MovinCool CM12 Service Manual

SERVICE MANUAL
DocID: 00G00088EB
CM 12
Unit Serial Number Range: 0211XXXXC12 to Present
SERIAL NUMBER LOCATION AND IDENTIFICATION
Nameplate Label Position
Nameplate Label
COOLING AMPS. WITH PUMP
COMPR. OUTPUT
REFRIGERANT/TOTAL CHARGE
DESIGN PRESSURE LO/HI
PART NO./WEIGHT
SERIAL NO.
Month
Model
Sequential
Number
Year
▲▲ XXXX ###
© 2015 DENSO PRODUCTS AND SERVICES AMERICAS, INC.
All rights reserved. This book may not be reproduced or copied, in
whole or in part, without the written permission of the publisher. DENSO
PRODUCTS AND SERVICES AMERICAS, INC. reserves the right to
make changes without prior notice. MovinCool
SpotCool
® are registered trademarks of DENSO Corporation.
®, Office Pro® and

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Operation Section
1. PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFETY
1.1 Foreword. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 Definition of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.3 General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2. CONSTRUCTION
2.1 Exterior Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Exterior Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Internal Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.4 Basic Construction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.5 Air Flow. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.1 Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.2 Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4. REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
4.1 Refrigeration System Construction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.2 Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4.3 Condenser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
4.4 Capillary Tube. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.5 Evaporator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.6 Accumulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.7 High-Pressure Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
5. ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
5.1 Circuit Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.2 Control Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5.3 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5.4 Relay Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.5 Compressor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5.6 Fan Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5.7 Capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.8 Temperature Thermistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.9 Drain Pump. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.10 Float Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30

Table of Contents
6. CONNECTION AND SETTING
6.1 Power Supply Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6.2 Millivolt Wall Thermostat Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.3 Warning Signal Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.4 Fire Alarm Control Panel Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35

Table of Contents
Repair Section
7. TROUBLESHOOTING
7.1 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.2 Alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
7.3 Troubleshooting Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
7.4 Basic Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
7.5 Inspection of Capacitor (For Fan Motor and Compressor) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7.6 Inspection of Compressor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7.7 Inspection of Fan Motor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7.8 Inspection of Thermistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7.9 Inspection of Wiring Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.10 Refrigeration System Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
8. DISASSEMBLY
8.1 Parts Construction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8.2 Disassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8.3 Removal of Evaporator Fan Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
8.4 Removal of Condenser Fan Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
8.5 Removal of Electrical Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
9. REFRIGERATION SYSTEM REPAIR
9.1 Repair of Refrigeration System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
9.2 Removal of Refrigeration System Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
9.3 Charging the System with R-410A Refrigerant. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
9.4 Refrigerant Charging Work . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
10. REASSEMBLY
10.1 Reassembly of Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
10.2 Compressor Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
10.3 Evaporator Fan Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
10.4 Condenser Fan Assembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
10.5 Wiring Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
10.6 Perform an Inspection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72

6
WARNING
WARNING
Operation Section
1. PRECAUTIONS FOR SAFETY
1.1 Foreword
• This manual has been published to service the MovinCool CM 12. Please use this service
manual only when servicing the CM 12.
1.2 Definition of Terms
Describes precautions that should be observed in order to prevent injury to
the user during installation or unit operation.
CAUTION
NOTE Provides additional information that facilitates installation or unit operation.
Describes precautions that should be observed in order to prevent damage to
the unit or its components, which may occur during installation or unit
operation if sufficient care is not taken.
1.3 General Precautions
• All electrical work should only be performed by qualified electrical personnel. Repair to
electrical components by non-certified technicians may result in personal injury and/or
damage to the unit. All electrical components replaced must be genuine MovinCool parts,
purchased from an authorized reseller.
• Before replacing any refrigeration components, recover the refrigerant using standard
recovery procedures and equipment.
• When handling refrigerant, always wear proper eye protection and do not allow the
refrigerant to come in contact with your skin.
• Do not expose refrigerant to an open flame.
• The power supply for this unit should be a dedicated single outlet circuit with a UL
recognized short-circuit and ground-fault protective breaker to prevent electrical shock
from the unit.
• When brazing any tubing, always wear eye protection, and work only in a well ventilated
area.
• Disconnect power before servicing unit.
• Be careful of any sharp edges when working on unit.
2. CONSTRUCTION
ILL00532-00
OPERATE
STOP
33.6
15.7
(34.8)
(2.8)
(9.2)
(1.3)
(7.6)
(19.9)(2.8)
(1.0)
(DIA. 10.0)
(DIA. 10.0)
(DIA. 0.6)
(DIA. 0.6)
(2.0)
(32.0)
(10.9)
(8.5)
(6.3)(2.3)
(4.5) (4.5)
(15.3)
(3.0)
(15.8)
(8.1)
(3.5)
(0.7)
(0.6)
UNIT: inch
Mount Bracket (t 0.08)
4 x DIA. 0.6
Ground Screw (M6)
With Washer
Fixing Hole (M4)
For Optional Outlet Ring
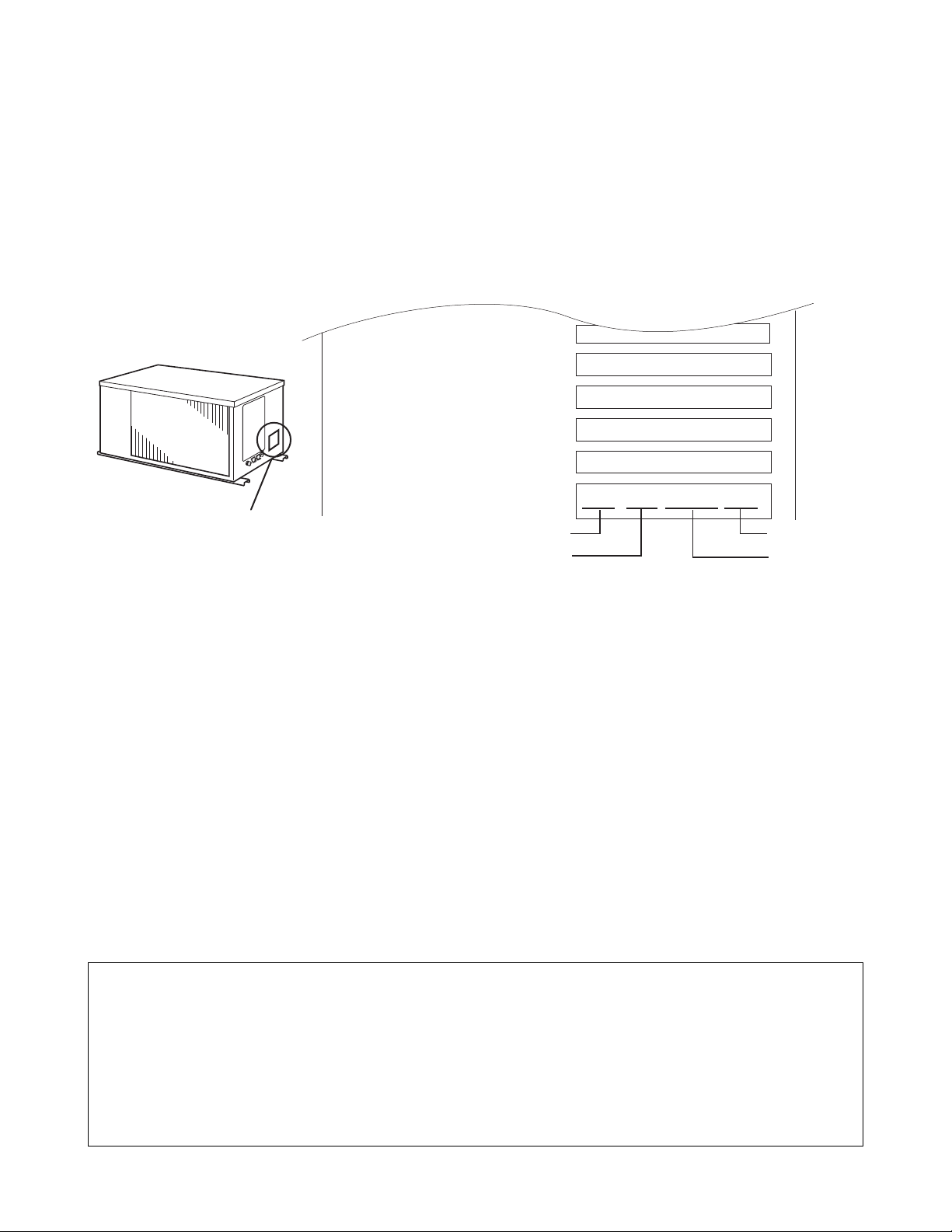
2.1 Exterior Dimensions
Operation Section
7
8
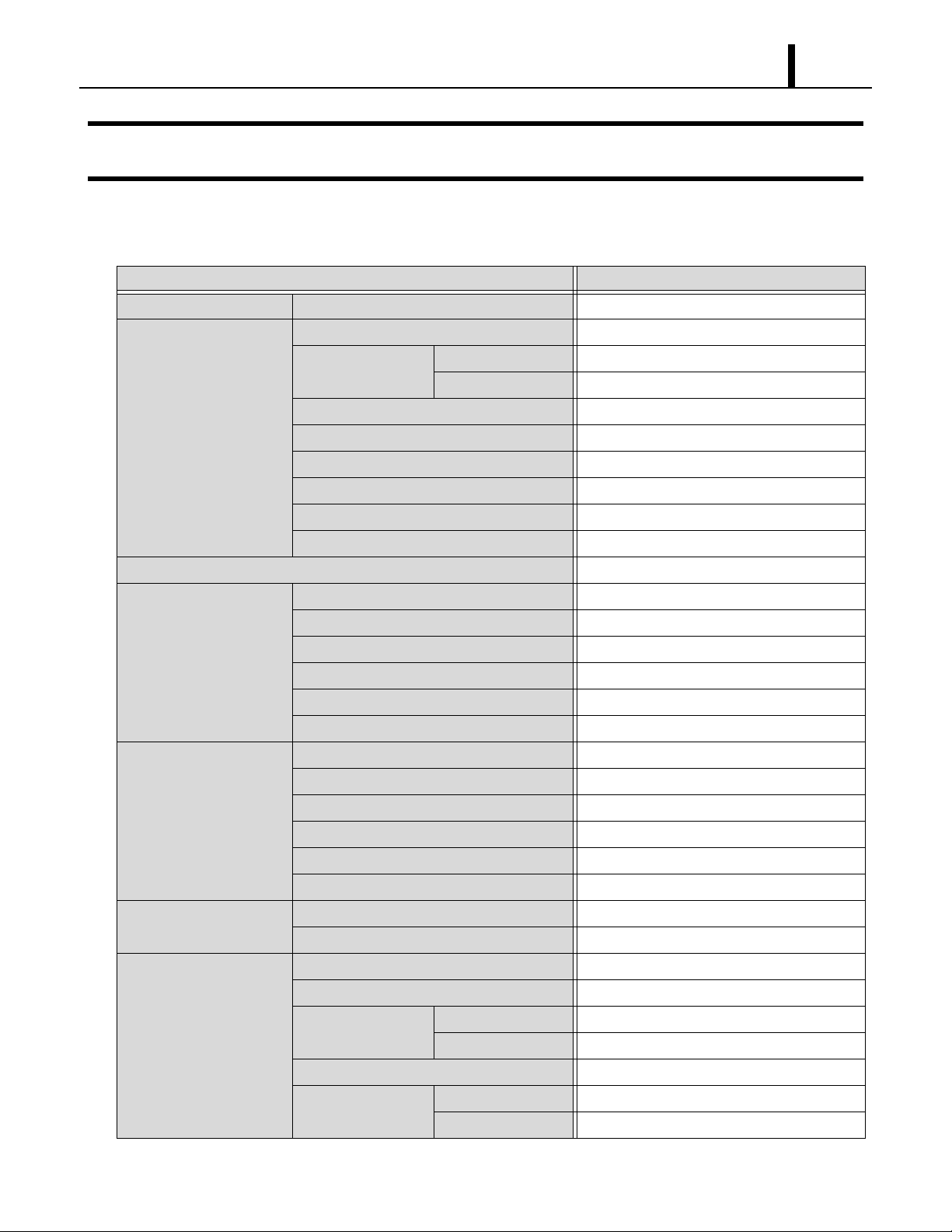
ILL00642-00
Cold Air Exhaust
(10 in.Dia.Flange)
Evaporator (Room)
Air Inlet
(10 in.Dia.Flange)
Mounting
Brackets
Service panel
Thermistor
Condenser Air Inlet
Power Cord Inlet
Override (Stop) Switch
Signal Input and
Output Wires
Thermostat Wires
Condenser (Hot)
Air Exhaust
Condensate Pan Drain for Maintenance
Drain Pipe for Pump
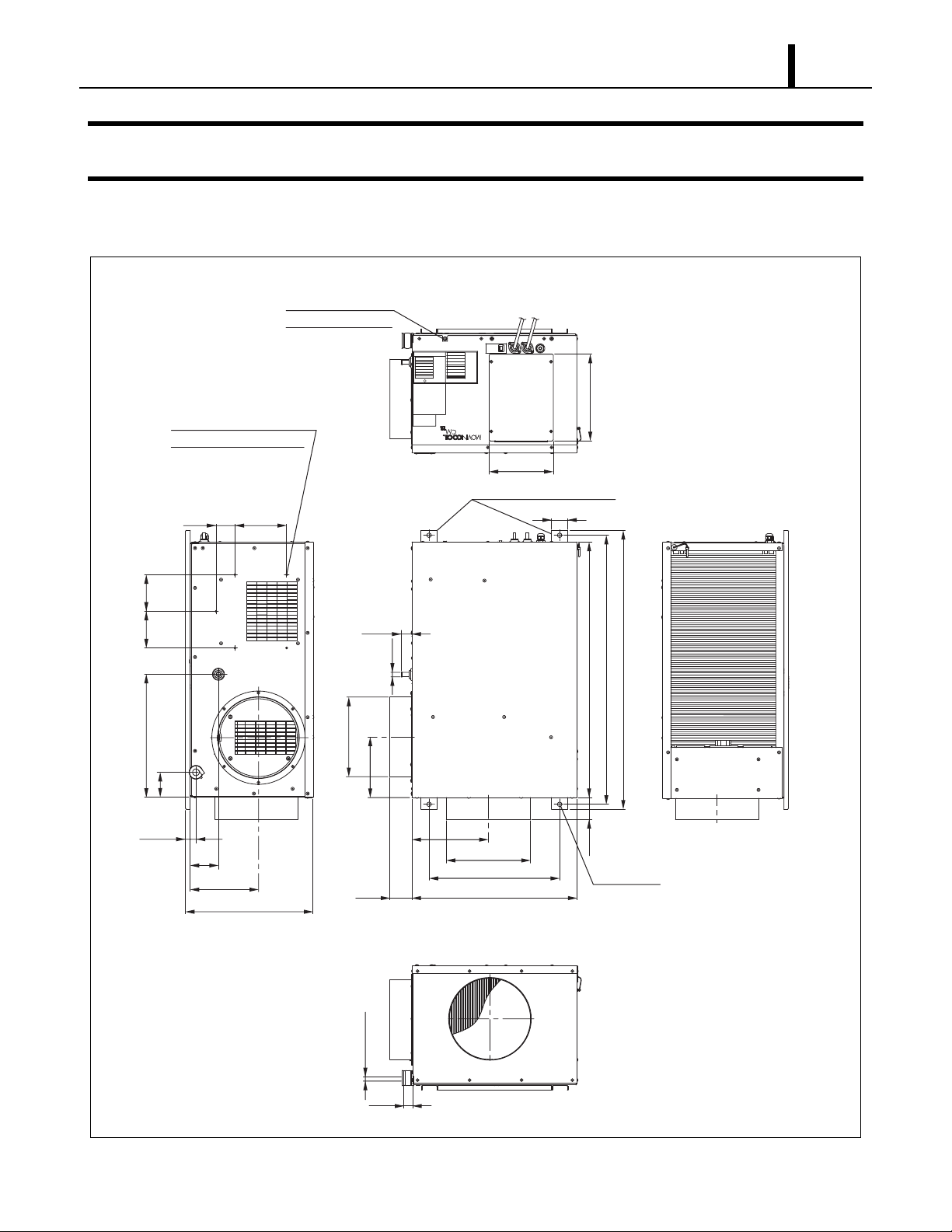
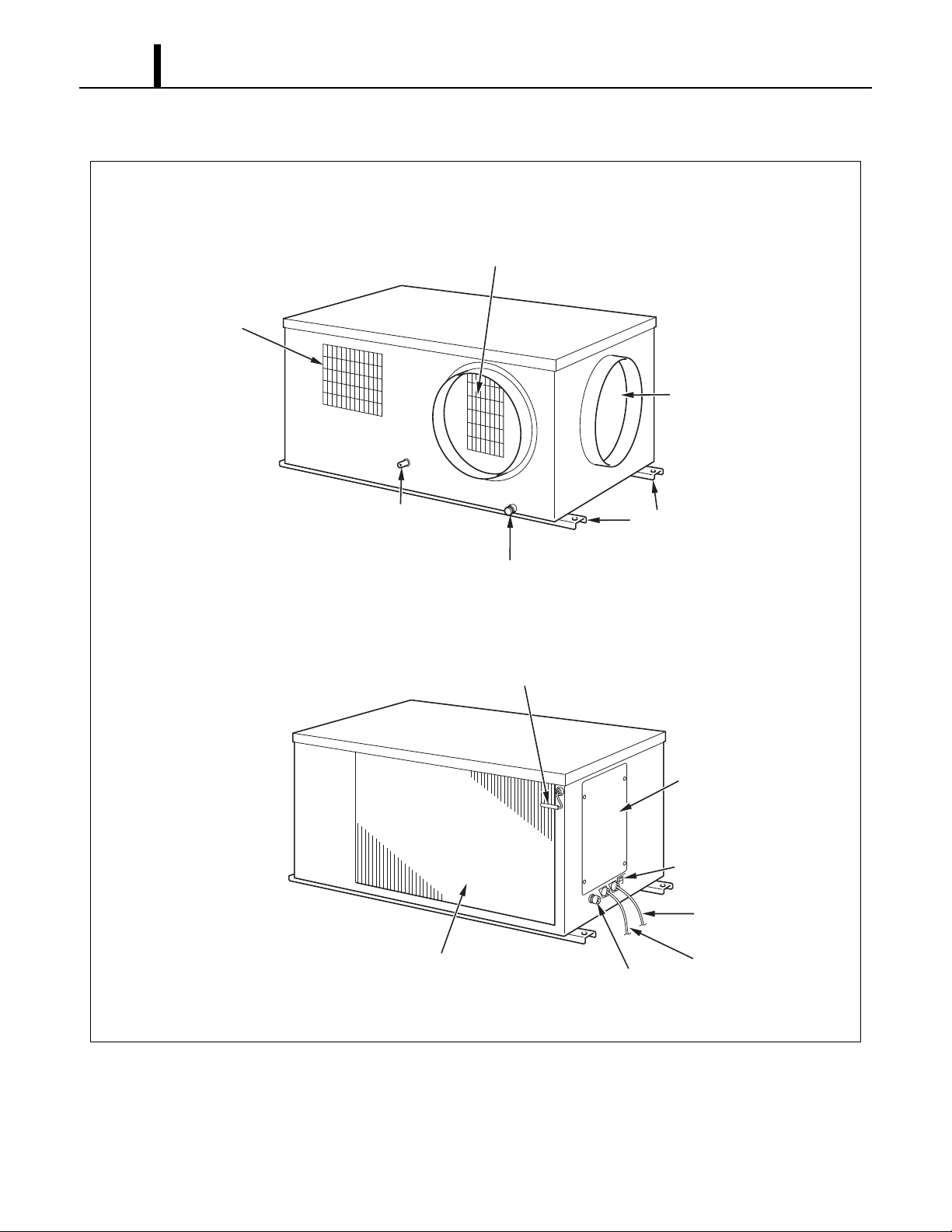
2.2 Exterior Overview
Operation Section
2.3 Internal Structure
ILL00533-01
Accumulator
Evaporator Fan Motor
Evaporator Fan
Drain Pump
Condenser Fan
Condenser Fan Motor
Control Box
Compressor
Evaporator
Condenser
Capillary Tube
Operation Section
9
10
ILL00649-00
Condenser
Control Box
Evaporator
Evaporator
Motor
Condenser
Motor
I002841
Condenser
Intake
Room
Air Intake
Cool Air
Supply
(Evaporator)
Condenser
Exhaust
Operation Section
2.4 Basic Construction
• The MovinCool CM 12 is compact in
construction due to the condenser and
evaporator being enclosed in one unit. The
interior of the unit is divided into two sections.
One section contains the evaporator which
cools room interior air. The other section is
comprised of the condenser, compressor and
control box.
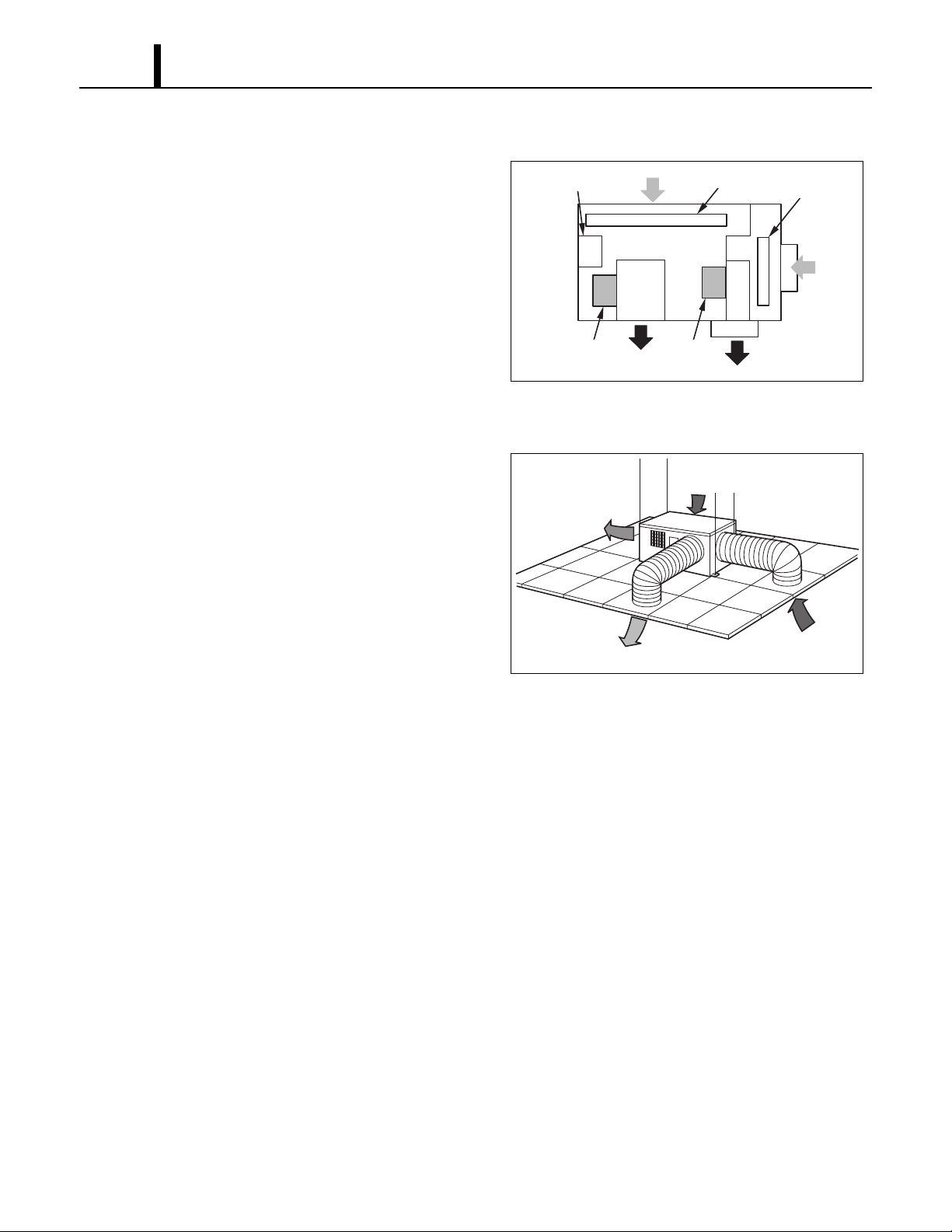
2.5 Air Flow
• Air drawn from the rear face passes over the
condenser which extracts heat from the
refrigerant. The hot air is blown out through the
front exhaust air vent. Air taken in from the
right side face is cooled by the evaporator and
then blown through the front cool air duct.
Operation Section
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.1 Technical Specifications
ITEM SPECIFICATIONS
Electronic Features Control Millivolt Thermostat (Field supplied)
Electrical Characteristics Voltage Requirement Single-Phase, 115 V, 60 Hz
Operating Voltage
Range
Starting Current 50 A
Recommended Fuse Size 15 A
FLA 11. 2 A
MCA 14.9 A
MOP 20 A
LRA 50 A
Max. 127 V
Min. 104 V
11
Cooling Capacity and Power Consumption
Evaporator: 80°F (27°C),
50% RH
Condenser: 95°F (35°C),
50% RH
Total Cooling Capacity
Sensible Cooling Capacity
Power Consumption
Current Consumption
*1
*1
*1
*1
10500 Btu/h (3090 W)
7200 Btu/h (2100 W)
1.23 kW
11. 2 A
EER 8.5
Power Factor 96%
Evaporator: 72°F (22°C),
50% RH
Condenser: 95°F (35°C),
50% RH
Total Cooling Capacity
Sensible Cooling Capacity
Power Consumption
Current Consumption
*1
*1
*1
*1
9300 Btu/h (2730 W)
7000 Btu/h (2040 W)
1.22 kW
11. 1 A
EER 7.6
Power Factor 96%
Compressor Typ e Hermetic Rotary
Output 0.91 kW
Evaporator Type of Evaporator Plate Fin
Typ e of Fan Centrifugal Fan
Air Flow High 324 CFM (550 m3/h)
Low 228 CFM (390 m3/h)
Max. External Static Pressure 0.16 IWG (40 Pa)
Motor Output High 0.04 kW
Low 0.01 kW
12
Operation Section
ITEM SPECIFICATIONS
Condenser Type of Condenser Plate Fin
Typ e of Fan Centrifugal Fan
Air Flow High 700 CFM (1190 m3/h)
Low 370 CFM (630 m3/h)
Max. External Static Pressure 0.12 IWG (30 Pa)
Motor Output High 0.09 kW
Low 0.06 kW
Refrigerant Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Typ e R-410A
Amount 1.59 lb (0.72 kg)
Signal Connection Fire Alarm Input (Signal Type) • No-voltage contact input
• Contact resistance less than 100 ohm
Warning Signal Output 2 A at 30 V DC/AC max. with resistive load
Dimension W × D × H Without Flange and
Mounting Bracket
32.0 ×19.9 × 15.2 in
(813
× 505 × 386 mm)
With Flange and
Mounting Bracket
34.8 × 22.7 × 15.8 in
(884
× 577 × 401 mm)
Weight Net 123 lb (56 kg)
Shipping 137 lb (62 kg)
Condensate Pump
Capacity
Operating Condition
*2
Range
Pump Rate 5.0 gal/h (19 L/h)
Max. Head 4 ft (1.2 m)
Evaporator Air Inlet Max. 95°F (35°C), 50% RH
Min. 65°F (18°C), 50% RH
Condenser Air Inlet Max. 113°F ( 45°C)
Min. 65°F (18°C)
Maximum Duct Length
*3
Cold Duct 20 ft (6.1 m)
Hot Duct 10 ft (3.0 m)
Maximum Sound Level
*4
High 52 dB(A)
Low 52 dB(A)
Safety Devices Compressor Overload Protector Included
Fan Motor Overload Protector Included
Freeze Protection Thermistor Included
Full Drain Pan Switch Included
Automatic Restart (Power Interruption) Included
High Pressure Interruption Included
Compressor Time Delay 120 sec
Signal Input/Output Included
Control Devices Temperature Control Included
Two Speed Fan Included

Operation Section
< NOTE >
13
• Specifications are subject to change without notice.
*1 : With two 6-foot (1.8 m) ducts containing one 90° bend each, supply grill and return grill with filter [0.16 IWG (40 Pa)
external static pressure] on high fan speed.
*2 : When ambient temperature is lower than 65°F (18°C), operation may be interrupted due to anti-freeze protection
activation.
*3 : Confirm pressure drop of duct, grills, and filter with manufacture's specifications.
*4 : Measured at 3 feet (1.0 m) under the ceiling with evaporator duct and ceiling tile.
14
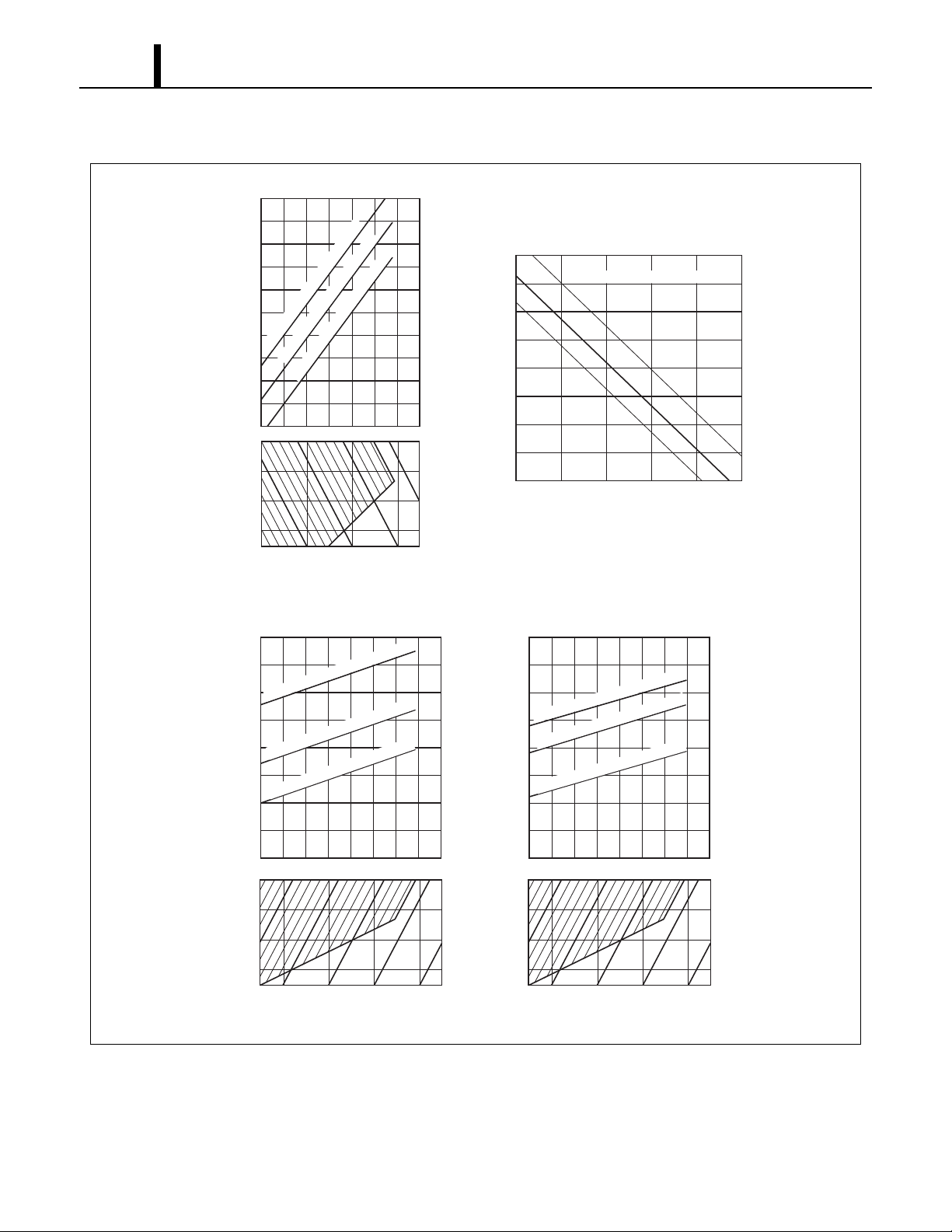
ILL00650-00
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 65F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 95F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature at 95F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 113F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 65F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 95F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 113F
8
10
30 40 50 60 70 80
15 20 25
(50) (59) (68) (77)
20 (68)
7(12.6)
8 (14.4)
9 (16.2)
10 (18.0)
11 (19.8)
12 (21.6)
13 (23.4)
14 (25.2)
15 (27.0)
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
25 (77)
30 (86)
35 (95)
20 25 30 35
(68) (77) (86) (95)
20(68)
25(77)
30(86)
35(95)
10
12
14
16
Cooling Capability Curve
Cool Air Temperature Difference Curve
Power Consumption Curve
Cooling capacity (x10
3
Btu/h)
Dry Bulb Temp.
°C (°F)
Delta-T
°C (°F)
Dry Bulb Temp.
°C (°F)
Power Consumption (kW)
Wet Bulb Temp.°C (°F)
Wet Bulb Temp.
°C (°F)
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 65F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 95F
Condenser Inlet Air Temperature 113F
14.0
12.0
10.0
8.0
20 25 30 35
(68) (77) (86) (95)
20(68)
25(77)
30(86)
35(95)
Current Consumption Curve
Dry Bulb Temp. °C (°F)
Current Consumption (A)
Wet Bulb Temp.°C (°F)
Relative Humidity (%)
Operation Section
3.2 Characteristics
Operation Section
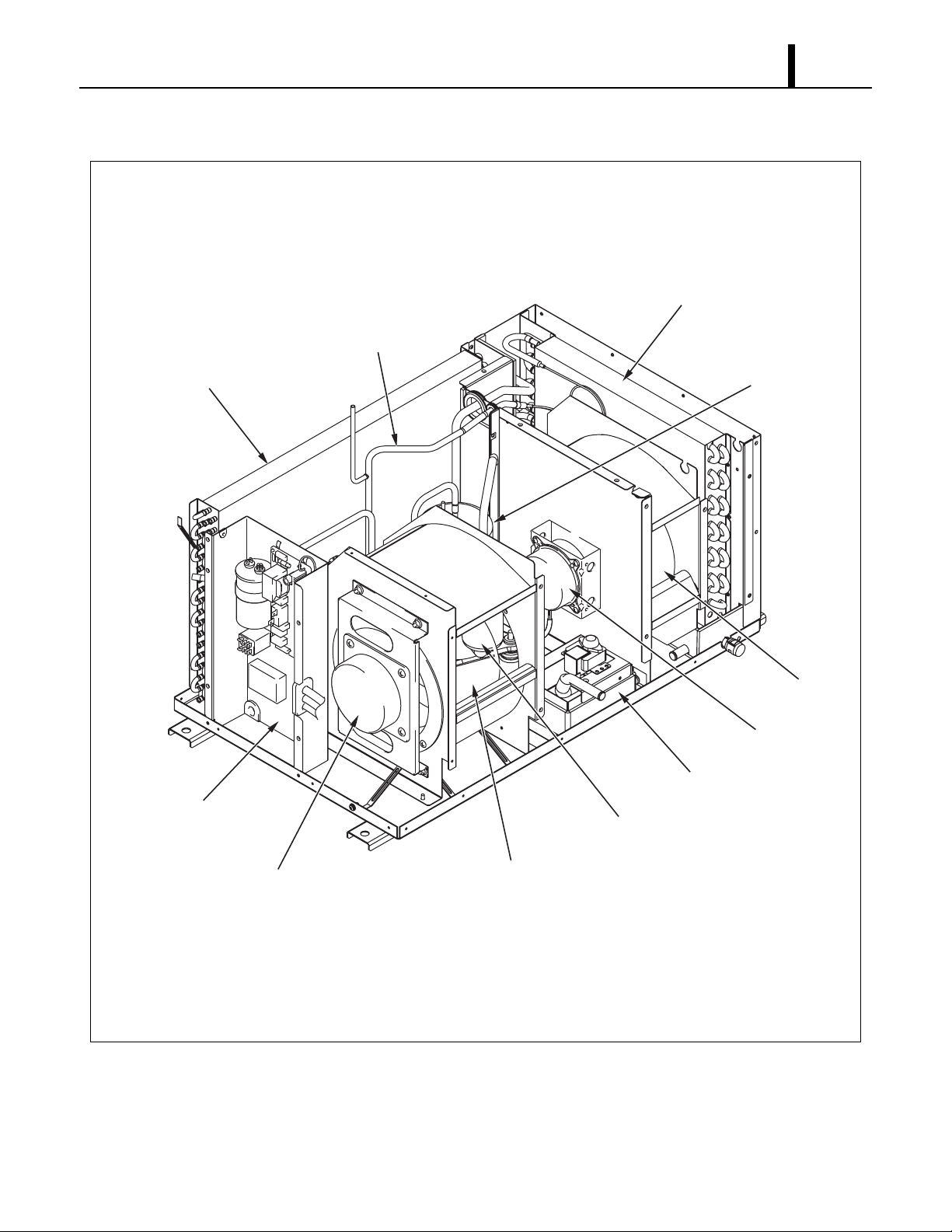
ILL00534-00
Accumulator
Compressor
Connecting Tube
High Pressure Switch
Evaporator
Accumulator
Compressor
Connecting Pipe
Evaporator Inlet Pipe
Condenser
Evaporator
Condenser
Condenser
Outlet Pipe
Condenser
Inlet Pipe
Compressor
Suction Pipe
(Insulated)
Evaporator Outlet PipeAssy
Compressor
Discharge Pipe
Capillary Tube
Fan
Motor
Capillary
Tube
Refrigerant
Flow
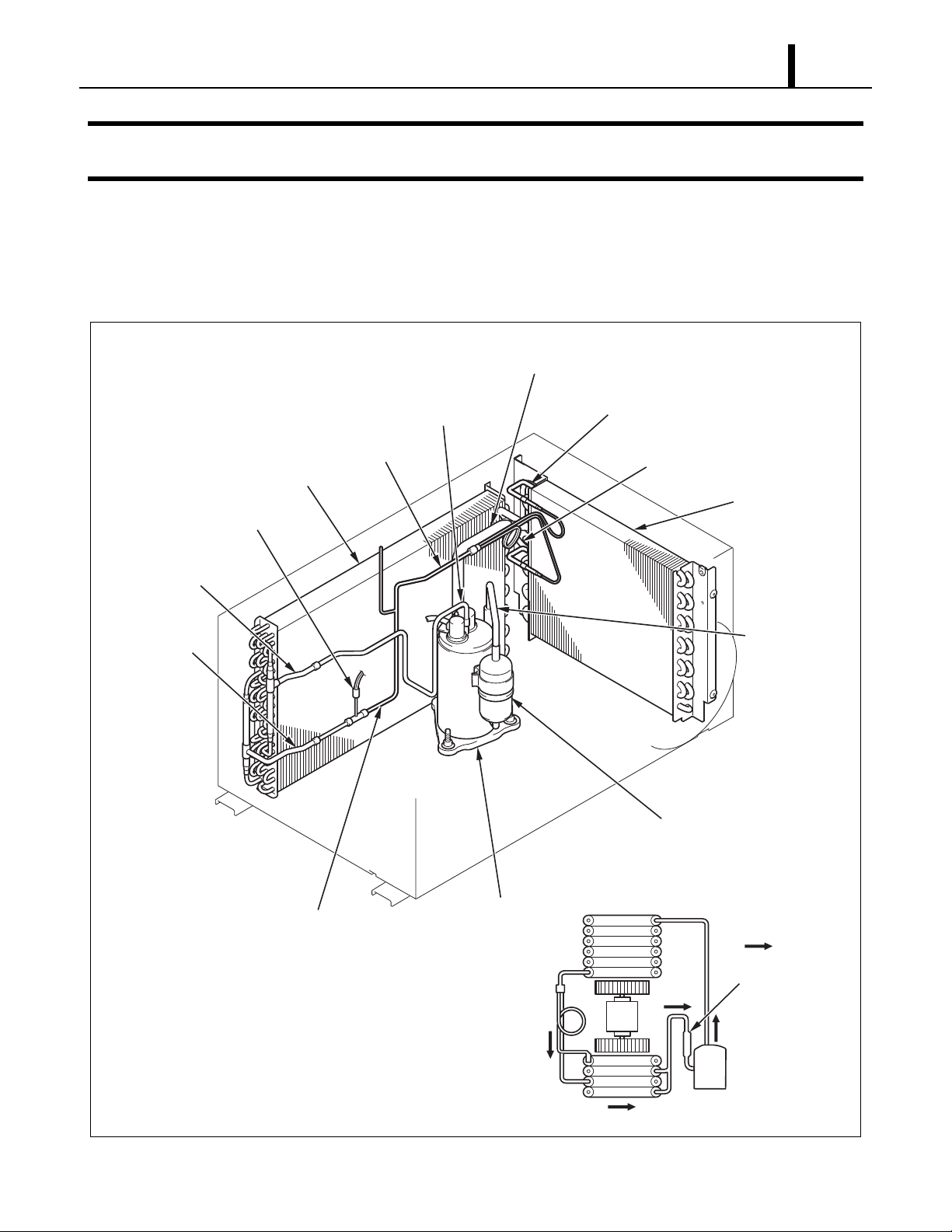
4. REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
4.1 Refrigeration System Construction
The component parts of the refrigeration system include the following:
• Compressor, Evaporator, Condenser, Accumulator, Capillary tube, High pressure switch
These parts are all connected by copper tubing. All the connections have been brazed.
15
16
I002753
I000510
Discharge
Hole
Cylinder
Blade
Spring
Suction
Hole
Discharge
Val ve
Shaft
Roller
Operation Section
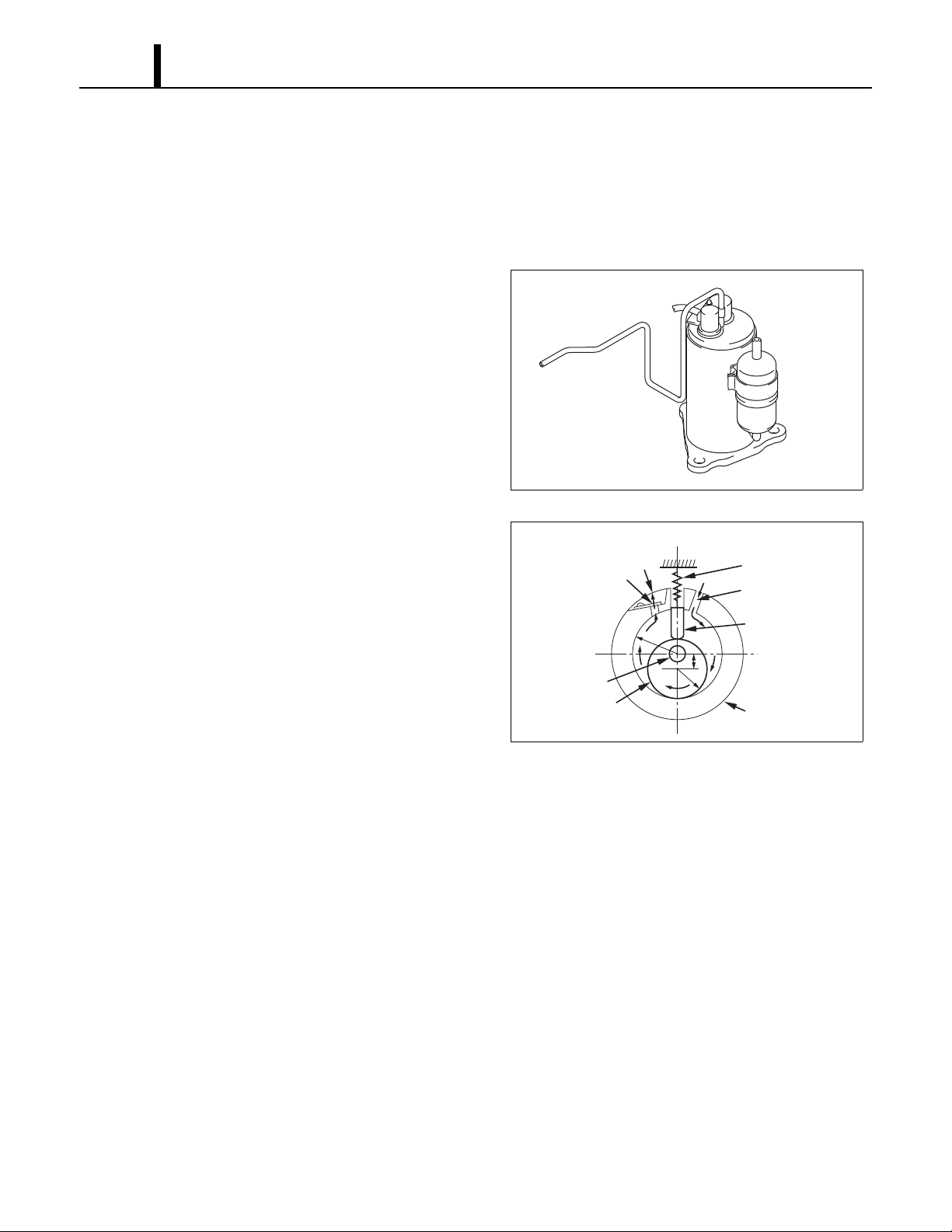
4.2 Compressor
• The compressor used for the unit is hermetically sealed. The compressor and the compressor
motor are in one casing.
(1) Compressor construction
• The construction of a rotary type compressor is
divided into two mechanisms; the drive
mechanism (compressor motor), and the
compression mechanism (compressor). When
the rotor shaft of the motor (drive mechanism)
turns, the roller (compression mechanism)
rotates to compress the refrigerant.
(2) Basic compressor operation
• The roller (compression mechanism) is set
eccentrically with a certain distance given from
the axis of the center of the cylinder. A spring
loaded blade is mounted on the cylinder. The
roller turns to compress the refrigerant in the
space between the cylinder and eccentrically
mounted roller. The blade is in contact with the
roller by means of spring force. The blade
partitions the space between the suction side
and the discharge side to keep compressed refrigerant from returning to the suction side. There
is no suction valve. The discharge valve is designed not to open until the pressure of the
refrigerant within the cylinder reaches or exceeds discharge side pressure. As a result, the
discharge valve prevents the backward flow of refrigerant gas.
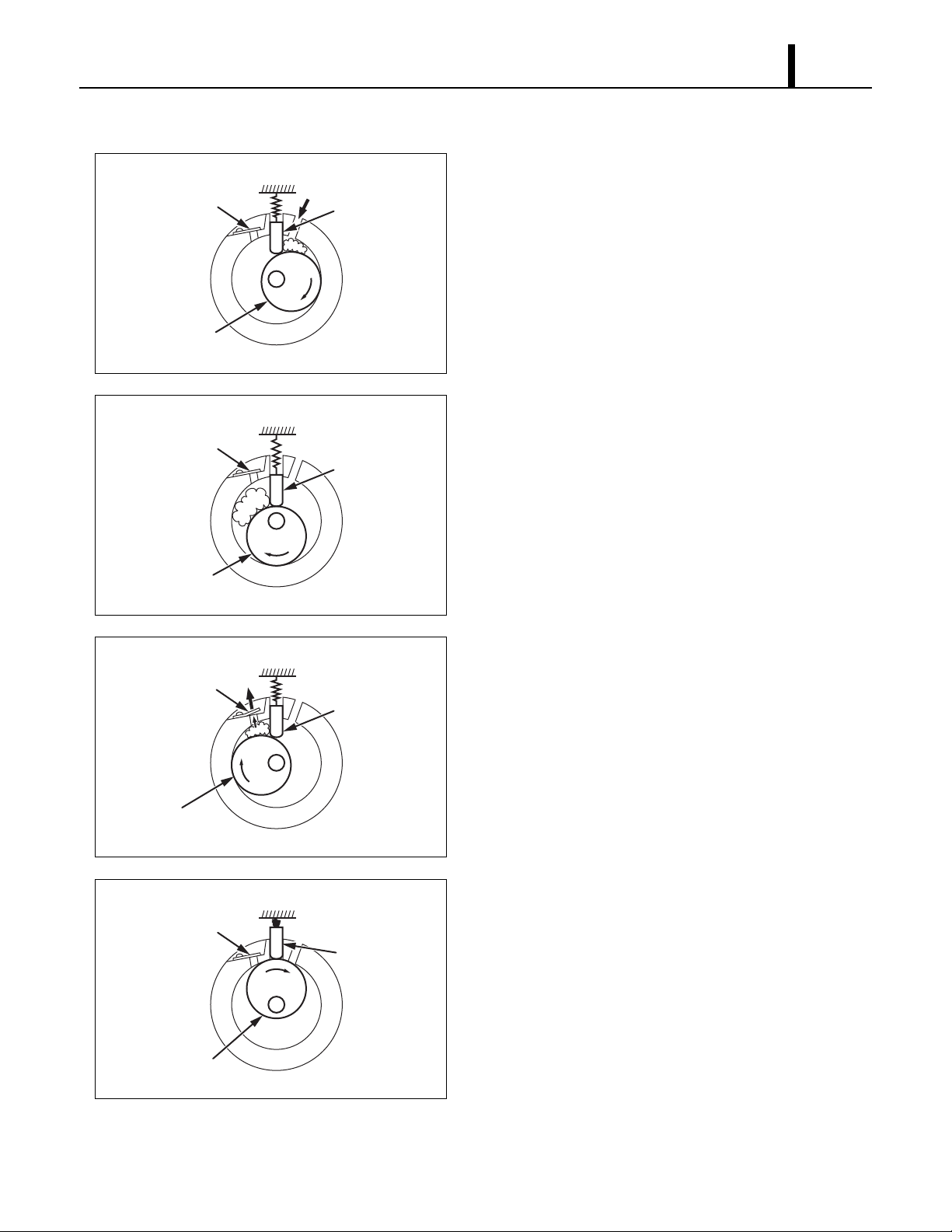
(3) Operation
I001676
Blade
Discharge
Val ve
Roller
I001677
Blade
Discharge
Val ve
Roller
I001678
Blade
Discharge
Val ve
Roller
I001679
Blade
Discharge
Val ve
Roller
Operation Section
17
1) Start of compression
1) The cylinder is filled with low pressure gas.
2) Since pressure in the discharge chamber is higher
than in the cylinder, the discharge valve is kept
closed.
2) Suction and compression
1) The pressure in the cylinder increases gradually.
2) Refrigerant suction begins on the suction side of
the cylinder.
3) The discharge valve remains closed.
3) Discharge
1) The pressure in the cylinder exceeds that in the
discharge chamber, and the discharge valve
opens.
2) On the suction side, refrigerant suction continues.
4) Completion of compression
1) When compression is completed, all of the
refrigerant has been drawn from the suction
chamber.
2) Operation then returns to step 1) (Start of
compression) and the above process of suction
and compression continues repeatedly in
succession.
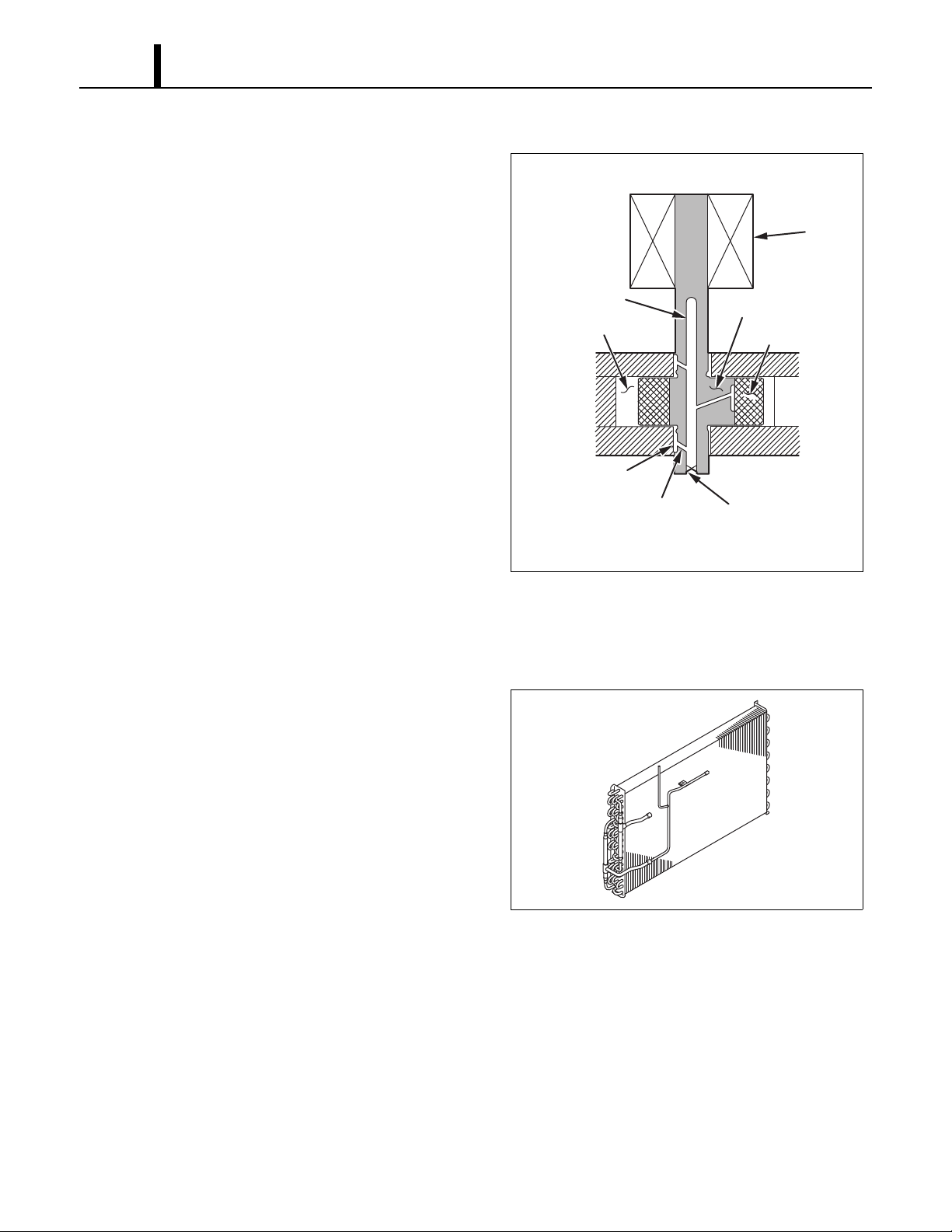
18
I001680
Oil Feed Groove
Oil Hole
Oil Scrapper
Roller
Rotor
Cylinder
Hollow Shaft
Eccentric Shaft
I002754
Operation Section
(4) Compressor lubrication
• The lubrication system is comprised of a
hollow shaft, an oil scraper mounted at the end
face, hollow shaft, a shaft journal (shaft
bearing), and the lubrication groove for the
shaft journal. The lubrication groove is wider
than the oil hole. When the shaft turns, oil is
scraped upward by the oil scraper along the
inside diameter of the hollow shaft. The oil is
fed through the oil hole by centrifugal force,
then supplied to the lubrication groove for each
shaft journal, lubricating the bearing. In this
lubrication system, oil enters into each bearing
separately and returns to the oil reservoir. This
system effectively prevents bearing
temperature increases, and offers high
reliability. In addition, the specially treated
shaft journal keeps the bearing from being damaged during high temperature operation.
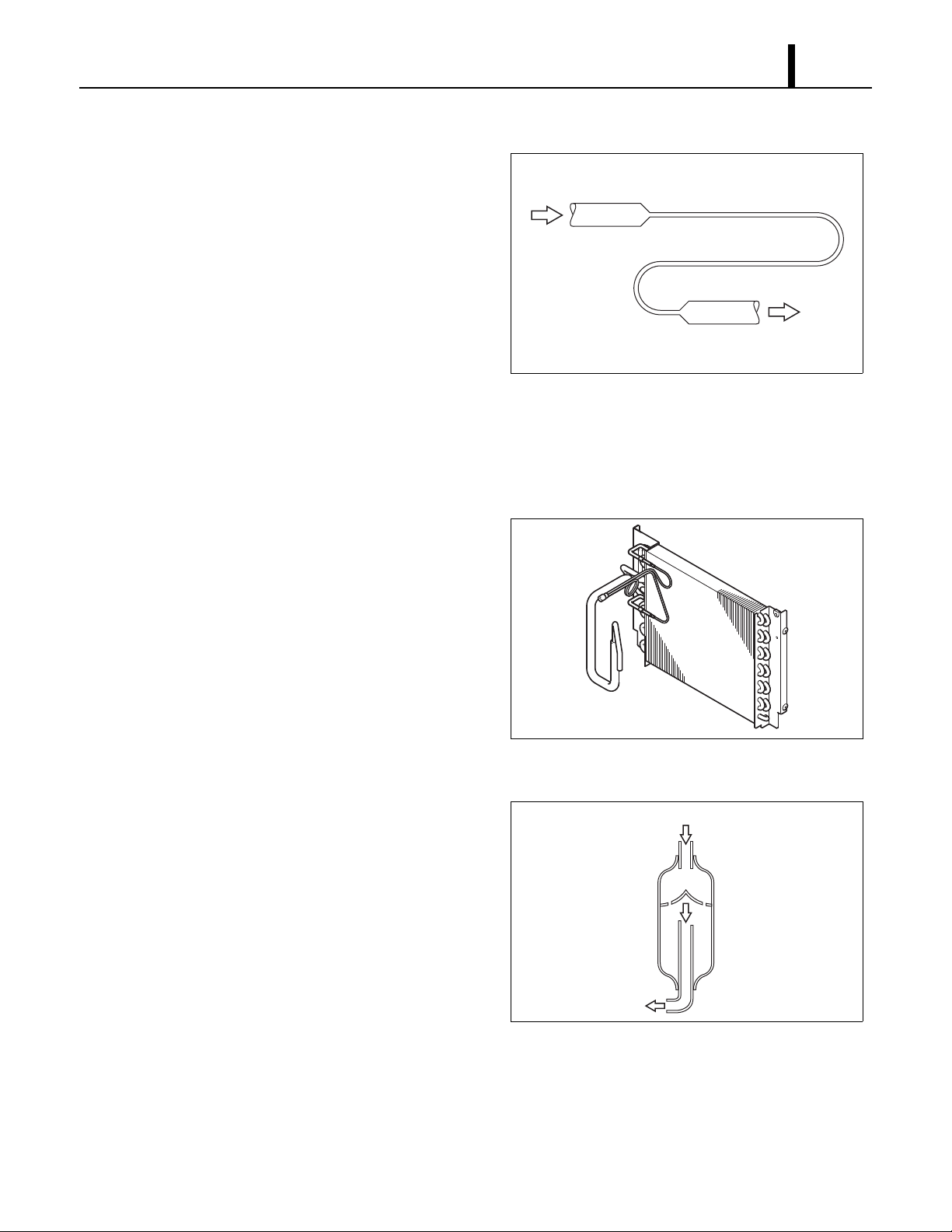
4.3 Condenser
• The condenser is a heat exchanger with
copper tubes that are covered with thin
aluminum projections called plate fins.
• Heat is given off and absorbed by air being
pulled across the condenser fins by the
centrifugal fan and then expelled through the
exhaust air duct.
Operation Section
I001887
High Temp./High Pressure
Liquid Refrigerant
Low Temp./Low Pressure
Gas and Liquid Mixture
ILL00535-00
I000514
From Evaporator
To Compressor
4.4 Capillary Tube
• The capillary tube is a long thin tube utilizing
line flow resistance to serve as an expansion
valve. The length and the inner diameter of the
capillary tube are determined by the capacity of
the refrigeration system, specified operating
conditions, and the amount of refrigerant. The
capillary tube causes the high pressure, high
temperature liquid refrigerant sent from the
condenser to expand rapidly as the refrigerant
is sprayed out through the fixed orifice in the capillary tube. As a result, the temperature and
state of the refrigerant becomes low and mist-like respectively, causing it to evaporate easily.
4.5 Evaporator
19
• The evaporator is a heat exchanger covered
with plate fins. Heat is removed from the air
being pulled across the evaporator by the
centrifugal fan and the resulting cool air is
expelled through the cool air vent.
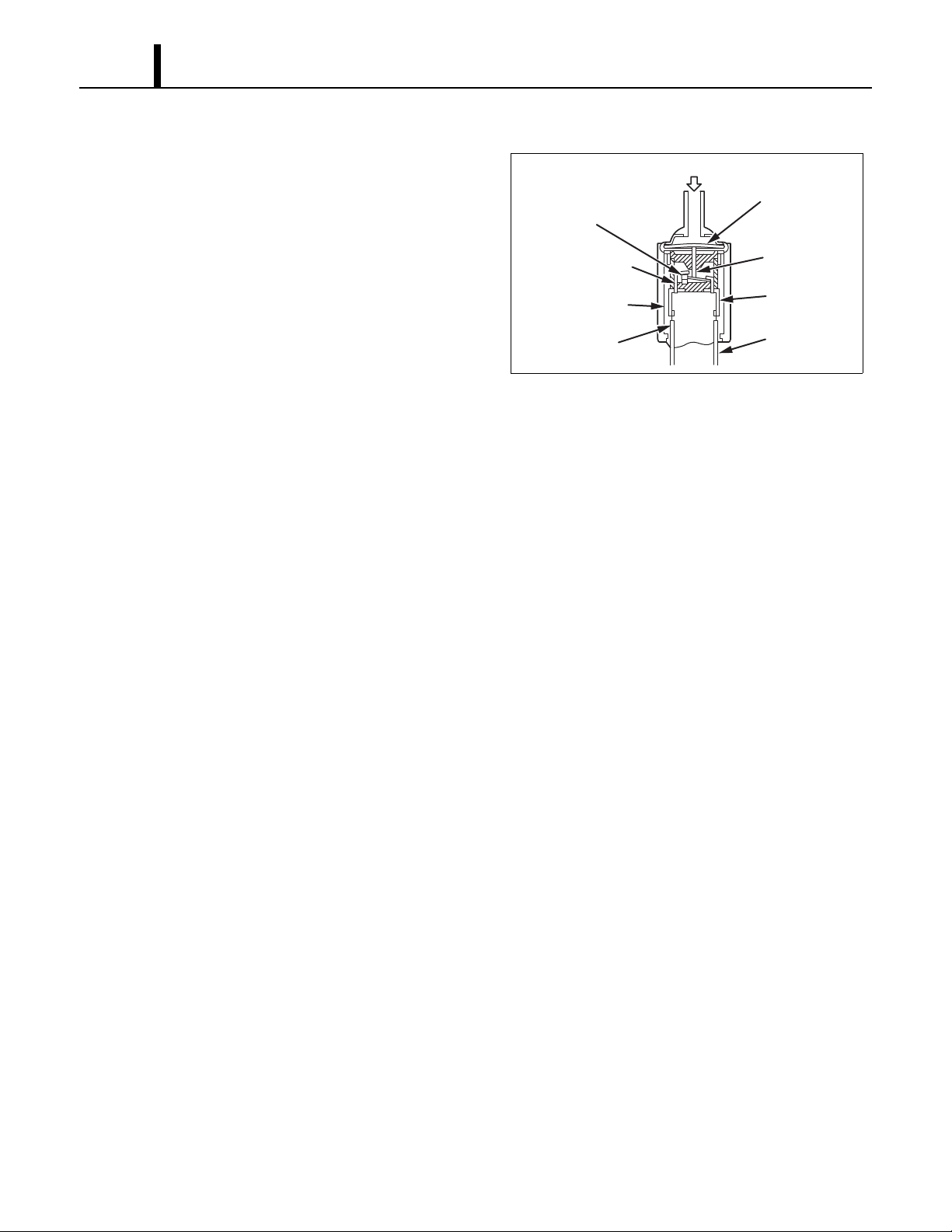
4.6 Accumulator
• The accumulator is mounted on the suction
gas piping between the evaporator and the
compressor. The accumulator separates the
liquid refrigerant from the gas refrigerant,
allowing only the gas refrigerant to enter the
compressor. In the accumulator, suction gas is
led into a cylindrical vessel where the speed of
the gas is decreased. This process separates
the refrigerant contained in the gas by the force
of gravity, causing the refrigerant to accumulate at the bottom of the vessel. As a result, the
compressor is protected from possible damage caused by liquid refrigerant intake.
20
I001768
Pressure of Refrigerant
Movable Point
Snap Disk
Pin
Terminal
Lead Wires
Stationary Point
Molding by Resin
Case
Operation Section
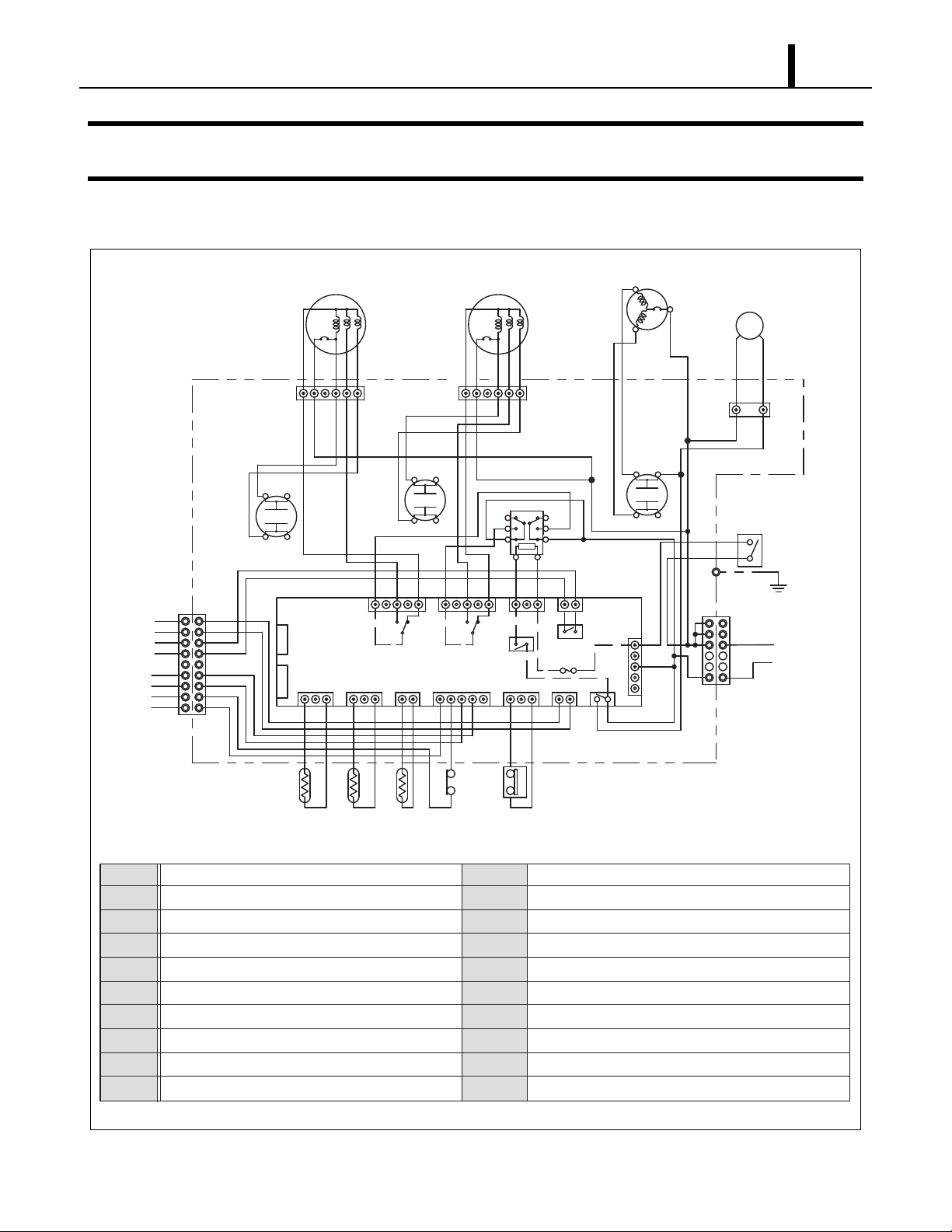
4.7 High-Pressure Switch
• The high-pressure switch prevents the
condenser and compressor from being
damaged by excessive high pressure in the
high-pressure line of the refrigeration cycle.
The switch is normally closed. The snap disk
responds to the variations in pressure and, if
pressure is abnormally high, the snap disk
moves down to push the pin down, causing the
internal contacts to open. This interrupts the
ground signal at the relay board which turns the compressor off.
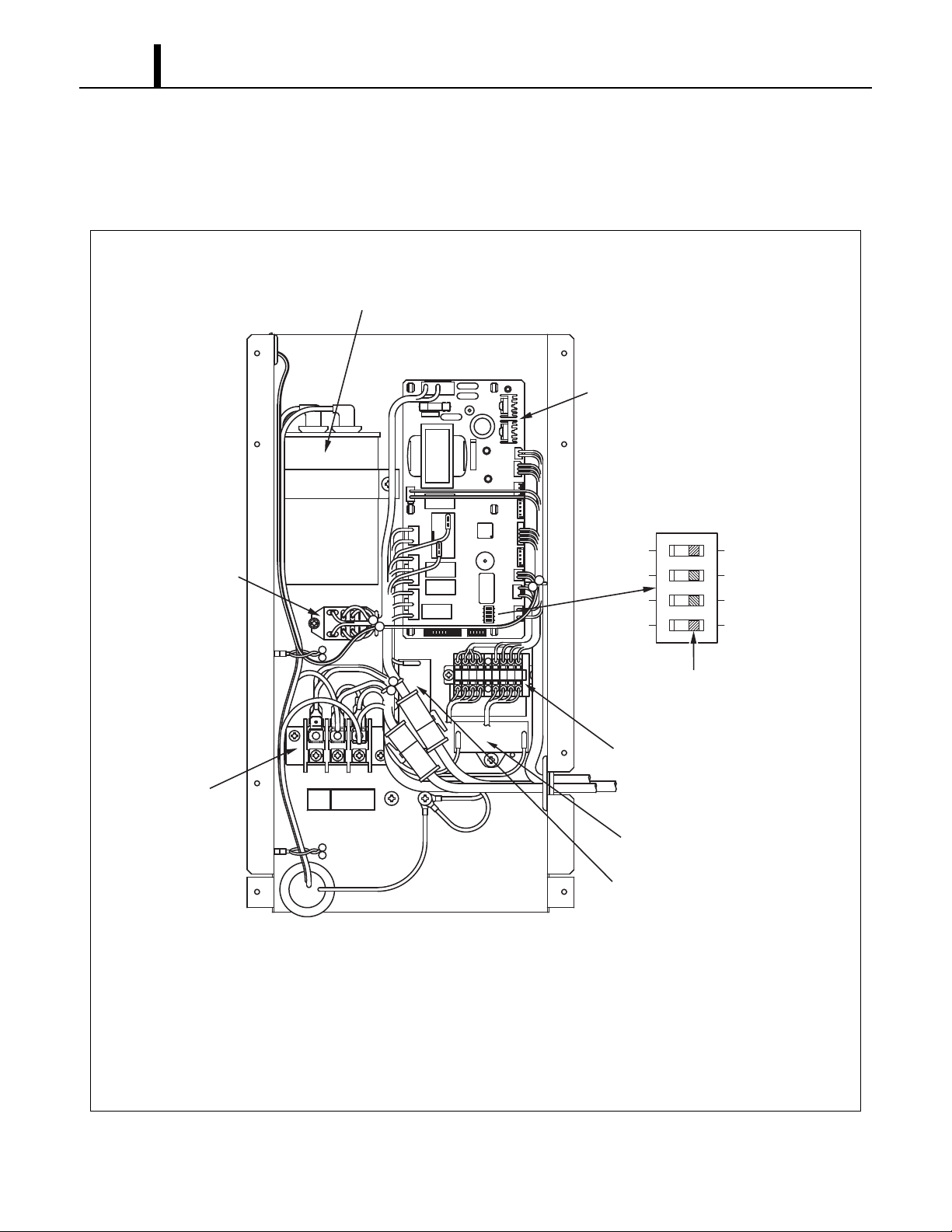
5. ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
TB1
CF1
TB2
CF2RB
CC
IDFM
OLODFM
DPMC
SW
RX
FLTSODS
GCTS
RTS
Capacitor For ODFM (Capacitor For Condenser Fan Motor)
FLTS
RTSCTSODS
CONTROL BOX
Fire Alarm
INPUT
TB2
TB1
EXTERNAL
OUTPUT
AC115 V
GROUND(G)
SW
1PHASE
60Hz
G1
G
Y
RC
IDFM
MC
C
S
R
ODFM
OL
M
DP
1
6
6
CN
1
1
1
2
2
CC
CN
BLACK
WHITE
GRAY
BLUE
RED
BLACK
WHITE
BLUE
RED
GRAY
1
2
CN
1
1
2
2
CF1
1
1
2
2
CF2
RX
78
4
2
1
3
5
6
HPRS
CN16
BROWN
RED
ORANGE
YELLOW
BROWN
BROWN
RED
RED
52ID
1
11
1 2
1
5
4 3
5
5
3
F1
CN22
52OD1
CN23
52OD2
CN21
CN13
RB
R
15
CN15
CN11 CN03
CN12
CN17
CN25
T
R
T
52CM
115V
COM
52CT
CN24
CN01
HPRS High Pressure Switch
ILL00536-01
Terminal Block 1
Terminal Block 2
Relay Board
Indoor Fan Motor (Evaporator Fan Motor)
Outdoor Fan Motor (Condenser Fan Motor)
Compressor Motor
Auxiliary Relay
Outdoor Thermistor (Condenser Inlet Air Thermistor)
Freeze Protection Thermistor
Capacitor For IDFM (Capacitor For Evaporator Fan Motor)
Capacitor For Compressor
Overload Protector
Drain Pump
Switch For Emergency (Override (Stop) Switch)
Float Switch
Ground
Room Thermistor (Evaporator Inlet Air Thermistor)
5.1 Circuit Diagram
Operation Section
21
22
12
ON
34
ILL00956-00
TR
CF1: Capacitor for
Evaporator Fan Motor
CF2: Capacitor for
Condenser Fan Motor
TB2: Terminal Block2
RB: Relay Board
TB1: Terminal Block1
CC: Capacitor for Compressor
4-Position Dipswitch
"OFF" Position
RX: Auxiliary Relay
Operation Section
5.2 Control Box
(1) For unit serial number from 0415XXXXC12 to Present
*
*:Please refer to page 2 for the position of the name plate showing the serial number on the unit.
 Loading...
Loading...