Page 1

EDR-G903/G902 User’s Manual
Second Edition, January 2011
www.moxa.com/product
© 2011 Moxa Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Page 2

EDR-G903/G902 User’s Manual
The software described in this manual is furnished under a license agreement and may be used only in accordance with
the terms of that agreement.
Copyright Notice
Copyright ©2011 Moxa Inc.
All rights reserved.
Reproduction without permission is prohibited.
Trademarks
The MOXA logo is a registered trademark of Moxa Inc.
All other trademarks or registered marks in this manual belong to their res pec tive manufacturers.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is subject to cha nge witho ut no tic e and doe s no t repres e nt a commitme nt o n the part of
Moxa.
Moxa provides this document as is, without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, including, but not limited
to, its particular purpose. Moxa reserves the rig ht to make improvements and/or changes to this manual, or to the
products and/or the programs described in this manual , at any time .
Information provided in this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, Moxa assumes no responsibility for
its use, or for any infringements on the rights of third parties that m ay res ult fr om its use.
This product might include unintentional tec hnic a l o r typographical errors. Changes are periodically made to the
information herein to correct such errors, and these changes are incorporated into new editions of the publica tio n.
Technical Support Contact Information
www.moxa.com/support
Moxa Americas
Toll-free: 1-888-669-2872
Tel: +1-714-528-6777
Fax: +1-714-528-6778
Moxa Europe
Tel: +49-89-3 70 03 99-0
Fax: +49-89-3 70 03 99-99
Moxa China (Shanghai office)
Toll-free: 800-820-5036
Tel: +86-21-5258-9955
Fax: +86-21-5258-5505
Moxa Asia-Pacific
Tel: +886-2-8919-1230
Fax: +886-2-8919-1231
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. Introduction ...................................................................................................................................... 1-1
Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 1-2
Package Checklist ............................................................................................................................... 1-2
Features ............................................................................................................................................ 1-2
Industrial Networking Capability .................................................................................................... 1-2
Designed for Industrial Applications ............................................................................................... 1-2
Useful Utility and Remote Configuration ......................................................................................... 1-2
2. Getting Star ted.................................................................................................................................. 2-1
RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100) .................................................................... 2-2
Using Telnet to Access the EtherDevice Router’ s Console ......................................................................... 2-4
Using a Web Browser to Configure the EtherDevice Router....................................................................... 2-5
3. Features and Functions ..................................................................................................................... 3-1
Configuring Basic Settings ................................................................................................................... 3-3
System Identification ................................................................................................................... 3-3
Accessible IP ............................................................................................................................... 3-4
Password.................................................................................................................................... 3-5
Time .......................................................................................................................................... 3-6
SettingCheck .............................................................................................................................. 3-8
System File Update—by Remote TFTP .......................................................................................... 3-10
System File Update—by Local Import/Export ................................................................................ 3-10
Restart ..................................................................................................................................... 3-11
Reset to Factory Default ............................................................................................................. 3-11
Network Settings .............................................................................................................................. 3-12
Mode Configuration ................................................................................................................... 3-12
WAN1 Configuration .................................................................................................................. 3-13
WAN2 Configuration (includes DMZ Enable ) .................................................................................. 3-15
Using DMZ Mode ....................................................................................................................... 3-19
LAN Interface............................................................................................................................ 3-19
DHCP Server ............................................................................................................................. 3-20
Static DHCP List ........................................................................................................................ 3-21
DHCP Leased List ...................................................................................................................... 3-22
Dynamic DNS ........................................................................................................................... 3-22
Network Redundancy ........................................................................................................................ 3-23
WAN Backup (EDR-G903 only) .................................................................................................... 3-23
Virtual Router Redundancy Proto col (VR RP) .................................................................................. 3-25
Static Routing and Dynamic Routing ................................................................................................... 3-26
Static Routing ........................................................................................................................... 3-26
RIP (Routing Information Protoc o l) .............................................................................................. 3-27
Routing Table ........................................................................................................................... 3-28
Network Address Translation (NAT) ..................................................................................................... 3-28
NAT Conc ept ............................................................................................................................. 3-28
N-to-1 NAT ............................................................................................................................... 3-28
Port Forwarding ........................................................................................................................ 3-29
1-to-1 NAT ............................................................................................................................... 3-31
Firewall Settings ............................................................................................................................... 3-33
Firewall Policy Concept ............................................................................................................... 3-33
Firewall Policy Overview ............................................................................................................. 3-33
Firewall Po l ic y Conf i g uration ....................................................................................................... 3-34
Layer 2 Policy Setup .................................................................................................................. 3-35
Quick Automation Profile ............................................................................................................ 3-37
PolicyCheck .............................................................................................................................. 3-38
Denial of Service (DoS) function .................................................................................................. 3-40
VPN (Virtual Private Network) ............................................................................................................ 3-41
Overview .................................................................................................................................. 3-41
IPSec Configuration ................................................................................................................... 3-42
X.509 Certification ..................................................................................................................... 3-47
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol) ................................................................................................... 3-49
Examples for Typical VPN Applications ......................................................................................... 3-51
Traffic Prioritization ........................................................................................................................... 3-52
How Traffic Prioritization Works ................................................................................................... 3-53
Traffic Prioritization Conf i g uration ................................................................................................ 3-53
Configuring SNMP ............................................................................................................................. 3-56
Using Auto Warning .......................................................................................................................... 3-58
Using Diagnosis ................................................................................................................................ 3-62
Using Monitor ................................................................................................................................... 3-63
Using System Log ............................................................................................................................. 3-64
Using HTTPs/SSL .............................................................................................................................. 3-65
Page 4

A. MIB Groups ....................................................................................................................................... A-1
Page 5

1
1. Introduction
Welcome to the Moxa EtherDevice Router (EDR-G903/G902), the Gigabit Firewall/VPN secure routers designed
for connecting Ethernet-enabled devices in industrial field applicatio ns .
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Overview
Package Checklist
Features
Industrial Networking Capability
Designed for Industrial Applications
Useful Utility and Remote Configuration
Page 6

EDR-G903/G902 Introduction
1-2
Overview
As the world’s network and information technology becomes more mature, the trend is to use Ethernet as the
major communications interface in many indus trial c o mmunications and automation applications. In f act, a
whole new industry has sprung up to provide Etherne t products tha t comply with the requirements of
demanding industrial applications.
The EtherDevice Router series is a Gigabit speed, all-in-one Firewall/VPN/Router for Ethernet s e c urity
applications in sensitive remote control and monitoring networks. The EtherDevice Router supports one WAN,
one LAN, and a user-configurable WAN/DMZ interface (EDR-G903) that provides high flexibility for differe nt
applications, such as WAN redundancy or Data/FTP ser ver security protection.
The Quick Automation Profile function of the EtherDevice Router’s firewall supports most common Fieldb us
protocols, including EtherCAT, EtherNet/IP, FOUNDATION Fieldbus, Modbus/TC P, and PROFIN ET. U ser s can
easily create a secure Ethernet Fieldbus ne twork fr o m a user-fr ie ndly web UI with a single clic k. In addition,
wide temperature models are available that ope rate reliably in hazardous, -40 to 75°C environments.
Package Checklist
The EtherDevice Router is shipped with the fo llo wing items. If any of these items are missing or damaged,
please contact your customer service representative for assist an ce.
• 1 Moxa EtherDevice Router
• RJ45 to DB9 console port cable
• Protective caps for unused ports
• DIN-Rail mounting kit (attached to the EtherDevice Router’s rear panel by default)
• Hardware Installation Guide (printed)
• CD-ROM with User’s Manual and Windows Utility
• Moxa Product Warranty statement
Features
Industrial Networking Capability
• Router/Firewall/VPN all in one
• 1 WAN, 1 LAN, and 1 user-configurable WAN or DMZ interface
• Network address translation (N-to-1, 1-to-1, and port forwarding)
Designed for Industrial Applications
• Dual WAN redundancy function
• Firewall with Quick Automation Profile for Fieldbus protocols
• Intelligent PolicyCheck and SettingChe c k too ls
• -40 to 75°C operating temperature (T models)
• Long-haul transmission distance of 40 km or 80 km (with optional mini-GBIC)
• Redundant, dual 12 to 48 VDC power inputs
• IP30, rugged high-strength metal case
• DIN-Rail or panel mounting ability
Useful Utility and Remote Configuration
• Configurable using a Web browser and T e lne t/S er ial c onsole
• Send ping commands to identify network segment integ rity
Page 7

2
2. Getting Started
This chapter explains how to access the EtherDevice Router for the first time. There are three ways to access
the switch: (1) serial console, (2) Telnet conso le , or (3) web brow ser. The serial console connection method,
which requires using a short serial cable to connect the EtherDevice Router to a PC’s COM port, can be used if
you do not know the EtherDevice Router’s IP address. The Telnet console and web browser connection methods
can be used to a ccess the EtherDevice Router over an Ethernet LAN, or over the Internet. A web browser can
be used to perform all monitoring and administration functions, but the serial console and Telnet console only
provide basic functions.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
Using Telnet to Access the EtherDevice Router’s Console
Using a Web Browser to Configure the EtherDevice Router
Page 8
EDR-G903/G902 Getting Started
2-2
We strongly suggest that you do NOT use more than one connection method at the same time. Following this
s
RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100)
NOTE Connection Caution!
advice will allow you to maintain better co ntro l over the config uration of your EtherDevice Router
NOTE
We recommend using Moxa PComm Terminal Emulator, which can be downloaded free of charge from Moxa’
website.
Before running PComm Terminal Emulator, use an RJ45 to DB9-F (or RJ45 to DB25-F) cable to connect the
EtherDevice Router’s RS-232 console port to your PC’s COM port (generally COM1 or COM2, depending on how
your system is set up).
After installing PComm Terminal Emulator , p erfor m the follo w i ng ste ps to acces s the RS -232 console utility.
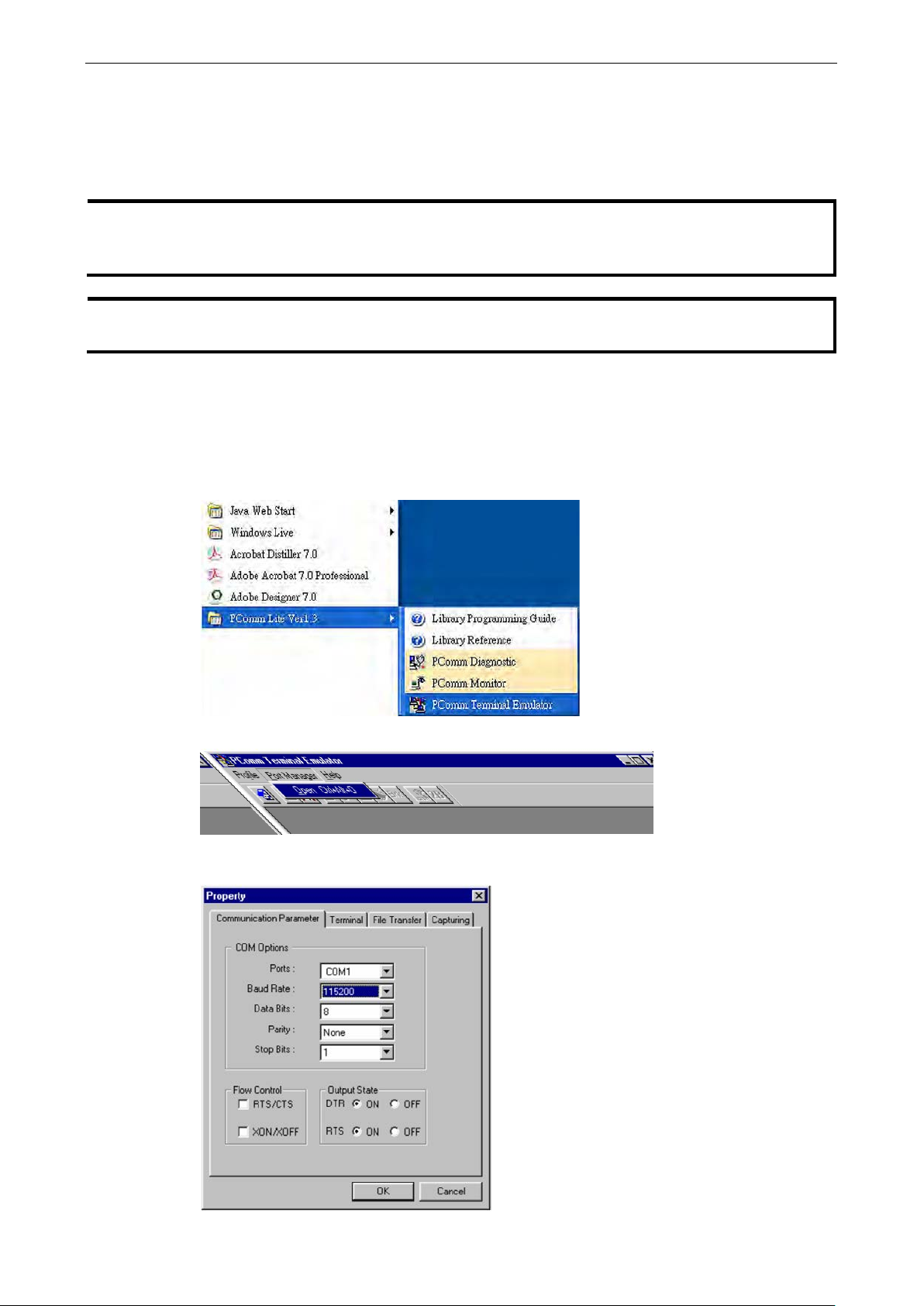
1. From the Windows desktop, click Start Programs PCommLite1.3 Terminal Emulator.
2. Select Open in the Port Manager menu to open a new connection.
3. The Communication Parameter page of the Prop erty window will appear. Select the appropriate COM
port for Console Connection, 115200 for Baud Rate, 8 for Data Bits, None for Parity, and 1 for Stop Bits
Page 9

EDR-G903/G902 Getting Started
2-3
4. Click the Terminal tab, and select VT100 for Terminal Type. Click OK to continue.
5. Type 1 to select ansi/VT100 terminal type, and then press Enter.
6. The Console login screen will appear. Use the keyboard to enter the login account (admin or user),
and then press Enter to jump to the Password field. Enter the console Password (this is the same as
the Web Browser password; leave the Password field blank if a console password has not been set), and
then press Enter.
7. Enter a question mark (?) to display the command list in the console.
The following table shows a list of commands that can be used when the EtherDevice Router is in console (serial
or Telnet) mode:
Login by Admin account:
Command Parameter/Example Description
disable Switch the Admin mode to User mode
exit/quit Exit this consol mode co nne c tion
lan lan ip address (A.B.C.D) netmask (A.B.C.D)
Example:
lan ip address 192.168.127.10 netmask
255.255.255.0
list Print com ma nd list
no no password admin Set the admin password to null
no password user Set the user password to null
password password admin (password)
Example:
Password admin 1234
password user (password)
Example:
Password user 1234
ping ping (IP address)
Example:
ping 192.168.127.10
Set the IP address of LAN interface
Set the admin password
Set the user password
Send echo message
reboot Reboot this device
reload default-config Reload default configuration and Reboot this
device
show show lan Show running system information
Page 10
EDR-G903/G902 Getting Started
2-4
s management and monitoring functions from a PC host connected to the same
s RJ45 Ethernet LAN ports
through or
telnet telnet (IP address)
Example:
telnet 192.168.127.10
telnet (IP address) (port number)
Example:
telnet 192.168. 127.10 23
ssh ssh (IP address)
Example:
ssh 192.168.127.10
Open a telnet connection
Open a telnet connection with port number
Open a ssh connection
Login by User account:
Command Parameter/Example Description
exit/quit Exit this consol mode co nne c tion
list Print com ma nd list
ping ping (IP address)
Example:
ping 192.168.127.10
show show lan Show running system information
ssh ssh (IP address)
Example:
ssh 192.168.127.10
telnet telnet (IP address)
Example:
telnet 192.168.127.10
telnet (IP address) (port number)
Example:
telnet 192.168. 127.10 23
Ping remote device via IP
Open a ssh connection
Open a telnet connection
Open a telnet connection with port number
Using Telnet to Access the EtherDevice Router’s Console
You may use Telnet to access the EtherDevice Router’s console utility ov e r a networ k. To access the EDR’s
functions over the network (by either Telnet or a web browser) from a PC host that is connected to the same
LAN as the EtherDevice Router, you need to make sure that the PC host and the EtherDevice Router are on the
same logical subnet. To do this, check your PC host’s IP address and subnet mask. By default, the EtherDevice
Router’s LAN IP address is 192.168.127.254 and the EtherDevice Router’s subnet mask is 255.255.255.0 (for
a Class C subnet). If you do not change these values, and your PC host’s subnet mask is 255.255.0.0, then its
IP address must have the form 192.168.xxx.xxx. On the other hand, if yo ur PC host’s subne t mask is
255.255.255.0, then its IP address must have the form, 192.168.127.xxx.
NOTE
NOTE
To use the EtherDevice Router’
LAN as the EtherDevice Router, you must make sure that the PC host and the EtherDevice Router are
connected to the same logical subnet.
Before accessing the console utility via Telnet, first connect the EtherDevice Router’
to your Ethernet LAN, or directly to your PC’s Ethernet card (NIC). You can use either a straightcross-over Ethernet cable.
NOTE The EtherDevice Router’s default LAN IP address is 192.168.127.254.
Page 11
EDR-G903/G902 Getting Started
2-5
s management and monitoring functions from a PC host connected to the same
s RJ45 Et hernet
Perform the following steps to access the conso le utility v ia Telnet.
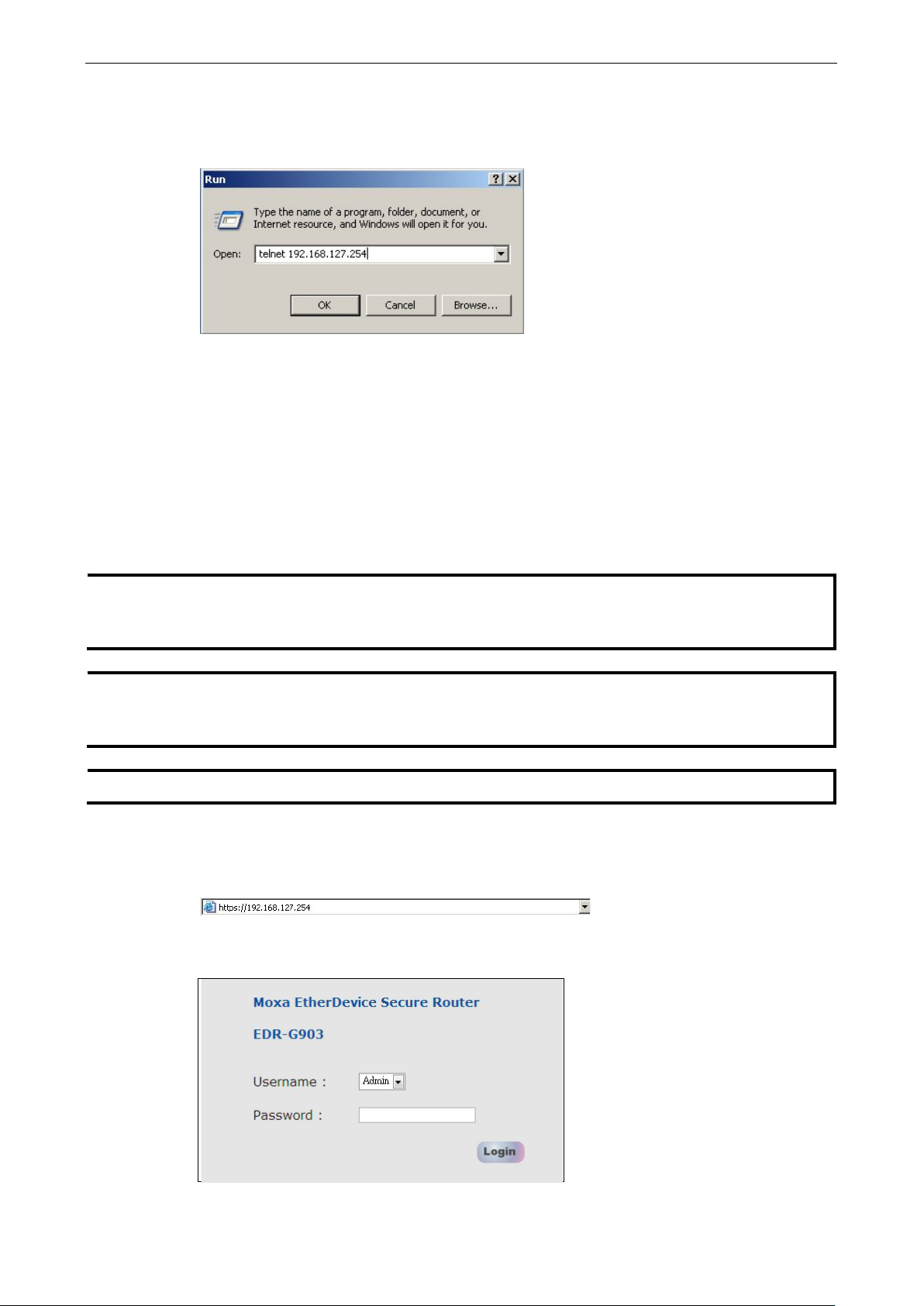
1. Click Start ( Run, and then telnet to the EtherDevice Router’s IP address from the Windows Run window.
(You may also issue the telnet command from the MS-DOS prompt.).
2. Refer to instructions 6 and 7 in the RS-232 Console Configuration (115200, None, 8, 1, VT100) section
on page 2-3.
Using a Web Browser to Configure the EtherDevice Router
The EtherDevice Router’s web browser interface provides a convenient way to modify the switch’s configuration
and access the built-in monitoring and network adminis tration functions. The recommended web br ows er is
Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 with JVM (Java Virtua l Mac hine) installe d.
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE The EtherDevice Router’s default LAN IP address is 192.168.127.254.
To use the EtherDevice Router’
LAN as the EtherDevice Router, you must make sure that the PC host and the EtherDevice Router are
connected to the same logical subnet.
Before accessing t he EtherDevice Router’s web browser, first connect the EtherDevice Router’
LAN ports to your Ethernet LAN, or directly to your PC’s Ethernet c ard (NIC ). You c an use either a
straight-through or cross-over Ethernet cable.
Perform the following steps to access the EtherDevice Router’s web browser interface.
1. Start Internet Explorer and type the EtherDevice Router’s LAN IP address in the Address field. Press
Enter to establish the connection.
2. The web login page will open. Select the login account (Admin or User) and enter the Password (this
is the same as the Console password), and then click Login to continue. Leave the Password field blank
if a password has not been set.
Page 12
EDR-G903/G902 Getting Started
2-6
NOTE By default, the EtherDevice Router’s password is not set (i.e., is blank).
You may need to wait a few moments for the web page to be downloaded to your computer. Use the menu tree
on the left side of the window to open the function pages to access eac h of the router’s functions.
Page 13

3
3. Features and Functions
In this chapter, we explain how to access the EtherDevice Router’s configuration options, perform monitoring,
and use administration functions. Ther e are thr ee ways to acces s thes e func tions: (1) RS-232 console, (2)
Telnet console, and (3) web browser.
The web browser i s the most u ser-friendly way to configure the EtherDevice Router, since you can both monitor
the EtherDevice Router and use administration functions from the web browser. An RS-232 or Telnet console
connection only provides basic functions. In this chapter, we use the web browser to introduce the EtherDevice
Router’s configuration and monitoring f unc tions.
The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Configuring Basic Settings
Network Settings
Network Redundancy
Static Routing and Dynamic Routing
Network Address Translation (NAT)
Firewall Settings
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Traffic Prioritization
Configuring SNMP
Using Auto Warning
Using Diagnosis
Using Monitor
Using System Log
Using HTTPs/SSL
Page 14
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-2
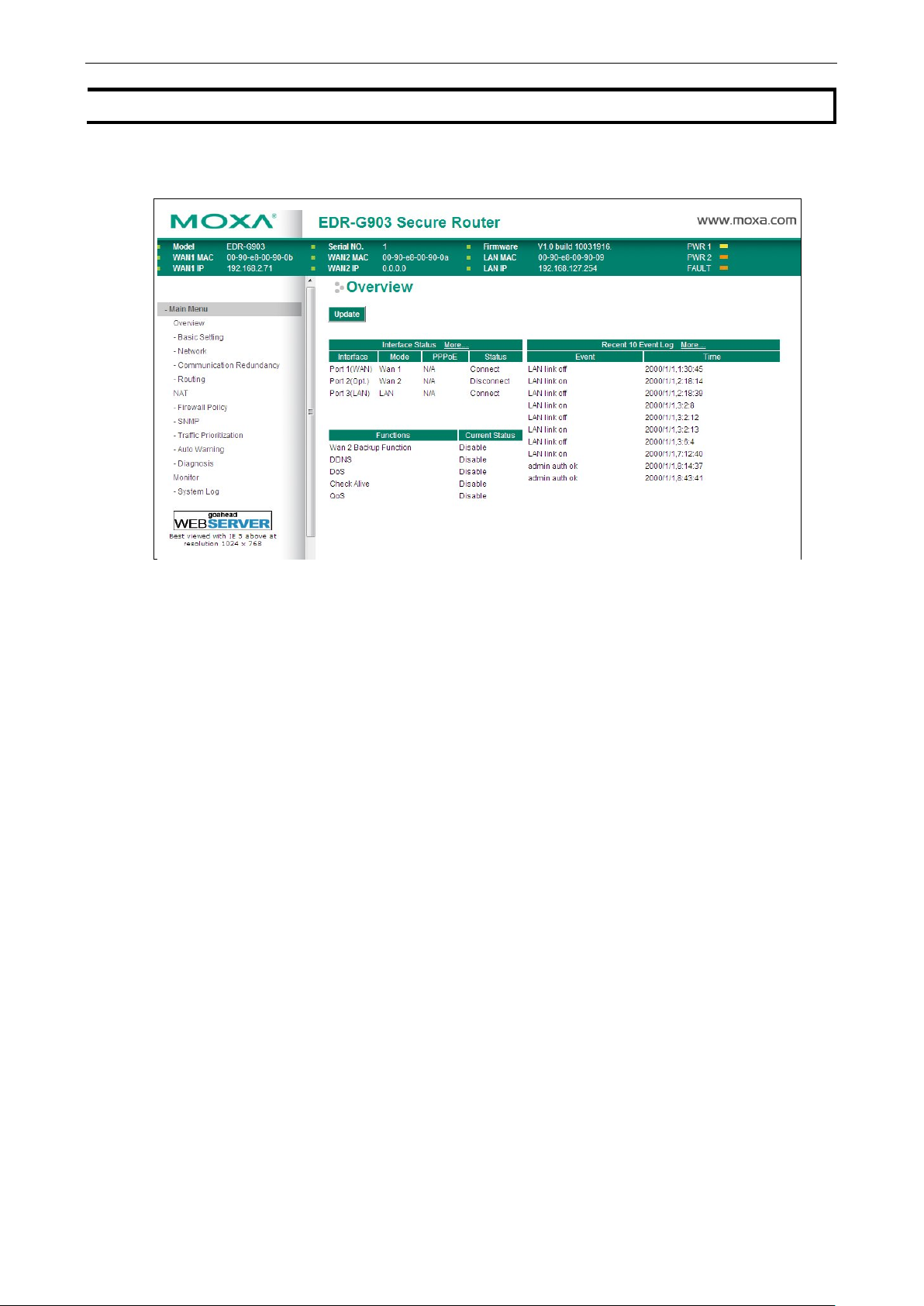
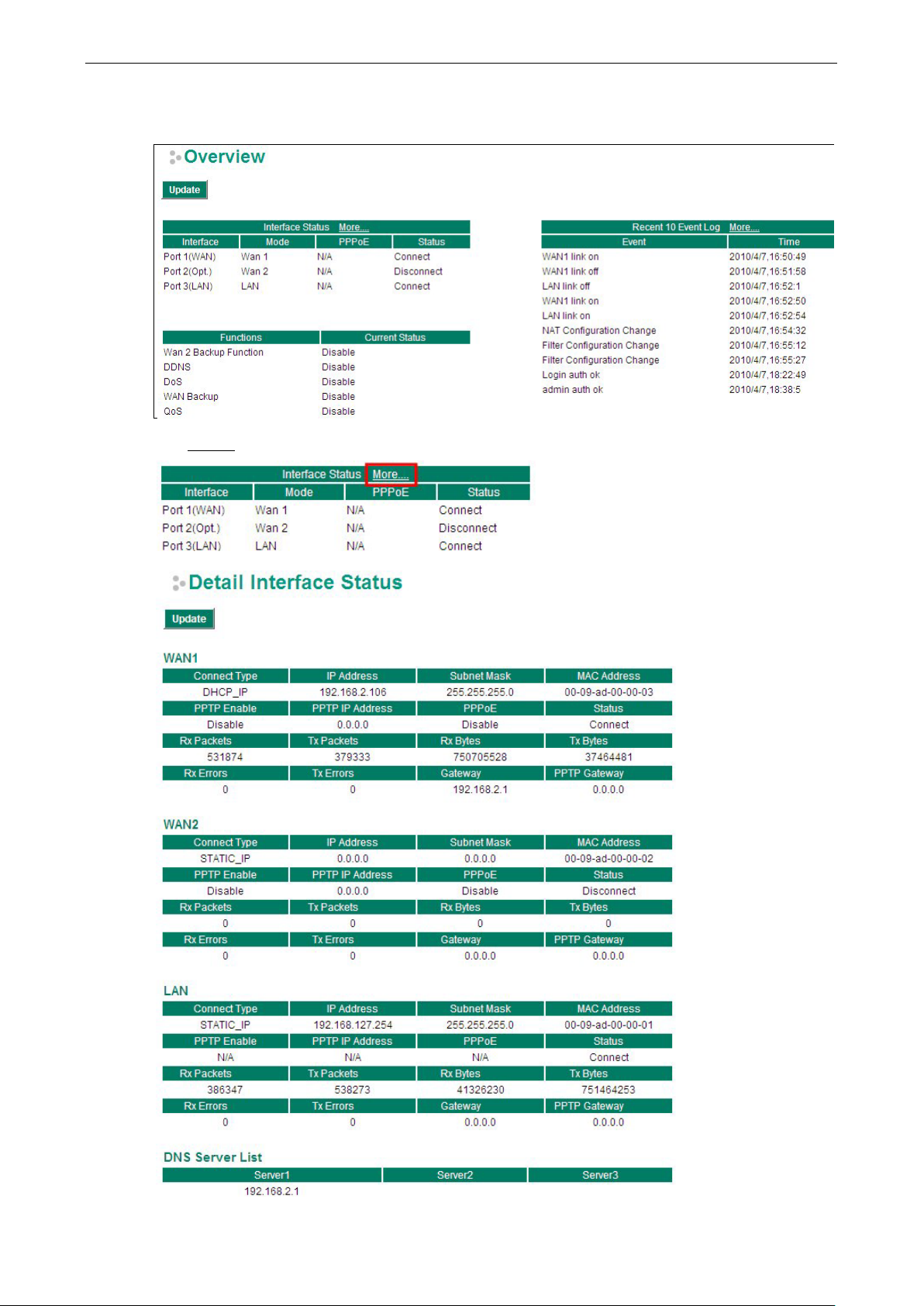
The Overview page is divided into three major parts: Interface Status, Basic function status, and Recent 10
Event logs, and gives users a quick overview of the EtherDevice Router’s current settings.
Click More… at the top of the Interface Status table to see detailed info rmation about all interfaces.
Page 15
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-3
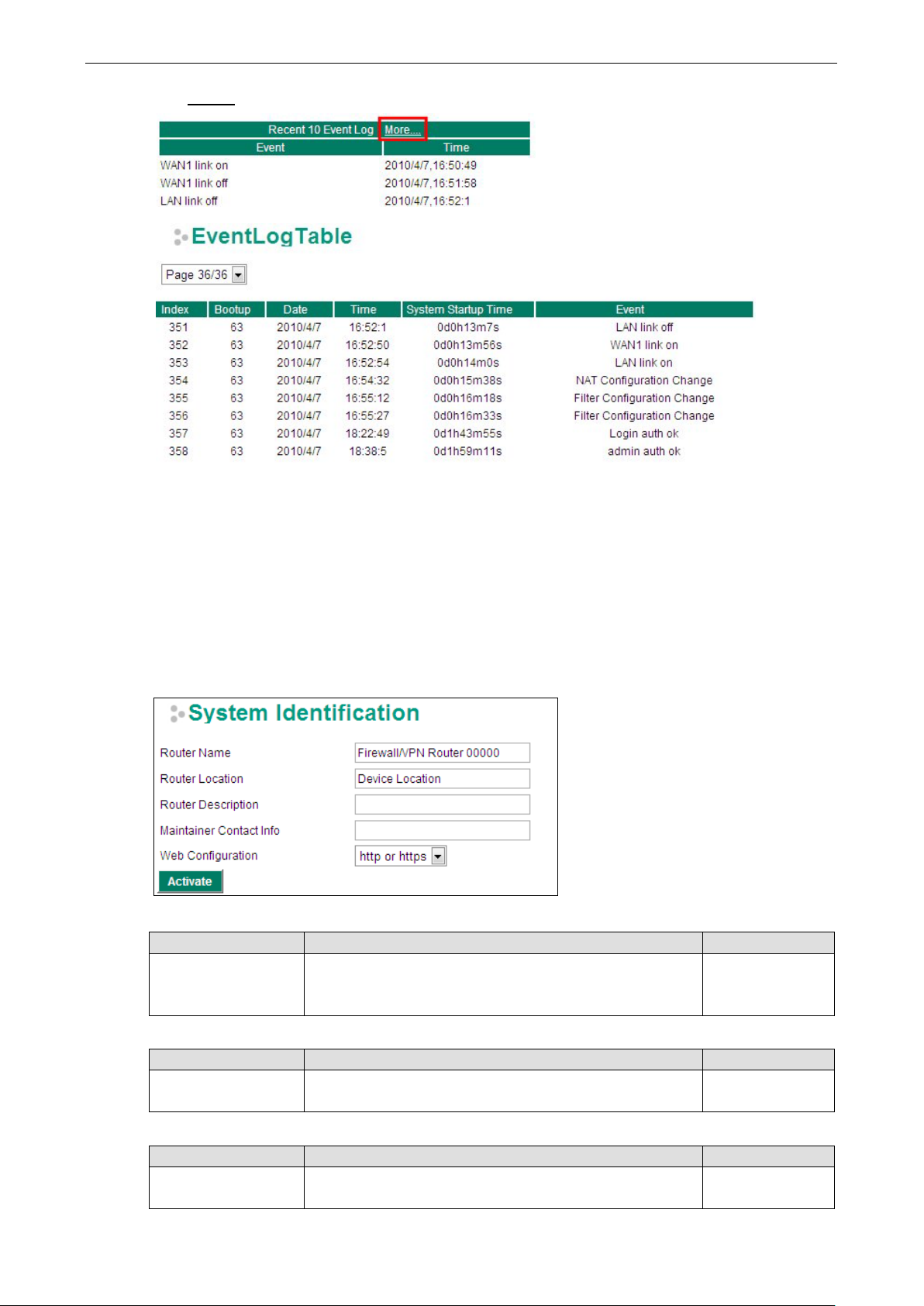
Click More… at the top of the “Recent 10 Event Log” table to open the EventLogTable page.
Configuring Basic Settings
The Basic Settings group includes the most commonly used settings required by administrators to maintain and
control the EtherDevice Router.
System Identification
The system identification section g ive s you an easy way to identif y the d ifferent switches connected to your
network.
Router name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters This option is useful for specifying the role or applic a tio n of
different EtherDevice Router units.
E.g., Factory Router 1.
Firewall/VPN router
[Serial No. of this
switch]
Router Location
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 80 Characters To specify the location of differe nt EtherDevice Router units.
E.g., production line 1.
Router Description
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters Use this field to enter a more detailed description of the
EtherDevice Router unit.
Device Location
None
Page 16
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-4
Maintainer Contact Info
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters Enter the contact informati o n of the person respons ible for
maintaining this EtherDevice Router
Web Configuration
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
http or https Users can connect to the EtherDevice Router router via http or
https protocol.
https only Users can connect to the EtherDevice Router router via https
protocol only.
None
http or https
Accessible IP
The EtherDevice Router uses an IP address-based filtering method to control access to EtherDevice Router
units.
Accessible IP Settings allows you to add or remove “Legal” remote host IP addresses to prevent unauthorized
access. Access to the EtherDevice Router is controlled by IP address. If a host’s IP address is in the accessible
IP table, then the host will have access to the EtherDevice Router. You can allow one of the following cases by
setting this parameter:
• Only one host with the specified IP address can access this device.
E.g., enter “192.168.1.1/255.255.255.255” to allow access to just the IP address 192.168.1.1.
• Any host on a specific subnetwork can access this device.
E.g., enter “192.168.1.0/255.255.255.0” to allow access to all IPs on the subnet defined by this IP
address/subnet mask combination.
• Any host can access th e EtherDevice Router. (Disable this function by deselecting the Enable the accessible
IP list option.)
• Any LAN can access the EtherDevice Router. (Disable this function by dese le c ting the LAN option to not
allow any IP at the LAN site to access this device.)
E.g., If the LAN IP Address is set to 192.168.127.254/255.255.255.0, then IP addresses 192.168.127.1 /24
to 192.168.127.253/24 can access the EtherDevice Router.
Page 17
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-5
The following table shows additional configuration examples:
Allowable Hosts Input Format
Ay host Disable
192.168.1.120 192.168.1.120 / 255.255. 255.255
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.25 5.0
192.168.0.1 to 192.168.255.254 192.168.0.0 / 255.255.0. 0
192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.126 192.168.1.0 / 255.255.25 5.128
192.168.1.129 to 192.168.1.254 192.168.1.128 / 255.255.255.128
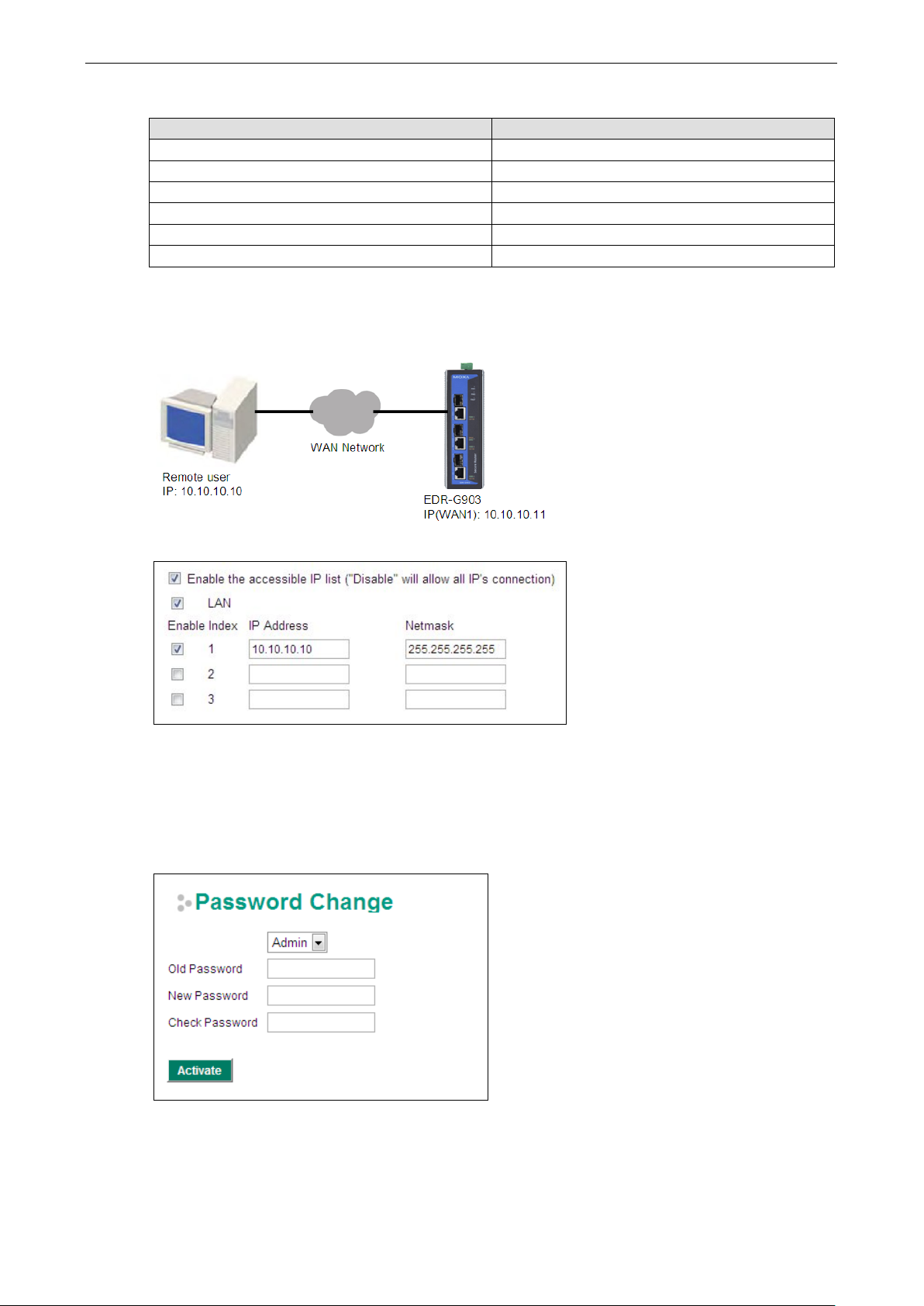
The Accessible IP list controls which devices can connect to the EtherDevice Router to change the configuration
of the device. In the example shown below, the Accessible IP list in the EtherDevice Router contains
10.10.10.10, which is the IP address of the remote user’s PC.
The remote u ser’s IP address is shown below in the EtherDevice Router’s Accessible IP list.
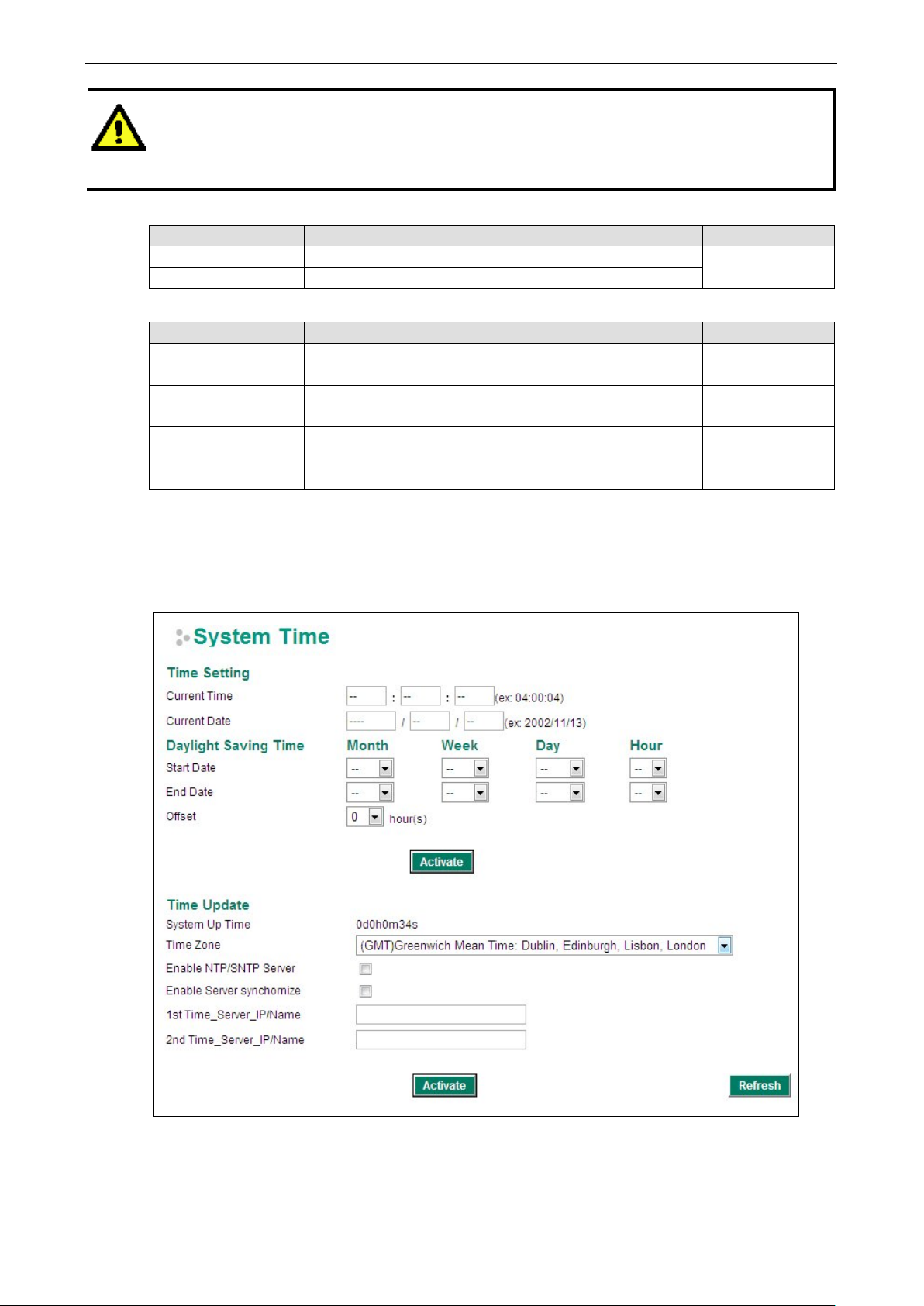
Password
The EtherDevice Router provid es two levels of acce ss privilege: “admin privilege” gives read/write acce ss to all
EtherDevice Router configuration parameters, and “user privilege” provides read access only. You will be able
to view the configuration, but will not be able to make modificatio ns .
Page 18
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-6
already set, then you will be required to
Time
• ATTENTION!
• By default, the Password field is blank. If a Password is
Account
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Admin “admin” privilege allows the user to modify all configurations. Admin
User “user” privilege only allows viewing device configurations.
Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Old password
(max. 16 Characters)
New password
(max. 16 Characters)
Retype password
(max. 16 Characters)
type the Password when logging into the RS-232 console, Telnet c o nso le , or web bro wser
interface.
Type current password when changing the password None
Type new password when changing the password None
If you type a new password in the Password field, you will be
required to retype the password in the Retype new password
field before updating the new password.
None
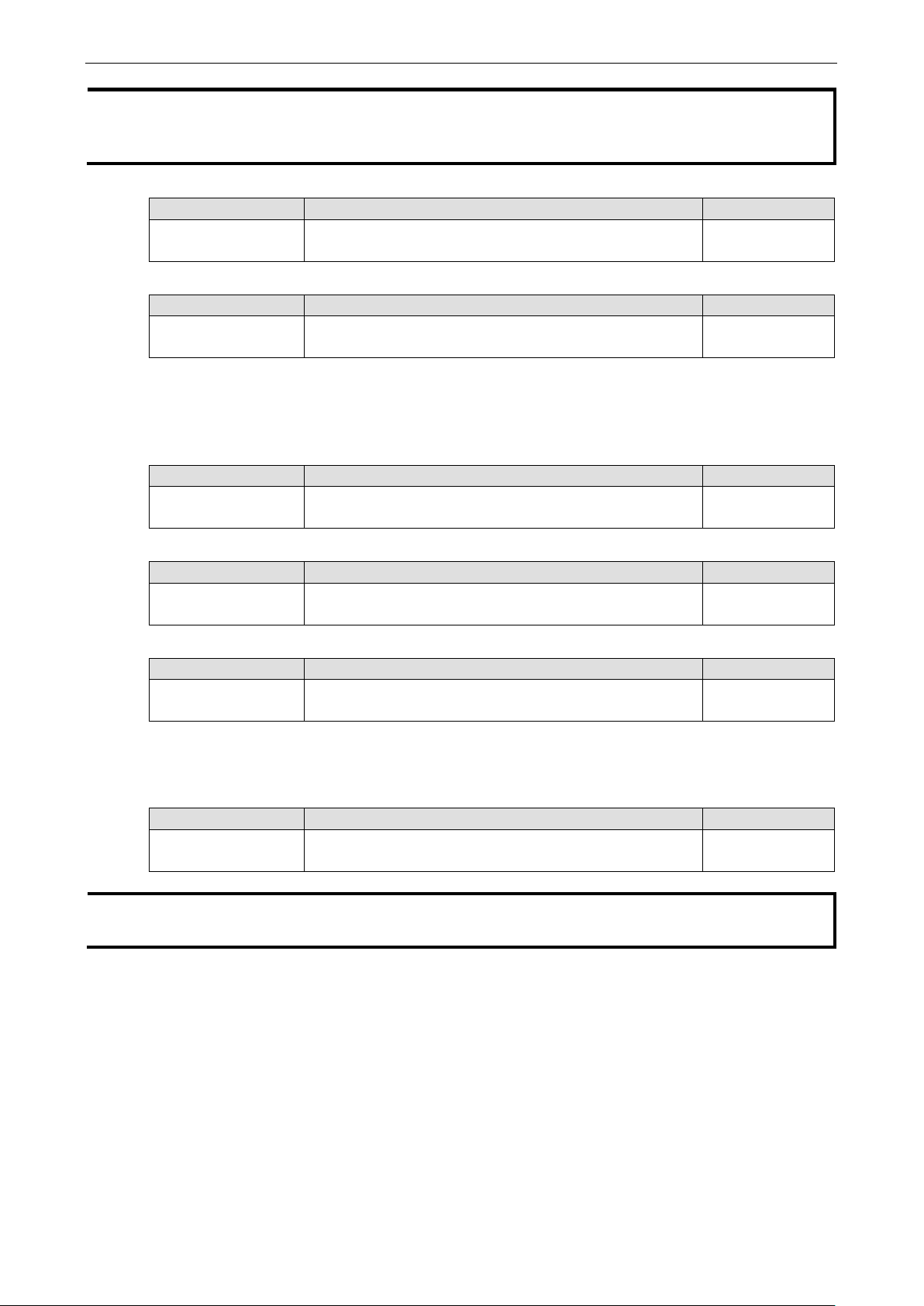
The Time configuration page lets users set the time, date, and other settings. An explanation of each setting
is given below.
The EtherDevice Router has a time calibr ation function based on information from an NTP server or user
specified Time and Date information. Functions such as Auto warning “Email” can add real-time information to
the message.
Page 19
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-7
when
.
NOTE The EtherDevice Router has a real time clock so the user does not need to update the Curr e nt Ti me and
Current Date to set the initial time for the EtherDevice Router after each reboot. This is especially useful
the network does not have an Internet connection for an NTP server, or there is no NTP server on the network
Current Time
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
User adjustable Time The time parameter allows configurati o n of the loca l time in
local 24-hour format.
Current Date
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
User adjustable date. The date parameter allows configuration of the local d ate in
yyyy/mm/dd f orm a t
Daylight Saving Time
Daylight Saving Time (also know as DST or summer time) involves advancing clocks 1 hour during the summer
to provide an extra hour of daylight in the evening.
Start Date
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
User adjustable date. The Start Date parameter allows users to enter the date that
daylight saving time begins.
End Date
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
User adjustable date. The End Date parameter allows users to enter the date that
daylight saving time begins.
None (hh:mm:ss)
None
(yyyy/mm/dd)
None
None
Offset
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
User adjustable date. The offset parameter indicates how many hours forward the
clock should be advanced.
System Up Time
Indicates the ED-G903’s up time from the last cold start. The unit is s eco nds .
Time Zone
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
User selectable time
zone
NOTE Changing the time zone will automatically cor re c t the current time. You should configure the time zone
before setting the time.
Enable NTP/SNTP Server
Enable this function to configure the EtherDevice Router as a NTP/SNTP server on the network.
Enable Server sync hr oni z e
Enable this function to configure the EtherDevice Router as a NTP/SNTP client, It will synchronize the time
information with another NTP/SNTP ser ver.
The time zone setting allows conversion from GMT (Greenwich
Mean Time) to local time.
None
GMT
Page 20

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-8
Time Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1st Time S er ver
IP/Name
2nd Time Server
IP/Name
IP or Domain address (e.g., 192.168.1.1, time.stdtime.gov.tw,
or time.nist.gov).
The EtherDevice Router will try to locate the 2nd NTP Server if
the 1st NTP Server fails to connect.
None
SettingCheck
SettingCheck is a safety function for industrial users using a secure router. It provides a double confirmation
mechanism for when a remote user changes the security policies , s uc h as Firewall filter, NAT, and
Accessible IP list. When a remote user changes these security polices, Setting C he ck prov i des a means of
blocking the connection from the remote user to the Firewall/VPN device. The only way to correct a wrong
setting is to get help from the local operator, or go to the local site and connect to the device through the
console port, which could take quite a bit of time and money. Enabling the SettingCheck function will execute
these new policy changes temporarily until doubly confirmed by the user. If the user does not click the confirm
button, the EtherDevice Router will revert to the previous setting.
Firewall Policy
Enables or Disables the SettingCheck function when the F irewall p olicies change.
NAT Policy
Enables or Disables the SettingCheck function when the NAT policies change.
Accessible IP List
Enables or Disables the SettingChe ck func tio n when the Acces s ible IP List changes.
Layer 2 Fiber
Enable or disable the SettingCheck functio n when the Lay er 2 filter changes.
Timer
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
10 to 3600 sec. The timer waits this amount of time to double confirm when the
user changes the policies
For example, if the remote user (IP: 10.10.10.10) connects to the EtherDevice Router and changes the
accessible IP address to 10.10.10.12, or deselects the Enable checkbox accidently after the remote u ser cli cks
the Activate button, connection to the EtherDevice Router will be lost because the IP address is not in the
EtherDevice Router’s Accessible IP list.
180 (sec.)
Page 21
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-9
If the user enables the SettingCheck function with the Accessible IP list and the confirmer Timer is set to 15
seconds, then when the user clicks the Activate button on the accessible IP list page, the EtherDevice Router
will execute the configuration change and the web browser will try to jump to the SettingCheck Confirmed page
automatically. Because the new IP list does not include the Remote user’s IP address, the remote us er cannot
connect to the SettingCheck Confirmed page. After 15 seconds, the EtherDevice Router will roll back to the
original Accessible IP List setting, allowing the remote user to reconnect to the EtherDevice Router and check
what’s wrong with the previous setting.
If the new configuration does not block the connectio n from the remote user to the EtherDevice Router, the
user will see the SettingCheck Confirmed page, shown in the following figure . Click Confirm to save the
configuration updates.
Page 22
EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-10
remote TFTP server. M u st be configured
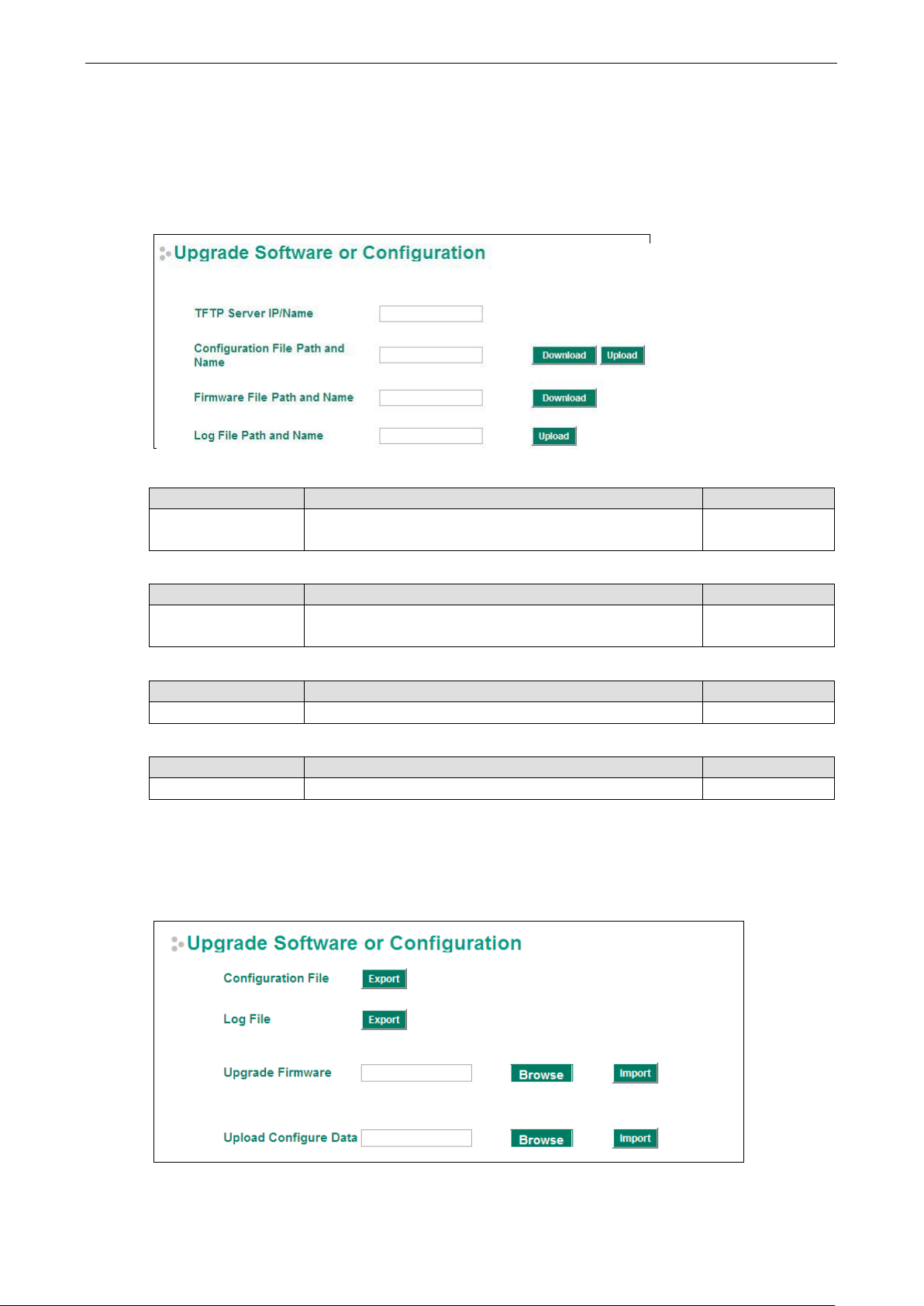
System File Update—by Remote TFTP
The EtherDevice Router supports saving your config uration file to a remote TFTP server or local host to allow
other EtherDevice Router routers to use the same configuration at a later time, or saving the Log file for future
reference. Loading pre-saved firmware or a configuration file from the TFTP server or local host is also
supported to make it easier to upgrade or configure the EtherDevice Router.
TFTP Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address of TFTP
Server
The IP or name of the
before downloading or uploading file s .
None
Configuration File Path and Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 40 Characters The path and filename of the EtherDevice Router’s
configuration file in the TFTP server.
Firmware File Path and Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 40 Characters The path and filename of the EtherDevice Router’s firmware file None
Log File Path and Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 40 Characters The path and filename of the EtherDevice Router’s log file None
After setting up the desired path and filename, click Activate to save the setting. Next, click Download to
download the file from the remote TFTP server, or click Upload to upload a file to the remote TFTP server.
System File Update—by Local Import/Export
None
Configuration File
Click Export to export the configuration file of the EtherDevice Router to the local host.
Page 23

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-11
Some operating systems will open the configuratio n file and log file directly in the web page. In such cases,
establish
Log File
Click Export to export the Log file of the EtherDevice Router to the local host.
NOTE
right click the Export button and then save as a file.
Upgrade Firmware
To import a firmware file into the EtherDevice Router, click Browse to select a firmware file already saved on
your computer. The upgrade procedure will pr oce ed automatically after clicking Import. This upgrade
procedure will take a couple of minutes to complete, including the boot-up time.
Upload Configuration Data
To import a configuration file to the EtherDevice Router, click Browse to select a configuration file already
saved on your computer. The upgrade procedure will proc eed auto ma tic ally after clicking Import.
Restart
This function is used to restart the EtherDevice Router router.
Reset to Factory Default
The Reset to Factory Default option gives users a quick way of restoring the EtherDevice Router’s
configuration settings to their fac tor y d ef ault v a lue s . This f unction is available in the console utility (serial or
Telnet), and web browser interface.
NOTE
After activating the Factory Default function, you will need to use the default network settings to rea web-browser or Telnet connec tion with your EtherDevice Router.
Page 24

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-12
Network Settings
Mode Configuration
Network Mode
EtherDevice Router provides Router Mode and Bridge Mode operation for different applications :
Router Mode
In this mode, EtherDevice Router operates as a gateway between different networks.
• Each interface (WAN1, WAN2 and LAN) has its own IP addresses & different subne t
• It provides Routing, Firewall, VPN and NAT func tio ns
• Default setting of EtherDevice Router
Bridge Mode
In this mode, EtherDevice Router operates as a Bridge mode firewall (or call transparent firewall) in a single
subnet. Users could simply insert EtherDevice Router into the existing single subnet without the need to
reconfigure the original subnet into different subnets and without the need to reconfigure the I P addr ess of
existing devices.
• EtherDevice Router only has one IP address, Network mask and Gateway.
• VPN, NAT, WAN backup, VRRP, DHCP, Dynamic DNS are not supported in this mode
User could select the appropriate oper a tio n mode and press Activate to change the mode of EtherDevice
Router. Change operation mode would take around 30-60 seconds to reboot system!!! If the webpage is no
response after 30-60 sec on ds, please refresh webpage or press F5.
Page 25

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-13
WAN1 Configuration
Connection
Note that there are there are three different connection types for the WAN1 interface: Dynamic IP, Static IP,
and PPPoE. A detailed explanation of the config ur a tio n settings for each type is given below.
Connection Mode
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable the WAN interface Enable
Connection Type
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Static IP, Dynamic IP,
PPPoE
Setup the connection type Dynamic IP
Detailed Explanation of Dynamic IP Type
PPTP Dialup
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is used for Virtual Private Networks (VPN). Remote users can use PPTP to
connect to private networks from public network s .
PPTP Connection
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable the PPTP connection None
IP Address
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
IP Address The PPTP service IP address None
User Name
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Max. 30 Characters The Login username when dialing up to PPTP service None
Password
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Max. 30 characters The password for dialing the PPTP service None
Page 26

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-14
Example: Suppose a remote user (IP: 10.10.10.10) wants to connect to the internal server (private IP:
30.30.30.10) via the PPTP protocol. The IP address for the PPTP server is 20.20.20.1 . The necessary
configuration settings are shown in the following figure.
DNS (Doman Name Server; optional setting for Dynamic IP and PPPoE types)
Server 1/2/3
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The DNS IP address None
NOTE The priority of a manually configured DNS will higher than the DNS from the PPPoE or DHCP server.
Detailed Explanation of Static IP Type
Address Information
IP Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The interface IP address None
Subnet Mask
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The subnet mask None
Page 27

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-15
Gateway
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The Gateway IP address None
Detailed Explanation of PPPoE Type
PPPoE Dialup
User Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The User Name for logging in to the PPPoE server None
Host Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters User-defined Host Name of this PPPoE server None
Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The login password for the PPPoE server None
WAN2 Configuration (includes DMZ Enable)
Connection
Note that there are there are three different connection types for the WAN2 interface: Dynamic IP, Static IP,
and PPPoE. A detailed explanation of the configuration settings for each type is given below.
Connection Mode
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable the WAN interface. None
Backup Enable WAN Backup mode
DMZ Enable DMZ mode (can only be enabled when the connection
type is set to Static IP)
Page 28

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-16
Connection Type
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Static IP, Dynamic IP,
PPPoE
Configure the connection type Dynamic IP
Detailed Explanation of Dynamic IP Type
PPTP Dialup
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is used for Virtual Private Networks (VPN). Remote users can use PPTP to
connect to private networks from public network s .
PPTP Connection
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable the PPTP connection None
IP Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The PPTP service IP address None
User name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters The Login username when dialing up to PPTP service None
Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The password for dialing the PPTP service None
Example: Suppose a remote user (IP: 10.10.10.10) wants to connect to the internal server (private IP:
30.30.30.10) via the PPTP protocol. The IP address for the PPTP server is 20.20.20.1 . The necessary
configuration settings are shown in the following figure.
Page 29

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-17
DNS (Doman Name Server; optional setting for Dynamic IP and PPPoE types)
Server 1/2/3
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The DNS IP Address None
NOTE The priority of a manually configured DNS will higher than the DNS from the PPPoE or DHCP server.
Detailed Explanation of Static IP Type
Address Information
IP Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The interface IP address None
Page 30

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-18
Subnet Mask
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The subnet mask None
Gateway
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The Gateway IP address None
Detailed Explanation of PPPoE Type
PPPoE Dialup
User Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The User Name for logging in to the PPPoE server None
Host Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters User-defined host name for this PPPoE server None
Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The login password for this PPPoE server None
Page 31

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-19
Using DMZ Mode
A DMZ (demilitarized zone) is an isolated network for devices—such as data, FTP, web, and mail servers
connected to a LAN network—that need to frequently connect with external networks. The deployment of an
FTP server in a DMZ is illustr ated in the follo w ing fig ure .
DMZ mode is configured on the WAN2 configuration web page. Set Connect Mode to Enable, Connect Type
to Static IP, and checkmark the DMZ Enable check box. You will also need to input the IP Address and Subnet
Mask. Click the Activate button to save the settings.
NOTE WAN2 configuration and DMZ mode a r e only available on EDR-G903
LAN Interface
A basic application of an industrial Firewall/VPN device is to provide protection when the device is connected to
a LAN. In this regard, the LAN port connects to a secure (or trusted) area of the network, whereas the WAN1
and WAN2/DMZ ports connect to an insecure (or untrusted) area.
Page 32

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-20
LAN IP Configuration
IP Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The LAN interface IP address 192.168.127.254
Subnet Mask
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The subnet mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP Server
The EtherDevice Router provides a DHCP (Dyna mic Ho s t Configur ati o n Pro toc o l) serv er function fo r LA N
interfaces. When configured, the EtherDevice Router will automatically assig n an IP address to a Ethernet
device from a defined IP range.
DHCP configuration
DHCP Server Enable/Disable
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable DHCP server function Enable
Lease Time
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
≥ 5 min. The lease time of the DHCP server 60 (min.)
DNS Server IP for Client
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The DHCP server’s IP address None
Offered IP Range
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP address The offered IP address range f or the DHCP server 192.168.127.1 to
NOTE 1. The DHCP server is only available for LAN interfaces.
2. The Offered IP address range must be in the same Subnet on the LAN.
192.168.127.252
Page 33

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-21
Static DHCP List
Use the Static DHCP list to ensure that devices connecte d to the EtherDevice Router always use the same IP
address. The static DHCP list matches IP addresses to MAC addresses.
In the above example, a device named “Device-01” was added to the Static DHCP list, with static IP address set
to 192.168.127 .101 and MAC address set to 00:09:ad:00:aa:01 . Whe n a device with MAC address of
00:09:ad:00:aa:01 is connected to the EtherDevice Router, the EtherDevice Router will offer the IP address
192.168.127.101 to this device.
Enable or Disable
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable the selected devi c e in the Static D HC P List Disabled
Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The name of the selected device in the Static DHCP List None
Static IP Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address The IP address of the selected device None
MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
MAC Address The MAC address of the selected device None
Clickable Buttons
Add: Use the Add button to input a new DHCP list. The Na me, Static IP, and MAC a ddress must be different
than for the existing list.
Delete: Use the Delete button to delete the Static DHCP list. Click on a list to select it (the background color
of the device will c hang e to blue) and then click the Delete button.
Modify: To modify the information for a particular list, click on a list to select it (the b ackgro und color of the
device will change to blue), modify the information as needed using the check boxes and text input boxes near
the top of the browser window, and then click Modify.
Page 34

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-22
DHCP Leased List
Use the DHCP Leased List to view the current DHCP clients.
Dynamic DNS
Dynamic DNS (Domain Name Server) allows you to use a domain name (e.g., moxa.edr-g903) to connect to
the EtherDevice Router. The EtherDevice Router can connect to 4 free DNS servers and register the user
configurable Domain name in these servers.
Service
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
> Disable
> freedns.afraid.org
> www.3322.org
> members.dyndns.org
> dynupdate.no-ip.com
User Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The DNS server’s user name None
Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The DNS server’s passw or d None
Verify Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters Verifies the DNS se rve r pass word None
Domain name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The DNS server’s domain name None
Disable or select the DNS server Disable
Page 35

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-23
Network Redundancy
Moxa EtherDevice Router provides 2 types of network redund a nc y f unc tio ns : WAN backup (ED R-G903 only)
and VRRP. The EtherDevice Router has two WAN interfaces: WAN1 is the primary WAN interface and WAN2 is
the backup interface. When the EtherDevice Router detects that connection WAN1 has failed (Link down or Ping
fails), it will switch the communication path from WAN1 to WAN2 automatically. When WAN1 recovers, the
major communication path will return to WAN1.
WAN Backup (EDR-G903 only)
How Dual WAN Backup Works
A power utility at a field site connects to a central offic e via two different ISPs (Internet Service Providers).
ISP-A uses Ethernet and ISP-B uses satellite for data transmission, with Ethernet used as the major connection
and the satellite as the backup connection. This makes sense since the cost of transmitting through the satellite
is greater than the cost of transmitting o ver the Ethernet. Trad itio na l s o luti o ns would us e two ro uter s to
connect to the different ISPs. In this case, if the connection to the primary ISP fails, the connection must be
switched to the backup ISP manually.
The EtherDevice Router’s WAN backup function checks the link status and the connection integrity between the
EtherDevice Router and the ISP or central office. When the primary WAN interface fails, it will switch to the
backup WAN automatically to keep the connec tion alive.
When configuring the EtherDevice Router, choose one of the two following conditions to activate the backup
path:
• Link Check: WAN1 link down
• Ping Check: Sends ping commands to a specific IP address (e.g., the IP address of the ISP’s server) from
WAN1 based on us er configurable Time Interval, Retry, and Timeout.
When the WAN backup function is enabled and the Link Check or Ping Check for the WAN1 interface fails, the
backup interface (WAN2) will be enabled as the primary interface.
WAN Backup Configuration
Select Backup for the WAN2/DMZ Connect Mode, and then go to the Netw ork Re dundan cy WA N Backu p
setting page for the WAN Backup configuration.
Page 36

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-24
Link Check
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Activate Backup function by checking the link status of WAN1 Disabled
Ping Check
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Activates the Backup function if unable to ping from the
EtherDevice Router to a specified IP address.
IP
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP address The EtherDevice Router will check the ping integrity of this IP
Address if the Ping Check function is Enabled
Disabled
None
NOTE The IP address for Ping Check function should be on the network segment of WAN1.
Interval
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 1000 sec User can set up a different Ping Interval for a different network
topology
Retry
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 100 User can configure the number of retries. If the number of
continuous retries exceeds this number , the EtherDevice
Router will activate the backup path.
Timeout
Setting Description Factory Default
100 to 10000 (ms) The timeout criterion of Ping Check 3000 ms
180 sec.
3
Page 37

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-25
become the
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
VRRP Settings
The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) feature can solve the problem with static configuration. VRRP
enables a group of routers to form a single virtual router with a virtual IP address. The LAN clients can then be
configured with the virtual router’s virtual IP address as their default gateway. The virtual router is the
combination of a group of routers, and is also known as a VRRP group .
Enable
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable Enables VRRP Disable
VRRP Interface Setting Entry
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable Enables VRRP entry Disabled
Virtual IP L3 switches / routers in the same VRRP group must be set to
the same virtual IP address as the VRRP ID. This virtual IP
address must belong to the same address range as the real IP
address of the interface.
Virtual Router ID Virtual Router ID is used to assign a VRRP group. The L3
switches / routers, which operate as master / backup, should
have the same ID. Moxa L3 switches / routers support one
virtual router ID for each interface. IDs can range from 1 to
255.
Priority Determines priority in a VRRP group. The priority value range is
1 to 255 and the 255 is the highest priority. If sev er al L3
switches / routers have the same priority, the router with
higher IP address has the higher priority. The usable range is “1
to 255”.
Preemption Mode Determines whether a backup L3 switch / router will take the
authority of master or not.
Track Interface The Track Interface is used to track specific interface within the
router that can change the status of the virtual route r for a
VRRP Group. For example, the WAN interface can be tracked
and if the link is down, the other backup router will
new master of the VRRP group.
0.0.0.0
0
100
Enabled
Disable
Page 38

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-26
Static Routing and Dynamic Routing
The EtherDevice Router supports two ro uting methods: static routing and dynamic routing. Dynam ic routing
makes use of RIP V1/V1c/V2. You can either choose one routing method, or combine the two methods to
establish your routing table. A routing entry includes the following items: the destination address, the next hop
address (which is the next router along the path to the destination address), and a metric that represents the
cost we have to pay to access a different network.
Static Route
You can define the routes yourself by specifying what is the next hop (or router) that the EtherDevice Router
forwards data for a specific subnet. The settings of the Static Route will be added to the routing table and stored
in the EtherDevice Router.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
RIP is a distance vector-based routing protocol that can be used to automatically build up a routing table in the
EtherDevice Router.
The EtherDevice Router can efficiently update a nd maintain the r outing table, and optimize the routing by
identifying the smallest metric and most matched mask prefix.
Static Routing
The Static Routing page is used to configure the EtherDevice Router’s static routing table.
Enable
Click the checkbox to enable Static Routing.
Name
The name of this Static Router list
Destination Address
You can specify the destination IP address.
Netmask
This option is used to specify the subnet mask for this IP address.
Next Hop
This option is used to specify the next router along the path to the destinatio n.
Metric
Use this option to specify a “cost” for accessing the neighboring netwo rk .
Page 39

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-27
s routing table until you
Clickable Buttons
Add
For adding an entry to the Static Routing Tab le .
Delete
For removing selected entries from the Static Routing Table.
Modify
For modifying the content of a selected entry in the Static Routing Ta b le .
NOTE
The entries in the Static Routing Table will not be added to the EtherDevice Router’
click the Activate button.
RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
RIP is a distance-vector routing protocol that employs the hop count as a routing metric. RIP prevents routing
loops by implementing a limit on the number of hops allowed in a path from the source to a destination.
The RIP page is used to set up the RIP parameters.
RIP State
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Enable/Disable Enable or Disable RIP protocol Disable
Enable WAN 1 RIP
Check the checkbox to enable RIP in the WAN 1 interface.
Enable WAN 2 RIP
Check the checkbox to enable RIP in the WAN 2 interface.
Enable LAN RIP
Check the checkbox to enable RIP in the LAN interface.
RIP V1 only
Check the checkbox to enable only RIP V1 interfaces.
Redistributed Static Route r
Check the checkbox to enable the Redistributed Static Route function. The entries that are set in a static route
will be re-distributed if this option is enabled.
Page 40

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-28
the packet
it will
Routing Table
The Routing Table page shows all routing entries.
All Routing Entry List
Setting Description Factory Default
All Show all routing entries N/A
Connected Show connected routing entries N/A
Static Show Static routing entries N/A
RIP Show RIP routing entries N/A
Others Show others routing entries N/A
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT Concept
NAT (Network Address Translation) is a common security function for changing the IP address during Ethernet
packet transmission. When the user wants to hid e the inte rnal IP address (LAN) from the external network
(WAN), the NAT function will translate the internal IP address to a specific IP a ddress, or an internal IP a ddress
range to one external IP address. The benefits of using NAT include :
• Uses the N- 1 or Port forwarding Nat function to hide the Internal IP address of a critical network or device
to increase the level of security of industrial network applications.
• Uses the same private IP address for different, but identica l, gr o ups of Ethernet devices. For example,
1-to-1 NAT makes it easy to duplicate or extend identical produc tion lines.
NOTE
NOTE The maximum number of NAT policies for the EtherDevice Router is 128.
The NAT function will check if incoming or outgoing packets match the policy. It starts by checking
with the first policy (Index=1); if the packe t ma tc hes this policy , the EtherDevice Router will translate the
address immediately and then start checking the next packet. If the packet does not match this policy,
check with the next policy.
N-to-1 NAT
If the user wants to hide the Internal IP address from users outside the LAN, the easiest way is to use the
N-to-1 (or N-1) NAT function. The N-1 NAT function replaces the source IP Address with an external IP address,
and adds a logical port number to identify the connection of this internal/external IP address. This function is
also called “Network Address Port Translation” (NAPT) or “IP Masquerading.”
The N-1 N AT function is a one way connection from an internal secure area to an external non-secure area. The
user can initialize the connection from the internal to the external network, but may not be able to initialize the
connection from the exte rnal to the internal network.
Page 41

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-29
1 policy from the source IP, 192.168.127.1 to 192.168.127.252 to the
Enable/Disable NAT Polic y
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the selected NAT policy Enabled
NAT Mode
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
N-1
1-1
Port Forwarding
Interface (N-1 mode)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Auto
WAN1
WAN2
The EtherDevice Router provides a Dual WAN backup function for network redundancy. If the interface is set to
Auto, the NAT Mode is set to N-1, and the WAN backup function is enabled, the primary WAN interface is WAN1.
If the WAN1 connection fails, the WAN interface of this N-1 policy will apply to WAN2 and switch to WAN2 for
N-1 outgoing traffic until the WAN1 interface recovers.
Select the NAT types N-1
Select the Interface for this NAT Policy Auto
IP Range
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP address Select the Internal IP range for IP translation to WAN IP
WAN IP (N-1 mode)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP address The IP address of the user selected interface (WAN1, WAN2,
NOTE
The EtherDevice Router will add an NWAN1 interface after activating the Factory Default.
Port Forwarding
If the initial connection is from outside the LAN, but the user still wants to hide the Internal IP address, one way
to do this is to use the Port Forwarding NAT function.
The user can specify the port number of an external IP address (WAN1 or WAN2) in the Port Forwarding policy
list. For example, if the IP address of a web server in the internal network is 192.168.127.10 with port 80, the
user can set up a port forwarding policy to let remote users connect to the internal web server from external IP
address 10.10.10.10 through port 8080. The EtherDevice Router will transfer the packet to IP address
192.168.127.10 through port 80.
None
address
None
and Auto) in this N-to-1 policy.
The Port Forwarding NAT function is one way of connecting from an external insecure area (WAN) to an internal
secure area (LAN). The user can initiate the connection from the external network to the internal network, but
will not able to initiate a connection from the internal ne twork to the external network.
Page 42

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-30
Enable/Disable NAT policy
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the selected NAT policy Enabled
NAT Mode
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
N-1
1-1
Port Forward
Select the NAT types N-1
Interface (Port Forward mode)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
WAN1
WAN2
Protocol (Port Forward mode)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
TCP
UDP
TCP & UDP
WAN Port (Port Forward mode)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 65535 Select a specific WAN port number None
LAN/DMZ IP (Port Forward mode)
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address The translated IP address in the internal netwo rk None
LAN/DMZ Port (Port Forward mode)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 65535 The translated port number in the internal network None
Select the Interface for this NAT Policy WAN1
Select the Protocol for NAT Policy TCP
Page 43

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-31
1-to-1 NAT
If the internal device and external devic e need to comm unicate with each other, choose 1-to-1 NAT, which
offers bi-directional communication (N-to-1 and Port forwarding are both single-directional communication
NAT functions).
1-to-1 NAT is usually used when you have a group of internal servers with private IP addresse s that mus t
connect to the external network. You can use 1-to-1 NAT to map the internal servers to public IP addresses.
The IP address of the internal device will not change.
The figure below illustrates how a user could extend production lines, and us e the same private IP addre sses
of internal devices in each production line. The inte rnal private IP addresses of these devices will map to
different public IP addresses. Configuring a g roup of devices for 1-to-1 NAT is easy and straightforward.
1-to-1 NAT Setting for EDR-G903 in Production Line 1
1-to-1 NAT Setting for EDR-G903 in Production Line 2
Page 44

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-32
an IP address via DHCP or PPPoE. However, if this dynamic IP address is
Enable/Disable NAT policy
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the selected NAT policy None
NAT Mode
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
N-1
1-1
Port Forward
Interface (1-1 NAT type)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
WAN1
WAN2
LAN/DMZ IP (1-1 NAT type)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address Select the Internal IP address in LAN/DMZ network ar e a None
Select the NAT types None
Select the Interface for this NAT Policy WAN1
NOTE
WAN IP (1-1 NAT type)
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address Select the external IP address in WAN network area None
The EtherDevice Router can obtain
the same as the WAN IP for 1-to-1 NAT, then the 1-to-1 NAT function will not work. For this reason, we
recommend disabling the DHCP/PPPoE func tio n w he n using the 1-to-1 NAT function.
Page 45

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-33
Firewall Settings
Firewall Policy Concept
A firewall device is commonly used to provide secure traffic control over an Ethernet network, as illustrated in
the following figure. Firewall devices are deployed at critical points between an external network (the
non-secure part) and an internal network (the secure part).
Firewall Policy Overview
The EtherDevice Router provides a Firewall Policy Overview that lists firewall policies by interface direction.
Select the From interface and To interface and then click the Show button. The Policy list table will show the
policies that match the From-To interface.
Interface From/To
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (WAN1/WAN2/LAN) Select the From Interface and To interface From All to All
WAN1
WAN2
LAN
Page 46

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-34
Firewall Policy Configuration
The EtherDevice Router’s Firewall policy provides secure traffic control, allowing users to control network traffic
based on the following parameters.
Interface From/To
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (WAN1/WAN2/LAN) Select the From Interface and To interface From All to All
WAN1
WAN2
LAN
Quick Automation Profile
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Refer to the “Quick
Automation Profile”
section on page 3-29.
Service
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Filter This Firewall policy will filter by IP addre ss IP Filter
MAC Filter This Firewall policy will filter by MAC address
Target
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Accept The packet will penetrate the firewall when it matches this
Drop The packet will not penetrate the firewall when it matches this
Source IP
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (IP Address) This Firewall Polic y wil l c heck all Source I P address e s in the
Single (IP Address) This Firewall Policy will check single Source IP addresses in the
Range (IP Address) This Firewall Polic y wil l c heck multiple S ource IP addresses in
Select the Protocol parameters in this Firewall Policy None
Accept
firewall policy
firewall policy
All
packet
packet
the packet
Source Port
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (Port number) This Firewall Policy will check all Source port numbers in the
packet
Single (Port number) This Firewall Policy will check single Source Port numbers in the
packet
Range (Port number) This Firewall Policy will check multiple Source port numbers in
the packet
All
Page 47

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-35
addresses
firewall function will check if incoming or outgoing packets match the firewall policy.
the packet with the first policy (Index=1); if the packet matches this policy, it will accept
check the next packet. If the packet does not match this policy it will
Destination IP
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (IP Address) This Firewall Policy will check all Destination IP addresses in the
packet
Single (IP Address) This Firewall Policy will check single Destination IP addresses in
the packet
Range (IP Address) This Firewall Policy will check multiple Destination IP
in the packet
Destination Port
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (Port number) This Firewall Policy will check all Destination port numbers in
the packet
Single (Port number) This Firewall Po lic y w ill c heck single Des tina tio n Port numbers
in the packet
Range (Port number) This Firewall Policy will check multiple Desti nation port
numbers in the packet
All
All
NOTE
NOTE The maximum number of Firewall po l ic ies for the EtherDevice Router is 256.
The EtherDevice Router’s
It starts by checking
or drop the packet immediately and then
check with the next policy.
Layer 2 Policy Setup
In Bridge Mode, the EtherDevice Router provides an advanced Layer 2 Firewall policy for secure traffic control,
which depends on the following parameters:
Interface From/To
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
All (WAN1/WAN2/LAN) Select the From Interface and To interface None
WAN1
WAN2
LAN
Protocol
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Refer to table
“EtherType for Layer 2
Protocol” for a more
detailed description
Select the Layer 2 Protocol in this Firewall Polic y None
Page 48

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-36
EtherType
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
0x0600 to 0xFFFF When Protocol is set to “Manual” you ca n set up EtherType
manually
Target
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Accept The packet will pass the Firewall when it matches this Firewall
policy
Drop The packet will not pass the Firewall when it matches this
Firewall policy
Source MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Mac Address This Firewall Policy will check all Source MAC addresses of the
packet
Destination MAC Address
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Mac Address This Firewall Policy will check all destination MAC address es of
the packet
None
None
None
00:00:00:00:00:00
00:00:00:00:00:00
The following table shows the Layer 2 protocol types commonly used in Ethernet frames.
EtherType for Layer 2 Protocol
Type Layer 2 Protocol
0x0800 IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4)
0x0805 X.25
0x0806 ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
0x0808 Frame Relay ARP
0x08FF G8BPQ AX.25 Ethernet Packe t
0x6000 DEC Assigned proto
0x6001 DEC DNA Dump/Load
0x6002 DEC DNA Remote Console
0x6003 DEC DNA Routing
0x6004 DEC LAT
0x6005 DEC Diagnostics
0x6006 DEC Customer use
0x6007 DEC Systems Comms Arch
0x6558 Trans Ether Bridging
0x6559 Raw Frame Relay
0x80F3 Appletalk AARP
0x809B Appletalk
0x8100 8021Q VLAN tagg ed frame
0x8137 Novell IPX
0x8191 NetBEUI
0x86DD IPv6 (Internet Protocol vers ion 6 )
0x880B PPP
0x884C MultiProtocol over ATM
0x8863 PPPoE discovery messages
0x8864 PPPoE session messages
0x8884 Frame-based ATM Transport over Ethernet
0x9000 Loopback
Page 49

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-37
Quick Automation Profile
Ethernet Fieldbus protocols are popular in industrial automation applications. In fact, many Fieldbus protocols
(e.g., EtheNet/IP and Modbus TCP/IP) can oper ate on an industri al Ethe rnet network, with the Ethernet port
number defined by IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority). The EtherDevice Router provides an easy t o
use function called Quick Automation Profile that includes 45 different pre-defined profiles (Modbus TCP/IP,
Ethernet/IP, etc.), allowing users to create an industrial Ethernet Fieldbus firewall policy with a single click.
For example, if the user wants to create a Modbus TCP/IP firewall policy for an internal network, the user just
needs to select the Modbus TCP/IP(TCP) or Modbus TCP/IP(UDP) protocol from the Protocol drop-down
menu on the Firewall Policy Setting page.
The following table shows the Quick Automation Profile for Ethernet Fieldb us Proto co l and the corresponding
port number
Ethernet Fieldbu s Pro toc o l Port Number
EtherCat port (TCP) 34980
EtherCat port (UDP) 34980
EtherNet/IP I/O (TCP) 2222
EtherNet/IP I/O (UDP) 2222
EtherNet/IP Messaging (TCP) 44818
EtherNet/IP Messaging (UDP) 44818
FF Annunciation (TCP) 1089
FF Annunciation (UDP) 1089
FF Fieldbus Message (TCP) 1090
FF Fieldbus Message (UDP) 1090
FF System Management (TCP) 1091
FF System Management (UDP) 1091
FF LAN Redundancy Port (TCP) 3622
FF LAN Redund a ncy Por t (UDP) 3622
LonWorks (TCP) 2540
LonWorks (UDP) 2540
LonWorks2 (TCP) 2541
LonWorks2 (UDP) 2541
Modbus TCP/IP (TCP) 502
Page 50

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-38
Modbus TCP/IP (UDP) 502
PROFInet RT Unicast (TCP) 34962
PROFInet RT Unicast (UDP) 34962
PROFInet RT Multicast (TCP) 34963
PROFInet RT Multicast (UDP) 34963
PROFInet Context Manager (TCP) 34964
PROFInet Context Manager (UDP) 34964
IEC 60870-5-104 (TCP) 2404
IEC 60870-5-104 (UDP) 2404
DNP (TCP) 20000
DNP (UDP) 20000
The Quick Automation Profile also includes the commonly used Ethernet protocols listed in the following table:
Ethernet Protocol Port Number
IPSec NAT Traversal (UDP) 4500
IPSec NAT traversal (TCP) 4500
FTP-data (TCP) 20
FTP-data (UDP) 20
FTP-control (TCP) 21
FTP-control (UDP) 21
SSH (TCP) 22
SSH (UDP) 22
Telnet (TCP) 23
Telnet (UDP) 23
HTTP (TCP) 80
HTTP (UDP) 80
IPSec (TCP) 1293
IPSec (UDP) 1293
L2F & L2TP (TCP) 1701
L2F & L2TP (UDP) 1701
PPTP (TCP) 1723
PPTP (UDP) 1723
Radius authentication (TCP) 1812
Radius authentication (UDP) 1812
RADIUS accounting (TCP) 1813
RADIUS accounting (UDP) 1813
PolicyCheck
The EtherDevice Router supports a PolicyCheck function for mai ntaining the firewall policy list. The
PolicyCheck function detects firewall po lic ie s that may be configured incorrectly.
PolicyCheck provides an auto detection function for detecting common configuration errors in the Firewall
policy (e.g., Mask, Include, and Cross conflict). When adding a new firewall policy, the user just needs to
click the PolicyCheck button to check each policy; warning messages will be generated that can be used for
further analysis. If the user decides to ignore a warning message, the EtherDevice Router firewall will run on
the configuration provided by the user.
The three most common types of configuration errors are related to Mask, Include, and Cross Conflict.
Page 51

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-39
Mask: Policy [X] is masked by Policy [Y]
The Source/Destination IP range or Source/Destination port number of policy [X] is smaller or equal to policy
[Y] but the action target (Accept/Drop) is different.
For example, two firewall policies are shown below:
Index Input Output Protocol Source IP Destination IP Target
1 WAN1 LAN All 10.10.10.10 192.168.127.10 ACCEPT
2 WAN2 LAN All 20.20.20.10
to 20.20.20.30
Suppose the user next adds a new policy with the following configuration:
Index Input Output Protocol Source IP Destination IP Target
3 WAN2 LAN All 20.20.20.20 192.168.127.20 DROP
After clicking the PolicyCheck button, the EtherDevice Router will issue a message informing the user that
policy [3] is masked by policy [2] because the IP range of policy [3] is smaller than the IP range of policy [2],
and the Target action is different.
192.168.127.20 ACCEPT
Include: Policy [X] is inc luded in Policy [Y]
The Source/Destination IP range or Source/Destination port number of policy [X] is less than or equal to policy
[Y], and the action target (Accept/Drop) is the same. In this case policy [X] will incre as e the load ing of the
EtherDevice Router and lower its performance.
For example, two firewall policies are shown in the following table:
Index Input Output Protocol Source IP Destination IP Target
1 WAN1 LAN All 10.10.10.10 192.168.127.10 ACCEPT
2 WAN2 LAN All 20.20.20.10
to 20.20.20.30
Suppose the user next adds a new policy with the following configuration:
Index Input Output Protocol Source IP Destination IP Target
3 WAN2 LAN All 20.20.20.20 192.168.127.20 ACCEPT
After clicking the PolicyCheck button, the EtherDevice Router will issue a message informing the user that
policy [3] is included in policy [2] because the IP range of policy [3] is smaller than the IP range of policy [2],
and the Target action is the same.
192.168.127.20 ACCEPT
Cross Conflict: Policy [X] cross conflicts with Policy [Y]
Two firewall policy configurations, such as Source IP, Destination I P, So urce port, and Destination port, in
policy [X] and policy [Y] are masked, and the action target (Accept/Drop) is different.
For example, two firewall policies are shown in the following table:
Index Input Output Protocol Source IP Destination IP Target
1 WAN1 LAN All 10.10.10.10 192.168.127.10 ACCEPT
2 WAN2 LAN All 20.20.20.20
to 20.20.20.30
192.168.127.25
ACCEPT
Page 52

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-40
Suppose the user next adds a new policy with the following configuration:
Index Input Output Protocol Source IP Destination IP Target
3 WAN2 LAN All 20.20.20.25 192.168.127.20
to 192.168.127.30
The source IP range in policy 3 is smaller than policy 2, but the destination IP of policy 2 is smaller than policy
3, and the target actions (Accept/Drop) of these two policies are different. If the user clicks the PolicyCheck
button, the EtherDevice Router will issue a messa ge informing the user that policy [3] is in Cross Conflic t with
policy [2].
DROP
Denial of Service (DoS) function
The EtherDevice Router provides 9 different DoS functions for detecting or defining abnormal packet format or
traffic flow. The EtherDevice Router will drop the packets when it detects an abnormal packe t form at. The
EtherDevice Router will also monitor some traffic flow parameters and activate the defense process when
abnormal traffic conditions are dete c te d.
Null Scan
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the Null Scan None
Xmas Scan
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the Xmas Scan None
NMAP-Xmas Scan
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the NMAP-Xmas None
SYN/FIN Scan
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the SYN/FIN Scan None
FIN Scan
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the FIN Scan None
NMAP-ID Scan
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the NMAP-ID Scan None
Page 53

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-41
SYN/RST Scan
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the SYN/RST Scan None
ICMP-Death
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the ICMP-Death defense None
Packet/Second The limit value to ac tiv a te ICMP-Death d ef e ns e None
SYN-Flood
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the Null Scan function None
Packet/Second The limit v alue to ac tiv a te SYN-Flood defense None
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Overview
This chapter describes how to use the EtherDevice Router to build a secure Remote Automation network with
the VPN (Virtual Private Network) feature. A VPN provides a highly cost effective solution of establishing secure
tunnels, so that data can be exchanged in a secure manner.
There are two common applications for secure remote communicatio n in an industrial automation network:
IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) VPN for LAN to LAN securit y: Data communication only in a
pre-defined IP range between two different LANs.
L2TP (Layer 2 T unnel Protocol) VPN for Remote roaming User: Secure data communication for remote
roaming users with dynamic IP. L2TP is a popular choice for remote roaming users for VPN applications because
the L2TP VPN protocol is a lready b uilt in to the Microsoft Windows operating syste m .
IPSec uses IKE (Internet Key Exchange) protocol for Authentication, Key exchange and provides a way for the
VPN gateway data to be protected by differe nt encry p tion methods.
There are 2 phases for IKE for negotiating the IPSec connections between 2 VPN gatew ays:
Key Exchang e (IPSec Phase 1):
The 2 VPN gateways will negotiate how IKE should be protected. Phase 1 will also authenticate the two VPN
gateways by the matched Per-shared Key or X.509 Certifi c ate.
Data Exchange (IPSe c Phase 2):
In Phase 2, the VPN gateways negotiate to determine additio nal I PS e c connec tion details, which include the
data encryption algorithm.
Page 54

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-42
IPSec Configuration
IPSec conf igur a tio n inc ludes 5 parts:
• Global Setting: Enable / Disable all IPSec Tunnels and NAT-Traversal function
• Tunnel Setting: Set up the VPN Connection type and VPN network plan
• Key Exchange: Authentication for 2 VPN gateways
• Data Exchange: Data encryption betwee n VPN gateway s
• Dead Peer Detection: The mechanism for VPN Tunnel maintenance .
Global Configuration
The EtherDevice Router provides 2 Global Settings for VPN applications.
All IPSec Connection
Users can Enable or Disable all VPN services with this configuration.
NOTE The factory default setting is Disable , so whe n the user wants to use VPN functio n, make sure the setting is
enabled.
IPSec NAT-T:
If there is an external NAT device between VPN tunnels, the use r mus t enable the NAT-T (NAT-Traversal)
function.
IPSec Quick Setting
The EtherDevice Router’s Quick Setting mode can be used to easily set up a site-to-site VPN tunne l fo r two
EtherDevice Router units.
When choosing the Quick setting mode, the user just needs to configure the following:
• Tunnel Setting
• Security Setting
Encryption Strength: Simple (AES-128), Standard (AES-192), Stro ng (AES-256)
Password of Per-shared Key
NOTE
The Encryption strength and Per-shared key should be configured the same for both EtherDevice Router units.
IPSec Advanced Setting
Click Advanced Setting to configure detailed VPN settings.
Page 55

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-43
for connecting
Tunnel Setting
Enable or Disable VPN Tunnel
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable this VPN Tunnel Disable
Name of VPN Tunnel
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Max. of 16 characters User defined name of this VPN Tunnel. None
NOTE The first character cannot be a number.
L2TP over IPSec Enable or Disable
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Enable or Disable Enable or Disable IPSec tunnel over L2TP protocol function None
VPN Connection T ype
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Site to Site VPN tunnel for Local and Remote subnets are fixed Site to Site
Site to Site (Any) VPN tunnel fo r Rem o te subnet a r e a is dynamic and Local
subnet is fixed
Remote VPN Gateway
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
IP Address Remote VPN Gateway’s IP Address None
Connection Interface
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
WAN1
WAN2
Default Route
Startup Mode
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Start in Initial This VPN tunnel will actively initiate the c onnection with the
Wait for Connecting This VPN tunnel will wait remote VPN gateway to initiate the
The interface of the VPN Tunnel
If the user enables the WAN backup function, WAN1 would be
the primary default route and WAN2 would be the backup
route.
Remote VPN Gateway.
connection
WAN1
Start in Initial
NOTE
The maximum number of Starts in the initial VPN tunnel is 5. The maximum number of Waits
to a VPN tunnel is 20.
Page 56

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-44
Local Network / Netmask / ID
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
IP Address IP address of local VPN network IP address of LAN
interface
Subnet Mask Subne t Mask of loc a l VPN network Netmask of LAN
interface
ID ID for indentifying the VPN tunnel connection.
The Local ID must be equal to the Remote ID of the VPN
Gateway. Otherwise, the VPN tunnel cannot be established
successfully
Remote Network / Netmask / ID
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
IP Address IP address of Remote VPN network 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask Subne t Mask of loc a l VPN network 0.0.0.0
ID ID for indentifying the VPN tunnel connection.
The Local ID must be equal to the Remote ID of the VPN
Gateway. Otherwise, the VPN tunnel cannot be established.
None
None
Key Exchange (IPSec phase I)
IKE Mode
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
Main In “Main” IKE Mode, both the Remote and Local V PN gateway
will negotiate which Encryption/Hash algorithm and DH groups
can be used in this VPN tunnel; both VPN gateways m us t use
the same algorithm to communicate.
Aggressive In “Aggressive” Mode, the Remote and Local VPN gateway will
not negotiate the algorithm; it will use the user’s configuration
only.
MAIN
Authentication Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Pre-shared K ey The authentication mode of IPSec VPN Per-Shared Key
X.509
In Per-Shared Key Mode, the user need s to key-in the same Per-Shared Key in the IPSec settin g between the
Local and Remote secure router.
Page 57

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-45
In X.509 Mode, the user needs to upload the Local and Remote certif ic ations first, and then select the
certifications from the drop-down list.
See the X.509 Certification section in this chapter for details.
Encryption Algor it hm
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
DES
3DES
AES-128
AES-192
AES-256
Hash Algorithm
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Any
MD5
SHA1
SHA256
Encryption Algorithm in key exchange 3DES
Hash Algorithm in key exchange SHA1
DH Group
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
DH1(modp 76 8)
DH2(modp 10 24)
DH5(modp 15 36)
DH14(modp 2048)
Negotiation Time
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
Negotiation time The number of allowed reconnect times when startup mode is
IKE Lifetime
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
IKE lifetime (hours) Lifetime for IKE SA 1 (hr)
Rekey Expire Time
Setting Description Factory Default
Rekey expire time
(minutes)
Rekey Fuzz Percent
Setting Description Factory Default
0-100 (%) The rekey expire time will change randomly to enhance the
Diffie-Hellman groups
(the Key Exchange group between the Remote and VPN
Gateways)
initiated. If the number is 0, this tunnel will always try
connecting to the remote gateway when the VPN tunnel is not
created successfully.
Start to Rekey before IKE lifetime expired 9 (min)
security.
Rekey fuzz percent is the maximum random change margin of
the Rekey expire time.
100% means the rekey expire time will not change randomly.
DH2(modp 1024)
0
100 (%)
Page 58

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-46
Data Exchange (IPSec phase II)
Perfect Forward Secrecy
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Enable or Disable Uses different security key for different IPSec phases to
enhance security
SA Lifetime
Setting Description Factory Default
SA lifetime (minutes) Lifetime for SA in Phase 2 4 80 (min)
Encryption Algor it hm
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
DES
3DES
AES-128
AES-192
AES-256
Encryption Algorithm in data exchang e 3DES
Disable
Hash Algorithm
Setting Description Factory Default
Any
MD5
SHA1
SHA256
Hash Algorithm in data exchange SHA1
Dead Peer Detection
Dead Peer Detection is a mech anism to det ect whether or not the connection between a local secure router and
a remote IPSec tunnel has been los t.
Action
Action when a dead peer is detected.
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Hold Hold this VPN tunnel Hold
Restart Reconnect this VPN tunnel
Clear Clear this VPN tunnel
Disable Disable Dead Peer Detection
Delay
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
Delay time (seconds) The period of dead peer detection messages 30 (sec)
Timeout
Setting Description Factory Defaul t
Timeout (seconds) Timeout to check if the connection is alive or not 120 (sec)
Page 59

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-47
IPSec Status
The user can check the VPN tunnel status in the IPSec Connection List.
This list shows the Name of the IPSec tunnel, IP address of Local and Remote Subnet/G a te w ay, and the
established status of the Key exchange phase and Data exchange p hase.
X.509 Certification
X.509 is a digital certificate method commonly used for IPSec Authentication. The EtherDevice Router can
generate a trusted Root Certification and then export/import the certific ate to the re mote VPN gateway .
The diagram below indicates the 5 steps you should follow to use X.509 for IPSec authentication with two VPN
gateways, referred to as EDR-G903(A) and EDR-G903(B) in the diagram:
1. Root Certifi c ate generation. Both EDR-G903(A) a nd EDR-G903(B) need to generate their own root
certificates.
2. EDR-G903(A) and EDR-G903(B) can request new certifications based on their own Root Certificates.
3. Generate PKCS#12 local certificate with password (.p12) and Certificate file for remote VPN tunnel (.crt)
• EDR-G903(A)Moxa-A.p12 and Moxa-A.crt
• EDR-G903(B)Moxa-B.crt and Moxa-B.crt
4. Upload the PKCS#12 certi f ic a te to the Loca l Certification list
• Moxa-A.p12 in EDR-G903(A)
• Moxa-B.p12 in EDR-G903(B)
5. Send the Certific a te file (.crt) to the remote VPN gateway and upload to the Remote certi f ic a te file
• Upload Moxa-B.crt to EDR-G903(A)
• Upload Moxa-A.crt to EDR-G903(B)
Page 60

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-48
Certificate Generation
The user must fill in the following information to generate the Root certification:
• Country name (2 Letter code)
• Certificate Days
• State or Province Name
• Locality Name
• Organization Name
• Organization Unit Name
• Common Name
• Email Address
After keyin in all information, press Activate to generate the Root Certification.
NOTE The default setting for Certificate Day is 0, which means that the certification will not terminated unless
modified by the user.
Certificate Setting
After Root Certification is activated, the user can generate different certifications for different VPN Tunnels. The
user needs to fill in the following information and press Add and Activate to add the new certificate to the
Certificate List.
• Certificate Days
• Organization Unit Name
• Certificate Name
• Email Address
• Certificate Password
The user can then choose certificat es from the list and press the PKCS#1 2 E xpor t button to generate a .p12
file for a local certificate and press Certificate Export to generate a .crt file for certificates on a Remote VPN
gateway.
Page 61

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-49
Local Certificate Upload
Upload the .p12 local certificate on this page. The Password must be the same as the .p12 certificate file. If the
password is not correct, the certificate impor t proc e ss will fail.
Label: User defined name for this local certificate
Name/Subject: Show the Name and subject when the certificate is imported successfully or the user selects
the certificate on the list
PKCS#12 Upload: Use Browser to select the .p12 file and press the Import button
Import Password: The Password for the .p12 certif ic a te
Remote Certificate Upload
Upload the .crt Remote certificate on this page.
Label: Use r defined name for this local certificate
Name/Subject: Show the Name and subject when the certificate is imported successfully or the user selects
a certificate from the list
Certificate Upload: Use the Browser to select a .p12 file and press the Import button.
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol)
L2TP is a popular choice for remote roaming users for VPN applications since an L2TP client is built in to the
Microsoft Windows operating system. Since L2TP does not provide an encryption function, it is usually
combined with IPSec to provide data encryption.
Page 62

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-50
L2TP Configuration
L2TP Server Mode
Setting Description Factory Default
Enable / Disable Enable or Disable the L2TP function on the WAN1 or WAN 2
interface
Local IP
Setting Description Factory Default
IP Address The IP address of the Local Subnet 0.0.0.0
Offered IP Range
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
IP Address Offered IP range is for the L2TP clients 0.0.0.0
Login User Name
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Max. to xx character. User Name for L2TP connection NULL
Login Password
Setting Description Factory Def a ult
Max. to xx character. Password for L2TP connection NULL
Disable
Page 63

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-51
Examples for Typical VPN Applications
Site to Site IPSec VPN tunnel with Per-shared Key
The following example shows how to cre ate a secure LAN to LAN VPN tunnel betw een the Central site and
Remote site via an Intrane t networ k .
VPN Plan:
• All communication from the Central site network (100.100.1.0/24 ) to the R e mote site Network
(100.100.3.0/24) needs to pass through the VPN tunnel.
• Intranet Network is 100.100.2.0/2 4
• The configuration of the WAN/LAN interface for 2 EtherDevice Routers is shown in the following table.
EDR-G903
Interface Setting
Configuration EtherDevice Router (1) EtherDevice Router (2)
WAN IP 100.100.2.1 100.100.2.2
LAN IP 100.100.1.1 100.100.3.1
Based on the requirement and VPN plan, the recommended configuration for VPN IPSec is shown in the
following table
Configuration EtherDevice Router (1) EtherDevice Router (2)
Tunnel Setting Connection Type Site to Site Site to Site
Remote VPN gateway 100.100.2.2 100.100.2.1
Startup mode Wait for Connection Start in Initial
Local Network /
Netmask
Remote Network /
Netmask
Key Exchange Per-shared Key 12345 12345
Data Exchange Encryption / Harsh 3DES / SHA1 3DES / SHA1
100.100.1.0 /
255.255.255.0
100.100.3.0 /
25.255.255.0
100.100.3.0 /
25.255.255.0
100.100.1.0 /
255.255.255.0
Page 64

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-52
L2TP for Remote User Maintenance
The following example shows how a Roaming user uses L2TP over IPSec to connect to theremote site network.
VPN Plan:
• All communication from the Roaming user (no fixed IP) to the Remote site Network (100.100.3.0/24) needs
to pass through the VPN tunnel.
• Communication goes through the Internet.
• The configuration of the WAN/LAN interface for the EtherDevice Router is shown in the following table.
Configuration EtherDevice Router (1)
EDR-G903
Interface Setting
WAN IP 100.100.2.1
LAN IP 100.100.3.1
Based on the requirement and VPN plan, the recommended configuration for L2TP over IPSec is shown in the
following table:
Configuration EtherDevice Router (1)
L2TP Server Setting L2TP Server Mode (WAN1) Enable
Local IP (L2TP Server IP) 100.100.4.1
Offer IP Range 100.100.4.1 ~100.100.4.100
Login User / Password User01 / 12345
Tunnel Setting Conne c tion Type Site to Site (Any)
L2TP Tunnel Enable
Local Network 100.100.3.1 / 24
Startup mode Wait for Connection
Key Exchange Per-shared Key 12345
Data Exchange Encryption Algorithm
Harsh Algorithm
Traffic Prioritization
The EtherDevice Router’s traffic prioritiz ation capability provides Quality of Servic e (QoS ) to your networ k by
making data delivery more reliable. You can prioritize traffic on your network to ensure that high priority data
is transmitted with minimum delay. Traffic can be controlled by a set of rules to obtain the required Quality of
Service for your network.
(Same as LAN Interface)
3DES
SHA1
NOTE The maximum number of Firewall po l ic ies for the EtherDevice Router is 256.
Page 65

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-53
How Traffic Prioritization Works
The EtherDevice Router provides four different priorities levels (0-3, high to low) for incoming and outgoing
traffic. The following figure illustrates incoming traffic, which refers to the traffic transmitted from WAN1 to LAN
or WAN2 to LAN interface. Outgoing traffic refers to the traffic transmitted from LAN to WAN1 or from LAN to
WAN2.
The following figures show the configuration for incoming and outgoing traffic. Users can manage the priority
of incoming traffic (WAN1 to LAN and WAN2 to LAN) and outgoing traff ic (LAN to WAN1 and LAN to WAN2).
Traffic Prioritization Configuration
Enable or Disable
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable the Traffic Prioritization function Disabled
Page 66

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-54
Max. Bandwidth
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 1,000,00 0
KBytes/s
Default Priority
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Priority 0/1/2/3 A packet without matching any incoming/outgoing policy w ill
Minimum Bandwidth of Priority 0/1/2/3
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 1,000,00 0
KBytes/s
Maximum Bandwidth of Priority 0/1/2/3
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
1 to 1,000,00 0
KBytes/s
The maximum bandwidth for total incoming or outgoing traffic 100 KBytes/s
Priority 3
adhere to the default priority
The minimum bandwidth for Priority 0/1/2 /3 Priority 0: 10 KBytes/s
Priority 1: 20 KBytes/s
Priority 2: 30 KBytes/s
Priority 3: 40 KBytes/s
The maximum bandwidth for Priority 0/1/2 /3 Priority 0: 10 KBytes/s
Priority 1: 20 KBytes/s
Priority 2: 30 KBytes/s
Priority 3: 40 KBytes/s
Outgoing/Incoming Policy Setup
After configuring the minimum/maximum
bandwidth for each priority, users can set up
the incoming or outgoing policies for Ethernet
traffic, providing the se tup meets all of the
following conditions:
Enable or Disable
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable this Incoming or Outgoing Policy Disabled
Packet To / From
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (WAN1 or WAN2) Se le c t the dire c tio n of Ethernet traffic for this policy
WAN1
WAN2
Protocol
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (TCP/UDP/ICMP) Select the Protocol fo r in this Policy All
TCP
UDP
ICMP
To: For outgoing policy
From: For incoming policy
All
Service
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
By IP Selec t the service type (IP address or MAC address) for this
By MAC
policy
By IP
Page 67

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-55
Priority
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Priority 0/1/2/3 Select the priority for this policy Priority 0
Source IP
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (IP Address) Select the Source IP address for this polic y All
Single (IP Address)
Range (IP Address)
Source Port
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (Port number) S e le c t the Sour c e port number for this policy All
Single (Port number)
Range (Port number)
Destination IP
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (IP Address) Select the Destination I P addres s for this polic y All
Single (IP Address)
Range (IP Address)
Destination Port
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
All (Port number) S e le c t the Destination port number for this policy All
Single (Port number)
Range (Port number)
The following table shows the management of outgoing traffic. The maximum bandwidth from LAN to WAN is
100 Kbytes. 10 Kbyte is res erved for traffic that matches the parameters of Priority 0. 20 Kbytes is reserved for
traffic that matches the parameters of priority 2 and so forth.
Set up the outgoing policies as below:
Page 68

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-56
The EtherDevice Router will manage the
bandwidth for outgoing packets. Based on the
four outgoing policies below, when the source
IP of the Ethernet traffic matches the
outgoing policies, the maximum bandwidth
for a packet sent from these source IP
addresses will be reserved by its target
priority.
If there are only two kinds of traffic packets,
priority 0 and priority 1, then transmission
will proceed fro m LAN to WAN1, and the
EtherDevice Router will reserve the minimum
bandwidth (10 KBytes/s and 20 Kbyte/s)
based on these two different IP addresses. In
this case, there are still 100 KBytes/s - 10
KBytes/s - 20 KBytes/s = 70 KBytes/s that do not belong to any priority. So, the EtherDevice Router will
increase the bandwidth from highest priority (0) to lowest priority (3). The EtherDevice Router will add this
70 KBytes/s bandwidth to priority 0 because the maximum bandwidth of priority 0 is 100 KBytes/s. The
following figure shows the bandwidth arrangement of the EtherDevice Router based on this configuration.
Configuring SNMP
The EtherDevice Router supports SNMP V1/V2c/V3. SNMP V1 and SNMP V2c use a community string match for
authentication, which means that SNMP s erve rs acce s s all obj e c ts with rea d-only permissions using the
community string public (default value). SNMP V3, which requires that the user selects an authentication level
of MD5 or SHA, is the most secure protocol. You can also enable data encryption to enhance data s ecur ity.
SNMP security modes and security levels supported by the EtherDevice Router are shown in the following table.
Select the security mode and level that will be used to communicate be tw een the SNMP agent and manag er .
Protocol
Version
SNMP V1, V2c V1, V2c Read
SNMP V3 MD5 or SHA Authentication based
These parameters are configured on the SNMP page. A more detailed explanati o n of each param e ter is give n
below.
UI Setting Authentication Type Data Encryp tion Method
Community string No Uses a community string
Community
on MD5 or SHA
MD5 or SHA Authentication based
on MD5 or SHA
match for authentication
No Provides authentication based
on HMAC-MD5, or HMAC-SHA
algorithms. 8-character
passwords are the minimum
requirement for
authentication.
Data encryption
key
Provides authentication based
onHMAC-MD5 or HMAC-SHA
algorithms, and data
encryption key. 8-character
passwords and a data
encryption key are the
minimum requirements for
authentication and
encryption.
Page 69

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-57
SNMP Read Settings
SNMP Versions
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Disable
V1, V2c, V3, or
V1, V2c, or
V3 only
Contact Person
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Admin or
user
Auth. Type
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
MD5 Prov ides authentic a tio n based on the HMAC-MD5 algorithms.
SHA Provides authentication based on the HMAC -SHA algorithm s .
Data Encryption Ke y
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters 8-character data encryption key is the minimum requir e m ent
Select the SNMP protocol version used to manage the secure
router.
Admin privilege allows access and authorization to read and
write the MIB file. User privilege only allows re ading the MIB
file, but does give authorization to write.
8-character passwords are the minimum requirement for
authentication.
8-character passwords are the minimum requirement for
authentication.
for data encryption
Disable
Admin
MD5
None
Community Name 1/2
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters Use a community string match for authenticatio n Public
Page 70

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-58
Access Control
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Read only (Public MIB
only)
No Access
Target IP Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address Enter the IP address of the Trap Server used by your network. Read only
Access control type after matching the community string Re ad o nly
SNMP Trap Type
SNMP Trap Types can be divided into two basic groups: System Events and Port Eve nts. System Event s are
related to the overall function of the router, whereas Port Events are related to the activity of a specific port.
System Events SNMP Trap is sent when…
Cold Start Power is cut off and then reconnected.
Warm Start The EtherDevice Router is rebooted, such as when network parameters are
changed (IP address, subnet mask, etc.).
Power Transition (On-Off) The EtherDevice Router is powered down.
Power Transition (Off-On) The EtherDevice Router is powered up.
DI (Off) Digital Input is triggered by an on to off transition
DI (On) Digital Input is triggered by an off to on transition
Config. Change A configuration ite m ha s been changed.
Auth. Failure An incorrect password is e ntered .
Port Events SNMP Trap is sent when…
Link-ON The port is connected to another device.
Link-OFF The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out or the opposing device
shuts down).
Using Auto Warning
Since industrial Ethernet devices are often located at the endpoints of a system, these devices will not always
know what is happening elsewhere on the network. This means that an industrial Ethernet router that connects
to these devices must provide system maintainers with real-time alarm messages . Even when co ntr ol
engineers are out of the control room for an extended period of time, they can still be informed of the status of
devices almost instantaneously when exceptions occur. The EtherDevice Router supports different approaches
to warn engineers automatically, such as by using email and relay output. It also supports one digital input to
integrate sensors with your syste m and automate alarms using email and relay output.
Configuring Email Warning
The Auto Email Warning function uses e-mail to alert the user when certain user-configured events take place.
Three basic steps are required to set up the Auto Warning function:
Page 71

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-59
1. Configu re Email Event Types
Select the desired Event types from the Web Browser Event type page (a description of each event type is
given later in the Email Alarm Events setting s ubse c tion).
2. Configure Ema il Se ttin gs
To configure the EtherDevice Router’s email setup from a browser interface, enter your Mail Server’s IP/Name
(IP address or name), Account Name, Account Password, the sender’s email address, and the email address to
which warning messages will be sent.
3. Activate your settings and if necessary, test the email
After configuring and activating your EtherDevice Router’s Event Types and Email Setup, you can use the Test
Email function to see if your e-mail addresses and mail server address have been properly configured.
Event Type
Email Warning Event Types can be divided into two basic groups: System Events and Port Events. System
Events are related to the overall function of the router, whereas Port Events are related to the activity of a
specific port.
System Events Warning email is sent when…
Cold Start Power is cut off and then reconnected.
Warm Start The EtherDevice Router is rebooted, such as when network parameters are
changed (IP address, subnet mask, etc.).
Power Transition (On-Off) The EtherDevice Router is powered down.
Power Transition (Off-On) The EtherDevice Router is powered up.
DI (Off) Digital Input is triggered by on to off transition
DI (On) Digital Input is triggered by off to on transition
Config. Change A configuration ite m ha s been changed.
Auth. Failure An incorrect password is entered .
Port Events Warning email is sent when…
Link-ON The port is connected to another device.
Link-OFF The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out or the opposing device
shuts down).
Page 72

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-60
authentication mechanism. We strongly recommend not entering your Account Name and Account Password
E-mail Setup
Main Server IP/Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP address The IP Address of your email server. None
Port
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Port number The port number of your email server. None
Account Name
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 Characters Your email account name (typically your user name) None
Email Password
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 30 characters The Password of your email account None
Sender Email Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP address The IP Address of the email send e r None
Recipient Email Address
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Max. 50 characters You can set up to 4 email addresses to receive alarm emails
from the EtherDevice Router.
None
Send Test Email
After configuring the email settings, y ou should first click Activate to activate those settings , and then c lic k
Send Test Email to verify that the settings are correct.
NOTE
Auto warning e-mail messages w ill be sent through an authentication protected SMTP server that supports
the CRAM-MD5, LOGIN, and PLAIN methods of SASL (Simple Authe ntic ation and Security Layer)
if auto warning e-mail messages can be delivered without using an authentication mechanism.
Page 73

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-61
Configuring Relay Warning
The Auto Relay Warning function uses relay output to alert the user when certain user-configured events take
place. There are two basic steps required to set up the Relay Warning function:
1. Configuring Rel ay E ve nt Ty pes
Select the desired Event types from the Web Browser Event type page (a descr iption of each event type is
given later in the Relay Alarm Events setting subse c ti o n).
2. Activate your settings
After completing the configuration procedure, you will need to activate your EtherDevice Router’s Relay Event
Types.
Event Types can be divided into two basic groups : System Events and Port Events. System Events are
related to the overall function of the router, whereas Port Events are related to the activ ity of a specific port.
System Events Warning Relay output is triggered when…
Power Input 1 failure (OnOff)
Power Input 2 failure (OnOff)
DI (Off) Digital Input is triggered by on to off transitio n
DI (On) Digital Input is triggered by off to on transition
Port Events Warning Relay output is triggered when…
Link-ON The po rt is connected to another device.
Link-OFF The port is disconnected (e.g., the cable is pulled out or the opposing
Ignore Ignore the status of the port
Power input 1 is down.
Power input 2 is down.
device shuts down).
Override relay ala rm sett i ng s
Select this option to override the relay warning se tting te mpor arily. Releasing the relay output will allow
administrators to fix any problems with the warning condition.
Warning List
Use this table to see if any relay alarms have been issued.
Page 74

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-62
Using Diagnosis
The EtherDevice Router provides Ping tools and LLDP for administrator s to diagnose network systems.
Ping
The Ping function uses the ping command to give users a simple but powerful tool for troubleshooting network
problems. The function’s most unique feature is that even though the ping command is entered from the user’s
PC keyboard, the actual ping command originates from the EtherDevice Router itself. In this way, the user can
essentially control the EtherDevice Router and send ping c ommands out through its ports. There are two basic
steps required to set up the Ping command to test network integrity:
1. Select which interface will be used to send the ping commands. You may choose from WAN1, WAN2, and
LAN.
2. Type in the desired IP address, and click Ping.
LLDP Function Overview
Defined by IEE E 80 2.1 1AB, Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is an OSI Layer 2 Protocol that standardizes
the methodology of self-identity advertisement. It allows each networking device, such as a Moxa managed
switch/router, to periodically inform its neighbors about itself and its configuration. In this way, all devices will
be aware of each other.
The router’s web interface can be used to enable or disable LLDP, and to set the LLDP Message Transmit
Interval. Users can view each switch’s neighbor-list, which is repor ted by its network ne ighb or s .
LLDP Setting
Enable LLDP
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
Enable or Disable Enable or disable LLDP function. Enable
Message Transmit Inte rv al
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
5 to 32768 sec. Set the transmit interval of LLDP messages. Unit is in seconds. 30 (sec.)
LLDT Table
Port: The port number that connects to the neighbor device.
Neighbor ID: A unique entity that identifies a neighbor device; this is typica lly the MAC address.
Neighbor Port: The port number of the neighbor device.
Page 75

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-63
Neighbor Port Descriptio n: A textual description of the neighbor device’s interface.
Neighbor System: Hostname of the neighbor device.
Using Monitor
You can monitor statistics in real time from the EtherDevice Router’s web console.
Monitor by System
Access the Monitor by selecting “System” from the left selection bar. Monitor by System allows the user to view
a graph that shows the combined data transmission activity of all the EtherDevice Router’s 3 ports. Click one
of the three options—Total Packets, TX Packets or RX Packets—to view transmission activity of specific types of
packets. Recall that TX Packets are packets sent out from the EtherDevice Router, and RX Packets are packets
received from connected devices. The Total Packets option displays a graph that combines TX and RX activity.
The graph displays data transmission activity by showing Packets/s (i.e., packets per second, or pps) versus
sec. (seconds).The graph is updated every few seconds, allowing you to analyze data transmission activity in
real time.
Monitor by Port
Access the Monitor by Port function by selecting the WAN1, WAN2, or LAN interface from the left drop-down list.
You can view graphs that show All Packets, TX Packets, or RX Packets, but in this case, only for an individual
port. The graph displays data transmissio n activ ity by showing Packets/s (i.e., packets per second, or pps)
versus sec. (seconds).The graph is updated every few seconds, allo wing you to analyze data transmission
activity in real time.
Page 76

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-64
Using System Log
The EtherDevice Router provides EventLog and Syslog functions to r ecor d important events.
Using EventLog
Field Description
Bootup This field shows how many times the EDR-G509 has been rebooted or cold started.
Date The date is updated based on how the current date is set in the “Basic Setting” page.
Time The time is updated based on how the current time is set in the “Basic Setting” page.
System Startup Time The system startup time related to this event.
Event Ev e nts that have occurred.
The following events will be recorded in the EtherDevice Router EventLog Table:
Event Status
Syslog Configuration change activated
DNS C o nfiguration change activated
Static Route Configuration change activated
SYSTEMINFO C onfiguration change activated
SNMPTRAP Configuration change activated
Filter Configuration change activated
NAT Configuration change activ ate d
DoS Configuration c ha nge activ ate d
QoS_Bandwith C onfiguration change activated
QoS_DownStream Configuration change activated
QoS_UpStream Configuration change activated
DHCP Configuration Change activated/ Enab le / Dis able
NTP Configuration Change activated/ Enab le / Dis able
SNMP Co nfiguration Change activated/ Enable / Disable
DDNS Configuration Change activated/ Enable / Disable
WAN Backup Configuratio n c ha nge activ ate d
LAN Link on / Link off / IP change
WAN2 Link on / Link off / IP change
WAN1 Link on / Link off / IP change
Password Conf igur a tio n c hange activa te d
Login Authentication Fail / Authe ntic ation Pass
Accessible IP function Enable / Disable
Power transition (On -> Off)
Power transition (Off -> On)
DI transition (Off -> On)
Page 77

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-65
DI transition (On -> Off)
Cold start
Factory default Warm start
System restart Warm start
Firmware Upgrade Warm start
Configuration Upgrade Warm start
NOTE The maximum number of event entrie s is 1000 .
Using Syslog
This function provides the event logs for the syslog server. The function supports 3 configurable syslog servers
and syslog server UDP port numbers. When an event occurs, the event will be sent as a syslog UDP packet to
the specified syslog servers.
Syslog Server 1/2/3
Setting Description Factory Defa ult
IP Address Enter the IP address of the Syslog Server used by your
network.
Port Destination
(1 to 65535)
Enter the UDP port of the Syslog Server. 514
Using HTTPs/SSL
To secure your HTTP acce ss, the EtherDevice Router supports HTTPS/SSL to encrypt all HTTP traffic. Perform
the following steps to access the EtherDevice Router’s web browser interface via HTTPS/SSL.
1. Open Internet Explorer and type https://< EtherDevice Router’s IP address> in the address field. Press
Enter to establish the connection.
None
Page 78

EDR-G903/G902 Features and Funct ions
3-66
2. A warning message will appear to warn the user that the security certificate was issued by a company
they have not chosen to trust.
3. Select Yes to enter the EtherDevice Router’s web browser interface and access the web browser
interface secured via HTTPS/SSL.
Page 79

A
A. MIB Groups
The EtherDevice Router comes with built-in SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) agent software that
supports cold start trap, line up/down trap, and RFC 1213 MIB -II. The standard MIB groups that the
EtherDevice Router series support are:
MIB II.1 – System Group
sysORTable
MIB II.2 – Interfaces Group
ifTable
MIB II.4 – IP Group
ipAddrTable
ipNetToMediaTable
IpGroup
IpBasicStatsGroup
IpStatsGroup
MIB II.5 – ICMP Group
IcmpGroup
IcmpInputStatus
IcmpOutputStats
MIB II.6 – TCP Group
tcpConnTable
TcpGroup
TcpStats
MIB II.7 – UDP Group
udpTable
UdpStats
MIB II.11 – SNMP Group
SnmpBasicGroup
SnmpInputStats
SnmpOutputStats
Public Traps:
1. Cold Start
2. Link Up
3. Link Down
4. Authentication Failure
Private Traps:
1. Configuration Changed
2. Power On
3. Power Off
4. DI Trap
The EtherDevice Router also provide s a MIB file, loc ated in the f ile “Moxa-EDRG903-MIB.my” on the
EtherDevice Router Series utility CD-ROM for SNMP trap message interpretation
 Loading...
Loading...