Page 1

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual
Seventh Edition, July 2006
www.moxa.com/product
MOXA Technologies Co., Ltd.
Tel: +886-2-8919-1230
Fax: +886-2-8919-1231
Web:
MOXA Technical Support
Worldwide:
www.moxa.com
support@moxa.com
Page 2

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual
The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in
accordance with the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2006 MOXA Technologies Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permi ssi on is pr ohibited.
Trademarks
MOXA is a registered trademark of The MOXA Group.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of MOXA.
MOXA provides this document “as is,” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but
not limited to, its particular purpose. MOXA reserves the right to make improvements and/or changes to this
manual, or to the products and/or the programs described in this manual, at any time.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, MOXA Technologies
assumes no responsibility for its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that may result from
its use.
This product might include unintentional technical or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the
publication.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction..............................................................................................1-1
Overview............................................................................................................................ 1-2
Package Checklist .............................................................................................................. 1-2
Product Features................................................................................................................. 1-2
Product Specifications........................................................................................................ 1-3
Chapter 2 Getting Started.........................................................................................2-1
Panel Layout....................................................................................................................... 2-2
Connecting the Hardware................................................................................................... 2-3
Wiring Requirements.............................................................................................. 2-3
Connecting NPort 5610/30/50-16/8’s Power.......................................................... 2-3
Connecting NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s Power............................................................ 2-3
Grounding NPort 5610-16/8-48V........................................................................... 2-4
Connecting to the Network..................................................................................... 2-4
Connecting to a Serial Device................................................................................. 2-5
LED Indicators........................................................................................................ 2-5
Link Indicator on the Rear Panel of NPort 5650 Fiber Model................................ 2-5
Real Time Clock..................................................................................................... 2-5
Adjustable Termination Resistor for the RS-485 Port............................................ 2-5
Chapter 3 Initial IP Address Configuration.............................................................3-1
Initializing NPort’s IP Address........................................................................................... 3-2
Factory Default IP Address ................................................................................................ 3-2
LCM Display...................................................................................................................... 3-2
NPort Administration Suite ................................................................................................ 3-5
ARP.................................................................................................................................... 3-5
Telnet Console.................................................................................................................... 3-6
Chapter 4 Choosing the Proper Operation Mode...................................................4-1
Overview............................................................................................................................ 4-2
Real COM Mode................................................................................................................ 4-2
TCP Server Mode............................................................................................................... 4-3
TCP Client Mode................................................................................................................4-4
UDP Mode..........................................................................................................................4-4
Pair Connection Mode........................................................................................................ 4-4
Reverse T elnet Mode.......................................................................................................... 4-5
Disabled Mode................................................................................................................... 4-5
RFC2217 Mode.................................................................................................................. 4-5
PPP Mode........................................................................................................................... 4-6
Chapter 5 Web Console Configuration...................................................................5-1
Opening Your Browser....................................................................................................... 5-2
Basic Settings..................................................................................................................... 5-3
Network Settings................................................................................................................ 5-5
Serial Settings..................................................................................................................... 5-9
Operating Settings.............................................................................................................5-11
Real COM Mode................................................................................................... 5-11
TCP Server Mode ................................................................................................. 5-14
TCP Client Mode.................................................................................................. 5-18
Page 4

UDP Mode............................................................................................................ 5-23
Pair Connection Mode .......................................................................................... 5-25
Reverse Telnet Mode............................................................................................ 5-27
Disabled Mode...................................................................................................... 5-28
RFC2217 Mode..................................................................................................... 5-28
PPP Mode ............................................................................................................. 5-30
Accessible IP Settings...................................................................................................... 5-31
PPP User Ta ble................................................................................................................. 5-32
Auto W a rning Settings..................................................................................................... 5-33
Auto warning: E-mail and SNMP Trap.................................................................5-33
Event Type............................................................................................................ 5-34
Monitor............................................................................................................................. 5-36
Monitor Line......................................................................................................... 5-36
Monitor Async...................................................................................................... 5-36
Monitor Async-Settings........................................................................................ 5-37
Change Password............................................................................................................. 5-37
Load Factory Defaults...................................................................................................... 5-38
Chapter 6 Configuring NPort Administrator...........................................................6-1
Overview............................................................................................................................ 6-2
Installing NPort Administrator........................................................................................... 6-2
Configuration ..................................................................................................................... 6-5
Broadcast Search..................................................................................................... 6-6
Unlock Password Protection................................................................................... 6-7
Configuring NPort 5600........................................................................................ 6-10
Upgrading Firmware............................................................................................. 6-12
Export/Import........................................................................................................ 6-13
Monitor............................................................................................................................. 6-14
Port Monitor..................................................................................................................... 6-20
COM Mapping ................................................................................................................. 6-20
On-line COM Mapping......................................................................................... 6-21
Off-line COM Mapping........................................................................................ 6-25
IP Location....................................................................................................................... 6-26
Chapter 7 IP Serial LIB..............................................................................................7-1
Overview............................................................................................................................ 7-2
IP Serial LIB Function Groups........................................................................................... 7-3
Example Program............................................................................................................... 7-3
Appendix A Pinouts and Cable Wiring......................................................................A-1
Port Pinout Diagrams........................................................................................................ A-2
Ethernet Port Pinouts ............................................................................................. A-2
Serial Port Pinouts.................................................................................................. A-2
Cable Wiring Diagram s..................................................................................................... A-3
Ethernet Cables...................................................................................................... A-3
Serial Cables for NPort 5610/5650 (RS-232)......................................................... A-3
Serial Cables for NPort 5630 (RS-422/4-wire RS-485)......................................... A-5
Serial Cables for NPort 5630 (2-wire RS-485)...................................................... A-6
Serial Cables for NPort 5650 (RS-422/4-wire RS-485)......................................... A-7
Serial Cables for NPort 5650 (2-wire RS-485)...................................................... A-8
Pin Assignments for DB9 and DB25 Connectors.................................................. A-9
Appendix B Well Known Port Numbers .................................................................... B-1
Page 5

Appendix C SNMP Agent with MIB II & RS-232 Like Group ....................................C-1
Appendix D Auto IP Report Protocol.........................................................................D-1
Appendix E Service Information................................................................................ E-1
MOXA Internet Services....................................................................................................E-2
Problem Report Form.........................................................................................................E-3
Product Return Procedure ..................................................................................................E-4
Page 6

1
1
Chapter 1 Introduction
The MOXA NPort 5600 Series of advanced serial device servers make it easy to network-enable
your serial devices. The NPort 5600 Series includes 8 models: NPort 5610-16, NPort 5610-8 (8 or
16 RS-232 ports, with AC power), NPort 5610-16-48V, NPort 5610-8-48V (8 or 16 RS-232 ports,
with DC power), NPort 5630-16, NPort 5630-8 (8 or 16 RS-422/485 ports, with AC power), and
NPort 5650-16, NPort 5650-8 (8 or 16 RS-232/422/285 ports, with AC power) . In this manual, we
often refer to the eight products collectively as “5600” or “5600 Series.”
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Product Features
Product Specifications
Page 7

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Getting Started
Overview
The NPort 5600 Series serial device servers are designed to make your industrial serial devices
Internet ready instantly. The compact size of the NPort 5600 device servers makes them the ideal
choice for connecting your RS-232 (NPort 5610-16/8), RS-422 /485 (NPort 5630-16/8), or
RS-232/422/485 (NPort 5650-16/8) serial devices—such as PLCs, meters, and sensors—to an
IP-based Ethernet LAN, making it possible for your software to access serial devices anywhere
over a local LAN or the Internet.
The NPort 5600 serial device servers ensure the compatibility of network software that uses a
standard network API (Winsock or BSD Sockets) by providing TCP Server Mode, TCP Client
Mode, and UDP Mode. And thanks to NPort’s Real COM/TTY drivers, software that works with
COM/TTY ports can be set up to work over a TCP/IP network in no time. This excellent feature
preserves your software investment and lets you enjoy the benefits of networking your serial
devices instantly.
The NPort 5600 serial device servers support automatic IP configuration protocols (DHCP,
BOOTP) and manual configuration via NPort ’ s han dy web browser console. Both methods ensure
quick and effective installation, and by using NPort 5600’s Windows Utility, installation is very
straightforward, since all system parameters can be stored and then copied to other device servers
simultaneously.
Package Checklist
The MOXA NPort 5600 Series products are shipped with the following items:
Standard Accessories
y 1 16- or 8-port serial device server
y NPort Documentation & Software CD
y NPort 5600 Quick Installation Guide
y Power cord
Optional Accessories
y CBL-RJ45M9-150 RJ45 8-pin to DB9 Male cable, 150 cm
y CBL-RJ45F9-150 RJ45 8-pin to DB9 Female cable, 150 cm
y CBL-RJ45M25-150 RJ45 8-pin to DB25 Male cable, 150 cm
y CBL-RJ45F25-150 RJ45 8-pin to DB25 Female cable, 150 cm
NOTE: Notify your sales representative if any of the above items is missing or damaged.
Product Features
The NPort 5600 Series products have the following features:
y Make your serial devices Internet ready
y Easy-to-use LCM (Liquid Crystal Module) interface for setting up the IP address
y Versatile socket operation modes, including TCP Server, TCP Client, and UDP
y Easy-to-use Windows Utility for mass installation
y Supports 10/100 Mbps Ethernet—auto-detectable
y Supports 16/8-port RS-232 or RS-422/485 interface or RS-232/422/485 interface
y Built-in 15 KV ESD protection for all serial signals
y Supports SNMP MIB-II for network management
1-2
Page 8

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Getting Started
Product Specifications
LAN
Ethernet 10/100 Mbps, RJ45
Protection Built-in 1.5 KV magnetic isolation
Optical Fiber
Distance
Min. TX Output Multi mode: -20 dBm
Max. TX Output Multi mode: -14 dBm
Sensitivity -36 to -32 dBm (Single), -34 to -30 dBm (Multi)
NPort 5610 Serial Interface
Interface RS-232
No. of Ports 16/8
Port Type RJ45 8-pin
Signals TxD, RxD, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, GND
Serial Line Protection 15 KV ESD for all signals
NPort 5630 Serial Interface
Interface RS-422/485
No. of Ports 16/8
Port Type RJ45 8-pin
Signals RS-422: Tx+, Tx-, Rx+, Rx-, GND
RS-485 (2-wire): Data+, Data-, GND
RS-485 (4-wire): Tx+, Tx-, Rx+, Rx-, GND
Serial Line Protection 15 KV ESD for all signals
RS-485 Data Direction ADDC™ (Automatic Data Direction Control)
NPort 5650 Serial Interface
Interface RS-232/422/485
No. of Ports 16/8
Port Type RJ45 8-pin
Signals RS-232: TxD, RxD, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD,
RS-422: Tx+, Tx-, Rx+, Rx-, GND
RS-485 (2-wire): Data+, Data-, GND
RS-485 (4-wire): Tx+, Tx-, Rx+, Rx-, GND
Serial Line Protection 15 KV ESD for all signals
Power Line Protection
4 KV Burst (EFT), EN61000-4-4
2 KV Surge, EN61000-4-5
Multi mode:
0 to 2 km, 1310 nm (62.5/125 µm, 500 MHz*km)
Single mode:
0 to 40 km, 1310 nm (9/125 µm, 3.5 PS/(nm*km))
Single mode: 0 to 40 km, -5 dBm
Single mode: 0 to 40 km, 0 dBm
GND
RS-485 Data Direction
ADDC™ (Automatic Data Direction Control)
1-3
Page 9

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Getting Started
Advanced Built-in Features
HMI LCM display with four push buttons
Buzzer
Real-Time Clock
Watch Dog Timer
Serial Communication Parameters
Parity None, Even, Odd, Space, Mark
Data Bits 5, 6, 7, 8
Stop Bit 1, 1.5, 2
Flow Control RTS/CTS, XON/XOFF, DSR/DTR (Exclu ded NPort 5630)
Transmission Speed 50 bps to 921.6 Kbps
Software Features
Protocols ICMP, IP, TCP, UDP, DHCP, BOOTP, Telnet, DNS, SNMP,
Utilities NPort Administrator for Windows 95/98/ME/NT/2000/XP/2003
OS Driver Support Windows 95/98/ME/NT/2000//XP/2003/x64 Real COM driver /
Configuration Web Browser, Telnet Console, or Windows Utility
Power Requirements
Power Input 100 to 240 VAC, 47 to 63 Hz, or 48 VDC
Power Consumption NPort 5610-16/8: 141 mA for 100V, 93 mA for 240V
NPort 5610-16/8-48V: 135 m A (at 48V max.)
NPort 5630-16/8: 152 mA for 100V, 98 mA for 240V
Mechanical
Material SECC sheet metal (1 mm)
Dimensions (W × H × D) 190 × 44.5 × 478 mm (including ears)
190 × 44.5 × 440 mm (without ears)
Environment
Operating Temperature 0 to 55°C (32 to 131°F), 5 to 95%RH
Storage Temperature -20 to 85°C (-4 to 185°F), 5 to 95%RH
Regulatory Approvals
EMC FCC Class A, CE Class A
Safety UL, CUL, TÜV
WARRANTY 5 years
HTTP, SMTP, SNTP, Rtelnet, ARP, PPP, RFC2217
Linux real TTY driver/SCO Unix/SCO Ope nSe rver 5/UnixWare
7/UnixWare 2.1/SVR4.2/QNX
NPort 5650-8/16: 158 mA @ 100 VAC, 102 mA @ 240 VAC
NPort 5650-S-SC-8/16: 164 mA @ 100 VAC, 110 mA @ 240
VAC
NPort 5650-M-SC-8/16: 174 mA @ 100 VAC, 113 mA @ 240
VAC
1-4
Page 10

2
Chapter 2 Getting Started
This chapter includes information about installing NPort 5600 Series. The following topics are
covered:
Panel Layout
Connecting the Hardware
¾ Wiring Requirements
¾ Connecting NPort 5610/30/50-16/8’s Power
¾ Connecting NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s Power
¾ Grounding NPort 5610-16/8-48V
¾ Connecting to the Network
¾ Connecting to a Serial Device
¾ LED Indicators
¾ Link Indicator on the Rear Panel of NPort 5650 Fiber Model
¾ Real Time Clock
¾ Adjustable Termination Resistor for the RS-485 Port
2
Page 11
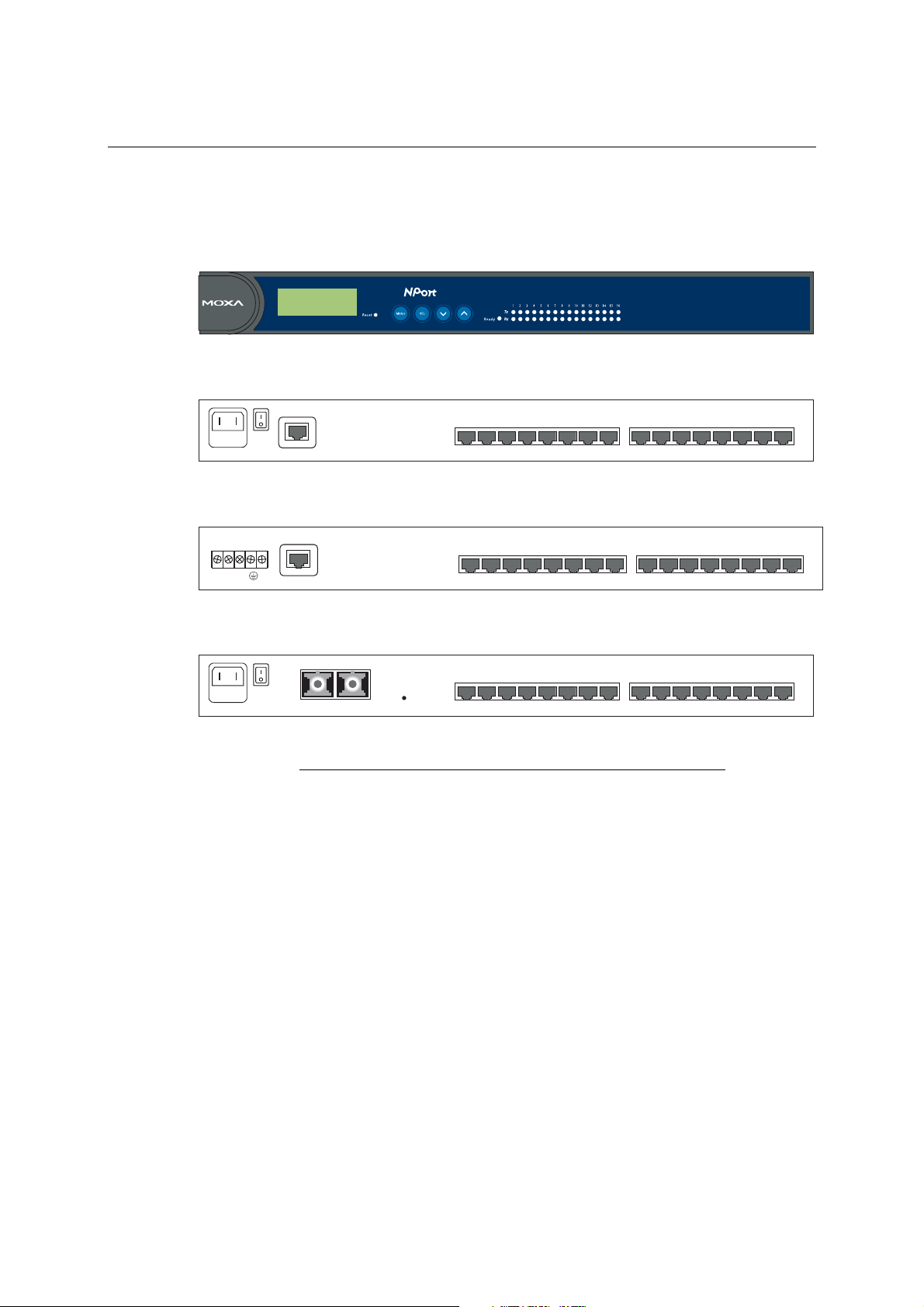
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Initial IP Address Configuration
Panel Layout
The following figures depict the front and rear panels of the NPort 5600 series.
Front panel of NPort 5600 series
5610-
16
Rear panel of NPort 5600 series (AC Power)
AC POWER 100-240V, 47-63Hz
Serial ports
12345678
LAN
9 10111213141516
Rear panel of NPort 5600 series (DC Power)
V+ V-
Serial ports
12345678
LAN
9 10111213141516
Rear panel of NPort 5650 Fiber model
AC POWER 100-240V, 47-63Hz
Fiber
Link
Serial ports
12345678
9 10111213141516
Reset Button—Press the Reset button continuously for 5 sec to load factory defaults
: Use a
pointed object, such as a straightened paper clip or toothpick, to press the reset button. This will
cause the Ready LED to blink on and off. The factory defaults will be loaded once the Ready LED
stops blinking (after about 5 seconds). At this point, you should release the reset button.
2-2
Page 12

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Initial IP Address Configuration
Connecting the Hardware
This section describes how to connect NPort 5600 Series to serial devices for first time testing
purposes. We cover Wiring Requirements, Connecting NPort 5610/30/50-16/8’s Power,
Connecting NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s Power, Grounding NPort 5610-16/8-48V, Connecting to
the Network, Connecting to a Serial Device, and LED Indicators.
Wiring Requirements
ATTENTION
Safety First!
Be sure to disconnect the power cord before installing and /or wiring your NPort 5600 Series.
Wiring Caution!
Calculate the maximum possible current in each power wire and common wire. Observe all
electrical codes dictating the maximum current allowable for each wire size.
If the current goes above the maximum ratings, the wiring could overheat, causing serious
damage to your equipment.
Temperature Caution!
Please take care when handling NPort 5600. When plugged in, NPort 5600’s internal
components generate heat, and consequently the casing may feel hot to the touch.
You should also pay attention to the following points:
y Use separate paths to route wiring for power and devices. If power wiring and device wiring
paths must cross, make sure the wires are perpendicular at the intersection point.
NOTE: Do not run signal or communication wiring and power wiring in the same wire
conduit. To avoid interference, wires with different signal characteristics should be routed
separately.
y You can use the type of signal transmitted through a wire to determine which wires should be
kept separate. The rule of thumb is that wiring that shares similar electrical characteristics can
be bundled together.
y Keep input wiring and output wirin g separate.
y Where necessary, it is strongly advised that you label wiring to all devices in the system.
Connecting NPort 5610/30/50-16/8’s Power
Connect NPort 5610/30-16/8’s 100-240 VAC power line with its AC connector. If the power is
properly supplied, the “Ready” LED will show a solid red color until the system is ready, at which
time the “Ready” LED will change to a green color.
Connecting NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s Power
To connect NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s power cord with its terminal block, follow the steps given
below:
2-3
Page 13
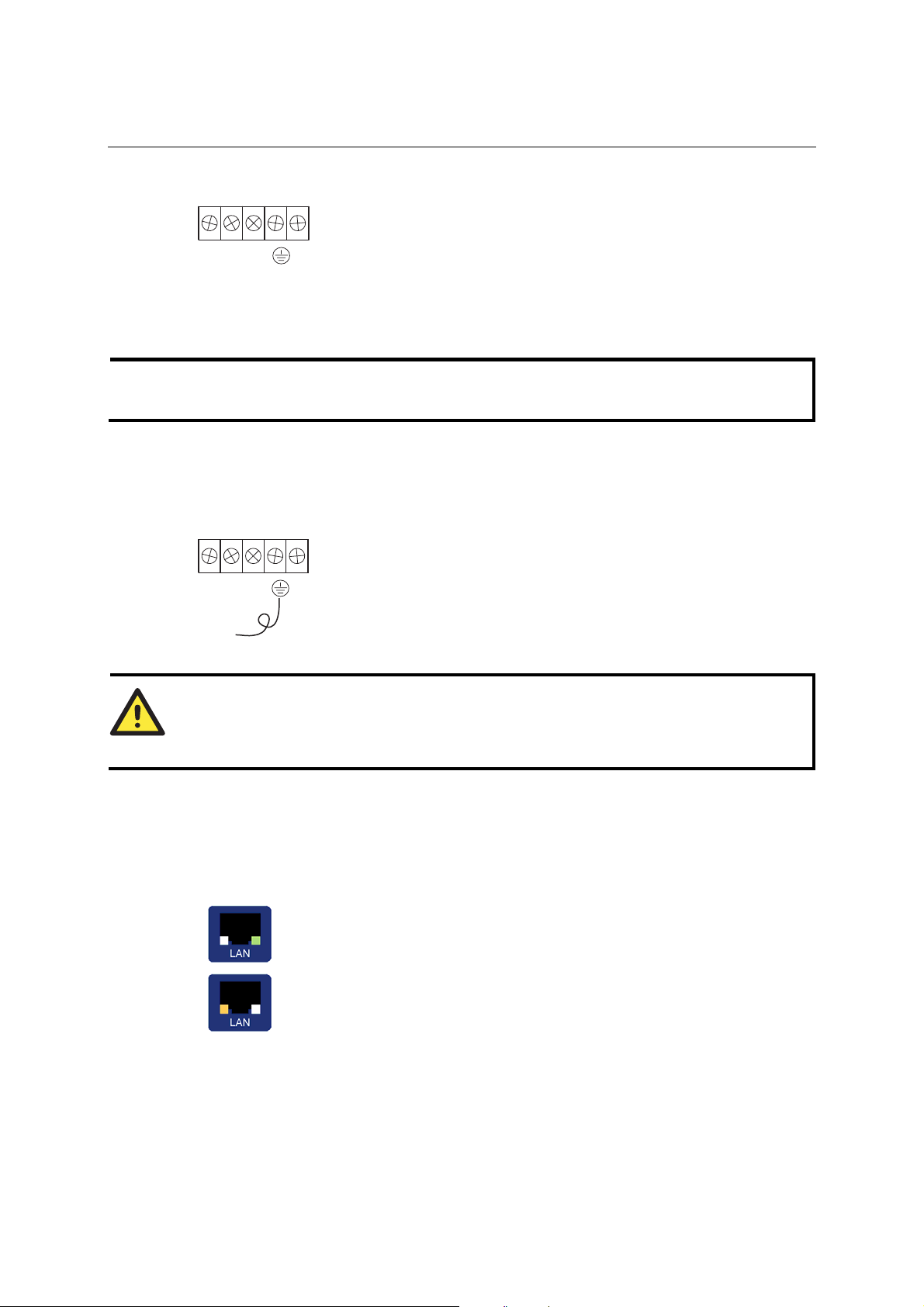
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Initial IP Address Configuration
1. Loosen the screws on the V
terminal block.
2. Connect the power cord’s 48 VDC wire to the terminal block’s V
terminal, and the power cord’s DC Power Ground wire to the terminal
block’s V
NPort 5610-16/8-48V can still operate even if the DC 48V and DC Power
Ground are reversed.)
terminal, and then tighten the terminal block screws. (Note:
-
NOTE
V+ V-
If the power is properly supplied, the “Ready” LED will show a solid red color until the system is
ready, at which time the “Ready” LED will change to a green color.
You should use 8 kg-cm of screw torque and 22-14 AWG of suitable electric wire to connect
NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s power cord to its terminal block.
Grounding NPort 5610-16/8-48V
Grounding and wire routing helps limit the effects of noise due to electromagnetic interference
(EMI). Run the ground connection from the ground screw to the grounding surface prior to
connecting devices.
The Shielded Ground (sometimes called Protected Ground) contact is the
second contact from the right of the 5-pin power terminal block connector
V+ V-
located on the rear panel of NPort 5610-16-48V/5610-8-48V. Connect the
SG wire to the Earth ground.
and V- terminals of NPort 5610-16/8-48V’s
+
+
SG
ATTENTION
This product is intended to be mounted to a well-grounded mounting surface such as a metal
panel.
Connecting to the Network
Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to NPort 5600’s 10/100M Ethernet port and the other end of
the cable to the Ethernet network. There are 2 LED indicators located on the bottom left and right
corners of the Ethernet connector. If the cable is properly connected, NPort 5600 will indicate a
valid connection to the Ethernet in the following ways:
The bottom right corner LED indicator maintains a solid green color when the
cable is properly connected to a 100 Mbps Ethernet network.
The bottom left corner LED indicator maintains a solid orange color when the
cable is properly connected to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network.
2-4
Page 14
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Initial IP Address Configuration
Connecting to a Serial Device
Connect the serial data cable between NPort 5600 and the serial device.
LED Indicators
The front panels of NPort 5600 have several LED indicators, as described in the following table.
LED Name LED Color LED Function
off Power is off, or power error condition exists.
Steady on: Power is on and NPort is booting up.
Ready
1-16
red
green
orange Serial port is receiving data.
green Serial port is transmitting data.
off
Blinking:
Steady on:
Blinking:
No data is being transmitted or received through the serial
port.
Indicates an IP conflict, or DHCP or BOOTP
server did not respond properly.
Power is on and NPort is functioning
normally.
The NPort has been located by NPort
Administrator’s Location function.
Link Indicator on the Rear Panel of NPort 5650 Fiber Model
The rear panels of NPort 5600 have a link indicator, as described in the following table.
LED Name LED Color LED Function
off Fiber is disconnected
Link
green Fiber is connected and no data is being transmitted
blinking Fiber is connected and data is being transmitted
Real Time Clock
NPort 5600’s real time clock is powered by a lithium battery. We strongly recommend that you do
not replace the lithium battery without the presence of MOXA’s technical support engineers. If
you need a battery change, contact MOXA for assistance.
ATTENTION
There is risk of explosion if the battery is replaced by an incorrect type. You need to dispose
used batteries according to the instructions.
Adjustable Termination Resistor for the RS-485 Port
In some critical environments, you may need to add termination resistors to prevent the reflection
of serial signals. When using terminat i on res i st or s, it is important to set the pull high/low resistors
correctly so that the electrical signal is not corrupted. Since a particular pull high/low resistor
value cannot fit all environments, the NPort 5650 uses DIP switches to set the pull high/low
resistor values for each serial port.
2-5
Page 15
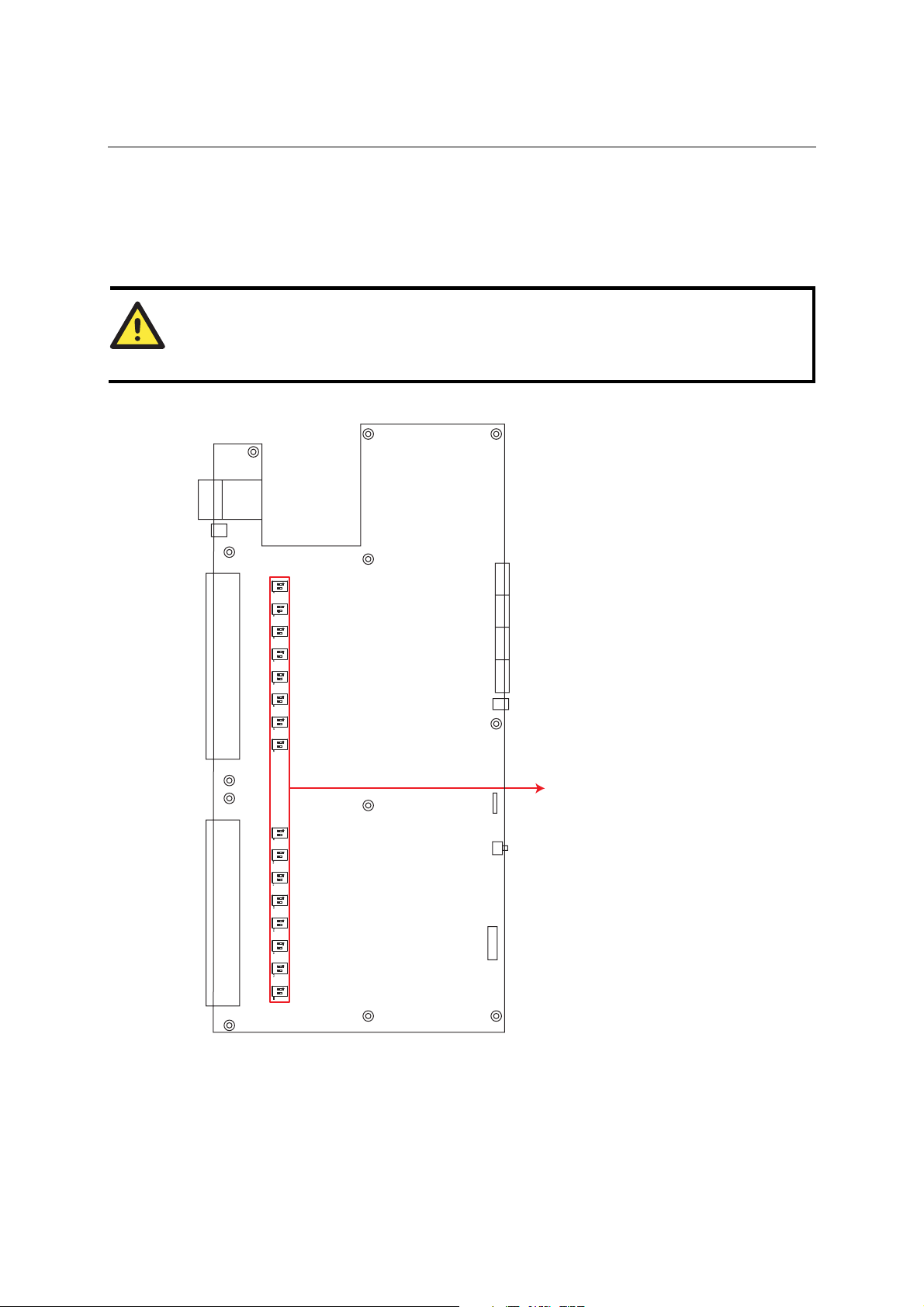
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Initial IP Address Configuration
To set a termination resistor to 150 KΩ, make sure both of the assigned DIP switches are in the
OFF position. This is the default setting.
To set a termination resistor to 1 KΩ, make sure both of the assigned DIP switches are in the ON
position.
ATTENTION
Do not use the 1 KΩ setting on the NPort 5650 when using the RS-232 interface. Doing so will
degrade the RS-232 signals and shorten the maximum allowed communication distance.
NPort 5650 DIP Switches
S1 for Port 1
S2 for Port 2
S3 for Port 3
S4 for Port 4
S5 for Port 5
S6 for Port 6
S7 for Port 7
S8 for Port 8
S9 for Port 9
S10 for Port 10
S11 for Port 11
S12 for Port 12
S13 for Port 13
S14 for Port 14
S15 for Port 15
S16 for Port 16
2-6
Page 16

3
3
Chapter 3 Initial IP Address Configuration
When setting up your NPort 5600 for the first time, the first thing you should do is configure the
IP address. This chapter introduces several methods to configure NPort’s IP address. Select the
method that is the most convenient for you. For more details about network settings, see the
Network Settings section from Chapter 5, Web Console Configuration.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Initializing NPort’s IP Address
Factory Default IP Address
LCM Display Å recommended configuration method
NPort Administration Suite Å recommended configuration method
ARP
Telnet Console
Page 17

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
Initializing NPort’s IP Address
1. Determine whether your NPort needs to use a Static IP or Dynamic IP (either DHCP or
BOOTP application).
2. If NPort is used in a Static IP environment, you can use NPort Administration Suite , A R P,
Web Console, or Telnet Console to configure the new IP address.
3. If NPort is used in a Dynamic IP environment, you can use NPort Administration suite, Web
Console, or Telnet Console to configure NPort to get an IP address dynamically with DHCP,
DHCP/BOOTP, or BOOTP.
ATTENTION
Consult your network administrator on how to reserve a fixed IP address (for your NPort) in the
MAC-IP mapping table when using a DHCP Server or BOOTP Server. In most applications, you
should assign a fixed IP address to your NPort.
Factory Default IP Address
NPort products are configured with the following default private IP address:
Default IP address: 192.168.127.254
(IP addresses of the form 192.168.xxx.xxx are referred to as private IP addresses, sin c e it is not
possible to directly access a device configured with a private IP address from a public network.
For example, you would not be able to ping such a device from an outside Internet connection.
NPort applications that require sending data over a public network, such as the Internet, require
setting up the server with a valid public IP address, which can be leased from a local ISP.)
LCM Display
We recommend using the LCM display and four push buttons to configure the IP address for the
first time.
Basic Operation
If the NPort is working properly, the LCM panel will display a green color. The red Ready LED
will also light up, indicating that the NPort is receiving power. After the red Ready LED turns
green, you will see a display similar to:
N P 5 6 1 0 - 1 6 _ 3 8
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 2 7 . 2 5 4
Where
• NP5610-16 is the NPort’s name
• 38 is the NPort’s serial number
• 192.168.127.254 is the NPort’s IP address
3-2
Page 18
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
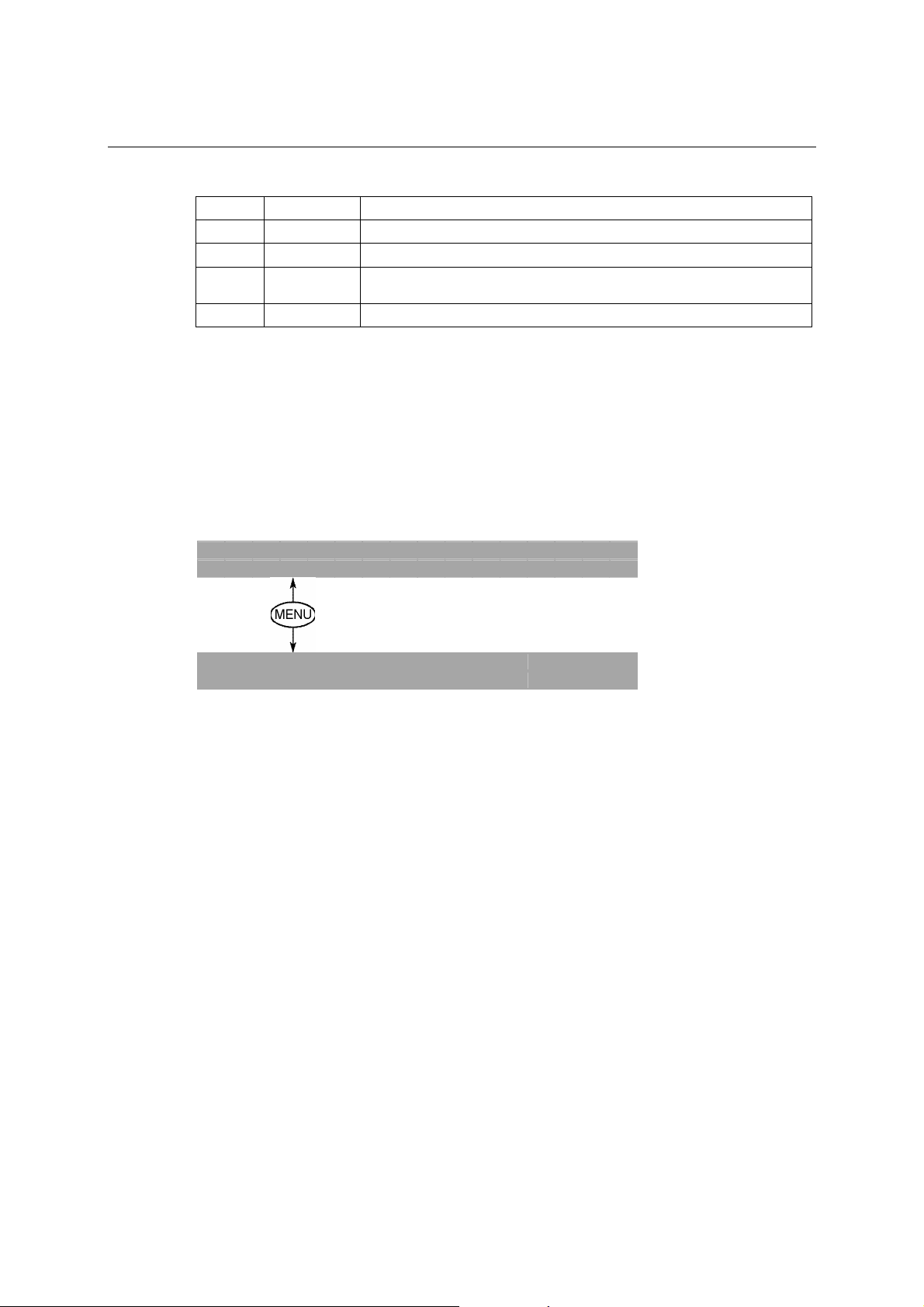
There are four push buttons on NPort’s nameplate. Going from left to right, the buttons are:
Button Name
MENU menu activates the main menu, or returns to an upper level
U
V
SEL
up cursor
down cursor
select
Action
scrolls up through a list of items shown on the LCM panel’s second line
scrolls down through a list of items shown on the LCM panel’s second
line
selects the option listed on the LCM panel’s second line
The buttons are manipulated in a manner similar to the way a modern cellular phone operates. As
you move through the various functions and setting options, note that the top line shows the
current menu or submenu name, and the bottom line shows the submenu name or menu item that is
activated by pressing the SEL button.
Detailed Menu Options
The best way to explain all of NPort’s LCM functions is to refer to the table shown on the next
page. There are three main levels—1, 2, and 3—with each level represented by a separate column.
The first thing to remember is that the MENU button is used to move back and forth between the
LCM panel’s default screen, and main menu screen:
N P 5 6 1 0 - 1 6 _ 3 8
1 9 2 . 1 6 8 . 1 2 7 . 2 5 4
M a i n M e n U
S e r v e r s e t t i n g ↓
In addition, you only need to remember to:
• Use the SEL button to move up one level (i.e., left to right on the tree graph)
• Use the MENU button to move down one level (i.e., right to left on the tree graph)
• Use the cursor keys, U and V, to scroll between the various options within a level (i.e.,
up and down on the tree graph).
As you use the buttons to operate the LCM display, you will notice that with v ery few
exceptions, moving up one level causes the bottom line of the display to move to the top
line of the display. You will also notice that the botto m three options in level 2, and all of
the options in level 3 have either a C or D attached. The meaning is as fo llows:
• C = configurable (i.e., you are allowed to change the setting of this option)
•
D = display only (i.e., the setting for this option is displayed, but it cannot be changed)
This does NOT necessarily mean that the number does not change; only that you cannot
change it.
3-3
Page 19
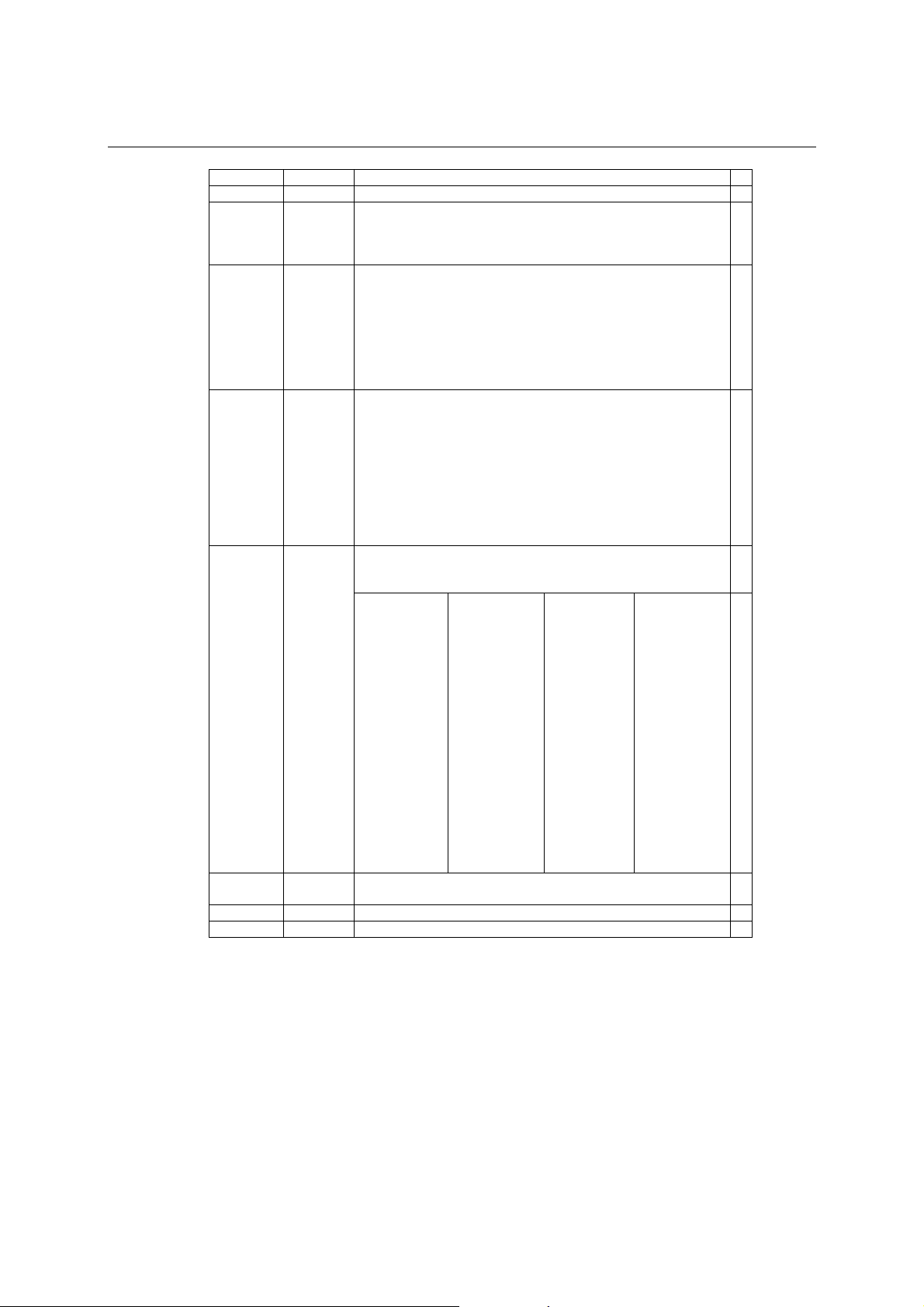
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
Main Menu
Server
setting
Network
setting
Serial set Select port
Op Mode set
Console Web console
Ping C
Save/Restart C
The part of the LCM operation that still requires some explanation is how to edit th e
configurable options. In fact, you will only encounter two types of configurable options.
The first type involves entering numbers, such as IP addresses, Netmasks, etc. In this case,
you change the number one digit at a time. The up cursor (U) is used to decrease the
highlighted digit, the down cursor (V) is used to increase the highlighted digit, and the sel
button is used to move to the next digit. When the last digit has been changed, pressing sel
simply enters the number into NPort 5600 Series’ memory.
The second type of configurable option is when there are only a small number of options
from which to choose (although only one option will be visible at a time). Consid er the
Serial number
Server name
Firmware ver
Model name
Ethernet status
MAC address
IP config
IP address
Netmask
Gateway
DNS server 1
DNS server 2
Baudrate
Data bit
Stop bit
Parity
Flow control
Tx/Rx fifo
Interface
Tx/Rx bytes
Line status
Select port
Select mode
[mode]
Real COM
Alive timeout
Max connection
Delimiter 1
Delimiter 2
Force Tx
Telnet console
TCP server
Alive timeout
Inact. time
Max connection
Delimiter 1
Delimiter 2
Force Tx
Local TCP port
Command port
TCP client
Alive timeout
Inact. time
Delimiter 1
Delimiter 2
Force Tx
Dest IP-1
TCP port-1
Dest IP-2
TCP port-2
Dest IP-3
TCP port-3
Dest IP-4
TCP port-4
TCP connect
UDP svr/cli
Delimiter 1
Delimiter 2
Force Tx
Dest IP start-1
Dest IP end-1
Dest port-1
Dest IP start-2
Dest IP end-2
Dest port-2
Dest IP start-3
Dest IP end-3
Dest port-3
Dest IP start-4
Dest IP end-4
Dest port-4
Local port
D
C
D
D
D
D
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
D
D
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
3-4
Page 20
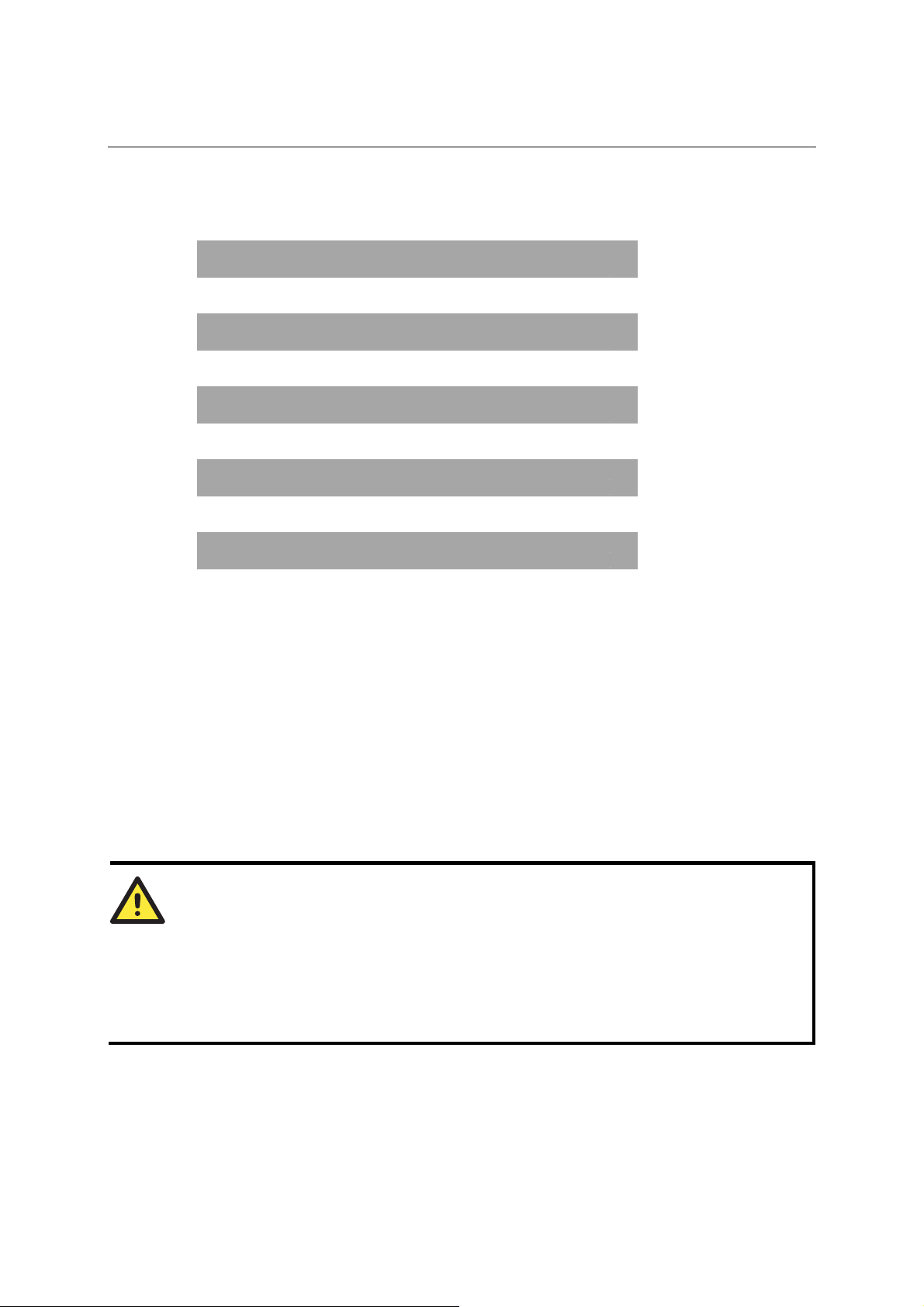
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
Parity attribute under Serial set as an example. Follow the tree graph to arrive at the
following Parity screen. The first option, None, is displayed, with a down arrow all the way
to the right. This is an indication that there are other options from which to choose.
P a r i t Y
N O n e
Press the down cursor button once to see Odd as the second option.
P a r i t Y
O D D
Press the down cursor button again to see Even as the third option.
P a r i t Y
E v e n
Press the down cursor button again to see Space as the fourth option.
P a r i t Y
S p a c e
Press the down cursor button yet again to see the last option, Mark .
P a r i t Y
M a r k
To choose the desired option, press the SEL button when the option is showing on the screen.
↓
↓
↓
↓
↓
NPort Administration Suite
NPort Administration Suite consists of some useful utility programs that are used to configure and
manage your NPorts.
See Chapter 6 for details on how to install NPort Administration Suite, and how to use this
suite of useful utilities to set up IP addresses and configure your NPort.
ARP
You can make use of the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) command to set up an IP address for
your NPort. The ARP command tells your computer to associate the NPort’s MAC address with
the intended IP address. You must then use Telnet to access the NPort, at which point the Device
Server’s IP address will be reconfigured.
ATTENTION
In order to use this setup method, both your computer and NPort must be connected to the same
LAN.
Or, you may use a cross-over Ethernet cable to connect the NPort directly to your computer’s
Ethernet card.
Your NPort must be configured with the factory default IP address—192.168.127.254—before
executing the ARP command, as described below.
3-5
Page 21
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
Take the following steps to use ARP to configure the IP address:
1. Obtain a valid IP address for your NPort from your network administrator.
2. Obtain the NPort’s MAC address from the label on its bottom panel.
3. Execute the ‘arp -s’ command from your computer’s MS-DOS prompt by typing:
arp –s 192.168.200.100 00-90-E8-xx-xx-xx
This is where 192.168.200.100 is the new IP address and 00-90-E8-xx-xx- xx is the MAC address
for your NPort. You will need to change both numbers, as described above in points 1 and 2.
4. Next, execute a special Telnet command by typing:
telnet 192.168.200.100 6000
After issuing this command, a Connect failed message will appear, as shown here. After the
NPort reboots, its IP address should be updated to the new address, and you can reconnect
using Telnet, Web, or Administrator to check that the update was successful.
Telnet Console
Depending on how your computer and network are configured, you may find it convenient to use
network access to set up your NPort’s IP address. This can be done using the Telnet program.
ATTENTION
Figures in this section will use 5610-8 as an example.
1. From the Windows deskt op, c l i ck Start and then select Run.
2. Type telnet 192.168.127.254 (use the correct IP address if different from the default)
in the Open text input box, and then click OK.
3. When the Telnet window opens, if you are prompted to input the Console password, input the
password and then press Enter.
Note that this page will only appear if the NPort is password protected.
3-6
Page 22
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
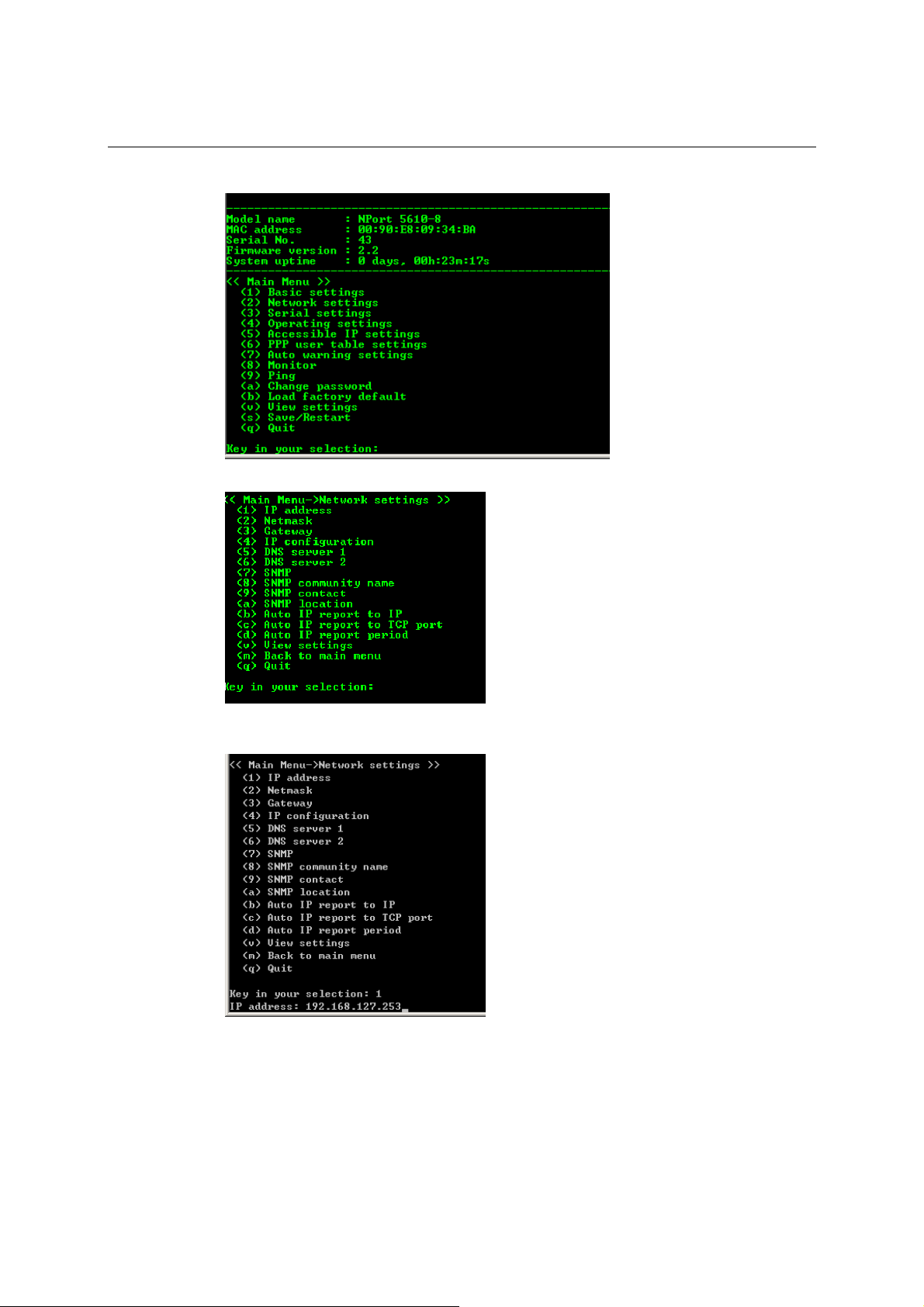
4. Type 2 to select Network settings, and then press Enter.
5. Type 1 to select IP address and then press Enter.
6. Use the Backspace key to erase the current IP address, type in the new IP address, and then
press Enter.
3-7
Page 23
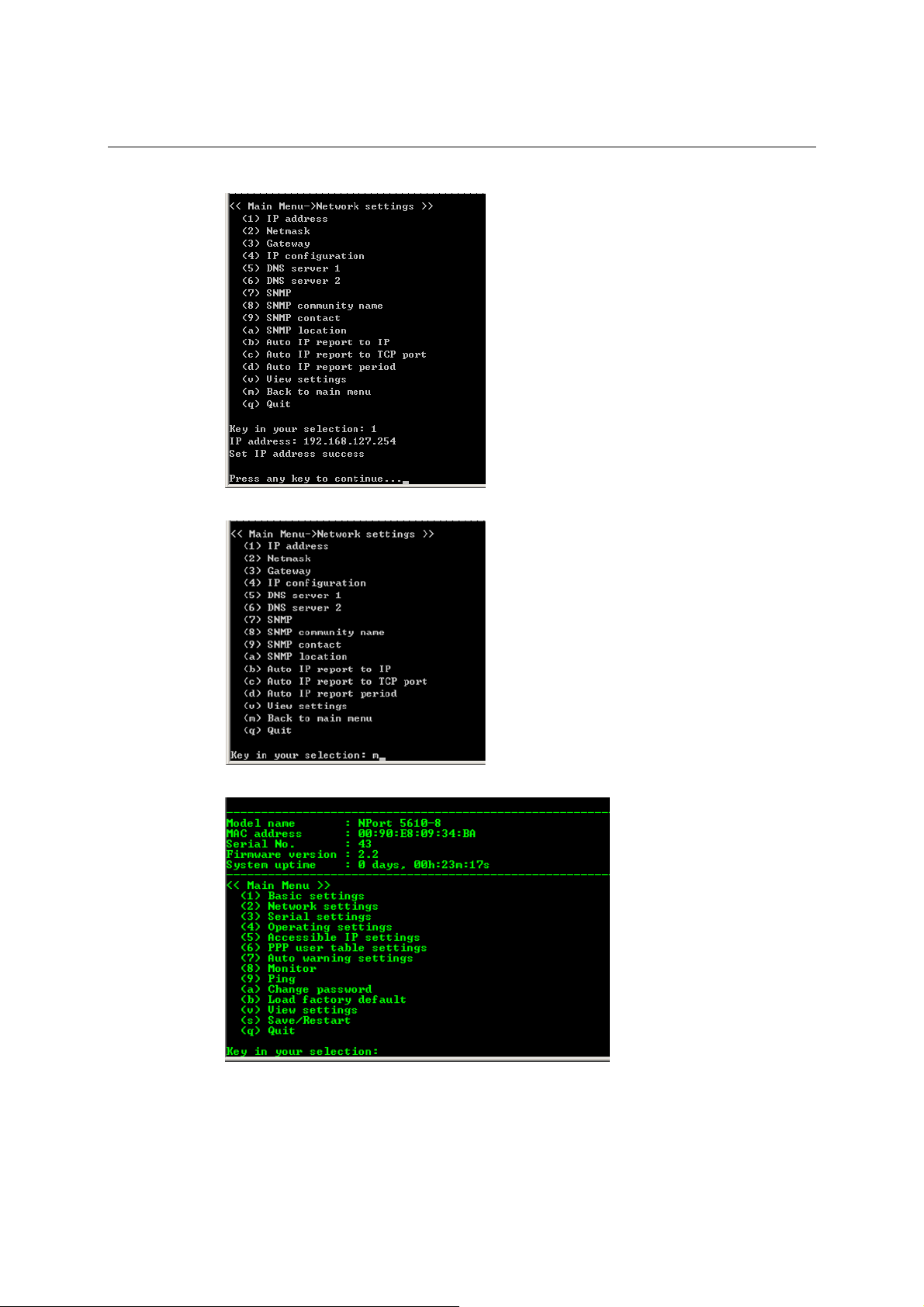
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
7. Press any key to continue…
8. Type m or M and then press Enter to return to the main menu.
9. Type s or S and then press Enter to Save/Restart the system.
3-8
Page 24

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
10. Type y or Y and then press Enter to save the new IP address and restart NPort.
3-9
Page 25

4
4
Chapter 4 Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
In this chapter, we describe the various NPort 5600 operation modes. The options include an
operation mode that uses a driver installed on the host computer, and operation modes that rely on
TCP/IP socket programming concepts. After choosing the proper operation mode in this chapter,
refer to Chapter 5 for detailed configuration parameter definitions.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Real COM Mode
TCP Server Mode
TCP Client Mode
UDP Mode
Pair Connection Mode
Reverse Telnet Mode
Disabled Mode
RFC 2217 Mode
PPP Mode
Page 26
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Web Console Configuration
Overview
NPort Device Servers network-enable traditional RS-232/422/485 devices, in which a Device
Server is a tiny computer equipped with a CPU, real-time OS, and TCP/IP protocols that can
bi-directionally translate data between the serial and Ethernet formats. Your computer can access,
manage, and configure remote facilities and equipment over the Internet from anywhere in the
world.
Traditional SCADA and data collection systems rely on serial prots (RS-232/422/485) to collect
data from various kinds of instruments. Since NPort Serial Device Servers network-enable
instruments equipped with an RS-232/422/485 communication port, your SCADA and data
collection system will be able to access all instruments connected to a standard TCP/IP network,
regardless of whether the devices are used locally or at a remote site.
NPort is an external IP-based network device that allows you to expand the number of serial ports
for a host computer on demand. As long as your host computer supports the TCP/IP protocol, you
won’t be limited by the host computer’s bus limitation (such as ISA or PCI), or lack of drivers for
various operating systems.
In addition to providing socket access, NPort also comes with a Real COM/TTY driver that
transmits all serial signals intact. This means that your existing COM/TTY-based software can be
preserved, without needing to invest in additional software.
Three different Socket Modes are available: TCP Server, TCP Client, and UDP Server/Client. The
main difference between the TCP and UDP protocols is that TCP guarantees delivery of data by
requiring the recipient to send an acknowledgement to the sender. UDP does not require this type
of verification, making it possible to offer speedier delivery. UDP also allows multicasting of data
to groups of IP addresses.
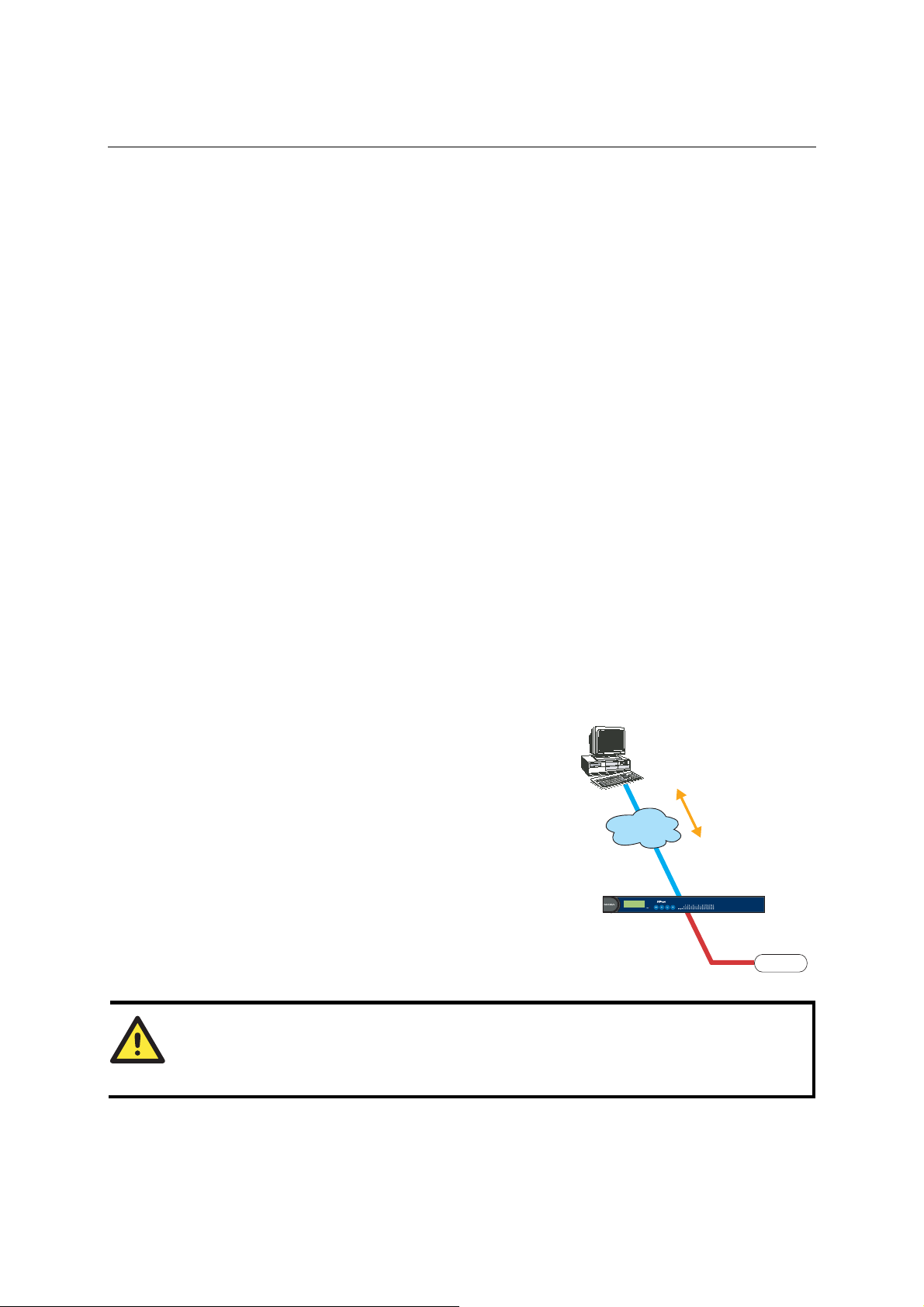
Real COM Mode
NPort comes equipped with COM drivers that work
with Windows 95/98/ME/NT/2000/XP systems,
and also TTY drivers for Linux systems. The driver
establishes a transparent connection between host
and serial device by mapping the IP:Port of the
NPort’s serial port to a local COM/TTY port on the
host computer. This operation mode also supports
up to 4 simultaneous connections, so that multiple
hosts can collect data from the same serial device at
the same time.
ATTENTION
The driver used for Real COM Mode comes with the NPort Windows Administrator. The driver
is installed automatically on your computer when you install NPort Administration Suite.
Real COM Mode
COM3 = IP Port
TCP/IP
Ethernet
5610-
16
Driver Mode
RS-232/422/485
Device
4-2
Page 27
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Web Console Configuration
The important point is that Real COM Mode allows users to continue using RS-232/422/485 serial
communications software that was written for pure serial communications applications. The driver
intercepts data sent to the host’s COM port, packs it into a TCP/IP packet, and then redirects it
through the host’s Ethernet card. At the other end of the connection, the NPort accepts the Ethernet
frame, unpacks the TCP/IP packet, and then transparently sends it to the appropriate serial device
attached to one of the NPort’s serial ports.
ATTENTION
Real COM Mode allows several hosts to have access control over the same NPort. The driver
that comes with your NPort controls host access to attached serial devices by checking the host’s
IP address.
Modify the Accessible IP Setting table when the legal IP address should be required in your
application
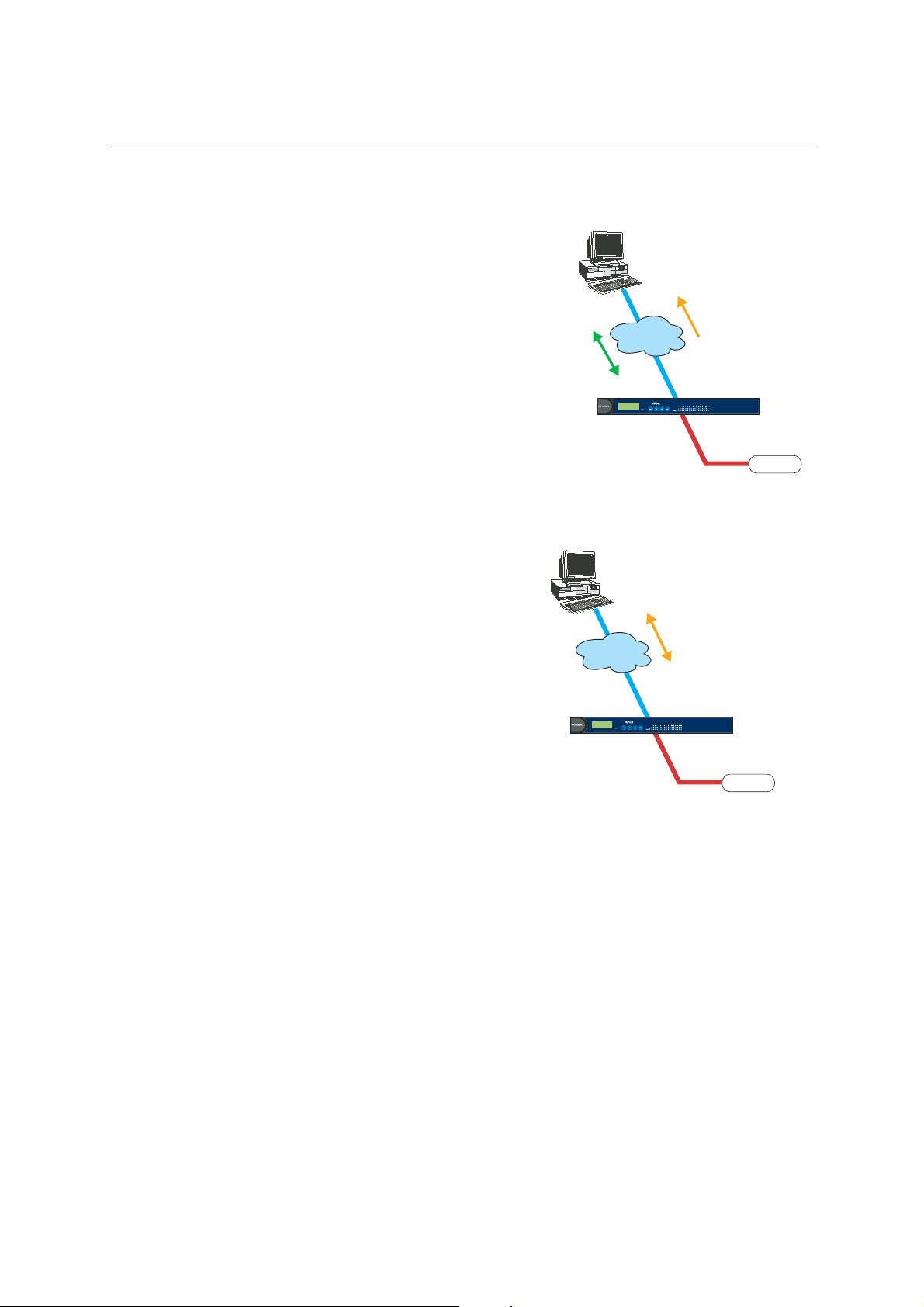
TCP Server Mode
In TCP Server mode, NPort provides a unique
IP:Port address on a TCP/IP network. NPort waits
passively to be contacted by the host computer,
allowing the host computer to establish a
connection with and get data from the serial device.
This operation mode also supports up to 4
simultaneous connections, so that multiple hosts
can collect data from the same serial device—at the
same time.
As illustrated in the figure, data transmission
proceeds as follows:
1. The host requests a connection from the NPort
configured for TCP Server Mode.
2. Once the connection is established, data can be
transmitted in both directions—from the host
to the NPort, and from the NPort to the host.
TCP Server Mode
1
TCP/IP
Ethernet
2
TCP Server
5610-
16
1Request a
connection
2Proceed with
data transmission
RS-232/422/485
Device
4-3
Page 28
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Web Console Configuration
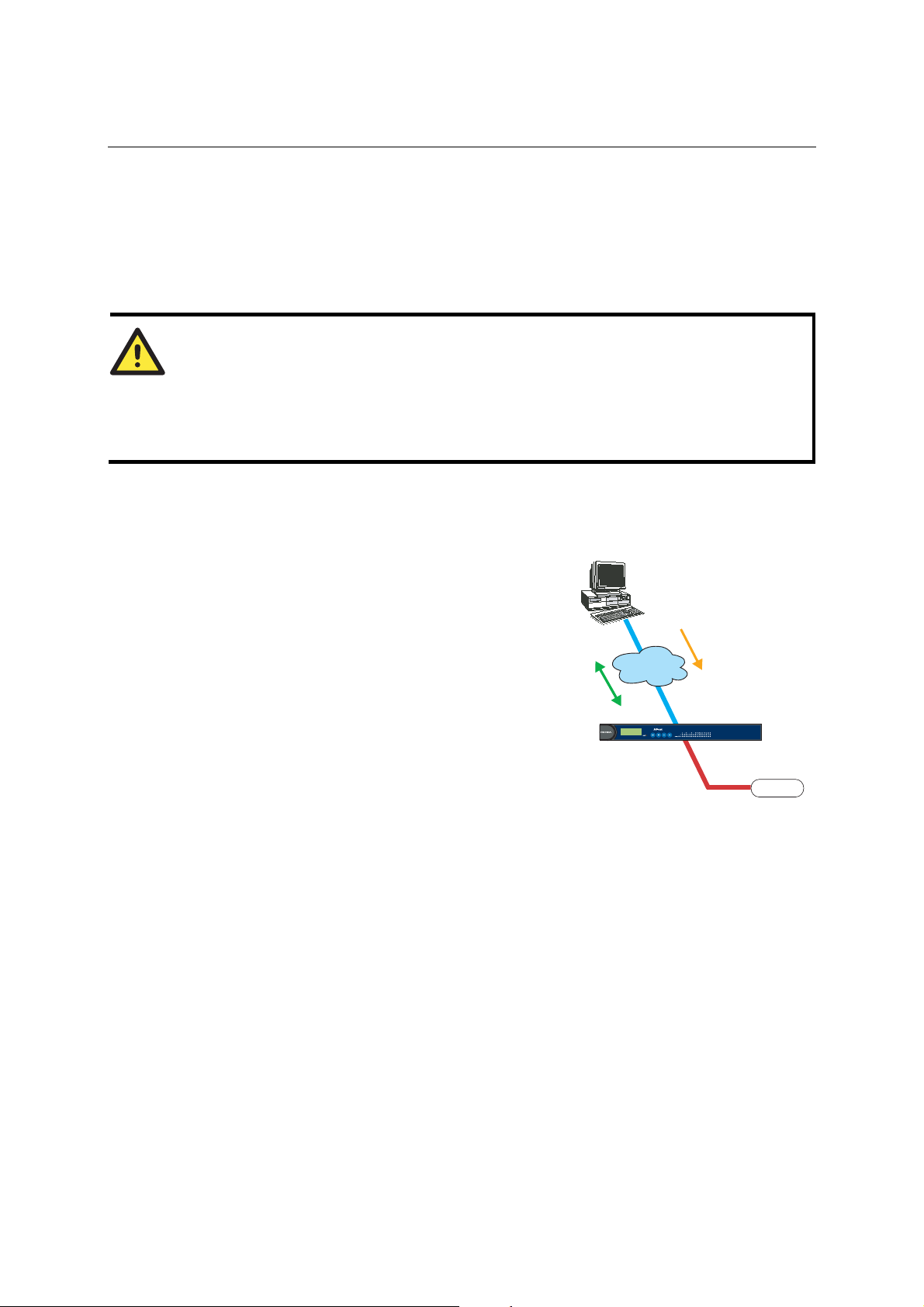
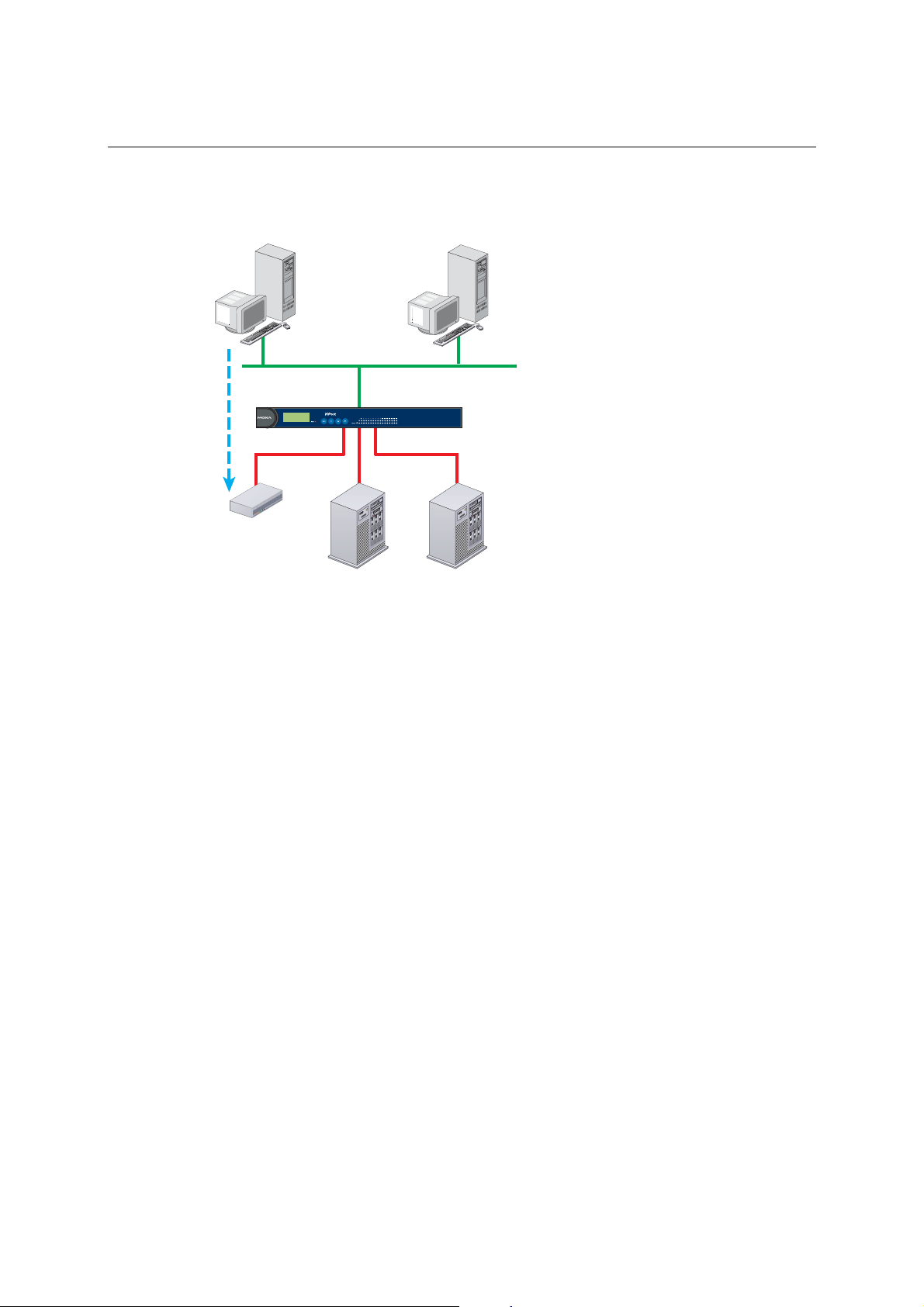
TCP Client Mode
In TCP Client mode, NPort can actively establish
a TCP connection to a pre-defined host computer
when serial data arrives.
After the data has been transferred, NPort can
automatically disconnect from the host computer
by using the TCP alive check time or Inactivity
time settings. Refer to chapter 5 for more details.
As illustrated in the figure, data transmission
proceeds as follows:
1. The NPort configured for TCP Client Mode
requests a connection from the host.
2. Once the connection is established, data can be
transmitted in both directions—from the host
to the NPort, and from the NPort to the host.
UDP Mode
Compared to TCP communication, UDP is faster
and more efficient. In UDP mode, you can
multicast data from the serial device to multiple
host computers, and the serial device can also
receive data from multiple host computers, making
this mode ideal for message display applications.
TCP Client Mode
TCP/IP
Ethernet
2
1Request a
connection
2Proceed with
data transmission
UDP Mode
TCP/IP
Ethernet
1
TCP Client
5610-
16
RS-232/422/485
Device
Directly proceed with
data transmission
(no connection required)
Pair Connection Mode
Pair Connection Mode employs two NPort 5600 in tandem, and can be used to remove the
15-meter distance limitation imposed by the RS-232 interface. One NPort 5600 is connected from
its RS-232 port to the COM port of a PC or other type of computer, such as hand-held PDAs that
have a serial port, and the serial device is connected to the RS-232 port of the other NPort 5600.
The two NPort 5600 units are then connected to each other with a cross-over Ethernet cable, both
are connected to the same LAN, or in a more advanced setup, they communicate with each other
over a WAN (i.e., through one or more routers). Pair Connection Mode transparently transfers
both data and modem control signals (although it cannot transmit the DCD signal) be tween the
two NPorts.
5610-
16
RS-232/422/485
Device
4-4
Page 29
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Web Console Configuration
Reverse Telnet Mode
Unix Windows NT
TCP/IP
Telnet
5610-
16
RS-232
NPort 5600
Series
Router Server Server
Console management is commonly used by connecting to Console/AUX or COM ports of routers,
switches, and UPS units. Rtelnet works the same as RAW mode in that only one TCP port is
listened to after booting up. The system then waits for a host on the network to initiate a
connection. The difference is that the RAW mode does not provide the conversion function
provided by Telnet. If the connected devices need to use the CR/LF conversion function when
controlling, then users must choose Rtelnet mode.
Disabled Mode
Setting the operation mode of a particular port to Disabled, disables that port.
RFC2217 Mode
RFC2217 is a standard driver that provides Virtual COM function. RFC2217 defines general com
port control options based on telnet protocol. Any 3rd party dri ver supporti ng RFC 2217 c an be used
to implement virtual COM on NPort 5600 series. The driver establishes a transparent connection
between host and serial device by mapping the IP:Port of the NPort 5600 series’ serial port to a local
COM port on the host computer. (RFC2217 Mode supports 1 connection)
4-5
Page 30
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Web Console Configuration
PPP Mode
NPort 5600 Device Server supports standard PPP service for out-of-band management if the Ethernet
network crashes. The PPP function enables dial-in access for users who need a remote access
solution. When a user at a remote site uses PPP dial-in to connect to NPort 5600, NPort 5600 plays
the role of a dial-in server. After the PPP connection is established, the user can remotely manage the
NPort 5600.
Please refer to Chapter 5 for detailed information and configuration instructions.
Web Server E-mail Server
TCP/IP
NPort 5600 Series
5610-
16
Router
Modem
Modem
PPP
Dialin
PC Notebook
PPP
Dialin
Internet
4-6
Page 31

5
5
Chapter 5 Web Console Configuration
The Web Console is the most user-friendly method available to configure NPort 5600 Series. This
chapter will introduce the Web Console function groups and function definitions. The figures in
this chapter were borrowed from the manual for NPort 5200, which uses the same Web Console
user interface as NPort 5600.
Opening Your Browser
Basic Settings
Network Settings
Serial Settings
Operating Settings
¾ Real COM Mode
¾ TCP Server Mode
¾ TCP Client Mode
¾ UDP Mode
¾ Pair Connection Mode
¾ Reverse Telnet Mode
¾ Disabled Mode
¾ RFC 2217 Mode
¾ PPP Mode
Accessible IP Settings
PPP User Table
Auto Warning Settings
¾ Auto warning: E-mail and SNMP Trap
¾ Event Type
Monitor
¾ Monitor Line
¾ Monitor Async
¾ Monitor Async-Settings
Change Password
Load Factory Default
Page 32
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
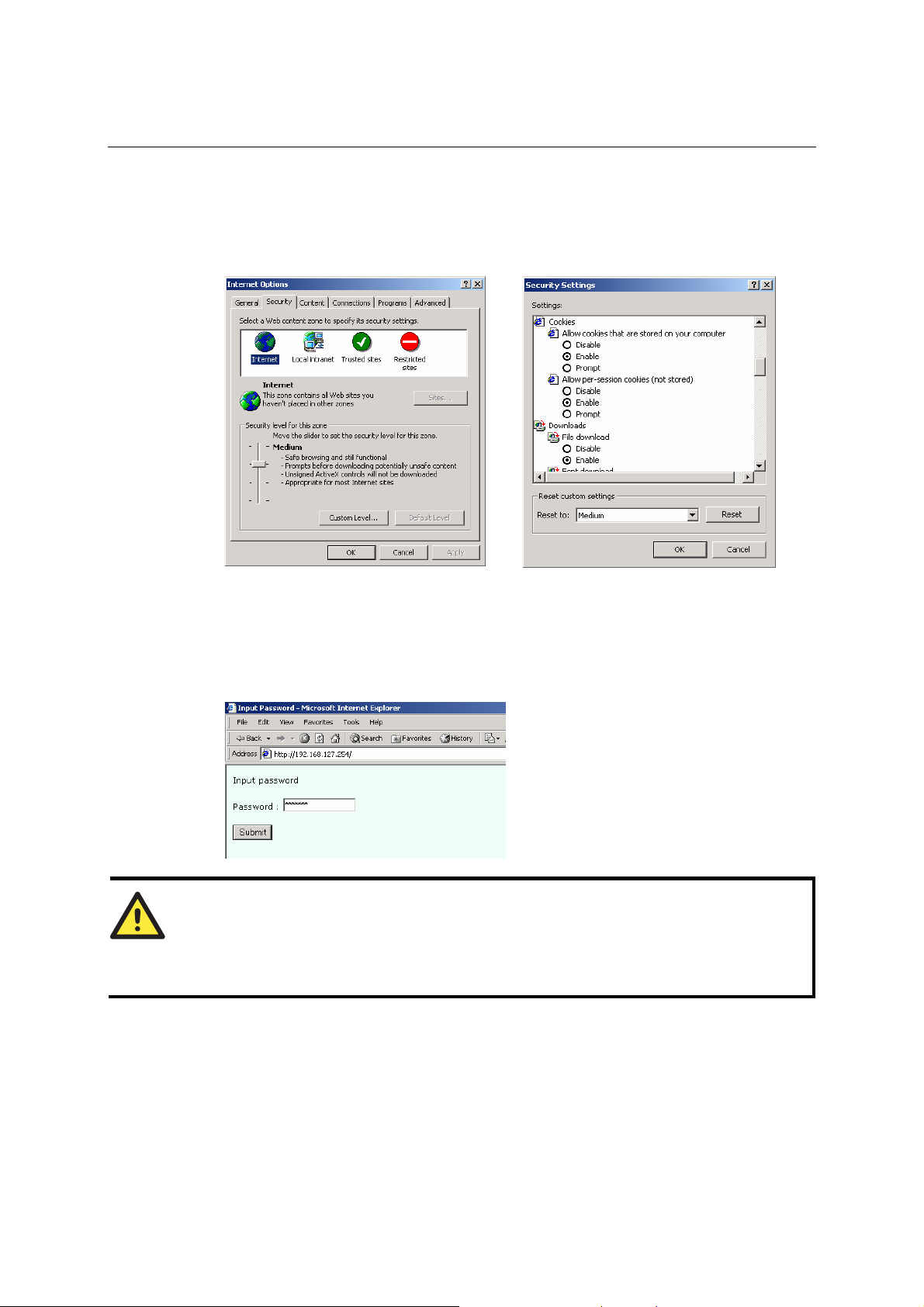
Opening Your Browser
1. Open your browser with the cookie function enabled. (To enable your browser for cookies,
right click your desktop Internet Explorer icon, select Proper ties, click the Security tab, and
then select the three Enable options as shown in the figure below.)
2. Type 192.168.127.254 in the Address input box (use the correct IP address if different from
the default), and then press Enter.
3. Input the password if prompted. The password will be transmitted with MD5 en cryption over
the Ethernet.
Note that you will not be prompted to enter the password if the NPort is not currently
password protected.
ATTENTION
If you use other web browsers, remember to Enable the functions to “allow cookies that are
stored on your computer” or “allow per-session cooki es.”
NPort 5600 series uses cookies only for “password” transmission.
5-2
Page 33
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
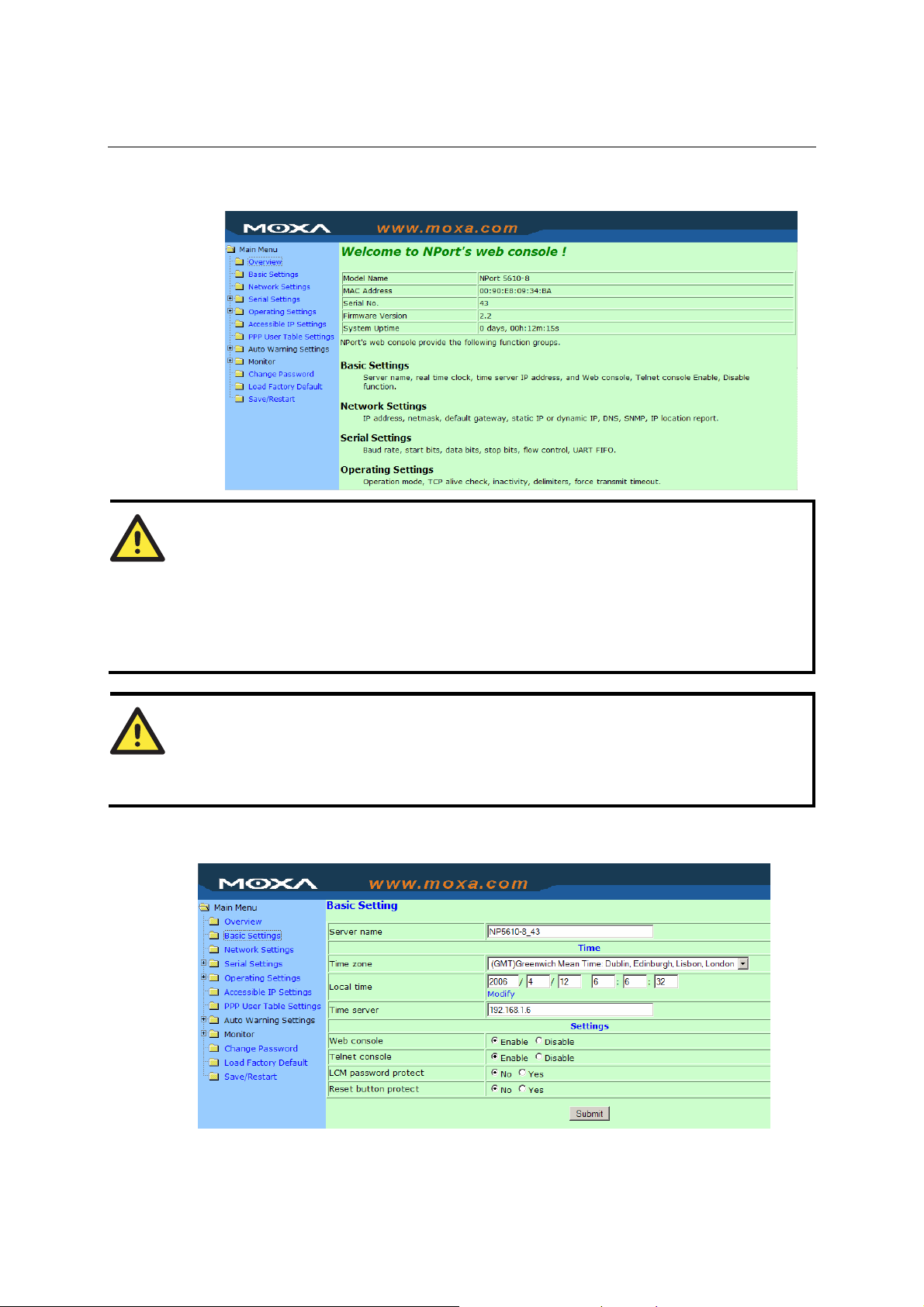
4. The NPort 5600 homepage will open. On this page, you can see a brief description of the Web
Console’s nine function groups.
ATTENTION
If you can’t remember the password, the ONLY way to start configuring NPort is to load factory
defaults by using the Reset button located near the NPort’s RJ45 Ethernet port.
Remember to use NPort Administrator to export the configuration file when you have finished
the configuration. After using the Reset button to load factory defaults, your configuration can be
easily reloaded into NPort by using the NPort Administrator Import function. Refer to Chapter 6
for more details about using the Export and Import functions.
ATTENTION
If your NPort application requires using password protection, you must enable the cookie
function in your browser. If the cookie function is disabled, you will not be allowed to enter the
Web Console Screen.
Basic Settings
5-3
Page 34
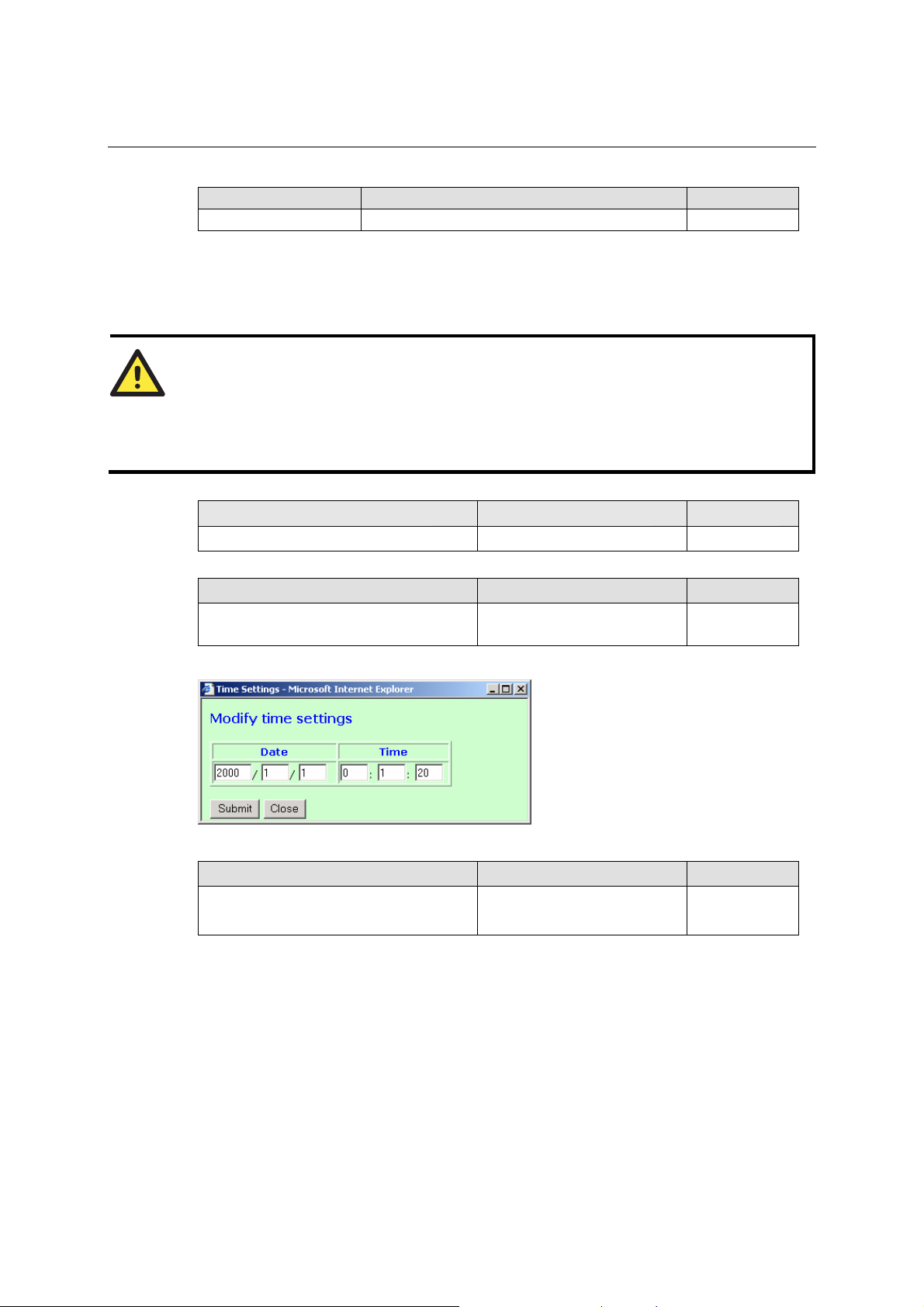
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Server name
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 39 characters NP[model name]-[Port No.]_ [Serial No.] Optional
This option is useful for specifying the location or application of different NPorts.
Time
NPort 5600 has a built-in Real-Time Clock for time calibration functions. Functions such as Auto
warning “Email” or “SNMP Trap” can add real-time information to the message.
ATTENTION
First time users should select the time zone first. The Console will display the “real time”
according to the time zone compared to GMT.
If you would like to modify the real time clock, select “Local time.” NPort’s firmware will
modify the GMT time according to the Time Zone.
Time zone
Setting Factory Default Necessity
User selectable time zone GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) Optional
Local time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
User adjustable time.
(1900/1/1-2037/12/31)
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) Optional
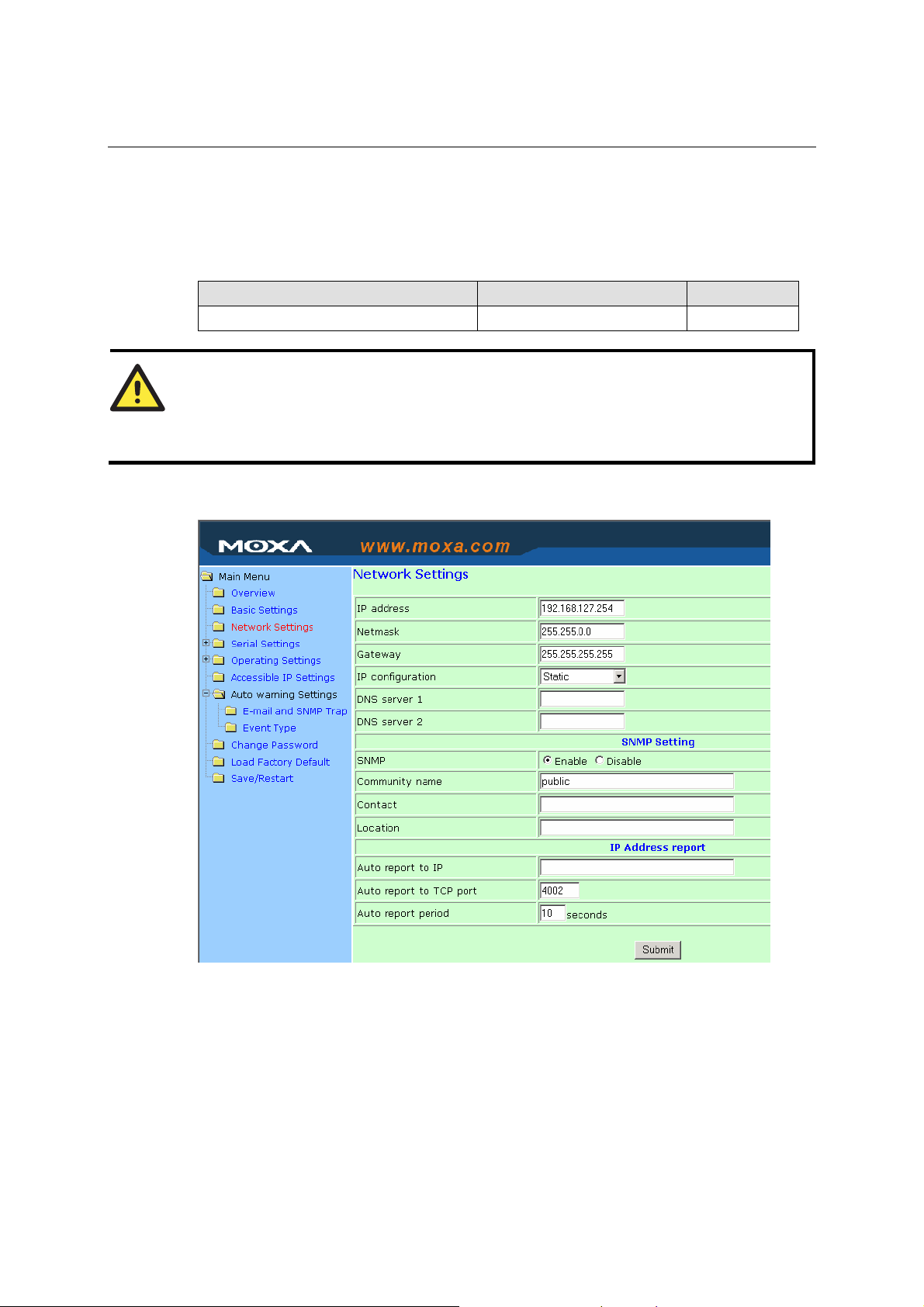
Click the Modify button to open the Modify time settings window to input the correct local time.
Time server
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP or Domain address
(E.g., 192.168.1.1 or time.stdtime.gov.tw)
NPort 5600 uses SNTP (RFC-2030) for auto time calibration.
Input the correct “Time server” IP address or domain address. Once NPort is configured with the
correct Time Server address, NPort will request time information from the “Time server” every 10
minutes.
None Optional
5-4
Page 35
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Console
The “Disable” option for Web Console and Telnet Console is included for security reasons. In
some cases, you may want to Disable one or both of these Console utilities as an extra precaution
to prevent unauthorized users from accessing your NPort. The factory default for both Web
Console and Telnet Console is Enable.
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Enable or Disable Enable Required
ATTENTION
If you disable both the “Web Console” and “Telnet Console,” you can still u se the LCM Display
to configure NPort locally, or Windows Administrator to configure NPort either locally or
remotely over the network.
Network Settings
You must assign a valid IP address to NPort 5600 before it will work in your network environment.
Your network system administrator should provide you with an IP address and related settings for
your network. The IP address must be unique within the network (otherwise, NPort 5600 will not
have a valid connection to the network). First time users can refer to Chapter 3, Initial IP Address
Configuration, for more information.
You can choose from four possible IP Configuration modes—Static, DHCP, DHCP/BOOTP, and
BOOTP—located under the web console screen’s IP configuration drop-down box.
5-5
Page 36
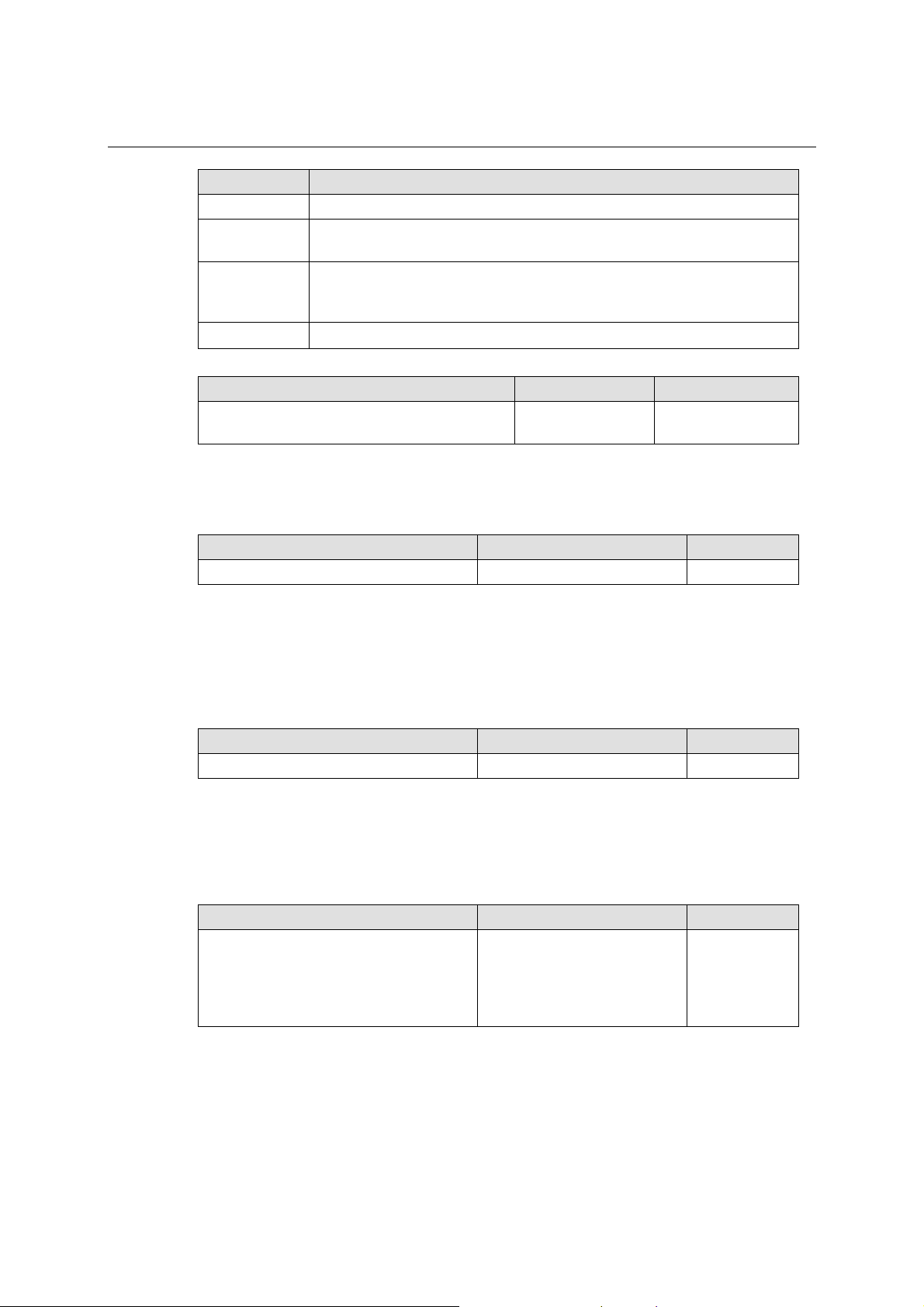
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Method Function Definition
Static User defined IP address, Netmask, Gateway.
DHCP
DHCP/BOOTP
BOOTP BOOTP Server assigned IP address
IP Address
Setting Factory Default Necessity
E.g., 192.168.1.1 (IP addresses of the form
x.x.x.0 and x.x.x.255 are invalid.)
An IP address is a number assigned to a network device (such as a computer) as a permanent
address on the network. Computers use the IP address to identify and talk to each other over the
network. Choose a proper IP address which is unique and valid in your network environment.
Netmask
Setting Factory Default Necessity
E.g., 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 Required
A subnet mask represents all the network hosts at one geographic location, in one building, or on
the same local area network. When a packet is sent out over the network, the NPort will use the
subnet mask to check if the desired TCP/IP host specified in the packet is on the local network
segment. If the address is on the same network segment as the NPort, a connection is established
directly from the NPort. Otherwise, the connection is established through the given default
gateway.
DHCP Server assigned IP address, Netmask, Gateway, DNS, and Time
Server
DHCP Server assigned IP address, Netmask, Gateway, DNS, and Time
Server, or BOOTP Server assigned IP address (if the DHCP Server does not
respond)
192.168.127.254 Required
Gateway
Setting Factory Default Necessity
E.g., 192.168.1.1 None Optional
A gateway is a network gateway that acts as an entrance to another network. Usually, the
computers that control traffic within the network or at the local Internet service provider are
gateway nodes. NPort needs to know the IP address of the default gateway computer in order to
communicate with the hosts outside the local network environment. For correct gateway IP
address information, consult the network administrator.
IP Configuration
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Static
DHCP
DHCP/BOOTP
BOOTP
Static Required
5-6
Page 37
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
ATTENTION
In Dynamic IP environments, the firmware will retry 3 times every 30 seconds until network
settings are assigned by the DHCP or BOOTP server. The Timeout for each try increases from 1
second, to 3 seconds, to 5 seconds.
If the DHCP/BOOTP Server is unavailable, the firmware will use the default IP address
(192.168.127.254), Netmask, and Gateway for IP setting s.
DNS server 1 / DNS server 2
Setting Factory Default Necessity
E.g., 192.168.1.1
(IP addresses of the form x.x.x.0 and
x.x.x.255 are invalid.)
When the user wants to visit a particular website, the computer asks a Domain Name System
(DNS) server for the website’s correct IP address, and the computer users the response to connect
to the web server. DNS is the way that Internet domain names are identified and translated into IP
addresses. A domain name is an alphanumeric name, such as moxa.com, that it is usually easier to
remember. A DNS server is a host that translates this kind of text-based domain name into the
numeric IP address used to establish a TCP/IP connection.
In order to use NPort’s DNS feature, you need to set the IP address of the DNS server to be able to
access the host with the domain name. NPort provides DNS server 1 and DNS server 2
configuration items to configure the IP address of the DNS server. DNS Server 2 is included for
use when DNS sever 1 is unavailable.
None Optional
NPort plays the role of DNS client. Functions that support domain name in NPort are Time Sever
IP Address, TCP Client-Destination IP Address, Mail Server, SNMP Trap IP Address, and
IP Location Server.
SNMP Settings
Community name
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 39 characters
(E.g., Support, 886-89191230 #300)
A community name is a plain-text password mechanism that is used to weakly authenticate queries
to agents of managed network devices.
Contact
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 39 characters
(E.g., Support, 886-89191230 #300)
The SNMP contact information usually includes an emergency contact name and telephone or
pager number.
Location
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 39 characters
(E.g., Floor 1, office 2)
Specify the location string for SNMP agents such as NPort. This string is usually set to the street
address where the NPort is physically located.
public Optional
None Optional
None Optional
5-7
Page 38
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
IP Address Report
When NPort 5600 series products are used in a dynamic IP environment, users must spend more
time with IP management tasks. For example, if NPort works as a server (TCP or UDP), then the
host, which acts as a client, must know the IP address of the server. If the DHCP server assigns a
new IP address to NPort, the host must have some way of determining NPort’s new IP address.
NPort 5000 series products help out by periodically reporting their IP address to the IP location
server, in case the dynamic IP has changed. The parameters shown below are used to configure the
Auto IP report function. There are two ways to develop an “Auto IP report Server” to receive
NPort’s Auto IP report.
1. Use NPort Administrator’s IP Address Report function.
2. “Auto IP report protocol,” which can automatically receive the Auto IP report on a regular
basis, is also available to help you develop your own software. Refer to Appendix E for the
“Auto IP report protocol”.
Auto report to IP
Setting Factory Default Necessity
E.g., 192.168.1.1
(IP addresses of the form x.x.x.0 and
x.x.x.255 are invalid.)
Reports generated by the Auto report function will be sent automatically to this IP address.
Auto report to TCP port
Setting Factory Default Necessity
E.g., 4001 None Optional
None Optional
Auto report period
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Time interval (in seconds) 10 Optional
5-8
Page 39
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Serial Settings
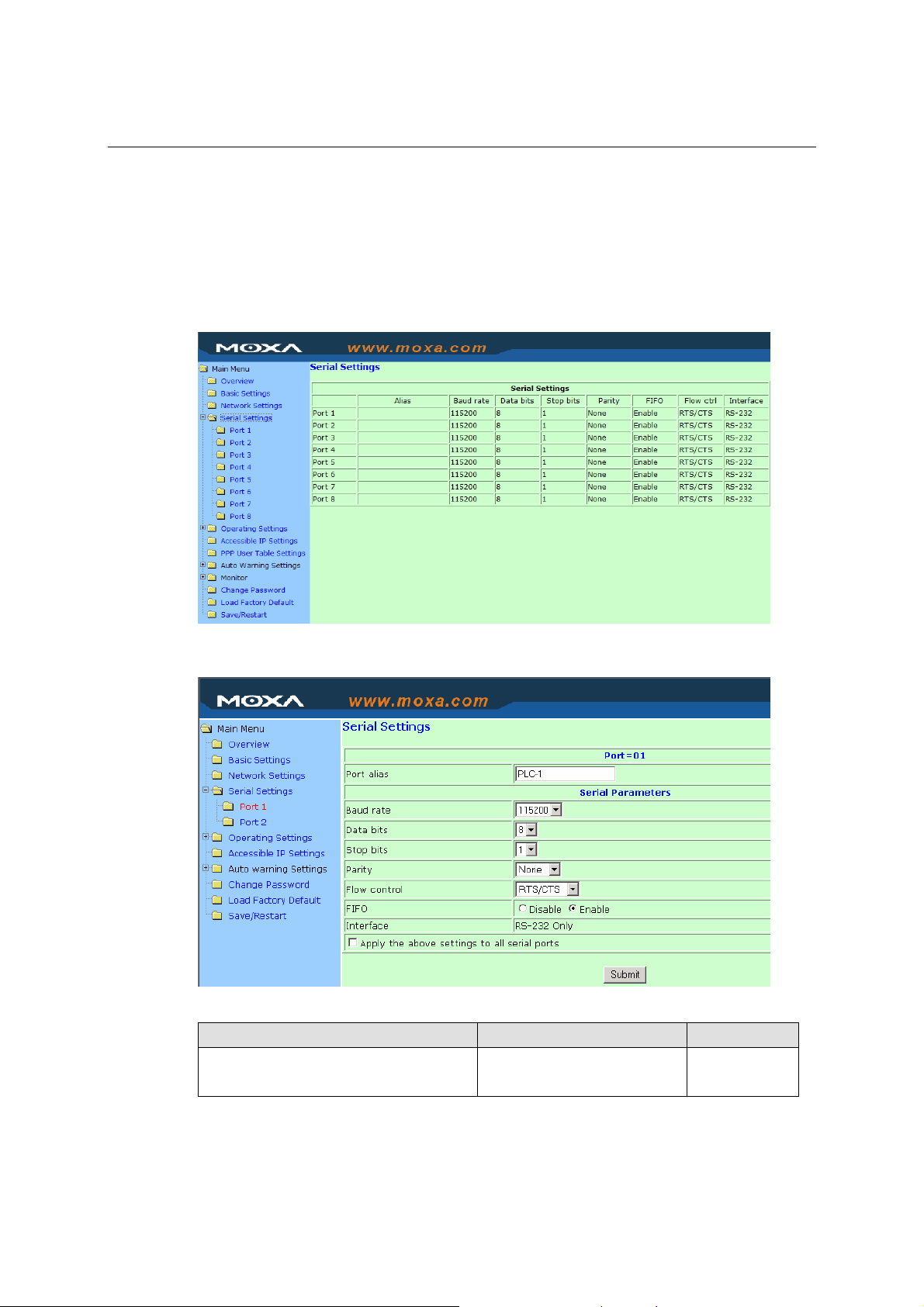
Click Serial Settings, located under Main Menu, to display serial port settings for ports 1 and 2.
NOTE: Since this figure was borrowed from the manual of NPort 5200, which has only 2 RS-232
ports, there are only 2 ports shown in this figure. Once you have completed the hardware
installation of NPort 5600, there should be either 16 or 8 ports shown in the figure, depending on
the model you installed. The steps for changing the settings of the other ports are the same as those
for Port 1 and Port 2.
To modify serial settings for a particular port, click either Port 1 or Port 2 under Serial Settings,
located under Main Menu on the left side of the browser window
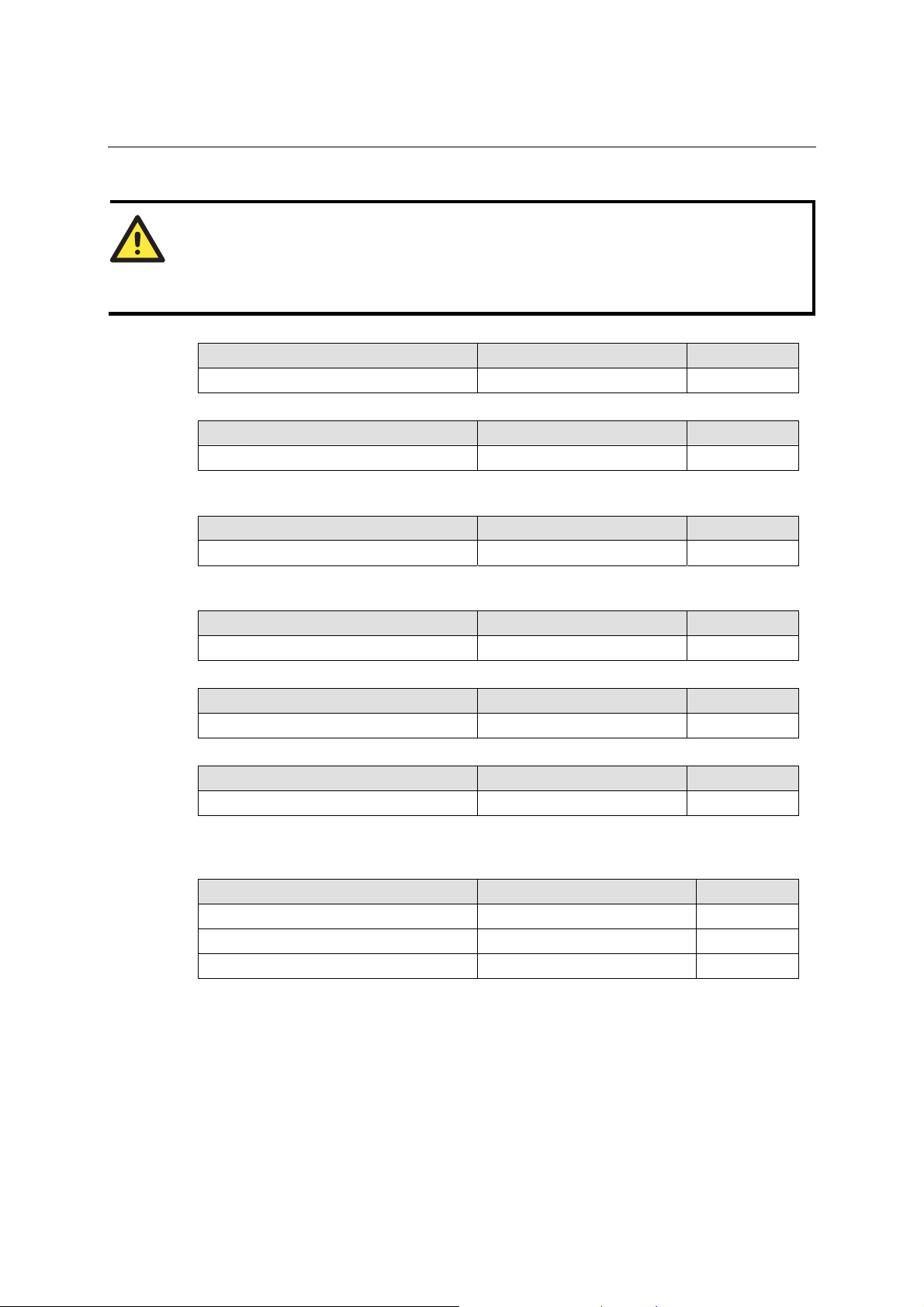
Port alias
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 15 characters
(E.g., PLC-No.1)
“Port Alias” is specially designed to allow easy identification of the serial devices which are
connected to NPort’s serial port.
None Optional
5-9
Page 40
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Serial Parameters
ATTENTION
Check the serial communication parameters in your Serial Device’s user’s manual. You should
set up NPort’s serial parameters with the same communication parameters used by your serial
devices.
Baudrate
Setting Factory Default Necessity
50 bps to921.6 Kbps 115.2 Kbps Required
Data bits
Setting Factory Default Necessity
5, 6, 7, 8 8 Required
When the user sets Data bits to 5 bits, the stop bits setting will automatically change to 1.5 bits.
Stop bits
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1, 1.5, 2 1 Required
Stop bits will be set to 1.5 when Data bits is set to 5 bits.
Parity
Setting Factory Default Necessity
None, Even, Odd, Space, Mark None Required
Flow control
Setting Factory Default Necessity
None, R TS/ C TS, DTR/DSR, Xon/Xoff RTS/CTS Required
FIFO
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Enable, Disable Enable Required
NPort’s serial ports provide a 16-byte FIFO both in the Tx and Rx directions. Disable the FIFO
setting when your serial device does not have a FIFO to prevent data loss during communication.
Interface
Setting Factory Default Necessity
NPort 5610-16/8: RS-232 only RS-232 only Required
NPort 5630-16/8: RS-422/485 only 4-wire RS-485 Required
NPort 5650-16/8 RS-232 Required
5-10
Page 41
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
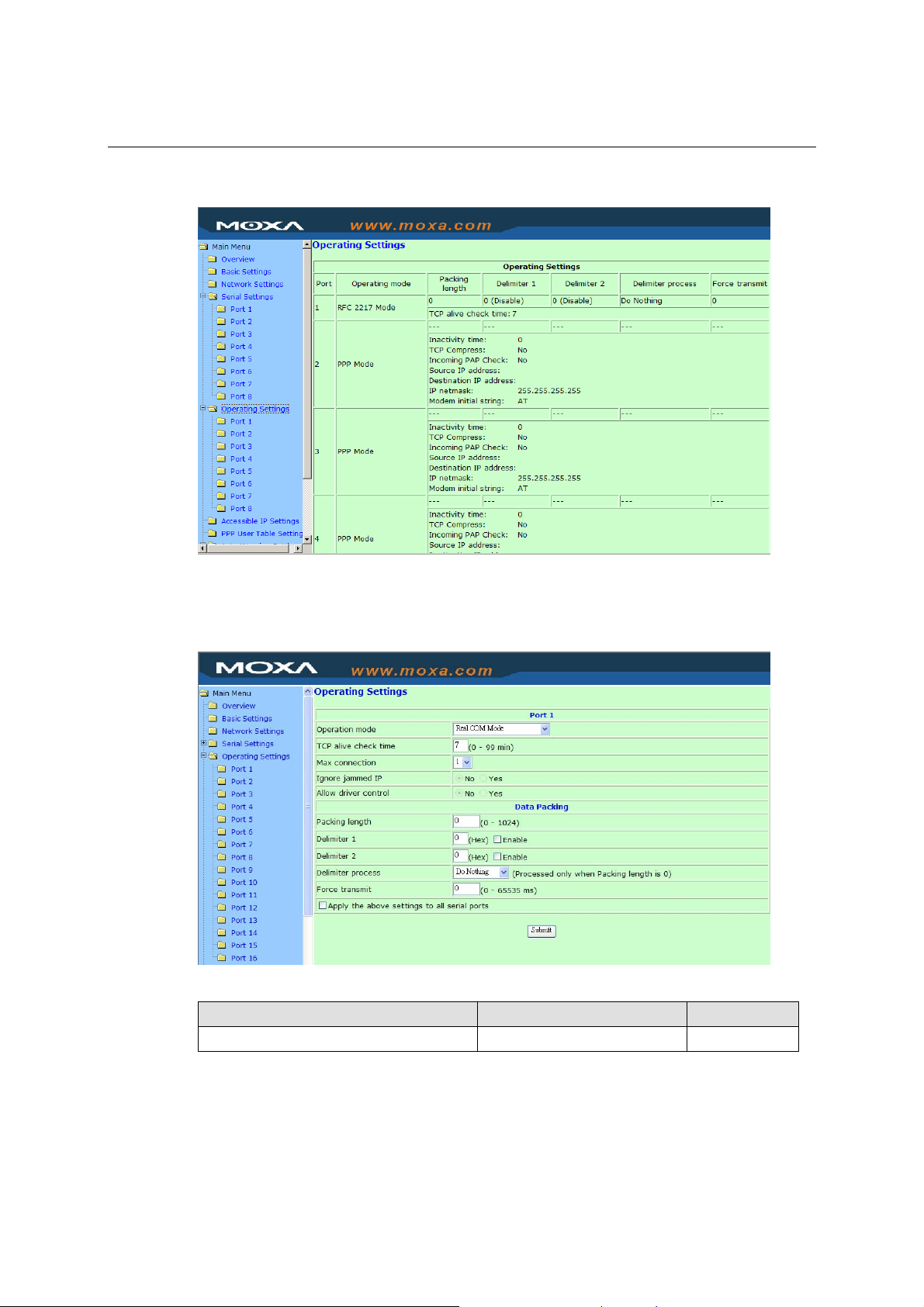
Operating Settings
Click Operating Settings located under Main Menu, to display the operating settings for all of
NPort’s serial ports.
Real COM Mode
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min 7 min Optional
0 min: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: NPort automatically closes TCP connection if there is no TCP activity for the given
time. After the connection is closed, NPort starts listening for another Real COM driver
connection from another host.
5-11
Page 42

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Max connection
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1, 2, 3, 4 1 Required
Max connection is usually used when the user needs to receive data from different hosts
simultaneously. The factory default is 1. In this case, only one specific host can access this port of
the NPort, and the Real COM driver on that host will have full control over the port.
Max. connection 1:
Allows only a single host’s Real COM driver to open the specific NPort serial port.
Max connection 2 to 4:
Allows 2 to 4 hosts’ Real COM drivers to open the specific NPort serial port at the same time.
When multiple hosts’ Real COM drivers open the serial port at the same time, the COM driver
only provides a pure data tunnel without control ability. That is, this serial port parameter will use
firmware’s settings, not depend on your appl i cat i on pr o gram (AP) .
Application software that is based on the COM driver will receive a driver response of “success”
when the software uses any of the Win32 API functions. The firmware will only send the data
back to the driver on the host.
Data will be sent first-in-first-out when data comes into the NPort from the Ethernet interface.
Ignore jammed IP
Setting Factory Default Necessity
No or Yes No Required
For previous versions of NPort 5200, when Max connections > 1, and the serial device is
transmitting data, if any one of the connected hosts was not responding NPort 5200 would wait
until the data had been transmitted successfully before transmitting the second group of data to all
hosts. For the current version of NPort 5200, if you select Yes for “Ignore jammed IP,” the host
that is not responding will be ignored, but the data will still be transmitted to the other hosts.
Allow driver control
Setting Factory Default Necessity
No or Yes No Required
If “max connection” is greater than 1, NPort will ignore driver control commands from all
connected hosts. However, if you set “Allow driver control” to YES, control commands will be
accepted. Note that since NPort 5200 may get configuration changes from multiple hosts, the most
recent command received will take precedence.
ATTENTION
When Max connection is set to 2, 3, or 4, this means that NPort will be using a “multi connection
application” (i.e., 2, 3, or 4 hosts are allowed access to the port at the same time). When using a
multi connection application, NPort will use the serial communication parameters set in the
console. All of the hosts connected to that port must use the same serial settings. If one of the
hosts opens the COM port with parameters that are different from NPort’s console setting, data
communication may not work properly.
5-12
Page 43

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Packing length
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 1024 0 Required
Default = 0, The Delimiter Process will be followed, regardless of the length of the data packet. If
the data length (in bytes) matches the configured value, the data will be forced out. The data length
can be configured for 0 to 1024 bytes. Set to 0 if you do not need to limit the length.
Delimiter 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Delimiter 2
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Once the NPort receives both delimiters through its serial port, it immediately packs all data
currently in its buffer and sends it to the NPort’s Ethernet port.
ATTENTION
Delimiter 2 is optional. If left blank, then Delimiter 1 alone trips clearing of the buffer. If the size
of the serial data received is greater than 1 KB, the NPort will automatically pack the data and
send it to the Ethernet. However, to use the delimiter function, you must at least enable Delimiter
1. If Delimiter 1 is left blank and Delimiter 2 is enabled, the delimiter function will not work
properly.
Delimiter process
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Do nothing, Delimiter + 1, Delimiter +
2, Strip Delimiter
When [Delimiter + 1] or [Delimiter + 2] is selected, the data will be transmitted when an
additional byte (for Delimiter +1), or an additional 2 bytes (for Delimiter +2) of data is received
after receiving the Delimiter.
When [Strip Delimiter] is selected, when the Delimiter is received, the Delimiter is deleted (i.e.,
stripped), and the remaining data is transmitted.
When [Do nothing] is selected, the data will be transmitted when the Delimiter is received.
Force transmit
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
Do Nothing Required
0: Disable the force transmit timeout.
1 to 65535: Forces the NPort’s TCP/IP protocol software to try to pack serial data received during
the specified time into the same data frame.
5-13
Page 44

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
This parameter defines the time interval during which NPort fetches the serial data from its
internal buffer. If data is incoming through the serial port, NPort stores the data in the internal
buffer. NPort transmits data stored in the buffer via TCP/IP, but only if the internal buffer is full or
if the Force transmit time interval reaches the time specified under Force transmit timeout.
The optimal Force transmit timeout depends on your application, but it must be at least larger than
one character interval within the specified baudrate. For example, assume that the serial port is set
to 1200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and none for parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed
to send a character is 10 bits, and the time required to transfer one character is
( 10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s) ) * 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set Force transmit timeout to be larger than 8.3 ms, so in this case, it must
be greater than or equal to 10 ms.
If the user wants to send the series of characters in the same packet, the serial device attached to
NPort should send that series of characters during a time interval less than the Force Transmit
timeout for NPort, and the total length of data must be less than or equal to NPort’s internal buffer
size. The serial communication buffer size for NPort is 1 KB per port.
TCP Server Mode
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min 7 min Optional
0 min: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: NPort automatically closes the TCP connection if there is no TCP activity for the
given time. After the connection is closed, NPort starts listening for another host’s TCP
connection.
5-14
Page 45

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Inactivity time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0 ms: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle serial line.
0-65535 ms: NPort automatically closes the TCP connection if there is no serial data activity for
the given time. After the connection is closed, NPort starts listening for another host’s TCP
connection.
This parameter defines the maintenances status as Closed or Listen on the TCP connection. The
connection is closed if there is no incoming or outgoing data through the serial port during the
specific Inactivity time.
If the Inactivity time is set to 0, the current TCP connection is kept active until a connection close
request is received. Although Inactivity time is disabled, the NPort will check the connection
status between the NPort and remote host by sending “keep alive” packets periodically. If the
remote host does not respond to the packet, NPort assumes that the connection was closed down
unintentionally. NPort will then force the existing TCP connection to close.
ATTENTION
The Inactivity time should at least be set larger than that of Force transmit timeout. To prevent
the unintended loss of data due to the session being disconnected, it is highly recommended that
this value is set large enough so that the intended data transfer is completed.
Max connection
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1, 2, 3, 4 1 Required
Max connection is usually used when the user needs to receive data from different hosts
simultaneously. The factory default only allows 1 connection at a time.
Max. connection 1:
NPort only allows 1 host to open the TCP connection to the specific serial port.
Max connection 2 to 4:
Allows 2 to 4 host’s TCP connection request to open this NPort serial port, at the same time. When
multiple hosts establish a TCP connection to the specific serial port at the same time, NPort will
duplicate the serial data and transmit to all of the hosts. Ethernet data is sent on a first-in-first-out
basis to the serial port when data comes into NPort from the Ethernet interface.
Ignore jammed IP
Setting Factory Default Necessity
No or Yes No Required
For previous versions of NPort 5200, when Max connections > 1, and the serial device is
transmitting data, if any one of the connected hosts was not responding NPort 5200 would wait
until the data had been transmitted successfully before transmitting the second group of data to all
hosts. For the current version of NPort 5200, if you select Yes for “Ignore jammed IP,” the host
that is not responding will be ignored, but the data will still be transmitted to the other hosts.
5-15
Page 46

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Allow driver control
Setting Factory Default Necessity
No or Yes No Required
If “max connection” is greater than 1, NPort will ignore driver control commands from all
connected hosts. However, if you set “Allow driver control” to YES, control commands will be
accepted. Note that since NPort 5200 may get configuration changes from multiple hosts, the most
recent command received will take precedence.
Packing length
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 1024 0 Required
Default = 0, The Delimiter Process will be followed, regardless of the length of the data packet. If
the data length (in bytes) matches the configured value, the data will be forced out. The data length
can be configured for 0 to 1024 bytes. Set to 0 if you do not need to limit the length.
Delimiter 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Delimiter 2
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Once the NPort receives both delimiters through its serial port, it immediately packs all data
currently in its buffer and sends it to the NPort’s Ethernet port.
Delimiter process
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Do nothing, Delimiter + 1, Delimiter +
2, Strip Delimiter
When [Delimiter + 1] or [Delimiter + 2] is selected, the data will be transmitted when an
additional byte (for Delimiter +1), or an additional 2 bytes (for Delimiter +2) of data is received
after receiving the Delimiter. When [Strip Delimiter] is selected, when the Delimiter is received,
the Delimiter is deleted (i.e., stripped), and the remaining data is transmitted. When [Do nothing]
is selected, the data will be transmitted when the Delimiter is received.
ATTENTION
Delimiter 2 is optional. If left blank, then Delimiter 1 alone trips clearing of the buffer. If the size
of the serial data received is greater than 1 KB, the NPort will automatically pack the data and
send it to the Ethernet. However, to use the delimiter function, you must at least enable Delimiter
1. If Delimiter 1 is left blank and Delimiter 2 is enabled, the delimiter function will not work
properly.
Do Nothing Required
5-16
Page 47

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Force transmit
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0: Disable the force transmit timeout.
1 to 65535: Forces the NPort’s TCP/IP protocol software to try to pack serial data received during
the specified time into the same data frame.
This parameter defines the time interval during which NPort fetches the serial data from its
internal buffer. If data is incoming through the serial port, NPort stores the data in the internal
buffer. NPort transmits data stored in the buffer via TCP/IP, but only if the internal buffer is full or
if the Force transmit time interval reaches the time specified under Force transmit timeout.
The optimal Force transmit timeout depends on your application, but it must be at least larger than
one character interval within the specified baudrate. For example, assume that the serial port is set
to 1200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and none for parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed
to send a character is 10 bits, and the time required to transfer one character is
( 10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s) ) * 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set Force transmit timeout to be larger than 8.3 ms, so in this case, it must
be greater than or equal to 10 ms.
If the user wants to send the series of characters in the same packet, the serial device attached to
NPort should send that series of characters during a time interval less than the Force Transmit
timeout for NPort, and the total length of data must be less than or equal to NPort’s internal buffer
size. The serial communication buffer size for NPort is 1 KB per port.
Local TCP port
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 65535 4001 Required
The “Local TCP port” is the TCP port that NPort uses to listen to connections, and that other
devices must use to contact NPort. To avoid conflicts with well known TCP ports, the default is
set to 4001.
Command port
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 65535 966 Optional
The “Command port” is a listen TCP port for IP-Serial Lib commands from the host. In order to
prevent a TCP port conflict with other applications, the user can set the Command port to another
port if needed. IP-Serial Lib will automatically check the Command Port on NPort so that the user
does not need to configure the program.
5-17
Page 48
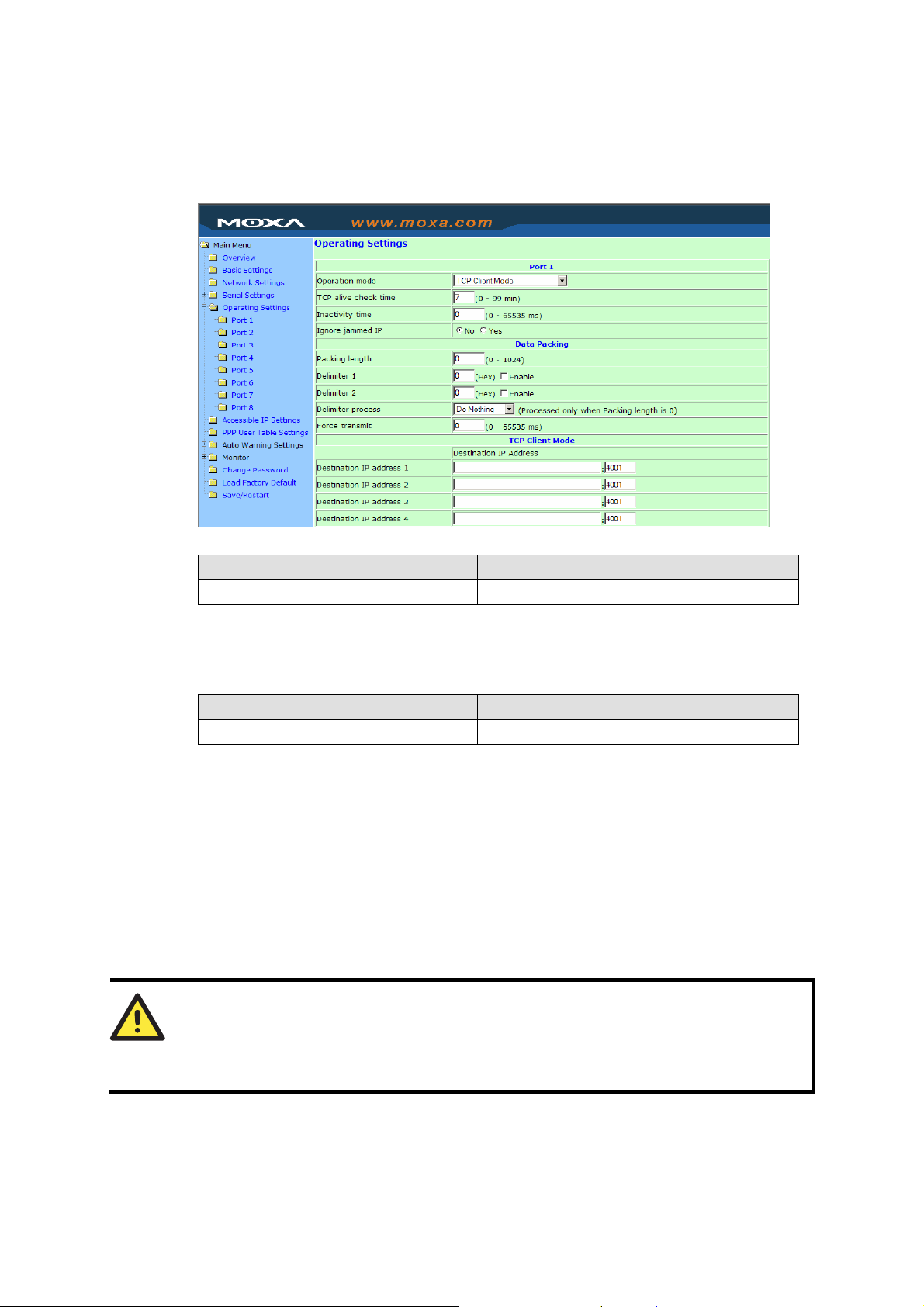
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
TCP Client Mode
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min 7 min Optional
0 min: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: NPort automatically closes the TCP connection if there is no TCP activity for the
given time.
Inactivity time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0 ms: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle serial line.
0-65535 ms: NPort automatically closes TCP connection, if there is no serial data activity for the
given time.
This parameter defines the maintenances status as Closed or Listen on the TCP connection. The
connection is closed if there is no incoming or outgoing data through the serial port during the
specific Inactivity time.
If the value of inactivity time is set to 0, the current TCP connection is maintained unless there’s
no connection close request. Although the inactivity time is disabled, the NPort will check the
connection status between the NPort and remote host by sending “keep alive” packets periodically.
If the remote host does not respond to the packets, it treats the connection as being down
unintentionally. NPort will then force the existing TCP connection to close.
ATTENTION
The Inactivity time should at least be set larger than that of Force transmit timeout. To prevent
the unintended loss of data due to the session being disconnected, it is highly recommended that
this value is set large enough so that the intended data transfer is completed.
5-18
Page 49
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
ATTENTION
Inactivity time is ONLY active when “TCP connect on” is set to “Any character.”
Ignore jammed IP
Setting Factory Default Necessity
No or Yes No Required
For previous versions of NPort 5200, when Max connections > 1, and the serial device is
transmitting data, if any one of the connected hosts was not responding NPort 5200 would wait
until the data had been transmitted successfully before transmitting the second group of data to all
hosts. For the current version of NPort 5200, if you select Yes for “Ignore jammed IP,” the host
that is not responding will be ignored, but the data will still be transmitted to the other hosts.
Allow driver control
Setting Factory Default Necessity
No or Yes No Required
If “max connection” is greater than 1, NPort will ignore driver control commands from all
connected hosts. However, if you set “Allow driver control” to YES, control commands will be
accepted. Note that since NPort 5200 may get configuration changes from multiple hosts, the most
recent command received will take precedence.
Packing length
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 1024 0 Required
Default = 0, The Delimiter Process will be followed, regardless of the length of the data packet. If
the data length (in bytes) matches the configured value, the data will be forced out. The data length
can be configured for 0 to 1024 bytes. Set to 0 if you do not need to limit the length.
Delimiter 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Delimiter 2
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Once the NPort receives both delimiters through its serial port, it immediately packs all data
currently in its buffer and sends it to the NPort’s Ethernet port.
5-19
Page 50
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
ATTENTION
Delimiter 2 is optional. If left blank, then Delimiter 1 alone trips clearing of the buffer. If the size
of the serial data received is greater than 1 KB, the Nport will automatically pack the data and
send it to the Ethernet. However, to use the delimiter function, you must at least enable Delimiter
1. If Delimiter 1 is left blank and Delimiter 2 is enabled, the delimiter function will not work
properly.
Delimiter process
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Do nothing, Delimiter + 1, Delimiter +
2, Strip Delimiter
When [Delimiter + 1] or [Delimiter + 2] is selected, the data will be transmitted when an
additional byte (for Delimiter +1), or an additional 2 bytes (for Delimiter +2) of data is received
after receiving the Delimiter.
When [Strip Delimiter] is selected, when the Delimiter is received, the Delimiter is deleted (i.e.,
stripped), and the remaining data is transmitted.
When [Do nothing] is selected, the data will be transmitted when the Delimiter is received.
Force transmit
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0: Disable the force transmit timeout.
Do Nothing Required
1 to 65535: Forces the NPort’s TCP/IP protocol software to try to pack serial data received during
the specified time into the same data frame.
This parameter defines the time interval during which NPort fetches the serial data from its
internal buffer. If data is incoming through the serial port, NPort stores the data in the internal
buffer. NPort transmits data stored in the buffer via TCP/IP, but only if the internal buffer is full or
if the Force transmit time interval reaches the time specified under Force transmit timeout.
The optimal Force transmit timeout depends on your application, but it must be at least larger than
one character interval within the specified baudrate. For example, assume that the serial port is set
to 1200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and none for parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed
to send a character is 10 bits, and the time required to transfer one character is
( 10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s) ) * 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set Force transmit timeout to be larger than 8.3 ms, so in this case, it must
be greater than or equal to 10 ms.
If the user wants to send the series of characters in the same packet, the serial device attached to
NPort should send that series of characters during a time interval less than the Force Transmit
timeout for NPort, and the total length of data must be less than or equal to NPort’s internal buffer
size. The serial communication buffer size for NPort is 1 KB per port.
5-20
Page 51
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Destination IP address 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP address or Domai n Address
(E.g., 192.168.1.1)
Allows NPort to connect actively to the remote host whose address is set by this parameter.
Destination IP address 2/3/4
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP address or Domai n Address
(E.g., 192.168.1.1)
Allows NPort to connect actively to the remote host whose address is set by this parameter.
Designated Local Port 1/2/3/4
Setting Factory Default Necessity
TCP Port No.
Connection control
Setting Factory Default Necessity
None Required
None Optional
5011(Port 1) 5012(Port 2)
5013(Port 3) 5014(Port 4)
Required
Startup/None,
Any Character/None,
Any Character/Inactivity Time,
DSR ON/DSR OFF,
DSR ON/None,
DCD ON/DCD OFF,
DCD ON/None
The meaning of each of the above settings is given in the table below. In general, both the Connect
condition and Disconnect condition are given.
Startup/None Required
5-21
Page 52

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Connect/Disconnect Description
Startup/None
(default)
Any Character/None
Any Character/
Inactivity Time
DSR On/DSR Off
DSR On/None
DCD On/DCD Off
DCD On/None
A TCP connection will be established on startup, and will remain
active indefinitely.
A TCP connection will be established when any character is
received from the serial interface, and will remain active
indefinitely.
A TCP connection will be established when any character is
received from the serial interface, and will be disconnected when
the Inactivity time out is reached.
A TCP connection will be established when a DSR “On” signal is
received, and will be disconnected when a DSR “Off” signal is
received.
A TCP connection will be established when a DSR “On” signal is
received, and will remain active indefinitely.
A TCP connection will be established when a DCD “On” signal is
received, and will be disconnected when a DCD “Off” signal is
received.
A TCP connection will be established when a DCD “On” signal is
received, and will remain active indefinitely.
ATTENTION
Up to 4 connections can be established between NPort and hosts. The connection speed or
throughput may be low if one of the four connections is slow, since the 1 slow connection will
slow down the other 3 connections.
ATTENTION
The “Destination IP address” parameter can use both IP address and Domain Name. For some
applications, the user may need to send the data actively to the remote destination domain name.
5-22
Page 53
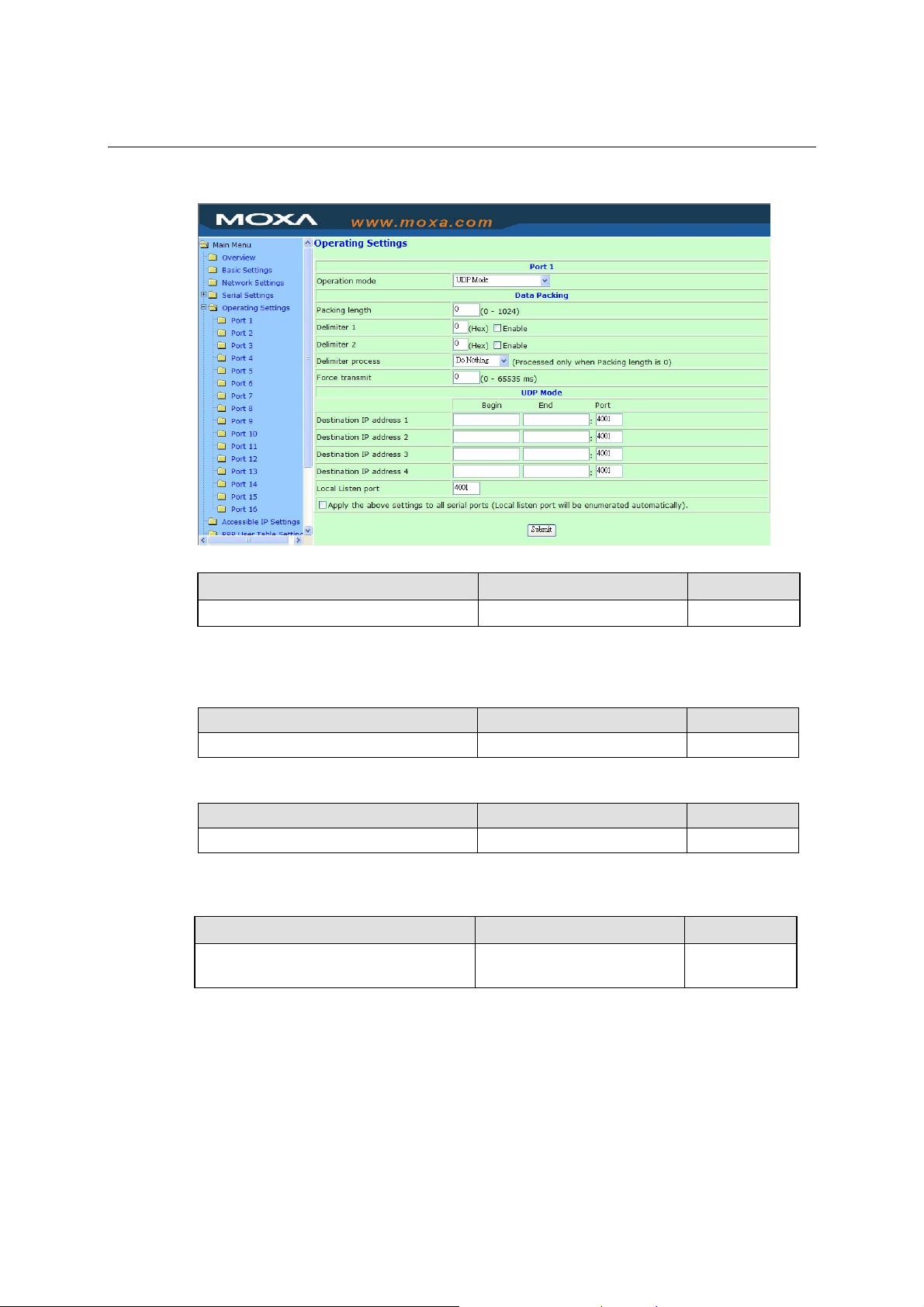
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
UDP Mode
Packing length
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 1024 0 Required
Default = 0, The Delimiter Process will be followed, regardless of the length of the data packet. If
the data length (in bytes) matches the configured value, the data will be forced out. The data length
can be configured for 0 to 1024 bytes. Set to 0 if you do not need to limit the length.
Delimiter 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Delimiter 2
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF None Optional
Once the NPort receives both delimiters through its serial port, it immediately packs all data
currently in its buffer and sends it to the NPort’s Ethernet port.
Delimiter process
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Do nothing, Delimiter + 1, Delimiter +
2, Strip Delimiter
When [Delimiter + 1] or [Delimiter + 2] is selected, the data will be transmitted when an
additional byte (for Delimiter +1), or an additional 2 bytes (for Delimiter +2) of data is received
after receiving the Delimiter.
When [Strip Delimiter] is selected, when the Delimiter is received, the Delimiter is deleted (i.e.,
stripped), and the remaining data is transmitted.
Do Nothing Required
When [Do nothing] is selected, the data will be transmitted when the Delimiter is received.
5-23
Page 54
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
ATTENTION
Delimiter 2 is optional. If left blank, then Delimiter 1 alone trips clearing of the buffer. If the size
of the serial data received is greater than 1 KB, the NPort will automatically pack the data and
send it to the Ethernet. However, to use the delimiter function, you must at least enable Delimiter
1. If Delimiter 1 is left blank and Delimiter 2 is enabled, the delimiter function will not work
properly.
Force transmit
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0: Disable the force transmit timeout.
1 to 65535: Forces the NPort’s TCP/IP protocol software to try to pack serial data received during
the specified time into the same data frame.
This parameter defines the time interval during which NPort fetches the serial data from its
internal buffer. If data is incoming through the serial port, NPort stores the data in the internal
buffer. NPort transmits data stored in the buffer via TCP/IP, but only if the internal buffer is full or
if the Force transmit time interval reaches the time specified under Force transmit timeout.
The optimal Force transmit timeout depends on your application, but it must be at least larger than
one character interval within the specified baudrate. For example, assume that the serial port is set
to 1200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and none for parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed
to send a character is 10 bits, and the time required to transfer one character is
( 10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s) ) * 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set Force transmit timeout to be larger than 8.3 ms, so in this case, it must
be greater than or equal to 10 ms.
If the user wants to send the series of characters in the same packet, the serial device attached to
NPort should send that series of characters during a time interval less than the Force Transmit
timeout for NPort, and the total length of data must be less than or equal to NPort’s internal buffer
size. The serial communication buffer size for NPort is 1 KB per port.
Destination IP address 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP address range
E.g., Begin: 192.168.1.1
End: 192.168.1.10
Destination IP address 2/3/4
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP address range
E.g., Begin: 192.168.1.11
End: 192.168.1.20
Begin: Empty
End: Empty
Port: 4001
Begin: Empty
End: Empty
Port: 4001
Required
Optional
5-24
Page 55
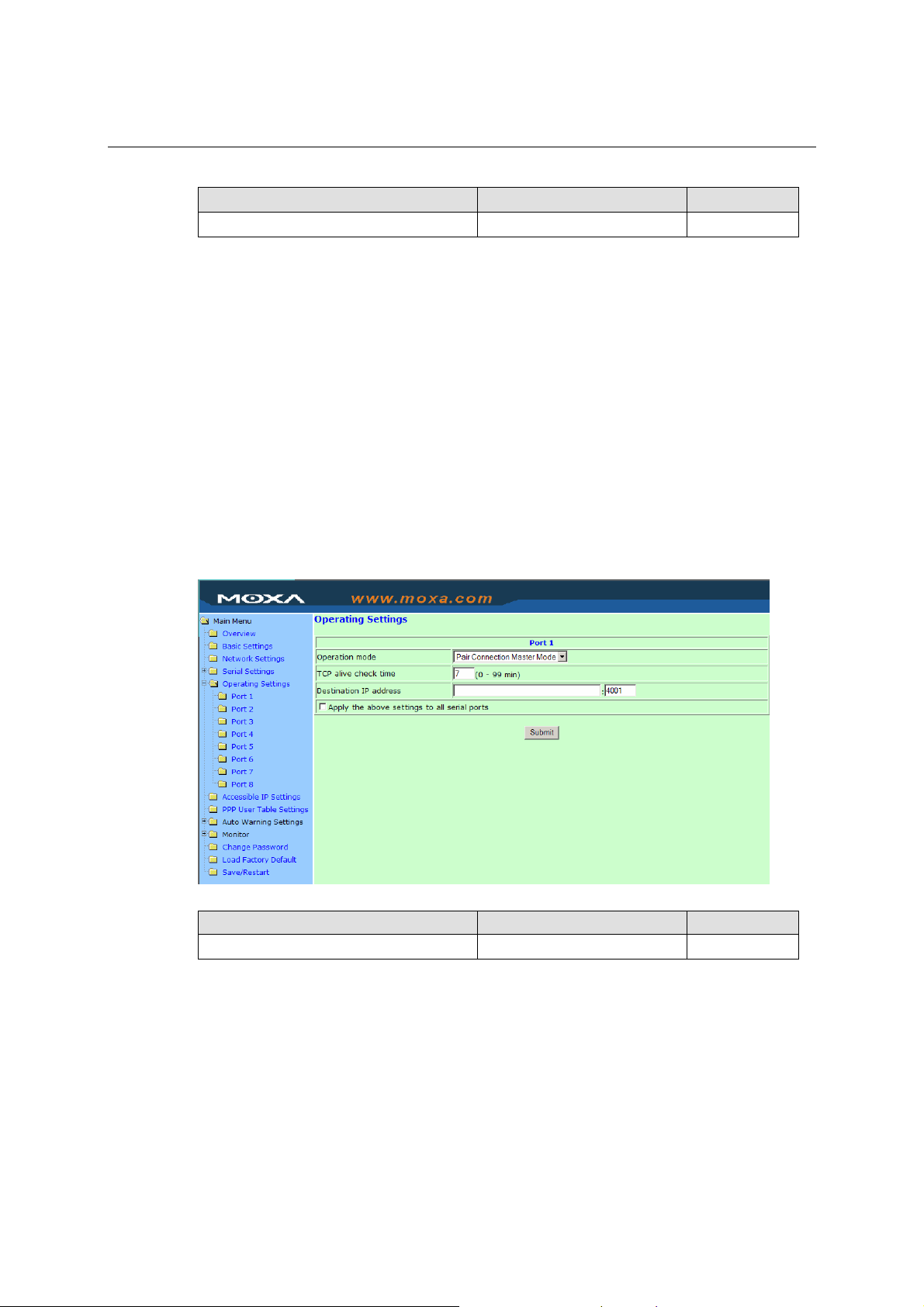
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Local listen port
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 65535 4001 Required
The UDP port that NPort listens to, and that other devices must use to contact NPort. To avoid
conflicts with well known UDP ports, the default is set to 4001.
Pair Connection Mode
Pair Connection Mode employs two NPort 5600 device servers in tandem, and can be used to
remove the 15-meter distance limitation imposed by the RS-232 interface. One NPort 5600 is
connected from its RS-232 port to the COM port of a PC or other type of computer, such as
hand-held PDAs that have a serial port, and the serial device is connected to the RS-232 port of the
other NPort 5600. The two NPort 5600 device servers are then connected to each other with a
cross-over Ethernet cable, both are connected to the same LAN, or in a more advanced setup, they
communicate with each other over a WAN (i.e., through one or more routers). Pair Connection
Mode transparently transfers both data and modem control signals (althoug h it cannot transmit the
DCD signal) between the two NPorts.
Pair Connection Master Mode
When using Pair Connection Mode, you must select Pair Connection Master Mode for the
Operation mode of one of the NPort 5600 device servers. In effect, this NPort 5600 will be acting
as a TCP client.
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min
0 min: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: NPort 5600 closes the TCP connection automatically if there is no TCP activity for
the given time.
7 min
Required
5-25
Page 56
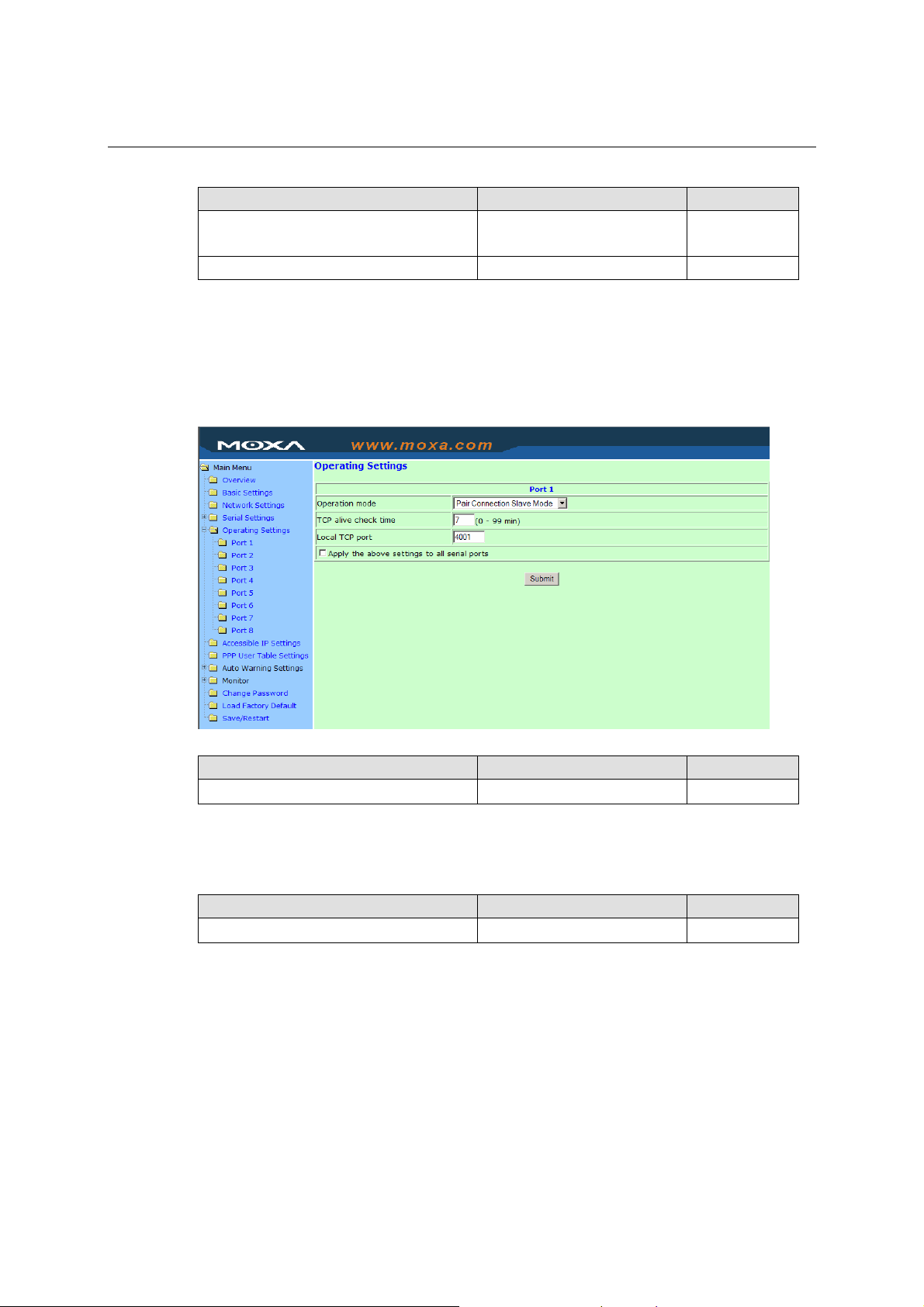
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Destination IP address
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP address or Domai n Name
(E.g., 192.168.1.1)
TCP port No. 4001 Required
The Pair Connection “Master” will contact the network host that has this IP address. Data will be
transmitted through the port No. (4001 by default). Note that you must configure the same TCP
port No. for the device server acting as the Pair Connection “Slave.”
blank Optional
Pair Connection Slave Mode
When using Pair Connection Mode, you must select Pair Connection Slave Mode for the
Operation mode of one of the NPort 5600 device servers. In effect, this NPort 5600 will be acting
as a TCP server.
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min
0 min: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: NPort 5600 closes the TCP connection automatically if there is no TCP activity for
the given time.
Local TCP port
Setting Factory Default Necessity
TCP port No. (e.g., 4001)
This Port No. must be the same port No. that you set up for the Pair Connection “Master” device
server.
7 min
4001
5-26
Required
Required
Page 57
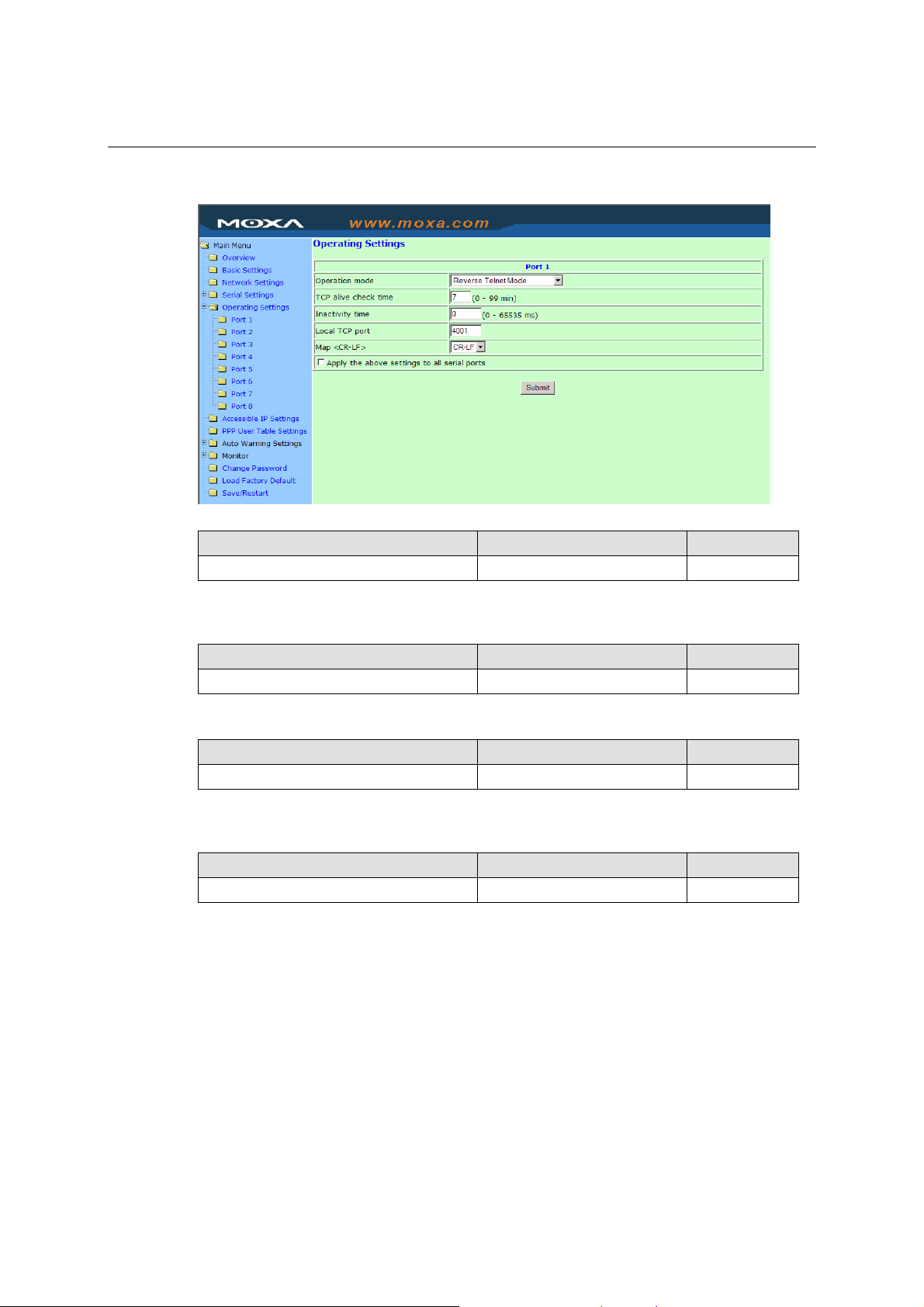
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Reverse Telnet Mode
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min 0 Optional
Specifies the time slice for checking if the TCP connection is alive. If there is no response, NPort
5600 series will disconnect the original connection.
Inactivity time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 Optional
Idle time setting for auto-disconnection. 0 min. means it will never disconnect.
Local TCP port
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 65535 4001 Optional
Each of NPort’s serial ports is mapped to a TCP port. To avoid conflicts with TCP ports, set port
numbers to 4001 for port1, 4002 for port 2, etc. (like the default values).
Map <CR-LF>
Setting Factory Default Necessity
CR, LF, or CR-LF CR-LF Optional
If data received through NPort 5600’s Ethernet port is sent using the “enter” command, the data will be
transmitted out the serial port with an added
1. “carriage return + line feed” if you select the <CR-LF> option
(i.e., the cursor will jum p to t he next li ne, and return to the first character of the line)
2. “carriage return” if you select the <CR> option
(i.e., the cursor will return to the first character of the line)
3. “line feed” if you select the <LF> option.
(i.e., the cursor will jump to the next line, but not mov horizontally)
5-27
Page 58

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Disabled Mode
When Operation mode is set to Disabled, that particular port will be disabled. Select the Apply the
above settings to all serial ports option to apply this setting to the other ports.
RFC2217 Mode
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 99 min 7 min Optional
0 min: TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: NPort 5600 automatically closes the TCP connection if there is no TCP activity for
the given time. After the connection is closed, NPort 5600 starts listening for another Real COM
driver connection from another host.
5-28
Page 59

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Packing length
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 1024 0 Optional
Default = 0, The Delimiter Process will be followed, regardless of the length of the data packet. If
the data length (in bytes) matches the configured value, the data will be forced out. The data length
can be configured for 0 to 1024 bytes. Set to 0 if you do not need to limit the length.
Delimiter 1
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF (hex) None Optional
Delimiter 2
Setting Factory Default Necessity
00 to FF (hex) None Optional
Once the NPort 5600 receives both delimiters through its serial port, it immediately packs all data
currently in its buffer and sends it to the NPort 5600’s Ethernet port.
ATTENTION
Delimiter 2 is optional. If left blank, then Delimiter 1 alone trips clearing of the buffer. If the size
of the serial data received is greater than 1 KB, the NPort 5600 will automatically pack the data
and send it to the Ethernet. However, to use the delimiter function, you must at least enable
Delimiter 1. If Delimiter 1 is left blank and Delimiter 2 is enabled, the delimiter function will not
work properly.
Delimiter process
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Do nothing
Delimiter + 1
Delimiter + 2
Strip Delimiter
[Delimiter + 1] or [Delimiter + 2]: The data will be transmitted when an additional byte (for
Delimiter +1), or an additional 2 bytes (for Delimiter +2) of data is received after receiving the
Delimiter.
[Strip Delimiter]: When the Delimiter is received, the Delimiter is deleted (i.e., stripped), and the
remaining data is transmitted.
[Do nothing]: The data will be transmitted when the Delimiter is received.
Force transmit
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0: Disable the force transmit timeout.
1 to 65535: Forces the NPort 5600’s TCP/IP protocol software to try to pack serial data received
during the specified time into the same data frame.
Do Nothing Optional
5-29
Page 60

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
This parameter defines the time interval during which NPort 5600 fetches the serial data from its
internal buffer. If data is incoming through the serial port, NPort 5600 stores the data in the
internal buffer. NPort 5600 transmits data stored in the buffer via TCP/IP, but only if the internal
buffer is full or if the Force transmit time interval reaches the time specified under Force transmit
timeout.
The optimal Force transmit timeout depends on your application, but it must be at least larger than
one character interval within the specified baudrate. For example, assume that the serial port is set
to 1200 bps, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed to
send a character is 10 bits, and the time required to transfer one character is
( 10 (bits) / 1200 (bits/s) ) * 1000 (ms/s) = 8.3 ms.
Therefore, you should set Force transmit timeout to be larger than 8.3 ms, so in this case, it must
be greater than or equal to 10 ms.
If the user wants to send a series of characters in the same packet, the serial device attached to
NPort 5600 should send that series of characters during a time interval less than the Force transmit
timeout for NPort 5600, and the total length of data must be less than or equal to NPort 5600’s
internal buffer size. The serial communication buffer size for NPort 56 0 0 is 1 KB per port .
PPP Mode
PPP provides standard PPP service for dial-in.
Inactivity time
Setting Factory Default Necessity
0 to 65535 ms 0 Optional
Idle time setting for auto-disconnection. 0 min. means it will never disconnect.
TCP/IP compression
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Yes or No No Optional
Depends on whether the remote user's application requests compression.
5-30
Page 61

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Incoming PAP check
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Yes or No No Optional
Depends on whether the remote user's application requests PAP check.
Source IP address
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Source IP address Required
Destination IP address
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Destination IP address Required
Designation IP address is IP address of remote dial-in server.
IP netmask
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP netmask Optional
NPort 5600 automatically assigns the netmask 255.255.255.255. We recommend leaving this space
blank.
Modem Initial stream
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Modem Initial stream
AT Optional
Accessible IP Settings
NPort has an IP address based filtering method to control access to itself.
Accessible IP Settings allows you to add or block remote host IP addresses to prevent
unauthorized access. Access to NPort is controlled by IP address. That is, if a host’s IP address is
in the accessible IP table, then the host will be allowed to access the NPort. You can allow one of
the following cases by setting the parameter.
5-31
Page 62

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
y Only one host with a specific IP address can access the NPort
Enter “IP address/255.255.255.255” (e.g., “192.16 8.1.1/255.255.255.255”).
y Hosts on a specific subnet can access the NPort
Enter “IP address/255.255.255.0” (e.g., “192.1 68.1.0/255.255.255.0”).
y Any host can access the NPort
Disable this function. Refer to the following table for more details about the configuration
example.
Allowable Hosts Input format
Any host Disable
192.168.1.120 192.168.1.120 / 255.255.255.255
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.255.0
192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254 192.16 8.0.0 / 255.255.0.0
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.255.128
192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.128 / 255.255.255.128
PPP User Table
5-32
Page 63

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Auto Warning Settings
Auto warning: E-mail and SNMP Trap
Mail Server
Mail server
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP or Domain Name None Optional
User name
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 15 characters None Optional
Password
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 15 characters None Optional
From E-mail address
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 63 characters None Optional
E-mail address 1/2/3/4
Setting Factory Default Necessity
1 to 63 characters None Optional
ATTENTION
Consult your Network Administ rator or ISP for the proper mail server settings. Aut o war ni n g
function may not work properly without proper settings. NPort SMTP AUTH support LOGIN,
PLAIN, CRAM-MD5 (RFC 2554).
5-33
Page 64
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
SNMP Trap Server
SNMP trap server IP or domain name
Setting Factory Default Necessity
IP or Domain Name None Optional
Event Type
Cold start
This refers to starting the system from power off (contrast this with warm start). When performing
a cold start, NPort will automatically issue an Auto warning message by e-mail, or send an SNMP
trap after booting up.
Warm start
This refers to restarting the computer without turning the power off. When performing a warm
start, NPort will automatically send an e-mail, or send an SNMP trap after rebooting.
Authentication failure
The user inputs a wrong password from the Console or Administrator. When authentication failure
occurs, NPort will immediately send an e-mail or send an SNMP trap.
IP address changed
The user has changed NPort’s IP address. When the IP address changes, NPort will send an e-mail
with the new IP address before NPort reboots. If the NPort is unable to send an e-mail message to
the mail server within 15 seconds, NPort will reboot anyway, and abort the e-mail auto warning.
Password changed
The user has changed NPort’s password. When the password changes, NPort will send an e-mail
with the password change notice before NPort reboots. If the NPort is unable to send an e-mail
message to the mail server within 15 seconds, NPort will reboot anyway, and abort the e-mail auto
warning.
5-34
Page 65
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
DCD changed
The DCD (Data Carrier Detect) signal has changed, also indicating that the modem connection
status has changed. For example, a DCD change to high also means “Connected” between local
modem and remote modem. If the DCD signal changes to low, it also means that the connection
line is down.
When the DCD changes, NPort 5610 will immediately send an e-mail or send an SNMP trap.
DSR changed
The DSR (Data Set Ready) signal has changed, also indicating that the data communication
equipment’s power is off. For example, a DSR change to high also means that the DCE is powered
ON. If the DSR signal changes to low, it also means that the DCE is powered off.
When the DSR changes, NPort 5610 will immediately send an e-mail or send an SNMP trap.
Mail
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Enable, Disable Disable Optional
This feature helps the administrator manage how the NPort sends e-mail to pre-defined e-mail
boxes when the enabled events—such as Cold start, Warm start, Authentication failure,
etc.—occur. To configure this feature, click the Event Type Mail checkbox.
Trap
Setting Factory Default Necessity
Enable, Disable Disable Optional
This feature helps the administrator manage how the NPort sends SNMP Trap to a pre-defined
SNMP Trap server when the enabled ev ents—such as Cold start, Warm start, Authentication
failure, etc.—occur. To configure this feature, click the Event Type Trap checkbox.
ATTENTION
DCD changed and DSR changed event only supported by those models, which have these two
signals. For example NPort 5210, 5410 and NPort 5610.
5-35
Page 66
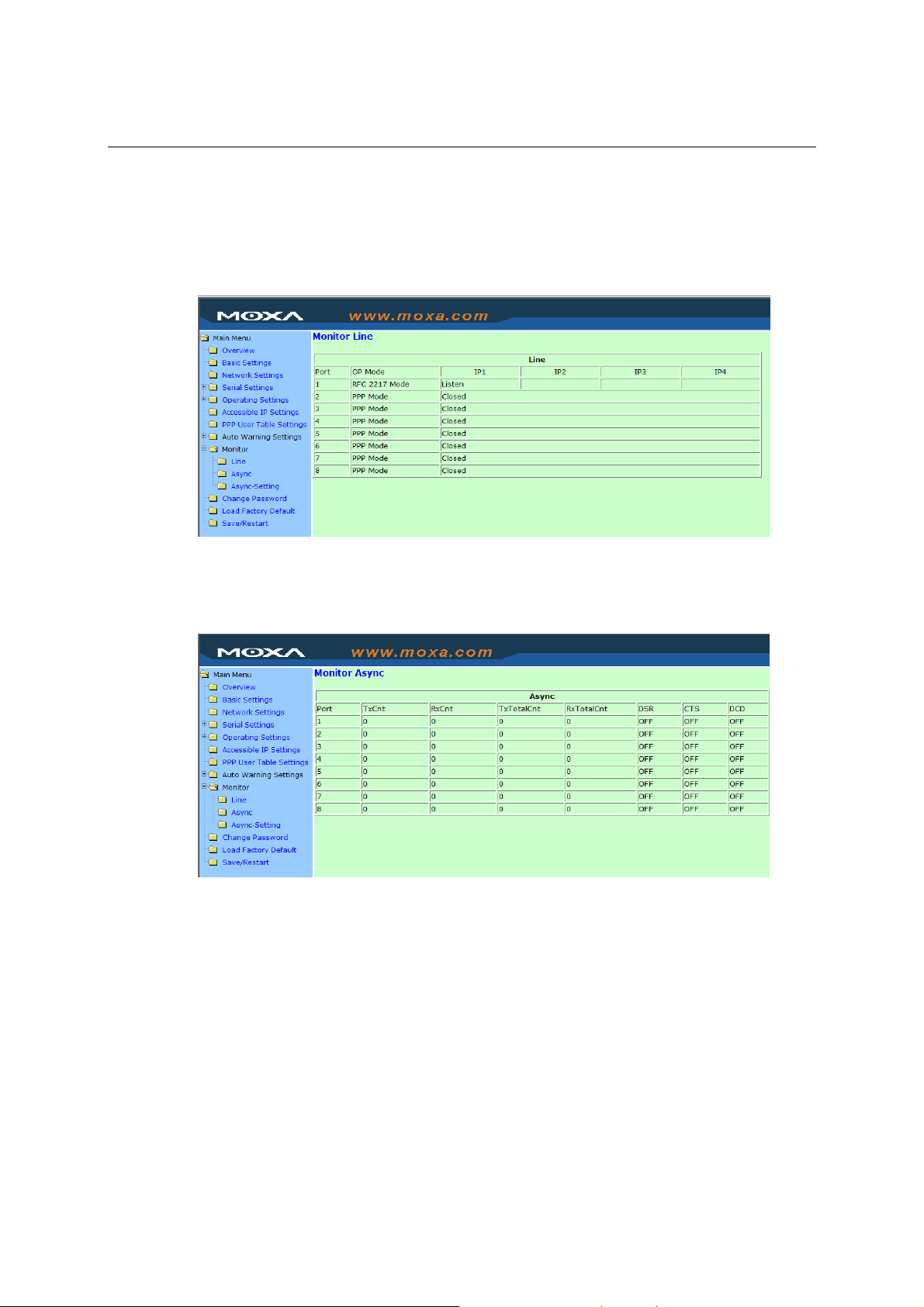
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Monitor
Monitor Line
Click Line under Monitor to show the operation mode and status of each connection (IPx), for
each of the four serial ports.
Monitor Async
Click Async under Monitor to show the current status of each of the four serial ports.
5-36
Page 67
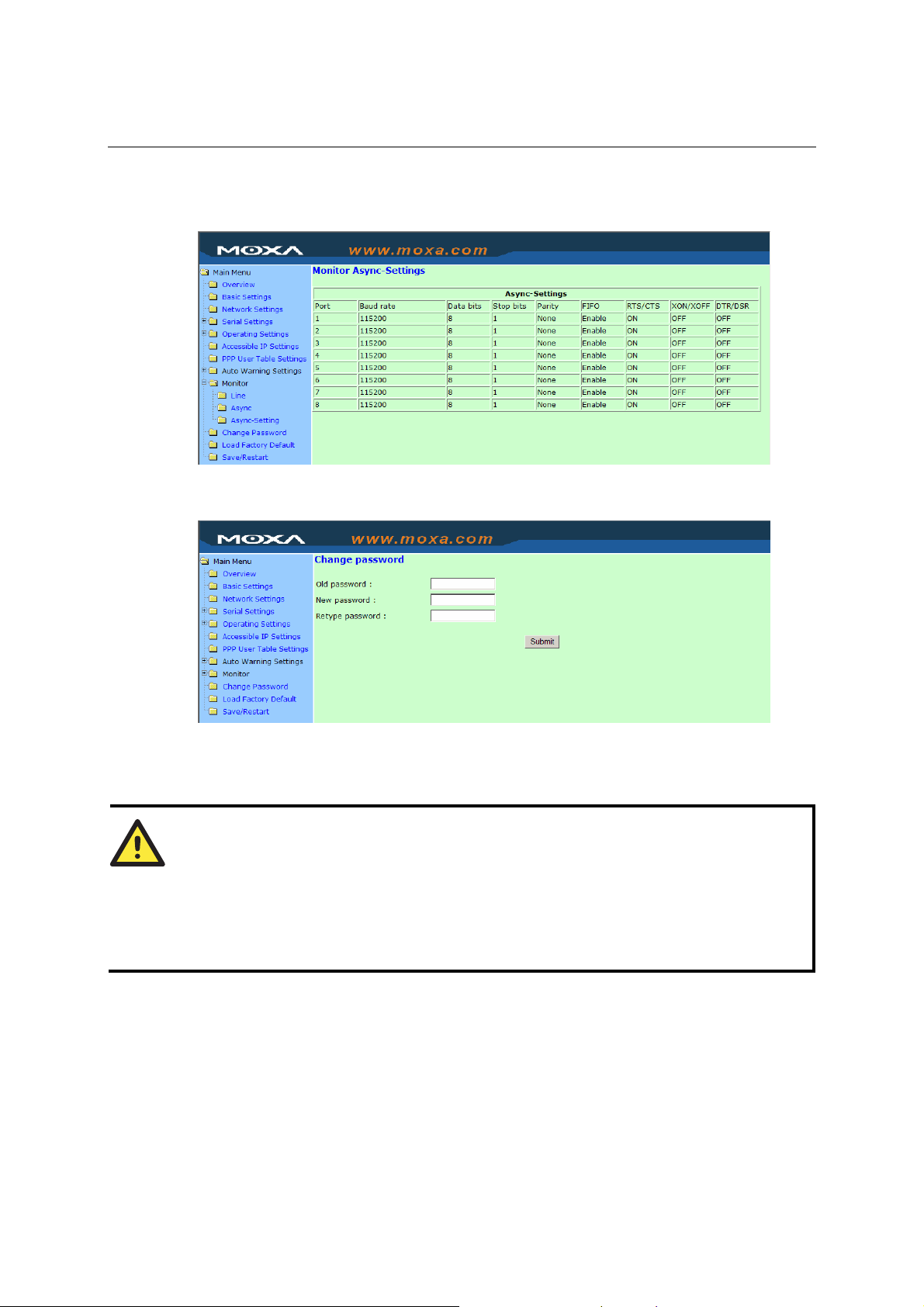
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Monitor Async-Settings
Click Async Setting under Monitor to show the run-time settings for each of the four serial ports.
Change Password
Input the “Old password” and “New password” to change the password. Leave the password boxes
blank to erase the password. In this case, the NPort will not have password protection.
ATTENTION
If you forget the password, the ONLY way to configure NPort is by using the Reset button on
NPort’s casing to Load Factory Defaults.
Remember to export the configuration file using Windows Administrator when you finish the
configuration. By using the Import function of Windows Administrator, your configuration can
be re-loaded into NPort after resetting the parameters to their factory defaults. Refer to Chapter 6
for more details about the Export and Import function.
5-37
Page 68
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Configuring NPort Administrator
Load Factory Defaults
This function will reset all of NPort’s settings to their factory default values. Be aware that
previous settings will be lost.
5-38
Page 69

6
6
Chapter 6 Configuring NPort Administrator
NPort Administrator and Web Console are two powerful tools that can be used to configure the
settings of your NPorts. Choose the method that is most convenient for you. Note that this chapter
uses NPort 5230 as an example to introduce the installation and configuration of NPort
Administration Suite. The functions and definitions are the same as for NPort 5600.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Installing NPort Administrator
Configuration
¾ Broadcast Search
¾ Unlock Password Protection
¾ Configuring NPort 5600
¾ Upgrading Firmware
¾ Export/Import
Monitor
Port Monitor
COM Mapping
¾ On-line COM Mapping
¾ Off-line COM Mapping
IP Location
Page 70
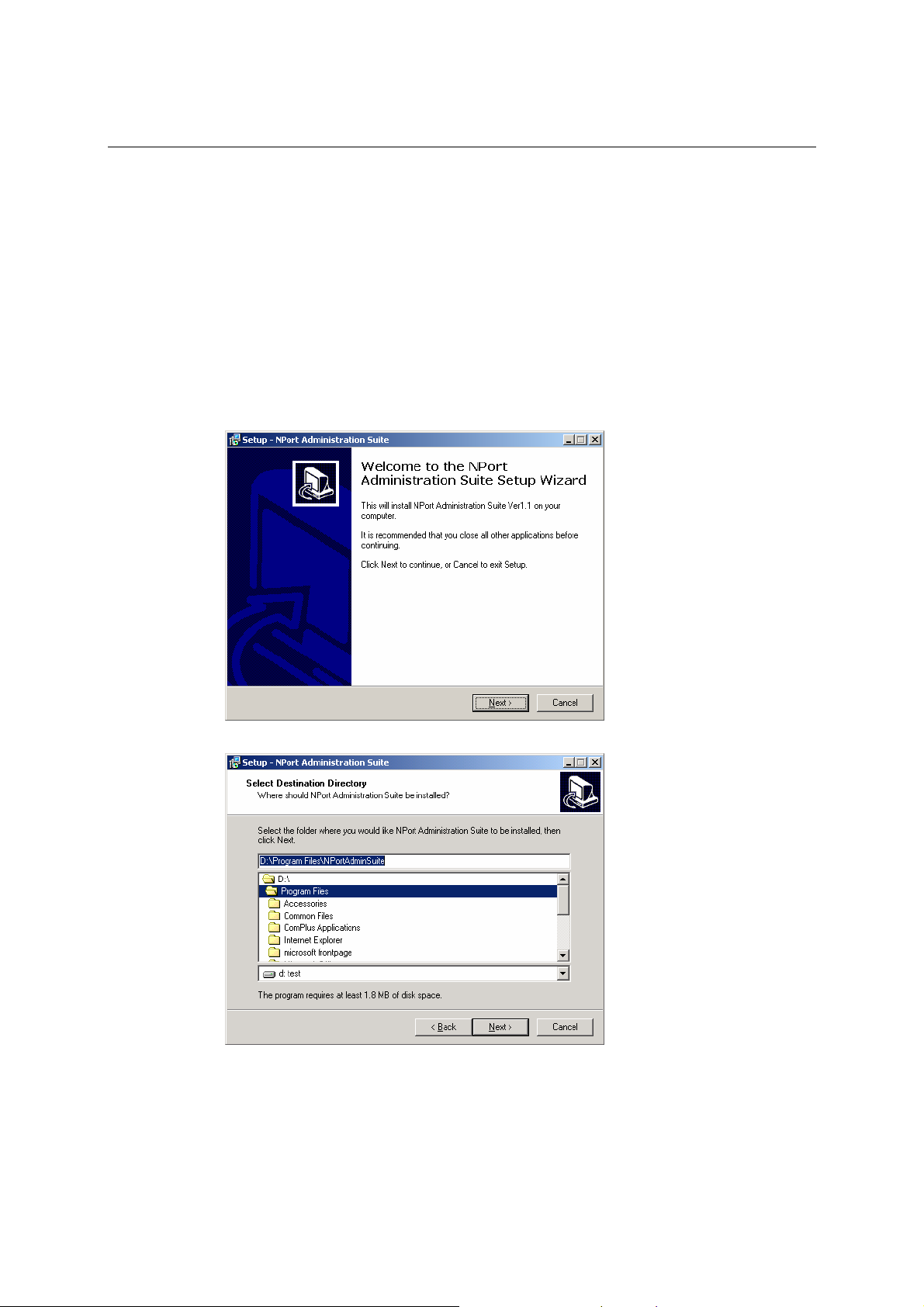
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Overview
NPort Administrator lets you easily install and configure your NPort 5600 Series product over the
network. NPort Administrator provides five function groups that ease the installation process,
allow off-line COM mapping, and provide monitoring and IP location server functions.
NPort Administrator is an integrated software suite that bundles NPort Administrator and the IP
Serial Library, and provides everything you need to remotely manage, monitor, and modify your
NPort from a remote location.
Installing NPort Administrator
1. Once the Setup program starts running , click Next when the Welcome window opens to
proceed with the installation.
2. Click Next to install program files in the default directory, or select an alternative location.
6-2
Page 71
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
3. Click Next to install the program using the default program name, or select a different name.
4. Click Install to proceed with the installation.
5. The Installing window reports the progress of the installation.
6-3
Page 72
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
6. Read through the installation notes and then click Next to proceed.
7. Click Finish to complete the installation of NPort Administration Suite.
6-4
Page 73
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Configuration
The Administrator-Configuration window is divided into four parts.
y The top section contains the function list and online help area. (Windows NT does not support
this .chm file format.)
y The five Administrator function groups are listed in the left section.
y A list of NPort 5600 serial device servers, each of which can be selected to process user
requirements, is displayed in the right section.
y The activity Log, which displays messages that record the user’s processing history, is shown
in the bottom section.
6-5
Page 74

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Broadcast Search
The Broadcast Search function is used to locate all NPorts that are connected to the same LAN as
your computer.
1. Since the Broadcast Search function searches by MAC address and not IP address, all NPorts
connected to the LAN will be located, regardless of whether or not they are part of the same
subnet as the host.
2. The Broadcast Search window will open and display the Model, IP Address, MAC Address,
and Progress (of the search for that particular device).
6-6
Page 75

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
3. When the search is complete, the Broadcast Search window closes, and the NPorts that were
located are displayed in the right pane of the Administrator window.
For the example shown here, NPort Admini strat or f ou n d 4 NPort Serial Device Servers on the
LAN. As you can see, 2 of the 4 NPorts have password protection, which is indicated by Lock
under Status.
To configure one of the listed NPorts, place the cursor over the row displaying that NPort’s
information, and then right click.
ATTENTION
Before modifying NPort 5600’s configuration, use Broadcast Search to locate all NPort 5600s
connected to the LAN, or use Specify by IP Address to locate a particular NPort 5600.
Unlock Password Protection
1. If the NPort is password protected, then you will not be able to use the right click method to
open the configuration page.
6-7
Page 76

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
2. Instead, select an NPort with “Lock” status, right click the locked NPort, and then select the
Unlock button.
3. After entering the correct password, the Administrator will display a message box as shown
here. The NPort is now unlocked.
6-8
Page 77

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
4. The previous “Lock” status will switch to “Unlock” status.
Administrator will keep this NPort in the Unlock status throughout this Administrator session.
The six states are as follows (note that the term Fixed is borrowed from the standard fixed IP
address networking terminology):
Lock
The NPort is password protected, “Broadcast Search” was used to locate it, and the password
has not yet been entered from within the current Administrator session.
Unlock
The NPort is password protected, “Broadcast Search” was used to locate it, and the password
has been entered from within the current Administrator session. Henceforth during this
Administrator session, activating various utilities for this NPort will not require re-entering
the server password.
Blank
The NPort is not password protected, and “Broadcast Search” was used to locate it.
Fixed
The NPort is not password protected, and “Search by IP address” was used to locate it.
Lock Fixed
The NPort is password protected, “Specify by IP address” was used to locate it, and the
password has not yet been entered from within the current Administrator session.
Unlock Fixed
The NPort is password protected, “Specify by IP address” was used to locate it, and the
password has been entered from within the current Administrator session. Henceforth during
this Administrator session, activating various utilities for this NPort will not require
re-entering the server password.
6-9
Page 78

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Configuring NPort 5600
1. To start NPort Administrator, click Start Æ NPort Administrati on Sui t e Æ NP ort
Administrator.
2. Input the password to Unlock the NPort.
Right click a specific NPort and select configure to start the configuration.
3. The progress bar shows that Administrator is retrieving configuration information from the
specific NPort.
6-10
Page 79

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
4. Refer to Chapter 5 for each parameter’s function definition.
To modify the configuration, you must first click in the modify box to activate the parameter
setting box.
6-11
Page 80
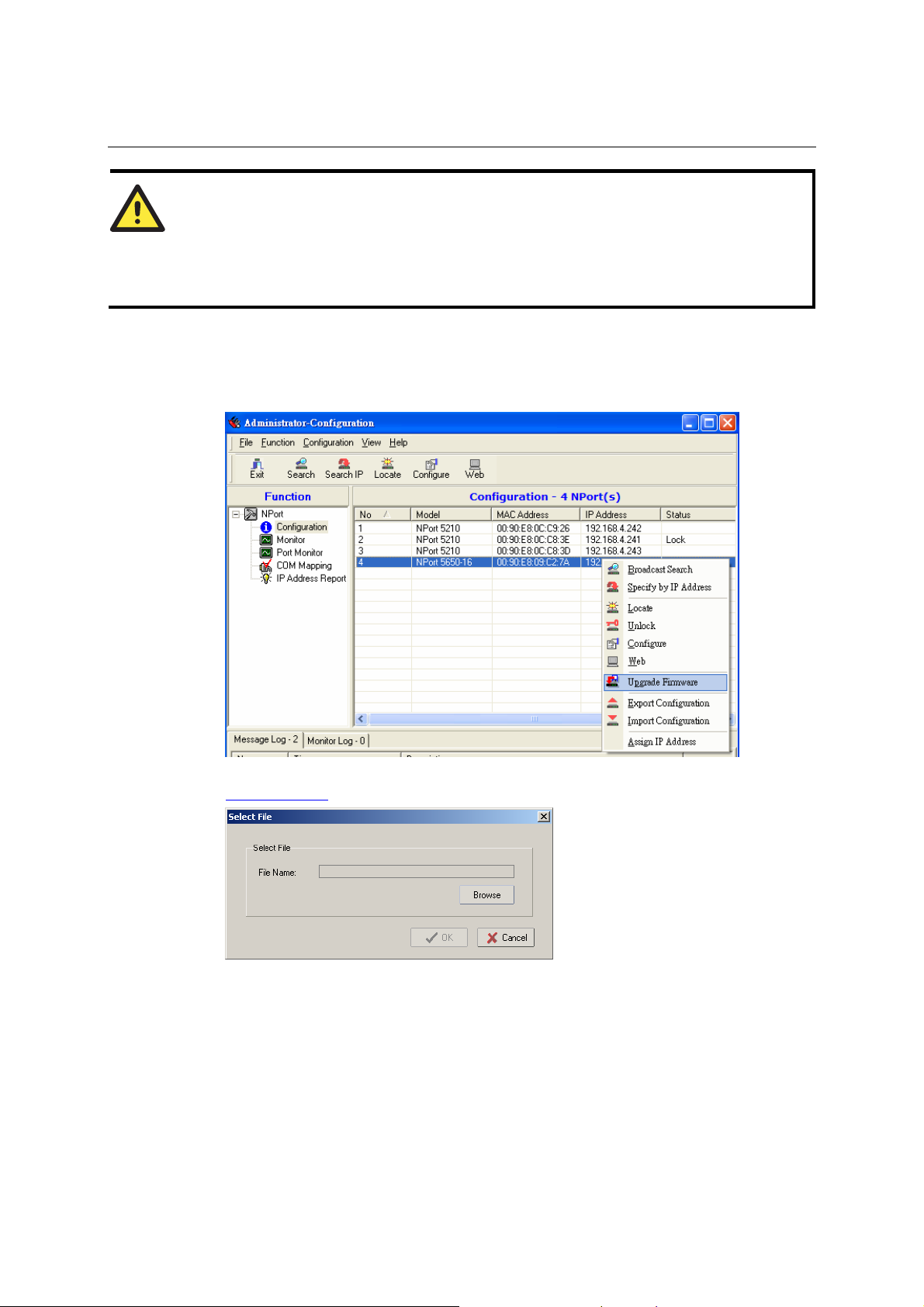
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
ATTENTION
You can simultaneously modify the configurations of multiple NPort 5600s that are of the same
model.
To select multiple NPort 5600s, hold down the Ctrl key when selecting additional NPort 5600s,
or hold down the Shift key to select a group of NPort 5600s.
Upgrading Firmware
1. Input the password to Unlock the NPort, and then right click a specific NPort and select the
Upgrade Firmware function to start upgrading the firmware.
2. Select the correct ROM file to be downloaded to the NPort. Visit MOXA’s website at
www.moxa.com for the latest firmware release.
6-12
Page 81
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
3. Wait patiently while the Upgrade Firmware action is being processed.
ATTENTION
You can simultaneously upgrade the firmware of multiple NPort 5600s that are of the same
model.
To select multiple NPort 5600s, hold down the Ctrl key when selecting an additional NPort
5600, or hold down the Shift key to select a block of NPort 5600s.
Export/Import
1. Input the password to Unlock the NPort, and then right click a specific NPort and select the
Export function to start Exporting the configuration file.
The Export Configuration function is a handy tool that can be used to produce a text file
containing the current configuration of a particular NPort.
6-13
Page 82
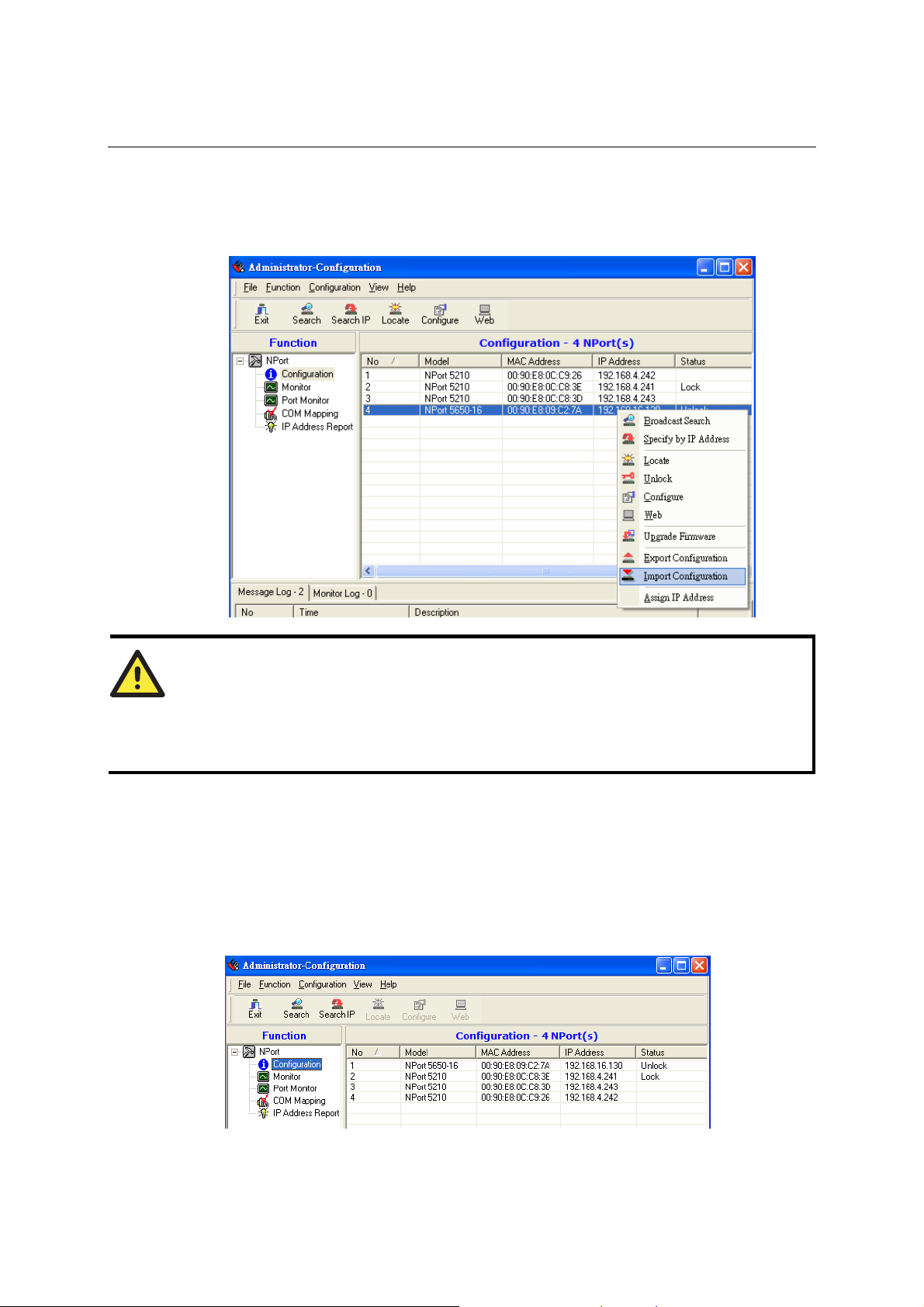
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
2. The Import Configuration function is used to import an NPort configuration from a file into
one or more of the same model NPort.
To import a configuration, first select the target servers (use the left mouse button to select
servers; simply hold down the Ctrl key when selecting the second, third, etc., NPort).
ATTENTION
Monitor
You can simultaneously import the same configuration file into multiple NPort 5600s that are of
the same model.
To select multiple NPort 5600s, hold down the Ctrl key when selecting an additional NPort
5600, or hold down the Shift key to select a block of NPort 5600s.
There are two methods available to start the Monitor function.
1. First use Broadcast Search under the Configuration Function group, and then click Monitor
Æ Add Target Æ Select target from the list.
2. First click Monitor, and then Add Target Æ Rescan.
3. Select Broadcast under the Configuration menu bar item.
6-14
Page 83
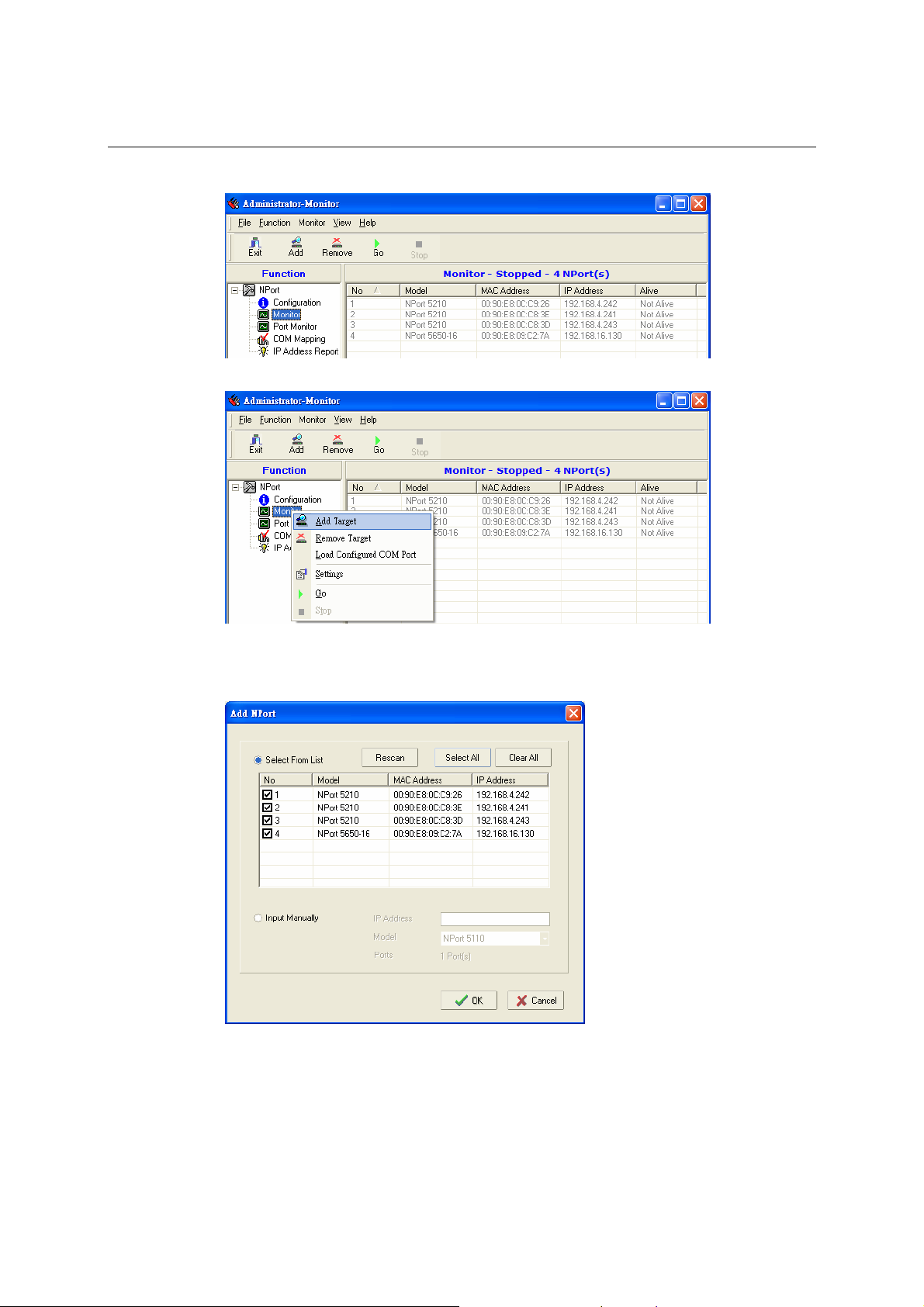
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
4. Click Monitor.
5. Select Add Target.
When you select add target, you will see an NPort list that looks the same as when using
Configuration Æ Broadcast Search.
6. Check the NPort you would like to Monitor, and then click OK.
6-15
Page 84
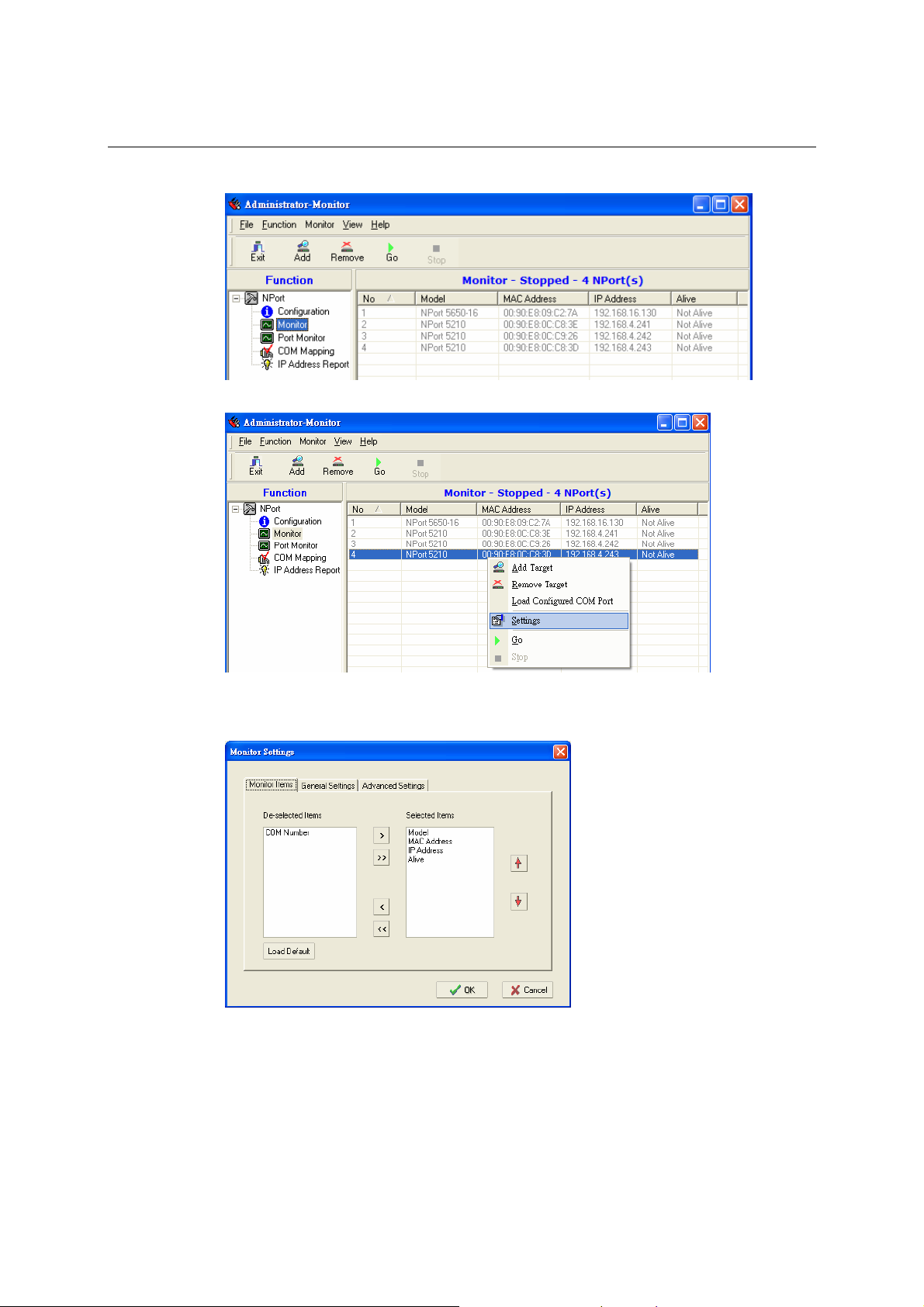
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
7. The NPort list will now appear on the Monitor screen.
8. Right click the panel and select Settings.
9. Select or de-select Monitor Items. Use the single arrowhead buttons to move highlighted
items from one box to the other. Use the double arrowhead buttons to move all items in one
box to the other.
6-16
Page 85
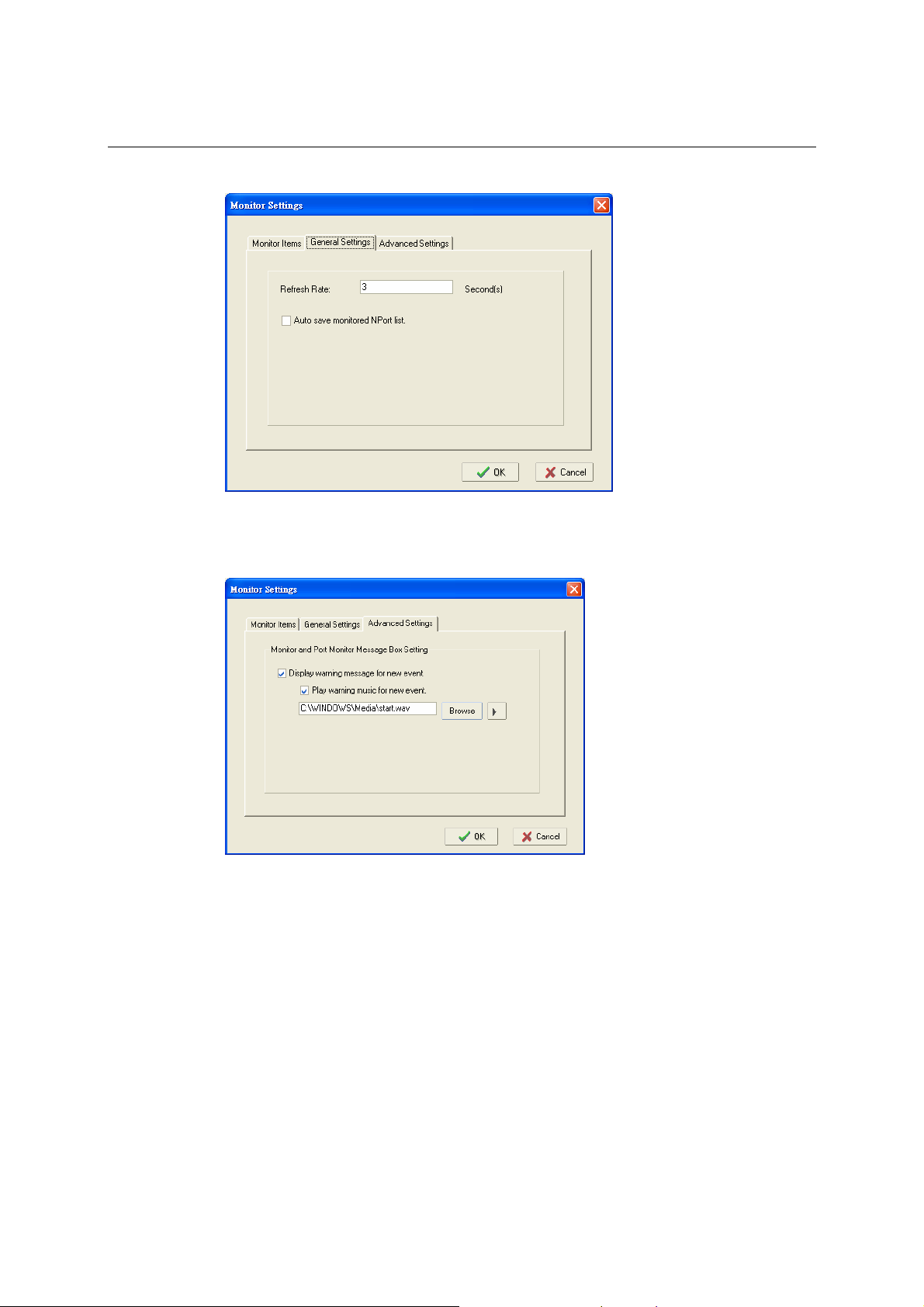
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
10. Select a Refresh Rate (the default is 3 seconds).
11. Select Display warning message for new event or Play warning music for new event. In the
second case, you must enter the path to the WAV file that you want to be played. “New event”
means that one of the 5600s in the monitor is “Alive” or “Not Alive,” or has lost connection
with the Monitor program.
6-17
Page 86
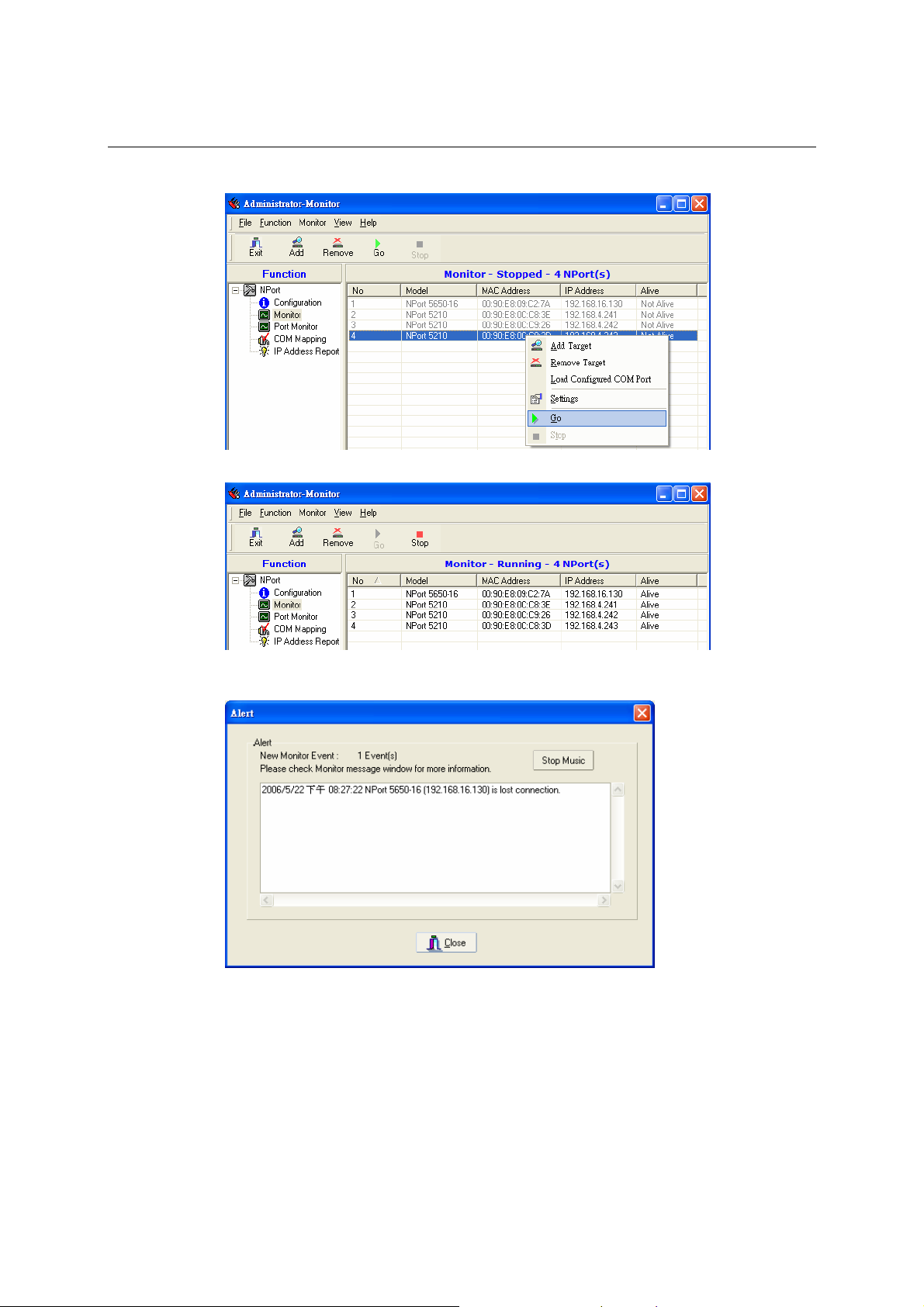
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
12. Right click and select Go to start the Monitor.
13. For this example, the 5 NPorts shown in the list will be monitored.
14. When one of the NPorts loses connection with the Monitor program, a warning alert will
display automatically. The warning music will be played at the same time.
6-18
Page 87
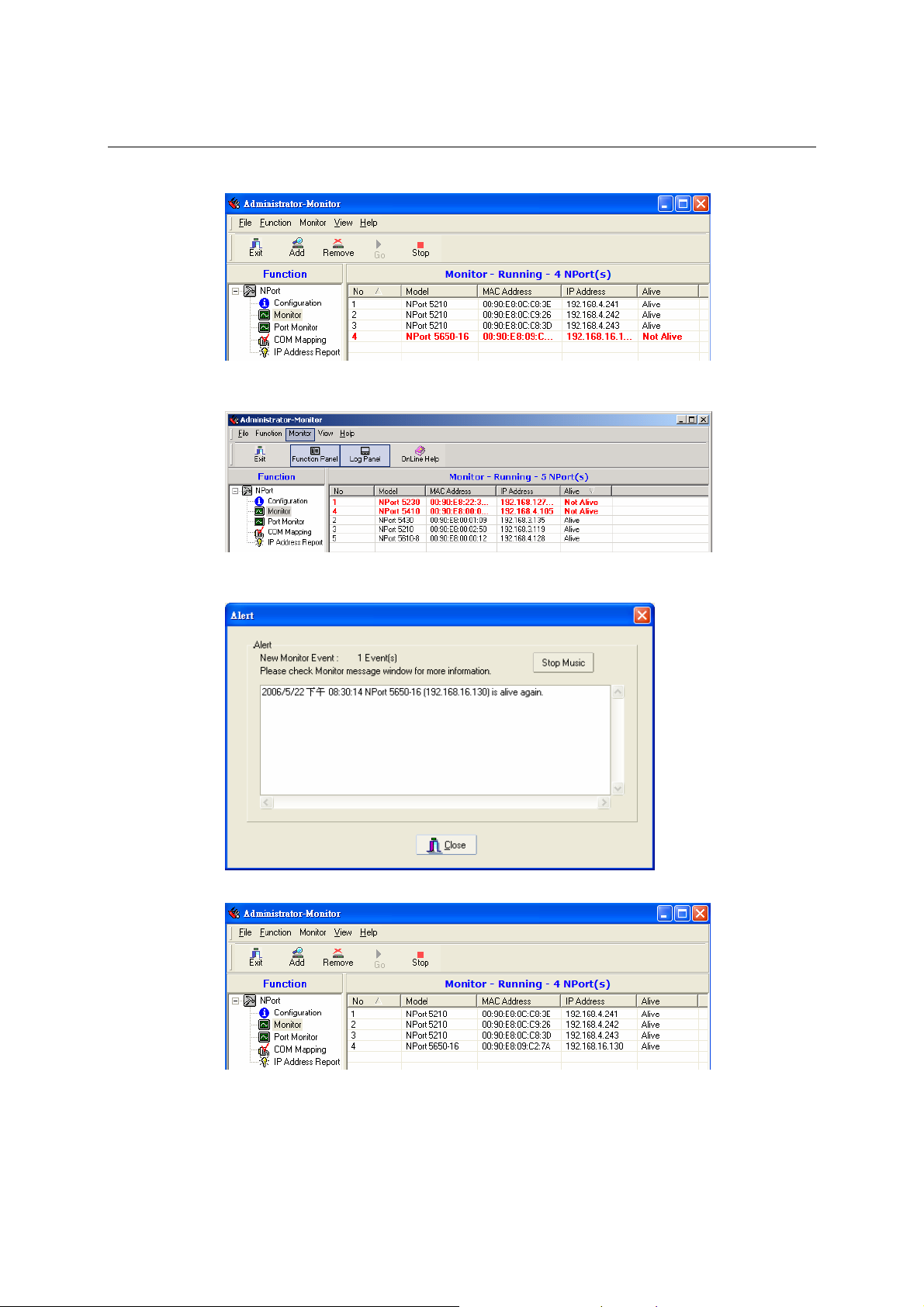
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
15. In the Monitor screen, you can see that the “Not Alive” NPort is marked with red color.
16. Click the Alive column. The Monitor program will sort the NPort list and put all “Not Alive”
NPorts at the top of the list.
17. If the NPort gets reconnected, a warning will be displayed to remind the user the NPort is now
“Alive.”
18. The NPort that was reconnected, and is now “Alive,” will be shown in black color.
6-19
Page 88
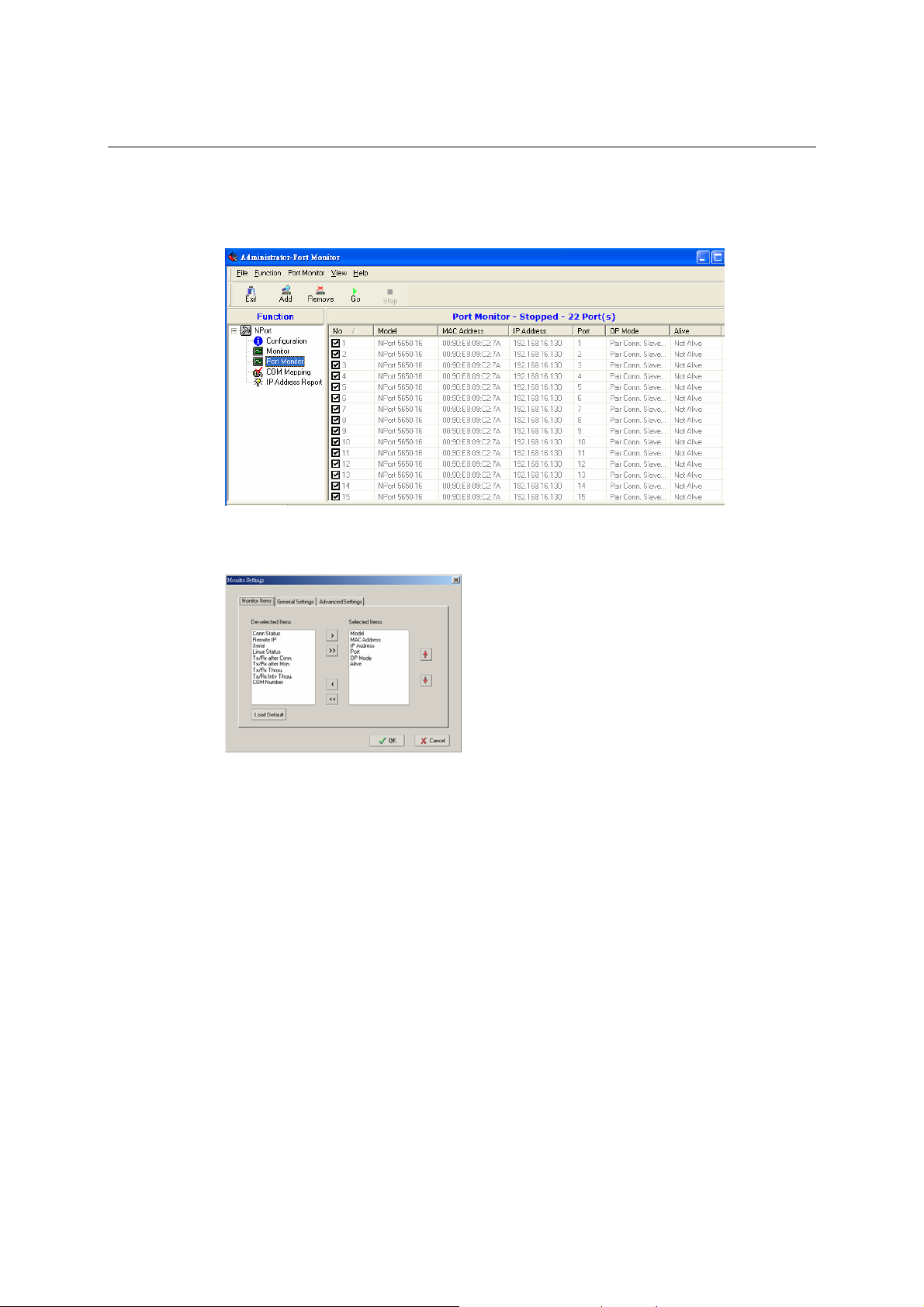
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Port Monitor
1. The process described here is the same as in the previous “Monitor” section. The only
difference is that you can select more items under Port Monitor than under Monitor.
2. Select or de-select Monitor Items. Use the single arrowhead buttons to move highlighted items
from one box to the other. Use the double arrowhead buttons to move all items from one box
to the other.
COM Mapping
NPort Administration Suite comes with Windows 95/98/ME/NT/2000/XP Real COM drivers.
After you install Windows Administration Suite, there are two ways to set up the NPort’s serial
port as your host’s remote COM port. The first way is with On-line COM Mapping. On-line
COM Mapping will check to make sure the NPort is connected correctly to the network and then
install the driver on the host computer.
The second way is with Off-line COM Installation, without connecting the NPort to the network
first. Off-line COM Mapping can decrease the system integrator’s effort by solving different field
problems. Via off-line installation, the user can process the host software installation and then
install the NPort to different fields.
Use the following procedure to map COM ports:
1. On-line COM Mapping:
Connect NPort to the network Æ Set NPort to the proper IP address Æ Map COMs to your
host Æ Apply Change.
2. Off-line COM Mapping:
Map COMs to your host Æ Apply Change Æ Connect NPort to the network Æ Configure
NPort’s IP address.
6-20
Page 89
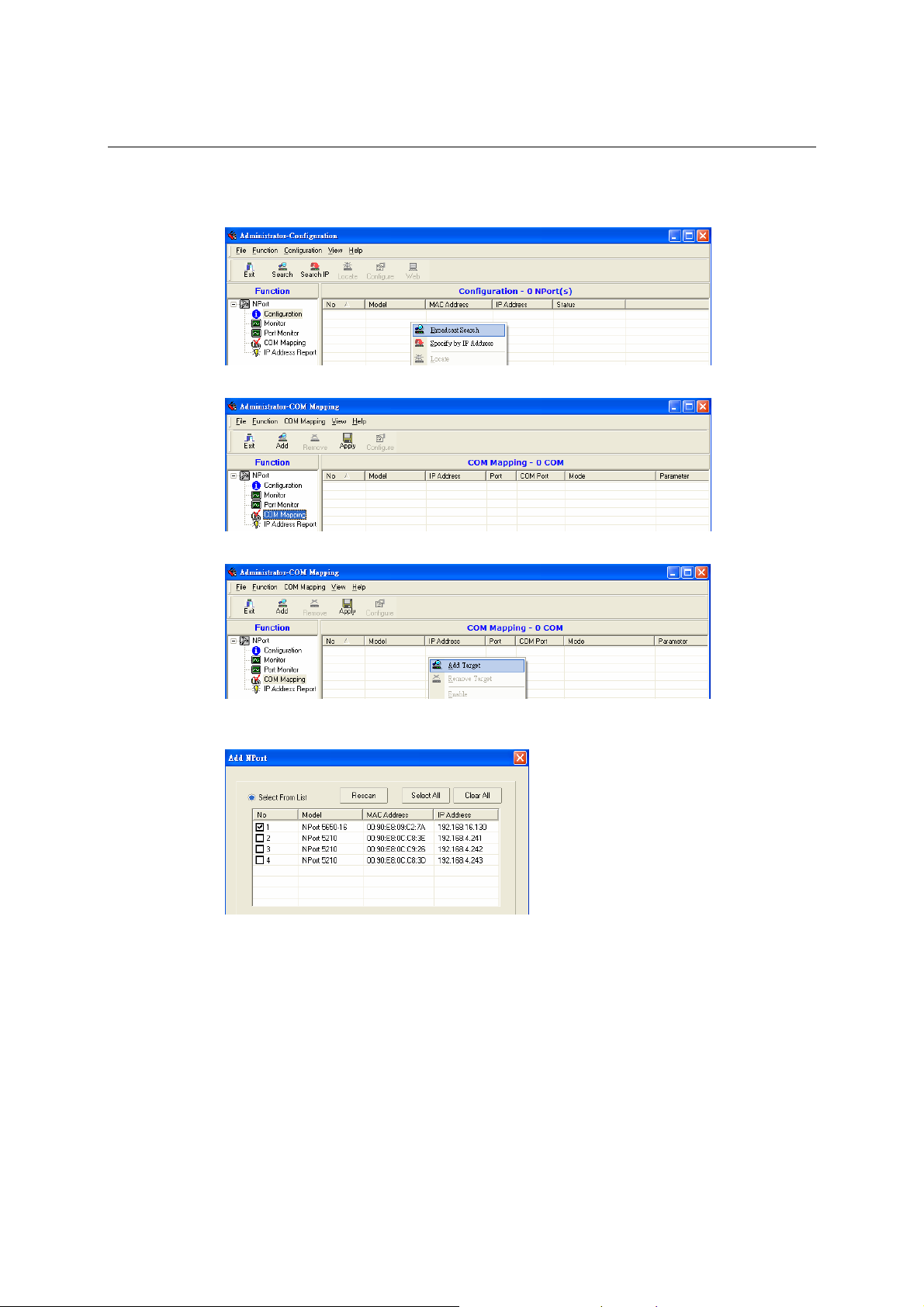
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
On-line COM Mapping
1. Broadcast Search for NPorts on the network.
2. Select the COM Mapping function group.
3. Add the target to which you would like to map COM ports.
4. The NPort list that appears is the list generated by the previous Broadcast Search. Select the
NPort to which you would like to map COM ports.
6-21
Page 90

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
5. Select COM Setting to modify COM No., default setting, etc.
6. Select the COM No. COM ports that are “In use” or “Assigned” will also be indicated in this
drop-down list.
If you select multiple serial ports or multiple NPorts, remember to check the “Auto
Enumerating” function to use the COM No. you select as the first COM No.
Hi-performance mode is the default for Tx mode. If the driver completes sending data out to
the NPort, the driver will respond “Tx Empty” to the program.
Under classical mode, the driver will not notify the user’s program that Tx is completed until
all Tx data has been sent out from the NPort; this mode will cause lower throughput. If you
want to ensure that all data is sent out before further processing, classical mode is
recommended.
Enable/Disable Tx/Rx FIFO. If disabled, NPort will send one byte each time the Tx FIFO
becomes empty; and an Rx interrupt will be generated for each incoming byte. This will result
in a faster response and lower throughput. If you want to use XON/XOFF flow control, we
recommend setting FIFO to Disable.
6-22
Page 91
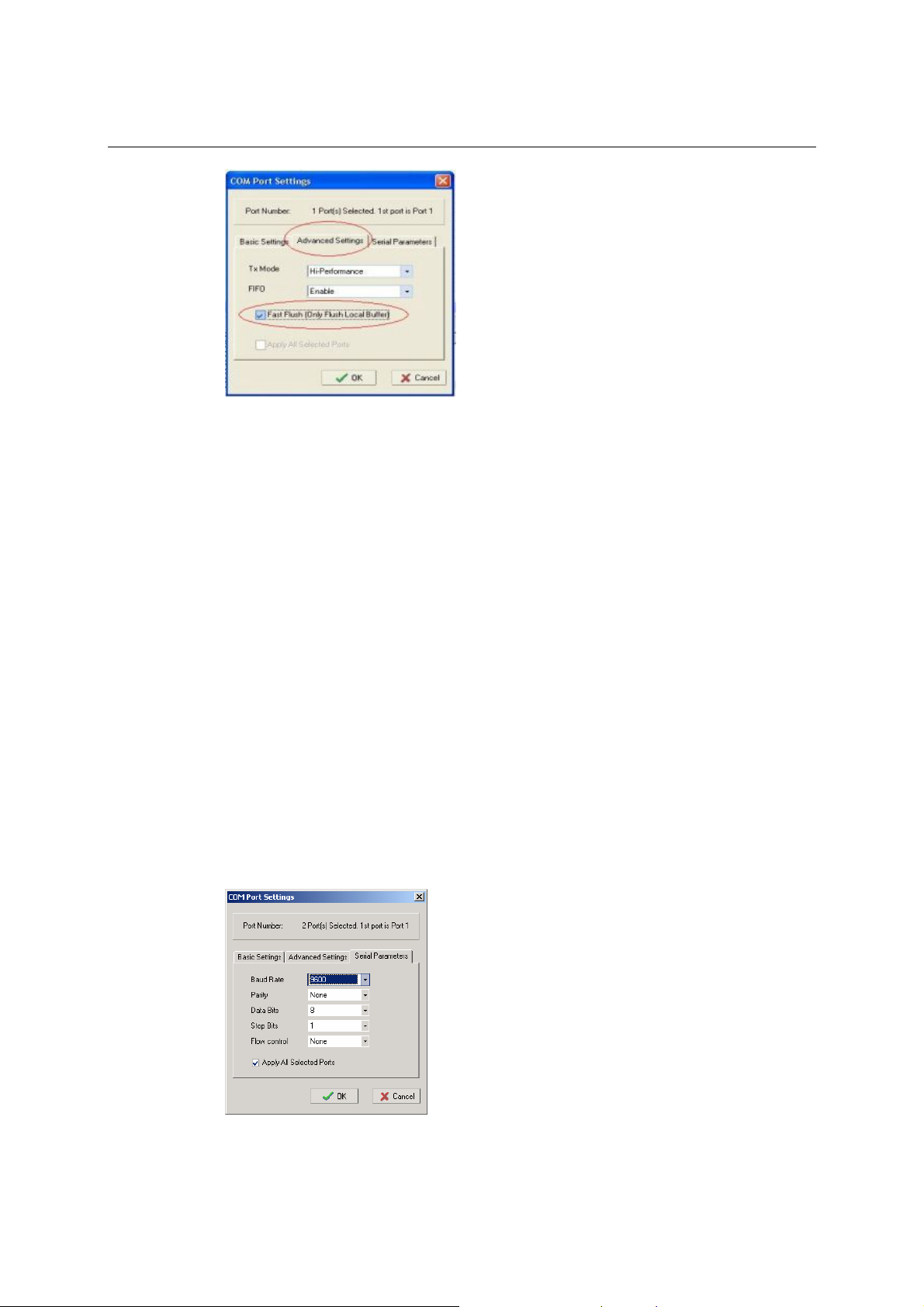
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Fast Flush (only flush local buffer)
We have added one optional Fast Flush function to Moxa’s new NPort Real COM driver.
NPort Administrator Suite fo r 2G NP o rt a dds it afte r version 1.2.
For some applications, the user’s program will use the Win32 “PurgeComm()” function
before it reads or writes data. With our design, after the program uses this Purge Comm()
function, the NPort driver will keep querying NPort’s firmware several times to make sure
there is really no data queued in the NPort firmware buffer, rather than just flushing the local
buffer. This kind of design is used because of some special considerations. However, it might
take more time (on the order of several hundred milliseconds) than a native COM1, because it
needs to work via Ethernet. That’s why the native COM ports on the motherboard can work
fast with this function call, but NPort requires much more time. In order to accommodate
other applications that require a faster response time, the new NPort driver implements a new
“Fast Flush” option. Note that by default, this function is disabled.
To begin with, make sure there are some “PurgeComm()” functions being used in your
application program. In this kind of situation, you might find that your NPort exhibits a much
poorer operation performance than when using the native COM1 port. Once you have enabled
the “Fast Flush” function, you can check to see if there has been an improvement in
performance.
By default, the optional “Fast Flush” function is disabled. If you would like to enable this
function, from the “NPort Administrator,” double click the COM ports that are mapped to the
NPort, and then select the “Fast Flush” checkbox. You should find that when “Fast Flush” is
enabled, the NPort driver will work faster with “PurgeComm().”
The Serial Parameter settings shown here are the default settings when the NPort is powered
on. However, the program can redefine the serial parameters to different values after the
program opens the port via Win 32 API.
6-23
Page 92

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
7. After setting the COM Mapping, remember to select Apply Change to save the information
in the host system registry. The host computer will not have the ability to use the COM port
until after Apply Change is selected.
8. Select Discard Change to tell Administrator NOT to save the COM Mapping information to
the host.
9. To save the configuration to a text file, select Export COM Mapping. You will then be able
to import this configuration file to another host and use the same COM Mapping settings in
the other host.
6-24
Page 93

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
Off-line COM Mapping
1. Add a target by entering the IP address and selecting the Model Name without physically
connecting the NPort to the network.
2. Select Apply change to effect the changes immediately.
6-25
Page 94

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
IP Location
When NPort 5600 series products are used in a dynamic IP environment, users must spend more
time with IP management tasks. NPort 5600 series products help out by periodically reporting
their IP address to the IP location server, in case the dynamic IP has changed.
y Receive NPort’s IP location report
y Centralize NPort’s IP management in a dynamic IP environment.
1. Configure NPort with Dynamic IP settings. For example, DHCP, BOOTP and DHCP/BOOTP.
Assign the remote Auto IP report server’s IP address and UDP port.
2. Select the IP Location Report, and click the right mouse button to select Settings.
3. Then configure the Local Listen Port to be the same as the NPort’s “Auto report to UDP port”
setting.
4. Click GO to start receiving the Auto IP address report from the NPort.
6-26
Page 95

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual IP Serial LIB
6-27
Page 96

The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
IP Serial LIB Function Groups
Example Program
7
7
Chapter 7 IP Serial LIB
Page 97
NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Pinouts and Cable Wiring
Overview
What is IP Serial Library?
IP Serial Library is a Windows library with frequently used serial command sets and subroutines.
IP Serial Library is designed to reduce the complexity and poor efficiency of serial communication
over TCP/IP. For example, Telnet can only transfer data, but it can't monitor or configure the serial
line's parameters.
Why Use IP Serial Library?
For programmers who are familiar with serial communication, IP Serial Library provides
well-designed function calls that have the same style as Moxa's PComm Library.
IP Serial Library is amazingly simple and easy to understand. By including it in your VB, C, or
Delphi programming environment, you can program your own TCP/IP application with the ability
to control serial communication parameters.
NPort Serial Device Servers use 2 TCP ports for communication between the NPort and host
computer's Real COM driver. NPort uses a data port and command po rt to provide pure data
transfer without decode and encode. Compared to using only one TCP port to control serial
communication (such as RFC 2217), IP Serial Library uses a command port to communicate with
NPort in user's program. IP Serial Library not only runs with excellent efficiency but also runs
without any decode or encode problems.
How to install IP Serial Library?
IP Serial Lib comes with the NPort Administration Suite. Refer to the IPSerial directory for more
detail about the function definitions.
7-2
Page 98

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Pinouts and Cable Wiring
IP Serial LIB Function Groups
Server Control Port Control Input/Output Data Port Status
nsio_init
nsio_end
nsio_resetserver
nsio_checkalive
Example Program
char nportip=”192.168.1.10”;
char buffer[255];
int port = 1;
int portid;
nsio_init();
portid = nsio_open(nportip, port);
nsio_ioctl(portid, B9600, (BIT_8 | STOP_1 |
P_NONE) );
sleep(1000);
nsio_read(port, buffer, 200);
nsio_close(portid);
nsio_end();
nsio_open
nsio_close
nsio_ioctl
nsio_flowctrl
nsio_DTR
nsio_RTS
nsio_lctrl
nsio_baud
nsio_resetport
nsio_read
nsio_SetReadTimeouts
nsio_write
nsio_SetWriteTimeouts
/*data buffer, 255 chars */
/*1st port */
/* port handle */
/*initial IP Serial Library */
/*1st port, nport IP=192.168.1 .1 0 */
/*set 9600, N81 */
/* wait for 1000 ms for data */
/* read 200 bytes from port 1 */
/* close this serial port */
/* close IP Serial Library */
Inquiry
nsio_lstatus
nsio_data_status
Miscellaneous
nsio_break
nsio_break_on
nsio_break_off
nsio_breakcount
7-3
Page 99

Appendix A Pinouts and Cable Wiring
In this appendix, we cover the following topics.
Port Pinout Diagrams
¾ Ethernet Port Pinouts
¾ Serial Port Pinouts
Cable Wiring Diagrams
¾ Ethernet Cables
¾ Serial Cables for NPort 5610/5650 (RS-232)
¾ Serial Cables for NPort 5630 (RS-422/4-wire RS-485)
¾ Serial Cables for NPort 5630 (2-wire RS-485)
¾ Serial Cables for NPort 5650 (RS-422/4-wire RS-485)
¾ Serial Cables for NPort 5650 (2-wire RS-485)
¾ Pin Assignments for DB9 and DB25 Connectors
A
A
Page 100

NPort 5600 Series User’s Manual Well Known Port Numbers
Port Pinout Diagrams
Ethernet Port Pinouts
Pin RS-232
1 Tx+
2 Tx3 Rx+
6 Rx-
Serial Port Pinouts
RS-232 Port Pinouts for NPort 5610
Pin RS-232
1 DSR (in)
2 RTS (out)
3 GND
4 TxD (out)
5 RxD (in)
6 DCD (in)
7 CTS (in)
8 DTR (out)
18
18
RS-422/485 Port Pinouts for NPort 5630
Pin
1 --- --2 --- --3 TxD+ --4 TxD- --5 RxD- Data6 RxD+ Data+
7 GND GND
8 --- ---
RS-232/422/485 Port Pinouts for NPort 5650
Pin RS-232
1 DSR --- --2 RTS TxD+ --3 GND GND GND
4 TxD TxD- --5 RxD RxD+ Data+
6 DCD RxD- Data7 CTS --- --8 DTR --- ---
RS-422
4-wire RS-485
2-wire
RS-485
RS-422
4-wire RS-485
18
2-wire
RS-485
18
A-2
 Loading...
Loading...