

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table of Contents
1 BOARD OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................... 7
1.1 P
1.2 F
2 HARDWARE DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................. 11
2.1 P
2.2 E
RODUCT INTRODUCTION
EATURES
.................................................................................................................................... 8
ROCESSOR
2.1.1 Core Features ..................................................................................................................... 11
2.1.2 External memory interfaces: .............................................................................................. 12
2.1.3 Interface to external devices .............................................................................................. 13
2.1.4 Advanced Power Management unit ................................................................................... 14
2.1.5 Hardware Accelerators ...................................................................................................... 14
XPANDED CHIP INTRODUCTION
2.2.1 MT41K256M16HA-125:E ................................................................................................... 15
2.2.2 MMPF0100NPAEP .............................................................................................................. 15
............................................................................................................................... 11
............................................................................................................... 7
.................................................................................................... 15
2.2.3 AR8035............................................................................................................................... 15
2.2.4 FE1.1 .................................................................................................................................. 16
2.2.5 SGTL5000 ........................................................................................................................... 16
2.3 E
XPANDED CHIP INTRODUCTION
2.3.1 Power Input Jack ................................................................................................................ 17
2.3.2 LVDS Interface .................................................................................................................... 18
2.3.3 HDMI Interface................................................................................................................... 19
2.3.4 Microphone Input Jack ....................................................................................................... 21
2.3.5 Audio Output Jack .............................................................................................................. 22
2.3.6 SD Card Interface ............................................................................................................... 23
2.3.7 uSD/MMC Card Interface ................................................................................................... 24
2.3.8 CSI Interface ....................................................................................................................... 25
2.3.9 Camera Interface ............................................................................................................... 26
.................................................................................................... 17
Page | 2

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.10 JTAG Interface ................................................................................................................ 28
2.3.11 Mini USB Interface ......................................................................................................... 29
2.3.12 Serial Port ...................................................................................................................... 30
2.3.13 Expansion Port Interface ................................................................................................ 31
2.3.14 Mini USB Interface (OpenSDA) ....................................................................................... 33
2.3.15 RGMII LAN Interface ...................................................................................................... 34
2.3.16 USB HUB Interface ......................................................................................................... 35
2.3.17 Boot Configuration Select .............................................................................................. 36
2.3.18 Reset Switch ................................................................................................................... 38
2.3.19 LEDs ............................................................................................................................... 39
3 GETTING STARTED ......................................................................................................................... 40
3.1 S
3.2 L
OFTWARE FEATURES
INUX SYSTEM
............................................................................................................................ 40
................................................................................................................... 40
3.3 A
3.4 S
4 DOWNLOADING AND RUNNING THE SYSTEM .............................................................................. 43
4.1 D
4.2 D
5 MAKING IMAGES ........................................................................................................................... 48
5.1 M
5.2 M
NDROID SYSTEM
ETTING UP TERMINAL EMULATION
OWNLOAD AND RUN LINUX OR ANDROID SYSTEM
ISPLAY MODE CONFIGURATIONS FOR LINUX & ANDROID SYSTEMS
AKING IMAGES FOR LINUX
5.1.1 Getting Tools and Source Code .......................................................................................... 48
5.1.2 Compiling System Images .................................................................................................. 48
AKING IMAGES FOR AN ANDROID SYSTEM
5.2.1 Getting Repo Source Code ................................................................................................. 49
5.2.2 Compiling System Images .................................................................................................. 50
....................................................................................................................... 41
................................................................................................ 42
........................................................................... 43
..................................................... 46
......................................................................................................... 48
..................................................................................... 49
6 ESD PRECAUTIONS AND PROPER HANDLING PROCEDURES......................................................... 52
Page | 3

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 7
Figure 1-2 RIoTboard top view ......................................................................................................... 8
Figure 1-3 RIoTboard bottom view .................................................................................................. 9
Figure 2-1 Block Diagram of i.MX 6Solo......................................................................................... 12
Figure 2-2 Power Interface............................................................................................................. 17
Figure 2-3 LVDS Interface ............................................................................................................... 18
Figure 2-4 HDMI Interface ............................................................................................................. 19
Figure 2-5 MIC Input ...................................................................................................................... 21
Figure 2-6 Audio Output Jack ......................................................................................................... 22
Figure 2-7 SD Card Interface .......................................................................................................... 23
Figure 2-8 uSD/MMC Card Interface .............................................................................................. 24
Figure 2-9 CSI Interface .................................................................................................................. 25
Figure 2-10 Camera Interface ........................................................................................................ 26
Figure 2-11 JTAG Interface ............................................................................................................. 28
Figure 2-12 Mini USB Interface ...................................................................................................... 29
Figure 2-13 Serial Port ................................................................................................................... 30
Figure 2-14 Expansion Port ............................................................................................................ 31
Figure 2-15 Mini USB (OpenSDA)Interface ..................................................................................... 33
Figure 2-16 RGMII LAN Interface ................................................................................................... 34
Figure 2-17 USB Host Interface ...................................................................................................... 35
Figure 2-18 Boot Configuration Select ........................................................................................... 36
Figure 2-19 Reset Switch ................................................................................................................ 38
Figure 2-20 LEDs ............................................................................................................................ 39
Page | 4

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Figure 3-1 COM Properties ............................................................................................................. 42
Figure 4-1 Boot Configuration Switch ............................................................................................ 43
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2-1 Power Interface .............................................................................................................. 17
Table 2-2 LVDS Interface ................................................................................................................ 18
Table 2-3 HDMI Interface ............................................................................................................... 19
Table 2-4 MIC Input Jack ................................................................................................................ 21
Table 2-5 Audio Output Jack .......................................................................................................... 22
Table 2-6 SD Card Interface ........................................................................................................... 23
Table 2-7 uSD/MMC Card Interface ............................................................................................... 24
Table 2-8 CSI Interface ................................................................................................................... 25
Table 2-9 Camera Interface ........................................................................................................... 27
Table 2-10 JTAG Interface .............................................................................................................. 28
Table 2-11 Mini USB Interface ....................................................................................................... 29
Table 2-12 Serial Port ..................................................................................................................... 30
Table 2-13 Expansion Port Interface .............................................................................................. 31
Table 2-14 Mini USB (OpenSDA) Interface ..................................................................................... 33
Table 2-15 RGMII LAN interface ..................................................................................................... 34
Table 2-16 USB Host Interface ....................................................................................................... 35
Table 2-17 Boot Configuration Select ............................................................................................ 37
Table 2-18 Reset Switch ................................................................................................................. 38
Table 2-19 LEDs .............................................................................................................................. 39
Table 3-1 OS and Drivers ................................................................................................................ 40
Table 3-2 Images Required by Linux ............................................................................................... 40
Page | 5

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 3-3 Storage Partitions for Linux ............................................................................................ 41
Table 3-4 Images Required by Android .......................................................................................... 41
Table 3-5 Storage Partitions for Android........................................................................................ 41
Table 4-1 Boot Switch Configuration – Serial Download ................................................................ 43
Table 4-2 Boot Switch Configuration - eMMC ................................................................................ 46
Table 4-3 Boot Switch Configuration – SD ..................................................................................... 46
Table 5-1 Images and Directories .................................................................................................. 51
Page | 6
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
1 Board Overview
1.1 Product Introduction
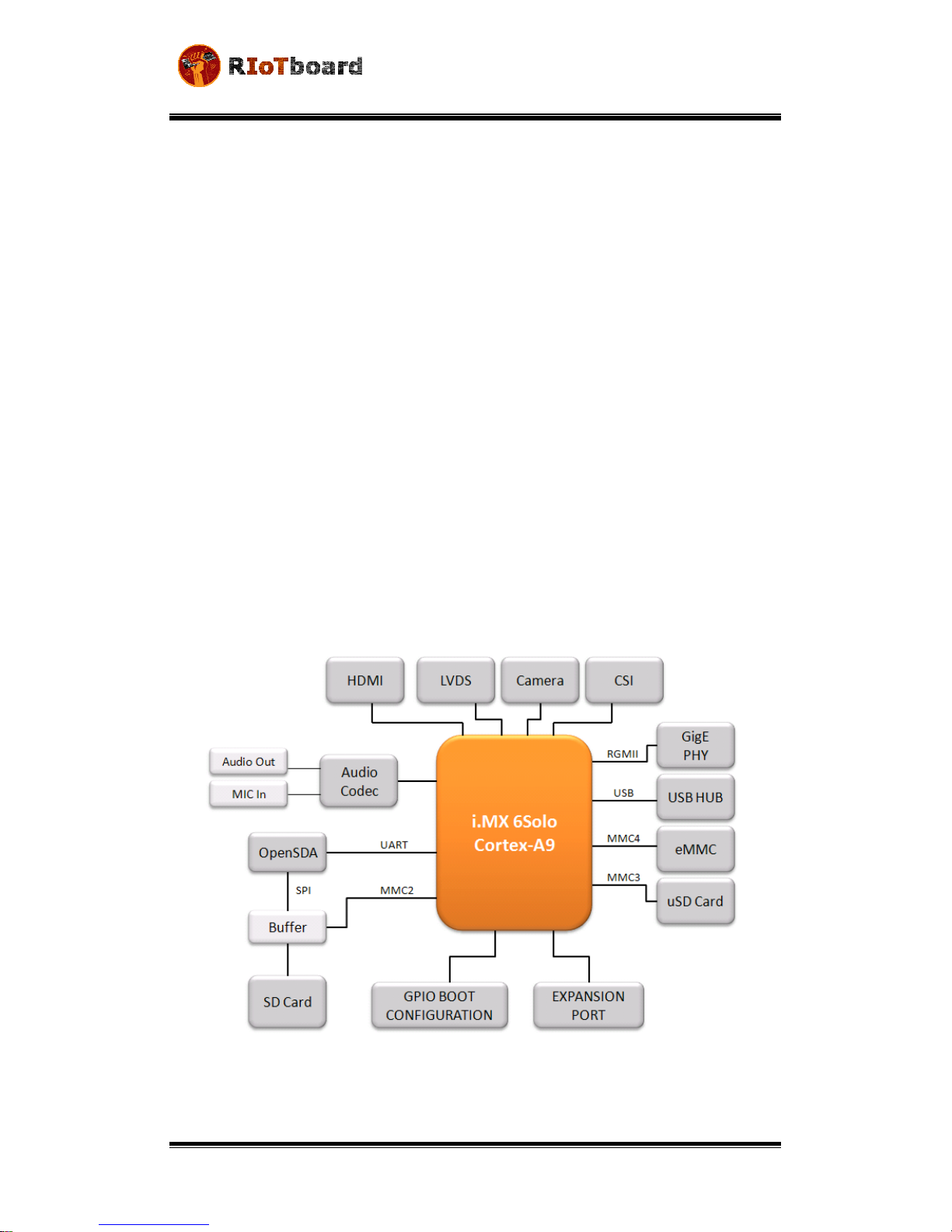
The RIoTboard is an evaluation platform featuring the powerful i.MX 6Solo, a
multimedia application processor with ARM Cortex-A9 core at 1 GHz from Freescale
Semiconductor. The platform helps evaluate the rich set of peripherals and includes
a 10/100/Gb Ethernet port, HDMI v1.4, LVDS, analog headphone/microphone, uSD
and SD card interface, USB, serial port, JTAG, 2 camera interfaces, GPIO boot
configuration interface, and expansion port, as shown in Figure 1-1.
The RIoTboard can be used in the following applications:
• Netbooks (web tablets)
• Nettops (Internet desktop devices)
• High-end mobile Internet devices (MID)
• High-end PDAs
• High-end portable media players (PMP) with HD video capability
• Portable navigation devices (PNDs)
• Industrial control and Test and measurement (T&M)
• Single board computers (SBCs)
Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram
Page | 7
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
1.2 Features
The RIoTboard is based on the i.MX 6Solo processor from Freescale Semiconductor
integrating all the functionalities of this multimedia application processor with the
following features:
• Mechanical Parameters
o Working Temperature: 0°C - 50°C
o Humidity Range: 20% - 90%
o Dimensions: 120mm x 75mm
o Input Voltage: +5V
• Processor
o ARM Cortex A9 MPCore™ Processor at 1 GHz
o High-performing video processing unit which covers SD-level and HD-
level video decoders and SD-level encoders as a multi-standard video
codec engine
o An OpenGL® ES 2.0 3D graphics accelerator with a shader and a 2D
graphics accelerator for superior 3D, 2D, and user interface
acceleration
• Memories
o 1GByte of 16-bit wide DDR3 @ 800MHz
o 4GB eMMC
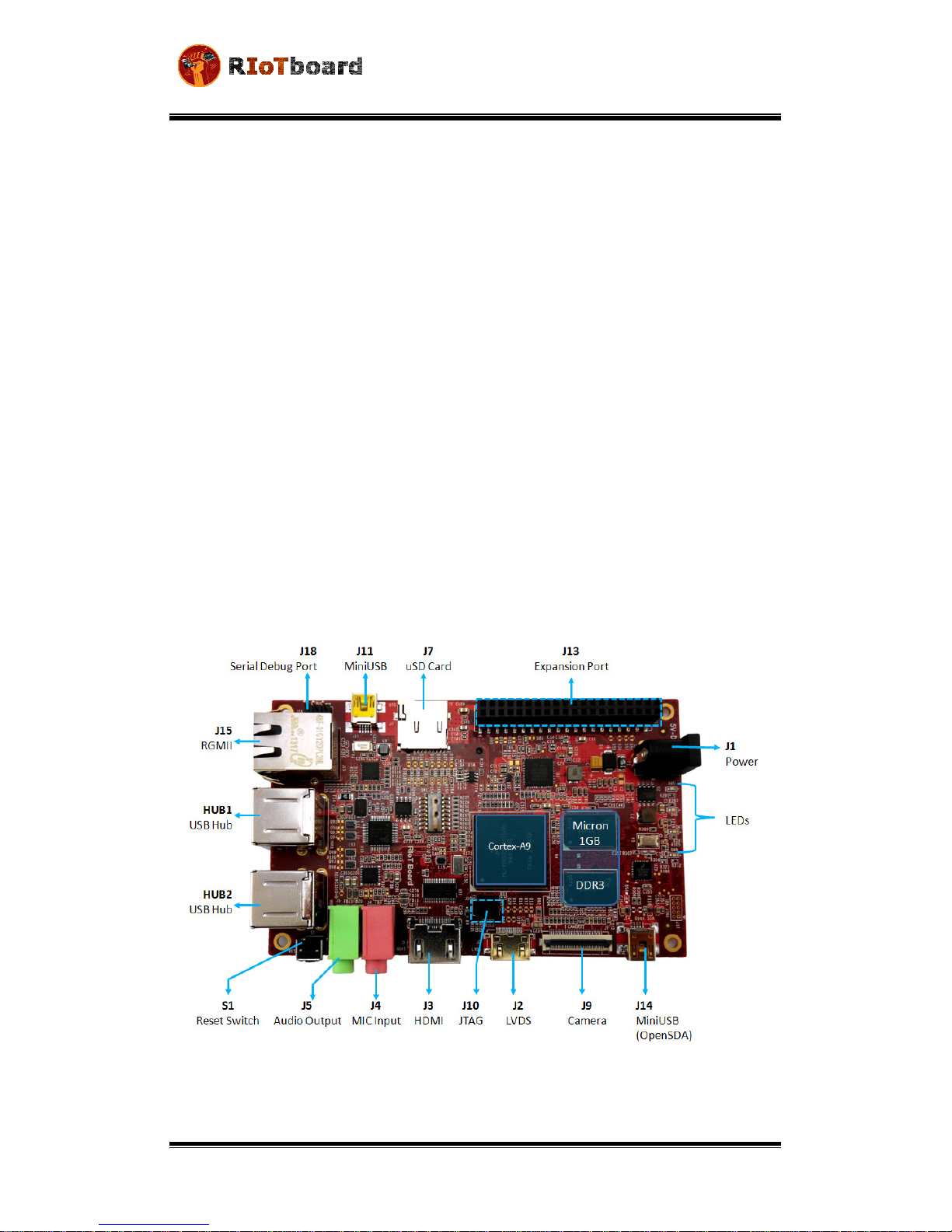
Figure 1-2 RIoTboard top view
Page | 8
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
• Media Interfaces
o Analog headphone/microphone, 3.5mm audio jack
o LVDS interface
o HDMI interface
o Parallel RGB interface(Expansion port)
o Camera interface (Support CCD or CMOS camera)
o MIPI lanes at 1 Gbps
Figure 1-3 RIoTboard bottom view
• Data Transfer Interfaces
o Debug Ports:
3 pin TTL level
o Serial Ports:
UART3,4,5, 3 line serial port, TTL Logic (Expansion port)
o USB Ports:
1 x USB2.0 OTG, mini USB, high-speed, 480Mbps
4 x USB2.0 HOST, Type A, high-speed, 480Mbps
o uSD card interface
o SD card interface
o 10M/100M/Gb Ethernet Interface (RJ45 jack)
Page | 9

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
o 2 channel I2C interface (Expansion port)
o 2 channel SPI interface (Expansion port)
o 3 channel PWM interface (Expansion port)
o GPIO (Expansion port)
o 10-pin JTAG interface
o Open SDA
• Others
o 1 Power LED
o 1 Open SDA LED
o 2 User-defined LEDs
o 1 DC Jack
o 1 Reset button
o Boot configuration interface
Page | 10

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2 Hardware Description
2.1 Processor
The i.MX 6Solo processor represents Freescale Semiconductor’s latest achievement in
integrated multimedia applications processors, which are part of a growing family of
multimedia-focused products that offer high performance processing and are
optimized for lowest power consumption.
The processor features Freescale’s advanced implementation of the single ARM™
Cortex-A9 core, which operates at speeds up to 1 GHz. It includes 2D and 3D graphics
processors, 3D 1080p video processing, and integrated power management. The
processor provides a 16/32-bit DDR3/LVDDR3-800 memory interface and a number of
other interfaces for connecting peripherals, such as WLAN, Bluetooth™, GPS, hard drive,
displays, and camera sensors.
2.1.1 Core Features
The i.MX 6Solo processor is based on the ARM Cortex A9 MPCore™ platform with the
following features:
• ARM Cortex A9 MPCore™ CPU Processor (with TrustZone)
• The core configuration is symmetric, where the core includes:
o 32 KByte L1 Instruction Cache
o 32 KByte L1 Data Cache
o Private Timer and Watchdog
o Cortex-A9 NEON MPE (Media Processing Engine) Co-processor
• The ARM Cortex A9 MPCore™ complex includes:
o General Interrupt Controller (GIC) with 128 interrupt support
o Global Timer
o Snoop Control Unit (SCU)
o 512 KB unified I/D L2 cache
o Two Master AXI (64-bit) bus interfaces output of L2 cache
o NEON MPE coprocessor
SIMD Media Processing Architecture
NEON register file with 32x64-bit general-purpose registers
NEON Integer execute pipeline (ALU, Shift, MAC)
NEON dual, single-precision floating point execute pipeline
(FADD, FMUL)
NEON load/store and permute pipeline
• The memory system consists of the following components:
o Level 1 Cache--32 KB Instruction, 32 KB Data cache per core
Page | 11
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
o Level 2 Cache--Unified instruction and data (512 KByte)
o On-Chip Memory:
Boot ROM, including HAB (96 KB)
Internal multimedia / shared, fast access RAM (OCRAM, 128 KB)
Secure/non-secure RAM (16 KB)
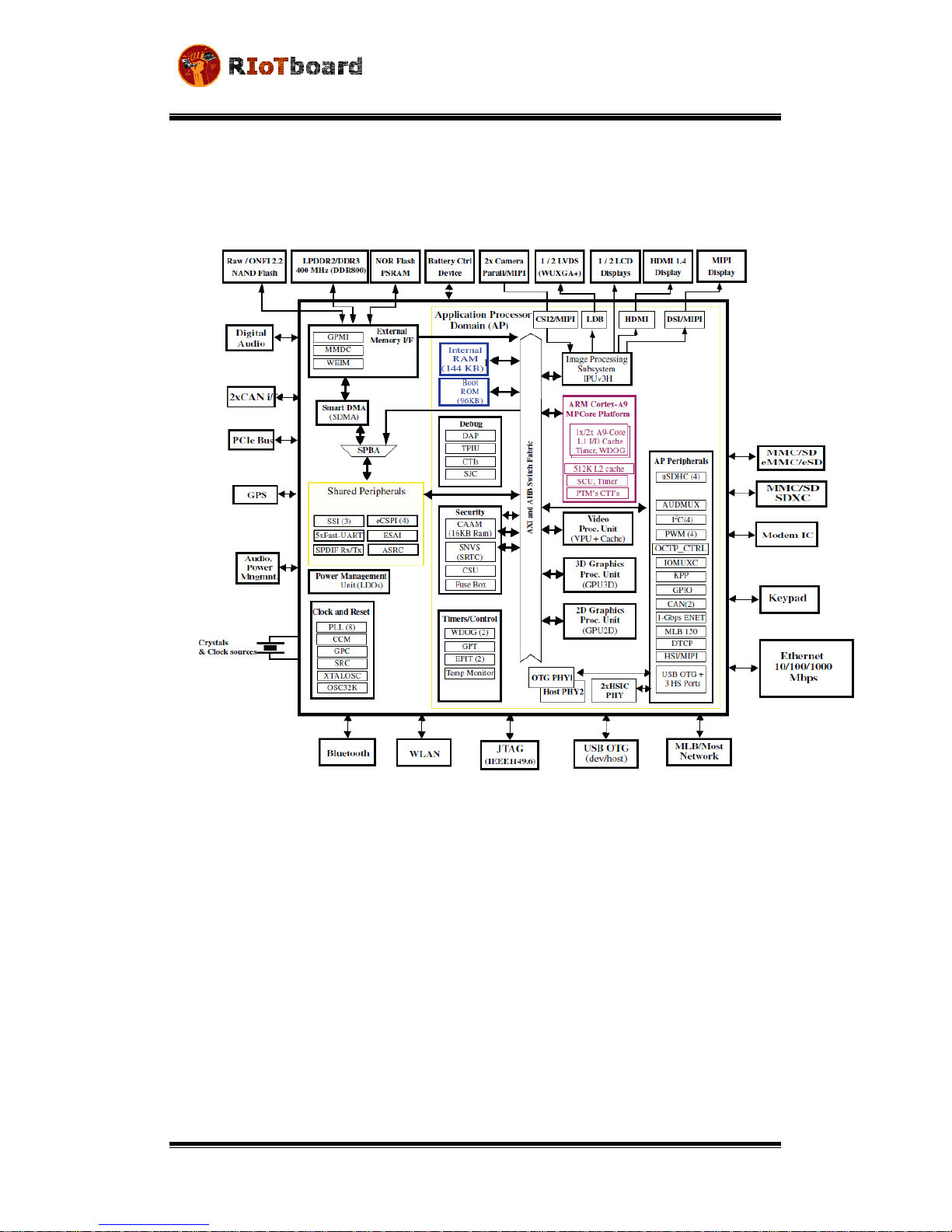
2.1.2 External memory interfaces:
• 16/32-bit LP-DDR2-800, 16/32-bit DDR3-800 and LV-DDR3-800.
• 8-bit NAND-Flash, including support for Raw MLC/SLC, 2 KB, 4 KB, and 8 KB
page size, BA-NAND, PBA-NAND, LBA-NAND, OneNAND™ and others. BCH ECC
up to 40 bit.
• 16/32-bit NOR Flash. All WEIMv2 pin are muxed on other interfaces.
• 16/32-bit PSRAM, Cellular RAM
Figure 2-1
Block Diagram of i.MX 6Solo
Page | 12

2.1.3 Interface to external devices
Each i.MX 6Solo processor enables the following interfaces to external devices
(some of them are muxed and not available simultaneously):
• Displays--Total five interfaces available. Total raw pixel rate of all interfaces is
up to 450 Mpixels/sec, 24 bpp. Up to two interfaces may be active in parallel.
o One Parallel 24-bit display port, up to 225 Mpixes/sec (for example,
WUXGA at 60 Hz or dual HD1080 and WXGA at 60 Hz)
o LVDS serial ports:One port up to 165 Mpixels/sec or two ports up to
85 MP/sec (for example, WUXGA at 60 Hz) each
o HDMI 1.4 port
o MIPI/DSI, two lanes at 1 Gbps
o EPDC, Color, and monochrome E-INK, up to 1650x2332 resolution and
5-bit grayscale
• Camera sensors:
o Two parallel Camera ports (up to 20 bit and up to 240 MHz peak)
o MIPI CSI-2 serial camera port, supporting from 80 Mbps to 1 Gbps
speed per data lane. The CSI-2 Receiver core can manage one clock
lane and up to two data lanes. Each i.MX 6Solo processor has two
lanes.
• Expansion cards:
o Four MMC/SD/SDIO card ports all supporting:
1-bit or 4-bit transfer mode specifications for SD and SDIO
cards up to UHS-I SDR-104 mode (104 MB/s max)
1-bit, 4-bit, or 8-bit transfer mode specifications for MMC cards
up to 52 MHz in both SDR and DDR modes (104 MB/s max)
• USB
o One high speed (HS) USB 2.0 OTG (Up to 480 Mbps), with integrated HS
USB PHY
o Three USB 2.0 (480 Mbps) hosts
One HS host with integrated High Speed PHY
Two HS hosts with integrated HS-IC USB (High Speed Inter-Chip
USB) PHY
• Expansion PCI Express port (PCIe) v2.0 one lane
o PCI Express (Gen 2.0) dual mode complex, supporting Root complex
operations and Endpoint operations. Uses x1 PHY configuration.
• Miscellaneous IPs and interfaces:
o Three I2S/SSI/AC97,up to 1.4 Mbps each
o Enhanced Serial Audio Interface ESAI), up to 1.4 Mbps per channel
o Five UARTs, up to 4.0 Mbps each
Providing RS232 interface
Supporting 9-bit RS485 multidrop mode
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Page | 13

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
One of the five UARTs (UART1) supports 8-wire while the other
four support 4-wire. This is due to the SoC IOMUX limitation,
since all UART IPs are identical
o Four eCSPI (Enhanced CSI)
o Four I2C, supporting 400 kbps
o Gigabit Ethernet Controller(IEEE1588 compliant), 10/100/1000 Mbps
o Four Pulse Width Modulators (PWM)
o System JTAG Controller (SJC)
o GPIO with interrupt capabilities
o 8x8 Key Pad Port (KPP)
o Sony Philips Digital Interface (SPDIF), Rx and Tx
o Two Controller Area Network (FlexCAN), 1 Mbps each
o Two Watchdog timers (WDOG)
o Audio MUX (AUDMUX)
o MLB (MediaLB) provides interface to MOST Networks (MOST25, MOST50,
MOST150) with the option of DTCP cipher accelerator
2.1.4 Advanced Power Management unit
The i.MX 6Solo processors integrate advanced power management unit and
controllers:
• Provide PMU, including LDO supplies, for on-chip resources
• Use Temperature Sensor for monitoring the die temperature
• Support DVFS techniques for low power modes
• Use SW State Retention and Power Gating for ARM and MPE
• Support various levels of system power modes
• Use flexible clock gating control scheme
2.1.5 Hardware Accelerators
The i.MX 6Solo processor uses dedicated hardware accelerators to meet the targeted
multimedia performance. The use of hardware accelerators is a key factor in obtaining
high performance at low power consumption numbers, while having the CPU core
relatively free for performing other tasks.
The i.MX 6Solo processor incorporates the following hardware accelerators:
• VPU--Video Processing Unit
• IPUv3H--Image Processing Unit version 3H
• GPU3Dv5--3D Graphics Processing Unit (OpenGL ES 2.0) version 5
• GPU2Dv2--2D Graphics Processing Unit (BitBlt)
• ASRC--Asynchronous Sample Rate Converter
Page | 14

Security functions are enabled and accelerated by the following hardware:
• ARM TrustZone including the TZ architecture (separation of interrupts, memory
mapping, etc.)
• SJC--System JTAG Controller. Protecting JTAG from debug port attacks by
regulating or blocking the access to the system debug features.
• CAAM--Cryptographic Acceleration and Assurance Module, containing
cryptographic and hash engines, 16 KB secure RAM and True and Pseudo
Random Number Generator (NIST certified)
• SNVS--Secure Non-Volatile Storage, including Secure Real Time Clock
• CSU--Central Security Unit. Enhancement for the IC Identification Module (IIM).
Will be configured during boot and by eFUSEs and will determine the security
level operation mode as well as the TZ policy.
• A-HAB Advanced High Assurance Boot--Hv4 with the new embedded
enhancements:SHA-256, 2048-bit RSA key, version control mechanism, warm
boot, CSU, and TZ initialization.
2.2 Expanded Chip Introduction
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.2.1 MT41K256M16HA-125:E
The board has 1GB of SDRAM (2x512MB). Micron’s MT41K256M16 is a 512MB DDR3
Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited for the main memory applications which require
large memory density and high bandwidth.
2.2.2 MMPF0100NPAEP
The PF0100 Power Management Integrated Circuit (PMIC) provides a highly
programmable/ configurable architecture, with fully integrated power devices and
minimal external components. With up to six buck converters, six linear regulators, RTC
supply, and coin-cell charger, the PF0100 can provide power for a complete system,
including applications processors, memory, and system peripherals, in a wide range of
applications. With on-chip One Time Programmable (OTP) memory, the PF0100 is
available in pre-programmed standard versions, or non-programmed to support
custom programming. The PF0100 is defined to power the entire embedded MCU
platform solution similar to i.MX6 based eReader, IPTV, medical monitoring and
home/factory automation.
2.2.3 AR8035
AR8035 is a single port 10/100/1000 Mbps tri-speed Ethernet PHY feaured with low
power and low cost. AR8035 supports MAC.TM RGMII interface and IEEE 802.3az-2010,
Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) standard through proprietary SmartEEE technology,
improving energy efficiency in systems using legacy MAC devices without 802.3az
Page | 15

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
support. The RIOT Board can be connected to a network hub directly through a cable. It
also can be directly connected with a computer through a crossover cable which is
provided with the kit.
2.2.4 FE1.1
FE1.1 is a USB 2.0 high-speed 4-port hub solution. It uses USB3320 to provide 4
extended USB interface with support for high-speed (480MHz), full-speed (2MHz) and
low-speed (1.5MHz) mode.
2.2.5 SGTL5000
The SGTL5000 is a low power stereo Codec with Headphone Amp from Freescale, and is
designed to provide a complete audio solution for portable products needing line-in,
mic-in, line-out, headphone-out, and digital I/O. Deriving its architecture from best-inclass Freescale-integrated products currently on the market, the SGTL5000 is able to
achieve ultra low-power with very high performance and functionality, all in one of the
smallest footprints available.
Designed with features such as capless headphone and an integrated PLL to allow clock
reuse within the system, it helps customers achieve a lower overall system cost.
Page | 16
J1
Pin Signal
Function
1 GND GND
2 NC NC
3 +5V Power supply (+5V)
4
A (Type)
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3 Expanded Chip Introduction
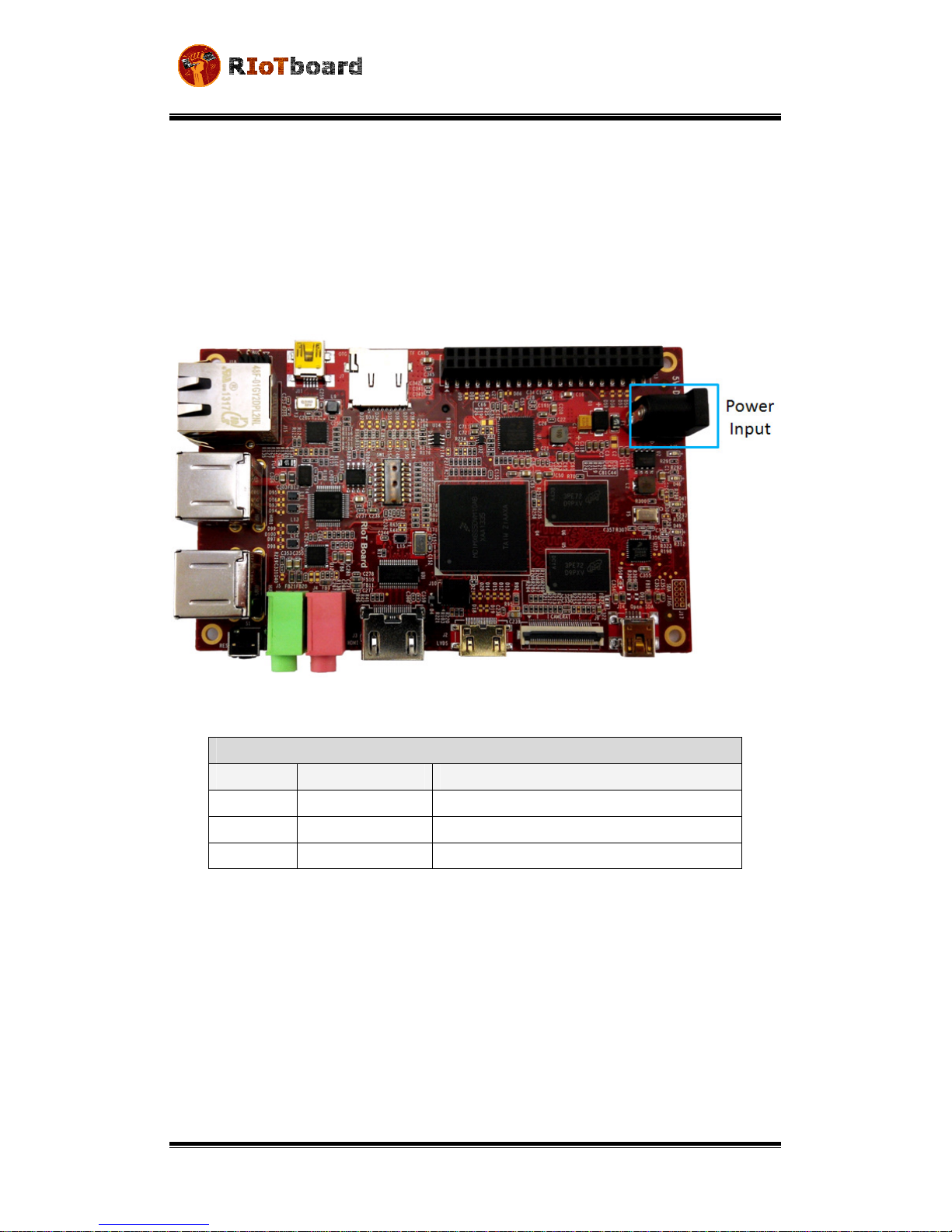
2.3.1 Power Input Jack
A 5V/4A AC-to-DC power supply needs to be plugged into the Power Jack (J1) on the
board. It is not recommended to use a higher voltage since possible damage to the
board may result due to failure of the protection circuitry.
Figure 2-2
Table 2-1
Power Interface
Power Interface
Page | 17

J2
Pin Signal
Function
1 3V3 +
3.3V
2 LV
DS_TX2_P
LVDS
data2+
3 LVDS_TX2_N
LVDS
data2-
4 GND GND
5 LVDS_TX1_P
LVDS
data1+
6 LVDS_TX1_N
LVDS
data1-
7 GND GND
8 LVDS_TX0_P
LVDS
data0+
9 LVDS_TX0_
N LVDS
data-
10 GND GND
11 LVDS_CLK_P
LVDS
CLK+
12 LVDS_CLK_
N LVDS
CLK-
2.3.2 LVDS Interface
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Figure 2-3
LVDS Interface
The LVDS Interface supports LVDS8000-97C designed by Embest.
Table 2-2 LVDS Interface
Page | 18

13 LCD_PWR_EN
Touch
r
eset
s
ignal
14 Touch_Int
Touch
i
nterrupt
signal
15 I2C_SCL
IIC master
s
erial
c
lock
16 I2C_SDA
IIC m
aster
s
erial
d
ata
17 LED_PWR_EN
Backlight
e
nable
18 5V +5V
19 PWM
Pulse Width Modulation
2.3.3 HDMI Interface
Figure 2-4 HDMI Interface
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Pin Signal Function
1 HDMI_D2P HDMI differential pairs data2+
2 GND GND
3 HDMI_D2M HDMI differential pairs data2-
4 HDMI_D1P HDMI differential pairs data1+
5 GND GND
Table 2-3 HDMI Interface
J3
Page | 19

6 HDMI_D1M
HDMI differential pairs data1
-
7 HDMI_D0P
HDMI differential pairs data0+
8 GND GND
9 HDMI_D0M
HDMI differential pairs data0
-
10 HDMI_CLKP
HDMI differential pairs clock+
11 GND GND
12 HDMI_CLKM
HDMI differential pairs
clock
-
13 NC NC
14 NC NC
15 BI2C2_SCL
IIC2 serial clock
16 BI2C2_SDA
IIC2 serial data
17 GND GND
18 5Vin 5V
19 HDMI_HPD
HDMI detect
20 GNF_DVI
GND
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Page | 20

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.4 Microphone Input Jack
The RIoTboard provides a 3.5mm stereo connector for a microphone input, as shown in
Figure 2-5. A mono microphone will input its signal though the tip of the 3.5mm plug.
Figure 2-5 MIC Input
Table 2-4 MIC Input Jack
J4
Pin Signal Function
1 GND_ANALOG Analog GND
2 MIC_IN_P MIC input analog GND
3 GND_ANALOG Analog GND
4 GND_ANALOG Analog GND
5 MIC_IN_P MIC input analog GND
Page | 21

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.5 Audio Output Jack
A headphone with a standard 3.5mm stereo jack can be connected to the Audio Output
jack at the point shown in Figure 2-6.
Figure 2-6 Audio Output Jack
Table 2-5
Pin Signal Function
1 GND_ANALOG Analog GND
2 LINEOUT_L Left output
3 LINEOUT_R Right output
4 LINEOUT_R Right output
5 LINEOUT_L Left output
Audio Output Jack
J5
Page | 22

2.3.6 SD Card Interface
Figure 2-7 SD Card Interface
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-6
SD Card Interface
Pin Signal Function
1 SD2_DAT3 Card data 3
2 SD2_CMD Command signal
3 GND GND
4 3P3V 3.3V
5 SD2_CLK Clock
6 VSS GND
7 SD2_DAT0 Card data 0
8 SD2_DAT1 Card data 1
9 SD2_DAT2 Card data 2
J6
Page | 23

10 SD2_CD Card detect
11 SD2_WP Card write protected
12 GND GND
13 GND GND
14 GND GND
15 GND GND
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.7 uSD/MMC Card Interface
The micro SD Card Connector (J7) connects a 4-bit parallel data bus to the SD3 port of
the i.MX 6 processor. The micro SD Card is inserted facing up at the location shown in
Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-8
uSD/MMC Card Interface
Pin Signal Function
1 SD3_DAT2 Card data 2
2 SD3_DAT3 Card data 3
3 CMD Card command signal
Table 2-7
uSD/MMC Card Interface
J7
Page | 24

4 3P3V
3P3V
5 SD3_CLK
Card clock
6 VSS GND
7 SD3_
DAT0
Card data 0
8 SD3_
DAT1
Card data 1
9 SD3_CD Card detect
10 PGND GND
2.3.8 CSI Interface
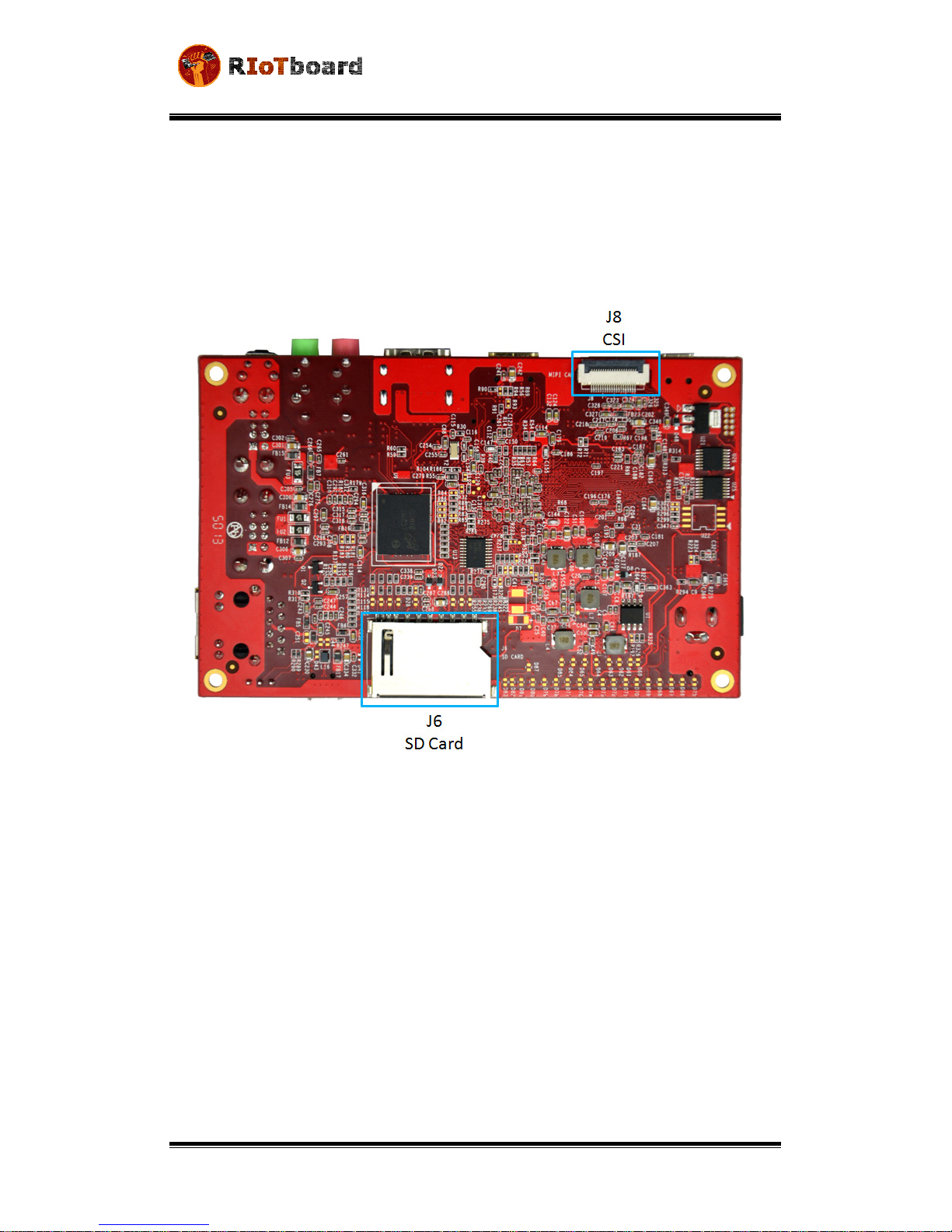
Figure 2-9 CSI Interface
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Pin Signal Function
1 5VIN 5V
2 5VIN 5V
3 GND GND
4 GND GND
Table 2-8 CSI Interface
J8
Page | 25

5 P2V8_VGEN6
2.8V
6 CSI_MCLK
CSI clock
7 GND GND
8 CSI_RST
CSI reset
9 CSI_EN
CSI data enable
10 I2C4_SCL IIC2 serial clock
11 I2C4_
SDA IIC2 serial data
12 GND GND
13 CSI_CLK0M
CSI differential pairs clock0
-
14 CSI_CLK0P
CSI differential pairs clock0+
15
GND GND
16
CSI_D0M
CSI differential pairs data0
-
17 CSI_D0P
CSI differential pairs data0+
18 GND GND
19 CSI_D1M
CSI different
ial pairs data1
-
20 CSI_D1P
CSI differential pairs data1+
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.9 Camera Interface
Figure 2-10 Camera Interface
Page | 26

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-9
Camera Interface
J9
Pin Signal Function
1 GND GND
2 NC NC
3 NC NC
4 CSI0_DAT12 CSI0 capture data bit 12
5 CSI0_DAT13 CSI0 capture data bit 13
6 CSI0_DAT14 CSI0 capture data bit 14
7 CSI0_DAT15 CSI0 capture data bit 15
8 CSI0_DAT16 CSI0 capture data bit 16
9 CSI0_DAT17 CSI0 capture data bit 17
10 CSI0_DAT18 CSI0 capture data bit 18
11 CSI0_DAT19 CSI0 capture data bit 19
12 NC NC
13 NC NC
14 GND GND
15 CSI0_PIXCLK CSI0 pixel clock
16 GND GND
17 CSI0_HSYNC CSIO HSYNC
18 NC NC
19 CSI0_VSYNC CSIO VSYNC
20 VDD_NVCC 3.3V
21 CAM_MCLK Camera clock
22 NC NC
23 GND GND
24 NC NC
25 CAM_RST CSI0 reset
26 CAM_EN CSI0 data enable
27 I2C4_SDA I2C2 serial data
28 I2C4_SCL I2C2 serial clock
29 GND GND
30 P1V8_SW4 1.8V
Page | 27

2.3.10 JTAG Interface
Figure 2-11 JTAG Interface
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-10 JTAG Interface
J10
Pin Signal Function
1 VDD_NVCC 3.3V
2 JTAG_TMS Test mode select
3 GND GND
4 JTAG_TCK Test clock
5 GND GND
6 JTAG_TDO Test data output
7 JTAG_MOD Test mode
8 JTAG_TDI Test data input
9 JTAG_nTRST Test system reset
10 RESET_N Reset
Page | 28

J11
Pin Signal
Function
1 USB_OTG_VBUS
+5V
2 USB_OTG_DN
USB data-
3 USB_OTG_DP
USB data+
4 USB_OTG_ID
USB ID
5 GND GND
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.11 Mini USB Interface
The mini USB connector is connected to the high-speed (HS) USB 2.0 OTG module of
the i.MX 6Solo processor and is cross connected with the lower USB Host port on J3.
When a 5V supply is seen on the mini USB connector (from the USB Host), the i.MX
6Solo processor will configure the OTG module to device mode, which will prevent the
lower USB Host port from operating correctly.
Figure 2-12
Mini USB Interface
Table 2-11
Mini USB Interface
Page | 29

J18
Pin Signal
Function
1 UART2_TXD
UART2
t
ransmit data
2 UART2_
RXD
UART2
r
eceive da
ta
3 GND GND
2.3.12 Serial Port
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Figure 2-13
Serial Port
Table 2-12 Serial Port
Page | 30

J13
Pin Signal
Function
1 VDD_NVCC
3.3V
2 5VIN
5V
3 GND GND
4 GND GND
5 GPIO4_16
GPIO
6 CSPI3_CLK
SPI
3 clock
7 GPIO4_17
GPIO
8 CSPI3_MOSI
SPI3 m
aster
o
utput
s
alve input
9 GPIO4_18
GPIO
10 CSPI3_MISO
SPI3 m
aster
in
put salve
out
put
11 GPIO4_19
GPIO
12 CSPI3_CS0
SPI3 chip select
0
13 CSPI3_CS1
SPI3 chi
p select 1
2.3.13 Expansion Port Interface
Figure 2-14 Expansion Port
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-13
Expansion Port Interface
Page | 31

14 CSPI2_CS1
SPI2 chip select 1
15 GPIO4_31
GPIO
16 CSPI2_MOSI
SPI2 m
aster
o
utput
s
alve input
17 GPIO5_05
GPIO
18 CSPI2_MISO
SPI2 m
aster
in
put salve
out
put
19 GPIO5_06
GPIO
20 CSPI2_CS0
SPI2 chip select 0
21 GPIO5_07
GPIO
22 CSPI2_CLK
SPI2 cl
ock
23 GPIO5_08
GPIO
24 UART3_RXD
UART
3 r
eceive da
ta
25 GPIO4_26
GPIO
26 UART3_TXD
UART
3 t
ransmit data
27 GPIO4_27
GPIO
28 UART4_RXD
UART
4 r
eceive da
ta
29 CSPI3_RDY
SPI3 data validation
30 UART4_TXD
UART
4 t
ransmit data
31 I2C3_SCL
I2C3 m
aste
r serial cloc
k
32 UART5_RXD
UART
5 r
eceive da
ta
33 I2C3_SDA
I2C3
m
aster serial data
34 UART5_TXD
UART
5 t
ransmit data
35 I2C4_SCL
I2C4 master serial cloc
k
36 PWM1
Pulse Width Modulation
37 I2C4_SDA
I2C4 master serial data
38 PWM2
Pulse Width Modulatio
n
39 GND GND
40 PWM3
Pulse Width Modulation
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Page | 32

J14
Pin Signal
Function
1 V5V_SDA
+5V
2 SDA_USB_DN
SDA
USB data-
3 SDA_USB_DP
SDA
USB data+
4 NC NC
5 GND GND
2.3.14 Mini USB Interface (OpenSDA)
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Figure 2-15
Mini USB (OpenSDA)Interface
Table 2-14
Mini USB (OpenSDA) Interface
Note:
The RIoTboard has hardware to support Freescale’s OpenSDA interface. Currently this
interface has not been enabled in software
Page | 33

J15
Pin Signal
Function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
2.3.15 RGMII LAN Interface
The Ethernet connector contains integrated magnetic which allows the Ethernet IC to
auto configure the port for the correct connection to either a switch or directly to a
host PC on a peer-to-peer network. It is not necessary to use a crossover cable when
connecting directly to another computer. The Ethernet connector is shown in Figure 2-
16.
Figure 2-16
Table 2-15
RGMII LAN Interface
RGMII LAN interface
TD1+ TD1+ output
TD1- TD1- output
TD2+ TD2+ output
TD2- TD2- output
TCT 2.5V power for TD
RCT 2.5V power for RD
RD1+ RD1+ input
RD1- RD1- input
RD2+ RD2+ input
RD2- RD2- input
Page | 34

11 GRLA
Gree
n LED link signal
12 GRLC
Power supply for
g
reen LED
13 YELC Yellow LED action signal
14 YELA
Power supply for
y
ellow LED
2.3.16 USB HUB Interface
Figure 2-17 USB Host Interface
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-16
USB Host Interface
HUB1
Pin Signal Function
1 USB_PWR3 +5V
2 USB_DM3 USB data-
3 USB_DP3 USB data+
4 GND GND
5 USB_PWR4 +5V
6 USB_DM4 USB data-
7 USB_DP4 USB data+
8 GND GND
Page | 35

HUB2
Pin Signal
Function
1 USB_PWR
1 +5V
2 USB_DM
1 USB data-
3 USB_DP
1 USB data+
4 GND GND
5 USB_PWR
2 +5V
6 USB_DM
2 USB data-
7 USB_DP
2 USB data+
8 GND GND
2.3.17 Boot Configuration Select
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Figure 2-18 Boot Configuration Select
Page | 36

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-17
Boot Configuration Select
SW1
Pin Signal Function
1 P3V0_STBY P3V0_STBY
2 P3V0_STBY P3V0_STBY
3 VDD_NVCC VDD_NVCC
4 VDD_NVCC VDD_NVCC
5 VDD_NVCC VDD_NVCC
6 VDD_NVCC VDD_NVCC
7 VDD_NVCC VDD_NVCC
8 VDD_NVCC VDD_NVCC
9 EIM_DA11 BT_CFG2_3
10 EIM_DA12 BT_CFG2_4
11 EIM_DA13 BT_CFG2_5
12 EIM_DA14 BT_CFG2_6
13 EIM_DA5 BT_CFG1_5
14 EIM_DA6 BT_CFG1_6
15 BOOT_MODE0 BOOT_MODE0
16 BOOT_MODE1 BOOT_MODE1
Page | 37

S1
Pin Signal
Function
1 GND GND
2 POR_B
System
r
eset
3 NC NC
4 NC NC
2.3.18 Reset Switch
Figure 2-19 Reset Switch
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 2-18
Reset Switch
Page | 38

2.3.19 LEDs
Figure 2-20 LEDs
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Reference Function
D45 User-defined LED
D46 User-defined LED
D47 Power LED
D49 OpenSDA LED
Table 2-19 LEDs
LED
Page | 39

NOTE:
All images and tools for Android and Linux can be downloaded
Types
Notes
Linux
Version 3.0.35
Ubuntu
Version
11.10
Android
Version 4.
3
Serial
Series driver
RTC Hardware clock driver
Net 10/100/Gb IEEE1588 Ethernet
Display
Two display ports (LVDS, and HDMI 1.4a)
MMC
/SD
Two SD 3.0/SDXC card slot & eMMC
USB 5 High speed USB ports
(4xHost, 1xOTG)
Audio
Analog (headphone
&
mic) and Digital (HDMI)
Camera
Two camera ports (1xParallel, 1x MIPI CSI
-2)
LED User leds driver
Images
Paths
u-boot image
u-
boot-mx6solo
-
riot.bin
kernel image
uImage
rootfs image
oneiric.tgz
USER MANUAL v1.0
3 Getting Started
Before you start to use RIoTboard, please read the following sections to get yourself
familiar with the system images, driver code and tools which might be involved during
development process.
from www.element14.com/riotboard
3.1 Software Features
The table shown below lists the versions of Linux and Android systems, as well as
the device drivers.
Table 3-1 OS and Drivers
Date: 01/20/2014
OS
Device
Drivers
3.2 Linux System
The following tables list the specific images and eMMC storage patitions required to
build a Linux system.
Table 3-2 Images Required by Linux
Page | 40

Partition
File
u-boot
-
N/A Kernel
1M
9MB N/A uImage
Total
-
Images
Paths
u-boot image
u-
boot-mx6solo
-
riot.bin
boot image
boot.img
Android system root image
system.img
Recovery root image
recovery.img
Partition type/index
Name
Start Offset
Size File System
Content
boot.img format,
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 3-3 Storage Partitions for Linux
type/index
N/A
Primary 1 Rootfs 10M
Name Start Offset Size
BOOT
Loader
0 1MB N/A
Other
System
mx6soloriot.bin
EXT3 oneiric.tgz
Partition type/index: defined in MBR.
Name: only meaningful in Android. You can ignore it when creating these partitions.
Start Offset: shows where partition starts with unit in MB.
3.3 Android System
The following tables list the specific images and eMMC storage patitions required to
build an Android system.
Table 3-4 Images Required by Android
Content
Table 3-5 Storage Partitions for Android
N/A
Primary 1 Boot 8M 8MB
Primary 2 Recovery Follow Boot 8MB
Logic 4
(Extended 3)
Logic 5
(Extended 3)
Logic 6 (Extended 3) CACHE
Logic 7(Extended 3) VENDOR follow CACHE 8MB
Logic 9
(Extended 3)
Primary 4 MEDIA Follow Misc Total - Other VFAT For internal media
BOOT
Loader
DATA
SYSTEM Follow DATA 512MB
Misc Follow DATA 8M N/A
0 1MB N/A bootloader
a kernel +
ramdisk
boot.img format,
a kernel +
ramdisk
follow
Recovery
follow
SYSTEM
> 1024MB
512MB
EXT4 Mount at
/data
EXT4. Mount as
/system
EXT4. Mount as
/cache
Ext4 Mount at
/device
boot.img
recovery.img
Application data
storage for system
application.
Android system files
under /system/ dir
Android cache, for
image store for OTA
For Store MAC address
files.
For recovery store
bootloader message,
reserve.
Page | 41

Partition type/index
Name
Start Offset
Size File System
Content
images partition, in
SYSTEM Partition: used to store Android system image.
DATA Partition: used to store applications’ unpacked data, system configuration
database, etc.
Under normal mode, the root file system is mounted from uramdisk. Under
recovery mode, the root file system is mounted from the RECOVERY partition.
3.4 Setting up Terminal Emulation
Connect the RIoTboard to a PC with the help of a serial cable. Launch a terminal
emulation program such as HyperTerminal or TeraTerm and configure the COM
parameters as show below.
Figure 3-1 COM Properties
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
/mnt/sdcard/ dir.
Page | 42

All images and tools for A
ndroid and Linux can be downloaded
Switch
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8
USER MANUAL v1.0
4 Downloading and Running the System
Now you can download the existing system to the RIoTboard and run it. The MFG tool
saved under linux\tools\ & android\tools\ will be used to download images.
NOTE:
from www.element14.com/riotboard
4.1 Download and Run Linux or Android System
1
))))
Copy all the system files to a root directory of your hard drive (assume C:\ is
the root directory).
2
))))
Use a Mini USB cable to connect USB OTG interface on RIoTboard to the USB
Date: 01/20/2014
Host on PC, and then open a Terminal window;
3
))))
Set the boot switch SW1 on the RIoTboard to
Serial Download Mode
according to the configurations as shown in the following table;
Table 4-1 Boot Switch Configuration – Serial Download
SW1 OFF ON ON ON OFF ON ON ON
Figure 4-1 Boot Configuration Switch
Page | 43

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
4
))))
Modify the MFG tool configuration
Currently the Linux system on the RIoTboard supports only booting from
eMMC, but the Android system supports booting from both eMMC and SD
card. To select the device you want to program to, follow the instruction
below:
Modify the value of “name” in cfg.ini under Android flash image tool
Mfgtools-Rel-4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER directory.
eMMC -- name = Android-RIOT-eMMC
SD -- name = Android-RIOT-SD
5
))))
Prepare the image files
For Linux: Copy the Linux image files oneiric.tgz, u-boot-mx6solo-riot.bin and
uImage to the Linux flash image tool Mfgtools-Rel-
4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER\ Profiles\MX6DL Linux Update\OS
Firmware\files\ to overwrite the files with the same names
For Android: Copy the Android image files: u-boot-mx6solo-riot.bin and
according to the boot mode (SD/eMMC) to copy the boot.img, recovery.img
and system.img under SD/eMMC directory to Android flash image tool
Mfgtools-Rel-4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER\ Profiles\MX6DL Linux
Update\OS Firmware\files\android\, for overwriting the files with the same
names
6
))))
According to the system you want to boot, run the corresponding MFG tool
on your PC and power up the RIoTboard; the software window is shown below;
(the PC will install HID driver automatically if it is the first time connecting to
the RIoTboard)
For Linux system, the MFG tool is located at :
linux\tools\Mfgtools-Rel-4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER;
For Android system, the MFG tool is located at :
android\tools\Mfgtools-Rel-4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER;
Page | 44

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
MFG tool window
7
))))
Click Start in the following window; when download process is done, click Stop to
finish.
Click Start
8
))))
When download process is done, click Exit to exit.
Page | 45

Switch
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8
Switch
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
9
))))
Power off the RIoTboard and set the boot switches SW1 on it to eMMC boot
mode according to the configuration as shown In the following table;
Table 4-2 Boot Switch Configuration - eMMC
SW1 ON OFF ON ON OFF ON ON ON
Table 4-3 Boot Switch Configuration – SD
SW1 ON OFF ON OFF OFF ON OFF ON
After the switch is set, power up the RIoTboard to boot the system.
4.2 Display Mode Configurations for Linux & Android Systems
The system supports multiple display modes. Users can select an appropriate mode by
configuring u-boot parameters.
Please reboot the RIOT Board and press any key on your PC’s keyboard when the system
prompts you with a countdown in seconds as shown below:
U-Boot 2009.08-dirty (Oct 17 2013 - 17:08:06)
CPU: Freescale i.MX6 family TO1.1 at 792 MHz
Thermal sensor with ratio = 201
Temperature: 42 C, calibration data 0x5f55765f
mx6q pll1: 792MHz
mx6q pll2: 528MHz
mx6q pll3: 480MHz
mx6q pll8: 50MHz
ipg clock : 66000000Hz
ipg per clock : 66000000Hz
uart clock : 80000000Hz
cspi clock : 60000000Hz
ahb clock : 132000000Hz
axi clock : 198000000Hz
emi_slow clock: 99000000Hz
ddr clock : 396000000Hz
usdhc1 clock : 198000000Hz
usdhc2 clock : 198000000Hz
usdhc3 clock : 198000000Hz
usdhc4 clock : 198000000Hz
nfc clock : 24000000Hz
Board: i.MX6DL/Solo-SABRESD: unknown-board Board: 0x61011 [POR ]
Boot Device: MMC
I2C: ready
DRAM: 1 GB
MMC: FSL_USDHC: 0,FSL_USDHC: 1,FSL_USDHC: 2,FSL_USDHC: 3
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Page | 46

Net: got MAC address from IIM: 00:00:00:00:00:00
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
----enet_board_init: phy reset
FEC0 [PRIME]
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0 ( press any key to enter u-boot command mode)
MX6Solo RIOT U-Boot >
1
))))
Display with 9.7” LVDS Only
Execute the following instructions in u-boot mode to configure for 9.7-inch display
mode;
MX6Solo RIOT U-Boot > setenv bootargs console=ttymxc1,115200
init=/init nosmp video=mxcfb0:dev=ldb,bpp=32 video=mxcfb1:off
fbmem=10M vmalloc=400M androidboot.console=ttymxc1
androidboot.hardware=freescale
MX6Solo RIOT U-Boot > saveenv
2
))))
Display with HDMI Only (Default mode)
Execute the following instructions in u-boot mode to configure for HDMI display
mode;
MX6Solo RIOT U-Boot > setenv bootargs console=ttymxc1,115200
init=/init nosmp video=mxcfb0:dev=hdmi,1280x720M@60,bpp=32
video=mxcfb1:off fbmem=10M vmalloc=400M
androidboot.console=ttymxc1 androidboot.hardware=freescale
MX6Solo RIOT U-Boot > saveenv
Page | 47

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
5 Making Images
This Chapter will introduce how to make images by using BSP contained in the ISO. The
BSP is a collection of binary, source code, and support files that can be used to create a
u-boot bootloader, Linux kernel image, and Android file system for i.MX 6Solo RIOT
Board.
Note:
The following instructions are all executed under Ubuntu system.
Each instruction has been put a bullets “” before it to prevent confusion caused by the long
instructions that occupy more than one line in the context.
5.1 Making Images for Linux
Please strictly follow the steps listed below to make images for Linux system.
5.1.1 Getting Tools and Source Code
1
))))
Execute the following instructions to get cross compiling toolchain;
$ cd ~
$ git clone git://github.com/embest-tech/fsl-linaro-toolchain.git
2
))))
Execute the following instructions to get u-boot source code;
$ cd ~
$ git clone git://github.com/embest-tech/u-boot-imx.git –b embest_imx_3.0.35_4.0.0
3
))))
Execute the following instructions to get kernel source code;
$ cd ~
$ git clone git://github.com/embest-tech/linux-imx.git -b embest_imx_3.0.35_4.0.0
5.1.2 Compiling System Images
1
))))
Execute the following instructions to compile u-boot image;
$ cd ~ /u-boot-imx
$ export ARCH=arm
$export CROSS_COMPILE=~/fsl-linaro-toolchain/bin/arm-fsl-linux-gnueabi-
$ make distclean
$ make mx6solo_riot_config
Page | 48

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
$ make
$ mv u-boot.bin u-boot-mx6solo-riot.bin
After executing the instructions, a file u-boot-mx6solo-riot.bin can be found in
the current directory ;
2
))))
Execute the following instructions to compile kernel image;
$export PATH=~/u-boot-imx/tools:$PATH
$ cd ~/linux-imx
$ export ARCH=arm
$export CROSS_COMPILE=~/ fsl-linaro-toolchain/bin/arm-fsl-linux-gnueabi-
$ make imx6_defconfig
$ make uImage
After executing the instructions, a kernel image named uImage can be found
under arch/arm/boot/.
Note:
The mkimage is used to build the kernel and ramfs images are automatically generated and
saved under tools/ after compiling u-boot.bin. So please make sure uboot is compiled first
before compiling kernel image.
Copy u-boot-mx6solo-riot.bin and uImage files that are generated by compiling to linux flash
image tool Mfgtools-Rel-4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER\ Profiles\MX6DL Linux Update\OS
Firmware\files\ to overwrite the files with the same names and then start over the operations
from step 2) in section 4.1 to verify the Linux system built.
5.2 Making Images for an Android System
Please strictly follow the steps listed below to make images for Android system.
5.2.1 Getting Repo Source Code
1
))))
Execute he following instructions to get repo tool;
$ mkdir ~/bin
$ curl https://raw.github.com/android/tools_repo/stable/repo > ~/bin/repo
$ chmod a+x ~/bin/repo
$ export PATH=~/bin:$PATH
Page | 49

2
))))
Execute the following instructions to initialize repo source code;
$ mkdir ~/android-imx6-jb4.3-1.0.0
$ cd ~/android-imx6-jb4.3-1.0.0
$ repo init --repo-url=git://github.com/android/tools_repo.git -u
git://github.com/embest-tech/imx-manifest.git –m embest_android_jb4.3_1.0.0
3
))))
Execute the following instructions to synchronize repo source code;
$ cd ~/android-imx6-jb4.3-1.0.0
$ repo sync
5.2.2 Compiling System Images
1
))))
You can choose to build Android image for eMMC or SD Boot:
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Open the “device/fsl/riot_6solo/BoardConfig.mk” file with Notepad; change
the “BUILD_TARGET_LOCATION” to select the boot device:
eMMC Boot -- BUILD_TARGET_LOCATION ?= emmc
SD Boot -- BUILD_TARGET_LOCATION ?= sdmmc
2
))))
Execute the following instructions to compile Android image;
$ cd ~/android-imx6-jb4.3-1.0.0
$ source build/envsetup.sh
$ lunch riot_6solo-user
$ make clean
$ make
After executing the instructions, the generated images can be found under
android-imx6-jb4.3-1.0.0/out/target/product/riot_6solo/;
Table 5-1 shown below lists all the images and directories after compilation is
completed.
Page | 50

Images/Directories
Notes
system/
Android system
directory,
mounted at /system
recovery/
Root filesystem when booting
in "recove
ry" mode
, n
ot used directly
USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
Table 5-1 Images and Directories
root/ root file system, mounted at /
data/ Android data area. mounted at /data
boot.img
ramdisk.img Ramdisk image generated from "root/", not directly used
system.img
userdata.img EXT4 image generated from "data/"
recovery.img
u-boot.bin uboot image with padding
A composite image which includes the kernel zImage, ramdisk, and
boot parameters
EXT4 image generated from "system/". Can be written to "SYSTEM"
partition of SD/eMMC card with "dd" command
EXT4 image generated from "recovery/". Can be written to
"RECOVERY" partition of SD/eMMC card with "dd" command
Note:
Android image should be built in user mode;
For more information, please visit http://source.android.com/source/building.html
3
))))
Execute the following instructions to compile boot.img;
$ source build/envsetup.sh
$ lunch riot_6solo-user
$ make bootimage
After executing the instructions, a boot.img image can be found under
android-imx6-jb4.3-1.0.0/out/target/product/riot_6solo/.
Note:
Copy the boot.img, recovery.img, system.img and u-boot.bin (rename this to u-boot-
mx6solo-riot.bin) files created upon compilation, to the Android flash tool folder Mfgtools-
Rel-4.1.0_130816_MX6DL_UPDATER\
Firmware\files\android to overwrite the files with the same names and repeat the operations
from step 2) in 4.1 to verify the Android system built.
Profiles\MX6DL Linux Update\OS
Page | 51

USER MANUAL v1.0
Date: 01/20/2014
6 ESD PRECAUTIONS AND PROPER HANDLING PROCEDURES
This section includes the precautions for mechanical handling and static precautions to
be taken to avoid ESD damage:
Avoid carpets in cool, dry areas. Leave development kits in their anti-static
packaging until ready to be installed.
Dissipate static electricity before handling any system components (development
kits) by touching a grounded metal object, such as the system unit unpainted
metal chassis.
If possible, use antistatic devices, such as wrist straps and floor mats.
Always hold a evaluation board by its edges. Avoid touching the contacts and
components on the board.
Take care when connecting or disconnecting cables. A damaged cable can cause a
short in the electrical circuit.
Prevent damage to the connectors by aligning connector pins before you connect
the cable. Misaligned connector pins can cause damage to system components at
power-on.
When disconnecting a cable, always pull on the cable connector or strain-relief
loop, not on the cable itself.
Page | 52

53

Mouser Electronics
Authorized Distributor
Click to View Pricing, Inventory, Delivery & Lifecycle Information:
RIoTboard:
MCIMX6 SOLO
 Loading...
Loading...