Page 1

VPort 2140
User’s Manual
www.moxa.com/product
First Edition, March 2004
Page 2

VPort 2140
User’s Manual
The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in
accordance with the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
Copyright 2004 Moxa Networking Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Trademarks
MOXA is a registered trademark of the Moxa Group.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of Moxa.
Moxa provides this document “as is,” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but
not limited to, its particular purpose. Moxa reserves the right to make improvements and/or changes to this
manual, or to the products and/or the programs described in this manual, at any time.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Moxa Technologies
assumes no responsibility for its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that may result from
its use.
This product might include unintentional technical or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the
publication.
Page 3

Before getting started
Before using your VPort 2140, pay attention to the following items.
After opening the VPort 2140 box, compare the contents of the box with the Package Checklist in
Chapter 1. Notify your sales representative if any of the items is missing or damaged.
To prevent damage or problems caused by unproper usage, read the Qucik Installation Guide (printed
handbook in the package) or Chapter 1, Introduction, under Product Description, and Chapter 2,
Getting Started, before assembling and operating the device and peripherals.
If you experience a system error, and the system does not recover easily, refer to the Troubleshooting
section in Chapter 7 to learn how to restore factory default settings and reinstall the system.
VPort 2140 Video Server has been designed for various environments and can be used to build various
applications for general security or demonstration purposes. For standard applications, refer to the
appropriate section in the Chapter 2, Getting Started, under Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the
First Time section to find your application, and then follow the steps to set up the system. To make the best
use of VPort, read Chapter 5, Advanced Applications, in the URL Command for Advanced Functions
section to get creative ideas, and review Chapter 4, System Configuration for detailed explanations of
system configurations.
Note
Surveillance devices may be prohibited by law in your country. Though VPort is both a high performance
surveillance system and networked video server, ensure that the operations of such devices are legal in your
local area before installing this unit for surveillance purposes.
Paragraphs preceded by the ATTENTION indicator must be fully understood and heeded. Ignoring
these warnings could result in serious hazards.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction ......................................................................................1-1
Overview ................................................................................................ 1-2
Package Checklist.................................................................................. 1-3
Product Features.................................................................................... 1-3
Typical Applications ............................................................................... 1-4
Ethernet Connection ................................................................................. 1-4
Modem Dial-up Connection ..................................................................... 1-4
Product Descriptions .............................................................................. 1-5
Front Panel................................................................................................ 1-5
Rear Panel................................................................................................. 1-7
Chapter 2 Getting Started .................................................................................2-1
Before Getting Started ........................................................................... 2-2
Setting up an Ethernet Environment ...................................................... 2-2
Cable Connection...................................................................................... 2-2
Running the IP Installer Program.............................................................. 2-3
Powering on the VPort 2140 Video Server............................................... 2-4
Assigning an IP Address to VPort 2140 Video Server ............................. 2-4
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time ........................... 2-6
Setting up a Modem Environment.......................................................... 2-7
Cable Connection...................................................................................... 2-7
Powering on VPort 2140 Video Server..................................................... 2-8
Configuring a Modem (Under Windows 2000 Environment) .................. 2-9
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time ......................... 2-14
Mounting VPort 2140 ........................................................................... 2-14
Panel Mounting....................................................................................... 2-14
Chapter 3 Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time ................3-1
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server...................................................... 3-2
Opening Your Browser............................................................................. 3-2
Authentication........................................................................................... 3-2
Installing the Plug-in Application............................................................. 3-3
Functions Featured on the Main Page ................................................... 3-3
Image Mode and Text Mode..................................................................... 3-3
Logo and Host Name ................................................................................ 3-4
Video Quality Selection............................................................................ 3-4
Image Size Selection................................................................................. 3-4
Camera View selection ............................................................................. 3-5
System Configuration ............................................................................... 3-5
Relay Output Control................................................................................ 3-5
Motorized (PTZ) Camera Control............................................................. 3-5
Custom Camera Commands ..................................................................... 3-5
Chapter 4 System Configuration......................................................................4-1
System Configuration Via Web Access ................................................. 4-3
Using Setup Wizard.................................................................................. 4-3
Using the Application Wizard .................................................................. 4-4
System....................................................................................................... 4-4
Security ..................................................................................................... 4-5
Network .................................................................................................... 4-6
Video......................................................................................................... 4-9
COM 1 & COM 2 ................................................................................... 4-11
Page 5

Application ............................................................................................. 4-13
Demo....................................................................................................... 4-17
Homepage layout .................................................................................... 4-17
View log file ........................................................................................... 4-18
View parameters ..................................................................................... 4-19
Factory default ........................................................................................ 4-19
System Configuration Via FTP............................................................. 4-20
CONFIG.INI........................................................................................... 4-20
System Configuration Via Telnet.......................................................... 4-27
Telnet Commands................................................................................... 4-27
System core debugging........................................................................... 4-27
Monitor changed status of digital inputs................................................. 4-27
Stop information dumping ...................................................................... 4-28
Query status of digital inputs .................................................................. 4-28
Set digital outputs ................................................................................... 4-28
Erase snapshots stored in Flash memory ................................................ 4-28
Skip installation at next boot................................................................... 4-28
Reset network for new settings ............................................................... 4-28
Restore factory default settings............................................................... 4-28
Reset system ........................................................................................... 4-28
Chapter 5 Advanced Applications ...................................................................5-1
Capturing Up-to-date Still Images .......................................................... 5-2
Getting snapshot via URL......................................................................... 5-2
Getting snapshot via FTP.......................................................................... 5-2
Video Embedded in Customers’ Homepage.......................................... 5-2
Download Event-triggered Snapshots ................................................... 5-3
Getting triggered snapshots via URL........................................................ 5-3
Getting triggered snapshots via FTP......................................................... 5-3
Customizing Graphics in Homepage...................................................... 5-4
Command Script for DI/DO & Camera’ Actions Settings ....................... 5-4
Command format ...................................................................................... 5-5
Parameter Explanations ............................................................................ 5-5
Practical Examples.................................................................................... 5-6
URL Commands for DI/DO & Camera’ Actions Settings ....................... 5-7
Query status of digital inputs .................................................................... 5-7
Drive digital outputs ................................................................................. 5-7
Moving motorized camera in PTZ direction............................................. 5-7
Recalling camera position......................................................................... 5-7
Transparent Remote Serial Driver ............................................................ 5-7
URL Commands for System Maintenance............................................. 5-8
Download System Log via FTP................................................................ 5-8
Restart System via URL............................................................................ 5-8
Restore Factory Default Settings via URL................................................ 5-8
Chapter 6 Upgrading System Firmware ..........................................................6-1
Using Upgrade Wizard to Upgrade Firmware Easily ............................. 6-2
Using FTP to Upgrade Firmware ........................................................... 6-3
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting...............................................................................7-1
Power On Self Test (POST)................................................................... 7-2
Frequently Asked Questions .................................................................. 7-2
Appendix A URL Commands of Video Server................................................... A-1
Page URL...............................................................................................A-1
System Resource URL...........................................................................A-2
General Format of Command URL ........................................................A-2
System Configuration URL..................................................................... A-2
Security Configuration URL.................................................................... A-2
Page 6

Network Configuration URL ...................................................................A-3
Video Configuration URL .......................................................................A-4
Image Quality Configuration URL ..........................................................A-4
COM 1 Configuration URL .....................................................................A-5
COM 2 configuration URL ......................................................................A-5
Camera custom command configuration URL .......................................A-6
Camera preset configuration URL..........................................................A-6
Custom camera configuration URL........................................................A-7
Application configuration URL................................................................A-7
Motion detection configuration URL....................................................... A-8
Demo configuration URL........................................................................ A-8
Homepage layout configuration URL .....................................................A-8
Appendix B Settings of Supported PTZ Cameras............................................. B-1
Appendix C Camera Control Cable ....................................................................C-1
Appendix D Time Zone Table.............................................................................. D-1
Appendix E Technical Specifications ................................................................ E-1
Appendix F Service Information ........................................................................ F-1
MOXA Internet Services......................................................................... F-2
Problem Report Form............................................................................. F-3
Product Return Procedure ..................................................................... F-4
Page 7

1
1
Chapter 1 Introduction
VPort 2140 is a high-performance networking video transmitter. In addition to meeting the basic
needs of video feed, many advanced features are included to help you set up surveillance or web
attraction applications. The state-of-the-art design strikes a good balance between stability,
robustness, ease-of-use, and flexibility.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Product Features
Typical Applications
Ethernet connection
Modem Dial-up Connection
Product Descriptions
Front Panel
Rear Panel
Page 8

Overview
Video Server is a high-performance networking video transmitter. Its powerful VLIW DSP core
and fully optimized algorithm compresses and transmits high quality real-time video over a
standard TCP/IP network. In addition to meeting the basic needs of video feed, many advanced
features are included to help you set up surveillance or web attraction applications. The
state-of-the-art design strikes a good balance between stability, robustness, ease-of-use, and
flexibility.
Real-time Motion-JPEG compression
Video input can be efficiently compressed into packets of JPEG images without delay, and the
optimized compression engine creates excellent images that take up much less memory space.
This is done without sacrificing remote monitoring capability or storage. Five levels of
compression ratio and three different image resolutions are provided to provide more versatility.
Robust system operation
The industrial real-time operating system prevents hackers and viruses from wreaking havoc on
both Windows and Linux systems, and the on-board watchdog improves reliability by continually
monitoring the system’s operation.
Easy Web access via standard browser
There is no need to install new software to access Video Server, since the embedded Web Server
allows users to access the Video Server anywhere over the Internet with any popular Web browser.
As long as you are connected to the network, you will be able to view the same images seen by
your cameras.
User’s Password protection
User’s Password protection is provided to prevent malicious intruders from accessing your system.
Once the administrator password is configured, all users will need a password to access the Video
Server.
Built-in VMD (Video Motion Detection)
External sensors are not required, since the video channel can be configured to detect motion,
making it easy to set up a security system in either your home or office. And the customizable
settings allow you to tune the system for both object size and sensitivity, making the Video Server
adaptable to different environments.
Weekly schedule for automated surveillance
The user-defined time period will repeat weekly to check security settings and send notifications
or drive external devices, making it easy to install in SOHOs, retail shops, and home security
systems.
Flexible I/O control for external devices
One opto-isolated sensor input and one relay output are provided to control external devices,
giving system integrators the option of turning an analog system into an advanced security
system.
MOXA SoftDVR™ Lite IP Surveillance Software
To extend the Video Server’s capabilities, MOXA SoftDVR Lite IP Surveillance Software, which
supports a maximum of 4 cameras in quad, is included free of charge, allowing users to turn their
PC into a digital video recorder. Scheduling or one-click recording saves important images on
your local hard disk, and the reliable motion detection and instant warning features make you
ready for any situation. A quick and easy to use search and playback function lets you easily find
the image you’re looking for, so that you can inspect the images more carefully, and also save the
output to an AVI file.
1-2
Remote system upgrade
Video Server users have round-the-clock access to the most up-to-date firmware on our website,
with a free upgrade wizard included to facilitate firmware installation.
Technical support for developers
The high-performance Video Server can be integrated into many applications—without busting
your budget—and the complete programming interface and standard JPEG format helps make the
developer’s job easy and straightforward. More ideas for Video Server applications can be found
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 9

on our website.
Package Checklist
1 VPort 2140 Video Server
Power adaptor
2 GPIO terminal connectors
L-type Fixed Aluminum pieces and 8
screws
Introduction
Camera control cable
Null modem cable
Software CD
NOTE: Notify your sales representative if any of the above items is missing or damaged.
Product Features
VPort 2140 products enjoy the following features:
Compact size, 4-ch MJPEG Video Server
4 BNC video inputs, 4 BNC video outputs (75Ω resistence switch off )
Stand-alone, with built-in web server for network interface
Industry-standard real-time operating system without virus threat
Real-time performance with powerful DSP
Optimal solution by adjustable frame rate, bandwidth, and quality
Video Motion Detection (VMD) with Pre/Event/Post images
General I/O for external sensor and alarm
Supports 2 RS-232/485 COM ports for PTZ camera control or Modem dial-up connection
Remote access of images via FTP or e-mail
Password protection and administrator privilege
Customized personal homepage
Remotely upgrade the firmware to keep it up to date
Easy but powerful utilities for installation and maintenance
MOXA SoftDVR IP Survaillance Software for viewing and recording bundled free
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
1-3
Page 10
NOTE: ActiveX Control SDK is supported with flexible interface and sample codes for third-party
developers (please contact Moxa sales representatives if you require this SDK.)
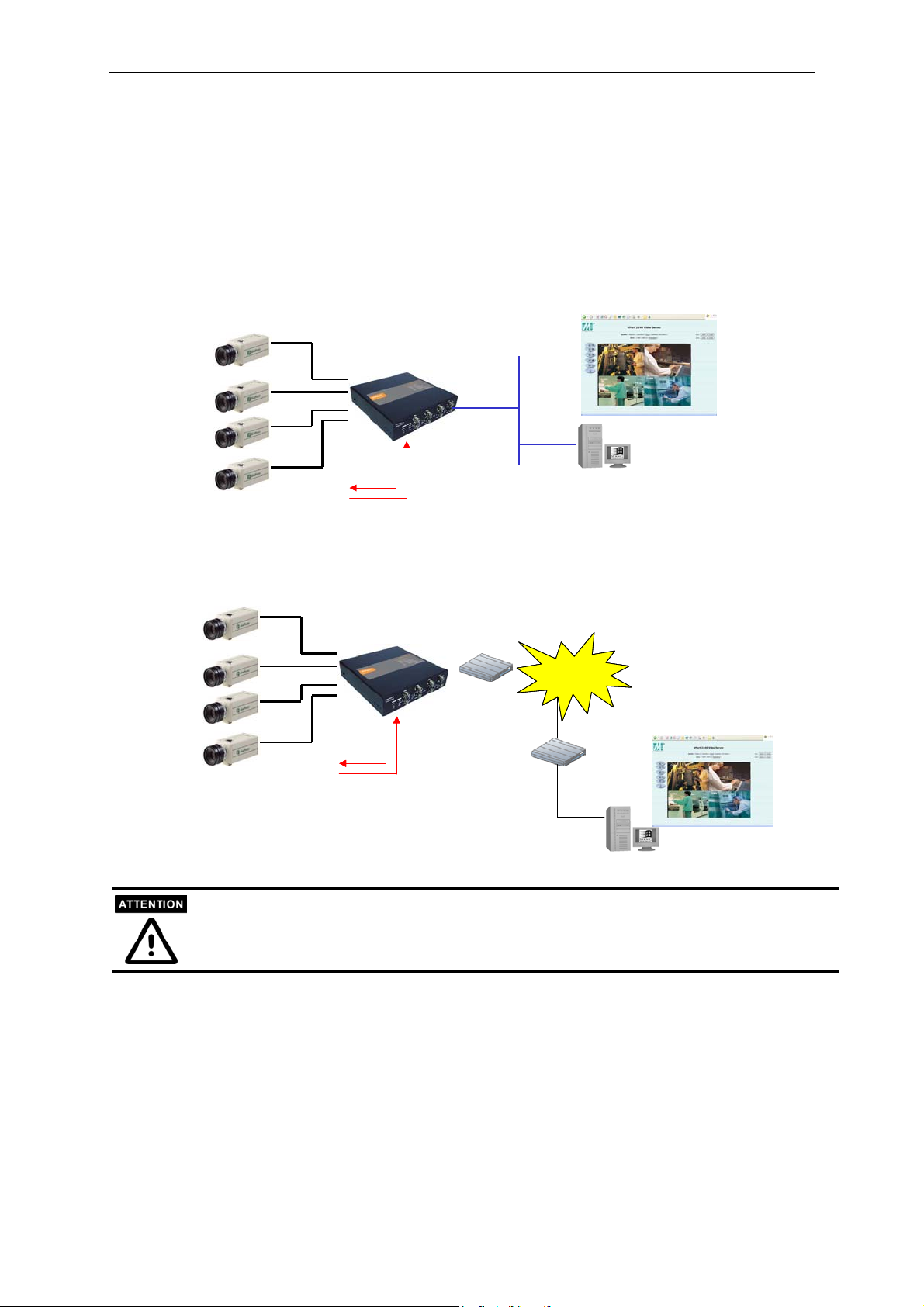
Typical Applications
Ethernet Connection
Analog
Analog
Cameras
Cameras
4DI/ 2DO
4DI/ 2DO
IP: 192.168.4.100
IP: 192.168.4.100
TCP/IP
TCP/IP
http://192.168.4.100
http://192.168.4.100
Server
Server
Modem Dial-up Connection
Analog
Analog
Cameras
Cameras
IP: 192.168.4.100
IP: 192.168.4.100
IP: 192.168.4.100
4DI/ 2DO
4DI/ 2DO
4DI/ 2DO
Since VPort 2140 Video Server only supports the Modem Dial-up connection, the snapshots
triggered by VMD, DI event or sequential mode will not be sent via the modem connection.
Modem
Modem
Modem
Modem
Modem
Modem
PSTN
PSTN
PSTN
http://192.168.4.100
http://192.168.4.100
http://192.168.4.100
Server
Server
Server
1-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 11
Product Descriptions
Front Panel
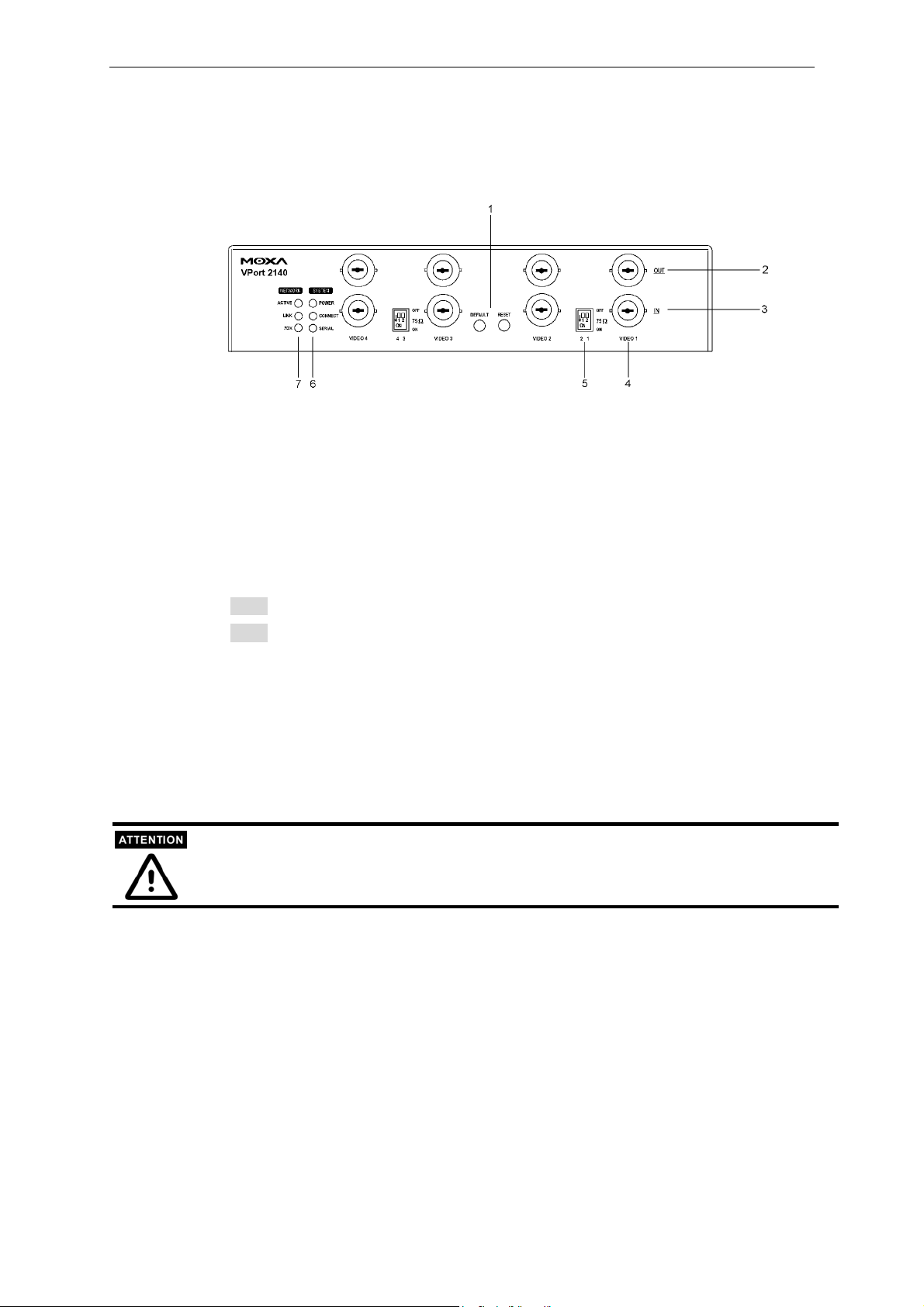
1: RESET & DEFAULT buttons for restoring the system
There are two buttons located at the center of the front panel. One is labeled “RESET” and the
other is labeled “DEFAULT.” “RESET” will force the system to restart at any point, meaning the
system will perform the system diagnosis, and software installation may be necessary if the IP
address is not fixed. “DEFAULT” will restore the default settings, and then force the system to
restart.
Introduction
When the system does not work properly, or VPort 2140’s IP address is not known, the
administrator can use the restore function to restore VPort 2140’s factory default settings.
Step1: Click the “RESET” button once.
Step2: Press the “DEFAULT” button firmly until the “CONNECT” and “SERIAL” LEDs
flash 2 times to run the system diagnosis and erase the system parameters.
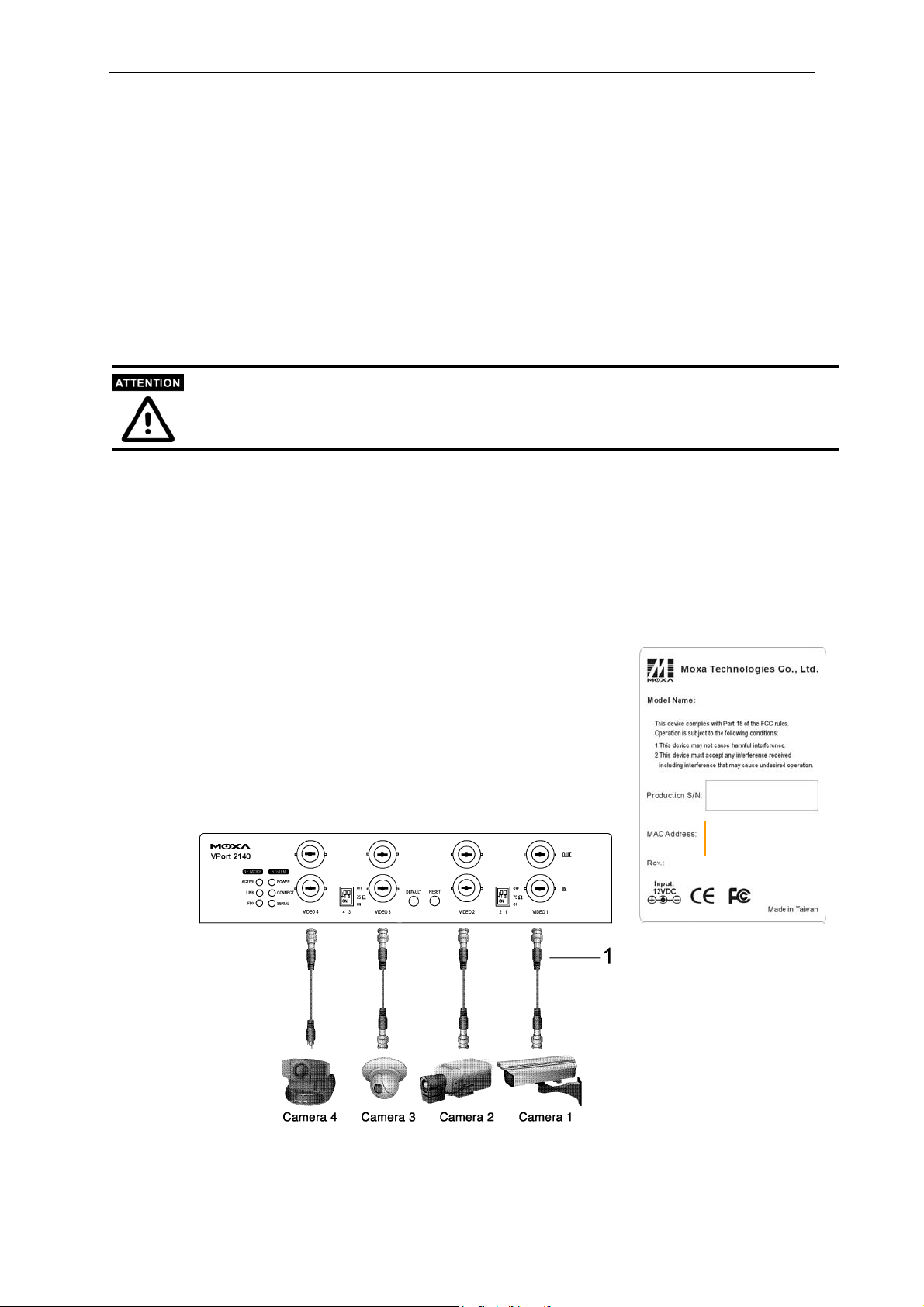
2 & 3: BNC video outputs “OUT” & inputs “IN”
VPort 2140 allows up to 4 cameras to be attached at the same time. To ensure that the correct
video modulation type is detected, cameras should be connected sequentially from “VIDEO 1” to
“VIDEO 4” and powered on before the VPort is powered on. Video outputs also have four
loop-through connectors for connecting with other capture devices, such as a time-lapsed VCR.
To use the video outputs, the 75 Ohm DIP switch should be turned to the “OFF” position.
Although the analog cameras have 2 different standards, NTSC or PAL, all of the cameras connected
to VPort 2140 Video Server should use the same standard.
4: Camera ID: “VIDEO 1,” “VIDEO 2,” “VIDEO 3,”and “VIDEO 4”
Each camera connected to VPort 2140 has a Camera ID used by VPort to identify the camera.
5: 75 Ohm DIP Switch
There are four 75 Ohm DIP switches numbered from “1” to “4” on the front panel. They are used
to enable the 75-Ohm resistance video impedance. DIP switches should be turned to the “ON”
position if cameras are connected to the video inputs. If users want to connect another device to
the video output, such as a VCR or multiplexer, the switches should be turned to the “OFF”
position to disable the impedance.
6: System LEDs: “POWER,” “CONNECT,” and “SERIAL”
Each time the Video Server starts up, it will perform a Power-On-Self-Test (POST) to examine
each hardware module. VPort 2140 has 3 LEDs:
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
1-5
Page 12
a. POWER: power indicator
b. CONNECT: checks if the Video Server is alive
c. SERIAL: checks if the RS-232/485 COM ports are in use
As soon as the administrator plugs in the power connector, both the CONNECT and SERIAL
LED’s will flash, one by one, until the diagnosis is finished. If the result is good, these 2 LEDs
will turn off momentarily, and then follow the pattern shown in the table below. If any of the
modules fails, refer to Chapter 7, Troubleshooting, under Power On Self Test for the error
pattern, and then follow the troubleshooting procedures. If the system still does not operate
normally, please contact your reseller for technical service.
Mode Condition
Ethernet Connection
Modem Dial-up
Connection
Connection
7: Network LEDs: “ACTIVE,” “LINK,” and “FDX”
When using the 10/ 100 Mbps Ethernet connection, VPort 2140 has 3 LEDs to show network
status:
Name Description Work Status
ACTIVE Check if the network is alive Flashing: Network alive
LINK Check the 10/ 100 Mbps Ethernet speed ON: 100 Mbps
FDX Check if transmission is full or half duplex ON: Full Duplex
Before installation ON OFF OFF
After installation ON Flash OFF
During camera control ON Flash Flash
After POST ON Flash ON
Before connected ON ON ON Null Modem Dial-up
After connected ON Flash ON
LED1
(POWER)
LED2
(CONNECT)
OFF: Network not alive
OFF: 10 Mbps
OFF: Half Duplex
LED3
(SERIAL)
1-6
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 13
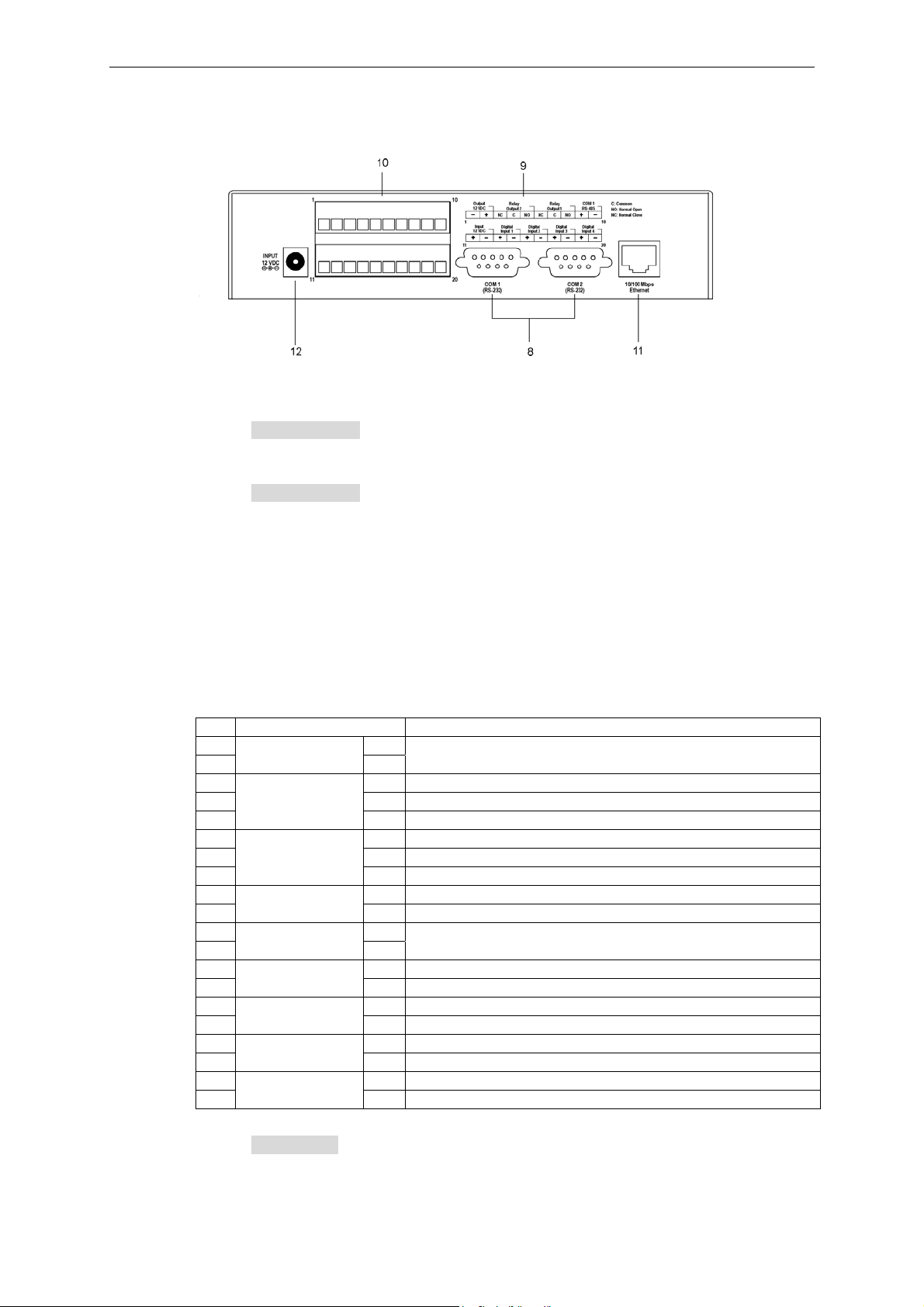
Rear Panel
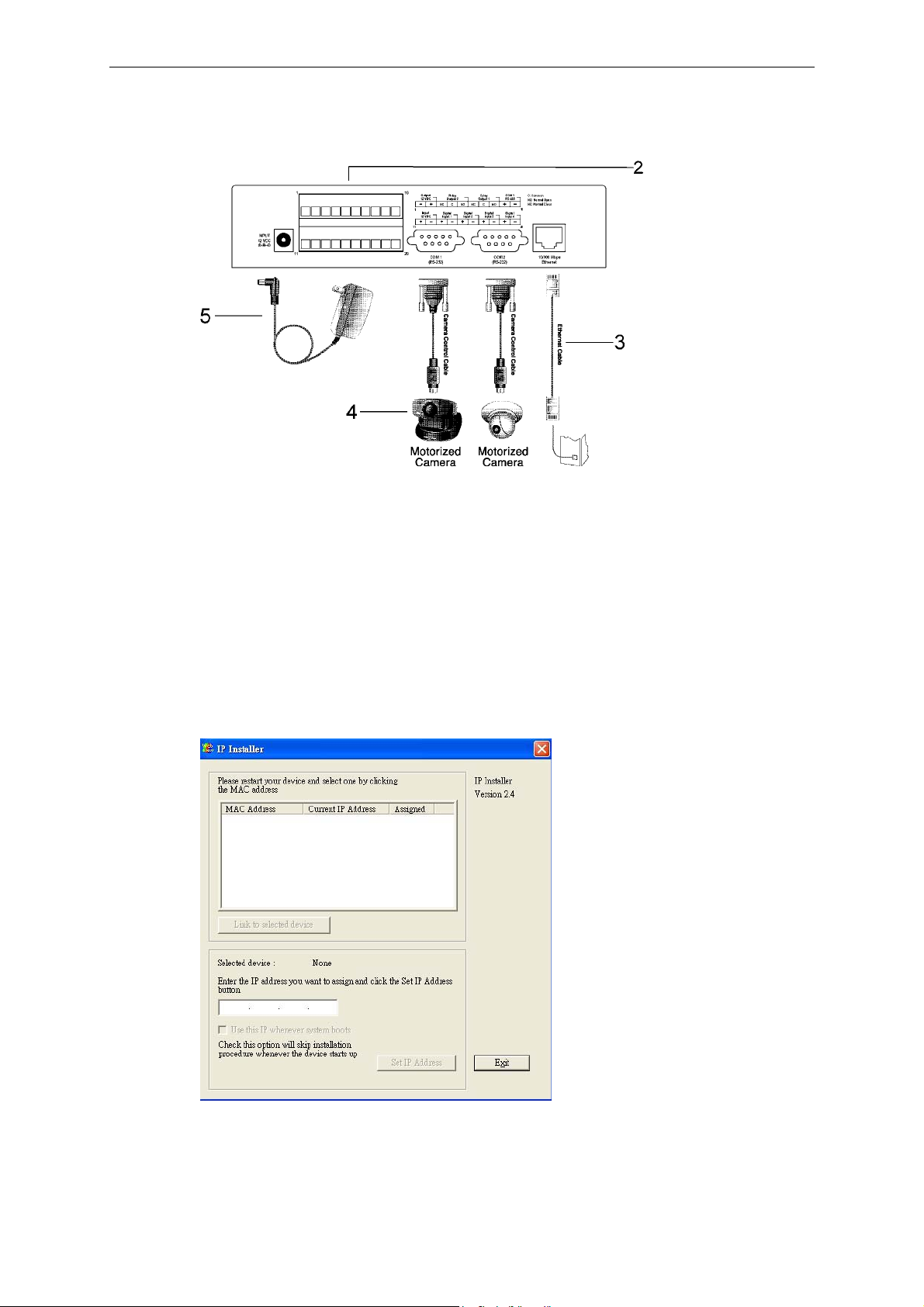
8: COM1 & COM 2
There are 2 COM ports on VPort 2140’s rear panel.
Introduction
a. COM 1 (RS-232): This RS-232 serial port can connect with an RS-232 PTZ camera. For
RS-485 PTZ cameras, the administrator can use the General I/O terminal block’s COM 1
(RS-485) .
b. COM 2 (RS-232): This RS-232 serial port can connect to a modem, or you can use the
included null modem cable to utilize a dial-up network when Ethernet is not available. If
the Video Server is connected to the network via the Ethernet interface, you can also use
this RS-232 serial port to control an RS-232 PTZ camera.
9 & 10: General I/O terminal block
VPort 2140 provides a very flexible general I/O interface that can be used with security devices,
such as sensors, alarms, lighting fixtures, or door locks. Two green connectors are included in the
package to connect external devices. The general I/O terminal block has 20 pins for device control.
These pins can be divided into three categories based on their functions, including power source,
RS-485 and digital inputs and outputs.
No. Pin description Regulation
Output
1 -
12 VDC
2
3 NC Normal Close, Max. 1A, 24V DC or 0.5A, 125V AC
Relay
4 C Common, Short with NC at initial state
Output 2
5
6 NC Normal Close, Max. 1A, 24V DC or 0.5A, 125V AC
Relay
7 C Common, Short with NC at initial state
Output 1
8
9 + RS-485, Data+
COM 1
RS-485
10
11 +
Input
12 VDC
12
13 + Max. 50 mA, 12V DC
Digital
Input 1
14
15 + Max. 50 mA, 12V DC
Digital
Input 2
16
17 + Max. 50 mA, 12V DC
Digital
Input 3
18
19 + Max. 50 mA, 12V DC
Digital
Input 4
20
Power Output, Max. 500 mA at 12V DC
+
NO Normal Open, Max. 1A, 24V DC or 0.5A, 125V AC
NO Normal Open, Max. 1A, 24V DC or 0.5A, 125V AC
- RS-485, Data-
External Power Input, Min. 1.5A, 12-15V AC or DC
-
- Ground
- Ground
- Ground
- Ground
a. Power Source: There are 2 ways to connect to the power source. One is using the power
adaptor. The other is using Pin 11 and Pin 12 of the terminal block, which are for DC
power input. This DC power source can be either AC or DC, and should fall in the output
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
1-7
Page 14
range between 12V and 15V. Polarity does not matter if you use AC. The DC output
through Pin 1 and Pin 2 is fed from the power adaptor of the Video Server or pin 11 and
pin 12 if an external power source is attached. The current of external devices is limited to
less than 500 mA.
b. COM 1 RS-485: If the device connected to the COM1 port has an RS-485 interface, such
as a PTZ camera control, wire the RS-485 Data+ and Data- control lines to COM RS-485
pin “+” and pin “ –”. If the distance from the controlled device is too long to allow
accurate function, an external power source may be used to pull the RS-485 signal to
“high” status.
c. Digital Input/Relay Output: VPort 2140 Video Server provides 4 digital inputs and 2
relay outputs. The Digital Input’s “+” pin and “-” pin can be connected to an external
sensor to monitor the voltage according to the programmed scripts in configuration (see
the “Command Script for DI/DO & Camera’s Actions Setting” in Chapter 5). The Relay
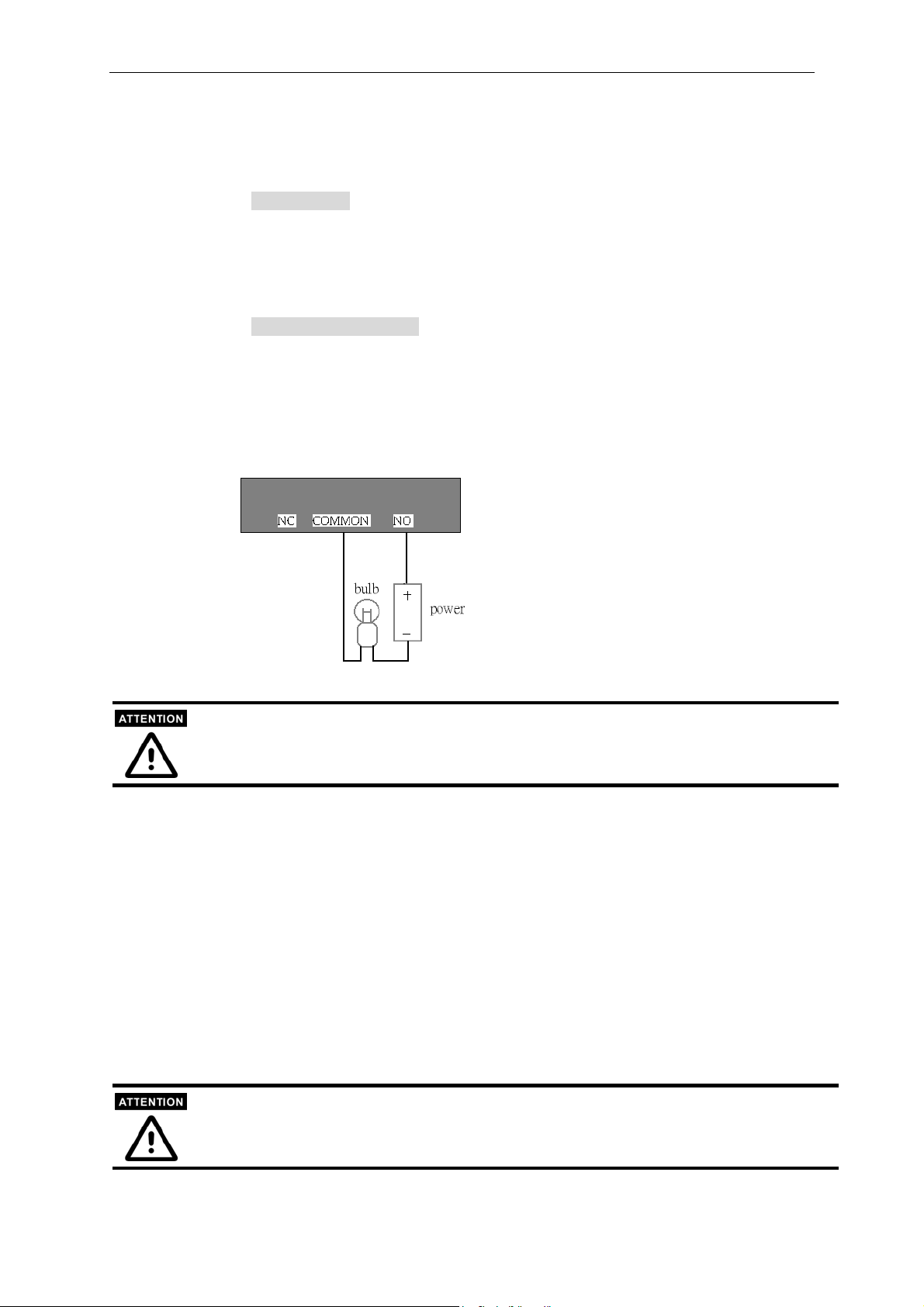
Output’s “NO” pin (Normal Open), “NC” (Normal Close) pin, and “C” pin (Common)
can be used to turn an external alarm on or off. When the system starts up, both relay
outputs’ “Common” pin will short the “NC” pin. A simple example is illustrated in the
diagram below.
If DI1 is configured to “rising” status, so
that DO1 is driven to “high” status
(resulting in DO1’s “Common” pin
shorting the “NO” pin), the light bulb
will light up when DI1’s signal changes
from 0V to 12V.
COM 1 RS-485 and COM 1 RS-232 share the same UART chip. If one of the ports is being used,
the other port will not be available.
11: 10/100 Mbps Ethernet
An RJ45 10/100 Mbps Ethernet connector can be connected to an Ethernet network with a UTP
category 5 cable of length shorter than 100 meters (according to the Ethernet standard). Once the
Ethernet cable is connected correctly, the Video Server will use the Ethernet interface before
using the modem attached to COM 2.
12: INPUT 12 VDC
Connect the power jack of the included 12 VDC power adaptor. Connecting the power adaptor
should be the last step involved in the Video Server hardware installation. Administrators may
feed an external power source through pins 11 and 12 of the GPIO terminal block to replace the
power adapter.
The Video Server power adaptor and the external power supply (from pins 11 and 12 of the Terminal
Block) cannot be used at the same time. Only one power source can be used to feed power to the
Video Server. Improper usage will result in serious damage to your Video Server.
1-8
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 15

Chapter 2 Getting Started
This chapter includes information about how to install a VPort 2140 Video Server.
The following topics are covered:
Before Getting Started
Setting up an Ethernet Environment
Cable Connection
Running the IP Installer Program
2
2
Powering on VPort 2140 Video Server
Assigning an IP Address to VPort 2140 Video Server
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time
Setting up a Modem Environment
Cable Connection
Powering on VPort 2140 Video Server
Configuring a Modem (Under Windows 2000 Environment)
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time
Mounting VPort 2140
Panel Mounting
Page 16
Before Getting Started
To adapt easily to different environments, the Video Server automatically detects the attached
interfaces and configures itself appropriately. For this reason, users do not need to worry about
whether the connected cameras are either NTSC or PAL, how to select between Ethernet or
modem, and whether the Ethernet speed is 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps.
The Video Server supports both Ethernet and modem dial-in connections. Refer to the installation
section that applies to your network environment. If both interfaces are available, we recommend
using Ethernet, which will be chosen automatically if an Ethernet cable and modem are both
connected to the Video Server.
Installing a different interface will automatically clear the previous network settings to start a new
installation.
In what follows, “user” refers to those who can access the Video Server, and “administrator”
refers to the person who knows the root password that allows changes to the Video Server’s
configuration, in addition to providing general access. Administrators should read this part of the
manual carefully, especially during installation.
Setting up an Ethernet Environment
Before installing multiple Video Servers at different locations, the
administrator should record the MAC Address (located on the
Video Server’s label) for future use, and then shut down all
peripheral devices prior to connecting the devices. The video BNC,
Ethernet cable, and power adaptor are needed to take advantage of
the basic viewing function provided by the Video Server.
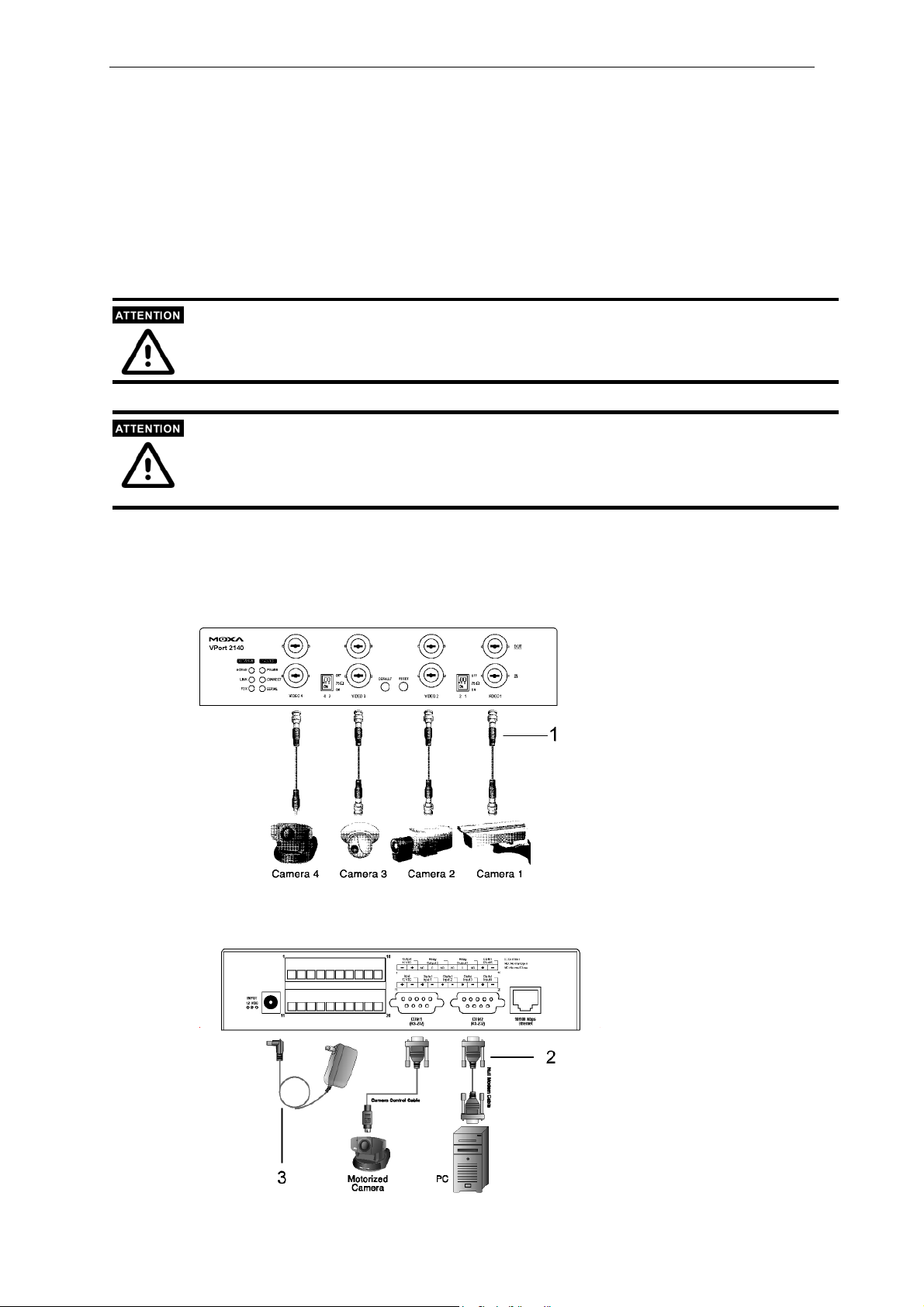
Cable Connection
Front Panel
00-02-xx-xx-xx-xx
2-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 17
Getting Started
Rear Panel
Before powering on the VPort 2140 Video Server:
1. Connect your camera’s video output with the BNC video input.
2. Connect I/O devices (such as sensors or alarms) with VPort’s GPIO Terminal Block.
3. Connect the hub or switch on the LAN to the VPort’s 10/100 Mbps Ethernet port.
4. Connect VPort’s COM port with your camera’s COM port if you are using a PTZ Camera.
Running the IP Installer Program
To run the IP installer program, double click on the “IPinstaller.exe” program located on the
software CD.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
2-3
Page 18
Powering on the VPort 2140 Video Server
First, make sure that all cables are correctly and firmly connected, and then turn on the cameras,
sensors, and alarm devices.
Next, power on the video server by attaching the Video Server’s power adaptor to an electrical
outlet. After the POST (Power-On Self Test) is completed successfully, the Video Server is ready
to be configured. At this point, the network speed and video modulation type will be detected
automatically.
Assigning an IP Address to VPort 2140 Video Server
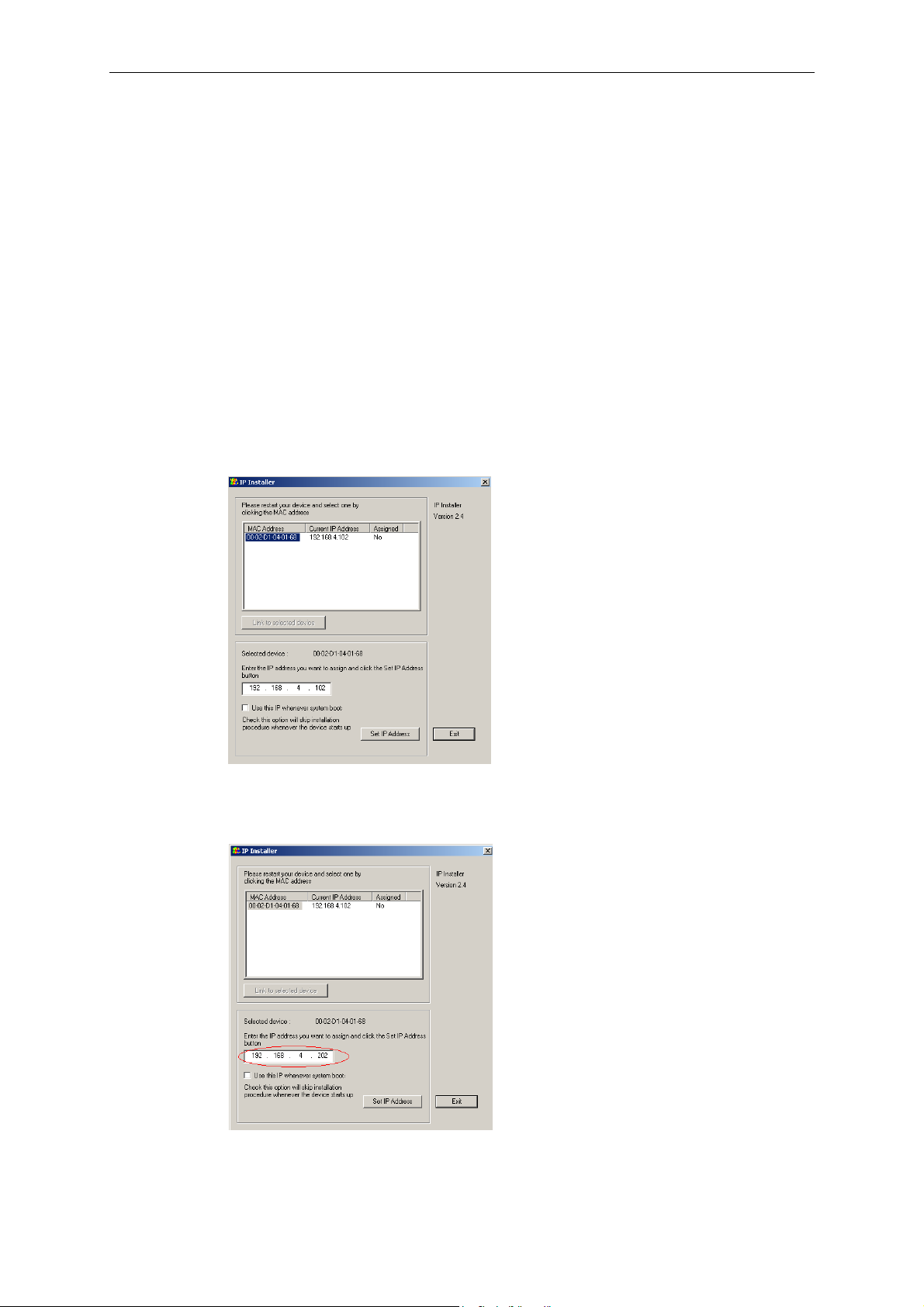
Using the IP Installer Program
1. Power on the VPort after running IPinstaller.exe.
2. Wait for auto-search to locate new video servers.
3. Click on the VPort whose MAC address matches the one you just installed to assign it an IP
address.
4. To assign an IP address to this VPort, manually type in the IP address you want to use if it
differs from the IP address given by the DHCP server.
5. Check Use the IP whenever system boots option if you wish to continue using this IP
2-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 19
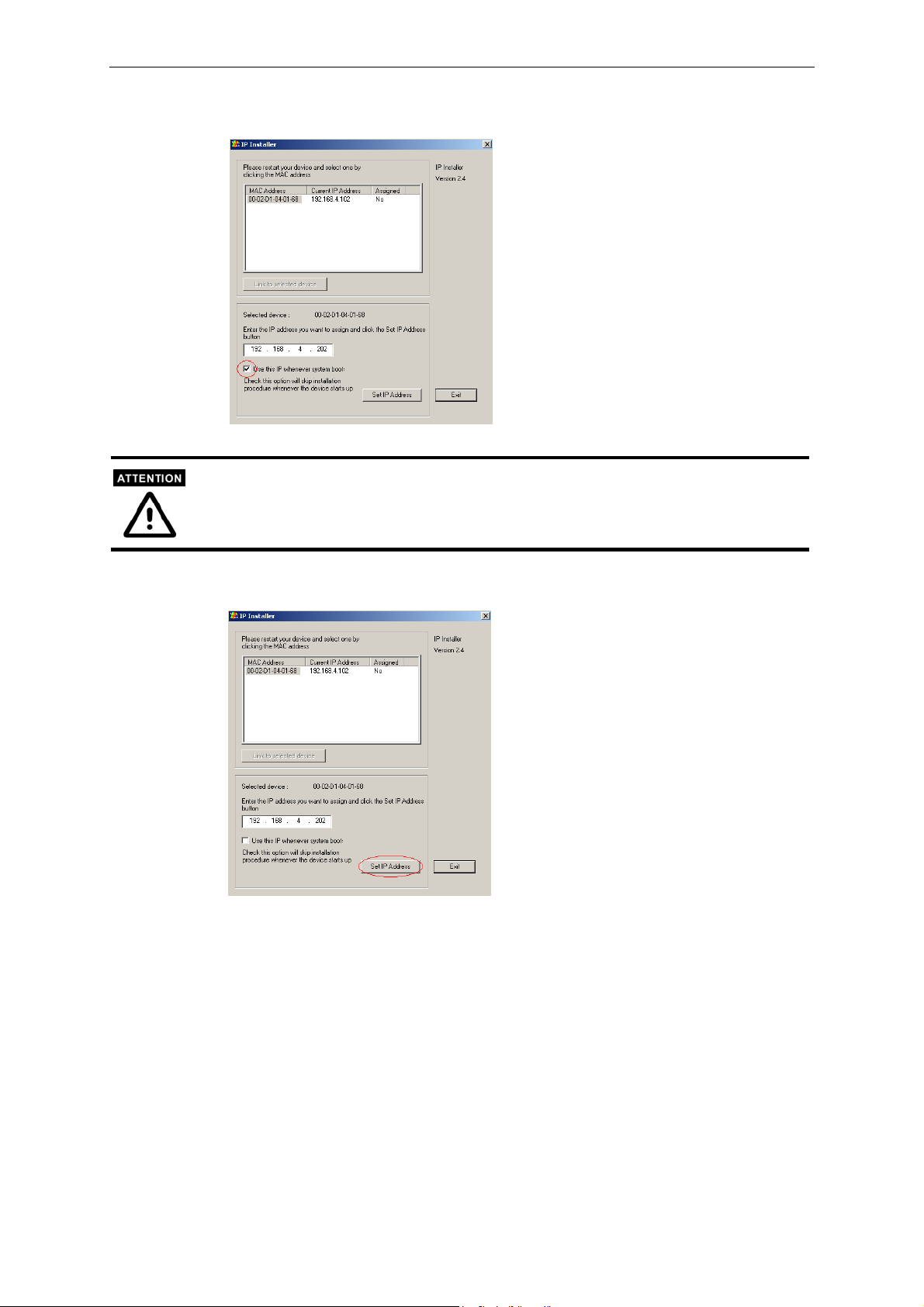
Getting Started
address for this VPort.
If you check Use this IP whenever system boots option, you will not see this VPort the next
time you run the IP installer program, unless you have restored the VPort. As a matter of
convenience, we strongly recommend that you check this option.
6. Click on Set IP Address to assign the IP address to this VPort.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
2-5
Page 20
7. If you check Use the IP whenever system boots option, then whenever you change the root
password and restart the system, a dialog window will open to ask for Server FTP Port and
Root Password, since they were already changed by the administrator to something other
than the default settings. If the settings made by the administrator are lost, restore default
settings and then rerun the IP installer program.
8. The system will check if the IP address is valid.
9. An Install OK message will appear if the installation is successful. Click on OK to close the
window.
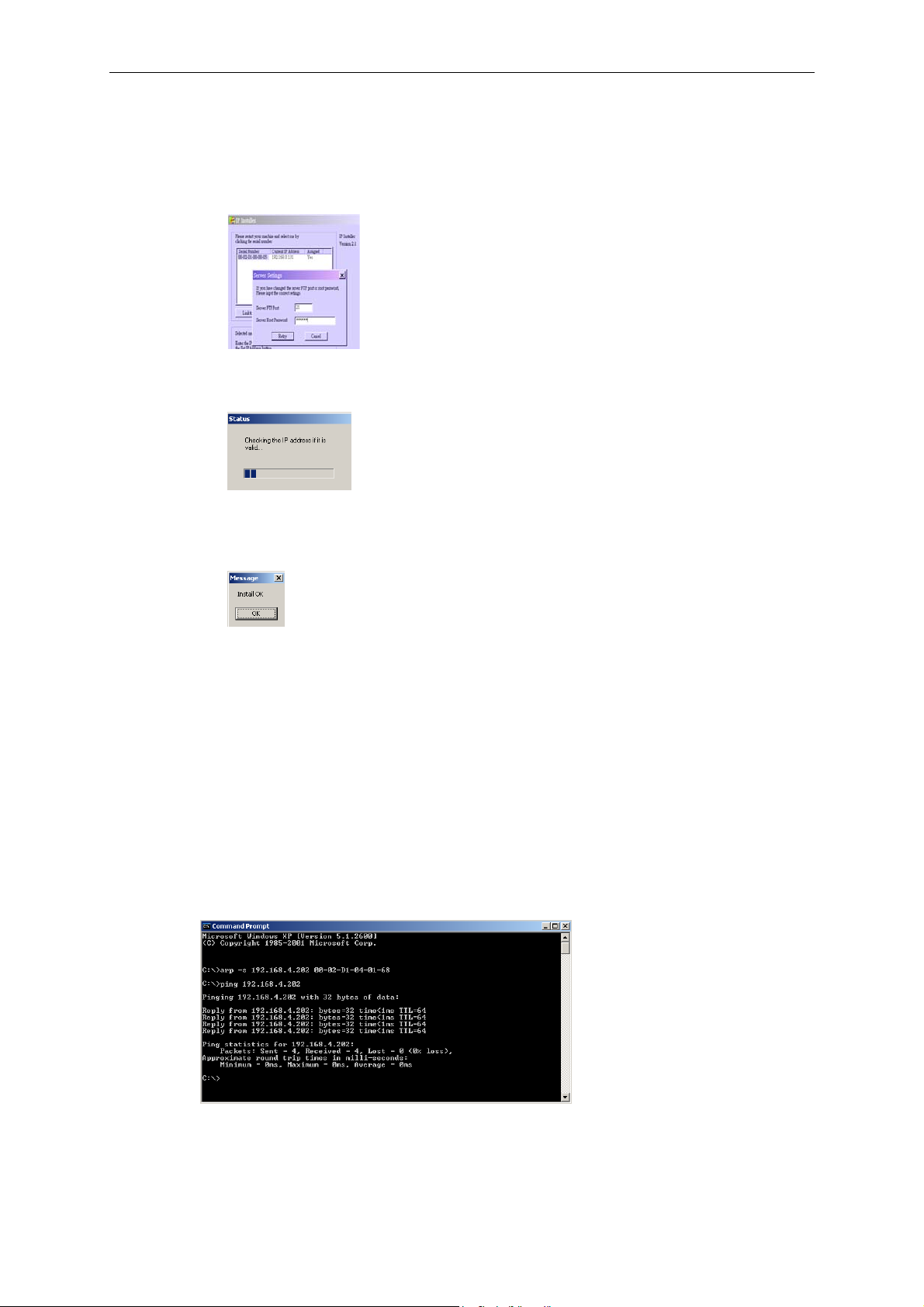
Using DOS Commands under Windows
For some environments, such as MAC, DOS, Linux, and UNIX, some common network tools,
including ARP and PING, can be used to install the VPort. Before proceeding further, make sure
that the ARP and PING programs are provided by your system.
1. Open a DOS command window.
2. Type arp –s <VPort’s IP Address> <MAC address>, and press enter.
3. Type ping <VPort’s IP address>, and then press enter.
4. A reply message will appear if the VPort is successfully installed.
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time
Once the installation is complete, administrators should follow the instructions described in the
next chapter, First Time Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server, to make necessary configurations.
2-6
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 21
Setting up a Modem Environment
VPort 2140 Video Server provides 2 modem modes: Modem and Null Modem. The null modem
mode can be used for point-to-point connections in a local environment. Although the baud rate
can be set up to 115.2 Kbps, the actual data rate depends on the Modem connection. For dial-up
connections, the VPort 2140 Video Server waits passively for a phone call to establish a
point-to-point connection.
The Modem and Null Modem dial-up connections are for initial usage of Video Server. If you have
already used an Ethernet connection, reset Video Server to factory defaults before using a dial-up
connection. In addition, when using a dial-up connection, the Ethernet socket must be disconnected.
The Modem and Null Modem connections for VPort 2140 Video Server only support the dial-in
function, which means that you can access the VPort 2140 Video Server, but VPort 2140 Video
Server cannot send alarm messages to you automatically via the Modem and Null Modem
connection.
Getting Started
Cable Connection
Null Modem
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
2-7
Page 22
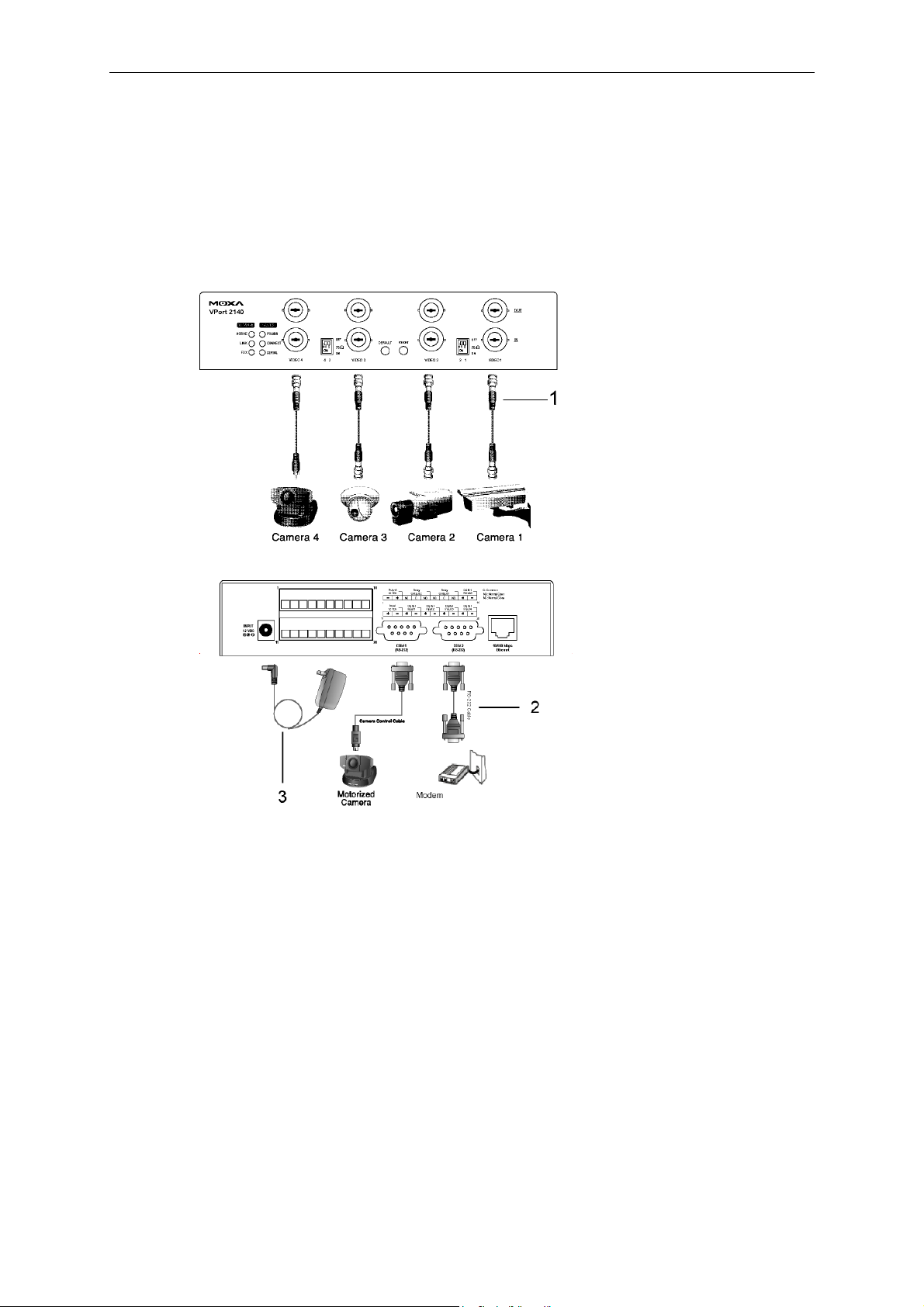
Before powering on the VPort 2140 Video Server:
1. Connect your cameras’ video outputs to the BNC video inputs.
2. Connect VPort’s COM port with your PC’s COM port.
3. Connect the power adaptor.
Modem
Before powering on the VPort 2140 Video Server:
1. Connect your cameras’ video outputs with the BNC video inputs.
2. Connect VPort’s COM port with your modem’s COM port.
3. Power on the Modem.
4. Connect the power adaptor.
Powering on VPort 2140 Video Server
After all cables are correctly and firmly connected, turn on all peripheral devices, including
cameras, sensors, and alarm devices. And then connect the VPort 2140 to the power supply.
After being powered on, the VPort will automatically detect if an external modem is connected to
the modem port. As soon as an external modem is detected, the CONNECT LED will blink
periodically. If no modem is detected, the VPort will assume that the included null modem cable
is connected to perform system configuration. Both CONNECT and SERIAL LEDs will show as
“steady on” until the dial-up connection over the null modem is established.
2-8
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 23
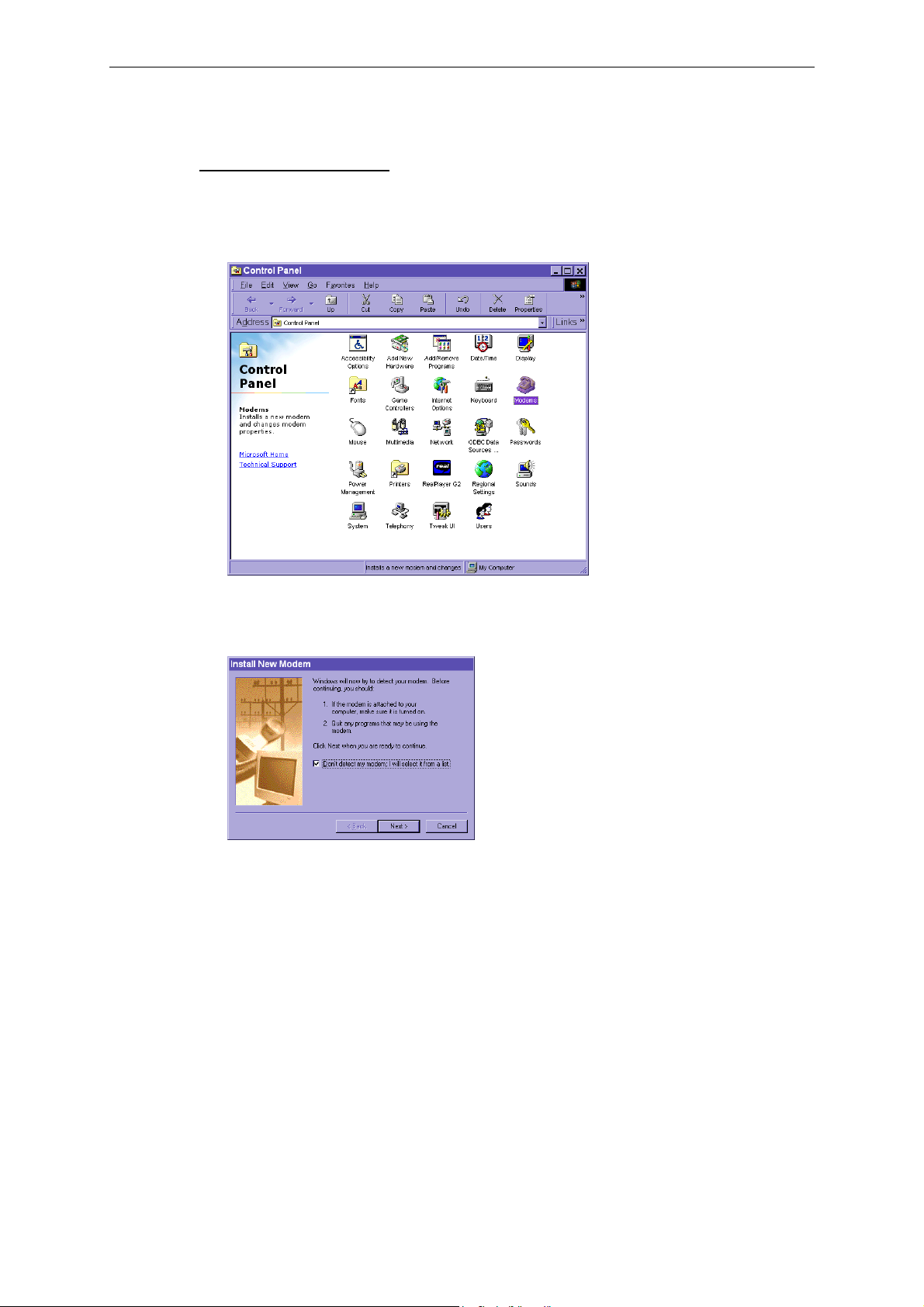
Configuring a Modem (Under Windows 2000 Environment)
Installing a new modem
Null Modem Mode
1. Click on StartControl PanelModems.
Getting Started
2. An Install New Modem message will appear. Check Don’t detect my modem; I will select
it from a list, and click on Next to continue.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
2-9
Page 24
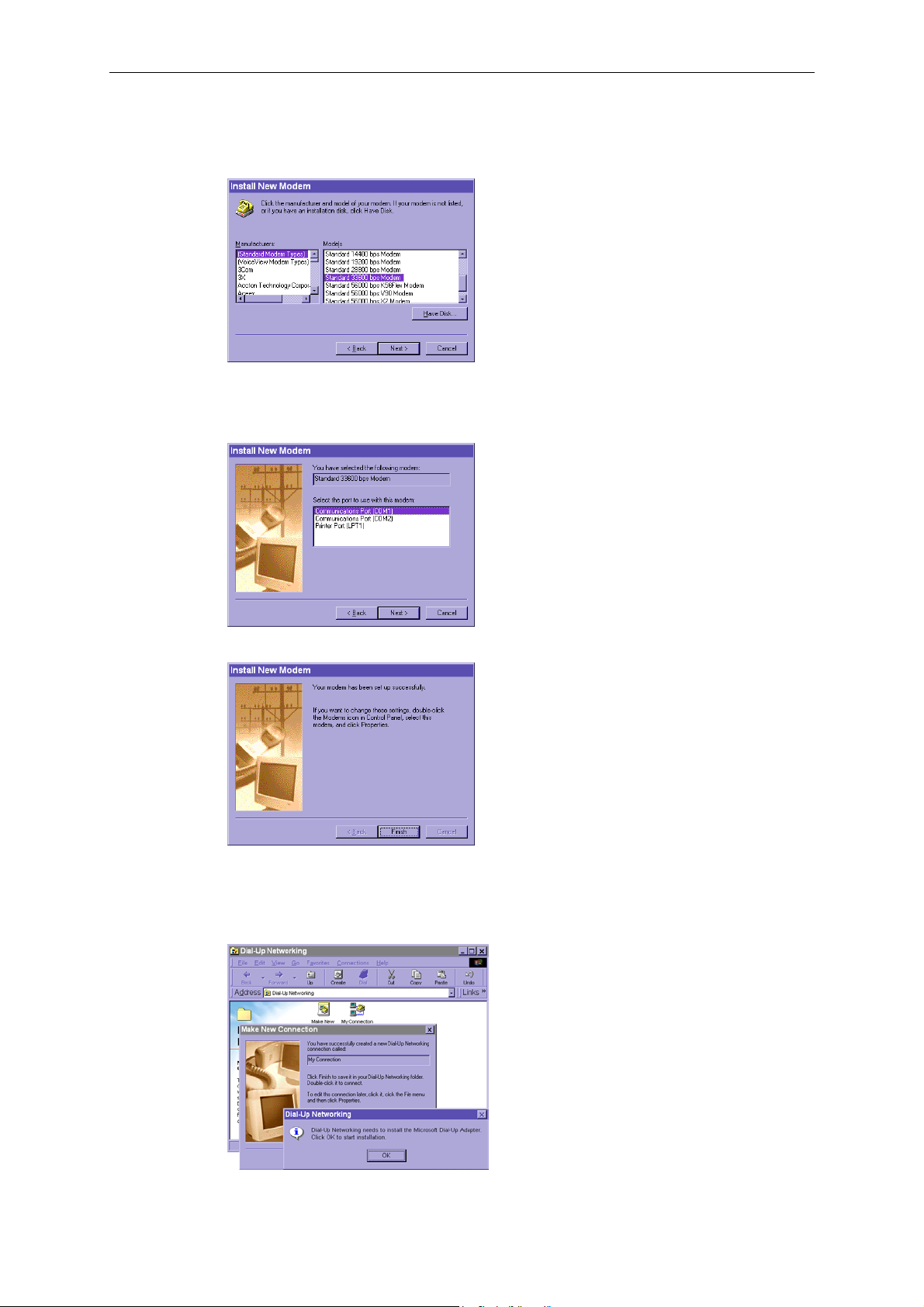
3. Under the Manufacturers column, select (Standard Modem Types). A number of modem
models will appear in the Models column. Select Standard 33600 bps Modem, and click on
Next to continue.
4. Select the serial port that the included null modem cable is connected to, and click on Next to
continue. The null modem is now ready for use.
5. If a Dial-Up adapter is not installed, Windows will automatically prompt you to install it.
Click on OK to continue. If the adapter does not start automatically, double click on the
Control Panel network icon install the Microsoft Dial-Up Adapter.
2-10
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 25
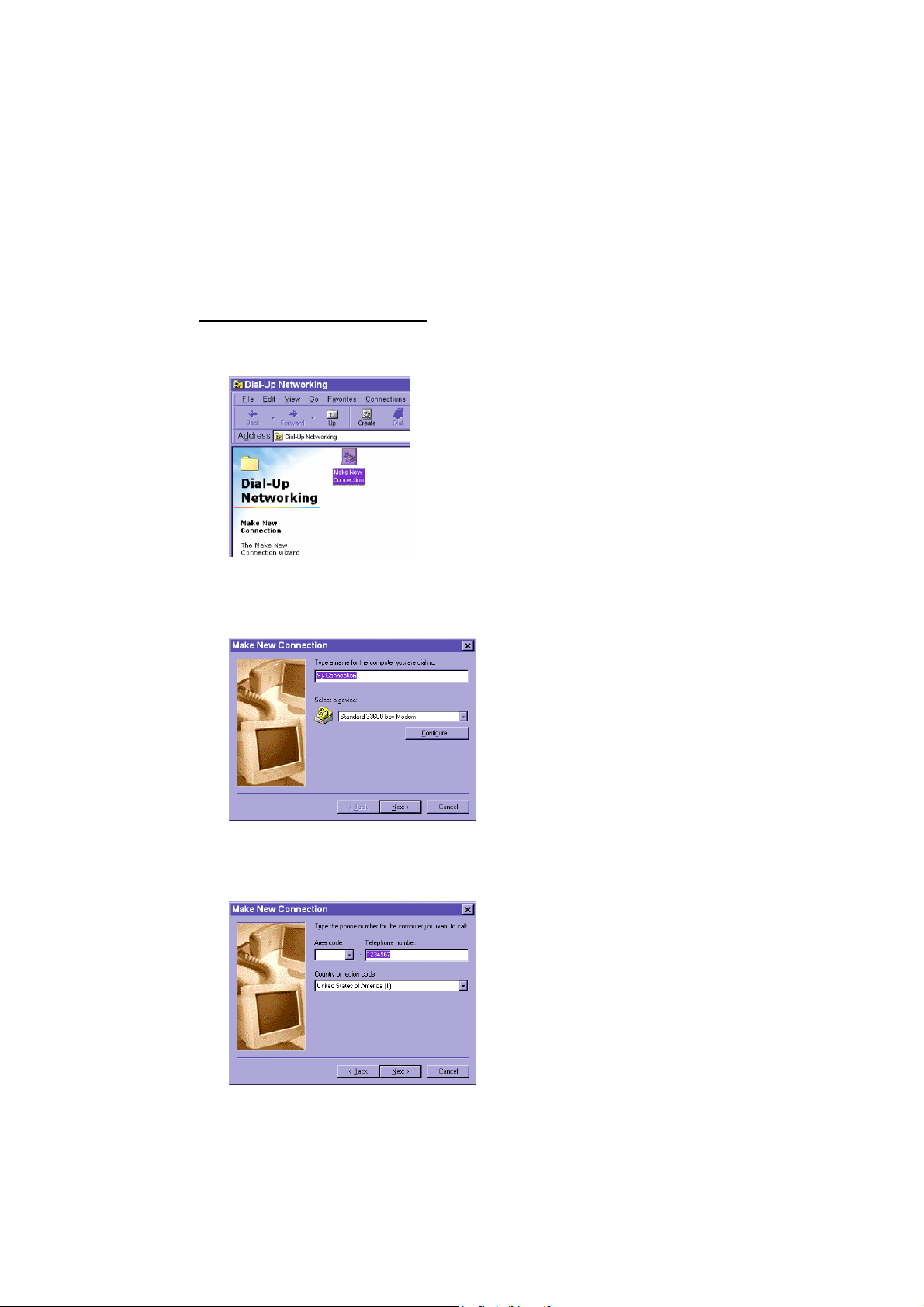
Modem Mode
1. Click on Start Control Panel Modems.
Getting Started
2. If you already have a Modem, read the Setting up a new connection
don’t have a modem, an Install New Modem message will appear. Click on Next, and the
system will detect the modem automatically. If your modem is not detected, you can select
the Modem from the manufacturers column.
section below. If you
Setting up a new connection.
1. After the modem is installed, open the dialup network folder in Windows to set up a new
connection.
2. Select the newly-installed Modem (for Modem connection) or Standard 33600 bps Modem
(for null modem connection), and then click on Next to continue.
3. In modem mode, enter the phone number used to connect to your VPort 2140; in null modem
mode, enter an arbitrary phone number, and then click on Next to continue.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
2-11
Page 26
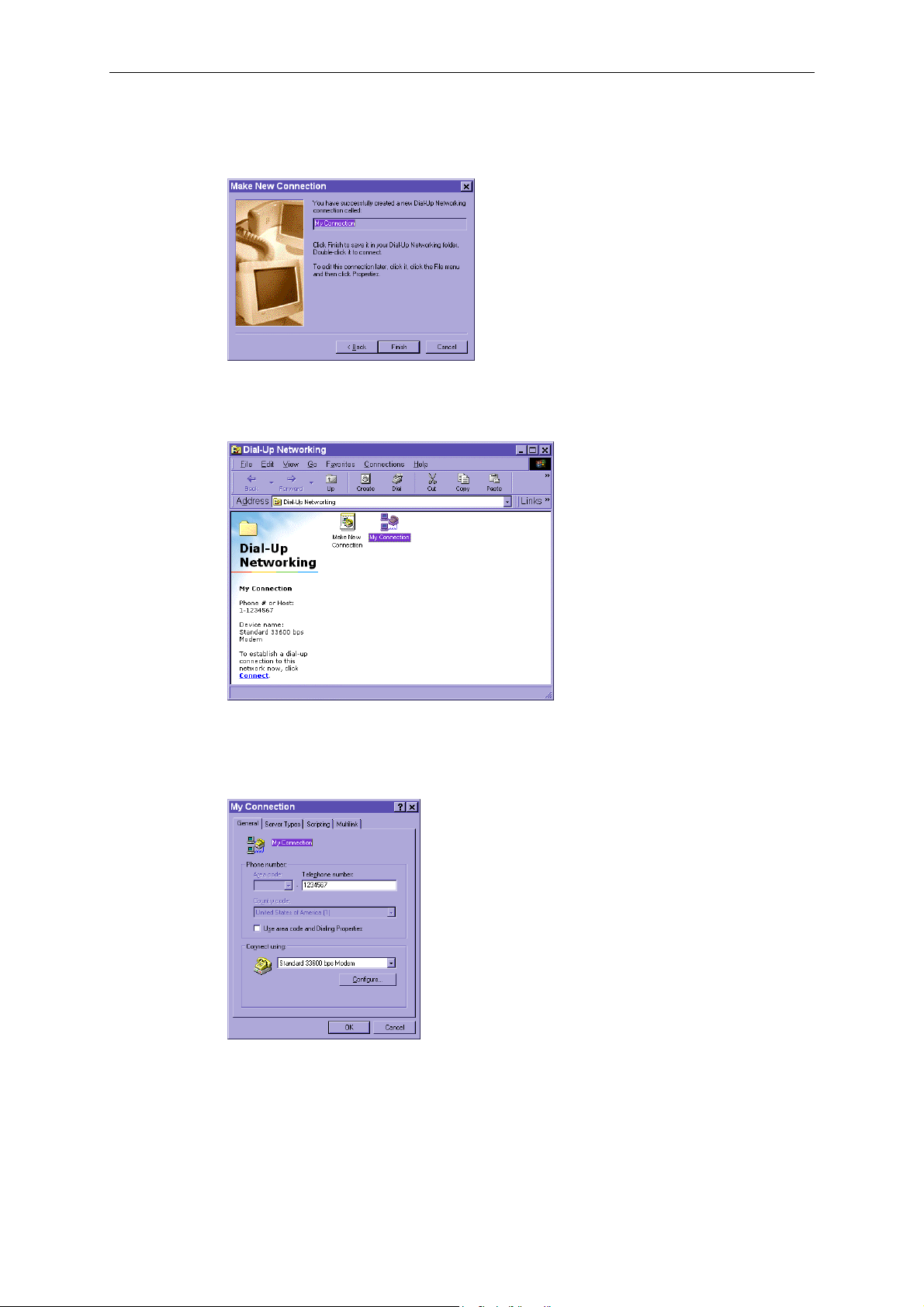
4. Click on Finish to complete the installation of the new modem. The new connection will be
displayed in the Dial-up Networking folder and will be used for modem or null modem
connections.
5. Open the Dial-Up Networking window, and then click on the icon for the connection (My
Connection) that was just installed to configure the connection’s properties.
6. When the My Connection window opens, right click on the General tab. In null modem
mode, you should uncheck Use area code and Dialing Properties. Then click on OK to
continue.
2-12
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 27

Getting Started
7. Click on Configure to modify the modem’s properties. Under Maximum speed, select
115200, and then click OK to continue.
8. Under the Server Types tab of my connection, checkmark the Enable software
compression option under Advanced options, and checkmark the TCP/IP option under
Allowed network protocols, as shown below. Leave settings under the other tabs as default
values, and then click on OK to continue.
Note that the location of the Enable software compression option and TCP/IP option might be
different from OS to OS.
9. The connection is now ready to use for modem and null modem mode. Double click on the
newly-installed connection icon. A dialing information window will appear. Enter root as
user name and the MAC address shown at the bottom of the window as the password, and
then click on Connect to connect to the Internet. Note that the letters in the MAC address
should be in capitals (for example, type A instead of a).
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
2-13
Page 28
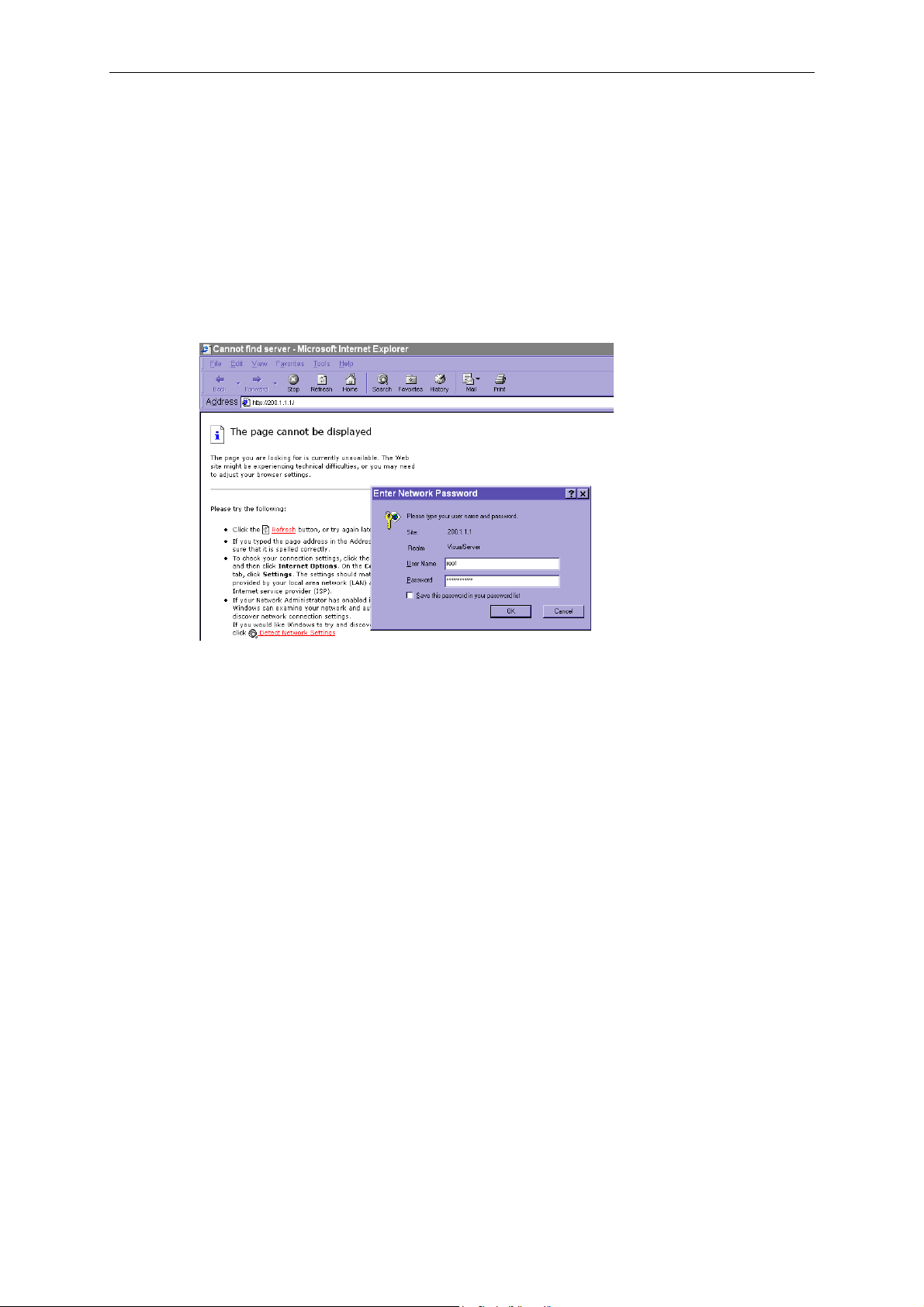
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time
In Null Modem Mode
Administrators can connect to http://200.1.1.1 from the web browser directly via the null modem
cable. 200.1.1.1 is VPort’s default IP address for the dial-up connection; and 200.1.1.100 is the IP
address assigned by VPort to the user’s PC. The user name and password are the same as what
were entered during the software installation. After successful authentication, administrators
should see the motion pictures on the main page. When using Microsoft Internet Explorer,
administrators must allow the installation of a plug-in provided by the VPort prior to viewing
motion pictures.
In Modem Mode
To dial the VPort, you need to establish a dial-up connection with the PC, in which the dial-up
phone number is the same as the phone line connected to the VPort. After the connection is
successfully established, open the Web browser and link to http://200.1.1.1. In this case, the VPort
runs as a dial-up server and assigns the IP address of 200.1.1.100 to the PC at the other end. When
the authentication message window appears, type root for user name and use VPort’s serial
number for the default password. The point-to-point connection allows users to connect to the
VPort for surveillance purpose at any time.
After the connection is successfully established, follow the instructions described in the next
chapter, Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time.
Mounting VPort 2140
Panel Mounting
Users can mount the VPort 2140 Video Server directly to the wall by using the 4 L-type Fixed
Aluminum pieces. First, attach these 4 L-type Fixed Aluminum pieces to the VPort 2140 with the
8 screws. Then use the screws that have diameter larger than 7 mm to mount the VPort 2140 to
the wall.
2-14
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 29

3
3
Chapter 3 Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for
the First Time
This chapter includes information about how to access VPort 2140 Video Server for the first time.
The following topics are covered:
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server
Opening Your Browser
Authentication
Installing the Plug-in Application
Functions Featured on the Main Page
Image Mode and Text Mode
Logo and Host Name
Video Quality Selection
Image Size Selection
Camera View Selection
System Configuration
Relay Output Control
Motorized (PTZ) Camera Control
Custom Camera Commands
Page 30
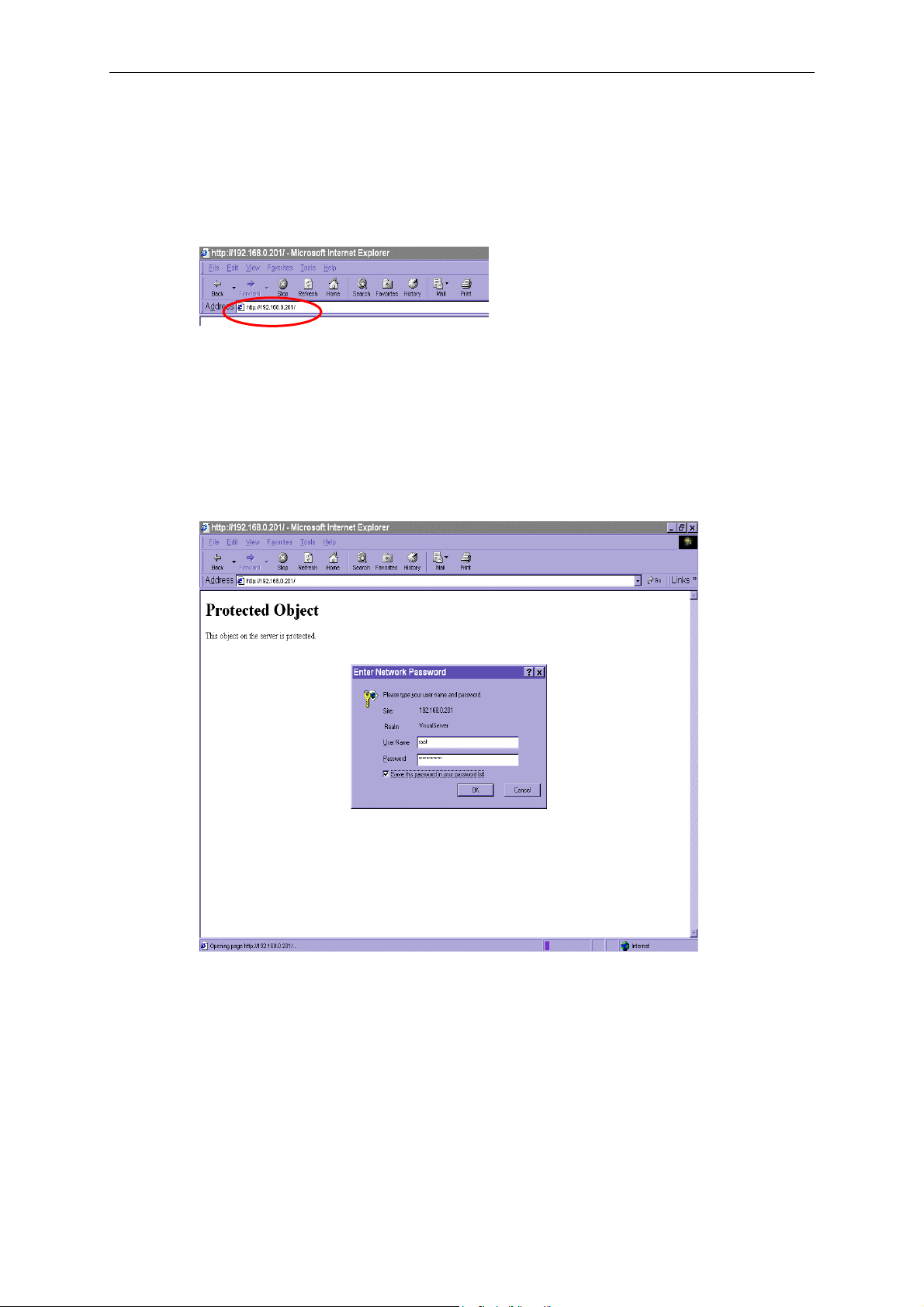
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server
Opening Your Browser
Open your browser, type the VPort’s IP address in the Address box, and then press Enter.
Authentication
After opening your browser and typing the VPort’s IP address, a dialogue window will appear,
asking you to enter the username and the password. When accessing the VPort for the first time,
administrators must enter root as the username, and the MAC address, in capital letters, as the
password. You can find the MAC address on the VPort’s label. Primary users will be allowed to
access the VPort as soon as the administrator finishes adding user profiles. Upon successful
authentication, the VPort’s main page will be displayed.
3-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 31

Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time
Installing the Plug-in Application
If you access the VPort for the first time via a browser that supports server push (e.g., Netscape),
the video images will be displayed directly. If you are using Windows’ Internet Explorer as your
browser, you will be asked to install a new plug-in application provided by the VPort. This
plug-in application has been registered for certification, and is used to display video images via
Internet Explorer. Click on Yes to install the plug-in application. If your browser does not allow
the user to install the plug-in, change the security option to a lower level, or contact your network
supervisor for assistance.
Functions Featured on the Main Page
Image Mode and Text Mode
Basic functions are displayed on the VPort’s main page. The first figure below shows image mode,
which has a better visual effect. The second figure shows text mode, which provides a shorter
download time. The main page may look different depending on the PTZ driver or the
authorization of the user.
Image Mode
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
3-3
Page 32

Text Mode
Logo and Host Name
The default logo is Moxa’s logo, and the host name is VPort 2140 Video Server. For customized
usage, the administrator can change the layout of the homepage from the Homepage Layout page.
Video Quality Selection
There are 5 options for video quality: Medium, Standard, Good, Detailed, and Excellent. Different
video quality selections result in different sized JPEG files. The table below is an example.
Video Quality JPEG File Size
Medium 9.3 KB
Standard 11.15 KB
Good 13.76 KB
Detailed 16.35 KB
Excellent 20.3 KB
Image Size Selection
There are 5 options for selecting image sizes:
Video Size (unit: pixels) NTSC PAL
Half
Half × 2 352 × 240 352 × 288
Standard
Standard × 2 704 × 480 704 × 576
Double
176 × 112 176 × 112
352 × 240 352 × 288
704 × 480 704 × 576
3-4
Half × 2 consumes the same file size and bandwidth as Half, but has the same resolution as
Standard. For this reason, the visual effect of Half × 2 is worse than Standard. Likewise,
Standard × 2 consumes the same file size and bandwidth as Standard, but has the same
resolution as Double. For this reason, the visual effect of Standard × 2 is worse than Double.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 33

Camera View selection
A maximum of 4 cameras can be connected to the VPort 2140 at the same time. Users can view
the image of each camera by selecting “Video 1,” “Video 2,” “Video 3,” and “Video 4,” or
selecting “Video All” to view all images in Quad screen.
In Quad viewing mode, the maximum image size is only 352 x 240 (NTSC) or 352 x 288 (PAL)
for each camera, in order to fit the monitor screen.
System Configuration
There is a button or text link on the left side of the system configuration window that only appears
on the administrators’ main page. For detailed system configuration instructions, refer to Chapter
4, System Configuration.
Accessing VPort 2140 Video Server for the First Time
Relay Output Control
VPort 2140 Video Server has 4 DI and 2 DO for external devices, such as sensors and alarms. If
external devices are attached to the digital output, administrators or permitted users can click on
Open to short the Common and Normal Open pins of the digital output, or click on Close to
short the Common and Normal Close pins of the digital output.
Motorized (PTZ) Camera Control
If a serial device, such as a motorized camera, is attached and correctly configured to the COM
port, the control panel will appear on the permitted users’ main page. The effective buttons will
change color when the cursor is passed over the button. Users can control the pan, tilt, zoom, and
focus functions of motorized cameras. The home button is used to return the camera to the center
position if the camera supports this command. Apart from near and far control for focus, an
AUTO button is provided for setting auto focus mode. To move the motorized camera more
precisely, the speed control for pan and tilt allows users to fine tune the aiming position. Users
can also click directly on any point in the image to force the motorized camera to focus on that
point, or select a preset location from the drop-down. The list of preset locations is pre-defined by
administrators. The detailed configurations are described in the related section in Chapter 4,
System Configuration.
Custom Camera Commands
There are a maximum of five buttons that can be set to custom commands for users to control the
attached motorized (PTZ) cameras, in addition to the default pan, tilt, zoom, and focus controls.
Custom commands are set up by administrators, and are used for functions such as activating or
deactivating the wiper of dome, according to the attached motorized device’s User’s Manual of.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
3-5
Page 34

Page 35

4
4
Chapter 4 System Configuration
After installing the hardware, the next task required is to configure VPort 2140’s settings. There
are 3 configuration methods: via web access, via FTP, and via Telnet.
This chapter includes the following sections:
System Configuration Via Web Access
Using Setup Wizard
Using the Application Wizard
System
Security
Network
Video
COM 1 & COM 2
Application
Demo
Homepage Layout
View log file
View parameters
Factory default
System Configuration Via FTP
CONFIG ini
System Configuration Via Telnet
Telnet Commands
System core debugging
Monitor changed status of digital inputs
Stop information dumping
Query status of digital inputs
Set digital outputs
Erase snapshots stored in Flash memory
Skip installation at next boot
Reset network for new settings
Page 36

Restore facotry default settings
Reset system
4-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 37

System Configuration Via Web Access
System configuration can be easily done remotely from Internet Explorer via the Web Server.
There are two wizards, in addition to classified categories of system configurations, which
provide user-friendly instructions to facilitate the setup task. Alternatively, administrators may
type the system configuration URL, “http://<IP address of Video Server>/setup/config.html”, to
enter the configuration page directly. Administrators who want to set certain options through the
URL should refer to the relevant section in Chapter 6, URL Commands for advanced functions.
System configuration serves 5 purposes:
1. Since VPort 2140 Video Server is a networked video server, administrators should run the
“Setup wizard,” or at least configure “Security,” “Network,” and “Video.”
2. To support external serial port devices, configure “COM 1,” “COM 2” and then “Camera
Setting” under “Video.”
3. To utilize the built-in security and web attraction features, run the “Application wizard” or
configure “Application” and “Demo.”
4. Administrators can adjust the system date and time under “System,” or configure different
homepage layouts by configuring “Homepage layout.”
System Configuration
5. Video Server also provides other system maintenance options, including “View log file,”
“View parameters,” and “Factory default.”
Using Setup Wizard
The setup wizard will guide the administrator to enter the required information, including:
1. Host name
2. Current date and time
3. Administrator’s password
4. Video configuration and captions
5. Network settings
The administrator can exit the setup wizard at any time to preserve the current configuration. The
setup wizard will give the administrator the option to reboot to validate the changes, or the
administrators can decide to reboot later.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-3
Page 38

Using the Application Wizard
VPort 2140 has two applications to choose from:
1. Surveillance System
Create a security system by configuring the built-in motion detection and external sensors to
integrate with an existing e-mail or FTP server, or external alarms. You may also use the
weekly schedule feature for timed monitoring.
2. Web Attraction
Customize the main page to your own style and set up accounts for your potential visitors.
To select one of these two applications, click on “Surveillance system” or “Web attraction” from
the Applications wizard window shown below. After using Applications Wizard, Administrators
can perform a more detailed configuration of the application parameters from the configuration’s
Application page.
System
Host name
The host name will appear as the homepage title of the main page and over the video window on
the main page. The maximum string length is 38 characters or 19 characters in
double-byte-character systems, such as Chinese or Japanese systems.
4-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 39

System Configuration
Date and Time
The default setting for Date and Time is Keep current date and time. You may also choose from
one of the following date and time configuration options:
1. The easiest way to adjust the date and time is to make the VPort Sync with computer time.
2. Select the Manual option if you wish to set the date and time manually by entering new
settings.
3. Select the Automatic option to make the VPort synchronize automatically with timeservers
over the Internet every month. However, synchronization may fail if the assigned NTP
server cannot be reached, or the VPort is connected to a local network. Leaving the NTP
server blank will force the VPort connect to default timeservers. Enter either the Domain
name or IP address format of the timeserver as long as the DNS server is available. Do not
forget to set the Time zone for local settings. Refer to Appendix G for your region’s time
zone.
Click on Save to validate changes.
Security
Root password
To change the administrator’s password, type the new password in both the Root password box
and Confirm password box. The passwords you enter will be displayed in asterisks for security
reasons. The maximum string length for a password is 14 characters. After clicking on Save to
validate the new password, a window will open to ask the administrator for the new password to
access the VPort.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-5
Page 40

Add user
To add a new user, type the new user’s name in the Username box, the password in the User
password box, and select authorization level by checking I/O access or Camera control. Click
on Add to insert the entry. The VPort 2140 Video Server has a total of 20 user accounts. Each
user can be given independent access right of the external I/O access and camera control.
Manage user
If the access rights of some users need to be changed, find the user name from the drop down list
and click on Edit. A new window will appear for administrators to change the password and
select a different authorization. Administrators can also delete the selected user by clicking on
Delete. A message window will open next to confirm.
Snapshot mode
A maximum of 20 users can view VPort’s images at the same time. Administrators can select the
Allow more guests with snapshot mode option to enable the snapshot mode for more users. In
this case, when the number of users exceeds 20, users will see the main page in snapshot mode
instead of seeing normal video images. Snapshot mode is very useful for web attraction. In this
case, configure the Snapshot interval to achieve better performance. Increasing the time interval
between snapshots allows more users to use snapshot mode.
Click on Save to validate changes.
Network
Reset network at next boot
To eliminate incautious mistakes during installation, VPort 2140 Video Server will be in
installation mode whenever it starts up, unless Reset network at next boot is disabled. This
option can also be disabled by selecting the IP Installer program’s Use this IP whenever system
boots option.
4-6
1. Use this IP whenever system boots = □ Reset network at next boot
VPort 2140 Video Server will skip the installation at the next boot, and the IP Installer
program will not show this VPort 2140. In this case, the VPort cannot be accessed and
reconfigured over the network using the IP Installer program if no one remembers the IP
address, unless the VPort’s reset button is used first to restore factory default settings. The
advantage of enabling the “Use this IP whenever the system boots” option is that the VPort
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 41

System Configuration
will automatically operate normally after being restarted after a power loss.
2. □ Use this IP whenever system boots = Reset network at next boot
In this case, the installation process must be performed again when system reboots. This is
the default setting.
You can ignore this option if you are using the Modem Dial-up connection.
General
Administrators may need to modify the network settings to connect to an existing network, since
the subnet mask in some broadband service may differ from the default value of 255.255.255.0,
and service providers may assign more specific network settings. Administrators should change
the configuration to the settings given by the service provider. The configuration may include IP
address, Subnet mask, Default router, Primary DNS server, and Secondary DNS server.
After changing network settings, make sure to uncheck the “Reset network at next boot option” to
avoid the installation starting up again the next time the system restarts. Otherwise, existing
network settings will be erased at the next start.
In addition, administrators can limit the bandwidth used by a VPort 2140 Video Server according
to priority and importance of location. Limiting bandwidth is useful for balancing network
utilization when multiple VPorts are installed on the same network. This method is more effective
than just changing image quality, and is able to achieve better performance with adequate image
size and quality.
HTTP
For security or network integration, administrators can hide the server from the general HTTP port
by changing the default HTTP port of 80 to a different port number. Administrators should have
enough network knowledge to change the default port.
SMTP
VPort 2140 Video Server not only plays the role of server, but also actively connects to outside
servers to send alarm messages or snapshots. If the administrator has set up some applications in
either event mode or sequential mode, the VPort will send out snapshots once these conditions
occur.
1. To activate the e-mail function, enter correct settings for SMTP (mail) server’s domain
name/IP address and Recipient email address.
2. Secondary SMTP (mail) server’s domain name/IP address and Secondary email address
are provided for a backup connection when the primary SMTP server fails.
3. Return email address is the address the email is returned to when the SMTP server rejects
email due to failure. Some ISPs may reject the email if the address is invalid.
If the settings are correct when the VPort starts up, it will send out a system log via e-mail
instead of uploading the log via FTP. Note that if the Return email address is not set, the
e-mail system will not work properly.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-7
Page 42

FTP
FTP is the other means available for VPort 2140 Video Server to send out alarm messages and
snapshots. To send the system log files described in the above paragraph via FTP, the SMTP
server should be erased.
1. Local FTP server port can also be changed to a setting different from the default setting of
21. Administrators should have enough network knowledge to change the default port.
2. Administrators must enter correct Primary FTP Server, Primary FTP user name, and
Primary FTP password.
3. Primary FTP remote folder is the sub-folder in the remote FTP server.
4. If the remote FTP server’s port is changed to a setting different from 21, make sure to set the
real port to Primary FTP server port.
5. If the local network is protected by a firewall to prevent it from initiating an FTP connection
from the remote FTP server, you may be able to connect to the FTP server, but be unable to
place a file on the server due to data channel connection failure. Check Primary FTP passive
mode for a passive transfer solution.
6. Another set of Secondary server settings is also provided for a backup connection.
In either e-mail or FTP, the primary server information should be entered first. If the primary
server is not set, the related FTP or email will be cancelled. Note that it may take time to
connect to the secondary server after the first one fails, and it may affect some applications
when conditions occur too often.
Save the modification
After all necessary modifications are made, click on Save to store the modifications. A warning
message will appear for confirmation. After clicking on OK, the VPort will automatically restart.
If the Reset network at next boot option is checked, perform the software installation again.
Otherwise, the VPort will boot up automatically using the new configuration settings.
If you make any changes to the settings in this web page, the system will restart to validate
those changes. Make sure that every field is correctly typed before clicking on Save. If the
VPort fails to respond due to incorrect settings, perform the restore procedures and run the
software installation.
Administrators should take note that the basic network settings, including IP address, subnet
mask, default router, and DNS servers, should be set to factory defaults before switching the
network interface from “Ethernet” to “modem” or from “modem” to “Ethernet.”
4-8
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 43

Video
System Configuration
To allow the VPort 2140 to show cameras’ video images, check the Enable item for each
camera. There are 3 kinds of settings for each camera’s video in this page.
Image setting
1. Show Time stamp in image and Text on image
When these options are enabled, Time stamp and Text on image will be shown on the image for
reference. The time stamp is captured from the Video Server’s date and time that are
maintained by an on-board real-time clock.
2. Color, Default size, and Default quality
The Color setting depends on the connected camera. The “B/W” option can speed up the
encoder. The Default size option is the default size of the video window when the user first
connects to the VPort. The Default quality option is the default quality when users first
connect to the VPort.
3. Brightness, Contrast, Saturation, and Hue
To adjust image settings for the best visual quality, click on Image Setting to open a motion
picture window. Four fields need to be configured, including Brightness, Contrast, Hue, and
Saturation. Each field has eleven levels, ranging from -5 to +5. While adjusting, administrators
can click on preview to see if the settings are appropriate before clicking on Save. If the
adjustment is not satisfactory, administrators can click on Restore to restore the original
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-9
Page 44

settings. After the configuration is done, click on Close to close this window. If the
configurations are changed without saving, they will only be used until the next time the system
starts up.
Camera Setting
1. Camera type
The default camera type of VPort 2140 is Fixed camera, which means it is a general camera
without motorized function. If you wish to select a PTZ camera, you also need to select the
COM port that this PTZ camera is connected to, and the PTZ camera’s ID to activate it.
Click on Save to validate the camera type.
2. Preset position setting of Motorized PTZ camera
Below the camera type setting is the image of this camera, the control buttons of PAN/ TILT/
ZOOM/ FOCUS and the preset position setting. The administrator can use the control
buttons to operate the camera’s image to set the preset position of this motorized PTZ
camera.
Motion Detection
4-10
Each camera has its own separate motion detection settings. The settings, which include Object
size and Sensitivity, allow administrators to fine tune the VPort to fit the environment:
1. Object size sets the minimum size of objects whose motion will be detected. (E.g., if Object
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 45

System Configuration
size = 30%, then the system will only detect the motion of objects that occupy an area larger
than 30% of the total monitored area; the motion of objects with size less than 30% of the
monitored area will NOT be detected.)
2. Sensitivity sets the measurable difference between two sequential images to indicate motion.
A larger object size and lower sensitivity will cause the VPort to ignore small variations in images.
When the motion amplitude of some objects in the monitored screen exceeds the settings, a white
letter M with red background color will appear in the upper-right corner to the window.
Motion detection is provided as a reference because it is environment-dependent. When the
settings are configured to be very sensitive to motion, some triggered events might be false
alarms, since in fact there is only a tiny difference between sequential images. False alarms can
be triggered by the flashing of florescent lights, shifting of shadows, etc.
Before completing the Video configuration, 3 items need to be confirmed.
Modulation
There are 3 types of Modulation. Administrators can set the auto-detected condition during
initialization by selecting Auto, but can still set it manually by selecting NTSC or PAL. When
you change the camera modulation, a warning message will pop up to inform you that the system
will restart to validate the new modulation.
Although the analog cameras have 2 different standards, NTSC or PAL, all of the cameras
connected to VPort 2140 Video Server should use the same standard.
Default Video Source
Administrators can set the default viewing mode for web home page in camera 1, 2, 3, 4, or all in
quad.
Save the modification
After all necessary modifications are made, click on Save to store the modifications. If you have
changed the modulation type, the VPort will automatically restart. If the Reset network at next
boot option is checked, perform the software installation again. Otherwise, the VPort will boot up
automatically using the new configuration settings.
COM 1 & COM 2
There are 2 COM ports, COM 1 and COM 2, in VPort 2140 Video Server for connecting the
external devices, such as Motorized PTZ controller, Modem, or Multiplexer.
COM 1
COM 2
RS-232 RS-485 Speed
DB9 Male Terminal block for Data+, Data- Max. 115. 2 Kbps
DB9 Male N/A Max. 115. 2 Kbps
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-11
Page 46

Interface mode
The COM 1 supports 2 serial interfaces, although only one interface can be used at a time.
Depending on the interface used by the attached device, administrators must set the Interface
mode to either RS-232 or RS-485.
The COM 2 only supports RS-232 interface. For this reason, there is no interface mode selection
for COM 2.
RS-232 interface is used via the DB9 COM port, and RS-485 interface is used via the GPIO.
These 2 interfaces in COM 1 cannot be used at the same time.
Purpose
The COM port connection has 3 purposes:
1. If the attached device is a PTZ camera, administrators must select the correct PTZ model
under PTZ driver options, since each PTZ camera has its own protocols for the PTZ functions.
Refer to Appendix B, Settings for Supported PTZ Cameras, to find out the PTZ cameras
that MOXA VPort 2140 Video Server supports. If the attached PTZ camera is not supported
by the VPort, administrators can select Custom Camera to enter the proprietary commands for
pan, tilt, zoom, and focus control.
2. If the attached device is not a PTZ camera, but another serial device, such as a video
multiplexer, etc., administrators can select the Generic CGI command to control the device
via CGI commands. For external device control, refer to Chapter 5, Advanced Applications,
under the URL Commands for DI/DO and Camera’s Actions settings section for more
details.
Port Settings
4-12
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
3. The default setting is None, which means that no other device is connected to the COM port.
After selecting the correct PTZ driver or Generic CGI command option, the next thing
administrators must do is configure Port settings, including Baud rate, Data bits, Stop bits, and
Parity bit. If the attached device is a PTZ camera, refer to Appendix B, Settings for Supported
Page 47

System Configuration
PTZ Cameras, for default settings of the supported PTZ cameras.
Custom command
VPort 2140 Video Server provides 5 custom commands in addition to the general pan, tilt, zoom,
and preset functions. Administrators can click on Custom Command to configure, and refer to
the manual enclosed with the attached PTZ camera to set up frequently-used functions. The
Command should be entered in ASCII format. The VPort will translate the commands into binary
code and send them out through the serial port. For instance, a text string of 8101ABCDEF will
be translated into five bytes of hexadecimal 81, 01, AB, CD, and EF. The maximum length of a
command string is 60, which is equivalent to 30 hexadecimal bytes. The Display string is for the
text on the command buttons and should be less than 8 characters. If Custom Camera is selected,
there will be more commands for PTZF that relate to custom camera.
Application
VPort 2140 Video Server provides 4 major applications.
1. Weekly schedule: Administrators can set up the Application schedule by week.
2. External script files: For advanced applications, administrators can program command
scripts, which can be uploaded to the VPort 2140 Video Server.
3. Event operation: Administrators can set trigger conditions by selecting Motion Detected, or
DI Condition, etc., options, and trigger actions by selecting Trigger output alarm while
input condition matched, etc., options.
4. Sequential mode: Administrators can set the sequential snapshot mode to send the snapshot
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-13
Page 48

by time interval.
Administrators can use combinations of options on the application web page to perform various
useful security applications. Although most settings will be done automatically by the
Application Wizard, administrators can also make adjustments to the settings from this page.
To set up the 4 applications that VPort 2140 Video Server provides, administrators must have a
certain level of knowledge about the setting items listed in the Application web page. Below is
the table that separates the setting items into 4 levels. Higher-level settings will not be activated
unless lower-level items are checked.
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4
□Weekly schedule
□All the time except
for the above schedule
□Enable the external script file to ignore the following settings
□Event operation
□Sequential mode Snapshot every □ tenth seconds
□Send snapshot by email
□Send snapshot by
FTP
□Sun □Mon □Tue □We d □Thu □Fri □Sat
snapshots begin at [hh:mm:ss]
snapshots stop at [hh:mm:ss]
□Show alert in image
Trigger
condition
Trigger action
□ Send
snapshot while
trigger
condition(s)
match
□FTP put snapshots with date and time suffix
Motion Detected on:
□Video 1 □Video 2 □Video 3 □Video 4
DI condition:
DI 1: Disable, High, Low, Rising, Falling
DI 2: Disable, High, Low, Rising, Falling
DI 3: Disable, High, Low, Rising, Falling
DI 4: Disable, High, Low, Rising, Falling
Delay □ second(s) to trigger output alarm
DO condition:
DO 1: Disable, Open, Close
DO 2: Disable, Open, Close
Snapshot on:
□Video 1 □Video 2 □Video 3 □Video 4
Take □ snapshot(s) with □ tenth seconds
interval after the event
Weekly schedule
The Weekly schedule is provided for daily security applications. Administrators can select any
weekday from Monday to Friday with the daily schedule set from 08:00 am to 20:00 pm when no
one is available to perform event checking. If the security system is installed in an office for
which no one is present on nights or weekends, administrators can still set the time period as
above, from 08:00 am to 20:00 pm, but remember to select All the time except for the above
schedule to let the program run during nights and weekends.
Either “Weekly schedule” or “All the time except for the above schedule” must be selected, or
the applications described in the following sections will not work properly.
4-14
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 49

System Configuration
Enable the external script file to exclude the following settings
Administrators can write a script named SCRIPT.TXT to match the additional software
according to the Command Script for DI/DO and Camera’s Actions Setting section from
Chapter 5. After uploading this script to the VPort via FTP, check the option Enable the external
script file to exclude the following settings. Otherwise the VPort will operate according to the
settings under Enable the external script file to exclude the following settings option.
Event operation
Event operation is for setting security applications.
1. Show alert in image.
VPort 2140 Video Server can show the event trigger condition in the video image on the
homepage. If motion is detected (based on the motion settings), an M will appear on the
upper-right corner of the image. As long as Show alert in image is checked, the M will
appear in the image to indicate that motions have been detected. If there are any sensors
attached to the digital inputs, the administrator can set the state to fire alarm.
The option Show alert in image may be set when running the application wizard or configuring
motion detection. Administrators should manually uncheck this option if no indication of
motion detection is needed in the image.
2. Trigger Condition
a. Motion Detected. The administrator can check the boxes of Video 1, Video 2, Video 3
and Video 4 to enable Video Motion Detection (VMD), which is set in the Video
configuration web page (or you can click on the *Click on each hyperlink of video to
configure motion detection link below to configure the appropriate parameters) as the
trigger condition.
b. DI Condition. There are 4 Digit Inputs in VPort 2140. The administrator can set the
DI’s conditions, including Input is High, Input is Low, Input is Rising, and Input is
Falling. The edge trigger like Rising or Falling is generally used to detect the emerging
signal from the external sensor.
3. Trigger Action
Once an event occurs, the administrator can set up 2 trigger actions: relay output alarms or
snapshot image.
a. DO Action. There are 2 DOs (Relay output) for connecting the alarms. Administrators
can set the trigger output alarm when the DI or Video Motion Detection conditions are
met. Once an event occurs, the administrator can select the Delay □ second(s) after
event option to drive a device attached to the digital outputs several seconds after the
event happens and/or send snapshots that are taken right at the moment.
b. Snapshot. The administrator can set up the snapshot action when the DI or Video
Motion Detection conditions are met. There are 3 snapshots will be taken when an
event occurs, which is in the tenth second interval by named as pre-event, the moment
of event and post-event. If the administrator thinks the snapshots are not enough, more
snapshots can be taken after the event by configuring Take □ snapshot(s) with □
tenth seconds interval after the event. Three snapshots of each channel can also be
downloaded via FTP or HTTP URL.The time interval of these 3 snapshot images can
be set on (refer to the “Download Event-triggered Snapshots” section from Chapter 5
for more details).
c. Send snapshot while trigger condition(s) match. To activate the function of snapshot
sent via E-mail or FTP server, this item should be checked.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-15
Page 50

Sequential Mode
With this feature, VPort 2140 Video Server can upload snapshots periodically to an external
E-mail or FTP server as a live video source. The interval can be set from a tenth of a second to
several hours in Snapshot every □ tenth seconds. The external E-mail or FTP server must be set
up in the Network configuration page.
Send Snapshot by Email or FTP
Snapshots taken by either event operation or sequential mode can be sent by E-mail or FTP,
which are set in the Network configuration page. If email is chosen, the snapshots of the video
channel will be attached to the emails. If FTP is chosen, administrators can choose to add date and
time in the file name of the snapshots by checking FTP file name with date and time suffix. If
the snapshots are used as the live video source, the date and time suffix can be eliminated to
update the same source file.
In Sequential mode, the VPort will send out snapshots according to interval and period settings.
If snapshot files are intended for quick updates, it is better to skip the date and time suffix, in
which case the file name will be video.jpg. If the snapshots are used for occasional monitoring,
suffixing with date and time can help administrators easily classify the snapshots.
Compared to the FTP method, email will induce more delay, although email can notify users
more promptly.
View Snapshot
The administrator can check the latest pre-event, the moment of event and post-event snapshots by
clicking on the View Snapshot button.
4-16
Save
Click on Save to activate the applications when you finish the settings.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 51

Demo
System Configuration
VPort 2140 Video Server provides a demonstration mode to allow general access for
demonstration purposes. To set up the demonstration mode, administrators must choose the
services to be permitted by each camera. If administrators select the view option, users may use
demo as the username to access the VPort. In this case, leave the password field blank.
Administrators also can select control camera for the demo account. Separating the demo account
from the primary users can prevent interference with normal operations.
Click on Save to validate changes.
Homepage layout
VPort 2140 Video Server allows administrators to customize the layout of the Video Server’s
homepage.
Logo graph
1. Select the blank option to hide the logo figure, which appears in the upper-left corner of the
homepage.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-17
Page 52

2. The “default” logo is the MOXA logo.
3. An external logo or image can be used by selecting the URL option, and typing the url for the
image in the text input box.
Logo link
Administrators set up the Logo with a Logo link, so that visitors are directed to another web
address when they click on the logo.
Background graph
As with Logo graph, Background graph gives administrators the ability to customize the
background as blank, default, or an external image by selecting the URL option, and typing the
url for the image in the text input box.
Font and Background color
The Font color and Background color can be chosen from sixteen custom colors.
The Background color option is active only when Background graph is set as blank.
Web page display mode
There are two homepage display modes. One is Image mode, which uses icons to link to the
various functions; the other is Text mode, which uses mostly text to link to the various functions.
Administrator can change the string content manually.
See the Customize graphics in homepage section from Chapter 5 to see how to replace the
default images for the Video Server’s log, background, and buttons.
View log file
The system log contains useful information, including current system configuration and activity
history with timestamp for tracking.
4-18
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 53

View parameters
System Configuration
Clicking on View parameters allows you to view all system parameters, which are listed by
category. The content is the same as CONFIG.INI of VPort 2140 Video Server.
Factory default
This function is used to restore the Video Server to its factory default settings, so that any changes
that were made previously will be lost. After clicking OK, the system will restart. Note that it will
take some time for the restore action to finish. You will need to run the software installation
program to set up the network.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-19
Page 54

System Configuration Via FTP
CONFIG.INI
FTP can be used to configure VPort 2140 Video Server much more quickly than configuring from
web browser, particularly when configuring multiple Video Servers. To configure a Video Server
via FTP, first download the parameter file, CONFIG.INI, customize each field, and then upload
the file to the Video Server to install the new settings. To log into the FTP daemon, enter “root” as
the user name, and use the same password used when connecting to the Web server. The MAC
address (no dash, all upper case) of Video Server is the password for initial access.
The CONFIG.INI file has eight categories: [SYSTEM], [LAYOUT], [NETWORK], [VIDEO],
[SERIAL1], [SERIAL2], [ALERT], and [DEMO]. The category names in square brackets
should be in upper case. The item names in angle braces should be in lower case. Some items
related to disable/enable should use the keywords “YES”/“NO”. The number zero (0) entry in
<user name> and <user password> is for administrators, i.e. “root”. Video Server will restart
automatically as soon as the file is uploaded and accepted. If administrators want to cancel the
reboot procedure after putting config.ini via FTP, then set the first item, <reset system>, to NO.
But it will take effect only once, and show YES in the download config.ini file the next time.
A sample CONFIG.INI is shown in the table below. The text in italics describes the
characteristics of the field, and the bold italic characters are the options for the field.
Video Server Initial Configuration file
[SYSTEM]
<reset system>
YES or NO
<host name>
VPort 2140 Video Server string with maximum of 38 characters
<serial number>
0002D1040972 read-only
<software version>
VS2402-MOXA-V1.0.6 read-only
<current date>
2003/01/01 read-only
<current time>
12:34:56 read-only
4-20
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 55

System Configuration
f
<time zone>
0
<user name>
(0)root read-only
(1) string with maximum of 14 characters
(2) the rest are the same as above
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
<user password>
(0)0002D1040972 string with maximum of 14 characters
(1) the rest are the same as above
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
<more guests enabled>
NO or YES to enable snapshot mode
<more guests interval>
0 snapshot interval in seconds
<language>
0
[LAYOUT]
<layout type>
1 image mode or 0 for text mode
<font color> 0-black, 1-white, 2-green, 3-maroon, 4-
1 olive, 5-navy, 6-purple, 7-gray, 8-yellow,
rom 12 to –12
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-21
Page 56

<background color> 9-lime, 10-aqua, 11-fuchsia, 12-silver,
0 13-red, 14-blue, 15-teal,
<logo type>
1 default image, or 0 for blank, or 2 from URL
<background type>
1 default image, or 0 for blank, or 2 from URL
<logo source>
http:// URL of logo type 2, maximum of 80 characters
<background source>
http:// URL of logo type 2, maximum of 80 characters
<logo link>
http:// reference link of logo, max. of 80 characters
<button name>
(0)Video1 Used in text mode, max. 14 characters
(1)Video2 Used in text mode, max. 14 characters
(2)Video3 Used in text mode, max. 14 characters
(3)Video4 Used in text mode, max. 14 characters
<com1 speedlink name> Name of custom PTZ commands
(0) string with maximum of 8 characters
(1) string with maximum of 8 characters
(2) string with maximum of 8 characters
(3) string with maximum of 8 characters
(4) string with maximum of 8 characters
<com2 speedlink name> Name of custom PTZ commands
(0) string with maximum of 8 characters
(1) string with maximum of 8 characters
(2) string with maximum of 8 characters
(3) string with maximum of 8 characters
(4) string with maximum of 8 characters
[NETWORK]
<install enabled>
YES reset IP whenever system boots or NO
<ppp enabled>
YES obsolete
<ethernet address>
00-02-D1-04-09-72 read-only
<host ip>
192.168.0.207 standard IP format
<subnet mask>
255.255.255.0 standard IP format
<gateway ip>
0.0.0.0 standard IP format
<primary name server>
0.0.0.0 standard IP format
<secondary name server>
0.0.0.0 standard IP format
<ntp enabled>
NO or YES
<network timing server>
IP address or domain name
<smtp mail server>
IP address or domain name
<mail recipient address>
string with maximum of 80 characters
<mail return address>
VPort 2140 Video Server string with maximum of 80 characters
<backup smtp mail server>
4-22
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 57

System Configuration
IP address or domain name
<backup mail recipient address>
string with maximum of 80 characters
<local ftp port>
21 or 1024 to 65535
<ftp server>
IP address or domain name
<ftp port>
21 or 1024 to 65535
<ftp username>
string with maximum of 14 characters
<ftp password>
string with maximum of 14 characters
<ftp init path>
string with maximum of 40 characters
<ftp passive>
NO or YES
<backup ftp server>
IP address or domain name
<backup ftp port>
21 or 1024 to 65535
<backup ftp username>
string with maximum of 14 characters
<backup ftp password>
string with maximum of 14 characters
<backup ftp init path>
string with maximum of 40 characters
<backup ftp passive>
NO or YES
<http server port>
80 or 1024 to 65535
<bandwidth limit>
0
[VIDEO]
<default video>
1 or 2, 3, 4, 5 (video all)
<camera modulation>
AUTO or MANUAL. NTSC or PAL will be ignored
NTSC or PAL, ignored when set to AUTO but can be
<video is open>
(0)YES or NO
(1)YES or NO
(2)YES or NO
(3)YES or NO
<video mapped to COM port>
(0)0 or 1, 2
(1)0 or 1, 2
(2)0 or 1, 2
(3)0 or 1, 2
<video mapped to ID>
(0)0 depending on the camera
(1)0 depending on the camera
(2)0 depending on the camera
(3)0 depending on the camera
<overlay timestamp>
or 64000, 128000, 256000, 512000,
768000, 1000000, 1500000, 2000000
when set to AUTO
notification
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-23
Page 58

(0)NO or YES
f
(1)NO or YES
(2)NO or YES
(3)NO or YES
<caption text>
(0) string of max. 14 characters
(1) string of max. 14 characters
(2) string of max. 14 characters
(3) string of max. 14 characters
<colored video>
(0)YES or NO for B/W
(1)YES or NO for B/W
(2)YES or NO for B/W
(3)YES or NO for B/W
<video quality>
(0)150 For Medium, 75 for Standard, 37 for Good,
(1)150 18 for Detailed, 8 for Excellent for
(2)150
(3)150
<default size>
(0)1
(1)1 4 for Halfx2, 5 for Standardx2
(2)1
(3)1
<brightness>
(0)0 between 5 and –5
(1)0 between 5 and –5
(2)0 between 5 and –5
(3)0 between 5 and –5
<contrast>
(0)0 between 5 and –5
(1)0 between 5 and –5
(2)0 between 5 and –5
(3)0 between 5 and –5
<hue>
(0)0 between 5 and –5
(1)0 between 5 and –5
(2)0 between 5 and –5
(3)0 between 5 and –5
<saturation>
(0)0 between 5 and –5
(1)0 between 5 and –5
(2)0 between 5 and –5
(3)0 between 5 and –5
[SERIAL 1]
<data bits>
0
<stop bits>
0
<parity bits>
0 None, 1 for Odd, 2 for Even
<baud rate>
0
<ccd model>
0 None, 1 for Generic, 2 for Sony VISCA,
or Half, 2 for Standard, 3 for Double,
3 for Canon VC-C1, 4 for Canon VC-C3,
5 for Canon VC-C4, 6 for DynaDome,
4-24
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 59

System Configuration
7 for Pelco D, 8 for LiLin, 9 for Ernitec,
10 for Custom Camera
<uart mode>
RS232 or RS485
<speedlink commands>
(0) string of maximum 60 characters
(1) string of maximum 60 characters
(2) string of maximum 60 characters
(3) string of maximum 60 characters
(4) string of maximum 60characters
<custom ccd commands>
HOME
string with maximum of 60 characters
UP
string with maximum of 60 characters
DOWN
string with maximum of 60 characters
LEFT
string with maximum of 60 characters
RIGHT
string with maximum of 60 characters
TELESCOPE
string with maximum of 60 characters
WIDE
string with maximum of 60 characters
NEAR
string with maximum of 60 characters
FAR
string with maximum of 60 characters
[SERIAL 2]
<data bits>
0
<stop bits>
0
<parity bits>
0 None, 1 for Odd, 2 for Even
<baud rate>
0
<ccd model>
0 As same as [SERIAL1]
<uart mode>
RS232
<speedlink commands>
(0) string of maximum 60 characters
(1) string of maximum 60 characters
(2) string of maximum 60 characters
(3) string of maximum 60 characters
(4) string of maximum 60characters
<custom ccd commands>
HOME
string with maximum of 60 characters
UP
string with maximum of 60 characters
DOWN
string with maximum of 60 characters
LEFT
string with maximum of 60 characters
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-25
Page 60

RIGHT
string with maximum of 60 characters
TELESCOPE
string with maximum of 60 characters
WIDE
string with maximum of 60 characters
NEAR
string with maximum of 60 characters
FAR
string with maximum of 60 characters
[ALERT]
<script file enabled>
NO or YES to activate external script
<motion detection channel enabled>
(0)NO or YES
(1)NO or YES
(2)NO or YES
(3)NO or YES
<snapshot channel enabled>
(0)NO or YES
(1)NO or YES
(2)NO or YES
(3)NO or YES
<series snapshot channel enabled>
(0)NO or YES
(1)NO or YES
(2)NO or YES
(3)NO or YES
<application mode>
0 disabled, 1 for Sequential, 10 for motion
detection event, 12 for DI event
<visual alert>
NO or YES
<upload method>
0 FTP, 1 for email
<file with time suffix>
YES or NO
<percentage of object size over screen>
(0)10 1 to 99
(1)10 1 to 99
(2)10 1 to 99
(3)10 1 to 99
<percentage of sensitivity>
(0)90 1 to 99
(1)90 1 to 99
(2)90 1 to 99
(3)90 1 to 99
<seconds to snapshot periodically>
0
<time to start snapshot>
00:00:00 24 hours format
<time to stop snapshot>
00:00:00 24 hours format
[DEMO]
<demo enabled>
NO or YES
4-26
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 61

<PTZ enabled>
(0)NO or YES
(1)NO or YES
(2)NO or YES
(3)NO or YES
<video is open>
(0)NO or YES
(1)NO or YES
(2)NO or YES
(3)NO or YES
[SYSTEM ADDON]
<NTP Update Interval>
3
System Configuration Via Telnet
Telnet Commands
Video Server has a Telnet daemon that allows administrators to access some seldom used
functions. Using any general terminal program to connect to Video Server will prompt the user for
a password. The Username is not requested since only administrators can access the Telnet
daemon. The password is the same as that used for web access. After logging in, type “help” for
the command list. If “debug” or “dinote” is not executed, Telnet will disconnect automatically
after being idle for 1 minute.
System Configuration
System core debugging
General activities are recorded into SYSTEM.LOG continuously, but information about abnormal
status is not recorded. Administrators can type the “debug” command to examine in-depth core
debugging information. This causes Video Server to start dumping the detailed debugging
information while the system is running. This is useful for examining if any errors have occurred
when the system operates abnormally. The stored information will be cleared automatically after
the dump. Video Server will continue to dump new messages unless the connection is broken. If
Telnet is not connected, messages will be stored until administrators re-login.
Monitor changed status of digital inputs
Typing “dinote” will make Video Server send the current status of all digital inputs. After that,
Video Server will continuously monitor DI status and send messages only when the state has
changed. For example, after typing “dinote” the terminal will display
DI1=L
DI2=L
DI3=L
DI4=L
and after DI2 changes to H, the terminal will display
DI2=H
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
4-27
Page 62

Stop information dumping
Typing “stop” will halt the dumping of debug information and the digital input status.
Query status of digital inputs
Typing “diquery” will display the status of all digital inputs once.
Set digital outputs
To set digital output to connect NO with COMMON, type “DO1=L”.
To set digital output to connect NC with COMMON, type “DO1=H”.
Erase snapshots stored in Flash memory
Typing “erase image” will clear all snapshots saved in Flash memory.
Skip installation at next boot
Typing “lock” will inform Video Server to lock the current network settings. You won’t need to
go through the installation procedure the next time the Video Server boots up.
Reset network for new settings
Typing “unlock” will cause Video Server to wait for the installation procedure the next time it
boots up.
Restore factory default settings
Typing “clear” will make Video Server restore factory settings but not restart. To validate new
settings, type “reset” to make the system restart.
Reset system
Typing “reset” will make Video Server perform a software reset.
4-28
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 63

Chapter 5 Advanced Applications
This chapter will introduce more advanced applications.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Capturing Up-to-date Still Images
Getting snapshot via URL
Getting snapshot via FTP
5
5
Video Embedded in Customers’ Homepage
Download Event-triggered Snapshots
Getting triggered snapshots via URL
Getting triggered snapshots via FTP
Customizing Graphics in Homepage
Command Script for DI/DO & Camera’s Actions Setting
Command Format
Parameter Explanations
Practical Examples
URL Commands for DI/DO & Camera’s Actions Setting
Query status of digital inputs
Drive digital outputs
Moving motorized camera in PTZ direction
Recalling camera position
Transparent Remote Serial Driver
Sending command to device attached to COM port
URL Commands for System Maintenance
Download System Log via FTP
Restart System via URL
Restore Factory Default Settings via URL
Page 64

Capturing Up-to-date Still Images
Getting snapshot via URL
Administrators and users can use a specific URL to capture the current still image.
Video Channel URL
Video 1 http://<IP of Video Server>/cgi-bin/video1.jpg[?<param>=<value>]
Video 2 http://<IP of Video Server>/cgi-bin/video2.jpg[?<param>=<value>]
Video 3 http://<IP of Video Server>/cgi-bin/video3.jpg[?<param>=<value>]
Video 4 http://<IP of Video Server>/cgi-bin/video4.jpg[?<param>=<value>]
Quad of all http://<IP of Video Server>/cgi-bin/videoall.jpg[?<param>=<value>]
Additional Parameters:
param Value Description
Quality 1 Medium
2 Standard
3 Good
4 Detailed
5 Excellent
Size 1 Half
2 Standard
3 Double
Getting snapshot via FTP
Administrators and users can log in to the Video Server FTP daemon to download the refreshed
JPEG image. The user name and password are the same as for web access. The zero file size in
file directory means it is captured by request.
Video Channel File Name
Video 1 Video1.jpg
Video 2 Video2.jpg
Video 3 Video3.jpg
Video 4 Video4.jpg
Quad of all Videoall.jpg
Video Embedded in Customers’ Homepage
In addition to the URL, some scripts should be added to download a plug-in for video images. The
following example simply displays title text and a real-time video window in Internet Explorer or
Netscape. The user name and password should be configured in advance. Those who are familiar
with HTML can easily add more components or rewrite the code to create a more vivid and useful
homepage.
<html>
<head><title>Video Server Sample Page</title></head>
<body>
5-2
<h2>Video Server Sample Page</h2>
<script language="JavaScript">
<!--
if ((navigator.appName == "Microsoft Internet Explorer")&&(navigator.platform != "MacPPC"))
{
document.write("<OBJECT ID=\"MjpegControl\" WIDTH=352 HEIGHT=240");
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 65

Advanced Applications
document.write(" CLASSID=\"CLSID:EAA105FE-7BBD-4196-8B96-D46743894195 \" ");
document.write("CODEBASE=\"http://username:password@192.168.0.201/plugin
/mjpegcontrol.cab#version=2,0,0,6\">");
document.write("<PARAM NAME=\"VSize\" VALUE=\"2\">");
document.write("<PARAM NAME=\"Url\" VALUE=\"http://username:password@
192.168.0.201/cgi-bin/video.jpg");
document.write("?cam=1&quality=3&size=2\">");
document.write("</OBJECT>");
} else {
document.write("<img width=352 height=240");
document.write("src=\"http://192.168.0.201/cgi-bin/video.jpg?cam=1&quality=3&size=2\">");
}
//-->
</script>
</body>
</html>
Download Event-triggered Snapshots
There are 12 video image files for the video channel of three stages: pre-alarm, the moment when
triggered, and post-alarm. Only the snapshots captured by the last event are preserved.
Administrator and users can use FTP or URL to get the saved snapshots. They can also be
browsed from the application page under system configuration.
Getting triggered snapshots via URL
/cgi-bin/snapshot.jpg?file=<value>
Video channel
Snapshot stage
snapshot before event pre1 pre2 pre3 pre4
snapshot upon event trg1 trg2 trg3 trg4
snapshot after event pos1 pos3 pos3 pos4
Video 1
Video 2 Video 3 Video 4
Getting triggered snapshots via FTP
File name Pre-alarm Upon alarm Post-alarm
Video 1 v1pre.jpg v1trg.jpg v1pos.jpg
Video 2 v2pre.jpg v2trg.jpg v2pos.jpg
Video 3 v3pre.jpg v3trg.jpg v3pos.jpg
Video 4 v4pre.jpg v4trg.jpg v4pos.jpg
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
5-3
Page 66

Customizing Graphics in Homepage
While in text mode, there is a small icon named BTN_TEXT.GIF preceding each link that can be
changed by administrators. While in image mode, the default method will use the image stored in
Flash memory. The table below shows the referenced file name and size limitation of each stored
image. Administrators may customize preferred image under the size limit and put it to the
specific name via FTP. Administrators can download the original images before uploading for
backup.
Object File name Maximal size
Logo logo.gif Logo and background share 8K bytes
Background back.gif Logo and background share 8K bytes
Link icon btn_text.gif 2K bytes
Camera 1 button btn_cam1.gif 5K bytes
Camera 2 button btn_cam2.gif 5K bytes
Camera 3 button btn_cam3.gif 5K bytes
Camera 4 button btn_cam4.gif 5K bytes
Camera All button btn_cama.gif 5K bytes
Configuration btn_confi.gif 5K bytes
Please do not try to upload the image, which the size is larger than the list, or it may cause the
unstable system operation.
Usage via FTP is illustrated below.
Command Script for DI/DO & Camera’s Actions Setting
Besides the application wizard, Video Server provides a more professional command script for
advanced applications. The command script will be executed exclusively with the settings in
Application page of system configuration except for the weekly schedule. To build an advanced
application, follow the steps below.
Step 1: Use any text editor to edit the appropriate command script according to the command
format. The script size cannot exceed 500 bytes.
Step 2: Save the script as a file named SCRIPT.TXT.
Step 3: Use FTP with administrator’s privilege to upload the script file.
Step 4: Enter the Application page in system configuration to define the time period in Weekly
Schedule. If it is supposed to run any time, keep the original settings but check the option All the
5-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 67

time except for the above schedule.
Step 5: Check the option Enable the external script file to exclude the following settings to
activate the command script.
Command format
[Event][“Operator”Event]……=[Action][+Action]……;
Event
[“Digital Input Number””Digital Input State”]
[“M” “Channel Number…”]
[“Channel Number””Video Input State”]
Operator
“+”: (OR)
“*”: (AND)
Action
[(“Delay Time”)“Digital Output Number””Digital Output State”]
[“V”“Channel Number”“P”“Preset Location Number”]
[“W”{“IP”:“Port”}{“Message”}]
[“U”“Method”]
[“S”“Channel Number…”]
[“N”{“filename”}];
Advanced Applications
Parameter Explanations
Items above in brackets show the options available for that item.
“Digital input number”: 1 to 4
“Digital input state”: H (high), L (low), / (low to high), \ (high to low)
“M”: motion detection event.
“Channel Number”: A, B, C, D for channel 1, 2, 3, 4
“Video input state”: / (signal from loss to presence), \ (signal from presence to loss), X (as
“Delay time”: seconds of delay for the following actions after events happen
“Digital output number”: 1 or 2
“Digital output state”: C (NC), O (NO)
“V”: set video channel to go to preset location
“P”: set preset location number to go to preset location
“W”: send warning to server
“IP”: server IP
“Port”: server port
“Message”: text to be sent to the server
“U”: upload snapshots
“Method”: ‘F’ is by FTP, ‘M’ is by e-mail
“S”: take snapshot on channels
“N”: define the format of the filename
“;”: end of line
The filename format is,
%a image characterization (pre, trg, pos)
%c video channel number
%y year
%M month
%d day
%h hour
%m minute
long as signal loss)
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
5-5
Page 68

%s second
%t tenth second
Practical Examples
Command line Description
MAB=1C; When any motion is detected on channel 1 or 2, “Normal
1H*2\=(5)1O; When DI1 high companied with DI2 transient from high
B\+C\+D\=W{192.168.0.1:6000}{no
signal!};
1H=VAP14; When sensor input 1 is high, drive the camera mapped to
MCD=UF+SABCD+N{video%c%a@
%y%M%d%h%m%s};
Close” of relay output 1 will short with “Common”.
to low, “Normal Open” of relay output 1 will short with
COMMON in 5 seconds.
If there is no signal on channel 2 or 3 or 4, a message “no
signal!” will be sent to port 6000 of 192.168.0.1 once.
video 1 to go to preset location 15.
If any motion is detected on channel 3 or 4, upload
snapshots taken on channel 1, 2, 3 and 4. If an event
triggered at 19:05:30 2002/10/15, the snapshot files will
be named as,
video1pre@20021015190530.jpg,
video2pre@20021015190530.jpg
video3pre@20021015190530.jpg,
video4pre@20021015190530.jpg
video1trg@20021015190530.jpg,
video2trg@20021015190530.jpg
video3trg@20021015190530.jpg,
video4trg@20021015190530.jpg
video1pos@20021015190531.jpg,
video2pos@20021015190531.jpg
video3pos@20021015190531.jpg,
video4pos@20021015190531.jpg
The script file is limited to a maximum of 500 characters. The actual performance will depend
on the complexity of the command script.
5-6
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 69

Advanced Applications
URL Commands for DI/DO & Camera’s Actions Setting
Query status of digital inputs
/cgi-bin/getdi.cgi
Video Server will return status of four digital inputs in one line.
Drive digital outputs
/cgi-bin/setdo.cgi?do1=<state>
<number> 1, 2 for DO1 and DO2
<state>: C, O denoting Normal Close or Normal Open respectively.
Moving motorized camera in PTZ direction
/cgi-bin/control.cgi?<param>=<value>&<param>=<value>……
Param Value Description
cam 1 Video 1
2 Video 2
3 Video 3
4 Video 4
move up Tilt up
down Tilt down
left Pan left
right Pan right
home Return to home position
zoom wide Zoom in
tele Zoom out
focus near Focus near
far Focus far
auto Automatic focus
panspeed -5 to 5
tiltspeed -5 to 5
Recalling camera position
/cgi-bin/recall.cgi?recall=<position>
<n>: video channel from 1 to 4
<position>: the text string of a location that is preset in system configuration.
Refer to Camera preset configuration URL for preset function.
Transparent Remote Serial Driver
Video Server provides a highly customized control support for third-party serial interface devices
(other than PTZ cameras). This means that in addition to setting up a custom camera with PAN/
TILT/ ZOOM/ FOCUS commands, users may utilize this mode and introduce a customized
homepage to transmit arbitrary user-defined commands from user-side to Video Server. The
third-party device connected to the serial port of Video Server will receive the same command
sent by the originator. The user only needs to attach the command in ASCII format after the
special URL. Video Server will parse the commands and translate into binary code to send out.
Send command to device attached to COM1
/cgi-bin/senddata.cgi?com=1&data=123456,ABCDEF&flush=yes&wait=1000&read=6
This hyperlink will inform Video Server to send out binary format commands to COM1 with
“0x12, 0x34, 0x56” followed by “0xAB, 0xCD, 0xEF”. Each comma separates the commands by
200 milliseconds. “flush=yes” means the receive data buffer of COM port must be cleared before
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
5-7
Page 70

read. Then read 6 bytes after waiting for 1000 milliseconds. The read data can be up to 128 bytes
and will return as ASCII coded hexadecimal value, e.g., 0x41, 0x42, 0x43 read from COM port
will show in returned homepage as 414243 instead of ABC.
Send command to device attached to COM2
/cgi-bin/senddata.cgi?com=2&data=123456,,,ABCDEF
This hyperlink will inform Video Server to send out binary format command to COM2 with
“0x12, 0x34, 0x56” followed by “0xAB, 0xCD, 0xEF” after 600 milliseconds of three comma.
URL Commands for System Maintenance
Download System Log via FTP
Besides viewing the system log from the web page, administrators can download the system log
file, SYSTEM.LOG, via FTP. To log into the FTP daemon, enter “root” as the user name and the
same administrator’s password used in Web access.
Restart System via URL
/cgi-bin/reset.cgi
Restart Video Server without warning.
Restore Factory Default Settings via URL
/cgi-bin/restore.cgi
Video Server will automatically restart after restoring factory default configurations.
5-8
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 71

6
Chapter 6 Upgrading System Firmware
Customers can check the appropriate product page on Moxa’s website to download the latest
firmware. Only administrators can upgrade the system firmware of Video Server.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Using Upgrade Wizard to Upgrade Firmware Easily
Using FTP to Upgrade Firmware
6
Page 72

Using Upgrade Wizard to Upgrade Firmware Easily
Step 1: Run the Upgrade Wizard (.exe) included in the product CD
Step 2: Key in the web address of the Video Server whose firmware you want to upgrade, and
type the administrators’ password. Then click Next.
Step 3 : The program will detect the Video Server.
If the password is wrong, a message window will appear asking you to check the FTP port and
password again.
Step 4: After the Video Server has been detected, you can select the firmware (Flash.bin) to
process the upgrade.
Step 5: Wait a few seconds for the upgrade process to finish.
Step 6: The following message appears once the firmware has been upgraded successfully.
Note that the power supply of VPort 2140 Video Server should not be turned off when the
Upgrade Wizard is upgrading the firmware. Otherwise, the firmware upgrade will fail, and you
will need to return the video server to Moxa for repair.
6-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 73

Using FTP to Upgrade Firmware
Step 1: Use the FTP program and change the working directory to the local folder where
FLASH.BIN resides.
Step 2: Connect to Video Server with user name as “root” and password.
Step 3: Use the PUT command to upload FLASH.BIN to Video Server. The file size is almost 1.8
MB. It will take approximately 3 seconds over a local network, 2 minutes by a null modem
connection, or 6 minutes by modem, but the actual time will depend on the status of the user's
network.
Step 4: After upload is complete, close the connection.
If the received FLASH.BIN is checked without error, Video Server will update the software in
Flash memory and restart automatically. When Video Server starts writing firmware, both
CONNECT and SERIAL LED indicators will stay on until the system restarts (this takes about
30 to 40 seconds). Users must keep the power stable during the update process. After the system
restarts, Video Server may need installation depending on whether the Reset network at next
boot option is enabled or not. After Video Server boots up, reload the web page in the browser.
Upgrading System Firmware
We strongly recommend that you use the upgrade wizard to upgrade the firmware for a
Microsoft Operating System, since if the power fails during the software upgrade, the program
in the memory of Video Server may be destroyed permanently. If Video Server cannot restart
properly, ask the dealer for technical service.
For customizing your VPort’s settings, we strongly recommend that you download config.ini
via FTP before you upgrade the firmware. The risk is that once the firmware has been
upgraded, the settings in config.ini might be restored to the the initial settings. For this reason,
after the firmware is upgraded, you need to upload the config.ini and overwrite the one existing
in your VPort. In this way, you don’t have to configure your VPort’s settings again.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
6-3
Page 74

Page 75

Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
This chapter describes some problems that might occur during installation or operation, and
provides the basic solutions to those problems.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Power On Self Test (POST)
Frequently Asked Questions
7
7
Page 76

Power On Self Test (POST)
b
After the power has been turned on, Video Server will perform a self-diagnostic to detect any
possible hardware defects. The CONNECT (LED 2) and SERIAL (LED 3) LEDs will blink
during the POST, and will keep blinking until the POST completes successfully, or a fatal error is
detected. If either status LED indicator is dim to start off with, the LED may be broken.
When certain fatal errors occur, LED2 and LED3 blink in a particular way to indicate the type of
failure, as described in the following table.
LED pattern after POST Failed function Troubleshooting
LED2 and LED3 blink at same
time
LED2 ON and LED3 OFF Ethernet network The PCI interface cannot work.
LED2 OFF and LED3 ON Ethernet network The Ethernet controller is
LED2 ON and LED3 ON Ethernet interface Ethernet interface failure
LED2 blink and LED3 ON System date and time The real-time clock is broken.
LED2 ON and LED3 blink Camera control via COM or
Video input The video decoder is broken.
modem interface
Ask your reseller for technical
service.
Ask your reseller for technical
service.
broken. Ask your reseller for
technical service.
includes not only components on
oard but also Ethernet cable and
the devices on the opposite end.
Ask your reseller for technical
service.
The UART controller is broken.
Ask your reseller for technical
service.
To reduce system failure caused by operation error, always read the related sections in this
user’s manual to prevent unexpected errors caused by “wild-guess configuration.”
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why can’t I see the Video Server in the installer after rebooting?
A: The installer is only used to install the IP address of the Video Server. If the IP address is fixed
by checking the option in the installer, the Video Server will no longer appear in the installer.
Q: Why can’t I connect the Video Server after rebooting?
A: If the IP address is not fixed, Video Server will always wait for the installing command to
provide a valid IP address. This means that the previous IP address will not be used if the
option in the installer is not checked; or the option in the network configuration is not cleared.
The benefit of waiting for a valid IP address by default is that administrators can find the Video
Server in the installer to prevent IP conflict. As long as the IP address is confirmed, we suggest
fixing the IP address to make Video Server automatically start up whenever regaining power.
Q: What if I forget my password?
A: Every access to Video Server needs authentication. If you are not a permitted user, you may
view the images or control the camera as long as the demo account is opened. The demo
account user may use username as “demo” without any password to access limited features. If
you are one of the managed users, you must ask the administrators for the password in the first
time. If you are the administrator, there is no way to recover the root password. The only way
to regain access to Video Server is to restore the factory settings and reinstall it.
7-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 77

Troubleshooting
Q: Why can’t I watch video from Video Server after it is authenticated?
A: There are many possible scenarios regarding this problem,
1. If you have just installed Video Server and are unable to watch the video, check if the video
input is enabled and check the video modulation on the Configuration page.
2. If Video Server is installed correctly and you are accessing Video Server for the first time
using Internet Explorer, adjust the security level of Internet Explorer to allow installation of
the plug-in.
3. If the problem still exists after making the adjustment, the current number of users may be
greater than what the system allows.
4. If you are using a demo account, the administrator may hide the video from public view.
Q: How can I use a name instead of the IP address to connect Video Server?
A: To allow users to connect to Video Server through an easily memorized name, administrators
must first configure the network’s domain name server. Here is an example: the administrator
installs the Video Server with a reserved IP address and assigns it a name on the domain name
service, then users can connect to Video Server by typing a name instead of an IP address. If
there is DHCP service on the network, the IP address must be excluded on the DHCP service to
prevent an IP conflict.
Q: What is the plug-in for?
A: The plug-in provided by Video Server is used to display motion pictures on versions of Internet
Explorer that do not support server push technology. If your system does not allow installation
of any plug-in software, the security level of the web browser may need to be lowered. It is
recommended that you consult the network supervisor in your office regarding adjusting the
security level.
Q: Why is the timestamp different from the system time of my PC or notebook?
A: The timestamp is based on the system time of Video Server. It is maintained by an internal
real-time clock, and automatically synchronizes with the time server if Video Server is
connected to the Internet and the function is enabled. Differences of several hours may result
from the time zone setting.
Q: Why does the image not refresh regularly?
A: In a modem environment, it is because the bandwidth of PPP connections is much lower than
for Ethernet. If the difference of the timestamp is not stable, use the modem property on the
control panel to adjust the UART FIFO to a lower level for both receiving and transmitting. In
an Ethernet environment, it may be due to the time taken for storing snapshots into memory
when events occur.
Q: How many users are allowed to watch Video Server at the same time?
A: To achieve the best effect, Video Server will allow a maximum of twenty users to connect at
the same time. Excess users can get an auto-refreshed still image on homepage instead. It is
recommended to build another web server to host a large quantity of users by retrieving images
from Video Server periodically.
Q: How fast is the video rate of Video Server?
A: The JPEG codec can process 30 frames per second internally. However, the overall
performance is subject to many different factors, such as:
1. network throughput,
2. bandwidth share,
3. number of users,
4. number of video inputs accessed at one time,
5. viewing complicated objects results in a larger image file,
6. the level of your PC or notebook that is responsible for displaying images.
In general, the transfer rate on a general local network environment can achieve over 200
Kbytes per second and approximately 10 to 20 pictures of normal environment per second. The
general frame size is illustrated in the following table for your reference.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
7-3
Page 78

Quality setting Size of each frame Bandwidth demand for 30 fps
Medium 9.3 Kbyte 2246 Kbps
Standard 11.15 Kbyte 2676 Kbps
Good 13.76 Kbyte 3303 Kbps
Detailed 16.35 Kbyte 3925 Kbps
Excellent 20.3 Kbyte 4886 Kbps
Q: How can I keep Video Server as private as possible?
A: Video Server is designed for surveillance purposes and has many flexible interfaces. The user
authentication and special confirmation during installation can keep Video Server from
unauthorized access. You may also change the HTTP port to a non-public number. You can
check system log to examine any abnormal activities and trace the origins.
Q: I have a PTZ camera that is not on the support list. How can I control it?
A: Video Server provides a custom camera command interface to control cameras that are not
supported. The details are described in this manual. Be sure that the COM port settings are
applied to the camera specifications. The camera control cable included is shown in the
package contents. Prepare your own cable if necessary. The general PTZ command is
composed of one start command and one stop command. When editing both commands in the
edit box of the configuration page, use comma(s) to separate commands. Each comma
represents 200 milliseconds. If the user has some serial control device other than the PTZ
camera, the special URL is provided to send the desired commands. For quick access, integrate
the URL to another homepage on your own web server.
Q: Why can I see image files when I use dir in FTP even if the alarm is not triggered?
A: Every time Video Server starts, it will capture the images as vpre.jpg. If there are previously
saved image files that are not retrieved, Video Server will keep them until they are accessed.
Q: How will the stored images be processed if Video Server loses power?
A: If a user has defined the snapshot interval, Video Server will capture images periodically as
pre-alarm stage. Once the pre-defined condition is match, the pre-alarm images will be kept
and the current images will be saved. The subsequent images will be stored as post-alarm stage.
Users may retrieve these files either by downloading via FTP, or direct Video Server to send
them in e-mails. This means that after monitoring conditions are met, Video Server will keep
these image files until user retrieval even if power is lost.
Q: If I set Video Server to send e-mails of images whenever the conditions are met, will my e-mail
account overflow?
A: It is recommended to use transient state instead of steady state. For instance, use ‘Input is
Rising’ and ‘Input is Falling’ rather than ‘Input is High’ and ‘Input is Low’ to let the condition
be triggered only when state is changed.
Q: The image is not clear enough. Is anything broken?
A: The lens can be focused by rotating the outer ring. Rotate it clockwise or counter-clockwise to
focus near or far.
7-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 79

Video Server can be easily integrated with existing websites or web control applications using
convenient URLs. This section lists the commands in URL format corresponding to the basic
functions of Video Server. Some RFC standards related to HTML may be a good reference for
implementation of the customized homepage.
Page URL
The configuration page has a frame layout that includes an option list frame and an option page
frame. Except for the configuration page, the Reference URLs shown below link just to the option
page frame. Some pages, such as image quality settings and preset settings, open in a new browser
window. These URLs can be accessed only by administrators.
Homepage name Reference URL
A
A
Appendix A URL Commands of Video Server
configuration page /setup/config.html
system option /setup/system.html
security option /setup/security.html
network option /setup/network.html
video option /setup/video.html
image quality option /setup/image.html
camera control /setup/serial.html
preset PTZ camera /setup/preset.html
custom command setting /setup/cuscom.html
custom camera setting /setup/custom.html
application option /setup/app.html
motion detection setting /setup/motion.html
view snapshots /setup/snap.html
demo option /setup/demo.html
homepage layout option /setup/layout.html
system log /setup/logfile.html
system parameters /setup/parafile.html
set factory default /setup/factory.html
Page 80

System Resource URL
Some images are used on the homepage when the homepage layout is in image mode.
Administrators may use the following links to show the images saved on Video Server on another
page. To change the logo or the background images referenced by the URL, refer to the homepage
layout section under configuration.
Resource name Reference URL
system logo image /logo.gif
background image /back.gif
button image for camera 1 /btn_cam1.gif
button image for camera 2 /btn_cam2.gif
button image for camera 3 /btn_cam3.gif
button image for camera 4 /btn_cam4.gif
button image for quad screen /btn_cama.gif
button image for configuration /btn_conf.gif
icon image for link indicator /btn_text.gif
General Format of Command URL
<general format>
URL[?[name=value][&name=value]……]
<method>
POST
<authorized user>
root
System Configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/system.cgi
Name Value Description
host <text string shorter than 15 characters> system name
method
date <yy/mm/dd> year, month and date separated by slash
time <hh:mm:ss> hour, minute and second separated by colon
ntp <domain name or IP address> NTP server
zone GMT±<n>:00 time zone, n ranged from 0 to 12
keep keep date and time unchanged
auto use NTP server to synchronize
manu directly adjust date and time
Security Configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/system.cgi
Name Value Description
rootpass <text string shorter than 14 characters> change root password
username <text string shorter than 14 characters> add new user
userpass <text string shorter than 14 characters> new user's password
v1allowed <not required> allow user to view video 1
A-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 81

v2allowed <not required> allow user to view video 2
v3allowed <not required> allow user to view video 3
v4allowed <not required> allow user to view video 4
ioallowed <not required> allow user to control DO
ptzallowed <not required> allow user to view PTZ panel
deluser <text string shorter than 14 characters> Existing user name
slow <not required> snapshot mode
delay <integer> refresh time in snapshot mode
Network Configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/network.cgi
Name Value Description
yes enable installation at next boot reset
<other than yes> disable installation at next boot
ip <IP address> Video Server's IP address
subnet <IP address> subnet mask
router <IP address> default gateway
domain <text string shorter than 38
characters>
dns1 <IP address> primary DNS server
dns2 <IP address> secondary DNS server
limit
Not limited use full network bandwidth
64Kbits/second use only 64Kbps of bandwidth
128Kbits/second use only 128Kbps of bandwidth
256Kbits/second use only 256Kbps of bandwidth
512Kbits/second use only 512Kbps of bandwidth
URL Commands of Video Server
domain name of Video Server
768Kbits/second use only 768Kbps of bandwidth
1Mbits/second use only 1Mbps of bandwidth
1.5Mbits/second use only 1.5Mbps of bandwidth
2Mbits/second use only 2Mbps of bandwidth
http <number less than 65535> HTTP port
smtp1 <domain name or IP address> primary SMTP server
mailto1 <text string shorter than 80
characters>
smtp2 <domain name or IP address> secondary SMTP server
mailto2 <text string shorter than 80
characters>
return <text string shorter than 80
characters>
ftp1 <domain name or IP address> primary FTP server
ftprp1 <number less than 65535> FTP server port
ftpuser1 <text string shorter than 14
characters>
ftppass1 <text string shorter than 15
characters>
mail recipient address
mail recipient address
return address
user name for primary FTP server
password for primary FTP server
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
A-3
Page 82

ftpfolder1 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
ftp2 <domain name or IP address> secondary FTP server
ftprp2 <number less than 65535> secondary FTP server port
ftpuser2 <text string shorter than 15
characters>
ftppass2 <text string shorter than 15
characters>
ftpfolder2 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
Video Configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/video.cgi
Name Value Description
enable1 <not required> enable video channel 1
enable2 <not required> enable video channel 2
enable3 <not required> enable video channel 3
enable4 <not required> enable video channel 4
mode Auto let Video Server detect video modulation
NTSC set directly to NTSC type
upload folder in primary FTP server
user name for secondary FTP server
password for secondary FTP server
upload folder in secondary FTP server
<other than above> set directly to PAL type
source <1, 2, 3, 4 or All> default video channel
Image Quality Configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/image.cgi
Name Value Description
cam <1 ~ 4> Video channel number
time <not required> enclose timestamp
text <text string shorter than 15
characters>
color B/W set encoder to monochrome
<other than B/W> set encoder to color
quality Medium lowest resolution
Standard lower resolution
Good normal setting
Detailed higher resolution
Excellent highest resolution
size Half set size to half
Standard set size to standard
Double set size to double
Half x 2 set size to half x 2
Standard x 2 set size to standard x 2
brightness <-5 ~ 5> adjust brightness of image
contrast <-5 ~ 5> adjust contrast of image
hue <-5 ~ 5> adjust hue of image
enclose caption
A-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 83

saturation <-5 ~ 5> adjust saturation of image
preview <not required> not save the parameters
restore <not required> recall the original settings
save <not required> save the parameters
COM 1 Configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/serial1.cgi
Name Value Description
RS232 switch COM to RS232 interface
RS485 switch COM to RS485
generic accept generic CGI commands detect
none no drivers
URL Commands of Video Server
driver
Sony VISCA
Canon VCC1
Canon VCC3
Canon VCC4
DynaDome/SmartDOME
Pelco D protocol
Lilin PIH-7x00
Ernitec
Custom Camera third party PTZ camera
COM 2 configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/serial2.cgi
Name
detect
Value Description
generic accept generic CGI commands
modem use modem
none no drivers
driver
Sony VISCA
Canon VCC1
Canon VCC3
Canon VCC4
DynaDome/SmartDOME
Pelco D protocol
Lilin PIH-7x00
Ernitec
Custom Camera third party PTZ camera
Tone (ATDT) make modem dial in tone method
Pulse (ATDP) make modem dial in pulse
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
A-5
Page 84

reatt <integer> redial attempts
discon <integer> minutes delay before disconnection
init <text string shorter than 40
characters>
phone1 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
user1 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
pass1 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
phone2 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
user2 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
pass2 <text string shorter than 40
characters>
command to initialize modem
phone number of primary ISP
user name for primary ISP
password for primary ISP
phone number of secondary ISP
user name for secondary ISP
password for secondary ISP
Camera custom command configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/cuscom.cgi
Name
str11 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 1 of COM1
str12 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 2 of COM1
str13 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 3 of COM1
str14 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 4 of COM1
str15 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 5 of COM1
com11 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 1 of COM1
com12 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 2 of COM1
com13 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 3 of COM1
com14 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 4 of COM1
com15 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 5 of COM1
str21 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 1 of COM2
str22 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 2 of COM2
str23 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 3 of COM2
str24 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 4 of COM2
str25 <text string shorter than 8 characters> button name of custom command 5 of COM2
com21 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 1 of COM2
com22 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 2 of COM2
com23 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 3 of COM2
com24 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 4 of COM2
com25 <text string shorter than 80 characters> custom command 5 of COM2
Value Description
Camera preset configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/preset.cgi
Value Description
fixed fixed camera camtype
cammap PTZ camera
A-6
Name
com 1, 2 Com port number
cam <1 ~ 4> Video channel number
id <integer> camera id
addpos <text string shorter than 40 characters> add preset position
delpos <existing position name> delete preset position
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 85

Custom camera configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/custom.cgi
Name
baud1 <integer> set baud rate of COM1
data1 <integer> set data bits of COM1
parity1
up1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> tilt up command string of COM1
down1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> tilt down command string of COM1
left1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> pan left command string of COM1
right1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> pan right command string of COM1
home1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> home command string of COM1
tele1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> zoom in command string of COM1
wide1 <text string shorter than 80 characters> zoom out command string of COM1
baud2 <integer> set baud rate of COM2
data2 <integer> set data bits of COM2
Value Description
1 set 1 stop bit of COM1 stop1
2 <other than 1> set 2 stop bits of COM1
None set parity check of COM1 to none
Odd set parity check of COM1 to odd
Even set parity check of COM1 to even
1 set 1 stop bit of COM2 stop2
URL Commands of Video Server
2 <other than 1> set 2 stop bits of COM2
parity2
up2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> tilt up command string of COM2
down2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> tilt down command string of COM2
left2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> pan left command string of COM2
right2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> pan right command string of COM2
home2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> home command string of COM2
tele2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> zoom in command string of COM2
wide2 <text string shorter than 80 characters> zoom out command string of COM2
None set parity check of COM2 to none
Odd set parity check of COM2 to odd
Even set parity check of COM2 to even
Application configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/app.cgi
Name
sun <not required> set Sunday in weekly schedule
mon <not required> set Monday in weekly schedule
tue <not required> set Tueday in weekly schedule
wed <not required> set Wednesday in weekly schedule
thu <not required> set Thursday in weekly schedule
fri <not required> set Friday in weekly schedule
sat <not required> set Saturday in weekly schedule
sbegin <hh:mm:ss> time to start in weekly schedule
send <hh:mm:ss> time to stop in weekly schedule
inv <not required> set inverse mode in weekly schedule
enfile <not required> enable script file
emode <not required> event operation
showalert <not required> show alert in image
Value Description
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
A-7
Page 86

mdch1 <not required> enable motion detection on video 1
mdch2 <not required> enable motion detection on video 2
mdch3 <not required> enable motion detection on video 3
mdch4 <not required> enable motion detection on video 4
di1 High, Low, Rising, Falling or Disable DI1 condition
di2 High, Low, Rising, Falling or Disable DI2 condition
di3 High, Low, Rising, Falling or Disable DI3 condition
di4 High, Low, Rising, Falling or Disable DI4 condition
delay <integer> delay time of DO after event
do1 High, Low or Disable DO1 action
do2 High, Low or Disable DO2 action
eventch1 <not required> take snapshots on ch1 while event happen
eventch2 <not required> take snapshots on ch2 while event happen
eventch3 <not required> take snapshots on ch3 while event happen
eventch4 <not required> take snapshots on ch4 while event happen
dura <integer> snapshots taken after event
inter <integer> tenth seconds interval after the event
mdmode <not required> enable motion detection(emode should
set)
smode <not required> sequential mode application
sinter <integer> tenth seconds interval for sequential
mode
mail upload snapshots by email smethod
ftp upload snapshots by FTP
suffix <not required> FTP file with date and time suffix
Motion detection configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/motion.cgi
Name
cam <1 ~ 4> Video channel number
per <integer> object size percentage
sen <integer> sensitivity percentage
Value Description
Demo configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/demo.cgi
Name
open <not required> enable demo account
camctr1 <not required> allow demo user to control PTZ camera on video 1
camctr2 <not required> allow demo user to control PTZ camera on video 2
camctr3 <not required> allow demo user to control PTZ camera on video 3
camctr4 <not required> allow demo user to control PTZ camera on video 4
view1 <not required> allow demo user to watch channel 1
view2 <not required> allow demo user to watch channel 2
view3 <not required> allow demo user to watch channel 3
view4 <not required> allow demo user to watch channel 4
Value Description
Homepage layout configuration URL
URL: /cgi-bin/layout.cgi
Value Description
A-8
Name
cuslogo blank hide logo
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 87

URL Commands of Video Server
logourl <text string shorter than 60
linkurl <text string shorter than 60
cusback
backurl <text string shorter than 60
fcolor <0 ~ 15> color index for font
bcolor <0 ~ 15> color index for background
strl <text string shorter than 38
str2 <text string shorter than 38
str3 <text string shorter than 38
str4 <text string shorter than 38
def use default logo
url use image from URL
URL of image for logo
characters>
URL to link when clicking on logo
characters>
blank hide background image
def use default background
url use image from URL
URL of image for background
characters>
image display homepage in image mode dismode
text display homepage in text mode
text for channel 1 in text mode
characters>
text for channel 2 in text mode
characters>
text for channel 3 in text mode
characters>
text for channel 4 in text mode
characters>
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
A-9
Page 88

Page 89

B
B
Appendix B Settings of Supported PTZ Cameras
Since the COM port settings can be adjusted to other than the default settings, check the correct
default settings for the attached camera.
Camera model Baud rate Data bits Stop bit Parity bit
Sony VISCA 9600 8 1 None
Canon VC-C1 9600 8 2 None
Canon VC-C3 9600 8 2 None
Canon VC-C4 9600 8 1 None
Pelco D protocol 2400 8 1 None
DynaDome/SmartDome 9600 8 1 None
Ernitec 9600 8 1 None
Lilin 9600 8 1 None
Page 90

Page 91

C
C
Appendix C Camera Control Cable
The included cable can be used to control motorized cameras of desktop types from Sony and
Canon. The pin assignment is illustrated in the following chart. To control cameras of another
brand, check the user’s manual of the motorized camera to see if the pin assignment of the control
cable is appropriate.
Page 92

Page 93

D
D
Appendix D Time Zone Table
The hour offsets for different time zones are shown below. You will need this information when
setting the time zone in automatic date/time synchronization. GMT stands for Greenwich Mean
Time, which is the global time that all time zones are measured from.
(GMT-12:00) International Date Line West
(GMT-11:00) Midway Island, Samoa
(GMT-10:00) Hawaii
(GMT-09:00) Alaska
(GMT-08:00) Pacific Time (US & Canada), Tijuana
(GMT-07:00) Arizona
(GMT-07:00) Chihuahua, La Paz, Mazatlan
(GMT-07:00) Mountain Time (US & Canada)
(GMT-06:00) Central America
(GMT-06:00) Central Time (US & Canada)
(GMT-06:00) Guadalajara, Mexico City, Monterrey
(GMT-06:00) Saskatchewan
(GMT-05:00) Bogota, Lima, Quito
(GMT-05:00) Eastern Time (US & Canada)
(GMT-05:00) Indiana (East)
(GMT-04:00) Atlantic Time (Canada)
(GMT-04:00) Caracas, La Paz
(GMT-04:00) Santiago
(GMT-03:30) Newfoundland
(GMT-03:00) Brasilia
(GMT-03:00) Buenos Aires, Georgetown
(GMT-03:00) Greenland
(GMT-02:00) Mid-Atlantic
(GMT-01:00) Azores
(GMT-01:00) Cape Verde Is.
(GMT) Casablanca, Monrovia
(GMT) Greenwich Mean Time: Dublin, Edinburgh, Lisbon, London
(GMT+01:00) Amsterdam, Berlin, Bern, Stockholm, Vienna
(GMT+01:00) Belgrade, Bratislava, Budapest, Ljubljana, Prague
(GMT+01:00) Brussels, Copenhagen, Madrid, Paris
(GMT+01:00) Sarajevo, Skopje, Warsaw, Zagreb
(GMT+01:00) West Central Africa
(GMT+02:00) Athens, Istanbul, Minsk
(GMT+02:00) Bucharest
(GMT+02:00) Cairo
(GMT+02:00) Harare, Pretoria
(GMT+02:00) Helsinki, Kyiv, Riga, Sofia, Tallinn, Vilnius
(GMT+02:00) Jerusalem
(GMT+03:00) Baghdad
(GMT+03:00) Kuwait, Riyadh
(GMT+03:00) Moscow, St. Petersburg, Volgograd
(GMT+03:00) Nairobi
Page 94

(GMT+03:30) Tehran
(GMT+04:00) Abu Dhabi, Muscat
(GMT+04:00) Baku, Tbilisi, Yerevan
(GMT+04:30) Kabul
(GMT+05:00) Ekaterinburg
(GMT+05:00) Islamabad, Karachi, Tashkent
(GMT+05:30) Chennai, Kolkata, Mumbai, New Delhi
(GMT+05:45) Kathmandu
(GMT+06:00) Almaty, Novosibirsk
(GMT+06:00) Astana, Dhaka
(GMT+06:00) Sri Jayawardenepura
(GMT+06:30) Rangoon
(GMT+07:00) Bangkok, Hanoi, Jakarta
(GMT+07:00) Krasnoyarsk
(GMT+08:00) Beijing, Chongqing, Hongkong, Urumqi
(GMT+08:00) Taipei
(GMT+08:00) Irkutsk, Ulaan Bataar
(GMT+08:00) Kuala Lumpur, Singapore
(GMT+08:00) Perth
(GMT+09:00) Osaka, Sapporo, Tokyo
(GMT+09:00) Seoul
(GMT+09:00) Yakutsk
(GMT+09:30) Adelaide
(GMT+09:30) Darwin
(GMT+10:00) Brisbane
(GMT+10:00) Canberra, Melbourne, Sydney
(GMT+10:00) Guam, Port Moresby
(GMT+10:00) Hobart
(GMT+10:00) Vladivostok
(GMT+11:00) Magadan, Solomon Is., New Caledonia
(GMT+12:00) Auckland, Wellington
(GMT+12:00) Fiji, Kamchatka, Marshall Is..
(GMT+13:00) Nuku’alofa
D-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 95

E
E
Appendix E Technical Specifications
System
CPU: Trimedia PNX1300
RAM: 16MB SDRAM
ROM: 2MB FLASH ROM
Networking
Adjustable bandwidth limit
Protocols
TCP/IP, HTTP, SMTP, FTP, Telnet, NTP, DNS
and DHCP
Modem
PPP (dial-up, direct cable connection)
Ethernet
10BaseT Ethernet or 100BaseT Fast Ethernet
Video
Algorithms Supported
JPEG, MJPEG
Video Inputs and Outputs
4 BNC video inputs with 75 ohm terminal
switch, NTSC/PAL auto-sensing
4 BNC loop-through video outputs
Features
Adjustable image size and quality
B/W or color control
Timestamp and text overlay
Resolution
NTSC
Up to 30 frames at 176x112
Up to 30 frames at 352x240
Up to 9 frames at 704x480 or quad
PAL
Up to 25 frames at 176x144
Up to 25 frames at 352x288
Up to 8 frames at 704x576 or quad
Serial Port
COM1
DB9 RS-232 or RS-485 Terminal block (PTZ
camera control) max.115.2Kbps
COM2
DB9 RS-232 (PTZ camera control or
modem), max.115.2Kbps
LED Indicators
NETWORK:
ACTIVE, LINK, FDX (full duplex)
SYSTEM:
POWER, CONNECT, SERIAL
Dimensions
193.71 x 195 x 44.3 mm (W x D x H)
Weight
Net. 890g
Power
Consumption: near 7.8W
Input: 100-240VAC, 50/60Hz, 0.4A
Output: 12VDC, 1.5A (12 VDC, 1.25A for UK
plug)
External Power Supply
Operating Environment
Operating Temperature: 0 to 65°C/ 32 to 149°F
Storage Temperature: -40 to 70°C/ -14 to 158°F
Humidity: 95%RH
Alarm Features
Motion detection with percentage and
sensitivity
Daily repeat timing schedule
3 color images per camera for pre/post alarm
Automatic transfer of stored images via email or
FTP with event-triggered actions
PAN/TILT/ZOOM
Multiple PTZ camera control through RS-232 or
RS-485
Supported devices and protocols:
Sony VISCA protocol, Canon VC-C1, VC-C3,
VC-C4, Dynacolor SmartDOME, Pelco
D-protocol, Lilin Speeddome, Ernitec
Speeddome
CGI command serial driver is supported
Software Development Kit
Open ActiveX control
Viewing System Requirement
Internet Explorer 4.x or above,
Netscape Navigator 4.x or above
Page 96

General I/O
4 Digital inputs (max. 12VDC 50 mA)
2 Relay outputs (max. 24 VDC 1A, 125 VAC
0.5A)
E-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 97

F
F
Appendix F Service Information
This appendix shows you how to contact Moxa for information about this and other products, and
how to report problems.
In this appendix, we cover the following topics.
MOXA Internet Services
Problem Report Form
Product Return Procedure
Page 98

MOXA Internet Services
Customer satisfaction is our number one concern, and to ensure that customers receive the full
benefit of our products, Moxa Internet Services has been set up to provide technical support,
driver updates, product information, and user’s manual updates.
The following services are provided
E-mail for technical support ............................... support@moxanet.com
World Wide Web (WWW) Site for product information:
............................ http://www.moxa.com
F-2
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
Page 99

Problem Report Form
Service Information
MOXA VPort 2140
Customer name:
Company:
Tel: Fax:
Email: Date:
1. Moxa Product: VPort 2140
2. Serial Number: _________________
Problem Description: Please describe the symptoms of the problem as clearly as possible, including any error
messages you see. A clearly written description of the problem will allow us to reproduce the symptoms, and
expedite the repair of your product.
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
F-3
Page 100

Product Return Procedure
For product repair, exchange, or refund, the customer must:
Provide evidence of original purchase.
Obtain a Product Return Agreement (PRA) from the sales representative or dealer.
Fill out the Problem Report Form (PRF). Include as much detail as possible for a shorter
product repair time.
Carefully pack the product in an anti-static package, and send it, pre-paid, to the dealer. The
PRA should be visible on the outside of the package, and include a description of the problem,
along with the return address and telephone number of a technical contact.
F-4
VPort 2140 User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...