Page 1

APPLICANT MOTOROLA INC. FCC ID: IHDT56LV1
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
A representative version of the user's manual follows:
Exhibit 8
Page 2

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
HSPA LGA module (HTM1100-L)
User Guide
DOCUMENT CONTROL NUMBER:
Version No.: 1.0
Date: March 2010
Copyright 2010 Motorola Inc. All rights reserved. This document and the
information contained in it is CONFIDENTIAL INFORMATION of Motorola,
and shall not be used, published, disclosed, or disseminated outside of Motorola
in whole or in part without Motorola’s consent. This document contains trade
secrets of Motorola. Copyright notice does not imply publication of this document.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 1 of 43
Page 3

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
HSPA LGA MODULE (HTM1100-L)........................................................................................................ 1
USER GUIDE ............................................................................................................................................... 1
1. INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................................... 4
1.1 REVISION HISTORY ...................................................................................................................... 4
1.2 PURPOSE ...................................................................................................................................... 4
1.3 SCOPE .......................................................................................................................................... 4
1.4 TARGET AUDIENCE ...................................................................................................................... 4
1.5 ABBREVIATIONS........................................................................................................................... 5
2. REFERENCES.................................................................................................................................... 6
3. PRODUCT OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................... 7
4. HARDWARE ARCHITECTURE..................................................................................................... 8
5. SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE ...................................................................................................... 9
5.1.1 Inter-Processor Communication........................................................................................... 10
5.1.2 Modem Software Architecture Overview .............................................................................. 10
5.1.3 ARM9 Software Architecture Overview................................................................................ 11
6. HTM1100-L MODULE FEATURE SUMMARY .......................................................................... 12
6.1 HARDWARE REVISION:............................................................................................................... 12
6.2 2G.............................................................................................................................................. 12
6.3 3G.............................................................................................................................................. 12
6.4 ADVANCED SERVICES ................................................................................................................ 12
6.5 AUDIO ........................................................................................................................................ 12
6.6 INTERNAL MEMORY................................................................................................................... 13
6.7 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS ............................................................................................................ 13
6.8 SECURITY................................................................................................................................... 13
6.9 CONNECTIVITY........................................................................................................................... 13
6.10 POWER UP SEQUENCE ................................................................................................................ 13
7. SPECIFICATIONS........................................................................................................................... 15
7.1.1 Electrical Specification......................................................................................................... 15
7.1.2 Mechanical Specification...................................................................................................... 15
8. LGA MODULE INTERFACES ...................................................................................................... 17
8.1.1 LGA Interface Signals .......................................................................................................... 17
8.1.2 SIM Interface ........................................................................................................................ 20
8.1.3 WWAN_LED......................................................................................................................... 20
8.1.4 Audio Interface ..................................................................................................................... 20
9. COMMUNICATION WITH HOST ............................................................................................... 21
9.1.1 Overview............................................................................................................................... 21
9.1.2 Link Details .......................................................................................................................... 22
9.1.3 Host Modem Wakeup Mechanism......................................................................................... 23
10. AT COMMANDS......................................................................................................................... 25
10.1 LGA MODULE AT COMMAND INTERFACE ALLOWS THE BELOW MENTIONED FUNCTIONALITY ON
HIGH LEVEL USING
10.1.1 Network Connection Management................................................................................... 25
10.1.2 Registration or Mobility Management............................................................................. 26
10.1.3 SMS.................................................................................................................................. 26
10.1.4 USIM and Phonebook...................................................................................................... 26
DIFFERENT AT COMMANDS:....................................................................................... 25
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 2 of 43
Page 4

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
11. NVM/FLASH................................................................................................................................27
12. RF CALIBRATION/PHASING.................................................................................................. 27
13. PLATFORM VALIDATION...................................................................................................... 28
13.1 RF PERFORMANCE TESTING....................................................................................................... 28
13.1.1 Equipment........................................................................................................................ 28
13.1.2 Equipment list .................................................................................................................. 28
13.1.3 Setup ................................................................................................................................29
14. HARDWARE INSTALLATION................................................................................................ 30
14.1 HTM1100 LGA MODULE REFLOW PROCESS ............................................................................. 30
15. LGA MODULE DRIVER INSTALLATION............................................................................ 32
16. LIVE NETWORK CONNECTION ........................................................................................... 35
16.1 PLUGGING IN THE CARD IN PC.................................................................................................... 35
16.2 SETTING UP DIAL UP NETWORKING (DUN) CONNECTION USING LGA MODULE AS A MODEM.. 35
17. KNOWN ISSUES......................................................................................................................... 43
17.1 LGA MODULE POWER UP TIMING.............................................................................................. 43
Figure 1: HTM1100-L Bottom Pad view............................................................................ 7
Figure 2: HTM1100 high level block diagram ................................................................... 8
Figure 3: Software Architecture Partitioning...................................................................... 9
Figure 4: Power Management by CPCAP ........................................................................ 14
Figure 5: HTM1100-L Component View and Pad View (Top View).............................. 16
Figure 6: Communication between Host and LGA Module............................................. 21
Figure 7: HTM1100-L Modem interface.......................................................................... 22
Figure 8: GPIO remote wakeup signaling ........................................................................ 24
Figure 9: LGA Module test set up .................................................................................... 28
Figure 10 : LGA module inside Test Socket .................................................................... 31
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 3 of 43
Page 5
MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
1. Introduction
1.1 Revision History
Revision Date Author Description
Customer
1.0 March 2010
1.2 Purpose
This document describes the product design and specification for HSPA LGA
module (HTM1100-L). The HTM1100-L supports multi-mode (2G/3G) with
HSDPA/HSUPA capabilities.
Operations –
Lauren Holmes
(GTJM87)
Initial Draft
1.3 Scope
This document describes platform architecture, hardware/software interactions,
Technical/Electrical Specifications.
1.4 Target Audience
This document is intended to provide design details about HSPA LGA module
(HTM1100-L) to the teams involved in product integration.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 4 of 43
Page 6

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
1.5 Abbreviations
AES Advanced Encryption Standard
AGPS Assisted Global Positioning System
AMR-NB Adaptive Multi-Rate Narrow Band
AMR-WB Adaptive Multi-Rate Wide Band
AP Applications Processor
BP Baseband Processor
DES Data Encryption Standard
DDR Double Data Rate
DTM Dual Transfer Mode
DUN Dial Up Networking
EDGE Enhanced Data rate for GSM Evolution
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
FPS Frames-Per-Second
FR Full Rate
GEA GSM Encryption Algorithm
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GPS Global Positioning System
GSM Global System for Mobile communications
HR Half Rate
HS High Speed
HSDPA High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
HSUPA High-Speed Uplink Packet Access
IMEI International Mobile Equipment Identity
IMS IP Multimedia Subsystems
IPC Inter Processor Communications
LGA Land Grid Array
NAND Not AND (electronic logic gate)
OHA Open Handset Alliance
OMA Open Mobile Alliance
OTG On-The-Go
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect
PMIC Power Management IC
RF Radio Frequency
SAM Stand Alone Modem
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
UEA UMTS Encryption Algorithm
UICC Universal Integrated Circuit Card
USB Universal Serial Bus
USIM Universal SIM
W3G Wrigley3G (Motorola 3G baseband processor)
WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
WLAN Wireless Local Area Network
WWAN Wireless Wide Area Network
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 5 of 43
Page 7

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
2. References
HTM1100-L is compliant with 3GPP specification Release6, December 2006 version.
Release 6 specifications can be found at www.3gpp.org
HTM1100-L pads comply with electrical specifications of PCIe Express specification 1.2.
PCIe Express specification 1.2 can be downloaded from
http://www.pcisig.com/specifications/pciexpress/
HTM1100-L USB signals and remote host wake up mechanism comply with USB
specification 2.0. USB2.0 specification can be downloaded from
http://www.usb.org/developers/docs/
JEDEC standards: http://www.jedec.org/
ESD protection is in compliance with JESD22-A114.
Moisture sensitivity level complies with Ref J-STD-020B section 7.
Reflow process is in compliant with J-STD-020C.
Linux source code drivers for HTM1100-L product are available at
http://opensource.motorola.com
Host Modem communication details are provided in the document HTM1100-L Host
Modem Communication 12-17-09 Ver 1-0-1.pdf
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 6 of 43
Page 8

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
3. Product Overview
HTM1100-L is a LGA module supporting tri-band HSPA and quad-band EDGE/GPRS,
with data rates of up to 10.1Mbps downlink and 5.76Mbps uplink. Signals on LGA
module comply with Electrical spec of PCIe interface Version 1.2.
HTM1100-L is based on a custom 3G baseband processor that was developed by
Motorola. Other main hardware components on this platform are the RF transceiver from
Infineon, the Power Management IC, the RF analog front end and Power amplifiers.
HTM1100-L has internal DDR SDRAM and NAND flash memories, which were
packaged on top of the baseband processor (POP). HTM1100-L uses USB signals to
connect with a PC, netbook or MID.
J
I
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
HTM1100-L Bottom View HTM1100-L Bottom view
(Engineering Sample) (Production version)
Figure 1: HTM1100-L Bottom Pad view
J
I
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 7 of 43
Page 9
MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
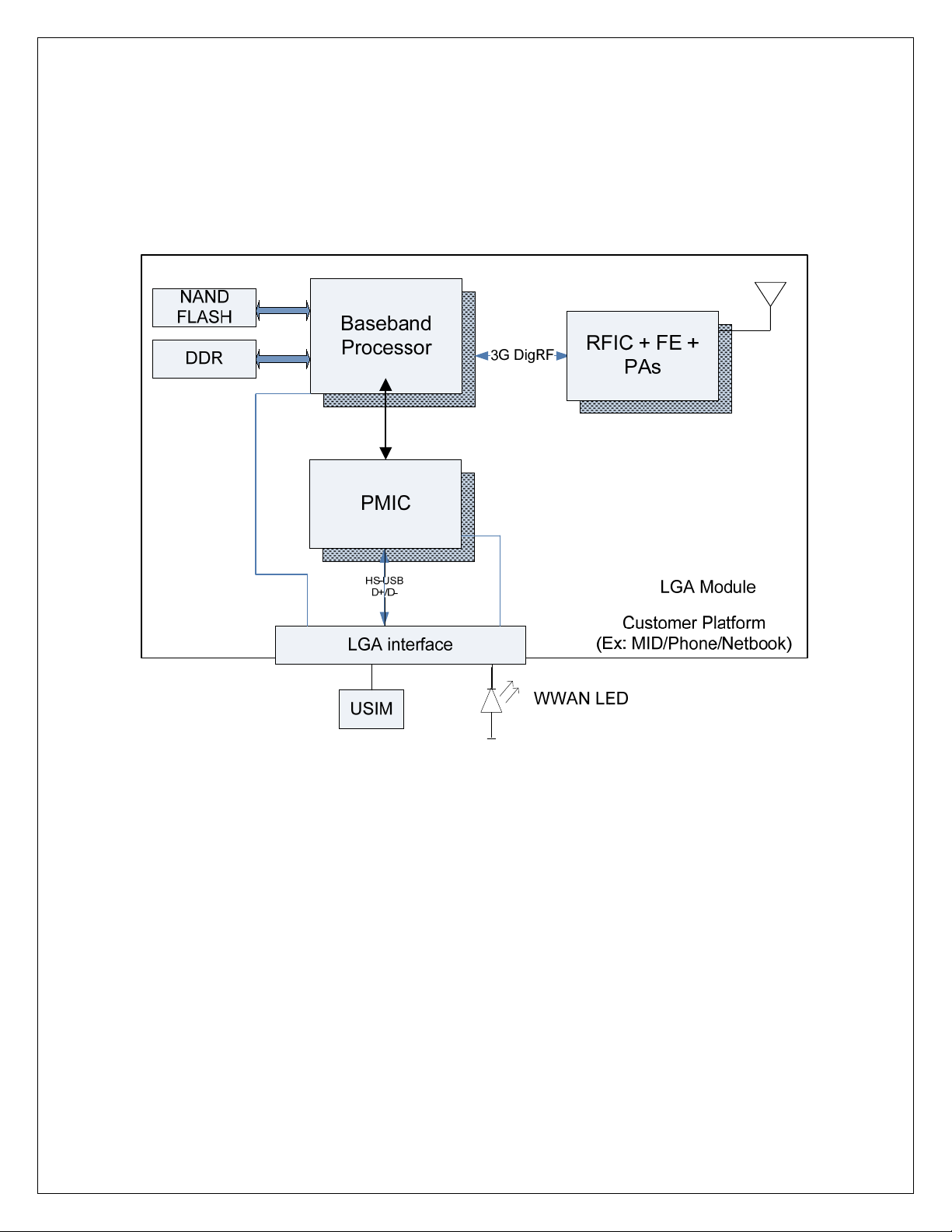
4. Hardware Architecture
Figure 2: HTM1100 high level block diagram
.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 8 of 43
Page 10
MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
_
_
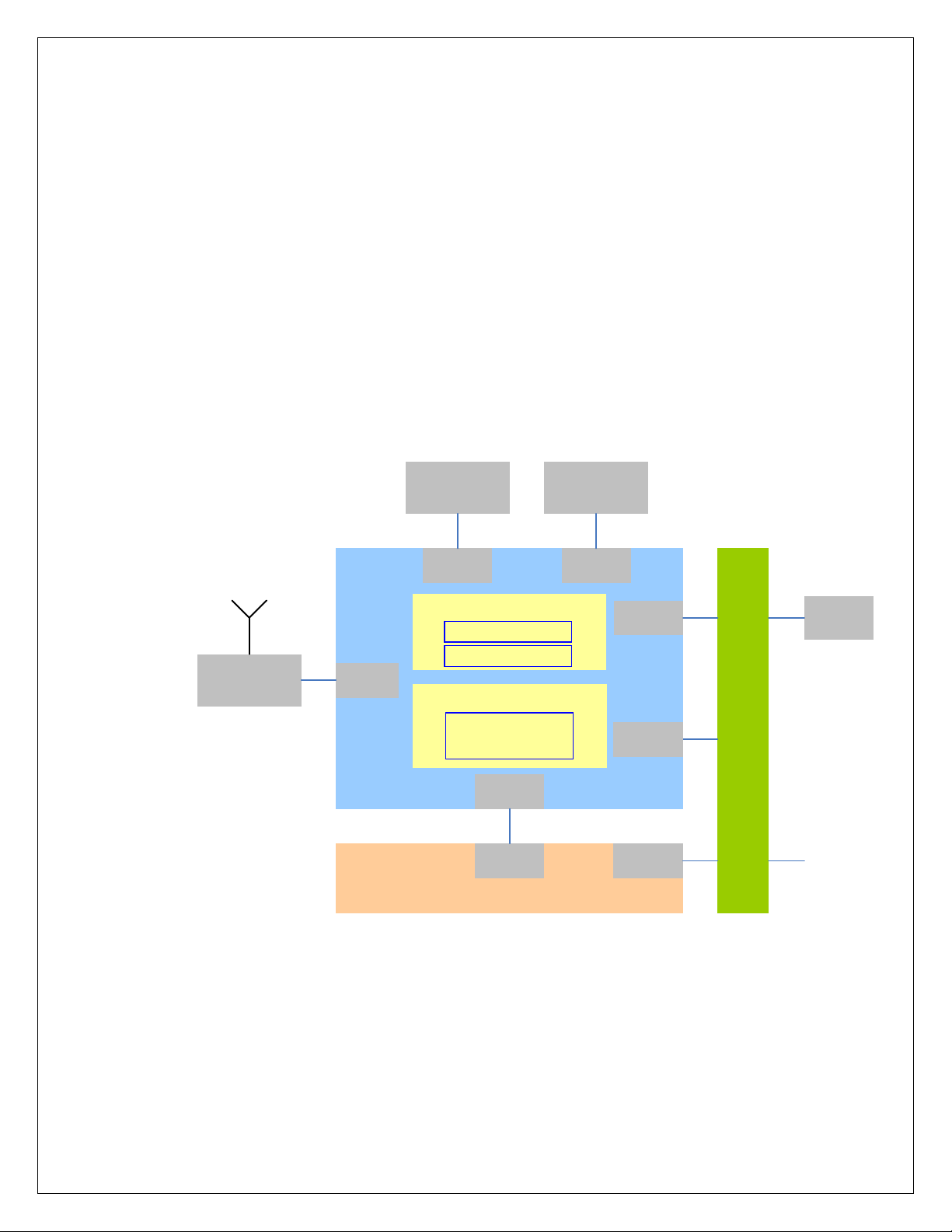
5. Software Architecture
The HTM1100-L module software architecture is based on:
• Linux kernel running on the ARM9 application processor of the W3G.
• Native services running on top of the Linux kernel in the user space.
• Hardware specific adapters, drivers and software stacks.
• A 3GSM Single Core Modem architecture running on the C55x+ DSP of the
W3G.
The following diagram shows a high level overview of the software partitioning:
SmartiUEMD
RF
W 3 G
RF IF
DDR SDRAM
SDRC
9
ARM
Native Services
Android Kernel
C
55
2G/3
G Stack
HSUSB
OTG
ULPI
CPCAP POWER IC
NAND
FLASH
GPMC
SIM IF
L
G
A
N
T
E
R
F
A
C
E
I
+x
GPIO
USB
XVR
UICC
USB
USB
D+
D-
Figure 3: Software Architecture Partitioning
The ARM9 in W3G hosts Linux kernel and some native services that are running
in the user space. The external peripherals that the LGA module supports are
limited to UICC and PCI Express connector which includes USB connectivity
lines. The internal peripherals that W3G supports are limited to DDR SDRAM
and NAND Flash memories, the RF transceiver SmartiUEMD from Infineon and
the CPCAP power management IC.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 9 of 43
Page 11

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
5.1.1 Inter-Processor Communication
The Inter-Processor Communication (IPC) infrastructure between the Single Core
Modem and Application Subsystem is made up of a shared RAM between the
ARM9 and the C55x+, and a mailbox mechanism, on top of which the NetMux
software infrastructure exposes virtual channels to client components on both
Application (AP) and Baseband Processor (BP) sides.
5.1.2 Modem Software Architecture Overview
In this platform, the W3G processor includes a C55x+ DSP that runs the whole
2G/3G modem stack (supporting HSDPA/HSUPA) thus leaving the ARM9 fully
dedicated to native services.
This approach enables native services to run on the application processor without
the complexity of mixing hard real-time software (modem) with the applications.
The SCM architecture enables running all the modem functions: 2G and 3G
Signal Processing Layer (SPL) and 2G Stack and 3G stack on the SAM core
(C55x+ core).
Only what is needed to support modem functions is implemented on the C55x+
DSP core.
Interfaces have been split into 3 main domains: SPL, Stack and Infrastructure.
The Single Core Modem Software architecture is composed of the following
elements:
• The Signal Processing Layer (SPL): this software layer implements the
physical layer.
o Uplink signal processing: channel coding and modulation, GSM
convolutional encoding and WCDMA convolutional encoding or
Turbo-encoding.
o Downlink signal processing: GSM equalization, GSM channel
decoding, WCDMA interface/control and WCDMA hardware
accelerators (3G Sub-System).
• Stack component is the component from L1 Control to L3 handling all the
logical part of the GSM/GPRS/EGPRS and WCDMA protocols:
o GSM/GPRS/EDGE protocols: Layer 1, Layer2-Link Access Protocol
on the Dm channel (L2-LAPDm), GPRS Radio Link Control (RLC),
Logical Link Control (LLC) and the Sub-Network Dependent
Convergence Protocol (SNDCP).
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 10 of 43
Page 12

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
o WCDMA protocols: WCDMA Layer 1, Radio Resource Control
(RRC), WCDMA Radio Link Control (W-RLC), Broadcast Message
Control (BMC) and the Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP).
o Dual Mode protocols: Layer 1, GPRS Radio Resource/Radio Resource
management (GRR/RR/RRC/RRLP), Mobility Management (MM),
GPRS Mobility Manager (GMM), Session Management (SM),
Intelligent Data Router (IDR) and Connection Management (CM),
which consists of Call Control (CC), Supplementary Services (SS) and
Short Message Management (SMS) entities. A new created entity is
the Translation Layer (TL) which allows the 2G/WCDMA Engine
Layer to interface with the AP (especially L3/L4 interface).
The Infrastructure: this is the component providing the low-level mechanisms required by
other SCM entities (Stack, SPL, IPC, AGPS and Audio control). It contains hardware
drivers required by the others components like interrupt, watchdog, GPIO, and also
entities for communicating with the application processor (IPC). Finally, it contains
modules to relay functions to the application processor like NVM proxy, SIM proxy and
Audio Proxy.
5.1.3 ARM9 Software Architecture Overview
The Application Software Architecture uses the MotoAndroid architecture. The
Android Linux kernel is made of the Linux Kernel with some additional patches
including alarm, ashmem, binder, power management, low memory killer, kernel
debugger, and logger. The Linux kernel version is 2.6.27 and includes several
improvements made by OHA to the reference release in kernel.org.
The layers provide a view in which system functionality is increasingly abstracted
from hardware at the bottom layer, towards user functionality at the top layer.
The Linux kernel provides the operating system kernel services. It separates all
higher layers from the device hardware. Android relies on Linux version 2.6.27
for core system services such as security, memory management, process
management, network stack, and driver model. The kernel also acts as an
abstraction layer between the hardware and the rest of the software stack.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 11 of 43
Page 13

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
6. HTM1100-L Module Feature Summary
Key capabilities of the LGA module and associated features of the platform are
listed below. The following summary describes some of the platform capabilities.
6.1 Hardware Revision:
6.2 2G
• 3GPP Release 6 December 2006 version compliant
• Quad-band GSM 850/900/1800/1900 MHz
• GPRS Class 12
• EDGE Class 12
• A5/1-3 (unused because no voice) and GEA/1-3 Encryption
• DARP (Downlink Advanced Receiver Performance)
• 2G to 3G handoffs based on 3GPP specification
• Sensitivity (2% BER in voice call): less than -106dBm (-108dBm typical)
• GPRS/EDGE Tx Output power(GMSK): Power Class 4, 33dBm(850 and
900Mhz) and Power Class1, 30dBm(1800MHz and 1900MHz)
• EDGE Tx Power (8-PSK): Power class E2 (27dBm in 850/900 MHz and
26dBm in 1800/1900 MHz)
6.3 3G
• 3GPP Release 6 December 2006 version compliant,
• Frequency Bands
o 850/1900/2100 MHz (Supported)
• WCDMA 384kbps uplink (UL) – 384kbps downlink (DL)
• HSDPA 7.2 / 10.1 Mbps
• HSUPA 1.46 / 2 / 5.76 Mbps
• UEA01, UEA02, UIA1, UIA2 Encryption
• 3G Rx Diversity in all bands
• 3G to 2G handoffs based on 3GPP specification
• Sensitivity (0.1% BER in 12.2k voice call): less than -108dBm (-110dBm
typical)
• Output Power 23dBm
6.4 Advanced Services
• GPS is not supported.
6.5 Audio
• PCM signals are available on the LGA module
• The master Clock is provided by LGA module. Support for Slave Clock will
be available upon request
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 12 of 43
Page 14

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
• Supports PCM data formats: Word (16-bit) and 4 slots network mode
• Mode 1 will be supported in initial release, Mode 2 is in development (see
section 7.1.3.1)
6.6 Internal Memory
• 64MByte NAND Flash Memory
• 32MByte DDR-333 166 MHz clock SDRAM
6.7 System Requirements
• Linux Android Kernel (2.6.27) in the ARM9 of the W3G
• VTRXmc in the C55x+ of the W3G
6.8 Security
• High Assurance Boot with Multiple Super Root Key Support
• MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, 3DES, AES 128, RC4, RSA
• Subsidy Lock
• IMEI Protection
6.9 Connectivity
• SIM or UICC (SIM and USIM)
• USB client 2.0 HS Support (PC connectivity)
• 3GDigRF RF interface version 3.07
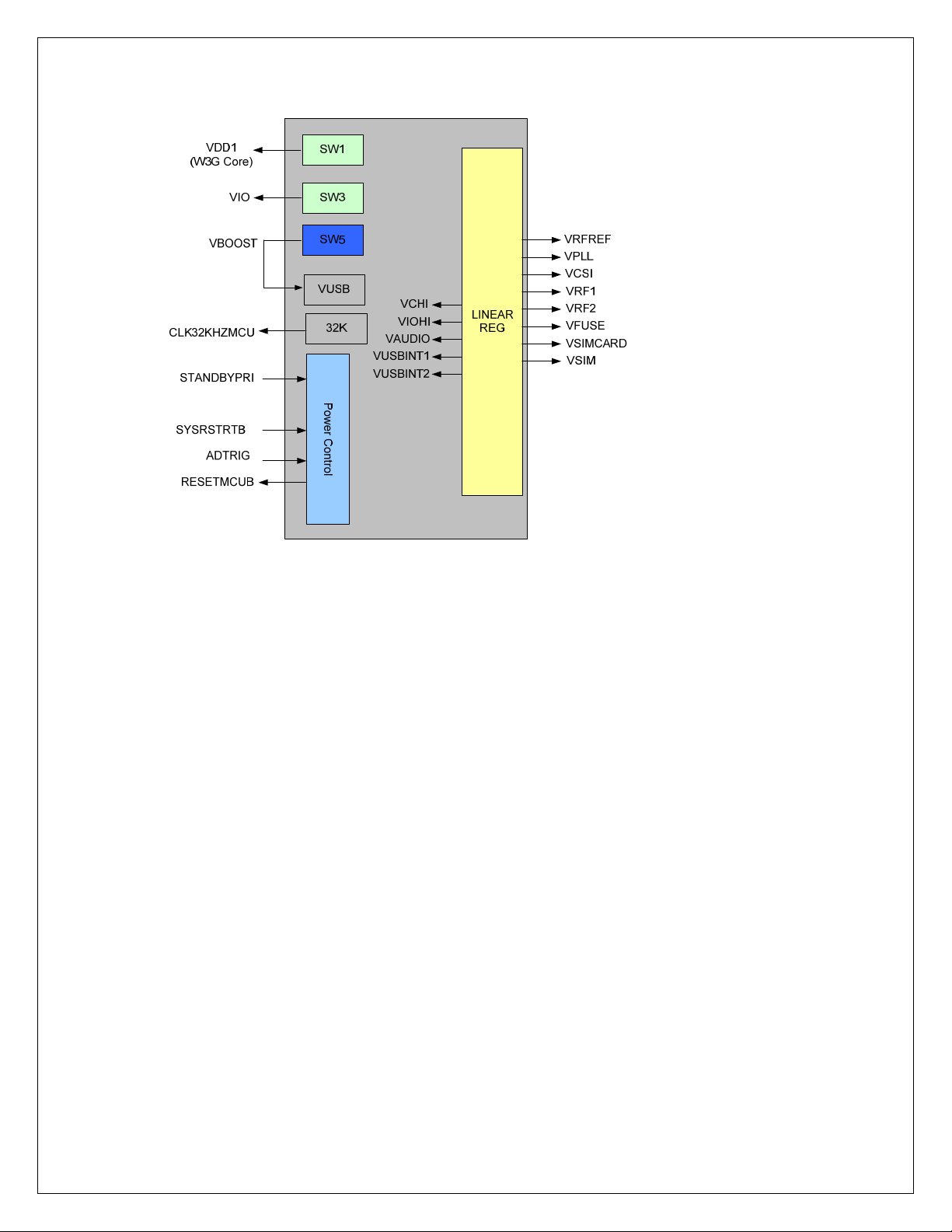
6.10 Power Up Sequence
The main power management function is performed by Power management IC (CPCAP),
which receives an input voltage of 3.3V.
CPCAP is capable of accepting input voltage in the range of 3V to 4.5V. This input
voltage range is being tested on LGA module.
CPCAP manages all the power requirements on module; it includes 2 bucks, 1 boost and
8 linear regulators.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 13 of 43
Page 15
MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Figure 4: Power Management by CPCAP
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 14 of 43
Page 16

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
7. Specifications
7.1.1 Electrical Specification
The HTM1100-L supports input voltage range of 3.0V to 4.2V supply. The module may
power down if the input voltage range drops below 2.9V.
Following table shows the power consumption of HTM1100-L. These measurements are
based on 00.16.01I software.
Mode Average Current at
3.3V (mA)
EDGE Downlink FTP Transfer
200kbps
HSDPA 10.1Mbps/ Power
level: 0dBm
2G Voice Call in PCL 5 DTX
(50%)
3G Voice Call 7dBm 260 858
Idle Mode in EDGE (DRX2),
no CM
Idle mode in WCDMA (K=7),
no CM
Airplane mode(RF off), no CM 3.3 <10
185 610
412 1360
200 660
4.6 <20
4.2 <20
Power Consumption
(mW)
7.1.2 Mechanical Specification
Physical dimensions of the card are: 29.3mm x 30.9mm
Height of the module with shield is 2.7mm (including label, label =0.1mm).
Weight of the module is ~6.1grams.
LGA module pad view as seen from the top is shown below. The actual bottom view of
the pads is shown in section 2.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 15 of 43
Page 17

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Figure 5: HTM1100-L Component View and Pad View (Top View)
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 16 of 43
Page 18

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
8. LGA module Interfaces
8.1.1 LGA Interface Signals
The HTM1100-L connects with netbook, notebook or MID using LGA module interface
signals. HTM1100-L uses USB interface on the module to connect with netbook,
notebook or MID. Electrically the module will be seen as a USB device since it uses a
standard USB2.0 connection. Power is supplied by motherboard. A SIM card must be
provided by PC manufacturer for user authentication.
A Radio disable (W_Disable) signal is connected from PC to the card; this allows the
user to enable/disable RF activity (Airplane mode) with a hardware switch. The module
controls one of the PC’s LEDs to indicate RF activity has been disabled or enabled. This
is driven by the signal LED_WWAN_B.
To summarize main characteristics of LGA Module:
• Standard USB interface
• B+ (3.0V to 4.2V) power supply from motherboard is used. Filter caps must
be added on these lines based on the PCB design.
• Expected max current in worst case scenario (with VSWR = 4) is around 1.1A
averaged over 1sec, 2.75A averaged over 100µs.
• W_DISABLE is used to enable/disable RF activity: 30s to disable, 1s to
enable.
• PC WWAN LED is controlled by the module.
The following table shows signals on LGA interface. The I/O level of all the pins is 1.8V.
Pin # Pin Name
A1 Ground
A2 Ground
A5 Ground
A6 Ground
A7 Ground
A8 Ground
A9 Ground
B1 Ground
B2 Ground
B3 USB_DM
B4 USB_DP
B5 VSIMCARD
B6 MICR_IN
B7 MICR_GND
B8 Ground
B9 Ground
C1 Ground
Direction
Input /
Output USB 2.0 DM pin 100 ohms matched impedance
Input /
Output USB 2.0 DP pin 100 ohms matched impedance
Output
Input
Pin Description
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
SIM card power.3.0V/1.8V supported.
Mic input
Mic ground pin
Ground
Ground
Ground
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 17 of 43
Page 19

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Input 3.3V module power.Max power <1.5W
(550mA).Add filter caps. 10K PullDown needed
C2 B+
C3 B+
C4 ON2B
C5 LED_WWAN_B
C6 MICR_RB
C7 Ground
C8 ANT_MAIN
D1 Ground
NC (Not
D2
D3 WATCHDOG_B
D4 SYS_RESTART
D5 LINE_OUT_R
D6 EAR_SPP
D7 Ground
D8 Ground
D9 Ground
E1 Ground
E2 HOST_WAKE
E3 PCM_IN
E4 Ground
E5 Ground
E6 EAR_SPM
E7 Ground
E8 Ground
E9 Ground
F1 Ground
F2 WAN_USB_EN
Connected)
Input 3.3V module power.Max power <1.5W
Input System Power on pin. Has an internal PullUp.
Output Signal to control a system LED/icon; L= RF
Output
RF
Input/Output
Input Watchdog interrupt, has an internal PullUp.
Input Do not Use (Debug interface). This pin has
Output
Output
Input /
Output
Input
Output
Input /
for correct power up.
(550mA).Add filter caps
If functionality is unused, the pin can be left
unconnected.
If functionality is used:
- pin should be high at boot
- if device was previously powered OFF by
assertion of WATCHDOG_B a falling edge on
ON2B will power ON the device. See section
7.1.5 for external circuit requirement.
inactive.
This signal shall be capable of sinking to ground
a minimum of 9.0mA at up to a maximum VOL
of 400mV.
Mic bias
Ground
Connect to antenna 50 ohms impedance.
External matching circuit is required. See
section 7.1.4
Ground
This pin can be left unconnected.
If driven by Host:
- must be high at boot
- can generate a Power OFF on falling edge
See section 7.1.5 for external circuit
internal PullUp.
Audio line output
Audio speaker output
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
GPIO9 Open drain active low signal to wake up
host. This pin has internal PullUp. Connect to a
GPIO on host apps processor or leave it un
connected if not used.
PCM input
Ground
Ground
Audio speaker output
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
GPIO8(LED_WLAN). This is still under
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 18 of 43
Page 20

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Output definition, can be connected to a GPIO on host
apps processor or left un connected.
F3 W_DISABLE
F4 JTAG_RTCK
F5 JTAG_TCK
F6 JTAG_EMU0
F7 Ground
F8 Ground
F9 Ground
G1 Ground
G2 COEX1
G3 PCM_FSX
G4 JTAG_TDO
G5 JTAG_NTRST
G6 JTAG_TMS
G7 Ground
G8 ANT_DIV
H1 Ground
GPS_TIMESTAM
H2
H3 UART_RX
H4 PCM_CLKX
H5 COEX2
H6 PCM_OUT
H7 Ground
H8 Ground
H9 Ground
J1 Ground
J2 Ground
J3 UART_TX
J4 SIM_IO
J5 SIM_CLK
J6 SIM_RST
J7 Ground
J8 Ground
J9 Ground
K1 Ground
K2 Ground
K3 UART3_RX
K4 UART3_TX
P
Input /
Output
Output
Input
Input /
Output Do not Use (Debug interface)
Input /
Output
Input /
Output
Output
Input
Input
RF Input Receive diversity antenna. Connect to antenna
Output CLK_REQ active low signal requesting for
Input
Input /
Output
Output SYS_CLKOUT2 output clk from W3G to
Output
Output
Input /
Output
Output
Output
Input
Output
GPIO10(signal from baseband; active low
=disable RF)
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
GPIO6 to coexist with other RF systems. Can be
left un connected.
PCM Frame sync
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Ground
50ohm impedance. External matching circuit is
required. See section 7.1.4
Ground
System clock/GPS time stamp. This is not
supported in SW, can be left unconnected.
Do not Use. (UART transmit )
PCM clock
coexist with other RF systems. Not supported in
SW. Can be left unconnected.
PCM output
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Do not Use. (UART transmit )
SIM interface data IO. This pin has an internal
PullUp.
SIM clock, This pin has an internal PullUp
SIM reset. This pin has an internal PullUp
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Ground
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 19 of 43
Page 21

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Input /
K5 JTAG_EMU1
K6 JTAG_TDI
K7 Ground
K8 Ground
K9 Ground
Table 1 – HTM1100 LGA module connector pin out
Output Do not Use (Debug interface)
Input
Do not Use (Debug interface)
Ground
Ground
Ground
8.1.2 SIM Interface
A standard ISO7816 SIM interface has been used on the card. SIM card is connected to
the SIM controller on ARM9.
A SIM slot must be provided by PC manufacturer on the final platform. SIM signals do
not have ESD protection. ESD protection is expected to be provided by PC manufacturer
and SIM connector should ne placed as close possible to the module by following the
guidelines in ISO7816 specification.
SIM signals are routed through the LGA module interface. SIM signals are shown in the
previous section.
SIM detection is done by SW polling. SW polls to see if SIM is present or not. SIM_CD
line is tied to w_disable and SIM_CD is not used for SIM detection.
8.1.3 WWAN_LED
WWAN_LED status indicator is in compliance with WWAN_LED signal in PCIe
specification 1.2. WWAN_LED signal is capable of sinking to ground as specified in
PCIe Specification 1.2.
WWAN_LED signal is a status indicator and the indicator is used to drive LED on the
host. WWAN_LED cannot change the brightness of the LED. Host is expected to provide
the source for LED and also capability to manage the brightness.
8.1.4 Audio Interface
HTM1000-L module will have the capability to support PCM Audio and Analog Audio.
Hardware support has been implemented; however SW support has not been
implemented yet. SW support for PCM audio and Analog audio will be available in the
future. Contact Motorola Applications Engineering for details.
Following PCM signals are routed to LGA interface.
Pin # Pin Name Description Voltage Level
E3 PCM_IN PCM input 1.8v
G3 PCM_FSX Frame Sync 1.8v
H4 PCM_CLK PCM Clock 1.8v
H6 PCM_OUT PCM output 1.8v
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 20 of 43
Page 22

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Table 2: PCM Audio Interface
Following Analog Audio signals are routed to LGA interface.
Pin # Pin Name Direction Pin Description
B6 MICR_IN
B7 MICR_GND
C6 MICR_RB
D5 LINE_OUT_R
D6 EAR_SPP
E6 EAR_SPM
Input
Output
Output
Output
Output
Mic input
Mic ground pin
Mic bias
Audio line output
Audio speaker output
Audio speaker output
Table 6: Analog Audio Interface
Recommended Connection if
analog not used
Ground
Ground
No connection
No connection
No connection
No connection
9. Communication with Host
This chapter describes the way the UMTS LGA module will communicate with
the Host, i.e. the PC.
9.1.1 Overview
The LGA module communicates with the host via the USB 2.0 link, and the
W_DISABLE# pin.
Figure 6: Communication between Host and LGA Module
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 21 of 43
Page 23

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
9.1.2 Link Details
Communication with the PC thru USB is made thru a composite driver. There is
only one enumeration which covers all the needs: final user, tests, factory, etc.
The details of this configuration are given by the figure below.
Figure 7: HTM1100-L Modem interface
The link between Card and PC is made of 3 data pipes:
• USB LAN: used to connect test services as TCMD, Log, as on LJ. The
channel may also be used for NGP services.
• ACM pipe 1: used for data connection. DUN services will send dial up AT
commands thru this channel. When a connection is established, PPP is
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 22 of 43
Page 24

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
used to transfer data across the link. On the LGA module side, IP frames
are routed directly (thru line discipline) to the appropriate Netmux
channel.
• ACM pipe 2: this ACM pipe is used for all control which is not related to
DUN. It is used by the connection manager on the PC side.
On the LGA module, ADB is not added on top of these three pipes as no external
developer will ever use ADB tools to develop on this card. And for AP log, the
same feature can be achieved by setting the variable ADBHOST on the PC to the
LGA module IP address.
The W_DISABLE# signal is also used to notify the card to go into airplane mode (signal
is active low, so setting it to ground will set the card to airplane mode). Setting
W_DISABLE# to low triggers an event on SCIM, and causes de-registration which is
handled at CommDrv level.
9.1.3 Host Modem Wakeup Mechanism
HTM1100-L supports optional USB remote wakeup capability by enabling the remote
wakeup flag in USB configuration descriptor and using electrical signaling as described
in Section 7.1.7.7 of USB Spec 2.0 to remote wakeup USB host. However, some USB
controllers and/or USB host software may not support USB remote wakeup. Therefore,
GPIO signaling is used to support remote wakeup.
During USB enumeration, HTM110-L will always enable USB remote wakeup flag in
USB configuration descriptor by default. That is to say, bit 5 of bmAttributes in USB
configuration descriptor is always 1 (enable).
Remote wakeup is implemented in two ways:
9.1.3.1 Using USB inband signalling
If USB host (HW and SW) supports USB remote wakeup, the built-in USB remote
wakeup functionality in device and host controller is used, HOST_WAKE is kept in its
default state as input and it is not used.
9.1.3.2 Using Host_Wakeup pad of HTM1100-L
If USB host does not support USB remote wakeup, it should disable this capability (see
sections 9.1.1.6, 9.2.5.2 and 9.4.1 of USB Spec 2.0) by clearing (disable) this feature. The
standard request to clear this feature is
0x0001010000000000. USB host should disable this
feature during or after USB enumeration but before USB suspend happens. HTM1100-L
can acknowledge this request, disable USB remote wakeup functionality and configure
HOST_WAKE as output LOW. If HTM110-L USB device is suspended and needed to
wakeup host, it will assert HOST_WAKE high. This should generate an interrupt to host
and host should start a standard USB resume process. HTM110-L USB will de-assert
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 23 of 43
Page 25

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
HOST_WAKE to low when it gets resume interrupt. The Figure 1 shows the GPIO
remote wakeup signaling.
Host gets interrupt and
starts normal USB
resume process
Device asserts
HOST_WAKE high to
remote wakeup host
USB suspended
Device gets resume
interrupt and clear
HOST_WAKE
Figure 8: GPIO remote wakeup signaling
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 24 of 43
Page 26

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
10. AT commands
The LGA module supports AT commands interface using TTY/ACM. There will be two
TTY ports supported for AT commands, and both allow all the AT commands. PC
Connection Manager client must use only one instance for PPP at any time. Since the PC
Connection Manager Client cannot execute AT commands when data is active using PPP,
a second TTY Port instance of AT parser was added to execute non-data commands like
SMS or SIM.
The PC Connection Manager client must use all the relevant dependent AT commands on
one instance of AT parser only. E.g. For CGACT to work CGDCONT and any other
dependent commands need to be issued on the same TTY port.
The LGA module supports only one PDP context/PPP and the Context ID 1 must be used.
AT parser allows only one PDP activation using AT+CGACT or ATD*99#, so any time
one PDP is active AT Parser returns an ERROR for the next PDP activation request.
LGA module supports only USIM based Phonebook and SMS.
LGA module supports 27.007 Rel5 Spec defined options and parameters and there are
some deviations from the specifications. Refer to HTM1000_AT_Commands_spec for
details.
LGA module AT parser checks the existence and validity of mandatory fields. If any
mandatory field is absent or validity check fails then LGA module AT parser returns
ERROR.
LGA module AT parser supports extended error reporting.
The PC Connection manager client must use ATD*99# to trigger the PPP and Data call
activation.
The values stored using any of the AT commands like CGDCONT are not persistent
across power cycle.
10.1 LGA module AT command interface allows the below mentioned functionality on high level using Different AT commands:
10.1.1 Network Connection Management
• LGA module allows AT commands for Network Connection Management like
APN management: Set, Read, and Reset.
• Activate and Deactivate network connection.
• GPRS Attach and Detach to the network.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 25 of 43
Page 27

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
• QOS Profile Management: Set QOS, Modify QOS, Minimum QOS.
• Get the PDP Context IP address.
10.1.2 Registration or Mobility Management
• Network Registration Event Notifications.
• PLMN selection: Manual, Automatic. Preferred PLMN list: Adding, deleting,
updating. Also for reading used entries from the USIM list of preferred PLMNs.
• Preferred PLMN list type: Selecting, Reading.
• Reading all the operator names.
• Reading the current activity status.
• Airplane mode and turning ON and OFF the RF.
• Enabling and Disabling the signal strength change event notification and also to
get current signal quality.
• Indications like Signal Strength, Service availability, Roam and SMS full status.
• GPRS mobile class: Setting, Reading
• GPRS registration change notification: Enabling, Disabling.
• Selection of network connection types, for example: GSM only Automatic,
WCDMA only Automatic, GSM and WCDMA Automatic.
• Service Supported in Current Cell and Packet Data activity indications.
10.1.3 SMS
• Supports SMS using PDU mode only. Messages are stored in the SIM/USIM.
• Writing, Sending and Receiving SMS messages.
• New SMS message indications.
• List SMS messages.
• Send SMS messages from Storage.
• Delete SMS message.
• Write message to memory.
10.1.4 USIM and Phonebook
• Query IMEI, IMSI, MSISDN’s of LGA module.
• Query FLEX version, CARRIER name and Country code of the LGA module
subscriber unit.
• Read a specific record from the phonebook entries (of USIM) or records of
specified range.
• Write the phonebook record into the storage entry specified i.e. only USIM is
supported. Capacity: It depends on the SIM/USIM card capacity.
• PIN management: activate/deactivate PIN, PIN lock, changing PIN, unblocking
by using the PUK.
• Subsidy Lock support.
• SIM file access: read, write facility.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 26 of 43
Page 28

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
11. NVM/FLASH
The LGA module uses Single Level Cell (SLC) Large Page (LP) NAND flash to store all
data. Flash block sizes is 128K, divided each in 64 pages of 2K each.. Default flash size
if fixed to 64 Mbytes.
NAND flash is shared for AP and BP needs, but can only be physically accessed by the
AP side.
12. RF Calibration/Phasing
All boards are calibrated and tested in order to meet 3GPP specifications with margins.
In 2G, output powers are calibrated for each PCL and with compensation over frequency.
2G Calibration points are then validated by testing output power levels in GMSK and
8PSK. Critical parameters such as modulation and switching spectrum are also tested.
RSSI levels are also calibrated across the range with frequency compensation. BLER and
BER level are measured to validate sensitivity meets expectations.
In 3G, output power is calibrated through the whole range (from below -55dBm up to the
maximum output power level for each band). The receive chain is calibrated for input
power levels. There are some compensations over frequency both in uplink and
downlink.
3G calibration points are also validated by checking output power together with ACLR
and EVM. BLER is measured is WCDMA for different transfer rates in order to validate
the downlink path.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 27 of 43
Page 29

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
13. Platform Validation
13.1 RF Performance Testing
13.1.1 Equipment
RF performance testing is performed using either Rhohde&Schwarz CMU200 or Agilent
8960
13.1.2 Equipment list
• HTM1100 LGA module LGA module
• USB adapter board
• CMU 200 or Agilent 8960
• RF connector: U.FL to SMA connector ( to connect from antenna port of LGA
module to equipment)
• Test SIM
Figure 9: LGA Module test set up
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 28 of 43
Page 30

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
13.1.3 Setup
Power for LGA module is provided by USB adapter board. Insert HTM1100 LGA
module into test socket as shown in the picture above. The PCB with test socket houses
PCIe connector. PCIe to USB adaptor board is used to connect with a PC. Use a ‘Y’
cable to connect USB adaptor board to PC. It is recommended that a ‘Y’ cable is used to
supply enough current to the card. Using U.FL to SMA connector, connect antenna port
of LGA module to CMU200. Insert test SIM in SIM slot which is located on PCIe to
USB adapter board.
• 2G testing configuration
• Network Support = GSM + EGPRS
• Main Service = Packet Data
• Service Selection = Test Mode A (for testing Tx)
• BCCH = TCH (or Aux TX - Channel type = BCCH)
• 3G testing configuration
• Choose WCDMA signaling Mode
• Operating Frequency Band, select UL or DL frequency
• Dedicated Channel (CS) = RMC
Follow the instructions in CMU200 or AG 8960 to set up the equipment. Instructions on
CMU200or AG8960 setup are beyond the scope of this document. RF performance tests
and through put testing can be performed using CMU200 or AG8960.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 29 of 43
Page 31

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
14. Hardware Installation
14.1 HTM1100 LGA module Reflow Process
The LGA module needs to be soldered on to a PCB. Pb-Free solder assembly processing
must be used. Reflow process should comply with JEDEC standard J-STD-020.
Avoid high temperature spikes to avoid module warpage.
Recommended Setting: PeakTemp =245oC (+5/-0) and Reflow Time =65-70 Secs.
Follow the guidelines given in the following table during soldering process to avoid
module warpage.
Condition Exposure
Average ramp-up rate (200oC to 245oC) Less than 3oC/second
Between 150 and 200oC Between 60-180 seconds
> 217oC Between 60-150 seconds
Peak Temperature 245oC (+5/-0)
Time within 5oC of peak 20-40 seconds
Ramp-down rate (Peak to 50oC) Less than 6oC/second
Time from 25oC to Peak No greater than 480 seconds
Following graph shows characterization of reflow process:
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 30 of 43
Page 32

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
A test socket was developed by Motorola to calibrate and test the modules. The test
socket is shown below. Module is placed in the test socket for phasing and testing.
J
I
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
U.FL
Connector
Figure 10 : LGA module inside Test Socket
Insert the module with
‘A1’ at this end. It is
marked with white
arrow.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 31 of 43
Page 33

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
15. LGA module Driver Installation
The Motorola driver package for LGA module is included in deliverables. The driver
package is available for Windows XP and Windows 7 operating systems. The driver
package is an .msi (Microsoft Installer) package.
Motorola driver package requires that the Windows XP operating system is at least
Service Pack 3 (SP3).
.
Double click on “Motorola_HTM1000_Datacard_Drivers_1.5.2.msi” to start installation.
Installation window opens, and click ‘Next’ on the window.
Agree to license terms, click on ‘Next’.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 32 of 43
Page 34

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Installation complete message comes up. Click Close to exit.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 33 of 43
Page 35

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
After successful installation of Motorola 3G Data Card driver, the LGA module appears
in device manager as shown in the picture below.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 34 of 43
Page 36

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
16. Live Network Connection
16.1 Plugging in the card in PC
After hardware and software installations as described in previous section, open device
manager to ensure device enumeration. The device enumerates as Motorola HTM1000
Modem under Modems as shown below. This device is also shown under ports as a COM
port.
16.2 Setting up Dial Up Networking (DUN) Connection using LGA module as a Modem
This section describes how one can setup dial up networking connection using LGA
module as a modem.
Open device manager, right click on Motorola 3G HTM1000 Modem under modems and
choose properties. Click on ‘Advanced’ tab and enter the initialization command:
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 35 of 43
Page 37

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
AT+CGDCONT = 1,”IP”,”APN”. Where APN is the access point name. APN
information must be obtained from the carrier that is supplying SIM card. Then click
on ’OK’ on the window to save settings.
By default the radio is turned off (Airplane Mode). Radio can be turned on by sending an
AT command to the Modem. Open HyperTerminal and connect to the modem using
Modem port. To turn ‘ON’ the radio send AT command AT+CFUN=1. This will enable
radio. If an LED is connected to WWAN_LED pin, LED will turn ON when the radio is
turned ‘ON’; this is an indication to ensure that the radio is ON.
Use the following steps to setup dial up connection. From StartÆSettingsÆnetwork
Connections open New Network Connection wizard and setup a new dial up network
connection.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 36 of 43
Page 38

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
To continue click ‘Next’
Choose “connect to the Internet” and click on ‘Next’
Choose to ‘Set up the connection manually” and click on ‘Next’
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 37 of 43
Page 39

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Choose ‘Connect using a dial-up modem” and click on ‘Next’
Choose Motorola 3G Datacard Modem and click ‘Next’
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 38 of 43
Page 40

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Enter a name for ISP and click ‘Next’
Enter phone number for data connection. The dial up number is provided by the carrier
and the number could vary from carrier to carrier. Typically the dial in number is *99# or
*99***1#. Enter the dial up number and click on ‘Next’
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 39 of 43
Page 41

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 40 of 43
Page 42

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Now you are ready to connect to live network. Double click on 3G Data Card icon on the
desktop. 3G Data Card connection window appears as shown below.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 41 of 43
Page 43

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
Click on properties and ensure that 3G HTM1000 modem is chosen for connection. Click
on ‘OK’ on Properties window and then Click on ‘Dial’ on 3G LGA module window.
The following window appears which shows dial up connection.
Once network connection is established, IP address of the connection can be verified by
typing ‘ipconfig” in command window.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 42 of 43
Page 44

MOTOROLA HSPA LGA Module User Guide
17. Known Issues
17.1 LGA Module Power up Timing
Issue: Power is provided to LGA module using B+. To turn Off the power to the module
B+ should be dropped down to 550mv or lower. If the supply voltage stays between 550
to 1150mV and then ramps to 3.3V the module will not turn ON when it’s powered up.
Resolution: Caution should be taken to drop the supply voltage to below 550mv while
designing a platform. If the supply voltage does not drop down to 550mv or lower, time
lapse between power down and power up should be at least 250ms.
Motorola Confidential Proprietary – Disclosed Under NDA
Page 43 of 43
Page 45

Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory Requirements
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) requires application for certification of digital
devices in accordance with CFR Title 47, Part 2 and Part 15. This includes MPE calculation. As
the modem is not a standalone transceiver but is an integrated module, the modem cannot be
tested by itself for EME certification. It is, however, the integrator’s responsibility to have the
completed device tested for EME certification.
Caution: Unauthorized repairs or modifications could result in permanent damage to the
equipment and void your warranty and your authority to operate this device under
Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
FCC Notice to Users
Motorola has not approved any changes or modifications to this device by the user. Any changes
or modifications could void the user's authority to operate the equipment. See 47 CFR Sec. 15.21.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation. See 47 CFR
Sec. 15.19(3).
The external label on the host device must include the following FCC ID information:
"This device contains TX FCC ID: IHDT56LV1"
If your mobile device or accessory has a USB connector, or is otherwise considered a computer
peripheral device whereby it can be connected to a computer for purposes of transferring data,
then it is considered a Class B device and the following statement applies:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates uses and can
Page 46

radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference.
(2) This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Precautions
Preface
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Interface connector and some of the module circuits are not shielded. Be sure to take appropriate
precautionary measures in order to avoid ESD while handling the module. ESD can damage the
modules. Integrators need to design ESD protection on all external interfaces.
Antenna and Transmission Safety Precautions
User Operation
Do not operate your unit when a person is within 8 inches (20 centimeters) of the antenna. A
person or object within 8 inches (20 centimeters) of the antenna could impair call quality and may
cause the phone to operate at a higher power level than necessary.
Important: The unit must be installed in a manner that provides a minimum separation distance
of 20 cm or more between the antenna and persons and must not be co-located or
operate in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter to satisfy FCC RF
exposure requirements for mobile transmitting devices.
Important: To comply with the FCC RF exposure limits and satisfy the categorical exclusion
requirements for mobile transmitters, the requirements described in the following
section, “Antenna Installation” , must be met.
Page 47

Standards
Antenna Installation
• The antenna installation must provide a minimum separation distance of 20 cm from users
and nearby persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
• Antenna installation should be done by a professional installer and should meet all FCC
requirement as given in FCC part 15.
• The combined cable loss and antenna gain must not exceed +5.0 dBi (850 band). The
combined cable
must
not exceed 2.0W EIRP in the PCS (1900) band in order to comply with the EIRP limit
of 24.232 (b). OEM installers must be provided with antenna installation instruction and
transmitter operating conditions for satisfying RF exposure compliance.
loss and antenna gain must not exceed +
2.9 dBi and total system output
Section 15.203 - Antenna Requirements
An intentional radiator shall be designed to ensure that no antenna other than that furnished by the
responsible party shall be used with the device. The use of a permanently attached antenna or of
an antenna that uses a unique coupling to the intentional radiator shall be considered sufficient to
comply with the provisions of this Section. The manufacturer may design the unit so that a
broken antenna can be replaced by the user, but the use of a standard antenna jack or electrical
connector is prohibited. This requirement does not apply to carrier current devices or to de-vices
operated under the provisions of Sections 15.211, 15.213, 15.217, 15.219, or 15.221. Further, this
requirement does not apply to intentional radiators that must be professionally installed, such as
perimeter protection systems and some field disturbance sensors, or to other intentional radiators
which, in accordance with Section 15.31(d), must be measured at the installation site. However,
the installer shall be responsible for ensuring that the proper antenna is employed so that the
limits in this Part are not exceeded.
 Loading...
Loading...