system
wakes up.
JGS1
2-34

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2.16 Power Saving LED Connector: JGL1
JGL1 can be connected with LED. This will lit while the system is in suspend
mode.
JGL1
2-35

CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-36
2.17 Keyboard Power: J7, J8
The J7 and J8 jumpers are for setting keyboard power .
J7 J8
J7 J8
Power Setting
5V
(default)
J7 J8
5V_Standby

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Chapter 3
AMI® BIOS USER GUIDE
The system configuration information and chipset register information is
stored in the CMOS RAM. This information is retained by a battery when
the power is off. Enter the BIOS setup (if needed) to modify this information.
The following pages will describe how to enter BIOS setup, and all about
options.
3-1

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
2 . When the “Hit <DEL>” message appears, press <DEL> key to
enter the BIOS setup screen.
3 . After pressing <DEL> key, the BIOS setup screen will appear .
AMIBIOS (C) 1996 American Megatrends Inc.
AGIOMS VXXX XXXXXX
Hit <DEL> if you want to run setup
(C) American Megatrends Inc.
61-XXXX-001169-00111111-071592-i82440FX-H
3.1 Enter BIOS Setup
Enter the AMI® setup Program’s Main Menu as follows:
1. Turn on or reboot the system. The following screen appears with
a series of diagnostic check.
Note: If you don’t want to modify CMOS original setting, then don’t press any
key during the system boot.
3-2

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Standard CMOS Setup
Advanced CMOS Setup
Advanced Chipset Setup
Power Management Setup
PCI/Plug and Play Setup
Peripheral Setup
Hardware Monitor Setup
Auto-Detect Hard Disks
Change User Password
Change Supervisor Password
Change Language Setting
Auto Configuration with Optimal Settings
Auto Configuration with Fail Safe Settings
Save Settings and Exit
Exit without Saving
4 . Use the <Up> and <Down> key to move the highlight scroll up or
down.
5 . Use the <ENTER> key to select the option.
6. T o exit, press <ESC>. To save and exit, press <F10>.
7. Section 3.2 to 3.7 will explain the option in more details.
AMIBIOS HIFLEX SETUP UTILITIES - VERSION 1.07
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
Standard CMOS setup for changing time, hard disk type, etc.
3-3

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
2 . Use <Up> and <Down> to choose the item and <PgUp> and
<PgDn> keys to modify the highlighted item.
3 . After you have finished with the Standard CMOS Setup, press
<ESC> to go back to the main menu.
3.2 Standard CMOS Setup
1. Press <ENTER> on “Standard CMOS Setup” of the main menu
screen .
AMIBIOS SETUP - STANDARD CMOS SETUP
(C)1996 American Megatrends,Inc.All Rights Reserved
Date (mm/dd/yyyy): Mon Jul 28, 1997
Time (hh/mm/ss): 17:09:25
Floppy Drive A: 1.44 MB 3 1/2
Floppy Drive B: Not Installed
LBA Blk PIO 32Bit
Type Size Cyln Head WPcom Sec Mode Mode Mode Mode
Pri Master : Auto ON ON AUTO ON
Pri Slave : Auto ON ON AUTO ON
Sec Master : Auto ON ON AUTO ON
Sec Slave : Auto ON ON AUTO ON
Boot Sector Virus Protection Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color
Month : Jan-Dec
Da y : 01-31
Year : 1901-2099
3-4

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
2 . Use <Up> and <Down> to choose the item and <PgUp> and
<PgDn> keys to modify the highlighted item.
3. After you have finished with the Advanced CMOS Setup, press
<ESC> to go back to the main menu.
AMIBIOS SETUP - ADVANCED CMOS SETUP
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
Quick Boot Enabled
Ist Boot Device Floppy
2nd Boot Device IDE 0
3rd Boot Device CD-ROM
Try Other Boot Devices Ye s
Initial Display Mode BIOS
Display Mode At ADD-ON ROM Init Force BIOS
Floppy Access Control Read-Write
Hard Disk Access Control Read-Write
BootUp Num-Lock On
Floppy Drive Swap Disabled
Floppy Drive Seek Disabled
PS/2 Mouse Support Enabled
Primary Display Abset
Password Check Setup
Parity Check Disabled
Boot to OS/2 64M No
System BIOS Cacheable Enabled
C000, 16k Shadow Cached
C400, 16k Shadow Cached
C800, 16k Shadow Disabled
CC00, 16k Shadow Disabled
D000, 16k Shadow Disabled
D400, 16k Shadow Disabled
D800, 16k Shadow Disabled
DC00, 16k Shadow Disabled
Available Options:
Enabled
Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color
3.3 Advanced CMOS Setup
1 . Press <ENTER> on “Advanced CMOS Setup” of the main menu
3-5

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Description of the item on screen follows:
Quick Boot
Set this option to Enabled to permit AMI® BIOS to boot within 5
seconds. This option replaces the old ABOVE 1 MB Memory Test option.
The Optimal default setting is Enabled. The Fail-Safe default setting is
Disabled.
1st Boot Device/2nd Boot Device/3rd Boot Device
This option sets the sequence of boot drives.
The settings are:
IDE0 The system will boot from the first HDD.
IDE1 The system will boot from the Second HDD.
IDE2 The system will boot from the Third HDD.
IDE3 The system will boot from the Fourth HDD.
F(optical) The system will boot from LS-120(120M Floppy).
SCSI The system will boot from the SCSI.
Netw ork The system will boot from the Network drive.
CD-ROM The system will boot from the CD-ROM.
Disable Disable this sequence.
Try other Boot Devices
This option sets the device boot, if all the Four Boot Devices failed.
Floppy Access Control
This option sets the Floppy to Read-only or Read-W rite.
HDD Access Control
This option sets the HDD to Read-only or Read-W rite. During
Read-only , if you try to write on the HDD, the system will halt.
3-6

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Boot up Num Lock
When this option is set to Off, AMI® BIOS turns off the Num Lock
key when the system is powered on. The end user can then use the arrow
keys on both the numeric keypad and the keyboard. The settings are On or
Off. The optimal default and Fail-Safe default settings are On.
Floppy Drive Swap
Set this option to Enabled to specify that floppy drives A: and B:
are swapped. The setting are Enabled and Disabled. The Optimal and FailSafe default settings are Disabled.
Floppy Drive Seek
When this option is set to Enabled, AMI® BIOS performs a Seek
command on floppy drive A: before booting the system. The settings are
Enabled and Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are
Disabled.
PS/2® Mouse Support
When this option is set to Enabled, AMI® BIOS supports a PS/2
®
mouse. The settings are Enabled and Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Enabled.
Primary Display
This option configures the primary display subsytem in the
computer . The settings are Mono(monochrome), 40CGA, 80CGA or VGA/
EGA. The optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are VGA/EGA.
Password Check
This option specifies the type of AMI® BIOS password protection
that is implemented. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Setup.
3-7

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Parity Check
Set this option to Enabled to use the Parity Check function. The
DIMM module need to have parity bit for this function to work.
Boot to OS/2
®
Set this option to Enabled to permit the BIOS to run properly, if
OS/2® is to be used with > 64MB of DRAM. The settings are Enabled or
Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-safe default settings are Disabled.
Internal Cache/External Cache
This option selects the type of caching algorithm used by AMI
®
BIOS and the CPU for L1 cache memory(internal/external to the CPU). The
settings are W riteback - a writeback algorithm is used, Write-through - a
write-through algorithm is used or Disabled - AMI® BIOS does not specify
the type of caching algorithm. The algorithm is set by the CPU. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are W riteback.
System BIOS Cacheable
AMI® BIOS always copies the system BIOS from ROM to RAM for
faster execution. Set this option to Enabled to permit the contents of the
F0000h RAM memory segment to be written to and read from cache memory .
The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The Optimal default setting is Enabled. The Fail-Safe default setting is Disabled.
C000, 16K Shadow/C400, 16k Shadow
These options specify how the contents of the video ROM are
handled. The settings are:
Disabled - the Video ROM is not copied to RAM.
Cached -the contents of the video ROM from C0000h -
C7FFFh are not only copied from ROM to RAM; it
can also be written to or read from cache memory .
Shadow - the Contents of the video ROM from C0000h -
C7FFFh are copied(shadowed) from ROM to RAM for
faster execution.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default setting is Cached.
3-8

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
C800, 16k Shadow/CC00, 16k Shadow/D000, 16K Shadow/
D400, 16k Shadow/D800, 16k Shadow/DC00, 16K Shadow
These options specify how the contents of the adaptor ROM
named in the option title are handled. The ROM area that is not used by ISA
adapter cards will be allocated to PCI adapter cards. The settings are;
Disabled - The specified ROM is not copied to RAM.
Cache - The contents of the ROM area are not only copied
from ROM to RAM for faster execution, it can also be
written to or read from cache memory .
Shadow - The contents of the ROM area are copied from ROM
to RAM for faster execution.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
3-9

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
3.4 Advanced Chipset Setup
1 . Press <ENTER> on “Advanced Chipset Setup” of the main menu
screen.
AMIBIOS SETUP - ADVANCED CHIPSET SETUP
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
Auto Configure EDO DRAM Timing Enabled
EDO DRAM Speed (ns) 60
EDO Read Burst Timing x222
EDO Write Burst Timing x222
EDO RAS Precharge Timing 3 clocks
EDO RAS to CAS Delay 3 clocks
MA wait State Slow
***** SDRAM Timing *****
SDRAM RAS to CAS Delay 2 Clks
SDRAM CAS Latency 3 Clks
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time 2 Clks
DRAM Integrity Mode Non ECC
VGA Frame Buffer USWC Disabled
PCI Frame Buffer USWC Disabled
Fixed Memory Hole Disabled
CPU To PCI IDE Posting Enabled
USWC Write I/O Post Disabled
AGP Aperture Size 64 MB
USB Passive Release Enabled
PIIX4 Passive Release Enabled
PIIX4 Delayed Transaction Enabled
USB Function Enabled
USB Keyboard Legacy Support Disabled
Available Options:
Enabled
Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color
3-10
2 . Use <Up> and <Down> to choose the item and <PgUp> and
<PgDn> keys to modify the highlighted item.
3. After you have finished with the Advanced Chipset Setup, press
<ESC> to go back to the main menu.

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Description of the item on screen follows:
Auto Configure EDO DRAM Timing
Choose Enabled(default) will automatically configure the DRAM
timing depending on the “DRAM Speed” selection. Choose disable to
customize setup.
EDO DRAM Speed (ns)
This option specifies the RAS access time (in nanoseconds) for the
DRAM used in the computer . The settings are 50,60 or 70. The Optimal
default setting is 60 and the Fail-Safe default setting is 70.
EDO DRAM Read Burst Timing
Choose DRAM read burst timing for the customize setup.
B stand for BEDO DRAM, E stand for EDO DRAM and F stand for FAST
P AGE DRAM.
EDO DRAM Write Burst Timing
Choose DRAM write burst timing for the customize setup.
EDO RAS Precharge Timing
This option defines the RAS# precharge requirements for the EDO
memory type in 66MHz clocks.
EDO RAS to CAS Delay
This operation decide the delay in assertion of CAS#(SCAS#) from
assertion of RAS#(SRAS#) in 66MHz.
MA Wait State
This option selects Fast or Slow MA bus timing. The Slow timing
is equal to Fast+1, in term of clock number for EDO DRAM.
SDRAM RAS to CAS Delay
This operation decide the delay in assertion of CAS#(SCAS#) from
assertion of RAS#(SRAS#) in 66MHz.
3-11

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
SDRAM CAS Latency
This option determines the CAS latency time parameter of SDRAM.
The settings are 2 clks or 3 clks.
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time
This option defines the RAS# precharge requirements for the
SDRAM memory type in 66MHz clocks.
DRAM Integrity Mode
During ECC, this will enable the DRAM ECC mechanism that allows
detection of single-bit and multiple-bit errors and recovery of single-bit
errors. During EC, the ECC logic will calculate 8-bit pattern written along
with 64-bit data into the main memory . During Read operation, 8-bit ECC
code is read along with 64-bit data and error checking is performed. No
correction of data will take place in this operation mode. During Disabled,
this will disable the ECC mechanism.
Note: If you choose ECC or EC modes, you must use a DIMM with ECC
byte.
VGA Frame Buffer USWC
The Pentium® II processor supports the Uncacheable Speculatable
Write-Combining (USWC) memory type. The processor provides a writecombining with buffering strategy for write operation. This is useful for
frame buf fering. Writing to USWC memory can be buffered and combined in
the processors write-combining buffer (WCB). The WCBs are viewed as a
special purpose outgoing write buffers, rather than a cache. The WCBs are
written into memory to allocate a different address, or after executing a
serializing, locked, or I/O instructions.
During Enabled, this will enable the processor memory location
A000 and B000 segment as USWC memory type.
3-12

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
PCI Frame Buffer USWC
The Pentium® II processor supports the Uncacheable Speculatable
Write-Combining (USWC) memory type. The processor provides a writecombining with buffering strategy for write operation. This is useful for
frame buf fering. Writing to USWC memory can be buffered and combined in
the processors write-combining buffer (WCB). The WCBs are viewed as a
special purpose outgoing write buffers, rather than a cache. The WCBs are
written into memory to allocate a different address, or after executing a
serializing, locked, or I/O instructions.
During Enabled, this will enable the processor memory location
C000 and DFFF segment as USWC memory type.
DRAM Refresh Queue
Choose Enabled, the system will provide 4-deep refresh queue. All
refresh request are queued, with the 4th refresh request being the priority
request. All refresh requests are priority when the refresh queue is Disabled.
Fixed Memory Hole
This option allows the end user to specify the location of a memory
hole. The cycle matching the selected memory hole will be passed to the
ISA bus. If Enabled, the selected hole is not remapped.
CPU To PCI IDE Posting
Set this option to Enabled to enable posted messages from the CPU
to the PCI bus or IDE controller. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The
Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Enabled.
USWC Write I/O Post
Set this option to Enabled to use USWC(Uncacheable,
Speculatable, Write-Combined) memory . The settings are Enabled or
Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
3-13

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
AGP Aperture Size
This option determines the effective size of the graphics aperture
used in the particular PAC configuration. The AGP aperture is memorymapped, while graphics data structure can reside in a graphics aperture. The
aperture range should be programmed as not cacheable in the processor
cache, accesses with the aperture range are forwarded to the main memory ,
then PAC will translate the original issued address via a translation table
that is maintained on the main memory. The option allows the selection of
an aperture size of 4MB, 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, and 256MB.
USB Passive Release
During Enabled, this will allow the PIIX4® to use passive
release(look at PIIX4® Passive Release) while transferring control
information or data for USB transaction. During Disabled, PIIX4
®
will perform PCI accesses for USB without using passive release.
PIIX4® Passive Release
The PIIX4® ISA bridge support GAT (Guaranteed Access T ime)
mode, which will now violate the spirit of the PCI specification. The systems
provides a programmable passive release mechanism to meet the required
master latencies. During Enabled, ISA masters may see long delays in
accessing PCI memory, including the main DRAM array. The ISA GA T mode
is also not supported during enable. ISA masters must honor IOCHRDY.
PIIX4® Delayed Transaction
During Enabled, the PIIX4® delay transaction mechanism is enabled
when the PIIX4® is the target of a PCI transaction. A read cycle from Host to
PCI is immediately retrived due to any pending PCI to DRAM cycle. During
Disabled, a read cycle from Host to PCI is waited until time-out due to any
pending PCI to DRAM cycle.
3-14

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
USB Function
Set this option to Enabled or Disabled the on-chip USB controller.
The Optional and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
USB Keyboard Legacy Support
Set this option to Enabled or Disabled USB keyboard/mouse.
The Optional and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
3-15

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
3.5 Power Management Setup
1 . Press <ENTER> on “Power Management Setup” of the main menu
screen.
2 . Use <Up> and <Down> to choose the item and <PgUp> and
<PgDn> keys to modify the highlighted item.
3 . After you have finished with the Power Management Setup, press
<ESC> to go back to the main menu.
AMIBIOS SETUP - POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
Power Management / APM Disabled
Green PC Monitor Power State Stand By
Video Power Down Mode Suspend
Hard Disk Power Down Mode Stand By
Standby Time Out 1
Suspend Time Out 1
Throttle Slow Clock Ratio 50-62.5%
Modem Use IO Port N/ A
Modem Use IRQ N/ A
Display Activity Ignore
Device 6(Serial Port 1) Monitor
Device 7(Serial Port 2) Monitor
Device 8(Parallel Port) Ignore
Device 5(Floppy Disk) Monitor
Device 0(Primary master IDE) Monitor
Device 1(Primary slave IDE) Ignore
Device 2(Secondary master IDE) Monitor
Device 3(Secondary slave IDE) Ignore
System Thermal Ignore
Thermal Slow Clock Ratio 50-62.5%
CPU Critical Temperature 40
o
c/104of
Power Button Function Suspend
Available Options:
Enabled
Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color
3-16
Ring Resume From Soft-Off Disabled
RTC Alarm Resume From Soft-Off Disabled
RTC Alarm Date 15
RTC Alarm Hour 12
RTC Alarm Minute 50
RTC Alarm Second 30

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Description of the item on screen follows:
Power Management/APM
Set this option to Enabled to enable the Intel® 82440LX ISA power
management features and APM(Advanced Power Management). The
settings are Enabled, Inst-On(instant-on) or Disabled. The Optimal and FailSafe default settings are Disabled.
Green PC Monitor Power State
This option specifies the power state that the green PC-compliant
video monitor enters when AMI® BIOS places it in a power savings state
after the specified period of display inactivity has expired. The settings are
Of f, Standby , Suspend or Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default
settings are Standby.
Video Power Down Mode
This option specifies the power conserving state that the VESA
VGA video subsystem enters after the specified period of display inactivity
has expired. The settings are Disabled, Standby or Suspend. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are Standby .
Hard Disk Power Down Mode
This option specifies the power conserving state that the hard disk
drive enters after the specified period of hard drive inactivity has expired.
The settings are Disabled, Standby or Suspend. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Disabled.
3-17

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Standby Time Out
This option specifies the length of a period of system inactivity
while in Full power on state. When this length of time expires, the computer
enters Standby power state. The settings are Disabled, 1 min, 2 min, 3 min, 4
min, 5 min, 6 min, 7 min, 8 min, 9 min, 10 min, 11 min, 12 min, 13 min, 14 min or
15 min. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
Suspend Time Out
This option specifies the length of a period of system inactivity
while in Standby state. When this length of time expires, the computer
enters Suspend power state. The settings are Disabled, 1 min, 2 min, 3 min, 4
min, 5 min, 6 min, 7 min, 8 min, 9 min, 10 min, 11 min, 12 min, 13 min, 14 min or
15 min. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
Throttle Slow Clock Ratio
This option specifies the speed at which the system clock runs in
power saving states. The settings are expressed as a ratio between the
normal CPU clock speed and the CPU clock speed when the computer is in
the power-conserving state.
Modem Use IO Port
This indicates which IO port will be used by the Modem(if there is a
Modem).
Modem Use IRQ
This indicates which IRQ no. will be used by the Modem(if there is
a Modem).
3-18

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Display Activity/Device 6/Device 7/Device 8/Device 5/Device
0/Device 1/Device 1/Device 2/Device 3/System Thermal
When set to Monitor, these options enable event monitoring on the
specified hardware interrupt request line. If set to Monitor and the computer
is in a power saving state, AMI® BIOS watches for activity on the specified
IRQ line. The computer enters the full on power state if any activity occurs.
AMI® BIOS reloads the Standby and Suspend timeout timers if
activity occurs on the specified IRQ line.
Power Button Function
During Suspend, if you push the switch one time, the system goes
into suspend mode and if you push it more than 4 seconds, the system will
be turned off. During On/Off, the system will turn off once you push the
switch.
Ring Resume from Soft-Off
During Disabled, the system will ignore any incoming call from the
modem. During Enabled, the system will boot up if there’ s an incoming call
from the modem.
Note: If you have change the setting, you must let the system boot up until
it goes to the operating system. Then, power off the system. This
function will work the next time you power on.
RTC Alarm Resume From Soft-Of f
This function is for setting the Date, Hour , Minute, and Second for
your computer to boot up. During Disabled, you cannot use this function.
During Enabled, Choose the Date, Hour , Minute, and Second:
RTC Alarm Date Choose which day the system will boot up.
RTC Alarm Hour Choose which hour the system will boot up.
RTC Alarm Minute Choose which minute the system will boot up.
RTC Alarm Second Choose which second the system will boot up.
Note: If you have change the setting, you must let the system boot up until
it goes to the operating system. Then, power off the system. This
function will work the next time you power on.
3-19

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
3.6 PCI/Plug and Play Setup
1. Press <ENTER> on “PCI/Plug and Play Setup” of the main menu
screen.
2 . Use <Up> and <Down> to choose the item and <PgUp> and
<PgDn> keys to modify the highlighted item.
3 . After you have finished with the PCI/Plug and Play Setup, press
<ESC> to go back to the main menu.
AMIBIOS SETUP - PCI/PLUG AND PLAY SETUP
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
Plug and Play Aware O/S N o
PCI Latency Timer (PCI Clocks) 64
PCI VGA Palette Snoop Disabled
Allocate IRQ to PCI VGA Y es
PCI IDE Busmaster Disabled
OffBoard PCI IDE Card Auto
OffBoard PCI IDE Primary IRQ Disabled
OffBoard PCI IDE Secondary IRQ Disabled
PCI Slot4 IRQ Priority Auto
DMA Channel 0 Pn P
DMA Channel 1 Pn P
DMA Channel 3 Pn P
DMA Channel 5 Pn P
DMA Channel 6 Pn P
DMA Channel 7 Pn P
IRQ3 PCI/PnP
IRQ4 PCI/PnP
IRQ5 PCI/PnP
IRQ7 PCI/PnP
IRQ8 PCI/PnP
IRQ9 PCI/PnP
IRQ10 PCI/PnP
IRQ11 PCI/PnP
IRQ12 PCI/PnP
Available Options:
Enabled
Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color
3-20
IRQ14 PCI/PnP
IRQ15 PCI/PnP
Reserved Memory Size Disabled
Reserved Memory Address C8000

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Description of the item on screen follows:
Plug and Play Aware O/S
Set this option to Yes if the operating system in this computer is
aware of and follows the Plug and Play specification. Currently , only
Windows® 95 is PnP-aware. The settings are Y es or No. The Optimal and
Fail-Safe default settings No.
PCI Latency Timer (PCI Clocks)
This option specifies the latency timings (in PCI clocks) for all PCI
devices on the PCI bus. The settings are 32, 64, 96, 128, 160, 192, 224 or 248.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are 64.
PCI VGA Palette Snoop
When this option is set to Enabled, multiple VGA devices operating
on different buses can handle data from the CPU on each set of palette
registers on every video device. Bit 5 of the command register in the PCI
device configuration space is the VGA Palette Snoop bit (0 is disabled). For
example, if there are two VGA devices in the computer (one PCI and ISA)
and the Bit settings are:
Disabled - Data read and written by the CPU is only directed to the
PCI VGA device’ s palette registers.
Enabled - Data read and written by the CPU is directed to
both the PCI VGA device’ s palette registers and the
ISA VGA device palette registers, permitting the
palette registers of both devices to be identical.
This option must be set to Enabled if an ISA adapter card requires
VGA palette snooping. The settings are Enabled or Disabled. The Optimal
and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
Allocate IRQ to PCI VGA
Choose the IRQ to be assigned to the PCI VGA display adapter card.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default setting is No.
3-21

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
PCI IDE BusMaster
Set this option to Enabled to specify that the IDE controller on the
PCI local bus includes a bus mastering capability . The settings are Enabled
or Disabled. The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Disabled.
Offboard PCI IDE Card
This option specifies if an offboard PCI IDE controller adapter card
is installed in the computer . You must specify the PCI expansion slot on the
mainboard where the offboard PCI IDE controller is installed. If an offboard
PCI IDE controller is used, the onboard IDE controller is automatically
disabled. The settings are Auto(AMI® BIOS automatically determines where
the offboard PCI IDE controller adaper card is installed), Slot1, Slot2, Slot3 or
Slot4. The Optimal and Fail-Safe settings are Auto.
If an offboard PCI IDE controller adapter card is installed in the
computer, you must also set the Offboard PCI IDE Primary IRQ and Offboard
PCI IDE Secondary IRQ options.
Offboard PCI IDE Primary IRQ/
Offboard PCI IDE Secondary IRQ
These options specify the PCI interrupt used by the Primary (or
Secondary) IDE channel on the offboard PCI IDE controller . The settings are
Disabled, Hardwired, INT A, INTB, INTC or INTD. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are Disabled.
3-22

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
DMA Channel 0/1/3/5/6/7
These options specify the bus that the specified DMA channel is
used. These options allow you to reserve DMAs for legacy ISA adapter
cards.
These options determine if AMI® BIOS should remove a DMA from
the available DMAs passed to devices that are configurable by the system
BIOS. The available DMA pool is determined by reading the ESCD
NVRAM. If more DMAs must be removed from the pool, the end user can
use these options to reserve the DMA by assigning an ISA/EISA setting to
it.
IRQ3/IRQ4/IRQ5/RQ7/IRQ9/IRQ10/IRQ11/IRQ14/IRQ15
These options specify the bus that the specified IRQ line is used
on. These options allow you to reserve IRQs for legacy ISA adapter cards.
These options determine if AMI® BIOS should remove an IRQ from
the pool of available IRQs passed to devices that are configurable by the
system BIOS. The available IRQ pool is determined by reading the ESCD
NVRAM. If more IRQs must be removed from the pool, the end user can use
these options to reserve the IRQ by assigning an ISA/EISA setting to it.
Onboard I/O is configured by AMI® BIOS. All IRQs used by onboard I/O
are configured as PCI/PnP. If all IRQs are set to ISA/EISA and IRQ14 and 15
are allocated to the onboard PCI IDE, IRQ9 will still be available for PCI and
PnP devices, because at least one IRQ must be available for PCI and PnP
devices. The settings are ISA/EISA or PCI/PnP . The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings are IRQ3 through 7 are ISA/EISA. The Optimal and Fail-Safe
default settings PCI/PnP.
Reserved Memory Size/Reserved Memory Address
Some ISA cards have ROM at 0C000h~0D000h segments, but in a
non-standard format. So Plug & Play BIOS can’t detect it. The end user
needs to set it up manually. Setting these options under this condition, will
inform the BIOS which location and how many location is occupied.
3-23

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
3.7 Peripheral Setup
1. Press <ENTER> on “Peripheral Setup” of the main menu screen.
2 . Use <up> and <down> to choose the item and <PgUp> and
<PgDn> keys to modify the highlighted item.
3 . After you have finished with the Peripheral Setup, press <ESC> to
go back to the main menu.
AMIBIOS SETUP - PERIPHERAL SETUP
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
OnBoard FDC Enabled
OnBoard Serial PortA 3F8h/COM1
OnBoard Serial PortB 2F8h/COM2
IR Port Support Disabled
IR Base Address Select 2F 8
IR IRQ Select 10
IR DMA Select Disabled
OnBoard Parallel Port 378
Parallel Port Mode EC P
EPP Version N/ A
Parallel Port IRQ 7
Parallel Port DMA Channel 3
Onboard IDE Both
Available Options:
Enabled
Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color
3-24

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
Description of the item on screen follows:
Onboard FDC
Choose Auto, for the BIOS to automatically detect the device
Choose Enabled, Enabling onboard FDC.
Choose Disabled, Disabling onboard FDC.
The Optimal and Fail-Safe default settings are Auto.
Onboard Serial Port A/Onboard Serial Port B
Choose 3F8, for the BIOS to automatically detect the device.
If the ISA add-on card has Onboard FDC to be set at
FDC exist
none FDC exist
Disabled
Enabled
üüüüDISABLED X DISABLED X
üüX X COM3 4 COM4 3
XXüü COM1 4 COM2 3
ü XXüCOM2 3 COM3 4
X üüX COM1 4 COM4 3
üüüX COM4 3 DISABLED X
üüXüCOM3 4 DISABLED X
ü X üü COM2 3 DISABLED X
X üüüCOM1 4 DISABLED X
X X X X COM1 4 COM2 3
ü X X X COM2 3 COM3 4
X ü X X COM1 4 COM3 4
XXüX COM1 4 COM2 3
XXXüCOM1 4 COM2 3
If the ISA add-on card has Onboard Serial port to be set at
COM1
(I/O:3F8H)
COM2
(I/O:3F8H)
COM3
(I/O:3E8H)
COM4
(I/O:2E8H)
PORT1 PORT2
IRQ
ASSIGNED
IRQ
ASSIGNED
Note: If the onboard serial port interrupt and ISA add-on card interrupt are in
conflict, the serial port will not work properly. Please disable one of the
devices.
3-25

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
IR Port Support
Choose Auto, the BIOS will automatically assigned onboard port
for IR.
IR Base Address Select
This option will assigned which base address will be used by IR
IR IRQ Select
This option is for selecting the IRQ for the IR.
IR DMA Select
This option is for selecting the DMA for the IR.
Onboard Parallel Port
Choose Auto, the BIOS automatically assigned onboard parallel
port to the available parallel port or disabled.
If the ISA add-on card has Onboard parallel port to be set as
üüüDisabled X
üüX LPT3 5
ü X ü LPT2 5
X üü LPT1 7
ü X X LPT2 5
X ü X LPT1 7
XXü LPT1 7
X X X LPT1 7
LPT1
I/O:378H
LPT2
I/O:278H
LPT3
I/O:3BCH
PORT
ASSIGNED
IRQ
ASSIGNED
Note: If the onboard parallel port interrupt and ISA add-on card interrupt are
in conflict, the parallel port will not work properly. Please disable one of
the devices.
3-26

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
EPP Version
This option is for setting which EPP version will be used. The
settings are 1.7 and 1.9.
Parallel Port Mode
This option allows user to choose the operating mode of the
onbaord parallel port. The settings are Normal, SPP/EPP or ECP mode.
Parallel Port IRQ
If the onboard parallel mode is not on auto mode, the user can
select the interrupt line for onboard parallel port. We suggest that the user
select the interrupt for the onboard parallel port as shown below:
Parallel Port DMA Channel
This option allows user to choose DMA channel 1 to 3 for the
onboard parallel port on ECP mode.
Onboard IDE
Set this option to enable or disable on board IDE controller.
Onboard parallel port set at Parallel Port IRQ
LPT1(378H)
LPT2(278H)
LPT3(3BCH)
7
5
5
3-27

CHAPTER 3
AMI® BIOS USERS GUIDE
3-28
3.8 Hardware Monitor Setup
The Hardware Monitor Setup is used to monitor the Current CPU
temperature, CPU Fan speed, Chassis Fan Speed, Power fan speed,
Vcore, and etc.
AMIBIOS SETUP - HARDWARE MONITOR SETUP
(C) 1996 American Megatrends, Inc. All Rights
Reserved
-=System Hardware Monitor= Current CPU Temperature 30
o
c/1000f
Current CPU Fan Speed 5273RPM
Current Chassis Fan Speed 0 RP M
Current Power Fan Speed 0 RPM
Vcore 2.2V
Vtt 1.5V
Vio 3.3V
+5,000V +5 V
+12,000V +12V
-12,000V -12V
-5,000V -5 V
Available Options:
Enabled
Disabled
ESC:Exit :Sel
PgUp/PgDn:Modify
F2/F3:Color


















 Loading...
Loading...