Page 1

MemoryLink UltraSync™ GPS-100M
GPS Synchronization Unit
for PTP 600 Series Wireless Ethernet Bridges
Page 2

Contents
Pg Section
3 Introduction
4 System Overview
5 Product Features and Benefits
6 Installation
The information in this publication is subject to change without notice.
Motorola shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions nor for any damages resulting from
the use of this material.
Each configuration described may or may not be the only available solution. The description is not a
determination of product quality or correctness, nor does it ensure compliance with any federal, state or
local requirements. Motorola does not warrant products other than its own strictly as stated in Motorola’s
product warranties.
2
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
Page 3
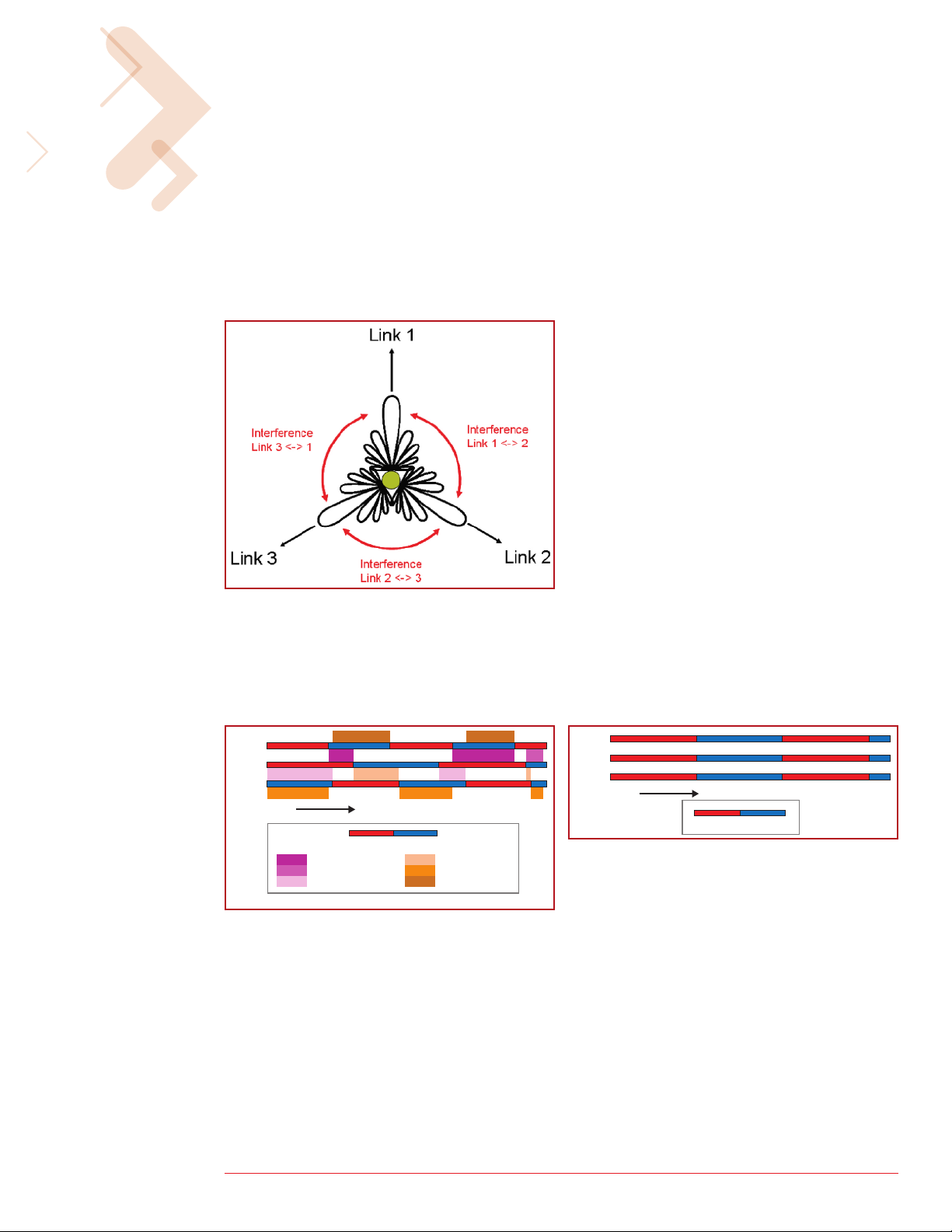
Simple example of cross-
Link 1
Link 3
Interference Link 3 to Link 2
Interference Link 1 to Link 3
Interference Link 3 to Link 1
Interference Link 2 to Link 1
Interference Link 1 to Link 2
Interference Link 2 to Link 3
Link 2
Time
Transmit Receive
Link 1
Link 3
Time
Link 2
Transmit Receive
interference when three links of
different lengths are mounted
on a mast and operating on the
same or adjacent channels
Introduction
The Motorola wi4 Fixed Point-To-Point (PTP) 600 Series Wireless Ethernet Link, which consists of a pair of
radios deployed one at each end of the link, operates on a single frequency channel in each direction using
Time Division Duplex (TDD). In situations where a number of radios are installed on the same mast or where
a large number of links are installed in a sizeable, dense network, it is possible that the performance or
throughput of some of the links can be reduced. In some cases, a number of the links may not work at all.
This is due to interference between the units, and the levels of interference can worsen when the links are
operating on the same or adjacent channels.
The effect of this cross interference between units can be reduced by ensuring that the radios are in
synchronism, meaning that transmit and receive frames of the units are synchronized so they do not
interfere with each other. TDD Synchronization introduces a fixed TDD framing mode and allows frame
timing in a PTP 600 link to be synchronized with an external reference – a Global Positioning System (GPS) unit.
Before TDD Synchronization
After TDD Synchronization
The result is that TDD synchronization minimizes the interference between links and promotes optimal
spectral re-use while greatly enhancing link performance. By timing and synchronizing transmit and receive
signals, network operators can co-locate multiple radios on a rooftop or tower without interference.
3
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
Page 4

MemoryLink UltraSync GPS-100M
GPS Synchronization Unit
(Motorola Part Number WB3001)
System Overview
To meet the high performance standards of a Motorola PTP broadband wireless network, Motorola has
partnered with MemoryLink to deploy the MemoryLink UltraSync™ GPS-100M in a Motorola wi4 Fixed
Point-to-Point (PTP) 600 Series network. With its integrated GPS receiver and internally-mounted antenna,
the UltraSync GPS-100M generates a precise, highly stable, proprietary synchronization signal that is used
by the PTP 600 Series radios to time and synchronize transmit and receive signals.
In fact, the UltraSync GPS-100M is critical to a wireless network’s efficiency and reliability as PTP 600
radios transport Time Division Duplex (TDD) data over the link, particularly in a high-interference coverage
area where multiple radios and channels are in use. The UltraSync GPS-100M’s high-quality components,
including an active antenna that functions even in low-signal environments, and its NEMA 4X and UL 508
outdoor-rated enclosure, ensure highly reliable performance. Like the Motorola PTP 600 Series units, the
UltraSync GPS-100M is rugged, performing consistently in harsh climates and challenging radio-frequency
(RF) environments.
The robust, reliable UltraSync GPS-100M generates a synchronization signal that originates from the atomic
clocks on the GPS satellites that orbit the earth.
Both existing and prospective operators of a Motorola PTP 600 Series network can reap the benefits of the
UltraSync GPS-100M’s superior GPS signal synchronization since the UltraSync GPS-100M comes
pre-wired for new systems, and can be retrofitted for existing PTP 600 Series links.
4
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
Page 5

Product Features and Benefits
UltraSync™ GPS-100M Features:
• Integral GPS receiver – 12 channel
• Passes 1000 Base-T protocol
• Supports Ethernet cable lengths of up to 330 feet (100 meters) from the PTP 600 PIDU Plus to the
UltraSync GPS-100M Eth1/PWR port
• Robust enclosure weighing approximately 23 ounces (650 grams)
• Small footprint – 5.92” (150 mm) height, 3.95” (100 mm) width and 2.79” (71 mm) depth
• Includes internally mounted GPS antenna, mounting bracket, screws, Ethernet cables and cable glands
for waterproof ingress/egress
• Connects via RJ-45 connector to PTP 600 Series radios equipped with a sync port
• Operates at temperatures from – 40° F to +140° F (-40° C to +60° C), even in high humidity
UltraSync GPS-100M Benefits:
• Minimizes interference between multiple links on a single mast
• Improves frequency re-use
• Reduces spatial / angular separation between PTP links when installed on the same mast
• Accurately provides the timing synchronization for PTP 600 Series links
• Internally mounted GPS antenna requires no antenna change to the PTP 600 Series link
• Robust operating features allow continuously high performance
• Small footprint and lightweight form factor allow easy installation
Ordering
The MemoryLink UltraSync GPS-100M can be ordered directly from Motorola under the following part
number and product description:
WB3001 – MemoryLink UltraSync GPS-100M for PTP 600
5
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
Page 6

UltraSync GPS-100M
Connections
Installation
Enabling TDD synchronization is a two-stage process:
• Install the GPS Synchronization Unit (Motorola part number WB3001)
• Enable TDD synchronization mode on the PTP 600 radio and configure related parameters using the
PTP 600 Web GUI interface
The following are deployment considerations for an UltraSync™ GPS-100M with a PTP 600 Series link:
• Fixed-frequency operations only
• Fixed TDD operation only – all synchronized links have the same ratio master to slave
• Not presently available when radar avoidance is enabled
• Networks need to be planned carefully
The following illustration shows the connections in the UltraSync GPS-100M:
Sync Port 1 to ODU
Pass Through Port 2 Ethernet
Pass Through Port 3 Ethernet
• Interface Specifications
> Sync Port (Port 1): Motorola proprietary differential 3.3V (nominal) peak-to-peak signal presented
on pins 4(+) and 5(-) of Port 1 (RJ-45 connector)
> Ethernet pass-through on Ports 2 and 3
• Maximum Cable Lengths
> Sync Port: 2’ (0.6 m)
> Ethernet Port 2: 330’ (100 m)
> Ethernet Port 3: 2’ (0.6 m)
Motorola strongly recommends purchasing and installing the Motorola wi4 Fixed PTP Lightning Protection
Unit (PTP-LPU) as an integral part of a PTP 600 Series network. Because PTP 600 Series radios are often
located in situations that can attract lightning, the PTP-LPU shields the radio from sudden power surges
caused by electro-magnetic activity (lightning) before they can harm the unit. Two Lightning Protection Units
are required for each radio – installed on the wall, tower or mast adjacent to the PTP 600 radio, and one
installed at the cable entry point of the building in which the network resides. When correctly installed, the
Motorola PTP-LPU gives the PTP 600 Series radio the best protection from the harmful effects of lightning.
However, 100% protection is neither implied nor possible.
6
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
Page 7

UltraSync GPS-100M
deployment diagram with a
PTP 600 Series radio and a
PTP Lightning Protection Unit
Installation continued
The following diagram shows how to connect the UltraSync™ GPS-100M to the PTP 600 ODU fitted with
a Lightning Protection Unit (PTP-LPU):
The UltraSync GPS-100M sits between the Lightning Protection Unit and the ODU (outdoor unit) of a PTP
600 Series link. One UltraSync GPS-100M is required for each link. The unit receives a stable, accurate timing
signal from its integrated GPS receiver, which obtains signals generated concurrently from 12 medium-earthorbit satellites. That signal is fed to the PTP 600 ODU via its SYNC port, giving the link a reference point for
timing synchronization.
Once the UltraSync GPS-100M has been installed, the PTP 600’s TDD synchronization capability can be
enabled and configured using the PTP 600’s installation wizard. For complete installation details, refer to the
UltraSync GPS-100M User Manual and the PTP 600 User Manual.
7
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
Page 8

GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT
MOTOwi4™
The wi4 Fixed PTP 600 Series bridges and the wi4 Fixed PTP Lightning Protection Unit are part of
Motorola’s MOTOwi4 portfolio of innovative wireless broadband solutions that create, complement and
complete IP networks. Delivering IP coverage to virtually all spaces, the MOTOwi4 portfolio includes wi4
Fixed, wi4 Mesh, wi4 Indoor and wi4 WiMAX solutions for private and public networks.
Motorola, Inc., 1303 E. Algonquin Road, Schaumburg, Illinois 60196 U.S.A. +1 877 515-0400 • www.motorola.com/ptp
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. All other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
© Motorola, Inc. 2008. All rights reserved.
8
GPS SYNCHRONIZATION UNIT GUIDE
GPS WB PTP GPS GD 021108
 Loading...
Loading...