Page 1

2015 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
P/N: 1802002051030
EDS-G205-1GTXSFP
Hardware Installation Guide
Moxa EtherDevice Switch
First Edition, April 2015
Page 2

- 2 -
Overview
The EDS-G205-1GTXSFP switches are equipped with 5 Gigabit Ethernet
ports (4 10/100/1000BaseT(X) ports and 1 combo 10/100/1000BaseT(X)
or 100/1000BaseSFP port), making them ideal, economical solutions for
demanding, high bandwidth Gigabit Ethernet applications. In addition,
the built-in relay warning function alerts system administrators when
power failures or port breaks occur, and the add-on 4-pin DIP switches
can be used to configure broadcast storm protection, jumbo frame rate,
IEEE 802.3az energy saving, and 100/1000 SFP speed switching. The
EDS-G205-1GTXSFP series includes 2 models: one with an operating
temperature range of -10 to 60°C, and the other with an extended
operating temperature range of -40 to 75°C. These 2 models have passed
a 100% burn-in test to ensure that they fulfill the special needs of
industrial automation control. The EDS-G205-1GTXSFP series can be
easily installed on a DIN rail or in distribution boxes.
Package Checklist
The EDS-G205-1GTXSFP is shipped with the following items.
• Moxa EDS-G205-1GTXSFP Switch
• Hardware installation guide
• Warranty card
Note: Please contact your customer service representative for assistance
if any of these items are missing or damaged.
Features
High Performance Network Switching Technology
• 10/100/1000BaseT(X) (RJ45), auto negotiation speed, F/H duplex
mode
• IEEE 802.3/802.3u/802.3ab/802.3z
• 100BaseSFP/1000BaseSFP; easily configure speed by DIP switch
• Store and Forward switching process type, 8K MAC address entries.
Industrial Grade Reliability and Efficiency
• Power failure, port break alarm by relay output
• Redundant dual 12/24/48 VDC power inputs
• IEEE 802.3az energy-efficient Ethernet settings by DIP switch
• Jumbo frame setting by DIP switch
Rugged Design
• Operating temperature range of -10 to 60°C, or extended operating
temperature of -40 to 75°C for T models
• IP30, rugged high-strength housing
• DIN rail or panel mounting capability
Page 3
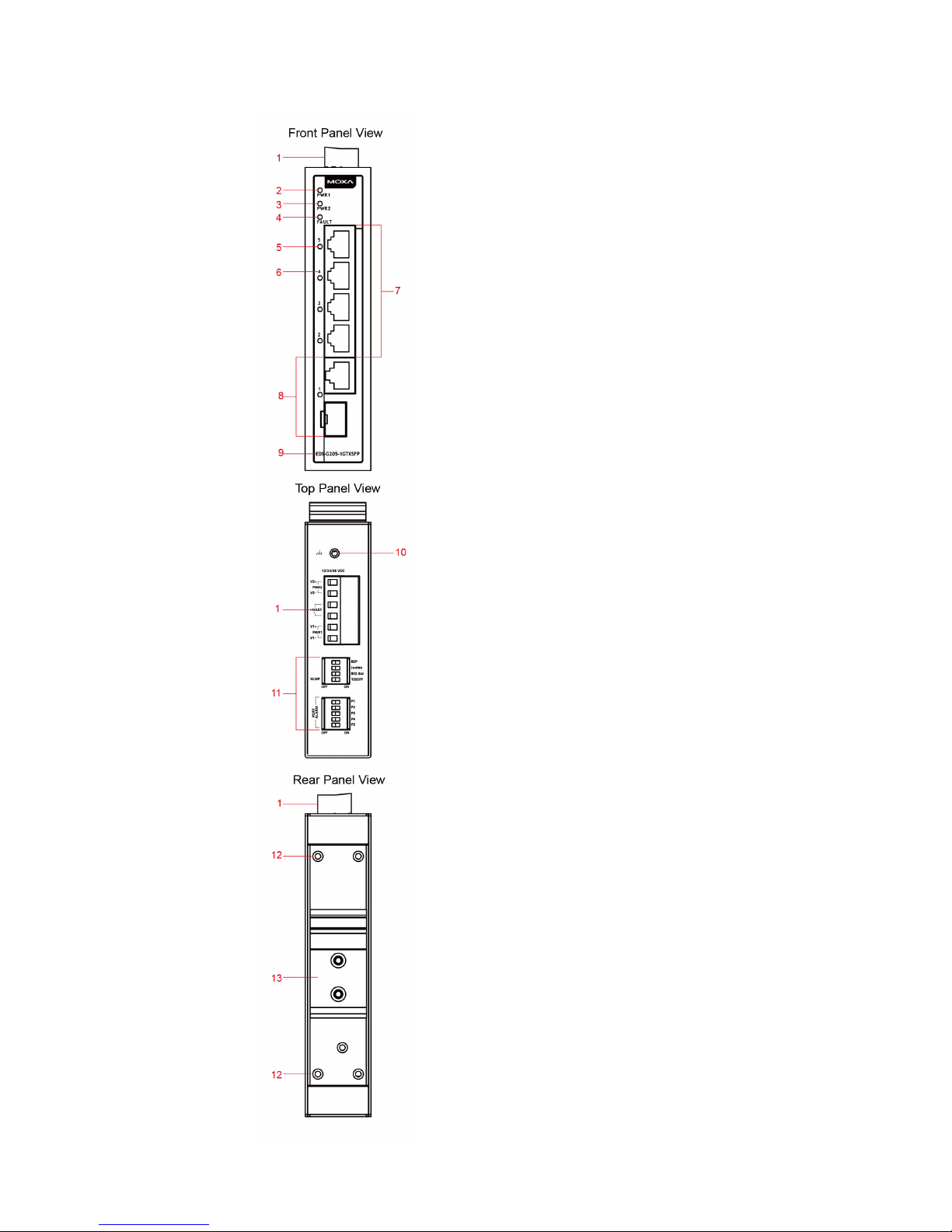
- 3 -
Panel Layout of the EDS-G205-1GTXSFP
1. Terminal block for power input
(PWR1, PWR2) and relay output
2. PWR1: LED for power input 1
3. PWR2: LED for power input 2
4. FAULT: LED indicator
5. 10/100/1000BaseT(X) LED
indicator (Amber: 10/100M;
Green: 1000M)
6. Port number
7. 2 to 5: 10/100/1000 BaseT(X)
ports
8. 1: 10/100/1000 BaseT(X) or
100/1000Base SFP slot combo
port
9. Model Name
10.
Grounding screw
11.
DIP switches
12.
Screw hole for wall mounting kit
13.
DIN rail kit
Page 4
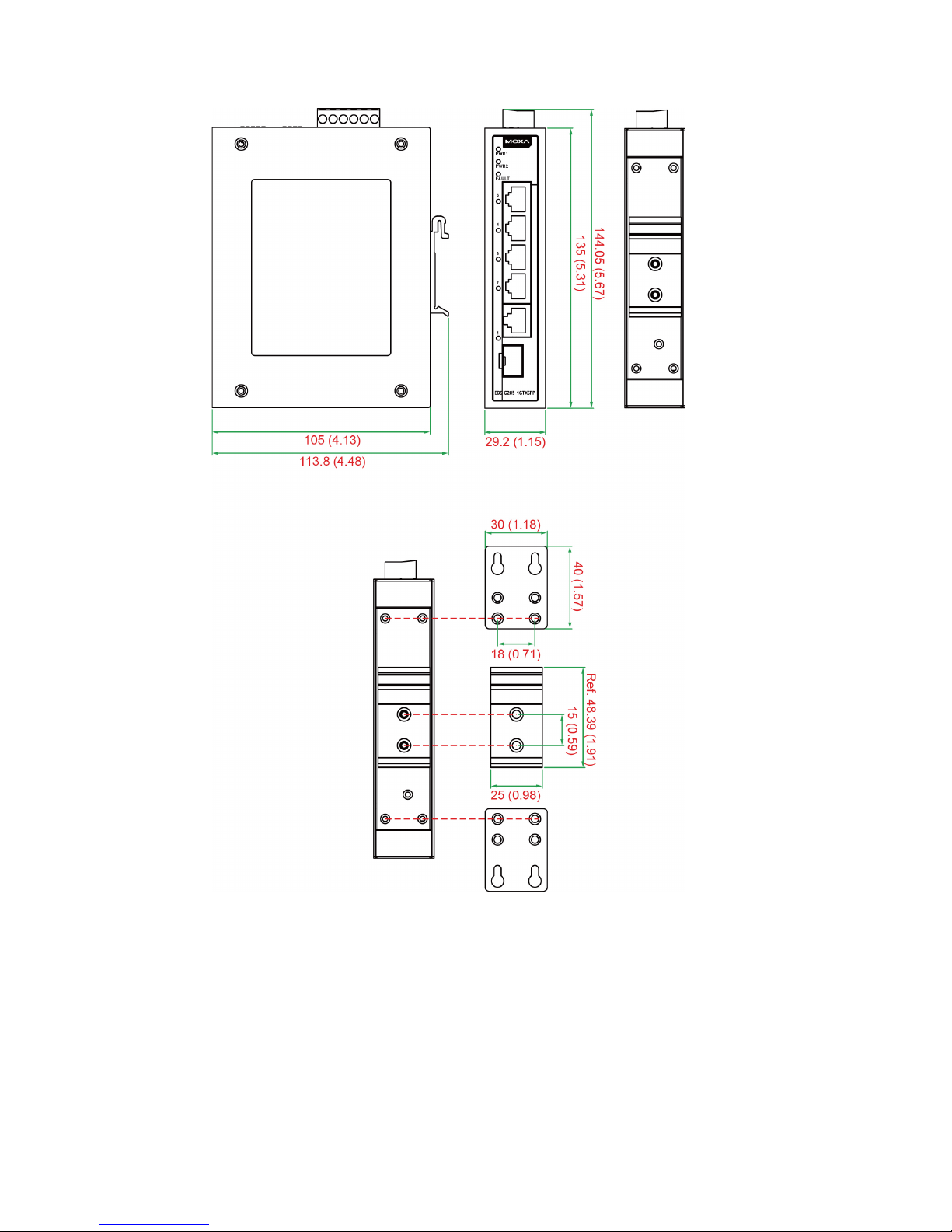
- 4 -
Mounting Dimensions, unit = mm (inch)
Page 5

- 5 -
DIN Rail Mounting
The aluminum DIN rail attachment plate should already be fixed to the
back panel of the switch when you take it out of the box. If you need to
reattach the DIN rail attachment plate, make sure the stiff metal spring is
situated towards the top, as shown in the figures below.
STEP 1:
Insert the top of the DIN
rail into
the slot just
below the stiff metal
spring.
STEP 2:
The DIN
rail attachment unit will
snap into place as shown below.
To remove the DIN rail from the switch, simply reverse Steps 1 and 2.
Wall Mounting (optional)
For some applications, you will find it convenient to mount the switch on
the wall, as illustrated below.
STEP 1:
Remove the aluminum DIN
rail attachment plate from
the
switch’s
rear panel, and
then attach the wall mount
plates, as shown in the
f
igure.
STEP 2:
Mounting
the switch
on the wall requires 4 screws. Use
the switch, with wall mount plates attached, as a guide
to mark the correct locations of the 4 s
crews. The
heads of the screws should be less than 6.0 mm in
diameter, and the shafts should be less than 3.5 mm in
diameter, as shown in the figure at the right.
NOTE
Before tightening the screws into the wall, make sure the screw
head and shank size are suitable by inserting the screw into one
of the keyhole-shaped apertures of the wall mounting plates.
Do not screw the screws in all the way—leave about 2 mm to allow room
for sliding the wall mount panel between the wall and the screws.
Page 6

- 6 -
STEP 3:
Once the screws are fixed in
the wall, insert the four screw
heads through the large parts
of the keyhole
-shaped
apertures, and then slide the
switch
downwards, as
indicated
. Tighten the four
screws for
added stability.
Wiring Requirements
WARNING
Safety First!
Turn
the power off before disconnecting modules or wires. The
proper power supply voltage is listed on the product label. Check
the voltage of your power source to make sure you are using the
correct voltage. Do NOT use a voltage greater than
what is
specified on the product label.
These devices must be supplied by an AELV source as defined in
the Low Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC and 2004/108/EC.
WARNING
Safety First!
Calculate the maximum possible current in each power wire and
common wire.
Observe all electrical codes dictating the
maximum current allowable for each wire size.
If the current goes above the maximum ratings, the wiring could
overheat, causing serious damage to your equipment.
You should also pay attention to the following items:
• Use separate paths to route wiring for power and devices. If power
wiring and device wiring paths must cross, make sure the wires are
perpendicular at the intersection point.
NOTE: Do not run signal or communications wiring and power wiring
in the same wire conduit. To avoid interference, wires with different
signal characteristics should be routed separately.
• You can use the type of signal transmitted through a wire to
determine which wires should be kept separate. The rule of thumb is
that wiring with similar electrical characteristics can be bundled
together.
• Keep input wiring and output wiring separated.
Page 7

- 7 -
• We strongly advise labeling the wiring for all devices in the system.
Grounding Your Moxa Switch
Grounding and wire routing help limit the effects of noise due to
electromagnetic interference (EMI). Run the ground connection from the
ground screw to the grounding surface prior to connecting devices.
ATTENTION
This produ
ct is intended to be mounted to a well-grounded
mounting surface, such as a metal panel.
Wiring the Alarm Contact
The alarm contact consists of the two middle contacts of the terminal
block on the switch’s top panel. You may refer to the next section for
detailed instructions on how to connect the wires to the terminal block
connector, and how to attach the terminal block connector to the terminal
block receptor.
In this section, we explain the meaning of the two contacts used to
connect the alarm contact.
FAULT: The two middle contacts of the
6
-contact terminal block connector
are used to
detect both power faults and port faults. The
two wires attached to the Fault contacts form
a
n open circuit when:
1. The switch has lost power from one of the
DC power inputs.
OR
2. The PORT ALARM DIP switch for one of
the ports is set to ON, but the port is not
connected properly.
If
neither of these two conditions is satisfied,
the Fault circuit will
be closed.
Wiring the Redundant Power Inputs
The top two contacts and the bottom two contacts of the 6-contact
terminal block connector on the switch’s top panel are used for DC inputs.
Top and front views of one of the terminal block connectors are shown
here.
Page 8

- 8 -
STEP 1: Insert the negative/positive DC
wires into the
V-/V+ terminals.
STEP 2: To keep the DC wires from pulling
loose, use a small flat-blade screwdriver to
tighten the wire-clamp screws on the front
of the terminal block connector.
STEP
3: Insert the plastic terminal block
connector prongs into the terminal block
receptor, which is
located on switch’s top
panel.
ATTENTION
Before connecting
the switch
to the DC power inputs, make sure
the DC power source voltage is stable.
Communication Connections
EDS-G205-1GTXSFP switches have 2 types of communication port:
• 4 10/100/1000BaseT(X) Ethernet ports
• 1 combination 10/100/1000T(X) or 100/1000BaseSFP port
10/100/1000BaseT(X) Ethernet Port Connection
The 10/100/1000BaseT(X) ports located on switch’s front panel are used
to connect to Ethernet-enabled devices. Most users will choose to
configure these ports for Auto MDI/MDI-X mode, in which case the port’s
pinouts are adjusted automatically depending on the type of Ethernet
cable used (straight-through or cross-over), and the type of device
(NIC-type or HUB/Switch-type) connected to the port.
In what follows, we give pinouts for both MDI (NIC-type) ports and MDI-X
(HUB/Switch-type) ports. We also give cable wiring diagrams for
straight-through and cross-over Ethernet cables.
10/100BaseT(x) RJ45 Pinouts
MDI Port Pinouts
MDI-X Port Pinouts
8-pin RJ45
Pin
Signal
1
Tx+
2
Tx-
3
Rx+
6
Rx-
Pin
Signal
1
Rx+
2
Rx-
3
Tx+ 6 Tx-
Page 9

- 9 -
1000BaseT RJ45 Pinouts
Pin
MDI
MDI-X
1
BI_DA+
BI_DB+
2
BI_DA-
BI_DB-
3
BI_DB+
BI_DA+
4
BI_DC+
BI_DD+
5
BI_DC-
BI_DD-
6
BI_DB-
BI_DA-
7
BI_DD+
BI_DC+
8
BI_DD-
BI_DC-
RJ45 (8-pin) to RJ45 (8-pin) Straight-Through Cable Wiring
RJ45 (8-pin) to RJ45 (8-pin) Cross-Over Cable Wiring
100/1000BaseSFP (mini-GBIC) Fiber Port
One of the Gigabit Ethernet ports on the EDS-G205-1GTXSFP is an SFP
slot, which requires 100M or 1G mini-GBIC fiber transceivers to work
properly. Moxa provides complete transceiver models for various distance
requirements.
The concept behind the LC port and cable is straightforward. Suppose you
are connecting devices I and II. Unlike electrical signals, optical signals do
not require a circuit in order to transmit data. Consequently, one of the
optical lines is used to transmit data from device I to device II, and the
other optical line is used to transmit data from device II to device I, for
full-duplex transmission.
Remember to connect the Tx (transmit) port of device I to the Rx (receive)
port of device II, and the Rx (receive) port of device I to the Tx (transmit)
port of device II. If you make your own cable, we suggest labeling the two
Page 10
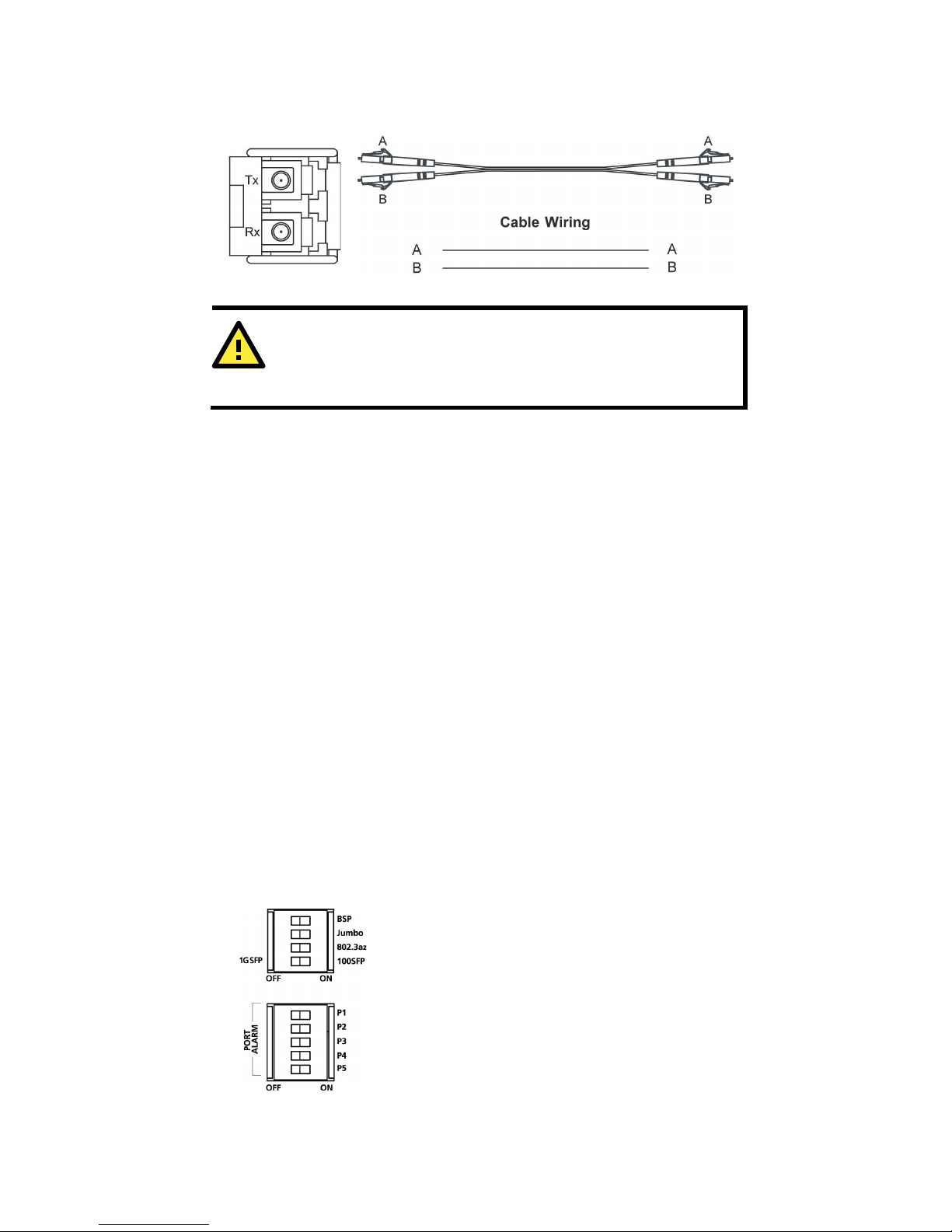
- 10 -
sides of the same line with the same letter (A-to-A and B-to-B, as shown
below, or A1-to-A2 and B1-to-B2).
LC-Port Pinouts
LC-Port to LC-Port Cable Wiring
ATTENTION
This is a Class 1 Laser/LED product. To avoid causing serious
damage to your eyes, do not stare directly into the laser beam.
Redundant Power Inputs
Both power inputs can be connected simultaneously to live DC power
sources. If one power source fails, the other live source acts as a backup,
and automatically supplies all of the switch’s power needs.
Alarm Contact
The EDS-G205-1GTXSFP has one alarm contact located on the top panel.
For detailed instructions on how to connect the alarm contact power wires
to the two middle contacts of the 6-contact terminal block connector, see
the Wiring the Alarm Contact section on page 7. A typical scenario
would be to connect the Fault circuit to a warning light located in the
control room. The light can be set up to switch on when a fault is detected.
The alarm contact has two terminals that form a Fault circuit for
connecting to an alarm system. The two wires attached to the Fault
contacts form an open circuit when (1) the switch has lost power from one
of the DC power inputs, or (2) one of the ports, for which the
corresponding PORT ALARM DIP switch is set to ON, is not properly
connected.
If neither of these two conditions occurs, the Fault circuit will be closed.
DIP Switch Settings
The default setting for each DIP switch is OFF.
The following table explains the effect of setting
the DIP switches to the ON positions.
Page 11

- 11 -
DIP Switch
Setting
Description
BSP
ON
Enables broadcast storm protection
OFF
Disables broadcast storm protection
Jumbo Frame
ON
Enables jumbo frame function
OFF
Disables jumbo frame function
802.3az
ON
Enables the energy-efficient Ethernet
function
OFF
Disables the energy-efficient Ethernet
function
100/1000BaseSFP
ON
Supports 100M SFP module
OFF
Supports 1000M SFP module
Port Alarm
ON
Enables the corresponding PORT
Alarm. If the port’s link fails, the relay
will form an open circuit and the fault
LED will light up
OFF
Disables the corresponding PORT
Alarm. If the port’s link fails, the relay
will form a closed
circuit and the fault
LED will never light up
ATTENTION
To actively update DIP switch settings, power off and then power
on the switch.
LED Indicators
The front panel of the EDS-G205-1GTXSFP switch contains several LED
indicators. The function of each LED is described in the table below.
LED
Color
State
Description
PWR1 AMBER
On
Power is being supplied to power input
PWR1
Off
Power is not being supplied to power input
PWR1
PWR2 AMBER
On
Power is being supplied to power input
PWR2
Off
Power is not being supplied to power input
PWR2
FAULT RED
On
When the corresponding PORT alarm is
enabled, and the port’s link is inactive.
Off
When the corresponding PORT alarm is
enabled and the port’s link is active, or
when the corresponding PORT alarm is
disabled.
10/100/
1000M
AMBER
On
TP port’s 10/100 Mbps or SFP port’s 100
Mbps link is active.
Blinking
Data is being transmitted at 10/100 Mbps
Off
TP port’s 10/100 Mbps or SFP port 100
Mbps link is inactive.
GREEN
On
TP/SFP port’s 1000 Mbps link is active.
Blinking
Data is being transmitted at 1000 Mbps
Off
TP/SFP port’s 1000 Mbps link is inactive
Page 12

- 12 -
Auto MDI/MDI-X Connection
The Auto MDI/MDI-X function allows users to connect the switch’s
10/100/1000BaseT(X) ports to any kind of Ethernet device, without
paying attention to the type of Ethernet cable being used for the
connection. This means that you can use either a straight-through cable
or cross-over cable to connect the switch to Ethernet devices.
Three Speed Functionality and Switching
The switch’s 10/100/1000 Mbps RJ45 switched port auto negotiates with
the connected device for the fastest data transmission rate supported by
both devices. The switch is a plug-and-play device, so software
configuration is not required at installation or during maintenance.
The half/full duplex mode for the RJ45 switched ports is user dependent
and changes (by auto-negotiation) to full or half duplex, depending on
which transmission speed is supported by the attached device.
Auto-Negotiation and Speed Sensing
The switch’s RJ45 Ethernet ports independently support auto-negotiation
for transmission speeds of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1000 Mbps, with
operation according to the IEEE 802.3 standard.
This means that some nodes could be operating at 10 Mbps, while at the
same time, other nodes are operating at 100 Mbps or 1000 Mbps.
Auto-negotiation takes place when an RJ45 cable connection is made, and
then each time a LINK is enabled. The switch advertises its capability for
using 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps transmission speeds, with the
device at the other end of the cable expected to advertise similarly.
Depending on what type of device is connected, this will result in
agreement to operate at a speed of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps.
If the switch’s RJ45 Ethernet port is connected to a non-negotiating
device, it will default to 10 Mbps speed and half-duplex mode, as required
by the IEEE 802.3 standard.
Specifications
Technology
Standards
IEEE 802.3 for 10BaseT
IEEE 802.3u for 100BaseT(X) and 100BaseFX
IEEE 802.3ab for 1000BaseT(X)
IEEE 802.3z for 1000BaseX
IEEE 802.3x for Flow Control
IEEE 802.3az for Energy-Efficient Ethernet
Interface
RJ45 Ports
10/100/1000BaseT(X) auto negotiation speed,
half/full duplex mode, and auto MDI/MDI-X
connection
Fiber Ports
Optional 1000BaseSX/LX/LHX/ZX (LC
connector) or 100BaseSFP
LED Indicators
PWR1, PWR2, FAULT, 10/100M/1000M
DIP Switch
Port break alarm, broadcast storm protection,
jumbo frame, IEEE 802.3az, 100/1000BaseSFP
Page 13

- 13 -
Alarm Contact
One relay output with current carrying capacity
of 1A @ 24 VDC
Power Requirements
Input Voltage
12/24/48 VDC (9.6 to 60 VDC), redundant input
Input Current @ 24VDC
0.16 A
Connection
One removable 6-pin terminal block
Overload Current
Protection
Present
Reverse Polarity
Protection
Present
Physical Characteristics
Housing
IP30 protection, metal case
Dimensions
29 x 135 x 105 mm (1.14 x 5.31 x 4.13 in)
Weight
290 g
Installation
DIN rail, wall mounting (optional kit)
Environmental Limits
Operating Temperature
-10 to 60°C (14 to 140°F)
-40 to 75°C (-40 to 167°F) for -T models
Storage Temperature
-40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F)
Ambient Relative
Humidity
5 to 95% (non-condensing)
Regulatory Approvals
Safety
UL 508
Hazardous Location
UL/cUL Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, and
D; ATEX Zone 2, Ex nA nC IIC T4 Gc
EMI
FCC Part 15, CISPR (EN 55022) Class A
EMS
EN 61000-4-2 (ESD), Level 3
EN 61000-4-3 (RS), Level 3
EN 61000-4-4 (EFT), Level 3
EN 61000-4-5 (Surge), Level 3
EN 61000-4-6 (CS), Level 3
EN 61000-4-8
Rail Traffic
EN 50121-4
Shock
IEC 60068-2-27
Freefall
IEC 60068-2-32
Vibration
IEC 60068-2-6
Warranty
Warranty Period
5 years
Details
See www.moxa.com/warranty
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
Moxa Americas:
Toll
-free: 1-888-669-2872
Tel:
1-714-528-6777
Fax:
1-714-528-6778
Moxa China (Shanghai office):
Toll
-free: 800-820-5036
Tel:
+86-21-5258-9955
Fax:
+86-21-5258-5505
Moxa Europe
:
Tel:
+49-89-3 70 03 99-0
Fax:
+49-89-3 70 03 99-99
Moxa Asia
-Pacific:
Tel:
+886-2-8919-1230
Fax:
+886-2-8919-1231
 Loading...
Loading...