Page 1

Moxa AirWorks AWK-6222 User’s Manual
Edition 2.0, August 2016
www.moxa.com/product
© 2016 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Moxa AirWorks AWK-6222 User’s Manual
Moxa Americas
Toll
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa China (Shanghai office)
Toll
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa Europe
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa Asia
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa
Tel:
Fax:
The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance with
the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
© 2016 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
The MOXA logo is a registered trademark of Moxa Inc.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
Moxa.
Moxa provides this document as is, without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited
to, its particular purpose. Moxa reserves the right to make improvements and/or changes to this manual, or to the
products and/or the programs described in this manual, at any time.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Moxa assumes no responsibility for
its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that may result from its use.
This product might include unintentional technical or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the publication.
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
-free: 1-888-669-2872
+1-714-528-6777
+1-714-528-6778
+49-89-3 70 03 99-0
+49-89-3 70 03 99-99
India
+91-80-4172-9088
+91-80-4132-1045
-free: 800-820-5036
+86-21-5258-9955
+86-21-5258-5505
-Pacific
+886-2-8919-1230
+886-2-8919-1231
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ...................................................................................................................................... 1-1
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Package Checklist ............................................................................................................................... 1-2
Product Features ................................................................................................................................ 1-2
Product Specifications ......................................................................................................................... 1-3
Functions ........................................................................................................................................... 1-5
LED Indicators ............................................................................................................................ 1-5
Reset Button ............................................................................................................................... 1-6
Relay (Digital Output) .................................................................................................................. 1-6
2. Getting Started ................................................................................................................................. 2-1
First-time Installation and Configuration ................................................................................................ 2-2
Communication Testing ....................................................................................................................... 2-3
Function Guide Map ............................................................................................................................ 2-5
3. Web Console Configuration ............................................................................................................... 3-1
Configuration by Web Browser ............................................................................................................. 3-2
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 3-3
Basic Settings .................................................................................................................................... 3-4
System Info Settings ................................................................................................................... 3-4
Network Settings ......................................................................................................................... 3-4
Time Settings ............................................................................................................................. 3-5
Wireless Settings ................................................................................................................................ 3-7
Operation Mode .......................................................................................................................... 3-7
Enabling Non-Redundant (Single RF) AP ....................................................................................... 3-10
WLAN Security Settings ............................................................................................................. 3-13
Advanced Wireless Settings ........................................................................................................ 3-21
WLAN Certification Settings (for EAP-TLS in Redundant Client, Client or Slave mode only) .................. 3-23
Advanced Settings ............................................................................................................................ 3-24
DHCP Server (for AP-Client operation mode’s AP mode only) .......................................................... 3-24
Packet Filters ............................................................................................................................ 3-26
RSTP Settings (for Master or Slave mode only) ............................................................................. 3-28
SNMP Agent ............................................................................................................................. 3-29
Storm Protection ....................................................................................................................... 3-31
Auto Warning Settings ....................................................................................................................... 3-32
System Log .............................................................................................................................. 3-32
Syslog ..................................................................................................................................... 3-33
E-mail ...................................................................................................................................... 3-34
Relay ....................................................................................................................................... 3-35
Trap ........................................................................................................................................ 3-36
Status ............................................................................................................................................. 3-38
Wireless Status ......................................................................................................................... 3-38
Associated Client List (for Redundant AP, AP, or Master Mode only) ................................................. 3-38
DHCP Client List (for AP mode only) ............................................................................................ 3-39
System Log .............................................................................................................................. 3-39
Relay Status ............................................................................................................................. 3-40
DI and Power Status .................................................................................................................. 3-40
Maintenance .................................................................................................................................... 3-40
Console Settings ....................................................................................................................... 3-41
Ping ......................................................................................................................................... 3-41
Firmware Upgrade ..................................................................................................................... 3-41
Config Import Export ................................................................................................................. 3-42
Load Factory Default .................................................................................................................. 3-42
Password ................................................................................................................................. 3-43
Misc. Settings ........................................................................................................................... 3-43
Save Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 3-43
Restart ............................................................................................................................................ 3-44
Logout ............................................................................................................................................ 3-44
4. Software Installation/Configuration ................................................................................................. 4-1
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 4-2
Wireless Search Utility ......................................................................................................................... 4-2
Installing Wireless Search Utility ................................................................................................... 4-2
Configuring the Wireless Search Utility ........................................................................................... 4-5
5. Other Console Configurations ............................................................................................................ 5-1
RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100) .................................................................... 5-2
Configuration by Telnet and SSH Consoles ............................................................................................. 5-4
Configuration by Web Browser with HTTPS/SSL ...................................................................................... 5-5
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access ..................................................................................................... 5-6
Page 4

6. References ........................................................................................................................................ 6-1
Beacon .............................................................................................................................................. 6-2
DTIM ................................................................................................................................................. 6-2
Fragment ........................................................................................................................................... 6-2
RTS Threshold .................................................................................................................................... 6-2
STP and RSTP .................................................................................................................................... 6-2
The STP/RSTP Concept ................................................................................................................ 6-2
Differences between RSTP and STP ................................................................................................ 6-3
7. Support Information ......................................................................................................................... 7-1
About This User’s Manual ..................................................................................................................... 7-2
DoC (Declaration of Conformity) ........................................................................................................... 7-2
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement ............................................................ 7-2
R&TTE Compliance Statement ....................................................................................................... 7-3
Firmware Recovery ............................................................................................................................. 7-3
Technical Support Contact Information .................................................................................................. 7-5
Page 5

1
1. Introduction
Moxa AirWorks AWK-6222 with dual-RF wireless capability allows wireless users to access network resources
more reliably. The AWK-6222 is rated to operate at temperatures ranging from -40 to 75°C and is rugged
enough for any harsh industrial environment.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Product Features
Product Specifications
Functions
LED Indicators
Reset Button
Relay (Digital Output)
Page 6
AWK-6222 Introduction
1-2
NOTE
The items above come with the standard AWK-6222. The package contents may vary for customized versions.
Overview
The AWK-6222 outdoor dual-RF wireless AP/bridge/client provides a flexible solution for industrial applications
in a demanding environment. The AWK-6222 is rated to operate at temperatures ranging from -40 to 75°C,
and its dustproof and weatherproof design is IP68-rated, allowing you to extend existing wired networks to
outdoor locations. With two independent RF modules, the AWK-6222 supports a greater variety of wireless
configurations and applications. It can also increase the reliability of entire wireless network by enabling
redundant wireless connections. The AWK-6222 also has two redundant DC power inputs to increase the
reliability of the power supply, and can be powered via PoE.
Package Checklist
Moxa’s AWK-6222 ships with the following items. If any of these items is missing or damaged, please contact
your customer service representative for assistance.
• 1 AWK-6222 wireless AP/bridge/client
• 2 dual-band omni-directional antennas (5/2 dBi, N-type male, 2.4/5 GHz)
• Wall mounting kit (includes 2 supports)
• Field-installable power plug
• Field-installable RJ45 plug
• 2 metal caps to cover RJ45 connectors
• Metal cap to cover M12-female DI/O connector
• 2 metal caps to cover N-type connectors
• Transparent plastic sticks for field-installable plugs
• Documentation and software CD
• Quick installation guide (printed)
• Warranty card
Product Features
• IEEE802.11a/b/g compliant.
• Three-in-one design (AP/Bridge/Client).
• Dual-RF design for redundant wireless communication.
• Advanced Wireless Security:
64-bit and 128-bit WEP/WPA/WPA2
SSID Hiding/IEEE 802.1X/RADIUS
Packet access control & filtering
• STP/RSTP support for network redundancy.
• Long-distance transmission support.
• Turbo Roaming™ enables rapid handover (Client mode).
• Dedicated antenna selection.
• RS-232 console management.
• 2DI+1DO for on-site monitoring and warming.
• -40 to 75°C operating temperature range (-T model).
• Redundant 24 VDC power inputs or IEEE802.3af Power over Ethernet.
• DIN-rail or wall mountable.
Page 7

AWK-6222 Introduction
1-3
WLAN Interface
Standards:
IEEE 802.11a/b/g for Wireless LAN
IEEE 802.11i for Wireless Security
IEEE 802.3 for 10BaseT(X)
IEEE 802.3u for 100BaseT(X)
IEEE 802.3af for Power
IEEE 802.
IEEE 802.1w for Rapid STP
IEEE 802.1Q for VLAN
Spread Spectrum and Modulation (typical):
• DSSS with DBPSK, DQPSK, CCK
• OFDM with BPSK, QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM
• 802.11b: CCK @ 11/5.5 Mbps, DQPSK @ 2 Mbps,
• 8
Operating Channels (central frequency):
US:
2.412 to 2.462 GHz (11 channels)
5.18 to 5.24 GHz (4 channels)
EU:
2.412 to 2.472 GHz (13 channels)
5.18 to 5.24 GHz (4
JP:
2.412 to 2.472 GHz (13 channels, OFDM)
2.412 to 2.484 GHz (14 channels, DSSS)
5.18 to 5.24 GHz (4 channels for W52)
Security:
• SSID broadcast enable/disable
• Firewall for MAC/IP/Protocol/Port
• 64
AES)
Transmission Rates:
802.11b: 1, 2, 5.5, 11
802.11a/g: 6, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 48, 54
TX Transmit Power:
802.11b:
Typ. 23±1.5 dBm @ 1 to 11 Mbps
802.11g:
Typ. 20±1.5 dBm @ 6 to 24 Mbps, Typ. 19±1.5 dBm @ 36 Mbps, Typ. 18±1.5 dBm @ 48 Mbps, Typ. 17±1.5
dBm @ 54 Mbps
802.11a:
Typ. 18±1.5 dBm @ 6 to 24 Mbps, Typ. 16±1.5 dBm @ 36 to 48 Mbps, Typ. 15±1.5 dBm @ 54 Mbps
• IP68 protected high-strength metal housing.
Product Specifications
-over-Ethernet
1D for Spanning Tree Protocol
DBPSK @ 11 Mbps
02.11a/g: 64QAM @ 54/48 Mbps, 16QAM @ 36/24 Mbps,
QPSK @ 18/12 Mbps, BPSK @ 9/6 Mbps
channels)
-based filtering
-bit and 128-bit WEP encryption, WPA/WPA2 Personal and Enterprise (IEEE 802.1X/RADIUS, TKIP, and
Mbps
Mbps
Page 8

AWK-6222 Introduction
1-4
RX Sensitivity:
802.11b:
-
802.11g:
-
80
dBm @ 36 Mbps,
802.11a:
-
79
dBm @ 36 Mbps,
Protocol Support
General Protocols: Proxy ARP, DNS, HTTP, HTTPS, IP, ICMP, SNTP, TCP, UDP, RADIUS, SNMP, PPPoE, DHCP
AP
Interface
Default Antennas:
type (male)
Connector for External Antennas:
RJ45 Ports:
X connection
Console Port:
Reset:
LED Indicators:
Alarm Contact (digital output, M12 female
1 relay output with current carrying capacity of 1
A @ 24 VDC
Digital Inputs (M12 female connector):
• +13 to +30 V for state “1”
• +3 to
• Max. input current: 8 mA
Physical Characteristics
Housing:
Weight:
Dimensions:
Installation:
Environmental Limits
Operating Temperature:
Storage Temperature:
Ambient Relative Humidity:
Power Requirements
Input Voltage:
Ethernet (IEEE 802.3af
compliant)
Connector:
Power Consumption:
Reverse Polarity Protection:
Standards and
Safety:
Hazardous Location:
EMC:
Radio:
Note: Please check Moxa’s web
MTBF
Time:
Warranty
Warranty Period:
Details:
97 dBm @ 1 Mbps, -94 dBm @ 2 Mbps, -92 dBm @ 5.5 Mbps, -90 dBm @ 11 Mbps
93 dBm @ 6 Mbps, -91 dBm @ 9 Mbps, -90 dBm @ 12 Mbps, -88 dBm @ 18 Mbps, -84 dBm @ 24 Mbps, -
-76 dBm @ 48 Mbps, -74 dBm @ 54 Mbps
90 dBm @ 6 Mbps, -89 dBm @ 9 Mbps, -89 dBm @ 12 Mbps, -85 dBm @ 18 Mbps, -83 dBm @ 24 Mbps, -
-75 dBm @ 48 Mbps, -74 dBm @ 54 Mbps
-only Protocols: ARP, BOOTP, DHCP, STP/RSTP (IEEE 802.1D/w)
2 dual-band omni-directional antennas, 5 dBi at 2.4 GHz, 2 dBi at 5 GHz, N-
N-type (female)
2, 10/100BaseT(X), auto negotiation speed, F/H duplex mode, and auto MDI/MDI-
RS-232 (waterproof RJ45-type)
Present
PWR, FAULT, STATE, WLAN1, WLAN2, LAN1, LAN2
connector):
2 electrically isolated inputs
-30 V for state “0”
Metal, IP68 protection
1.8 kg
224 x 148 x 67 mm (8.82 x 5.82 x 2.62 in)
Wall mounting (standard), DIN-rail mounting (optional), pole mounting (optional)
-40 to 75°C (-40 to 167°F)
-40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F)
5% to 100% (non-condensing)
12 to 48 VDC, redundant dual DC power inputs or 48 VDC Power-over-
M12 male connector with A-coding
12 to 48 VDC, 1.066 to 0.312 A
Present
Certifications
UL 60950-1, EN 60950-1
UL/cUL Class I Division 2, ATEX Zone 2
EN 301 489-1/17, FCC Part 15 Subpart B, EN 55022/55024
EN 300 328, EN 301 893, TELEC, FCC ID SLE-WAPA003
site for the most up-to-date certification status.
(mean time between failures)
284,072 hrs
See www.moxa.com/warranty
5 years
Page 9
AWK-6222 Introduction
1-5
ATTENTION
The AWK
body. The AWK
trained technician is required to safely
deploy AWK
ATTENTION
When the LEDs for
one
issue
Firmware
Recovery
Patent http://www.moxa.com/doc/operations/Moxa_Patent_Marking.pdf
-6222 is NOT a portable mobile device and should be located at least 20cm away from the human
-6222 is NOT designed for the general consumer. A well-
-6222s and establish a wireless network.
Functions
LED Indicators
The LEDs on the front panel help you to quickly identity the status and wireless settings of the AWK-6222. The
following table gives a summary:
LED Color State Description
PWR Green
FAULT Red
STATE Green/Red
WLAN 1/
WLAN 2
LAN 1/
LAN 2
Green/Amber
Yellow/Green
On Power is being supplied (from power input 1 or 2, or PoE)
Off Power is not being supplied.
On Relay output is triggered by an event.
Blinking (slow
at 1-second
intervals)
Blinking (fast
at 0.5-second
intervals)
Off Normal status.
Green
Green
(blinking at
1-second
intervals)
Red Booting or Error condition.
Green On WLAN is functioning in client/slave mode.
Green Blinking WLAN’s is transmitting data in client/slave mode.
Amber On WLAN is functioning in AP/bridge/master mode.
Amber
Blinking
Off WLAN is not in use or not working properly.
Yellow On LAN port’s 10 Mbps link is active.
Yellow Blinking Data is being transmitted at 10 Mbps.
Yellow Off LAN port’s 10 Mbps link is inactive.
Green On LAN port’s 100 Mbps link is active.
Green Blinking Data is being transmitted at 100 Mbps.
Cannot get an IP address from the DHCP server.
IP address conflict.
System startup is complete and the system is in operation.
The Wireless Search Utility has located the AWK.
WLAN’s is transmitting data in AP/bridge/master mode.
-second intervals, it means that the system failed to boot. This may be due to an improper operation or
s such as an unexpected shutdown during a firmware update. To recover the firmware, refer to “
” in Chapter 6.
STATE (Green), FAULT, WLAN1, and WLAN2 all light up simultaneously and blink at
Page 10
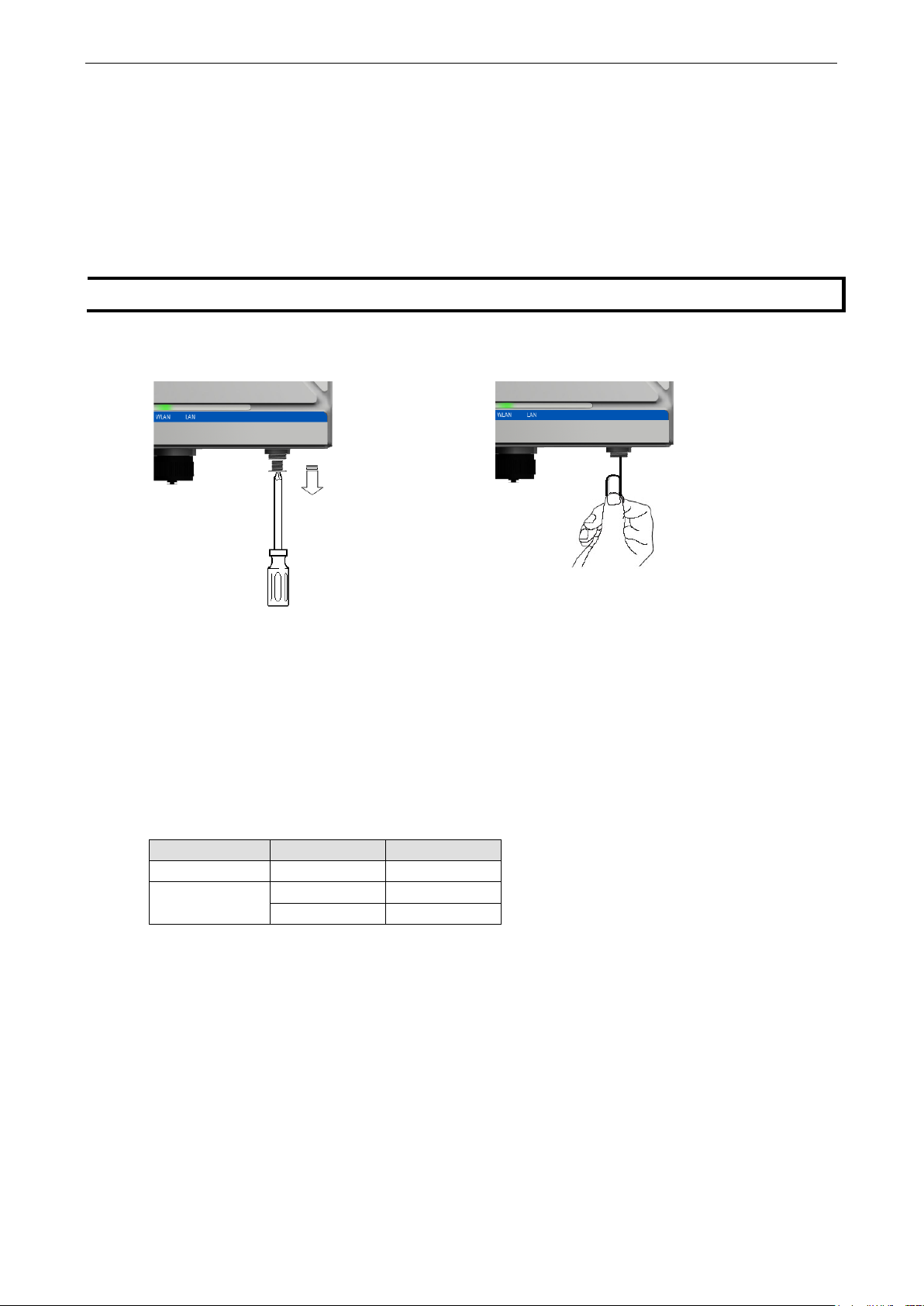
AWK-6222 Introduction
1-6
NOTE
Each time the system is turned on the reset button
S
STEP 2
reset button
Reset Button
The RESET button is located on the bottom panel of the AWK-6222. You can reboot the AWK-6222 or reset it
to factory default settings by pressing the RESET button with a pointed object such as an unfolded paper clip.
• System reboot: Hold the RESET button down for less than 5 seconds and then release.
• Reset to factory default: Hold the RESET button down for over 5 seconds until the STATE LED starts
blinking green. Release the button to reset the AWK-6222.
TEP 1: Remove the reset button cover.
Relay (Digital Output)
The AWK-6222 has one relay output, which consists of the 2 contacts for the 8-pin M12 connector on the
bottom panel, as shown below. These relay contacts forward system failure and user-configured events.
can be disabled for 60 seconds.
: Using a pointed object, press and hold the
.
The two wires attached to the relay contacts form an open circuit when a user-configured event is triggered. If
a user-configured event does not occur, the relay circuit will remain closed. For safety reasons, the relay circuit
is kept open when the AWK-6222 is not powered.
The AWK-6222’s relay status is shown below:
Power Status Event Relay
Off – Open
On Yes Open
No Short
Page 11
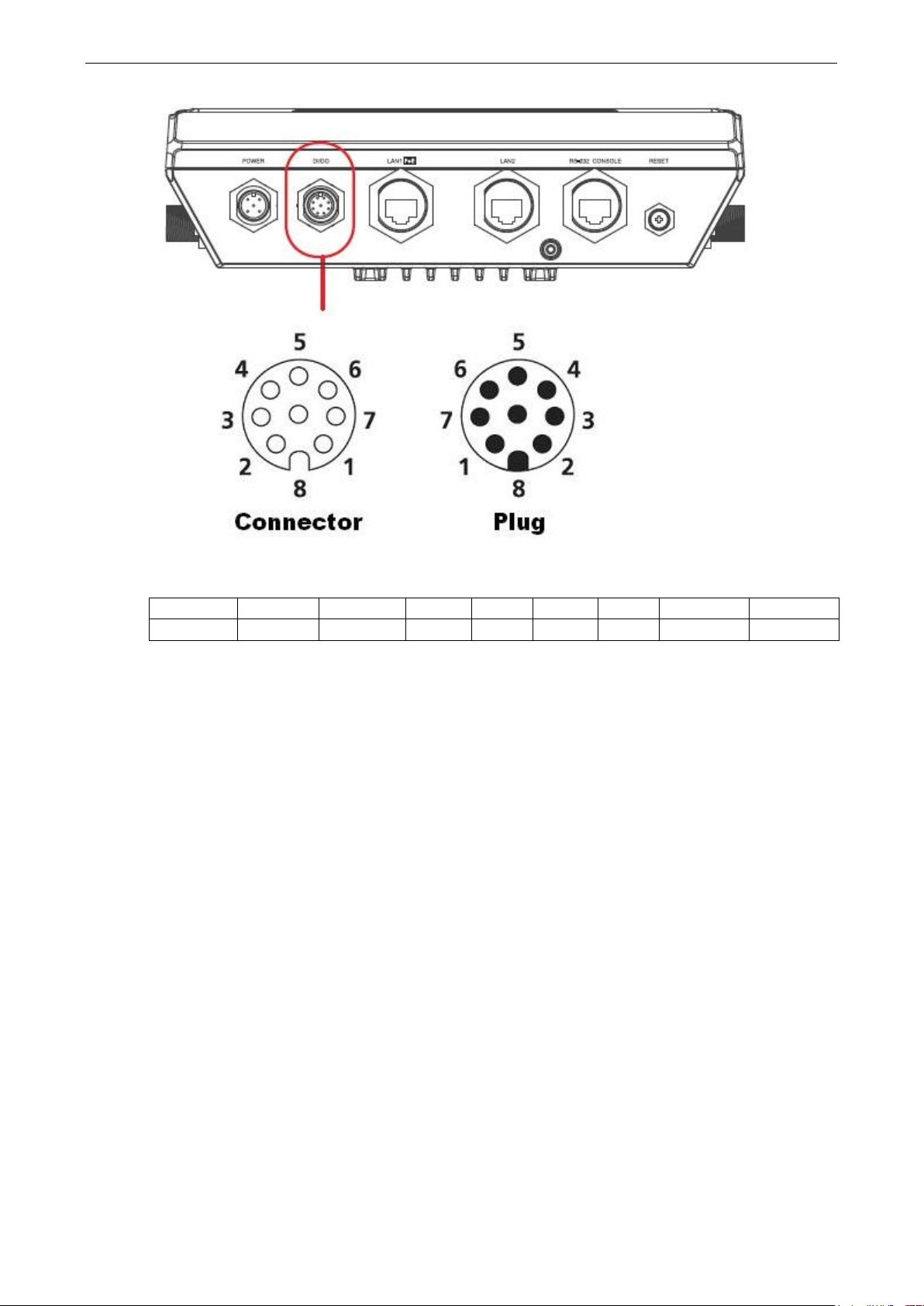
AWK-6222 Introduction
1-7
Digital Inputs and Relay-out Pin Assignment (8-pin M12 connector)
PIN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Function DOUT_I DOUT_O DI0+ DI0- DI1+ DI1- reserved reserved
Page 12

2
2. Getting Started
This chapter explains how to install Moxa’s AirWorks AWK-6222 for the first time, quickly set up your wireless
network, and test whether the connection is running properly. The function guide helps you find the functions
that you need easily.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
First-time Installation and Configuration
Communication Testing
Function Guide Map
Page 13

AWK-6222 Getting Started
2-2
NOTE
The information technology equipment (ITE) power supply unit is to be connected only to PoE networks without
routing it to the outside plant.
NOTE
After yo
be
reset to
First-time Installation and Configuration
Before installing the AWK-6222, make sure that all items in the Package Checklist are in the box. In addition,
you will need access to a notebook computer or PC equipped with an Ethernet port. The AWK-6222 has a
default IP address that you must use when connecting to the device for the first time.
Step 1: Select the power source.
The AWK-6222 can be powered by DC power input or PoE (Power over Ethernet).
Step 2: Connect the AWK-6222 to a notebook or PC.
Since the AWK-6222 supports MDI/MDI-X auto-sensing, you can use either a straight-through cable or
crossover cable to connect the AWK-6222 to a computer. If the LED indicator on the AWK-6222’s LAN port
lights up, it means the connection is established.
Step 3: Set up the computer’s IP address.
Set an IP address on the same subnet as the AWK-6222. Since the AWK-6222’s default IP address is
192.168.127.253, and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, you should set the IP address of the computer to
192.168.127.xxx.
Step 4: Use the web-based manager to configure AWK-6222
Open your computer’s web browser and type in http://192.168.127.253 in the address field to access the
homepage of the web-based Network Manager. Before the homepage opens, you will need to enter the
username and password as shown in the following figure. For first-time configuration, enter the default
username and password and then click on the Login button:
u select Maintenance Load Factory Default and click the Submit button, the AWK-6222 will
factory default settings and the IP address will also reset to 192.168.127.253.
Page 14

AWK-6222 Getting Started
2-3
NOTE
Default U
For security reasons, we strongly recommend changing the default password. T
Password
NOTE
Clicking on
” and a blinking
reminder will be displayed on the upper
To make the changes effective, click
The
AWK
Step 5: Select the operation mode
By default, the AWK-6222’s operation mode is set to Wireless redundancy. You can change the setting at
Wireless Settings
Detailed information about configuring the AWK-6222’s operation mode can be found in Chapter 3.
Step 6: Test communications.
sername and Password:
Username: admin
Password: root
o do so, select Maintenance
, and then follow the on-screen instructions.
Submit will apply your changes and refresh the web page. The string “(Updated)
-right corner of the page as shown below.
Restart and then Save and Restart after you change the settings.
-6222 will take about 30 seconds to complete its restart process.
Operation mode if you would like to use Wireless bridge or AP-Client mode instead.
In the following sections we will describe two test methods that can be used to ensure that a network
connection has been established.
Communication Testing
After installation, you can run a sample test to make sure the AWK-6222 and wireless connection are
functioning normally. Two testing methods are explained in the following sections. Use the first method if you
are using only one AWK-6222 device, and use the second method if you are using two or more AWK-6222s.
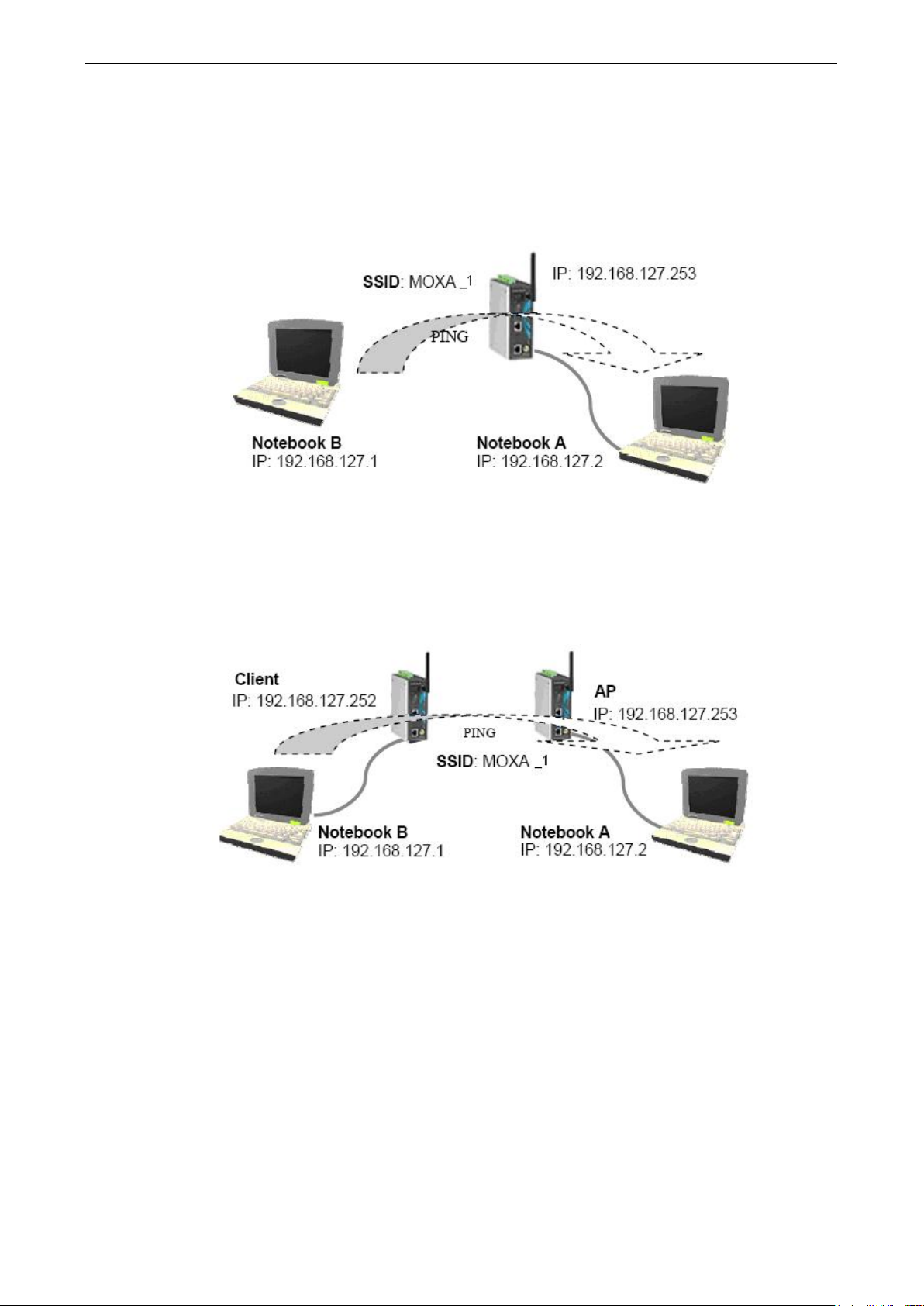
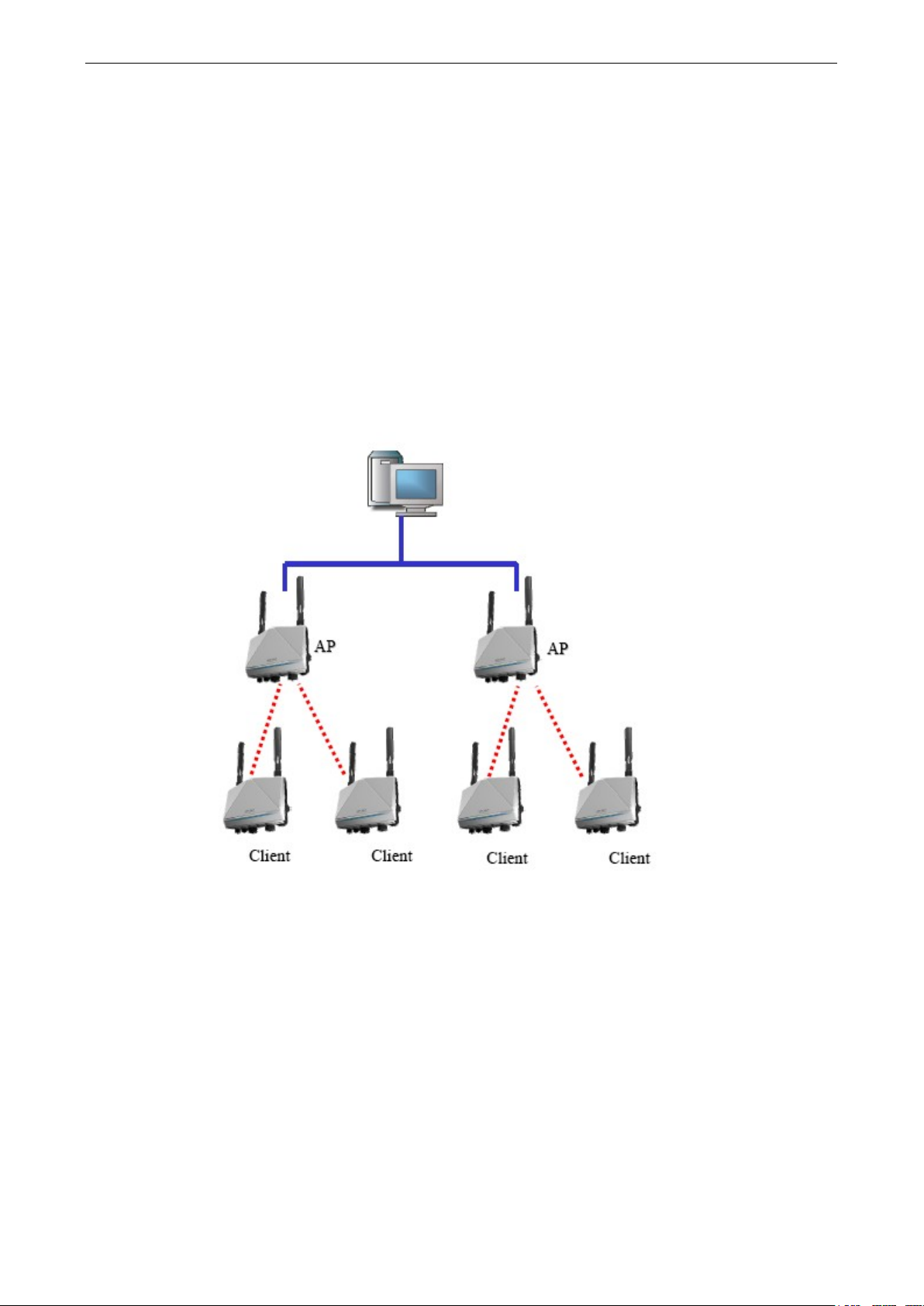
Testing Method for One AWK-6222 with AP-Client Operation Mode
If you are only using one AWK-6222, you will need a second notebook computer equipped with a WLAN card.
Configure the WLAN card to connect to the AWK-6222 (NOTE: the default SSID is MOXA_1), and change the
IP address of the second notebook (B) so that it is on the same subnet as the first notebook (A), which is
connected to the AWK-6222.
Page 15
AWK-6222 Getting Started
2-4
After configuring the WLAN card, establish a wireless connection with the AWK-6222 and open a DOS window
on Notebook B. At the prompt, type
ping <IP address of notebook A>
and then press Enter (see the figure below). A “Reply from IP address …” response means the communication
was successful. A “Request timed out.” response means the communication failed. In this case, check the
configuration to make sure the connections are correct.
Testing Method for Two or More AWK-6222s with AP-Client Operation Mode
If you have two or more AWK-6222s, you will need a second notebook computer (B) equipped with an Ethernet
port. Use the default settings for the first AWK-6222 connected to notebook A and change the second or third
AWK-6222 connected to notebook B to Client mode. Then, configure the notebooks and AWK-6222s as
illustrated below:
After setting up the testing environment, open a DOS window on notebook B. At the prompt, type
ping <IP address of notebook A>
and then press Enter. A “Reply from IP address …” response means the communication was successful. A
“Request timed out” response means the communication failed. In this case, recheck the configuration to make
sure the connections are correct.
Page 16
AWK-6222 Getting Started
2-5
A quick overview of the AWK-6222’s status
Essential settings related to establishing
Advanced features to support additional
Real-time status information to monitor
Functions to maintain the AWK-6222 and
diagnose the network
On-demand functions to support the
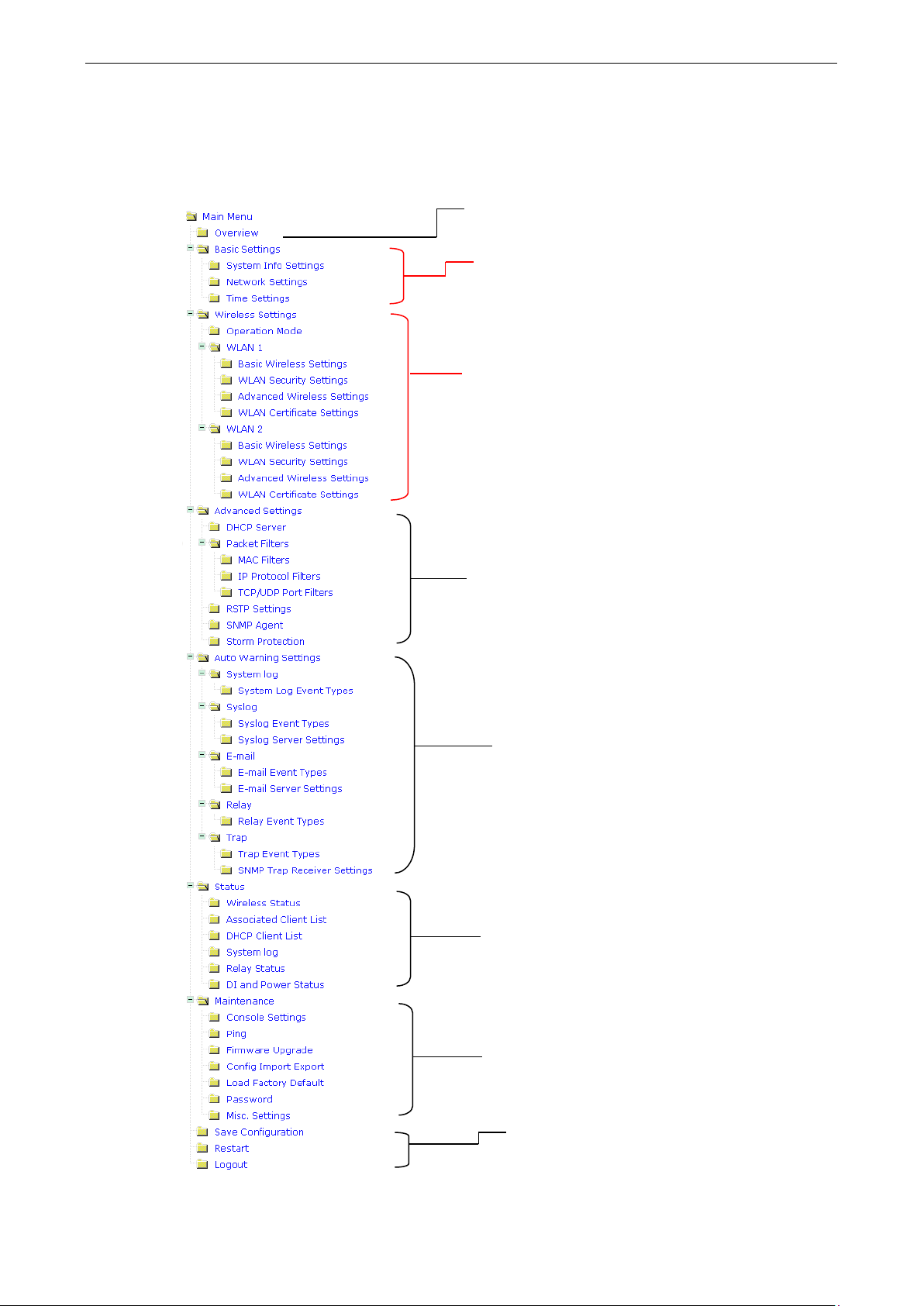
Function Guide Map
The management functions are organized in a tree and shown in the left field of the web-based management
console. You can efficiently locate the function you need with the following guiding map.
Basic settings for administering the AWK-6222
a wireless network
network management and secure wired and
wireless communication
* These advanced functions are all optional.
Application-oriented device management
functions to set up events, traps, and
reactions via relay warning, e-mail and
SNMP notification
* These functions are all optional.
wired/wireless network performance,
advanced services, and device
management functions
operations of web-based console management
Page 17

3
operation mode’s
Slave mode only)
Redundant AP, AP,
3. Web Console Configuration
In this chapter, we explain each item in the web-based configuration and management tool. Moxa’s
easy-to-use management functions will help you set up your AWK-6222 as well as establish and maintain your
wireless network easily.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Configuration by Web Browser
Overview
Basic Settings
System Info Settings
Network Settings
Time Settings
Wireless Settings
Operation Mode
Enabling Non-Redundant (Single RF) AP
WLAN Security Settings
Advanced Wireless Settings
WLAN Certification Settings (for EAP-TLS in
Redundant Client, Client or Slave mode only)
Advanced Settings
DHCP Server (for AP-Client
AP mode only)
Packet Filters
RSTP Settings (for Master or
SNMP Agent
Storm Protection
Auto Warning Settings
System Log
Syslog
E-mail
Relay
Trap
Status
Wireless Status
Associated Client List (for
or Master Mode only)
DHCP Client List (for AP mode only)
System Log
Relay Status
DI and Power Status
Maintenance
Console Settings
Ping
Firmware Upgrade
Config Import Export
Load Factory Default
Password
Misc. Settings
Save Configuration
Restart
Logout
Page 18
AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-2
NOTE
To use the AWK-6222’s management and monitoring functions from a PC host connected to the same LAN as
the AWK
6222 are on the same logical subnet. Similarly,
if the AWK
nfigured for other VLAN settings, you must make sure your PC host is on the management
VLAN.
The Moxa AWK
Configuration by Web Browser
Moxa AWK-6222’s web browser interface provides a convenient way to modify its configuration and access the
built-in monitoring and network administration functions. The recommended web browser is Microsoft
Internet Explorer 5.5 or higher with JVM (Java Virtual Machine) installed.
-6222, you must make sure that the PC host and AWK-
-6222 is co
-6222’s default IP is 192.168.127.253.
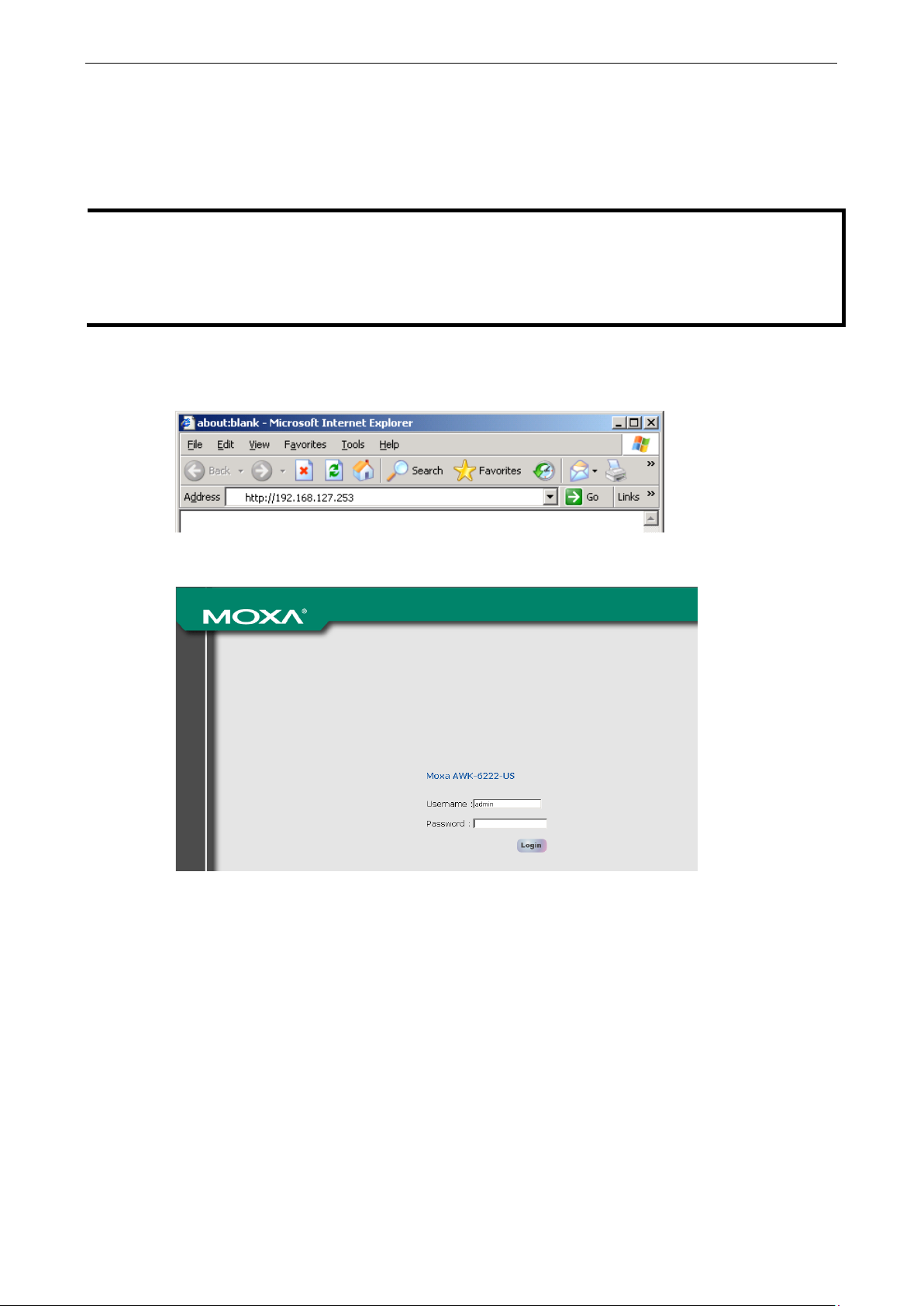
To access the AWK-5222’s web-based console management:
1. Open your web browser (e.g. Internet Explorer) and type the AWK-6222’s IP address in the address field.
Then press Enter to establish the connection.
2. In the web console login page, enter the password (the default Username is admin and the Password is
root if a new password has not been set.) and then click Login to continue.
®
You may need to wait a few moments for the web page to download onto your computer. The model name and
IP address of your AWK-6222 are both shown on the title of web page title. This information can help you
identify multiple AWK-6222s.
You can use the menu tree on the left panel of the window to open the function pages to access each of
AWK-6222’s functions.
Page 19

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-3
ATTENTION
The model name of the AWK
XX where XX indicates the country code. The country
code represents the AWK
as an example in
the following figures. The country code of model name on the screen may vary if you are using a different
version (band) AWK
ATTENTION
For
In the following sections, we will review each of the AWK-6222’s management functions in detail. You can also
get a quick overview of these functions in the “Function Guide Map” section of Chapter 2.
security reasons, you will need to log back into the AWK-6222 after a 5-minute time-out.
Overview
The Overview page summarizes the AWK-6222’s current status. The information is categorized into several
groups: System info, Device info and 802.11 info.
-6222 is shown as AWK-6222-
-6222 version and which bandwidth it uses. We use AWK-6222-US
-6222.
Page 20
AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-4
record contact information
Basic Settings
The Basic Settings group includes the most commonly used settings required by administrators to maintain and
control the AWK-6222.
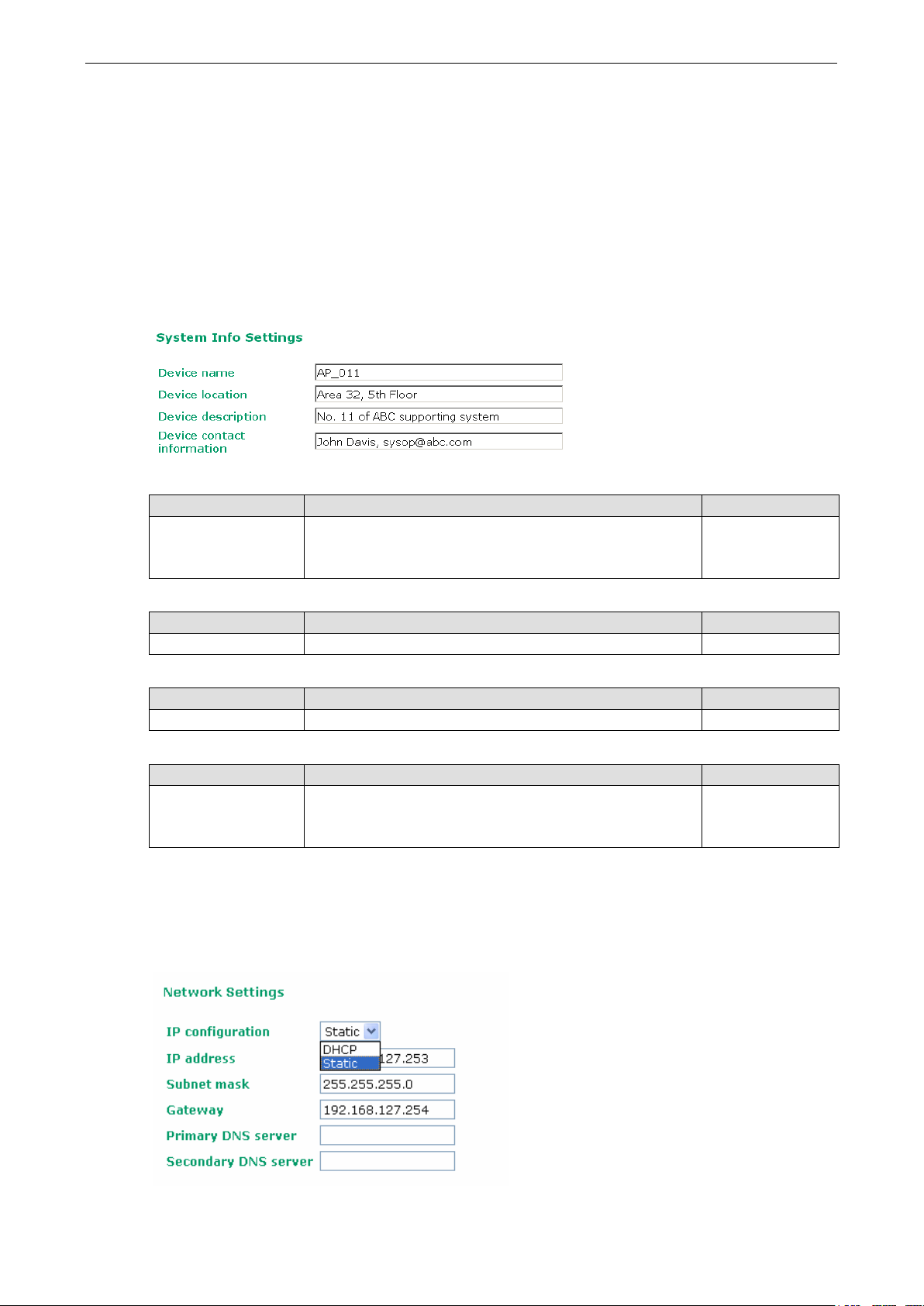
System Info Settings
The System Info items, especially Device name and Device description, are displayed and included on the
Overview page, SNMP information, and alarm emails. Setting System Info items makes it easier to identify
the different AWK-6222s connected to your network.
Device name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 Characters This option is useful for specifying the role or application of
different AWK-6222 units.
AWK-6222_<Serial
No. of this
AWK-6222>
Device location
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 Characters To specify the location of different AWK-6222 units. None
Device description
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 Characters Use this space to record more detailed description of AWK-6222 None
Device contact information
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 Characters To provide information about whom to contact in order to
Network Settings
The Network Settings configuration allows you to modify the usual TCP/IP network parameters. An explanation
of each configuration item is given below.
None
resolve problems. Use this space to
of the person responsible for maintaining this AWK-6222.
Page 21

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-5
The IP address of the DNS Server used by your network. After
(e.g., http://ap11.abc.com) in your browser’s
address field instead of entering the IP address. The Secondary
IP configuration
Setting Description Factory Default
DHCP The AWK-6222’s IP address will be assigned automatically by
the network’s DHCP server
Static Set up the AWK-6222’s IP address manually.
IP address
Setting Description Factory Default
AWK-6222’s IP address Identifies the AWK-6222 on a TCP/IP network. 192.168.127.253
Subnet mask
Setting Description Factory Default
AWK-6222’s subnet
mask
Gateway
Setting Description Factory Default
AWK-6222’s default
gateway
Identifies the type of network to which the AWK-6222 is
connected (e.g., 255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, or
255.255.255.0 for a Class C network).
The IP address of the router that connects the LAN to an
outside network.
Static
255.255.255.0
None
Primary/ Secondary DNS server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address of Primary/
Secondary DNS server
Time Settings
The AWK-6222 has a time calibration function based on information from an NTP server or user specified Date
and Time information. Functions such as Auto warning can add real-time information to the message.
None
entering the DNS Server’s IP address, you can input the
AWK-6222’s URL
DNS server will be used if the Primary DNS server fails to
connect.
Current local time shows the AWK-6222’s system time when you open this web page. You can click on the
Set Time button to activate the update after adjusting the date and time parameters. An “(Updated)” string
will appear to indicate that the change is complete. Local time settings will be immediately activated in the
system without running Save and Restart.
Page 22
AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-6
NOTE
The AWK
for the
AWK
k does not have an Internet
connection for
GMT (Greenwich
ATTENTION
Changing the time zone will automatically adjust the
Time zone
before setting the
involves advancing clocks (usually 1 hour) during the summer
IP or Domain address of NTP time server. The 2nd time will be
the time is updated from
Current local time
Setting Description Factory Default
User adjustable time The date and time parameters allow configuration of the local
Time zone
Setting Description Factory Default
User selectable time
zone
Daylight saving time
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/ Disable Daylight saving time (also known as DST or summer time)
-6222 has a real time clock (RTC). Users are strongly recommended to update the Local time
-6222 after initial setup or long-term shutdown, especially when the networ
accessing the NTP server or there is no NTP server on the LAN.
None
time with immediate activation.
The time zone setting allows conversion from
Mean Time) to local time.
Current local time. You should configure the
Current local time.
(yyyy/mm/dd
hh:mm:ss format;
24-hour format.)
GMT (Greenwich
Mean Time)
Disable
time to provide an extra hour of daylight in the afternoon.
When Daylight saving time is enabled, the following parameters can be shown:
• The Starts at parameter allows users to enter the date that daylight saving time begins.
• The Stops at parameter allows users to enter the date that daylight saving time ends.
• The Time offset parameter indicates how many hours forward the clock should be advanced.
Time server 1/ 2
Setting Description Factory Default
The 1st/ 2nd time
server IP/Name
Query period
Setting Description Factory Default
Query period time
(1- 9999 seconds)
used if the 1st NTP server fails to connect.
This parameter determines how often
the NTP server.
None
600 (seconds)
Page 23
AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-7
Wireless Settings
The essential settings for wireless networks are presented in this function group. Settings must be properly set
before establishing your wireless network.
Operation Mode
The AWK-6222 supports three operation modes that are used for different wireless network applications:
Wireless Redundancy
In traditional architectures, most vendors only provide a single RF AP and Client, in which the AP connects one
or more Clients to the network. Since the AP and Client are connected by a single RF connection, if the RF
connection is disconnected the system or network behind the Client will be disconnected, too.
With the new wireless redundancy technology, you can set up a redundant wireless connection between a
redundant client device and a redundant AP device. The redundant structure involves using the
AWK-6222’s two RF modules to set up two independent wireless connections between the redundant client
and redundant AP devices. If either of the two wireless connections fails, the other wireless connection will
continue transmitting packets between the redundant client and redundant AP devices. In addition to
carrying one or more redundant clients, standard single RF clients can also associate with the redundant AP.
One of the biggest advantages of the AWK-6222’s wireless redundancy mode is that you can expect “zero data
loss.”
Page 24

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-8
The following figure shows the Wireless Redundancy operation mode:
WLAN Operation mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Redundant AP AP with Dual RF redundancy capable of serving dual RF clients. Redundant AP
Redundant Client Dual RF redundant clients can join dual RF redundant APs.
Page 25
AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-9
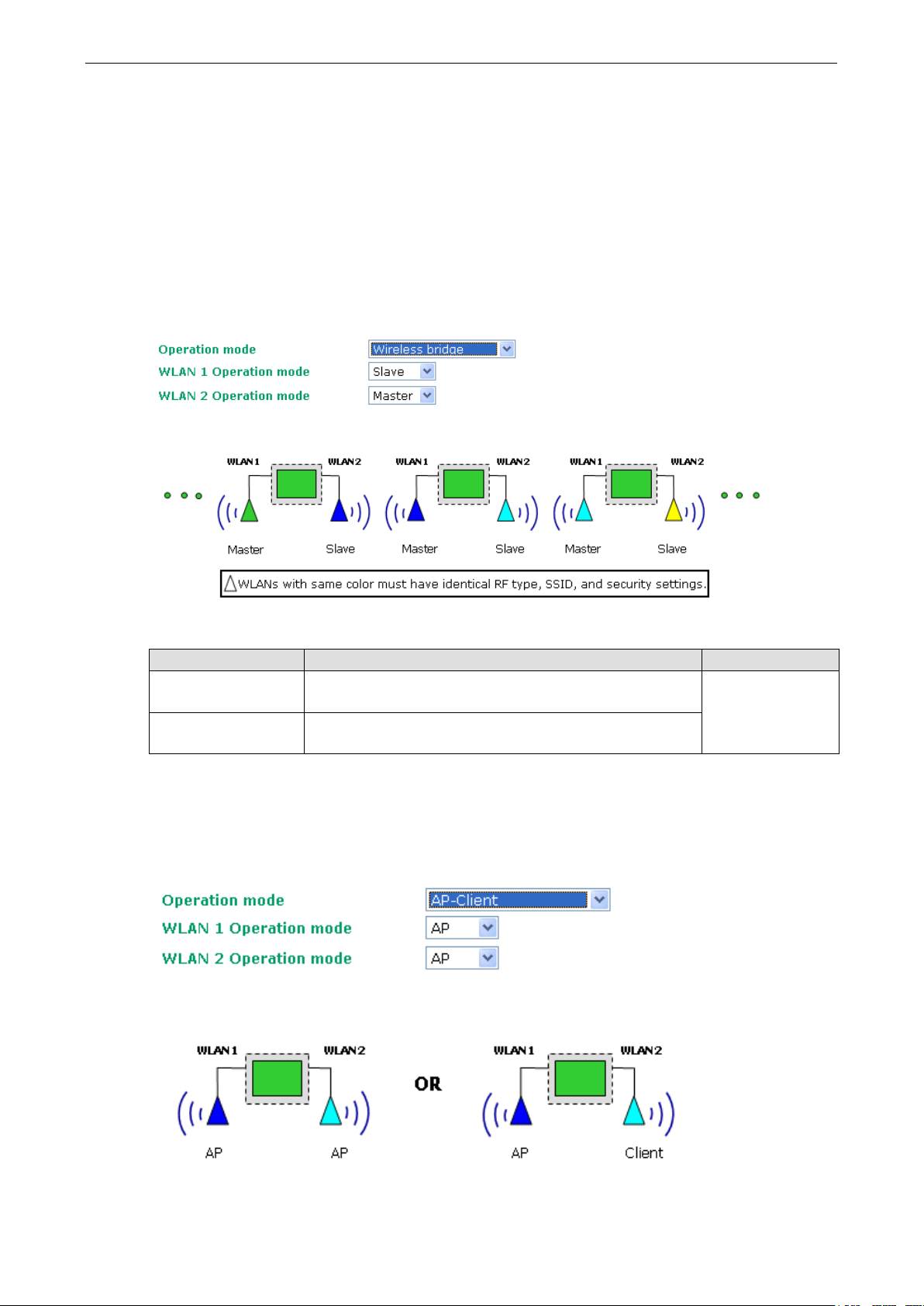
Wireless Bridge
A bridge is a network component that connects two networks. AWK-6222’s bridge operation is based on the AP
(master) and Client (Slave) concept. Both sides of the connection must have the same RF type, SSID, and
security settings.
For single RF mesh networks, we can use WDS to establish a static bridge link. In this case, the APs at both ends
of the WDS link must be configured manually with each other’s MAC addresses. The performance of a single RF
bridge will be poor if more nodes are added.
The AWK-6222’s dual RF bridge concept is different from using a single RF, because the AWK-6222 has dual
RFs, and offer users a cascade link to bridge the two ends without narrowing down the throughput.
WLAN 1/WLAN 2 Operation mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Master Master can build a connection with a Slave that has the same
RF type, SSID, and security settings.
Slave Slave can build a connection with a master that has the same
RF type, SSID, and security settings.
AP for WLAN 1
Master for WLAN 2
AP-Client
AP-Client mode provides a more flexible topology to allow the user to configure the 2 RF modules for an AP or
Client.
Page 26
AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-10
The following table lists the combinations for AP-Client WLANs:
WLAN 1 WLAN 2 Allowable Setting
AP AP Allow
AP Client Allow
Client Client Do not allow
Client AP Allow
Enabling Non-Redundant (Single RF) AP
WLAN 1/WLAN 2
This section describes WLAN1 and WLAN2 settings. Each WLAN setting must be configured separately.
Some applications already have existing clients in the environment. The AWK-6222 can not only carry dual RF
clients to the Ethernet LAN, but also single RF or existing Clients. This function is available in Wireless
Redundancy mode’s Redundant AP, or Wireless Bridge mode’s Master page. Descriptions of other
operation modes can be found in the “Basic Wireless Settings” section.
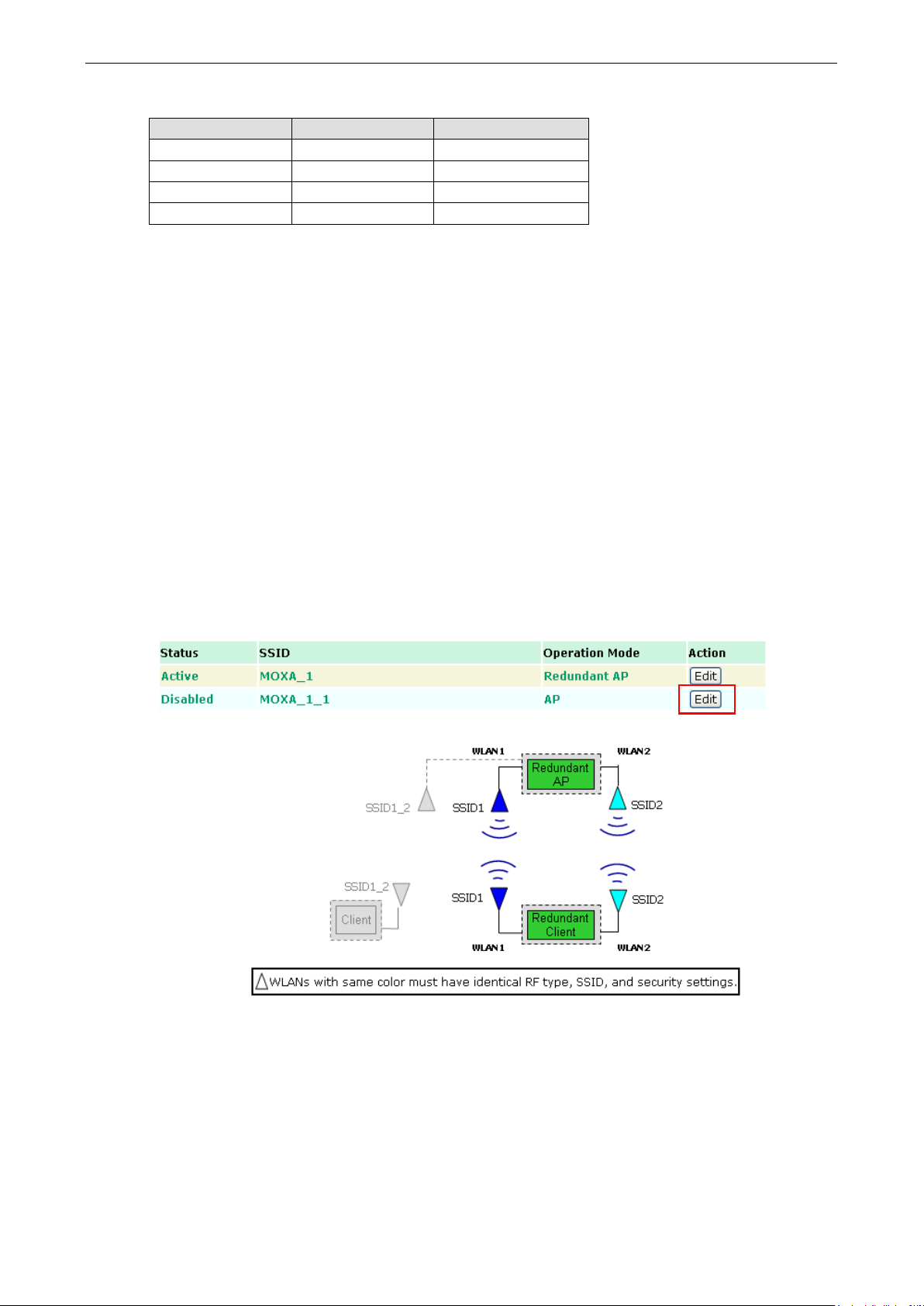
Wireless Redundancy Mode’s Redundant AP
This AP functionality can be set to Enable or Disable on the basic wireless settings page. If AP functionality is
set to Enable, the Status will appear as Active, which means that the WLAN is ready to operate in the operation
mode you are setting. For AP functionality settings, click on Edit for the AP operation mode, as described on the
following page.
Page 27

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-11
You can Enable or Disable the AP functionality in the Edit mode.
AP functionality
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable Redundant AP cannot serve non-redundant Clients. Disable
Enable Redundant AP can serve non-redundant Clients.
Wireless Bridge Mode’s Master
You are allowed to edit this AP functionality to Enable or Disable on the basic wireless settings page. If AP
functionality is set to Enable, the Status will appear as Active, which means that the WLAN is ready to operate
in the operation mode you are setting. For AP functionality settings, click on Edit, as described below.
You can Enable or Disable the AP functionality in the Edit mode.
Page 28

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-12
NOTE
Please note that
mode is not available. WLAN 2’s
RF type does support
channels vary
The SSID of a client and the SSID of the AP must be identical for
_1 for WLAN1,
AP functionality
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable Master can only serve a single slave. Disable
Enable Master can serve single RF clients.
Basic Wireless Settings
The following figure shows the Basic Wireless Settings page. The parameters and options are described below:
RF type
Setting Description Factory Default
A Supports IEEE802.11a standard only B/G Mixed
B Supports IEEE802.11b standard only
G Supports IEEE802.11g standard only
B/G Mixed Supports both IEEE 802.11b/g standards, but 802.11g’s
WLAN 1’s RF type supports 802.11b/g mode only; 802.11a
802.11a/b/g.
throughput may suffer when 802.11b clients are on the
network
Channel (for Redundant AP, AP, or Master Mode only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Available
with RF type
SSID
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 Characters
SSID broadcast (for Redundant AP, AP, or Master Mode only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/ Disable Whether the SSID is broadcast or not. Enable
AWK-6222 plays the role of wireless AP. 6 (in B/G Mixed
mode)
MOXA
them to communicate with each other.
MOXA_2 for WLAN2
Page 29

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-13
NOTE
If your device uses
button
on basic wireless settings page. The button supports site survey and pops up a dialog box
information for available APs, as
SSID of an entity and bring
the value of its SSID onto the SSID fi
button will
re
NOTE
When you switch to
overview page. Please click on
-scan and update the table.
redundant Client, Client, or Slave mode, you can find an additional Site Survey
listing the
shown in the following figure. You can click on the
eld of the Basic Wireless Settings page. Clicking on the Refresh
WLAN Security Settings
The following figure shows the WLAN1/2 Security Settings page. The parameters and options are described
below:
The AWK-6222 provides four standardized wireless security modes: Open, WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy),
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2. Several types of security models are available in AWK-6222 by
selecting Security mode and WPA type:
• Open: No authentication, no data encryption.
• WEP: Static WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) keys must be manually configured.
• WPA/WPA2-Personal: also known as WPA/WPA2-PSK. You need to specify the Pre-Shared Key in the
Passphrase field, which will be used by the TKIP or AES engine as a master key to generate keys that
actually encrypt outgoing packets and decrypt incoming packets.
• WPA/WPA2-Enterprise: also called WPA/WPA2-EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol). In addition to
device-based authentication, WPA/WPA2-Enterprise enables user-based authentication via IEEE802.1X.
The AWK-6222 can support three EAP methods: EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, and EAP-PEAP.
Wireless Redundancy mode, you will see an additional WLAN Security Setting
Edit to modify WLAN security settings.
Page 30

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-14
Security mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Open No authentication Open
WEP Static WEP is used
WPA WPA is used
WPA2 Fully supports IEEE802.11i with “TKIP/AES + 802.1X”
Open
For security reasons, it is highly recommended that the security mode should be set to an option other than
Open System. When the security mode is set to Open System, no authentication or data encryption will be
performed.
WEP
According to the IEEE802.11 standard, WEP can be used for authentication and data encryption
(confidentiality). Shared (or Shared Key) authentication type is used if WEP authentication and data
encryption are both needed. Normally, Open (or Open System) authentication type is often used when WEP
data encryption is run with authentication.
When WEP is enabled as a security mode, the length of a key (so-called WEP seed) can be specified as 64/128
bits, which is actually a 40/104-bit secret key with a 24-bit initialization vector. The AWK-6222 provides 4
entities of WEP key settings that can be selected to use with Key index. The selected key setting specifies the
key to be used as a send-key for encrypting traffic from the AP side to the wireless client side. All 4 WEP keys
are used as receive-keys to decrypt traffic from the wireless client side to the AP side.
The WEP key can be presented in two Key type, HEX and ASCII. Each ASCII character has 8 bits, so a 40-bit
(or 64-bit) WEP key contains 5 characters, and a 104-bit (or 128-bit) key has 13 characters. In hex, each
character uses 4 bits, so a 40-bit key has 10 hex characters, and a 128-bit key has 26 characters.
Page 31

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-15
Authentication type
Setting Description Factory Default
Open Data encryption is enabled, but no authentication. Open
Shared Data encryption and authentication are both enabled.
Key type
Setting Description Factory Default
HEX Specifies WEP keys in hex-decimal number form HEX
ASCII Specifies WEP keys in ASCII form
Key length
Setting Description Factory Default
64 bits Uses 40-bit secret keys with 24-bit initialization vector 64 bits
128 bits Uses 104-bit secret key with 24-bit initialization vector
Key index
Setting Description Factory Default
1-4 Specifies which WEP key is used Open
WEP key 1-4
Setting Description Factory Default
ASCII type:
64 bits: 5 chars
128 bits: 13chars
HEX type:
64 bits: 10 hex chars
128 bits: 26 hex chars
A string that can be used as a WEP seed for RC4 encryption
engine.
None
WPA/WPA2-Personal
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) and WPA2 are significantly improved encryption methods over WEP. WPA is a
security standard based on 802.11i draft 3, while WPA2 is based on the fully ratified version of 802.11i. The
initial vector is transmitted, encrypted, and enhanced with its 48 bits, twice as long as WEP. The key changes
regularly so that true session is secured.
Even though AES encryption is only included in the WPA2 standard, it is widely available in the WPA security
mode of some wireless APs and clients as well. The AWK-6222 also supports AES algorithms in WPA and WPA2
for better compatibility.
Personal versions of WPA/WPA2, also known as WPA/WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key), provide a simple way of
encrypting a wireless connection for high confidentiality. A Passphrase is used as a basis for encryption
methods (or cipher types) in a WLAN connection. The passphrases should be complex and as long as possible.
The number of ASCII characters of the Passphrase must be at least 8 and can go up to 63. For security reasons,
disclose this passphrase to the relevant users only and change it regularly.
Page 32

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-16
*This option
NOTE
The value for key renewal
the wireless AP how often it should change the encryption keys. Usually the
security level will be higher if you set this value shorter so that the encryption keys change more often. Default
value is 3600 seconds
WPA Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Personal Provides Pre-Shared Key-enabled WPA and WPA2 Personal
Enterprise Provides enterprise-level security for WPA and WPA2
Encryption method
Setting Description Factory Default
TKIP Temporal Key Integrity Protocol is enabled TKIP
AES Advance Encryption System is enabled
Mixed* Provides TKIP broadcast key and TKIP+AES unicast key for
some legacy AP clients. This option is rarely used.
is available in Redundant AP, AP, or Master mode only, and
cannot support AES-enabled clients.
Passphrase
Setting Description Factory Default
8 – 63 characters Master key to generate keys for encryption and decryption None
Key renewal (for Redundant AP, AP, or Master Mode only)
Setting Description Factory Default
60 – 86400 seconds
(1 minute to 1 year)
Specifies the time period of group key renewal 3600 (seconds)
instructs
(6 minutes). Longer time periods can be considered if traffic is low.
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise (for Redundant AP, AP, or Master Mode)
By selecting WPA type as Enterprise, you can use EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol), a framework
authentication protocol used by 802.1X to provide network authentication. In these Enterprise-level security
modes, a back-end RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server is needed if IEEE 802.1X
functionality is enabled in WPA /WPA2. The IEEE 802.1X protocol also offers the possibility of carrying out an
efficient connection authentication in a large-scaled network. It is not necessary to exchange keys or pass
phrases.
Page 33

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-17
*This option
WPA Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Personal Provides Pre-Shared Key-enabled WPA and WPA2 Personal
Enterprise Provides enterprise-level security for WPA and WPA2
Encryption method
Setting Description Factory Default
TKIP Temporal Key Integrity Protocol is enabled TKIP
AES Advance Encryption System is enabled
Mixed* Provides TKIP broadcast key and TKIP+AES unicast key for
some legacy AP clients. This option is rarely used.
is available in Redundant AP, AP, or Master mode only, and
cannot support AES-enabled clients.
Primary/ Secondary RADIUS server IP
Setting Description Factory Default
The IP address of
RADIUS server
Primary/ Secondary RADIUS port
Setting Description Factory Default
Port number Specifies the port number of the delegated RADIUS server 1812
Specifies the delegated RADIUS server for EAP None
Primary/ Secondary RADIUS shared key
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 characters The secret key shared between AP and RADIUS server None
Key renewal
Setting Description Factory Default
60 – 86400 seconds
(1 minute to 1 year)
Specifies the time period of group key renewal 3600 (seconds)
WPA/WPA2-Enterprise (for Redondant Client, Client, or Slave mode)
In a client role, the AWK-6222 can support three EAP methods (or EAP protocols): EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, and
EAP-PEAP, corresponding to WPA/WPA-Enterprise settings on the AP side.
Encryption method
Setting Description Factory Default
TKIP Temporal Key Integrity Protocol is enabled TKIP
AES Advance Encryption System is enabled
Page 34

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-18
EAP Protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
TLS Specifies Transport Layer Security protocol TLS
TTLS Specifies Tunneled Transport Layer Security
PEAP Specifies Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol, or
Protected EAP
Before choosing the EAP protocol for your WPA/WPA2-Enterpise settings on the client end, please contact the
network administrator to make sure the system supports the protocol on the AP end. Detailed information on
these three popular EAP protocols is presented in the following sections:
EAP-TLS
TLS is the standards-based successor to the Secure Socket Layer (SSL). It can establish a trusted
communication channel over a distrusted network. TLS provides mutual authentication through certificate
exchange. EAP-TLS is also secure to use. You are required to submit a digital certificate to the authentication
server for validation, but the authentication server must also supply a certificate.
You can use WLAN 1/2 WLAN Certificate Settings to import your WLAN certificate and enable EAP-TLS
on the client end.
You can check the current certificate status in Current Status if it is available.
Certificate issued to: shows the certificate user.
Certificate issued by: shows the certificate issuer.
Certificate expiration date: indicates when the certificate becomes invalid.
EAP-TTLS
It is usually much easier to re-use existing authentication systems, such as a Windows domain or Active
Directory, LDAP directory, or Kerberos realm, rather than create a parallel authentication system. As a result,
TTLS (Tunneled TLS) and PEAP (Protected EAP) are used to support the use of so-called “legacy authentication
methods.”
TTLS and PEAP work in a similar way. First, they establish a TLS tunnel, like EAP-TLS, and validate whether the
network is trustworthy with digital certificates on the authentication server. This step is run to establish a
tunnel that protects the next step (or “inner” authentication) so it is sometimes referred to as the “outer”
authentication. Then the TLS tunnel is used to encrypt an older authentication protocol that authenticates the
user for the network.
Page 35

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-19
As you can see, digital certificates are still needed for the outer authentication in a simplified form. Only a small
number of certificates are required, which can be generated by a small certificate authority. Certificate
reduction makes TTLS and PEAP much more popular than EAP-TLS.
The AWK-6222 provides some non-cryptographic EAP methods including PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP, and
MS-CHAP-V2. These EAP methods are not recommended for direct use on wireless networks. However, they
may be useful as inner authentication methods with TTLS or PEAP.
Because the inner and outer authentications can use distinct user names in TTLS and PEAP, you can use an
anonymous user name for the outer authentication, while the true user name is shown only through the
encrypted channel. Remember, not all client software supports anonymous altercation. Confirm this with the
network administrator before you enable identity hiding in TTLS and PEAP.
TTL Inner Authentication
Setting Description Factory Default
PAP Password Authentication Protocol is used MS-CHAP-V2
CHAP Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol is used
MS-CHAP Microsoft CHAP is used
MS-CHAP-V2 Microsoft CHAP version 2 is used
Anonymous
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 characters A distinct name used for outer authentication None
User name & Password
Setting Description Factory Default
User name and password used in inner authentication None
Page 36

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-20
PEAP
There are a few differences in the inner authentication procedures for TTLS and PEAP. TTLS uses the encrypted
channel to exchange attribute-value pairs (AVPs), while PEAP uses the encrypted channel to start a second EAP
exchange inside of the tunnel. The AWK-6222 provides MS-CHAP-V2 merely as an EAP method for inner
authentication.
Inner EAP protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
MS-CHAP-V2 Microsoft CHAP version 2 is used MS-CHAP-V2
Anonymous
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 characters A distinct name used for outer authentication None
User name & Password
Setting Description Factory Default
User name and password used in inner authentication None
Page 37

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-21
Advanced Wireless Settings
Additional wireless-related parameters are presented in this section to help you set up your wireless network
in detail.
Transmission Rate
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto AWK-6222 will sense and adjust the data rate automatically Auto
Available rates User can manually select a target transmission data rate
Transmission Power
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto Specifies wireless signal coverage by automatically selecting
the strength of Tx power
Full Equivalent to 100% of maximum Tx power
High Equivalent to 75% of maximum Tx power
Medium Equivalent to 50% of maximum Tx power
Low Equivalent to 25% of maximum Tx power
Beacon Interval (for Redundant AP, AP, Master mode only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Beacon Interval
(40-1000 ms)
DTIM Interval (for Redundant AP, AP, Master mode only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Data Beacon Rate
(1-16384)
This value indicates the frequency interval of the beacon 100 (ms)
This value indicates how often the AWK-6222 sends out a
Delivery Traffic Indication Message
Full
1
Fragment threshold
Setting Description Factory Default
Fragment Length
(256-2346)
This parameter specifies the maximum size a data packet
before splitting and creating a new packet
2346
Page 38

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-22
Access Point coordinates transmission and reception to ensure
NOTE
You can refer to the related
mentioned
settings. By setting these parameters properly, you can better tune the performance of your wireless network.
Distance or max. range
The distance specifies the transmission distance or max. range
communication distances of under 500 meters and disable it for
This setting can enhance communication by strengthening the
NOTE
Make sure the same
Master and Slave. When this parameter is more than 500, an optimal algorithm will be enabled to support
long
Please note that
supported.
Transmission enhancement
long
improve performance. (Select
antenna is in
EAPOL version 1 is specified in the 2001 version of 802.1X, and
RTS threshold
Setting Description Factory Default
RTS/CTS Threshold
(256-2346)
This setting determines how large a packet can be before the
efficient communication
2346
Transmission distance
Setting Description Factory Default
for transmission
(500-11000m)
Noise protection
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable The setting enhances the ability of the AWK-6222 to filter
Transmission enhancement
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable
glossaries in Chapter 5 for more detailed information about the above-
500
between two AWK devices. This parameter should be set
properly, especially for long-distance communication.
Enable
wireless interference. You should enable this option for
communication distances of over 500 meters.
Disable
AWK-6222’s transmission power. It is quite useful for
long-distance transmission or countering environmental
interference. Before enabling this option you should carefully
evaluate and measure the transmission power of whole
system, and confirm that it is still below regulatory limits.
-distance transmission.
-distance transmission is required. A high-gain antenna installed at a fixed antenna connector can also
Antenna
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto The AWK-6222 uses four antennas (two MAIN and two AUX)
MAIN 1 and MAIN 2 Diversity function is disabled. Only MAIN 1 and 2
AUX 1 and AUX 2 Diversity function is disabled. Only AUX 1 and 2 antenna is in
EAPOL Version
Setting Description Factory Default
1
2 EAPOL version 2 is specified in 802.1X-2004.
Transmission distance parameters are set in both AP and Client sides, and both
Transmission enhancement only supports 802.11b/g mode; 802.11a mode is not
is also recommended to enable communication at both ends when
Antenna at MAIN or AUX.)
and enables the diversity function for reducing multipath effect.
use.
use.
is much more commonly implemented.
Auto
1
Page 39

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-23
Turbo Roaming (for AP-Client operation mode's Client mode only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/ Disable Moxa’s Turbo Roaming can enable rapid handover when the
AWK-6222, as a client, roams among a group of APs.
When Turbo Roaming is enabled, RF type and Scan channels will be shown as follows. RF type shows the
current RF type, which this client is using now. You can set up Scan channels for the APs among which this
client is going to roam. There are three Scan channels available. Please note that the Scan channels may need
to be modified when the RF type is changed. (For example, channel 36 is not available in B, G or B/G Mix
mode.)
Disable
WLAN Certification Settings (for EAP-TLS in Redundant Client,
Client or Slave mode only)
When EAP-TLS is used, a WLAN Certificate will be required at the client end to support WPA/WPA2-Enterprise.
The AWK-6222 can support the PKCS #12, also known as Personal Information Exchange Syntax Standard,
certificate formats that define file formats commonly used to store private keys with accompanying public key
certificates, protected with a password-based symmetric key.
Current Status displays information for the current WLAN certificate imported into the AWK-6222. Nothing
will be displayed if no certificate is available.
Certificate issued to: shows the certificate user
Certificate issued by: shows the certificate issuer
Certificate expiration date: indicates when the certificate becomes invalid
You can import a new WLAN certificate in Import WLAN Certificate by following these steps:
1. Input the corresponding password (or key) in the Certificate private password field. Then click Submit
to set the password.
2. You can see the password displayed in the Certificate private password field. Then click on the Browse
button in Select certificate/key file and select the certificate file.
3. Click Upload Certificate File to import the certificate file. If it succeeds, you can see the information
uploaded in Current Certificate. If it fails, you may need to return to step 1 to set the password correctly
and then import the certificate file again.
Page 40

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-24
NOTE
The WLAN certificate will
, it can still be seen on
Current Certificate
remain after the AWK-6222 reboots. Even though it is expired
.
Advanced Settings
Several advanced functions are available to increase the functionality of your AWK-6222 and wireless network
system. The DHCP server helps you deploy wireless clients efficiently. Packet filters provide security
mechanisms, such as firewalls, in different network layers. Moreover, the AWK-6222 can support the STP/RSTP
protocols to increase reliability across the entire network. In addition, SNMP support can ease the network
management via SNMP protocols.
DHCP Server (for AP-Client operation mode’s AP mode only)
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a networking protocol that allows administrators to assign
temporary IP addresses to network computers by “leasing” an IP address to a user for a limited amount of time,
instead of assigning permanent IP addresses.
The AWK-6222 can act as a simplified DHCP server and easily assign IP addresses to your wireless clients by
responding to the DHCP requests from the client ends. The IP-related parameters you set on this page will also
be sent to the client.
You can also assign a static IP address to a specific client by entering its MAC address. The AWK-6222 provides
a Static DHCP mapping list with up to 16 entities. Remember to check the Active check box for each entity
to activate the setting.
You can check the IP assignment status under Status DHCP Client List.
Page 41

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-25
The IP address of the DNS Server used by your network. After
DHCP server (AP only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables the DHCP server function Disable
Disable Disable DHCP server function
Default gateway
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address of a default
gateway
Subnet mask
Setting Description Factory Default
subnet mask Identifies the type of sub-network (e.g., 255.255.0.0 for a
Primary/ Secondary DNS server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address of Primary/
Secondary DNS server
Start IP address
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address Indicates the starting IP address which the AWK-6222 can
Maximum number of users
Setting Description Factory Default
1 – 999 Specifies how many IP address can be assigned continuously None
The IP address of the router that connects to an outside
network
Class B network, or 255.255.255.0 for a Class C network)
entering the DNS Server’s IP address, you can use URLs. The
Secondary DNS server will be used if the Primary DNS server
fails to connect.
assign.
None
None
None
None
Client lease time
Setting Description Factory Default
1 – 10 days The lease time for which an IP address is assigned. The IP
address may expire after the lease time is reached.
10 (days)
Page 42

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-26
ATTENTION
Be careful when you enable the filter function:
Drop +
Accept +
Packet Filters
The AWK-6222 includes various filters for IP-based packets going through LAN and WLAN interfaces. You can
set these filters as a firewall to help enhance network security.
MAC Filter
The AWK-6222’s MAC filter is a policy-based filter that can allow or filter out IP-based packets with specified
MAC addresses. The AWK-6222 provides eight fields for filtered MAC addresses. Remember to check the
Active check box for each entity to activate the setting.
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables MAC filter Disable
Disable Disables MAC filter
Policy
Setting Description Factory Default
Accept Only the packets from the listed addresses will be allowed. Drop
Drop Any packet from the listed addresses will be denied.
“no entity on list is activated” = all packets are allowed
“no entity on list is activated” = all packets are denied
IP Protocol Filter
The AWK-6222’s IP protocol filter is a policy-based filter that can allow or filter out IP-based packets with
specified IP protocol and source/destination IP addresses.
The AWK-6222 provides eight fields for setting IP protocol and source/destination IP addresses in your filtering
policy. Four IP protocols are available: All, ICMP, TCP, and UDP. You must specify either the Source IP or the
Destination IP. By combining IP addresses and netmasks, you can specify a single IP address or a range of IP
addresses to accept or drop. For example, “IP address 192.168.1.1 and netmask 255.255.255.255” refers to
the sole IP address 192.168.1.1. “IP address 192.168.1.1 and netmask 255.255.255.0” refers to the range of
IP addresses from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.255. Remember to check the Active check box for each entity to
activate the setting.
Page 43

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-27
ATTENTION
Be careful when you enable the filter function:
Drop +
Accept +
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables IP protocol filter Disable
Disable Disables IP protocol filter
Policy
Setting Description Factory Default
Accept Only the packets from the listed addresses will be allowed Drop
Drop Any packet from the listed addresses will be denied
“no entity on list is activated” = all packets are allowed.
“no entity on list is activated” = all packets are denied.
TCP/UDP Port Filter
The AWK-6222’s TCP/UDP port filter is a policy-based filter that can allow or filter out TCP/UDP-based packets
with a specified source or destination port.
The AWK-6222 provides eight fields for setting the range of source/destination ports of a specific protocol. In
addition to selecting TCP or UDP protocol, you can set either the source port, destination port, or both. The end
port can be left empty if only a single port is specified. Of course, the end port cannot be larger than the start
port.
The Application name is a text string that describes the corresponding entity with up to 31 characters.
Remember to check the Active check box for each entity to activate the setting.
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables TCP/UDP port filter Disable
Disable Disables TCP/UDP port filter
Page 44

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-28
ATTENTION
Be careful when you enable the filter function:
Drop +
Accept +
to be
The root of the Spanning Tree topology periodically sends out a
“hello” message to other devices on the network to check if the
Policy
Setting Description Factory Default
Accept Only the packets from the listed ports be allowed. Drop
Drop Any packet from the listed ports will be denied.
“no entity on list is activated” = all packets are allowed
“no entity on list is activated” = all packets are denied
RSTP Settings (for Master or Slave mode only)
The AWK-6222 supports IEEE802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol and IEEE802.1w Rapid STP standards. In addition
to eliminating unexpected path looping, STP/RSTP can provide a backup recovery path if a wired/ wireless path
fails accidentally. The reliability and availability of the network can increase because this fail-over function.
The AWK-6222’s STP/RSTP feature is disabled by default. To be completely effective, you must enable
RSTP/STP on every AWK-6222 connected to your network.
The following figures indicate which Spanning Tree Protocol parameters can be configured. A more detailed
explanation of each parameter is given below the figure.
RSTP status
This field will appear only when STP/RSTP is enabled. It indicates whether this AWK-6222 is the Root of the
Spanning Tree (the root is determined automatically) or not.
Bridge priority
Setting Description Factory Default
User-selected
numerical value
Hello time
Setting Description Factory Default
User-selected
numerical value
(1 – 10 seconds)
You can increase the bridge priority by selecting a lower
number. Units with higher bridge priority are more likely
chosen as the root of the Spanning Tree topology.
topology is healthy. Hello time indicates how often the root
sends hello messages.
32768
2 (seconds)
Page 45

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-29
30
checking to see if it
40
message from the root longer than Max. age, it will reconfigure
port is less suitable as a
go through, as an
NOTE
We
sub
unnecessary
waiting and
receives
BPDUs, it can still
Setting an edge port is different from disabling STP/RSTP on a port. If you disable STP/RSTP, a port will not deal
with STP/RST
Forwarding delay
Setting Description Factory Default
User-selected
numerical value (4 –
seconds)
Max. age
Setting Description Factory Default
User-selected
numerical value (6 –
seconds)
Enable RSTP
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/ disable Enables or disables the port as a node on the Spanning Tree
Port priority
Setting Description Factory Default
User-selected
numerical value
The amount of time this device waits before
should change to a different topology.
As a non-root role, if the device has not received a hello
itself as a root. Once two or more devices on the network are
recognized as a root, the devices will renegotiate to set up a
new Spanning Tree topology.
topology.
Increase this port’s priority as a node on the Spanning Tree
topology by inputting a lower number.
15 (seconds)
20 (seconds)
Disable (unchecked)
128
Port cost
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/ Disable Input a higher cost to indicate that this
Edge port
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked/ unchecked Sets a port, which no BPDU are expected to
recommend you set use the edge port setting for ports that are only connected to non-STP/RSTP
-networks or end devices (PLC, RTU, etc.) as opposed to network equipment. This can prevent
negotiation of STP/RSTP protocol, and accelerate system initialization. When an edge port
Port Status
Port Status indicates the current Spanning Tree status of this port. Use Forwarding for normal transmission,
or Blocking to block transmission.
SNMP Agent
node for the Spanning Tree topology
edge port
function as an STP/RSTP port and start negotiation.
P BPDUs at all.
2000000
unchecked, except
WLAN1/2 ports
The AWK-6222 supports SNMP V1/V2c/V3. SNMP V1 and SNMP V2c use a community string match for
authentication, which means that SNMP servers access all objects with read-only or read/write permissions
using the community string public/private (default value). SNMP V3, which requires you to select an
authentication level of MD5 or SHA, is the most secure protocol. You can also enable data encryption to
enhance data security.
The AWK-6222’s MIB can be found in the software CD and supports reading the attributes via SNMP. (Only get
method is supported.)
Page 46

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-30
agent
agent
SNMP security modes and security levels supported by the AWK-6222 are shown in the following table. Select
the security mode and level that will be used to communicate between the SNMP agent and manager.
Protocol
Version
SNMP
V1, V2c
SNMP V3
The following parameters can be configured on the SNMP Agent page. A more detailed explanation of each
parameter is given below the following figure.
Setting on UI
web page
V1, V2c Read
Community
V1, V2c
Write/Read
Community
No-Auth None No
MD5 or SHA
MD5 or SHA
Authentication
Type
Community string No
Community string No
Authentication
based on MD5 or
SHA
Authentication
based on MD5 or
SHA
Data
Encryption
No
Data
encryption
key
Method
Use a community string match for
authentication
Use a community string match for
authentication
Use admin or user account to access
objects
Provides authentication based on
HMAC-MD5, or HMAC-SHA algorithms.
8-character passwords are the minimum
requirement for authentication.
Provides authentication based on
HMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA algorithms, and
data encryption key. 8-character
passwords and a data encryption key are
the minimum requirements for
authentication and encryption.
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables SNMP Agent Disable
Disable Disables SNMP Agent
Read community (for V1, V2c, V3 or V1, V2c)
Setting Description Factory Default
Read Community Use a community string match with a maximum of 31
characters for authentication. This means that the SNMP
can access all objects with read-only permissions using this
community string.
Write community (for V1, V2c, V3 or V1, V2c)
Setting Description Factory Default
Read /Write
Community
Use a community string match with a maximum of 31
characters for authentication. This means that the SNMP
can access all objects with read/write permissions using this
community string.
public
private
Page 47

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-31
option will show up. You can Enable or Disable Broadcast Storm
Protection globally for unknown multicast and unknown unicast
SNMP agent version
Setting Description Factory Default
V1, V2c, V3, or
V1, V2c, or V3 only
Admin auth type (for V1, V2c, V3, and V3 only)
Setting Description Factory Default
No Auth Use admin account to access objects. No authentication No Auth
MD5 Provide authentication based on the HMAC-MD5 algorithms.
SHA Provides authentication based on HMAC-SHA algorithms.
Admin private key (for V1, V2c, V3, and V3 only)
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable No data encryption Disable
DES DES-based data encryption
AES AES-based data encryption
Select the SNMP protocol version used to manage the switch. V1, V2c
8-character passwords are the minimum requirement for
authentication.
8-character passwords are the minimum requirement for
authentication.
Private Key
A data encryption key is the minimum requirement for data encryption (maximum of 63 characters)
Private MIB Information Device Object ID
Also known as OID. This is the AWK-6222’s enterprise value. It is fixed.
Storm Protection
In general, one host should not be allowed to occupy unlimited bandwidth, particularly when the device
malfunctions. For example, so-called “broadcast storms” could be caused by an incorrectly configured topology
or a malfunctioning device.
Storm Protection
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Enable or disable Broadcast Storm Protection globally for
Enable
multicast packets
Multicast and flooding
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable If you enable Storm Protection, the Multicast and flooding
packets.
Disable
Page 48

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-32
6222 is rebooted, such as when its settings are changed
Auto Warning Settings
Since industrial-grade devices are often located at the endpoints of a system, these devices will not always
know what is happening elsewhere on the network. This means that these devices, including wireless APs or
clients, must provide system maintainers with real-time alarm messages. This way even when system
administrators are out of the control room for an extended period, they can still be informed of the status of
devices almost instantaneously when exceptions occur.
In addition to logging these events, the AWK-6222 supports different approaches to warn engineers
automatically, such as SNMP trap, e-mail, and relay output. It also supports two digital inputs to integrate
sensors into your system to automate alarms by email and relay output.
System Log
System Log Event Types
Detailed information for grouped events is shown in the following table. You can check the Enable log box to
enable event groups. By default all the values are enabled (checked). The log for system events can be seen in
Status
System Log.
System-related events Event triggers when…
System restart (warm start) The AWK-
(IP address, subnet mask, etc.).
Network-related events Event triggers when…
LAN 1 or LAN 2 link on The LAN port is connected to a device or network.
LAN 1 or LAN 2 link off The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out, or the
opposing device shuts down).
Client joined/ left for WLAN 1 or WLAN 2
(for Redundant AP, AP, or Master mode)
WLAN 1 or WLAN 2 connected to AP
(for Redundant Client, Client, or Slave
mode)
WLAN 1 or WLAN 2 disconnected
(for Redundant Client, Client, or Slave
mode)
Config-related events Event triggers when…
Configuration Changed A configuration item has been changed.
Configuration file import via Web Console The configuration file is imported to the AWK-6222.
Console authentication failure An incorrect password is entered.
Firmware upgraded The AWK-6222’s firmware is updated.
Power events Event triggers when…
Power 1/2 transition (On Off) The AWK-6222 is powered down in PWR1/2.
PoE transition (On Off) The AWK-6222 is powered down in PoE.
Power 1/2 transition (Off On) The AWK-6222 is powered via PWR1/2.
A wireless client is associated or disassociated.
The AWK-6222 is associated with an AP.
The AWK-6222 is disassociated from an AP.
Page 49

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-33
PoE transition (Off On) The AWK-6222 is powered via PoE.
DI events Event is triggered when…
DI1/2 transition (On Off) Digital Input 1/2 is triggered by on to off transition
DI1/2 transition (Off On) Digital Input 1/2 is triggered by off to on transition
Syslog
This function provides the event logs for the Syslog server. The function supports up to three configurable
Syslog servers and Syslog server UDP port numbers. When an event occurs, the event will be sent as a Syslog
UDP packet to the specified Syslog servers.
Syslog Event Types
Detail information for the grouped events is shown in the following table. You can check the Enable log box to
enable event groups. By default all values are enabled (checked). Details for each event group can be found on
the “System log Event Types” table on page 3-31.
Syslog Server Settings
You can configure the parameters for your Syslog servers in this page.
Syslog server 1/ 2/ 3
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address Enter the IP address of the 1st/ 2nd/ 3rd Syslog Server None
Syslog port
Setting Description Factory Default
Port destination
(1 to 65535)
Enter the UDP port of the corresponding Syslog server 514
Page 50

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-34
E-mail Event Types
Check the Active box to enable the event items. By default all values are deactivated (unchecked). Details for
each event item can be found on the “System log Event Types” table on page 3-31.
Page 51

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-35
mail address which will be shown in
E-mail Server Settings
You can set up to four e-mail addresses to receive alarm emails from the AWK-6222. The following parameters
can be configured on the E-mail Server Settings page. In addition, a Send Test Mail button can be used to
test whether the Mail server and e-mail addresses are working. More detailed explanations about these
parameters are given after the following figure.
Mail server (SMTP)
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address The IP Address of your email server. None
Relay
User name & Password
Setting Description Factory Default
User name and password used in the SMTP server None
From e-mail address
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 63 characters Enter the administrator’s e-
the “From” field of a warning e-mail.
To E-mail address 1/ 2/ 3/ 4
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 63 characters Enter the receivers’ e-mail addresses. None
The AWK-6222 has one relay output, which consists of two terminal block contacts on the AWK-6222’s top
panel. These relay contacts are used to indicate user-configured events and system failure.
The two wires attached to the relay contacts form an open circuit when a user-configured event is triggered. If
a user-configured event does not occur, the relay circuit will remain closed. For safety reasons, the relay circuit
is kept open when the AWK-6222 is not powered.
None
Page 52

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-36
Relay Event Types
You can check the Active box to enable the event items. By default all values are deactivated (unchecked).
Details for each event item can be found in the “System log Event Types” table on page 3-31.
Trap
Traps can be used to signal abnormal conditions (notifications) to a management station. This trap-driven
notification can make your network more efficient.
Because a management station usually takes care of a large number of devices that have a large number of
objects, it will be overwhelming for the management station to poll or send requests to query every object on
every device. It would be more effective for the managed device agent to notify the management station when
necessary by sending a message known as a trap.
Page 53

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-37
Trap Event Types
SNMP Trap Receiver Settings
SNMP traps are defined in SMIv1 MIBs (SNMPv1) and SMIv2 MIBs (SNMPv2c). The two styles are basically
equivalent, and it is possible to convert between the two. You can set the parameters for SNMP trap receivers
through the web page.
1st / 2nd Trap version
Setting Description Factory Default
V1 SNMP trap defined in SNMPv1 V1
V2 SNMP trap defined in SNMPv2
1st / 2nd Trap server IP/name
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address or host
name
Enter the IP address or name of the trap server used by your
network.
None
1st / 2nd Trap community
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 31 characters Use a community string match with a maximum of 31
characters for authentication.
alert
Page 54

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-38
Status
Wireless Status
The status for 802.11 info parameters, such as Operation mode and Channel, are shown on the Wireless
Status page. The status will refresh every 5 seconds if the Auto refresh box is checked.
Certain 802.11 info values may not appear in certain operation modes. For example, Current BSSID and
RSSI are not available in Redundant AP, AP, or Master modes.
It is helpful to use the continuously updated information option on this page, such as RSSI, to monitor the
signal strength of the AWK-6222 in Redundant Client, Client, or Slave modes.
Associated Client List (for Redundant AP, AP, or Master Mode
only)
Associated Client List shows all the clients that are currently associated to a particular AWK-6222. You can click
Select all to select all the content in the list for further editing. You can click Refresh to refresh the list.
Page 55

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-39
DHCP Client List (for AP mode only)
When you enable the DHCP server, the DHCP Client List shows all the clients that require and have successfully
received IP assignments. You can click the Refresh button to refresh the list.
You can press Select all button to select all content in the list for further editing.
System Log
Triggered events are recorded in System Log. You can export the log contents to an available viewer by clicking
Export Log. You can use the Clear Log button to clear the log contents and the Refresh button to refresh the
log.
Page 56

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-40
Relay Status
The status of user-configurable events can be found under Relay Status. The status will refresh every 5
seconds if the Auto refresh box is checked.
If an event is triggered, it will be noted on this list. System administrators can click Acknowledge Event when
he has acknowledged the event and addressed it.
DI and Power Status
The status of power inputs and digital inputs is shown on this web page. The status will refresh every 5 seconds
if the Auto refresh box is checked.
Maintenance
Maintenance functions provide the administrator with tools to manage the AWK-6222 and wired/wireless
networks.
Page 57

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-41
Console Settings
You can enable or disable access permission for the following consoles: HTTP, HTTPS, Telnet and SSH
connections. For more security, we recommend you only allow access to the two secured consoles, HTTPS and
SSH.
Ping
Ping helps to diagnose the integrity of wired or wireless networks. By inputting a node’s IP address in the
Destination field, you can use the ping command to make sure it exists and discover whether or not the
access path is available.
If the node and access path are available, you will see that all packets were successfully transmitted with no
loss. Otherwise, some, or even all, packets may be lost, as shown in the following figure.
Firmware Upgrade
The AWK-6222 can be enhanced with more value-added functions by installing firmware upgrades. The latest
firmware is available at Moxa’s download center.
Before running a firmware upgrade, make sure the AWK-6222 is off-line. Click the Browse button to specify
the firmware image file and click Firmware Upgrade and Restart to start the firmware upgrade. After the
progress bar reaches 100%, the AWK-6222 will reboot itself.
When upgrading your firmware, the AWK-6222’s other functions are deactivated.
Page 58

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-42
ATTENTION
Please make sure the power source is stable when you
interruption
may damage your AWK-6222.
Config Import Export
You can back up or restore the AWK-6222’s configuration with Config Import Export.
In the Config Import section, click Browse to specify the configuration file and click Config Import button
to begin importing the configuration.
In the Config Export section, click the Config Export button and save the configuration file onto your local
storage media. The configuration file is a text file and you can view and edit it with a general text-editing tool.
upgrade your firmware. An unexpected power
Load Factory Default
Use this function to reset the AWK-6222 and roll all settings back to the factory default values. You can also
reset the hardware by pressing the reset button on the top panel of the AWK-6222.
Page 59

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-43
Password
You can change the administration password for each of the AWK-6222’s console managers by using the
Password function. Before you set up a new password, you must input the current password and reenter the
new password for confirmation. For your security, do not use the default password root, and remember to
change the administration password regularly.
Misc. Settings
Additional settings to help you manage your AWK-6222, are available on this page.
Reset button
Setting Description Factory Default
Always enable The AWK-6222’s Reset button works normally. Always enable
Disable after 60 sec The AWK-6222’s Reset button will become invalid 60 seconds
after the AWK-6222 completes booting.
Save Configuration
The following figure shows how the AWK-6222 stores the setting changes into volatile and non-volatile memory.
All data stored in volatile memory will disappear when the AWK-6222 is shutdown or rebooted unless they are
saved. Because the AWK-6222 starts up and initializes with the settings stored in flash memory, all new
changes must be saved to flash memory before restarting the AWK-6222.
This also means the new changes will not work unless you run either the Save Configuration function or the
Restart function.
Page 60

AWK-6222 Web Console Configuration
3-44
After you click on Save Configuration in the left menu box, the following screen will appear. Click Save if you
wish to update the configuration settings in the flash memory at this time. Alternatively, you may choose to run
other functions and put off saving the configuration until later. However, the new setting changes will remain
in the non-volatile memory until you save the configurations.
Restart
If you submitted configuration changes, you will find a blinking string in the upper right corner of the screen.
After making all your changes, click the Restart function in the left menu box. One of two different screens will
appear.
If you made changes recently but did not save, you will be given two options. Clicking the Restart button here
will reboot the AWK-6222 directly, and all setting changes will be ignored. Clicking the Save and Restart
button will apply all setting changes and then reboot the AWK-6222.
If you run the Restart function without changing any configurations or saving all your changes, you will see
just one Restart button on your screen.
You will not be able to run any of the AWK-6222’s functions while the system is rebooting.
Logout
Logout helps users disconnect the current HTTP or HTTPS session and go to the Login page. For security
reasons, we recommend you logout before quitting the console manager.
Page 61

4
4. Software Installation/Configuration
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Wireless Search Utility
Installing Wireless Search Utility
Configuring the Wireless Search Utility
Page 62

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-2
Overview
The Wireless Search Utility can be downloaded from the Moxa website at www.moxa.com.
Wireless Search Utility
Installing Wireless Search Utility
Once the Wireless Search Utility is downloaded, run the setup executable to start the installation.
1. Click Next on the Welcome screen to proceed with the installation.
Page 63

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-3
2. Click Next to install program files in the default directory, or click Browse to select an alternate location.
3. Click Next to create and place the program’s shortcut files in the default directory, or click Browse to
specify a different location.
Page 64

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-4
4. Click Next to select additional tasks.
5. Click Next to proceed with the installation. The installer then displays a summary of the installation options.
6. Click Install to begin the installation. The setup window will report the progress of the installation. To
change the installation settings, click Back and navigate to the previous screen.
Page 65

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-5
7. Click Finish to complete the installation of the Wireless Search Utility.
Configuring the Wireless Search Utility
The Broadcast Search function is used to locate all AWK-6222 APs that are connected to the same LAN as your
computer. After locating an AWK-6222, you will be able to change its IP address. Since the Broadcast Search
function searches by TCP packet and not IP address, it doesn’t matter if the AWK-6222 is configured as an AP
or Client. In either case, APs and Clients connected to the LAN will be located, regardless of whether or not they
are part of the same subnet as the host.
1. Start the Wireless Search Utility program.
2. In the Login page, select the Device Search Only option to search for devices and view the configuration,
or the Device Management option to assign IPs, upgrade firmware, and locate devices.
Page 66

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-6
3. To search for devices, open the Wireless Search Utility and click the Search icon.
The “Searching” window indicates the progress of the search. When the search is complete, all AWKs that
were located will be displayed in the Wireless Search Utility window.
Page 67

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-7
ATTENTION
For security purposes, we suggest
Click Locate to cause a selected device to beep.
Make sure the device is unlocked before using the other functions of the search utility. The device will
unlock automatically if the password is set to the default. Otherwise you must enter the new password
manually.
To unlock devices, go to Tools Utility Login Options
Use the scroll down list to select the MAC addresses of the AWK devices that you would like to manage, and
then click Add. Key in the password for the device and then click OK to save. If you return to the search
page and search for the AWK again, you will find that the AWK will unlock automatically.
changing the default password of the Wireless Search Utility login.
Page 68

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-8
To modify the configuration of the selected device, click on the Web icon. This will take you to the web
console, where you can make all configuration changes. Refer to Chapter 3, “Using the Web Console,” for
information on using the web console.
Click on Telnet if you would like to use telnet to configure your devices.
Page 69

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-9
Click Assign IP to change the IP setting.
The three advanced options available under the Tools menu—Search, Connection, and
Miscellaneous—are explained below:
Search
Retry count (default=5): Use this option to set the number of times a search will be automatically retried.
Retry interval (ms): The time interval between retries.
Page 70

AWK-6222 Software Installation/Configuration
4-10
Connection
Connection timeout (secs): Use this option to set the waiting time for the Default Login, Locate, Assign
IP, Upload Firmware
Upgrade timeout (secs): Use this option to set the connection timeout while the firmware is upgrading,
which is the time required for the firmware to be written to the flash memory.
, and Unlock functions to complete their tasks.
Misc.
Search on start: Select this option if you would like the search function to start searching for devices after you
log in to the Wireless Search Utility.
Page 71

5
5. Other Console Configurations
This chapter explains how to access the AWK-6222 for the first time. In addition to HTTP access, there are four
ways to access AWK-6222: serial console, Telnet console, SSH console, and HTTPS console. The serial console
connection method, which requires using a short serial cable to connect the AWK-6222 to a PC’s COM port, can
be used if you do not know the AWK-6222’s IP address. The other consoles can be used to access the
AWK-6222 over an Ethernet LAN, or over the Internet.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
Configuration by Telnet and SSH Consoles
Configuration by Web Browser with HTTPS/SSL
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access
Page 72

AWK-6222 Other Console Configurations
5-2
ATTENTION
6222 with two or more of these console configurations simultaneously.
use more than one connection method at the same time.
6222.
ATTENTION
Do not use the RS
even though reverse voltage
If you need to connect the RS
NOTE
We rec
Terminal Emulator, which can be downloaded free of charge from
Moxa’s website.
1. You CANNOT connect to the AWK-
2. You can connect to the AWK-6222 simultaneously by web browser and serial/ Telnet /SSH console.
However, we strongly suggest that you do NOT
Following this advice will allow you to maintain better control over the configuration of your AWK-
RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
The serial console connection method, which requires using a short serial cable to connect the AWK-6222 to a
PC’s COM port, can be used if you do not know the AWK-6222’s IP address. It is also convenient to use serial
console configurations when you cannot access the AWK-6222 over Ethernet LAN, such as in the case of LAN
cable disconnections or a broadcast storm.
ommend using Moxa PComm (Lite)
Before running PComm Terminal Emulator, use an RJ45 to DB9-F (or RJ45 to DB25-F) cable to connect the
AWK-6222’s RS-232 console port to your PC’s COM port (generally COM1 or COM2, depending on how your
system is set up). After installing PComm Terminal Emulator, take the following steps to access the RS-232
console utility.
1. From the Windows desktop, open the Start menu and start PComm Terminal Emulator in the PComm
(Lite) group.
2. Select Open under Port Manager to open a new connection.
-232 console manager when the AWK-6222 is powered at reversed voltage (ex. -48VDC),
protection is supported.
-232 console at reversed voltage, Moxa’s TCC-82 isolator is your best solution.
Page 73

AWK-6222 Other Console Configurations
5-3
3. The Communication Parameter page of the Property window opens. Select the appropriate COM port for
Console Connection, 115200 for Baud Rate, 8 for Data Bits, None for Parity, and 1 for Stop Bits.
4. Click on the Terminal tab, and select VT100 (or ANSI) for Terminal Type. Click on OK to continue.
5. The Console login screen will appear. Log into the RS-232 console with the login name (default: admin)
and password (default: root, if no new password is set).
Page 74

AWK-6222 Other Console Configurations
5-4
NOTE
To modify the appearance of the PComm Terminal Emulator window, select
and then choose the
desired formatting options.
ATTENTION
If you unplug the RS
network security.
NOTE
The
(for
a Class C network). If you do not set these values properly, please check the network settings of your PC host
a
6. The AWK-6222’s device information and Main Menu will be displayed. Please follow the description on
screen and select the administration option you wish to perform.
-232 cable or trigger DTR, a disconnection event will be invoked to enforce logout for
You will need to log in again to resume operation.
Edit Font
Configuration by Telnet and SSH Consoles
You may use a Telnet or SSH client to access the AWK-6222 and manage the console over a network. To access
the AWK-6222’s functions over the network from a PC host that is connected to the same LAN as the AWK-6222,
you need to make sure that the PC host and the AWK-6222 are on the same logical subnet. To do this, check
your PC host’s IP address and subnet mask.
AWK-6222’s default IP address is 192.168.127.253 and the default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
nd then change the IP address to 192.168.127.xxx and subnet mask to 255.255.255.0.
Follow the steps below to access the console utility via Telnet or SSH client.
1. From Windows Desktop, run Start Run, and then use Telnet to access the AWK-6222’s IP address from
the Windows Run window. (You may also issue the telnet command from the MS-DOS prompt.)
Page 75

AWK-6222 Other Console Configurations
5-5
When using SSH client (ex. PuTTY), please run the client program (ex. putty.exe) and then input the
AWK-6222’s IP address, specifying 22 for the SSH connection port.
2. The Console login screen will appear. Please refer to the previous paragraph “RS-232 Console Configuration”
and for login and administration.
Configuration by Web Browser with HTTPS/SSL
To secure your HTTP access, the AWK-6222 supports HTTPS/SSL encryption for all HTTP traffic. Perform the
following steps to access the AWK-6222’s web browser interface via HTTPS/SSL.
1. Open your web browser and type https://<AWK-6222’s IP address> in the address field. Press Enter to
establish the connection.
2. Warning messages will pop up to warn users that the security certificate was issued by a company they
have not yet chosen to trust.
Page 76

AWK-6222 Other Console Configurations
5-6
3. Select Yes to accept the certificate issued by Moxa IW and then enter the AWK-6222’s web browser
interface secured via HTTPS/SSL. (You can see the protocol in URL is https.) Then you can use the menu
tree on the left side of the window to open the function pages to access each of AWK-6222’s functions.
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access
If you are connecting the AWK-6222 to a public network but do not intend to use its management functions
over the network, then we suggest disabling both Telnet Console and Web Configuration. Please run
Maintenance
Console Settings to disable them, as shown in the following figure.
Page 77

6
6. References
This chapter provides more detailed information about wireless-related technologies. The information in this
chapter can help you administer your AWK-6222s and plan your industrial wireless network better.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Beacon
DTIM
Fragment
RTS Threshold
STP and RSTP
The STP/RSTP Concept
Differences between RSTP and STP
Page 78

AWK-6222 References
6-2
Beacon
A beacon is a packet broadcast by the AP to keep the network synchronized. A beacon includes the wireless LAN
service area, the AP address, the Broadcast destination address, a time stamp, Delivery Traffic Indicator Maps
(DTIM), and the Traffic Indicator Message (TIM). Beacon Interval indicates the frequency interval of AP.
DTIM
Delivery Traffic Indication Map (DTIM) is contained in beacon frames. It indicates that broadcast and multicast
frames buffered by the AP will be delivered shortly. Lower settings result in more efficient networking, while
preventing your PC from dropping into power-saving sleep mode. Higher settings allow your PC to enter sleep
mode, thus saving power.
Fragment
A lower setting means smaller packets, which will create more packets for each transmission. If you have
decreased this value and experience high packet error rates, you can increase it again, but it will likely decrease
overall network performance. Only minor modifications of this value are recommended.
RTS Threshold
RTS Threshold (256-2346) – This setting determines how large a packet can be before the Access Point
coordinates transmission and reception to ensure efficient communication. This value should remain at its
default setting of 2,346. When you encounter inconsistent data flow, only minor modifications are
recommended.
STP and RSTP
The STP/RSTP Concept
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was designed to help reduce link failures in a network, and provide protection
from loops. Networks that have a complicated architecture are prone to broadcast storms caused by
unintended loops in the network. The STP protocol is part of the IEEE802.1D standard, 1998 Edition bridge
specification.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) implements the Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol defined by
IEEE802.1w-2001 standard. RSTP provides the following benefits:
• The topology of a bridged network will be determined much more quickly compared to STP.
• RSTP is backward compatible with STP, making it relatively easy to deploy. For example:
Defaults to sending 802.1D-style BPDUs if packets with this format are received.
STP (802.1D) and RSTP (802.1w) can operate on the LAN ports and WLAN ports (AP and WDS1-WDS8)
of the same AWK-6222.
This feature is particularly helpful when the AWK-6222 connects to older equipment, such as legacy switches.
Page 79

AWK-6222 References
6-3
Differences between RSTP and STP
RSTP is similar to STP, but includes additional information in the BPDUs that allow each bridge to confirm that
it has taken action to prevent loops from forming when it decides to enable a link to a neighboring bridge.
Adjacent bridges connected via point-to-point links will be able to enable a link without waiting to ensure that
all other bridges in the network have had time to react to the change. The main benefit of RSTP is that the
configuration decision is made locally rather than network-wide, allowing RSTP to carry out automatic
configuration and restore a link faster than STP.
Page 80

7
7. Support Information
This chapter presents additional information about this manual and product. You can also learn how to contact
Moxa for technical support.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
About This User’s Manual
DoC (Declaration of Conformity)
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
R&TTE Compliance Statement
Firmware Recovery
Technical Support Contact Information
Page 81

AWK-6222 Support Information
7-2
NOTE
You can find out the hardware revision number of AWK
The firmware version number can be seen on the Overview page, as follow:
About This User’s Manual
This manual is mainly written for, but not limited to, the following hardware and firmware for the AWK-6222:
• Hardware Revision: 1.0
• Firmware Version: 1.1
You are strongly recommended to visit Moxa’s website (http://www.moxa.com) and find the latest product
datasheet, firmware, QIG (Quick Installation Guide), UM (User’s Manual) and related information.
-6222 on the back label.
DoC (Declaration of Conformity)
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in
a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one of the
following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example – use only shielded interface cables when connecting
to computer or peripheral devices). Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment. This transmitter must not
be co-located or operated in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Page 82

AWK-6222 Support Information
7-3
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This
equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20 cm between the radiator & your
body.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC 15.407(e): Within the 5.15-5.25 GHz band, U-NII devices will be restricted to indoor operations to reduce
any potential for harmful interference to co-channel MSS operations.
R&TTE Compliance Statement
This equipment complies with all the requirements of DIRECTIVE 1999/5/CE OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT
AND THE COUNCIL OF 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and telecommunication terminal equipment and the
mutual recognition of their conformity (R&TTE).
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC (Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment and Satellite Earth Station Equipment) as of April 8, 2000.
Safety
This equipment is designed with the utmost care for the safety of those who install and use it. However, special
attention must be paid to the dangers of electric shock and static electricity when working with electrical
equipment. All guidelines of this and of the computer manufacturer must therefore be allowed at all times to
ensure the safe use of the equipment.
EU Countries Intended for Use
The ETSI version of this device is intended for home and office use in Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland,
France (with Frequency channel restrictions), Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Portugal, Spain,
Sweden, The Netherlands, and United Kingdom.
The ETSI version of this device is also authorized for use in EFTA member states Norway and Switzerland.
EU Countries Not Intended for Use
None.
Potential Restrictive Use
France: only channels 10, 11, 12, and 13.
CE Warning
This is a class B product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case
the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Firmware Recovery
When FAULT and STATE LEDs all light up simultaneously and blink at one-second intervals, it means the
system boot has failed. This may result from an improper operation or issues such as an unexpected shutdown
during a firmware update. The AWK-6222 is designed to help administrators recover from such damage and
resume system operation rapidly. You can refer to the following instructions to recover the firmware:
Page 83

AWK-6222 Support Information
7-4
Connect to the AWK-6222’s RS-232 console with 115200bps and N-8-1. You will see the following message
shown on the terminal emulator every second.
Press Ctrl - C and the following message will appear.
Enter 2 to change the network setting. Specify the location of the AWK-6222’s firmware file on the TFTP server
and press y to write the settings into flash memory.
AWK-6222 restarts, and the “Press Ctrl-C to enter Firmware Recovery Process…” message will reappear. Press
Ctrl-C to enter the menu and select 1 to start the firmware upgrade process.
Page 84

AWK-6222 Support Information
7-5
Select 0 in the sub-menu to load the firmware image via LAN, and then enter the file name of the firmware to
start the firmware recovery.
Technical Support Contact Information
Customer satisfaction is our number one concern, and to ensure that customers receive the full benefit of our
products, Moxa Internet Services has been set up to provide technical support, driver updates, product
information, certification status, installation guide and user’s manual updates.
The following services are provided:
• E-mail for technical support:
support@moxa.com (Worldwide)
support@usa.moxa.com (The Americas)
• World Wide Web (WWW) Site for product information:
http://www.moxa.com
 Loading...
Loading...