MPL MAGBES Technical Reference Manual

MAGBES Technical Reference Manual
The MAGBES Manageable GigaBit Ethernet Switch is an Industrial 5-Port Gigabit Switch available in several
mechanical and electrical variants:
Electrical Variants:
● 5 Copper ports (4 x RJ45 and one 2.54mm Header)
● 3 Copper ports (2 x RJ45 and one 2.54mm Header) and 2 x SFP (Small Form factor Pluggable)
Mechanical Variants:
● Stand Alone Switch.
● PC/104 Stackable Switch.
● PIP Build-In Switch.
Supported Functions
● Configuration via Web Interface
● Automatic or manual Port Settings
● Switch Statistics
● Port Based VLAN
● IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
● Quality of Service
● MAC Authentication
● SNMP Support
● IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree
● Port Monitoring
2012 by MPL AG 1 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................. 6
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL.........................................................................................................6
1.2 MANUAL REVISIONS............................................................................................................6
1.2.1 RELATED PRODUCTS.................................................................................................. 6
1.2.2 REVISION HISTORY.....................................................................................................6
1.3 RELATED DOCUMENTATION.............................................................................................. 6
2 ACCESSING MAGBES MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE ..................................................7
2.1 Factory default system configuration parameters............................................................. 7
2.2 Login...................................................................................................................................... 7
3 SYSTEM CONFIGURATION...........................................................................................8
3.1 System Status....................................................................................................................... 8
3.2 System Setup........................................................................................................................ 9
3.3 System Admin .................................................................................................................... 10
3.4 System Configuration........................................................................................................ 11
4 SWITCH CONFIGURATION......................................................................................... 12
4.1 Port Status.......................................................................................................................... 12
4.1.1 Port Configuration (Copper).......................................................................................... 13
4.1.2 Port Configuration (SFP).............................................................................................. 15
4.1.2.1 SFP Diagnostic.....................................................................................................................16
4.2 Switch Statistics................................................................................................................. 18
4.2.1 Detailed Switch Statistics.............................................................................................. 19
4.3 Port Based VLAN................................................................................................................ 21
4.3.1 Port Based VLAN Example........................................................................................... 22
4.4 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.............................................................................................................. 23
4.4.1 Configuring IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Groups...................................................................... 24
4.4.2 Configuring the Ports for IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ..............................................................25
4.4.3 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Example....................................................................................... 26
4.4.4 Important Notes using IEEE 802.Q VLAN.................................................................... 28
4.5 Quality Of Service (QoS).................................................................................................... 29
4.5.1 Priority Mapping for MAC, VID, IEEE 802.1ac and Default Priority .............................30
4.5.2 Priority Mapping for ToS / TC and DSCP.................................................................... 31
4.5.3 Replace Priority............................................................................................................ 32
4.6 MAC Authentication........................................................................................................... 33
4.7 IEEE 802.1X Source MAC checking..................................................................................36
4.8 SNMP Configuration........................................................................................................... 37
4.9 Spanning Tree Protocol .................................................................................................... 38
4.9.1 Spanning Tree Example............................................................................................... 38
4.10 Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol.............................................................................. 41
4.10.1 Bridge Configuration................................................................................................... 41
4.10.1.1 Bridge parameters............................................................................................................... 42
4.10.2 STP Port Options........................................................................................................ 43
4.10.2.1 STP Port Parameters.......................................................................................................... 43
4.10.3 STP Configuration Parameters...................................................................................44
4.10.3.1 Root Bridge selection.......................................................................................................... 44
4.10.3.2 Alternate Root Bridge Selection.......................................................................................... 44
4.10.3.3 Path Modification................................................................................................................. 44
4.10.3.4 Performance Parameters.................................................................................................... 45
4.10.3.5 Edge Ports..........................................................................................................................45
2012 by MPL AG 2 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
4.10.4 Important Notes for the Spanning Tree....................................................................... 46
4.10.4.1 Forwarding Loop when disabling STP................................................................................46
4.10.4.2 Forwarding Loop with unidirectional Links..........................................................................46
4.10.4.3 STP and VLAN....................................................................................................................46
4.10.4.4 STP and DHCP................................................................................................................... 46
4.11 Port Monitoring................................................................................................................. 47
5 TELNET COMMAND LINE INTERFACE......................................................................48
5.1 Login.................................................................................................................................... 48
5.2 Commands.......................................................................................................................... 48
5.3 Help Command................................................................................................................... 49
5.4 System................................................................................................................................. 49
5.4.1 IP Settings.................................................................................................................... 49
5.4.2 DHCP Options.............................................................................................................. 49
5.4.3 System Information....................................................................................................... 50
5.4.4 System wide settings.................................................................................................... 50
5.5 Port Configuration.............................................................................................................. 51
5.6 SFP Support........................................................................................................................ 53
5.7 Switch Statistics................................................................................................................. 54
5.8 Port based VLAN................................................................................................................ 55
5.9 IEEE802.1Q VLAN............................................................................................................... 56
5.9.1 IEEE802.1Q VLAN Administration................................................................................ 56
5.9.2 EEE802.1Q VLANs......................................................................................................57
5.9.3 EEE802.1Q VLAN ports............................................................................................... 58
5.10 QOS.................................................................................................................................... 59
5.11 MAC Address Authentication.......................................................................................... 62
5.12 SNMP Configuration......................................................................................................... 64
5.13 Spanning Tree................................................................................................................... 65
5.14 Firmware update procedure:...........................................................................................68
5.15 Configuration file handling.............................................................................................. 68
5.15.1 Upload a configuration file.......................................................................................... 68
5.15.2 Load the uploaded configuration file...........................................................................69
5.15.3 Save the configuration file or the current configuration as alternate configuration......69
5.15.4 Apply the configuration file.......................................................................................... 69
5.15.5 Download the current configuration as configuration file............................................69
6 CONFIGURATION FILE................................................................................................70
6.1 File format........................................................................................................................... 70
6.2 File rules.............................................................................................................................. 70
6.2.1 Root tag........................................................................................................................ 70
6.2.2 System section............................................................................................................. 70
6.2.2.1 System ID.............................................................................................................................. 70
6.2.2.2 IP Settings.............................................................................................................................70
6.2.2.3 Jumbo Frame........................................................................................................................ 71
6.2.2.4 Telnet CLI.............................................................................................................................. 71
6.2.2.5 Web UI.................................................................................................................................. 71
6.2.2.6 Hostname..............................................................................................................................71
6.2.2.7 Location................................................................................................................................. 71
6.2.2.8 Password..............................................................................................................................71
6.2.2.9 Login Timeout.......................................................................................................................71
6.2.3 Port section................................................................................................................... 71
6.2.3.1 Port........................................................................................................................................ 71
6.2.4 Port-Based VLAN section.............................................................................................72
6.2.4.1 PVLAN..................................................................................................................................72
6.2.5 IEEE802.1Q VLAN section...........................................................................................72
2012 by MPL AG 3 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
6.2.5.1 QVLAN.................................................................................................................................. 72
6.2.6 QOS............................................................................................................................. 72
6.2.6.1 IEEE802.1p Priority mapping section....................................................................................72
6.2.6.2 DSCP Priority mapping section.............................................................................................72
6.2.6.3 QOS port settings.................................................................................................................. 73
6.2.7 MAC Address authentication section............................................................................73
6.2.8 SNMP section............................................................................................................... 73
6.2.9 Spanning Tree section.................................................................................................. 74
7 OS INFORMATION....................................................................................................... 75
7.1 OS Copyright and Disclaimer............................................................................................ 75
8 COPYRIGHT.................................................................................................................76
9 DISCLAIMER................................................................................................................76
10 TRADEMARKS........................................................................................................... 76
11 SUPPORT...................................................................................................................76
11.1 SERIAL NUMBER AND REVISION................................................................................... 76
11.2 CONTACT MPL AG........................................................................................................... 76
2012 by MPL AG 4 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
TABLE OF FIGURES
Figure 1: MAGBES Login....................................................................................................................................... 7
Figure 2: System Status......................................................................................................................................... 8
Figure 3: System Setup......................................................................................................................................... 9
Figure 4: System Admin....................................................................................................................................... 10
Figure 5: System Configuration............................................................................................................................ 11
Figure 6: Port Status............................................................................................................................................ 12
Figure 7: Port Configuration (Copper)..................................................................................................................13
Figure 8: Port Configuration (SFP)....................................................................................................................... 15
Figure 9: SFP Diagnistics.................................................................................................................................... 16
Figure 10: Switch Statistics.................................................................................................................................. 18
Figure 11: Detailed Switch Statistics.................................................................................................................... 19
Figure 12: Port Based VLAN................................................................................................................................ 21
Figure 13: Port Based VLAN Example................................................................................................................. 22
Figure 14: Port Based VLAN Example MAGBES Configuration.......................................................................... 22
Figure 15: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN............................................................................................................................. 23
Figure 16: Add new IEEE 802.1Q VLAN.............................................................................................................. 24
Figure 17: Edit IEEE 802.1Q VLAN..................................................................................................................... 24
Figure 18: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Port Settings....................................................................................................... 25
Figure 19: Edit IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Settings....................................................................................................... 25
Figure 20: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Example.............................................................................................................. 26
Figure 21: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Example MAGBES Configuration.......................................................................27
Figure 22: Quality Of Service (QoS).................................................................................................................... 29
Figure 23: Priority Mapping for MAC, VID, IEEE 802.1ac and Default Priority ....................................................30
Figure 24: Priority Mapping for ToS / TC Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP).........................................31
Figure 25: Port Settings for QoS.......................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 26: MAC Authentication............................................................................................................................ 33
Figure 27: MAC Address Properties.................................................................................................................... 34
Figure 28: List known MAC address page........................................................................................................... 35
Figure 29: IEEE 802.1X Source MAC checking...................................................................................................36
Figure 30: SNMP Configuration........................................................................................................................... 37
Figure 31: Spanning Tree Example..................................................................................................................... 38
Figure 32: Spanning Tree Example, STP on....................................................................................................... 39
Figure 33: STP Bridge Configuration................................................................................................................... 41
Figure 34: STP Port Options................................................................................................................................ 43
Figure 35: Port Monitoring................................................................................................................................... 47
2012 by MPL AG 5 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 ABOUT THIS MANUAL
This manual and the MAGBES User Manual provide all the information necessary to handle and configure the
MAGBES.
The manual is written for technical personnel responsible for integrating the MAGBES into their systems.
1.2 MANUAL REVISIONS
1.2.1 RELATED PRODUCTS
Manual
Revisions
Related To
A
• MAGBES Management Firmware V 0.0.1
B
• MAGBES Management Firmware V 0.0.1
C
• MAGBES Management Firmware V 0.0.9
D
• MAGBES Management Firmware V 0.2.0
1.2.2 REVISION HISTORY
Manual
Revisions
Date Description
A 2008-02-27
Initial release of this document.
B 2008-06-02
Fixed some typos
C 2010-02-09
Changed to reflect current Firmware
D 2012-07-05
Changed to reflect current Firmware
1.3 RELATED DOCUMENTATION
The following documents are related to this manual. For detailed Information about a specific MAGBES feature
or setting please refer to this additional manual.
Reference Description Available from
[1] MAGBES User Manual MPL AG: www.mpl.ch
2012 by MPL AG 6 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual

2 Accessing MAGBES Management Software
The MAGBES is manageable via a Web Interface. To access the MAGBES an IP Address is necessary. This
address may be fixed, or retrieved from a DHCP Server.
To login a Password is required, which should be changed after the first login.
On first power-up or after loading the “Factory Default Values” (either by pressing the “Default” switch for more
than 4 sec, or clicking the Load Factory Default button on the System Configuration Page), the MAGBES uses
following IP Parameters:
2.1 Factory default system configuration parameters
Parameter First 12 seconds after Power-Up After the first 12 seconds
IP Address DHCP 192.168.1.254
Netmask DHCP 255.0.0.0
Gateway DHCP 0.0.0.0
Login user name admin
Login Password 1234
System Name Magbes
Location
Notes:
● After Power-Up, the MAGBES waits for a valid Link before starting the DHCP Client.
● If no DHCP server has been found 12 seconds after the detection of a valid link, the IP address
192.168.1.254 will be used.
● The “Login user name” is not changeable.
● The “System Name” and “Location” are changeable and should contain useful information for the
Network Administrator to identify the Switch.
● If using DHCP, the IP Address of the switch can be found in the log file of the DHCP Server.
2.2 Login
After entering the IP Address in the address field of your Internet browser, you have to login as “admin” User:
Enter the Password to access the MAGBES Management Web Interface.
2012 by MPL AG 7 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 1: MAGBES Login
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
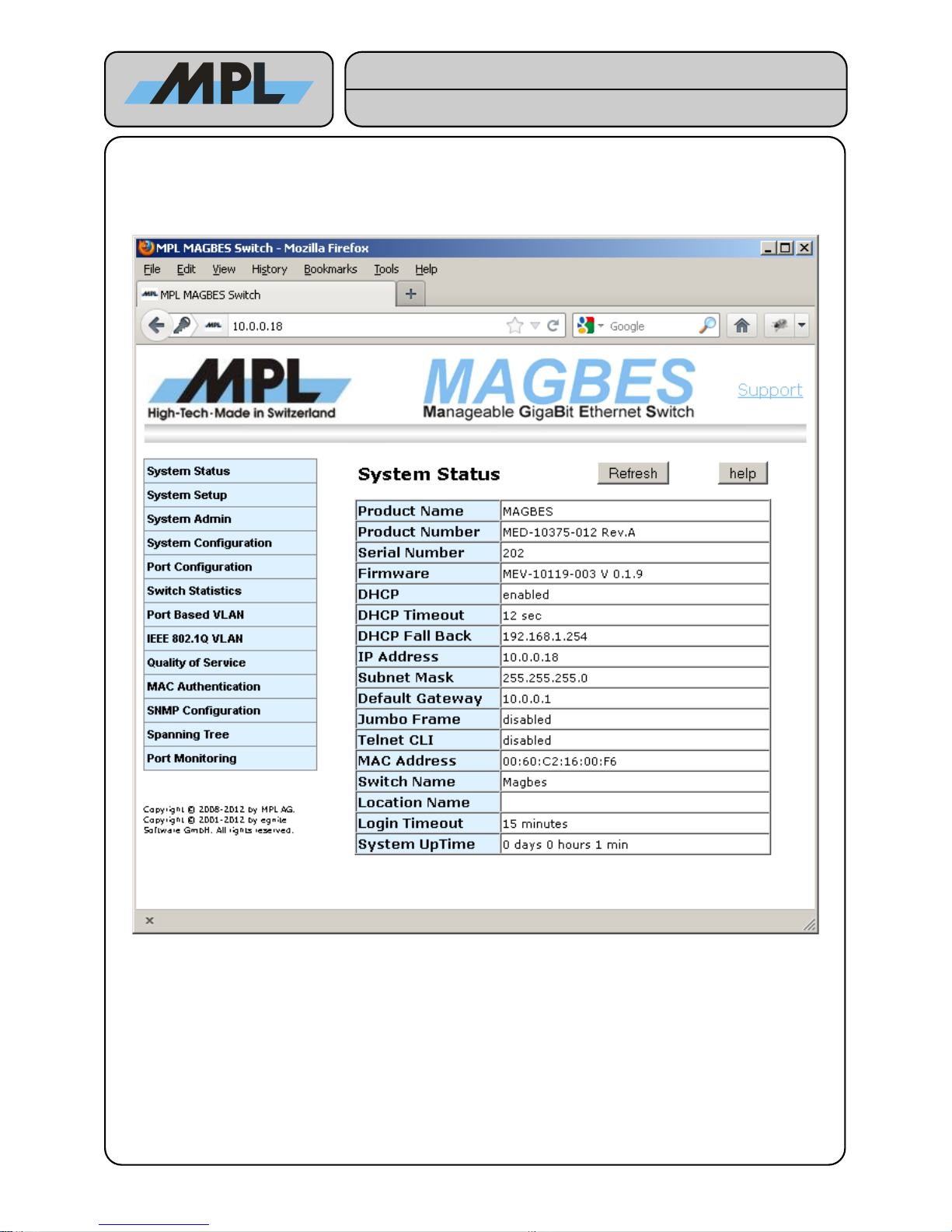
3 System Configuration
3.1 System Status
The System Status shows information about the MAGBES Revisions and the System Configuration:
● The Product Name, Product Number, Serial Number, and the Firmware are used to identify the
MAGBES.
● The DHCP, DHCP Fall Back, IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway show the Network
configuration.
● The Switch Name, Location Name and Login Timeout are configurable.
2012 by MPL AG 8 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 2: System Status
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
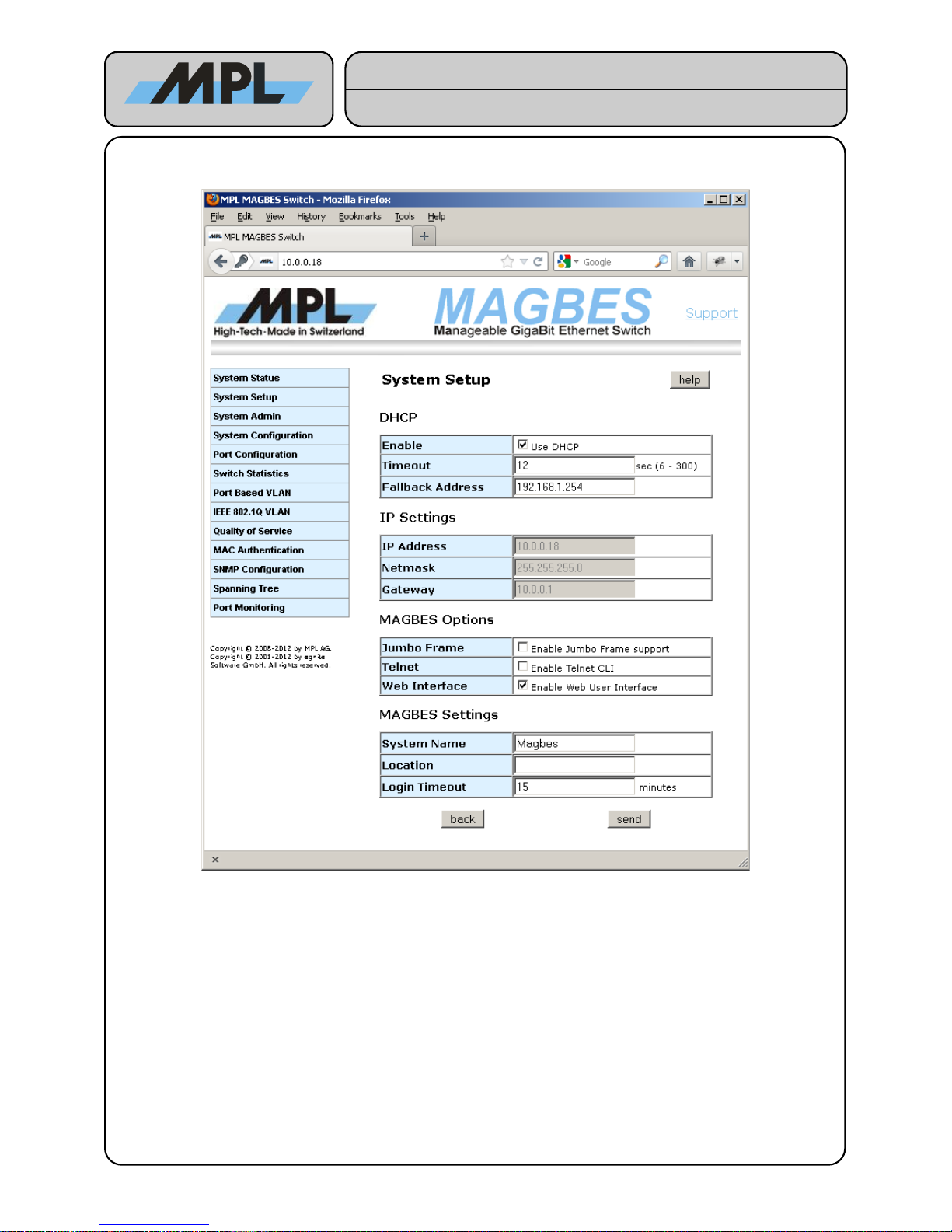
3.2 System Setup
On this page the System Parameters can be configured.
Notes:
● The DHCP Fallback Address will be used if DHCP Timeout sec have been elapsed after valid link
detection and no DHCP offer has been received.
● If using DHCP the IP Address, Netmask, and Gateway Settings are ignored.
● Jumbo Frame support is only available on MAGBES-11, MAGBES-12 and MAGBES-13.
● Telnet CLI enables the Telnet Command line Interface. See chapter 5 Telnet Command Line Interface
for further information.
● If disable both Web Interface and Telnet Command Line Interface, the MAGBES will disable the
configuration interface of the MAGBES. This means that the MAGBES will not use any IP address but
will still do the configured jobs as long as they don't require an IP Address (SNMP will not work). To
revert in the configurable mode the "default switch" has to be pressed for at least 4 sec.
● System Name (max Length 15 chars) and Location (max Length 15 chars) are only used to inform
the Network Administrator, on which MAGBES she/he is logged in.
● If the Login Timeout is elapsed without any activity on the Web Interface, the user is automatically
logged out.
2012 by MPL AG 9 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 3: System Setup
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
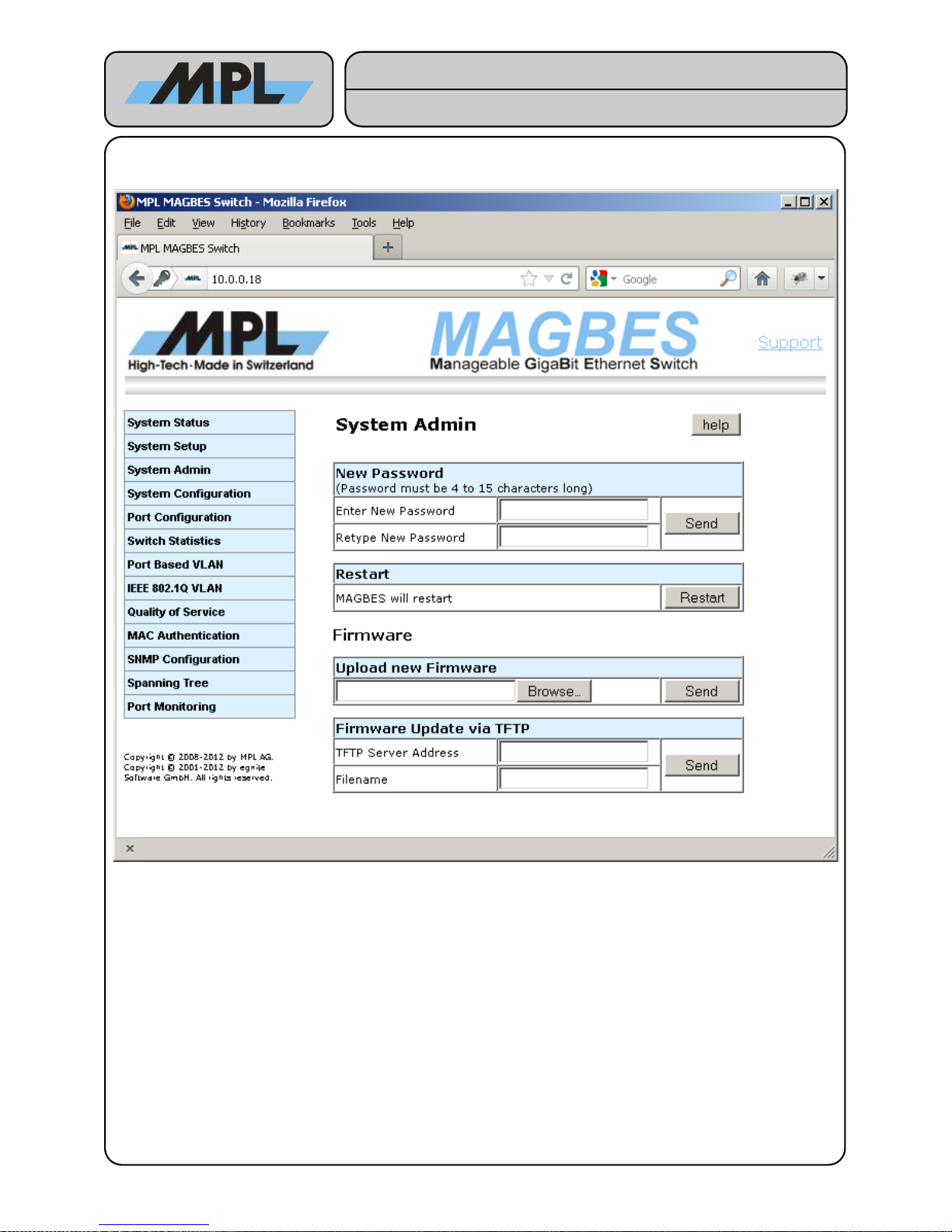
3.3 System Admin
This page allows to change the Password, Restart the MAGBES and Update the Firmware.
● The Password must be between 4 and 15 characters long. This is used for the login (see Figure 2:
System Status). The Password must be retyped to ensure that no typos have been filled in. If you have
forgotten the Password you have to set the MAGBES to default as it is described in the MAGBES User
Manual.
● Restart forces the MAGBES to restart (reset). No configuration will change.
● Firmware Update can be done either via a direct File Upload, or loading the firmware from a TFTP
Server. Please note that after updating the Firmware all configuration are lost.
2012 by MPL AG 10 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 4: System Admin
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
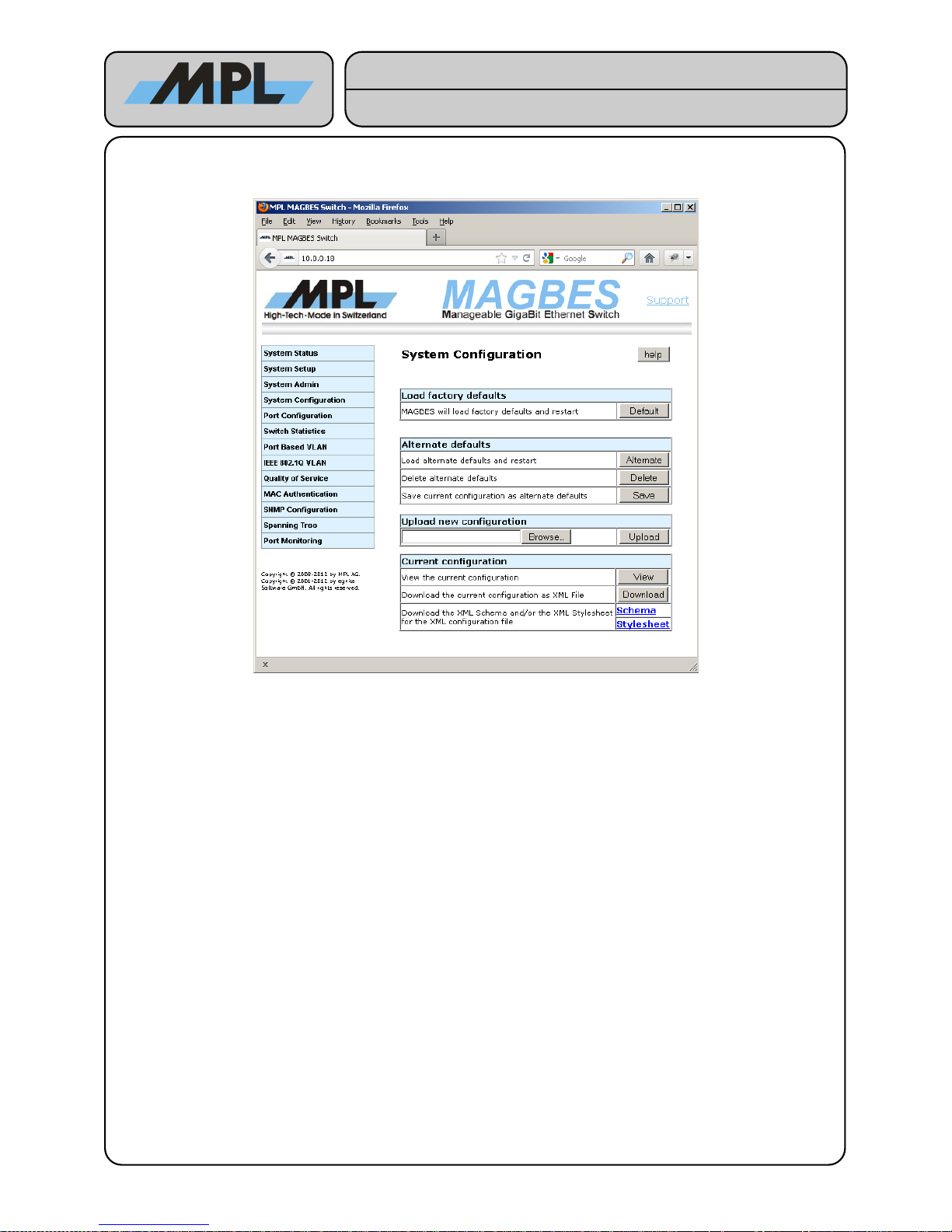
3.4 System Configuration
This page allows to change the configuration of the entire switch:
● Default forces the MAGBES to load factory defaults and restart. The same effect has the pressing of
the “Default Switch” for more than 4 seconds.
The MAGBES allows the use of a customer specific default configuration. This is called the Alternate defaults
in this Manual.
● Alternate: Loads the alternate defaults and restarts. The same effect has the pressing of the “Default
Switch” (less than 4 seconds). If no alternate defaults are stored, the MAGBES uses the factory default
for this purpose.
● Delete: Invalidate the alternate defaults.
● Save: Save the current configuration as alternate defaults.
The configuration of the MAGBES can also be uploaded. See chapter 6 Configuration File for further information
on configuration file support.
● Upload: Uploads the chosen configuration file. After the upload, the file will be validated and a new
page allows to select one of the following actions:
● Apply: The new configuration will be saved and the MAGBES will restart.
● Discard: The new configuration will be discarded and the previous configuration restored.
● Save: The new configuration will be saved as alternate defaults.
The current configuration can also be viewed or downloaded for modifications.
● View: Shows the current configuration, using the XML configuration file along the XML Stylesheet.
● Download: Allows to download the XML configuration file.
For offline viewing and validation of the configuration file, MAGBES allows also to download the
appropriate XML Stylesheet and XML Schema file.
WARNING: Upload, viewing and download XML files uses much memory. Using large XML files may
lead to an “out of RAM” condition, which may lead to a restart of the MAGBES. So it is not
recommended to use this feature in a production network.
2012 by MPL AG 11 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
Figure 5: System Configuration
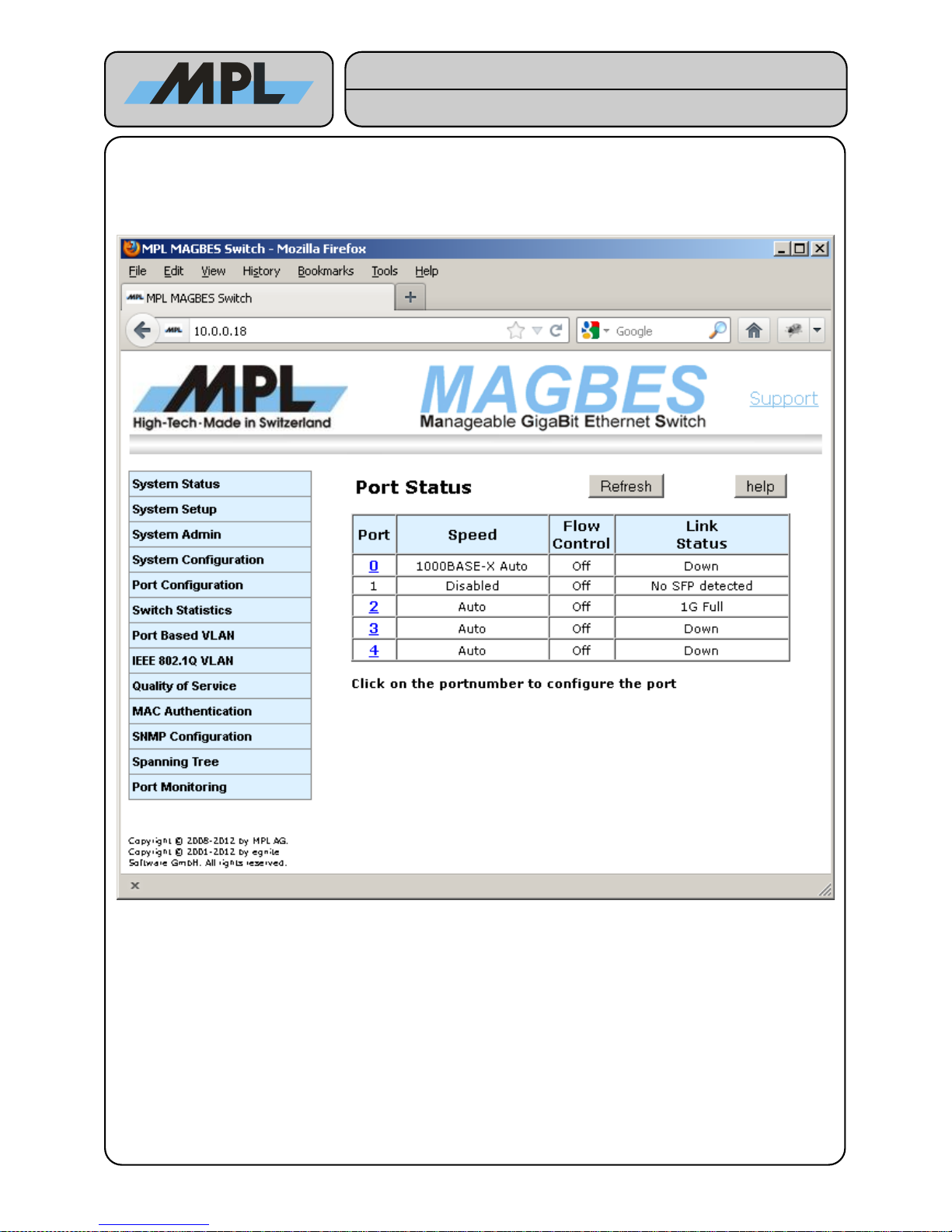
4 Switch Configuration
4.1 Port Status
By clicking on the Port number you can configure the port.
2012 by MPL AG 12 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 6: Port Status
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
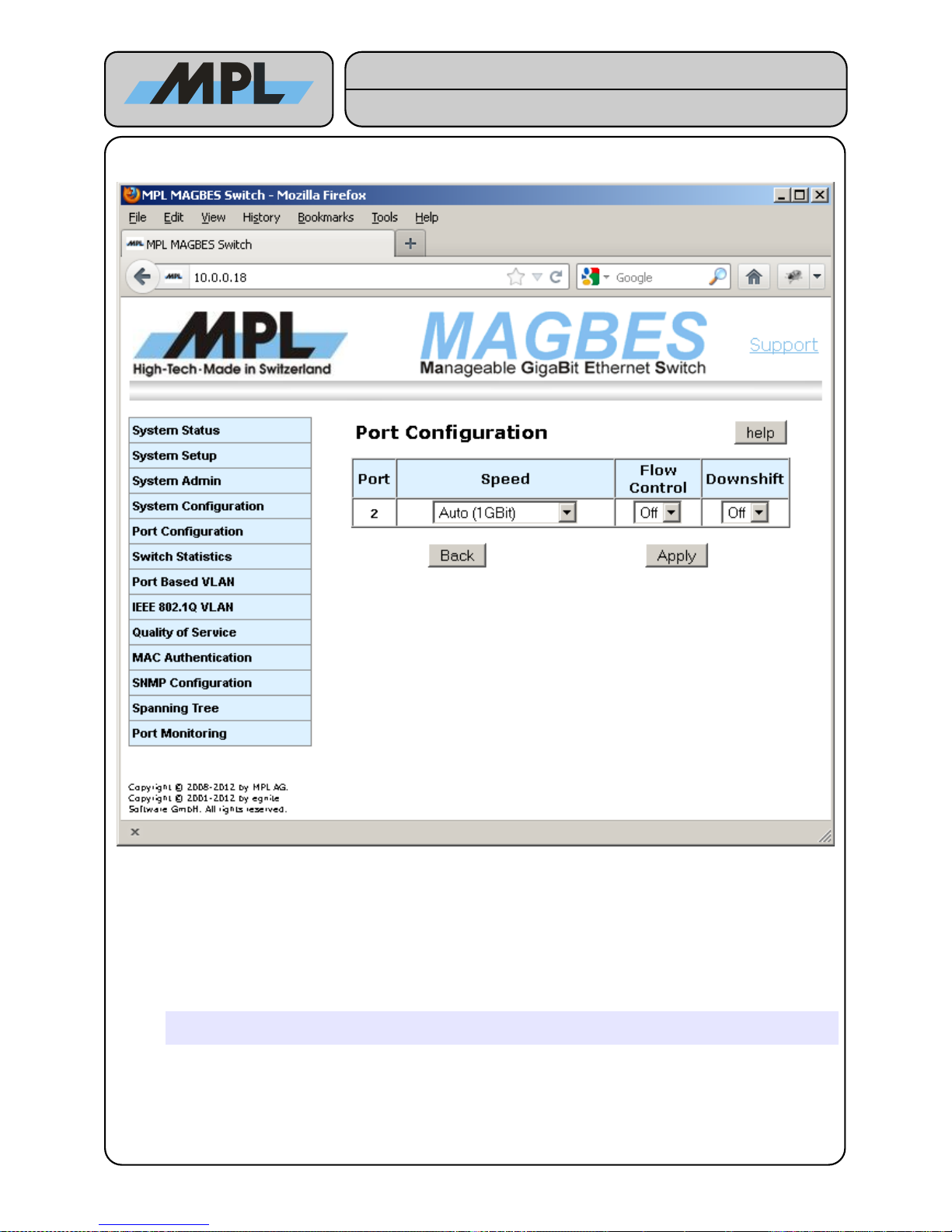
4.1.1 Port Configuration (Copper)
Speed:
Used to select the Speed and the duplex mode of the Port. Following choices are possible:
● Auto (1GBit): According IEEE 802.3 1000Base-T link are only possible with Auto-Negotiation. In this
Mode the Speed and duplex mode are negotiated between the two link partners. The Flow-Control
settings in this mode is used to advertise the ability of Flow-Control. If the Link partner doesn't support
this, the MAGBES will not use Flow-Control.
The Downshift setting is only active during the Auto Setting.
● 100MBit Full-Duplex, 100MBit Half-Duplex, 10MBit Full-Duplex, and 10MBit Half-Duplex: these
settings are used to force the MAGBES to these Speeds and Duplex-Modes.
Warning: When using one of these Modes, the Link Partner must be set to the exact same
settings.
● Disabled: If set to Disabled, the port enters a Power-Down Mode and doesn't receive or transmit any
Frames.
2012 by MPL AG 13 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 7: Port Configuration (Copper)
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
Flow Control:
In Auto (1GBit) mode, this setting is only used to advertise the ability to use Flow-Control.
● Off: No Flow-Control is used
● On: Flow Control on a half duplex enabled port is used to throttle the throughput rate of an end station
to avoid packet dropping during network congestion. Only ports involved in the congestion are flow
controlled. If the half duplex flow control is not set, incoming packets may be discarded during network
congestion. Flow Control on a half duplex enabled port is not defined by IEEE.
Flow Control on a full duplex enabled port has the same purpose as on a half duplex enabled port.
IEEE 802.3 flow control requires the two link partners to auto-negotiate and advertise their flow control
capabilities. Flow-Control on full duplex ports is achieved by sending Pause-Frames to the Link partner.
Downshift:
● Off: No Downshift is used
● On: If both link partners support 1000Base-T, but are connected with an Ethernet Cable containing only
2 pairs instead of the required 4 pairs, they may negotiate to 1000Base-T but will fail to link. If downshift
is enabled MAGBES will advertise the next lower speed after the 1000Base-T link fails 3 times.
This feature is ignored in other modes than Auto (1GBit).
2012 by MPL AG 14 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
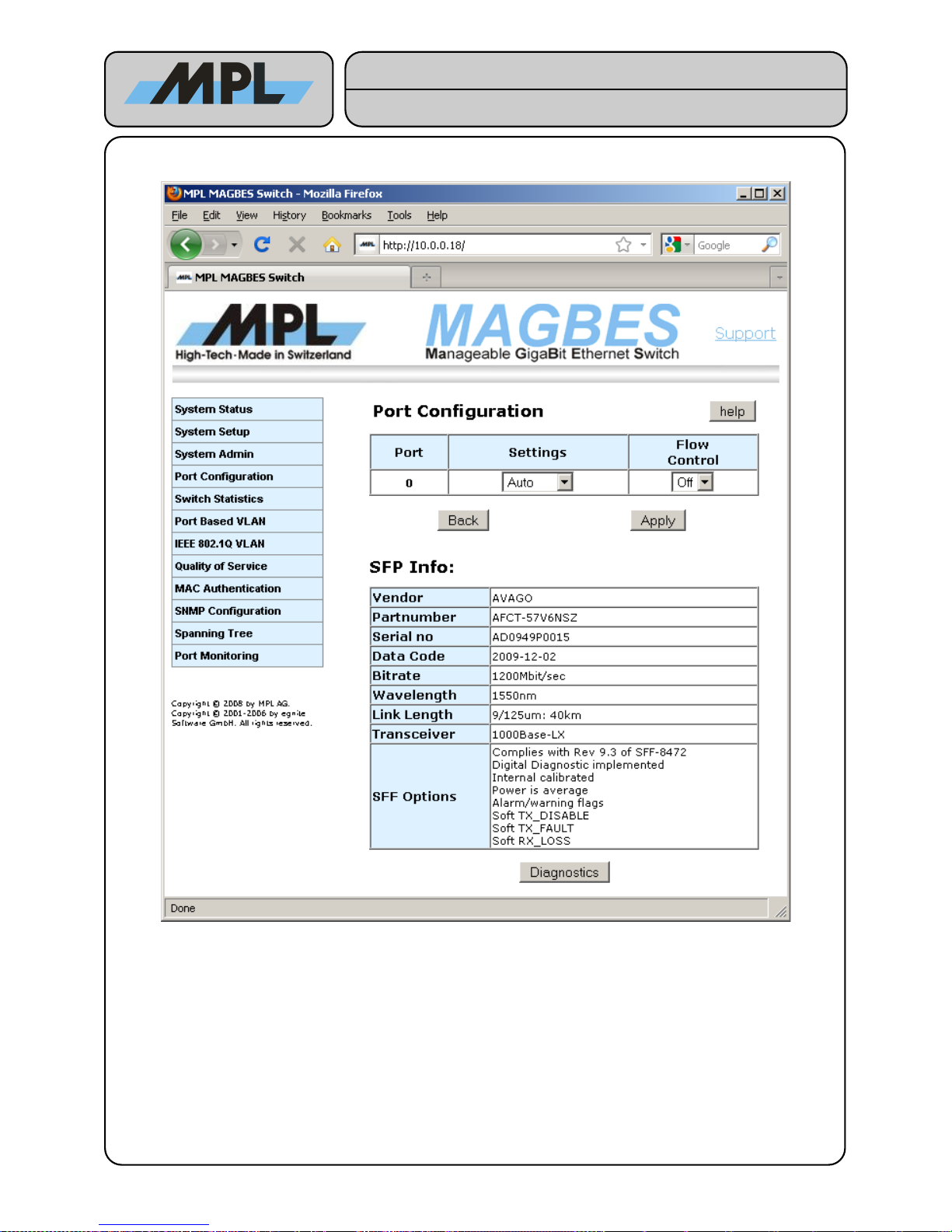
4.1.2 Port Configuration (SFP)
The Port Configuration for SFP works similar to the one for Copper with the difference, that the settings allow
only the SPF supported Speeds. If the SFP is not supported by the MAGBES the Settings drop down box is
fixed on Disabled.
● Most 100Base-FX, 1000Base-SX and 1000Base-LX SFP's are supported as long as they comply
Ethernet compatibility.
● Copper SFP is also supported, but this is only tested with the FINISAR FCLF-8520-3 A.
● The SFP Info shows the contents of the serial EEPROM of the SFP.
● If the EEPROM of the SFP has a wrong Checksum, the MAGBES tries to get as much information as
possible from the SFP and guess the possible Settings according this information. This mode is marked
with a red Checksum invalid.
● If no useful information can be retrieved, all Settings are possible. In this case the user is responsible to
choose the correct setting. Wrong Speed settings may damage the SFP! This mode is marked with a
red Checksum invalid
2012 by MPL AG 15 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 8: Port Configuration (SFP)
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
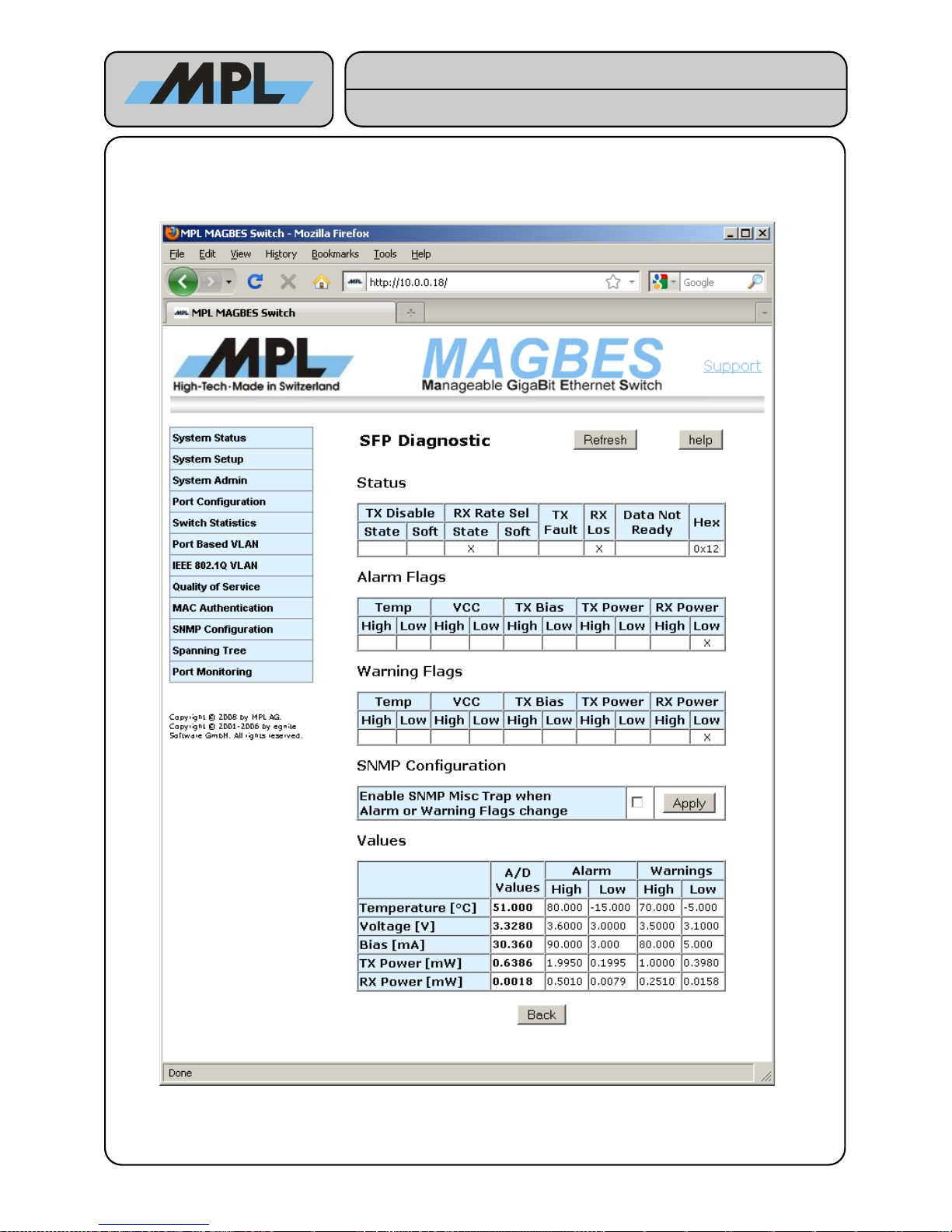
4.1.2.1 SFP Diagnostic
If the SFP supports Digital Diagnostics the button Diagnostics will be displayed. By pressing this button the
SFP Diagnostic page will be show.
2012 by MPL AG 16 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 9: SFP Diagnistics
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
On the SFP Diagnostic page information from the SFP is shown:
Status:
The contents of the Status byte of the SFP:
● TX Disable: The State of the TX Disable Pin as well as the Software settings for the TX Disable of the
SFP.
● RX Rate Sel: The State of the RX Rate Select Pin as well as the Software settings for RX Rate Select
of the SFP.
● TX Fault: The State of the TX Fault Pin of the SFP.
● RX Los: The State of the RX Los Pin (Link Los) of the SFP.
● Data Not Ready: If set, the Data of the Diagnostic is not valid.
● Hex: The value of the status byte in hexadecimal.
Alarm Flags:
The state of the alarm flags of the SFP.
Warning Flags:
The state of the warning flags of the SFP.
TX Disable:
The State of the TX Disable Pin as well as the Software settings for the TX Disable of the SFP.
SNMP Configuration:
Enables a SNMP Misc Trap when Alarm or Warning Flags change. Please note that the SNMP must be
configured and enabled for this. Please refer to 4.8 SNMP Configuration for more information.
Values:
The A/D Values and the Alarm and Warnings threshold Values.
2012 by MPL AG 17 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
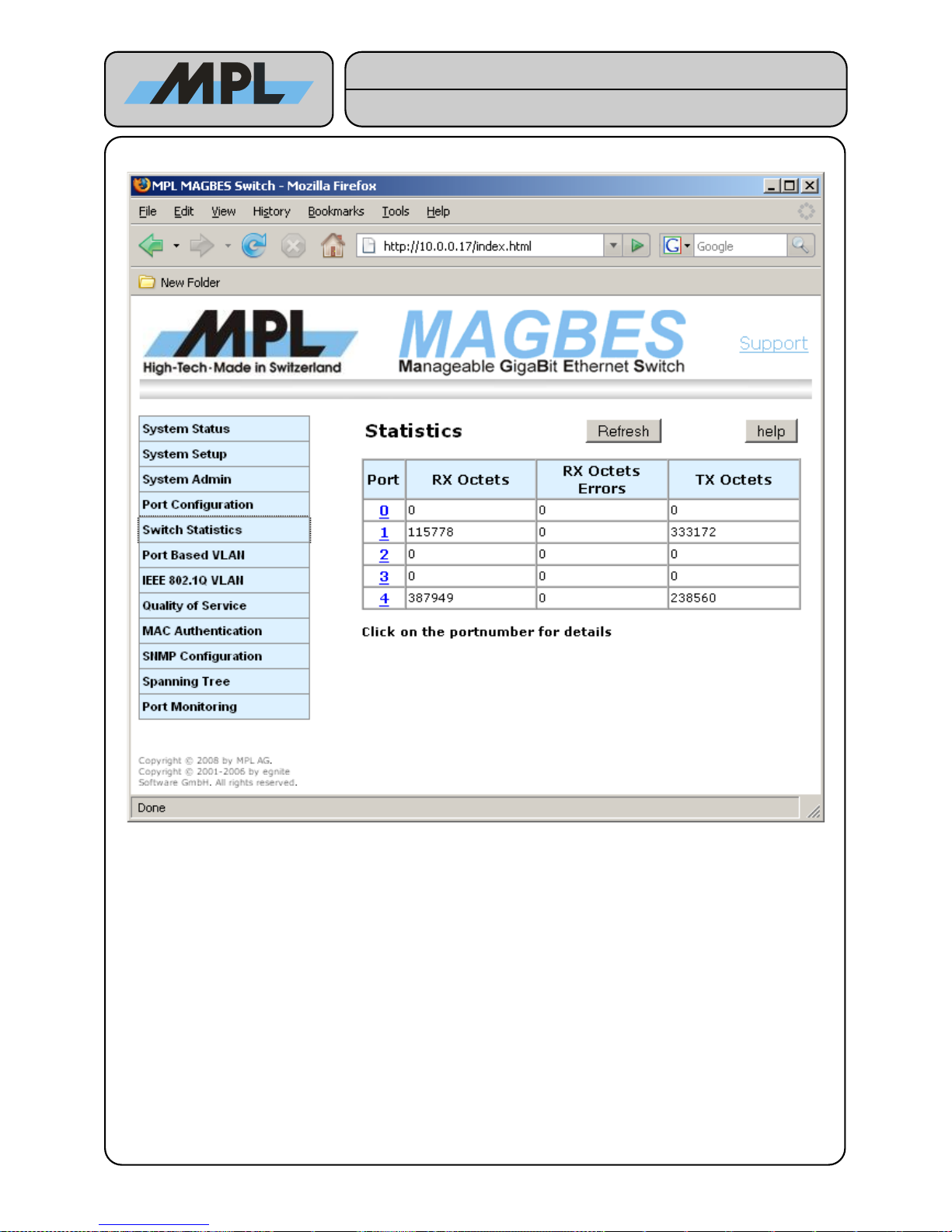
4.2 Switch Statistics
RX Octets:
The total length of all good Ethernet Frames received.
RX Octets Errors:
The total length of all bad Ethernet Frames received.
TX Octets:
The total length of all Ethernet Frames sent.
2012 by MPL AG 18 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 10: Switch Statistics
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
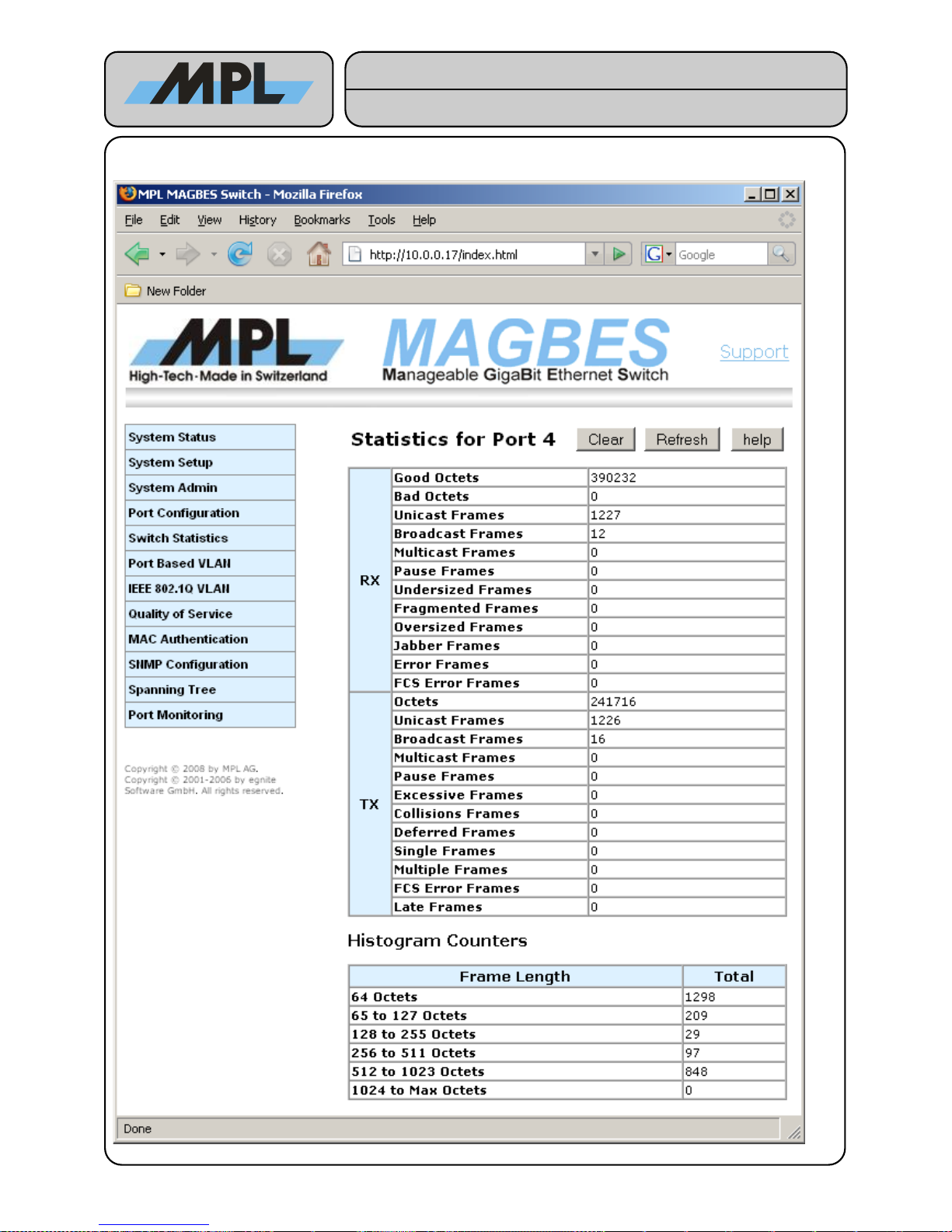
4.2.1 Detailed Switch Statistics
2012 by MPL AG 19 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 11: Detailed Switch Statistics
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
These Counter have following meaning:
Name Description
RX
Good Octets The total length of all good Ethernet Frames received.
Bad Octets The total length of all bad Ethernet Frames received.
Unicast Frames Good Frames received with a Unicast Destination Address.
Broadcast Frames Good Frames received with a Broadcast Destination Address.
Multicast Frames Good Frames received with a Multicast Destination Address.
Pause Frames The number of good Flow-Control Frames received.
Undersized Frames Received Frames with a length smaller than 64 octets with a valid FCS.
Fragmented Frames Received Frames with a length smaller than 64 octets with an invalid FCS.
Oversized Frames Received Frames with a length of more than Max Length octets with a valid FCS
Jabber Frames Received Frames with a length of more than Max Length octets with an invalid FCS
Error Frames Received Frames which have been marked as Error Frames by the Phy.
FCS Error Frames Received Frames with a length between 64 and Max Length and an invalid FCS.
TX
Octets The total length of all sent Ethernet Frames.
Unicast Frames Frames sent to a Unicast Destination Address.
Broadcast Frames Frames sent to a Broadcast Destination Address.
Multicast Frames Frames sent to a Multicast Destination Address.
Pause Frame The number of Flow-Control Frames sent.
Excessive Frames Frames dropped after 16 consecutive collisions (Half-Duplex Only)
Collisions Frames The number of Collision Frames. (Half-Duplex Only)
Deferred Frames
Frames successfully sent without collision but delayed because medium was busy (HalfDuplex Only)
Single Frames Frames successfully sent after exactly one collision (Half-Duplex Only).
Multiple Frames Frames successfully sent after more than one collision (Half-Duplex Only).
FCS Error Frames Frames sent with an invalid FCS.
Late Frames Frames where the collision is detected 512 bit-times into the transmission.
The Histogram Counters shows the total Frames (received and sent) with their length.
By clicking on the Clear button, all statistics Counters will be reset for this port.
2012 by MPL AG 20 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
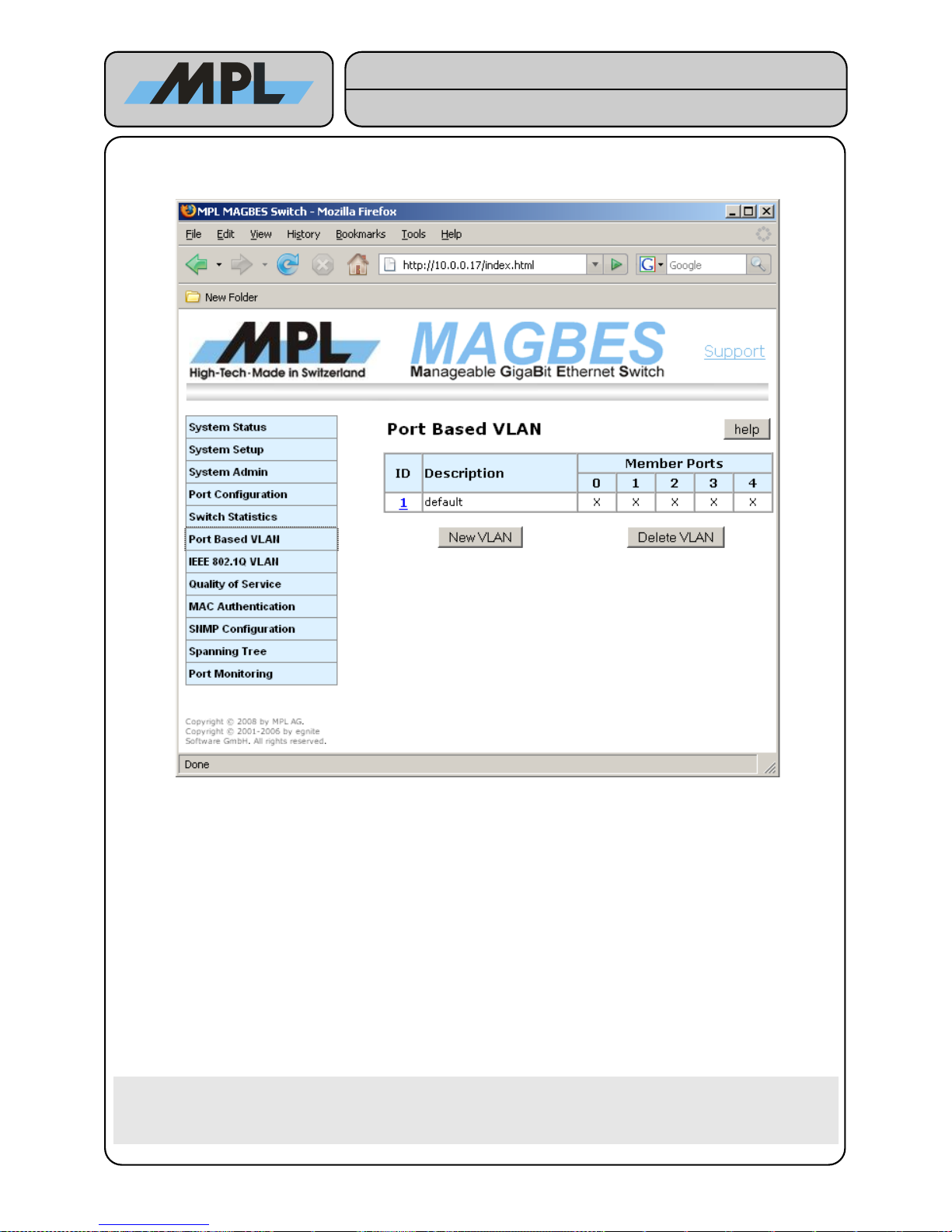
4.3 Port Based VLAN
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) are used to separate different LAN segments from each other. This has
following advantages:
● Smaller Broadcast Traffic. Broadcast Frames on one LAN segment are only forwarded to the same LAN
segment.
● Enhanced Security. It is not possible to send a frame from one LAN Segment to another.
Port based VLAN allows to create simple VLAN which exist only within the Switch. Frames are not modified
and the devices connected to the MAGBES do not need to support VLAN.
Parameter description:
ID: Is just an arbitrary Number and has no influence on the functionality of the Port Based VLAN.
Description: Used to identify the Port Based VLAN Segment. Up to 15 Characters Length.
Member Ports: Each Port with an 'X' in the table is member of this VLAN. In the example above, this means
that Port0 (Marketing Workstation) can reach Port2 (Marketing Workstation) and Port4 (Server),
but it cannot reach Port1 (Production Workstation) or Port2 (Production Workstation).
Warning: Please make sure that the Port you use to configure the MAGBES is enabled in one
VLAN. Otherwise the connection to the internal CPU is lost, and you have to press the
Default Switch to enable access to the internal CPU again. Note that the internal CPU is
member of all IDs.
2012 by MPL AG 21 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 12: Port Based VLAN
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
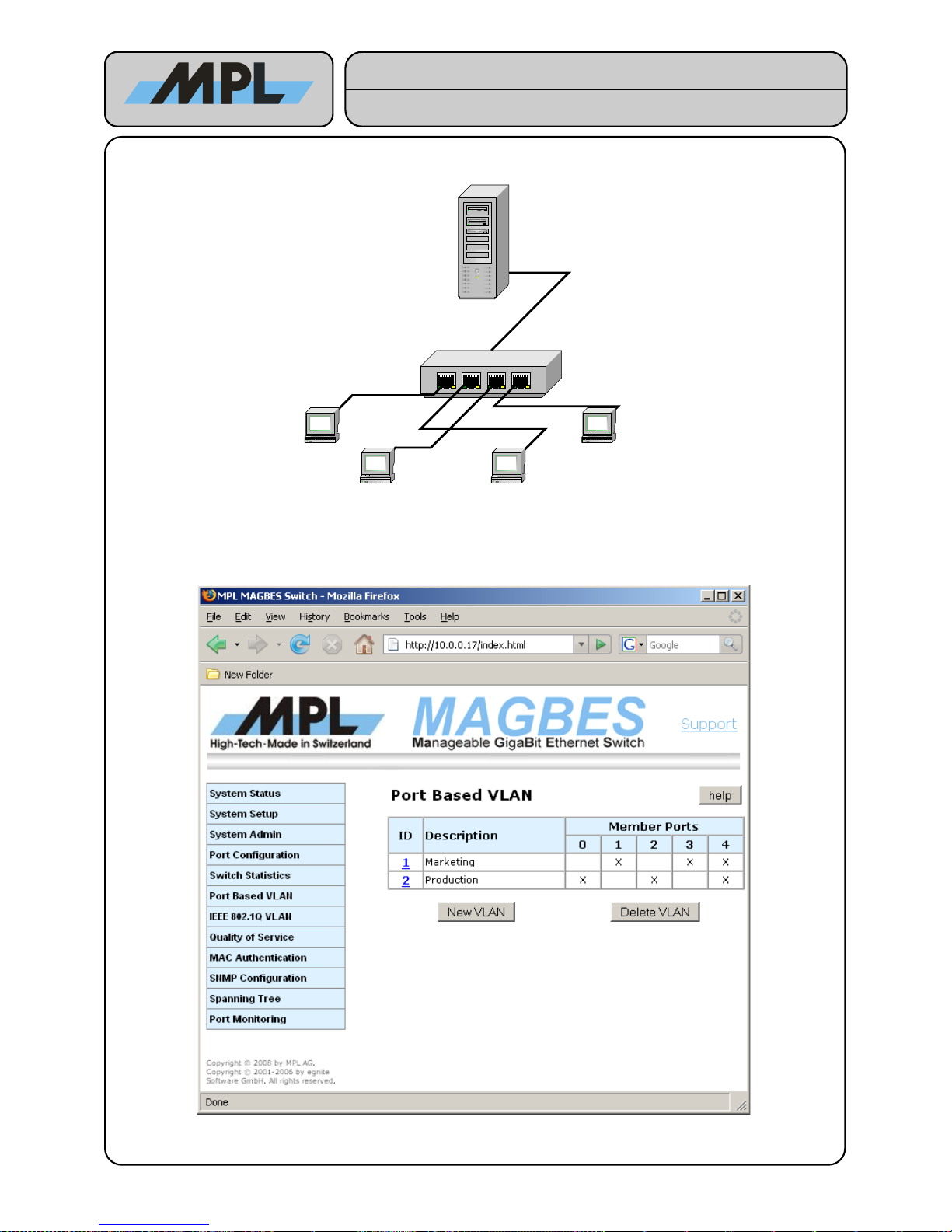
4.3.1 Port Based VLAN Example
In this example two simple VLAN are created:
● Marketing Workstation 1 has connection to Marketing Workstation 2 and to the Server / Router.
● Production Workstation 1 has connection to Production Workstation 2 and to the Server / Router.
This can be achieved with following configuration:
2012 by MPL AG 22 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 13: Port Based VLAN Example
MAGBES 1
Server / Router
Production 1
Marketing 1 Production 2
Marketing 2
Figure 14: Port Based VLAN Example MAGBES Configuration
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
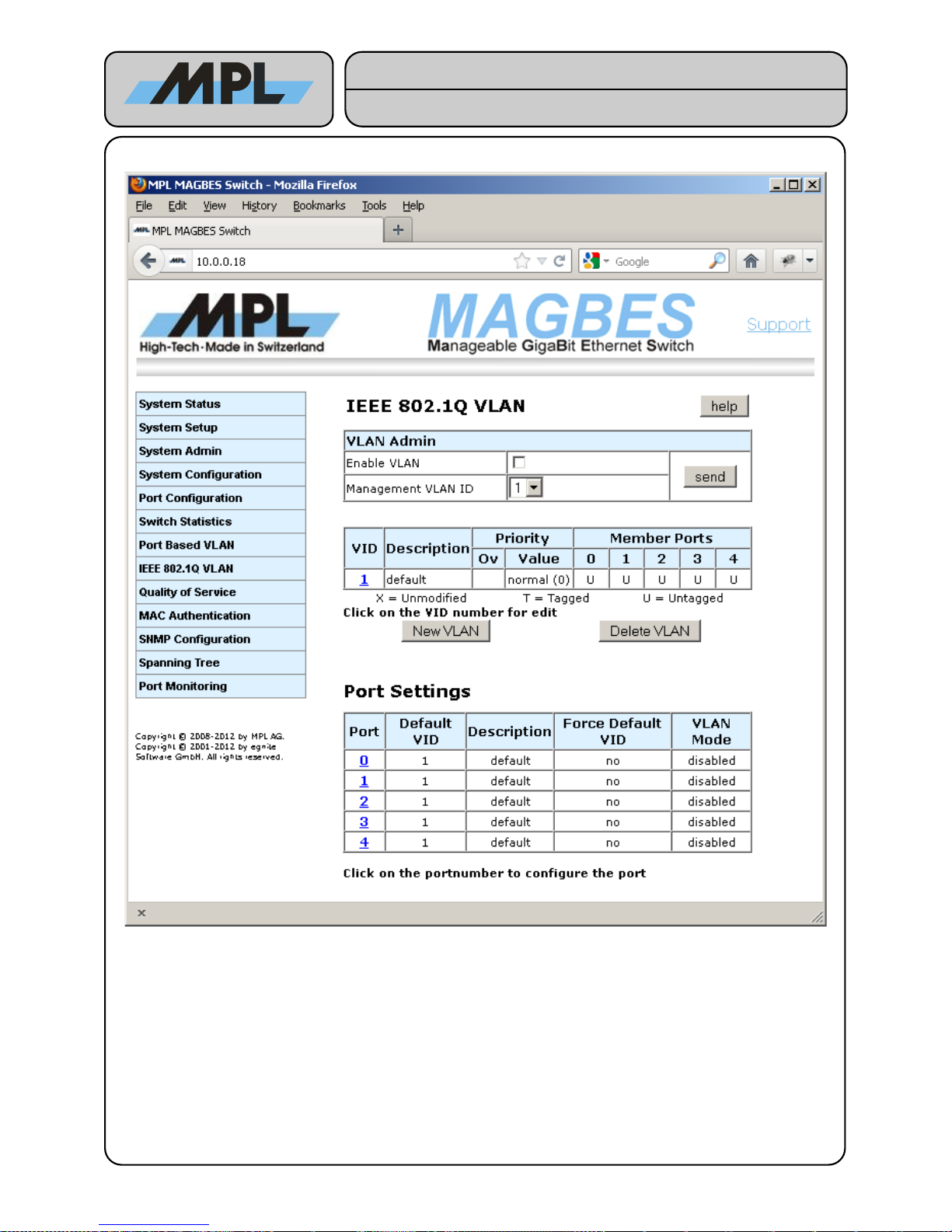
4.4 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
The IEEE 802.1Q VLAN allows to define VLAN over the entire Network. For this purpose a special tag is
inserted into the Frame containing information of the VLAN.
VLAN Admin
• Enable VLAN: If checked the VLAN is enabled and the management is only possible within the
"Management VLAN ID" VLAN. If not checked the VLAN is not enabled and the management is
possible from all VID. All changes to the VLAN configuration takes only place when check it and press
the send button.
• Management VLAN ID: The ID of the VLAN within management of the MAGBES is possible, if the
VLAN is enabled.
2012 by MPL AG 23 MEH-10134-201 Rev. D
Figure 15: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
High-Tech • Made in Switzerland
MAGBES
Technical Reference Manual
 Loading...
Loading...