Page 1

Moxa Managed Ethernet Switch
(UI_2.0_FW_5.x) User’s Manual
Version 1.8, September 2020
www.moxa.com/product
Models covered by this user's manual (only applies to products
using firmware version 5.0 or higher):
EDS-510E, EDS-518E, EDS-528E, EDS-G508E, EDS-G512E, EDS-
G516E, EDS-P506E-4PoE, EDS-G512E-8PoE, IKS-6726A, IKS-6728A,
IKS-6728A-8PoE, IKS-G6524A, ICS-G7526A, ICS-G7528A, ICS-
G7748A, ICS-G7750A, ICS-G7752A, IKS-G6824A, ICS-G7826A, ICS-
G7828A, ICS-G7848A, ICS-G7850A, ICS-G7852A
© 2020 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2

Moxa Managed Ethernet Switch
Moxa Americas
Toll
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa China (Shanghai office)
Toll
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa Europe
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa Asia
Tel:
Fax:
Moxa India
Tel:
Fax:
(UI_2.0_FW_5.x) User’s Manual
The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance
with the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
© 2020 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Trademarks
The MOXA logo is a registered trademark of Moxa Inc.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their respective manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of
Moxa.
Moxa provides this document as is, without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not
limited to, its particular purpose. Moxa reserves the right to make improvements and/or changes to this manual, or to
the products and/or the programs described in this manual, at any time.
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Moxa assumes no responsibility
for its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that may result from its use.
This product might include unintentional technical or typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the publication.
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
-free: 1-888-669-2872
+1-714-528-6777
+1-714-528-6778
+49-89-3 70 03 99-0
+49-89-3 70 03 99-99
+91-80-4172-9088
+91-80-4132-1045
-free: 800-820-5036
+86-21-5258-9955
+86-21-5258-5505
-Pacific
+886-2-8919-1230
+886-2-8919-1231
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. About this Manual ............................................................................................................................. 1-1
2. Getting Started ................................................................................................................................. 2-1
USB Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100) ......................................................................... 2-2
Configuration by Command Line Interface (CLI) ..................................................................................... 2-5
Configuration by Web Console .............................................................................................................. 2-6
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access ..................................................................................................... 2-8
3. Featured Functions ........................................................................................................................... 3-1
Home ................................................................................................................................................ 3-2
System Settings ................................................................................................................................. 3-2
System Information ..................................................................................................................... 3-2
User Account .............................................................................................................................. 3-4
Password Login Policy .................................................................................................................. 3-6
Network ..................................................................................................................................... 3-6
Date and Time ............................................................................................................................ 3-9
IEEE 1588 PTP .......................................................................................................................... 3-12
Warning Notification .................................................................................................................. 3-16
MAC Address Table .................................................................................................................... 3-23
System Files ............................................................................................................................. 3-24
Turbo Ring DIP Switch ............................................................................................................... 3-27
Restart..................................................................................................................................... 3-28
Factory Default ......................................................................................................................... 3-28
PoE (PoE Models Only) ...................................................................................................................... 3-29
PoE Settings ............................................................................................................................. 3-29
VLAN ............................................................................................................................................... 3-39
The Virtual LAN (VLAN) Concept .................................................................................................. 3-39
Sample Applications of VLANs Using Moxa Switches ....................................................................... 3-42
Configuring a Virtual LAN ........................................................................................................... 3-43
VLAN Name Setting ................................................................................................................... 3-45
QinQ Settings ........................................................................................................................... 3-46
VLAN Table ............................................................................................................................... 3-46
Port ................................................................................................................................................ 3-47
Port Settings ............................................................................................................................. 3-47
Port Status ............................................................................................................................... 3-48
Link Aggregation ....................................................................................................................... 3-48
Link-Swap Fast Recovery ........................................................................................................... 3-50
Multicast .......................................................................................................................................... 3-51
The Concept of Multicast Filtering ................................................................................................ 3-51
IGMP Snooping ......................................................................................................................... 3-54
IGMP Snooping Setting .............................................................................................................. 3-54
IGMP Group Status .................................................................................................................... 3-55
Stream Table ............................................................................................................................ 3-56
Static Multicast Address ............................................................................................................. 3-56
GMRP ...................................................................................................................................... 3-57
Multicast Filtering Behavior ......................................................................................................... 3-57
QoS ................................................................................................................................................ 3-58
The Traffic Prioritization Concept ................................................................................................. 3-58
Configuring Traffic Prioritization .................................................................................................. 3-60
CoS Classification ...................................................................................................................... 3-60
Priority Mapping (Type 1) ........................................................................................................... 3-61
Priority Mapping (Type 2) ........................................................................................................... 3-62
DSCP Mapping .......................................................................................................................... 3-63
Rate Limiting ............................................................................................................................ 3-63
Security ........................................................................................................................................... 3-70
Management Interface ............................................................................................................... 3-70
Trusted Access .......................................................................................................................... 3-72
SSL Certificate Management ....................................................................................................... 3-73
SSH Key Management ............................................................................................................... 3-73
Authentication .......................................................................................................................... 3-73
Port Security ............................................................................................................................. 3-80
Port Access Control Table ........................................................................................................... 3-83
Broadcast Storm Protection ........................................................................................................ 3-83
Loop Protection ......................................................................................................................... 3-84
Access Control List .................................................................................................................... 3-84
DHCP .............................................................................................................................................. 3-91
IP-Port Binding ......................................................................................................................... 3-91
DHCP Relay Agent ..................................................................................................................... 3-91
SNMP .............................................................................................................................................. 3-94
SNMP Read/Write Settings.......................................................................................................... 3-95
Page 4

Trap Settings ............................................................................................................................ 3-96
Industrial Protocols ......................................................................................................................... 3-100
Diagnostics .................................................................................................................................... 3-100
LLDP ...................................................................................................................................... 3-100
Ping ....................................................................................................................................... 3-101
Port Mirroring ......................................................................................................................... 3-101
Monitoring ..................................................................................................................................... 3-103
CPU/Memory Utilization ............................................................................................................ 3-103
Statistics ................................................................................................................................ 3-104
Fiber Digital Diagnostics Monitoring (SFP DDM and Fiber Check) ................................................... 3-105
Event Log ............................................................................................................................... 3-108
Tracking ........................................................................................................................................ 3-108
Interface Tracking ................................................................................................................... 3-109
Ping Tracking .......................................................................................................................... 3-111
Logic Tracking ......................................................................................................................... 3-112
Tracking Table ........................................................................................................................ 3-113
A. MIB Groups ....................................................................................................................................... A-1
Page 5

1
1. About this Manual
Thank you for purchasing a Moxa managed Ethernet switch. Read this user’s manual to learn how to
connect your Moxa switch to Ethernet-enabled devices used for industrial applications.
A synopsis of chapters 2 and 3 are given below:
Chapter 2: Getting Started
In this chapter, we explain the initial installation process for a Moxa switch. Moxa switches provide three
interfaces to access the configuration settings: USB console interface, command line interface, and web
console interface.
Chapter 3: Featured Functions
In this chapter, we explain how to access a Moxa switch’s various configuration, monitoring, and
management functions. The functions can be accessed by USB console, Telnet console, and web console
(web browser). We describe how to configure the switch functions via web console, which provides the
most user-friendly way to configure a Moxa switch.
Page 6

2
2. Getting Started
In this chapter, we explain how to install a Moxa switch for the first time. There are three ways to access
the Moxa switch’s configuration settings: USB console, command line interface, or web-based interface. If
you do not know the Moxa switch’s IP address, you can open the USB console by connecting the Moxa
switch to a PC’s USB port with a USB cable. You can open the Telnet or web-based console over an Ethernet
LAN or over the Internet.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
USB Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
Configuration by Command Line Interface (CLI)
Configuration by Web Console
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access
Page 7
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-2
NOTE
A
console (serial or Telnet) at the same time.
NOTE
We recommend
. This software can be
downloaded free of charge from the Moxa website.
USB Console Configuration (115200, None, 8,
1, VT100)
Moxa switch allows multi-session connections (up to 6) by connecting to the web console and another
Before running PComm Terminal Emulator, first install the USB console driver on your PC and then connect
the Moxa switch’s USB console port to your PC’s USB port with a USB cable.
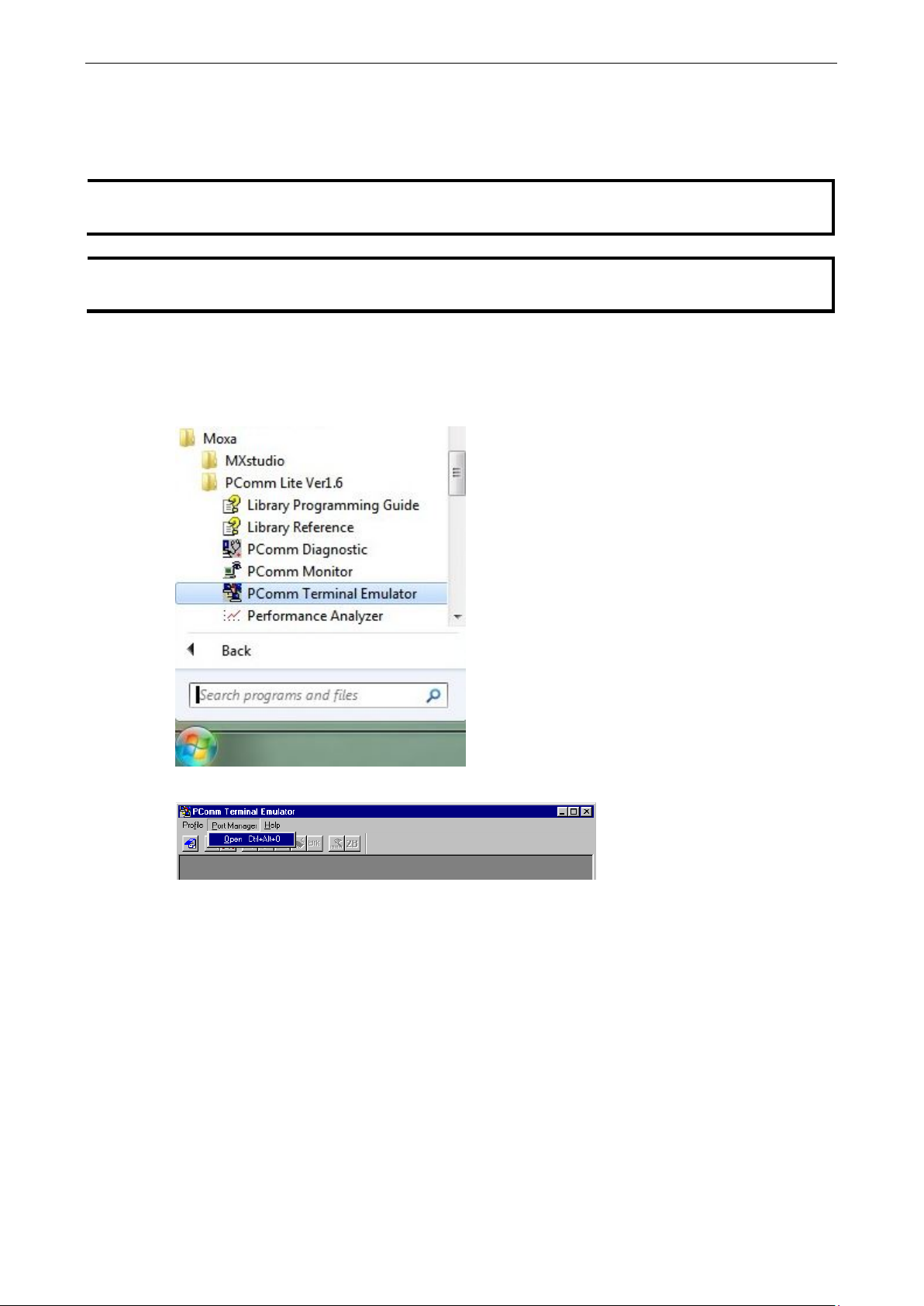
After installing PComm Terminal Emulator, open the Moxa switch’s USB console as follows:
1. From the Windows desktop, click Start
using PComm Terminal Emulator when opening the USB console
Moxa PComm Lite Ver1.6 Terminal Emulator.
2. Select Open under the Port Manager menu to open a new connection.
Page 8
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-3
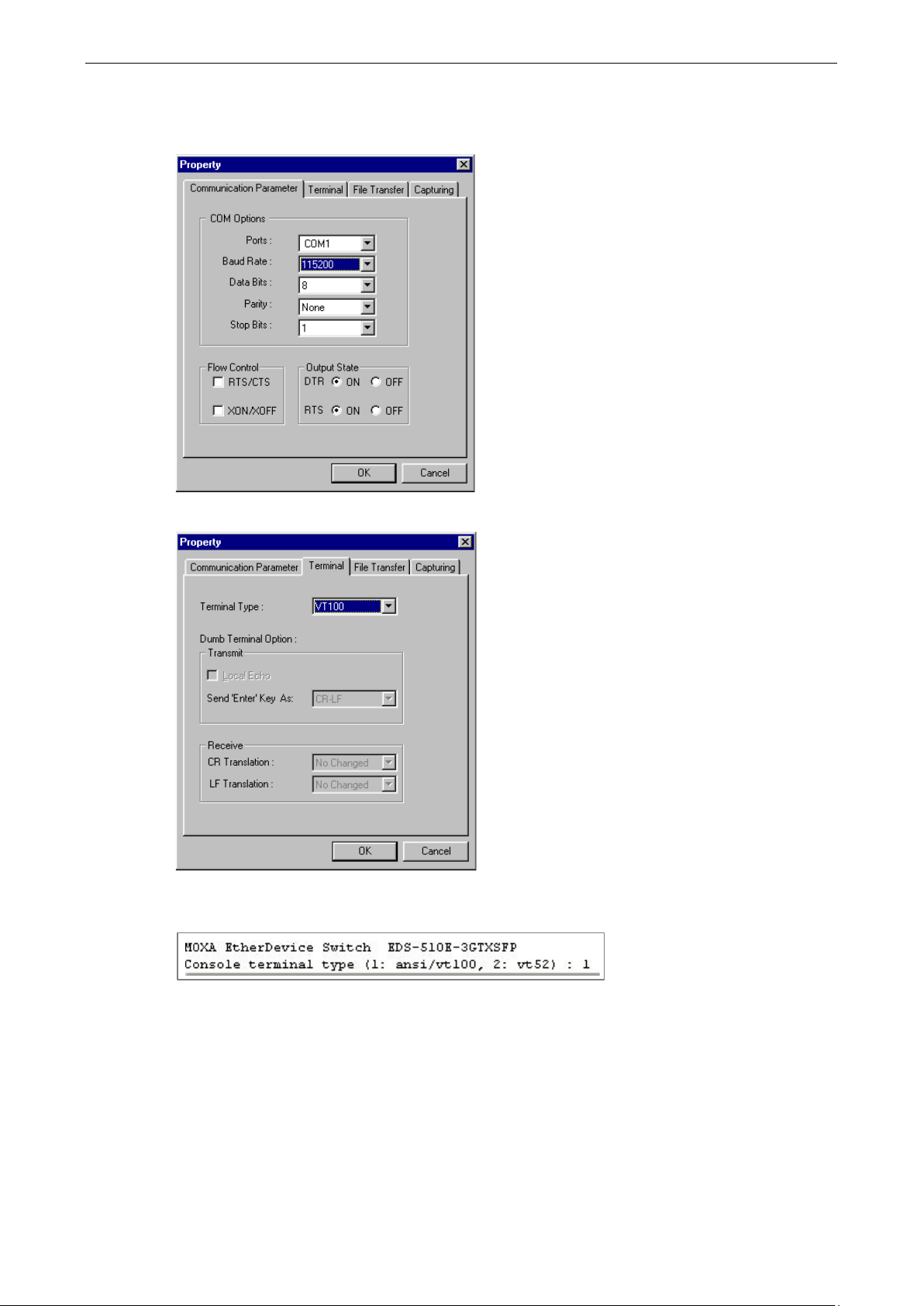
3. The Property window should open. On the Communication Parameter tab for Ports, select the COM
port that is being used for the console connection. Set the other fields as follows: 115200 for Baud
Rate, 8 for Data Bits, None for Parity, and 1 for Stop Bits.
4. On the Terminal tab, select VT100 for Terminal Type, and then click OK to continue.
5. In the terminal window, the Moxa switch will prompt you to select a terminal type. Enter 1 to select
ansi/vt100 and then press Enter.
Page 9

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-4
NOTE
By default, the
after
6. The USB console will prompt you to log in. Press Enter and select admin or user. Use the down arrow
key on your keyboard to select the Password field and enter a password if desired. This password will
be required to access any of the consoles (web, serial, Telnet).
you first log in to help keep your system secure.
7. The Main Menu of the Moxa switch’s USB console should appear. (In PComm Terminal Emulator, you
can adjust the font by selecting Font… from the Edit menu.)
password assigned to the Moxa switch is moxa. Be sure to change the default password
8. Use the following keys on your keyboard to navigate the Moxa switch’s USB console:
Key Function
Up, down, right, left arrow keys, Tab Move the onscreen cursor
Enter Display and select options
Space Toggle options
Esc Previous menu
Page 10
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-5
NOTE
To connect to the Moxa switch’s Telnet or web console, your PC host and the Moxa switch must be on the
same logical subnet.
NOTE
When connecting to the Moxa switch’s Telnet or web console, first connect one of the Moxa
Ethernet ports to your Ethernet LAN, or directly to your PC’s Ethernet port. You may use either a straight
through or cross
NOTE
The Moxa switch’s default IP address is 192.168.127.253.
Configuration by Command Line Interface
(CLI)
Opening the Moxa switch’s Telnet or web console over a network requires that the PC host and Moxa switch
are on the same logical subnet. You may need to adjust your PC host’s IP address and subnet mask. By
default, the Moxa switch’s IP address is 192.168.127.253 and the Moxa switch’s subnet mask is
255.255.255.0 (referred to as a Class B network). Your PC’s IP address must be set to 192.168.xxx.xxx if
the subnet mask is 255.255.0.0, or to 192.168.127.xxx if the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
-over Ethernet cable.
After making sure that the Moxa switch is connected to the same LAN and logical subnet as your PC, open
the Moxa switch’s Telnet console as follows:
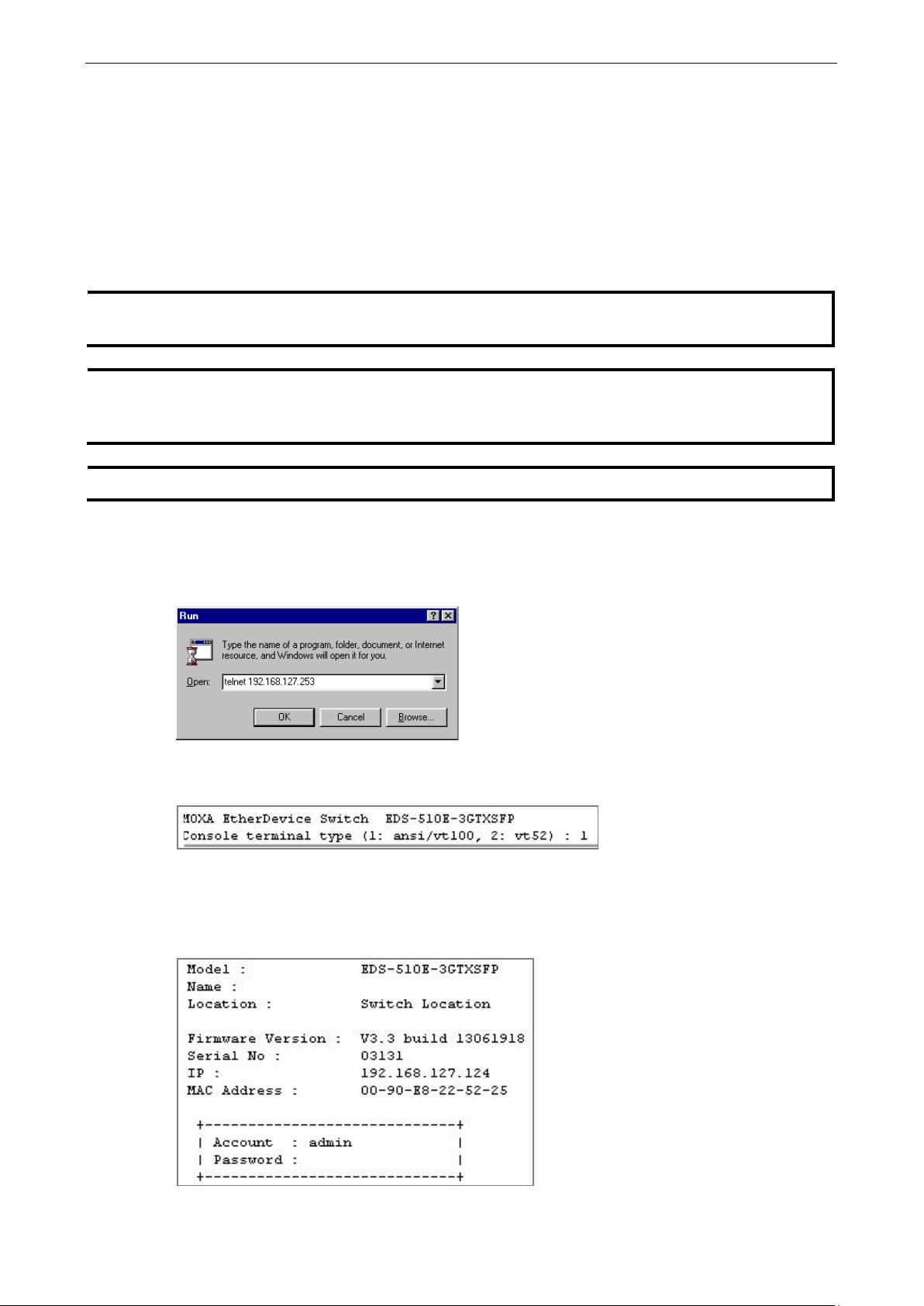
1. Click Start
the Windows Run window. You may also issue the Telnet command from a DOS prompt.
2. In the terminal window, the Telnet console will prompt you to select a terminal type. Type 1 to choose
ansi/vt100, and then press Enter.
Run from the Windows Start menu and then Telnet to the Moxa switch’s IP address from
switch’s
-
3. The Telnet console will prompt you to log in. Press Enter and then select admin or user. Use the down
arrow key on your keyboard to select the Password field and enter a password if desired. This
password will be required to access any of the consoles (web, serial, Telnet). If you do not wish to create
a password, leave the Password field blank and press Enter.
Page 11

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-6
NOTE
The Telnet console looks and operates in precisely the same manner as the
NOTE
When connecting
on the same logical subnet.
NOTE
If the Moxa switch is configured for other VLAN settings, you must make sure your PC host is on the
management
4. The Main Menu of the Moxa switch’s Telnet console should appear.
5. In the terminal window, select Preferences… from the Terminal menu on the menu bar.
6. The Terminal Preferences window should appear. Make sure that VT100 Arrows is checked.
7. Use the following keys on your keyboard to navigate the Moxa switch’s Telnet console:
Key Function
Up, down, right, left arrow keys, Tab Move the onscreen cursor
Enter Display and select options
Space Toggle options
Esc Previous menu
Configuration by Web Console
The Moxa switch’s web console is a convenient platform for modifying the configuration and accessing the
built-in monitoring and network management functions. You can open the Moxa switch’s web console using
a standard web browser, such as Internet Explorer.
to the Moxa switch’s Telnet or web console, your PC host and the Moxa switch must be
USB console.
VLAN.
Page 12
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-7
NOTE
When connecting to the Moxa switch’s Telnet or web console, first connect one of the Moxa switch’s
Ethernet ports to your Ethernet LAN, or directly to your PC’s Ethernet port. You may use either a straight
through or cross
NOTE
The Moxa switch’s default IP address is 192.168.127.253.
NOTE
By default, the
after
-
-over Ethernet cable.
After making sure that the Moxa switch is connected to the same LAN and logical subnet as your PC, open
the Moxa switch’s web console as follows:
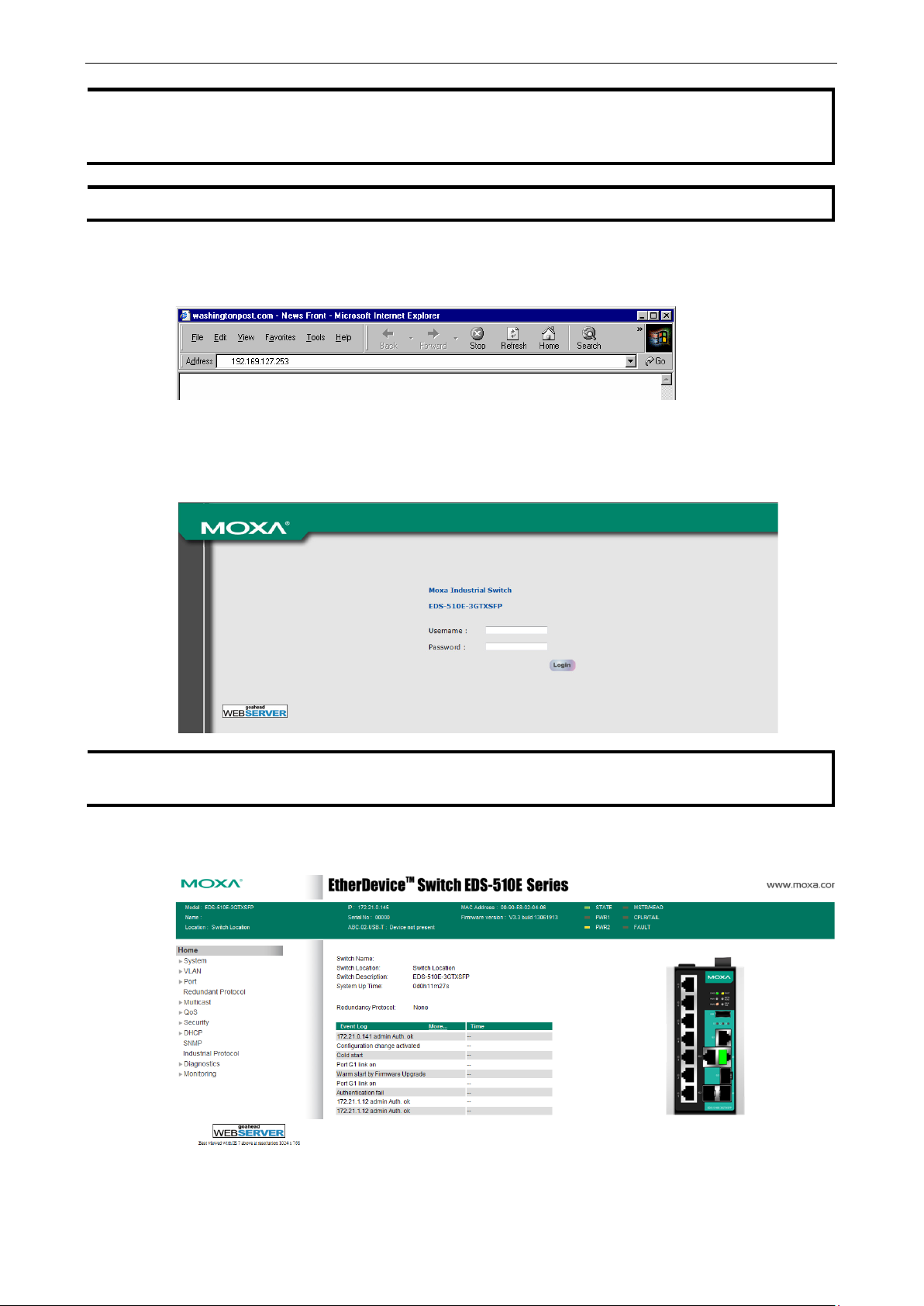
1. Connect your web browser to the Moxa switch’s IP address by entering it in the Address or URL field.
2. The Moxa switch’s web console will open, and you will be prompted to log in. Select the login account
(admin or user) and enter the Password. This password will be required to access any of the consoles
(web, serial, Telnet). If you do not wish to create a password, leave the Password field blank and press
Enter.
you first log in to help keep your system secure.
3. After logging in, you may need to wait a few moments for the web console to appear. Use the folders in
the left navigation panel to navigate between different pages of configuration options.
password assigned to the Moxa switch is moxa. Be sure to change the default password
Page 13

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Getting Started
2-8
Disabling Telnet and Browser Access
If you are connecting the Moxa switch to a public network but do not intend to manage it over the network,
we suggest disabling both the Telnet and web consoles. This is done from the USB console by navigating to
System Identification under Basic Settings
Console and Web Configuration as shown below:
System Information. Disable or enable the Telnet
Page 14

3
3. Featured Functions
In this chapter, we explain how to access the Moxa switch’s various configuration, monitoring, and
management functions. These functions can be accessed by USB console, Telnet console, or web console.
The USB console can be used if you do not know the Moxa switch’s IP address. To access the USB console,
connect switch’s USB port to your PC’s COM port. The Telnet and web consoles can be opened over an
Ethernet LAN or the Internet.
The web console is the most user-friendly interface for configuring a Moxa switch. In this chapter, we use
the web console interface to introduce the console functions. There are only a few differences between the
web console, USB console, and Telnet console.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Home
System Settings
PoE (PoE Models Only)
VLAN
Port
Multicast
QoS
Security
DHCP
SNMP
Industrial Protocols
Diagnostics
Monitoring
Tracking
Page 15
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-2
Home
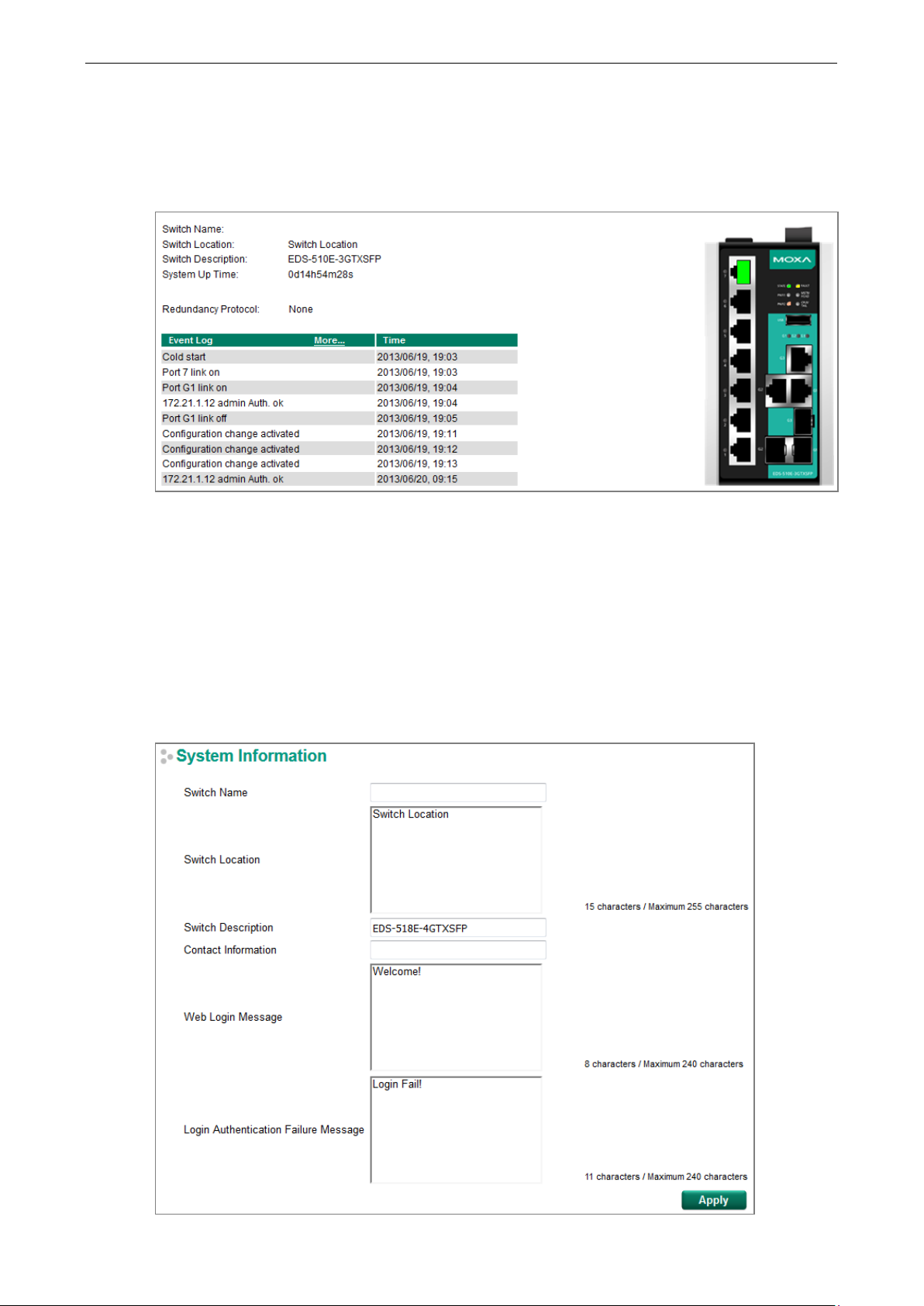
The Home page shows the summary of the Moxa switch information including System Information,
Redundancy Protocol, Event Log, and Device virtualization panel. By showing the switch's information and
event log, the operators can easily understand the system and port link status at a glance.
System Settings
The System Settings section includes the most common settings required by administrators to maintain
and control a Moxa switch.
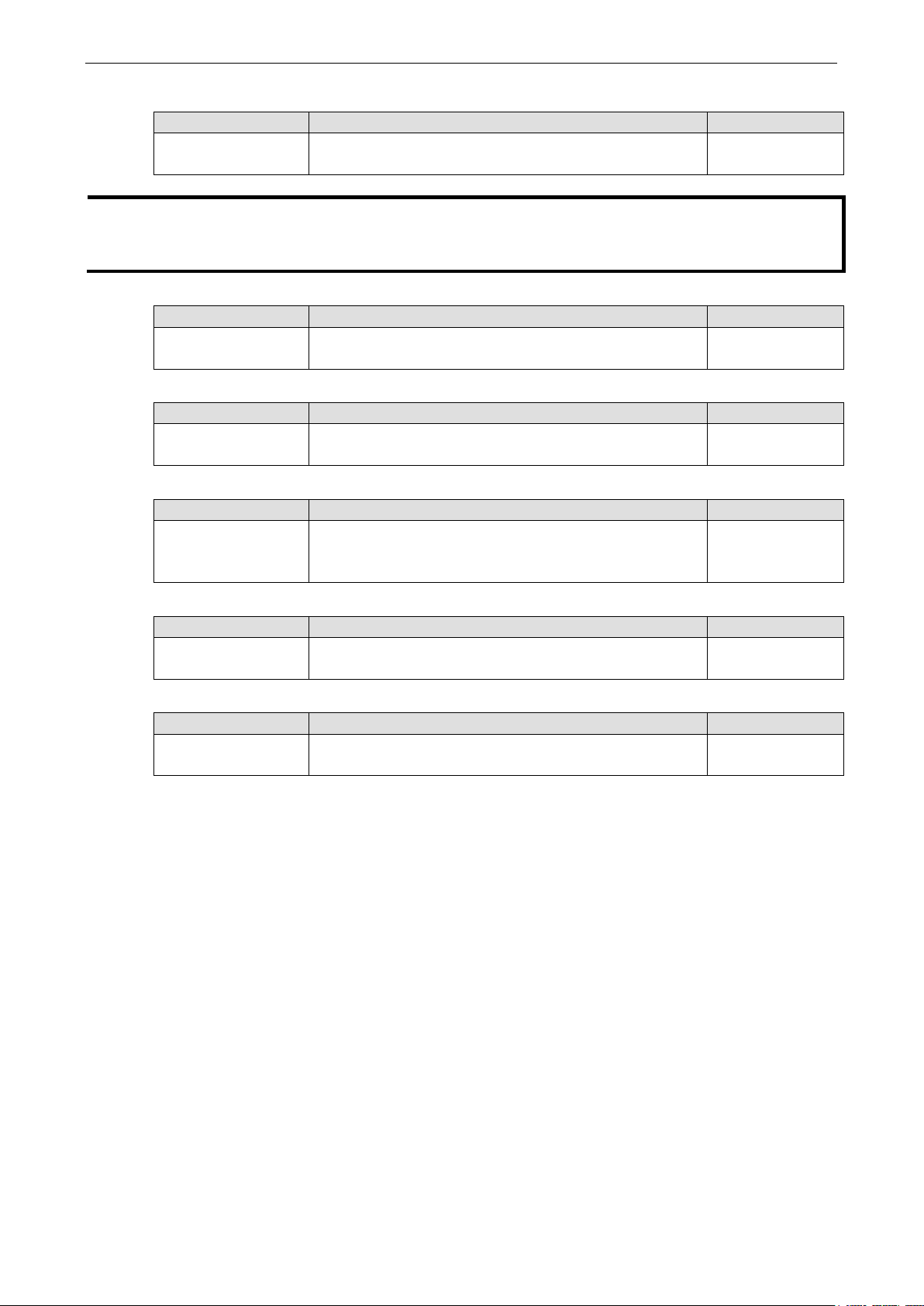
System Information
Define System Information items to make it easier to identify different switches that are connected to
your network.
Page 16
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-3
NOTE
The Switch Name field follows
character
xyzabcde=0...9 or
Switch Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30 characters This option is useful for differentiating between the roles or
applications of different units. Example: factorySwitch1
none
s, a-z/A-Z/0-9/-/., and the name cannot start with port-xyz or port-xyz-abcde where
is in the form n.n.n.n where n=0...9
Switch Location
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 255 characters This option is useful for differentiating between the locations
Switch Description
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30 characters This option is useful for recording a more detailed description
Contact Information
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30 characters This option is useful for providing information about who is
Web Login Message
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 240 characters This option is useful as it shows a message when a user’s
the PROFINET I/O naming rule. The name can only include any of these
Switch Location
of different switches. Example: production line 1.
Switch Model name
of the unit.
None
responsible for maintaining this unit and how to contact this
person.
Switch Location
login is successful
Login Authentication Failure Message
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 240 characters This option is useful as it shows a message when a user’s
login has failed
Switch Location
Page 17
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-4
NOTE
1.
change the password after
2.
User Account
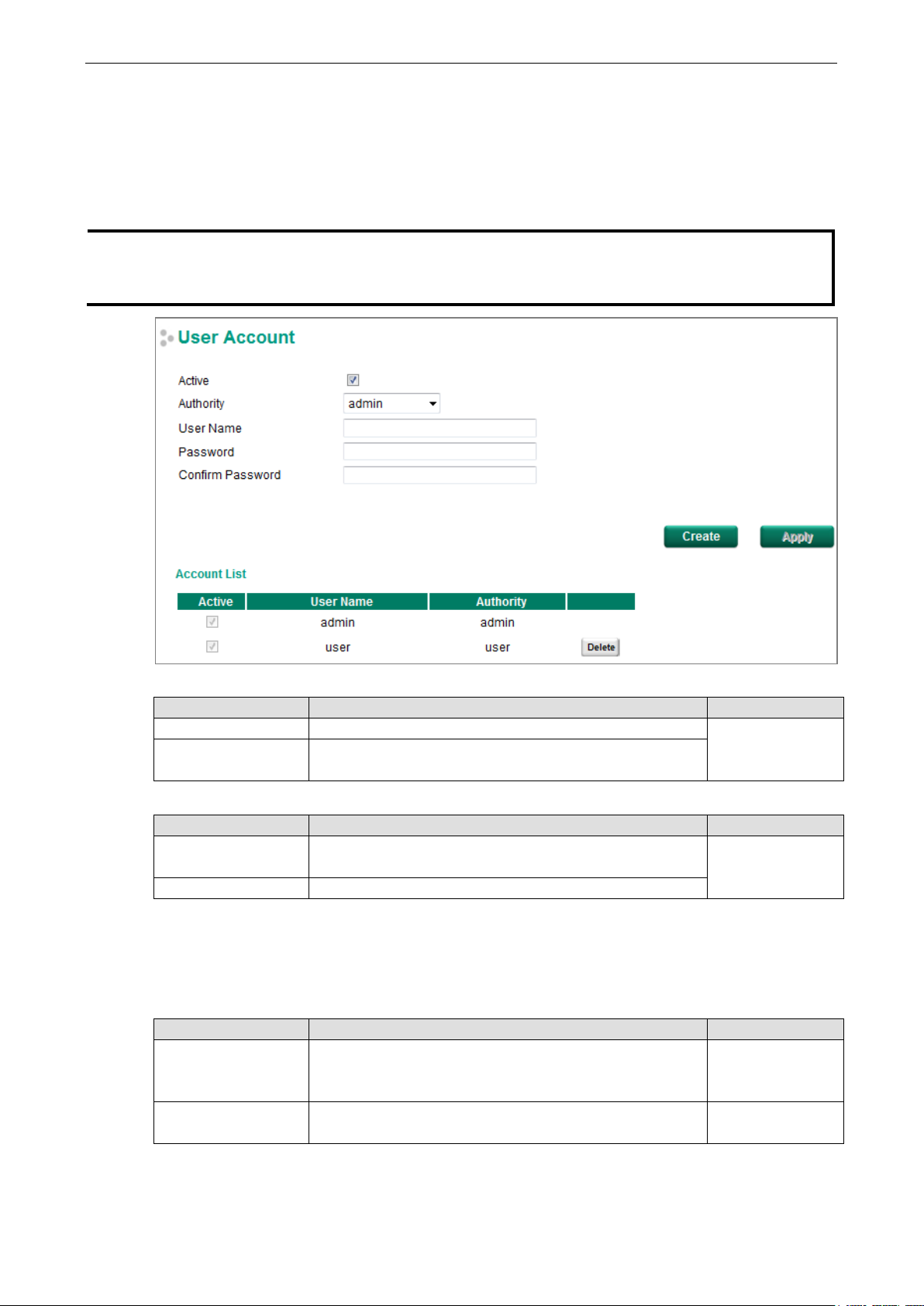
The Moxa switch supports the management of accounts, including establishing, activating, modifying,
disabling, and removing accounts. There are two levels of configuration access: admin and user. Accounts
with admin authority have read/write access of all configuration parameters, whereas accounts with user
authority only have read access to view configuration items.
In order to maintain a higher level of security, we strongly suggest that you
you first log in.
By default, the admin user account cannot be deleted or disabled.
Active
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked This account can access the switch’s configuration settings. Checked
Unchecked This account cannot access the switch’s configuration
Authority
Setting Description Factory Default
admin This account has read/write access of all configuration
user This account can only view configuration parameters.
Creating a New Account
Click Create, type in the user name and password, and assign an authority to the new account. Click Apply
to add the account to the Account List table.
Setting Description Factory Default
User Name
(Max. of 30
characters)
Password Password for the user account.
settings.
admin
parameters.
User Name None
None
(between 4 and 16 characters)
Page 18
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-5
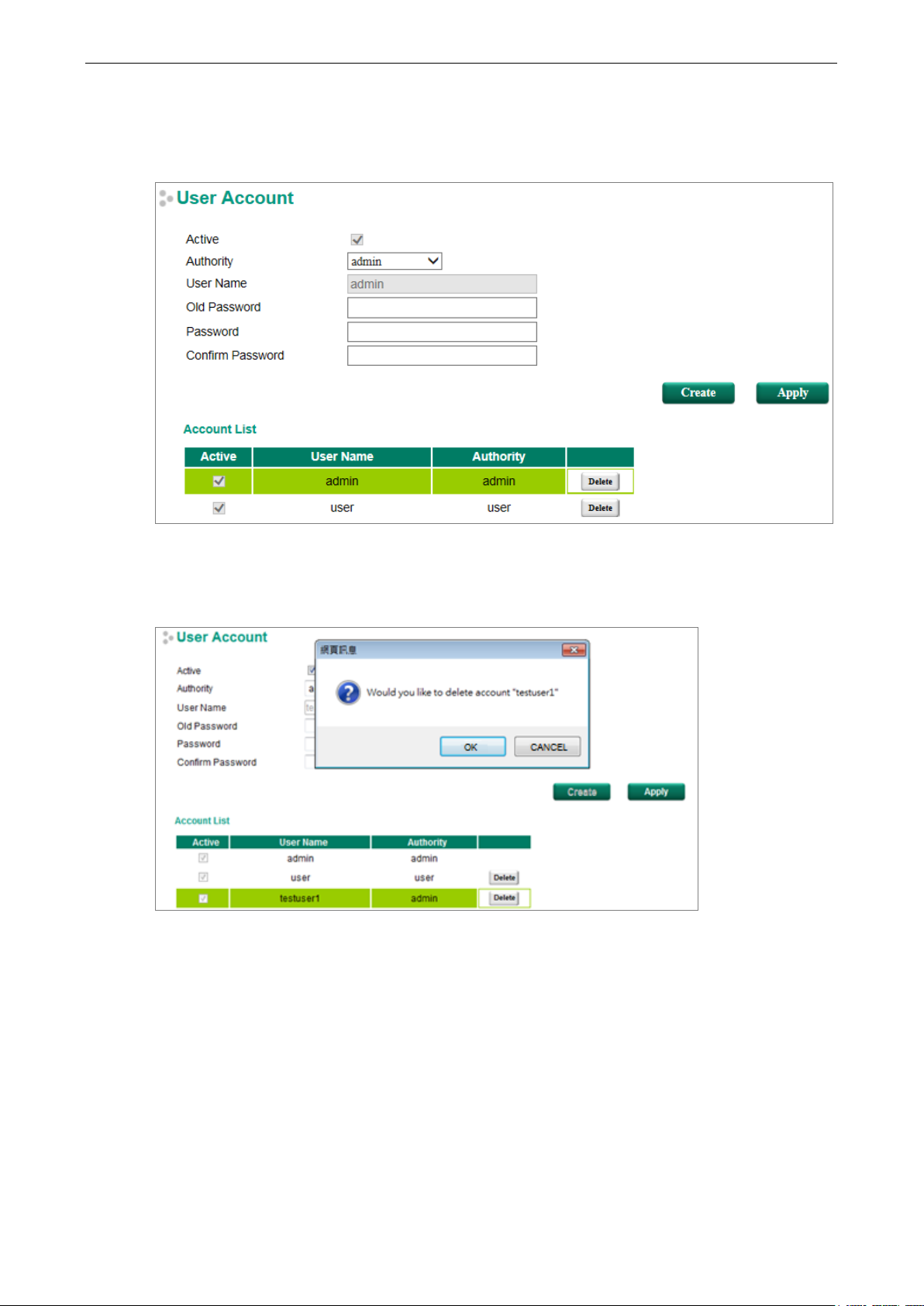
Modifying an Existing Account
Select an existing account from the Account List table, modify the account details, and then click Apply to
save the changes.
Deleting an Existing Account
Select an account from the Account List table and then click Delete to delete the account.
Page 19

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-6
Password Login Policy
In order to prevent hackers from cracking the password, Moxa switches allow users to configure a password
for their account and lock the account in the event that the wrong password is entered. The account
password policy requires passwords to be of a minimum length and complexity with a strength check. If
Account Login Failure Lockout is enabled, you will need to configure the Retry Failure Threshold and
Lockout Time parameters. If the number of login attempts exceeds the Retry Failure Threshold, users will
need to wait the number of minutes configured in Lockout Time before trying again.
Network
Network configuration allows users to configure both IPv4 and IPv6 parameters for management access
over the network. The Moxa switch supports both IPv4 and IPv6, and can be managed through either of
these address types.
Page 20
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-7
Class B network, or 255.255.255.0
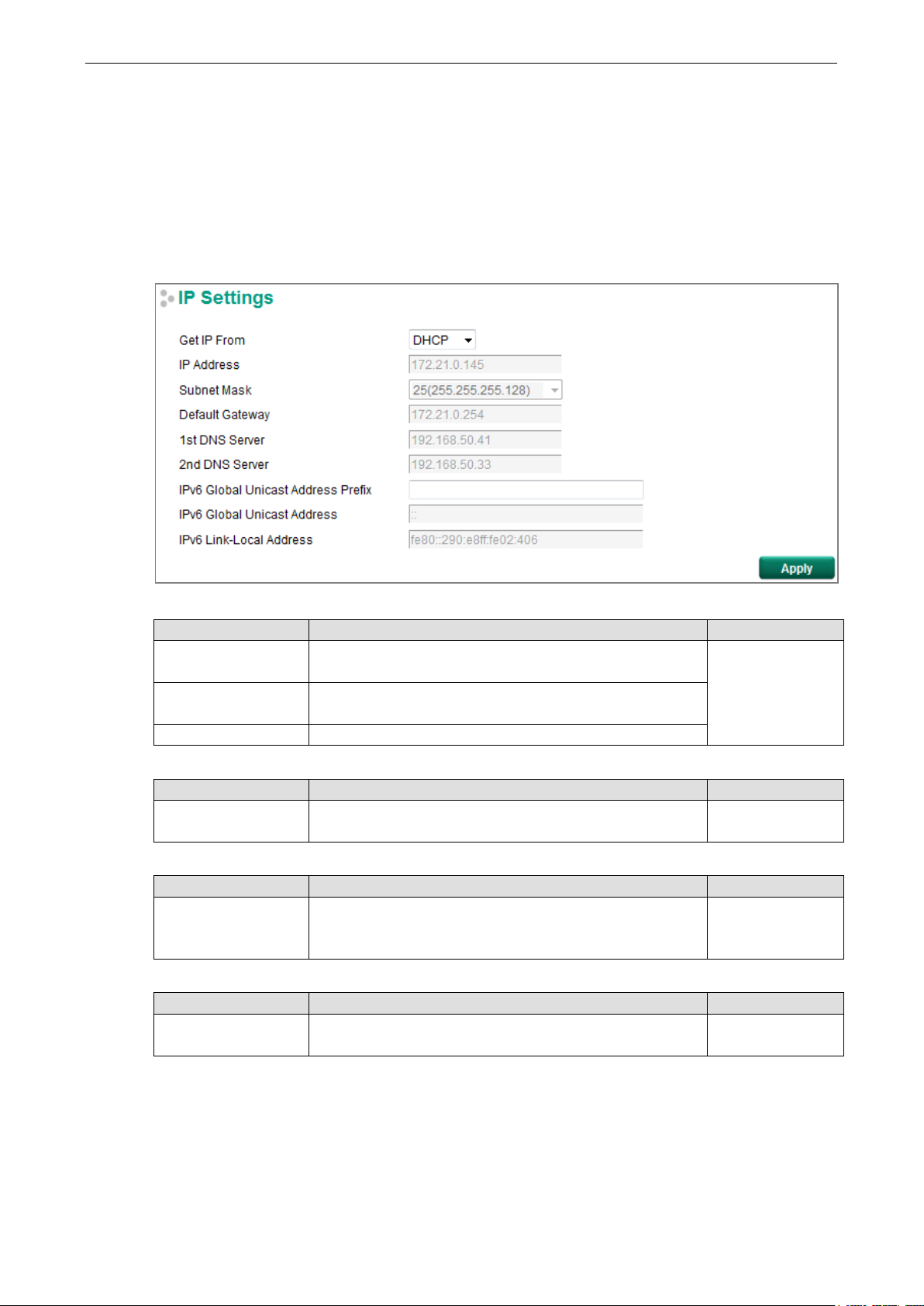
IP Settings
The IPv4 settings include the switch’s IP address and subnet mask, as well as the IP address of the default
gateway. In addition, input cells are provided for the IP addresses of a 1st and 2nd DNS server.
The IPv6 settings include two distinct address types—Link-Local Unicast addresses and Global Unicast
addresses. A Link-Local address makes the switch accessible over IPv6 for all devices attached to the same
local subnet. To connect to a larger network with multiple segments, the switch must be configured with a
Global Unicast address.
Get IP From
Setting Description Factory Default
DHCP The Moxa switch’s IP address will be assigned automatically
by the network’s DHCP server.
BOOTP The Moxa switch’s IP address will be assigned automatically
by the network’s BootP server.
Manual The Moxa switch’s IP address must be set manually.
IP Address
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for the
Moxa switch
Subnet Mask
Setting Description Factory Default
Subnet mask for the
Moxa switch
Default Gateway
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address for gateway Specifies the IP address of the router that connects the LAN
Assigns the Moxa switch’s IP address on a TCP/IP network. 192.168.127.253
Identifies the type of network the Moxa switch is connected
to (e.g., 255.255.0.0 for a
for a Class C network).
to an outside network.
Manual
24(255.255.255.0)
None
Page 21
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-8
Local address is FE80 and the
DNS Server IP Addresses
Setting Description Factory Default
1st DNS Server Specifies the IP address of the DNS server used by your
network. After specifying the DNS server’s IP address, you
can use the Moxa switch’s URL (e.g., www.PT.company.com)
to open the web console instead of entering the IP address.
2nd DNS Server Specifies the IP address of the secondary DNS server used by
your network. The Moxa switch will use the secondary DNS
server if the first DNS server fails to connect.
IPv6 Global Unicast Address Prefix (Prefix Length: 64 bits) Default Gateway
Setting Description Factory Default
Global Unicast Address
Prefix
IPv6 Global Unicast Address
Setting Description Factory Default
None Displays the IPv6 Global Unicast address. The network
The prefix value must be formatted according to the RFC
2373 “IPv6 Addressing Architecture,” using 8 colon-separated
16-bit hexadecimal values. One double colon may be used in
the address to indicate the appropriate number of zeros
required to fill the undefined fields.
portion of the Global Unicast address can be configured by
specifying the Global Unicast Prefix and using an EUI-64
interface ID in the low order 64 bits. The host portion of the
Global Unicast address is automatically generated using the
modified EUI-64 form of the interface identifier (Switch’s MAC
address).
None
None
None
None
IPv6 Link-Local Address
Setting Description Factory Default
None The network portion of the Link-
host portion of the Link-Local address is automatically
generated using the modified EUI-64 form of the interface
identifier (Switch’s MAC address).
None
IPv6 Neighbor Cache
The IPv6 neighbor cache includes the neighboring node’s IPv6 address, the corresponding Link-Layer
address, and the current state of the entry.
Page 22
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-9
NOTE
The user must update the Current Time and Current Date after powering off the switch for a long period of
time (for example a few days). The user must pay particular attention to this when there is no NTP server,
LAN, or Internet connection.
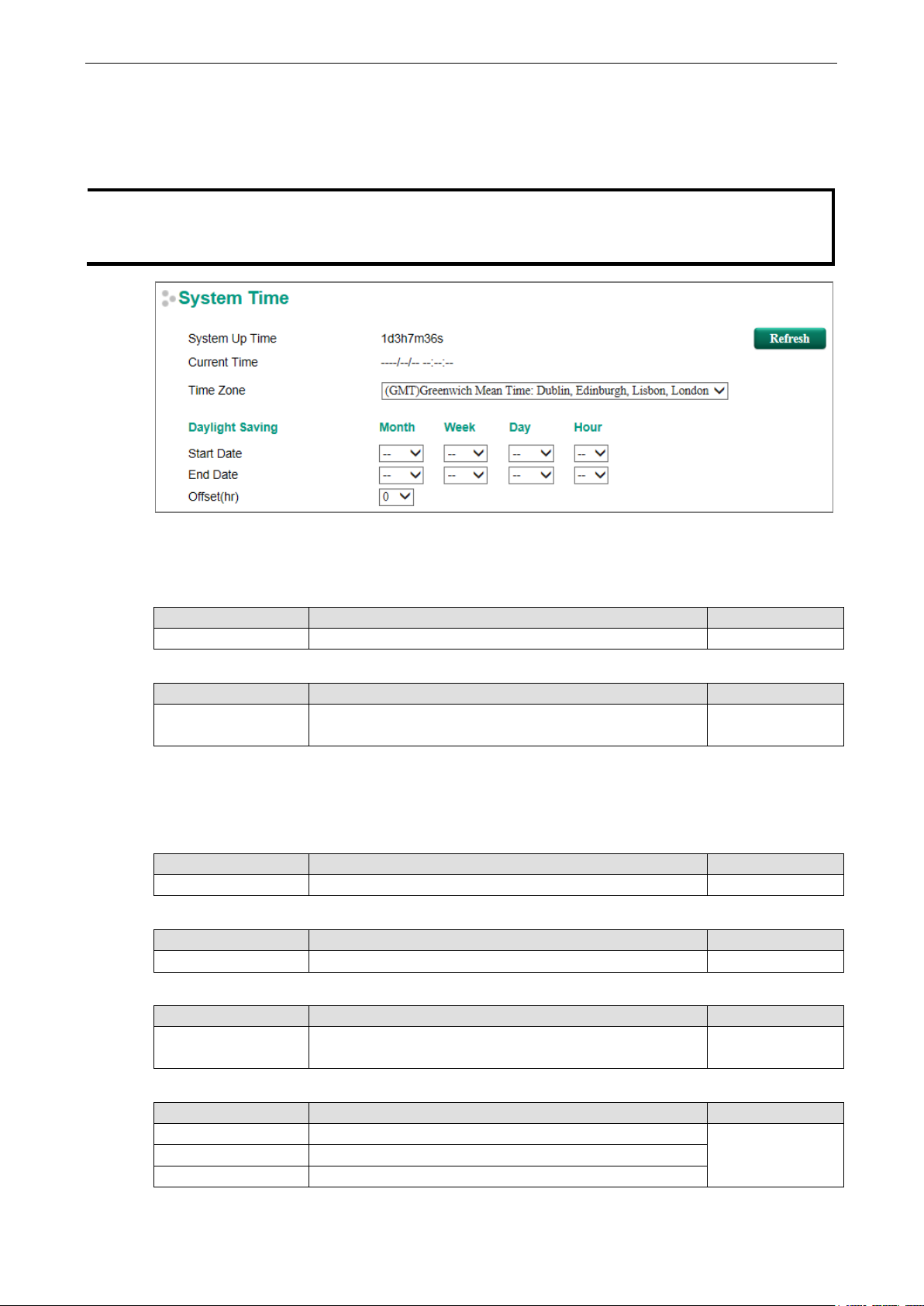
Date and Time
The Moxa switch has a time calibration function based on information from an NTP server or user specified
time and date, allowing functions such as automatic warning emails to include a time and date stamp.
System Up Time
Indicates how long the Moxa switch has been up and running since the last cold start.
Current Time
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified time Indicates time in yyyy-mm-dd format. None
Time Zone
Setting Description Factory Default
Time zone Specifies the time zone, which is used to determine the local
time offset from GMT (Greenwich Mean Time).
GMT (Greenwich
Mean Time)
Daylight Saving Time
The Daylight Saving Time settings are used to automatically set the Moxa switch’s time ahead according to
national standards.
Start Date
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified date Specifies the date that Daylight Saving Time begins. None
End Date
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified date Specifies the date that Daylight Saving Time ends. None
Offset
Setting Description Factory Default
User-specified hour Specifies the number of hours that the time should be set
forward during Daylight Saving Time.
Clock Source
Setting Description Factory Default
Local Configure clock source from local time Local
NTP Configure clock source from NTP
SNTP Configure clock source from SNTP
None
Page 23
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-10
Clock Source is from Local
Time Setting
The Time settings are set manually or synced automatically with Moxa’s switch time.
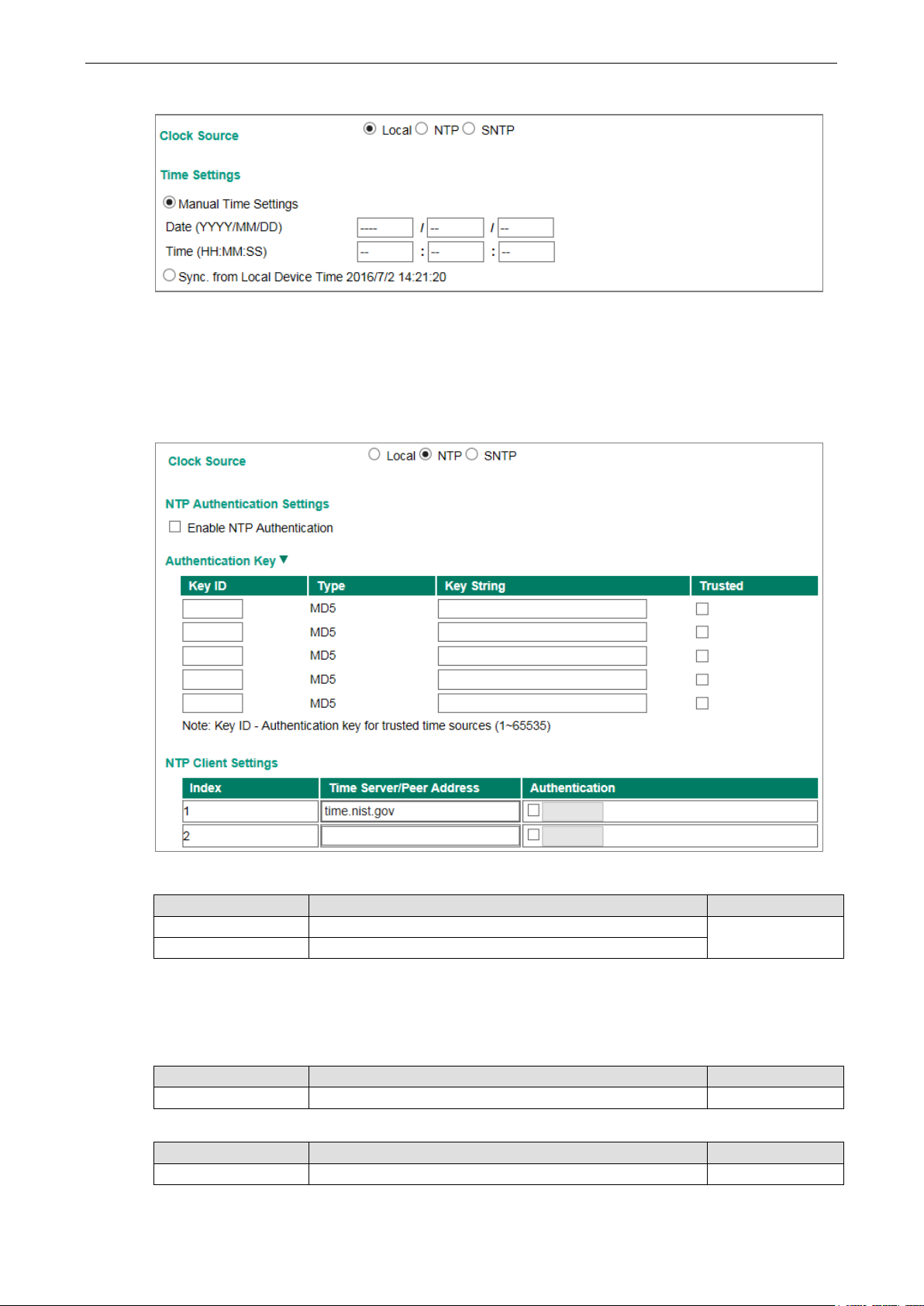
Clock Source is from NTP
The Moxa switch can work as an NTP client or NTP server. The user can enable the NTP Authentication
function to do authentication with configured Authentication Key between the NTP client and NTP server.
NTP Authentication Settings
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Enable NTP Authentication Unchecked
Unchecked Disable NTP Authentication
Authentication Key
The user is able to configure up to five Authentication Keys in Moxa’s switch database. Those Keys are
encrypted by type MD5 and authorized between the NTP server and the NTP client.
Key ID
Setting Description Factory Default
Key ID The ID of Authentication Key Unchecked
Key String
Setting Description Factory Default
Key String The Password of Authentication Key Unchecked
Page 24
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-11
NOTE
Changing the time zone will automatically correct the current time. Be sure to set the time zone before
setting the time.
Trusted
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Enable the Authentication Key Unchecked
Unchecked Disable the Authentication Key
NTP Client Settings
The NTP server should be set when the Moxa switch is configured to work as an NTP client.
Setting Description Factory Default
Time Server/Peer
Address
Authentication
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Enable NTP Authentication Unchecked
Unchecked Disable NTP Authentication.
Key ID Set Key ID that is used to be authorized Null
The domain of Time Server or Peer Address time.nist.gov
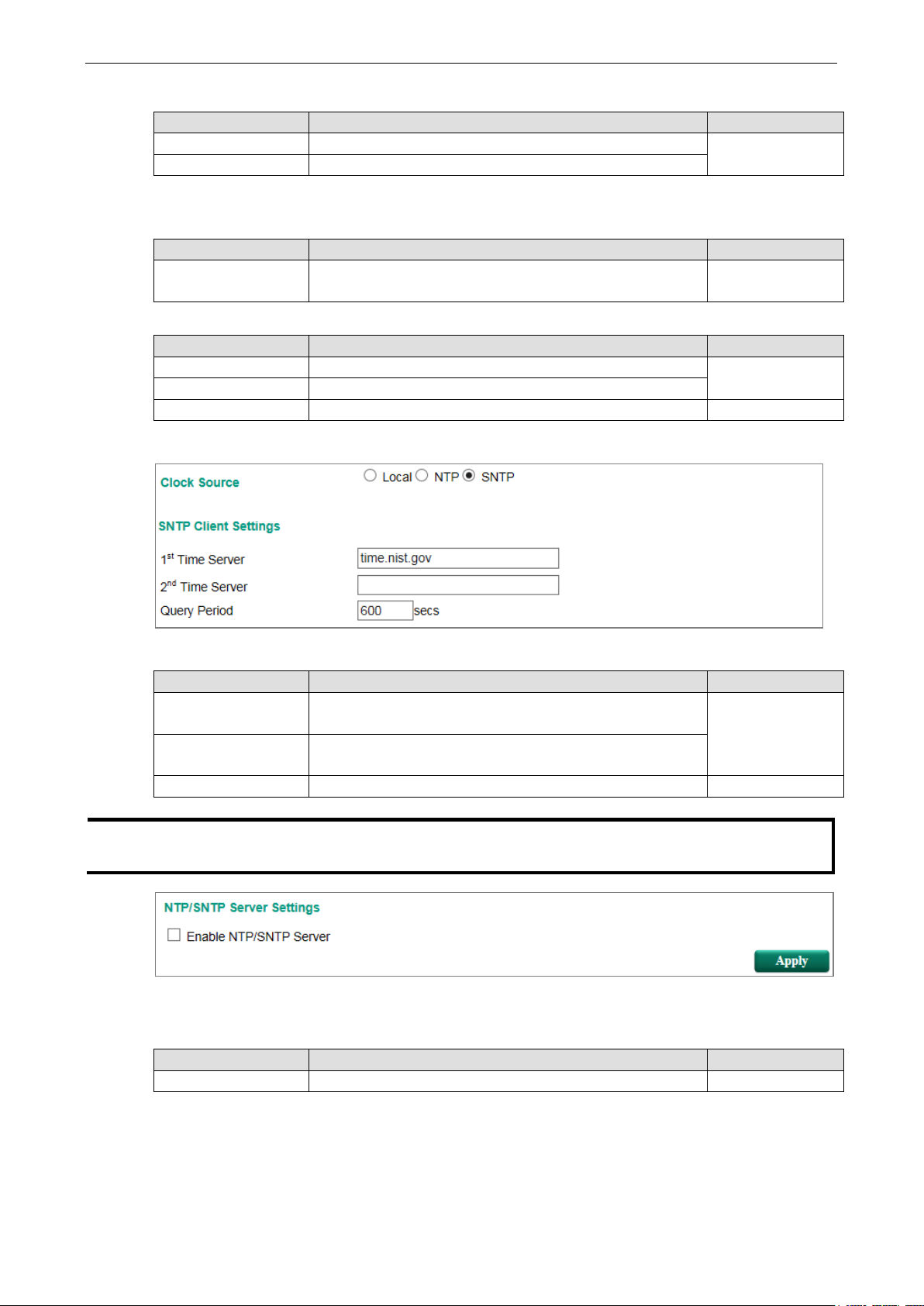
Clock Source is from SNTP
SNTP Client Settings
Setting Description Factory Default
1st Time Server The IP or domain address (e.g., 192.168.1.1,
time.stdtime.gov.tw, or time.nist.gov).
2nd Time Server The Moxa switch will try to locate the secondary SNTP server
if the first SNTP server fails to connect.
Query Period The time period to sync with time server 600secs
The NTP server should be enabled when the Moxa switch is configured to work as an NTP server.
Enable NTP/SNTP Server
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Enables SNTP/NTP server functionality for clients Disabled
Time.nist.gov
Page 25
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-12
IEEE 1588 PTP
The following information is taken from the NIST website at http://ieee1588.nist.gov/intro.htm:
“Time measurement can be accomplished using the IEEE Standard for a Precision Clock Synchronization
Protocol for Networked Measurement and Control Systems (IEEE 1588-2008) to synchronize real-time
clocks incorporated within each component of the electrical power system for power automation
applications.
IEEE 1588, which was published in November 2002, expands the performance capabilities of Ethernet
networks to control systems that operate over a communication network. In recent years an increasing
number of electrical power systems have been using a more distributed architecture with network
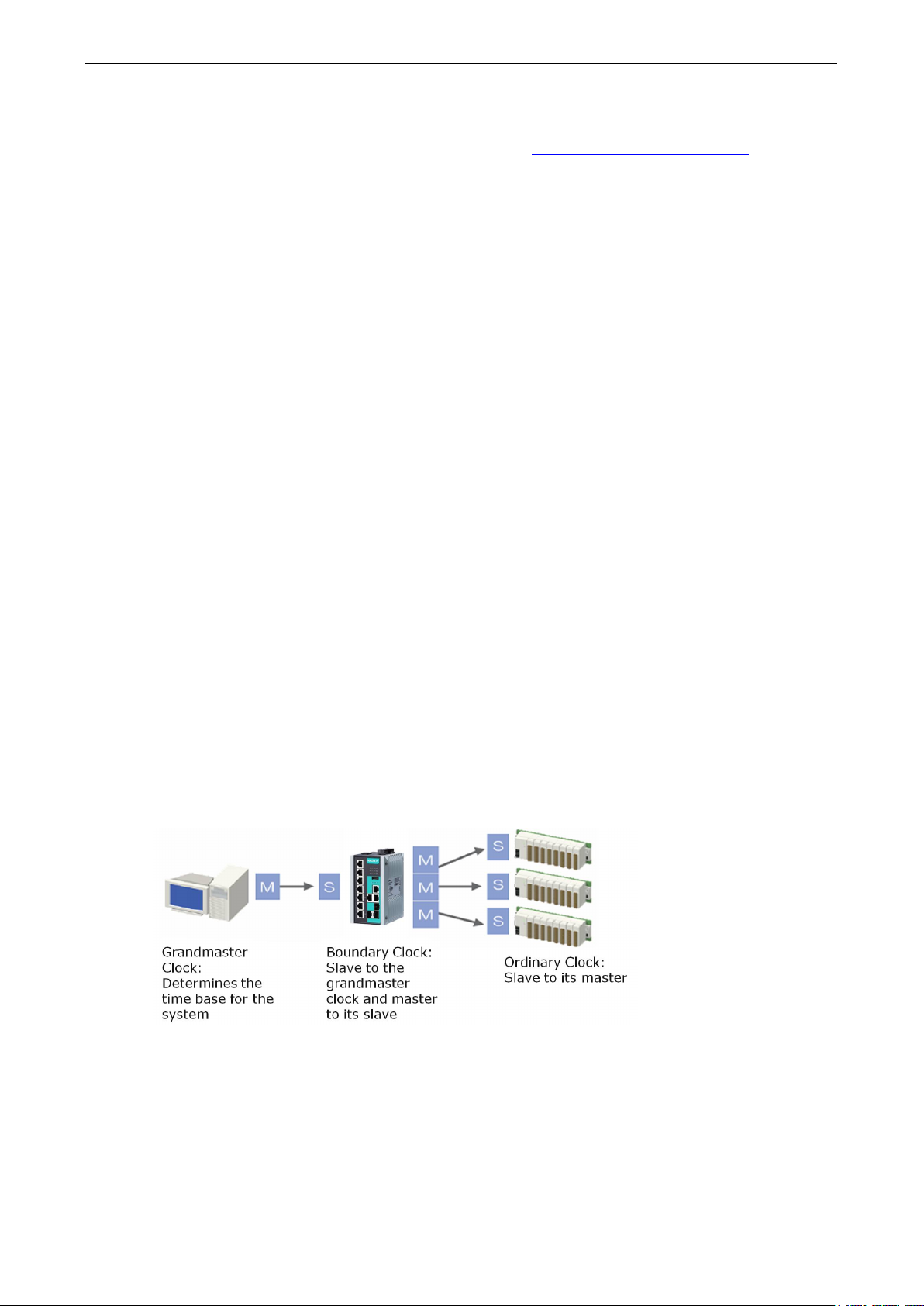
technologies that have less stringent timing specifications. IEEE 1588 generates a master-slave relationship
between the clocks, and enforces the specific timing requirements in such power systems. All devices
ultimately get their time from a clock known as the grandmaster clock. In its basic form, the protocol is
intended to be administration free.”
How Does an Ethernet Switch Affect 1588 Synchronization?
The following content is taken from the NIST website at http://ieee1588.nist.gov/switch.htm:
“An Ethernet switch potentially introduces multi-microsecond fluctuations in the latency between the 1588
grandmaster clock and a 1588 slave clock. Uncorrected these fluctuations will cause synchronization errors.
The magnitude of these fluctuations depends on the design of the Ethernet switch and the details of the
communication traffic. Experiments with prototype implementations of IEEE 1588 indicate that with suitable
care the effect of these fluctuations can be successfully managed. For example, use of appropriate statistics
in the 1588 devices to recognize significant fluctuations and use suitable averaging techniques in the
algorithms controlling the correction of the local 1588 clock will be good design means to achieve the
highest time accuracy.”
Can Ethernet switches be designed to avoid the effects of these
fluctuations?
A switch can be designed to support IEEE 1588 while avoiding the effects of queuing. In this case two
modifications to the usual design of an Ethernet switch are necessary:
1. The Boundary Clock and Transparent Clock functionalities defined by IEEE 1588 must be
implemented in the switch.
2. The switch must be configured so that it does not pass IEEE 1588 message traffic using the normal
communication mechanisms of the switch.
Such an Ethernet switch will synchronize clocks directly connected to one of its ports to the highest possible
accuracy.
Page 26

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-13
PTP Settings
Operation
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable IEEE 1588 PTP Globally disables or enables IEEE 1588 operation. Disabled
Clock Mode (sets the switch’s clock mode)
Setting Description Factory Default
v1 BC Operates as an IEEE 1588 v1 boundary clock. v1 BC
v2 E2E 2-step TC Operates as an edge-to-edge IEEE 1588 v2 transparent clock
with 2-step method.
v2 P2P 2-step TC Operates as a peer-to-peer IEEE 1588 v2 transparent clock
with 2-step method.
v2 E2E BC Operates as an edge-to-edge IEEE 1588 v2 boundary clock
v2 P2P BC Operates as a peer-to-peer IEEE 1588 v2 boundary clock
SyncInterval (sets the synchronization message time interval)
Setting Description Factory Default
0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 0 (1 s), 1 (2 s), 2 (4 s), 3 (8 s), or 4 (16 s). Supported by
IEEE 1588 V1.
-3, -2, -1, 0, or 1 -3 (128 ms), -2 (256 ms), -1 (512 ms), 0 (1 s), or 1 (2 s).
Supported in IEEE 1588 V2.
Delay-request Minimum Interval
Setting Description Factory Default
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 Minimum delay request message interval 0 (1 sec.)
0
Domain
Setting Description Factory Default
_DFLT (0), _ALT(1),
_ALT(2), or _ALT(3)
Transport mode
Setting Description Factory Default
IPv4 or 802.3/Ethernet IEEE 1588 PTP V1 supports IPv4 only
Subdomain name (IEEE 1588-2002) or the domain Number
(IEEE 1588-2008) fields in PTP messages
IEEE 1588 PTP V2 supports both IPv4 and IPv6.
0(default domain)
IPv4
Page 27
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-14
Slave
Master during
Role
Setting Description Factory Default
Member or Master Set this switch to be the Member or Grand Master Member
If a different mode is selected, you will also need to configure the following settings.
Announce Interval (sets the announce message interval)
Setting Description Factory Default
0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 0 (1 s), 1 (2 s), 2 (4 s), 3 (8 s), or 4 (16 s) 1 (2 s)
Announce Timeout
Setting Description Factory Default
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
or 10
PDelay-request Minimum Interval
Setting Description Factory Default
-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 Minimal delay request message interval:
The timeout period between Announce messages. If the
hasn’t received an Announce message from the
this time period, the Slave becomes the Master and
renegotiation begins.
-1 (512 ms), 0 (1 s), 1 (2 s), 2 (4 s), 3 (8 s), 4 (16 s),
5(32s)
(Available in Clock Mode: v2 P2P 2-step TC, and v2 P2P BC)
3
0 (1 sec)
priority1
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 255 Set first priority value; 0 = highest priority, 255 = lowest
priority.
priority2
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 255 Set second priority value; 0 = highest priority, 255 = lowest
priority.
Clock Class
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 255 The clock Class attribute denotes the traceability of the time
or frequency distributed by the grandmaster clock.
Clock Accuracy
Setting Description Factory Default
0x21 The Clock Accuracy characterizes a clock for the purpose of
the best master clock (BMC) algorithm. This value is fixed at
0x21, which means the time of the EDS switch is accurate to
within 100 ns.
128
128
248
0x21
Page 28
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-15
Timescale Type
Setting Description Factory Default
PTP or ARB • PTP timescale: In normal operation, the epoch is the PTP
epoch and the timescale is continuous. The time unit is SI
seconds, as realized on the rotating geoid (SI:
International System).
• ARB timescale: In normal operation, the epoch is set by
an administrative procedure. The epoch can be reset
during normal operation. Between invocations of the
administrative procedure, the timescale is continuous.
Additional invocations of the administrative procedure
may introduce discontinuities in the overall timescale.
ARB Time
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 255 The geoid of the PTP clock reference time (seconds). 0
Leap59
Setting Description Factory Default
True or False The last minute of the current UTC day contains 59 seconds.
If the epoch is not PTP, the value will be set to FALSE.
PTP
False
Leap61
Setting Description Factory Default
True or False The last minute of the current UTC day contains 61 seconds.
If the epoch is not PTP, the value will be set to FALSE.
UTC Offset Valid
Setting Description Factory Default
True or False The initialization value will be TRUE if the value of the current
UTC offset is known to be correct; otherwise, it will be FALSE.
UTC Offset
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 255 The known UTC offset (seconds). 0
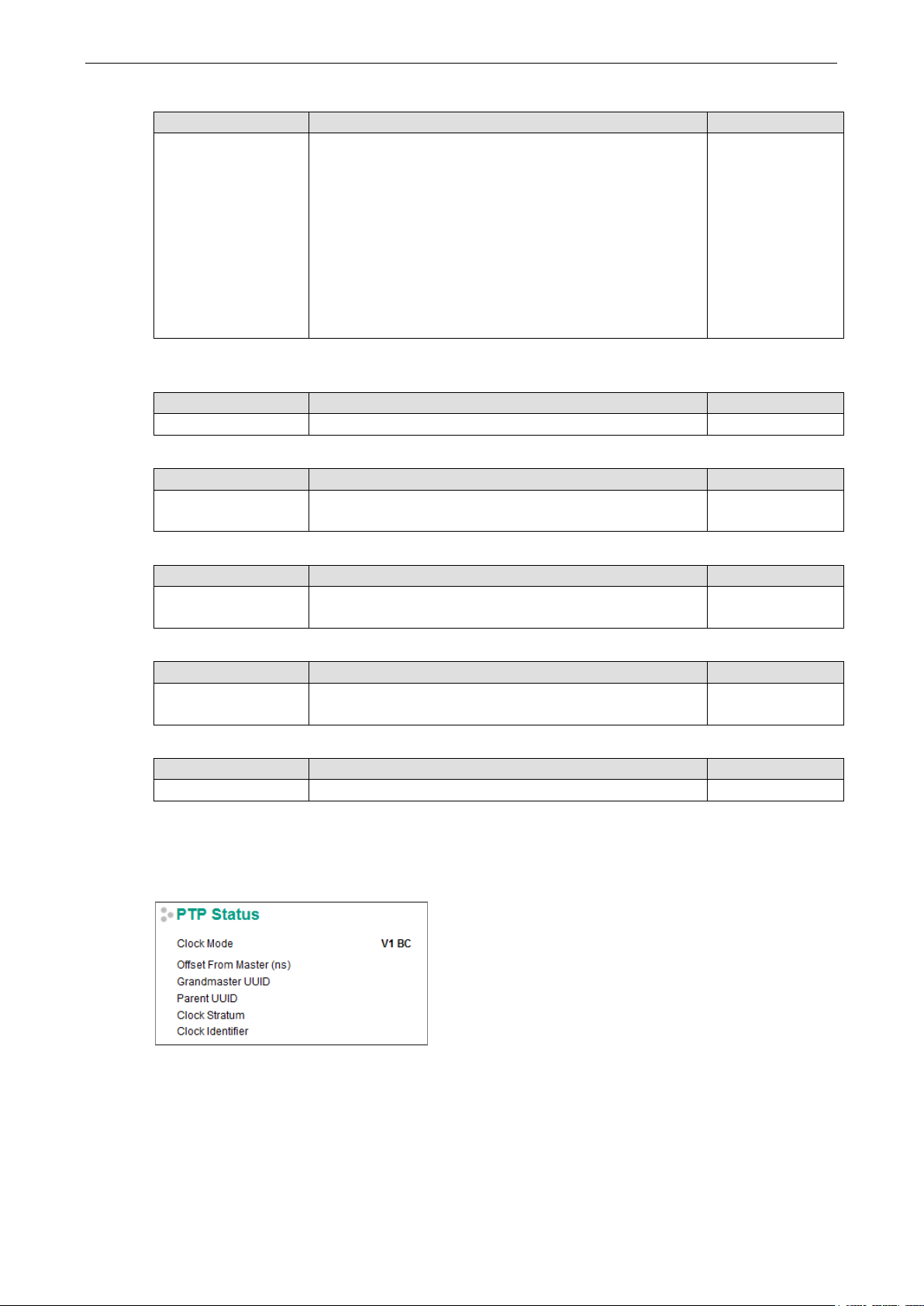
PTP Status
Indicates the current IEEE 1588 PTP status.
False
False
Page 29
Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-16
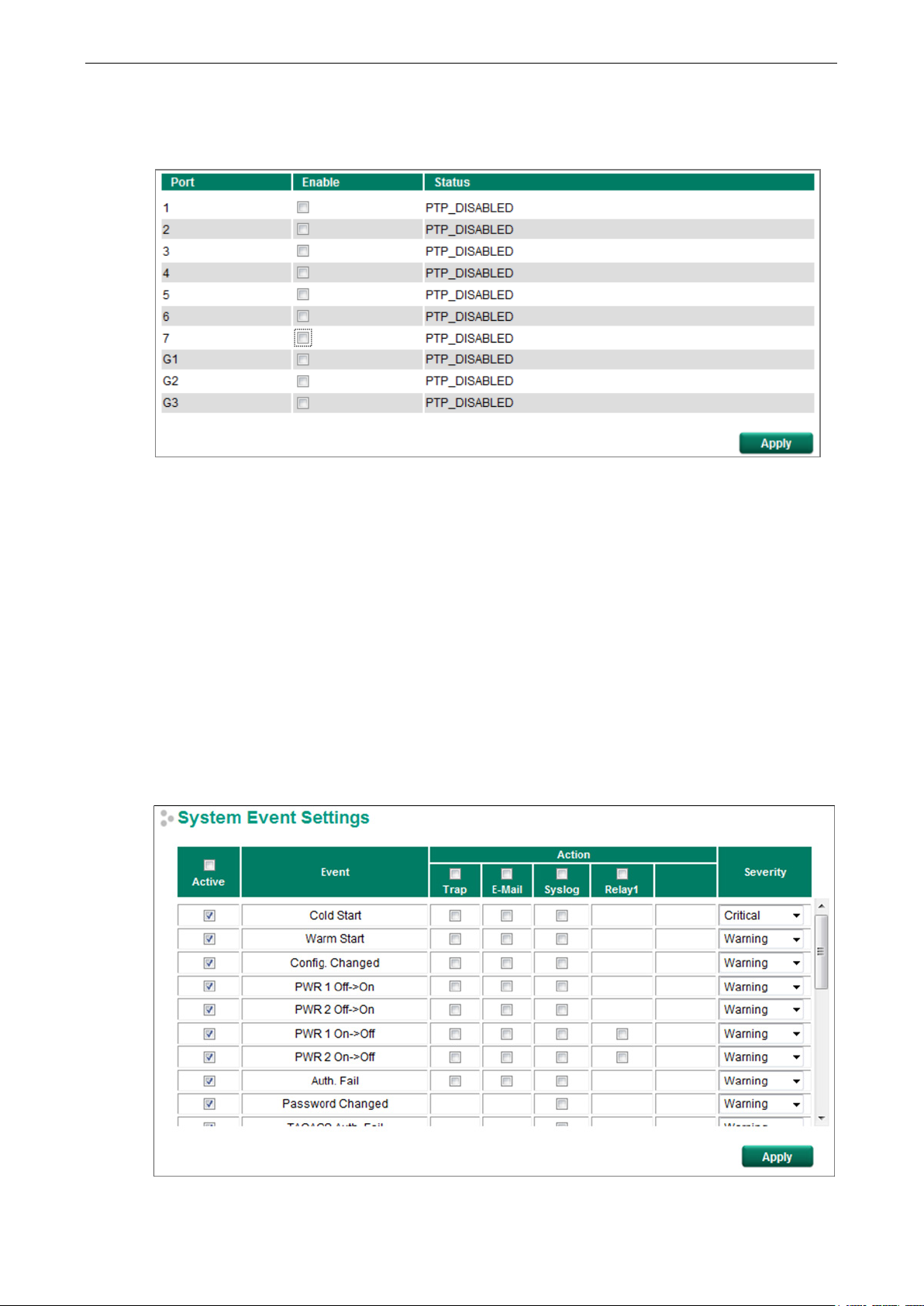
PTP Port Settings
Enable/Disable the PTP setting for each port.
Warning Notification
Since industrial Ethernet devices are often located at the endpoints of a system, these devices will not
always know what is happening elsewhere on the network. This means that an industrial Ethernet switch
that connects to these devices must provide system maintainers with real-time alarm messages. Even when
control engineers are out of the control room for an extended period of time, they can still be informed of
the status of devices almost instantaneously when exceptions occur. The Moxa switch supports different
approaches to warn engineers automatically, such as email, trap, syslog and relay output. It also supports
two digital inputs to integrate sensors into your system to automate alarms by email and relay output.
System Event Settings
System Events are related to the overall function of the switch. Each event can be activated independently
with different warning approaches. The Administrator can decide the severity of each system event.
Page 30

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-17
System Events Description
Cold Start Power is cut off and then reconnected.
Warm Start The Moxa switch is rebooted, such as when network parameters are
changed (IP address, subnet mask, etc.).
Configuration Change Any configuration item has been changed.
Power Transition (OnOff) The Moxa switch is powered down. (The relay will not be triggered when
the device is powered up.)
Power Transition (OffOn) The Moxa switch is powered up.
Login Success The account logins to the switch
Login Fail An incorrect password was entered.
TACACS+ Auth. Success The account is authorized by a TACACS+ server
TACACS Auth. Fail Incorrect authentication details were entered
RADIUS Auth. Success The account is authorized by a RADIUS server
RADIUS Authentication Fail Incorrect authentication details were entered
Password Change User changes the account password
Topology Changed • If the Master of the Turbo Ring has changed or the backup path is
activated
• If the Turbo Ring path is disconnected
• If the MSTP topology has changed
Coupling Changed Backup path is activated
Master Changed Master of the Turbo Ring has changed
Master Mismatch When the duplicate master (two or more) or non-master is set up, if any
Turbo Ring path/switch fails, the duplicate master switches will
automatically renegotiate to determine a new master.
RSTP Root Changed If the RSTP root has changed
RSTP Topo. Changed If any Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol switches have changed their position
(applies only to the root of the tree)
Turbo Ring Break Turbo Ring path is disconnected
DI1 (OnOff) Digital Input 1 is triggered by an on to off transition
DI1 (OffOn) Digital Input 1 is triggered by an off to on transition
ABC-02 Status Detects if the ABC-02-USB-T is connected or disconnected to the switch
when the ABC-02-USB-T automatically imports/exports/backs-up the
configuration
Rate Limited On (Disable Port) When the port is disabled due to the ingress throughput exceeding the
configured rate limit.
Rate Limited Off (Disable Port) The port disable function is off because it exceeds the traffic duration or
the user changes “Port Disable” mode to “Drop Packet” mode.
Port Looping Port looping event is triggered
LLDP Table Change Nearly connected devices are changed and shown in the LLDP table
Login Failure Lockout The attempt to log in exceeds the threshold
Account Info Changed The account information has been changed
Configuration is Imported When the configuration is successfully imported
SSL Certification is Imported When SSL Certification is successfully imported
Fiber Check Warning* If the corresponding value of the fiber port status exceeds the threshold
defined by the Fiber Check function
MAC Sticky Violation Port Disable Any port with MAC sticky function is disabled because of a rule violation
*The Fiber Check Warning event is only supported by the EDS-518E series.
Page 31

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-18
Four response actions are available on the EDS E series when events are triggered.
Action Description
Trap The EDS E series will send a notification to the trap server when an event is triggered.
E-Mail The EDS E series will send a notification to the email server defined in the Email Setting.
Syslog The EDS E series will record a syslog to syslog server defined in Syslog Server Setting.
Relay The EDS E series supports digital inputs to integrate sensors. When an event is triggered,
the device will automate alarms through the relay output.
Severity
Severity Description
Emergency System is unusable
Alert Action must be taken immediately
Critical Critical conditions
Error Error conditions
Warning Warning conditions
Notice Normal but significant condition
Information Informational messages
Debug Debug-level messages
Port Event Settings
Port Events are related to the activity of a specific port.
Port Events Warning e-mail is sent when…
Link-ON The port is connected to another device.
Link-OFF The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out, or the opposing
device shuts down).
Traffic-Overload The port’s traffic surpasses the Traffic-Threshold for that port (provided
this item is Enabled).
Traffic-Threshold (%) Enter a nonzero number if the port’s Traffic-Overload item is Enabled.
Traffic-Duration (sec.) A Traffic-Overload warning is sent every Traffic-Duration seconds if the
average Traffic-Threshold is surpassed during that time period.
Page 32

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-19
NOTE
The Traffic
you Enable the Traffic
well as a Traffic
Four response actions are available on the EDS E series when events are triggered.
Action Description
Trap The EDS E series will send a notification to the trap server when an event is triggered.
E-Mail The EDS E series will send a notification to the email server defined in the Email Setting.
Syslog The EDS E series will record a syslog to syslog server defined in Syslog Server Setting.
Relay The EDS E series supports digital inputs to integrate sensors. When an event is triggered,
the device will automate alarms through the relay output.
Severity
Severity Description
Emergency System is unusable
Alert Action must be taken immediately
Critical Critical conditions
Error Error conditions
Warning Warning conditions
Notice Normal but significant condition
Information Informational messages
Debug Debug-level messages
-Overload, Traffic-Threshold (%), and Traffic-Duration (sec.) Port Event items are related. If
-Overload event, then be sure to enter a nonzero Traffic-Threshold percentage, as
-Duration between 1 and 300 seconds.
Event Log Settings
This function is used to inform the user what the event log capacity status is and decide what action to take
when an event log is oversized. Select the Enable Log Capacity Warning checkbox to set the threshold
percentage. When the event log capacity is over the percentage, the switch will send a warning message by
SNMP Trap or Email.
Event Log Oversize Action
Setting Description Factory Default
Overwrite The Oldest
Event Log
Stop Recording Event
Log
The oldest event log will be overwritten when the event log
exceeds 1000 records.
Additional events will not be recorded when the event log
exceeds 1000 records.
Overwrite The
Oldest Event Log
Page 33

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-20
Email Settings
Mail Server
Setting Description Factory Default
IP address or url The IP Address or url of the email server. None
TCP Port
Setting Description Factory Default
TCP Port number The TCP port number of your email server. 25
User Name
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. of 45 characters Your email account name None
Password Setting
Setting Description Factory Default
Password The email account password. None
Email Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. of 30 characters You can set up to 4 email addresses to receive alarm emails
from the Moxa switch.
Sender Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 30 characters Sender Email Address admin@localhost
None
User TLS
Setting Description Factory Default
Yes/No Enables TLS(Transport Layer Security) No
SMTP Server Auth Method
Setting Description Factory Default
Plain/Login/ CRAM-
MD5
Sending a Test Email
After you complete the email settings, you should first click Apply to activate those settings, and then press
the Test button to verify that the settings are correct.
choose an authentication mechanism, PLAIN, LOGIN, and
CRAM-MD5, to login SMTP Server
Plain
Page 34

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-21
NOTE
Auto warning e-mail messages will be sent through an authentication protected SMTP server that supports
the CRAM
authentication mechanism.
We strongly recom
messages can be delivered without using an authentication mechanism.
-MD5, LOGIN, and PAIN methods of SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer)
mend not entering your Account Name and Account Password if auto warning e-mail
Page 35

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-22
NOTE
The following events will be recorded into the Moxa switch’s Event Log table, and will then be
specified Syslog Server:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Syslog Server Settings
The Syslog function provides the event logs for the syslog server. The function supports 3 configurable
syslog servers and syslog server UDP port numbers. When an event occurs, the event will be sent as a
syslog UDP packet to the specified syslog servers. Each Syslog server can be activated separately by
checking the appropriate checkbox to enable it.
Syslog Server 1/2/3
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address Enter the IP address of Syslog server 1/2/3, used by your
network.
Port Destination
(1 to 65535)
Cold start
Warm start
Configuration change activated
Power 1 or 2 transition: Off to On or On to Off
Authentication fail
Password change
Redundancy protocol/topology change
Master setting mismatch
ABC-02 status
Web log in
Rate Limit on/off(Disable port)
Port looping
Port traffic overload
dot1x Auth Fail
Port link off/on
Enter the UDP port of Syslog server 1/2/3. 514
None
sent to the
Page 36

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-23
NOTE
Relay 1 Alarm Cut
Relay Warning Status
When a relay warning is triggered by either the system or port events, the administrator can turn off the
hardware warning buzzer by clicking the Apply button. The event will still be recorded in the event list.
-Off (ACO) setting will not be changed by configuration file import.
MAC Address Table
The MAC address table shows the MAC address list passed through the Moxa switch. The Aging Time (15 to
3825 seconds) defines the length of time that a MAC address entry can remain in the Moxa switch. When an
entry reaches its aging time, it “ages out” and is purged from the switch, effectively cancelling frame
forwarding to that specific port.
The MAC Address table can be configured to display the following Moxa switch MAC address groups, which
are selected from the drop-down list.
Drop Down List
ALL Select this item to show all of the Moxa switch’s MAC addresses.
ALL Learned Select this item to show all of the Moxa switch’s Learned MAC addresses.
ALL Static Select this item to show all of the Moxa switch’s Static, Static Lock, and Static
Multicast MAC addresses.
ALL Multicast Select this item to show all of the Moxa switch’s Static Multicast MAC addresses.
Port x Select this item to show all of the MAC address’s dedicated ports.
Page 37

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-24
The table displays the following information:
MAC This field shows the MAC address.
Type This field shows the type of this MAC address.
Port This field shows the port that this MAC address belongs to.
System Files
Firmware Upgrade
There are three ways to update your Moxa switch’s firmware: from a local *.rom file, by remote TFTP
server, and with Auto Backup Configurator (ABC-02).
Local
1. Download the updated firmware (*.rom) file from Moxa’s website (www.moxa.com).
2. Browse for the (*.rom) file, and then click the Upgrade button
TFTP Server
1. Enter the TFTP Server’s IP address.
2. Input the firmware file name (*.rom) and click the Upgrade button.
Auto Backup Configurator (ABC-02)
1. Download the updated firmware (*.rom) file from Moxa’s website (www.moxa.com).
2. Save the file to the ABC-02’s Moxa folder. The file name cannot be longer than 8 characters, and the file
extension must be .rom.
3. Browse for the firmware (*.rom) file from the ABC-02, and then click the Upgrade button.
Page 38

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-25
NOTE
MAC.ini is
Configuration Backup and Restore
There are three ways to back up and restore your Moxa switch’s configuration: from a local configuration
file, by remote TFTP server, and with Auto Backup Configurator (ABC-02).
Local
1. Click the Backup button to back up the configuration file to a local drive.
2. Browse for a configuration on a local disk, and then click the Restore button.
TFTP Server
1. Enter the TFTP Server’s IP address.
2. Input the backup/restore file name (supports up to 54 characters, including the .ini file extension) and
then click the Backup/Restore button.
Auto Backup Configurator (ABC-02)
1. Click Backup to save the configuration file to the ABC-02. The file will be saved in the ABC-02’s Moxa
folder as a *.ini file (e.g., Sys.ini).
Note that two files will be saved to the ABC-02-USB’s Moxa folder: Sys.ini and MAC.ini. The purpose of
saving the two files is to identify which file will be used when Auto load configuration from ABC to
system when boot up is activated.
2. Click Browse to select the configuration file, and then click Restore to start loading the configuration
3. Configuration File Encryption Setting
4. Auto load configuration from ABC to system when boot up
named using the last 6 digits of the switch’s MAC address, without spaces.
into your switch.
Select the Configuration File Encryption Setting checkbox, input the password, and then click Apply.
Select the Auto load configuration from ABC to system when boot up checkbox and then click
Apply. Note that this function is enabled by default.
Power off your switch first, and then plug in the ABC-02. When you power on your switch, the system
will detect the configuration file on the ABC-02 automatically. The switch will recognize the file name,
with the following sequence priority:
Page 39

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-26
NOTE
MAC.ini is named using the last 6 digits of the switch’s MAC
NOTE
MM=month, DD=day, HH=hour, mm=minutes, from the system time.
First priority: MAC.ini
Second priority: Sys.ini
If no matching configuration file is found, the fault LED light will turn on, and the switch will boot up
normally.
5. Auto backup to ABC-02 when configuration changes
Select the Auto backup to ABC-02 when configuration change checkbox and then click Apply. This
function is disabled by default.
The ABC-02 is capable of backing up switch configuration files automatically. While the ABC-02 is
plugged into the switch, enable the Auto backup to ABC-02 when configuration change option, and
then click Apply. Once this configuration is modified, the switch will back up the current configuration to
the /His_ini folder on the ABC-02. The file name will be the system date/time (MMDDHHmm.ini).
Log File Backup
There are three ways to back up Moxa switch’s log files: from a local drive, by remote TFTP server, or with
Auto Backup Configurator (ABC-02).
address, without spaces.
Local
Click the Backup button to back up the log file to a local drive.
TFTP Server
Enter the TFTP Server’s IP address and file name and then click the Backup button.
Auto Backup Configurator (ABC-02)
Click Backup to save the configuration file to the ABC-02. The file will be saved in the ABC-02’s Moxa
folder with filename Sys.ini.
Auto backup of event log to prevent overwrite
This function is designed to maintain a long-term record of the switch’s log files. Moxa Ethernet switches are
capable of saving 1000 event log entries. When the 1000-entry storage limit is reached, the switch will
delete the oldest saved event log. The ABC-02 can be used to back up these event logs. When the number
of switch log entries reaches 1000, the ABC-02 will save the oldest 100 entries from the switch.
Enable the Auto backup of event log to prevent overwrite, and then click Apply. After that, when the
ABC-02 is plugged into the switch, the event logs will always be saved to the ABC-02 automatically when
the number of switch log entries reaches 1000. Each backup action saves the oldest 100 logs to the ABC-02
in one file, with the filename generated by the current system time as MMDDHHmm.ini. The file is saved
to the His_log folder.
Page 40

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-27
NOTE
Note: MM=month, DD=day, HH=hour, mm=minutes, from
NOTE
DO NOT remove the ABC
Set DIP switch as Turbo Ring
The log file includes the following information:
Index An event index assigned to identify the event sequence.
Bootup
Number
Date The date is updated based on how the current date is set on the System Settings page.
Time The time is updated based on how the current time is set on the System Settings page.
System
Startup Time
Event Events that have occurred.
This field shows how many times the Moxa switch has been rebooted or cold started.
The system startup time related to this event.
Switch Reset Button
The Moxa switch reset button can be used to quickly reset the switch’s configuration, and save the current
configuration and log files to the ABC-02. Press the Reset button on top of the EDS switch to back up the
current system configuration files and event logs to the ABC-02.
-02 when performing an upgrade, backup, or restore.
Turbo Ring DIP Switch
the system time.
The Turbo Ring DIP Switch page allows users to disable the 4th DIP switch located on the EDS’s outer
casing. The default is enabled with Turbo Ring v2 protocol. Once the user changes the 4th hardware DIP
switch configuration to ON, the switch will start to initiate the Turbo Ring redundancy protocol based on the
configuration. The detailed description is given below:
Setting Description Factory Default
Unchecked:
The Turbo Ring protocol will be activated automatically
Disable the Turbo Ring DIP
switch
Set DIP switch as Turbo Ring
v2
when the 4th DIP switch is moved to the ON position.
Checked:
The Turbo Ring protocol will not be activated
automatically, regardless of the position of the 4th DIP
switch.
If the DIP switch is enabled, Turbo Ring protocol will be
enabled when the DIP switch is moved to the ON
position.
If the DIP switch is enabled, Turbo Ring v2 protocol will
be enabled when the DIP switch is moved to the ON
position.
unchecked
Set DIP switch as
Turbo Ring v2
Page 41

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-28
NOTE
If the 4
switch from the web interface, console, or Telnet.
NOTE
If the 4
the
DIP switch (Turbo
Ring) to OFF.
NOTE
If you would like to enable VLAN and/or port trunking on any of the last four ports,
DIP switch to activate Turbo Ring. In this case, you should use the Web, Telnet, or Serial console to activate
Turbo Ring.
NOTE
After restoring the factory default configuration, you will need to use the default network settings to re
establish the web or Telnet console connection with the Moxa switch.
Restart
The Restart function provides users with a quick way to restart the switch’s operating system.
th
DIP switch (Turbo Ring) is configured to ON, you will not be able to disable the Turbo Ring DIP
th
DIP switch (Turbo Ring) is configured to ON, and this configuration is saved again in CLI mode,
n the redundancy mode will not be able to change to default RSTP by switching the 4th
do not use the fourth
Factory Default
The Factory Default function provides users with a quick way of restoring the Moxa switch’s configuration
to factory defaults. The function can be activated from the USB serial interface, via Telnet, through the web-
based console, or with the hardware reset button.
-
Page 42

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-29
PoE (PoE Models Only)
Power over Ethernet has become increasingly popular, due in large part to the reliability provided by PoE
Ethernet switches that supply the power to Powered Devices (PD) when AC power is not available, or is too
expensive to provide locally.
Power over Ethernet can be used with the following types of devices:
• Surveillance cameras
• Security I/O sensors
• Industrial wireless access points
• Emergency IP phones
In fact, it’s not uncommon for video, voice, and high-rate industrial application data transfers to be
integrated onto one network. Moxa’s PoE switches are equipped with many advanced PoE management
functions, providing vital security systems with a convenient and reliable Ethernet network. Moreover,
Moxa’s advanced PoE switches support the high power PoE+ standard, a 24 VDC direct power input, and 20
ms fast recovery redundancy with Turbo Ring and Turbo Chain.
PoE Settings
The PoE settings interface gives users control over the system’s PoE power output, PoE power threshold,
PoE port configuration, and PD failure check. The PoE settings page is divided into three parts: PoE System
Configuration, PoE Port Configuration, and PoE Device Failure Check. Each part is discussed
separately below.
Page 43

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-30
NOTE
The configuration is different,
“Allocated Power” or “Measured Power.”
PoE System Configuration
depending on whether the “PoE power output managed by” item is set to
PoE Power Management by Allocated Power
PoE Power Management by Measured Power
Page 44

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-31
PoE System Configuration Settings
PoE Power Output
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables PoE power transmission to a PD Enable
Disable Disables PoE power transmission to a PD
PoE power management Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Allocated Power If a powered device is connected that would cause the total
amount of power needed by all connected devices to exceed
the total allocated power limit, the switch will not power up
the device.
Disable
Measured Power If a powered device is connected that would cause the total
amount of power needed by all connected devices to exceed
the total measured power limit, the switch with will deny
power to the device with the lowest priority.
PoE system power budget
Setting Description Factory Default
wattage Assigns the “Total measured power” limit for all PoE ports
combined.
Enable
IKS-6728A-8PoE
and EDS-G512E-
8PoE: 240W
EDS-P506E-4PoE:
depend on input
voltage (12VDC:
62W, 24VDC:
150W, 48VDC:
180W)
PoE Port Configuration
Power
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Allows data and power to be transmitted through the port. Checked
Unchecked Immediately shuts off power to that port
Page 45

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-32
Allocation can be set from 0 to 36 W. When the Output Mode
NOTE
O
Output Mode
Setting Description
802.3 af/at Auto Power transmission follows the IEEE 802.3 af/at protocols. The acceptable PD
resistance range is 17 kΩ to 29 kΩ.
High Power / 2-Pair
High Power 36W
(only for EDS-P506E-
4PoE)
Force / 2-Pair Force -
36W (only for EDS-
P506E-4PoE)
4-Pair High Power
60W
4-Pair Force - 60W Provides a higher power output to the 4-Pair PDs. The acceptable PD resistance
Power Allocation
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 60 When the Output Mode is set to 2-Pair Force, the Power
Provides a higher power output to the 2-Pair PD. The acceptable PD resistance range
is 17 kΩ to 29 kΩ and the power allocation of the port is automatically set to 36 W.
Provides power output to non-802.3 af/at PDs. The acceptable PD resistance is over
2.4 kΩ and the range of power allocation is 0 to 36 W.
Provides a higher power output to the 4-Pair PDs. The acceptable PD resistance
range is 17 kΩ to 29 kΩ and the power allocation of the port is automatically set to
60 W.
range is over 2.4 kΩ and the range of power allocation is 0 to 60 W.
2-Pair Force: 36W
4-Pair Force: 60W
is set to 4-Pair Force, the Power Allocation can be set from 0
to 60 W.
nly the EDS-P506E-4PoE can support PoE output over 36W and 4-Pair PD.
Legacy PD Detection
The PoE Ethernet Switch provides a Legacy PD Detection function. When the capacitance of the PD is
higher than 2.7 μF, checking the Legacy PD Detection checkbox enables the system to output power to
the PD. In this case, it will take 10 to 15 seconds for PoE power to be output through this port after the
switch is turned on.
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Enables legacy PD detection Unchecked
Unchecked Disables legacy PD detection
Power Priority
Use Power Priority when managing PoE power with measured power mode. The smaller the number, the
higher the priority. You may set the same priority for different PoE ports, but if you configure two ports with
the same priority, then the port with the lower port number has the higher priority. The setting can range
from 1 up to the total number of ports. When the PoE measured power exceeds the assigned limit, the
switch will disable the PoE port with the lowest priority.
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to “number of PoE
ports”
The smaller the number, the higher the PoE port priority.
When the PoE measured power exceeds the assigned limit,
the switch will disable the PoE port with the lowest priority.
The PoE port index
number
Page 46

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-33
PoE Device Failure Check
The PoE Ethernet switch can monitor the status of a PD via its IP address. If the PD fails, the switch will not
receive a PD response after the defined period, and the authentication process will be restarted. This
function is extremely useful for ensuring your network’s reliability and reducing your management burden.
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Enables the PD Failure Check function Unchecked
Unchecked Disables the PD Failure Check function
PoE Device IP Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 15 Characters Enter the PD’s IP address None
No Response Timeout
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to 10 The maximum number of IP checking cycles. 3
Check Period
Setting Description Factory Default
5 to 300 Enter maximum time allowed for each IP checking cycle. 10
No Response Action
Setting Description Factory Default
No Action The PSE has no action on the PD No Action
Reboot PD The PSE reboots the PD after the PD Failure Check
Power Off PD The PSE powers off the PD after the PD Failure Check
Page 47

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-34
Powered devices usually do not need to be running 24
hours a day, 7 days a week.
provides a PoE timetabling mechanism t
economize the system
flexible working schedule for each PoE port.
PoE Timetabling
The PoE Ethernet switch
hat lets users
’s power burden by setting a
Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Port Select which port you would like to configure. Port 1
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Enables the PoE function of the port for the defined time
period.
Unchecked Enables the PoE function of the port all the time.
Unchecked
MON, TUE, WED, THU, FRI, SAT, SUN
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Select those days on which you would like the port to be
enabled (you will then be able to modify the StartTime and
EndTime)
Unchecked The port will not provide PoE power on days that are not
check marked.
Start/End Time
Setting Description Factory Default
Configured time
period
Enter the hour of the day the configuration will be enabled,
and the hour of the day the configuration will be disabled.
PoE Warning Event Settings
Since industrial Ethernet devices are often located at the endpoints of a system, these devices do not
always know what is happening elsewhere on the network. This means that a PoE port connected to a PD
must provide system administrators with real-time alarm messages. Even when control engineers are out of
the control room for an extended period of time, they can still be informed of the status of the PD almost
instantaneously when exceptions occur. The PoE Ethernet switch supports different methods for warning
engineers automatically, including SNMP trap, email, and relay output. It also supports two digital inputs to
integrate sensors into your system to automate alarms using email and relay output. The PoE warning event
settings are on the System Event Settings page.
Disable
0 to 24
Page 48

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-35
NOTE
The Relay Output does not support three Event Types:
temperature
Warning Type
Action Description
Trap The EDS E series will send a notification to the trap server when
an event is triggered.
E-Mail The EDS E series will send a notification to the email server
defined in Email Settings.
Syslog The EDS E series will record a syslog to a syslog server defined
in Syslog Server Settings.
Relay1 The EDS E series supports digital inputs to integrate sensors.
When an event is triggered, the device will automatically activate
an alarm through the relay output.
Event Type
Port Events Description
PoE PD power on Power is being output to the PD.
PoE PD power off The PoE power output is cut off.
PoE over current When the current of the port exceeds the following limits:
802.3 af: 350 mA
802.3 at: 600 mA
High Power: 720 mA
Force: 600 mA
PoE PD Failure Check When the switch does not receive a PD response after the
defined period.
Over Measured Power Limitation When the total PD power consumption exceeds the total
measured power limit.
PoE FETBad When the MOSFET of the port is out of order (please contact
Moxa for technical service)
PoE over Temperature Check the temperature of the environment. If you cannot keep
the temperature under 75°C, contact Moxa for technical support.
PoE VEE Uvlo - VEE (PoE input voltage)
under Voltage Lockout
Over Allocated Power Limitation When the total PD power consumption exceeds the total
The voltage of the power supply has dropped below 44 VDC.
Adjust the voltage to between 46 and 57 VDC to eliminate this
issue.
allocated power.
, and VEE (PoE input voltage) under voltage lockout.
External FET has failed, PSE chip is over
Page 49

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-36
PoE Diagnostic
PoE Diagnostic helps users determine the PD conditions. The system provides the user with configuration
options; select the best option for your PDs. It will automatically detect and suggest the configurations when
users click on this page and the status will be refreshed when you click the refresh button.
Diagnose Configuration
Device Type
Item Description
Not Present No connection to the port
NIC A NIC is connected to the port
IEEE 802.3af An IEEE 802.3af PD is connected to the port
IEEE 802.3 at An IEEE 802.3at PD is connected to the port
Legacy PoE Device A legacy PD is connected to the port, and the PD’s detected voltage is too high or
low, or the PD’s detected capacitance is too high.
Unknown Unknown PD connected to the port
2-Pair PD A 802.af, 802.3 at, or legacy 2-pair PD
4-Pair 60W A 4-Pair PD that uses all 8 pins of the RJ-45 connector to receive PoE output
Classification
Item Description
N/A The port is not classified
0 to 4 Class 0 to 4
Unknown Unknown class for the port; in this case it will usually be higher than class 4
Voltage (V)
Item Description
N/A No voltage output on the port
Voltage Display the voltage of the port
PoE Port Configuration Suggestion
Item Description
Disable PoE power output When detecting a NIC or unknown PD, the system suggests disabling PoE
power output.
Enable “Legacy PD Detection” When detecting a higher capacitance of PD, the system suggests enabling
Legacy PD Detection.
Select Force Mode When detecting higher/lower resistance or higher capacitance, the system
suggests selecting Force Mode.
Select IEEE 802.3af/at auto
mode
When detecting an IEEE 802.3 af/at PD, the system suggests selecting
802.3 af/at Auto mode.
Page 50

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-37
Item Description
Select high power output When detecting an unknown classification, the system suggests selecting
High Power output.
Raise the external power
supply voltage to greater than
46 VDC
Enable PoE function for
detection
Select 4-Pair High Power 60W
mode
Select 2-Pair Force Mode or 4-
Pair Force Mode
When the external supply voltage is detected at under 46 V, the system
suggests raising the voltage.
The system suggests enabling the PoE function.
When detecting 4-Pair PD, the system suggests selecting 4-Pair High Power
60W mode.
When configuring at 4-Pair PoE Mode and detecting higher/lower resistance
or higher capacitance, the system suggests selecting 2-Pair Force Mode or
4-Pair Force Mode.
PoE Port Status
Monitoring Configuration
Refresh Rate
Setting Description Factory Default
5 to 300 The period of time for the system to refresh the PoE Port
Status (in seconds)
5
Page 51

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-38
NOTE
ICS
VEE Voltage.
PSE Status
VEE Voltage
Setting Description Factory Default
Read-only The VEE voltage supplied by the PSE. None
-G7748A, G7750A, G7752A, ICS-G7848A, G7850A, G7852A, EDS-P506E-4PoE do not support to show
Port Status
Status Description
Item Description
Not Present No connection to the port. PoE power is not being provided.
Powered PoE power is being provided by the PSE.
NIC System has detected a NIC connected to the port. PoE power is not being provided.
Disabled The PoE function of the port is disabled. PoE power is not being provided.
Fault In Force mode; the system has detected an out-of-range PD.
Legacy Powered In Force mode; the system has detected a legacy PD.
Potential Legacy PD In 802.3af/at or High Power mode; the system has detected a potential legacy PD.
PoE power is not being provided.
Port Description
Item Description
Status Indicates if the PoE function is enabled or disabled.
Power Output Indicates the power output of each PoE port.
Class Indicates the classification of each PoE port.
Current (mA) Indicates the actual current consumed by each PoE port.
Voltage (V) Indicates the actual voltage consumed by each PoE port.
Consumption (Watts) Indicates the actual Power consumed by each PoE port.
PD Failure Check Status Indicates the PD Failure Check status of each PoE port.
Alive: The system receives a response from all pings to the PD.
Not Alive: The system receives no response from pings to the PD.
Disabled: The PD Failure Check function is not activated.
Page 52

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-39
PoE System Status
Monitoring Configuration
Refresh Rate
Setting Description Factory Default
5 to 300 If the Refresh Rate = T, then the PoE Port Status will be
System Power Status
System Power Status shows a graph of Sum of measured power, Sum of allocated power, and Max of
allocated power. “Sum of measured power” (in green) shows the total measured power of all PDs, “Sum
of allocated power” (in blue) shows the total allocated power, and “Max of allocated power” (in red) shows
the threshold of total PoE power output. The graphs show Current (mA) versus Sec. (second), and are
refreshed at the configured Refresh Rate.
Patent http://www.moxa.com/doc/operations/Moxa_Patent_Marking.pdf
VLAN
Setting up Virtual LANs (VLANs) on your Moxa switch increases the efficiency of your network by dividing
the LAN into logical segments, as opposed to physical segments. In general, VLANs are easier to manage.
5
refreshed every T seconds.
The Virtual LAN (VLAN) Concept
What is a VLAN?
A VLAN is a group of devices that can be located anywhere on a network, but which communicate as if they
are on the same physical segment. With VLANs, you can segment your network without being restricted by
physical connections—a limitation of traditional network design. With VLANs you can segment your network
into:
Page 53

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-40
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8
Switch A
Switch B
Department 1
VLAN 1
Department 2
VLAN 2
Department 3
VLAN 3
Backbone connects multiple switches
• Departmental groups—You could have one VLAN for the marketing department, another for the
finance department, and another for the product development department.
• Hierarchical groups—You could have one VLAN for directors, another for managers, and another for
general staff.
• Usage groups—You could have one VLAN for email users and another for multimedia users.
Benefits of VLANs
The main benefit of VLANs is that they provide a network segmentation system that is far more flexible than
traditional networks. Using VLANs also provides you with three other benefits:
• VLANs ease the relocation of devices on networks: With traditional networks, network
administrators spend much of their time dealing with moves and changes. If users move to a different
subnetwork, the addresses of each host must be updated manually. With a VLAN setup, if a host
originally on the Marketing VLAN, is moved to a port on another part of the network, and retains its
original subnet membership, you only need to specify that the new port is on the Marketing VLAN. You
do not need to do any re-cabling.
• VLANs provide extra security: Devices within each VLAN can only communicate with other devices on
the same VLAN. If a device on the Marketing VLAN needs to communicate with devices on the Finance
VLAN, the traffic must pass through a routing device or Layer 3 switch.
• VLANs help control traffic: With traditional networks, congestion can be caused by broadcast traffic
that is directed to all network devices, regardless of whether or not they need it. VLANs increase the
efficiency of your network because each VLAN can be set up to contain only those devices that need to
communicate with each other.
VLANs and the Rackmount switch
Your Moxa switch provides support for VLANs using IEEE Std 802.1Q-1998. This standard allows traffic from
multiple VLANs to be carried across one physical link. The IEEE Std 802.1Q-1998 standard allows each port
on your Moxa switch to be placed as follows:
• On a single VLAN defined in the Moxa switch
• On several VLANs simultaneously using 802.1Q tagging
The standard requires that you define the 802.1Q VLAN ID for each VLAN on your Moxa switch before the
switch can use it to forward traffic:
Page 54

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-41
Managing a VLAN
A new or initialized Moxa switch contains a single VLAN—the Default VLAN. This VLAN has the following
definition:
• VLAN Name—Management VLAN
• 802.1Q VLAN ID—1 (if tagging is required)
All the ports are initially placed on this VLAN, and it is the only VLAN that allows you to access the
management software of the Moxa switch over the network.
Communication Between VLANs
If devices connected to a VLAN need to communicate with devices on a different VLAN, a router or Layer 3
switching device with connections to both VLANs needs to be installed. Communication between VLANs can
only take place if they are all connected to a routing or Layer 3 switching device.
VLANs: Tagged and Untagged Membership
The Moxa switch supports 802.1Q VLAN tagging, a system that allows traffic for multiple VLANs to be
carried on a single physical link (backbone, trunk). When setting up VLANs you need to understand when to
use untagged or tagged membership of VLANs. Simply put, if a port is on a single VLAN it can be an
untagged member, but if the port needs to be a member of multiple VLANs, a tagged membership must be
defined.
A typical host (e.g., clients) will be an untagged member of one VLAN, defined as an Access Port in a Moxa
switch, while an inter-switch connection will be a tagged member of all VLANs, defined as a Trunk Port in a
Moxa switch.
The IEEE Std 802.1Q-1998 defines how VLANs operate within an open packet-switched network. An 802.1Q
compliant packet carries additional information that allows a switch to determine which VLAN the port
belongs to. If a frame is carrying the additional information, it is known as a tagged frame.
To carry multiple VLANs across a single physical link (backbone, trunk), each packet must be tagged with a
VLAN identifier so that the switches can identify which packets belong in which VLAN. To communicate
between VLANs, a router must be used.
The Moxa switch supports three types of VLAN port settings:
• Access Port: The port connects to a single device that is not tagged. The user must define the default
port PVID that assigns which VLAN the device belongs to. Once the ingress packet of this Access Port
egresses to another Trunk Port (the port needs all packets to carry tag information), the Moxa switch will
insert this PVID into this packet so the next 802.1Q VLAN switch can recognize it.
• Trunk Port: The port connects to a LAN that consists of untagged devices, tagged devices, and/or
switches and hubs. In general, the traffic of the Trunk Port must have a Tag. Users can also assign a
PVID to a Trunk Port. The untagged packet on the Trunk Port will be assigned the default port PVID as
its VID.
• Hybrid Port: The port is similar to a Trunk port, except users can explicitly assign tags to be removed
from egress packets.
The following section illustrates how to use these ports to set up different applications.
Page 55

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-42
Sample Applications of VLANs Using Moxa Switches
In this application:
• Port 1 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 5; it should be configured as an Access
Port with PVID 5.
• Port 2 connects a LAN with two untagged devices belonging to VLAN 2. One tagged device with VID 3
and one tagged device with VID 4. It should be configured as a Hybrid Port with PVID 2 for untagged
device and Fixed VLAN (Tagged) with 3 and 4 for tagged device. Since each port can only have one
unique PVID, all untagged devices on the same port must belong to the same VLAN.
• Port 3 connects with another switch. It should be configured as a Trunk Port. GVRP protocol will be
used through the Trunk Port.
• Port 4 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 2; it should be configured as an Access
Port with PVID 2.
• Port 5 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 3; it should be configured as an Access
Port with PVID 3.
• Port 6 connect a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 5; it should be configured as an Access
Port with PVID 5.
• Port 7 connects a single untagged device and assigns it to VLAN 4; it should be configured as an Access
Port with PVID 4.
After the application is properly configured:
• Packets from Device A will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 5. Switch B will recognize its
VLAN, pass it to port 6, and then remove tags received successfully by Device G, and vice versa.
• Packets from Devices B and C will travel through Hybrid Port 2 with tagged VID 2. Switch B recognizes
its VLAN, passes it to port 4, and then removes tags received successfully by Device F, and vice versa.
• Packets from Device D will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 3. Switch B will recognize its
VLAN, pass to port 5, and then remove tags received successfully by Device H. Packets from Device H
will travel through Trunk Port 3 with PVID 3. Switch A will recognize its VLAN and pass it to port 2, but
will not remove tags received successfully by Device D.
• Packets from Device E will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 4. Switch B will recognize its
VLAN, pass it to port 7, and then remove tags received successfully by Device I. Packets from Device I
will travel through Trunk Port 3 with tagged VID 4. Switch A will recognize its VLAN and pass it to port
2, but will not remove tags received successfully by Device E.
Page 56

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-43
Remove the
Configuring a Virtual LAN
To configure 802.1Q VLAN and port-based VLANs on the Moxa switch, use the VLAN Settings page to
configure the ports for either an 802.1Q VLAN or Port-based VLAN.
VLAN Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
802.1Q VLAN Sets VLAN mode to 802.1Q VLAN 802.1Q VLAN
Port-based VLAN Sets VLAN mode to Port-based VLAN
VLAN Settings: 802.1Q
When VLAN Mode is set to 802.1Q VLAN, the configuration options will be divided into the Quick Setting
Panel and VLAN ID Configuration Table. The Quick Setting Panel is generally used to configure VLAN
settings for groups of ports, with the settings pushed down to the VLAN ID Configuration Panel when the
user clicks the Add button. The VLAN ID Configuration Table can be used to configure the settings for
individual ports.
Quick Setting Panel
The EDS E series provides a Quick Setting Panel that administrators can use to quickly configure VLAN
settings for single ports or groups of ports. To configure a group of ports, type the port names in the Port
column, separated commas (,) for individual port names, or colons (:) to indicate a range of ports. For
example, typing “G1,G3” applies the settings to ports G1 and G3, whereas typing “G1:G3” applies the
settings to ports G1, G2, and G3. Next, if necessary configure Type, PVID, Tagged VLAN, Untagged
VLAN, and Forbidden VLAN, and then click the Add button to move the settings down to the table at the
bottom of the window.
VLAN ID Configuration Table
Enable GVRP
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked/Unchecked Check the checkbox to enable the GVRP function.
checkmark to disable the GVRP function.
Disabled
Page 57

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-44
ATTENTION
For communication redundancy in the VLAN environment, set
Coupling Control Por
fr
NOTE
The
Management VLAN ID
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to 4094 Assigns the VLAN ID to this Moxa switch. 1
Note: Some of the following settings can be modified in the Quick Setting Panel.
Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Port name Read only N/A
Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Access When this port is connected to a single device, without tags. Access
Trunk When this port is connected to another 802.1Q VLAN aware
switch.
Hybrid When this port is connected to another Access 802.1Q VLAN
aware switch or another LAN that combines tagged and/or
untagged devices and/or other switches/hubs.
om different VLANs to different Moxa switch units.
PVID
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to 4094 Sets the default VLAN ID for untagged devices connected to
Tagged VLAN
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to 4094 This field will be active only when selecting the Trunk or
Untagged VLAN
Setting Description Factory Default
VID range from 1 to
4094
ts to Trunk Port, since these ports act as the backbone for transmitting packets
the port.
Hybrid port type. Set the other VLAN ID for tagged devices
that connect to the port. Use commas to separate different
VIDs.
This field is only active when the Hybrid port type is selected.
Set the other VLAN ID for tagged devices that connect to the
port and tags that need to be removed in egress packets. Use
commas to separate different VIDs.
Redundant Port Coupling Ports and
1
None
None
Forbidden VLAN
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to 4094 This field is only active when Trunk or Hybrid port type is
selected. Set the other VLAN IDs that will not be supported
by this port. Use commas to separate different VIDs.
Quick Setting Panel provides a quick way of configuring multiple VLAN ports with the same setting.
None
Page 58

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-45
NOTE
Port
•
•
Port
•
•
•
NOTE
When Port
VLAN Settings: Port-based
When VLAN Mode is set to Port-based VLAN, the VLAN Settings window will appear as shown below.
Select the appropriate checkbox under a port to assign the port to a VLAN. The maximum VLAN ID equals
the number of switch ports. In the following example, all of the ports are assigned to VLAN 1.
-Based VLAN is supported by:
EDS series switches (not including the EDS-728/828)
IKS-6726A/6728A
-Based VLAN is NOT supported by:
EDS-728/828
IKS-G6524A/G6824A
ICS series switches
-based VLAN is configured, IGMP will be disabled.
VLAN Name Setting
For the 802.1Q VLAN, the user is able to set VLAN name of each VLAN ID (VID).
VLAN Name Setting
Setting Description Factory Default
Name The VLAN name can only include these characters, a-z/A-Z/0-
9/-/_/
Null
Page 59

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-46
NOTE
Moxa
headers into a single Ethernet frame
QinQ Settings
’s layer 3 switches support the IEEE 802.1ad QinQ function, which allows users to tag double VLAN
.
TPID
Setting Description Factory Default
8100 to FFFF Assign the TPID of the second VLAN tag 8100
QinQ Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Enable VLAN QinQ function Disable
VLAN Table
Use the 802.1Q VLAN table to review the VLAN groups that were created, VLAN Name, Joined Access
Ports, Trunk Ports, and Hybrid Ports, and use the Port-based VLAN table to review the VLAN groups
and Joined Ports.
Page 60

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-47
Port
Port Settings
Port settings are included to give the user control over port access, port transmission speed, flow control,
and port type (MDI or MDIX).
Enable
Setting Description Factory Default
Checked Allows data transmission through the port. Checked
Unchecked Immediately shuts off port access.
Media Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Media type Displays the media type for each module’s port N/A
Description
Setting Description Factory Default
Max. 63 characters Specifies an alias for the port to help administrators
differentiate between different ports. Example: PLC 1
Speed
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto Allows the port to use the IEEE 802.3u protocol to negotiate
with connected devices. The port and connected devices will
determine the best speed for that connection.
100M-Full Choose one of these fixed speed options if the connected
100M-Half
10M-Full
10M-Half
Ethernet device has trouble auto-negotiating for line speed.
None
Auto
Page 61

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-48
NOTE
For
FDX Flow Ctrl
This setting enables or disables flow control for the port when the port’s Speed is set to Auto. The final
result will be determined by the Auto process between the Moxa switch and connected devices.
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Enables flow control for this port when the port’s Speed is set
to Auto.
Disable Disables flow control for this port when the port’s Speed is
set to Auto.
MDI/MDIX
Setting Description Factory Default
Auto Allows the port to auto-detect the port type of the connected
Ethernet device and change the port type accordingly.
MDI Choose MDI or MDIX if the connected Ethernet device has
MDIX
trouble auto-negotiating for port type.
Disabled
Auto
the Gigabit ports, MDI/MDIX is only Auto mode.
Port Status
The following table shows the status of each port, including the media type, link status, flow control, and
port state.
Link Aggregation
Link aggregation involves grouping links into a link aggregation group. A MAC client can treat link
aggregation groups as if they were a single link.
The Moxa switch’s port trunking feature allows devices to communicate by aggregating up to 4 trunk
groups, with a maximum of 8 ports for each group. If one of the 8 ports fails, the other seven ports will
automatically provide backup and share the traffic.
Port trunking can be used to combine up to 8 ports between two Moxa switches. If all ports on both
switches are configured as 100BaseTX and they are operating in full duplex, the potential bandwidth of the
connection will be 1600 Mbps.
Page 62

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-49
Step 1:
Select the desired
Step 2:
Select the
Step 3:
Select the
The Port Trunking Concept
Moxa has developed a port trunking protocol that provides the following benefits:
• Greater flexibility in setting up your network connections, since the bandwidth of a link can be doubled,
tripled, or quadrupled.
• Redundancy—if one link is broken, the remaining trunked ports share the traffic within this trunk group.
• Load sharing—MAC client traffic can be distributed across multiple links.
To avoid broadcast storms or loops in your network while configuring a trunk, first disable or disconnect all
ports that you want to add to the trunk or remove from the trunk. After you finish configuring the trunk,
enable or re-connect the ports.
If all ports on both switch units are configured as 100BaseTX and they are operating in full duplex mode,
the potential bandwidth of the connection will be up to 1.6 Gbps. This means that users can double, triple,
or quadruple the bandwidth of the connection by port trunking between two Moxa switches.
Each Moxa switch can set a maximum of 3 port trunking groups. When you activate port trunking, certain
settings on each port will be reset to factory default values or disabled:
• Communication redundancy will be reset.
• 802.1Q VLAN will be reset.
• Multicast Filtering will be reset.
• Port Lock will be reset and disabled.
• Set Device IP will be reset.
• Mirror will be reset.
After port trunking has been activated, you can configure these items again for each trunking port.
Port Trunking
The Port Trunking Settings page is where ports are assigned to a trunk group.
Trunk Type (Static or LACP).
Trunk Group to modify the desired ports if necessary
Trunk Group
Page 63

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-50
Trunk Group (maximum of 4 trunk groups)
Setting Description Factory Default
Trk1, Trk2, Trk3, Trk4
(depends on switching
chip capability; some
Moxa switches only
support 3 trunk
groups)
The EDS 400A series does not support Port Trunking. The number of Trunk Groups for other models are
listed in the following table:
No. of Trunk Groups Model
2 EDS-505A, EDS-P506A-4PoE, EDS-516A
3 EDS-518A
4 For other models
Trunk Type
Setting Description Factory Default
Static Selects Moxa’s static trunking protocol. Static
LACP Selects LACP (IEEE 802.3ad, Link Aggregation Control
Specifies the current trunk group. Trk1
Static
Protocol).
Trunking Status
The Trunking Status table shows the Trunk Group configuration status.
Link-Swap Fast Recovery
The Link-Swap Fast Recovery function, which is enabled by default, allows the Moxa switch to return to
normal operation extremely quickly after devices are unplugged and then re-plugged into different ports.
The recovery time is on the order of a few milliseconds (compare this with standard commercial switches for
which the recovery time could be on the order of several minutes). To disable the Link-Swap Fast Recovery
function, or to re-enable the function after it has already been disabled, access either the Console utility’s
Link-Swap recovery page, or the Web Browser interface’s Link-Swap fast recovery page, as shown
below.
Link-Swap-Fast-Recovery
Setting Description Factory Default
Page 64

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-51
Enable/Disable Select the checkbox to enable the Link-Swap-Fast-Recovery
function
Multicast
Multicast filtering improves the performance of networks that carry multicast traffic. This section explains
multicasts, multicast filtering, and how multicast filtering can be implemented on your Moxa switch.
The Concept of Multicast Filtering
What is an IP Multicast?
A multicast is a packet sent by one host to multiple hosts. Only those hosts that belong to a specific
multicast group will receive the multicast. If the network is set up correctly, a multicast can only be sent to
an end-station or a subset of end-stations on a LAN or VLAN that belong to the multicast group. Multicast
group members can be distributed across multiple subnets, so that multicast transmissions can occur within
a campus LAN or over a WAN. In addition, networks that support IP multicast send only one copy of the
desired information across the network until the delivery path that reaches group members diverges. To
make more efficient use of network bandwidth, it is only at these points that multicast packets are
duplicated and forwarded. A multicast packet has a multicast group address in the destination address field
of the packet’s IP header.
Benefits of Multicast
The benefits of using IP multicast are:
Enable
• It uses the most efficient, sensible method to deliver the same information to many receivers with only
one transmission.
• It reduces the load on the source (for example, a server) since it will not need to produce several copies
of the same data.
• It makes efficient use of network bandwidth and scales well as the number of multicast group members
increases.
• Works with other IP protocols and services, such as Quality of Service (QoS).
Multicast transmission makes more sense and is more efficient than unicast transmission for some
applications. For example, multicasts are often used for video-conferencing, since high volumes of traffic
must be sent to several end-stations at the same time, but where broadcasting the traffic to all end-stations
would cause a substantial reduction in network performance. Furthermore, several industrial automation
protocols, such as Allen-Bradley, EtherNet/IP, Siemens Profibus, and Foundation Fieldbus HSE (High Speed
Ethernet), use multicast. These industrial Ethernet protocols use publisher/subscriber communications
models by multicasting packets that could flood a network with heavy traffic. IGMP Snooping is used to
prune multicast traffic so that it travels only to those end destinations that require the traffic, reducing the
amount of traffic on the Ethernet LAN.
Multicast Filtering
Multicast filtering ensures that only end-stations that have joined certain groups receive multicast traffic.
With multicast filtering, network devices only forward multicast traffic to the ports that are connected to
registered end-stations. The following two figures illustrate how a network behaves without multicast
filtering, and with multicast filtering.
Page 65

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-52
All hosts receive the multicast
traffic, even if they don’t need it.
Hosts only receive dedicated
traffic from other hosts belonging
to the same group.
NOTE
IGMP Snooping Enhanced mode is only provided in Layer 2 switches.
NOTE
Moxa
protocols. Layer 2 switches only support IGMP v1/v2.
Network without multicast filtering
Network with multicast filtering
Multicast Filtering and Moxa’s Industrial Rackmount Switches
There are three ways to achieve multicast filtering with a Moxa switch: IGMP (Internet Group Management
Protocol) Snooping, GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol), and adding a static multicast MAC
manually to filter multicast traffic automatically.
Snooping Mode
Snooping Mode allows your switch to forward multicast packets only to the appropriate ports. The switch
snoops on exchanges between hosts and an IGMP device, such as a router, to find those ports that want to
join a multicast group, and then configures its filters accordingly.
Query Mode
Query mode allows the Moxa switch to work as the Querier if it has the lowest IP address on the subnetwork
to which it belongs.
IGMP querying is enabled by default on the Moxa switch to ensure that query election is activated. Enable
query mode to run multicast sessions on a network that does not contain IGMP routers (or queriers). Query
mode allows users to enable IGMP snooping by VLAN ID. Moxa switches support IGMP snooping version 1,
version 2, and version 3. Version 2 is compatible with version 1.The default setting is IGMP V1/V2.
Layer 3 switches are compatible with any device that conforms to the IGMP v2 and IGMP v3 device
Page 66

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-53
IGMP Multicast Filtering
IGMP is used by IP-supporting network devices to register hosts with multicast groups. It can be used on all
LANs and VLANs that contain a multicast capable IP router, and on other network devices that support
multicast filtering. Moxa switches support IGMP version 1, 2 and 3. IGMP version 1 and 2 work as follows:
• The IP router (or querier) periodically sends query packets to all end-stations on the LANs or VLANs that
are connected to it. For networks with more than one IP router, the router with the lowest IP address is
the querier. A switch with IP address lower than the IP address of any other IGMP queriers connected to
the LAN or VLAN can become the IGMP querier.
• When an IP host receives a query packet, it sends a report packet back that identifies the multicast
group that the end-station would like to join.
• When the report packet arrives at a port on a switch with IGMP Snooping enabled, the switch knows that
the port should forward traffic for the multicast group, and then proceeds to forward the packet to the
router.
• When the router receives the report packet, it registers that the LAN or VLAN requires traffic for the
multicast groups.
• When the router forwards traffic for the multicast group to the LAN or VLAN, the switches only forward
the traffic to ports that received a report packet.
IGMP version 3 supports “source filtering,” which allows the system to define how to treat packets from
specified source addresses. The system can either white-list or black-list specified sources.
IGMP version comparison
IGMP Version Main Features Reference
V1 Periodic query RFC-1112
V2 Compatible with V1 and adds:
a. Group-specific query
b. Leave group messages
c. Resends specific queries to verify leave message was the last one
in the group
d. Querier election
V3 Compatible with V1, V2, and adds:
Source filtering
- accept multicast traffic from specified source
- accept multicast traffic from any source except the specified source
RFC-2236
RFC-3376
GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol)
Moxa switches support IEEE 802.1D-1998 GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol), which is different
from IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol). GMRP is a MAC-based multicast management protocol,
whereas IGMP is IP-based. GMRP provides a mechanism that allows bridges and end stations to register or
de-register Group membership information dynamically. GMRP functions similarly to GVRP, except that
GMRP registers multicast addresses on ports. When a port receives a GMRP-join message, it will register
the multicast address to its database if the multicast address is not registered, and all the multicast packets
with that multicast address are able to be forwarded from this port. When a port receives a GMRP-leave
message, it will de-register the multicast address from its database, and all the multicast packets with this
multicast address will not be able to be forwarded from this port.
Static Multicast MAC
Some devices may only support multicast packets, but not support either IGMP Snooping or GMRP. The
Moxa switch supports adding multicast groups manually to enable multicast filtering.
Enabling Multicast Filtering
Use the USB console or web interface to enable or disable IGMP Snooping and IGMP querying. If IGMP
Snooping is not enabled, then IP multicast traffic is always forwarded, flooding the network.
Page 67

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-54
NOTE
IGMP Snooping will be disabled when Port
to
IGMP Snooping
IGMP Snooping provides the ability to prune multicast traffic so that it travels only to those end destinations
that require that traffic, thereby reducing the amount of traffic on the Ethernet LAN.
IGMP Snooping Setting
-Based VLAN is enabed.
Enable IGMP Snooping (Global)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Select the Enable IGMP Snooping checkbox near the top of
the window to enable the IGMP Snooping function globally.
Query Interval (sec)
Setting Description Factory Default
Numerical value, input
by the user
Enable Multicast Fast Forwarding Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Select the Enable Multicast Fast Forwarding Mode checkbox
Enable IGMP Snooping
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Enables or disables the IGMP Snooping function on that
Sets the query interval of the Querier function globally. Valid
settings are from 20 to 600 seconds.
achieve fast multicast forwarding path re-learning while the
ring redundant network is down.
Note: Turbo Ring V2 or Turbo Chain must be enabled.
particular VLAN.
Disabled
125 seconds
Disabled
Enabled if IGMP
Snooping is enabled
globally
Page 68

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-55
NOTE
If a router or layer 3 switch is connected to the
Querier option will be disabled on all Moxa layer 2 switches.
If all switches on the network are Moxa layer 2 switches, then only one layer 2 switch will act as Querier.
NOTE
Multicast Fast Forw
layer 3 switches. For
(UI 2.0) User’s Manual
Querier
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable Disables the Moxa switch’s querier function. V1/V2
V1/V2 and V3
checkbox
Static Multicast Querier Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the ports that will connect to the multicast routers.
V1/V2: Enables the switch to send IGMP queries that are
compatible for both V1 and V2.
V3: Enables the switch to send IGMP snooping version 3
queries
Disabled
These ports will receive all multicast packets from the source.
This option is only active when IGMP Snooping is enabled.
arding Mode is one function of V-ON technology that should be enabled in layer 2 and
a detailed introduction, refer to Moxa Managed Ethernet Switch Redundancy Protocol
.
IGMP Group Status
The Moxa switch displays the current active IGMP groups that were detected. On this page, you can view
IGMP group settings by VLAN ID.
network, it will act as the Querier, and consequently this
The information shown in the table includes:
• Dynamic Router Port: Indicates that a multicast router connects to or sends packets from these port(s).
• Static Router Port: Displays the static multicast querier port(s).
• Querier Connected Port: Displays the port that is connected to the querier.
• Role: Indicates if the switch is a querier. Displays Querier or Non-Querier.
• Group: Displays the multicast group addresses.
• Port: Displays the port that receives the multicast stream or the port the multicast stream is forwarded
to
• Version: Displays the IGMP Snooping version.
Page 69

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-56
NOTE
IGMP Stream Status is only
NOTE
The MAC address (
Snooping to implement automatic classification
• Filter Mode: Indicates that the multicast source address is included or excluded. Displays Include or
Exclude when IGMP v3 is enabled
• Sources: Displays the multicast source address when IGMP v3 is enabled
Stream Table
This page displays the multicast stream forwarding status. It allows you to view the status by VLAN ID.
Stream Group: Multicast group IP address
Stream Source: Multicast source IP address
Port: The port that receives the multicast stream
Member Ports: Ports the multicast stream is forwarded to
supported by Moxa’s Layer 3 switches.
Static Multicast Address
MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Integer Type the MAC address in the MAC Address field to specify a
01:00:5E:XX:XX:XX) will appear on the Static Multicast Address page. Activate IGMP
.
None
static multicast address.
Page 70

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-57
Member Port
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to define the join ports for
this multicast group.
None
GMRP
GMRP is a MAC-based multicast management protocol, whereas IGMP is IP-based. GMRP provides a
mechanism that allows bridges and end stations to register or un-register Group membership information
dynamically.
Enable GMRP
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to define which ports are
to be GMRP enabled.
GMRP Status
The Moxa switch displays the current active GMRP groups that were detected.
MAC Address: The Multicast MAC address
Static Port: This multicast address is defined by static multicast
Learned Port: This multicast address is learned by GMRP
Multicast Filtering Behavior
Multicast Filtering Behavior supports two options: Forward Unknown and Filter Unknown.
Note: Only supported by the EDS-518E, EDS-528E, IKS-6726A, IKS-6728A, IKS-6728A-8PoE,IKS-G6524A,
IKS-G6824A, ICS-G7526A, ICS-G7826A, ICS-G7528A, ICS-G7828A, ICS-G7748A, ICS-G7848A, ICS-
G7750A, ICS-G7850A, ICS-G7752A, and ICS-G7852A Series.
None
Page 71

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-58
Multicast Filtering Behavior
Setting Description Factory Default
Forward Unknown Allows the switch to forward all unknown Multicast streams Forward Unknown
Filter Unknown Allows the switch to drop all unknown Multicast steams
QoS
The Moxa switch’s traffic prioritization capability provides Quality of Service (QoS) to your network by
making data delivery more reliable. You can prioritize traffic on your network to ensure that high priority
data is transmitted with minimum delay. Traffic can be controlled by a set of rules to obtain the required
Quality of Service for your network. The rules define different types of traffic and specify how each type
should be treated as it passes through the switch. The Moxa switch can inspect both IEEE 802.1p/1Q layer 2
CoS tags, and even layer 3 TOS information to provide consistent classification of the entire network. The
Moxa switch’s QoS capability improves the performance and determinism of industrial networks for mission-
critical applications.
There are two types of QoS settings, depending on which model of switch you are using.
Type Model
Type 1 EDS-510E,EDS-518E, EDS-G512E-8PoE EDS-G508E, EDS-G512E-4GSFP, EDS-G516E-
4GSFP, IKS-6726A, IKS-6728A, IKS-6728A-8PoE
Type 2 IKS-G6524A, IKS-G6824A, ICS-G7526A, ICS-G7826A, ICS-G7528A, ICS-G7828A,
ICS-G7748A, ICS-G7848A, ICS-G7750A, ICS-G7850A, ICS-G7752A, ICS-G7852A
The Traffic Prioritization Concept
Traffic prioritization allows you to prioritize data so that time-sensitive and system-critical data can be
transferred smoothly and with minimal delay over a network. The benefits of using traffic prioritization are:
• Improve network performance by controlling a wide variety of traffic and by managing congestion.
• Assign priorities to different categories of traffic. For example, set higher priorities for time-critical or
business-critical applications.
• Provide predictable throughput for multimedia applications, such as video conferencing or voice over IP,
and minimize traffic delay and jitter.
• Improve network performance as the amount of traffic grows. Doing so will reduce costs since it will not
be necessary to keep adding bandwidth to the network.
Traffic prioritization uses the four traffic queues that are present in your Moxa switch to ensure that high
priority traffic is forwarded on a different queue from lower priority traffic. Traffic prioritization provides
Quality of Service (QoS) to your network.
Moxa switch traffic prioritization depends on two industry-standard methods:
• IEEE 802.1D—a layer 2 marking scheme.
• Differentiated Services (DiffServ)—a layer 3 marking scheme.
IEEE 802.1D Traffic Marking
The IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition marking scheme, which is an enhancement to IEEE Std 802.1D, enables
Quality of Service on the LAN. Traffic service levels are defined in the IEEE 802.1Q 4-byte tag, which is used
to carry VLAN identification as well as IEEE 802.1p priority information. The 4-byte tag immediately follows
the destination MAC address and Source MAC address.
The IEEE Std 802.1D, 1998 Edition priority marking scheme assigns an IEEE 802.1p priority level between 0
and 7 to each frame. The priority marking scheme determines the level of service that this type of traffic
should receive. Refer to the table below for an example of how different traffic types can be mapped to the
eight IEEE 802.1p priority levels.
Page 72

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-59
IEEE 802.1p Priority Level IEEE 802.1D Traffic Type
0 Best Effort (default)
1 Background
2 Standard (spare)
3 Excellent Effort (business critical)
4 Controlled Load (streaming multimedia)
5 Video (interactive media); less than 100 milliseconds of latency and jitter
6 Voice (interactive voice); less than 10 milliseconds of latency and jitter
7 Network Control Reserved traffic
Even though the IEEE 802.1D standard is the most widely used prioritization scheme for LAN environments,
it still has some restrictions:
• It requires an additional 4-byte tag in the frame, which is normally optional for Ethernet networks.
Without this tag, the scheme cannot work.
• The tag is part of the IEEE 802.1Q header, so to implement QoS at layer 2, the entire network must
implement IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging.
• It is only supported on a LAN and not across routed WAN links, since the IEEE 802.1Q tags are removed
when the packets pass through a router.
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) Traffic Marking
DiffServ is a Layer 3 marking scheme that uses the DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) field in the IP header to
store the packet priority information. DSCP is an advanced intelligent method of traffic marking that allows
you to choose how your network prioritizes different types of traffic. DSCP uses 64 values that map to user-
defined service levels, allowing you to establish more control over network traffic.
The advantages of DiffServ over IEEE 802.1D are:
• You can configure how you want your switch to treat selected applications and types of traffic by
assigning various grades of network service to them.
• No extra tags are required in the packet.
• DSCP uses the IP header of a packet to preserve priority across the Internet.
• DSCP is backwards compatible with IPV4 TOS, which allows operation with existing devices that use a
layer 3 TOS enabled prioritization scheme.
Traffic Prioritization
Moxa switches classify traffic based on layer 2 of the OSI 7 layer model, and the switch prioritizes received
traffic according to the priority information defined in the received packet. Incoming traffic is classified
based upon the IEEE 802.1D frame and is assigned to the appropriate priority queue based on the IEEE
802.1p service level value defined in that packet. Service level markings (values) are defined in the IEEE
802.1Q 4-byte tag, and consequently traffic will only contain 802.1p priority markings if the network is
configured with VLANs and VLAN tagging. The traffic flow through the switch is as follows:
• A packet received by the Moxa switch may or may not have an 802.1p tag associated with it. If it does
not, then it is given a default 802.1p tag (which is usually 0). Alternatively, the packet may be marked
with a new 802.1p value, which will result in all knowledge of the old 802.1p tag being lost.
• Because the 802.1p priority levels are fixed to the traffic queues, the packet will be placed in the
appropriate priority queue, ready for transmission through the appropriate egress port. When the packet
reaches the head of its queue and is about to be transmitted, the device determines whether or not the
egress port is tagged for that VLAN. If it is, then the new 802.1p tag is used in the extended 802.1D
header.
Page 73

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-60
• The Moxa switch will check a packet received at the ingress port for IEEE 802.1D traffic classification,
and then prioritize it based on the IEEE 802.1p value (service levels) in that tag. It is this 802.1p value
that determines which traffic queue the packet is mapped to.
Traffic Queues
The hardware of Moxa switches has multiple traffic queues that allow packet prioritization to occur. Higher
priority traffic can pass through the Moxa switch without being delayed by lower priority traffic. As each
packet arrives in the Moxa switch, it passes through any ingress processing (which includes classification,
marking/re-marking), and is then sorted into the appropriate queue. The switch then forwards packets from
each queue.
Moxa switches support two different queuing mechanisms:
• Weight Fair: This method services all the traffic queues, giving priority to the higher priority queues.
Under most circumstances, the Weight Fair method gives high priority precedence over low priority, but
in the event that high priority traffic does not reach the link capacity, lower priority traffic is not blocked.
• Strict: This method services high traffic queues first; low priority queues are delayed until no more high
priority data needs to be sent. The Strict method always gives precedence to high priority over low
priority.
Configuring Traffic Prioritization
Quality of Service (QoS) provides a traffic prioritization capability to ensure that important data is delivered
consistently and predictably. The Moxa switch can inspect IEEE 802.1p/1Q layer 2 CoS tags, and even layer
3 TOS information, to provide a consistent classification of the entire network. The Moxa switch’s QoS
capability improves your industrial network’s performance and determinism for mission critical applications.
CoS Classification
Scheduling Mechanism
Setting Description Factory Default
Weight Fair The Moxa switch has 4 priority queues. In the weight fair
scheme, an 8, 4, 2, 1 weighting is applied to the four
Weight Fair
Page 74

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-61
transmission with only a
NOTE
The priority of an ingress frame is determined in the following order:
NOTE
The designer can enable these classifications individually or in combination. For instance, if a “hot” higher
priority port is required for a network design,
can be disabled.
This setting leaves only port default priority active, which results in all ingress frames being assigned the
same priority on that port.
priorities. This approach prevents the lower priority frames
from being starved of opportunity for
slight delay to the higher priority frames
Strict In the Strict-priority scheme, all top-priority frames egress a
port until that priority’s frames egress. This approach can
cause the lower priorities to be starved of opportunity for
transmitting frames but ensures that all high priority frames
will egress the switch as soon as possible.
TOS/DSCP Inspection
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Enables or disables the Moxa switch for inspecting Type of
Server (TOS) bits in the IPV4 frame to determine the priority
of each frame.
COS Inspection
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Enables or disables the Moxa switch for inspecting 802.1p
COS tags in the MAC frame to determine the priority of each
frame.
Enable
Enable
Priority
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 7 The port priority has 8 priority queues: from 0 (lowest) to 7
(highest)
1. ToS/DSCP Inspection
2. CoS Inspection
3. Priority
Priority Mapping (Type 1)
3
TOS/DSCP Inspection and Cos Inspection
Page 75

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-62
CoS Priority and Queues
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 3 Maps different CoS values to 4 different egress queues. CoS 0, 1: 0
CoS 2, 3: 1
CoS 4, 5: 2
CoS 6, 7: 3
Priority Mapping (Type 2)
CoS Value and Priority Queues
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 7 Maps different CoS values to 8 different egress queues. CoS 0: 0
CoS 1: 1
CoS 2: 2
CoS 3: 3
CoS 4: 4
CoS 5: 5
CoS 6: 6
CoS 7: 7
Page 76

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-63
DSCP Mapping
DSCP Value and Priority
Setting Description Factory Default
0 to 7
8 to 15 1
16 to 23 2
24 to 31 3
32 to 39 4
40 to 47 5
48 to 55 6
56 to 63 7
Rate Limiting
In general, one host should not be allowed to occupy unlimited bandwidth, particularly when the device
malfunctions. For example, so-called “broadcast storms” could be caused by an incorrectly configured
topology, or a malfunctioning device. Moxa industrial Ethernet switches not only prevent broadcast storms,
but can also be configured to a different ingress rate for all packets, giving administrators full control of
their limited bandwidth to prevent undesirable effects caused by unpredictable faults.
Traffic Rate Limiting Settings
There are four types of bandwidth management settings, depending on which model of switch you are
using.
0
Different DSCP values map to one of 8 different priorities.
Type Model
Type 1 EDS-510E
Type 2 EDS-G508E, EDS-G512E-4GSFP, EDS-G516E-4GSFP, EDS-G512E-8PoE
Type 3 EDS-518E, IKS-6726A, IKS-6728A, IKS-6728A-8PoE, EDS-P506E-4PoE
Type 4 IKS-G6524A, IKS-G6824A, ICS-G7526A, ICS-G7826A, ICS-G7528A, ICS-G7828A, ICS-
G7748A, ICS-G7848A, ICS-G7750A, ICS-G7850A, ICS-G7752A, ICS-G7852A
Page 77

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-64
(% of max.
Type 1
For Type 1, the Control Mode setting on the Rate Limiting page can be set to Normal or Port Disable.
Control Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Normal Set the max. ingress rate limit for different packet types Normal
Port Disable When the ingress multicast and broadcast packets exceed the
ingress rate limit, the port will be disabled for a certain
period. During this period, all packets from this port will be
discarded.
Rate Limiting: Normal
Ingress Rate Limit
Policy Description Factory Default
Limit All Select the ingress rate limit for different packet types from
Limit Broadcast,
Multicast, Flooded
Unicast
Limit Broadcast,
Multicast
Limit Broadcast
the following options: Unlimited, 128K, 256K, 512K, 1M, 2M,
4M, 8M
Limit Broadcast 8M
Egress Rate Limit
Setting Description Factory Default
Egress rate
throughput)
Select the egress rate limit (% of max. throughput) for all
packets from the following options: Not Limited, 3%, 5%,
10%, 15%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 65%, 85%
Unlimited
Page 78

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-65
NOTE
The
Rate Limiting: Port Disable
Setting Description Factory Default
Port disable duration
(1-65535 seconds)
Ingress (frames per
second)
When the ingress multicast and broadcast packets exceed the
ingress rate limit, the port will be disabled for this period of
time. During this time, all packets from this port will be
discarded.
Select the ingress rate (fps) limit for all packets from the
following options: Not Limited, 4464, 7441, 14881, 22322,
37203, 52084, 74405
30 seconds
Unlimited
Rate Limiting function is for broadcast packets only.
Type 2
For Type 2, the Action setting on the Rate Limiting page can be set to Drop Packet or Port Disable.
Action
Setting Description Factory Default
Drop Packet Set the max. ingress rate limit for ingress packets Drop Packet
Port Disable When the ingress packets exceed the ingress rate limit, the
port will be disabled for a certain period. During this period,
all packets from this port will be discarded.
Page 79

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-66
NOTE
The
Rate Limiting: Drop Packet
Setting Description Factory Default
Ingress rate (% of
max. throughput)
Select the ingress rate limit (% of max. throughput) for all
packets from the following options: Not Limited, 3%, 5%,
10%, 15%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 65%, 85%
Unlimited
Rate Limiting: Port Disable
Setting Description Factory Default
Duration (1-65535
seconds)
Ingress (frame per
second)
When the ingress packets exceed the ingress rate limit, the
port will be disabled for a certain period.
Select the ingress rate (fps) limit for all packets from the
following options: Not Limited, 4464, 7441, 14881, 22322,
37203, 52084, 74405
30 seconds
Unlimited
Port Disable function of Rate Limiting is for broadcast packets only.
Page 80

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-67
NOTE
The
Type 3
For Type 3, the Action setting on the Rate Limiting page can be set to Drop Packet or Port Disable.
Action
Setting Description Factory Default
Drop Packet Set the max. ingress/egress rate limit for ingress/egress
packets
Port Disable When the ingress packets exceed the ingress rate limit, the
port will be disabled for a certain period. During this period,
all packets from this port will be discarded.
Rate Limiting: Drop Packet
Drop Packet
Setting Description Factory Default
Ingress rate (% of
max. throughput)
Egress rate (% of
max. throughput)
Drop Packet function of Rate Limiting is for multicast packets and broadcast packets.
Select the ingress rate limit (% of max. throughput) for all
packets from the following options: Not Limited, 3%, 5%,
10%, 15%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 65%, 85%
Select the egress rate limit (% of max. throughput) for all
packets from the following options: Not Limited, 3%, 5%,
10%, 15%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 65%, 85%
Unlimited
Unlimited
Page 81

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-68
NOTE
The
Rate Limiting: Port Disable
Type 4
Setting Description Factory Default
Port disable
duration (1-65535
seconds
Ingress (frame per
second)
Port Disable function of Rate Limiting is for multicast packets and broadcast packets.
For Type 4, the Control Mode setting on the Rate Limiting page can be set to Normal or Port Disable.
Control Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Normal Set the max. ingress rate limit for different packet types 30 seconds
Port Disable When the ingress multicast and broadcast packets exceed the
When the ingress packets exceed the ingress rate limit, the
port will be disabled for a certain period.
Select the ingress rate (fps) limit for all packets from the
following options: Not Limited, 4464, 7441, 14881, 22322,
37203, 52084, 74405
ingress rate limit, the port will be disabled for a certain
period. During this period, all packets from this port will be
discarded.
30 seconds
Unlimited
Unlimited
Page 82

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-69
Rate Limiting: Normal
Ingress Rate Limit
Policy Description Factory Default
Limit All Select the ingress rate limit for different packet types from
Limit Broadcast,
Multicast, Flooded
Unicast
Limit Broadcast,
Multicast
Limit Broadcast
the following options: Unlimited, 128K, 256K, 512K, 1M, 2M,
4M, 8M, 10%(100Mbps), 15%(150Mbps), 25%(250Mbps),
35%(350Mbps), 50%(500Mbps), 65%(650Mbps),
85%(850Mbps).
Limit Broadcast 8M
Egress Rate Limit
Setting Description Factory Default
Egress rate Select the egress rate limit (% of max. throughput) for all
packets from the following options: Not Limited, 3%, 5%,
10%, 15%, 25%, 35%, 50%, 65%, 85%
Unlimited
Page 83

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-70
Rate Limiting: Port Disable
Setting Description Factory Default
Port disable
duration (1-65535
seconds)
Ingress (frames per
second)
When the ingress packets exceed the ingress rate limit, the
port will be disabled for a certain period.
Select the ingress rate (fps) limit for all packets from the
following options: Not Limited, 4464, 7441, 14881, 22322,
37203, 52084, 74405
30 seconds
Unlimited
Security
Security can be categorized into two levels: the user name/password level, and the port access level. Moxa
switches provide many kinds of security functions, including Management Interface, Trusted Access,
SSL/SSH Authentication certificate, Login Authentication, IEEE 802.1X, MAC Authentication Bypass, Port
Security, Broadcast Storm Protection, Loop Protection, and Access Control List.
Management Interface
Enable HTTP
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable HTTP. TCP Port: 80
Page 84

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-71
Enable HTTPS
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable HTTPS. TCP Port: 443
Enable Telnet
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable Telnet. TCP Port: 23
Enable SSH
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable SSH. TCP Port: 22
Enable SNMP
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable SNMP. TCP Port: 161
Enable Moxa Service
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable Moxa Service.
NOTE: Moxa Service is only for Moxa network management
software suite.
TCP Port: 4000
UDP Port: 4000
Enable Moxa Service (Encrypted)
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the appropriate checkboxes to enable Moxa Service
(Encrypted). NOTE: Moxa Service (Encrypted) is only for
Moxa network management software suite.
Maximum Login Users for HTTP+HTTPS
Setting Description Factory Default
Integer (1 to 10) Sets the maximum number of login users for HTTP and
HTTPS
Maximum Login Users for Telnet+SSH
Setting Description Factory Default
Integer (1 to 5) Sets the maximum number of login users for Telnet and SSH 1
Auto Logout Setting (min)
Setting Description Factory Default
Integer (0 to 1440) Sets the web auto logout period.
(Enter 0 to disable this function.)
TCP Port: 443
UDP Port: 40404
5
5
Page 85

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-72
Trusted Access
The Moxa switch uses an IP address-based filtering method to control access.
You may add or remove IP addresses to limit access to the Moxa switch. When the Trusted Access list is
enabled, only addresses on the list will be allowed access to the Moxa switch. Each IP address and netmask
entry can be tailored for different situations:
• Grant access to one host with a specific IP address
For example, enter IP address 192.168.1.1 with netmask 255.255.255.255 to allow access to
192.168.1.1 only.
• Grant access to any host on a specific subnetwork
For example, enter IP address 192.168.1.0 with netmask 255.255.255.0 to allow access to all IPs on the
subnet defined by this IP address/subnet mask combination.
• Grant access to all hosts
Make sure the Trusted Access list is not enabled by removing the checkmark from Enable trusted
access.
The following table shows additional configuration examples:
Hosts That Need Access Input Format
Any host Disable
192.168.1.120 192.168.1.120 / 255.255.255.255
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.255.0
192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254 192.168.0.0 / 255.255.0.0
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.255.128
192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.128 / 255.255.255.128
Page 86

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-73
SSL Certificate Management
Certificate Import
1. Click Browse and select Public-Key Cryptography Standard (PKCS) #12 certificate file
2. Enter the Import Password and click Import
3. The SSL certificate is updated
Regenerate SSL Certificate
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Enable the SSL Certificate Regeneration Deselect
SSH Key Management
SSH Key Re-generate
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Enable SSH Key Re-generate Deselect
Authentication
Login Authentication
Moxa switches provide three different user login authentications: TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller
Access-Control System Plus), RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial In User Service), and Local. The
TACACS+ and RADIUS mechanisms are centralized “AAA” (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting)
systems for connecting to network services. The fundamental purpose of both TACACS+ and RADIUS is to
provide an efficient and secure mechanism for user account management.
Page 87

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-74
There are five combinations for users:
1. TACACS+, Local: Check TACACS+ database first. If checking the TACACS+ database fails, then check
the Local database
2. RADIUS, Local: Check RADIUS database first. If checking the RADIUS database fails, then check the
Local database
3. TACACS+: Only check TACACS+ database
4. RADIUS: Only check the RADIUS database
5. Local: Only check the Local database
Setting Description Factory Default
Authentication Protocol Authentication protocol selection. Local
Server IP/Name Sets the IP address of an external TACACS+/RADIUS server
as the authentication database.
TCP/UDP Port Sets the communication port of an external
TACACS+/RADIUS server as the authentication database.
Shared Key Sets specific characters for server authentication verification. None
Authentication Type Authentication mechanism selection. ASCII, PAP, CHAP, and
MSCHAP are for TACACS+; PAP and CHAP are for RADIUS.
Timeout (sec) The timeout period for waiting for a server response. 3
None
TACACS+: 49
RADIUS: 1812
ASCII for TACACS+
PAP for RADIUS
Page 88

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-75
NOTE
The account privilege level is authorized
under
RADIUS Server
TACACS+ Server
• TACACS+ privilege level= 1 to 14 = read only = user
TACACS+.
• RADIUS Service type = 6 = read/write = administrator
• RADIUS Service type = 1 = read only = user
• TACACS+ privilege level= 15 = read/write = administrator
under service type settings in RADIUS, and the privilege level is
IEEE 802.1X Settings
The IEEE 802.1X standard defines a protocol for client/server-based access control and authentication. The
protocol restricts unauthorized clients from connecting to a LAN through ports that are open to the Internet,
and which otherwise would be readily accessible. The purpose of the authentication server is to check each
client that requests access to the port. The client is only allowed access to the port if the client’s permission
is authenticated.
Three components are used to create an authentication mechanism based on 802.1X standards:
Client/Supplicant, Authentication Server, and Authenticator.
Client/Supplicant: The end station that requests access to the LAN and switch services and responds to
the requests from the switch.
Authentication Server: The server that performs the actual authentication of the supplicant.
Authenticator: Edge switch or wireless access point that acts as a proxy between the supplicant and the
authentication server, requesting identity information from the supplicant, verifying the information with the
authentication server, and relaying a response to the supplicant.
The Moxa switch acts as an authenticator in the 802.1X environment. A supplicant and an authenticator
exchange EAPOL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) frames with each other. We can either use
an external RADIUS server as the authentication server, or implement the authentication server in the Moxa
switch by using a Local User Database as the authentication look-up table. When we use an external
RADIUS server as the authentication server, the authenticator and the authentication server exchange EAP
frames.
Authentication can be initiated either by the supplicant or the authenticator. When the supplicant initiates
the authentication process, it sends an EAPOL-Start frame to the authenticator. When the authenticator
initiates the authentication process or when it receives an EAPOL Start frame, it sends an EAP
Request/Identity frame to ask for the username of the supplicant.
Page 89

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-76
Authentication Protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
802.1X Local
(Max. of 32 users)
RADIUS Select this option to set an external RADIUS server as the
RADIUS, 802.1X Local Select this option to make using an external RADIUS server
Select this option when setting the 802.1X Local User
Database as the authentication database.
authentication database. The authentication mechanism is
EAP-MD5.
as the authentication database the first priority. The
authentication mechanism is EAP-MD5. The second priority is
to set the 802.1X Local User Database as the authentication
database.
802.1X Local
Re-Auth (Global)
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Select enable to require re-authentication of the client after a
Re-Auth Period (sec)
Setting Description Factory Default
60 to 65535 Sets the Re-Auth period 3600
Enable 802.1X
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select the checkbox under the 802.1X column to enable IEEE
Re-Auth
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Select enable to require re-authentication of the client by port Deselect
Enable
preset time period of no activity has elapsed.
Deselect
802.1X for one or more ports. All end stations must enter
usernames and passwords before access to these ports is
allowed.
Page 90

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-77
the MAC
NOTE
The user name for the
IEEE 802.1X Local Database
When selecting the 802.1X Local as the authentication protocol, set the IEEE 802.1X Local Database first.
IEEE 802.1X Local Database Setup
Setting Description Factory Default
User Name
(Max. of 30
characters)
Password
(Max. of 16
characters)
Confirm Password
(Max. of 16
characters)
Description
(Max. of 30
characters)
User Name for the Local User Database None
Password for the Local User Database. Input the MAC address
without ":", while using MAC Authentication Bypass with the
Local database.
Confirm Password for the Local User Database. Input
address without ":", while using MAC Authentication Bypass
with the Local database.
Description for the Local User Database None
IEEE 802.1X Local Database is not case sensitive.
None
None
Page 91

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-78
NOTE
If RADIUS Server is case sensitive,
NOTE
MAC Authentication Bypass is not available on the
MAC Authentication Bypass Settings
Authentication Protocol
Setting Description Factory Default
RADIUS Authenticated by the RADIUS protocol. RADIUS
Local Input authorized MAC address in IEEE802.1X Local Database
Re-Auth
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Select enable to require re-authentication of the client after a
preset time period of no activity has elapsed
Re-Auth Period (sec)
Setting Description Factory Default
60 to 65535 Sets the Re-Auth period 3600
Re-Start
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable/Disable Select enable to require a present time period to re-start
authentication after failure of authentication
Re-Start Period (sec)
Setting Description Factory Default
5 to 300 Sets the Re-Start period 60
Enable MAC Authentication Bypass
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Check the checkbox under the MAC Authentication Bypass
column to enable MAC Authentication Bypass for one or more
ports
Disable
Disable
Deselect
use lower-case characters for the username and password.
EDS-510E Series.
Page 92

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-79
RADIUS Server Settings
Apply Login Authentication Setting
Setting Description Factory Default
Select/Deselect Enables using the same setting as Auth Server. Deselect
Server Setting
Setting Description Factory Default
Server IP/Name Specifies the IP/name of the server None
Server Port Specifies the port of the server 1812
Server Shared Key Specifies the shared key of the server None
Page 93

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-80
NOTE
S
the
Port Security
Moxa switches provide a Port Security function that lets packets with allowed MAC Addresses access the
switch’s ports. Two Port Security modes are supported: Static Port Lock and MAC Address Sticky.
Static Port Lock: Allows users to configure specific MAC addresses that are allowed to access the port.
MAC Address Sticky: Allows users to configure the maximum number of MAC addresses (the Limit) that a
port can “learn.” Users can configure what action should be taken (under Violation Port Disable) when a new
MAC address tries to access a port after the maximum number of MAC addresses have already been
learned. The total number of allowed MAC addresses cannot exceed 1024.
The whitelist (or blacklist) of the EDS-G500E Series, including EDS-G508E Series, EDS-G512E(-8PoE)
eries, and EDS-G516E Series, cannot regulate the traffic from the target host through the specified port to
CPU because of a chipset limitation.
Port Security Mode
Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Static Port Lock The switch will block unauthorized MAC addresses and allow
access to packets with a MAC address defined in the Static
Unicast MAC Address Table.
MAC Address Sticky If Limit is set to n, the switch will learn the first n MAC
addresses that access the port, and automatically store them
in the MAC Address Control Table.
None
Page 94

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-81
Limit (only active for MAC Address Sticky)
Setting Description Factory Default
1 to 1024 The maximum number of learned MAC addresses allowed for
that port.
Violation Port Disable (only active for MAC Address Sticky)
Setting Description Factory Default
Disable When the port receives a packet with an unlearned MAC
address, the packet will be discarded.
Enable When the port receives a packet with an unlearned MAC
address, the port will be disabled.
1
Disable
Static Port Lock
Port Number
Setting Description Factory Default
Port Number Associates the static address to a dedicated port None
VID
Setting Description Factory Default
VLAN ID Associates the static address to a dedicated VLAN on the port None
MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Default
Page 95

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-82
MAC Address Adds the static unicast MAC address into the address table None
MAC Address Sticky
Port Number
Setting Description Factory Default
Port Number Associates the static address to a dedicated port None
VID
Setting Description Factory Default
VLAN ID Associates the static address to a dedicated VLAN on the port None
MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Default
MAC Address Adds the static unicast MAC address into the address table None
Page 96

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-83
Broadcast storm protection is activated. In this case, you may
Include Multicast Packet
When checked,
traffic is over
Include Unknown Unicast Packet
When checked,
Unknown Unicast packet traffic is over
Port Access Control Table
The port status will be indicated as authorized or unauthorized.
Broadcast Storm Protection
Broadcast Storm Protection is only supported by the EDS-G508E, EDS-G512E-4GSFP, EDS-G516E-4GSFP,
IKS-6726A/6728A/6728A-8PoE, EDS-G512E-8PoE, EDS-518E, and EDS-528E series.
Broadcast Storm Protection
Setting Description Factory Default
Unchecked Broadcast storm protection is not activated. Checked
Checked
check either one or both of Include Multicast Packet and
Include Unknown Unicast Packet.
:
the switch will discard Multicast packets if the Multicast
the Multicast packet limit.
:
the switch will discard Unknown Unicast packets if the
the limit.
Page 97

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-84
NOTE
Access Control Lists are available in
EDS
Ingress ACL.
Loop Protection
The switch is designed with a loop checking mechanism whereby it sends a control BPDU from the Ethernet
port and check if this control PBDU will be sent back to the switch again. If the looping occurs, the switch
will automatically block the Ethernet port to prevent looping.
Enable Loop Protection
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable Select the Enable checkbox to enable the loop protection
function.
Disable Deselect the Enable checkbox to disable the loop protection
function.
Disable
Access Control List
-518E. EDS-G508E, EDS-G512E, EDS-G516E, and EDS-G512E-8PoE. Layer 2 switches only support
Access control lists (ACLs) increase the flexibility and security of networking management. ACLs provide
traffic filtering capabilities for ingress and egress packets. Moxa ACLs can manage filter criteria for a diverse
range of protocols and allow users to configure customized filter criteria. For example, users can deny
access to specific source or destination IP/MAC addresses. The Moxa ACL configuration interface is easy to
use. Users can quickly establish filtering rules, manage rule priorities, and view overall settings on the
display page.
The ACL Concept
What is ACL?
An access control list is a basic traffic filter for ingress and egress packets. The ACL can examine each
Ethernet packet’s information and take the necessary action. Moxa Layer 3 switches provide complete
filtering capabilities. Access list criteria could include the source or destination IP address of the packets, the
source or destination MAC address of the packets, IP protocols, or other information. The ACL can check
these criteria to decide whether to permit or deny access to a packet.
Moxa Layer 3 switches and the following layer 2 switches: EDS-528E,
Benefits of ACL
ACLs support per interface, per packet direction, and per protocol filtering capability. These features can
provide basic protection by filtering specific packets. The main benefits of an ACL are:
• Manage authority of hosts: An ACL can restrict specific devices through MAC address filtering. The
user can deny all packets or only permit packets that come from specific devices.
• Subnet authority management: Configure filtering rules for specific subnet IP addresses. An ACL can
restrict packets from or to specific subnets.
Page 98

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-85
• Network security: The demand for networking security is growing. An ACL can provide basic protection
that works in a similar manner to an Ethernet firewall device.
• Control traffic flow by filtering specific protocols: An ACL can filter specific IP protocols such as TCP
or UDP packets.
How an ACL Works
The ACL working structure is based on access lists. Each access list is a filter. When a packet enters into or
exits from a switch, the ACL will compare the packet to the rules in the access lists, starting from the first
rule. If a packet is rejected or accepted by the first rule, the switch will drop or pass this packet directly
without checking the rest of the lower-priority rules. In other words, Access Control Lists have “Priority
Index” as an attribute to define the priority in the web configuration console.
There are two types of settings for an ACL: list settings and rule settings. In order to be created, an Access
Control List needs the following list settings: Name, Priority Index, Filter Type, and Ports to Apply. Once
created, each Access Control List has its own set of rule settings. Priority Index represents the priority of the
names in the access list. Names at Priority Index 1 have first priority in packet filtering. The Priority Index is
adjustable whenever users need to change the priority. Two types of packet filtering can be used:
• IP based
• MAC Based
MAC Based ACL rules will only apply for non-IP (or pure Ethernet without IP headers) packets, while IP
Based ACL rules will apply for the other IP packets. The type affects what detailed rules can be edited. You
can then assign the ports you would like to apply the list to. You can also define Ingress and Egress per
port.
After adding a new access control list, you can also create new rules for the access control list. Each ACL
group accepts 10 rules. Rules can filter packets by source and destination IP/MAC address, IP protocol,
TCP/UDP Port, Ethernet Type, and VLAN ID.
After all rules are set, the ACL starts to filter the packets by the rule with the highest Priority Index (smaller
number, higher priority). Once a rule denies or accepts its access, the packet will be dropped or passed.
Page 99

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-86
Access Control List Configuration and Setup
Access Control Profile Settings
On this page, you can configure two settings: (1) Add/Modify Access Control list, and (2) Adjust ACL ID.
Add/Modify Access Control List
This function lets you add a new access control profile or modify an existing access control profile. The
operation depends on the ACL ID you select. If the selected ACL ID is still empty, you can start by creating
a new access control profile. Parameters for editing are as follows:
• ACL ID: The ACL checking sequence is based on these IDs. Smaller ID numbers have a higher priority
for packet filtering. If a packet is filtered by an access control profile with a higher priority, those access
control profiles with a lower priority will not be executed.
Note that the ACL ID is not unique with respect to the profile name. The ID changes when swapping the
priority of different access control profiles.
The maximum Priority Index number is 16.
• Name: You can name the access control profile in this field.
• Filter Name: Select filtering by either IP or MAC address. Detailed settings can be configured in the
Access Control Rule Settings page.
If a selected ACL ID is already in the access control list, then you can modify the parameters listed above.
After the configuration is complete, click Apply to confirm the settings. A new list will appear in the Access
Control List Table.
Adjust ACL ID
Changing an established access control profile’s priority is easy. Moxa provides a simple interface to let you
easily adjust the priority. Follow the three steps below to adjust the priority:
Step 1: Select the profile
Step 2: Click the Up/Down button to adjust the sequence. The ACL ID will change with the profile’s
position.
Step 3: Click the Apply button to confirm the settings.
Page 100

Managed Ethernet Switch (UI_2.0_FW_5.x) Featured Functions
3-87
Access Control Rule Settings
You can edit access control rules on this page. Each ACL includes up to 10 rules. First, select the access
control profile you would like to edit based on the ACL ID, and then set up the rule content and
ingress/egress ports. After configuring, click the Add button to add the rule to the list. Finally, click Apply to
activate the settings.
An access control rule displays setting options based on the filtering type used:
IP Based (Layer 2 Device)
 Loading...
Loading...