Page 1
www.moxa.com
NPort IA5000 Series
1 and 2-port serial device servers for industrial automation
Features and Benefits
• Socket modes: TCP server, TCP client, UDP
• Patented ADDC® (Automatic Data Direction Control) for 2-wire and 4-wire
RS-485
• Cascading Ethernet ports for easy wiring (applies only to RJ45 connectors)
• Redundant DC power inputs
• Warnings and alerts by relay output and email
• 10/100BaseTX (RJ45) or 100BaseFX (single mode or multi-mode with SC
connector)
• IP30-rated housing
Certifications
Introduction
NPort® IA device servers provide easy and reliable serial-to-Ethernet connectivity for industrial automation applications. The device servers can
connect any serial device to an Ethernet network, and to ensure compatibility with network software, they support a variety of port operation
modes, including TCP Server, TCP Client, and UDP. The rock-solid reliability of the NPort® IA device servers makes them an ideal choice for
establishing network access to RS-232/422/485 serial devices such as PLCs, sensors, meters, motors, drives, barcode readers, and operator
displays. All models are housed in a compact, rugged housing that is DIN-rail mountable.
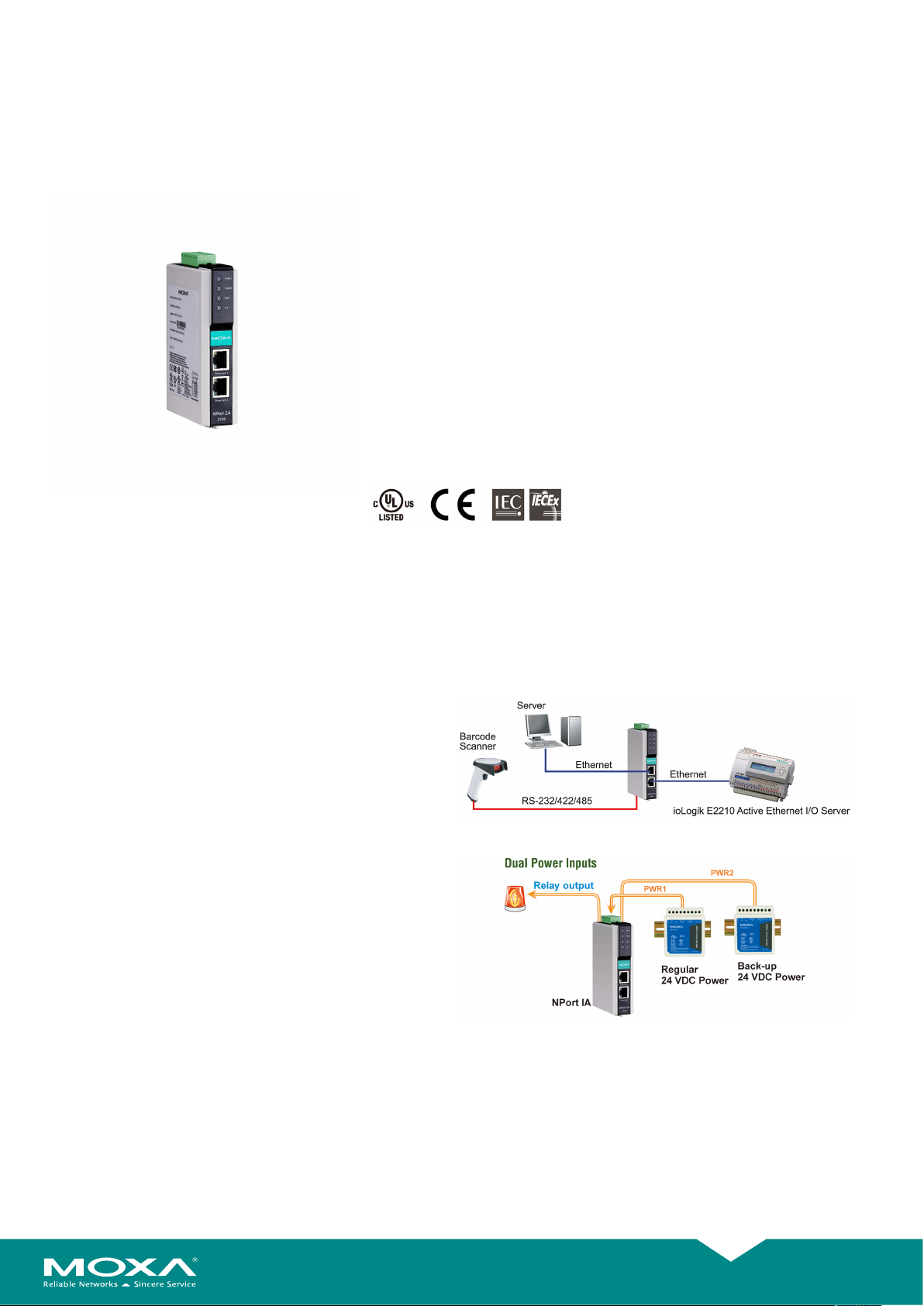
Cascading Ethernet Ports Make Wiring Easy (10/100BaseTX models)
The NPort® IA5150 and IA5250 device servers each have two
Ethernet ports that can be used as Ethernet switch ports. One port
connects directly to the network or server, and the other port can be
connected to either another NPort® IA device server or an Ethernet
device. The dual Ethernet ports help reduce wiring costs by
eliminating the need to connect each device to a separate Ethernet
switch.
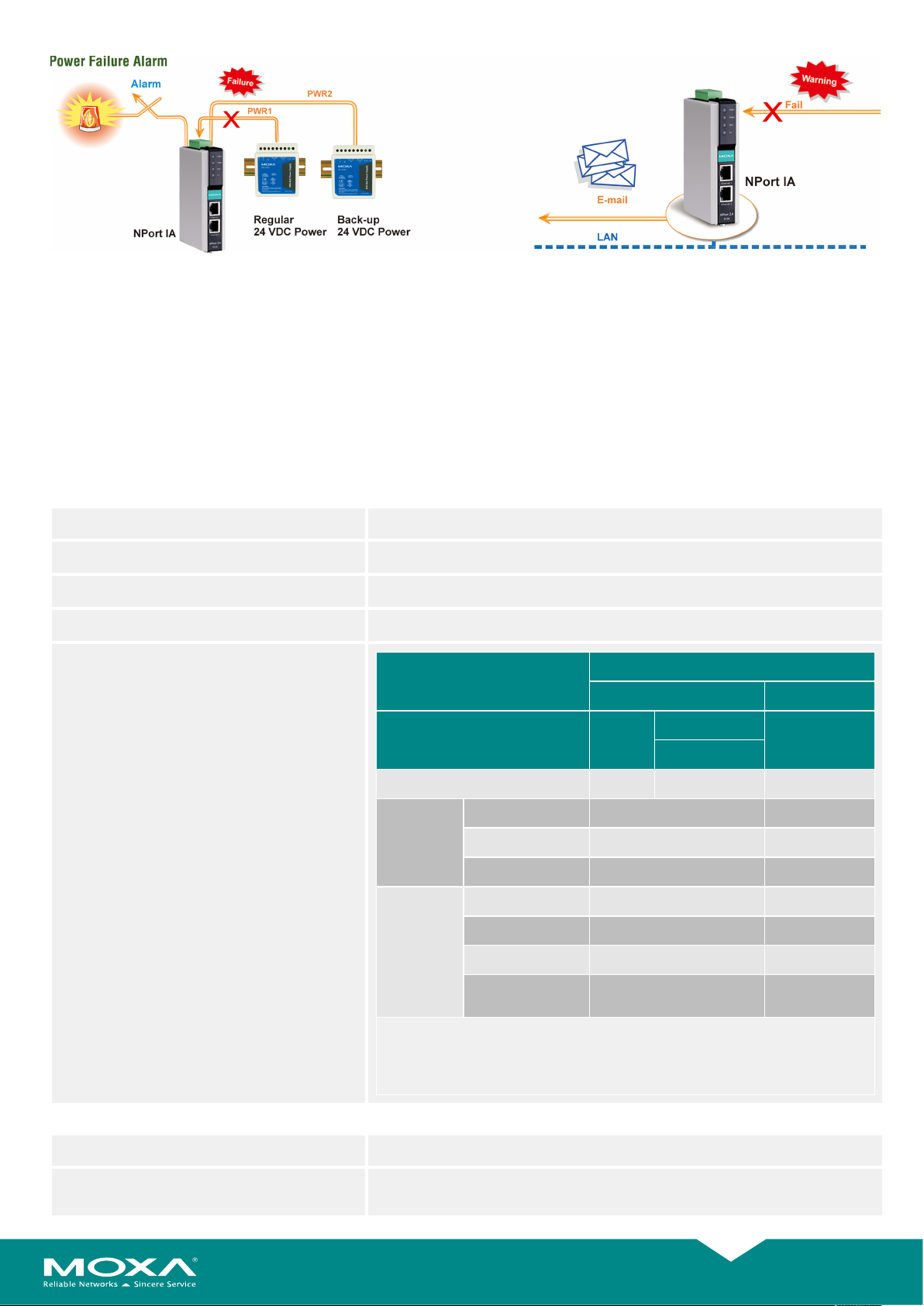
Redundant Power Inputs
The NPort® IA5000 device servers have two power inputs that can be
connected simultaneously to live DC power sources. If one power
source fails, the other source takes over automatically. Redundant
power inputs help assure that your device server will operate
nonstop.
Relay Output Warning and Email Alerts
The built-in relay output can be used to alert administrators of problems with the Ethernet links or power inputs, or when there is a change in the
DCD or DSR serial signals. The web console indicates which Ethernet link or power input has failed, or which serial signal has changed. An email
warning can also be issued when an exception is detected. These functions are valuable tools that enable maintenance engineers to react promptly
to emergency situations.
1
Page 2
www.moxa.com
Optical Fiber for Ethernet Communication
The NPort® IA5000 Series includes 100BaseFX fiber models that support transmission distances up to 5 km for multi-mode models, and up to 40
km for single-mode models. Optical fiber is well-suited for industrial applications because it is immune to electromagnetic noise and interference.
For environments that experience high ground loop voltages, fiber provides the best isolation protection, and because there is no danger of
sparking, optical fiber is safer than copper wire to use in hazardous environments.
Industrial-grade Certification
To ensure safe and reliable operation in industrial environments, the NPort® IA5000 device servers have obtained various industrial certifications,
including an IP30 rating for mechanical protection, UL 508 safety certification for industrial control equipment, and explosion-safe certifications for
hazardous locations. Certifications include UL/cUL Class 1 Division 2 Groups A, B, C, D, as well as ATEX Class 1 Zone 2, and IECEx Zone 2.
Specifications
Ethernet Interface
10/100BaseT(X) Ports (RJ45 connector) 2 (NPort IA-5150/5150I/5250)
100BaseFX Ports (multi-mode SC connector) NPort IA-5000-M-SC Models: 1
100BaseFX Ports (single-mode SC connector) NPort IA-5000-S-SC Models: 1
Magnetic Isolation Protection 1.5 kV (built-in)
Optical Fiber
100BaseFX
Multi-Mode Single-Mode
Fiber Cable Type OM1
Typical Distance 4 km 5 km 40 km
Wavelength
Optical Power
Typical (nm) 1300 1310
TX Range (nm) 1260 to 1360 1280 to 1340
RX Range (nm) 1100 to 1600 1100 to 1600
TX Range (dBm) -10 to -20 0 to -5
RX Range (dBm) -3 to -32 -3 to -34
Link Budget (dB) 12 29
Dispersion Penalty
(dB)
50/125 µm
G.652
800 MHz x km
3 1
Note: When connecting a single-mode fiber transceiver, we recommend using an
attenuator to prevent damage caused by excessive optical power.
Note: Compute the “typical distance” of a specific fiber transceiver as follows: Link
budget (dB) > dispersion penalty (dB) + total link loss (dB).
Ethernet Software Features
Configuration Options Web Console (HTTP), Windows Utility, Telnet Console, Serial Console
Management DHCP Client, IPv4, SMTP, SNMPv1, Telnet, ARP, BOOTP, DNS, HTTP, TCP/IP, UDP,
ICMP, Rtelnet
2
Page 3

www.moxa.com
Windows Real COM Drivers Windows 95/98/ME/NT/2000, Windows XP/2003/Vista/2008/7/8/8.1/10 (x86/x64),
Linux Real TTY Drivers Kernel versions: 2.4.x, 2.6.x, 3.x, 4.x, and 5.x
Windows 2008 R2/2012/2012 R2/2016/2019 (x64), Windows Embedded CE 5.0/6.0,
Windows XP Embedded
Fixed TTY Drivers SCO UNIX, SCO OpenServer, UnixWare 7, QNX 4.25, QNX 6, Solaris 10, FreeBSD, AIX 5.
Android API Android 3.1.x and later
Time Management SNTP
MIB RFC1213, RFC1317
x, HP-UX 11i, Mac OS X, macOS 10.12, macOS 10.13, macOS 10.14, macOS 10.15
Serial Interface
Connector NPort IA-5150: DB9 male for RS-232, terminal block for RS-422/485
No. of Ports NPort IA-5150 Models: 1
Serial Standards RS-232, RS-422, RS-485
Baudrate Supports standard baudrates (unit=bps): 110, 134, 150, 300, 600, 1200, 1800, 2400,
Data Bits 5, 6, 7, 8
Parity None, Even, Odd, Space, Mark
Stop Bits 1, 1.5, 2
NPort IA-5250: DB9 male for RS-232/422/485
NPort IA-5250 Models: 2
4800, 7200, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 230400
Flow Control RTS/CTS (RS-232 only), DTR/DSR (RS-232 only), XON/XOFF
Isolation 2 kV isolation protection (NPort IA-5150I, NPort IA-5150I-M-SC, NPort IA-5150I-S-SC)
Serial Signals
RS-232 TxD, RxD, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD, GND
RS-422 Tx+, Tx-, Rx+, Rx-, GND
RS-485-4w Tx+, Tx-, Rx+, Rx-, GND
RS-485-2w Data+, Data-, GND
Power Parameters
Input Current NPort IA-5150 Models: 238 mA @ 12 VDC
Input Voltage 12 to 48 VDC
No. of Power Inputs 2
NPort IA-5150I Models: 257 mA @ 12 VDC
NPort IA-5150-M-SC Models: 315 mA @ 12 VDC
NPort IA-5150I-M-SC Models: 339 mA @ 12 VDC
NPort IA-5150-S-SC Models: 328 mA @ 12 VDC
NPort IA-5150I-S-SC Models: 333 mA @ 12 VDC
NPort IA-5250 Models: 238 mA @ 12 VDC
Power Connector Terminal block
Physical Characteristics
Housing Plastic
IP Rating IP30
3
Page 4

www.moxa.com
Dimensions 29 x 89.2 x 118.5 mm (0.82 x 3.51 x 4.57 in)
Weight NPort IA-5150: 360 g (0.79 lb)
Installation DIN-rail mounting
NPort IA-5250: 380 g (0.84 lb)
Environmental Limits
Operating Temperature Standard Models: 0 to 55°C (32 to 131°F)
Storage Temperature (package included) -40 to 75°C (-40 to 167°F)
Ambient Relative Humidity 5 to 95% (non-condensing)
Wide Temp. Models: -40 to 75°C (-40 to 167°F)
Standards and Certifications
Freefall IEC 60068-2-32
EMC EN 55032/24
EMI CISPR 32, FCC Part 15B Class A
EMS IEC 61000-4-2 ESD: Contact: 6 kV; Air: 8 kV
IEC 61000-4-3 RS: 80 MHz to 1 GHz: 10 V/m
IEC 61000-4-4 EFT: Power: 4 kV; Signal: 2 kV
IEC 61000-4-5 Surge: Power: 2 kV; Signal: 1 kV
IEC 61000-4-6 CS: 150 kHz to 80 MHz: 10 V/m; Signal: 10 V/m
IEC 61000-4-8 PFMF
IEC 61000-4-11
Hazardous Locations ATEX, Class I Division 2, IECEx (for -IEX models)
Safety UL 508, UL 60950-1
Vibration IEC 60068-2-6
Declaration
Green Product RoHS, CRoHS, WEEE
MTBF
Time NPort IA-5150 Models: 183,747 hrs
Standards Telcordia (Bellcore) Standard TR/SR
NPort IA-5150I Models: 195,614 hrs
NPort IA-5250 Models: 194,765 hrs
Warranty
Warranty Period 5 years
Details See www.moxa.com/warranty
Package Contents
Device 1 x NPort IA-5000 Series device server
Documentation 1 x quick installation guide
1 x warranty card
4
Page 5

www.moxa.com
Dimensions
Ordering Information
Model Name
NPort IA-5150 2 RJ45 0 to 55°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150-T 2 RJ45 -40 to 75°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150I 2 RJ45 0 to 55°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150I-T 2 RJ45 -40 to 75°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150-M-SC 1 Multi-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150-M-SC-T 1 Multi-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150I-M-SC 1 Multi-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150I-M-SC-T 1 Multi-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150-S-SC 1 Single-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150-S-SC-T 1 Single-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150I-S-SC 1 Single-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150I-S-SC-T 1 Single-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5150-IEX 2 RJ45 0 to 55°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
No. of Ethernet
Ports
Ethernet Port
Connector
Operating
Temp.
No. of Serial
Ports
Serial
Isolation
Certification: Hazardous
Locations
NPort IA-5150-T-IEX 2 RJ45 -40 to 75°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
5
Page 6

www.moxa.com
Model Name
NPort IA-5150I-IEX 2 RJ45 0 to 55°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150I-T-IEX 2 RJ45 -40 to 75°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150-M-SC-IEX 1 Multi-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150-M-SC-T-IEX 1 Multi-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150I-M-SC-IEX 1 Multi-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150I-M-SC-T-IEX 1 Multi-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150-S-SC-IEX 1 Single-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150-S-SC-T-IEX 1 Single-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150I-S-SC-IEX 1 Single-mode SC 0 to 55°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5150I-S-SC-T-IEX 1 Single-mode SC -40 to 75°C 1 2 kV ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5250 2 RJ45 0 to 55°C 2 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5250-T 2 RJ45 -40 to 75°C 2 – ATEX, C1D2
NPort IA-5250-IEX 2 RJ45 0 to 55°C 2 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
NPort IA-5250-T-IEX 2 RJ45 -40 to 75°C 2 – ATEX, C1D2, IECEx
No. of Ethernet
Ports
Ethernet Port
Connector
Operating
Temp.
No. of Serial
Ports
Serial
Isolation
Certification: Hazardous
Locations
Accessories (sold separately)
Cables
CBL-F9M9-150 DB9 female to DB9 male serial cable, 1.5 m
CBL-F9M9-20 DB9 female to DB9 male serial cable, 20 cm
CBL-RJ458P-100 8-pin RJ45 CAT5 Ethernet cable, 1 m
CBL-RJ45SF9-150 8-pin RJ45 to DB25 male serial cable with shielding, 1.5m
Connectors
ADP-RJ458P-DB9F DB9 female to RJ45 connector
Mini DB9F-to-TB DB9 female to terminal block connector
© Moxa Inc. All rights reserved. Updated Feb 25, 2021.
This document and any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever without the express written permission of
Moxa Inc. Product specifications subject to change without notice. Visit our website for the most up-to-date product information.
6
 Loading...
Loading...