Page 1

Motorola
SM56 Modem
Quick Start User's Guide
Contents
1 Overview
2 Introduction
3 Personal Computer Requirements
4 Preparing the Computer for SM56 Installation
5 Understanding Sound Card Compatibility and Installing Hardware
6 Installing SM56 Software on Windows 95/98
7 Installing SM56 Software on Windows NT 4.0
8 Verifying Proper Modem Installation
9 Changing the Operating System
10 Using the SM56 Modem
11 Un-installing and Upgrading the SM56 Modem
12 Troubleshooting
13 Reporting Problems and Contacting the Modem Supplier
14 Understanding Microsoft Windows Logo Certification
15 An Overview of the V.90 Protocol
Appendix A SM56 Features
Appendix B Software License Agreement
1 Overview
This document helps the OEM, system integrator, VAR, and end user with host system selection
and proper modem hardware and software installation. It lists qualified personal computer
systems, and explains proper modem usage. This document helps you select CPUs, and it
explains the tradeoffs associated with different processors. It explains the use of the SM56
Data/Fax/Voice modem with various sound card configurations. It also aids you in
troubleshooting and testing the SM56 equipped system.
2 Introduction
Motorola's SM56 Modem is a feature-rich modem at an attractive price. It provides high-speed
communications between your personal computer and a remote location, such as an Internet
Service Provider (ISP), so you can:
• Receive data at up to 56 Kbps in V.90 or K56flex modes
Page 2

• Get automatic fallback to V.34 (33.6 Kbps) rates in bad line conditions and on non-
V.90/K56flex headends
• Send and receive faxes on your personal computer at rates up to 14.4 Kbps
• Use your computer as a video phone to place and receive video phone calls.
• Use your computer as a telephone answering machine (TAM) -- not available on Data/Fax
modems.
• Use your computer to conduct hands-off speakerphone voice calls (Data/Fax/Speakerphone
modems only).
Important: There are three different SM56 modem types, and each supports a different featureset, as follows:
Product Name Modem Type
Main Feature-set
Supported
1.Motorola SM56 PCI Fax Modem Data/Fax only All data and fax modes
2. Motorola SM56CPQ PCI Modem No telephone answering
machine (TAM)
No speakerphone
No caller ID
No distinctive ring
______________________________________________________________________________
________
1. Motorola SM56 PCI Voice Modem Data/Fax/TAM All data and fax modes
Telephone answering
machine (TAM)
Caller ID and
distinctive ring
No speakerphone
______________________________________________________________________________
________
1. Motorola SM56 PCI Speakerphone Data/Fax/TAM/Speakerphone All data and fax modes
Modem Telephone answering
machine (TAM)
Full duplex
speakerphone
______________________________________________________________________________
________
You can check which modem you have by opening the SM56 Control Panel application (Start-
>Settings->Control Panel, then double click on the SM56 Modem icon). On the applications'
main window the product name of your installed modem is displayed.
Page 3

Personal-computer OEMs that bundle the SM56 can benefit from sizable cost reductions,
hardware reduction, and lower power consumption. End users benefit from quick, easy and
affordable software upgrades, which help them keep current with the latest communications
technology.
Please check with your direct modem supplier for the latest software updates and other product
information.
3 Personal Computer Requirements
Motorola performs rigorous, exhaustive testing on its modems. It has developed a list of
recommended personal computer features that perform well with the SM56. The information
includes qualified CPUs, Level 2 cache requirements, operating systems, RAM requirements,
and third-party sound card compatibility. However, in today's dynamic technology markets, it is
not possible to test all components and combinations on all systems.
This section outlines minimum system requirements for SM56 operation. On these systems,
CPU loading was found to be acceptable and the modem demonstrated good performance over
the entire network model.
Important: SM56 operation is not limited to the personal computer systems listed here.
Recommended CPUs
The SM56 modem has been qualified (tested for processor loading and TSB network model
coverage) on the following processors:
• Intel Pentium, 150MHz with MMX, 256K Level 2 (L2) cache minimum
• Intel Pentium, 200MHz, 256K L2 cache minimum
• Intel Pentium II
• Intel Pentium Pro
• Intel Celeron (Pentium II, 266MHz, no L2 cache)
• AMD K6-2 with 3DNow!, 256K L2 cache
The SM56 functions satisfactorily on the following systems. However, it has not been fully
qualified (it was not tested for processor loading or TSB performance):
• AMD K6, 233 MHz, 256K L2 cache
• Cyrix MII, 266MHz, 256K L2 cache
The SM56 does not function on the following CPUs, whose floating-point performance is
insufficient:
• Cyrix MediaGX
• Cyrix MediaGXM
• Cyrix 6x86
Page 4

Level 2 Cache Benefits
Level 2 (L2) cache is an instruction memory (SRAM) bank that resides outside the CPU core. It
holds many instructions close to the CPU, to reduce the need for the processor to use slow access
cycles fetching instructions from main memory (DRAM). Eliminating most CPU accesses to
main memory considerably improves overall system performance.
The SM56 modem works best when a minimum of 256K L2 Cache is installed on the computer
system motherboard to minimize processor loading. Intel's Celeron (266MHz PII) systems do not
have L2 cache. Although the SM56 operates on those systems, host processor loading increases
in the absence of L2 cache.
Compatible Operating Systems
The SM56 modem will run on the following operating systems:
• Windows 95 (OEM Service Release 2.0 or later)
• Windows 98
• Windows NT
• DOS Box under Windows 95/98.
System RAM Requirements
The SM56 operates on systems that have the minimum RAM required by the installed operating
system. As with L2 cache, the more main memory, the better. This reduces slow hard-disk
swapping and improves overall system performance....especially when executing numerous
concurrent processes.
4 Preparing the Computer for SM56 Installation
To ensure problem-free installation of the SM56, ensure that an Interrupt Request (IRQ) line is
available, as follows.
1. In Win95/98, open the Control Panel.
2. Double click the System icon.
3. Select the Device Manager tab.
4. Highlight the Computer icon.
5. Select the Properties radio button.
6. Ensure that the Interrupt Request (IRQ) radio button is selected.
This displays the IRQ lines that are in use on the computer. Available/unused lines are not shown
on the list. The SM56 PCI software modem can use an IRQ in the range 3 through 15, inclusive.
Page 5

If there is no IRQ line available for the SM56 disable one of the COM ports in the BIOS and use
it's IRQ.
Note: If you are using a Windows 95/98 DOS box application, the modem requires two IRQs.
Refer to the Troubleshooting section in this document, or to the on-line User's Guide for more
information on DOS application support. You can access the User's Guide through the SM56
modem Control Panel application.
Also, you must ensure that one of COM Port 2, 3, or 4 is available for the SM56, as follows:
1. Open the Windows Control Panel.
2. Double click the System icon.
3. Choose the Device Manager tab.
4. Expand the Ports (COM and LPT) branch to see which COM ports are already installed.
To install the SM56 so that it is accessible to older application software and DOS programs, the
modem needs to be installed on one of COM port 2, 3, or 4. If none of these ports are available,
you must disable one of them in the BIOS.
5 Understanding Sound Card Compatibility and Installing the SM56
Hardware
Note: This section applies only to Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems.
Before discussing modem board installation, let's review the optional sound card connections for
the SM56. Recall that SM56 Data/Fax/TAM modems do not support the sound subsystem, even
though you can record and play back answering machine messages through your sound card
using them.
Sound Card Compatibility:
The SM56 requires a sound card to use its speakerphone capabilities. The Data/Fax/TAM modem
requires the sound card for local message playback which occurs through the host PC bus, not via
external wire connections. For this reason there are typically no TAPI connectors or
speaker/microphone jacks provided on Data/Fax/TAM and Data/Fax modems. Instead, these
modems usually have a local call progress speaker mounted on them, while speakerphone
supporting modems do not (since they can be connected to the sound board).
Typically, there are two methods for interfacing the Data/Fax/TAM/Speakerphone modem to a
sound card:
• Internal speaker/microphone TAPI connector/header
• Microphone and Speaker jacks mounted on the modem board
TAPI Connector
Page 6

Using the on-board TAPI connector requires a sound card that also has a TAPI-style connector,
which has pins that provide analog microphone output and speaker input connections. Many
sound cards have one or more CD or auxiliary connectors, but these do not provide the required
microphone output for the SM56. To ensure compatibility, check the sound card specifications;
one connector must provide a microphone output as well as a speaker input.
You can make up or purchase a cable that routes SM56 microphone and speaker signals to the
sound card. Locate the 4-pin header connector on the SM56 card. The SM56 reference design
connector pin-out is as follows.
SM56 Pin Signal
1 Ground
2 Microphone In
3 Ground
4 Speaker Out
Important: Different modem manufacturers may vary this pinout. Consult their modem
documentation to verify. Also, different sound card connector pinouts may be different, in which
case the audio cable will need to have cross-over wires to match the pin signals. Make sure to
consult your sound card documentation for pin-signal details.
On-Board Microphone and Speaker Jacks
If the sound card does not provide a TAPI-style connector, you can connect the SM56 modem to
the sound card through optional on-board microphone and speaker jacks. Ask your modem
supplier for a board with this option. The microphone jack allows for the direct connection of a
microphone to the SM56 modem card. The sound card also has a microphone input.
• To use speakerphone applications with the modem, connect your microphone to the
microphone input jack on the SM56 modem card. You can then talk into your
microphone and hold a conversation with the remote party.
• To record audio (such as a voice mail greeting) on the personal computer, attach the
microphone to the microphone input jack on the sound card. Note that some
telephony applications may support audio recording through the modem jacks, e.g.
Bitware, in which case you do not need to switch the microphone to the sound card input
jack.
You may be able to create a special cable or use a T-splitter to connect one microphone to the
input on the modem and the sound board simultaneously.
The speaker out jack on the modem board can be used in one of two ways:
• To directly connect powered speakers to it.
• To connect it to the sound card line-in jack (this allows the speakers to remain plugged
into the sound card at all times).
SM56 Hardware Installation Procedure:
1. Power down the personal computer.
Page 7
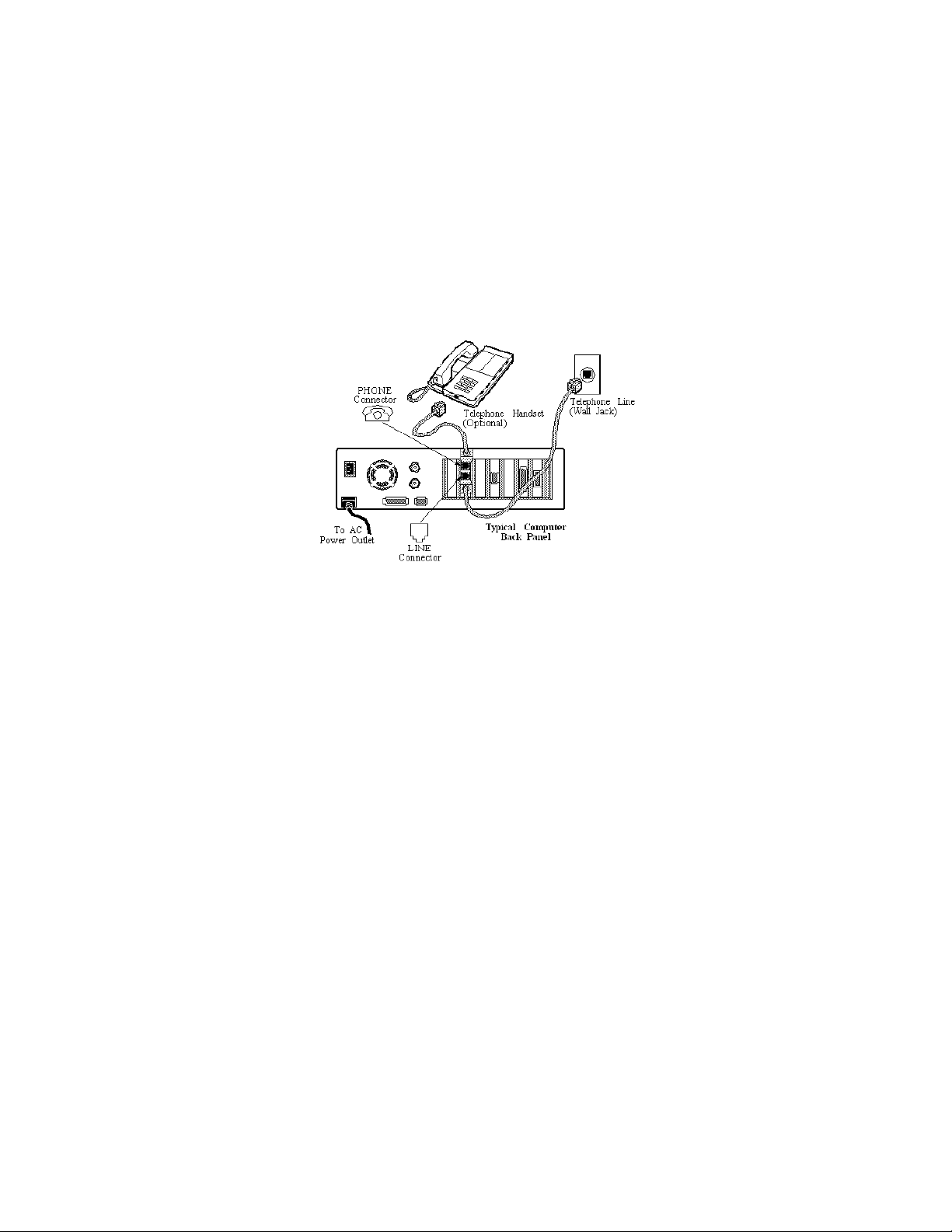
2. Locate a vacant PCI bus connector.
3. If using the SM56 Data/Fax/Speakerphone modem, connect the sound subsystem interface
cable(s) to the modem card (via the internal TAPI connector or using the audio jacks -- refer
to the information above on sound card compatibility.)
4. Connect the modem Line input to an analog phone jack using an RJ-11 phone cable.
Optionally, connect a telephone handset to the Phone input on the line interface card.
5. Replace the personal computer cover and power it back on.
6 Installing SM56 Software on Windows 95/98
Note: Windows 95/98 assigns the modem a COM port number. To support older software
applications and DOS games the SM56 installation software attempts to negotiate a COM port
number in the range of 1-4. If the install picks a higher COM port, you can force the COM port
selection via the Control Panel application after install is complete.
Installing on Windows 95/98
(Note: The Install Wizard may vary slightly with different versions of the OS and different
service packs)
On starting Windows for the first time after installing the SM56 line interface card, the Windows
Configuration Manager detects the new hardware, assigns resources to it, and then displays a
window requesting the modem software drivers. This indicates that the Configuration Manager is
looking for the information (INF) file, which contains information about the modem, including
device type (Modem), device driver information (the name of the driver that will control the
modem) and the AT command/response sets that it supports.
Page 8

In response to the request window. Select Driver from Disk Provided by Hardware
Manufacturer (or Have Disk depending on the OS version) and browse to where the SM56
drivers are located. Windows should find the information on the disk and identify the device as a
SM56 Modem. It then copies the files from the install disk to the computer.
Important: The install program may display a message box that reports Cannot locate file.... If
this occurs, browse and re-point to where the SM56 driver files are located. Then click OK.
Installation will now complete.
On Data/Fax/TAM and Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems, another device is found after the
modem has been installed. Windows notifies you that it has found a Serial Wave Device for the
modem and prompts for a Wave Device driver. Re-point to the SM56 driver location and click
OK.
When these two devices are installed, the SM56 Modem Setup program runs.
The modem setup program for PCI does not prompt for user input during installation. It defaults
to USA country code and Domestic English as the language for the online Help file. If you wish
to change these settings, and/or the COM port selection, you may do so via the SM56 Control
Panel application (Start->Settings->Control Panel, then double-click the SM56 Modem icon)
after setup is complete. Also, for SM56 Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems the microphone and
speaker gain selections may be done via the Control Panel application (under the Advanced tab).
Also, DOS box support is disabled after the SM56 is installed. After install is complete, you
must enable it via the Advanced tab in the SM56 Control Panel application. Make sure the DOS
box check box is checked. If not, click it to check it, exit the SM56 Control Panel application and
restart the computer. You must restart the computer to complete DOS box enabling.
7 Installing SM56 Software on Windows NT 4.0
Important -- The SM56 software for Windows NT is Data/Fax only, there is no
speakerphone or TAM supported.
Windows NT 4.0 does not fully support plug and play (PnP). Therefore, after installing the
modem board in the computer and booting, the operating system will not automatically recognize
that new hardware is present. You must manually install the modem as follows:
Step 1 -- Install a COM port for the modem
You must install a COM port for the SM56 modem as follows:
1. Open the Windows NT Control Panel.
2. Double click the Ports icon. The Ports window opens.
3. Select Add.
4. Select a COM port number (in the range 1-4 preferably) that is not already installed, and
allocate to it the standard resources as follows:
COM Port IO Address IRQ
Page 9

1 3F8 4
2 2F8 3
3 3E8 4
4 2E8 3
5. When your selections are complete click OK.
6. You will be prompted to restart the computer, do not do so yet. Select Don't Restart Now.
7. Close the Ports window.
Step 2 -- Install the SM56 modem software
1. Open the Windows NT Control Panel.
2. Double click the Modems icon....the Install New Modem dialog appears.
3. Click the "Don't detect my modem; I will select it from a list" check box. Then click Next.
4. Click the Have Disk button.
5. Browse to the Windows NT SM56 modem install software. Click misgmodm.inf to highlight
it. Then click Open, then click OK.
6. Select the Motorola SM56 Modem (note that the product name listed will vary depending on
which modem you have -- Data/Fax/, Data/Fax/TAM, etc.) from the list. Click Next.
7. Click the port number selected in Step 1 above to highlight it as the COM port for the modem.
Then click Next. The wizard will now copy all the necessary files and install the SM56 modem
on your PC.
8. When complete, restart the PC to activate and start the COM port and SM56 modem devices.
You are now ready to use the modem.
8 Verifying Proper Modem Installation
Verify that the SM56 software and hardware installation has completed correctly as follows.
Verifying SM56 Software Installation
1. Verify correct COM port selection.
You can check COM port installation through the Modems icon in the Control Panel or through
the SM56 Control Panel application (see below). Normally, the SM56 will install on COM2,
COM3, or COM4. Sometimes, however, depending on your computer system setup or Windows
setup, the SM56 may install on COM5 (or higher). Although the modem functions correctly on
any COM port, many software applications do not work if the modem is on a COM port number
higher than 4. If the SM56 installs on COM5 (or higher), you can force it to a lower COM port
via the SM56 Control Panel applet.
2. Run modem diagnostic from the SM56 Control Panel.
The SM56 software modem provides an informative Control Panel application that reports:
• Modem status: in use/not in use; dialing; negotiating a connection; actual connect rate
(updated in real time during a connection).
Page 10

• A button to access the on-line User's Guide.
• COM port selections.
• Country and language selections.
• Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems only -- microphone and speaker gain selections.
The SM56 Control Panel program also provides access to two Windows components:
• COM port and IRQ information
• A diagnostic utility that issues various ATI commands to the modem and displays the
responses: software build, modem type, and more.
To open the SM56 Control Panel application, selection Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then
double click the SM56 Modem icon. To access the diagnostics option from the Control Panel
applet, click Properties; select the Diagnostics tab; select the COM port corresponding to the
SM56 Modem from the list; and then click More Info. If the driver is properly installed, within
a few seconds a dialog box appears, with responses to the ATI commands. Refer to the AT
Commands section in the on-line User's Guide for an explanation of these commands and
responses.
Verifying SM56 Hardware Operation
To verify correct SM56 modem card hardware operation (up to the isolation transformer), you
can use the following local analog loopback (LAL) test procedure.
1. Important: Remove the telephone line connector from the modem card.
2. Select Start.
3. Select Programs-->Accessories-->HyperTerminal.
4. Double click the Hypertrm.exe icon.
5. Optionally, select a connection name and icon.
6. In the Connect Using window, select Motorola SM56...... modem. Click OK.
7. Enter a number in the Phone Number box...any number since we will not be dialing it. Click
OK.
8.On the next screen select Cancel.
9. Enter AT and hit <Enter>.
The response OK should appear.
10. Enter ATS46 = 23 and hit <Enter>.
11. Enter AT&T1 and hit <Enter>. Wait a few seconds.
12. Type some letters at the keyboard. If the hardware is functioning correctly, the letters you
type appear on the HyperTerminal display.
13. To exit this test mode, type +++ in quick succession (note no carriage return) to escape to
command mode, then type ATH <Enter>.
9 Changing the Operating System
The SM56 Modem software is the same for Windows 9 and Windows 98. If the modem is
installed on Windows 95 and you upgrade to Windows 98, the SM56 will continue to function as
before. No new drivers are required.
Page 11

However, if you change from Windows 95 or Windows 98 to Windows NT you must get a new
set of drivers for that operating system. The SM56 modem software for Windows 9x will not
work under Windows NT. Contact your direct modem vendor or PC supplier for drivers, or visit
their Web sites.
10 Using the SM56 Modem
32-Bit Windows 95/98 Applications
Because 32-bit Windows 95/98 applications use TAPI for communicating with modems, using
the SM56 is as easy as selecting the SM56 modem by name from the list of available modems.
16-Bit Windows 95/98 Applications
Because 16-bit applications cannot use the TAPI interface, there is a bit more setup required.
1. Select Motorola SM56 modem from the list of supported modems (if the SM56 modem is
not shown, select Hayes Compatible modem...see also REVHIST.TXT for other selections).
2. Configure the application's COM port selection. Use the COM port assigned to the SM56
modem, e.g. COM 2.
3. If the application requires it, enter specific AT commands for the SM56 modem. Normally you
will not need to do this. (For a full list of AT commands supported by the SM56 refer to the
SM56 on-line User's Guide). Some of the more common AT commands are listed below.
DOS-Based Applications and Games
Importnt: DOS box support is disabled after the SM56 is installed. After install is complete, you
must enable it via the Advanced tab in the SM56 Control Panel application (Start->Settings-
>Control Panel, then double-click the SM56 Modem icon). Make sure the DOS box check box
is checked. If not, click it to check it, exit the SM56 Control Panel application and restart the
computer. You must restart the computer to complete DOS box enabling.
The SM56 can be used by DOS applications only through a Windows 95/98 DOS box. Win 9x
DOS box support is achieved by virtualizing the standard I/O and IRQ assigned to a COM port.
This means that the SM56 drivers capture and redirect all I/O to/from the standard I/O address
for the COM port to which it assigned. In simpler terms, you tell the application the COM port
that the SM56 modem is installed on, and then use all the standard I/O and IRQ settings.
Standard I/O addresses and IRQs for COM Ports 1-4 are as follows:
COM Port IO Address IRQ
1 3F8 4
2 2F8 3
3 3E8 4
4 2E8 3
To determine the SM56 COM port number, open the SM56 Control Panel application (Start-
>Settings->Control Panel and double click the SM56 Modem icon), and select the Diagnostics
tab. The COM port number to which the SM56 modem is assigned is listed here. Configure your
Page 12

application to use this COM port. For example, if the SM56 modem has been assigned COM 2,
configure your application to communicate through COM 2.
Some of the more common AT commands used by applications are:
Initialization* AT&F
Hangup ATH0
Dialing string ATDT
Answer string ATA
*Some games require that the modem refrain from performing error correction and data
compression. In these cases, use the initialization string AT&F\N0.
For a full list of AT commands supported by the SM56 please refer to the on-line User's Guide.
11 Un-installing and Upgrading the SM56 Modem
SM56 Un-Install Procedure
1. Open the Control Panel.
2. Select Add\Remove Programs.
3. In the dialog box, select Motorola SM56 Modem Uninstall.
4. Select Add/Remove.
5. When asked to close the Control Panel window do so to allow the SM56 Control Panel applet
to be removed.
6. Shut down the computer.
7. Remove the SM56 hardware from the computer. (Note: If you do not remove the SM56
modem board, the SM56 will be automatically re-installed when Windows 95/98 restarts.)
The SM56 modem software remains on the PC hard disk for later installs without needing a
complete software install again. Simply install the modem card back in the PC (any vacant
slot)and the software will automatically self-install. Make sure to always run the un-install
utility before removing the modem board from the PC.
SM56 Software Upgrade Procedure (Windows 95/98)
Upgrade the SM56 modem to a newer version as follows.
Page 13

1. Obtain the latest software version from your direct modem supplier.
2. Run sm56set.exe and follow the Upgrade Wizard prompts. The upgrade utility retains a
backup of your previous modem version in a folder called \Windows\Motorola\Motbak95. It also
retains the current modem COM port so all communication applications will continue to function
correctly.
Recovering From an Unsuccessful Upgrade (Windows 95/98)
If , after an SM56 upgrade, you have problems with the new driver, you can restore your
previous SM56 software installation as follows. Perform all of the following steps.
1. Open the Control Panel. Select Add/Remove programs.
2. If SM56 Modem is in the list of installed programs, click on SM56 Modem, then Click
Add/Remove to run the un-install program.
3. Open the \Windows\Inf\Other folder. Delete all Motorola INF files that are listed there.
4. Open the Control Panel and determine if the SM56 Modem Control Panel icon is there. If
so, close the Control Panel; open the windows\system folder; and delete the mca.cpl file.
5. Restart the computer.
6. Upon restart, re-install the SM56 modem from the backup directory --
\Windows\Motorola\Motbak95. This will reinstall your previous modem software.
SM56 Software Upgrade Procedure (Windows NT 4.0)
1. Make a backup of your current modem software version -- copy all the files in
\Windows\Motorola\MotsetNT folder.
2. Un-install your current software -- run the SM56 Modem Uninstall from Add/Remove
Programs in the WindowsControl Panel.
3. Delete the Motorola SM56 modem INF files from \Program Files\Inf\Other
4. Restart the computer and perform a complete SM56 modem install (including COM port)
again using the new drivers.
Recovering From an Unsuccessful Upgrade (Windows NT 4.0)
2. Un-install your current software -- run the SM56 Modem Uninstall from Add/Remove
Programs in the Windows Control Panel.
3. Delete the Motorola SM56 modem INF files from \Program Files\Inf\Other.
4. Restart the computer and perform a complete SM56 modem install (including COM port)
again, this time using your previous software version backup files (see Step 1 of NT 4.0 upgrade
procedure).
12 Troubleshooting
If there is a problem making or receiving a call or transmitting data, and your communications
application does not explain the problem, check the following list of symptoms and tips.
Page 14

• The modem installs at COM 5 (or higher)
Some communications applications do not communicate with a COM port higher than COM4. If
the SM56 installs on COM5 or higher, force the modem to a lower COM port as follows.
1. Open the SM56 Control Panel application.
2. Select the Advanced tab.
3. Click on the radio button for the desired COM port. Note that unavailable COM ports are
grayed out and not selectable.
• Windows 95/98 DOS box applications do not work with the modem
By default DOS box support is disabled after installing the SM56 modem. You must enable it via
the Advanced tab in the SM56 Control Panel application (Start->Settings->Control Panel, then
double-click the SM56 Modem icon). Make sure the DOS box check box is checked. If not, click
it to check it, exit the SM56 Control Panel application and restart the computer. You must restart
the computer to complete DOS box enabling.
If the Enable DOS box check box is already checked (i.e. enabled), and DOS box application still
do not work, try:
1. Open the Control Panel.
2. Double click the System icon.
3. Expand the Modem branch.
4. Double click the Motorola SM56 modem.
5. Select the Modem tab. Make a note of the COM port number.
6. Select the Resources tab. Make a note of the IRQ number listed.
7. For DOS support to operate correctly, the SM56 modem cannot occupy the standard IRQ for
the COM port number.
8. Uncheck the Use Automatic Resources check box.
Double click on the Interrupt Request label and change the IRQ to a different number that
is not in conflict with another device. (If there is no free IRQ: free one, or change other
device IRQ levels to free a non-standard IRQ).
• There is no dial tone
Page 15

1. Ensure that the telephone cable is securely connected at both ends.
2. Unplug the telephone line cable from the computer, and connect it directly to a telephone
from the wall outlet. Check for a dial tone. If there is none, the problem is in the telephone
line or system. Call the service provider.
• The modem cannot complete a connection to another modem
1. Ensure that your modem is dialing the correct number. Ensure that you've specified the
correct area code, if one is required.
2. Determine whether the remote modem is correctly configured to communicate with yours.
• The modem does not answer incoming calls
1. Ensure that the automatic answer parameter is set to one of the enabled options, using the
ATS0 command (ATS0=1 to answer after one ring, ATS0=2 to answer after two rings, and
so on).
2. Ensure that no other devices, such as fax or answering machines, are answering calls before
the modem does.
• The modem disconnects while transmission is in progress
1. Ensure that the telephone cable is securely connected at both ends.
2. Ensure that call-waiting is disabled. In most areas, the command *70 or #70 disables call-
waiting. Check with your telephone company for the correct key sequence. (With callwaiting, the incoming call's click sound may be disrupting your call.)
• Data is not transmitted or received for unusually long periods of time
1. Re-dial the call. (The telephone line connection may be poor.)
2. Try another ISP number, the server could be busy.
3. Call your ISP and find out if they are having server problems or any suggestions why data
transmission is lethargic.
• The computer runs slower than usual
1. Close any open applications that you are not using.
Page 16

• You cannot enter tone selections successfully when calling tone-driven
applications
1. When dialing a remote system that requires you to enter selections using the telephone keys,
such as a voice-mail depot or bank-account information provider, you can lengthen the
duration of the tones your modem sends, so that the remote system can detect them better.
To adjust DTMF tone length, use the AT+VTDn command, where n specifies the tone
duration.
• The modem does not respond to AT commands
1. Ensure that your communications software is configured to use the same COM port as the
modem's COM port.
2. Reset modem parameters to default options by entering AT&F; then re-enter custom options.
3. SM56 builds after Build 50 require setting the S46 register to 23 before AT&T1 will perform
the Local Analog Loopback (LAL) hardware test.
• The modem responds to commands, but they do not appear on the screen
Ensure that the local display echo option is enabled by entering ATE1.
• You've installed a new peripheral device; now the modem does not work
1. In the Windows desktop tray, select Start.
2. Select Help. The Windows Help Topics window appears.
3. Select the Contents tab.
4. Select If You Have a Hardware Conflict.
5. A series of troubleshooting actions appears. Follow the appropriate sequence.
• You hear feedback (noise) from the PC sound system
(Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems)
1. Position the speakers at least three feet (1 M) away from the microphone.
2. Ensure that the speakers are facing away from the microphone.
3. Turn down the speaker volume.
Page 17

4. Speak into the microphone at a distance of at least 12 inches (30 cm) from your mouth.
Minimize background noise.
5. If there is still feedback, turn off the microphone boost, under the volume control panel.
• The modem connects; then meaningless characters appear
1. Open the Control Panel. Double click the Modem icon.
2. Select the Motorola SM56 modem
3. Click on Properties.
4. Select Connection.
5. Click on Advanced.
6. Check the Use Error Control-Required to Connect box.
• The modem cannot connect; the Error Control option is selected
The modem may be connecting at a rate higher than appropriate for the line conditions.
1. Use the AT%B command to limit the SM56 maximum connection rate. (For a list of AT
commands, refer to the on-line User's Guide.)
2. Lower the rate, using AT commands, until the problem is corrected. You can add AT
commands to do this; refer to the next section .
• How to Add AT Commands
1. Open the Control Panel.
2. Double-click the Modem icon.
3. Select the Motorola SM56 modem.
4. Click on Properties.
5. Select Connection.
6. Click on Advanced.
7. In the Extra Settings box, add commands as needed. You do not need to enter the AT prefix,
but it will not hurt if you do.
Page 18

13 Reporting Problems and Contacting the Modem Supplier
If you have a problem with the modem, ensure that the problem and its solution are not shown in
the Troubleshooting section. If you cannot resolve it through troubleshooting, send the following
information in an email to your direct modem supplier
able to resolve the problem.
Information about your computer:
• Brand and model
• CPU type (Pentium, Pentium II, AMD, etc.) Specify if MMX
• CPU clock rate
• Amount of Level 2 cache memory
• Operating system and version (Windows 95 OSR revision level, Windows 98, etc.)
Information about your modem:
• SM56 modem card version; modifications to your SM56 modem card
• SM56 version number (find this with the ATI3 command; or with the More Info button in
the SM56 Control Panel appplication)
Information about your setup:
• The telephone number you are calling from
• The telephone number you are calling to
• If performing a lab test, a detailed description of the equipment used
• The remote modem information
or PC vendor, so that they will be better
Information about the problem:
• The actions and steps that you performed
• A description of what you saw; be specific
• A description of what you expected to see
14 Understanding Microsoft Windows Logo Certification
Microsoft's WHQL (Windows Hardware Quality Logo) is targeted at commercially marketed
desktop applications that run on the latest released versions of Windows 95, Windows 98, and
Windows NT Workstation. It is not intended for client/server or Windows NT Server
applications. The goals of the logo certification program are to improve Windows hardware and
software quality, increase end-user satisfaction, and reduce support costs.
To receive the logo, a product must show proof of compatibility with Windows 95/98 and NT.
These include making sure that a device:
• Installs and registers itself properly with the operating system
• Is reliably functional and stable
• Removes itself (minus its core components) using an automated uninstaller
• Supports Universal Naming Conventions (UNC) and Long File Names (LFN)
Page 19

What does the logo mean for a product such as the SM56 modem? It means that Motorola and its
OEMs, system integrators, and VARs can use the Windows logo on their products and
packaging, and on advertising, collateral, and marketing materials. This signals end users that the
SM56 software modem is tested and fully functional on Windows 95/98 and Windows NT; that
it is designed to provide optimum usability and compatibility; and that it takes advantage of the
latest technologies provided by these operating systems. It makes users feel more comfortable
about purchasing the product, and it assures them of more complete satisfaction while using it.
The Windows logo also means that the qualified product gets included on Microsoft's Windows
Hardware Compatibility List (HCL) under "Logo," reinforcing to customers and end-users alike
that it meets Microsoft's strict requirements and operates properly with Windows operating
systems.
15 An Overview of the V.90 Protocol
In February 1998, the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) formulated the V.90
industry-standard protocol for 56K modems. Before the adoption of the V.90 standard, 56K
modems complied with one of two pre-standard implementations: K56flex or X2 technology.
Unfortunately for ISPs and end-users, these technologies were not compatible. ISPs had to worry
about which standard to employ. End users had to be sure to purchase modems compatible with
their ISP's equipment.
Upgrading Motorola's SM56 K56flex modems to V.90 is a software-only upgrade. There is no
change to the line interface hardware. This makes it easy for pre-V.90 users to upgrade their
system to V.90 compliance.
Note: sometimes V.90 is referred to as V.PCM. PCM is an acronym for Pulse Code Modulation.
With V.90, high-speed downstream (from Internet to personal computer) data transmission is
accomplished using PCM techniques. Before the ITU formulated its standard V.90 protocol, the
industry typically referred to it as V.PCM. This name is fading from use.
V.90 technology allows users to connect to the Internet at rates up to twice as fast as those of
V.34 (33.6Kbps) modems. The maximum receive (downstream) rate is 56Kbps, while the return
path (upstream) connects at V.34 rates up to 33.6 Kbps. This is perfect for Internet connections,
where most data is transferred downstream.
The SM56 begins connections by attempting a V.90 connection to the headend. If the headend is
not V.90, the SM56 automatically switches to K56flex mode. If K56flex mode fails (when, for
example, the headend uses X2 technology, or there is a noisy phone line condition), the SM56
drops to V.34 rates. This auto-mode switching mechanism ensures maximum compatibility with
all remote headends.
On the Web you can visit www.v90.com for a wealth of information on V.90 technology,
including:
• A list of ISPs that support V.90
• The latest news on V.90
Page 20

• White papers on the V.90 standard
• Technology descriptions
• Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Appendix A: SM56 Specifications
• Compatibility with Windows 95/98 and Windows NT 4.0/5.0 communication applications
• Compatibility with communication applications that run in an Windows 95/98 DOS box.
• An powerful installation engine.
• Plug and Play operation
• Support for various data modulation modes:
- V.90 connection rates if the headend is a true V.90 location. V.90 downstream rates to
56Kbps. Upstream rates to 33.6Kbps (V.34).
- Fallback to K56flex® mode if the headend is K56flex, not V.90. K56flex®
downstream rates to 56Kbps. Upstream rates to 33.6Kbps(V.34).
- Connection at V.34 rates (33.6 Kbps) if the headend is not V.90 or K56flex®.
- V.32bis, V.32, V.22bis, V.23, V.22/B212, V.21, Bell 103.
• Error correction - V.42, LAPM, MNP2-4.
• Data compression - V.42bis, MNP5.
• Fax modes supported - V.17, V.27ter, V.29.
• Data, fax, and telephone answering machine (TAM) support on Data/Fax/TAM and
Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems.
• Full voice support on Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems, including full-duplex speaker phone
with acoustic and line echo cancellation.
• Answering machine capability with PCM and IMA ADPCM audio formats -- Data/Fax/TAM
and Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems.
• Caller ID (USA and Canada) -- not available on Data/Fax modems.
• Distinctive Ring (USA and Canada) -- not available on Data/Fax modems.
• Pulse and tone dialing and call progress monitoring.
• Adaptive rate re-negotiation (up and down) during a connection to compensate for line
dynamics.
• Auto dial and answer.
• Informative Control Panel applet that includes microphone and speaker gain selection sliders
(Data/Fax/Speakerphone modems only, COM port selection buttons, country and language
selections, and real time modem status reporting (dialing, negotiating, connect rate, etc.).
• On-line user's guide accessible through the Control Panel applet, which includes a list of
supported AT commands.
Appendix B: Software License Agreement
THE FOLLOWING AGREEMENT IS A LEGAL AGREEMENT BETWEEN
YOU (EITHER AN INDIVIDUAL OR ENTITY), AND MOTOROLA, INC. (FOR
ITSELF AND ITS LICENSORS). THE RIGHT TO USE THIS SOFTWARE IS
Page 21

BASED ON THE CONDITION THAT YOU AGREE TO THE FOLLOWING
LICENSE. USING THIS PRODUCT CONSTITUTES ACCEPTANCE OF THE
TERMS AND CONDITIONS SET FORTH IN THIS AGREEMENT. IF YOU DO
NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, THEN DO NOT USE
THE SOFTWARE
The enclosed computer program(s), SM56 Software Modem ("Software") is licensed, not
sold, to you by Motorola, Inc. ("Motorola") for use only under the terms of this License,
and Motorola reserves any rights not expressly granted to you. Motorola and its licensors
retain ownership of the Software itself and its accompanying written materials, which are
protected by the copyright laws of your country and international treaty provisions.
1. License. This License allows you to use one copy of the Software with the Beta
Kit (Intel PIIX Bus Master IDE Driver for Windows NT) supplied from Intel. To "use"
the Software means that the Software is either loaded in the temporary memory (e.g.,
RAM) of a computer or installed on the permanent memory of a computer (e.g., hard
disk). Licensee hereby acknowledges that the licenses granted under this Agreement may
be suspended in some cases if Licensee assert an Essential patent for an ITU or prior
CITT analog modem standard against Motorola or a third party. The use of the Software
is restricted to personal, non-commercial testing of the Software. Any other use is
expressly prohibited.
2. Restrictions. The Software contains trade secrets in a human or machine
perceivable form and, to protect them, you may not REVERSE ENGINEER,
DECOMPILE, DISASSEMBLE OR OTHERWISE REDUCE THE SOFTWARE
TO ANY HUMAN OR MACHINE PERCEIVABLE FORM. YOU MAY NOT
MODIFY, ADAPT, TRANSLATE, RENT, LEASE, LOAN OR CREATE
DERIVATIVE WORKS BASED UPON THE SOFTWARE OR ANY PART
THEREOF.
3. Termination. This License is effective until terminated. This License will
terminate immediately without notice form Motorola or judicial resolution if you fail to
comply with any provision of this License. Motorola can terminate this license at will
upon proper notice to you. In any event this License will terminate 6 months from the
date you received this Software. Upon such termination you must destroy the Software,
all accompanying written materials and all copies thereof, and Sections 5, 6, 7 and 8 will
survive any termination.
4. Export Law Assurances. You agree that neither the Software nor any direct
product thereof is being or will be shipped, transferred or re-exported, directly or
indirectly, into any country prohibited by the United States Export Administration Act and
the regulations thereunder or will be used for any purpose prohibited by the Act.
5. Warranty. The Software and written materials are provided "AS IS" and without
warranty of any kind. Motorola's entire liability and your sole and exclusive remedy for
Page 22

any breach of the foregoing limited warranty will be, at Motorola's option, replacement of
the disk(s) or refund the amount paid for this Software License.
NO OTHER WARRANTY IS PROVIDED BY MOTOROLA, AND MOTOROLA
AND ITS LICENSORS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ALL OTHER WARRANTIES,
EITHER EXPRESS OF IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. MOTOROLA DOES
NOT WARRANT THAT THE OPERATION OF THE SOFTWARE WILL BE
UNINTERRUPTED OR ERROR-FREE, OR THAT DEFECTS IN THE
SOFTWARE WILL BE CORRECTED. NO ORAL OR WRITTEN
REPRESENTATIONS MADE BY MOTOROLA OR AN AGENT THEREOF
SHALL CREATE A WARRANTY OR IN ANY WAY INCREASE THE SCOPE
OF THIS WARRANTY. BECAUSE SOME JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW
THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES, THE
ABOVE LIMITATIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
6. Limitation of Remedies and Damages. Regardless of whether any remedy set forth
herein fails of its essential purpose, in no event shall Motorola or any of the licensors,
directors, officers, employees or affiliates of the foregoing be liable to you for any
consequential, incidental, indirect, special or similar damages whatsoever (including,
without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business interruption, loss of
business information and the like), whether foreseeable or unforeseeable, arising out of the
use or inability to use the Software or accompanying written materials, regardless of the
basis of the claim and even if Motorola or a Motorola representative has been advised of
the possibility of such damage. Motorola's liability to you for direct damages for any
cause whatsoever, and regardless of the basis of the form of the action, will be limited to
the price paid for the Software that caused the damages. THIS LIMITATION WILL
NOT APPLY IN CASE OF PERSONAL INJURY ONLY WHERE AND TO THE
EXTENT THAT APPLICABLE LAW REQUIRES SUCH LIABILITY WITHOUT
THIS LIMITATION. BECAUSE SOME JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW
THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL
OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY
TO YOU.
7. Complete Agreement. This License constitutes the entire agreement between the
parties with respect to the use of the Software and related documentation, and supersedes
all prior or contemporaneous understandings or agreements, written or oral, regarding
such matter. No amendment to or modification of this License will be binding unless in
writing and signed by a duly authorized representative of Motorola.
______________
Readme 04/12/99
JHowley
 Loading...
Loading...