Page 1

Version 1.1
G52-B6269X4
User’s Guide
MPC 865
Page 2
ii
FCC-B Radio Frequency Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment
is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at his own expense.
Notice 1
The changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible
for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Notice 2
Shielded interface cables and AC. power cord, if any, must be used in order to
comply with the emission limits.
VOIR LA NOTICE D’INSTALLATION AVANT DE RACCORDER AU RESEAU.
Micro-Star International
MPC 865
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
(1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference
that may cause undesired operation.
Page 3

iii
Lithium Battery Statement
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the
same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by
method claims of certain U.S. patents and other intellectual property rights owned
by Macrovision Corporation and other rights owners. Use of this copyright protection technology must be authorized by Macrovision Corporation, and is intended for home and other limited viewing users only unless otherwise authorized by Macrovision Corporation. Reverse engineering or disassembly is
prohibited.
Macrovision
®
Statement
Page 4

iv
1. Always read the safety instructions carefully.
2. Keep this User’s Manual for future reference.
3. Keep this equipment away from humidity.
4. Lay this equipment on a reliable flat surface before setting it up.
5. The openings on the enclosure are for air convection hence protects the
equipment from overheating. DO NOT COVER THE OPENINGS.
6. Make sure the voltage of the power source and adjust properly 115/230V
before connecting the equipment to the power inlet.
7. Place the power cord such a way that people can not step on it. Do not
place anything over the power cord.
8. Always Unplug the Power Cord before inserting any add-on card or module.
9. All cautions and warnings on the equipment should be noted.
10. Never pour any liquid into the opening that could damage or cause electrical shock.
11. If any of the following situations arises, get the equipment checked by a
service personnel:
- The power cord or plug is damaged.
- Liquid has penetrated into the equipment.
- The equipment has been exposed to moisture.
- The equipment has not work well or you can not get it work according to
User’s Manual.
- The equipment has dropped and damaged.
- The equipment has obvious sign of breakage.
12. DO NOT LEAVE THIS EQUIPMENT IN AN ENVIRONMENT
UNCONDITIONED, STORAGE TEMPERATURE ABOVE 600 C (1400F), IT MAY
DAMAGE THE EQUIPMENT.
CAUTION: Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by
the manufacturer.
Safety Instructions
Page 5
v
Trademarks
All trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
Intel® and Pentium® are registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
PS/2 and OS®/2 are registered trademarks of International Business Machines
Corporation.
Windows® 95/98/2000/NT/XP are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netware® is a registered trademark of Novell, Inc.
Award® is a registered trademark of Phoenix Technologies Ltd.
AMI® is a registered trademark of American Megatrends Inc.
Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
V1.0 First Release January 2004
v1.1 Update BIOS and spec. April 2004
Page 6

vi
CONTENTS
Introduction
Chapter 1. Getting Started ---------------------------------------------------------- 1-1
1.1 Introduction ----------------------------------------------------------------- 1-2
1.2 System Specification ----------------------------------------------------- 1-4
Chapter 2. Introducing Mainboard ---------------------------------------- 2-1
2.1 Mainboard Layout --------------------------------------------------------- 2-2
2.2 CPU --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-3
2.3 Memory ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-3
Introduction to DDR SDRAM----------------------------------------- 2-3
Memory Speed /CPU FSB Support Matrix------------------------- 2-4
DIMM Module Combination ----------------------------------------- 2-4
2.4 Power Supply --------------------------------------------------------------- 2-5
2.5 Front Panel ------------------------------------------------------------------ 2-6
IEEE 1394 Port: J1394-2 ------------------------------------------------ 2-6
IEEE 1394 Port: J1394-1 ------------------------------------------------ 2-7
USB Ports------------------------------------------------------------------- 2-7
Mic-in/Head-Phone ----------------------------------------------------- 2-8
OPTICAL SPDIF-in ------------------------------------------------------ 2-8
2.6 Back Panel ------------------------------------------------------------------ 2-9
Serial Port ------------------------------------------------------------------ 2-9
Mouse/Keyboard Connectors ----------------------------------------2-10
VGA Port ------------------------------------------------------------------2-10
RJ45 LAN Jack-----------------------------------------------------------2-11
USB Ports------------------------------------------------------------------2-11
OPTICAL SPDIF-out ----------------------------------------------------2-11
Parallel Port --------------------------------------------------------------2-12
Audio Port-----------------------------------------------------------------2-13
2.7 Connectors------------------------------------------------------------------2-14
IDE Connectors: PIDE1&SIDE1--------------------------------------2-14
FDD Connector: FDD1 ------------------------------------------------2-14
Page 7

vii
Serial ATA RAID Connector: SATA1 ------------------------------2-15
TV-Tuner Card Connector: CN3-------------------------------------2-15
CPU/System Fan Connectors ----------------------------------------2-15
Modem Module Connector: MDC1 (Optional) -----------------2-16
Card Reader Connector: CR1 ----------------------------------------2-16
Front Panel Power Connector: JFP1 --------------------------------2-17
2.8 Jumper....................................................................................... 2-18
Clear CMOS Jumper: JBAT1..................................................2-18
2.9 Slots .......................................................................................... 2-19
PCI Slot .................................................................................. 2-19
AGP Slot ................................................................................. 2-19
Mini PCI Slot..........................................................................2-19
Chapter 3: Setting BIOS Function .................................................... 3-1
3.1 Entering Setup ............................................................................ 3-2
Control Keys.............................................................................3-2
Getting Help ............................................................................ 3-3
Main Menu .............................................................................. 3-3
Sub-Menu.................................................................................3-3
General Help<F1>...................................................................3-3
3.2 The Main Menu..........................................................................3-4
3.3 Standard CMOS Features...........................................................3-6
3.4 Advanced BIOS Features...........................................................3-8
3.5 Advanced Chipset Features ..................................................... 3-11
3.6 Integrated Peripherals .............................................................. 3-14
3.7 Power Management Setup ....................................................... 3-19
3.8 PNP/PCI Configurations ........................................................... 3-22
3.9 PC Health Status ...................................................................... 3-23
3.10 Frequency/Voltage Control....................................................3-24
3.11 Load Default Setting .............................................................. 3-26
3.12 Set Supervisor/User Password ................................................ 3-27
Chapter 4: Wireless LAN Card (for Deluxe Model)................................. 4-1
4.1 Introduction ................................................................................ 4-2
Page 8

viii
4.2 Wireless Network Utility ........................................................... 4-4
4.3 Networking ................................................................................. 4-8
4.4 Encryption................................................................................. 4-14
4.5 Status ........................................................................................ 4-15
4.6 Information ............................................................................... 4-17
Page 9

1-1
Getting Started
Getting Started
1.1 Introduction
1.2 System Specification
1
1
Page 10
1-2
Chapter 1
Front Panel
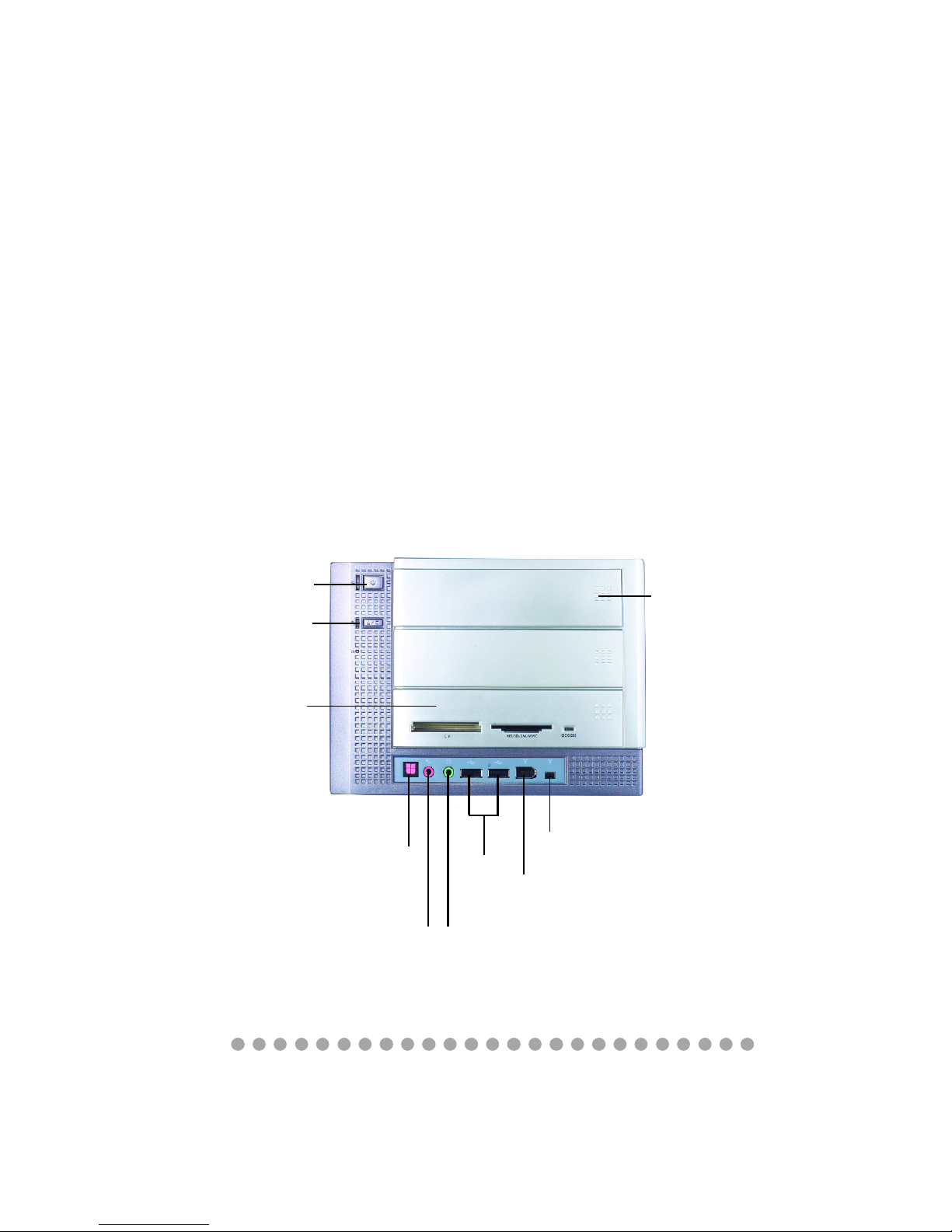
1.1 Introduction
Unlike the traditional PC, the MPC 865 comes with a fancy design case
and multimedia I/O ports for quick connection and use. The embedded 6-in-1
card reader (for Deluxe model) provides a total solution for accessing your various types of memory cards instead of finding the respective card readers. With
an optional TV tuner card installed, the MPC 865 can be a multimedia platform.
You can record, capture and schedule all the TV programs with the proprietary
application.
In addition, you can surf the Internet with the optional wireless LAN card
(for Deluxe model) to enhance the mobility of your MPC 865. Now, you can
enjoy it anywhere.
SPDIF-In
1394 port
(6-pin)
USB 2.0
ports
MIC
Eject / Stop
PC Power Switch
Card Reader
(for Deluxe model)
Line-In
1394 port
(4-pin)
Optical Drive
(Optional)
Page 11
1-3
Getting Started
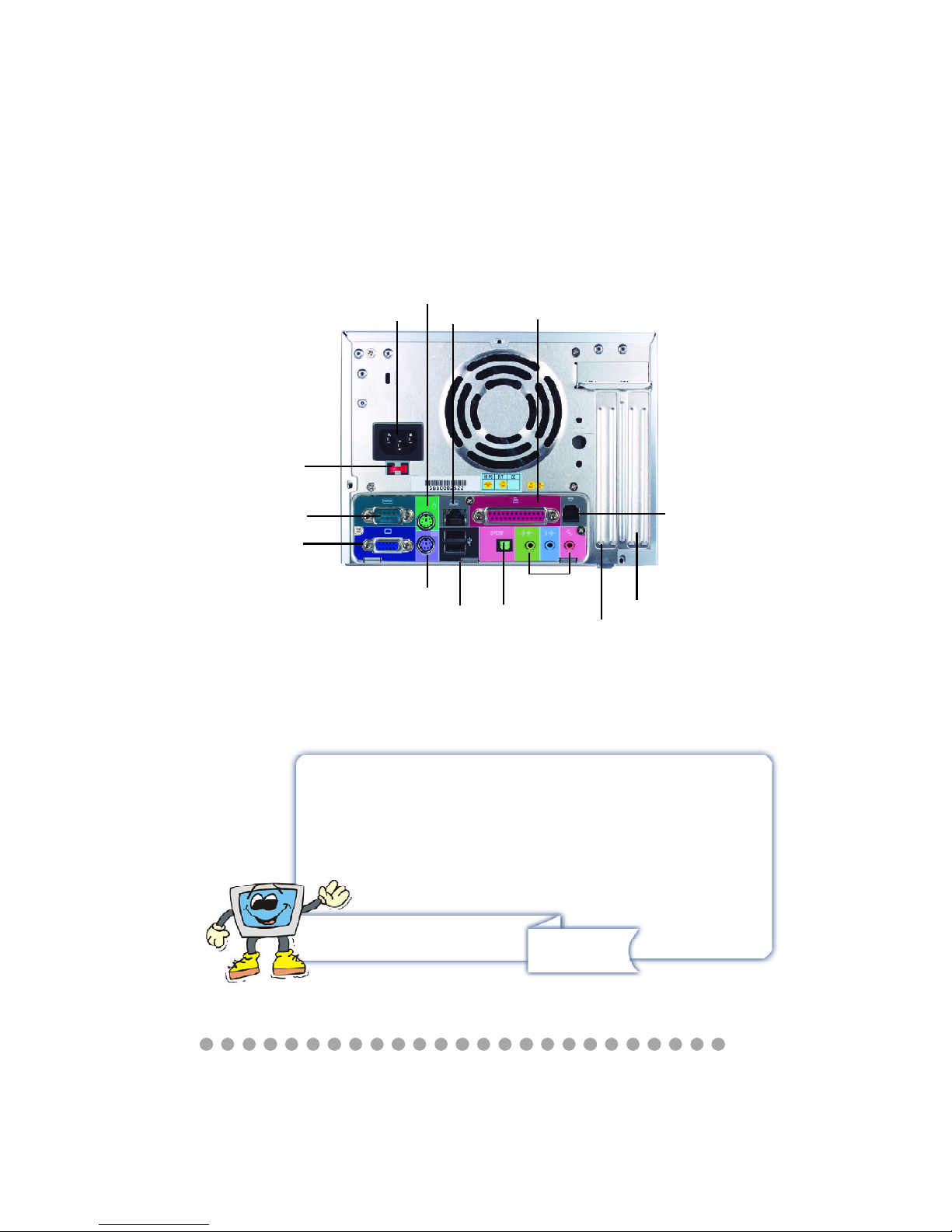
Back Panel
Power Jack
Serial Port
USB x 2
AGP Slot
PCI Slot
Modem
Mouse
LAN Port
Parallel Port
Audio Ports
SPDIF-out
Keyboard
VGA Port
ATTENTION!!!
Check the AC power voltage switch on the back panel.
Select the voltage that is appropriate to the country you
are in.
Powe Voltage
Switch
Page 12

1-4
Chapter 1
1.2 System Specification
M/B
- MS-6797 (Proprietary F/F), 185 x 290 mm (6 layer)
CPU:
- Support Socket 478 for Intel
®
NorthwoodTM up to 3.2GHz
(For the latest information about CPU, please visit our Web site at http://www.
msi.com.tw/program/products/slim_pc/slm/pro_slm_cpu_support.php)
Chipset:
- Intel 865G + FW82801EB (Springdale G + ICH5)
Memory:
- DDR 400 x 2, support memory up to 2.0GB (Dual Channel support)
On-Board Audio:
- AC’97 Codec integrated in Realtek658, support 5.1 channel, SPDIF In/Out
On-Board VGA:
- Integrated in Intel 865G (AGP 8X)
- On-Board VGA memory: None
On-Board Communication
- LAN: BCM5705 (10/100/1000M)
- Modem: MDC module
- WLAN: Mini-PCI
On-Board USB
- USB2.0 x 6 (Front x 2; Rear x 2; On-Board x 2 for Card Reader & RF K/B, M/S)
On-Board IEEE 1394:
- NEC PD72874 (2 ports), Front x 2 (4 pin, 6 pin)
Expansion Slots:
- PCI 2.2 x 1, AGP (8X) x1, Mini PCI x 1, SATA x 1
TV Tuner Function
- MS-8606 (optional PCI card with remote control)
Power Supply:
- 210W (PFC 5V/12V SB) Full Range
Page 13
1-5
Getting Started
Chassis:
- 202(W) x 320(D) x 151(H) mm
On-Board Headers & Connectors
- Rear Panel: Parallel Port x 1, VGA x 1, Serial Port x 1, PS/2 x 2, Mic in/Line in/
Line out x 1, USB x 2, LAN (RJ45) x 1, SPDIF/O x 1, Modem (RJ11) x 1
- Front Panel: Mic-in x 1, Headphone x 1, USB x 2, SPDIF/I x 1, 1394 x 1 (4-pin),
1394 x 1(6-pin)
BIOS
- 4MB Flash
Clock Generator
- Integrated in ICS952617
Others
- Microsoft
®
PC 2001
- LAN Wake Up Function
- Suspend to RAM/Disk function
- Top Tech III (Thermal Overheat Protection Technology)
- PC Alert System Hardware Monitor
- Support Windows XP only
ATTENTION!!!
The file system format in Compact Disc (CD) is based on
ISO9660. However, the format on DVD disc is a subset of
UDF (Universal Disk Format) called micro UDF (M-UDF),
which is based on ISO13346.
So far BVL+ does not support DVD format. That is the reason you see strange symptom when using DVD discs.
Page 14
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-1
Introducing Mainboard
Introducing MainboardIntroducing Mainboard
Introducing MainboardIntroducing Mainboard
Introducing Mainboard
2.1 Mainboard Layout2.1 Mainboard Layout
2.1 Mainboard Layout2.1 Mainboard Layout
2.1 Mainboard Layout
2.2 CPU2.2 CPU
2.2 CPU2.2 CPU
2.2 CPU
2.3 Memory2.3 Memory
2.3 Memory2.3 Memory
2.3 Memory
2.4 Power Supply2.4 Power Supply
2.4 Power Supply2.4 Power Supply
2.4 Power Supply
2.5 Front Panel2.5 Front Panel
2.5 Front Panel2.5 Front Panel
2.5 Front Panel
2.6 Back Panel2.6 Back Panel
2.6 Back Panel2.6 Back Panel
2.6 Back Panel
2.7 Connectors2.7 Connectors
2.7 Connectors2.7 Connectors
2.7 Connectors
2.8 Jumper2.8 Jumper
2.8 Jumper2.8 Jumper
2.8 Jumper
2.9 Slots2.9 Slots
2.9 Slots2.9 Slots
2.9 Slots
2
2
Page 15
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-2
Chapter 2
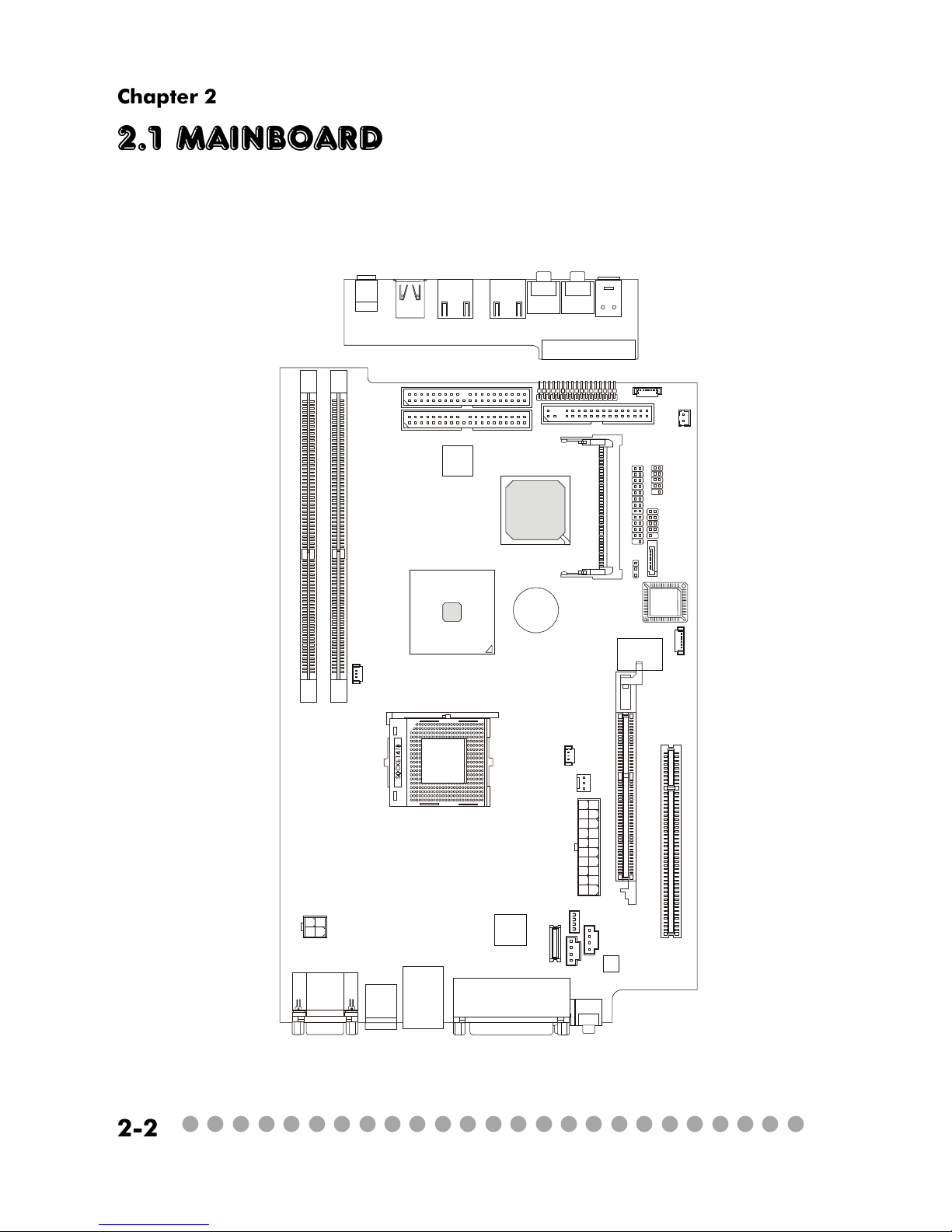
2.1 Mainboard layout
MS-6797 v1.X Mainboard
J1
CN1
SPDIF-In
MIC-In
Headphone
AUDIO 1
AUDIO2
USB1
USB2
J1394-1
J1394-2
BATT
+
ICH5
Intel
865G
DIMM 1
SM
BluebirdVL+
DIMM 2
JFP1
SATA1
USB1
JBAT1
J1
LCM1
ATX
Power Supply
BIOS
PCI Slot 1
To p : m ou se
Bottom: keyboard
To p : C OM 1
Bottom: VGA Port
Top: LAN Jack
Bottom: USB
ports
CN2
CN3
Broadcom
BCM4401
SMSC
LPC47M192-NC
Codec
FDD1
MINIPCI1
SIDE1
PIDE1
CR1
JKBMS1
FIO1
PWR1
MDC1
JPW1
CPUFAN1
SYSFAN1
CPUFAN2
AGP Slot
Top :
Parallel Port
Bottom:
SPDIF
Line_Out
Line_In
Mic
Page 16
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-3
Introducing Mainboard
2.2 CPU
The MEGA 865 supports Intel® Northwood® processors up to 3.2GHz. The
mainboard uses a CPU socket called PGA478 for easy CPU installation. When
you are installing the CPU, make sure the CPU has a heat sink and a cooling fan
attached on the top to prevent overheating.
Overheating
Overheating will seriously damage the CPU and system, always
make sure the cooling fan can work properly to protect the CPU
from overheating.
Introduction to DDR SDRAM
DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM is
similar to conventional SDRAM, but
doubles the rate by transferring data twice
per cycle. It uses 2.5 volts as opposed to
3.3 volts used in SDR SDRAM, and requires
184-pin DIMM modules rather than 168pin DIMM modules used by SDR SDRAM.
High memory bandwidth makes DDR an
ideal solution for high performance PC,
workstations and servers.
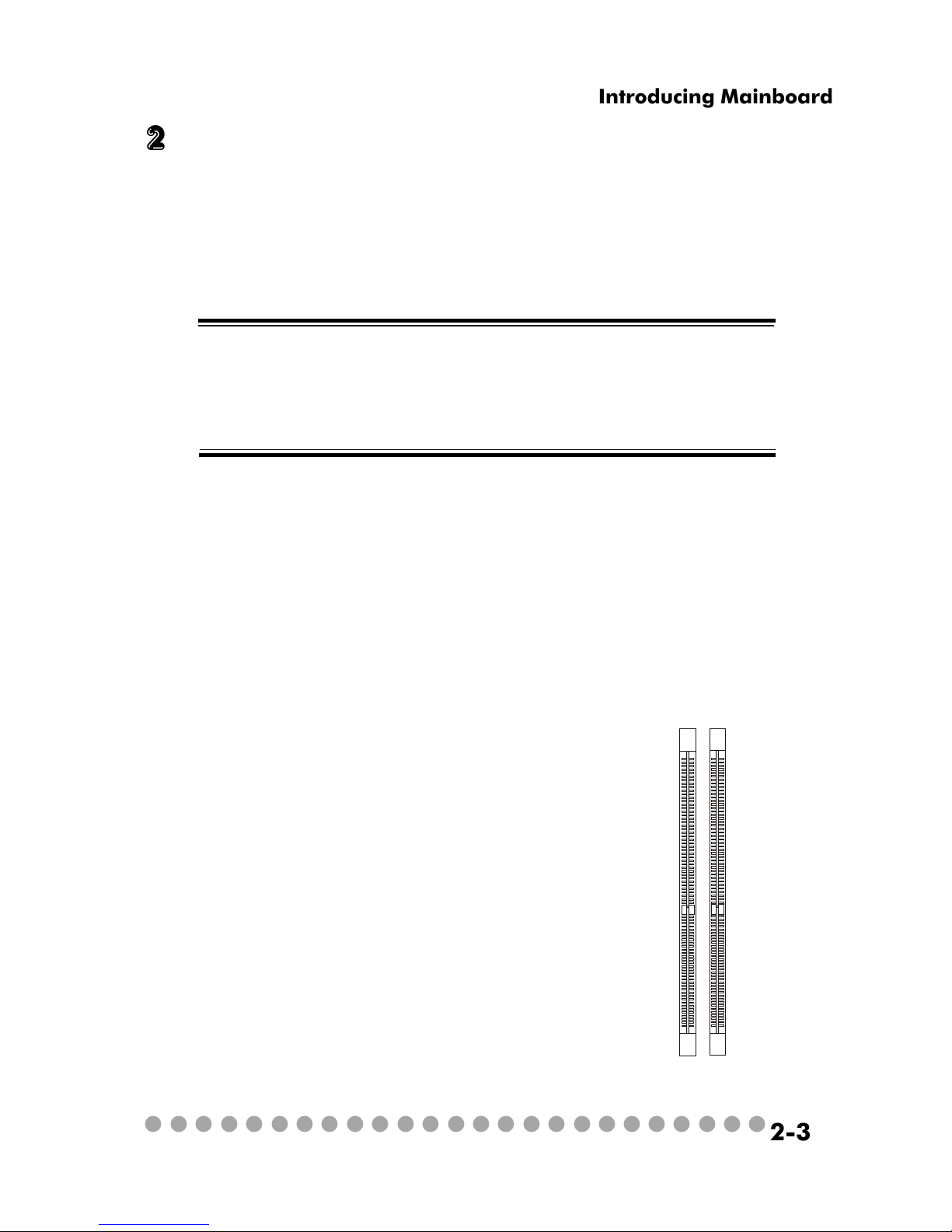
The mainboard provides 2 slots for 184-pin DDR SDRAM DIMM (Double
In-Line Memory Module) modules and supports the memory size up to 2GB. You
can install PC3200/DDR400, PC2700/DDR333 or PC2100/DDR266 modules into
the DDR DIMM slots.
2.3 memory
DIMM 1
DIMM 2
Page 17
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-4
Chapter 2
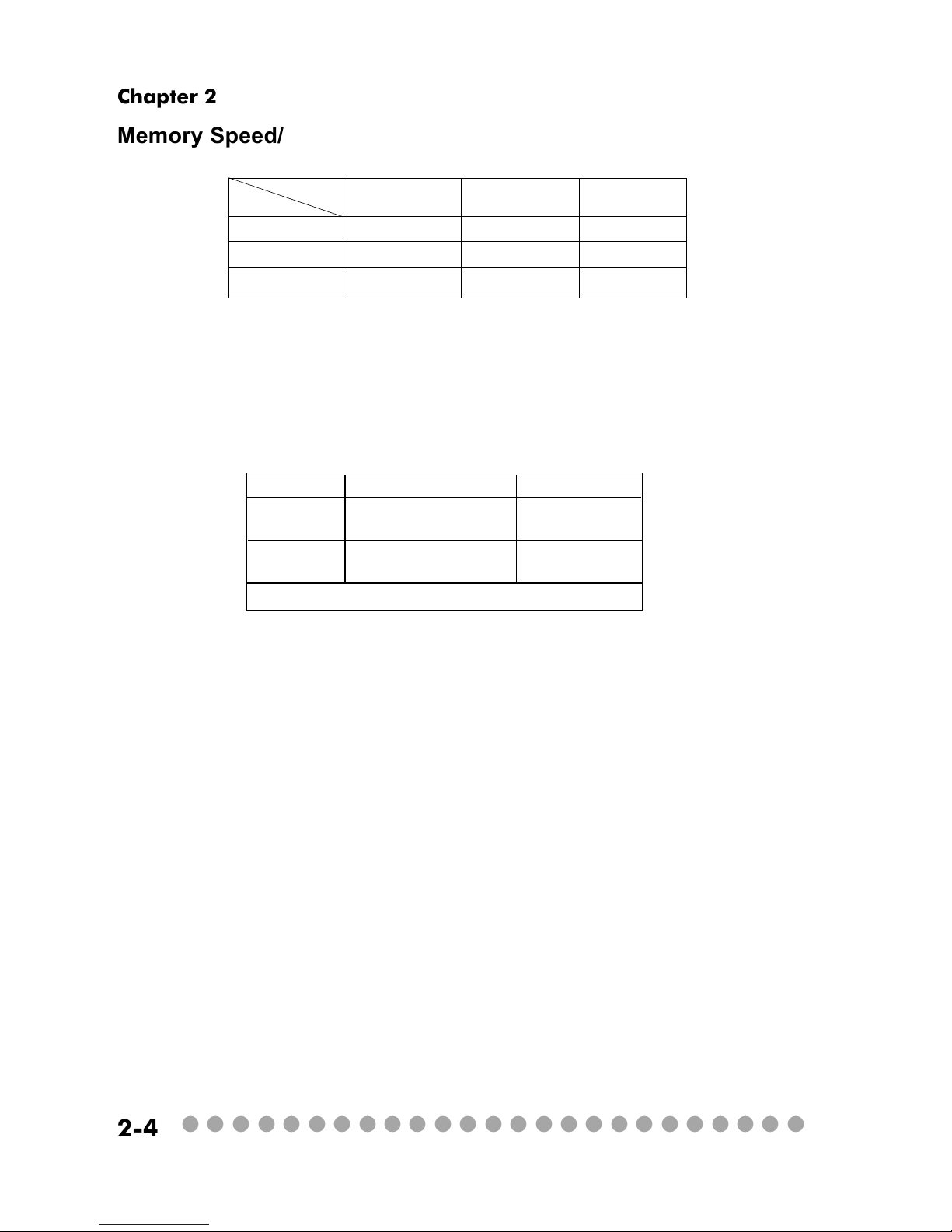
Memory Speed/CPU FSB Support Matrix
DIMM Module Combination
Install at least one DIMM module on the slots. You can install either
single- or double-sided modules in any order to meet your own needs. Memory
modules can be installed in any combination as follows:
S: Single Side
D: Double Side
Slot Memory Module Total Memory
DIMM 1 DDR S/D 64MB~1GB
(Bank 0 & 1)
DIMM 2 DDR S/D 64MB~1GB
(Bank 2 & 3)
Maximum System Memory Supported 64MB~2GB
DDR266 DDR333 DDR400
FSB400 OK N/A N/A
FSB533 OK OK N/A
FSB800 OK OK OK
FSB
Memory
Page 18
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-5
Introducing Mainboard
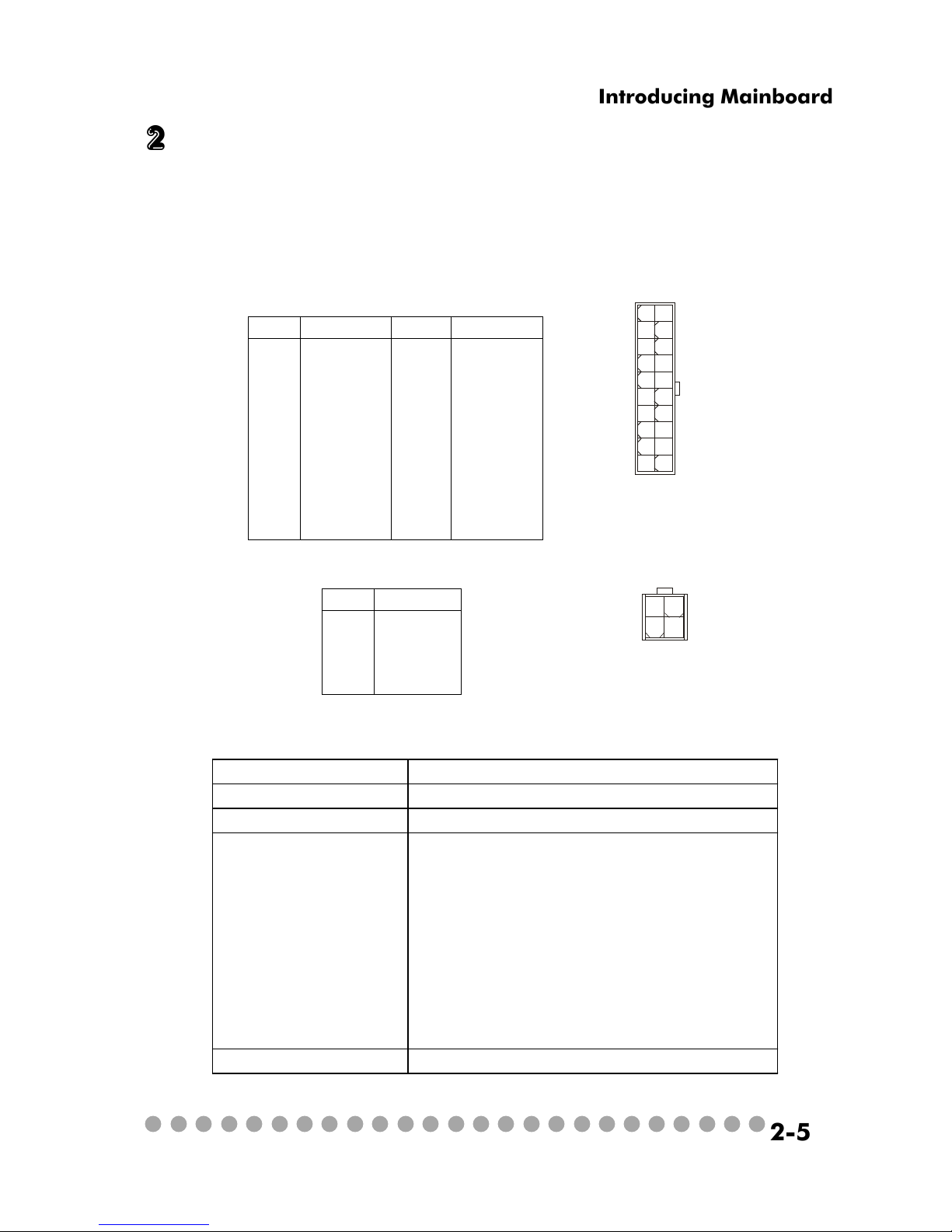
2.4 Power Supply
The system is equipped with a 210W(PFC) ATX power supply. The power
cord of power supply has been connected to the connector JWR1 on the mainboard
when shipped out. Except the 20-pin connector ATX1, you can find another
4-pin power connector JPW1 on the mainboard.
1
11
ATX1
20
10
PIN SIGNAL
11 3.3V
12 -12V
13 GND
14 PS_ON
15 GND
16 GND
17 GND
18
19 5V
20 5V
PIN SINGAL
1 3.3V
2 3.3V
3 GND
45V
5 GND
65V
7 GND
8 PW_OK
9 5V_SB
10 12V
JWR1 Pin Definition
PIN SINGAL
1 GND
2 GND
3 12V
4 12V
JPW1 Pin Definition
1
3
4
2
JPW1
Dim ension 70 (H)x1450(W )x105(D) m m
PF C Yes (passive)
W attage 210W M ax
Electrical D esign
Specification
AC O utput :100-127/200-240 VAC ,
Switch Selectable, Auto Protection
DC O utput :+3.3V 17A
:+5V 12A
:+12V 13.5A
:-12V 0.5A
:+5Vsb 3A
:+12Vsb 2.5A
80 m m PW M Fan
Certificate FCC/UL/CUL/BSMI/CB/NEMKO/TUV
Power Supply Specification
Page 19
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-6
Chapter 2
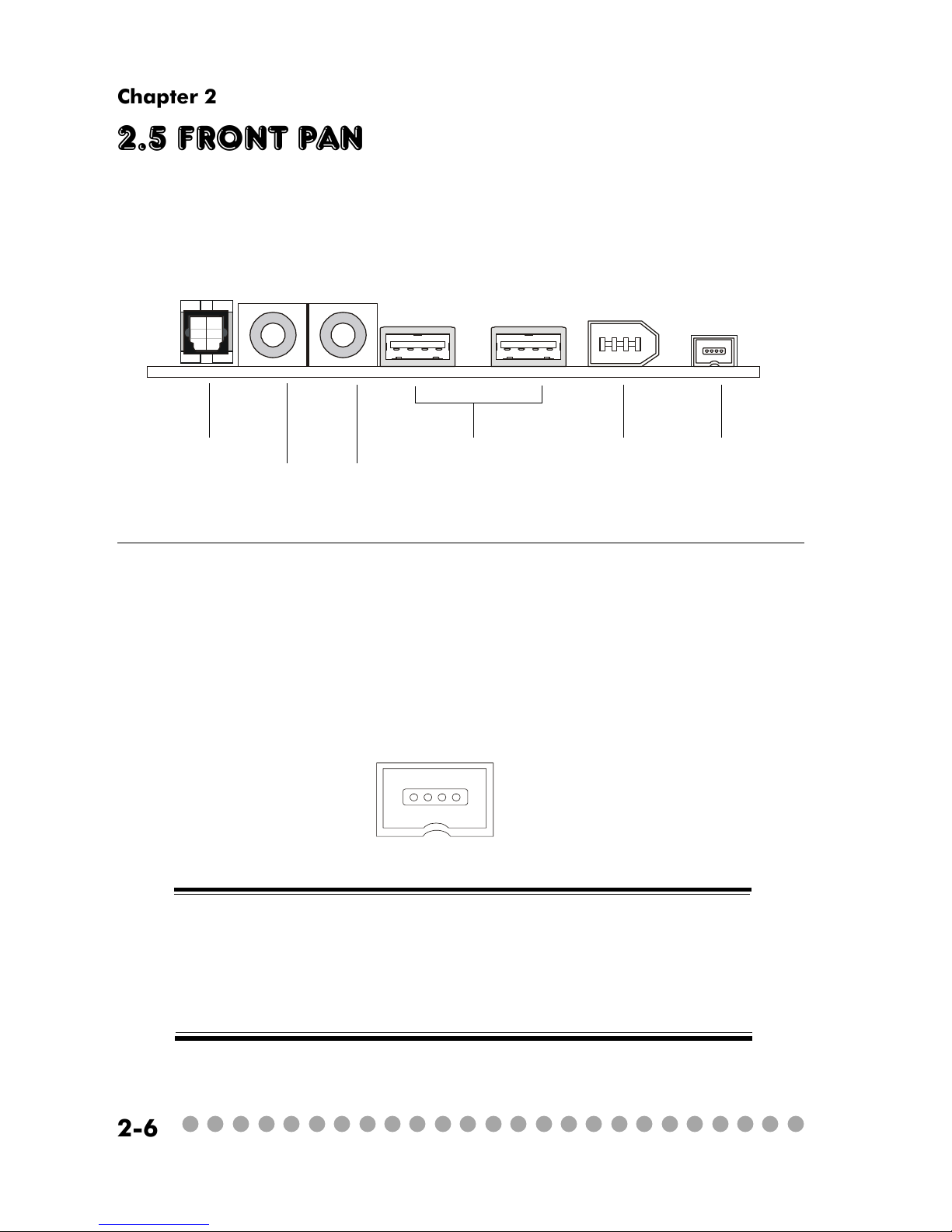
2.5 Front panel
The Front Panel is independent and extended from the mainboard. It’s
connected to the Front I/O Connector on the mainboard. You can find the
following ports on the Front Panel.
Optical SPDIF-In
Mic-In
Head-Phone
USB x 2 J1394-1 J1394-2
IEEE 1394 Port: J1394-2
The mainboard provides two IEEE 1394 ports. This smaller one is designed for you to connect the IEEE 1394 device with external power. The IEEE
1394 high-speed serial bus complements USB by providing enhanced PC connectivity for a wide range of devices, including consumer electronics audio/video
(A/V) appliances, storage peripherals, other PCs, and portable devices.
Software Support
IEEE 1394 Driver is provided by Windows® 98 SE, Windows® XP,
Windows® ME and Windows® 2000. Just plug in the IEEE 1394 connector into the port. These Operating Systems will install the driver
for IEEE 1394.
Page 20
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-7
Introducing Mainboard
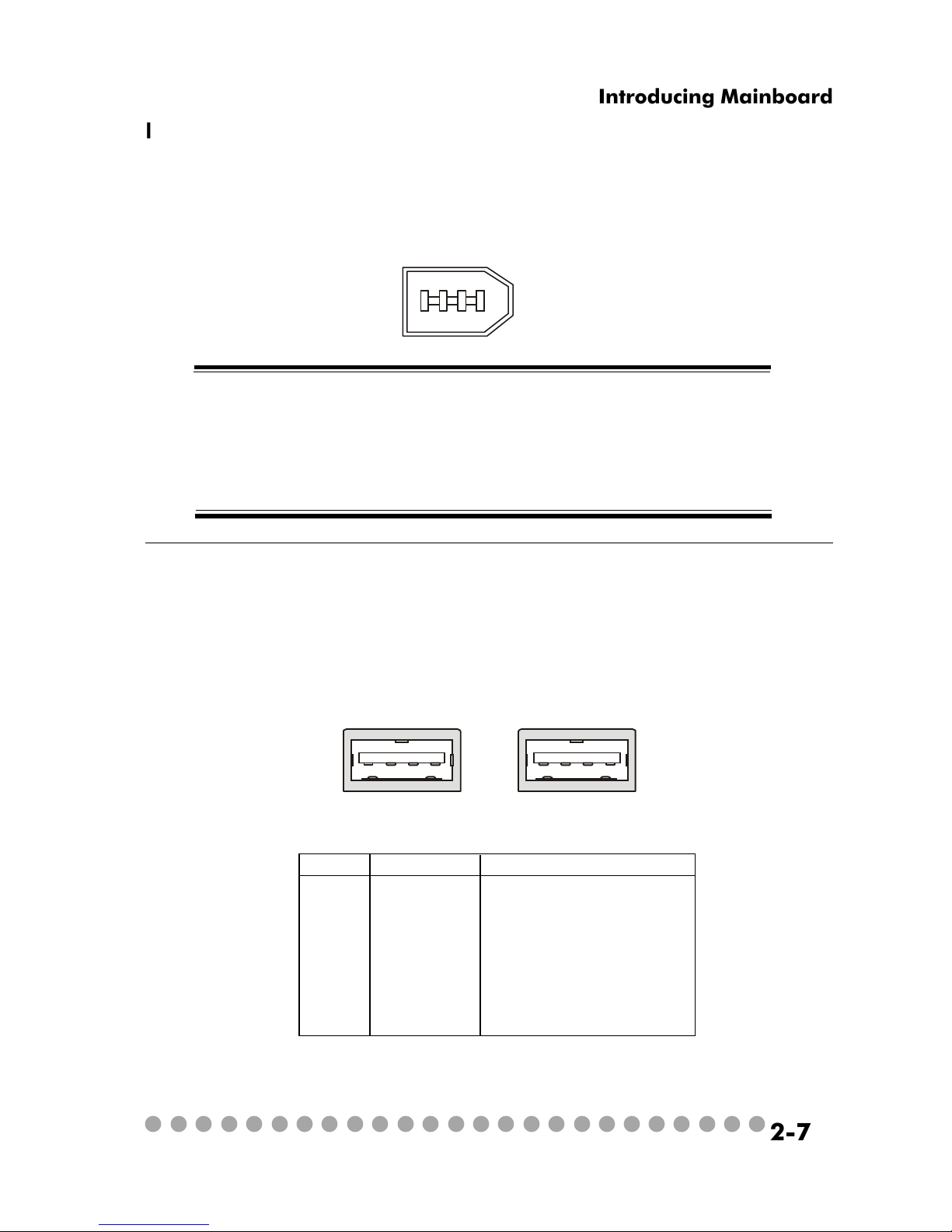
IEEE 1394 Port: J1394-1
The bigger 6-pin IEEE 1394 Port on the back panel is designed for you to
connect to IEEE 1394 devices without external power. That means the mainboard
can provide the power for the devices connected to this port.
Software Support
IEEE 1394 Driver is provided by Windows® 98 SE, Windows® XP,
Windows® ME and Windows® 2000. Just plug in the IEEE 1394
connector into the port. These Operating Systems will install the
driver for IEEE 1394.
USB Ports
The mainboard provides an OHCI (Open Host Controller Interface) Universal Serial Bus root for attaching USB devices such as keyboard, mouse or
other USB-compatible devices. You can plug the USB device directly into the
connector.
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 VCC +5V
2 -Data 0 Negative Data Channel 0
3 +Data 0 Positive Data Channel 0
4 GND Ground
5 VCC +5V
6 -Data 1 Negative Data Channel 1
7 +Data 1 Positive Data Channel 1
8 GND Ground
USB Port Description
Page 21
○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-8
Chapter 2
Mic-in/Head-Phone
Mic-in is a connector for microphone. Head-Phone is a connector for
Speakers or Headphones.
OPTICAL SPDIF-in
The OPTICAL connector allows you to receive the audio file of SPDIF
interface for recording and playing.
The SPDIF (Sony & Philips Digital Interface) is developed jointly by the
Sony and Philips corporations . A standard audio file transfer format, SPDIF
allows the transfer of digital audio signals from one device to another without
having to be converted first to an analog format.
Page 22

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-9
Introducing Mainboard
2.6 Back panel
The Back Panel provides the following ports:
VGA Port
Keyboard
USB x 2
Optical SPDIF-out
Speaker-out
Line-in
Mic-in
Parallel Port
LAN Port
Mouse
Serial Port
9-Pin Male DIN Connector
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9
Serial Port
The mainboard offers a 9-pin male DIN serial port . The port is 16550A
high speed communication ports that sends/receives 16 bytes FIFOs. You can
attach a serial mouse or other serial devices directly to the connector.
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 DCD Data Carry Detect
2 SIN Serial In or Receive Data
3 SOUT Serial Out or Transmit Data
4 DT R Data Terminal Ready
5 GN D Ground
6 DSR Data Set Ready
7 RTS Request To Send
8 CTS Clear To Send
9 RI Ring Indicate
Pin Definition
Page 23

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-10
Chapter 2
Mouse/Keyboard Connectors
The mainboard provides two standard mini DIN connectors for attaching
PS/2® mouse and keyboard. You can plug a PS/2® mouse or keyboard directly
into the connector.
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 Mouse DATA Mouse DATA
2 NC No connection
3 GND Ground
4 VCC +5V
5 Mouse Clock Mouse clock
6 NC No connection
Pin Definition
PS/2 Mouse (6-pin Female)
2
1
3
4
5
6
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 Keyboard DATA Keyboard DATA
2 NC No connection
3 GND Ground
4 VCC +5V
5 Keyboard Clock Keyboard clock
6 NC No connection
Pin Definition
PS/2 Keyboard (6-pin Female)
2
1
3
4
5
6
Pin Definition
Analog Video Display Connector (DB-15s)
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 Red
2 Green
3 Blue
4 Not used
5 Ground
6 Ground
7 Ground
8 Ground
9 Power
10 Ground
11 Not used
12 SDA
13 Horizontal Sync
14 Vertical Sync
15 SCL
DB 15-Pin Female Connector
5 1
15 11
VGA Port
The mainboard provides one DB 15-pin female connector to connect a
VGA monitor.
Page 24

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-11
Introducing Mainboard
OPTICAL SPDIF-out
The OPTICAL connector allows you to play the audio file of SPDIF interface.
The mainboard provides one standard RJ-45 jack for connection to Local
Area Network (LAN). You can connect a network cable to the LAN jack.
Pin Definition
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 TDP Transmit Differential Pair
2 TDN Transmit Differential Pair
3 RDP Receive Differential Pair
4 NC Not Used
5 NC Not Used
6 RD N Receive Differential Pair
7 NC Not Used
8 NC Not Used
RJ45 LAN Jack
USB Ports
The mainboard provides two USB2.0 EHCI/USB1.1 OHCI Universal Serial Bus root for attaching USB devices such as keyboard, mouse or other USBcompatible devices. You can plug the USB device directly into the connector.
USB Ports
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 VCC +5V
2 -Data 0 Negative Data Channel 0
3 +Data 0 Positive Data Channel 0
4 GND Ground
5 VCC +5V
6 -Data 1 Negative Data Channel 1
7 +Data 1 Positive Data Channel 1
8 GND Ground
USB Port Description
Page 25

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-12
Chapter 2
Parallel Port
The mainboard provides a 25-pin female centronic connector as LPT. A
parallel port is a standard printer port that supports Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP)
and Extended Capabilities Parallel Port (ECP) mode.
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 STROBE Strobe
2 DATA0 Data0
3 DATA1 Data1
4 DATA2 Data2
5 DATA3 Data3
6 DATA4 Data4
7 DATA5 Data5
8 DATA6 Data6
9 DATA7 Data7
10 ACK# Acknowledge
11 BUSY Busy
12 PE Paper End
13 SELECT Select
14 AUTO FEED# Automatic Feed
15 ERR# Error
16 INIT# Initialize Printer
17 SLIN# Select In
18 GND Ground
19 GND Ground
20 GND Ground
21 GND Ground
22 GND Ground
23 GND Ground
24 GND Ground
25 GND Ground
Pin Definition
14
25
13 1
Page 26

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-13
Introducing Mainboard
Audio Port
Speaker-out is a connector for Speakers or Headphones. Line In is used
for external CD player, Tape player, or other audio devices. Mic-in is a connec-
tor for microphones. These three ports can also be used for 5.1 channel audio
output.
NOTE: When used for 5.1 channel audio output, Speaker-out is used for “left/
right”, Line-in is used for “surround left/right” while Mic-in is used for “Center/
LFE (Subwoofer).
Speaker-out
Line-in Mic-in
Page 27

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-14
Chapter 2
2.7 Connectors
PIDE1 (Primary IDE Connector)
- PIDE1 can only connect a HDD.
SIDE1 (Secondary IDE Connector)
- SIDE1 can only connect a CD-ROM drive.
IDE Connectors: PIDE1 & SIDE1
The mainboard has a 32-bit Enhanced PCI IDE and Ultra DMA 33/66/100
controller that provides PIO mode 0~4, Bus Master, and Ultra DMA/33/66/100
function. The two connectors on the mainboard allows you to connect to two
IDE devices.
FDD Connector: FDD1
The mainboard provides you with a standard floppy disk drive connector
that supports 1.44M floppy disk type.
FDD1
PIDE1
SIDE1
If you install two hard disks on cable, you must configure the
second drive to Slave mode by setting its jumper. Refer to the
hard disk documentation supplied by hard disk vendors for jumper
setting instructions.
Page 28

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-15
Introducing Mainboard
CPU/System Fan Connectors: CPUFAN1/CPUFAN2/SYSFAN1
The CPU and System Fan connectors support system cooling fans with
+12V that is controlled by PWM. When connecting the wire to the three-pin
head connectors, always note that the red wire is the positive and should be
connected to the +12V (that is controlled by PWM), the black wire is Ground
and should be connected to GND.
CPUFAN1 CPUFAN2
TV-Tuner Card Connector: CN3
The mainboard provides the connector to connect the TV-Tuner card.
You can insert the TV-Tuner card into the PCI Slot 1.
GND
R
L
Serial ATA RAID Connector: SATA1
The mainboard provides the connector to connect the hard disk of Serial
ATA interface. One Serial ATA cable is included in the package.
SATA1 Pin Definition
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GND TXP
3 TXN GND
5 RXN RXP
7 GND
1
7
2
4
6
SENSOR
+12V
GND
+12V
SENSOR
GND
SYSFAN1
Power
GDD
Page 29

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-16
Chapter 2
Card Reader Connector: CR1
The mainboard provides a connector to connect the USB Card Reader (for
Deluxe Model) on the Front Panel.
Modem Module Connector: MDC1 (Optional)
The mainboard provides the connector to connect the modem module.
The modem module is directly inserted into the connector without an extra cable.
MDC1
Page 30

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-17
Introducing Mainboard
Front Panel Power Connector: JFP1
The mainboard provides a Front Panel connector for electrical connection to the Front Panel switches and LEDs. JFP1 is compliant with Intel® Front
Panel I/O Connectivity Design Guide.
PIN SIGNAL DESCRIPTION
1 HD_LED_P Hard disk LED pull-up
2 FP PWR/SLP MSG LED pull-up
3 HD_LED_N Hard disk active LED
4 FP PWR/SLP MSG LED pull-up
5 RST_SW_N Reset Switch low reference pull-down to GND
6 PWR_SW_P Power Switch high reference pull-up
7 RST_SW_P Reset Switch high reference pull-up
8 PWR_SW_N Power Switch low reference pull-down to GND
9 RSVD_DNU Reserved. Do not use.
JFP1 Pin Definition
1
910
JFP1
HDD
LED
Reset
Switch
Power LED
Power
Switch
2
Page 31

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-18
Chapter 2
2.8 Jumper
There is a CMOS RAM on board that has a power supply from external
battery to keep the data of system configuration. With the CMOS RAM, the system can automatically boot OS every time it is turned on. That battery has long
life time for at least 2 years. If you want to clear the system configuration, use
the JBAT1 (Clear CMOS Jumper ) to clear data. Follow the instructions below to
clear the data:
Clear Data
1
3
Keep Data
1
3
Clear CMOS Jumper: JBAT1
You can clear CMOS by shorting 2-3 pin while the system is off.
Then return to 1-2 pin position. Avoid clearing the CMOS while
the system is on; it will damage the mainboard.
Page 32

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
2-19
Introducing Mainboard
2.9 Slots
PCI 1
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) Slot
The AGP slot allows you to insert the AGP graphics
card. AGP is an interface specification designed for the
throughput demands of 3D graphics. It introduces a 66MHz,
32-bit channel for the graphics controller to directly access
main memory and provides three levels of throughputs: 1x
(266Mbps), 2x (533Mbps) , 4x (1.07Gbps) and 8x.
PCI Slot
The PCI slot allows you to insert PCI card or TV Tuner
card.
When adding or removing expansion cards, make sure
that you unplug the power supply first. Meanwhile, read the
documentation for the expansion card to make any necessary hardware or software settings
NOTE: You can install the OPTIONAL MS8606 card into
the PCI slot to enjoy watching TV.
AGP Slot
Mini PCI
Mini PCI Slot
The motherboard provides a mini PCI slot for connecting a mini PCI interface card.
Page 33

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-1
Setting BIOS Function
Setting BIOS FunctionSetting BIOS Function
Setting BIOS FunctionSetting BIOS Function
Setting BIOS Function
3.1 Entering Setup3.1 Entering Setup
3.1 Entering Setup3.1 Entering Setup
3.1 Entering Setup
3.2 The Main Menu3.2 The Main Menu
3.2 The Main Menu3.2 The Main Menu
3.2 The Main Menu
3.3 Standard CMOS Features3.3 Standard CMOS Features
3.3 Standard CMOS Features3.3 Standard CMOS Features
3.3 Standard CMOS Features
3.4 Advanced BIOS Features3.4 Advanced BIOS Features
3.4 Advanced BIOS Features3.4 Advanced BIOS Features
3.4 Advanced BIOS Features
3.5 Advanced Chipset Features3.5 Advanced Chipset Features
3.5 Advanced Chipset Features3.5 Advanced Chipset Features
3.5 Advanced Chipset Features
3.6 Integrated Peripherals3.6 Integrated Peripherals
3.6 Integrated Peripherals3.6 Integrated Peripherals
3.6 Integrated Peripherals
3.7 Power Management Setup3.7 Power Management Setup
3.7 Power Management Setup3.7 Power Management Setup
3.7 Power Management Setup
3.8 PnP/PCI Configurations3.8 PnP/PCI Configurations
3.8 PnP/PCI Configurations3.8 PnP/PCI Configurations
3.8 PnP/PCI Configurations
3.9 PC Health Status3.9 PC Health Status
3.9 PC Health Status3.9 PC Health Status
3.9 PC Health Status
3.10 Frequency/V3.10 Frequency/V
3.10 Frequency/V3.10 Frequency/V
3.10 Frequency/V
oltage Controloltage Control
oltage Controloltage Control
oltage Control
3.11 Load Default Setting3.11 Load Default Setting
3.11 Load Default Setting3.11 Load Default Setting
3.11 Load Default Setting
3.12 Set Supervisor/User Password3.12 Set Supervisor/User Password
3.12 Set Supervisor/User Password3.12 Set Supervisor/User Password
3.12 Set Supervisor/User Password
3
3
Page 34

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-2
Chapter 3
3.1 Entering Setup
Power on the computer and the system will start POST (Power On Self
Test) process. When the message below appears on the screen, press <DEL> key
to enter Setup.
Press DEL to enter SETUP
If the message disappears before you respond and you still wish to enter
Setup, restart the system by turning it OFF and On or pressing the RESET button.
You may also restart the system by simultaneously pressing <Ctrl>, <Alt>, and
<Delete> keys.
Control Keys
<↑>
Move to the previous item
<↓>
Move to the next item
<←>
Move to the item in the left hand
<→>
Move to the item in the right hand
<Enter> Select the item
<Esc> Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the main menu from a submenu
<+/PU> Increase the numeric value or make changes
<-/PD> Decrease the numeric value or make changes
<F1> General help, only for Status Page Setup Menu and Option Page
Setup Menu
<F5> Restore the previous CMOS value from CMOS, only for Option Page
Setup Menu
<F7> Load Optimized defaults
<F10> Save all the CMOS changes and exit
Page 35

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-3
Setting BIOS Function
Getting Help
After entering the Setup menu, the first menu you will see is the Main
Menu.
Main Menu
The main menu lists the setup functions you can make changes to. You
can use the control keys ( ↑↓ ) to select the item. The on-line description of the
highlighted setup function is displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Sub-Menu
If you find a right pointer symbol (as shown in the right view) appears to the left
of certain fields that means a sub-menu containing additional options can be
launched from this field. You can use control keys (↑↓ ) to highlight the field
and press <Enter> to call up the sub-menu. Then you can use the control keys
to enter values and move from field to field within a sub-menu. If you want to
return to the main menu, just press <Esc >.
8IDE Primary Master
8IDE Primary Slave
8IDE Secondary Master
8IDE Secondary Slave
General Help <F1>
The BIOS setup program provides a General Help screen. You can call up
this screen from any menu by simply pressing <F1>. The Help screen lists the
appropriate keys to use and the possible selections for the highlighted item. Press
<Esc> to exit the Help screen.
Page 36

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-4
Chapter 3
3.2 The main menu
Once you enter Phoenix-Award® BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, the Main Menu
(Figure 1) will appear on the screen. The Main Menu allows you to select from
eleven setup functions and two exit choices. Use arrow keys to select among
the items and press <Enter> to accept or enter the sub-menu.
Standard CMOS Features
Use this menu for basic system configurations, such as time, date etc.
Advanced BIOS Features
Use this menu to setup the items of AWARD® special enhanced features.
Advanced Chipset Features
Use this menu to change the values in the chipset registers and optimize your
system’s performance.
Integrated Peripherals
Use this menu to specify your settings for integrated peripherals.
Page 37

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-5
Setting BIOS Function
Power Management Setup
Use this menu to specify your settings for power management.
PnP/PCI Configurations
This entry appears if your system supports PnP/PCI.
PC Health Status
This entry shows your PC health status.
Frequency/Voltage Control
Use this menu to specify your settings for frequency/voltage control.
Load Default Setting
Use this menu to load factory default settings into the BIOS for stable system
performance operations.
Set Supervisor Password
Use this menu to set Supervisor Password.
Set User Password
Use this menu to set User Password.
Save & Exit Setup
Save changes to CMOS and exit setup.
Exit Without Saving
Abandon all changes and exit setup.
Page 38

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-6
Chapter 3
3.3 standard cmos features
The items in Standard CMOS Features Menu are divided into 8 categories.
Each category includes no, one or more than one setup items. Use the arrow keys
to highlight the item and then use the <PgUp> or <PgDn> keys to select the value
you want in each item.
Date
This allows you to set the system to the date that you want (usually the current
date). The format is <day><month> <date> <year>.
Time
This allows you to set the system time that you want (usually the current time).
The time format is <hour> <minute> <second>.
IDE Channel 0/Channel 1 Master/Slave
Press PgUp/<+> or PgDn/<-> to select [Manual], [None] or [Auto] type. Note
that the specifications of your drive must match with the drive table. The hard
disk will not work properly if you enter improper information for this category. If
your hard disk drive type is not matched or listed, you can use [Manual] to
define your own drive type manually.
Page 39

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-7
Setting BIOS Function
If you select [Manual], related information is asked to be entered to the following items. Enter the information directly from the keyboard. This information
should be provided in the documentation from your hard disk vendor or the
system manufacturer.
Access Mode The settings are CHS, LBA, Large, Auto.
Capacity The formatted size of the storage device.
Cylinder Number of cylinders.
Head Number of heads.
Precomp Write precompensation.
Landing Zone Cylinder location of the landing zone.
Sector Number of sectors.
Drive A
This item allows you to set the type of floppy drives installed.
Halt On
The setting determines whether the system will stop if an error is detected at boot.
Available options are:
[All Errors] The system stops when any error is detected.
[No Errors] The system doesn’t stop for any detected error.
[All, But Keyboard] The system doesn’t stop for a keyboard error.
[All, But Diskette] The system doesn’t stop for a disk error.
[All, But Disk/Key] The system doesn’t stop for either a disk or a key
CPU Type/BIOS Version/Video Memory/System Memory/Total Memory
The items show the CPU type, BIOS version and memory status of your system
(read only).
Page 40

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-8
Chapter 3
3.4 advanced bios features
Quick Boot
Setting the item to [Enabled] allows the system to skip certain tests while booting.
This will decrease the time needed to boot the system. Available options:
[Enabled], [Disabled].
Full Screen LOGO Show
This item enables you to show the company logo on the bootup screen. Settings
are:
[Enabled] Shows a still image (logo) on the full screen at boot.
[Disabled] Shows the POST messages at boot.
Boot Sequence
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu. Then you may use the arrow keys to
select the desired device, then press <+>, <-> or <PageUp>, <PageDown>
key to move it up/down in this hard disk boot priority list.
Hard Disk Boot Priority
Press [Enter] to enter a sub menu which shows every current hard drive
installed. Use [PageUp] or [PageDown] key to select the first boot hard
disk.
Page 41

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-9
Setting BIOS Function
CD-ROM Boot Priority
Press [Enter] to enter a sub menu which shows every current CD-ROM
installed. Use [PageUp] or [PageDown] key to select the first boot CDROM.
1st/2nd/3rd Boot Device
The items allow you to set the sequence of boot devices where BIOS attempts to load the disk operating system.
Boot Other Device
Setting the option to [Enabled] allows the system to try to boot from other
device if the system fails to boot from the 1st/2nd/3rd boot device.
Boot Up Num-Lock LED
This setting is to set the Num Lock status when the system is powered on.
Setting to [On] will turn on the Num Lock key when the system is powered
on. Setting to [Off] will allow users to use the arrow keys on the numeric
keypad. Setting options: [On], [Off].
Seek Floppy
Setting to [Enabled] will make BIOS seek floppy drive A: before booting the
system. Settings: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Security Option
This specifies the type of BIOS password protection that is implemented. Settings are described below:
The password prompt appears only when end users try
to run Setup.
A password prompt appears every time when the computer
is powered on or when end users try to run Setup.
DescriptionOption
[Setup]
[System]
Page 42

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-10
Chapter 3
Hyper-Threading Technology
The processor uses Hyper-Threading technology to increase transaction rates
and reduces end-user response times. The technology treats the two cores inside
the processor as two logical processors that can execute instructions
simultaneously. In this way, the system performance is highly improved. If you
disable the function, the processor will use only one core to execute the
instructions. Settings: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Page 43

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-11
Setting BIOS Function
3.5 advanced chipset features
NOTE: Change these settings only if you are familiar with the chipset.
DRAM Timing Selectable
Selects whether DRAM timing is controlled by the SPD (Serial Presence Detect)
EEPROM on the DRAM module. Setting to [By SPD] enables DRAM timings to
be determined by BIOS based on the configurations on the SPD. Selecting
[Manual] allows users to configure the DRAM timings manually.
CAS Latency Time
This controls the timing delay (in clock cycles) before SDRAM starts a read
command after receiving it. Settings: [2], [2.5], [3] (clocks). [2] (clocks) increases the system performance the most while [3] (clocks) provides the most
stable performance.
Active to Precharge Delay
The field specifies the idle cycles before precharging an idle bank. Settings: [8],
[7], [6], [5] (clocks).
Page 44

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-12
Chapter 3
DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
This field allows you to set the number of cycles for a timing delay between the
CAS and RAS strobe signals, used when DRAM is written to, read from or
refreshed. Fast speed offers faster performance while slow speed offers more
stable performance. Settings: [4], [3], [2] (clocks).
DRAM RAS# Precharge
This item controls the number of cycles for Row Address Strobe (RAS) to be
allowed to precharge. If insufficient time is allowed for the RAS to accumulate
its charge before DRAM refresh, refresh may be incomplete and DRAM may fail
to retain data. This item applies only when synchronous DRAM is installed in
the system. Available settings: [4], [3], [2] (clocks).
Memory Frequency For
Use this item to configure the clock frequency of the installed DRAMs. Setting
options: [Auto], [DDR266], [DDR333], [DDR320], [DDR400].
AGP Aperture Size (MB)
This setting controls just how much system RAM can be allocated to AGP for
video purposes. The aperture is a portion of the PCI memory address range
dedicated to graphics memory address space. Host cycles that hit the aperture
range are forwarded to the AGP without any translation. The option allows the
selection of an aperture size of [4MB], [8MB], [16MB], [32MB], [64MB], [128MB],
and [256MB].
Page 45

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-13
Setting BIOS Function
**On-Chip VGA Setting**
The following items allow you to configure the settings about On-Chip VGA.
On-Chip VGA
This setting determines whether the system RAM can be allocated to on-chip
video controller for video purposes. When setting to [Enabled], up to 128MB
system RAM will be allocated to on-chip video controller. Settings: [Disabled],
[Enabled].
On-Chip Frame Buffer Size
Frame Buffer is the video memory that stores data for video display (frame). This
field is used to determine the memory size for Frame Buffer. Larger frame buffer
size increases video performance. Settings: [1M], [8M], [16M].
Page 46

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-14
Chapter 3
3.6 integrated peripherals
OnChip IDE Device
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
IDE DMA Transfer Access
This item is used to enable or disable the DMA transfer function of the IDE Hard
Drive. The settings are: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Page 47

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-15
Setting BIOS Function
On-Chip Primary/Secondary PCI IDE
The chipset contains a PCI IDE interface with support for two IDE channels.
Select [Enabled] to activate the IDE interface. Select [Disabled] to deactivate
this interface.
**On-Chip Serial ATA Setting**
On-Chip Serial ATA
This setting is used to specify the SATA controller. Settings: [Disable], [Auto],
[Legacy Mode], [Native Mode]. If [Legacy Mode] is selected, PATA and SATA
will be combined. If [Native Mode] is selected, PATA and SATA will both be
enabled. If [Auto] is selected, PATA and SATA will be arranged by BIOS, and
you will be able to see the IDE Device status listed in Standard CMOS Features.
Serial ATA Port 0 Mode
When On-Chip Serial ATA is set to [Legacy Mode], setting options will show as
follows:
1. [Primary Master]
Serial ATA Port 0 will be set to Primary Master.
2. [Primary Slave]
Serial ATA Port 0 will be set to Primary Slave.
3. [Secondary Master]
Serial ATA Port 0 will be set to Secondary Master.
4. [Secondary Slave]
Serial ATA Port 0 will be set to Secondary Slave.
When On-Chip Serial ATA is set to [Native Mode], setting options will show as
follows:
1. [SATA1 Master]
Serial ATA Port 0 will be set to Native Mode Master.
2. [SATA1 Slave]
Serial ATA Port 0 will be set to Native Mode Slave.
Page 48

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-16
Chapter 3
Onboard Device
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
USB Controller
Select [Enabled] if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller
and you have USB peripherals.
USB 2.0 Controller
This setting is used to enable/disable the onboard USB2.0 controller. This setting works only when the operating system installed supports USB2.0 driver,
such as Windows 2000/XP/ME. Setting options: [Disabled], [Enabled].
USB Keyboard/Mouse Support
Select [Enabled] if you need to use a USB keyboard/mouse in the operating
system that does not support or have any USB keyboard/mouse driver installed,
such as DOS and SCO Unix. Setting options: [Enabled], [Disabled].
AC97 Audio
[Auto] allows the motherboard’s BIOS to detect whether you’re using any audio
device. If so, the onboard audio controller will be enabled. If not, the onboard
audio controller will be disabled. If you want to use different controller cards to
Page 49

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-17
Setting BIOS Function
connect audio connectors, set the field to [Disabled]. Setting options: [Disabled],
[Auto].
AC97 Modem
[Auto] allows the mainboard to detect whether a modem is used. If a modem is
detected, the onboard AC’97 modem controller will be enabled; if not, it is
disabled. Disable the controller if you want to use other controller cards to
connect a modem. Settings: [Auto], [Disabled].
Onboard LAN Device
This setting controls the onboard LAN device. Setting options: [Disabled],
[Enabled].
Onboard 1394 Device
This setting controls the onboard 1394 device. Setting options: [Disabled],
[Enabled].
SuperIO Device
Press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu and the following screen appears:
Page 50

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-18
Chapter 3
Onboard FDC Controller
Select [Enabled] if your system has a floppy disk controller (FDD) installed on
the system board and you wish to use it. If you install add-on FDC or the system
has no floppy drive, select [Disabled] in this field. The settings are: [Enabled]
and [Disabled].
Onboard Serial Port 1
These items specify the base I/O port address and IRQ for the onboard Serial Port
A (COM A). Selecting [Auto] allows BIOS to automatically determine the correct base I/O port address. Settings: [Disabled], [3F8/IRQ4], [2F8/IRQ3], [3E8/
IRQ4], [2E8/IRQ3], [Auto].
Onboard Parallel Port
This specifies the I/O port address and IRQ of the onboard parallel port. Settings:
[378/IRQ7], [278/IRQ5], [3BC/IRQ7], [Disabled].
Parallel Port Mode
Select an operating mode for the onboard parallel (printer) port.
SPP: Standard Parallel Port
EPP: Enhanced Parallel Port
ECP: Extended Capability Port
Options: [SPP], [EPP1.9+SPP], [ECP], [EPP1.9+ECP], [PRINTER], [EPP1.7+SPP],
[EPP1.7+ECP].
ECP Mode Use DMA
The ECP mode has to use the DMA channel, so choose the onboard parallel port
with the ECP feature. After selecting it, the following message will appear:
“ECP Mode Use DMA.” At this time, the user can choose between DMA channel [3] or [1].
Page 51

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-19
Setting BIOS Function
3.7 Power management setup
Sleep State
This item specifies the power saving mode for ACPI function. If your operating
system supports ACPI, such as Windows 98SE, Windows ME and Windows 2000,
you can choose to enter the Standby mode in S1(POS) or S3(STR) fashion through
the setting of this field. Options are:
[S1(POS)] The S1 sleep mode is a low power state. In this state, no
system context (CPU or chipset) is lost and hardware main
tains all system context.
[S3(STR)] The S3 sleep mode is a power-down state in which power is
supplied only to essential components such as main memory
and wake-capable devices and all system context is saved
to main memory. The information stored in memory will be
used to restore the PC to the previous state when an “wake
up” event occurs.
[Auto] BIOS determines the mode automatically.
Page 52

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-20
Chapter 3
Run VGABIOS if S3 Resume
When Sleep State is set to [S3] or [Auto], users can select the options in this
field. Selecting [Yes] allows BIOS to call VGABIOS to initializet he VGA card
when system wakes up (resumes) from S3 sleep state. The system resume time
is shortened when you disable the function, but system will need an AGP driver
to initialize the VGA card. Therefore, if the AGP driver of the card does not
support the initialization feature, the display may work abnormally or not function after resuming form S3. Options: [Auto], [Yes], [No].
Wake Up On PME
When set to [Enabled], the feature allows your system to be awakened from
the power saving modes through any event on PME (Power Management
Event). Settings: [Enabled], [Disabled].
USB Wake-Up From S3
This item allows the USB device to wake up the system from S3 sleep state.
Settings: [Enabled], [Disabled].
PS/2 KB/MS Wake-Up from S3
This setting allows you to enter “Any Key” (max. 8 numbers) to wake up the
system from S3 state. Settings are: [Hot Key] and [Disable].
Resume By Alarm
The field is used to enable or disable the feature of booting up the system on a
scheduled time/date.
Date(of Month) Alarm
The field specifies the date for Resume By Alarm. Settings: [0]~[31].
Time(hh:mm:ss) Alarm
The field specifies the time for Resume By Alarm. Format is <hour>
<minute><second>.
Page 53

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-21
Setting BIOS Function
After AC Power Lost
This setting specifies whether your system will reboot after a power failure or
interrupt occurs. Available settings are:
[Off] Leaves the computer in the power off state.
[On] Leaves the computer in the power on state.
Page 54

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-22
Chapter 3
3.8 pnp/pci configurations
This section describes configuring the PCI bus system and PnP (Plug &
Play) feature. PCI, or Peripheral Component Interconnect, is a system which
allows I/O devices to operate at speeds nearing the speed the CPU itself uses
when communicating with its special components. This section covers some
very technical items and it is strongly recommended that only experienced users
should make any changes to the default settings.
Clear ESCD
Normally, you leave this field [Disabled]. Select [Enabled] to reset Extended
System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have installed a
new add-on and the system reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict
that the operating system cannot boot.
Primary Graphic Adaptor
This setting specifies which VGA card is your primary graphics adapter. Setting
options are:
[Onboard/AGP] The system initializes the installed AGP card first.
If the AGP card is not available, it will initialize the
PCI VGA card.
[PCI Slot] The system initialize the installed PCI VGA card first.
If the PCI VGA card is not available, it will initialize the AGP card.
Page 55

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-23
Setting BIOS Function
Current CPU/System Temperature, Current CPU/System FAN Speed, Vcore,
+2.5V, Vcc, +3.3V, +5V, +12V,
These items display the current status of all of the monitored hardware devices/
components such as CPU voltages, temperatures and all fans’ speeds.
3.9 PC health status
Page 56

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-24
Chapter 3
3.10 Frequency/Voltage Control
Auto Detect PCI Clk
This option allows you to enable/disable the feature of auto detecting the clock
frequency of the installed PCI bus. The settings are: [Enabled], [Disabled].
Spread Spectrum
When the motherboard’s clock generator pulses, the extreme values (spikes) of
the pulses creates EMI (Electromagnetic Interference). The Spread Spectrum
function reduces the EMI generated by modulating the pulses so that the spikes
of the pulses are reduced to flatter curves. If you do not have any EMI problem,
leave the setting at [Disable] for optimal system stability and performance. But
if you are plagued by EMI, set to [Enabled] for EMI reduction. Remember to
disable Spread Spectrum if you are overclocking because even a slight jitter can
introduce a temporary boost in clock speed which may just cause your
overclocked processor to lock up.
CPU Clock
This item specifies the clock frequency of CPU host bus (FSB), AGP (3V66) and
Page 57

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-25
Setting BIOS Function
PCI bus. It provides a method for end users to overclock the processor. Setting
options: Give a DEC value by entering a number between maximum [233 MHz]
to minimum [100 MHz].
Page 58

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-26
Chapter 3
The default setting is the default value set by the BIOS vendor for stable
system performance. When you select Load BIOS Setup Defaults, a message
as below appears:
Press [Y] to load the default values for the most stable system performance.
3.11 Load Default setting
Page 59

○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○○
3-27
Setting BIOS Function
3.12 Set Supervisor/user password
When you select this function, a message as below will appear on the
screen:
Type the password, up to six characters in length, and press <Enter>. The
password typed now will replace any previously set password from CMOS
memory. You will be prompted to confirm the password. Retype the password
and press <Enter>. You may also press <Esc> to abort the selection and not
enter a password.
To clear a set password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to
enter the password. A message will show up confirming the password will be
disabled. Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you can
enter Setup without entering any password.
When a password has been set, you will be prompted to enter it every
time you try to enter Setup. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of your system configuration.
Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also have Award BIOS
to request a password each time the system is booted. This would prevent
unauthorized use of your computer. The setting to determine when the password prompt is required is the Security Option of the ADVANCED BIOS FEA-
TURES menu. If the Security Option is set to [System], the password is required
both at boot and at entry to Setup. If set to [Setup], password prompt only
occurs when you try to enter Setup.
MSI Reminds You...
About Supervisor Password & User Password:
Supervisor password: Can enter and change the settings of the
setup menu.
User password: Can only enter but do not have the right to
change the settings of the setup menu.
Page 60

4-1
Wireless LAN Card
Wireless LAN Card
(for Deluxe Model)
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Wireless Network Utility
4.3 Encryption
4.4 Status
4.5 Information
4
4
Page 61

4-2
Chapter 4
The Wireless LAN Card, compliant with IEEE802.11b, is a high-efficiency
wireless adapter for wireless networking at home, in office or in public places.
The data transfer rate can be auto-negotiated to 1, 2, 5.5Mbps or up to
11Mbps, and is compatible with any existing IEEE802.11b devices.
With Wireless LAN Card, you can roam between conference room and office
without being disconnected the LAN cables; in addition, sharing files and
printers can be easy tasks.
The Wireless LAN Card is available to Microsoft Windows operating systems
(Windows® XP/2000/ME/98SE) and can be integrated into networking with
either Ad-hoc mode (computer-to-computer, without an Access Point) or
Infrastructure mode (computer-to-access point, an Access Point is required).
4.1 Introduction
Page 62

4-3
Wireless LAN Card
4.1.1 Hardware Specifications
Compliant Standards
- IEEE802.11b
Bus and Connector Types
- 32-bit 3.3V Type IIIA
- 124-pin Golden Finger
Security Mechanism
- Hardware-based WEP Privacy
Operational Environment
- Operational Temperature: 0~55OC
- Humidity: 10~90% (Non-Condensing)
Weight and Dimension
- Weight:12g
- Dimension: 50.8 x 59.6 x 4.9mm
4.1.2 Radio Frequency Specifications
Raw Data Rates and Modulation Types
- IEEE802.11b (Auto-Fallback)
CCK: 11 and 5.5Mbps
DQPSK: 2Mbps
DBPSK: 1Mbps
Communication Protocol
- DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) with
ACK
- Half-Duplex
Access Method
- Infrastructure Mode: Station-To-LAN Architecture
- Ad-Hoc Mode: Station-To-Station Architecture
Page 63

4-4
Chapter 4
Right-clicking the icon will bring up a sub-menu containing more
settings:
After installing the driver, the Wireless LAN Card provides a convenient and
powerful utility that allows you to set up, configure, and know your networking status easily and clearly.
- Not connected to the network.
- Connected to the network.
- Receiving/transmitting data from/to the network.
When you move the mouse over the icon, it shows the current
connection information.
4.2 Wireless network utility
4.2.1 The Wireless LAN Icon
Page 64

4-5
Wireless LAN Card
Language
You can select language according to your operating system.
Switch to AP Mode (optional)
If your wireless LAN adapter supports Software AP function, you can
see this item in the sub-menu, and which allows you to use your wireless adapter as a virtual access point. For details, refer to the Soft-
ware AP/Gateway User’s Guide.
Switch to Gateway Mode (optional)
If your wireless LAN adapter supports Software Gateway function,
you can see this item in the sub-menu, and which allows you to use
your wireless adapter as a virtual gateway. For details, refer to the
Software AP/Gateway User’s Guide.
Open Network Connections
Select to open the Network Connections window.
View Available Wireless Networks
Launch the utility to configure your network settings.
Exit
Close the program.
Clicking the icon will launch the utility as shown below to configure
your network settings.
Page 65

4-6
Chapter 4
If you use Windows XP, the wireless LAN is controlled by the operating system
(default). To take full advantage of your wireless adapter, it is recommended to
use the Wireless Network Utility to control your wireless LAN.
Clic k
Doubl e-click
To change the control setting:
1. Right-click the Wireless LAN icon and select the Network
Connections option.
2. In the Network Connections window, double-click the Wireless
Network Connection icon to bring up the following dialog
window.
4.2.2 Changing the Control Setting(for Windows XP Only)
Page 66

4-7
Wireless LAN Card
3. Click Advanced, and the Properties window will appear as below.
Uncheck this option
Clic k
4. Uncheck the Use Windows to configure my wireless network
settings option. Then, click OK.
5. Now, you can use the Wireless Network Utility to configure your
network.
Page 67

4-8
Chapter 4
Since the wireless LAN card is installed in your computer, you have to configure
the settings for communication to start working in your network environment.
Select
Connecting to the Access Point:
Infrastructure mode allows your computer to communicate with the other computers in the network through an Access Point. The following tasks should be
done before you configure the settings:
- The Access Point must be turned on.
- Your computer with wireless adapter installed and the Access
Point must be located with the communication range of the
Access Point (see the Access Point's manual for details).
Clic k
Clic k
4.3 networking
4.3.1 Infrastructure Mode
1. Click the Wireless LAN icon to bring up the Wireless Network
Connection window.
2. In the list of Available wireless networks, select (highlight) the
network you want, and then click Connect.
Page 68

4-9
Wireless LAN Card
1. Click Advanced in the Wireless Network Connection window.
2. The Available Networks field contains a list of available Access
Points in your network. Select (highlight) one network you want,
and then click Configure to set up the selected network. You
can click Refresh to search the available Access Points in the
network again.
WEP settings
Only the network administrator
can change the SSID and WEP
settings in the Association
window; if you have problem of
accessing the network, please
ask the administrator for help.
Clic k
If you want to configure the network settings:
3. Setup the Network Key (if needed) in the Wireless Network Key
(WEP) field according to the network’s settings.
Page 69

4-10
Chapter 4
con nected
Clic k
4. Click OK. The selected network will appear in the Preferred
Networks field. If it contains two or more networks in the list,
you can use Move up/Move down to set the priority.
5. Click OK to complete the configuration, and an icon indicating
connected to the network will appear in the status area.
Page 70

4-11
Wireless LAN Card
Ad-hoc mode allows your computer to communicate directly with any computer
installed with compatible wireless adapter. If you want to use the network in
Ad-hoc mode:
- All the computers conn ected should be set to Ad-hoc mode.
- The computers have the same SSID (n etwork name) setting.
Clic k
Clic k
4.3.2 Ad-hoc Mode
To configure the settings:
1. Click the Wireless LAN icon to bring up the Wireless Network
Connection window. Then, click Advanced.
Page 71

4-12
Chapter 4
Enter a Network
Nam e (SSID)
IMPO RTANT
Check this to enable Adhoc mode.
Check this option
and cancel the
bottom option
Clic k
Clic k
3. Set up the Network Name (SSID) and Network Key (if needed) for
the network. Then, check the This is a computer-to-computer [ad
hoc] network; wireless access points are not used option and
click OK to enable the Ad-hoc mode.
2. You can build up the Ad-hoc network by clicking Add in the
Preferred Networks field.
Page 72

4-13
Wireless LAN Card
con nected
Clic k
5. The computer set up with this Ad-hoc network in step 3 is the
designated administrator of the network. Any computer can
access the network by selecting Connect in the Wireless Network Connection window.
4. The Ad-hoc network will appear in the Available Networks field.
Click OK, and an icon indicating connected to the network
appears in the status area.
Page 73

4-14
Chapter 4
Network key
Enter a key for the network.
Key format
You can decide the network key to be encoded by ASCII characters or
hexadecimal digitals.
Key length
In ASCII characters format, it can be 5 or 13 characters. In hexadecimal digitals format, it would be 10 or 26 digitals.
Key index
There can be up to 4 sets of WEP key (1~4). The 4 sets of WEP key
must have the identical sequence with the key settings on the Access
Point.
In the wireless network environment, the administrator can set up password
(Network Key) to protect the network from being attacked or unauthorized access.
When building the network, you can set up 4 sets of WEP keys, which can be 5
characters (10 hex-adecimal digital) or 13 characters (26 hex-adecimal digital)
and specify one of them to use.
Check this
Can cel this
To setu p the Network Key,
check Encryption opt ion
first, then cancel The key is
provided for me automatically option.
4.4 Encryption
Page 74

4-15
Wireless LAN Card
In the Status tab, you can configure more network settings.
Channel
Specifies the operating radio frequency channel in Ad-hoc mode, which
should be set to the same channel as the other points in the wireless
network.
Speed
This field sets the current transmitting rate. The speed should be set to
Auto rate to optimize performance and range, which will adjust the
transfer speed for best performance and longest range automatically.
Radio
Set to On to activate the radio.
SSID
Means Service Set Identifier, a unique name shared among all points
in a wireless network. It must be identical for all points in the network.
Then the card will be able to connect to an access point with the
same SSID.
Signal Strength:
shows the received signal
strength level.
Link Quality:
shows the measured signal
level and connection status.
4.5 Status
Click Advance, and you can get more information about the LAN traffic status
and more detailed settings.
Page 75

4-16
Chapter 4
Fragmentation Threshold
You may set the length of the fragment in this field. Please note that
each fragment should not be larger than the Fragmentation Threshold.
RTS/CTS Threshold
You may set the length threshold.
Preamble Type
You may set the length of preamble in this field. The available options
are:
- Long: It is set to 144 bits.
- Short: It is set to 72 bits.
- Auto: The card supports an auto-detection feature,
it will automatically select the Preamble Type
depending on the Access Point Preamble Type if this
option is selected.
Country
Display the country that you are in (read only).
Power save
The card will turn into power save mode when idle.
It is not recomm ended to
change these settings if
you are not familiar with the
advanced configuration.
Page 76

4-17
Wireless LAN Card
In the Information tab, you can get some information about the manufacturer,
hardware and software.
4.6 information
 Loading...
Loading...