MPS MP1469GJ Schematic [ru]
MP1469
The Future of Analog IC Technology
DESCRIPTION
The MP1469 is a high-frequency, synchronous,
rectified, step-down, switch-mode converter
with internal power MOSFETs. It offers a very
compact solution to achieve a 1.5A continuous
output current over a wide input supply range,
with excellent load and line regulation. The
MP1469 has synchronous-mode operation for
higher efficiency over the output current-load
range.
Current-mode operation provides fast transient
response and eases loop stabilization.
Protection features include over-current
protection and thermal shutdown.
The MP1469 requires a minimal number of
readily-available, standard, external
components and is available in a space-saving
6-pin TSOT23 package.
High-Efficiency, 1.5A, 16V, 500kHz
Synchronous, Step-Down Converter
In 6 Pin SOT 23
FEATURES
• Wide 4.7V-to-16V Operating Input Range
• 255m/160m Low-R
Internal Power
DS(ON)
MOSFETs
• Proprietary Switching-Loss–Reduction
Technique
• High-Efficiency Synchronous-Mode
Operation
• Fixed 500kHz Switching Frequency
• AAM Power-Save Mode for High Efficiency
at Light Load
• Internal Soft-Start
• Over-Current Protection and Hiccup
• Thermal Shutdown
• Output Adjustable from 0.8V
• Available in a 6-pin TSOT-23 package
APPLICATIONS
• GameStations
• Digital Set-Top Boxes
• Flat-Panel Television and Monitors
• General Purposes
All MPS parts are lead-free and adhere to the RoHS directive. For MPS green
status, please visit MPS website under Products, Quality Assurance page.
“MPS” and “The Future of Analog IC Technology” are registered trademarks of
Monolithic Power Systems, Inc.
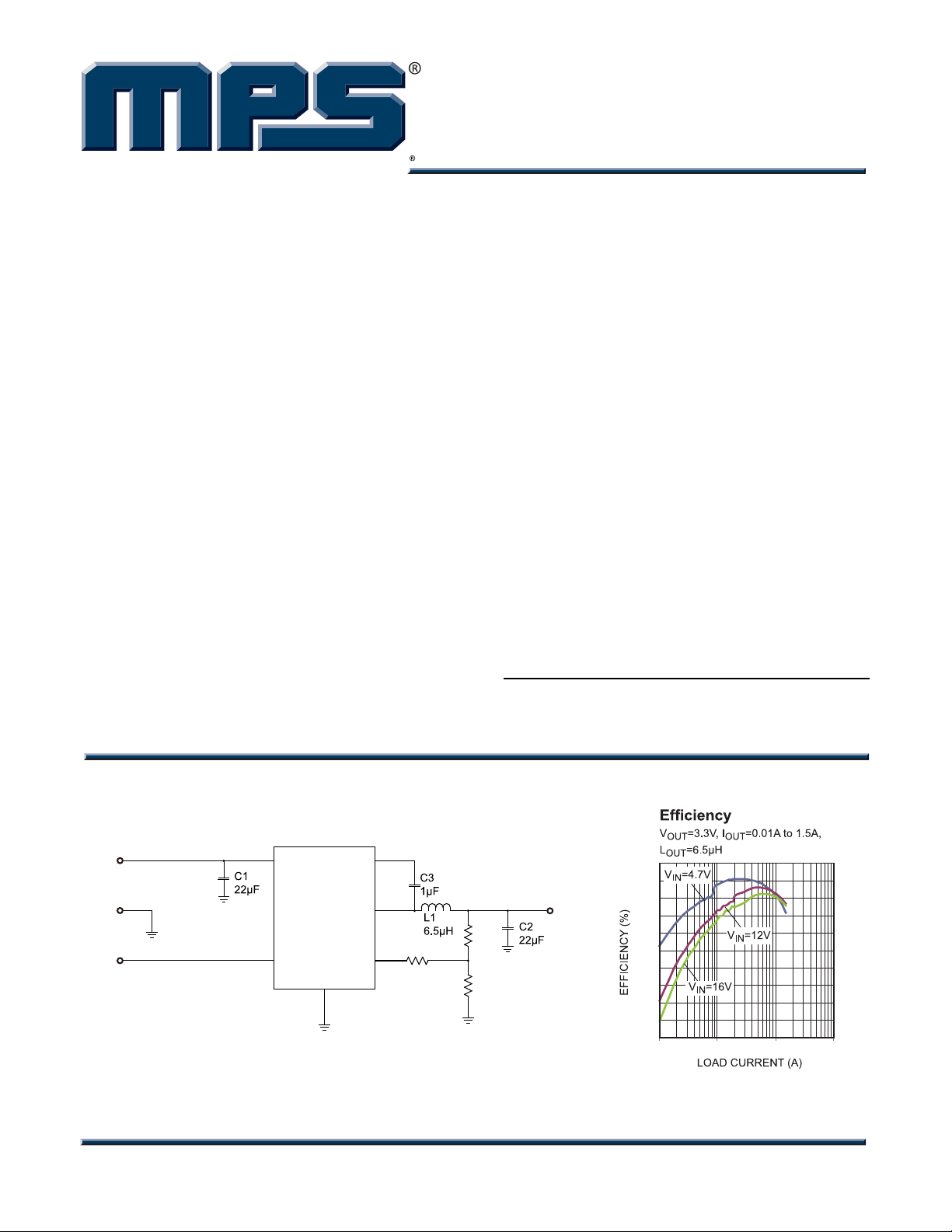
TYPICAL APPLICATION
VIN
GND
EN
MP1469 Rev. 1.01 www.MonolithicPower.com 1
8/26/2013 MPS Proprietary Information. Patent Protected. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2013 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
1
5
IN
U1
MP1469
EN
GND
2
BST
SW
FB
4
3
R3
6
59k
3.3V/1.5A
VOUT
R1
40.2k
R2
13k
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
0.01 0.1 1 10
MP1469 – SYNCHRONOUS, STEP-DOWN CONVERTER WITH INTERNAL MOSFETS
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number* Package Top Marking
MP1469GJ TSOT23-6 ADM
* For Tape & Reel, add suffix –Z (e.g. MP1469GJ–Z);
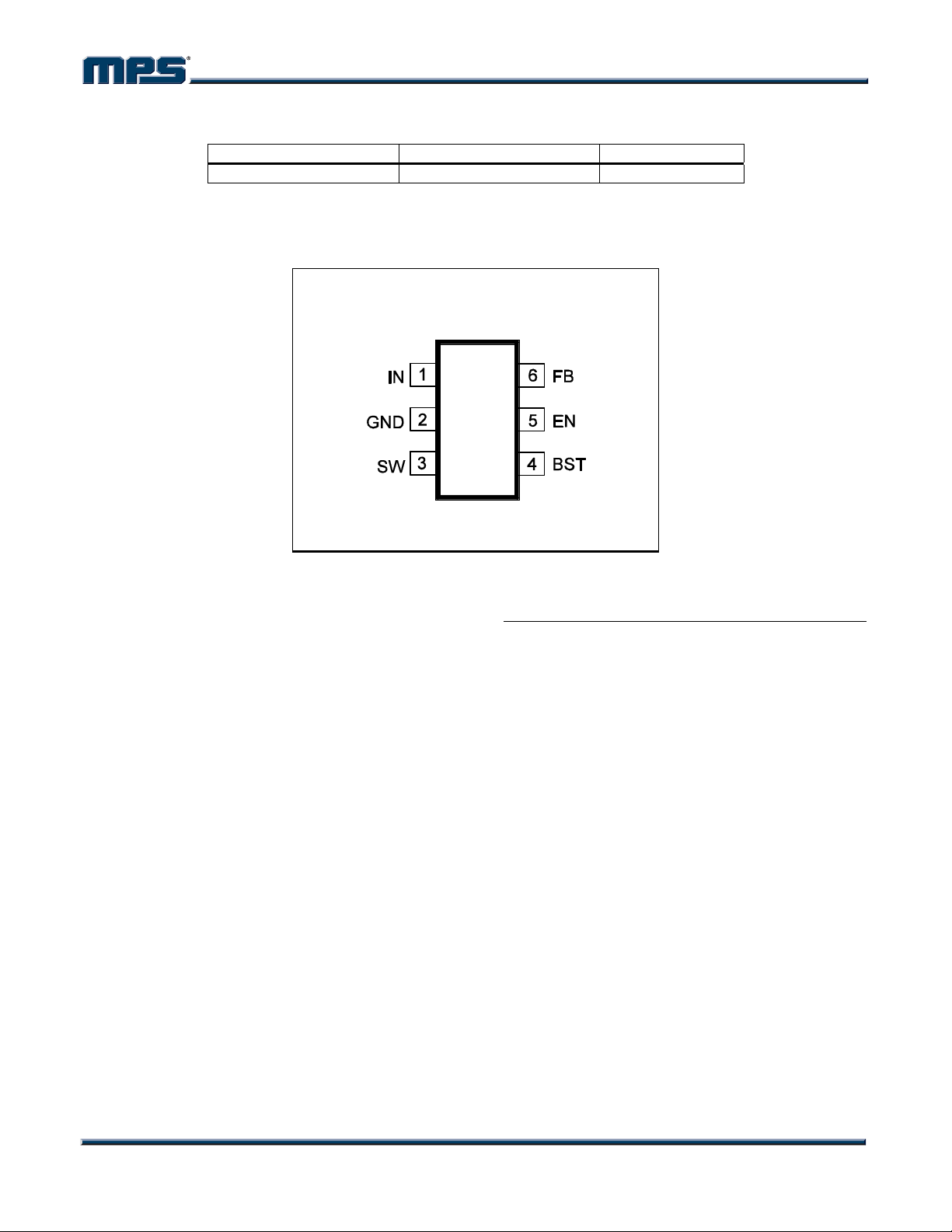
PACKAGE REFERENCE
TOP VIEW
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
VIN ..................................................-0.3V to 17V
V
......................................................................
SW
-0.3V (-5V for <10ns) to 17V (19V for <10ns)
V
......................................................... VSW+6V
BS
All Other Pins...................................–0.3V to 6V
Continuous Power Dissipation (T
= +25°C)
A
(2)
........................................................... 0.57W
Junction Temperature...............................150°C
Lead Temperature ....................................260°C
Storage Temperature................. -65°C to 150°C
Recommended Operating Conditions
(3)
Supply Voltage VIN...........................4.7V to 16V
Output Voltage V
Operating Junction Temp. (T
.................... 0.8V to Vin-3V
OUT
). -40°C to +125°C
J
Thermal Resistance
(4)
θ
JA
θJC
TSOT-23-6............................. 220 .... 110.. °C/W
Notes:
1) Exceeding these ratings may damage the device.
2) The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of the
maximum junction temperature T
ambient thermal resistance
. The maximum allowable continuous power dissipation at
T
A
any ambient temperature is calculated by P
(MAX)-TA)/JA. Exceeding the maximum allowable power
dissipation will cause excessive die temperature, and the
regulator will go into thermal shutdown. Internal thermal
shutdown circuitry protects the device from permanent
damage.
3) The device is not guaranteed to function outside of its
operating conditions.
4) Measured on JESD51-7, 4-layer PCB.
(MAX), the junction-to-
J
, and the ambient temperature
JA
(MAX) = (T
D
J
MP1469 Rev. 1.01 www.MonolithicPower.com 2
8/26/2013 MPS Proprietary Information. Patent Protected. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2013 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
MP1469 – SYNCHRONOUS, STEP-DOWN CONVERTER WITH INTERNAL MOSFETS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(5)
VIN = 12V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Parameter Symbol Condition Min Typ Max Units
Supply Current (Shutdown) IIN VEN = 0V 1 A
Supply Current (Quiescent) Iq VEN = 2V, VFB = 1V 0.83 mA
HS Switch-On Resistance HS
LS Switch-On Resistance LS
Switch Leakage SW
Current Limit
AAM Peak Current I
(5)
I
AAM_PEAK
Oscillator Frequency fSW VFB=0.75V 400 490 580 kHz
Maximum Duty Cycle D
Minimum On Time
(5)
t
ON_MIN
Feedback Voltage VFB 776 800 824 mV
EN Rising Threshold V
EN Falling Threshold V
EN_RISING
EN_FALLING
V
RDS-ON
Vcc=5V 160 m
RDS-ON
VEN = 0V, VSW =12V 1 A
LKG
2.5 3.0 A
LIMIT
=5V 255 m
BST-SW
0.5 A
VFB=700mV 88 92 %
MAX
90 ns
1.4 1.5 1.6 V
1.23 1.32 1.41 V
EN Input Current IEN
VEN=2V 1.6 A
=0 0 A
V
EN
VIN Under-Voltage Lockout
Threshold—Rising
VIN Under-Voltage Lockout
Threshold—Hysteresis
INUV
INUV
3.85 4.2 4.55 V
Vth
340 mV
HYS
Soft-Start Period tSS 1 ms
Thermal Shutdown
Thermal Hysteresis
Notes:
5) Guaranteed by design.
(5)
150 °C
(5)
20 °C
MP1469 Rev. 1.01 www.MonolithicPower.com 3
8/26/2013 MPS Proprietary Information. Patent Protected. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2013 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
MP1469 – SYNCHRONOUS, STEP-DOWN CONVERTER WITH INTERNAL MOSFETS
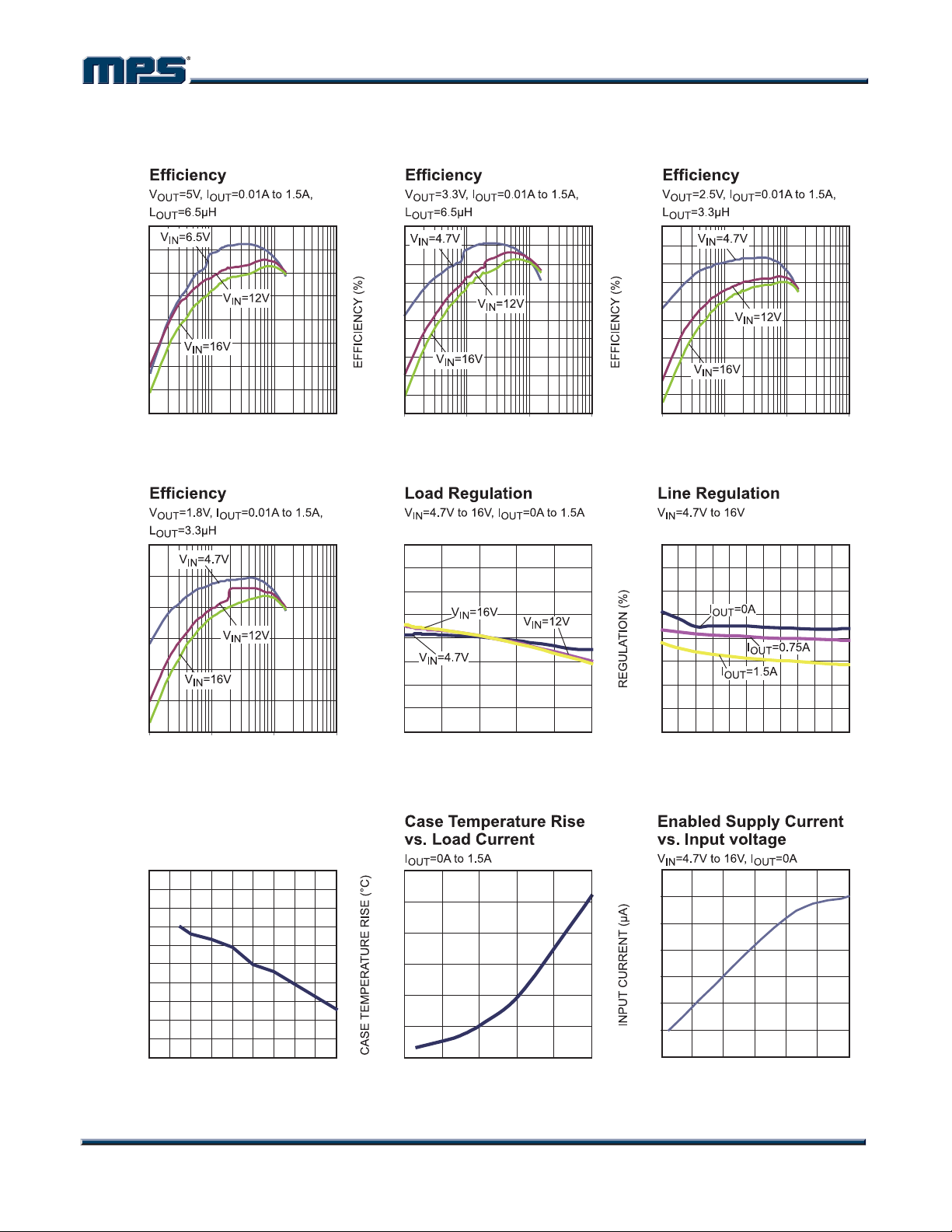
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VIN = 12V, V
= 3.3V, L = 6.5µH, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
100
95
90
85
80
75
EFFICIENCY (%)
70
65
60
0.01 0.1 1 10 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.01 0.1 1 10
100
90
80
70
60
EFFICIENCY (%)
50
40
0.01 0.1 1 10
LOAD CURRENT (A)
LOAD CURRENT (A)
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
LOAD CURRENT (A)
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
-0.5
-1
REGULATION (%)
-1.5
-2
0 0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 1.5
LOAD CURRENT (A)
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
LOAD CURRENT (A)
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
-0.5
-1
-1.5
-2
5678910111213141516
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Peak Current vs. Duty Cycle
4.0
3.8
3.6
3.4
3.2
3.0
2.8
2.6
PEAK CURRENT (A)
2.4
2.2
2.0
01020304050607080 90
DUTY CYCLE (%)
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0.0 0.3 0.6 0.9 1.2 1.5
LOAD CURRENT (A)
MP1469 Rev. 1.01 www.MonolithicPower.com 4
8/26/2013 MPS Proprietary Information. Patent Protected. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2013 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
870
860
850
840
830
820
810
800
46810121416
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
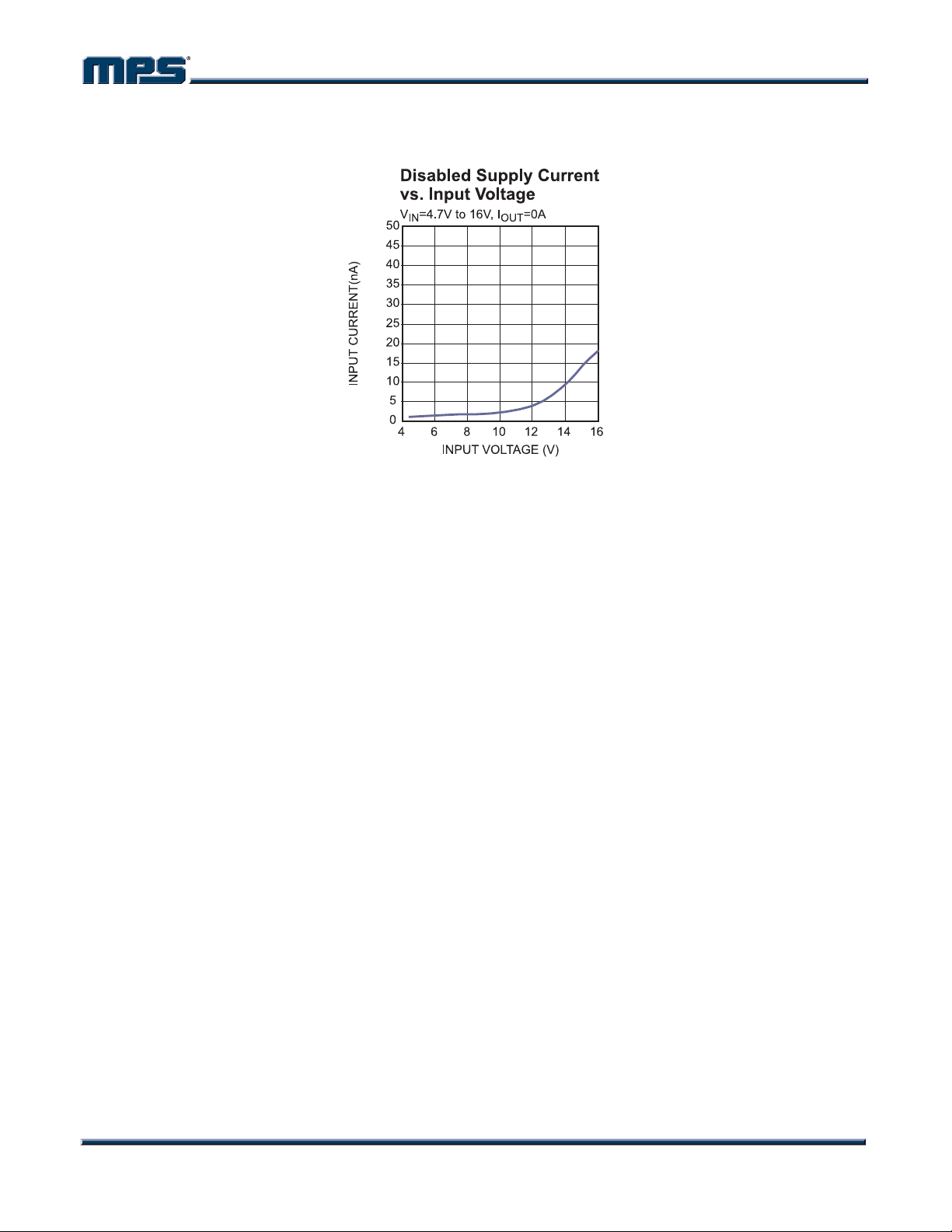
MP1469 – SYNCHRONOUS, STEP-DOWN CONVERTER WITH INTERNAL MOSFETS
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
VIN = 12V, V
= 3.3V, L = 6.5µH, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
MP1469 Rev. 1.01 www.MonolithicPower.com 5
8/26/2013 MPS Proprietary Information. Patent Protected. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2013 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
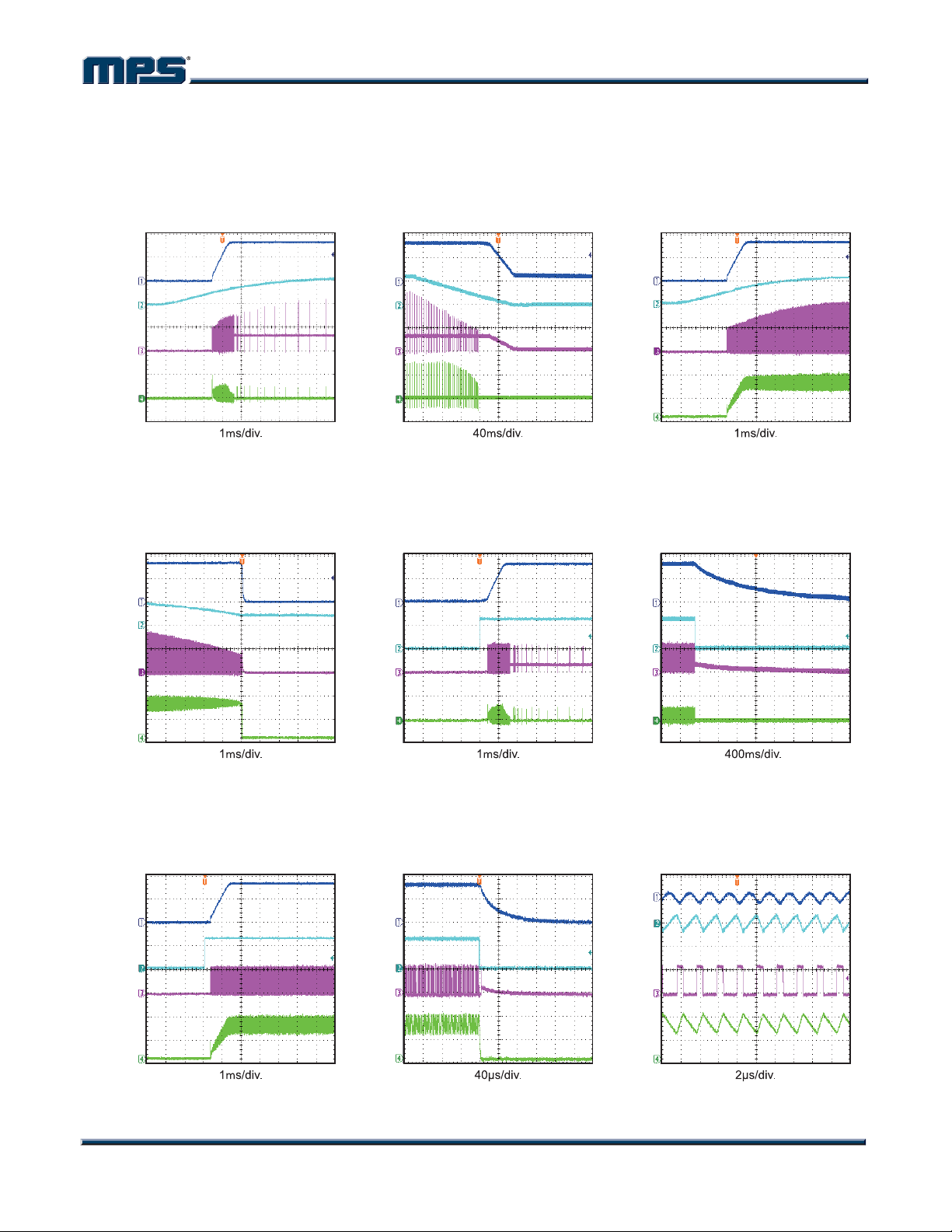
MP1469 – SYNCHRONOUS, STEP-DOWN CONVERTER WITH INTERNAL MOSFETS
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
VIN = 12V, V
Startup through
Input Voltage
I
OUT
= 3.3V, L = 6.5µH, TA = +25°C, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
Shutdown through
Input Voltage
= 0A
I
OUT
= 0A
Startup through
Input Voltage
I
= 1.5A
OUT
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
10V/div.
V
SW
5V/div.
500mA/div.
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
10V/div.
V
SW
5V/div.
1A/div.
IN
I
L
Shutdown through
Input Voltage
I
= 1.5A
OUT
IN
I
L
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
10V/div.
V
SW
5V/div.
200mA/div.
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
EN
2V/div.
V
SW
10V/div.
500mA/div.
IN
I
L
Startup through Enable
I
= 0A
OUT
I
L
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
10V/div.
V
SW
5V/div.
1A/div.
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
EN
2V/div.
V
SW
10V/div.
500mA/div.
IN
I
L
Shutdown through Enable
I
= 0A
OUT
I
L
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
2V/div.
V
SW
10V/div.
1A/div.
Startup through Enable
I
= 1.5A
OUT
EN
I
L
Shutdown through Enable
I
= 1.5A
OUT
V
OUT
2V/div.
V
EN
2V/div.
V
SW
10V/div.
I
L
1A/div.
V
OUT/AC
50mV/div.
V
IN/AC
200mV/div.
V
SW
10V/div.
1A/div.
Input/Output Ripple
I
= 1.5A
OUT
I
L
MP1469 Rev. 1.01 www.MonolithicPower.com 6
8/26/2013 MPS Proprietary Information. Patent Protected. Unauthorized Photocopy and Duplication Prohibited.
© 2013 MPS. All Rights Reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...