Page 1

Moxa PowerTrans Switch
PT-7828 User’s Manual
www.moxa.com/product
Third Edition, September 2010
© 2010 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Page 2

Moxa PowerTrans Switch
PT-7828 User’s Manual
The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in
accordance with the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2010 Moxa Inc.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Trademarks
MOXA is a registered trademark of Moxa Inc.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of Moxa.
Moxa provides this document “as is,” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but
not limited to, its particular purpose. Moxa reserves the right to make improvements and/or changes to this
manual, or to the products and/or the programs described in this manual, at any time.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Moxa assumes no
responsibility for its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that may result from its use.
This product might include unintentional technical or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the
publication.
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
Moxa Americas:
Toll-free: 1-888-669-2872
Tel: +1-714-528-6777
Fax: +1-714-528-6778
Moxa China (Shanghai office)
:
Toll-free: 800-820-5036
Tel: +86-21-5258-9955
Fax: +86-21-5258-5505
Moxa Europe
:
Tel: +49-89-3 70 03 99-0
Fax: +49-89-3 70 03 99-99
Moxa Asia-Pacific
:
Tel: +886-2-8919-1230
Fax: +886-2-8919-1231
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction ............................................................................................... 1-1
Overview .............................................................................................................................. 1-2
Package Checklist ................................................................................................................. 1-2
Software Features ................................................................................................................. 1-2
Chapter 2 Getting Started .......................................................................................... 2-1
Serial Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100) ................................................ 2-2
Configuration by Telnet Console .......................................................................................... 2-5
Configuration by Web Browser ............................................................................................ 2-7
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access .................................................................................. 2-9
Chapter 3 Featured Functions ................................................................................... 3-1
Configuring Basic Settings ................................................................................................... 3-3
System Identification ................................................................................................. 3-3
Password ................................................................................................................... 3-4
Accessible IP ............................................................................................................. 3-5
Port ............................................................................................................................ 3-6
Network ..................................................................................................................... 3-7
Time .......................................................................................................................... 3-9
Daylight Saving Time ............................................................................................... 3-9
IEEE 1588 PTP................................................................................................................... 3-10
How Does an Ethernet Switch Affect 1588 Synchronization? ............................................ 3-11
PTP Setting ......................................................................................................................... 3-12
System File Update—By Remote TFTP ................................................................. 3-13
System File Update—By Local Import/Export ....................................................... 3-14
System File Update - By Backup Media ................................................................. 3-15
Restart ..................................................................................................................... 3-15
Factory Default ........................................................................................................ 3-15
Using Port Trunking ........................................................................................................... 3-16
The Port Trunking Concept ..................................................................................... 3-16
Configuring Port Trunking ...................................................................................... 3-17
Configuring SNMP ............................................................................................................. 3-18
SNMP Read/Write Settings ..................................................................................... 3-19
Trap Settings ........................................................................................................... 3-21
Private MIB information ......................................................................................... 3-22
Using Communication Redundancy ................................................................................... 3-22
The Turbo Ring Concept ......................................................................................... 3-23
Configuring Turbo Ring and Turbo Ring V2 .......................................................... 3-27
The Turbo Chain Concept ................................................................................................... 3-31
Configuring “Turbo Chain” ................................................................................................ 3-32
Head Switch Configuration ..................................................................................... 3-32
Member Switch Configuration ................................................................................ 3-33
Tail Switch Configuration ....................................................................................... 3-33
Explanation of “Current Status” Items .................................................................... 3-33
The STP/RSTP Concept .......................................................................................... 3-34
Configuring STP/RSTP ........................................................................................... 3-40
Using Traffic Prioritization ................................................................................................. 3-42
The Traffic Prioritization Concept .......................................................................... 3-42
Configuring Traffic Prioritization ........................................................................... 3-45
Page 4

Using Virtual LAN ............................................................................................................. 3-47
The Virtual LAN (VLAN) Concept ........................................................................ 3-47
Sample Applications of VLANs using PT-7828 ..................................................... 3-49
Configuring Virtual LAN ........................................................................................ 3-50
Using Multicast Filtering .................................................................................................... 3-52
The Concept of Multicast Filtering ......................................................................... 3-52
Configuring IGMP Snooping .................................................................................. 3-55
Add Static Multicast MAC ...................................................................................... 3-56
Configuring GMRP ................................................................................................. 3-57
GMRP Table ........................................................................................................... 3-57
Using Bandwidth Management .......................................................................................... 3-58
Broadcast Storm Protection ..................................................................................... 3-58
Traffic Rate Limiting Settings ................................................................................. 3-58
Using Port Access Control .................................................................................................. 3-59
Configuring Static Port Lock .................................................................................. 3-60
Configuring IEEE 802.1X ....................................................................................... 3-60
Using IP Filter .................................................................................................................... 3-63
Using Auto Warning ........................................................................................................... 3-63
Configuring Email Warning .................................................................................... 3-63
Event Type .............................................................................................................. 3-64
Email Setup ............................................................................................................. 3-65
Configuring Relay Warning .................................................................................... 3-66
Event Setup ............................................................................................................. 3-67
Warning List ............................................................................................................ 3-68
Using Line-Swap-Fast-Recovery........................................................................................ 3-68
Configuring Line-Swap Fast Recovery ................................................................... 3-68
Using Set Device IP ............................................................................................................ 3-68
Configuring Set Device IP ...................................................................................... 3-69
DHCP Relay Agent (Option 82) ......................................................................................... 3-70
Using Diagnosis .................................................................................................................. 3-72
Mirror Port .............................................................................................................. 3-72
Ping ......................................................................................................................... 3-73
LLDP Function Overview .................................................................................................. 3-73
LLDP Web Interface ............................................................................................... 3-74
LLDP Settings ......................................................................................................... 3-74
LLDP Table ............................................................................................................. 3-74
Using Monitor .................................................................................................................... 3-75
Monitor by Switch ................................................................................................... 3-75
Monitor by Port ....................................................................................................... 3-75
Using the MAC Address Table ........................................................................................... 3-76
Using System Log .............................................................................................................. 3-77
Event Log ................................................................................................................ 3-77
Syslog ...................................................................................................................... 3-78
Using HTTPS/SSL ............................................................................................................. 3-79
Using Layer 3 Settings ....................................................................................................... 3-80
The Layer-3 Switching Concept .............................................................................. 3-80
Interface Setting ...................................................................................................... 3-81
RIP .......................................................................................................................... 3-82
OSPF Settings ..................................................................................................................... 3-83
OSPF Global Settings .............................................................................................. 3-83
OSPF Area Settings ................................................................................................. 3-84
Page 5

OSPF Interface Settings .......................................................................................... 3-85
OSPF Virtual Link Settings ..................................................................................... 3-86
OSPF Area Aggregation Settings ............................................................................ 3-87
OSPF Neighbor Table ............................................................................................. 3-87
VRRP Settings ........................................................................................................ 3-88
Static Route ............................................................................................................. 3-89
Routing Table .......................................................................................................... 3-90
Using System Log .............................................................................................................. 3-90
Event Log ................................................................................................................ 3-90
Syslog Settings ........................................................................................................ 3-91
Using HTTPS/SSL ............................................................................................................. 3-92
Appendix A MIB Groups ............................................................................................... A-1
Appendix B Specifications ........................................................................................... B-1
Appendix C Modbus/TCP Map ..................................................................................... C-1
Page 6

1
1
Chapter 1 Introduction
Welcome to the PowerTrans PT-7828, a managed redundant Gigabit Ethernet switch designed
especially for connecting Ethernet-enabled devices for industrial field applications.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Software Features
Page 7

PT-7828 User’s Manual Introduction
1-2
Overview
The PowerTrans PT-7828 is certified for use in power substation automation systems (IEC
61850-3, IEEE 1613), traffic control systems (NEMA TS 2), and railway applications
(EN50121-4). It can be used for Gigabit or Fast Ethernet backbones and supports redundant ring
topologies. It also supports dual power inputs (24/48 VDC or 110/220 VDC/VAC) to increase the
reliability of communication.
The PT-7828 has a modular design that makes network planning easy and allows greater flexibility.
You can install up to 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports and 24 Fast Ethernet ports. Optional front or rear
wiring makes the PT-7828 suitable for different applications.
Package Checklist
The PowerTrans PT-7828 is shipped with the following items. If any of these items is missing or
damaged, please contact your customer service representative for assistance.
y 1 PowerTrans PT-7828
y Hardware installation guide
y CD-ROM with user’s manual and SNMP MIB file
y Warranty statement
y RJ45-to-DB9 console port cable
y Protective caps for unused ports
y 2 rackmount attachments
Software Features
y Static routing and RIP V1/V2 supported
y Turbo Ring, Turbo Chain, and RSTP/STP (IEEE 802.1W/D)
y VRRP ensures redundant routing paths
y IEEE 1588 PTP (Precision Time Protocol) for precise time synchronization of networks
y DHCP Option 82 for IP address assignment for different policies
y Supports Modbus TCP for easy integration in HMI
y Supports LLDP (Link Layer Discovery Protocol)
y Redundant Gigabit Turbo Ring, RSTP/STP (IEEE 802.1w/D), and Turbo Chain
y IGMP snooping, GMRP to filter multicast traffic from industrial Ethernet protocols
y IEEE 802.1Q VLAN, GVRP for easier network planning
y QoS-IEEE 802.1p/1Q and TOS/DiffServ to increase determinism
y 802.3ad, LACP for bandwidth optimization
y IEEE 802.1X and https/SSL to enhance network security
y SNMP V1/V2c/V3 for differential network management
y RMON for efficient, proactive network monitoring
y Supports ABC-01 for system configuration backup
y Access restriction by MAC address
y Port mirroring for online debugging
y Automatic warnings by email, relay output
y Automatic recovery of connected device’s IP addresses
y Line-swap fast recovery
y Configuration through web browser, Telnet/serial console, Windows utility, and ABC-01
Page 8

2
2
Chapter 2 Getting Started
This chapter explains how the initial installation process for the PT-7828. There are three ways to
access PT-7828’s configuration settings: the serial console, Telnet console, and web console. If
you do not know the PT-7828’s IP address, you can open the serial console by connecting the
PT-7828 to a PC’s COM port with a short serial cable. You can open the Telnet or web console
over an Ethernet LAN or over the Internet.
The following topics are covered:
Serial Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
Configuration by Telnet Console
Configuration by Web Browser
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access
Page 9
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-2
Serial Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
NOTE
y You cannot connect to the serial and Telnet console at the same time.
y You can connect to the web console and another console (serial or Telnet) at the same time.
However, it is strongly recommended that you do NOT do so. Following this advice will
allow you to maintain better control over the PT-7828’s configuration.
NOTE
We recommend using PComm Terminal Emulator when opening the serial console. This
software can be downloaded free of charge from the Moxa website.
Before running PComm Terminal Emulator, use an RJ45 to DB9-F (or RJ45 to DB25-F) cable to
connect the PT-7828’s console port to your PC’s COM port (generally COM1 or COM2,
depending on how your system is set up).
After installing PComm Terminal Emulator, open the PT-7828’s serial console as follows:
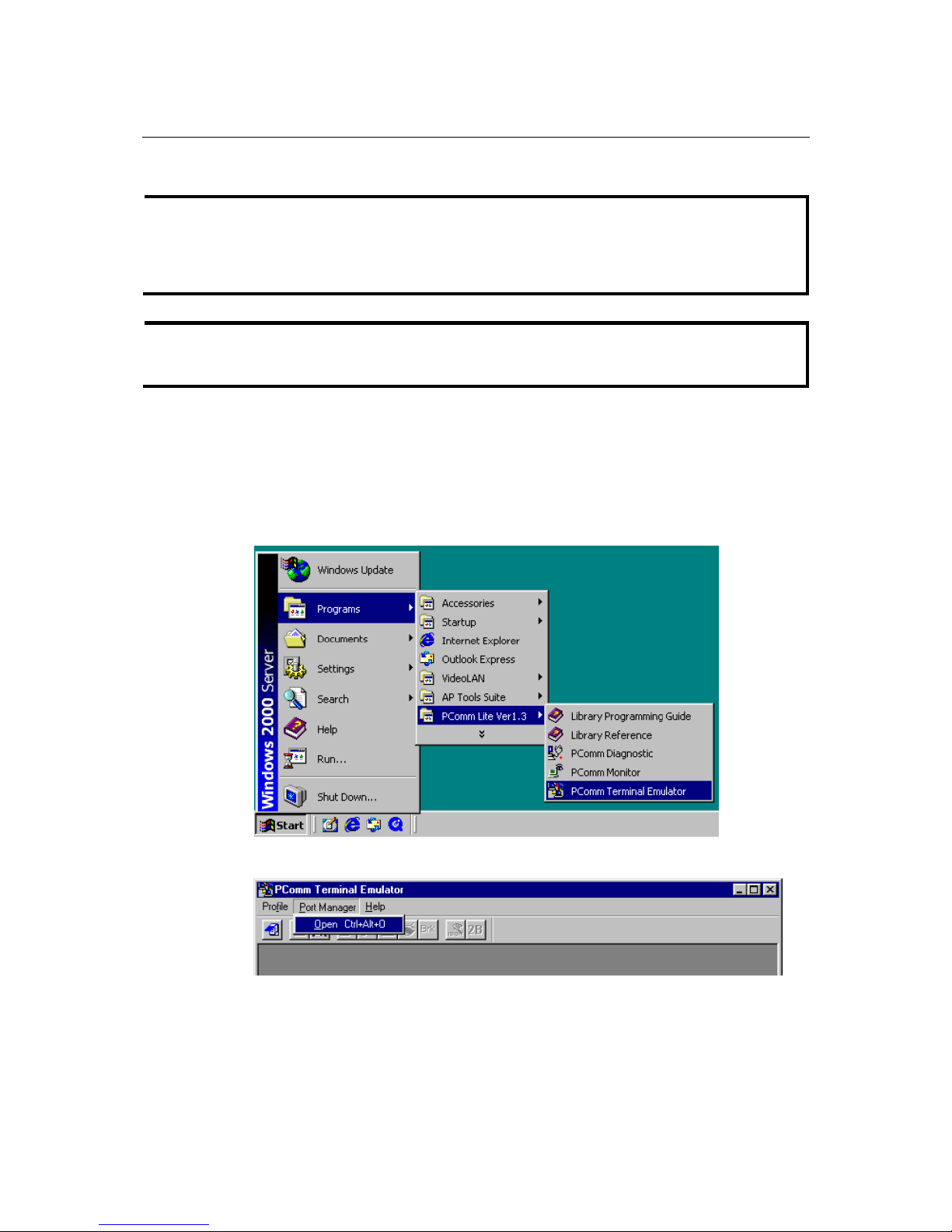
1. From the Windows desktop, click Start Æ Programs Æ PComm Lite 1.3 Æ Terminal
Emulator.
2. Select Open under the Port Manager menu to open a new connection.
Page 10
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-3
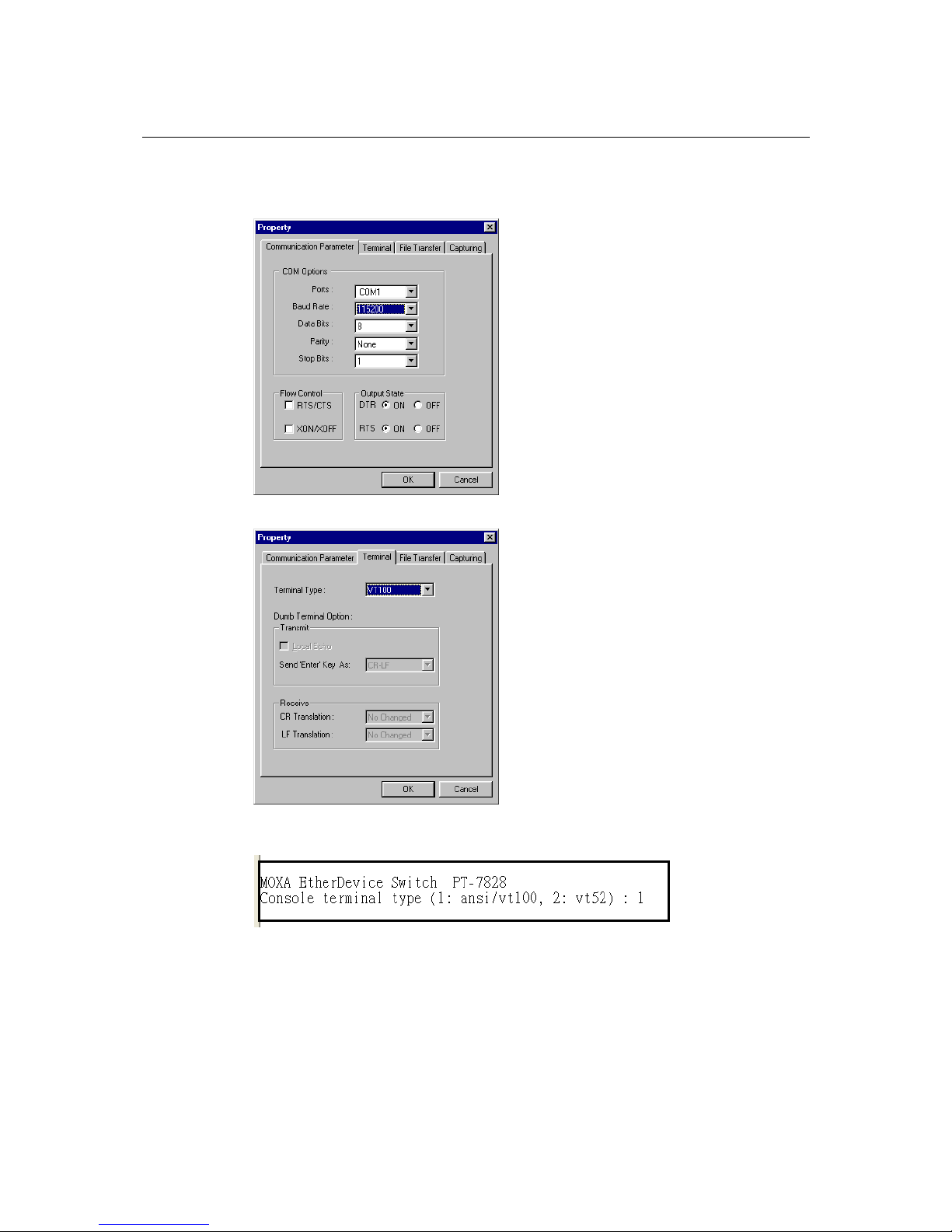
3. The Property window should open. On the Communication Parameter tab for Ports, select
the COM port that is being used for the console connection. Set the other fields as follows:
115200 for Baud Rate, 8 for Data Bits, None for Parity, and 1 for Stop Bits.
4. On the Terminal tab, select VT100 for Terminal Type. Click OK.
5. In the terminal window, the PT-7828 will prompt you to select a terminal type. Enter 1 to
select ansi/vt100 and press Enter.
Page 11
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-4
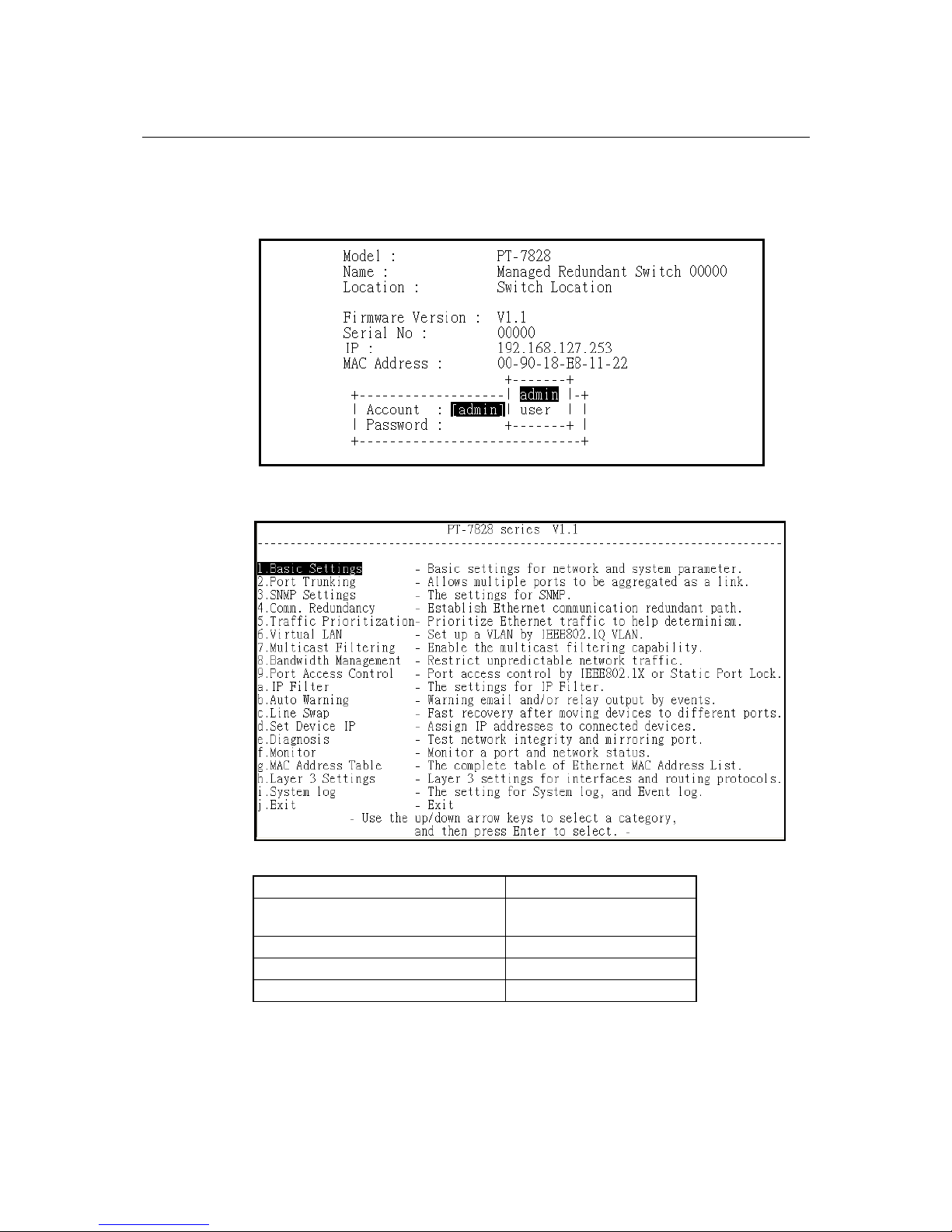
6. The serial console will prompt you to log in. Press Enter and select admin or user. Use the
down arrow key on your keyboard to select the Password field and enter a password if
desired. This password will be required to access any of the consoles (web, serial, Telnet). If
you do not wish to create a password, leave the Password field blank and press Enter.
7. The Main Menu of the PT-7828’s serial console should appear. (In PComm Terminal
Emulator, you can adjust the font by selecting Font… in the Edit menu.)
8. Use the following keys on your keyboard to navigate the PT-7828’s serial console:
Key Function
Up, down, right, left arrow keys
Tab
Move the onscreen cursor
Enter Display and select options
Space Toggle options
Esc Previous menu
Page 12
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-5
Configuration by Telnet Console
You may open the PT-7828’s Telnet or web console over a network. This requires that the PC host
and PT-7828 are on the same logical subnet. You may need to adjust your PC host’s IP address
and subnet mask. By default, the PT-7828’s IP address is 192.168.127.253 and PT-7828’s subnet
mask is 255.255.255.0 (for a Class C network). This means that your PC’s IP address must be set
to 192.168.xxx.xxx for a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0, or to 192.168.127.xxx with a subnet mask of
255.255.255.0.
NOTE
To connect to the PT-7828’s Telnet or web console, your PC host and the PT-7828 must be on
the same logical subnet.
NOTE
When connecting to the PT-7828’s Telnet or web console, first connect one of PT-7828’s
Ethernet ports to your Ethernet LAN or directly to your PC’s Ethernet port. You may use either a
straight-through or cross-over Ethernet cable.
NOTE
The PT-7828’s default IP address is 192.168.127.253.
After making sure that the PT-7828 is connected to the same LAN and logical subnet as your PC,
open the PT-7828’s Telnet console as follows:
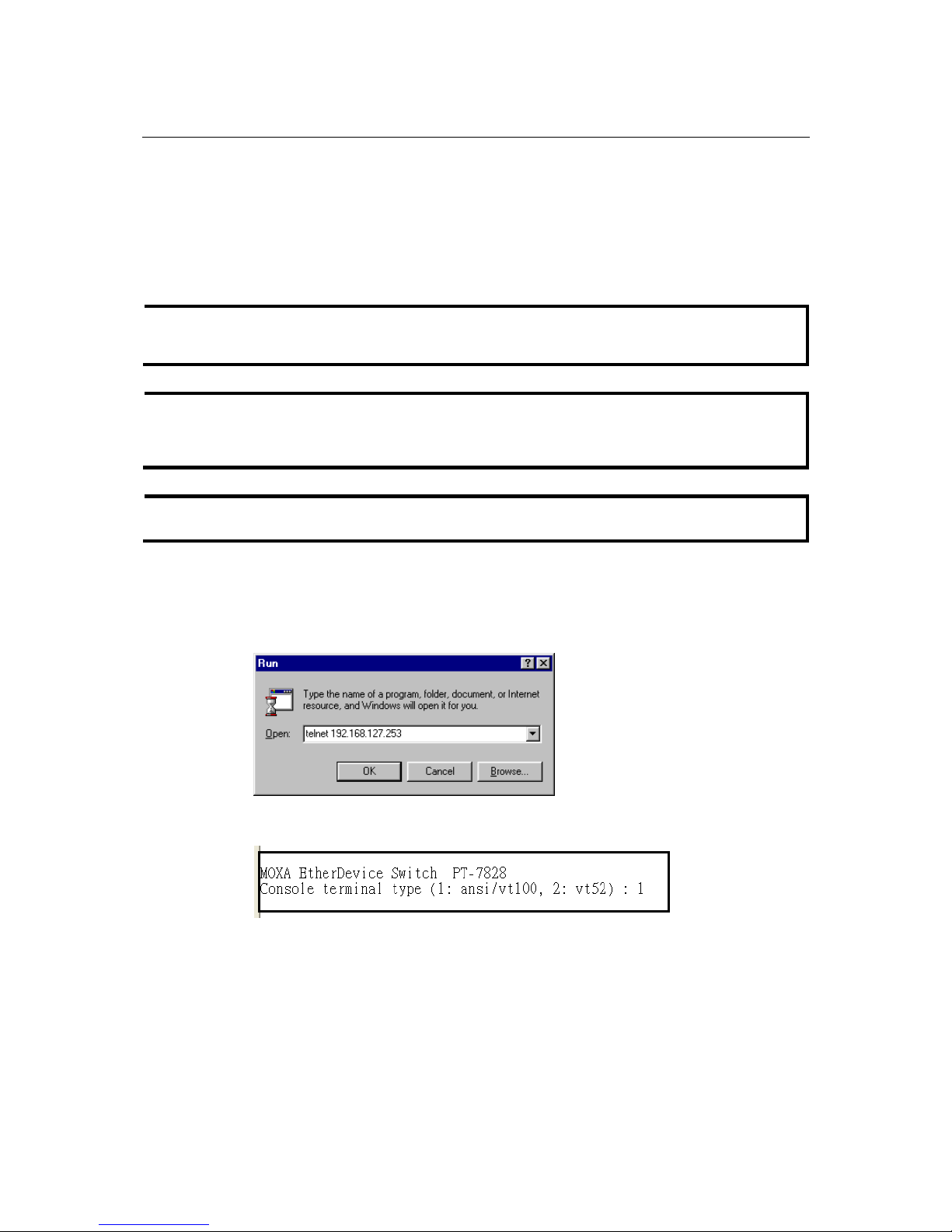
1. Click Start Æ Run from the Windows Start menu. Telnet to the PT-7828’s IP address from
the Windows Run window. You may also issue the Telnet command from a DOS prompt.
2. In the terminal window, the Telnet console will prompt you to select a terminal type. Type 1
to choose ansi/vt100, and then press Enter.
Page 13
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-6
3. The Telnet console will prompt you to log in. Press Enter and select admin or user. Use the
down arrow key on your keyboard to select the Password field and enter a password if
desired. This password will be required to access any of the consoles (web, serial, Telnet). If
you do not wish to create a password, leave the Password field blank and press Enter.
4. The Main Menu of the PT-7828’s Telnet console should appear.
5. In the terminal window, select Preferences… from the Terminal menu on the menu bar.
6. The Terminal Preferences window should appear. Make sure that VT100 Arrows is
checked.
Page 14
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-7
7. Use the following keys on your keyboard to navigate the PT-7828’s Telnet console:
Key Function
Up, down, right, left arrow keys
Tab
Move the onscreen cursor
Enter Display and select options
Space Toggle options
Esc Previous menu
NOTE
The Telnet console looks and operates in precisely the same manner as the serial console.
Configuration by Web Browser
The PT-7828’s web console is a convenient way to modify the configuration and access the
built-in monitoring and network administration functions. You can open the PT-7828’s web
console using a standard web browser such as Internet Explorer or Netscape.
NOTE
To connect to the PT-7828’s Telnet or web console, your PC host and the PT-7828 must be on
the same logical subnet.
NOTE
If the PT-7828 is configured for other VLAN settings, you must make sure your PC host is on the
management VLAN.
NOTE
When connecting to the PT-7828’s Telnet or web console, first connect one of PT-7828’s
Ethernet ports to your Ethernet LAN or directly to your PC’s Ethernet port. You may use either a
straight-through or cross-over Ethernet cable.
NOTE
The PT-7828’s default IP address is 192.168.127.253.
Page 15
PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-8
After making sure that the PT-7828 is connected to the same LAN and logical subnet as your PC,
open the PT-7828’s web console as follows:
1. Point your web browser to the PT-7828’s IP address by entering it in the Address or URL
field.
2. The PT-7828’s web console will open, and you will be prompted to log in. Select the login
account (admin or user) and enter the Password. This password will be required to access any
of the consoles (web, serial, Telnet). If you do not wish to create a password, leave the
Password field blank and press Enter.
NOTE
By default, no password is assigned to the PT-7828’s web, serial, and Telnet consoles.
3. After logging in, you may need to wait a few moments for the web console to appear. Use the
folders in the left navigation panel to navigate between different pages of configuration
options.
Page 16

PT-7828 User’s Manual Getting Started
2-9
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access
If you are connecting the PT-7828 to a public network but do not intend to manage it over the
network, we suggest disabling both the Telnet and web consoles. This is done through the serial
console, by navigating to System Identification under Basic Settings. Disable or enable the
Telnet Console and Web Configuration as shown below:
Page 17

3
3
Chapter 3 Featured Functions
This chapter explains how to access PT-7828’s various configuration, monitoring, and
administration functions. These functions can be accessed by serial, Telnet, or web console. The
serial console can be used if you do not know PT-7828’s IP address and requires that you connect
the PT-7828 to a PC COM port. The Telnet and web consoles can be opened over an Ethernet
LAN or the Internet.
The web console is the most user-friendly way to configure PT-7828. In this chapter, we use the
web console interface to introduce the functions. There are only a few differences between the web
console, serial console, and Telnet console.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Configuring Basic Settings
IEEE 1588 PTP
How Does an Ethernet Switch Affec
t 1588 Synchronization?
PTP Setting
Using Port Trunking
Configuring SNMP
Using Communication Redundancy
The Turbo Chain Concept
Configuring “Turbo Chain”
Using Traffic Prioritization
Using Virtual LAN
Using Multicast Filtering
Using Bandwidth Management
Using Port Access Control
Using IP Filter
Using Auto Warning
Using Line-Swap-Fast-Recovery
Using Set Device IP
DHCP Relay Agent (Option 82)
Using Diagnosis
LLDP Function Overview
Using Monitor
Using the MAC Address Table
Page 18

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-2
Using System Log
Using HTTPS/SSL
Using Layer 3 Settings
OSPF Settings
Using System Log
Using HTTPS/SSL
Page 19

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-3
Configuring Basic Settings
Basic Settings includes the most common settings required by administrators to maintain and
control the PT-7828.
System Identification
System Identification items are displayed at the top of the web console and will be included in
alarm emails. You can set the System Identification items to make it easier to identify different
switches that are connected to your network.
Switch Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30
characters
This option is useful for differentiating between
the roles or applications of different units.
Example: Factory Switch 1.
Managed Redundant Switch
[Serial no. of this switch]
Switch Location
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 80
characters
This option is useful for differentiating between
the locations of different units. Example:
production line 1.
Switch Location
Switch Description
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30
characters
This option is useful for recording a more
detailed description of the unit.
None
Maintainer Contact Info
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30
characters
This option is useful for providing information
about who is responsible for maintaining this
unit and how to contact this person.
None
Page 20

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-4
Password
The PT-7828 provides two levels of configuration access. The admin account has read/write
access of all configuration parameters, and the user account has read access only. The user
account can only view the configuration, but will not be able to make modifications.
ATTENTION
By default, no password is assigned to the PT-7828’s web, Telnet, and serial consoles. If a
password is assigned, you will be required to enter the password when you open the serial
console, Telnet console, or Web console.
Account
Setting Description Factory Default
Admin This account can modify the PT-7828’s
configuration.
admin
User This account can only view the PT-7828’s
configurations.
Password
Setting Description Factory Default
Old password
(max. 16 characters)
Enter the current password None
New password
(Max. 16 characters)
Enter the desired new password. Leave it blank if
you want to remove the password.
None
Retype password
(Max. 16 characters)
Enter the desired new password again. Leave it
blank if you want to remove the password.
None
Page 21

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-5
Accessible IP
The PT-7828 uses an IP address-based filtering method to control access.
You may add or remove IP addresses to limit access to the PT-7828. When the accessible IP list is
enabled, only addresses on the list will be allowed access to the PT-7828. Each IP address and
netmask entry can be tailored for different situations:
y Grant access to one host with a specific IP address
For example, enter IP address 192.168.1.1 with netmask 255.255.255.255 to allow access to
192.168.1.1 only.
y Grant access to any host on a specific subnetwork
For example, enter IP address 192.168.1.0 with netmask 255.255.255.0 to allow access to all
IPs on the subnet defined by this IP address/subnet mask combination.
y Grant acces to all hosts
Make sure the accessible IP list is not enabled. Remove the checkmark from Enable the
accessible IP list.
The following table shows additional configuration examples:
Hosts That Need Access Input Format
Any host Disable
192.168.1.120 192.168.1.120 / 255.255.255.255
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.255.0
192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254 192.168.0.0 / 255.255.0.0
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.255.128
192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.128 / 255.255.255.128
Page 22

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-6
Port
Port settings are included to give the user control over port access, port transmission speed, flow
control, and port type (MDI or MDIX).
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked This allows data transmission through the port.
Enabled
Unchecked This immediately shuts off port access.
ATTENTION
If a connected device or sub-network is wreaking havoc on the rest of the network, the Disable
option under Advanced Settings/Port gives the administrator a quick way to shut off access
through this port immediately.
Description
Setting Description Factory Default
Media type This displays the media type for each module’s
port
N/A
Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 63 characters This specifies an alias for the port to help
administrators differentiate between different
ports. Example: PLC 1
None
Page 23

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-7
Speed
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto This allows the port to use the IEEE 802.3u
protocol to negotiate with connected devices. The
port and connected devices will determine the
best speed for that connection.
Auto
100M-Full Choose one of these fixed speed options if the
connected Ethernet device has trouble
auto-negotiating for line speed.
100M-Half
10M-Full
10M-Half
FDX Flow Ctrl
This setting enables or disables flow control for the port when the port's Speed is set to Auto. The
final result will be determined by the Auto process between the PT-7828 and connected devices.
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable This enables flow control for this port when the
port's Speed is set to Auto.
Disable
Disable This disables flow control for this port when the
port's Speed is set to Auto.
MDI/MDIX
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto This allows the port to auto-detect the port type of
the connected Ethernet device and change the
port type accordingly.
Auto
MDI Choose MDI or MDIX if the connected Ethernet
device has trouble auto-negotiating for port type.
MDIX
Network
Network settings allow users to modify the usual TCP/IP network parameters.
Page 24

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-8
Auto IP Configuration
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable Select this to set the PT-7828’s IP address
manually.
Disable
By DHCP The PT-7828’s IP address will be assigned
automatically by the network’s DHCP server.
By BootP The PT-7828’s IP address will be assigned
automatically by the network’s BootP server.
Switch IP Address
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for the PT-7828 This assigns the PT-7828’s IP address on a
TCP/IP network.
192.168.127.253
Switch Subnet Mask
Setting Description Factory Default
Subnet mask for the
PT-7828
This identifies the type of network to which the
PT-7828 is connected (e.g., 255.255.0.0 for a
Class B network, or 255.255.255.0 for a Class
C network).
255.255.255.0
Default Gateway
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for gateway This specifies the IP address of the router that
connects the LAN to an outside network.
None
DNS IP Address
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for DNS server This specifies the IP address of the DNS server
used by your network. After specifying the
DNS server’s IP address, you can use the
PT-7828’s URL (e.g., www.PT.company.com)
to ope
n the web console instead of entering the
IP address.
None
IP address for 2nd DNS
server
This specifies the IP address of the secondary
DNS server used by your network. The
PT-7828 will use the secondary DNS server if
the first DNS server fails to connect.
None
Page 25

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-9
Time
The PT-7828 has a time calibration function based on information from an NTP server or user
specified time and date. Functions such as automatic warning emails can therefore include time
and date stamp.
NOTE
The PT-7828 does not have a real time clock. The user must update the Current Time and
Current Date to set the initial time for PT-7828 after each reboot, especially when there is no
N
TP server on the LAN or Internet connection.
Current Time
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified time This allows configuration of the local time in
local 24-hour format.
00h:00m:00s
Current Date
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified date This allows configuration of the local date in
yyyy-mm-dd format.
1970/01/01
Daylight Saving Time
The Daylight Saving Time settings are used to automatically offset the PT-7828’s time forward
according to national standards.
Start Date
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified date This specifies the date that Daylight Savings
Time begins.
None
End Date
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified date This specifies the date that Daylight Savings
Time ends.
None
Page 26

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-10
Offset
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified hour This specifies the number of hours that the time
should be offset forward during Daylight
Savings Time.
None
System Up Time
This indicates how long the PT-7828 remained up since the last cold start. The up time is indicated
in seconds.
Time Zone
Setting Description Factory Default
Time zone This specifies the time zone, which is used to
determine the local time offset from GMT
(Greenwich Mean Time).
GMT (Greenwich
Mean Time)
NOTE
Changing the time zone will automatically correct the current time. Make sure to set the time
zone before setting the time.
Time Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address or name of time
server
This is the IP or domain address (e.g.,
192.168.1.1, time.stdtime.gov.tw, or
time.nist.gov).
None
IP address or name of
secondary time server
The PT-7828 will try to locate the secondary
NTP server if the first NTP server fails to
connect.
Time Server Query Period
Setting Description Factory Default
Query period This parameter determines how frequently the
time is updated from the NTP server.
600 seconds
IEEE 1588 PTP
The following information is taken from the NIST website at http://ieee1588.nist.gov/intro.htm:
Time measurement can be accomplished using the IEEE Standard for a Precision Clock
Synchronization Protocol for Networked Measurement and Control Systems (IEEE 1588-2008) to
synchronize real-time clocks incorporated within each component of the electrical power system
for power automation applications.
IEEE 1588, which was published in November 2002, expands the performance capabilities of
Ethernet networks to control systems that operate over a communication network. In recent years
an increasing number of electrical power systems have been using a more distributed architecture
with network technologies that have less stringent timing specifications. IEEE 1588 generates a
master-slave relationship between the clocks, and enforces the specific timing requirements in
such power systems. All devices ultimately get their time from a clock known as the grandmaster
clock. In its basic form, the protocol is intended to be administration free.
Page 27

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-11
How Does an Ethernet Switch Affect 1588
Synchronization?
The following content is taken from the NIST website at http://ieee1588.nist.gov/switch.htm:
An Ethernet switch potentially introduces multi-microsecond fluctuations in the latency between
the 1588 grandmaster clock and a 1588 slave clock. Uncorrected these fluctuations will cause
synchronization errors. The magnitude of these fluctuations depend on the design of the Ethernet
switch and the details of the communication traffic. Experiments with prototype implementations
of IEEE 1588 indicate that with suitable care the effect of these fluctuations can be successfully
managed. For example, use of appropriate statistics in the 1588 devices to recognized significant
fluctuations and use suitable averaging techniques in the algorithms controlling the correction of
the local 1588 clock will be the good design means to achieve the highest time accuracy.
Can Ethernet switches be designed to avoid the effects of these fluctuations?
A switch may be designed to support IEEE 1588 to avoide the effects of queuing. In this case two
modifications to the usual design of an Ethernet switch are necessary:
z The Boundary Clock functionality defined by IEEE 1588 must be implemented in the switch
z The switch must be configured such that it does not pass IEEE 1588 message traffic using the
normal communication mechanisms of the switch.
Such an Ethernet switch will synchronize clocks directly connected to one of its ports to the
highest possible accuracy.
S
S
S
M
S
M
M
M
Grandmaster
Clock:
Determines the
time base for the
system
Boundary Clock:
Slave to the
grandmaster clock
and master to its
slave
Ordinary Clock:
Slave to its master
Page 28

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-12
PTP Setting
Operation IEEE 1588/PTP
Setting Description Factory Default
Operation Disable or enable IEEE 1588(PTP) operation Disable
Configuration IEEE 1588/PTP
Setting Description Factory Default
Clock Mode Support software-based IEEE 1588(PTP) mode Disable
Sync Interval Period for sending synchronization message (in
seconds)
Disable
Sub-domain Name Support _DFLT(Default) domain only _DFLT
Status
Setting Description Factory Default
Offset To Master (nsec) Deviation between local time and the reference
clock (in nanoseconds).
Grandmaster UUID When the clock has a port in PTP_SLAVE
state, this member’s value is the value of the
grand master clock's Uuid field of the last Sync
message received from the parent of the slave
port.
Parent UUID When the clock has a port in PTP_SLAVE
state, this member’s value is the value of the
source-Uuid field of the last Sync message
received from the parent of the slave port.
Page 29

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-13
Clock Stratum The stratum number describes one measure of
the quality of a clock. Each clock is
characterized by a stratum number used by the
best master clock algorithm as one parameter of
clock quality.
4
Clock Identifier Properties of the clock. DFLT
PTP Port Settings
Setting Description Factory Default
Port Enable Enable or disable PTP port operation. None
Port Status Display PTP port real status. PTP_DISABLED
System File Update—By Remote TFTP
The PT-7828 supports saving your configuration or log file to a remote TFTP server or local host.
Other PT-7828 switches can also load the configuration at a later time. The PT-7828 also supports
loading firmware or configuration files from the TFTP server or a local host.
TFTP Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address of TFTP
server
This specifies the IP address or name of the remote
TFTP server. This must be specified before
downloading or uploading files.
None
Configuration Files Path and Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 40 characters This specifies the path and file name of the
PT-7828’s configuration file on the TFTP server.
None
Firmware Files Path and Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 40 characters This specifies the path and file name of the
PT-7828’s firmware file.
None
Log Files Path and Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 40 characters This specifies the path and file name of the
PT-7828’s log file.
None
Page 30

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-14
After setting the desired paths and file names, click Activate to save the setting. Click Download
to download the prepared file from the remote TFTP server, or click Upload to upload the desired
file to the remote TFTP server.
System File Update—By Local Import/Export
Configuration File
Click Export to save the PT-7828’s configuration file to the local host.
Log File
Click Export to save the PT-7828’s log file to the local host.
NOTE
Some operating systems will open the configuration file and log file directly in the web page. In
such cases, right click the Export button to save the file.
Upgrade Firmware
To import a new firmware file onto the PT-7828, click Browse to select the firmware file that is
saved on your computer. The upgrade procedure will proceed automatically after clicking Import.
Upload Configure Data
To import a configuration file onto the PT-7828, click Browse to select the configuration file
already saved on your computer. The upgrade procedure will proceed automatically after clicking
Import.
Page 31

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-15
System File Update - By Backup Media
User can use Moxa’s Automatic Backup Configurator to save and load the configuration of
PT-7828 managed switches through the switch’s RS-232 console port.
Restart
This Restart function provides users with a quick way to restart the system.
Factory Default
This function provides users with a quick way of restoring the PT-7828’s configuration to factory
defaults. This function is available in the serial, Telnet, and web consoles.
NOTE
After restoring the factory default configuration, you will need to use the default network settings
to re-establish the web or Telnet console connection with the PT-7828.
Page 32

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-16
Using Port Trunking
Link aggregation involves grouping links to into a link aggregation group. A MAC client can treat
link aggregation groups as if they were a single link.
The PT-7828’s port trunking feature allows devices to communicate by aggregating up to 4 trunk
groups, with a maximum of 8 ports for each group. If one of the 8 ports fails, the other seven ports
will automatically provide backup and share the traffic.
Port trunking can be used to combine up to 8 ports between two PT-7828 switches. If all ports on
both switch units are configured as 100BaseTX and they are operating in full duplex, the potential
bandwidth of the connection will be 1600 Mbps.
The Port Trunking Concept
Moxa has developed a proprietary port trunking protocol that provides the following benefits:
y More flexibility in setting up your network connections, since the bandwidth of a link can be
doubled, tripled, or quadrupled
y Redundancy — if one link is broken, the remaining trunked ports share the traffic within this
trunk group
y Load sharing — MAC client traffic may be distributed across multiple links
To avoid broadcast storms or loops in your network while configuring a trunk, first disable or
disconnect all ports that you want to add to the trunk or remove from the trunk. After you finish
configuring the trunk, enable or re-connect the ports.
If all ports on both switch units are configured as 100BaseTX and they are operating in full duplex
mode, the potential bandwidth of the connection will be up to 1.6 Gbps. This means that users can
double, triple, or quadruple the bandwidth of the connection by port trunking between two PT
series switches.
Each PT-7828 can set a maximum of 4 port trunking groups. When you activate port trunking,
certain settings on each port will be reset to factory default values or disabled:
y Communication redundancy will be reset
y 802.1Q VLAN will be reset
y Multicast Filtering will be reset
y Port Lock will be reset and disabled.
y Set Device IP will be reset
y Mirror will be reset
After port trunking has been activated, you may configure these items again for each trunking
ports.
Page 33

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-17
Configuring Port Trunking
The Port Trunking Settings page is where ports are assigned to a trunk group.
Step 1: Select the desired Trunk Group (Trk1, Trk2, Trk3, Trk4).
Step 2: Select the Trunk Type (Static or LACP).
Step 3: Select the desired ports under Available Ports and click Up to add to the Trunk Group.
Step 4: Select the desired ports under Member Ports and click Down to remove from the group.
Trunk Group (Maximum of 4 trunk groups)
Setting Description Factory Default
Trk1, Trk2, Trk3, Trk4 This specifies the current trunk group. Trk1
Trunk Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Static This selects Moxa’s proprietary trunking protocol. Static
LACP
This selects LACP (IEEE 802.3ad, Link
Aggregation Control Protocol).
Static
Available Ports/Member Ports
Setting Description Factory Default
Member/available ports This lists the ports in the current trunk group and the
ports that are available to be added.
N/A
Check box This selects the port to be added or removed from
the group.
Unchecked
Port This is how each port is identified. N/A
Port description This displays the media type for each port. N/A
Name This displays the specified name for each port. N/A
Speed
This indicates the transmission speed for each port
(100M-Full, 100M-Half, 10M-Full, or 10M-Half).
N/A
FDX flow control
This indicates if the FDX flow control of this port is
enabled or disabled.
N/A
Page 34

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-18
Up
This is used to add selected ports into the trunk
group from available ports.
N/A
Down
This is used to remove selected ports from the trunk
group.
N/A
Trunk Table
Setting Description
Trunk group Displays the trunk type and trunk group.
Member port Displays the member ports that belong to the trunk group.
Status Success means port trunking is working properly.
Fail means port trunking is not working properly.
Standby means port trunking is working as a standby port. When there
are more than eight ports trunked as a trunking group, the 9
th
port will be
the standby port.
Configuring SNMP
The PT-7828 supports SNMP V1, V2c, and V3. SNMP V1 and SNMP V2c use a community
string match for authentication, which means that SNMP servers access all objects with read-only
or read/write permissions using the community strings public and private by default. SNMP V3
requires that you select an authentication level of MD5 or SHA, and is the most secure protocol.
You can also enable data encryption to enhance data security.
Supported SNMP security modes and levels are shown in the following table. Select the security
mode and level that will be used to communicate between the SNMP agent and manager.
Protocol
Version
UI Setting Authentication Encryption Method
SNMP V1,
V2c
V1, V2c
Read
Community
Community
string
No
This uses a community string
match for authentication.
V1, V2c
Write/Read
Community
Community
string
No
This uses a community string
match for authentication.
SNMP V3
No-Auth No No
This uses an account with admin
or user to access objects
MD5 or SHA
Authentication
based on MD5
or SHA
No
This provides authentication based
on HMAC-MD5, or HMAC-SHA
algorithms. 8-character passwords
are the minimum requirement for
authentication.
Page 35

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-19
MD5 or SHA
Authentication
based on MD5
or SHA
Data
encryption
key
This provides authentication based
on HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA
algorithms, and data encryption
key. 8-character passwords and a
data encryption key are the
minimum requirements for
authentication .and encryption.
These parameters are configured on the SNMP page. A more detailed explanation of each
parameter is given below the figure.
SNMP Read/Write Settings
SNMP Versions
Setting Description Factory Default
V1, V2c, V3, or
V1, V2c, or
V3 only
This specifies the SNMP protocol version
used to manage the switch.
V1, V2c
V1, V2c Read Community
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30 characters
This specifies the community string to
authenticate the SNMP agent for read-only
access. The SNMP agent will access all
objects with read-only permissions using
this community string.
Public
Page 36
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-20
V1, V2c Write/Read Community
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30 characters
This specifies the community string to
authenticate the SNMP agent for
read/write access. The SNMP server will
access all objects with read/write
permissions using this community string.
Private
For SNMP V3, there are two levels of privilege for different accounts to access the PT-7828.
Admin privilege provides access and authorization to read and write the MIB file. User privilege
allows reading of the MIB file only.
Admin Auth. Type (for SNMP V1, V2c, V3, and V3 only)
Setting Description Factory Default
No-Auth
This allows the admin account to access
objects without authentication.
No
MD5Auth
Authentication will be based on the
HMAC-MD5 algorithms. 8-character
passwords are the minimum requirement
for authentication.
No
SHAAuth
Authentication will be based on the
HMAC-SHA algorithms. 8-character
passwords are the minimum requirement
for authentication.
No
Admin Data Encryption Key (for SNMP V1, V2c, V3, and V3 only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable
This enables data encryption using the
specified data encryption key (between 8
and 30 characters).
No
Disable
This specifies that data will not be
encrypted.
No
User Auth. Type (for SNMP V1, V2c, V3 and V3 only)
Setting Description Factory Default
No-Auth
This allows the admin account and user
account to access objects without
authentication.
No
MD5-Auth
Authentication will be based on the
HMAC-MD5 algorithms. 8-character
passwords are the minimum requirement
for authentication.
No
SHA-Auth
Authentication will be based on the
HMAC-SHA algorithms. 8-character
passwords are the minimum requirement
for authentication.
No
Page 37

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-21
User Data Encryption Key (for SNMP V1, V2c, V3 and V3 only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable
This enables data encryption using the
specified data encryption key (between 8
and 30 characters).
No
Disable No data encryption No
Trap Settings
SNMP Trap Mode
In Trap mode, the SNMP agent sends a SNMPv1 trap PDU to the NMS. No acknowledgment is
sent back from the NMS so the agent has no way of knowing if the trap reached the NMS.
SNMP Inform Mode
SNMPv2 provides an inform mechanism. When an inform message is sent from the SNMP agent
to the NMS, the receiver sends a response to the sender acknowledging receipt of the event. This
behavior is similar to that of the get and set request. If the SNMP agent doesn’t receive a response
from the NMS for a period of time, the agent will resend the trap to the NMS agent. The maximum
timeout time is 300 seconds (default is 1 second), and the maximum number of retries is 99 times
(default is 1 time). When the SNMP agent receives acknowledgement from the NMS, it will stop
resending the inform messages.
1
st
Trap Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Default
IP or Name Enter the IP address or name of the Trap
Server used by your network.
None
1st Trap Community
Setting Description Factory Default
character string Use a community string match for
authentication (maximum of 30
characters).
public
Page 38

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-22
2nd Trap Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Retries Enter Inform Retry number 1
Time out Enter Inform Timeout window 1
Private MIB information
Switch Object ID
Setting Description Factory Default
8691.7.15
This indicates the PT-7828’s enterprise
value.
Fixed
NOTE: The Switch Object ID cannot be changed.
Using Communication Redundancy
Communication redundancy on your network helps protect critical links against failure, protects
against network loops, and keeps network downtime at a minimum.
Communication redundancy functions allow the user to set up redundant loops in the network to
provide a backup data transmission route in the event that a cable is inadvertently disconnected or
damaged. This is a particularly important feature for industrial applications, since it could take
several minutes to locate the disconnected or severed cable. For example, if the PT-7828 is used as
a key communications component of a production line, several minutes of downtime can result in
a big loss in production and revenue. The PT-7828 supports three different protocols for
communication redundancy—Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE-802.1w) and Turbo Ring,
and Turbo Ring V2.
When configuring a redundant ring, all switches on the same ring must be configured using the
same redundancy protocol. You cannot mix the Turbo Ring, Turbo Ring V2, and STP/RSTP
protocols within a ring. The following table lists the key differences between each feature. Use this
information to evaluate each the benefits of each, and then determine which features are most
suitable for your network.
Turbo Ring V2 Turbo Ring STP RSTP
Topology Ring Ring Ring, Mesh Ring, Mesh
Recovery Time < 20 ms < 300 ms Up to 30 sec. Up to 5 sec
NOTE
Most managed switches by Moxa support two proprietary Turbo Ring protocols:
y Turbo Ring refers to the original version of Moxa’s proprietary redundant ring protocol,
which has a recovery time of under 300 ms.
y Turbo Ring V2 refers to the new generation Turbo Ring, which has a recovery time of under
20 ms.
Page 39

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-23
The Turbo Ring Concept
Moxa developed the proprietary Turbo Ring protocol to optimize communication redundancy and
achieve a faster recovery time on the network.
The Turbo Ring and Turbo Ring V2 protocols designate one switch as the master of the network,
and then automatically block packets from traveling through any of the network’s redundant loops.
In the event that one branch of the ring gets disconnected from the rest of the network, the protocol
automatically readjusts the ring so that the part of the network that was disconnected can
reestablish contact with the rest of the network.
Initial setup for Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2
1. For each switch in the ring, select any two
ports as the redundant ports.
2. Connect redundant ports on neighboring
switches to form the redundant ring.
The user does not need to manually assign the master with Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2. If no
switch is assigned as the master, the protocol automatically selects one of the switches to be the
master. The master is only used to identify which segment in the redundant ring acts as the backup
path. In the following subsections, we explain how the redundant path is selected for rings
configured for Turbo Ring and Turbo Ring V2.
Determining the Redundant Path for Turbo Ring
In this case, the redundant segment (i.e., the segment that will be blocked during normal operation)
is determined by the number of PT series Ethernet switches in the ring and by the location of the
master switch.
Turbo Ring with even number of switches
Master
If the number of Ethernet switches in the Turbo
Ring is 2N (an even number), the backup
segment is one of the two segments connected
to the (N+1)st switch (i.e., the unit directly
opposite the master).
Page 40

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-24
T urbo Ring with odd number switches
Master
Segment N+1
If the number of Ethernet switches in the Turbo
Ring is 2N+1 (an odd number), the backup
segment is the (N+1)st segment counting
counterclockwise.
For the example shown here, N=1, so that
N+1=2.
Determining the Redundant Path for Turbo Ring V2
Master
For Turbo Ring V2, the backup segment is the
segment connected to the 2nd redundant port on
the master.
Please refer to Configuring Turbo Ring V2
later in this chapter.
Ring Coupling Configuration
For some systems, it may not be convenient to connect all devices in the system in a single
redundant ring, since some devices could be located in a remote area. For these systems, Ring
Coupling can be used to group devices into smaller redundant rings that communicate with each
other.
ATTENTION
In a VLAN environment, the user must set Redundant Port Coupling Port and Coupling
Control Port to join all VLANs, since these ports act as the backbone to transmit all packets of
different VLANs to the different PT series Ethernet switches.
Page 41

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-25
Ring Coupling for Turbo Ring
Switch A: "Coupler"
Switch B Switch D
Switch C
Main Path
Coupling Port
Backup Path
Coupling
Control Port
To configure the ring coupling for a Turbo Ring, select two PT series Ethernet switches (e.g.,
Switch A and B in the above figure) in the ring, and another two PT series Ethernet switches in the
adjacent ring (e.g., Switch C and D).
Select two ports on each switch to be used as coupling ports and link them together. Next, assign
one switch (e.g., Switch A) to be the coupler and connect the coupler’s coupling control port with
Switch B (for this example).
The coupler switch (i.e., Switch A) will monitor switch B through the coupling control port to
determine whether or not the coupling port’s backup path should be recovered.
Ring Coupling for Turbo Ring V2
Switch B
Switch A
Switch D
Switch C
Main Path
Coupling Port (Primary)
Coupling Port (Backup)
Backup Path
Note that the ring coupling settings for a Turbo Ring V2 are different from a Turbo Ring. For
Turbo Ring V2, ring coupling is enabled by configuring the Coupling Port (Primary) on Switch
B and the Coupling Port (Backup) on Switch A only. You do not need to set up a coupling
control port, so Turbo Ring V2 does not require a coupling control line.
The Coupling Port (Backup) on Switch A is used for the backup path and connects directly to a
network port on Switch C. The Coupling Port (Primary) on Switch B monitors the status of the
main path, and connects directly to an extra network port on Switch D. With ring coupling
established, Switch A can activate the backup path as soon as it detects a problem with the main
path.
Page 42

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-26
ATTENTION
Ring coupling only needs to be enabled on one of the switches serving as the ring coupler. The
coupler must assign separate ports for the two Turbo Ring ports and the coupling port.
NOTE
You do not need to use the same PT series Ethernet switch for both ring coupling and ring
master.
Dual-Homing Configuration for Turbo Ring V2
Dual-homing is only supported with Turbo Ring V2 and is used to connect two networks through
a single Ethernet switch. The primary path is the operating connection, and the backup path is a
back-up connection that is activated in the event that the primary path connection fails.
Dual-Homing for Turbo Ring V2
Primary
Path
Ring A
Master
Master
Ring B
Backup
Path
Page 43
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-27
Configuring Turbo Ring and Turbo Ring V2
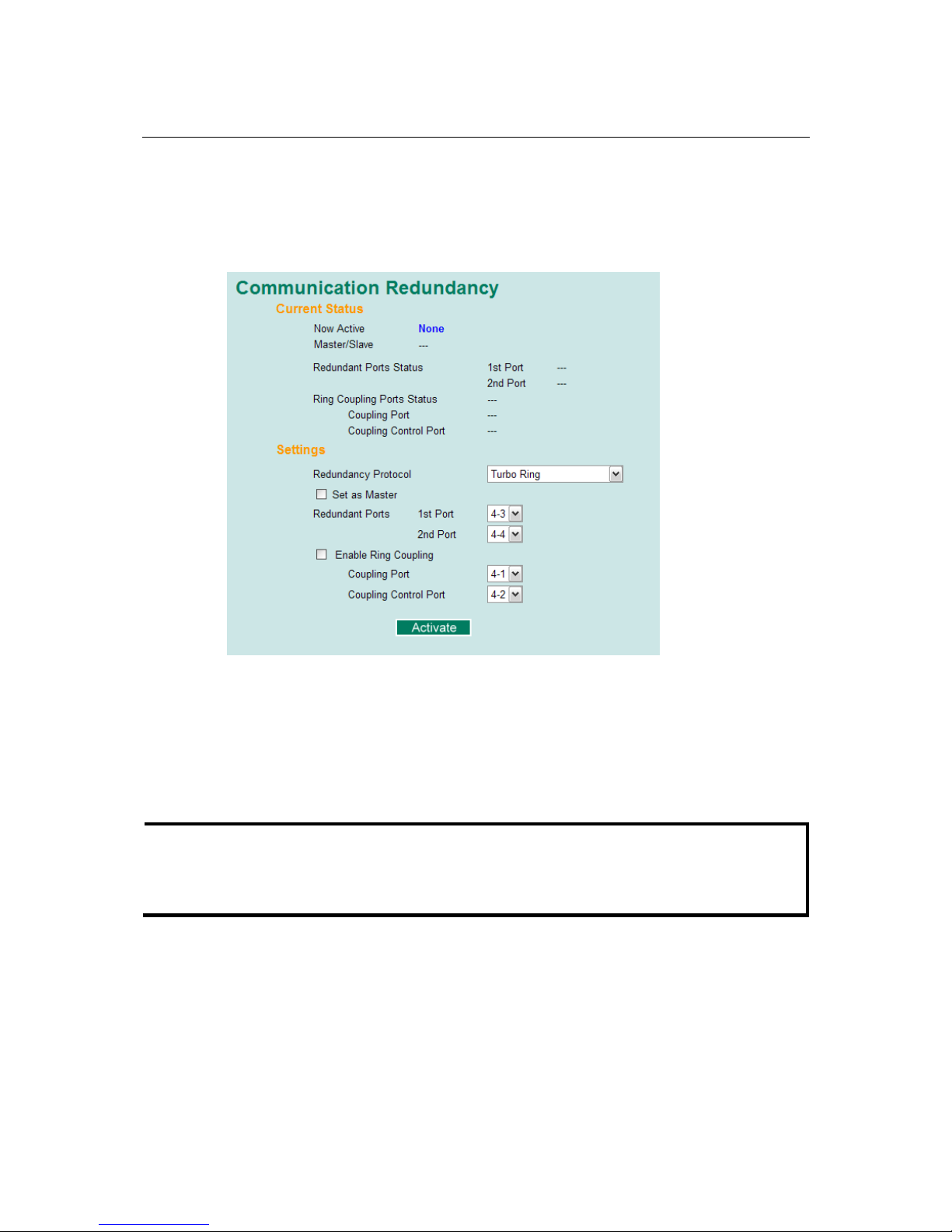
On the Communication Redundancy page, select Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2 as the
Redundancy Protocol. Note that each protocol's configuration page is different.
Configuring Turbo Ring
"Current Status" Items
Now Active
This shows which communication protocol is in use: Turbo Ring, Turbo Ring V2, RSTP, or
none.
Master/Slave
This indicates whether or not the PT-7828 is the master of the Turbo Ring. This field appears only
for Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2.
NOTE
The user does not need to assign the master to use Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2. If no master is
assigned, the Turbo Ring protocol will automatically assign master status to one of the PT series
Ethernet switches in the ring. The master is only used to determine which segment serves as the
backup path.
Redundant Ports Status (1st Port, 2nd Port)
Ring Coupling Ports Status (Coupling Port, Coupling Control Port)
The Ports Status indicators show Forwarding for normal transmission, Blocking if the port is
part of a backup path that is currently blocked, and Link down if there is no connection.
Page 44
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-28
"Settings" Items
Redundancy Protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
Turbo Ring
This selects the Turbo Ring
protocol.
None
Turbo Ring V2
This selects the Turbo Ring V2
protocol.
RSTP (IEEE
802.1w/1D)
This selects the RSTP protocol.
None This disables ring redundancy.
Set as Master
Setting Description Factory Default
Enabled
The PT-7828 is manually selected
as the master.
Not checked
Disabled
The Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2
protocol will automatically select
the master.
Redundant Ports
Setting Description Factory Default
1st Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the first
redundant port.
None
2nd Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the second
redundant port.
None
Enable Ring Coupling
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable
This specifies that this PT-7828
will be a ring coupler.
Not checked
Disable
This specifies that this PT-7828 is
not a ring coupler.
Coupling Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Coupling Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the
coupling port.
None
Coupling Control Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Coupling Control Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the
coupling control port.
None
Page 45

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-29
Configuring Turbo Ring V2
NOTE
When using a dual-ring architecture, users must complete configuration for both Ring 1 and Ring
2. The status of both rings will appear under Current Status.
"Current Status" Items
Now Active
This shows which communication protocol is in use: Turbo Ring, Turbo Ring V2, RSTP, or
none.
Ring 1/2—Status
This shows Healthy if the ring is operating normally, and shows Break if the ring’s backup link is
active.
Ring 1/2—Master/Slave
This indicates whether or not the PT-7828 is the master of the Turbo Ring. This field appears only
when selected to operate in Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2 mode.
NOTE
The user does not need to assign the master to use Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2. If no master is
assigned, the Turbo Ring protocol will automatically assign master status to one of the PT series
Ethernet switches in the ring. The master is only used to determine which segment serves as the
backup path.
Page 46

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-30
Ring 1/2—1st Ring Port Status
Ring 1/2—2nd Ring Port Status
The Ports Status indicators show Forwarding for normal transmission, Blocking if this port is
connected to a backup path and the path is blocked, and Link down if there is no connection.
Coupling—Mode
This indicates either None, Dual Homing, or Ring Coupling.
Coupling—Coupling Port status
This indicates either Primary, or Backup.
"Settings" Items
Redundancy Protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
Turbo Ring
This selects the Turbo Ring
protocol.
None
Turbo Ring V2
This selects the Turbo Ring V2
protocol.
RSTP (IEEE
802.1W/1D)
This selects the RSTP protocol.
None This disables ring redundancy.
Enable Ring 1
Setting Description Factory Default
Enabled This enables Ring 1.
Not checked
Disabled This disables Ring 1.
Enable Ring 2*
Setting Description Factory Default
Enabled This enables Ring 2.
Not checked
Disabled This disables Ring 2.
*Both Ring 1 and Ring 2 must be enabled when using the dual-ring architecture.
Set as Master
Setting Description Factory Default
Enabled
The PT-7828 is manually selected
as the master.
Not checked
Disabled
The Turbo Ring or Turbo Ring V2
protocol will automatically select
the master.
Redundant Ports
Setting Description Factory Default
1st Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the first
redundant port.
None
2nd Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the second
redundant port.
None
Page 47

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-31
Enable Ring Coupling
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable
This specifies that this PT-7828
will be a ring coupler.
Not checked
Disable
This specifies that this PT-7828 is
not a ring coupler.
Coupling Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Dual Homing
This enables dual homing through
the PT-7828.
None
Ring Coupling
(backup)
This specifies that the PT-7828 will
be used for a ring coupling backup
connection.
None
Ring Coupling
(primary)
This specifies that the PT-7828 will
be used for a ring coupling primary
connection.
None
Primary/Backup Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Primary Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as primary
port.
None
Backup Port
This specifies which port on the
PT-7828 will be used as the backup
port.
None
The Turbo Chain Concept
Moxa’s Turbo Chain is an advanced software-technology that gives network administrators the
flexibility of constructing any type of redundant network topology. When using the “chain”
concept, you first connect the Ethernet switches in a chain and then simply link the two ends of the
chain to an Ethernet network, as illustrated in the following figure.
Turbo Chain can be used on industrial networks that have a complex topology. If the industrial
network uses a multi-ring architecture, Turbo Chain can be used to create flexible and scalable
topologies with a fast media-recovery time.
Page 48

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-32
Setting Up Turbo Chain
LAN Network
Head Port
Member Port
Member Port
Member Port
Member Port
Ta i l P o r t
Ta i l
Head
1. Select the Head switch, Tail switch, and Member switches.
2. Configure one port as the Head port and one port as the Member port in the Head switch,
configure one port as the Tail port and one port as the Member port in the Tail switch, and
configure two ports as Member ports in each of the Member switches.
3. Connect the Head switch, Tail switch, and Member switches as shown in the diagram.
The path connecting to the Head port is the main path, and the path connecting to the Tail port is
the back up path of the Turbo Chain. Under normal conditions, packets are transmitted through the
Head Port to the LAN Network. If any Turbo Chain path is disconnected, the Tail Port will be
activated to continue packet transmission.
Configuring “Turbo Chain”
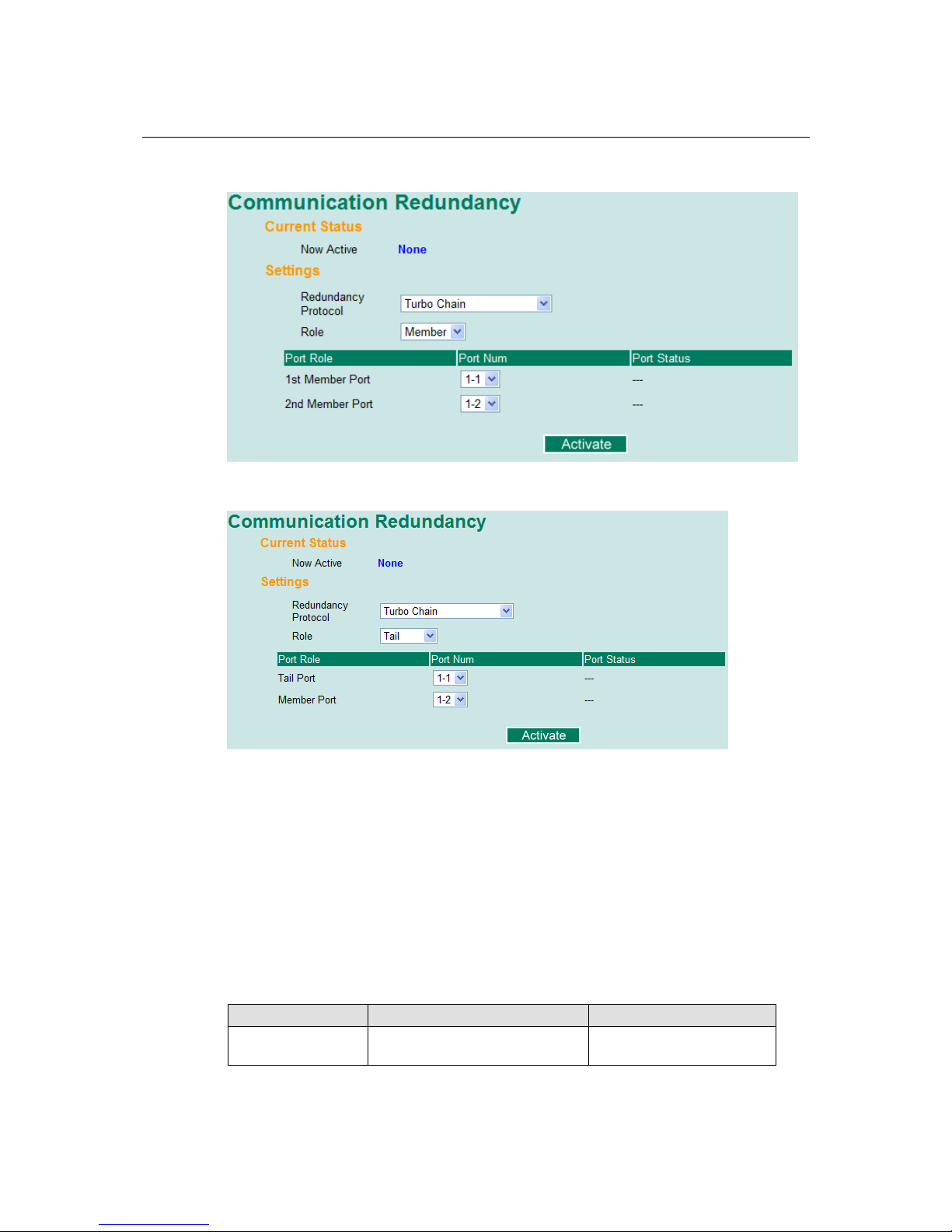
Head Switch Configuration
Page 49
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-33
Member Switch Configuration
Tail Switch Configuration
Explanation of “Current Status” Items
Now Active
Shows which communication protocol is in use: Turbo Ring, Turbo Ring V2, RSTP, Turbo
Chain or None.
The “Ports Status” indicators show Forwarding for normal transmission, Blocked if this port is
connected to the Tail port as a backup path and the path is blocked, and Link down if there is no
connection.
Explanation of “Settings” Items
Redundancy Protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
Turbo Ring Select this item to change to the
Turbo Ring configuration page.
None
Page 50

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-34
Turbo Ring V2 Select this item to change to the
Turbo Ring V2 configuration page.
Turbo Chain Select this item to change to the
Turbo Chain configuration page
RSTP (IEEE
802.1W/1D)
Select this item to change to the
RSTP configuration page.
None Ring redundancy is not active
Enable Ring Coupling
Setting Description Factory Default
Head Select this EDS as Head Switch
Member
Member Select this EDS as Member Switch
Tail Select this EDS as Tail Switch
Enable Ring Coupling
Setting Description Factory Default
Head Port Select any port of the EDS to be the
head port.
port 1-1
Member Port Select any port of the EDS to be the
member port.
port 1-2
Enable Ring Coupling
Setting Description Factory Default
1st Member port Select any port of the EDS to be the
1st member port
port 1-1
2nd Member port Select any port of the EDS to be the
2nd member port
port 1-2
Enable Ring Coupling
Setting Description Factory Default
Tail Port Select any port of the EDS to be the
tail port.
port 1-1
Member Port Select any port of the EDS to be the
member port.
port 1-2
The STP/RSTP Concept
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was designed to help reduce link failures in a network and provide
protection from loops. Networks that have a complicated architecture are prone to broadcast
storms caused by unintended loops in the network. The PT-7828’s STP feature is disabled by
default. To be completely effective, you must enable RSTP/STP on every PT-7828 connected to
your network.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) implements the Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol
defined by IEEE Std 802.1w-2001. RSTP provides the following benefits:
y The topology of a bridged network will be determined much more quickly compared to STP.
y RSTP is backward compatible with STP, making it relatively easy to deploy. For example:
¾ It defaults to sending 802.1D style BPDUs if packets with this format are received.
Page 51

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-35
¾ STP (802.1D) and RSTP (802.1w) can operate on different ports of the same PT-7828.
This feature is particularly helpful when PT-7828 ports connect to older equipment, such
as legacy switches.
You get essentially the same functionality with RSTP and STP. To see how the two systems
different, please refer to Differences between RSTP and STP later in this chapter.
NOTE
The STP protocol is part of the IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition bridge specification. The
explanation given below uses bridge instead of switch.
What is STP?
STP (802.1D) is a bridge-based system that is used to implement parallel paths for network traffic.
STP uses a loop-detection process to:
y Locate and then disable less efficient paths (i.e., paths that have a lower bandwidth)
y Enable one of the less efficient paths if the most efficient path fails
The figure below shows a network made up of three LANs separated by three bridges. Each
segment uses at most two paths to communicate with the other segments. Since this configuration
can give rise to loops, the network will overload if STP is not enabled.
If STP is enabled, it will detect duplicate paths and prevent, or block, one of them from forwarding
traffic. In the following example, STP determined that traffic from LAN segment 2 to LAN
segment 1 should flow through Bridges C and A because this path has a greater bandwidth and is
therefore more efficient.
Page 52

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-36
What happens if a link failure is detected? As shown in next figure, the STP process reconfigures
the network so that traffic from LAN segment 2 flows through Bridge B.
STP will determine which path between each bridged segment is most efficient, and then assign a
specific reference point on the network. When the most efficient path has been identified, the other
paths are blocked. In the above 3 figures, STP first determined that the path through Bridge C was
the most efficient, and as a result, blocked the path through Bridge B. After the failure of Bridge C,
STP re-evaluated the situation and opened the path through Bridge B.
How STP Works
When enabled, STP determines the most appropriate path for traffic through a network. The
method is described below:
STP Requirements
Before STP can configure the network, the system must satisfy the following requirements:
y Communication must be established between all bridges. This communication is carried out
using Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs), which are transmitted in packets with a known
multicast address.
Page 53

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-37
y Each bridge must have a Bridge Identifier that specifies which bridge acts as the central
reference point, or Root Bridge, for the STP system. Bridges with a lower Bridge Identifier
are more likely to be designated as the Root Bridge. The Bridge Identifier is calculated using
the MAC address of the bridge and a priority defined for the bridge. The default priority of
PT-7828 is 32768.
y Each port has a cost that specifies the efficiency of each link. The efficiency cost is usually
determined by the bandwidth of the link, with less efficient links assigned a higher cost. The
following table shows the default port costs for a switch:
Port Speed Path Cost 802.1D,
1998 Edition
Path Cost
802.1w-2001
10 Mbps 100 2,000,000
100 Mbps 19 200,000
1000 Mbps 4 20,000
STP Calculation
The first step of the STP process is to perform calculations. During this stage, each bridge on the
network transmits BPDUs. The following items will then be calculated:
y The bridge that will act as the Root Bridge. The Root Bridge is the central reference point
from which the network is configured.
y The Root Path Costs for each bridge. This is the cost of the paths from each bridge to the Root
Bridge.
y The identity of each bridge’s Root Port. The Root Port is the port on the bridge that connects
to the Root Bridge via the most efficient path. In other words, this port connects to the Root
Bridge via the path with the lowest Root Path Cost. The Root Bridge itself does not have a
Root Port.
y The identity of the Designated Bridge for each LAN segment. The Designated Bridge is the
bridge with the lowest Root Path Cost from that segment. If several bridges have the same
Root Path Cost, the one with the lowest Bridge Identifier becomes the Designated Bridge.
Traffic transmitted in the direction of the Root Bridge will flow through the Designated
Bridge. The port on this bridge that connects to the segment is called the Designated Bridge
Port.
STP Configuration
After all the bridges on the network agree on the identity of the Root Bridge and all relevant
parameters have been established, each bridge is configured to forward traffic only between its
Root Port and the Designated Bridge Ports for their respective network segments. All other ports
are blocked, which means that they will not be allowed to receive or forward traffic.
STP Reconfiguration
Once the network topology has stabilized, each bridge listens for "Hello" BPDUs that are
transmitted from the Root Bridge at regular intervals. If a bridge does not receive a "Hello" BPDU
after a certain interval (the Max Age time), the bridge assumes that the Root Bridge, or a link
between itself and the Root Bridge, has gone down. This will trigger the bridge to reconfigure the
network to account for the change. If you have configured an SNMP trap destination, the first
bridge to detect a topology change in your network sends out an SNMP trap.
Differences between RSTP and STP
RSTP is similar to STP, but includes additional information in the BPDUs that allow each bridge
to confirm that it has taken action to prevent loops from forming when it decides to enable a link
to a neighboring bridge. Adjacent bridges connected via point-to-point links will be able to enable
a link without waiting to ensure that all other bridges in the network have had time to react to the
Page 54

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-38
change. The main benefit of RSTP is that the configuration decision is made locally rather than
network-wide, allowing RSTP can carry out automatic configuration and restore a link faster than
STP.
STP Example
The LAN shown below has three segments, with adjacent segments connected using two possible
links. The various STP factors, such as Cost, Root Port, Designated Bridge Port, and Blocked Port
are shown in the figure.
y Bridge A has been selected as the Root Bridge, since it was determined to have the lowest
Bridge Identifier on the network.
y Since Bridge A is the Root Bridge, it is also the Designated Bridge for LAN segment 1. Port 1
on Bridge A is selected as the Designated Bridge Port for LAN Segment 1.
y Ports 1 of Bridges B, C, X, and Y are all Root Ports sine they are nearest to the Root Bridge,
and therefore have the most efficient path.
y Bridges B and X offer the same Root Path Cost for LAN segment 2. However, Bridge B was
selected as the Designated Bridge for that segment since it has a lower Bridge Identifier. Port
2 on Bridge B is selected as the Designated Bridge Port for LAN Segment 2.
y Bridge C is the Designated Bridge for LAN segment 3, because it has the lowest Root Path
Cost for LAN Segment 3:
y The route through Bridges C and B costs 200 (C to B=100, B to A=100)
y The route through Bridges Y and B costs 300 (Y to B=200, B to A=100)
y The Designated Bridge Port for LAN Segment 3 is Port 2 on Bridge C.
Page 55

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-39
Using STP on a Network with Multiple VLANs
IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition, does not take into account VLANs when calculating STP
information—the calculations only depend on the physical connections. Consequently, some
network configurations will result in VLANs being subdivided into a number of isolated sections
by the STP system. You must ensure that every VLAN configuration on your network takes into
account the expected STP topology and alternative topologies that may result from link failures.
The following figure shows an example of a network that contains VLANs 1 and 2. The VLANs
are connected using the 802.1Q-tagged link between Switch B and Switch C. By default, this link
has a port cost of 100 and is automatically blocked because the other Switch-to-Switch
connections have a port cost of 36 (18+18). This means that both VLANs are now
subdivided—VLAN 1 on Switch units A and B cannot communicate with VLAN 1 on Switch C,
and VLAN 2 on Switch units A and C cannot communicate with VLAN 2 on Switch B.
Block
802.1Q tagged,
10BaseTx
half-duplex Link
camies VLAN1, 2
(path cost = 100)
100BaseTX
full-duplex Link;
only carries VLAN1
(path cost =18)
100BaseTX
full-duplex Link;
only carries VLAN2
(path cost =18)
LNK/ACTSPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTERCOUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3
7
4 8
2
6
1
5
3
7
482 6
1
5
4
3
2
1
3
7
4826
1
5
M1
M2
M3
M4
LNK/ACTSPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTERCOUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3 7
4 82
6
1
5
3
7
4 82 6
1
5
4
32
1
3 7
4
826
1 5
M1
M2
M3
M4
1
2
3
45678
M3
PT-7728
M4
1
2
3
4
4
1
3
2
1
3
5
24
6
M1
TXRXTX
RX TX
RX
24
6
13
5
M2
TX
RX TX RX TX RX
LNK/ACTSPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTERCOUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3
7
4 8
2
6
1
5
3
7
482 6
1
5
4
3
2
1
3
7
4826
1
5
M1
M2
M3
M4
LNK/ACTSPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTERCOUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3 7
4 82
6
1
5
3
7
4 82 6
1
5
4
32
1
3 7
4
826
1 5
M1
M2
M3
M4
1
2
3
45678
M3
PT-7728
M4
1
2
3
4
4
1
3
2
1
3
5
24
6
M1
TXRXTX
RX TX
RX
24
6
13
5
M2
TX
RX TX RX TX RX
LNK/ACTSPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTERCOUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3
7
4 8
2
6
1
5
3
7
482 6
1
5
4
3
2
1
3
7
4826
1
5
M1
M2
M3
M4
LNK/ACTSPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTERCOUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3 7
4 82
6
1
5
3
7
4 82 6
1
5
4
32
1
3 7
4
826
1 5
M1
M2
M3
M4
1
2
3
45678
M3
PT-7728
M4
1
2
3
4
4
1
3
2
1
3
5
24
6
M1
TXRXTX
RX TX
RX
24
6
13
5
M2
TX
RX TX RX TX RX
To avoid subdividing VLANs, all inter-switch connections should be made members of all
available 802.1Q VLANs. This will ensure connectivity at all times. For example, the connections
between Switches A and B, and between Switches A and C should be 802.1Q tagged and carrying
VLANs 1 and 2 to ensure connectivity.
See the Configuring Virtual LANs section for more information about VLAN Tagging.
Page 56

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-40
Configuring STP/RSTP
The following figures indicate which Spanning Tree Protocol parameters can be configured. A
more detailed explanation of each parameter is given below the figure.
At the top of this page, the user can check the Current Status of this function. For RSTP, you will
see:
Now Active:
This field shows which communication protocol is being used—Turbo Ring, RSTP, or neither.
Root/Not Root
This field appears only for RSTP mode. It indicates whether or not this PT-7828 is the Root of the
Spanning Tree (the root is determined automatically).
At the bottom of this page, the user can configure the Settings for the selected protocol. For RSTP,
you can configure:
Protocol of Redundancy
Setting Description Factory Default
Turbo Ring This selects the Turbo Ring protocol. None
RSTP (IEEE 802.1W/1D) This selects the RSTP protocol. None
Bridge Priority
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value selected
by user
This specifies the PT-7828's bridge priority. A
lower number means a higher priority, which
means a greater chance of being established as
the root of the Spanning Tree topology.
32768
Forwarding Delay
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value input by
user
This specifies the amount of time this device
will wait before checking to see if it should
change to a different state.
15 (sec.)
Page 57

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-41
Hello Time (sec.)
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value input by
user
This specifies the time interval between "hello"
messages broadcast by the root of the Spanning
Tree topology. The "hello" message is used to
check if the topology is healthy.
2
Max. Age (sec.)
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value input by
user
This specifies the amount of time to wait for a
"hello" message from the root before the
PT-7828 will reconfigure itself as a root. When
two or more devices on the network are
recognized as a root, the devices will
renegotiate to set up a new Spanning Tree
topology.
20
Enable STP per Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This includes the selected port as a node on the
Spanning Tree topology.
Disabled
NOTE
We suggest that you disable the Spanning Tree Protocol for ports that are connected directly to a
device (PLC, RTU, etc.) as opposed to network equipment. This will prevent unnecessary
negotiation.
Port Priority
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value selected
by user
This specifies the port’s priority as a node on
the Spanning Tree topology. Lower values
correspond to higher priority.
128
Port Cost
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value input by
user
This specifies the port cost. Higher costs
correspond to lower suitability as a node for the
Spanning Tree topology.
200000
Port Status
Indicates the current Spanning Tree status of this port. Forwarding indicates normal transmission
and Blocking indicates blocked transmission.
Configuration Limits of RSTP/STP
The Spanning Tree Algorithm places limits on three of the configuration items:
[Eq. 1]: 1 sec Hello Time 10 sec≦≦
[Eq. 2]: 6 sec Max. Age 40 sec≦≦
[Eq. 3]: 4 sec Forwarding Delay 30 sec≦≦
These three variables are further restricted by the following two inequalities:
Page 58

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-42
[Eq. 4]: 2 * (Hello Time + 1 sec) Max. Age 2 * (Forwardin≦≦ g Delay – 1 sec)
The PT-7828’s firmware will alert you immediately if any of these restrictions are violated. For
example, suppose Hello Time = 5 sec, Max. Age = 20 sec, and Forwarding Delay = 4 sec. This
does not violate Eqs. 1 through 3, but it violates Eq. 4:
2 * (Hello Time + 1 sec) = 12 sec, and 2 * (Forwarding Delay – 1 sec) = 6 sec.
You can remedy the situation in any number of ways. One solution is simply to increase the
Forwarding Delay value to at least 11 seconds.
HINT: Take the following steps to avoid guessing:
Step 1: Assign a value to “Hello Time” and then calculate the left most part of Eq. 4 to get the
lower limit of Max. Age.
Step 2: Assign a value to “Forwarding Delay” and then calculate the right most part of Eq. 4 to
get the upper limit for Max. Age.
Step 3: Assign a value to Forwarding Delay that satisfies the conditions in Eq. 3 and Eq. 4.
Using Traffic Prioritization
The PT-7828’s traffic prioritization capability provides Quality of Service (QoS) to your network
by making data delivery more reliable. You can prioritize traffic on your network to ensure that
high priority data is transmitted with minimum delay. Traffic can be controlled by a set of rules to
obtain the required Quality of Service for your network. The rules define different types of traffic
and specify how each type should be treated as it passes through the switch. The PT-7828 can
inspect both IEEE 802.1p/1Q layer 2 CoS tags, and even layer 3 TOS information to provide
consistent classification of the entire network. The PT-7828’s QoS capability improves the
performance and determinism of industrial networks for mission critical applications.
The Traffic Prioritization Concept
What is Traffic Prioritization?
Traffic prioritization allows you to prioritize data so that time-sensitive and system-critical data
can be transferred smoothly and with minimal delay over a network. The benefits of using traffic
prioritization are:
y Improve network performance by controlling a wide variety of traffic and managing
congestion.
y Assign priorities to different categories of traffic. For example, set higher priorities for
time-critical or business-critical applications.
y Provide predictable throughput for multimedia applications, such as video conferencing or
voice over IP, and minimize traffic delay and jitter.
y Improve network performance as the amount of traffic grows. This will save cost by reducing
the need to keep adding bandwidth to the network.
How Traffic Prioritization Works
Traffic prioritization uses the four traffic queues that are present in your PT-7828 to ensure that
high priority traffic is forwarded on a different queue from lower priority traffic. This is what
provides Quality of Service (QoS) to your network.
The PT-7828 traffic prioritization depends on two industry-standard methods:
y IEEE 802.1D—a layer 2 marking scheme.
Page 59

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-43
y Differentiated Services (DiffServ)—a layer 3 marking scheme.
IEEE 802.1D Traffic Marking
The IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition marking scheme, which is an enhancement to IEEE Std
802.1D, enables Quality of Service on the LAN. Traffic service levels are defined in the IEEE
802.1Q 4-byte tag, which is used to carry VLAN identification as well as IEEE 802.1p priority
information. The 4-byte tag immediately follows the destination MAC address and Source MAC
address.
The IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition priority marking scheme assigns an IEEE 802.1p priority
level between 0 and 7 to each frame. This determines the level of service that that type of traffic
should receive. Refer to the table below for an example of how different traffic types can be
mapped to the eight IEEE 802.1p priority levels.
IEEE 802.1p Priority Level IEEE 802.1D Traffic Type
0 Best Effort (default)
1 Background
2 Standard (spare)
3 Excellent Effort (business critical)
4 Controlled Load (streaming multimedia)
5 Video (interactive media); less than 100 milliseconds
of latency and jitter
6 Voice (interactive voice); less than 10 milliseconds of
latency and jitter
7 Network Control Reserved traffic
Even though the IEEE 802.1D standard is the most widely used prioritization scheme in the LAN
environment, it still has some restrictions:
y It requires an additional 4-byte tag in the frame, which is normally optional in Ethernet
networks. Without this tag, the scheme cannot work.
y The tag is part of the IEEE 802.1Q header, so to implement QoS at layer 2, the entire network
must implement IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging.
It is only supported on a LAN and not across routed WAN links, since the IEEE 802.1Q tags are
removed when the packets pass through a router.
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) Traffic Marking
DiffServ is a Layer 3 marking scheme that uses the DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) field in the IP
header to store the packet priority information. DSCP is an advanced intelligent method of traffic
marking because you can choose how your network prioritizes different types of traffic. DSCP
uses 64 values that map to user-defined service levels, allowing you to establish more control over
network traffic.
Advantages of DiffServ over IEEE 802.1D are:
y Configure how you want your switch to treat selected applications and types of traffic by
assigning various grades of network service to them.
y No extra tags are required in the packet.
y DSCP uses the IP header of a packet and therefore priority is preserved across the Internet.
y DSCP is backward compatible with IPV4 TOS, which allows operation with existing devices
that use a layer 3 TOS enabled prioritization scheme.
Traffic Prioritization
The PT-7828 classifies traffic based on layer 2 of the OSI 7 layer model, and the switch prioritizes
Page 60

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-44
received traffic according to the priority information defined in the received packet. Incoming
traffic is classified based upon the IEEE 802.1D frame and is assigned to the appropriate priority
queue based on the IEEE 802.1p service level value defined in that packet. Service level markings
(values) are defined in the IEEE 802.1Q 4-byte tag, and consequently traffic will only contain
802.1p priority markings if the network is configured with VLANs and VLAN tagging. The traffic
flow through the switch is as follows:
y A packet received by the PT-7828 may or may not have an 802.1p tag associated with it. If
it does not, then it is given a default 802.1p tag (which is usually 0). Alternatively, the
packet may be marked with a new 802.1p value, which will result in all knowledge of the
old 802.1p tag being lost.
y Because the 802.1p priority levels are fixed to the traffic queues, the packet will be placed
in the appropriate priority queue, ready for transmission through the appropriate egress
port. When the packet reaches the head of its queue and is about to be transmitted, the
device determines whether or not the egress port is tagged for that VLAN. If it is, then the
new 802.1p tag is used in the extended 802.1D header.
The PT-7828 will check a packet received at the ingress port for IEEE 802.1D traffic classification,
and then prioritize it based upon the IEEE 802.1p value (service levels) in that tag. It is this 802.1p
value that determines which traffic queue the packet is mapped to.
Traffic Queues
The PT-7828 hardware has multiple traffic queues that allow packet prioritization to occur. Higher
priority traffic can pass through the PT-7828 without being delayed by lower priority traffic. As
each packet arrives in the PT-7828, it passes through any ingress processing (which includes
classification, marking/re-marking), and is then sorted into the appropriate queue. The switch then
forwards packets from each queue.
The PT-7828 supports two different queuing mechanisms:
y Weight Fair: This method services all the traffic queues, giving priority to the higher priority
queues. Under most circumstances, this method gives high priority precedence over
low-priority, but in the event that high-priority traffic except the link capacity, lower priority
traffic is not blocked.
y Strict: This method services high traffic queues first; low priority queues are delayed until no
more high priority data nePT to be sent. This method always gives precedence to high priority
over low-priority.
Page 61

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-45
Configuring Traffic Prioritization
Quality of Service (QoS) provides a traffic prioritization capability to ensure that important data is
delivered consistently and predictably. The PT-7828 can inspect IEEE 802.1p/1Q layer 2 CoS tags,
and even layer 3 TOS information, to provide a consistent classification of the entire network. The
PT-7828’ QoS capability improves your industrial network’s performance and determinism for
mission critical applications.
QoS Classification
The PT-7828 supports inspection of layer 3 TOS and/or layer 2 CoS tag information to determine
how to classify traffic packets.
Queuing Mechanism
Setting Description Factory Default
Weight Fair PT-7828 has 4 priority queues. In the weight fair
scheme, an 8, 4, 2, 1 weighting is applied to the four
priorities. This approach prevents the lower priority
frames from being starved of opportunity for
transmission with only a slight delay to the higher
priority frames.
Weight Fair
Strict In the Strict-priority scheme, all top-priority frames
egress a port until that priority’s queue is empty, and
then the next lower priority queue’s frames egress. This
approach can cause the lower priorities to be starved of
opportunity for transmitting any frames but ensures all
high priority frames to egress the switch as soon as
possible.
Inspect TOS
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables the PT-7828 to inspect the Type
of Service (TOS) bits in IPV4 frame to determine the
priority of each frame.
Enable
Page 62

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-46
Inspect COS
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables the PT-7828 to inspect the
802.1p COS tag in the MAC frame to determine the
priority of each frame.
Enable
CoS Mapping
Setting Description Factory
Low/Normal/
Medium/High
This maps different CoS values to 4 different egress
queues.
0: Low
1: Low
2: Normal
3: Normal
4: Medium
5: Medium
6: High
7: High
TOS/DiffServ Mapping
Page 63

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-47
Setting Description Factory Default
Low/Normal/
Medium/High
This maps different TOS values to 4 different egress
queues.
1 to 16: Low
17 to 32: Normal
33 to 48: Medium
49 to 64: High
Using Virtual LAN
Setting up Virtual LANs (VLANs) on your PT-7828 increases the efficiency of your network by
dividing the LAN into logical segments, as opposed to physical segments. In general, VLANs are
easier to manage.
The Virtual LAN (VLAN) Concept
What is a VLAN?
A VLAN is a group of devices that can be located anywhere on a network, but which
communicate as if they are on the same physical segment. With VLANs, you can segment your
network without being restricted by physical connections—a limitation of traditional network
design. As an example, with VLANs you can segment your network according to:
y Departmental groups—You could have one VLAN for the marketing department, another
for the finance department, and another for the product development department.
y Hierarchical groups—You could have one VLAN for directors, another for managers, and
another for general staff.
y Usage groups—You could have one VLAN for email users and another for multimedia users.
Benefits of VLANs
The main benefit of VLANs is that they provide a network segmentation system that is far more
flexible than traditional networks. Using VLANs also provides you with three other benefits:
y VLANs ease the relocation of devices on networks. With traditional networks, network
administrators spend much of their time dealing with moves and changes. If users move to a
different subnetwork, the addresses of each host must be updated manually. With a VLAN
setup, if a host on VLAN Marketing, for example, is moved to a port in another part of the
Page 64

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-48
network, and retains its original subnet membership, you only need to specify that the new
port is on VLAN Marketing. You do not need to carry out any re-cabling.
y VLANs provide extra security. Devices within each VLAN can only communicate with
other devices on the same VLAN. If a device on VLAN Marketing nePT to communicate with
devices on VLAN Finance, the traffic must pass through a routing device or Layer 3 switch.
y VLANs help control traffic. With traditional networks, congestion can be caused by
broadcast traffic that is directed to all network devices, regardless of whether or not they need
it. VLANs increase the efficiency of your network because each VLAN can be set up to
contain only those devices that need to communicate with each other.
VLANs and the PowerTrans
Your PT-7828 provides support for VLANs using IEEE Std 802.1Q-1998. This standard allows
traffic from multiple VLANs to be carried across one physical link. The IEEE Std 802.1Q-1998
standard allows each port on your PT-7828 to be placed as follows:
y In a single VLAN defined on the PT-7828
y In several VLANs simultaneously using 802.1Q tagging
The standard requires that you define the 802.1Q VLAN ID about each VLAN on your PT-7828
before the switch can use it to forward traffic:
Managing a VLAN
A new or initialized PT-7828 contains a single VLAN—the Default VLAN. This VLAN has the
following definition:
y VLAN Name—Management VLAN
y 802.1Q VLAN ID—1 (if tagging is required)
All the ports are initially placed in this VLAN, and it is the only VLAN that allows you to access
the management software of the PT-7828 over the network.
Communication between VLANs
If devices connected to a VLAN need to communicate to devices on a different VLAN, a router or
Layer 3 switching device with connections to both VLANs needs to be installed. Communication
between VLANs can only take place if they are all connected to a routing or Layer 3 switching
device.
VLANs: Tagged and Untagged Membership
The PT-7828 supports 802.1Q VLAN tagging, a system that allows traffic for multiple VLANs to
be carried on a single physical (backbone, trunk) link. When setting up VLANs you need to
understand when to use untagged and tagged membership of VLANs. Simply put, if a port is on a
single VLAN it can be an untagged member, but if the port needs to be a member of multiple
VLANs, tagged membership must be defined.
A typical host (e.g., clients) will be untagged members of one VLAN, defined as Access Port in
PT-7828, while inter-switch connections will be tagged members of all VLANs, defined as Trunk
Port in PT-7828.
The IEEE Std 802.1Q-1998 defines how VLANs operate within an open packet-switched network.
An 802.1Q compliant packet carries additional information that allows a switch to determine
which VLAN the port belongs to. If a frame is carrying the additional information, it is known as a
tagged frame.
To carry multiple VLANs across a single physical (backbone, trunk) link, each packet must be
Page 65

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-49
tagged with a VLAN identifier so that the switches can identify which packets belong in which
VLAN. To communicate between VLANs, a router must be used.
The PT-7828 supports two types of VLAN port settings:
y Access Port: The port connects to a single device that is not tagged. The user must define the
default port PVID that assigns which VLAN the device belongs to. Once the ingress packet of
this Access Port egresses to another Trunk Port (the port nePT all packets to carry tag
information), PT-7828 will insert this PVID into this packet to help the next 802.1Q VLAN
switch recognize it.
y Trunk Port: The port connects to a LAN that consists of untagged devices/tagged devices
and/or switches and hubs. In general, the traffic of the Trunk Port must have a Tag. Users can
also assign PVID to a Trunk Port. The untagged packet on the Trunk Port will be assigned the
port default PVID as its VID.
The following section illustrates how to use these ports to set up different applications.
Sample Applications of VLANs using PT-7828
In this application,
y Port 1 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 5; it should be configured as
Access Port with PVID 5.
y Port 2 connects a LAN with two untagged devices belonging to VLAN 2. One tagged device
with VID 3 and one tagged device with VID 4. It should be configured as Trunk Port with
PVID 2 for untagged device and Fixed VLAN (Tagged) with 3 and 4 for tagged device. Since
each port can only have one unique PVID, all untagged devices on the same port can only
belong to the same VLAN.
y Port 3 connects with another switch. It should be configured as Trunk Port GVRP protocol
will be used through the Trunk Port.
y Port 4 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 2; it should be configured as
Access Port with PVID 2.
y Port 5 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 3; it should be configured as
Access Port with PVID 3.
y Port 6 connect a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 5; it should be configured as
Page 66

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-50
Access Port with PVID 5.
y Port 7 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 4; it should be configured as
Access Port with PVID 4.
After proper configuration:
y Packets from Device A will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 5. Switch B will
recognize its VLAN, pass it to port 6, and then remove tags received successfully by Device G,
and vice versa.
y Packets from Devices B and C will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 2. Switch B
recognizes its VLAN, passes it to port 4, and then removes tags received successfully by
Device F, and vice versa.
y Packets from Device D will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 3. Switch B will
recognize its VLAN, pass to port 5, and then remove tags received successfully by Device H.
Packets from Device H will travel through Trunk Port 3 with PVID 3. Switch A will
recognize its VLAN and pass it to port 2, but will not remove tags received successfully by
Device D.
y Packets from Device E will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 4. Switch B will
recognize its VLAN, pass it to port 7, and then remove tags received successfully by Device I.
Packets from Device I will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 4. Switch A will
recognize its VLAN and pass it to port 2, but will not remove tags received successfully by
Device E.
Configuring Virtual LAN
VLAN Settings
To configure 802.1Q VLAN on the PT-7828, use the VLAN Setting page to configure the ports.
Management VLAN ID
Setting Description Factory Default
VLAN ID from 1
to 4094
This assigns the VLAN ID of this PT-7828. 1
Page 67

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-51
Port Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Access This port type is used to connect single devices without
tags.
Access
Trunk Select Trunk port type to connect another 802.1Q
VLAN aware switch or another LAN that combines
tagged and/or untagged devices and/or other
switches/hubs.
ATTENTION
For communication redundancy in the VLAN environment, set Redundant Port Coupling Port
and Coupling Control Port as Trunk Port since these ports act as the backbone to transmit all
packets of different VLANs to different PT-7828 units.
Port PVID
Setting Description Factory Default
VID range from 1
to 4094
This sets the default VLAN ID for untagged devices that
connect to the port.
1
Fixed VLAN List (Tagged)
Setting Description Factory Default
VID range from 1
to 4094
This field will be active only when selecting the Trunk
port type. Set the other VLAN ID for tagged devices that
connect to the Trunk port. Use commas to separate
different VIDs.
None
Forbidden VLAN List
Setting Description Factory Default
VID range from 1
to 4094
This field will be active only when selecting the Trunk
port type. Set the VLAN IDs that will not be supported
by this trunk port. Use commas to separate different
VIDs.
None
VLAN Table
In 802.1Q VLAN table, you can review the VLAN groups that were created, Joined Access Ports,
and Trunk Ports, and in Port-based VLAN table, you can review the VLAN group and Joined port.
Page 68

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-52
NOTE
The physical network can have a maximum of 64 VLAN settings.
Using Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering improves the performance of networks that carry multicast traffic. This section
explains multicasts, multicast filtering, and how multicast filtering can be implemented on your
PT-7828.
The Concept of Multicast Filtering
What is an IP Multicast?
A multicast is a packet sent by one host to multiple hosts. Only those hosts that belong to a
specific multicast group will receive the multicast. If the network is set up correctly, a multicast
can only be sent to an end-station or a subset of end-stations on a LAN or VLAN that belong to the
multicast group. Multicast group members can be distributed across multiple subnets, so that
multicast transmissions can occur within a campus LAN or over a WAN. In addition, networks
that support IP multicast send only one copy of the desired information across the network until
the delivery path that reaches group members diverges. To make more efficient use of network
bandwidth, it is only at these points that multicast packets are duplicated and forwarded. A
multicast packet has a multicast group address in the destination address field of the packet’s IP
header.
Benefits of Multicast
The benefits of using IP multicast are that it:
y Uses the most efficient, sensible method to deliver the same information to many receivers
with only one transmission.
y Reduces the load on the source (for example, a server) since it will not need to produce
several copies of the same data.
y Makes efficient use of network bandwidth and scales well as the number of multicast group
members increases.
y Works with other IP protocols and services, such as Quality of Service (QoS).
Multicast transmission makes more sense and is more efficient than unicast transmission for some
applications. For example, multicasts are often used for video-conferencing, since high volumes of
traffic must be sent to several end-stations at the same time, but where broadcasting the traffic to
all end-stations would cause a substantial reduction in network performance. Furthermore, several
industrial automation protocols, such as Allen-Bradley, EtherNet/IP, Siemens Profibus, and
Foundation Fieldbus HSE (High Speed Ethernet), use multicast. These industrial Ethernet
protocols use publisher/subscriber communications models by multicasting packets that could
flood a network with heavy traffic. IGMP Snooping is used to prune multicast traffic so that it
travels only to those end destinations that require the traffic, reducing the amount of traffic on the
Ethernet LAN.
Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering ensures that only end-stations that have joined certain groups receive multicast
traffic. With multicast filtering, network devices only forward multicast traffic to the ports that are
connected to registered end-stations. The following two figures illustrate how a network behaves
without multicast filtering, and with multicast filtering.
Page 69

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-53
Network without multicast filtering
LNK/ACT SPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTER COUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3
7
4 8
2
6
1
5
3
7
482 6
1
5
4
3
2
1
3
7
4826
1
5
M1
M2
M3
M4
LNK/ACT SPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTER COUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3 7
4 82
6
1
5
3
7
4 82 6
1
5
4
32
1
3 7
4
826
1 5
M1
M2
M3
M4
1
2
3
45678
M3
PT-7728
M4
1
2
3
4
4
1
3
2
1
3
5
24
6
M1
TXRXTX
RX TX
RX
24
6
13
5
M2
TX
RX TX RX TX RX
All hosts receive the multicast traffic, even if they don’t need it.
Network with multicast filtering
IGMP Group2
Group 1 Multicast Stream Group 2 Multicast Stream
IGMP Group1 IGMP Group2 IGMP Group1
LNK/ACT SPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTER COUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3
7
4 8
2
6
1
5
3
7
482 6
1
5
4
3
2
1
3
7
4826
1
5
M1
M2
M3
M4
LNK/ACT SPEED FDX/HDX
FAULT MASTER COUPLER
STAT PWR1 PWR2
RING PORT
COUPLER
PORT
MODE
3 7
4 82
6
1
5
3
7
4 82 6
1
5
4
32
1
3 7
4
826
1 5
M1
M2
M3
M4
1
2
3
45678
M3
PT-7728
M4
1
2
3
4
4
1
3
2
1
3
5
24
6
M1
TXRXTX
RX TX
RX
24
6
13
5
M2
TX
RX TX RX TX RX
Hosts only receive dedicated traffic from other hosts belonging to the same group.
Multicast Filtering and Moxa PowerTrans Switch
The PT-7828 has three ways to achieve multicast filtering: IGMP (Internet Group Management
Protocol) Snooping, GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol), and adding a static multicast
MAC manually to filter multicast traffic automatically.
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
Snooping Mode
Snooping Mode allows your switch to forward multicast packets only to the appropriate ports. The
switch snoops on exchanges between hosts and an IGMP device, such as a router, to find those
ports that want to join a multicast group, and then configures its filters accordingly.
Page 70

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-54
Query Mode
Query mode allows the PT-7828 to work as the Querier if it has the lowest IP address on the
subnetwork to which it belongs. IGMP querying is enabled by default on the PT-7828 to help
prevent interoperability issues with some multicast routers that may not follow the lowest IP
address election method. Enable query mode to run multicast sessions on a network that does not
contain IGMP routers (or queriers).
NOTE
PT-7828 is compatible with any device that conforms to the IGMP v2 and IGMP v3 device
protocol.
IGMP Multicast Filtering
IGMP is used by IP-supporting network devices to register hosts with multicast groups. It can be
used on all LANs and VLANs that contain a multicast capable IP router, and on other network
devices that support multicast filtering. IGMP works as follows:
1. The IP router (or querier) periodically sends query packets to all end-stations on the LANs or
VLANs that are connected to it. For networks with more than one IP router, the router with
the lowest IP address is the querier. A switch with IP address lower than the IP address of any
other IGMP queriers connected to the LAN or VLAN can become the IGMP querier.
2. When an IP host receives a query packet, it sends a report packet back that identifies the
multicast group that the end-station would like to join.
3. When the report packet arrives at a port on a switch with IGMP Snooping enabled, the switch
knows that the port should forward traffic for the multicast group, and then proceeds to
forward the packet to the router.
4. When the router receives the report packet, it registers that the LAN or VLAN requires traffic
for the multicast groups.
5. When the router forwards traffic for the multicast group to the LAN or VLAN, the switches
only forward the traffic to ports that received a report packet.
GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol)
The PT-7828 supports IEEE 802.1D-1998 GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol), which
differs from IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol). GMRP is a MAC-based multicast
management protocol, whereas IGMP is IP-based. GMRP provides a mechanism that allows
bridges and end stations to register or de-register Group membership information dynamically.
GMRP functions similarly to GVRP, except that GMRP registers multicast addresses on ports.
When a port receives a GMRP-join message, it will register the multicast address to its database if
the multicast address is not registered, and all the multicast packets with that multicast address are
able to be forwarded from this port. When a port receives a GMRP-leave message, it will
de-register the multicast address from its database, and all the multicast packets with this multicast
address are not able to be forwarded from this port.
Static Multicast MAC
Some devices may only support multicast packets, but not support either IGMP Snooping or
GMRP. The PT-7828 supports adding multicast groups manually to enable multicast filtering.
Enabling Multicast Filtering
Use the serial console or Web interface to enable or disable IGMP Snooping and IGMP querying.
If IGMP Snooping is not enabled, then IP multicast traffic is always forwarded, flooding the
network.
Page 71

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-55
Configuring IGMP Snooping
IGMP Snooping provides the ability to prune multicast traffic so that it travels only to those end
destinations that require that traffic, thereby reducing the amount of traffic on the Ethernet LAN.
IGMP Snooping Settings
IGMP Snooping Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Click the checkbox to enable the IGMP Snooping
function globally.
Disabled
Query Interval
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value
input by user
This sets the query interval of the Querier function
globally. Valid settings are from 20 to 600 seconds.
125 seconds
IGMP Snooping
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables the IGMP Snooping function
per VLAN.
Enabled if IGMP
Snooping Enabled
Globally
Querier
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables the PT-7828’s querier function. Enabled if IGMP
Snooping is
Enabled Globally
Static Multicast Router Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect This selects the ports that will connect to the multicast
routers. It is active only when IGMP Snooping is
enabled.
Disabled
Page 72

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-56
NOTE
At least one switch must be designated the Querier or enable IGMP snooping and GMRP when
enabling Turbo Ring and IGMP snooping simultaneously.
IGMP Table
The PT-7828 displays the current active IGMP groups that were detected.
The information includes VID, Auto-learned Multicast Router Port, Static Multicast Router
Port, Querier Connected Port, and the IP and MAC addresses of active IGMP groups.
Add Static Multicast MAC
If required, the PT-7828 also supports adding multicast groups manually.
Add New Static Multicast Address to the List
Setting Description Factory Default
MAC Address Input the multicast MAC address of this host. None
MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Integer Input the number of the VLAN that the host with this
MAC address belongs to.
None
Join Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Checkmark the appropriate check boxes to select the
join ports for this multicast group.
None
Page 73

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-57
Configuring GMRP
GMRP is a MAC-based multicast management protocol, whereas IGMP is IP-based. GMRP
provides a mechanism that allows bridges and end stations to register or un-register Group
membership information dynamically.
GMRP enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables the GMRP function for the port
listed in the Port column
Disable
GMRP Table
The PT-7828 displays the current active GMRP groups that were detected
Setting Description
Fixed Ports This multicast address is defined by static multicast.
Learned Ports This multicast address is learned by GMRP.
Page 74

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-58
Using Bandwidth Management
In general, one host should not be allowed to occupy unlimited bandwidth, particularly when the
device malfunctions. For example, so-called “broadcast storms” could be caused by an incorrectly
configured topology, or a malfunctioning device. The PT-7828 not only prevents broadcast storms,
but can also be configured to a different ingress rate for all packets, giving administrators full
control of their limited bandwidth to prevent undesirable effects caused by unpredictable faults.
Broadcast Storm Protection
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables Broadcast Storm Protection for
unknown broadcast packet globally.
Enable
This enables or disables Broadcast Storm Protection for
unknown multicast packets globally.
Disable
Traffic Rate Limiting Settings
Ingress
Setting Description Factory Default
Ingress rate Select the ingress rate for all packets from the following
options: not limited, 3%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 25%, 35%,
50%, 65%, 85%
N/A
Page 75

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-59
Using Port Access Control
The PT-7828 provides two kinds of Port-Base Access Control. One is Static Port Lock and the
other is IEEE 802.1X.
Static Port Lock
The PT-7828 can also be configured to protect static MAC addresses for a specific port. With the
Port Lock function, these locked ports will not learn any additional addresses, but only allow
traffic from preset static MAC addresses, helping to block hackers and careless usage.
IEEE 802.1X
The IEEE 802.1X standard defines a protocol for client/server-based access control and
authentication. The protocol restricts unauthorized clients from connecting to a LAN through ports
that are open to the Internet, and which otherwise would be readily accessible. The purpose of the
authentication server is to check each client that requests access to the port. The client is only
allowed access to the port if the client’s permission is authenticated.
The IEEE 802.1X Concept
Three components are used to create an authentication mechanism based on 802.1X standards:
Client/Supplicant, Authentication Server, and Authenticator.
Supplicant: The end station that requests access to the LAN and switch services and responds to
the requests from the switch.
Authentication server: The server that performs the actual authentication of the supplicant.
Authenticator: Edge switch or wireless access point that acts as a proxy between the supplicant
and the authentication server, requesting identity information from the supplicant, verifying the
information with the authentication server, and relaying a response to the supplicant.
The PT-7828 acts as an authenticator in the 802.1X environment. A supplicant and an
authenticator exchange EAPOL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) frames with each
other. We can either use an external RADIUS server as the authentication server, or implement the
authentication server in PT-7828 by using a Local User Database as the authentication look-up
table. When we use an external RADIUS server as the authentication server, the authenticator and
the authentication server exchange EAP frames between each other.
Authentication can be initiated either by the supplicant or the authenticator. When the supplicant
initiates the authentication process, it sends an EAPOL-Start frame to the authenticator. When the
authenticator initiates the authentication process or when it receives an EAPOL Start frame, it
sends an EAP Reque st/Ide ntity frame to ask for the username of the supplicant.
Page 76

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-60
Configuring Static Port Lock
The PT-7828 supports adding unicast groups manually if required.
Setting Description Factory Default
MAC Address Add the static unicast MAC address into the address
table.
None
Port Fix the static address with a dedicated port. 1-1
Configuring IEEE 802.1X
Database Option
Setting Description Factory Default
Local
(Max. 32 users)
Select this option when setting the Local User Database
as the authentication database.
Local
Radius Select this option to set an external RADIUS server as
the authentication database. The authentication
mechanism is EAP-MD5.
Local
Radius, Local Select this option to make using an external RADIUS
server as the authentication database the second priority.
The authentication mechanism is EAP-MD5 The first
priority is to set the Local User Database as the
authentication database.
Local
Radius Server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address or
domain name
The IP address or domain name of the RADIUS server local host
Page 77

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-61
Server Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical The UDP port of the RADIUS server 1812
Shared Key
Setting Description Factory Default
alphanumeric
(Max. 40
characters)
A key to be shared between the external RADIUS server
and PT-7828. Both ends must be configured to use the
same key.
None
Re-Auth
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Select to require re-authentication of the client after a
preset time period of no activity has elapsed.
Disable
Re-Auth Period
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical
(60 to 65535 sec.)
Specify how frequently the end stations need to reenter
usernames and passwords in order to stay connected.
3600
802.1X
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Click the checkbox under the 802.1X column to enable
IEEE 802.1X for one or more ports. All end stations
must enter usernames and passwords before access to
these ports is allowed.
Disable
802.1X Re-Authentication
The PT-7828 can force connected devices to be re-authorized manually.
802.1X Re-Authentication
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable This enables or disables 802.1X Re-Authentication Disable
Page 78

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-62
Local User Database Setup
When setting the Local User Database as the authentication database, set the database first.
Local User Database Setup
Setting Description Factory Default
User Name
(Max. 30 characters)
User Name for Local User Database None
Password
(Max. 16 characters)
Password for Local User Database None
Description
(Max. 30 characters)
Description for Local User Database None
NOTE
The user name for the Local User Database is case-insensitive.
Port Access Control Table
The port status will show authorized or unauthorized.
Page 79

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-63
Using IP Filter
IP filtering lets users control which IP addresses are allowed to access the port.
Using Auto Warning
Since industrial Ethernet devices are often located at the endpoints of a system, these devices will
not always know what is happening elsewhere on the network. This means that an industrial
Ethernet switch that connects to these devices must provide system maintainers with real-time
alarm messages. Even when control engineers are out of the control room for an extended period
of time, they can still be informed of the status of devices almost instantaneously when exceptions
occur. The PT-7828 supports different approaches to warn engineers automatically, such as email
and relay output. It also supports two digital inputs to integrate sensors into your system to
automate alarms by email and relay output.
Configuring Email Warning
The Auto Email Warning function uses e-mail to alert the user when certain user-configured
events take place.
Three basic steps are required to set up the Auto Warning function:
1. Configuring Email Event Types
Select the desired Event types from the Console or Web Browser Event type page (a
description of each event type is given later in the Email Alarm Events setting subsection).
2. Configuring Email Settings
To configure PT-7828’s email setup from the serial, Telnet, or web console, enter your Mail
Server IP/Name (IP address or name), Account Name, Account Password, Retype New
Password, and the email address to which warning messages will be sent.
3. Activate your settings and if necessary, test the email
After configuring and activating your PT-7828’s Event Types and Email Setup, you can use
the Test Email function to see if your e-mail addresses and mail server address have been
properly configured.
Page 80
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-64
Event Type
Event Types can be divided into two basic groups: System Events and Port Events. System
Events are related to the overall function of the switch, whereas Port Events are related to the
activity of a specific port.
System Events Warning e-mail is sent when…
Switch Cold Start Power is cut off and then reconnected.
Switch Warm Start PT-7828 is rebooted, such as when network
parameters are changed (IP address, subnet mask,
etc.).
Power Transition (OnÆOff) PT-7828 is powered down.
Power Transition (OffÆOn) PT-7828 is powered up.
Configuration Change Activated Any configuration item has been changed.
Authentication Failure An incorrect password is entered.
Comm. Redundancy Topology
Changed
If any Spanning Tree Protocol switches have changed
their position (applies only to the root of the tree).
If the Master of the Turbo Ring has changed or the
backup path is activated.
Port Events Warning e-mail is sent when…
Link-ON The port is connected to another device.
Link-OFF
The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out,
or the opposing device shuts down).
Traffic-Overload
The port’s traffic surpasses the Traffic-Threshold for
that port (provided this item is Enabled).
Traffic-Threshold (%)
Enter a nonzero number if the port’s Traffic-Overload
item is Enabled.
Traffic-Duration (sec.)
A Traffic-Overload warning is sent every
Traffic-Duration seconds if the average
Traffic-Threshold is surpassed during that time
period.
Page 81

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-65
NOTE
The Traffic-Overload, Traffic-Threshold (%), and Traffic-Duration (sec.) Port Event items
are related. If you Enable the Traffic-Overload event, then be sure to enter a nonzero
Traffic-Threshold percentage, as well as a Traffic-Duration between 1 and 300 seconds.
NOTE
Warning e-mail messages will have sender given in the form:
Moxa_PowerTrans_Switch_0001@Switch_Location
where Moxa_PowerTrans_Switch is the default Switch Name, 0001 is PT-7828’s serial number,
and Switch_Location is the default Server Location.
Refer to the Basic Settings section to see how to modify Switch Name and Switch Location.
Email Setup
Mail Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address The IP Address of your email server. None
Account Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 45 Charters Your email account. None
Page 82

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-66
Password Setting
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable/Enable to
change password
To reset the password from the Web Browser interface,
click the Change password check-box, type the Old
password, type the New password, retype the New
password, and then click Activate; Max. 45 characters.
Disable
Old password Type the current password when changing the password None
New password Type new password when enabled to change password;
Max. 45 characters.
None
Retype password If you type a new password in the Password field, you
will be required to retype the password in the Retype
new password field before updating the new password.
None
Email Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30
characters
You can set up to 4 email addresses to receive alarm
emails from PT-7828.
None
Send Test Email
After finishing with the email settings, you should first click Activate to activate those settings,
and then press the Send Test Email button to verify that the settings are correct.
NOTE
Auto warning e-mail messages will be sent through an authentication protected SMTP server that
supports the CRAM-MD5, LOGIN, and PAIN methods of SASL (Simple Authentication and
Security Layer) authentication mechanism.
We strongly recommend not entering your Account Name and Account Password if auto warning
e-mail messages can be delivered without using an authentication mechanism.
Configuring Relay Warning
The Auto Relay Warning function uses relay output to alert the user when certain user-configured
events take place. There are two basic steps required to set up the Relay Warning function:
1. Configuring Relay Event Types
Select the desired Event types from the Console or Web Browser Event type page (a
description of each event type is given later in the Relay Alarm Events setting subsection).
2. Activate your settings
After completing the configuration procedure, you will need to activate your PT-7828’s Relay
Event Types.
Page 83

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-67
Event Setup
Event Types can be divided into two basic groups: System Events and Port Events. System
Events are related to the overall function of the switch, whereas Port Events are related to the
activity of a specific port.
The PT-7828 supports two relay outputs. You can configure which relay output is related to which
events. This helps administrators identify the importance of the different events.
System Events Warni ng Relay output is triggered when…
Power Transition (OnÆOff) PT-7828 is powered on.
Power Transition (OffÆOn) PT-7828 is powered down.
Port Events Warning e-mail is sent when…
Link-ON The port is connected to another device.
Link-OFF
The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out,
or the opposing device shuts down).
Traffic-Overload
The port’s traffic surpasses the Traffic-Threshold for
that port (provided this item is Enabled).
Traffic-Threshold (%)
Enter a nonzero number if the port’s Traffic-Overload
item is Enabled.
Traffic-Duration (sec.)
A Traffic-Overload warning is sent every
Traffic-Duration seconds if the average
Traffic-Threshold is surpassed during that time
period.
NOTE
The Traffic-Overload, Traffic-Threshold (%), and Traffic-Duration (sec) Port Event items
are related. If you Enable the Traffic-Overload event, then be sure to enter a nonzero
Traffic-Threshold percentage, as well as a Traffic-Duration between 1 and 300 seconds.
Page 84

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-68
Override relay alarm settings
Click the checkbox to override the relay warning setting temporarily. Releasing the relay output
will allow administrators to fix any problems with the warning condition.
Warning List
Use this table to see if any relay alarms have been issued.
Using Line-Swap-Fast-Recovery
The Line-Swap Fast Recovery function, which is enabled by default, allows PT-7828 to return to
normal operation extremely quickly after devices are unplugged and then re-plugged into different
ports. The recovery time is on the order of a few milliseconds (compare this with standard
commercial switches for which the recovery time could be on the order of several minutes). To
disable the Line-Swap Fast Recovery function, or to re-enable the function after it has already
been disabled, access either the Console utility’s Line-Swap recovery page, or the Web Browser
interface’s Line-Swap fast recovery page, as shown below.
Configuring Line-Swap Fast Recovery
Enable Line-Swap-Fast-Recovery
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Check-mark the check box to enable the
Line-Swap-Fast-Recovery function
Enable
Using Set Device IP
To reduce the effort required to set up IP addresses, the PT-7828 comes equipped with
DHCP/BootP server and RARP protocol to set up IP addresses of Ethernet-enabled devices
automatically.
When enabled, the Set device IP function allows PT-7828 to assign specific IP addresses
automatically to connected devices that are equipped with DHCP Client or RARP protocol. In
effect, PT-7828 acts as a DHCP server by assigning a connected device with a specific IP address
stored in its internal memory. Each time the connected device is switched on or rebooted, PT-7828
sends the device the desired IP address.
Page 85

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-69
Take the following steps to use the Set device IP function:
STEP 1—Set up the connected devices
Set up those Ethernet-enabled devices connected to
PT-7828 for which you would like IP addresses to be
assigned automatically. The devices must be configured
to obtain their IP address automatically.
The devices’ configuration utility should include a
setup page that allows you to choose an option similar
to Obtain an IP address automatically.
For example, Windows’ TCP/IP Properties window is
shown at the right. Although your device’s
configuration utility may look quite a bit different, this
figure should give you some idea of what to look for.
You also need to decide which of PT-7828’s ports your
Ethernet-enabled devices will be connected to. You
will need to set up each of these ports separately, as
described in the following step.
STEP 2
Configure PT-7828’s Set device IP function, either from the Console utility or from the Web
Browser interface. In either case, you simply need to enter the Desired IP for each port that needs
to be configured.
STEP 3
Be sure to activate your settings before exiting.
• When using the Web Browser interface, activate by clicking on the Activate button.
• When using the Console utility, activate by first highlighting the Activate menu option, and
then press Enter. You should receive the Set device IP settings are now active! (Press any
key to continue) message.
Configuring Set Device IP
Page 86

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-70
Desired IP Address
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address Set the desired IP of connected devices. None
DHCP Relay Agent (Option 82)
The DHCP Relay Agent makes it possible for DHCP broadcast messages to be sent over routers.
The DHCP Relay Agent enables DHCP clients to obtain IP addresses from a DHCP server on a
remote subnet, or those that are not located on the local subnet.
Option 82 is used by the relay agent to insert additional information into the client’s DHCP request.
The Relay Agent Information option is inserted by the DHCP relay agent when forwarding
client-originated DHCP packets to a DHCP server. Servers can recognize the Relay Agent
Information option and use the information to implement IP addresses to Clients.
When Option 82 is enabled on the switch, a subscriber device is identified by the switch port
through which it connects to the network (in addition to its MAC address). Multiple hosts on the
subscriber LAN can be connected to the same port on the access switch and are uniquely
identified.
The Option 82 information contains 2 sub-options: Circuit ID and Remote ID, which define the
relationship between end device IP and the DHCP Option 82 server. The “Circuit ID” is a 4-byte
number generated by the Ethernet switch—a combination of physical port number and VLAN ID.
The format of the “Circuit ID” is as described below:
FF–VV–VV–PP
Where the first byte “FF” is fixed to “01”, the second and the third byte “VV-VV” is formed by
the port VLAN ID in hex, and the last byte “PP” is formed by the port number in hex. For
example,
01–00–0F–03 is the “Circuit ID” of port number 3 with port VLAN ID 15.
The “Remote ID” is to identify the relay agent itself and it can be one of the following:
1. The IP address of the relay agent.
2. The MAC address of the relay agent.
3. A combination of IP address and MAC address of the relay agent.
4. A user-defined string.
Page 87

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-71
Server IP Address
1st Server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for the
1st DHCP server
This assigns the IP address of the 1st DHCP server that
the switch tries to access.
None
2nd Server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for the
2nd DHCP server
This assigns the IP address of the 2nd DHCP server that
the switch tries to access.
None
3rd Server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for the
3rd DHCP server
This assigns the IP address of the 3rd DHCP server that
the switch tries to access.
None
4th Server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for the
4th DHCP server
This assigns the IP address of the 4th DHCP server that
the switch tries to access.
None
Page 88

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-72
DHCP Option 82
Enable Option82
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable or Disable Enable or disable DHCP Option 82 function. Disable
Type
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Use switch IP address as the remote ID sub-option. IP
MAC Use switch MAC address as the remote ID sub-option. IP
Client-ID Use the combination of switch MAC address and IP
address as the remote ID sub-option.
IP
Other Use the user-defined value as the remote ID sub-option. IP
Value
Setting Description Factory Default
Displays the value which you’ve set.
Max. 12
characters
If you set the DHCP Option 82 type as Other, you will
need to set it here.
switch IP address
Display
Setting Description Factory Default
The actual hexdecimal value set at the DHCP server for
the Remote-ID. This value is automatically generated
according to the Value field. Users can not modify it.
COA87FFD
DHCP Function Table
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable or Disable Enable or disable DHCP Option 82 function for this
port.
Disable
Using Diagnosis
The PT-7828 provides two important tools for administrators to diagnose network systems.
Mirror Port
Page 89

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-73
The Mirror port function can be used to monitor data being transmitted through a specific port.
This is done by setting up another port (the mirror port) to receive the same data being transmitted
from, or both to and from, the port under observation. This allows the network administrator to
sniff the observed port and thus keep tabs on network activity.
Take the following steps to set up the Mirror Port function:
STEP 1
Configure PT-7828’s Mirror Port function from either the Console utility or Web Browser
interface. You will need to configure three settings:
Monitored Port
Select the port number of the port whose network activity will be
monitored.
Mirror Port
Select the port number of the port that will be used to monitor the
activity of the monitored port.
Watch Direction
Select one of the following two watch direction options:
y Output data stream
Select this option to monitor only those data packets being sent out
through PT-7828’s port.
y Bi-directional
Select this option to monitor data packets both coming into, and
being sent out through, PT-7828’s port.
STEP 2
Be sure to activate your settings before exiting.
• When using the Web Browser interface, activate by clicking on the Activate button.
• When using the Console utility, activate by first highlighting the Activate menu option, and
then press Enter. You should receive the Mirror port settings are now active! (Press any key
to continue) message.
Ping
The Ping function uses the ping command to give users a simple but powerful tool for
troubleshooting network problems. The function’s most unique feature is that even though the
ping command is entered from the user’s PC keyboard, the actual ping command originates from
PT-7828 itself. In this way, the user can essentially sit on top of PT-7828 and send ping commands
out through its ports.
To use the Ping function, type in the desired IP address, and then press Enter from the Console
utility, or click Ping when using the Web Browser interface.
LLDP Function Overview
Defined by IEEE 802.11AB, LLDP is an OSI Layer 2 Protocol that standardizes the self-identity
advertisement methodology. It allows each networking device, e.g. a Moxa managed switch, to
Page 90
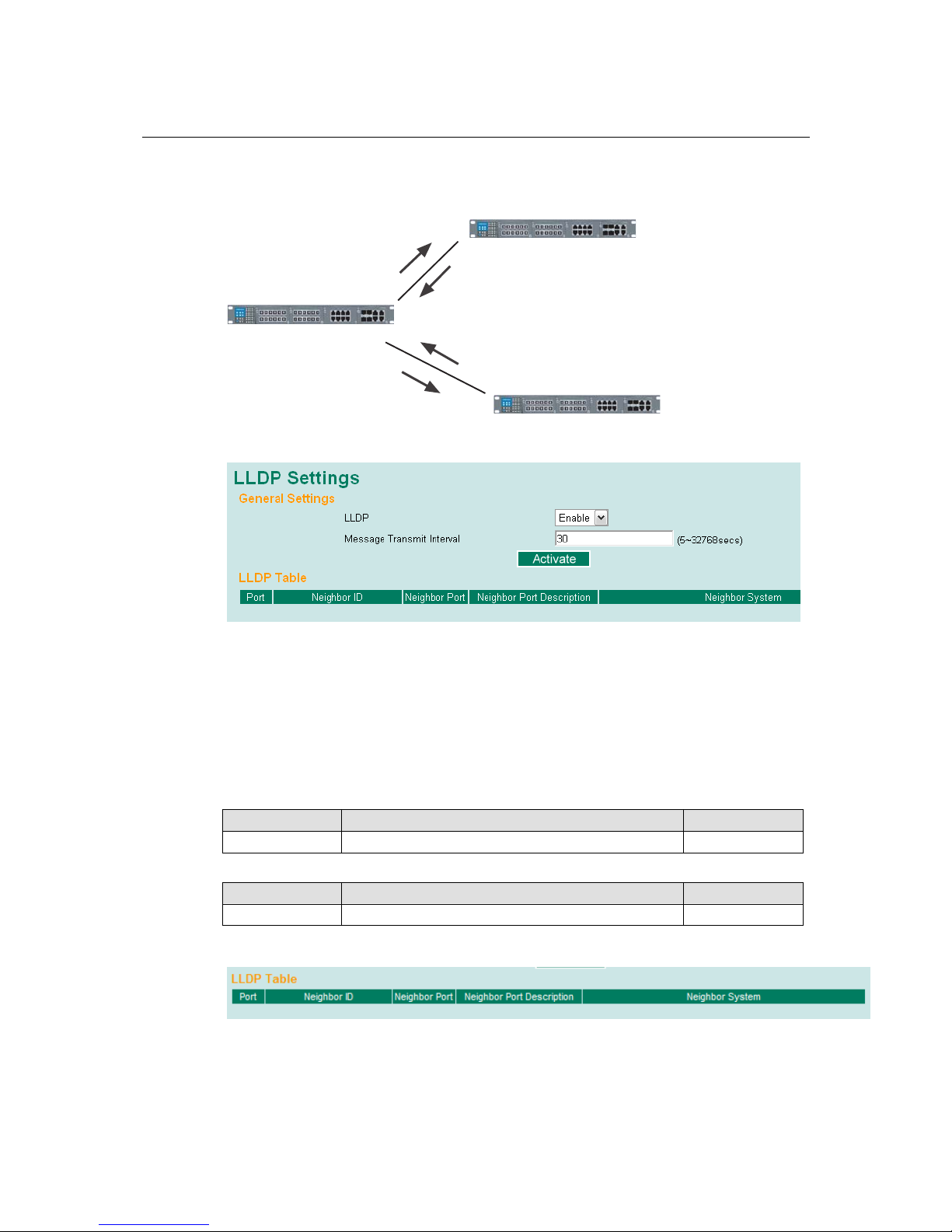
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-74
periodically inform its neighbors about its self-information and configurations. As a result, all of
the devices will have knowledge about each other; and through SNMP, this knowledge can be
transferred to Moxa’s MXview for auto-topology and network visualization.
LLDP Web Interface
From the switch’s web interface, users have the option of either enabling or disabling the LLDP,
as well as setting the LLDP transmit interval (as shown in the figure below). In addition, users are
able to view each switch’s neighbor-list, which is reported by its network neighbors. Most
importantly, enabling the LLDP function allows Moxa’s MXview to automatically display the
network’s topology as well as system setup details such as VLAN, and Trunking for the entire
network.
LLDP Settings
Enable LLDP
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable or Disable Enable or disable LLDP function. Enable
Message Transmit Interva
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address Set the desired IP of connected devices. None
LLDP Table
Port: The port number that connects to the neighbor device.
Neighbor ID: A unique entity which identifies a neighbor device; this is typically the MAC
Page 91

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-75
address.
Neighbor Port: The port number of the neighbor device.
Neighbor Port Description: A textual description of the neighbor device’s interface.
Neighbor System: Hostname of the neighbor device.
Using Monitor
You can monitor statistics in real time from PT-7828’s web console and serial console.
Monitor by Switch
Access the Monitor by selecting System from the left selection bar. Monitor by System allows the
user to view a graph that shows the combined data transmission activity of all of PT-7828’s 18
ports. Click one of the four options—Total Packets, TX Packets, RX Packets, or Error
Packets—to view transmission activity of specific types of packets. Recall that TX Packets are
packets sent out from PT-7828, RX Packets are packets received from connected devices, and
Error Packets are packets that did not pass TCP/IP’s error checking algorithm. The Total Packets
option displays a graph that combines TX, RX, and TX Error, RX Error Packets activity. The
graph displays data transmission activity by showing Packets/s (i.e., packets per second, or pps)
versus sec. (seconds). In fact, three curves are displayed on the same graph: Uni-cast packets (in
red color), Multi-cast packets (in green color), and Broad-cast packets (in blue color). The graph
is updated every few seconds, allowing the user to analyze data transmission activity in real-time.
Monitor by Port
Access the Monitor by Port function by selecting ALL 10/100M or 1G Ports or Port i, in which
i= 1-1, 1-2, …, 4-4, from the left pull-down list. The Port i options are identical to the Monitor by
System function discussed above, in that users can view graphs that show All Packets, TX Packets,
RX Packets, or Error Packets activity, but in this case, only for an individual port.
The All Ports
option is essentially a graphical display of the individual port activity that can be viewed with the
Console Monitor function discussed above. The All Ports option shows three vertical bars for each
port. The height of the bar represents Packets/s for the type of packet, at the instant the bar is
Page 92

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-76
being viewed. That is, as time progresses, the height of the bar moves up or down so that the user
can view the change in the rate of packet transmission. The blue colored bar shows Uni-cast
packets, the red colored bar shows Multi-cast packets, and the orange colored bar shows
Broad-cast packets. The graph is updated every few seconds, allowing the user to analyze data
transmission activity in real-time.
Using the MAC Address Table
This section explains the information provided by PT-7828’s MAC address table.
The MAC Address table can be configured to display the following PT-7828 MAC address
groups.
ALL Select this item to show all PT-7828 MAC addresses
ALL Learned Select this item to show all PT-7828 Learned MAC addresses
ALL Static Lock Select this item to show all PT-7828 Static Lock MAC addresses
ALL Static Select this item to show all PT-7828 Static/Static Lock /Static
Multicast MAC addresses
ALL Static
Multicast
Select this item to show all PT-7828 Static Multicast MAC
addresses
Port x Select this item to show all MAC addresses of dedicated ports
The table will display the following information:
MAC This field shows the MAC address
Type This field shows the type of this MAC address
Port This field shows the port that this MAC address belongs to
Page 93

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-77
Using System Log
Event Log
Bootup This field shows how many times the PT-7828 has been rebooted or cold started.
Date The date is updated based on how the current date is set in the Basic Setting
page.
Time The time is updated based on how the current time is set in the Basic Setting
page.
System
Startup Time
The system startup time related to this event.
Events Events that have occurred.
NOTE
The following events will be record into PT-7828’s Event Log Table.
y Cold start
y War m s t a r t
y Configuration change activated
y Power 1/2 transition (Off Æ On), Power 1/2 transition (On Æ Off)
y Authentication fail
y Topology changed
y Master setting is mismatched
y Port traffic overload
y dot1x Auth Fail
y Port link off / on
Page 94

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-78
Syslog
This function provides the event logs for the syslog server. The function supports 3 configurable
syslog servers and syslog server UDP port numbers. When an event occurs, the event will be sent
as a syslog UDP packet to the specified syslog servers.
Syslog Server 1
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address Enter the IP address of 1st Syslog server used by your
network.
None
Port Destination
(1 to 65535)
Enter the UDP port of 1st Syslog server. 514
Syslog Server 2
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address Enter the IP address of 2nd Syslog server used by your
network.
None
Port Destination
(1 to 65535)
Enter the UDP port of 2nd Syslog server. 514
Syslog Server 3
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address Enter the IP address of 3rd Syslog server used by your
network.
None
Port Destination
(1 to 65535)
Enter the UDP port of 3rd Syslog server. 514
NOTE
The following events will be recorded into the PT-7828’s Event Log table, and will then be
sent to the specified Syslog Server:
y Cold start
y Warm start
y Configuration change activated
y Power 1/2 transition (Off Æ On), Power 1/2 transition (On Æ Off)
y Authentication fail
y Topology changed
y Master setting is mismatched
y Port traffic overload
Page 95

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-79
y dot1x Auth Fail
y Port link off / on
Using HTTPS/SSL
To secure your HTTP access, the PT-7828 supports HTTPS/SSL to encrypt all HTTP traffic.
Perform the following steps to access the PT-7828’s web browser interface via HTTPS/SSL.
1. Open Internet Explorer and type https://PT-7828’s IP address in the address field. Press
Enter to establish the connection.
2. Warning messages will pop out to warn the user that the security certificate was issued by a
company they have not chosen to trust.
3. Select Yes to enter the PT-7828’s web browser interface and access the web browser interface
secured via HTTPS/SSL.
NOTE
Moxa provides a Root CA certificate .After installing this certificate into your PC or Notebook,
you can access the web browser interface direc
t
ly and will not see any warning messages again.
You may download the certificate from the PT-7828A’s CD-ROM.
Page 96

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-80
Using Layer 3 Settings
The PT-7828 is a Layer-3 switch uses the Network Layer (layer 3) of the ISO’s OSI layer model
for data switching. Unlike Layer-2 switching for which the MAC address is used for exchanging
data, a Layer-3 switch uses the IP address to determine the destination of a data packet.
Layer-2 switching Layer-3 switching
Layer 1
Layer 1
Layer 1
Layer 2 Layer 2
Layer 2
EDS-7828
Layer 3 Layer 3
Layer 4
Layer 4
Layer 5
Layer 5
Layer 6
Layer 6
Layer 7
Layer 7
Layer 1
Layer 1
Layer 1
Layer 2 Layer 2
Layer 3
Layer 2
EDS-7828
Layer 3 Layer 3
Layer 4
Layer 4
Layer 5
Layer 5
Layer 6
Layer 6
Layer 7
Layer 7
The Layer-3 Switching Concept
IP (Internet Protocol) is a protocol defined on layer 3 of the OSI 7-layer model. The IP address is
used to address data packets on the Network Layer, and is not tied to the hardware of a device or
PC. The IP address can be assigned by the system operator or network administrator.
Whereas a layer 2 switch uses the MAC address of a network card to determine the destination of
data packets, a layer 3 switch uses IP address currently assigned to the network card to transmit
data packets. Switches use ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to establish the relationship
between MAC addresses and IP addresses.
When a PC sends out an ARP request, which is a broadcast packet requiring the IP address owner
to send back his MAC address, one of two situations could be encountered:
y If your PC and the IP address owner are on the same subnet, the IP address owner will use a
unicast packet, which contains his MAC address, to reply to your PC. Henceforth, your PC will
use this MAC address to transmit to the IP address owner directly.
y If your PC and the IP address owner are not on the same subnet, your PC will not receive a
reply, so it will ask for the MAC address of the Layer-3 switch (gateway/ router). To transmit
data packets to IP address owner, your PC packs the data packet with IP address and sends this
packet to the Layer-3 switch (gateway/ router) with its MAC address. The Layer-3 switch
(gateway/ router) receives the data packet, and then repacks and forwards it to the next hop,
based on the routing rules.
Static Routing and Dynamic Routing
The PT-7828 supports both static and dynamic routing. Dynamic routing can use either RIP V1
and/or V2. You can either choose one of the routing methods, or combine the two methods to
establish your routing table.
A routing entry includes the following items: the destination address, the next hop address (which
is the next router along the path to the destination address), and the metric that gives the cost we
have to pay to access a different network.
Static Routing
You can define the routes yourself by specifying the next hop (or router) that PT-7828 should
forward data to for a specific subnet. The Static Route settings will be stored in the PT-7828’s
routing table.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
RIP is a distance vector-based routing protocol that can automatically build up a routing table in
Page 97

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-81
the PT-7828.
The PT-7828 can efficiently update and maintain the routing table and optimize the routing with
the smallest metric and most matched mask prefix.
Interface Setting
The IP Interface Setting page is used to assign the interface.
Interface Name
Use this option to describe this interface (Max. of 30 characters).
IP Address
Use this option to specify the IP address of this interface.
Subnet Mask
Use this option to specify the subnet mask for this IP address.
VLAN ID
Setting Description Fact or y Default
ID numbers
Display all available VLAN ID that you have set in
Virtual LAN. To establish a interface, you have to
assign an available ID for this interface firstly. If a
VLAND ID is assigned twice, a warning message
will be shown.
N
one (if no VLAN
ID is available)
Proxy ARP
Setting Description Fact or y Default
Enable/Disable
This option is used to enable or disable the function
of Proxy ARP.
Disabled
There are three action buttons for setting up the IP Interface Table:
Add
For adding an entry into the IP Interface Table.
Page 98

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-82
Delete
For removing the selected entries in the IP Interface Table.
Modify
For modifying the content of a selected entry in the IP Interface Table.
NOTE
The entries in the IP Interface Table will not be added into the PT-7828’s interface table until you
click the Activate button.
RIP
The RIP page is used to set up the RIP parameters.
RIP Enable
Setting Description Fact or y Default
Enable/Disable
This option is used to enable or disable the RIP
function globally.
Disabled
RIP Version
You can specify which version the RIP should follow. You can also select V1 Compatibility to
make sure that Version 1 PIP packets can also be received.
RIP Distribution
Setting Description Fact or y Default
Connected
The entries that are learned from the connected ports
will be re-distributed if this option is enabled.
Unchecked
(disabled)
Static
The entries that are set in a static route will be
re-distributed if this option is enabled.
Unchecked
(disabled)
RIP Enable Table
This is a table showing the entries learned from RIP.
NOTE
The RIP settings will not function until you click the Activate button.
Page 99

PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-83
OSPF Settings
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a dynamic routing protocol for use in Internet Protocol (IP)
networks. Specifically, it is a link-state routing protocol and falls into the group of interior
gateway protocols, operating within a single autonomous system. As a link-state routing protocol,
OSPF establishes and maintains neighbor relationships in order to exchange routing updates with
other routers. The neighbor relationship table is called an adjacency database in OSPF. OSPF
forms neighbor relationships only with the routers directly connected to it. In order to form a
neighbor relationship between two routers, the interfaces used to form the relationship must be in
the same area. An interface can only belong to a single area. With OSPF enabled, PT-7828 is
capable to exchange routing information with other L3 switches or routers more efficiently in a
large system. The OSPF Settings page is used to set up OSPF configurations.
OSPF Global Settings
Each L3 switch/router has an OSPF router ID, customarily written in the dotted decimal format
(e.g., 1.2.3.4) of an IP address. This ID must be established in every OSPF instance. If not
explicitly configured, the default ID (0.0.0.0) will be regarded as the router ID. Since the router ID
is an IP address, it does not have to be a part of any routable subnet in the network.
OSPF State, OSPF Router ID, Current Router ID, Redistribute
Setting Description Factory Default
OSPF State Select the option to enable/disable the OSPF Function. Disable
OSPF Router ID Set the L3 switch’s Router ID. 0.0.0.0
Current Router ID Show the current L3 switch’s Router ID. 0.0.0.0
Redistribute Redistribute routing information to other protocols Connected
Page 100
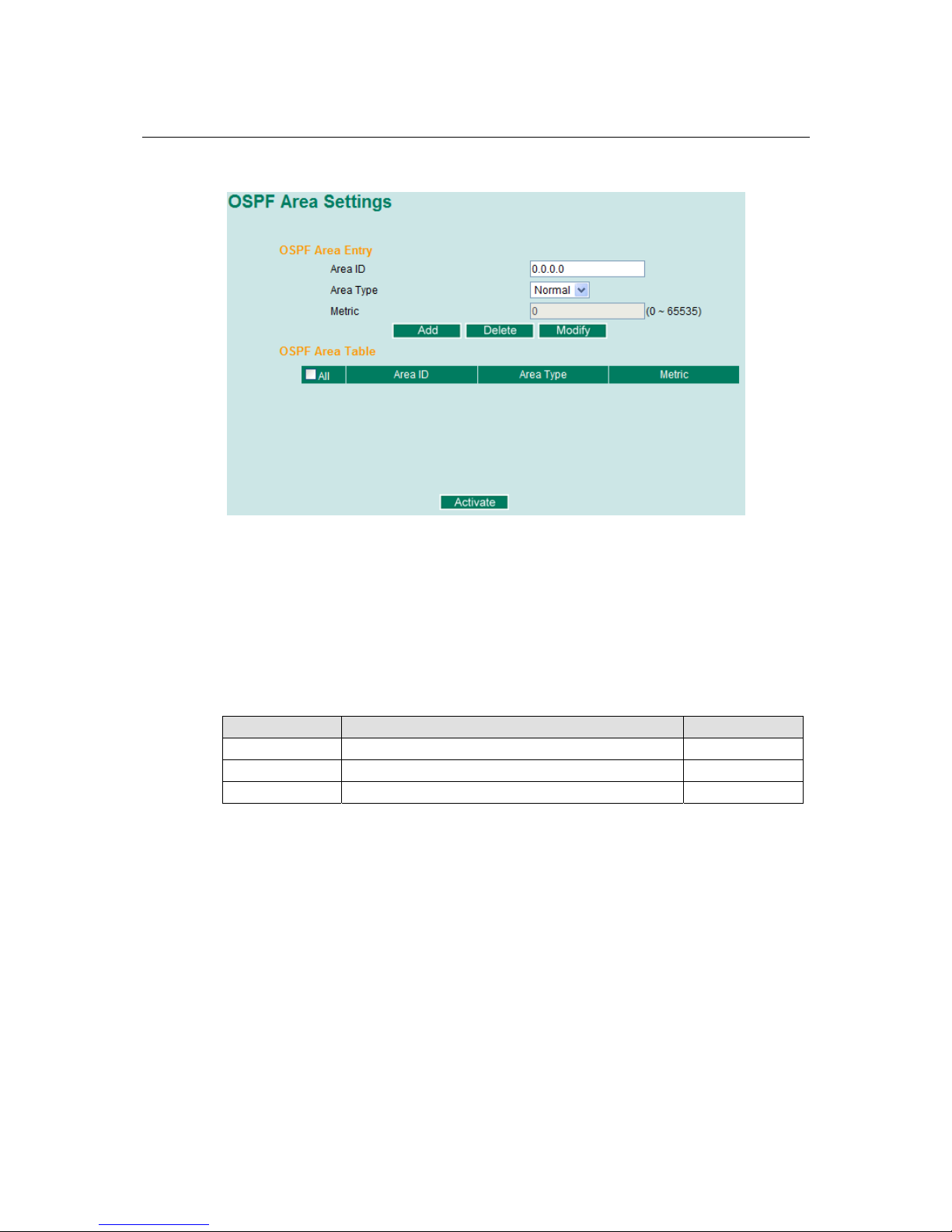
PT-7828 User’s Manual Featured Functions
3-84
OSPF Area Settings
An OSPF domain is divided into areas that are labeled with 32-bit area identifiers which are
commonly written in the dot-decimal notation of an IPv4 address. Areas are used to divide a large
network into smaller network areas. They are logical groupings of hosts and networks, including
their routers having interfaces connected to any of the included networks. Each area maintains a
separate link state database whose information may be summarized towards the rest of the network
by the connecting router. Thus, the topology of an area is unknown outside of the area. This
reduces the amount of routing traffic between parts of an autonomous system.
OSPF Area Entry
Area ID, Area Type, Metric
Setting Description Factory Default
Area ID Define the areas that this L3 switch/router connects to. 0.0.0.0
Area Type Define the area type, Stub Area or NSSA. Normal
Metric Define the metric value. 0
OSPF Area Table
Shows the current OSPF area table in the L3 switch/router.
 Loading...
Loading...