Page 1

P/N: 1802020160012
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
2021 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
EDS-2016-ML Series
Quick Installation Guide
Moxa EtherDevice Switch
Version 1.2, March 2021
*1802020160012*
Page 2
Overview
NOTE
Throughout this Quick Installation Guide, we use EDS as an
abbreviation for M oxa EtherDevice Switch:
EDS = Moxa EtherDevice Switch
ATTENTION
This device c omplies with part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not
cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
The EDS-2016-ML Series industrial Ethernet switches have 16 10/100M
ports and up to two optical fiber ports with SC/ST connector type options.
The EDS-2016-ML provides 12/24/48 VDC redundant power inputs, and
the switches are available with a standard operating temperature range
from -10 to 60°C, or with a wide operating temperature range from -40 to
75°C. The switches are rugged enough to operate reliably in harsh
industrial environments.
To provide greater versatility for u se with applicat ions from d ifferent
industries, the EDS-2016-ML a lso allow users to enable or disable
broadcast storm protection, Quality of Service (QoS) function, and port
break alarm function with DIP switches on the outer panel.
The EDS-2016-ML switches can be easily installed with DIN-Rail
mounting as well as distribution boxes. The DIN-rail mounting capability
and IP30 metal housing with LED indicators make the plug-and-play
EDS-2016-ML switches reliable and easy to use.
Package Checklist
Your EDS is shipped with the following items. If any of these items are
missing or damaged, please contact your customer service
representative for assistance.
• Moxa EtherDevice™ Switch
• Quick installation guide (printed)
• Warranty card
• Protective caps for unused ports
- 2 -
Page 3
Features
WARNING
The
for this product is intended to be supplied by a Listed
Power Supply, with output marked LPS, and rated to deliver 12 to
48 VDC at a maximum
The DC
deliver 12 to 48 VDC at a minimum of 1.1A. The product should
not be disassembled by operators or service people.
High Performance Network Switching Technology
• 10/100BaseT(X) auto-negotiation speed, full/half duplex mode, auto
MDI/MDI-X connection, and 100BaseFX (SC/ST type, Multi/Single
mode).
• IEEE 802.3 for 10BaseT, IEEE 802.3u for 100BaseT(X) and
100BaseFX.
• IEEE 802.1p for Quality of Service (QoS) traffic prioritized function.
• Store-and-forward switching process type.
Industrial-grade Reliability
• Power failure, port break alarm by relay output
• Redundant dual DC power inputs
• Broadcast storm protection to prevent network devices from crashing
Rugged Design
• Operating temperature range from -10 to 60°C, or extended
operating temperature from -40 to 75°C for “-T” models
• IP30, rugged high-strength case
• DIN-rail or panel mounting ability
power
of 0.62 A.
jack should be used with an LPS unit that is rated to
- 3 -
Page 4
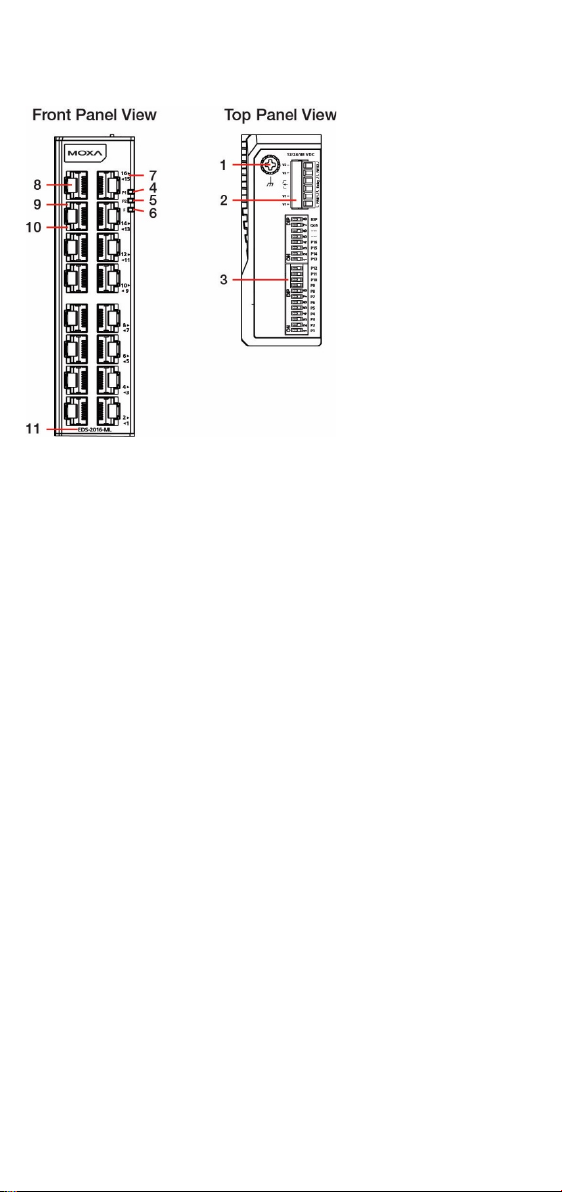
Panel Layout of EDS-2016-ML (Standard type)
1. Grounding screw
2. Terminal block for power input
(PWR1, PWR2) and relay output
3. DIP switch
4. Power input PWR1 LED
5. Power input PWR2 LED
6. Fault LED
7. Port number
8. 10/100 BaseT(X) Port
9. TP port’s 100 Mbps LED
10. TP port’s 10 Mbps LED
11. Model name
- 4 -
Page 5

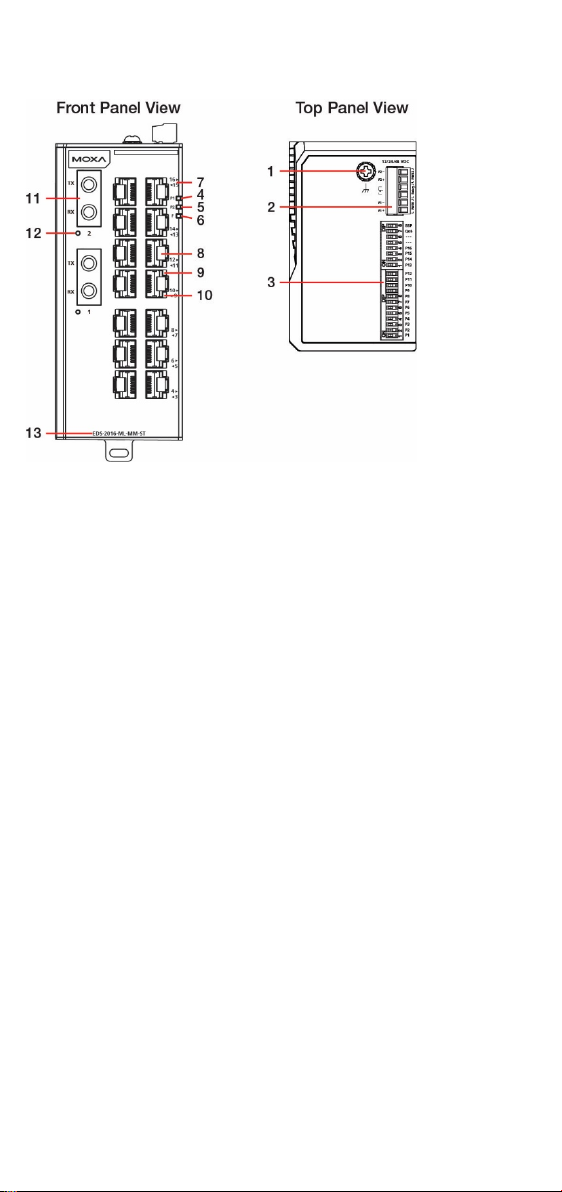
Panel Layout of EDS-2016-ML (SC type)
1. Grounding screw
2. Terminal block for power input
(PWR1, PWR2) and relay output
3. DIP switch
4. Power input PWR1 LED
5. Power input PWR2 LED
6. Fault LED
7. Port number
8. 10/100 BaseT(X) Port
9. TP port’s 100 Mbps LED
10. TP port’s 10 Mbps LED
11. 100BaseFX Port
12. FX port’s 100 Mbps LED
13. Model name
- 5 -
Page 6
Panel Layout of EDS-2016-ML (ST type)
1. Grounding screw
2. Terminal block for power input
(PWR1, PWR2) and relay output
3. DIP switch
4. Power input PWR1 LED
5. Power input PWR2 LED
6. Fault LED
7. Port number
8. 10/100 BaseT(X) Port
9. TP port’s 100 Mbps LED
10. TP port’s 10 Mbps LED
11. 100BaseFX Port
12. FX port’s 100 Mbps LED
13. Model name
- 6 -
Page 7

Mounting Dimensions
EDS-2016-ML Series
EDS-2016-ML Fiber Series
- 7 -
Page 8

DIN-Rail Mounting
STEP 1:
Insert the upper lip of the DIN-rail
kit into the mounting rail.
S
Press the device towards the
mounting rail until it snaps into
place.
STEP 1:
Pull down the latch on the DIN-rail
kit with a screwdriver.
STEP 2:
Slightly
and lift up to remove it from the
mounting rail.
There are two options for DIN-rail mounting that can be used on an EDS.
Option 1 is the default type when the product is shipped.
Option 1 (Default):
When shipped, the metal DIN-rail mounting kit is fixed to the back panel
of the EDS. Mount the EDS on the corrosion-free mounting rail that
adheres to the EN 60715 standard.
Suggested Installation Method
TEP 2:
Suggested Removal Method
pull the device forward
Option 2 (when side cabling is needed):
The metal DIN-rail mounting kit can be fixed to the side panel (mold s ide)
of the EDS (horizontal or vertical). Mount the EDS on the corrosion-free
mounting rail that adheres to the EN 60715 standard.
- 8 -
Page 9

Suggested Installation Method
STEP 2:
Insert the upper lip of the DIN
into the mounting rail.
STEP 3:
Press the device towards the mounting
rail until it snaps into place
STEP 1:
Pull down the latch on
with a screwdriver.
STEP 2:
Slightly pull the device forward and lift
up to remove it from the mounting rail.
NOTE
Screws that are used to fix the DIN-rail kit on the EDS should be
securely fastened before mounting on the mounting rail. Please
make sure that if you remove the DIN
fastened when it is reattached.
STEP 1:
Detach the metal DIN-rail mounting kit from the back panel and attach it
to the s ide panel (mold side) in either the horizontal or vertica l direction
as indicated in the figure below.
-rail kit
.
Suggested Removal Method
the DIN-rail kit
- 9 -
-rail, it must be securely
Page 10

Wall Mounting (optional)
EDS-2016-ML Series
EDS-2016-ML Fiber Series
STEP 2:
Mounting
the switch, with wall mount plates attached, as a guide
to mark the correct locations of the 4 screws. The
heads of the screws should be less than 6.0 mm in
diameter, and the shafts should be less than 3.5 mm in
diameter, as shown in the figure at the right.
NOTE
Before tightening screws into the wall, make sure the screw head
and shank size are suitable by inserting the screw into one of the
keyhole-shaped apertures of the Wall Mounting Plates.
STEP 3:
Once the screws are fixed in the
wall, insert the four screw heads
through the large parts of the
keyhole
t
indicated. Tighten the four
screws for added stability.
WARNING
External metal parts can be hot. Take necessary precautions if it
is necessary to touch.
For some applications, you will find it convenient to mount EDS on the
wall, as illustrated below.
STEP 1:
Remove the aluminum DIN-Rail attachment plate from EDS’s rear panel,
and then attach the wall mount plates, as shown in the diagram below.
the EDS on the wall requires 4 screws. Use
Do not screw the screws in all the way—leave about 2 mm to allow room
for sliding the wall mount panel between the wall and the screws.
-shaped apertures, and
hen slide EDS downwards, as
- 10 -
Page 11

Wiring Requirements
WARNING
Do not disconnect modules or wires unless the power supply has
been switched off or the area is known to be non
The
devices may only be connected to the supply voltage shown on
the type plate.
The devices are designed for operation with a
ow
Voltage. Thus, they may only be connected to the supply voltage
connections and to the signal contact with the
ow
Voltages (SELV) in compliance with IEC950/ EN60950/ VDE0805.
WARNING
Safety First!
Be sure to disconnect the power cord before installing and/or
wiring your
Calculate the maximum possible current in each power wire and
common wire. Observe all electrical codes dictating the
maximum current allowable for each wire
If the current goes above the maximum ratings, the wiring could
overheat, causing serious damage to your equipment.
ATTENTION
This product is intended to be mounted to a well
mounting surface, such as a metal panel.
-hazardous.
Safety Extra-L
Safety Extra-L
Moxa EtherDevice Switch.
size.
You should also pay attention to the following items:
• Use separate paths to route wiring for power and devices. If power
wiring and device wiring paths must cross, make sure the wires are
perpendicular at the intersection point.
NOTE: Do not run signal or communications wiring and power wiring
in the same wire conduit. To avoid interference, wires with different
signal characteristics should be routed separately.
• You can use the type of signal transmitted through a wire to
determine which wires should be kept separate. The ru le of thum b is
that wiring that shares similar electrical characteristics can be
bundled together.
• Keep input wiring and output wiring separated.
• It is strongly advised that you label wiring to all devices in the system
when necessary.
Grounding Moxa EtherDevice Switch
Grounding and wire routing help limit the effects of noise due to
electromagnetic interference (EMI). Run the ground connection from the
ground screw to the grounding surface prior to connecting devices.
2
A 4 mm
grounding screw is utilized.
conductor must be used when a connection to the external
- 11 -
-grounded
Page 12

Wiring the Alarm Contact
FAULT:
6
are used to
detect both power faults and port faults. The
two wires attached to the Fault contacts form
a
corresponding PORT ALARM DIP Switch is
If
the Fault circuit will be closed.
STEP 1:
Insert the negative/positive DC wires into the
V
STEP 2:
To keep the DC wires from pulling loose, use a
small flat
wire-clamp screws on the front of the terminal
block connector.
STEP 3:
Insert the plastic terminal block connector
prongs into the ter minal block receptor, which
is
ATTENTION
Before connecting
EDS to the DC power inputs, make sure the
DC power source voltage is stable.
ATTENTION
One individual conductor in a clamping point with 28
wire size, and a torque value of 1.7 lb-in should be used.
The Alarm Contact consists of the two middle contacts of the terminal
block on the EDS’s top panel. You may refer to the next section for
detailed instructions on how to connect the wires to the terminal block
connector, and how to attach the terminal block connector to the terminal
block receptor. In this section, we explain the meaning of the two
contacts used to connect the Alarm Contact.
The two middle contacts of the
-contact terminal block connector
n open circu it when:
1. The EDS has lost power from one of the
DC power inputs.
OR
2. One of the ports for which the
set to ON is not properly connected.
neither of these two conditions is satisfied,
Wiring the Redundant Power Inputs
The top two contacts and the bottom two contacts of the 6-contact
terminal block connector on the EDS’s top panel are used for the EDS’s
two DC inputs. Top and front views of one of the terminal block
connectors are shown here.
-/V+ termina ls.
-blade screwdriver to tighten the
located on the EDS’s top panel.
the
- 12 -
-14 AWG
Page 13

Communication Connections
MDI Port Pinouts
MDI-X Port Pinouts
8-pin RJ45
Pin
Signal
1
Tx+ 2 Tx- 3 Rx+ 6 Rx-
Pin
Signal
1
Rx+ 2 Rx- 3 Tx+ 6 Tx-
The EDS-2016-ML models have 14 or 16 10/100BaseT(X) Ethernet ports,
and 0 or 2 100BaseFX (SC/ST-type connector) fiber ports.
10/100BaseT(X) Ethernet Port Connection
The 10/100BaseT(X) ports located on the EDS’s front panel are used to
connect to Ethernet-enabled devices.
Below we show pinouts for both MDI (NIC-type) ports and MDI-X
(HUB/Switch-type) ports, and also show cab le wiring diagrams for
straight-through and cross-over Ethernet cables.
10/100Base T(x) RJ45 Pinouts
RJ45 (8-pin) to RJ45 (8-pin) Straight-through Cable Wiring
RJ45 (8-pin) to RJ45 (8-pin) Cross-over Cable Wiring
100BaseFX Ethernet Port Connection
The concept behind the SC/ST port and cable is very straightforward.
Suppose you are connecting devices I and II. Contrary to electrical signals,
optical signals do not require a cir cuit in order to transmit data.
Consequently, one of the optical lines is used to transmit data from device
I to device II, and the other optical line is used transmit data from device
II to device I, for full-duplex transmission.
- 13 -
Page 14
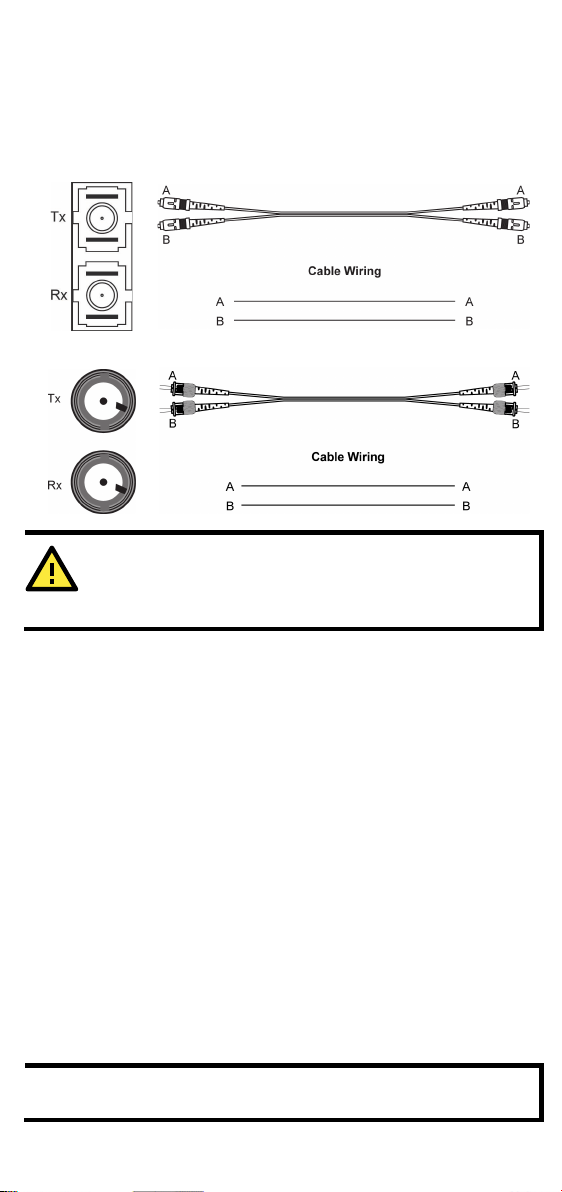
All you need to remember is to connect the Tx (transmit) port of device I
SC-Port Pinouts
SC-Port to SC-Port Cable Wiring
ST-Port Pinouts
ST-Port to ST-Port Cable Wiring
ATTENTION
This is a Class 1 Laser/LED product.
damage to your eyes, do not stare directly into the Laser Beam.
NOTE
The DIP settings will be activated when the device is powered on
the next time.
to the Rx (receive) port of device II, and the Rx (receive) port of device I
to the Tx (transmit) port of device II. If you make your own cable, we
suggest labeling the two sides of the same line with the same letter
(A-to-A and B-to-B, as shown below, or A1-to-A2 and B1-to-B2).
To avoid causing serious
Redundant Power Inputs
Both power inputs can be connected simultaneously to live DC power
sources. If one power source fails, the other live source acts as a backup,
and automatically supplies all of EDS’s power needs.
Alarm Contact
The Moxa EtherDevice Switch has one Alarm Contact located on the top
panel. For detailed instructions on how to connect the Alarm Contact
power wires to the two middle contacts of the 6-contact terminal block
connector, see the Wiring the Alarm Contact section on page 10. A typical
scenario would be to connect the Fault circuit to a warning light located in
the control room. The light can be set up to switch on when a fault is
detected.
The Alarm Contact has two terminals that form a Fault circuit for
connecting to an alarm system. The two wires attached to the Fault
contacts form an open circuit when (1) EDS has lost power from one of
the DC power inputs, or (2) one of the ports for which the corresponding
PORT ALARM DIP Switch is set to ON is not properly connected.
If neither of these two conditions occurs, the Fault circuit will be closed.
- 14 -
Page 15

DIP Switch Settings
DIP Switch
Setting
Description
Enables the corresponding PORT Alarm. If the
circuit and the fault LED will light up.
LED will never light up.
Quality of
ON
Enable the Quality of Service to handle packet
ping matrix in
CoS Priority
7,6
5,4
3,2
1,0
ToS/DSCP
Priority
63 to
48
47 to
32
31 to
16
15 to 0
Queues
3 2 1 0 WRR 8 4 2 1
OFF
Disable the Qualit y of Service.
(BSP)
second) in the EDS switch for all ports.
OFF
Disables broadcast storm protection.
LED
Color
State
Description
System LEDs
module’s power input PWR1.
Power is not being supplied to the main
module’s power input PWR1.
Power is being supplied to the main
module’s power input PWR2.
module’s power input PWR2.
enabled, and the port’s link is inactive.
When the corresponding PORT alarm is
disabled.
EDS-2016-ML Series DIP Switches
Port Alarm
Function
P1 to P16
Service (QoS)
Broadcast
Storm
Protection
ON
port’s link fails, the relay will form an open
OFF Disables the corresponding PORT Alarm. The
relay will form a c losed circu it and the Fault
priorities in four WRR queues.
QoS and ToS/DSCP priority map
each queue
ON Enables broadcast storm protection (at a
maximum of 2000 broadcast packets per
LED Indicators
The front panel of the Moxa EtherDevice Switch contains several LED
indicators. The function of each LED is described in the table below.
Power is being supplied to the main
PWR1 Amber
On
Off
PWR2 Amber
FAULT Red
On
Power is not being supplied to the main
Off
When the corresponding PORT alarm is
On
enabled and the port’s link is active, or
Off
when the corresponding PORT alarm is
- 15 -
Page 16

LED
Color
State
Description
100M
Fiber
On
TP port’s 100Mbps link is active.
Blinkin g
Data is being transmitted at 100Mbps.
Off
TP port’s 100Mbps link is inactive.
LED
On
TP port’s 100Mbps link is active.
Blinkin g
Data is being transmitted at 100Mbps.
Off
TP port’s 100Mbps link is inactive.
10M/100M
On
TP port’s 10Mbps link is active.
Blinkin g
Data is being transmitted at 10Mbps.
Off
TP port’s 10Mbps link is inactive.
LED
10M/100M
Copper top
Green
Green
Copper
bottom LED
Green
Auto MDI/MDI-X Connection
The Auto MDI/MDI-X function allows users to connect the EDS’s
10/100BaseT(X) ports to any kind of Ethernet de vice, without pa ying
attention to the type of Ethernet cable being used for the connection. This
means that you can use either a straight-through cable or cross-over
cable to connect the EDS to Ethernet devices.
Dual Speed Functionality and Switching Moxa EDS’s 10/100 Mbps
switched RJ45 port auto negotiates with the connected device for the
fastest data transmission rate supported by both devices. All models of
Moxa EtherDevice Switch are plug-and-play devices, so that software
configuration is not required at installation, or during maintenance. The
half/full duplex mode for the switched RJ45 ports is user dependent and
changes (by auto-negotiation) to full or half duplex, depending on which
transmission speed is supported by the attached device.
Fiber Ports
Moxa EDS's fiber switched ports operate at a fixed 100 Mbps speed and
full-duplex mode to provide the best performance. The fiber ports are
factory-built as either a multi-mode or sin gle-mode SC/ST connector.
Consequently, you should use fiber cables that have SC/ST connectors at
both ends. When plugging the connector into the port, make sure the
slider guide is positioned to the r ight side so that it fit s snuggly into the
port.
The 100 Mbps fiber ports are switched ports, and perform as a domain,
providing a high bandwidth backbone connection that supports long fiber
cable distances (up to 5 km for multi-mode, and 40 km for single-mode)
for installation versatility.
- 16 -
Page 17

Switching, Filtering, and Forwarding
Technology
Standards
IEEE 802.3 for 10BaseT,
IEEE 802.1p for Class of Service
Flow Control
EEE 802.3x flow control, back pressure flow control
Interface
RJ45 Ports
10/100BaseT(X) auto negotiation speed
Fiber Ports
100BaseFX ports (SC/ST connector)
LED Indicators
PWR1, PWR2, Fault, 10/100M, 100M
DIP Switch
Port break alarm, QoS, BSP
Alarm Contact
One relay output with current carrying capacity of
1A @ 24 VDC
Each time a packet arrives at one of the switched ports, a decision is
made to either filter or forward the packet. Packets with source and
destination addresses belonging to the same port segment will be filtered,
constraining those packets to one port, and relieving the rest of the
network from the need to process them. A packet with destination
address on another port segment will be forwarded to the appropriate
port, and will not be sent to the other ports where it is not needed.
Packets that are used in maintaining the operation of the network (such
as the occasional multi-cast packet) are forwarded to all ports. EDS
operates in the store-and-forward switching mode, which eliminates bad
packets and enables peak performance to be achieved when there is
heavy traffic on the network.
Switching and Address Learning
Moxa EDS has an address table that can hold up to 8K node addresses,
which makes it suitable for use with large networks. The address tables
are self-learning, so that as nodes are added or removed, or moved from
one segment to another, EDS automatically keeps up with new node
locations. An address-aging alg orithm causes the lea st-used addresses to
be deleted in favor of newer, more frequently used addresses. To reset
the address buffer, power down the unit and then power it back up.
Auto-Negotiation and Speed Sensing
The EDS’s RJ45 Ethernet ports independently support auto-negotiation
for transmission speeds of 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps with operation
according to the IEEE802.3 standard. This means that some nodes could
be operating at 10 Mbps, while at the same time, other nodes are
operating at 100 Mbps.
Auto-negotiation takes place when an RJ45 cable connection is made, and
then each time a LINK is enabled. The EDS advertises its capability for
using 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps transmission speeds, with the device at the
other end of the cable expected to advertise similarly.
Depending on what type of device is connected, this will result in
agreement to operate at a speed of 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps.
If an EDS’s RJ45 Ethernet port is connected to a non-negotiating device,
it will default to 10 Mbps speed and half-duplex mode, as required by the
IEEE802.3 standard.
Specifications
IEEE 802.3u for 100BaseT(X) and 100Base FX,
- 17 -
Page 18

Optical Fiber
100Base FX
Single-mode
40 km
Single-mode
80 km
µm
800
MHz*Km
Typical Distance
4 km
5 km
40 km
80 km
Typical
(nm)
(nm)
(nm)
TX Range
(dBm)
RX Range
(dBm)
(dB)
Dispersion
Penalty (dB)
distance, we recommend putting an attenuator to prevent the transceiver
Switch Properties
MAC Table Size
8 K
Packet Buffer Size
2 Mbits
Processing Type
Store and Forward
Power
Input Voltage
12/24/48 VDC redundant dual inputs
Relay output: 24 VDC, 1 A, Resistance
Connection
Removable 6-contact terminal block 28-14 AWG, 1.7
All wires must be able to withstand at least 85°C
Protection
Reverse Polarity
Protection
Present
Mechanical
Casing
IP30 protection, metal case
Dimensions
EDS-2016-ML Copper model:
58 x 135 x 95 mm (2.28 x 5.31 x 3.74 in)
Fiber Cable T ype OM1
Wavelength
TX Range
RX Range
Multi-mode
1260 to 1360 1280 to 1340 1530 to 1570
1100 to 1600 1100 to 1600 1100 to 1600
-10 to -20 0 to -5 0 to -5
50/125
G.652 G.652
1300 1310 1550
Optical
Power
Note: When connecting 40 km or 80 km single-mode fiber over a short
from being damaged by excessive optical power.
Typical Distance: To reach the typical distance of a specified fiber
transceiver, please refer to the following formula: Link budget(dB) >
dispersion penalty(dB) + total link loss(dB).
Input Current EDS-2016-ML: 0.171 A (max.)
Overload Current
Link Budget
EDS-2016-ML-MM-SC: 0.291 A (max.)
EDS-2016-ML-MM-ST: 0.303 A (max.)
EDS-2016-ML-SS-SC: 0.325 A (max.)
lb-in
Present
-3 to -32 -3 to -34 -3 to -34
12 29 29
3 1 1
(W x H x D)
36 x 135 x 95 mm (1.41 x 5.31 x 3.74 in)
EDS-2016-ML Fiber model:
- 18 -
Page 19

Weight
EDS-2016-ML Copper model: 486 g (1.07 lb)
EDS-2016-ML Fiber model: 648 g (1.43 lb)
Installation
DIN-rail, Wall Mounting (optional kit)
Environmental Limits
Operating
Temperature
-10 to 60°C (32 to 140°F)
-40 to 75°C (-40 to 167°F) for -T models
Storage
Temperature
-40 to 85°C (-40 to 185°F)
Ambient Relative
Humidity
Altitude
Up to 2,000 m
enclosure
Regulatory Approvals
Note: Only for indoor use.
Safety
UL 61010-2-201, EN 62368-1(LVD)
EMI
FCC Part 15, CISPR (EN55032) class A
EN61000-4-8
Location*
UL/cUL Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C, and D;
ATEX Zone 2, Ex nA nC IIC T4 Gc
Rail Traffic
EN 50121-4
Shock
IEC60068-2-27
Free Fall
IEC60068-2-32
Vibration
IEC60068-2-6
Warranty
Warranty Period
5 years
Details
See www.moxa.com/warranty
NOTE
Please check Moxa’s website for the latest certification status.
Note This device must be installed within a su itable, final
5 to 95% (non-condensing)
EMS EN61000-4-2 (ESD), Level 3
Hazardous
EN61000-4-3 (RS), Level 3
EN61000-4-4 (EFT), Level 3
EN61000-4-5 (Surge), Level 3
EN61000-4-6 (CS), Level 3
- 19 -
 Loading...
Loading...