Page 1

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK User’s Manual
Edition 2.1, November 2017
www.moxa.com/product
© 2017 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK User’s Manual
Moxa Americas
Toll
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa China (Shanghai office)
Toll
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa Europe
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa Asia
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa India
Tel:
Fax:
the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
© 2017 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
The MOXA logo is a registered trademark of Moxa Inc.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
Moxa.
Moxa provides this document as is, without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited
to, its particular purpose. Moxa reserves the right to make improvements and/or changes to this manual, or to the
products and/or the programs described in this manual, at any time.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Moxa assumes no responsibility for
its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that may result from its use.
This product might include unintentional technical or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the publication.
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
-free: 1-888-669-2872
+1-714-528-6777
+1-714-528-6778
+49-89-3 70 03 99-0
+49-89-3 70 03 99-99
+91-80-4172-9088
+91-80-4132-1045
-free: 800-820-5036
+86-21-5258-9955
+86-21-5258-5505
+886-2-8919-1230
-Pacific
+886-2-8919-1231
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ...................................................................................................................................... 1-1
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Package Checklist ............................................................................................................................... 1-2
Product Features ................................................................................................................................ 1-2
Panel Layout ...................................................................................................................................... 1-3
MiiNePort E1-SDK Evaluation Board Panel Layout ............................................................................ 1-3
MiiNePort E2-SDK Evaluation Board Panel Layout ............................................................................ 1-4
Block Diagram .................................................................................................................................... 1-5
For MiiNePort E1-SDK Module ....................................................................................................... 1-5
For MiiNePort E2-SDK Module ....................................................................................................... 1-6
LED Indicators .................................................................................................................................... 1-6
2. Getting Started.................................................................................................................................. 2-1
Wiring Precautions .............................................................................................................................. 2-2
Selecting the Serial Interface ............................................................................................................... 2-2
Connecting Power ............................................................................................................................... 2-3
Connecting MiiNePort USB to PC ........................................................................................................... 2-3
Connecting to the Network ................................................................................................................... 2-5
Connecting to a Serial Device ............................................................................................................... 2-5
Digital I/O Channel Settings ................................................................................................................. 2-5
Schematic Design Guide ...................................................................................................................... 2-6
3. Choosing the Proper Operation Mode ................................................................................................ 3-1
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 3-2
RealCOM Mode ................................................................................................................................... 3-2
Ethernet Modem Mode ......................................................................................................................... 3-3
4. Utility Console and Driver Installation .............................................................................................. 4-1
Device Search Utility (DSU) ................................................................................................................. 4-2
Installing the Device Search Utility ................................................................................................ 4-2
Device Search Utility Configuration ................................................................................................ 4-4
NPort Windows Driver Manager ............................................................................................................ 4-5
Installing NPort Windows Driver Manager ....................................................................................... 4-5
Using NPort Windows Driver Manager ............................................................................................ 4-7
Command Line Installation/Removal .............................................................................................. 4-9
Linux Real TTY Drivers ...................................................................................................................... 4-11
Installing Linux Real TTY Driver Files ................................................................................................... 4-11
Mapping TTY Ports ..................................................................................................................... 4-11
Removing Mapped TTY Ports ....................................................................................................... 4-12
Removing Linux Driver Files ........................................................................................................ 4-12
UNIX Fixed TTY Drivers ..................................................................................................................... 4-12
Installing the UNIX Driver........................................................................................................... 4-13
Configuring the UNIX Driver ....................................................................................................... 4-13
5. MiiNePort IDE Development Tool ...................................................................................................... 5-1
Installing MiiNePort IDE ....................................................................................................................... 5-2
Starting MiiNePort IDE ......................................................................................................................... 5-6
Create MiiNePort-SDK Project ............................................................................................................... 5-6
RealCOM Mode ............................................................................................................................ 5-8
Ethernet Modem Mode ................................................................................................................. 5-9
Sample Application .................................................................................................................... 5-10
Data Packing ............................................................................................................................ 5-11
Serial Command Mode ............................................................................................................... 5-13
Web Console ............................................................................................................................. 5-17
CLI .......................................................................................................................................... 5-18
SNMP agent .............................................................................................................................. 5-18
TFTP Server .............................................................................................................................. 5-19
NTP Client ................................................................................................................................ 5-19
CPU Monitor.............................................................................................................................. 5-20
Wizards ........................................................................................................................................... 5-21
Modify project dependency ......................................................................................................... 5-21
CLI Wizard ............................................................................................................................... 5-21
Configuration Wizard ................................................................................................................. 5-24
SCM Wizard .............................................................................................................................. 5-26
SNMP Wizard ............................................................................................................................ 5-28
User App Wizard ....................................................................................................................... 5-31
Build project ............................................................................................................................. 5-32
Upload debug version firmware to MiiNePort ................................................................................. 5-32
Debug current active project ....................................................................................................... 5-32
Upload your customized firmware to MiiNePort .............................................................................. 5-32
Page 4

6. NetEZ Technologies ........................................................................................................................... 6-1
SCM (Serial Command Mode) ............................................................................................................... 6-2
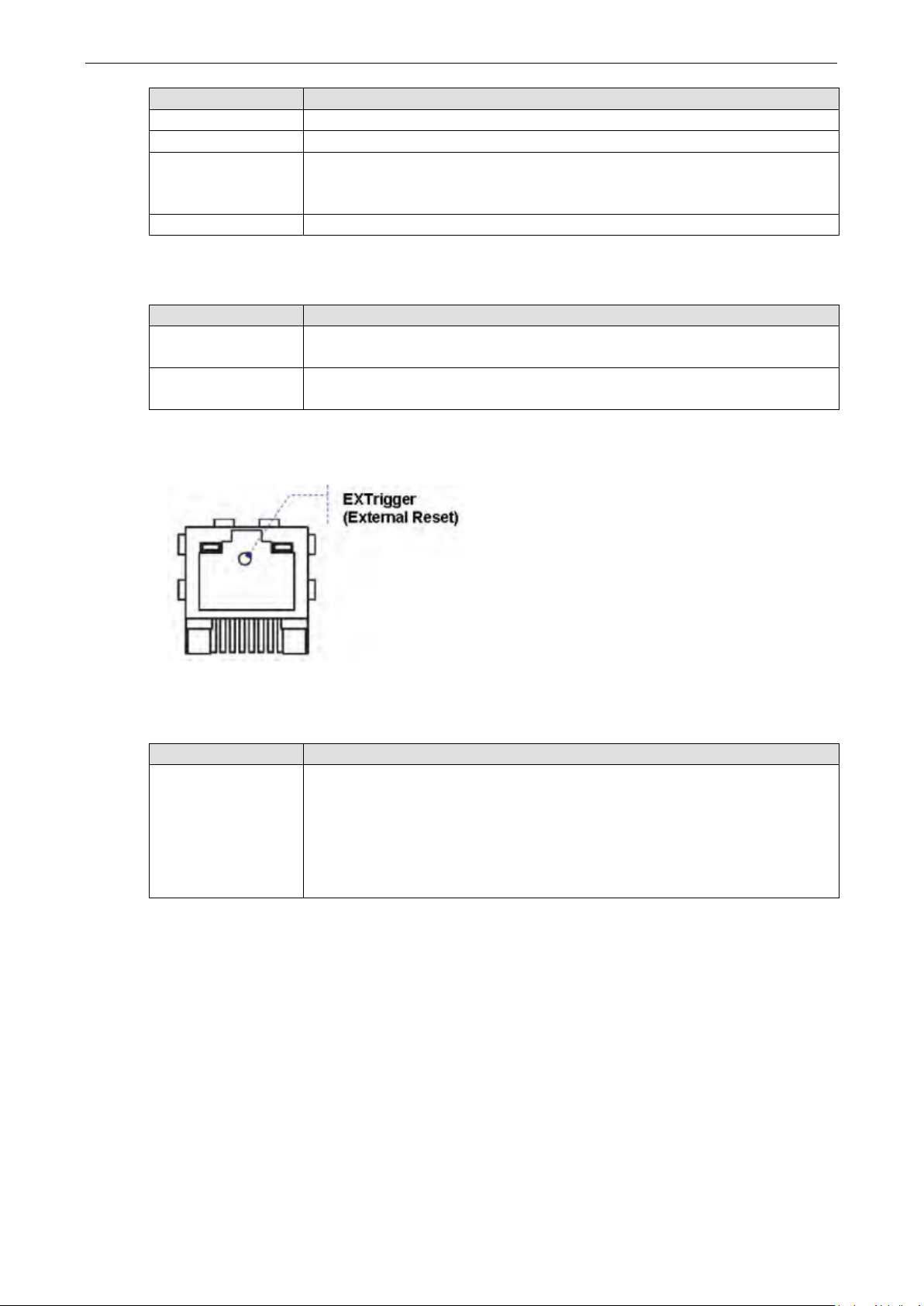
EXTrigger (External Trigger) ................................................................................................................ 6-3
EZPower ............................................................................................................................................ 6-4
A. Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set ............................................................. A-1
Command/Reply Format ...................................................................................................................... A-2
Single Line Command Format ....................................................................................................... A-2
Single Line Reply Format .............................................................................................................. A-2
Head and Tail Format ................................................................................................................... A-2
Operation Codes ......................................................................................................................... A-2
Status Codes .............................................................................................................................. A-2
Restriction .................................................................................................................................. A-2
Command Code .................................................................................................................................. A-3
Command Code for Getting the Configuration ................................................................................. A-3
Command Codes for Retrieving Running Configuration ..................................................................... A-5
Command Codes for Viewing the Status ......................................................................................... A-7
Control Command Codes .............................................................................................................. A-7
B. Well-Known Port Numbers ................................................................................................................ B-1
C. SNMP Agent with MIB II and RS-232 Like Groups ............................................................................. C-1
D. Supported File Systems ..................................................................................................................... D-1
Page 5

1
1. Introduction
The MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Series of embedded device servers is compact drop-in modules that can be
integrated with your serial devices to enable connectivity to an Ethernet network. All MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK
Series modules come equipped with built-in TCP/IP protocols and other easy-to-use network enabling tools for
fast integration, allowing you to provide network access to any electronic device with a serial port.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Product Features
MiiNePort E1-SDK Evaluation Board Panel Layout
MiiNePort E2-SDK Evaluation Board Panel Layout
Block Diagram
For MiiNePort E1-SDK Module
For MiiNePort E2-SDK Module
LED Indicators
Page 6
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction
1-2
NOTE
Please notify your sales representative if any of the above items is missing or damaged.
Overview
The Moxa MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Series products are serial-to-Ethernet embedded modules. Moxa provides
development and debug kit which includes JTAG, an Eclipse-based integrated software development tool, and
a source-level debugger. The following table lists the model names of all MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK series modules,
along with the model names of the corresponding starter kits.
Package Checklist
Available Models:
• MiiNePort E1-SDK: Software Development Kit for the MiiNePort E1 Series, MiiNePort E1 module included
• MiiNePort E2-SDK: Software Development Kit for the MiiNePort E2 Series, MiiNePort E2 module included
Package Checklist:
• MiiNePort E2-SDK module or MiiNePort E1-SDK module
• MiiNePort E2-SDK evaluation board or MiiNePort E1-SDK evaluation board
• Universal power adapter
• 2 power cords
• Null modem cable
• Crossover Ethernet cable
• Documentation and software CD
• Quick installation guide (printed)
• Warranty card
Product Features
All MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules have the following general features:
• Eclipse-based integrated software development tool
• Source-level debugger
• Easy to build proprietary SNMP/CLI console
• Various serial-to-Ethernet sample code
• Mass production tool for easy firmware upload
• Supports RealCOM mode operation functions
Page 7
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction
1-3
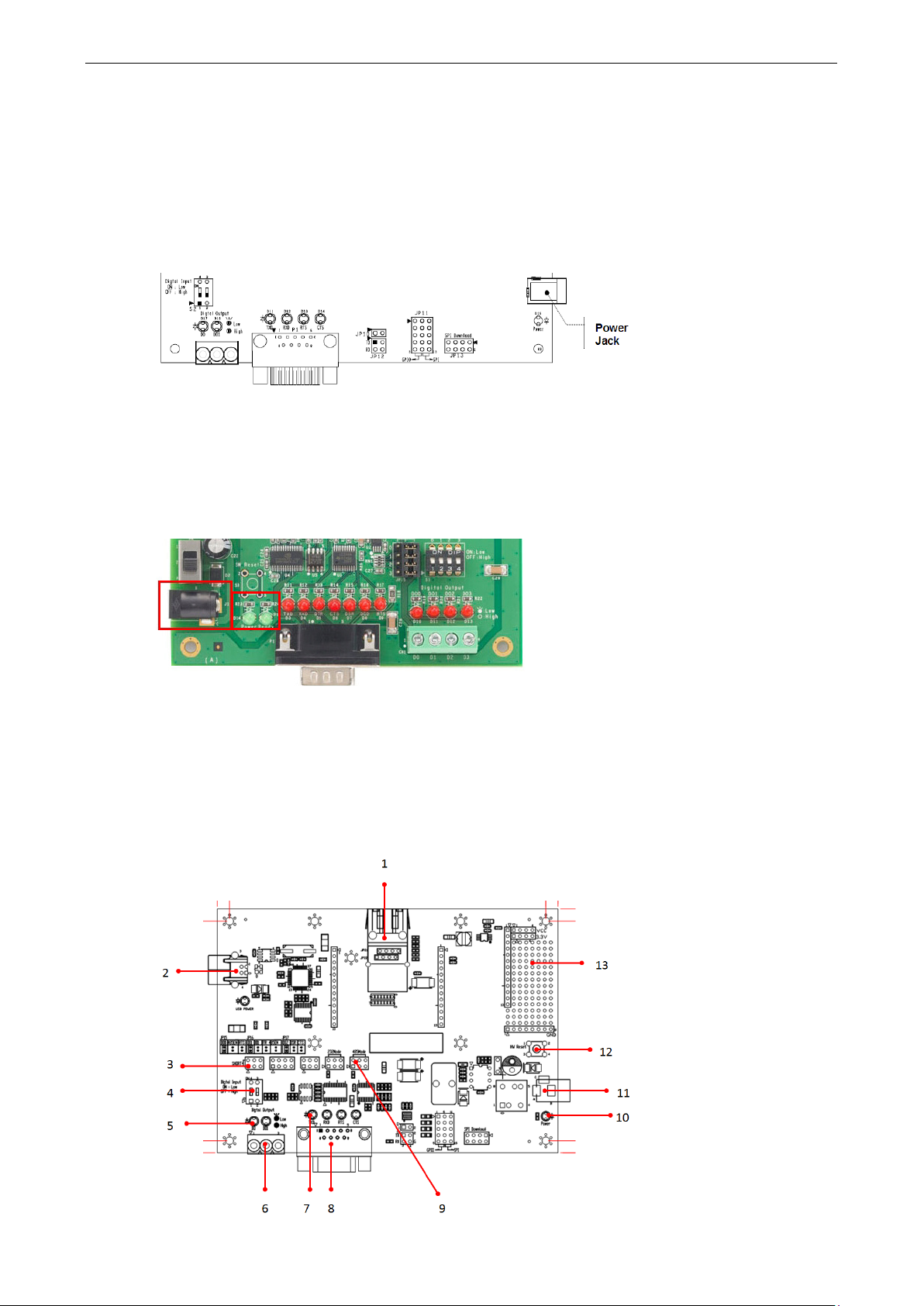
USB Type B Connector (Debug)
3
Configurable Pin Jumper
13
Circuit Pad
ATTENTION
Users must set
respectively, to ensure that the evaluation board works properly.
ATTENTION
When you are in RS
pin jumper must
be moved from JP19 to JP20.
Panel Layout
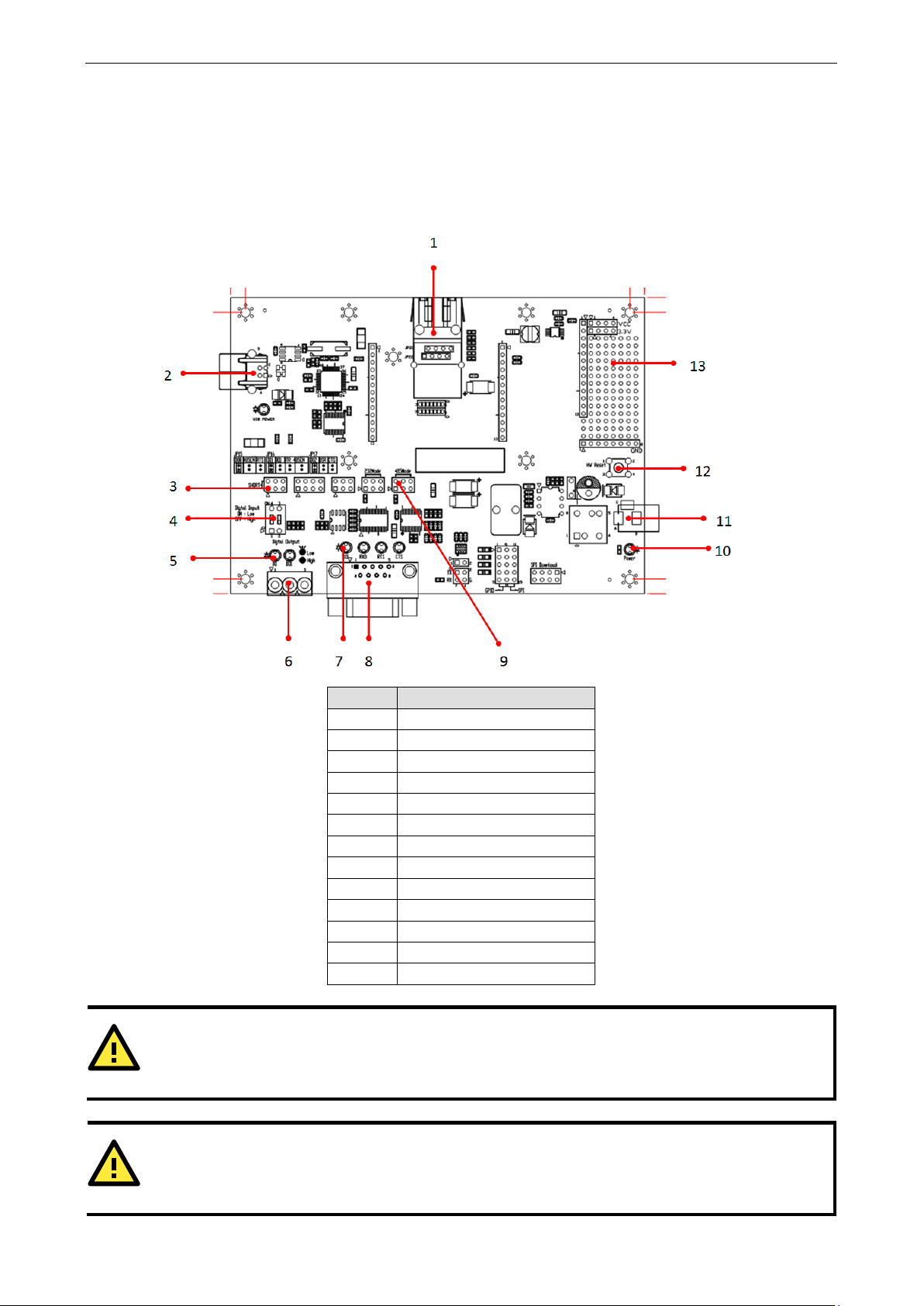
MiiNePort E1-SDK Evaluation Board Panel Layout
Number Description
1 MiiNePort E1 Module Location
2
4 Digital Input Switch
5 Digital Output LED
6 Digital IO Terminal Block
7 Serial Port Status LED
8 DB9 Male Connector
9 Serial Interface Jumper
10 Power LED
11 Power Jack
12 Restart Button
jumpers JP15, JP16, and JP17 to correspond with the functions of pins 6, 7, and 8,
-485 mode, 485EN must be configured by either JP15 or JP16, and the 6-
Page 8
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction
1-4
ATTENTION
Before you manipulate the jumpers, be sure to disconnect the power first.
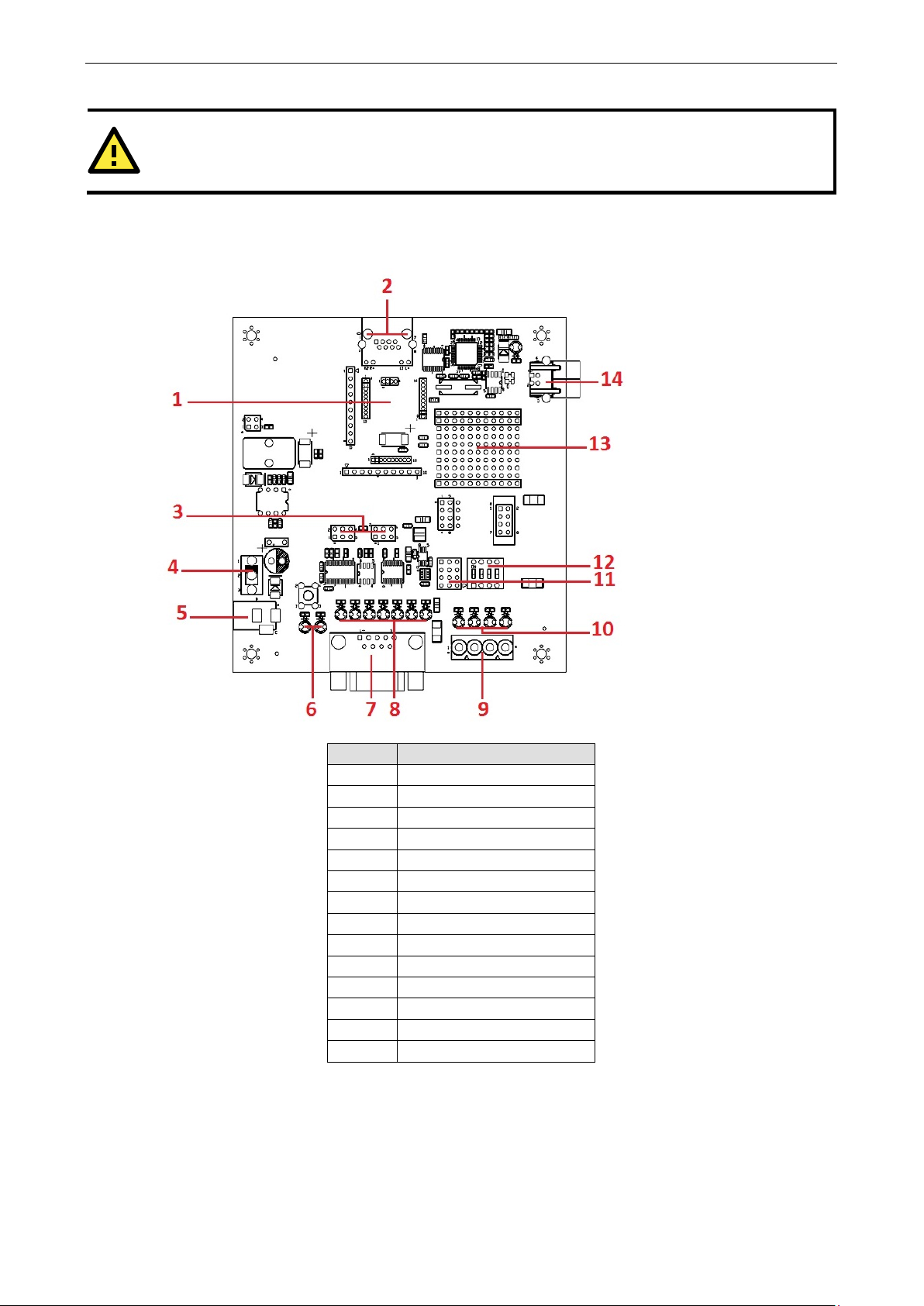
MiiNePort E2-SDK Evaluation Board Panel Layout
Number Description
1 MiiNePort E2 Module Location
2 Ethernet RJ45 Connector
3 Serial Interface Jumper
4 Power Switch
5 Power Jack
6 Power & Ready LED
7 DB9 Male Connector
8 Serial Port Status LED
9 Digital IO Terminal Block
10 Digital Output LED
11 Digital Input/Output Mode
12 Digital Input Switch
13 Circuit Pad
14 USB Type B Connector (Debug)
Page 9
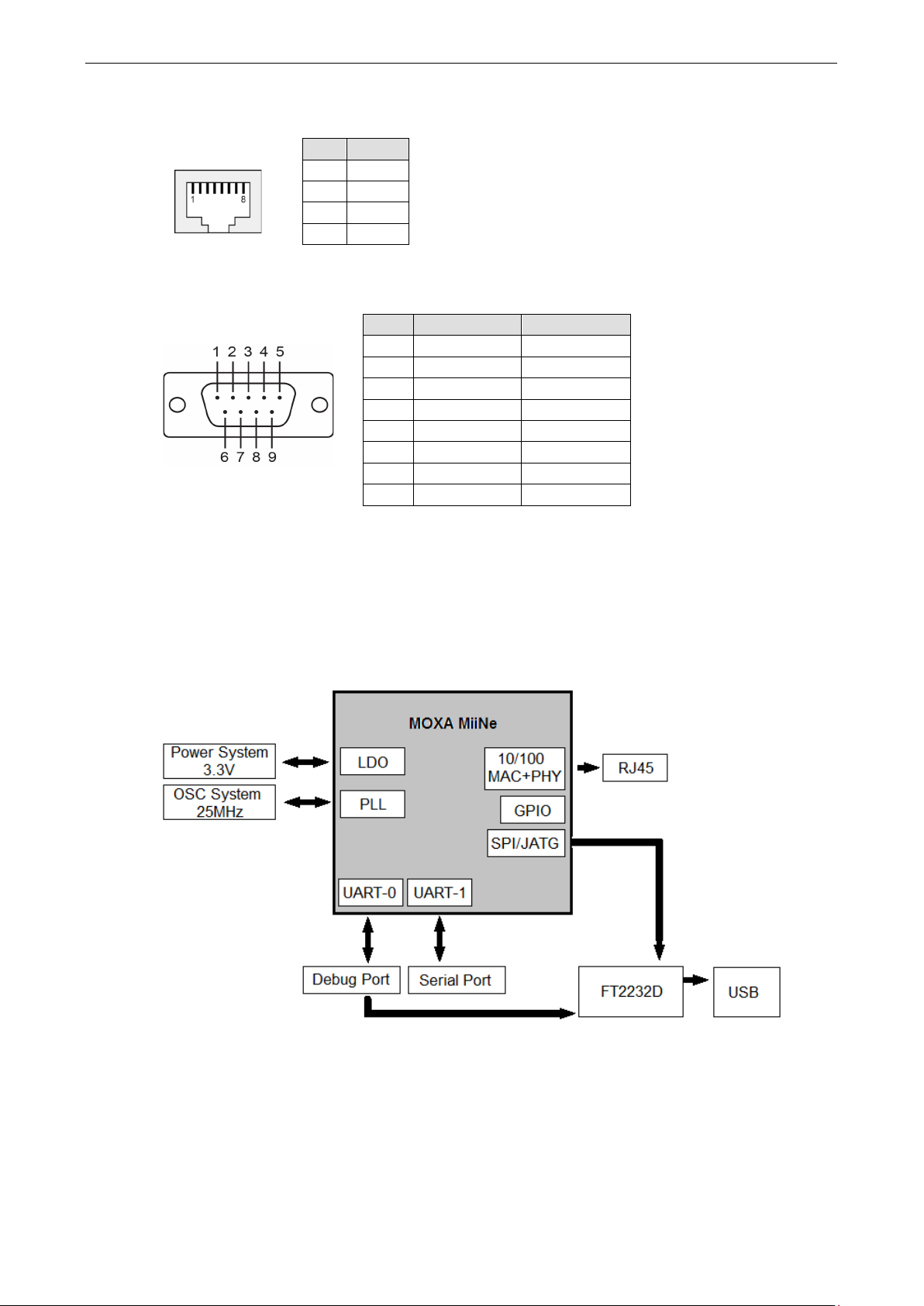
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction
1-5
3
Rx+
1
DCD
–
Ethernet Port Pins for MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Modules
RJ45
Pin Signal
1 Tx+
2 Tx-
6 Rx-
Serial Pin Signals for the MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Evaluation Board
DB9 Male
Pin RS-232 2-wire RS-485
2 RxD –
3 TxD Data+
4 DTR Data-
5 GND GND
6 DSR –
7 RTS –
8 CTS –
Block Diagram
For MiiNePort E1-SDK Module
Page 10

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction
1-6
For MiiNePort E2-SDK Module
LED Indicators
MiiNePort E1-SDK Series Modules
LED Color Description
Left
Right
MiiNePort E1-SDK Evaluation Board
LED Color Description
Serial Signal TxD / LED D11 Red Indicates that TxD has a signal
Serial Signal RXD / LED D12 Red Indicates that RxD has a signal
Serial Signal RTS / LED D13 Red Indicates that RTS has a signal
Power Signal / LED D43 Green Indicates power input status
Digital Output / LED D17 Red Indicates DO 0 “low” (0) status
Digital Output / LED D18 Red Indicates DO 1 “low” (0) status
Green 100BASE-TX Link Activity (constant on when link exists, blinks when data transmitting)
Amber 10BASE-T Link Activity (constant on when link exists, blinks when data transmitting)
Green In Use (constant on when connection established)
Amber Fault (blinks when IP fault)
Page 11
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction
1-7
2. Auto Config complete.
DHCP or BOOTP server did
DTR / LED D5
Red
Indicates that DTR has a signal.
MiiNePort E2-SDK Evaluation Board
LED Name Color Description
Power Off 1. Power is off
2. Power error
3. System error
Green, Steady On Indicates that the power is on.
Ready Green, Blinking every 1
sec.
1. The device server has been located by NPort search utility’s
location function.
Green, Blinking every
0.5 sec.
TxD / LED D3 Red Indicates that TxD has a signal.
RxD / LED D4 Red Indicates that RxD has a signal.
CTS / LED D6 Red Indicates that CTS has a signal.
DSR / LED D7 Red Indicates that DSR has a signal.
DCD / LED D8 Red Indicates that DCD has a signal.
RTS / LED D9 Red Indicates that RTS has a signal.
DO0 / LED D10 Red Indicates that DO0 is in “low” (0) status.
DO1 / LED D11 Red Indicates that DO1 is in “low” (0) status.
DO2 / LED D12 Red Indicates that DO2 is in “low” (0) status.
DO3 / LED D13 Red Indicates that DO3 is in “low” (0) status.
USB (Debug) Power Green Indicates that the USB cable is connected to PC
Indicates a LAN IP conflict, or the
not respond properly.
Page 12

2
2. Getting Started
This chapter includes information about how to install MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules for development and
testing.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Wiring Precautions
Selecting the Serial Interface
Connecting Power
Connecting MiiNePort USB to PC
Connecting to the Network
Connecting to a Serial Device
Digital I/O Channel Settings
Schematic Design Guide
Page 13

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Getting Started
2-2
ATTENTION
Be sure to disconnect the power cord before installing or
ATTENTION
Determine the maximum possible current
in each power wire and common wire. Observe all electrical
codes dictating the maximum current allowable for each wire size. If the current goes above the maximum
capacity
ATTENTION
Take care when handling the evaluation boards. When plugged in, the evaluation boards’ internal components
generate heat, and consequently the board may
Wiring Precautions
This section describes some important safety precautions that you should pay attention to before proceeding
with installation.
, the wiring could overheat, causing serious damage to your equipment.
You should also pay attention to the following:
• Do not run signal or communication wiring and power wiring in the same wire conduit. To avoid interference,
wires with different signal characteristics should be routed separately. Separate paths should be used to
route wiring for power and devices. You can use the type of signal transmitted through a wire to determine
which wires should be kept separate. The rule of thumb is that wires sharing similar electrical
characteristics may be bundled together.
• Keep input wiring and output wiring separate.
• If power wiring and device wiring paths must cross paths, make sure the wires are perpendicular at the
intersection point.
• All wiring should be clearly labeled.
allowed
be too hot to touch.
wiring the evaluation board.
Selecting the Serial Interface
RS-232
MiiNePort E1-SDK: To use an RS-232 serial interface, place the 6-pin jumper on JP19.
MiiNePort E2-SDK: To use an RS-232 serial interface, place the 6-pin jumper on JP13.
RS-485
MiiNePort E1-SDK: To use an RS-485 serial interface, place the 2-pin jumper on the middle two pins of JP15 or
the right-most two pins of JP16 (labeled as 485EN), and place the 6-pin jumper on JP20.
MiiNePort E2-SDK: Place the 6-pin jumper on JP14.
Page 14
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Getting Started
2-3
Connecting Power
For MiiNePort E1-SDK Evaluation Board Layout
Connect the 12-48 VDC power line with the power jack of the evaluation board. If the power is properly
supplied, the power LED (D15, as shown in the following figure) on the evaluation board will show a solid red
color until the system is ready, at which time the ready LED on the module will show a solid green color.
For MiiNePort E2-SDK Evaluation Board Layout
Connect the 12-48 VDC power line with the evaluation board’s power jack. If the power is properly supplied, the
power LED on the evaluation board (D14) will show a solid green color until the system is ready. When the
system is ready, the ready LED on the module will show a solid green color.
Connecting MiiNePort USB to PC
First, connect the MiiNePort USB port to the PC. Please use the USB cable to connect the USB port on the
evaluation board to the PC. The figures below indicate the location of the USB port on the evaluation board.
E1 Evaluation Board
Page 15
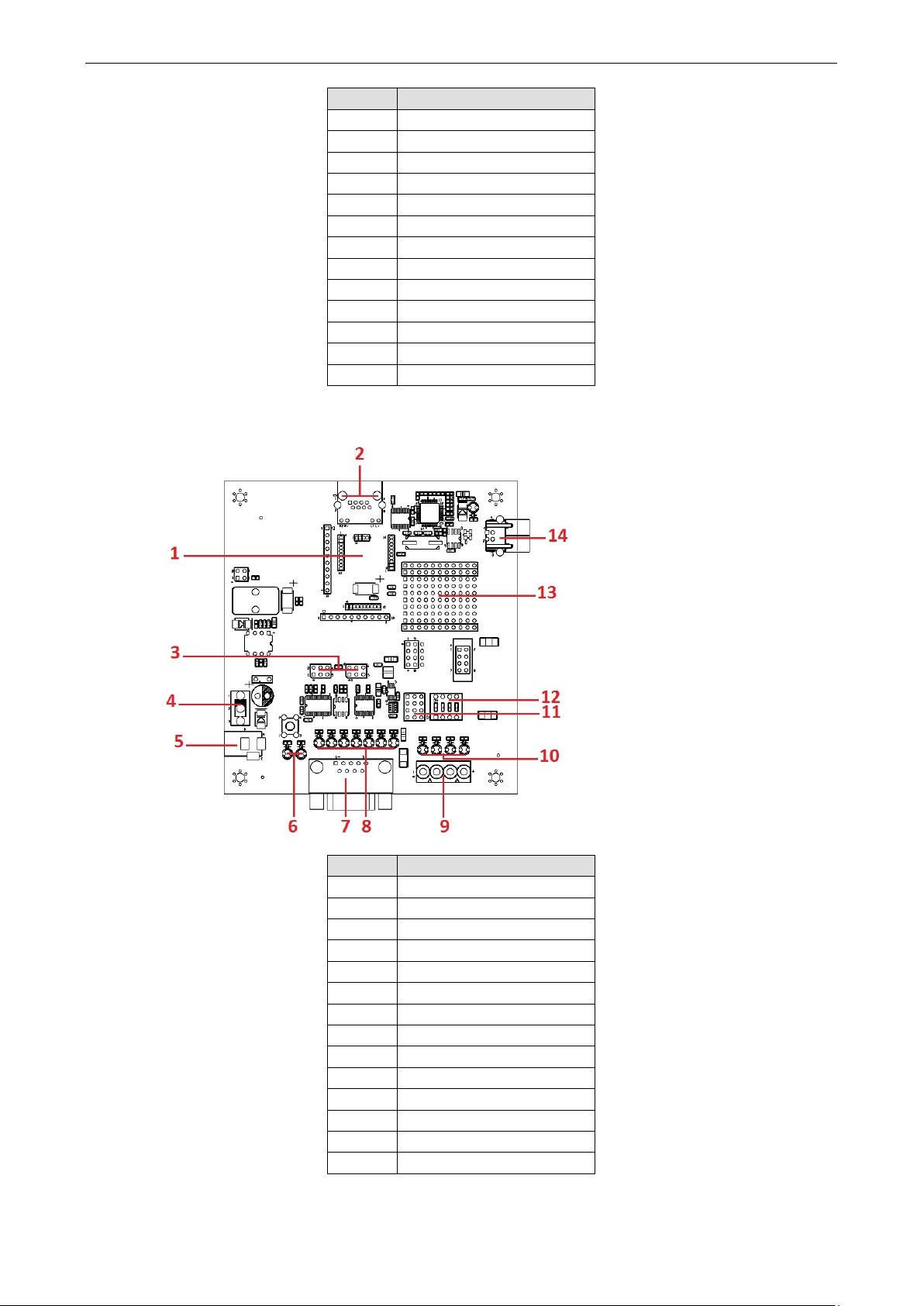
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Getting Started
2-4
USB Type B Connector (Debug)
4
Power Switch
Number Description
1 MiiNePort E1 Module Location
2
3 Configurable Pin Jumper
4 Digital Input Switch
5 Digital Output LED
6 Digital IO Terminal Block
7 Serial Port Status LED
8 DB9 Male Connector
9 Serial Interface Jumper
10 Power LED
11 Power Jack
12 Restart Button
13 Circuit Pad
E2 Evaluation Board
Number Description
1 MiiNePort E2 Module Location
2 Ethernet RJ45 Connector
3 Serial Interface Jumper
5 Power Jack
6 Power & Ready LED
7 DB9 Male Connector
8 Serial Port Status LED
9 Digital IO Terminal Block
10 Digital Output LED
11 Digital Input/Output Mode
12 Digital Input Switch
13 Circuit Pad
14 USB Type B Connector (Debug)
Page 16
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Getting Started
2-5
Green
In Use (always on when connection is established)
Connecting to the Network
To connect to the network for testing and development purposes, install the module on the evaluation board
and then plug the Ethernet cable into the RJ45 jack on the module. If the cable is properly connected, the LED
on the module will indicate a valid connection to the Ethernet as follows:
MiiNePort E1-SDK
LED Color Meaning
Left
Green
Amber 10BASE-T Link Activity (constant on when link exists, blinks when transmitting data)
100BASE-TX Link Activity (constant on when link exists, blinks when transmitting data)
Right
Amber Fault (blinks when an IP fault exists)
MiiNePort E2-SDK
LED Color Meaning
Left Amber 10BASE-T Link Activity
(does not blink when not transmitting; blinks when transmitting)
Right Green 100BASE-TX Link Activity
(does not blink when not transmitting; blinks when transmitting)
When using a private IP address (factory default) for the module, make sure the netmask and IP settings are
configured properly to access the module from a host on the network.
Connecting to a Serial Device
To connect to a serial device for testing and development purposes, the module should be installed on the
evaluation board. Make sure the serial interface is configured correctly before connecting the evaluation board
to the serial device. (Refer to Selecting the Serial Interface section above when you are using jumper blocks
to select the serial interface on the evaluation board.) The module’s serial signals are routed to and from the
RS-232 or RS-485 COM port on the evaluation board. Use a serial data cable to connect the serial device to the
COM port on the evaluation board.
Digital I/O Channel Settings
For MiiNePort E1-SDK Evaluation Board Layout
Each module has three digital I/O (DIO) channels. (Refer to the Pin Assignments section above for the
module’s configurable DIO pin description. Refer to Configurable Pin Jumpers to select the corresponding
setting on the evaluation board.) All three DIO channels may be configured by software. A DI channel is a
channel that is operating in digital input mode; a DO channel is a channel that is operating in digital output
mode. You may use the evaluation board’s Digital Output LEDs and Digital Input DIP switches as the digital
input and output devices, or you may connect digital input/output devices to the DIO Terminal Block.
For channels in digital output mode, Low and High status is controlled from within the web console. When
using a Digital Output LED as your output device, Low status will be expressed by the LED lighting up, and
High status will be expressed by the LED turning off.
Page 17

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Getting Started
2-6
ATTENTION
When using a digital input device connected to the DIO Terminal Block, the corresponding Digital Input DIP
switch must be set to
will interfere with the signal from your
digital input device.
For MiiNePort E2-SDK Evaluation Board Layout
Each module has four digital I/O (DIO) channels. (Refer to the Pin Assignment section in Chapter 1 for the
module’s configurable DIO pin descriptions. Refer to the Evaluation Board Layout section in Chapter 1 to select
corresponding settings on the evaluation board.) All four DIO channels can be configured by software. A DI
channel is a channel that operates in digital input mode; a DO channel is a channel that operates in digital
output mode. You can use the evaluation board’s Digital Output LEDs and Digital Input DIP switches as the
digital input and output devices, or you can connect digital input/output devices to the DIO Terminal Block.
For channels in digital output mode, the Low versus High setting is controlled from the web console. When
using a Digital Output LED as your output device, the LED will be on to indicate that the status is Low and the
LED will be off to indicate that the status is High.
OFF or High. Setting the DIP switch to ON or Low
Schematic Design Guide
For guidance and suggestions on integrating your device’s hardware with the MiiNePort, refer to the MiiNePort
Schematic Design Guide in the Document and software CD.
Page 18

3
3. Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
In this chapter, we will describe the operation modes supported by MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules. Modes are
available for COM port mapping from the host computer, as well as operation modes for TCP/IP protocols. After
choosing the operation mode in this chapter, refer to subsequent chapters for configuration details.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
RealCOM Mode
Ethernet Modem Mode
Page 19
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
3-2
ATTENTION
The
the
MiiNePort E1
Overview
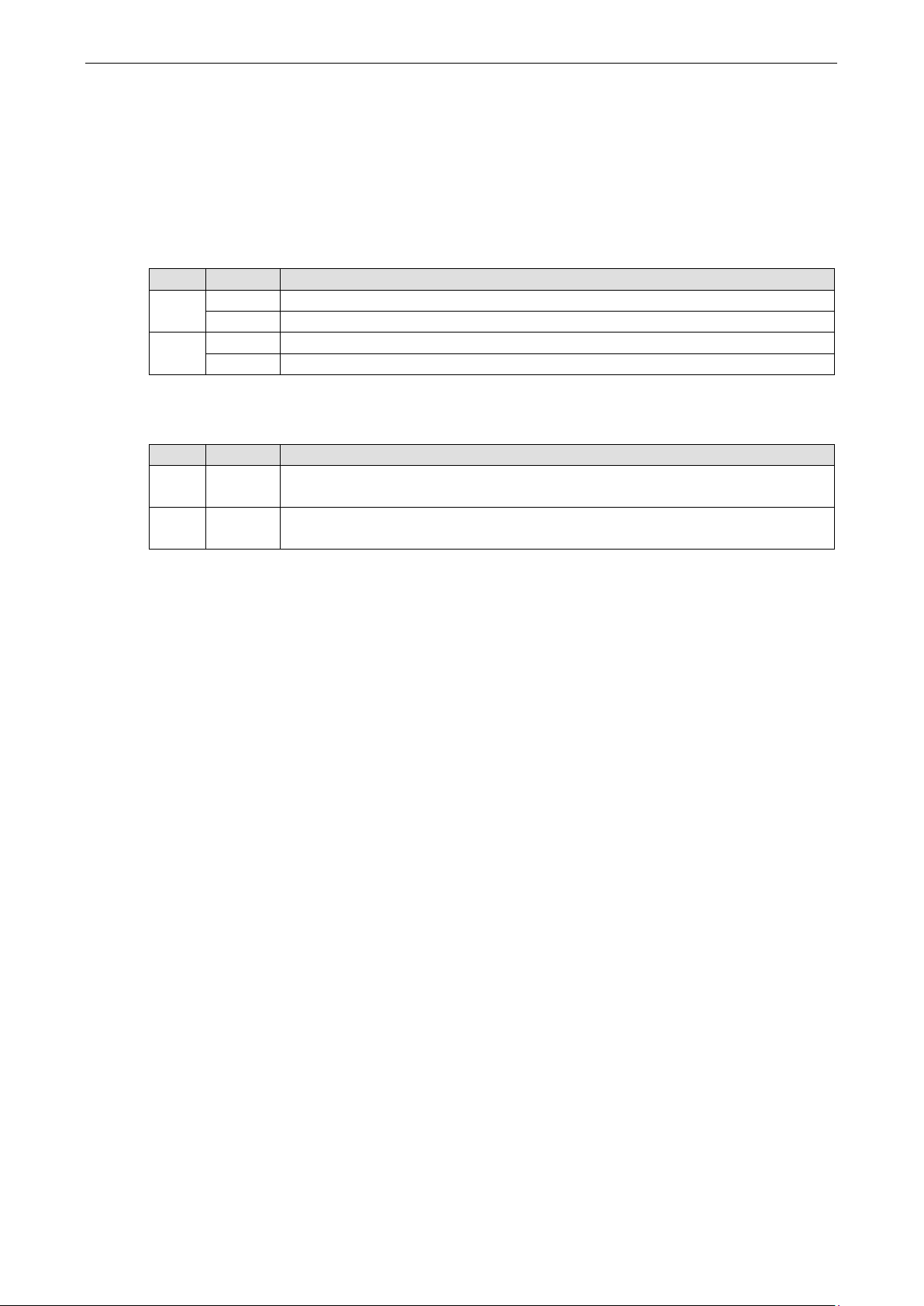
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules act as a bridge to connect your serial devices to the Ethernet. The built-in TCP/IP
stack frees you from the tedious task of programming networking protocols. With one step you can choose the
proper operation mode, and then use your computer to access, manage, and configure your serial devices from
anywhere in the world over the Internet.
Traditional SCADA and data collection systems rely on serial ports (RS-232/422/485) to collect data from a
variety of instruments. Since MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules convert between serial and Ethernet signals, your
SCADA and data collection system can be made accessible from any device connected to a standard TCP/IP
network, regardless of whether the devices are used locally or at a remote site.
The MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK supports RealCOM mode and Ethernet Modem mode. You don't need to take effort to
development these two kinds of complex serial to Ethernet operating mode. Only do some setting to complete
the function.
RealCOM Mode
RealCOM mode allows users to continue using software that was written for pure serial communications
applications. Each module comes equipped with COM drivers for Windows systems (95 and above). The
module’s serial port is mapped by the driver to an IP address and port number. The driver intercepts data sent
to the host’s COM port, packs it into a TCP/IP packet, and then redirects it through the host’s Ethernet card. At
the other end of the connection, the module accepts the Ethernet frame, unpacks the TCP/IP packet, and then
transparently sends the data to the attached serial device. The driver thus establishes a transparent connection
between the host and serial device, allowing the host to treat the networked device as if it were directly
attached.
RealCOM driver comes with the NPort Windows Driver Manager, which is included on the CD-ROM for
/E2-SDK package.
Page 20

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Choosing the Proper Operation Mode
3-3
Ethernet Modem Mode
Ethernet Modem mode is designed for use with legacy operating systems, such as MS-DOS, that do not support
TCP/IP Ethernet. By connecting the properly configured MiiNePort serial port to the MS-DOS computer’s serial
port, it is possible to use legacy software to transmit data over the Ethernet when the software was originally
designed to transmit data over a modem.
Page 21

4
4. Utility Console and Driver Installation
This chapter describes the installation of the MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK’s utilities, which are used to perform simple
configurations and driver installations.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Device Search Utility (DSU)
Installing the Device Search Utility
Device Search Utility Configuration
NPort Windows Driver Manager
Installing NPort Windows Driver Manager
Using NPort Windows Driver Manager
Command Line Installation/Removal
Linux Real TTY Drivers
Installing Linux Real TTY Driver Files
Mapping TTY Ports
Removing Mapped TTY Ports
Removing Linux Driver Files
UNIX Fixed TTY Drivers
Installing the UNIX Driver
Configuring the UNIX Driver
Page 22
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-2
Device Search Utility (DSU)
Installing the Device Search Utility
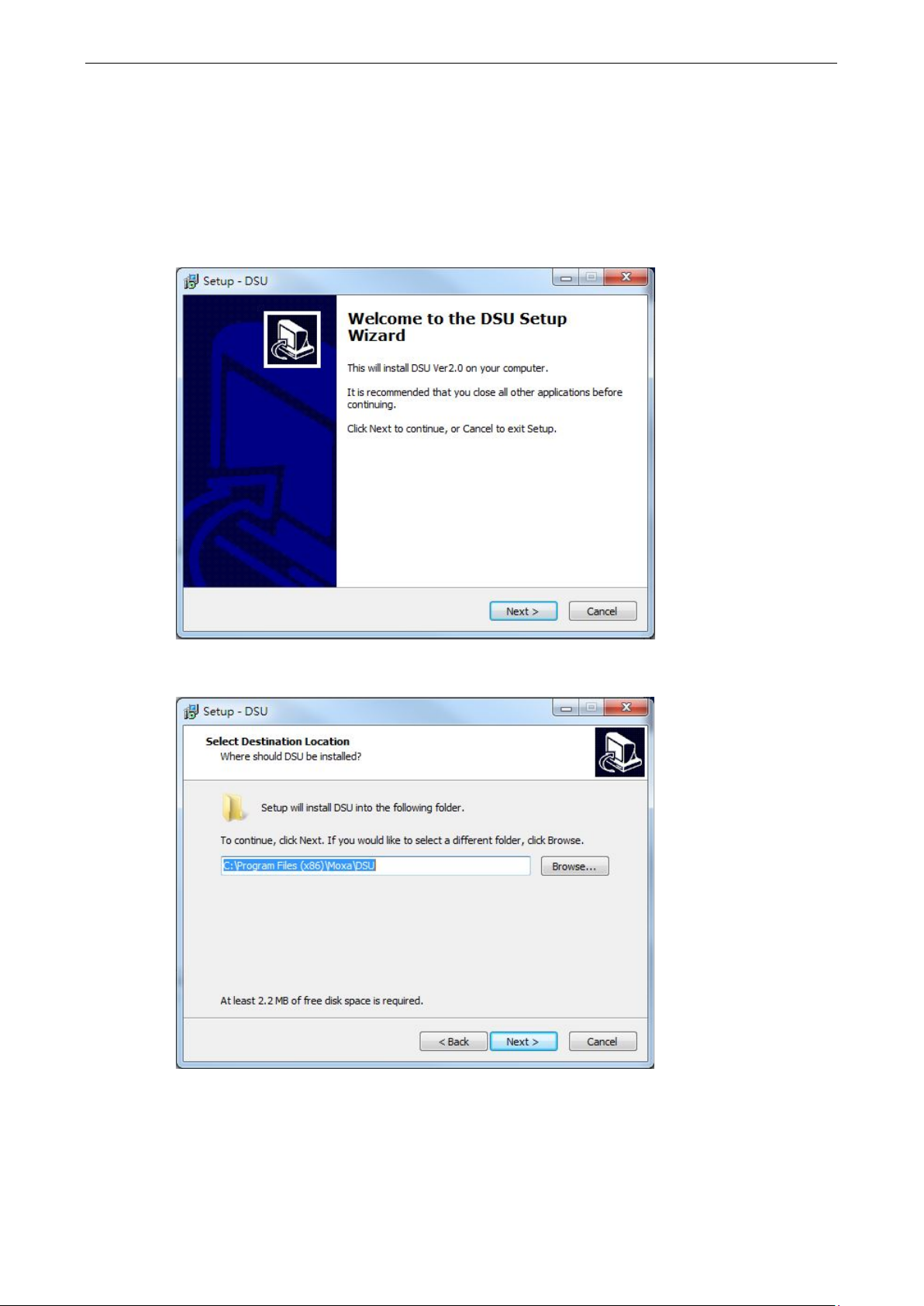
1. Click the INSTALL UTILITY button in the MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK (Installation CD) auto-run window to
install the Device Search Utility. Once the program starts running, click Yes to proceed.
2. Click Next when the Welcome screen opens to proceed with the installation.
3. Click Browse to select an alternate location and then click Next to install program files to the directory
displayed in the input box.
Page 23
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-3
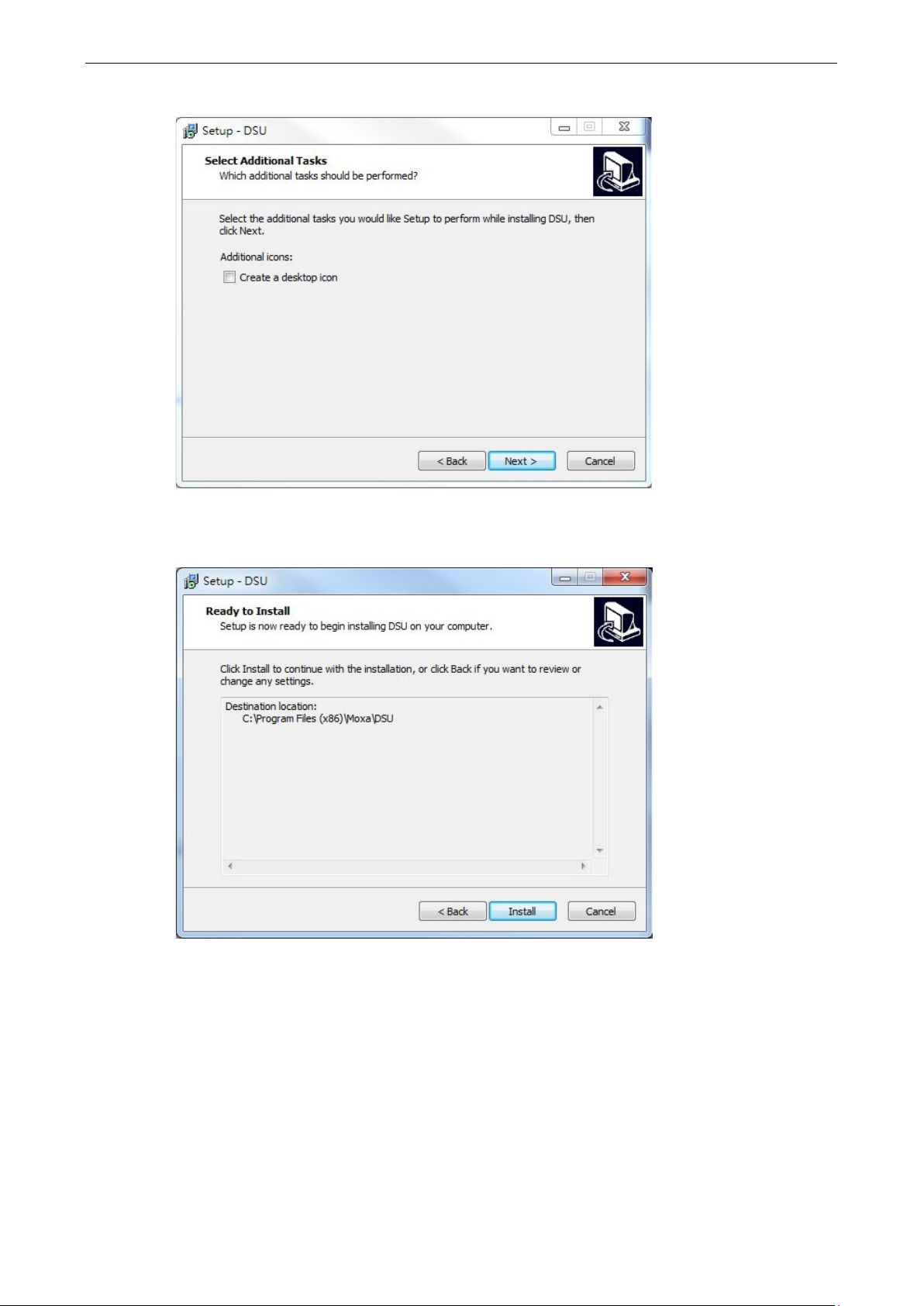
4. Select the additional tasks you would like to set up to be performed while installing DSU; then, click Next.
5. The installer will display a summary of the installation options. Click Install to begin the installation. The
setup window will report the progress of the installation. To change the installation settings, click Back and
navigate to the previous screen.
Page 24
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-4
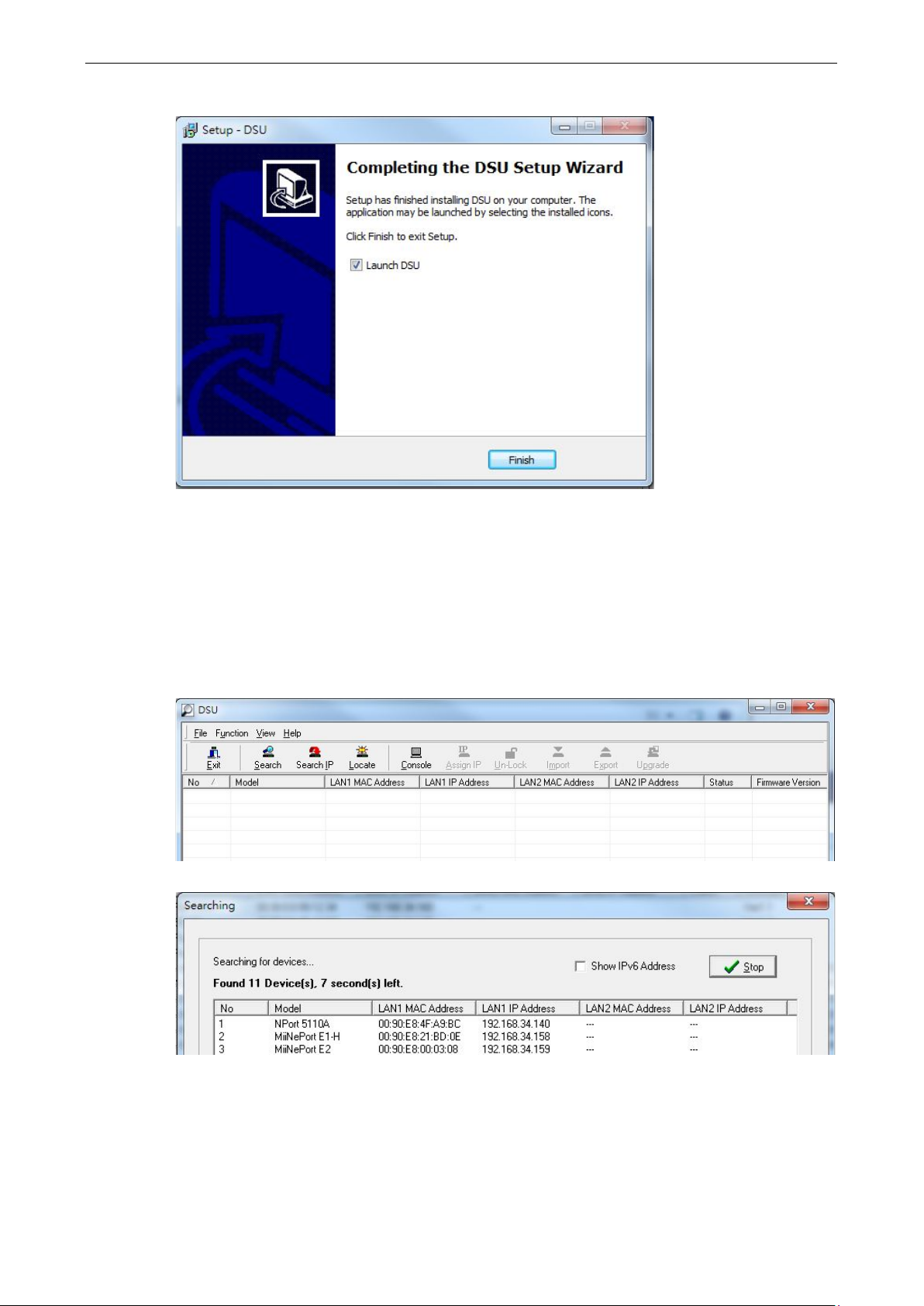
6. Click Finish to complete the installation of the Device Search Utility.
Device Search Utility Configuration
The Broadcast Search function is used to locate all MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules that are connected to the
same LAN as your computer. After locating a MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK, you will be able to change its IP address.
Since the Broadcast Search function searches by MAC address and not IP address, all MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK
modules connected to the LAN will be located, regardless of whether or not they are part of the same subnet
as the host.
1. Start the Device Search Utility and then click the Search icon.
2. The Searching window indicates the progress of the search.
Page 25

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-5
ATTENTION
The information below is only for RealCOM mode.
3. When the search is complete, all MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK modules that were located will be displayed in the
Device Search Utility window.
4. To modify the configuration of the highlighted MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK, click the Console icon to open the web
console. This will take you to the web console, where you can make configuration changes.
5. To upload your custom software, click the Upgrade icon to upload your firmware.
NPort Windows Driver Manager
Installing NPort Windows Driver Manager
The NPort Windows Driver Manager is intended for use with serial ports that are set to RealCOM mode. The
software manages the installation of drivers that allow you to map unused COM ports on your PC to your device
presented by the MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK’s serial port. These drivers are designed for use with Windows 98, ME,
NT, and Windows 7. When the drivers are installed and configured, devices that are embedded with the
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK will be treated as if they are attached to your PC’s COM ports.
1. Click the INSTALL COM Driver button in the MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Installation CD auto-run window to
install the NPort Windows Driver. Once the installation program starts running, click Yes to proceed.
2. Click Next when the Welcome screen opens to proceed with the installation.
Page 26
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-6
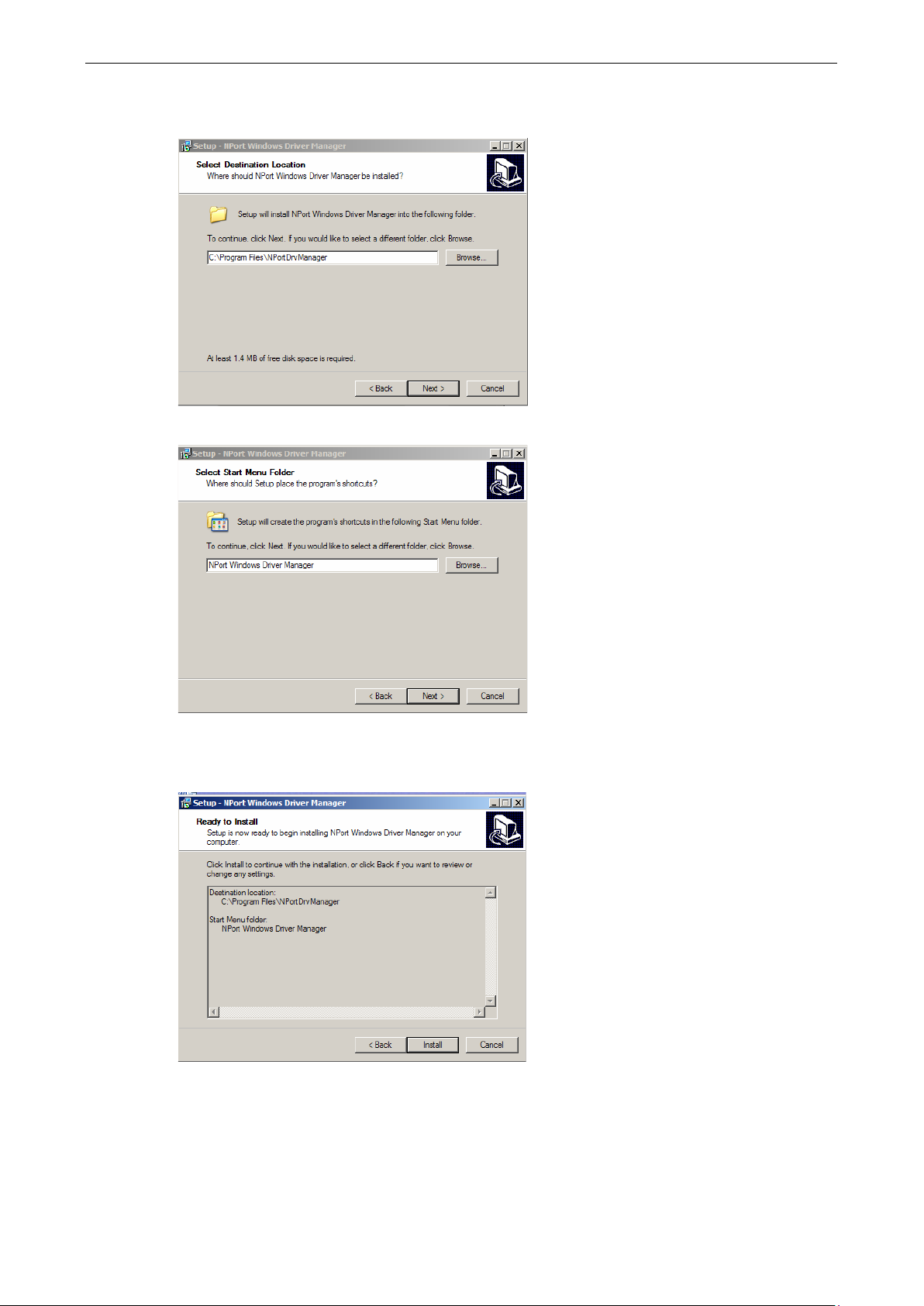
3. Click Browse to select the destination directory and then click Next to install program files to the directory
displayed in the input box.
4. Click Next to install the program’s shortcuts in the appropriate Start Menu folder.
5. The installer will display a summary of the installation options. Click Install to begin the installation. The
setup window will report the progress of the installation. To change the installation settings, click Back and
navigate to the previous screen.
Page 27

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-7
6. Click Finish to complete the installation of NPort Windows Driver Manager.
Using NPort Windows Driver Manager
After you have installed the NPort Windows Driver Manager, you can set up the MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK serial port,
which is connected to the device mainboard, as remote COM ports for your PC host. Make sure that the serial
port on your MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK is already set to RealCOM mode when mapping COM ports with the NPort
Windows Driver Manager.
1. Go to Start NPort Windows Driver Manager NPort Windows Driver Manager to start the COM
mapping utility.
2. Click the Add icon.
3. Click Search to search for the MiiNePort E1 modules. From the list that is generated, select the server to
which you will map COM ports, and then click OK.
Page 28

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-8
4. Alternatively, you can select Input Manually and then manually enter the MiiNePort E1 module’s IP
Address, 1st Data Port, 1st Command Port, and Total Ports to which COM ports will be mapped. Click
OK to proceed to the next step. Note that the NPort IP Adress column supports FQDN (Fully Qualified
Domain Name), in which case the IP address will be filled in automatically.
5. COM ports and their mappings will appear in blue until they are activated. Activating the COM ports saves
the information in the host system registry and makes the COM port available for use. The host computer
will not have the ability to use the COM port until the COM ports are activated. Click Yes to activate the COM
ports at this time, or click No to activate the COM ports later.
6. Ports that have been activated will appear in black.
Page 29

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-9
Command Line Installation/Removal
The NPort Windows Driver Manager v1.19 and above comes with command-line script tool – npcli.exe for
installation, removal of the driver, and configuring NPort driver functions.
After successfully installing the NPort Windows Driver Manager v1.19 (or above), the default file path is
C:\Program Files\NPortDrvManager as shown below. The main files that support the NPort command-line
tool are npcli.exe and GIdMap.dat. You may move these two files to your preferred location.
Once the NPort Windows Driver Manager v1.19 (or above) is installed, call up the cmd screen on your
computer. Change the directory to the drive where you placed the above two files.
Type npcli /? to get detailed information of what command lines are supported and the function descriptions.
Page 30

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-10
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
npcli /device /set 1 /network /ip 192.168.10.7 /mask 255.255.255.0
The usage instructions will show up for user’s reference.
NPort Command-Line Interface Ver2.0 Build 16052400
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Usage:
1. NPort Driver operation:
npcli /driver [/install | /uninstall | /upgrade] [PATH_NAME]
/install Install specified driver to host.
/uninstall Uninstall current installed driver from host.
/upgrade Upgrade specified driver without modifying the mapped ports.
PATH_NAME Specify the installer file of NPort Driver Manager to install
or upgrade.
2. RealCOM port operation:
npcli /driver /add IP_ADDR /port PORT_NO /com COM_NO [/txmode [hiperf |
classical]] [/fifo [enable | disable]] [/flush [fast | normal]]
npcli /driver /remove /com [COM_NO | all]
/add Add a RealCOM with a valid IP address (IP_ADDR).
/port Specify the NPort port number (PORT_NO) to add.
/com Specify the COM number to add or remove (COM_NO).
/txmode Set the TX mode as hi-performance (hiperf) or classical. The
default is hiperf.
/fifo Set the FIFO as enable or disable. The default is enable.
/flush Set to enable fast flush(fast) or disable fast flush(normal).
The default is fast.
/remove Remove specified COM number (COM_NO) or all RealCOM ports.
3. NPort devices operation:
npcli /devicd /search
npcli /device /set ID /network [/ip IP_ADDR] [/mask SUBNET]
[/gateway IP_ADDR] [/password CIPHER]
npcli /device /apply ID [/password CIPHER]
/search Search the NPort and store the list to the memory.
/set Specify the ID to set. Users must specify one of the searched
NPorts for further operations. The default is 1.
/port Specify the NPort port number (PORT_NO) to set.
/password Specify the password (CIPHER) if the NPort has one.
/network Set to change the network settings.
/ip Change the IP address (IP_ADDR) of NPort.
/mask Change the subnet mask (SUBNET) of NPort.
/gateway Change the IP address (IP_ADDR) of gateway.
/apply Specify the ID to save changes and restart the NPort.
4. Examples
npcli /driver /install D:\Users\drvmgr_setup_Ver1.19.0_Build_15122492
npcli /driver /uninstall
npcli /driver /add 192.168.127.254 /port 1 /com 3
npcli /driver /add 192.168.127.254 /port 2 /com 4 /flush normal
npcli /device /search
Page 31

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-11
/password moxa
npcli /device /apply 1
Note:
Npcli.exe requires an administrator privilege to change device settings.
It support only IPv4 and it must be run under Windows XP and later versions.
Linux Real TTY Drivers
Real TTY drivers are provided to map Linux host TTY ports to MiiNePort serial (TTL) ports. Once the mapping
has been set up, Linux users and applications can connect to a serial (TTL) port as if it were a local TTY port.
These drivers have been designed and tested for the majority of Linux distributions, including Linux kernel
version 2.4.x, 2.6.x and 3.0.x, 4.x. Please check Moxa’s website (http://www.moxa.com) for the latest
Linux kernel support. For more detail, please refer to README.TXT.
Installing Linux Real TTY Driver Files
1. Obtain the driver file from the accompanying CD-ROM or the Moxa website, at http://www.moxa.com.
2. Log in to the console as a super user (root).
3. Execute cd / to go to the root directory.
4. Copy the driver file npreal2xx.tgz to the / directory.
5. Execute tar xvfz npreal2xx.tgz to extract all files into the system.
6. Execute /tmp/moxa/mxinst.
For RedHat AS/ES/WS and Fedora Core1, append an extra argument as follows:
# /tmp/moxa/mxinst SP1
The shell script will install the driver files automatically.
7. After installing the driver, you will be able to see several files in the /usr/lib/npreal2/driver folder:
> mxaddsvr (Add Server, mapping TTY port)
> mxdelsvr (Delete Server, un-mapping TTY port)
> mxloadsvr (Reload Server)
> mxmknod (Create device node/TTY port)
> mxrmnod (Remove device node/TTY port)
> mxuninst (Remove TTY port and driver files)
At this point, you will be ready to map the MiiNePort E1 serial port to the system TTY port.
Mapping TTY Ports
Make sure that you set the operation mode of the serial port of the MiiNePort E1 to RealCOM mode. After
logging in as a super user, enter the directory /usr/lib/npreal2/driver and then execute mxaddsvr to map
the target MiiNePort E1 serial port to the host TTY ports. The syntax of mxaddsvr is as follows:
mxaddsvr [MiiNePort E1 IP Address] [Total Ports] ([Data port] [Cmd port])
The mxaddsvr command performs the following actions:
1. Modifies npreal2d.cf.
2. Creates TTY ports in directory /dev with major and minor number configured in npreal2d.cf.
3. Restarts the driver.
Page 32

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-12
Mapping TTY ports automatically
To map TTY ports automatically, you may execute mxaddsvr with just the IP address and number of ports, as
in the following example:
# cd /usr/lib/npreal2/driver
# ./mxaddsvr 192.168.3.4 16
In this example, 16 TTY ports will be added, all with IP 192.168.3.4, with data ports from 950 to 965 and
command ports from 966 to 981.
Mapping TTY ports manually
To map TTY ports manually, you may execute mxaddsvr and manually specify the data and command ports,
as in the following example:
# cd /usr/lib/npreal2/driver
# ./mxaddsvr 192.168.3.4 16 4001 966
In this example, 16 TTY ports will be added, all with IP 192.168.3.4, with data ports from 4001 to 4016 and
command ports from 966 to 981.
Removing Mapped TTY Ports
After logging in as root, enter the directory /usr/lib/npreal2/driver and then execute mxdelsvr to delete
a server. The syntax of mxdelsvr is:
mxdelsvr [IP Address]
Example:
# cd /usr/lib/npreal2/driver
# ./mxdelsvr 192.168.3.4
The following actions are performed when executing mxdelsvr:
1. Modifies npreal2d.cf.
2. Removes the relevant TTY ports in directory /dev.
3. Restart the driver.
If the IP address is not provided in the command line, the program will list the installed servers and total ports
on the screen. You will need to choose a server from the list for deletion.
Removing Linux Driver Files
A utility is included that will remove all driver files, mapped TTY ports, and unload the driver. To do this, you
only need to enter the directory /usr/lib/npreal2/driver, and then execute mxuninst to uninstall the driver.
This program will perform the following actions:
1. Unload the driver.
2. Delete all files and directories in /usr/lib/npreal2.
3. Delete directory /usr/lib/npreal2.
4. Modify the system initializing script file.
UNIX Fixed TTY Drivers
A fixed TTY driver is provided that will map UNIX host TTY ports to the MiiNePort. Once the mapping has been
set up, UNIX users and applications can connect to a device port as if it were a local TTY port. This driver has
been designed and tested for the majority of UNIX systems. Please check Moxa’s website
(http://www.moxa.com) for the latest UNIX systems support. For more detail, please refer to README.TXT.
Page 33

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-13
Installing the UNIX Driver
Log in to UNIX and create a directory for the Moxa TTY. To create a directory named /usr/etc, execute the
command:
# mkdir –p /usr/etc
Copy moxattyd.tar to the directory you created. For the /usr/etc directory, execute the following
commands:
# cp moxattyd.tar /usr/etc
# cd /usr/etc
Extract the source files from the tar file by executing the command:
# tar xvf moxattyd.tar
The following files will be extracted:
README.TXT
moxattyd.c --- source code
moxattyd.cf --- an empty configuration file
Makefile --- makefile
VERSION.TXT --- fixed TTY driver version
FAQ.TXT
Compile and link.
For SCO UNIX:
# make sco
For UnixWare 7:
# make svr5
For UnixWare 2.1.x, SVR4.2:
# make svr42
Configuring the UNIX Driver
Modify the configuration:
The configuration used by moxattyd is defined in the text file moxattyd.cf, which is in the same directory.
You may use vi or any text editor to modify the file, as follows:
ttyp1 192.168.1.1 950
You can refer to moxattyd.cf for detailed descriptions of the various configuration parameters. Please note
that “Device Name” depends on the OS. See the Device Naming Rule section in README.TXT for more
information.
To start the moxattyd daemon after system boot-up, add an entry into /etc/inittab using the TTY name you
defined in moxattyd.cf, as in the following example:
ts:2:respawn:/usr/etc/moxattyd/moxattyd –t 1
Device naming rule
For UnixWare 7, UnixWare 2.1.x, and SVR4.2, use:
pts/[n]
For all other UNIX operating systems, use:
ttyp[n]
The value of [n] should be equal or larger than 11 in order to prevent conflicts with the device names of
functional keys in some UNIX systems.
Starting moxattyd
Execute the command init q or reboot your UNIX operating system.
Page 34

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Utility Console and Driver Installation
4-14
Adding an additional server
Modify the text file moxattyd.cf to add an additional server. User may use vi or any text editor to modify the
file. For more configuration information, refer to moxattyd.cf, which contains detailed descriptions of the
various configuration parameters.
Find the process ID (PID) of the moxattyd.
# ps -ef | grep moxattyd
Update the configuration of moxattyd.
# kill -USR1 [PID]
(e.g., if moxattyd PID = 404, kill -USR1 404)
This completes the process of adding an additional server.
Page 35

5
5. MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Installing MiiNePort IDE
Starting MiiNePort IDE
Create MiiNePort-SDK Project
RealCOM Mode
Ethernet Modem Mode
Sample Application
Data Packing
Serial Command Mode
Web Console
CLI
SNMP agent
TFTP Server
NTP Client
CPU Monitor
Wizards
Modify project dependency
CLI Wizard
Configuration Wizard
SCM Wizard
SNMP Wizard
User App Wizard
Build project
Upload debug version firmware to MiiNePort
Debug current active project
Upload your customized firmware to MiiNePort
Page 36

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-2
Installing MiiNePort IDE
Eclipse is an open source community, whose projects are focused on building an open development platform
comprised of extensible frameworks, tools and runtimes for building, deploying, and managing software across
the lifecycle. MOXA provides an Eclipse-based integrated software development tool and a step-by-step
source-level debugger, which is called MiiNePort IDE. The following instructions explain how to install Eclipse.
1. Insert the Document and software CD into the CD-ROM drive. Locate and run the following setup program
to begin the installation process:
MiiNePort-SDK_Setup_[Version]_build_[DateTime].exe
2. You will be greeted by the Welcome window. Click Next to continue.
3. Next page is license agreement. Select I accept the agreement, then click Next.
Page 37
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-3
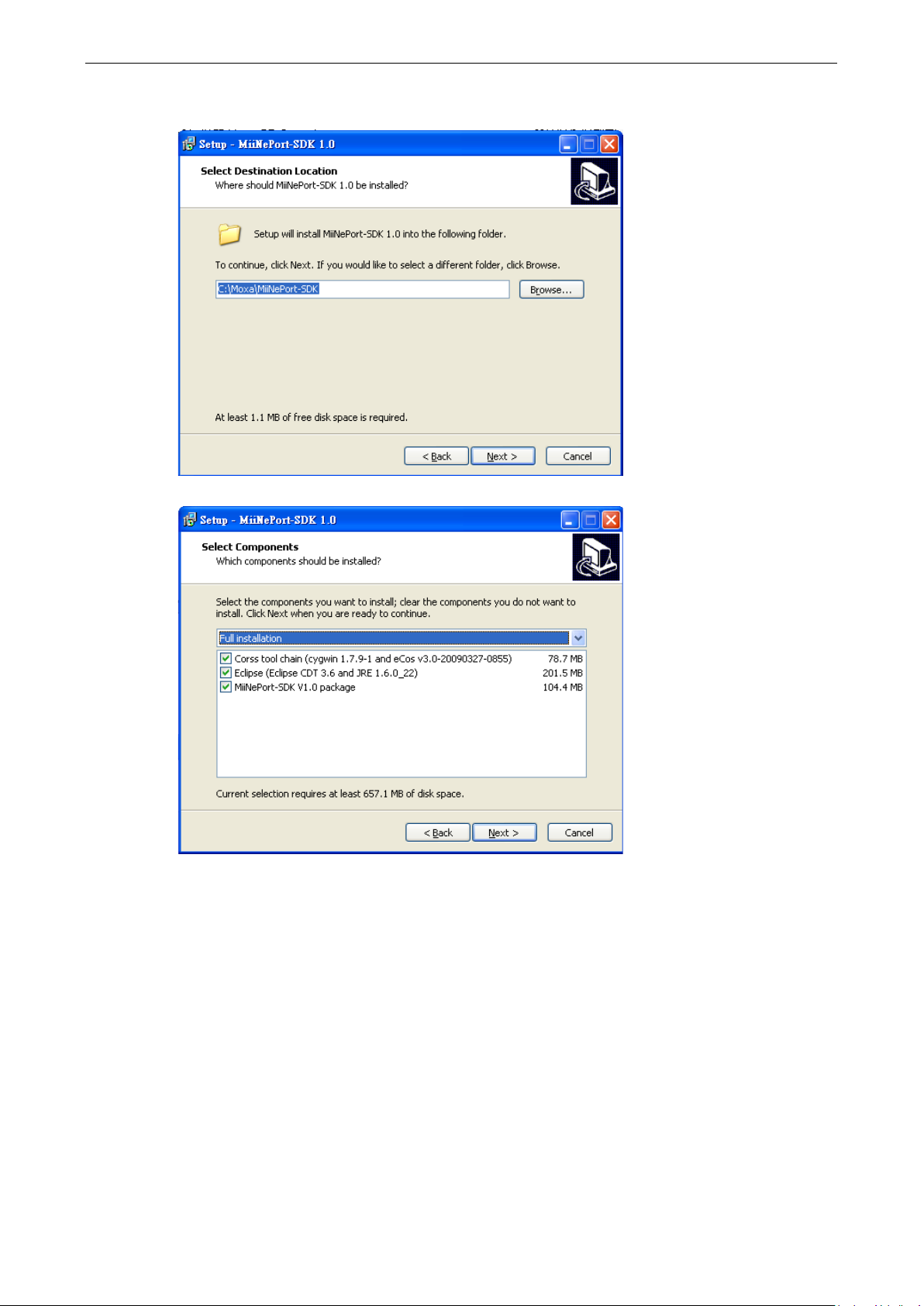
4. When the Select Destination Location window appears, click Next to continue. You may change the
destination directory by first clicking on Browse....
5. In this page, you can select what components you would like to install, then click Next.
Page 38

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-4
6. Then creating the program’s shortcuts. When the Select Destination Location window appears, click Next
to continue. You may change the destination directory by first clicking on Browse....
7. Click Next to start copying the software files.
Page 39
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-5
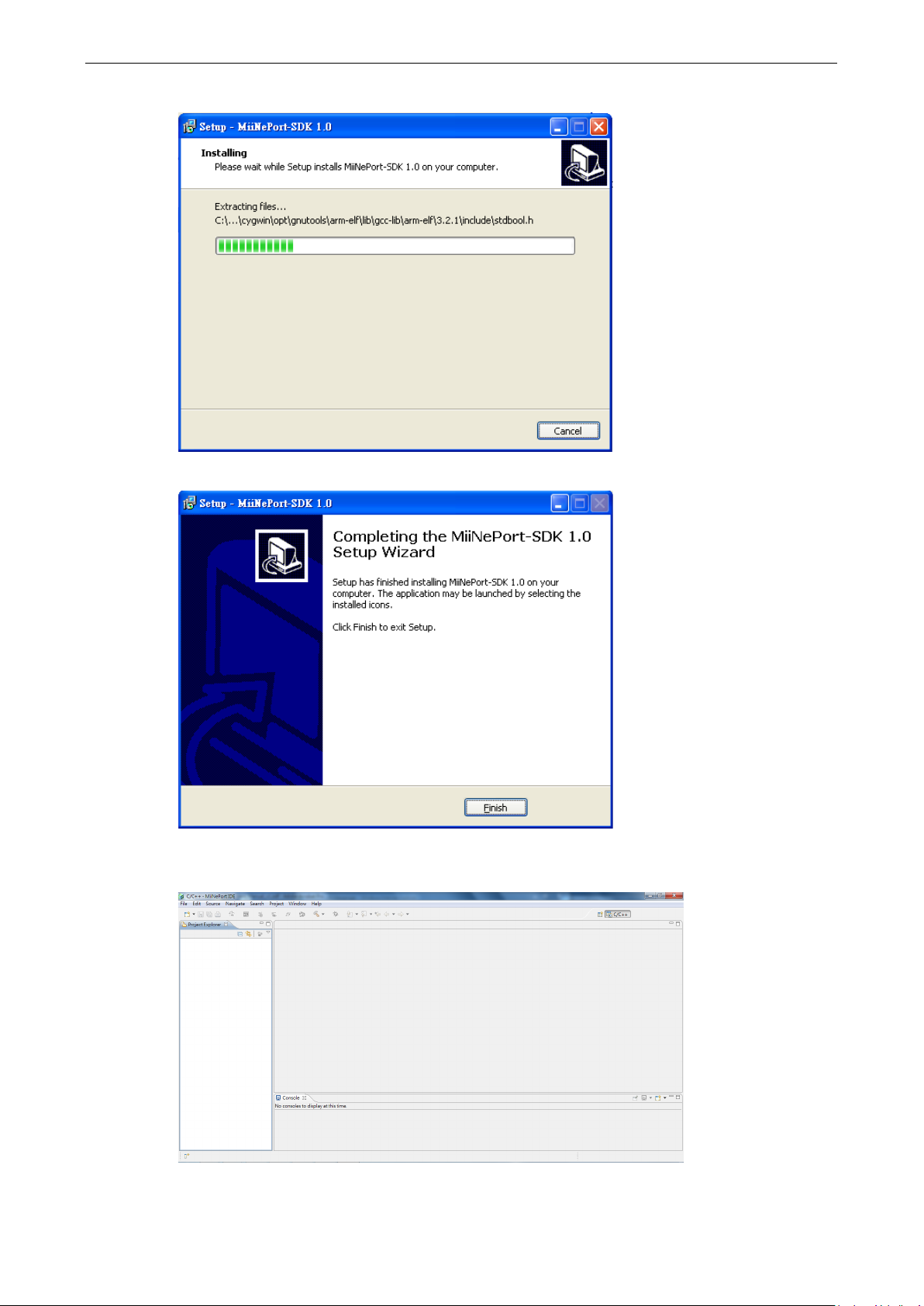
8. A progress bar will appear. The procedure should take only a few seconds to complete.
9. A message will indicate that MiiNePort IDE is successfully installed.
10. You may also open MiiNePort IDE through Start Programs MOXA MiiNePort-SDK
MiiNePort-IDE, as shown below.
Page 40

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-6
Starting MiiNePort IDE
MiiNePort IDE is an Eclipse-based integrated software development tool and a step-by-step source-level
debugger that is used to configure the MiiNePort-SDK.
Before running MiiNePort IDE, make sure that the MiiNePort-SDK device is connected to your PC. Please refer
to Chapter 2 for more details.
You may open MiiNePort IDE from the Windows Start menu by clicking Start Programs MOXA
MiiNePort-SDK
MiiNePort-IDE. The MiiNePort IDE window should appear as shown below.
Create MiiNePort-SDK Project
Prior to firmware development, the MiiNEPort-SDK device must be connected to the unit. For developing
customized firmware, MOXA provides a powerful tool called EZStack. You can compose the desired functions
step by step. The following section will show you how to build a customized firmware. First, create a new
project by clicking File -> New -> MiiNePort-SDK Project.
The project wizard will then begin, as shown in the figure below. Just fill your desired value into each field and
click Next to continue. The description of each parameter is shown in the table below.
Page 41
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-7
2. MiiNePort E2
the 3 configurable pins (Pin 6, 7, and 8), refer to Chapter 1: Pin Assignments for
Parameter Description
Project name The project name
Location The location path of project
Platform The development platform
1. MiiNePort E1
Kernel Version SDK version
For MiiNePort E1-SDK
Parameter Description
DIO For
their default settings and change to the appropriate function for your application.
Restart The restart function is enabled by default and is not subject to be disabled. You can
choose to enable or disable the Restart function in the Pin and IO Settings.
EXTrigger is designed to provide an easy tool for network troubleshooting without interrupting device
operation.
For MiiNePort E2-SDK
Parameter Description
DIO Mode
Select Input or Output under Mode to specify digital input or digital output operation.
State
Select Low or High under State to specify a high or low state for digital output
channels. Note that when Mode is set to Input (as shown in the above screenshot),
the State option is deactivated.
Page 42

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-8
ATTENTION
To use
driver
on Windows or Linux.
The next page is regarding serial to Ethernet application, data packing and serial command mode.
RealCOM Mode
RealCOM mode, refer to Chapter 6: Utility Console and Driver Installation to install the RealCOM
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 99 min 7 min Optional
0 min: The TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: The module automatically closes the TCP connection if there is no TCP activity for the given time.
After the connection is closed, the module starts listening for another host’s TCP connection.
Max connection
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
1, 2, 3, 4 1 Required
Page 43

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-9
ATTENTION
When Max connection is greater than
, the MiiNePort E1 module will use a multiple connection application
(i.e.,
application, the module will use the serial communication parameters as defined here in the web console, and
all hosts connected to the port must use identical serial settings. If one of the hosts opens the COM port with
different serial settings
Enable, Disable
Disable
Required when Max connection greater than1
NOTE
Ignore Jammed IP is only valid when the Max connection is greater than
NOTE
Allow drive control is only valid when Max connection is greater than 1.
Max connection is used when the device needs to receive data from different hosts simultaneously.
The factory default only allows 1 connection at a time. When Max Connection is set to 1, the RealCOM driver on
the specific host has full control.
Max connection 1: The module will only allow one host’s RealCOM driver to open a connection to the module’s
serial port.
Max connection 2 to 4: When set to two or higher, RealCOM drivers for up to the specified number of hosts
may open this port at the same time. When RealCOM drivers for multiple hosts open the port at the same time,
the
COM driver only provides a pure data tunnel with no control ability. The serial port parameters will use firmware
settings instead of your application program (AP) settings.
Application software that is based on the COM driver will receive a driver response of “success” when the
software uses any of the Win32 API functions. The firmware will only send data back to the driver on the host.
Data will be sent first-in, first-out when data is received by the MiiNePort E1 from the Ethernet interface.
two to four hosts are allowed access to the port at the same time). When using a multi-connection
, data will not be transmitted properly.
Ignore jammed IP
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
This option determines how the port will proceed if multiple hosts are connected and one or more of the hosts
stops responding as the port is transmitting data. If you select Disable, the port will wait until the data has been
transmitted successfully to all hosts before transmitting the next group of data. If you select Enable, the port
will ignore the host that stopped responding and continue data transmission to the other hosts.
Allow driver control
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
Enable, Disable Disable Required when Max connection greater than1
one
1.
This option determines how the port will proceed if driver control commands are received from multiple hosts
that are connected to the port. If Disable is selected, driver control commands will be ignored. If Enable is
selected, control commands will be accepted, with the most recent command received taking precedence.
Ethernet Modem Mode
Page 44
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-10
TCP alive check time
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 99 min 7 min Optional
0 min: The TCP connection is not closed due to an idle TCP connection.
1 to 99 min: The module automatically closes the TCP connection if there is no TCP activity for the given time.
After the connection is closed, the module starts listening for another host’s TCP connection.
TCP Port
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
1 to 65535 4001 Required
Use this field to indicate the TCP port that the module will use to listen to connections, and that other devices
must use to contact the module. To avoid conflicts with well-known TCP ports, the default is set to 4001
Sample Application
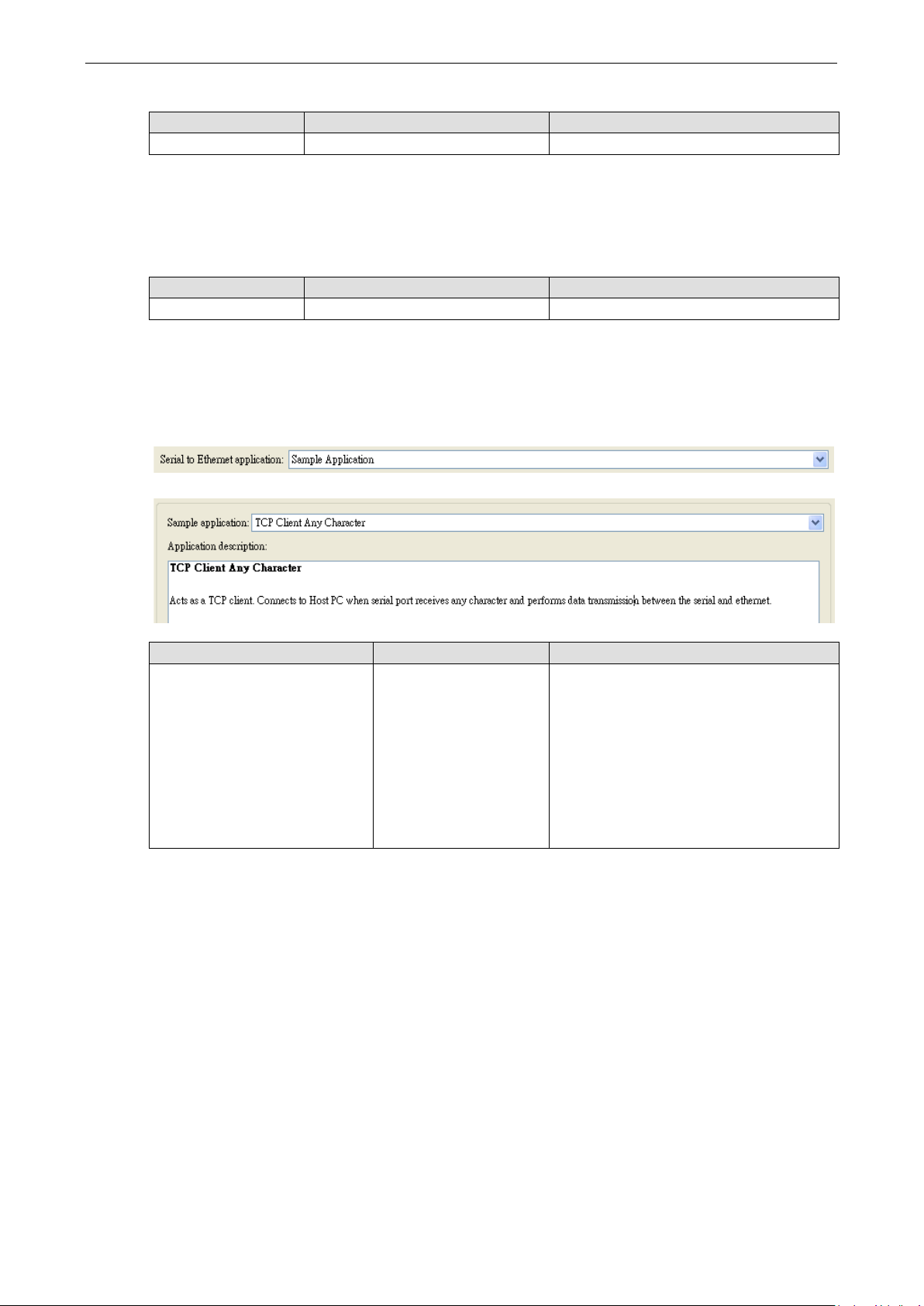
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
TCP Client Any Character
TCP Client Ask Destination
TCP Client Echo
TCP Client Startup
TCP Server Echo
TCP Server Multiple Connections
TCP Server Single Connection
UDP Echo
UDP Mode
TCP Client Any Character: Acts as a TCP client. Connects to Host PC when serial port receives a character and
performs serial-to-Ethernet data transmissions.
TCP Client Ask Destination: Acts as a TCP client. Connects to Host PC after destination IP is got via serial port
and then performs data transmission between the serial and Ethernet.
TCP Client Echo: Acts as a TCP client. Connects to Host PC and echoes all the received data to server.
TCP Client Startup: Acts as a TCP client. Connects to Host PC on startup and performs data transmission
between the serial and Ethernet.
TCP Server Echo: Acts as a TCP server. Accepts connection and echoes all the received data to client.
TCP Client Any Character Optional
TCP Server Multiple Connections: Acts as a TCP server. Accepts multiple connections and performs data
transmission between the serial and Ethernet.
TCP Server Single Connection: Acts as a TCP server. Accepts single connection and performs data
transmission between the serial and Ethernet.
UDP Echo: Creates a UDP socket and echoes the data received from the Ethernet port.
UDP Mode: Creates a UDP socket and performs data transmission between the serial port and Ethernet port.
Page 45

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-11
Data Packing
Packet length
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 1024 bytes 0 byte Required
The Packet length setting refers to the maximum amount of data that is allowed to accumulate in the serial port
buffer before sending. At the default of 0 for packet length, no maximum amount is specified and data in the
buffer will be sent as specified by the delimiter settings or when the buffer is full. When a packet length between
1 and 1024 bytes is specified, data in the buffer will be sent as soon as it reaches the specified length.
Delimiter 1
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
00 to FF “0” for None Optional
Delimiter 2
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
00 to FF “0” for None Optional
The delimiter fields are used to specify a character or two-character sequence which will act as a marker to
control packing of serial data. By default, no delimiter characters are defined, so the module transmits data as
soon as it is received. When a delimiter character or characters are defined, the module will hold data in its
buffer until it receives the delimiter character or two-character sequence. When the delimiter is received, the
module will pack up the data in its buffer and send it through the Ethernet port.
Use Delimiter 1 to define the first delimiter character in hex. If only one delimiter character will be used,
Delimiter 2 should be set to “0”. If the delimiter will be a two-character sequence, use Delimiter 2 to define the
second character. To disable the use of delimiters, set both Delimiter 1 and Delimiter 2 to “0”.
Note that data packing is not only controlled by the delimiter; it is also influenced by the module’s buffer size
and the Force transmit field. If the delimiter has not been received by the time the 1K buffer is full, the module
will pack the data for network transmission and clear the buffer. Also, if the module will also pack data for
network transmission if the next byte of data is not received within the Force transmit time.
Match bytes
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
1 byte to 2 bytes 2 bytes (only effective when Delimiter is enabled) Optional
1 byte: MiiNePort E1 packs the serial data and sends out TCP/IP packets once it receives either one of Delimiter
1 and Delimiter 2.
2 bytes: MiiNePort E1 only packs the serial data and sends out TCP/IP packets once it receives both of
Delimiter 1 and Delimiter 2. And the receiving order should be first Delimiter 1 then Delimiter 2.
Delimiter process
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
Do Nothing,
Delimiter+1,
Delimiter+2
Do Nothing (only effective when Delimiter is enabled) Optional
Page 46

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-12
The delimiter process field determines how the data is handled when a delimiter is received. Delimiter 1 must
be enabled for this field to have effect. If Delimiters 1 and 2 are both enabled, both characters must be received
for the delimiter process to take place.
Do Nothing: Data in the buffer will be transmitted when the delimiter is received.
Delimiter + 1: Data in the buffer will be transmitted after one additional byte is received following the
delimiter.
Delimiter + 2: Data in the buffer will be transmitted after two additional bytes are received following the
delimiter.
Force transmit
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 65535 ms 0 ms Optional
0: The force transmit timeout is disabled.
1 to 65535: If the module does not receive the next byte of data within the time specified, it will pack the data
in its buffer into the same data frame for network transmission.
The Force transmit field is typically used in conjunction with the delimiter fields to specify how data in the
module’s buffer is packed for network transmission. When delimiters are used, the module accumulates data in
its buffer as it waits to receive a delimiter. If there is a break in communication, data will be held in the buffer
as the module continues to wait for a delimiter. The Force transmit field allows you to specify the maximum
amount of time that the module will wait for data. With Force transmit enabled, the module will automatically
pack the data in the buffer for network transmission if no data is received for the specified time.
When set to 0, Force transmit is disabled, which means there is no time limit for how long the module will wait
to receive data. When set between 1 and 65535, the module will pack data as soon as there is no serial
communication for the specified time.
The optimal force transmit time depends on your application, but it should be larger than one character interval
within the specified baud rate to have any effect. For example, assume that the serial port is set to 1200 bps,
8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity. In this case, the total number of bits needed to send one character is 10
bits, and the time required to transfer one character is
(10 bits / 1200 bits/s) × 1000 ms/s = 8.3 ms.
Since it requires about 9 ms to send one character, the Force transmit should be 10 ms or more to have any
effect. At 9 ms or less, the module will simply pack every character as it is received, which would be the same
as if no delimiter characters or Force transmit time were specified at all.
Page 47

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-13
Serial Command Mode
SCM (Serial Command Mode) uses serial communication between the MiiNePort E1 and your device’s main
system to configure the MiiNePort E1, usually during device operation. For more details about SCM commands,
refer to Chapter 7: NetEZ Technologies.
Port number
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
Port 1 Port 1 Optional
SCM trigger mode
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
HW trigger
SW trigger
Bootup SW trigger
Break trigger
HW trigger: Entering the SCM mode by HW DIO and DIO trigger mode.
SW trigger: Entering the SCM mode by the continuous three characters. The default value is 0x58, 0x58, 0x58
Bootup SW trigger: Entering the SCM mode by the continuous three characters during the timeout period.
The default value is 0x58, 0x58, 0x58
Break trigger: Break signals are caused by sending continuous Spacing values (no Start or Stop bits). When
there is no electricity present on the data circuit, the line is considered to be sending a Break. The Break signal
must be of duration longer than the time it takes to send a complete byte plus Start, Stop, and Parity bits.
SW trigger Optional
Page 48

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-14
ATTENTION
In Dynamic IP environments, the module will attempt to obtain an IP address from the DHCP or BOOTP server
three
seconds, and the last try will be 5 seconds.
If the DHCP/BOOTP Server is unavailable, the module will use the default IP address (192.168.127.254),
net
The Next page is network settings, you can assign IP configuration in this page.
Device name
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
1 to 40 characters [model name]_[Serial No.] Optional
This option can be used to specify the location or application of the module, which may be useful when
managing more than one module on the network.
IP configuration
Method Function Definition
Static User defined IP address, Netmask, Gateway.
DHCP DHCP Server assigned IP address, Netmask, Gateway, DNS
BOOTP BOOTP Server assigned IP address
IP configuration is a required field. The default setting is Static.
times at 30-second intervals. The timeout for the first try will be 1 second, the second try will be 3
mask, and gateway settings.
IP Address
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
E.g., 192.168.1.1
(IP addresses of the
form x.x.x.0 and
x.x.x.255 are invalid.)
An IP address is a number assigned to a network device, such as a computer, as a permanent address on the
network. Computers use the IP address to identify and talk to each other over the network. Choose a proper IP
address that is unique and valid in your network environment.
192.168.127.254 Required
Page 49

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-15
x.x.x.255 are invalid)
Netmask
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
E.g., 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 Required
A subnet mask represents all the network hosts at one geographic location, in one building, or on the same
local area network. When a packet is sent out over the network, the module will use the subnet mask to check
whether the host specified in the packet is on a local network segment. If the address is on the same network
segment as the module, a connection is established directly from the module. Otherwise, the connection is
established through the default gateway.
Gateway
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
E.g., 192.168.1.1 None Optional
A gateway acts as an entrance to another network. Usually, the computers that control traffic within the
network or at the local Internet service provider are gateway nodes. The module needs to know the IP address
of the default gateway computer in order to communicate with the hosts outside the local network environment.
For correct gateway IP address information, consult your network administrator.
DNS server 1 / DNS server 2
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
E.g., 192.168.1.1
(IP addresses of the
form x.x.x.0 and
None Optional
Domain Name System (DNS) is how Internet domain names are identified and translated into IP addresses. A
domain name is an alphanumeric name, such as moxa.com, that it is usually easier to remember. A DNS server
is a host that translates the text-based domain name into the corresponding numeric IP address which is used
to establish a TCP/IP connection. When the user enters a website address, the computer asks a DNS server for
the website’s IP address to connect to the web server.
When a DNS server is specified, the module acts as DNS client and will allow domain names instead of IP
addresses to be used on the web console. The following web console fields support the use of domain names:
TCP Client-Destination IP Address, and IP Address Report Server. Two DNS servers may be specified, DNS
server 1 and DNS server 2. DNS server 2 is included for use when DNS server 1 is unavailable.
The Next page is about serial parameters settings, all serial parameters settings can be adjusted in this page.
Page 50

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-16
50 bps to 921.6 Kbps
ATTENTION
Baudrate 460800 and 921600 are for High speed model only. If you don’t want to use High speed mode, please
remove jumper first.
DTR/DSR, XON/XOFF
Baudrate
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
115200 Required
IP configuration is a required field. The default setting is Static.
Data Bits
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
5, 6, 7, 8 8 Required
Stop Bits
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
1, 1.5, 2 1 Required
Stop Bits will be set to 1.5 when Data Bits is set to 5 bits.
Parity
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
None, Even, Odd,
Space, Mark
Flow control
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
None, RTS/CTS,
FIFO
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
Enable, Disable Enable Required
None Required
RTS/CTS Required
Each module’s serial port provides a 16-byte FIFO both in the Tx and Rx directions. Disable the FIFO setting
when your serial device does not have a FIFO to prevent data loss during communication.
Page 51

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-17
MOXA provides a lot of applications to customers; as long as you check the checkbox, the desired application
will be applied into your customized firmware.
Web Console
The Web Console is the most user-friendly way to configure the MiiNePort device. We use the Web Console
interface to introduce the functions. There are only a few differences between the Web Console and Serial
Console.
HTTP port
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0~65535 80 Required
Connections
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
>0 5 Required
Session timeout
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0~6553 300 Required
Keep-Alive timeout
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0~65535 25 Required
Page 52

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-18
CLI
For telnet/serial console access, MiiNePort device provides Command-Line Interface (CLI) to do some
configuration or monitor work of the device, such as network configuration, serial parameter configuration, etc.
The programmer can build user-defined CLI by using system CLI APIs, and a function is provided to add the
user-defined CLI to the command list. The project sample code provides a set of default CLI commands is for
user to reference when developing new CLI or for modification to suit for the user application.
Telnet port
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0~65535 23 Required
SNMP agent
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an Internet standard for managing devices on IP networks.
The SNMP consists of two kinds of devices, the managed device that is known as SNMP agent and the SNMP
manager that controls the SNMP agent. MiiNePort will be the SNMP agent, which supports the SNMP V1
(Version 1) and V2 (Version 2).
SNMP version
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
V1, V2 V1, V2 Required
Read community
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters public Optional
A read community name is a plain-text password mechanism that is used to authenticate queries to agents of
managed network devices.
Write community
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters private Optional
Page 53

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-19
ATTENTION
For MIB wizard, it works after you create project. Please refer to the ‘Wizards’ section for more
A write community name is a plain-text password mechanism that is used to authenticate queries to agents of
managed network devices.
Description
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters None Optional
Contact
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters None Optional
The SNMP contact information usually includes an emergency contact name and telephone or pager number.
Name
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters None Optional
Location
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters None Optional
Enter a location string for SNMP agents. This string is usually set to the street address where the module is
physically located.
Service
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
>=0 0 Optional
OID
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 256 characters None Optional
TFTP Server
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a file transfer protocol known for its simplicity. It is generally used for
automated transfer of configuration or boot files between machines in a local environment.
NTP Client
NTP (Network Time Protocol) is a protocol for synchronizing the clocks of computer systems over
packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. It is designed particularly to resist the effects of variable
latency by using a jitter buffer. NTP uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port number 123. Please refer
official web site for more information
details.
Page 54

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-20
Time server IP/name 1/2:
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
0 to 40 characters None Required
Time offset:
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
-720~720 min 0 Optional
Time server query period:
Setting Factory Default Recommended Setting
>30 600 Optional
CPU Monitor
Enable this function to monitor status of the CPU.
The next page will display the result you select. Then click Next to create this project.
Finally the project will be created on project explorer list. Then you can modify or add source code to develop
your firmware.
Page 55
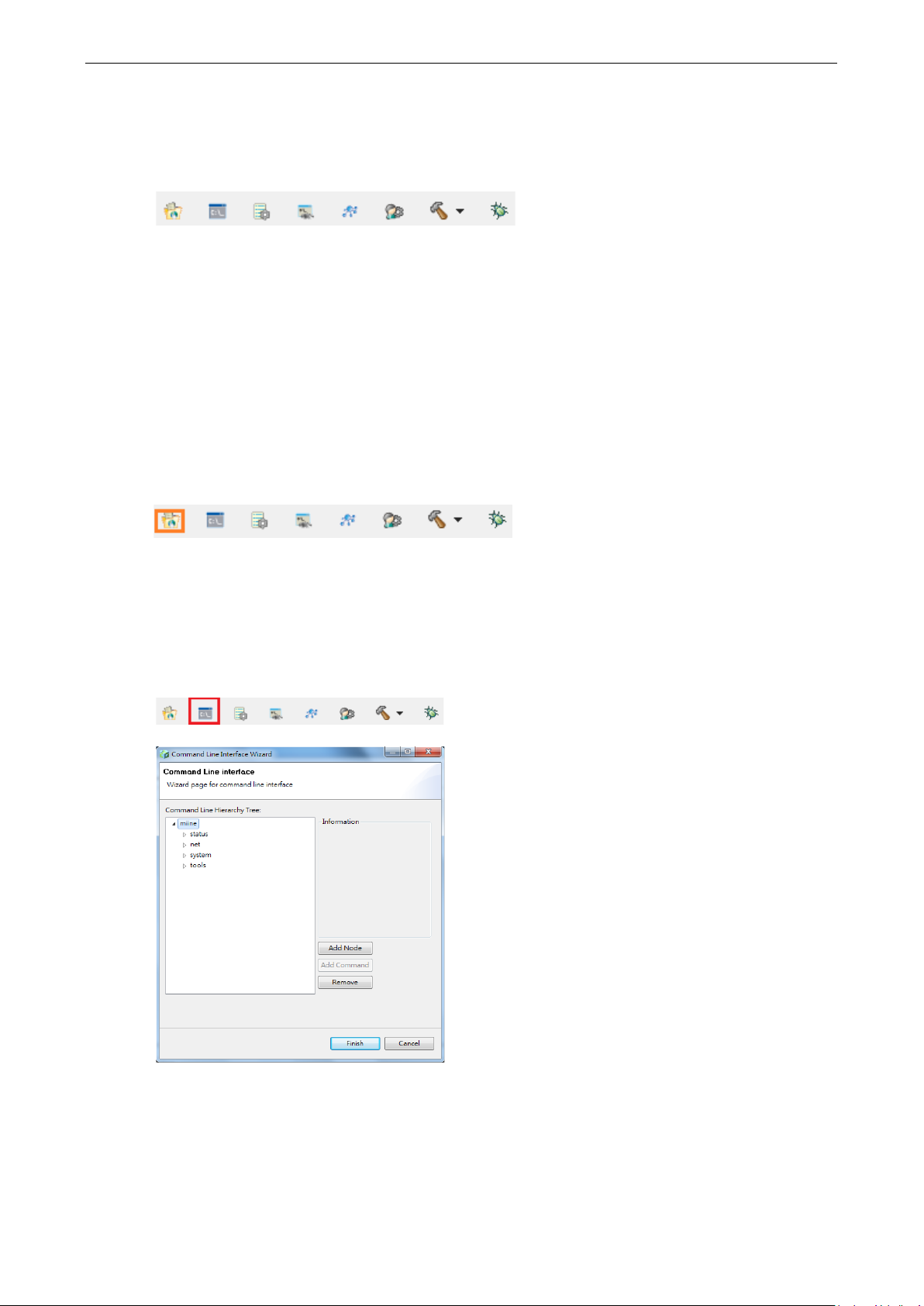
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-21
Wizards
Moxa provides wizards to help you modify source codes. Then MiiNePort IDE can create the functions
automatically. Below is the list of wizards (You can find it on the tool bar):
From the left to right, they are:
• CLI Wizard: Help to add CLI commands
• Configuration Wizard: Help to make configuration variables
• SCM Wizard: Help to add SCM command
• SNMP MIB Wizard Action: Help to add SNMP MIB
• User App Wizard: Help to create user application (subroutine)
• Project Wizard: Help to change function and property of project
• MiiNePort-SDK debug: Debug MiiNePort project
• Build: Release build and debug build (download firmware)
Modify project dependency
The function is used to modify the settings of MiiNePort project. The section “Create MiiNePort-SDK Project”
includes the description of all settings. Please refer the before section.
The following section will introduce more details about each wizard.
CLI Wizard
This wizard is used to add CLI command. The command-line interface is a tree structure, and each leaf is a
command. You can do some configuration or monitor work of the device by these commands you define.
Page 56

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-22
Select the location you want to add command.
First, click Add Node to add a node.
A window will pop up, you can edit node name and node brief. And then click the Confirm button.
Page 57

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-23
Then click Add Command to add a new command.
Then window will show up and you have to enter Command Name, Function, and Node Brief. After you have
filled in, click Confirm.
Then the new command is created. You can modify and remove it. When you finish setting CLI, click the Finish
button.
Then you can develop the behavior of this “moxa_command” in the moxa_function() in this example.
Page 58

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-24
Configuration Wizard
This wizard is used to help to make configuration variables. You can define the attribute you need in this page.
By this way, you can build up your own configuration.
First, click the Add button.
Page 59
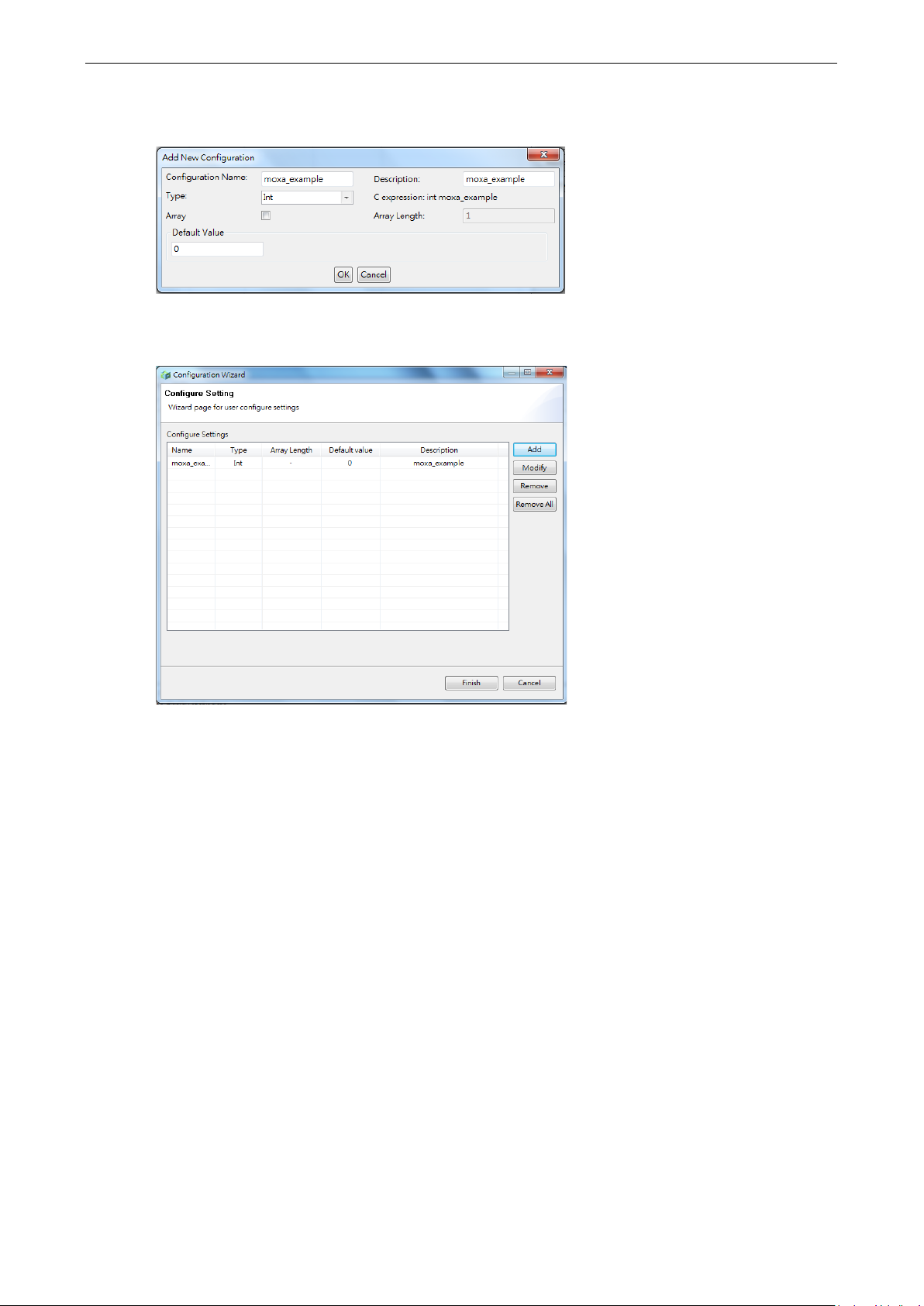
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-25
Then the configuration window will pop up and you can fill in the value into each filed. After determining the
new attribute, please click Confirm.
Then your attribute will be showed on the configuration settings list. Besides, you can modify or remove them
easily. After you have completed all desired attributes, click Finish
Page 60

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-26
Finally, your configuration will be saved into config_init.c. The picture below is the configuration settings we set
before.
SCM Wizard
This wizard is used to help add SCM commands. You can add the serial command you need in this page. With
these serial commands, you can configure your device to help add SCM commands.
Page 61

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-27
Click Add button to add a new serial command. Regarding the format of serial command, please refer to
appendix A
Then a serial command mode window will pop up. Fill in each field. Click Confirm to add a new serial command.
The result of all serial commands will be listed in the serial command list. Click Finish to apply your settings
Page 62

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-28
ATTENTION
For MIB wizard, a node has a max of 255 subnodes.
Finally, your command will be saved into scmcmd.c file. You can add other behavior in this method.
SNMP Wizard
This wizard is used to help to add a private MIB. You can add the private MIB you need in this page. By these
OIDs in private MIB, you can manage your device by SNMP protocol.
Page 63

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-29
NOTE
Node name is the root name you would like
First, click Add button.
Select the private MIB by the Browse button, and fill in this node name. After you have completed it, click
Confirm.
to generate
Page 64
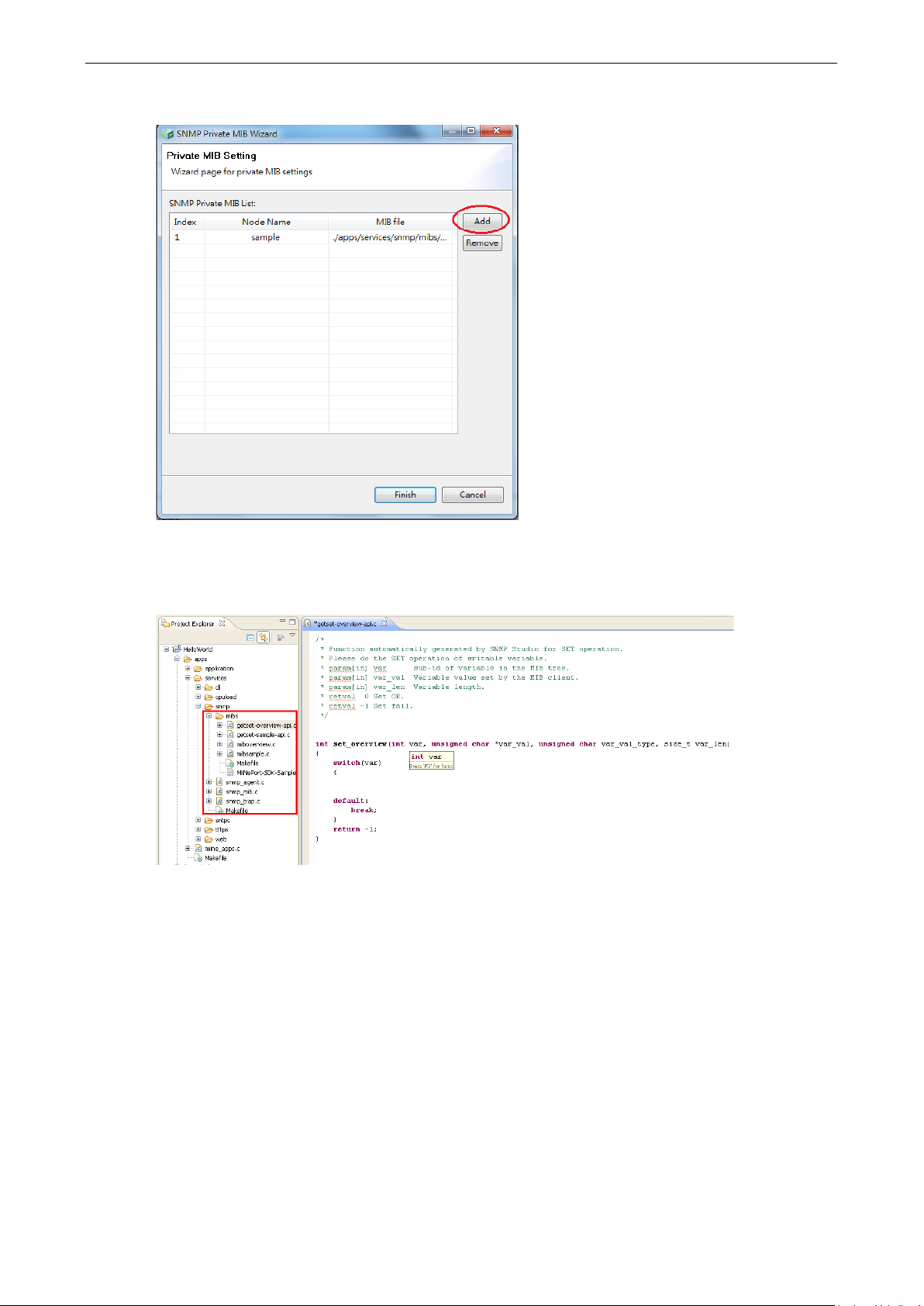
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-30
The private MIB will be showed on the MIB list. Then click Finish.
The MiiNePort IDE will generate some get and set functions for this MIB file under snmp folder. Besides, it will
also generate the file regarding your MIB file. Then you can implement the SNMP behavior you expect from
these functions.
Page 65

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-31
User App Wizard
This wizard is used to help you to create your application (subroutine). If you would like to develop your own
application, you can use this wizard. It will show you how to add a new application.
Fill in all fields, click Finish button.
The file templates will be created, so you can develop your application with them.
Page 66

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-32
Build project
The function is used to build a customized firmware which you develop. This function can build two different
types of firmware. If you select debug type, the firmware will be downloaded onto the MiiNePort. Then you can
debug step by step. On the other hand, if you build release version firmware, it will generate a customized
firmware without debug message. Besides, it won’t write onto the MiiNePort, and you can upgrade it into the
MiiNePort by utility.
Upload debug version firmware to MiiNePort
After compiling the source code, you have to upload your debug firmware file to the MiiNePort to verify all
functions. Moxa provides a source-level debug tool. In this way, you can debug it step by step to find your
programming issues.
First, you need to build a debug firmware, and then the MiiNePort will create a folder, which is called “Debug,”
and put the firmware into this folder. Click the debug button to upload firmware onto the MiiNePort by a USB
port automatically.
After uploading successfully, you can start to debug step by step.
Debug current active project
The function is used to debug a MiiNePort project. Your project will be downloaded into the MiiNePort SDK and
then it will execute your project. In addition, if you set break point, you can debug step by step.
Upload your customized firmware to MiiNePort
After the development of your customized firmware has been completed, you have to deploy your firmware file
to the MiiNePort. Please remember connect an Ethernet cable to the MiiNePort first, then use the NPort Search
Utility, as it can help you upload your firmware to the MiiNePort easily.
First, you need to build a release firmware, then the MiiNePort IDE will ask you to confirm if you want to reset
the default to MiiNePort device. Click Yes to go to the next step.
Page 67

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK MiiNePort IDE Development Tool
5-33
ATTENTION
For E1, user can upgrade MiiNePort SDK firmware into MiiNePort device from MiiNePort E1 standard firmware
V1.7
For E2, user can upgrade MiiNePort SDK firmware into MiiNePort device from MiiNePort E2 standard firmware
V1.3
After upgrading successfully, the setting of MiiNePort will be reset to
Then the MiiNePort will create a folder which is called “Release.” Put the firmware into this folder, so that you
can find your firmware in the sub-folder ‘objs’.
Please copy the .rom file to your desired path. In this way, you can upgrade the firmware by the Device Search
utility.
Select the target devices and the firmware you saved in the desired path, then click OK to start uploading the
firmware to the MiiNePort devices via Ethernet.
After uploading it successfully, the MiiNePort devices will be updated with all the new firmware.
.
.
default.
Page 68

6
6. NetEZ Technologies
This chapter introduces the NetEZ technology family and its innovative functions.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
SCM (Serial Command Mode)
EXTrigger (External Trigger)
EZPower
Page 69

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK NetEZ Technologies
6-2
SCM (Serial Command Mode)
The MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK’s SCM (Serial Command Mode) allows the module’s parameters to be retrieved or
configured through the serial port, rather than over the network. This is done through the use of specially
parsed commands sent to the module through the serial port.
SCM is often used when your device has already been used in actual applications and you need to change the
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK’s configuration, such as changing the device’s IP address by using your device’s keypad.
The details are shown below:
Page 70

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK NetEZ Technologies
6-3
NOTE
The Restart function of ExTrigger is disabled in Moxa
Press the button anytime
Refer to Appendix A: Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set for detailed
instructions on using SCM commands.
EXTrigger (External Trigger)
This function is for MiiNePort E1-SDK only.
The MiiNePort E1-SDK’s EXTrigger has two functions: (1) Resetting the module to Moxa’s default configuration,
and (2) Restarting the module. EXTrigger is designed to provide you with an easy network troubleshooting tool
that can be used without stopping the device’s normal operation.
The Reset-to-Default function is enabled by default and cannot be disabled. This design prevents device
deadlock in the future if you or your customer forgets the password and is unable to access the console to
troubleshoot the device. To activate the EXTrigger’s Reset to Default function, press the button inside the RJ45
jack for five seconds while your device and the MiiNePort E1-SDK is starting up.
The Restart function simply shuts down the module and then turns it back on. This does not affect any settings
in the module but is a commonly used method for initial troubleshooting. Simply hold the button for five
seconds at any time during device operation to restart the MiiNePort E1-SDK module.
’s factory default settings.
Refer to the following table describing the LED interaction with EXTrigger.
EXTrigger Fault/In Use
LED Behavior
Restart 0.5 time/sec
(Blinks amber
slowly)
Blinking
Duration
5 sec
Trigger Timing Note
When LED is Off (stops
during operation.
blinking)
1. Function active
2. Release button
Page 71

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK NetEZ Technologies
6-4
EXTrigger is actually an external Digital Input (DI) that can be accessed by you or your device’s end user. You
can design your own application by leveraging this external DI. Contact Moxa for information about custom
EXTrigger functions.
EZPower
Note: This function is only available for the MiiNePort E2-SDK.
The EZPower function makes it easy to configure the MiiNePort’s input voltage. Use EZPower to configure the
MiiNePort’s system power input to either 3.3 VDC or 5 VDC.
Page 72

A
A. Introduction to SCM (Serial Command
Mode) Command Set
The following topics are covered in this appendix:
Command/Reply Format
Single Line Command Format
Single Line Reply Format
Head and Tail Format
Operation Codes
Status Codes
Restriction
Command Code
Command Code for Getting the Configuration
Command Codes for Setting the Configuration
Command Codes for Retrieving Running Configuration
Command Codes for Viewing the Status
Control Command Codes
Page 73

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set
A-2
Command/Reply Format
Single Line Command Format
Head
1 byte
Op
1 byte
Cmd.
2 bytes
Single Line Reply Format
Head
1 byte
Op
1 byte
Cmd.
2 bytes
Head and Tail Format
Command ? ---
Reply ! --- LF
Head
1 byte
---
Operation Codes
Operation Code Meaning
G Get configuration from MiiNePort’s RAM
S Set configuration to MiiNePort’s RAM
R Retrieve running configuration
V View status
C Control
ST
1 byte
Tail
1 or 2 bytes
CR
LF
CR-LF
Parameters
0 to n bytes
Parameters
0 to n bytes
Tail
1 to 2 bytes
Tail
1 to 2 bytes
Status Codes
Status Code Meaning
E Enter Serial Command Mode
0 Command was executed successfully
1 Unrecognized format
2 Operation is not valid
3 Command is not valid
4 Parameter is incorrect
5 Parameter is too long
Restriction
The total number of parameters in a single command cannot exceed 1024 characters.
Page 74

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set
A-3
MiiNePort reports device name as MiiNePort_E1_9527
MiiNePort reports IP address as ‘192.168.127.254’.
Command Code
Command Code for Getting the Configuration
Device Name
Command code: BN
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s name.
?GBN
!GBN0MiiNePort_E1_9527
IP configuration
Command code: NC
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s IP configuration index as follows.
0 Static
1 DHCP
2 DHCP/BOOTP
3 BOOTP
4 AUTOIP
?GNC
!GNC00
IP address
Command code: NI
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s IP address.
System requests configured device name for this MiiNePort.
System requests IP configuration for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports IP configuration as ‘Static’.
?GNI
!GNI0192.168.127.254
Netmask
Command code: NM
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s Netmask address.
?GNM
!GNM0255.255.255.0
System requests IP address for this MiiNePort.
System requests Netmask address for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports netmask as ‘255.255.255.0’.
Page 75
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set
A-4
MiiNePort reports command executed successfully.
Gateway
Command code: NG
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s Gateway address.
?GNG
!GNG0255.255.255.255
DNS
Command code: ND
Command parameters: The index (1 or 2) of DNS server.
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s DNS address.
?GND1
!GND0192.168.1.2
IP configuration
Command code: NC
Command parameters: MiiNePort’s IP configuration index as shown in the following table
Reply parameters: N/A
0 Static
1 DHCP
2 DHCP/BOOTP
3 BOOTP
4 AutoIP
?SNC0
!SNC0
System requests Gateway address for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports Gateway address as ‘255.255.255.255’.
System requests DNS server 1 address for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports DNS server 1 address as ‘192.168.1.2’.
System sets IP configuration as ‘Static’.
MiiNePort reports command executed successfully.
IP address
Command code: NI
Command parameters: MiiNePort’s IP address.
Reply parameters: N/A
?SNI192.168.1.2
!SNI0
Netmask
Command code: NM
Command parameters: MiiNePort’s Netmask address.
Reply parameters: N/A
?SNM255.255.255.0
!SNM0
System sets IP address as ‘192.168.1.2’.
MiiNePort reports command executed successfully.
System sets Netmask as ‘255.255.255.0’.
Page 76

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set
A-5
Gateway
Command code: NG
Command parameters: MiiNePort’s Gateway address.
Reply parameters: N/A
?SNG192.168.1.254
!SNG0
System sets Gateway as ‘192.168.1.254’.
MiiNePort reports command executed successfully.
DNS
Command code: ND
Command parameters: The index (1,2) and DNS server address, separated by a semicolon (;).
Reply parameters: N/A
?SND1;192.168.1.123
!SND0
System sets DNS1 as ‘192.168.1.123’.
MiiNePort reports command executed successfully.
Command Codes for Retrieving Running Configuration
Device Name
Command code: BN
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s name.
?RBN
!RBN0MiiNePort_9527
System requests configured device name for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports device name as ‘MiiNePort_9527’.
IP configuration
Command code: NC
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s IP configuration index as follows.
0 Static
1 DHCP
2 DHCP/BOOTP
3 BOOTP
4 AutoIP
?RNC
!RNC00
IP address
Command code: NI
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s IP address.
?RNI
!RNI0192.168.127.254
System requests IP configuration for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports IP configuration as ‘Static’.
System requests IP address for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports IP address as ‘192.168.127.254’.
Page 77

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set
A-6
MiiNePort reports build number is 09021208.
Netmask
Command code: NM
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s Netmask address.
?RNM
!RNM0255.255.255.0
System requests Netmask address for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports netmask as ‘255.255.255.0’.
Gateway
Command code: NG
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s Gateway address.
?RNG
!RNM0255.255.255.255
System requests Gateway address for this MiiNePort.
MiiNePort reports Gateway address as ‘255.255.255.255’.
Serial Number
Command code: @S
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s serial number, in digit notation.
?R@S
!R@S09527
System requests MiiNePort’s serial number.
MiiNePort reports serial number is 9527.
Firmware Version
Command code: @V
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s firmware version. Version parts are separated by a single dot, with at least two
parts (major.minor) and at most three parts (major.minor.rev).
?R@V
!R@V01.0
System requests MiiNePort’s firmware version.
MiiNePort reports firmware version is 1.0.
Firmware Build Number
Command code: @B
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s firmware build number, eight digits.
?R@B
!R@B009021208
System requests MiiNePort’s firmware build number.
MAC address
Command code: @M
Command parameters: N/A
Reply parameters: MiiNePort’s MAC address.
?R@M
!R@M000:90:E8:71:00:10
System requests MiiNePort’s firmware build number.
MiiNePort reports MAC address is 00:90:E8:71:00:10.
Page 78

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Introduction to SCM (Serial Command Mode) Command Set
A-7
Command Codes for Viewing the Status
Control Command Codes
PING
Command code: NP
Command parameters: Target host name or IP address.
Reply parameters: A single minus symbol indicates the target host did not reply in 1000 milliseconds.
Otherwise, one decimal number indicating the reply latency in milliseconds is returned.
?CNPwww.moxa.com
!CNP010
?CNP192.168.1.1
!CNP0-
System requests to PING www.moxa.com.
Target host replies in 10 milliseconds.
System requests to PING 192.168.1.1.
Target host did not reply in 1000 milliseconds.
Load Factory Default
Command code: LD
Note that this command is not applied to the configuration until you save and restart the MiiNePort.
Command parameters: ‘1’ for “All setting”, ‘0’ for “Keep IP setting”.
Reply parameters: N/A
?CLD0
!CLD0
System requests to load factory default.
System loads factory default successfully.
Page 79

B
0
Reserved
23
Telnet
B. Well-Known Port Numbers
This appendix is included for your reference. Listed below are port numbers that already have a
well-established use. These port numbers should be avoided when assigning a port number to your MiiNePort
E1 Series module; otherwise you may experience network problems. Refer to the RFC 1700 standard for
Well-Known Port Numbers or refer to the following introduction from IANA.
• The port numbers are divided into three ranges: the Well-Known Ports, the Registered Ports, and the
Dynamic and/or Private Ports.
• The Well-Known Ports are those from 0 through 1023.
• The Registered Ports are those from 1024 through 49151.
• The Dynamic and/or Private Ports are those from 49152 through 65535.
The Well-Known Ports are assigned by IANA, and on most systems, can only be used by system processes or
by programs executed by privileged users. The following table shows famous port numbers among the
well-known port numbers. For more details, visit the IANA website at
http://www.iana.org/assignments/port-numbers
.
TCP Socket Application Service
1 TCP Port Service Multiplexor
2 Management Utility
7 Echo
9 Discard
11 Active Users (systat)
13 Daytime
15 Netstat
20 FTP data port
21 FTP CONTROL port
25 SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
37 Time (Time Server)
42 Host name server (names server)
43 Whois (nickname)
49 (Login Host Protocol) (Login)
53 Domain Name Server (domain)
79 Finger protocol (Finger)
80 World Wide Web HTTP
119 Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)
123 Network Time Protocol
213 IPX
160 – 223 Reserved for future use
Page 80
MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Well-Known Port Numbers
B-2
79
Finger Protocol
UDP Socket Application Service
0 Reserved
2 Management Utility
7 Echo
9 Discard
11 Active Users (systat)
13 Daytime
35 Any private printer server
39 Resource Location Protocol
42 Host name server (names server)
43 Whois (nickname)
49 (Login Host Protocol) (Login)
53 Domain Name Server (domain)
69 Trivial Transfer Protocol (TETP)
70 Gopler Protocol
80 World Wide Web HTTP
107 Remote Telnet Service
111 Sun Remote Procedure Call (Sunrpc)
119 Network news Tcanster Protocol (NNTP)
123 Network Time protocol (nnp)
161 SNMP (Simple Network Mail Protocol)
162 SNMP Traps
213 IPX (Used for IP Tunneling)
Page 81

C
ifInNUcastPkts
ipReasmTimeout
IcmpOutMsgs
C. SNMP Agent with MIB II and RS-232 Like
Groups
MiiNePort E1 Series modules have SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) agent software built in. The
software supports RFC1317 RS-232 like groups and RFC 1213 MIB-II. The following table lists the standard
MIB-II groups, as well as the variable implementations for the MiiNePort E1 Series modules.
RFC1 213 MIB-II supported SNMP variables:
System MIB Interfaces MIB IP MIB ICMP MIB
SysDescr itNumber ipForwarding IcmpInMsgs
SysObjectID ifIndex ipDefaultTTL IcmpInErrors
SysUpTime ifDescr ipInreceives IcmpInDestUnreachs
SysContact ifType ipInHdrErrors IcmpInTimeExcds
SysName ifMtu ipInAddrErrors IcmpInParmProbs
SysLocation ifSpeed ipForwDatagrams IcmpInSrcQuenchs
SysServices ifPhysAddress ipInUnknownProtos IcmpInRedirects
ifAdminStatus ipInDiscards IcmpInEchos
ifOperStatus ipInDelivers IcmpInEchoReps
ifLastChange ipOutRequests IcmpInTimestamps
ifInOctets ipOutDiscards IcmpTimestampReps
ifInUcastPkts ipOutNoRoutes IcmpInAddrMasks
ifInDiscards ipReasmReqds IcmpOutErrors
ifInErrors ipReasmOKs IcmpOutDestUnreachs
ifInUnknownProtos ipReasmFails IcmpOutTimeExcds
ifOutOctets ipFragOKs IcmpOutParmProbs
ifOutUcastPkts ipFragFails IcmpOutSrcQuenchs
ifOutNUcastPkts ipFragCreates IcmpOutRedirects
ifOutDiscards ipAdEntAddr IcmpOutEchos
ifOutErrors ipAdEntIfIndex IcmpOutEchoReps
ifOutQLen ipAdEntNetMask IcmpOutTimestamps
ifSpecific ipAdEntBcastAddr IcmpOutTimestampReps
ipAdEntReasmMaxSize IcmpOutAddrMasks
IpNetToMediaIfIndex IcmpOutAddrMaskReps
IpNetToMediaPhysAddress
IpNetToMediaNetAddress
IpNetToMediaType
IpRoutingDiscards
Page 82

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK SNMP Agent with MIB II and RS-232 Like Groups
C-2
UDP MIB TCP MIB SNMP MIB
UdpInDatagrams tcpRtoAlgorithm snmpInPkts
UdpNoPorts tcpRtoMin snmpOutPkts
UdpInErrors tcpRtoMax snmpInBadVersions
UdpOutDatagrams tcpMaxConn snmpInBadCommunityNames
UdpLocalAddress tcpActiveOpens snmpInASNParseErrs
UdpLocalPort tcpPassiveOpens snmpInTooBigs
tcpAttempFails snmpInNoSuchNames
Address Translation MIB tcpEstabResets snmpInBadValues
AtIfIndex tcpCurrEstab snmpInReadOnlys
AtPhysAddress tcpInSegs snmpInGenErrs
AtNetAddress tcpOutSegs snmpInTotalReqVars
Page 83

D. Supported File Systems
There are two file systems in MiiNePort-SDK for you to access via file operation APIs: ROM file system and FAT
ROM File System
When you create your project under MiiNePort-IDE, you can find a directory named <romfs> under your
project directory, as shown in the following:
D
All files in <romfs> directory will be compiled into ROM file system of MiiNePort-SDK. The files in ROM file
system are available through the mount point "/sys". The maximum storage size of ROM file system is 512K
bytes.
All files in ROM file system are read only. In your application, if you need to read contents from some files but
do not need to write data to these files, you can put these read-only files in <romfs> directory under your
project, and open these files under "/sys" direcotry with O_RDONLY flag in your program.
Note:In your program, the files under "/sys" directory are read only, and you cannot create/delete files under
this directory.
FAT File System
There is a FAT file system with maximum storage size of 512K bytes in MiiNePort-SDK for you to
create/read/write/delete files. In your program, you can access FAT file system under "/usr" directory. This FAT
file system only supports 8.3 filename format. A 8.3 filename has at most eight characters, optionally followed
by a period "." and a filename extension of at most three characters. The long filename is not supported.
Example: File write/read
Page 84

MiiNePort E1/E2-SDK Supported File Systems
D-2
The following example uses POSIX library to write/read a file.
Example:
 Loading...
Loading...