Page 1

MVME187
RISC Single Board Computer
Installation Guide
MVME187IG/D4
Page 2

Notice
While reasonable efforts have been made to assure the accuracy of this document,
Motorola, Inc. assumes no liability resulting from any omissions in this document,
or from the use of the information obtained therein. Motorola reserves the right to
revise this document and to make changes from time to time in the content hereof
without obligation of Motorola to notify any person of such revision or changes.
No part of this material may be reproduced or copied in any tangible medium, or
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form, or by any means, radio,
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or facsimile, or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of Motorola, Inc.
It is possible that this publication may contain reference to, or information about
Motorola products (machines and programs), programming, or services that are
not announced in your country. Such references or information must not be
construed to mean that Motorola intends to announce such Motorola products,
programming, or services in your country.
Restricted Rights Legend
If the documentation contained herein is supplied, directly or indirectly, to the U.S.
Government, the following notice shall apply unless otherwise agreed to in
writing by Motorola, Inc.
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set
forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer
Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013.
Motorola, Inc.
Computer Group
2900 South Diablo Way
Tempe, Arizona 85282-9602
Page 3
Preface
This manual provides a general board level hardware description, hardware
preparation and installation instructions, debugger general information, and
information about using the debugger.
This manual applies to the following MVME187 RISC Single Board Computers:
Assembly Item Board Description
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME187
MVME
MVME187
MVME187
-001B 25MHZ, 4MB Parity
-002B 25MHZ, 8MB Parity
-003B 25MHZ, 16MB Parity
-004B 25MHZ, 32MB Parity
-023B 33MHZ, 16MB ECC, 128
-024B 33MHZ, 32MB ECC, 128C
-031B 33MHZ, 4MB ECC
-032B 33MHZ, 8MB ECC
-033B 33MHZ, 16MB ECC
187-034B 33MHZ, 32MB ECC
-035B 33MHZ, 64MB ECC
-036B 33MHZ, 128MB ECC
This manual is intended for anyone who wants to provide OEM systems, supply
additional capability to an existing compatible system, or work in a lab
environment for experimental purposes.
Anyone using this manual should have a basic knowledge of computers and
digital logic.
Page 4
Safety Summary
Safety Depends On You
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service, and
repair of this equipment. Failure to comply with these precautions or with speciÞc warnings elsewhere in
this manual violates safety standards of design, manufacture, and intended use of the equipment.
Motorola, Inc. assumes no liability for the customer's failure to comply with these requirements.
The safety precautions listed below represent warnings of certain dangers of which Motorola is aware. You,
as the user of the product, should follow these warnings and all other safety precautions necessary for the
safe operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
Ground the Instrument.
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and enclosure must be connected to an electrical ground.
The equipment is supplied with a three-conductor ac power cable. The power cable must be plugged into
an approved three-contact electrical outlet. The power jack and mating plug of the power cable meet
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) safety standards.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
Do not operate the equipment in the presence of ßammable gases or fumes. Operation of any electrical
equipment in such an environment constitutes a deÞnite safety hazard.
Keep Away From Live Circuits.
Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers. Only Factory Authorized Service Personnel or
other qualiÞed maintenance personnel may remove equipment covers for internal subassembly or
component replacement or any internal adjustment. Do not replace components with power cable
connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the power cable removed. To
avoid injuries, always disconnect power and discharge circuits before touching them.
Do Not Service or Adjust Alone.
Do not attempt internal service or adjustment unless another person capable of rendering Þrst aid and
resuscitation is present.
Use Caution When Exposing or Handling the CRT.
Breakage of the Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) causes a high-velocity scattering of glass fragments (implosion).
To prevent CRT implosion, avoid rough handling or jarring of the equipment. Handling of the CRT should
be done only by qualiÞed maintenance personnel using approved safety mask and gloves.
Do Not Substitute Parts or Modify Equipment.
Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install substitute parts or perform any
unauthorized modiÞcation of the equipment. Contact your local Motorola representative for service and
repair to ensure that safety features are maintained.
Dangerous Procedure Warnings.
Warnings, such as the example below, precede potentially dangerous procedures throughout this manual.
Instructions contained in the warnings must be followed. You should also employ all other safety
precautions which you deem necessary for the operation of the equipment in your operating environment.
Dangerous voltages, capable of causing death, are
!
WARNING
present in this equipment. Use extreme caution when
handling, testing, and adjusting.
Page 5

All Motorola PWBs (printed wiring boards) are manufactured by UL-recognized
manufacturers, with a ßammability rating of 94V-0.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate electro-
!
WARNING
magnetic energy. It may cause or be susceptible to
electro-magnetic interference (EMI) if not installed and
used in a cabinet with adequate EMI protection.
European Notice: Board products with the CE marking comply with the
EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). Compliance with this directive implies
conformity to the following European Norms:
EN55022 (CISPR 22) Radio Frequency Interference
EN50082-1 (IEC801-2, IEC801-3, IEEC801-4) Electromagnetic Immunity
The product also fulÞlls EN60950 (product safety) which is essentially
the requirement for the Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC).
This board product was tested in a representative system to show
compliance with the above mentioned requirements. A proper
installation in a CE-marked system will maintain the required
EMC/safety performance.
The computer programs stored in the Read Only Memory of this device contain
material copyrighted by Motorola Inc., 1995, and may be used only under a license
such as those contained in MotorolaÕs software licenses.
¨
Motorola
and the Motorola symbol are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc.
All other products mentioned in this document are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
©Copyright Motorola 1997
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the United States of America
March 1997
Page 6

Page 7

Contents
This Chapter Covers 1-1
About this Manual 1-1
Terminology, Conventions, and DeÞnitions Used in this Manual 1-2
Data and Address Parameter Numeric Formats 1-2
Signal Name Conventions 1-2
Assertion and Negation Conventions 1-3
Data and Address Size DeÞnitions 1-3
Big-Endian Byte Ordering 1-3
Control and Status Bit DeÞnitions 1-4
True/False Bit State DeÞnitions 1-4
Bit Value Descriptions 1-4
Related Documentation 1-5
xx
Document Set for MVME187-0
Additional Manuals for this Board 1-6
Other Applicable Motorola Publications 1-6
Non-Motorola Peripheral Controllers Publications Bundle 1-7
Applicable Non-Motorola Publications 1-9
This Chapter Covers 2-1
General Description 2-1
Onboard Memory Mezzanine Module 2-2
SCSI Mass Storage Interface 2-2
Serial Ports 2-3
Parallel (Printer) Port 2-3
Ethernet Transceiver Interface 2-3
187Bug Firmware 2-4
Features 2-4
SpeciÞcations 2-6
Conformance to Requirements 2-6
Board Level Overview 2-7
Connectors 2-7
Adapters 2-7
Transition Modules 2-8
ASICs 2-8
VMEchip2 ASIC 2-9
PCCchip2 ASIC 2-9
MEMC040 Memory Controller ASIC 2-10
Board 1-5
Page 8

MCECC Memory Controller ASIC 2-10
Functional Description 2-10
Front Panel Switches and LEDs 2-11
Data Bus Structure 2-12
Local Bus Arbitration 2-12
M88000 MPU 2-12
EPROM 2-13
Programmable EPROM Features 2-13
Static RAM 2-13
Optional SRAM Battery Backup 2-14
Onboard DRAM 2-15
Stacking Mezzanines 2-16
DRAM Programming Considerations 2-16
Battery Backed Up RAM and Clock 2-17
VMEbus Interface 2-18
I/O Interfaces 2-18
Serial Port Interface 2-18
Parallel Port Interface 2-20
Ethernet Interface 2-21
SCSI Interface 2-22
Local Resources 2-23
Programmable Tick Timers 2-23
Watchdog Timer 2-23
Software-Programmable Hardware Interrupts 2-23
Local Bus Timeout 2-23
Memory Maps 2-24
Local Bus Memory Map 2-24
Normal Address Range Devices 2-24
VMEbus Memory Map 2-28
VMEbus Accesses to the Local Bus 2-28
VMEbus Short I/O Memory Map 2-28
This Chapter Covers 3-1
Unpacking the Equipment 3-1
Overview of Startup Procedure 3-2
Preparing the Hardware 3-5
Modifying ConÞguration before Installation 3-5
Option Modification 3-5
Checking the 187Bug EPROMs 3-7
EPROM Location 3-7
EPROM Orientation 3-7
User-programmed EPROMs 3-7
Page 9

Jumper Settings 3-7
Optional Jumper Settings 3-8
General Purpose Software Readable Header J1 3-8
System Controller Header J2 3-10
Optional SRAM Backup Power Source Select Header J6 3-11
Serial Port 4 Clock Configuration Select Headers J7 and J8 3-11
Preparing the MVME187 for Installation 3-14
Preparing the System Chassis 3-15
Installing the Hardware 3-16
Installing the MVME187 in the Chassis 3-16
Transition Modules and Adapter Boards Overview 3-17
Equipment Connections 3-19
Installing Transition Modules and Adapter Boards 3-20
Connecting Peripherals 3-20
Completing the Installation 3-24
Starting the System 3-24
Powering Up the System 3-25
Initializing the Real-Time Clock 3-25
Examining and/or Changing Environmental Parameters 3-25
Programming the PCCchip2 and VMEchip2 3-26
System Considerations 3-27
Backplane Power Connections 3-27
Memory Address Ranges 3-27
DRAM Addressing 3-27
Global Bus Timeout 3-27
Multiple Module Cage Configuration 3-28
GCSR Location Monitor Register 3-28
Ethernet LAN (+12 Vdc) Fuse 3-28
SCSI Bus Termination 3-29
Storage and the Real-Time Clock 3-29
This Chapter Covers 4-1
Introduction to MVME187Bug 4-1
Overview of M88000 Firmware 4-1
Description of 187Bug 4-2
Command Facilities 4-2
Trap #496 Routines 4-2
Debugger or Diagnostic Directories 4-3
Keyboard Control 4-3
Comparison with M68000-Based Firmware 4-4
187Bug Implementation 4-4
Memory Requirements 4-5
Page 10

Booting and Restarting 187Bug 4-5
Starting Up 187Bug 4-6
Autoboot 4-6
Autoboot Sequence 4-6
ROMboot 4-7
ROMboot Sequence 4-7
Network Boot 4-8
Network Boot Sequence 4-8
Restarting the System 4-9
Reset 4-10
Abort 4-10
Break 4-11
SYSFAIL* Assertion/Negation 4-12
MPU Clock Speed Calculation 4-12
Disk I/O Support 4-13
Disk Support Facilities 4-13
Parameter Tables 4-13
Supported Controllers 4-13
Blocks Versus Sectors 4-14
Device Probe Function 4-14
Disk I/O via 187Bug Commands 4-15
IOI (Input/Output Inquiry) 4-15
IOP (Physical I/O to Disk) 4-15
IOT (I/O Teach) 4-15
IOC (I/O Control) 4-15
BO (Bootstrap Operating System) 4-15
BH (Bootstrap and Halt) 4-16
Disk I/O via 187Bug System Calls 4-16
Controller Command Packets 4-16
Default 187Bug Controller and Device Parameters 4-17
Disk I/O Error Codes 4-18
Network I/O Support 4-19
Intel 82596 LAN Coprocessor Ethernet Driver 4-19
UDP/IP Protocol Modules 4-19
RARP/ARP Protocol Modules 4-20
BOOTP Protocol Module 4-20
TFTP Protocol Module 4-20
Network Boot Control Module 4-20
Network I/O Error Codes 4-21
Multiprocessor Support 4-21
Multiprocessor Control Register (MPCR) Method 4-21
Page 11

MPCR Status Codes 4-22
Multiprocessor Address Register (MPAR) 4-22
MPCR Powerup Sequence 4-22
Global Control and Status Register (GCSR) Method 4-24
Diagnostic Facilities 4-25
187Bug Diagnostic Test Groups 4-27
This Chapter Covers 5-1
Entering Debugger Command Lines 5-1
Terminal Input/Output Control 5-1
Debugger Command Syntax 5-3
Syntactic Variables 5-4
Expression as a Parameter 5-4
Address as a Parameter 5-5
Address Formats 5-6
Offset Registers 5-7
Port Numbers 5-7
Entering and Debugging Programs 5-8
Creating a Program with the Assembler/Disassembler 5-8
Downloading an S-Record Object File 5-8
Read the Program from Disk 5-9
Calling System Utilities from User Programs 5-9
Preserving the Debugger Operating Environment 5-10
187Bug Vector Table and Workspace 5-10
Hardware Functions 5-11
Exception Vectors Used by 187Bug 5-11
CPU/MPU Registers 5-11
Floating Point Support 5-11
Single Precision Real 5-13
Double Precision Real 5-13
ScientiÞc Notation 5-14
The 187Bug Debugger Command Set 5-15
This Appendix Covers A-1
ConÞguring the Board Information Block A-1
Setting Environment to Bug/Operating System A-3
Disk/Tape Controller Modules Supported B-1
Disk/Tape Controller Default ConÞgurations B-2
IOT Command Parameters for Supported Floppy Types B-4
Network Controller Modules Supported C-1
Introduction E-1
Levels of Implementation E-3
Page 12

Signal Adaptations E-4
Sample ConÞgurations E-4
Proper Grounding E-7
Page 13

List of Figures
MVME187 General Block Diagram 2-7
MVME187 Switches, Headers, Connectors, Fuses, and LEDs 3-6
Typical Internal SCSI and Serial Port Connections 3-18
Using MVME712A/AM and MVME712B 3-22
Typical Transition Module Peripheral Port Connectors 3-23
Page 14

List of Tables
MVME187 General SpeciÞcations 2-6
Bus Transfers 2-9
Front Panel Switches 2-11
Front Panel LEDs 2-11
Local Bus Memory Map 2-25
Local I/O Devices Memory Map 2-26
Startup Overview 3-2
J1 Bit Descriptions 3-9
Factory Settings for J1 General Purpose Readable Jumpers 3-9
Settings for J2 System Controller Header 3-10
Settings for Optional J6 SRAM Backup Power Source
Select Header 3-12
Settings for J7 and J8 Serial Port 4 Clock ConÞguration
Select Headers 3-13
MVME187 Preparation Procedure 3-14
Chassis Preparation/Slot Selection Procedure 3-15
MVME187 Installation Procedure 3-16
Peripheral Connections 3-19
Transition Module and Adapter Board Installation Overview 3-20
Peripheral Connection Procedures 3-21
Installation Completion Procedure 3-24
System Startup Overview 3-24
RTC Initialization Procedure 3-26
Diagnostic Monitor Commands/PreÞxes 4-25
Diagnostic Utilities 4-26
Diagnostic Test Groups 4-27
Debugger Commands 5-15
xiv
Page 15

1Introduction to the MVME187
Installation Guide
This Chapter Covers
Details about this manual
❏
Terminology, conventions, and definitions used
❏
Other publications relevant to the MVME187
❏
About this Manual
This manual supports the setup, installation, and debugging of the
RISC-based MVME187 Single Board Computer; a highperformance engine for VMEbus-based low- and mid-range OEM
and integrated systems, embedded controllers, and other singleboard computer applications.
This manual provides:
A general
❏
Board Level Hardware Description
1
in Chapter 2
Hardware Preparation and Installation
❏
Debugger General Information
❏
Debugger/monitor commands, and other information about
❏
Using the 187Bug Debugger
Other information needed for start-up and troubleshooting of
❏
the MVME187 RISC Single Board Computer, including
Ð
Configure and Environment Commands
Ð
Disk/Tape Controller Data
modules supported by 187Bug
Ð
Network Controller Data
Ð Procedures for
Ð
EIA-232-D Interconnections
Troubleshooting CPU Boards
in Chapter 4
in Chapter 5
in Appendix B for controller
in Appendix C
instructions in Chapter 3
in Appendix A
in Appendix D
in Appendix E
1-1
Page 16
1
Introduction to the MVME187 Installation Guide
Terminology, Conventions, and Definitions
Used in this Manual
Data and Address Parameter Numeric Formats
Throughout this manual, a character identifying the numeric
format precedes data and address parameters as follows:
$ dollar speciÞes a hexadecimal character
% percent speciÞes a binary number
& ampersand speciÞes a decimal number
For example, Ò12Ó is the decimal number twelve, and Ò$12Ó is the
decimal number eighteen.
Unless otherwise specified, all address references are in
hexadecimal.
Signal Name Conventions
An asterisk (*) follows signal names for signals which are level or
edge significant:
Term * Indicates
level
signiÞcant
edge
signiÞcant
1-2
The signal is true or valid when the signal is low.
The actions initiated by that signal occur on high
to low transition.
Page 17
Terminology, Conventions, and Definitions Used in this Manual
Assertion and Negation Conventions
Assertion and negation are used to specify forcing a signal to a
particular state. These terms are used independently of the voltage
level (high or low) that they represent.
Term Indicates
1
Assertion and assert
Negation and negate
The signal is active or true.
The signal is inactive or false.
Data and Address Size Definitions
Data and address sizes are defined as follows:
Name Size Numbered SigniÞcance Called
Byte 8 bits 0 through 7
Two-byte 16 bits 0 through 15
Four-byte 32 bits 0 through 31
Big-Endian Byte Ordering
bit 0 is the
least
signiÞcant
bit 0 is the
least
signiÞcant
bit 0 is the
least
signiÞcant
halfword
word
This manual assumes that the MPU on the MVME187 always
programs the CMMUs with big-endian byte ordering, as shown
below. Any attempt to use little-endian byte ordering will
immediately render the MVME187Bug debugger unusable.
BIT BIT
31 24 23 16 15 08 07 00
ADR0 ADR1 ADR2 ADR3
1-3
Page 18
1
Introduction to the MVME187 Installation Guide
Control and Status Bit Definitions
The terms control bit and status bit are used extensively in this
document to describe certain bits in registers.
Term Describes
Control bit
Status bit
The status bit can be read by software to determine
❏
The bit can be set and cleared under software
control
.
The bit reflects a specific condition
operational or exception conditions.
True/False Bit State Definitions
True and False indicate whether a bit enables or disables the
function it controls:
Term Indicates
True
False
Enables the function it controls.
Disables the function it controls.
Bit V alue Descriptions
In all tables, the terms 0 and 1 are used to describe the actual value
that should be written to the bit, or the value that it yields when
read.
.
1-4
Page 19
Related Documentation
The MVME187 ships with a start-up installation guide
(MVME187IG/D, the document you are presently reading) which
includes installation instructions, jumper configuration
information, memory maps, debugger/monitor commands, and
any other information needed for start-up of the board.
If you wish to develop your own applications or need more detailed
information about your MVME187 Single Board Computer, you
may purchase the additional documentation (listed on the
following pages) through your local Motorola sales office.
If any supplements have been issued for a manual or guide, they
will be furnished along with the particular document. Each
Motorola Computer Group manual publication number is suffixed
with characters which represent the revision level of the document,
such as Ò/D2Ó (the second revision of a manual); a supplement
bears the same number as a manual but has a suffix such as
Ò/D2A1Ó (the first supplement to the second edition of the
manual).
Related Documentation
1
Document Set for MVME187-0xx Board
You may order the manuals in this list individually or as a set. The
manual set
68-M187SET
Motorola
Publication Number
MVME187/D MVME187 RISC Single Board Computer UserÕs Manual
88KBUG1/D
88KBUG2/D
MVME187BUG MVME187Bug Debugging Package UserÕs Manual
VMESBCA1/PG
VMESBCA2/PG
Debugging Package for Motorola 88K RISC CPUs UserÕs
Manual (Parts 1 and 2)
Single Board Computer ProgrammerÕs Reference Guide
(Parts 1 and 2)
includes:
Description
1-5
Page 20
1
Introduction to the MVME187 Installation Guide
Motorola
Publication Number
SBCSCSI/D Single Board Computers SCSI Software UserÕs Manual
Description
Additional Manuals for this Board
Also available but
Motorola
Publication Number
MVME187IG/D MVME187 RISC Single Board Computer Installation
Guide (this manual)
SIMVME187/D MVME187 RISC Single Board Computer Support
Information
The SIMVME187 manual contains the connector
interconnect signal information, parts lists, and the
schematics for the MVME187.
not
included in the set:
Description
Other Applicable Motorola Publications
The following publications are applicable to the MVME187 and
may provide additional helpful information. They may be
purchased through your local Motorola sales office.
Motorola
Publication Number
MVME712M MVME712M Transition Module and P2 Adapter
Board User's Manual
MVME712A MVME712-12, MVME712-13, MVME712A,
MVME712AM, and MVME712B Transition Modules
and LCP2 Adapter Board User's Manual
1-6
Description
Page 21
Related Documentation
1
Motorola
Publication Number
MC88100UM MC88100 RISC Microprocessor User's Manual
MC88200UM MC88200 Cache/Memory Management Unit
(CMMU) User's Manual
MC88204 MC88204 64K-Byte Cache/Memory Management
Unit (CMMU) data sheet A
Description
Non-Motorola Peripheral Controllers Publications Bundle
For your convenience, we have collected user's manuals for each of
the peripheral controllers used on the MVME187 from the
suppliers. This bundle, which can be ordered as part number
1X7DS
Part Number Description
NCR53C710DM NCR 53C710 SCSI I/O Processor Data Manual
NCR53C710PG NCR 53C710 SCSI I/O Processor ProgrammerÕs Guide
, includes the following manuals:
68-
CL-CD2400/2401 Cirrus Logic CD2401 Serial Controller UserÕs Manual
UM95SCC0100 Zilog Z85230 Serial Communications Controller
UserÕs Manual
290218 Intel Networking Components Data Manual
290435 Intel i28F008 Flash Memory Data Sheet
290245 Intel i28F020 Flash Memory Data Sheet
292095 Intel i28F008SA Software Drivers Application Note
292099 Intel i28F008SA Automation and Algorithms
Application Note
1-7
Page 22
1
Introduction to the MVME187 Installation Guide
Part Number Description
MK48T08/18B SGS-THOMSON MK48T08 Time Clock/NVRAM
Data Sheet
MC68230/D MC68230 Parallel Interface Timer (PI/T) Data Sheet
SBCCOMPS/L Customer Letter for Component Alternatives
1-8
Page 23
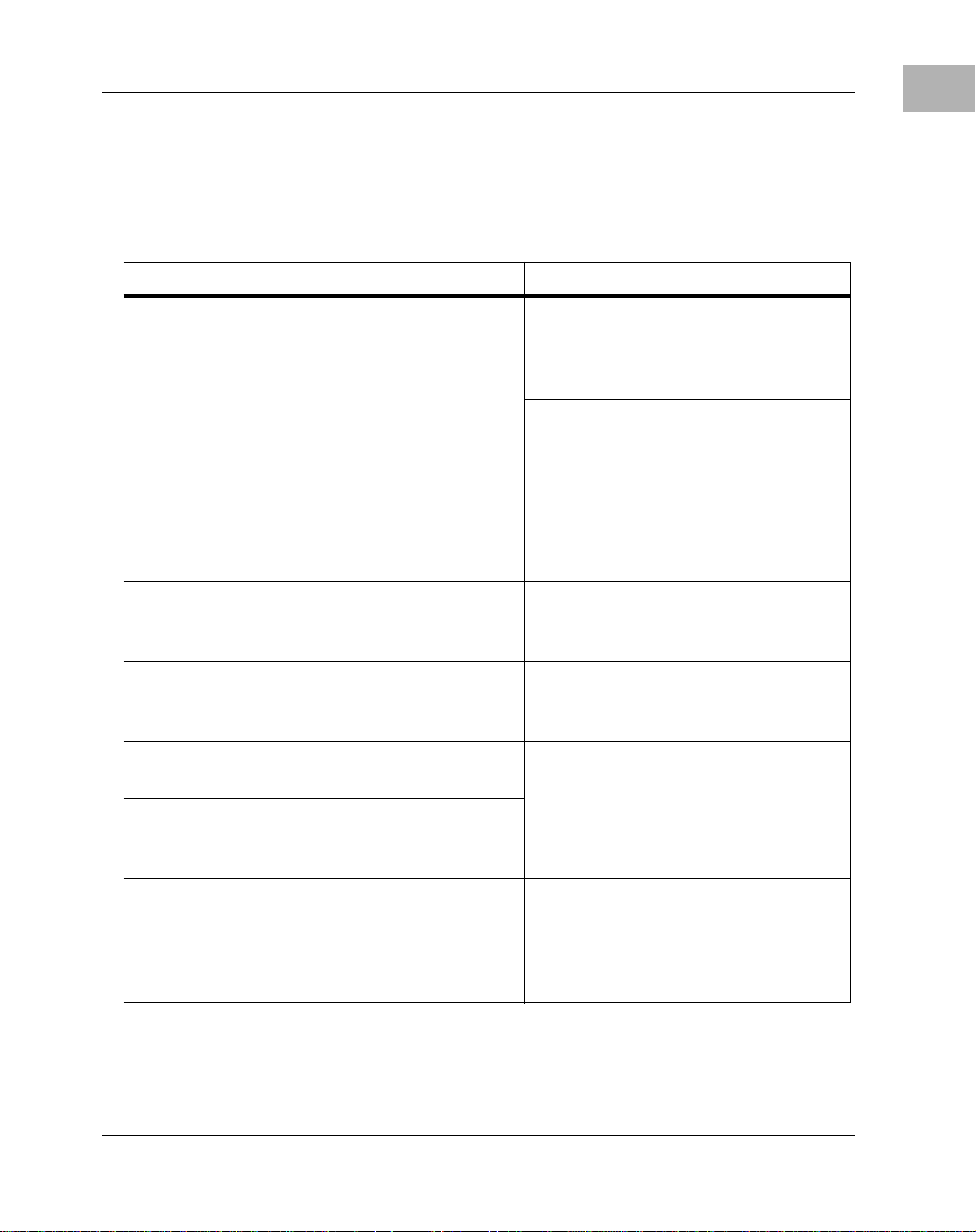
Applicable Non-Motorola Publications
The following non-Motorola publications are also available from
the sources indicated.
Document Title Source
Related Documentation
1
Versatile Backplane Bus: VMEbus,
ANSI/IEEE Std 1014-1987
(VMEbus SpeciÞcation) (This is also
Microprocessor System Bus for 1 to 4 Byte
Data, IEC 821
ANSI Small Computer System Interface-2
(SCSI-2), Draft Document X3.131-198X,
Revision 10c
CL-CD2400/2401 Four-Channel MultiProtocol Communications Controller Data
Sheet, order number 542400-003
82596CA Local Area Network Coprocessor
Data Sheet, order number 290218; and
82596 User's Manual, order number 296853
NCR 53C710 SCSI I/O Processor Data
Manual, order number NCR53C710DM
NCR 53C710 SCSI I/O Processor
ProgrammerÕs Guide, order number
BUS)
NCR53C710PG
MK48T08(B) Timekeeper
Zeropower
RAMs Databook, order number DBSRAM71
TM
RAM data sheet in Static
TM
and 8Kx8
The Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers, Inc.
345 East 47th St.
New York, NY 10017
Bureau Central de la Commission
Electrotechnique Internationale
3, rue de VarembŽ
Geneva, Switzerland
Global Engineering Documents
15 Inverness Way East
Englewood, CO 80112-5704
Cirrus Logic, Inc.
3100 West Warren Ave.
Fremont, CA 94538
Intel Corporation, Literature Sales
P.O. Box 58130
Santa Clara, CA 95052-8130
NCR Corporation
Microelectronics Products Division
1635 Aeroplaza Dr.
Colorado Springs, CO 80916
SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics
Group
Marketing Headquarters
1000 East Bell Rd.
Phoenix, AZ 85022-2699
1-9
Page 24

1
Introduction to the MVME187 Installation Guide
1-10
Page 25

2Board Level Hardware
This Chapter Covers
❏ A general description of the MVME187 RISC Single Board
Computer
❏ Features and specifications
❏ A board-level hardware overview
❏ A detailed hardware functional description, including front
panel switches and indicators
❏ Memory maps
General Description
The MVME187 is a high functionality VMEbus RISC single board
computer designed around the M88000 chip set. It features:
Description
2
❏ Onboard memory expansion mezzanine module with
4, 8, 16, 32, 64 or 128MB of onboard DRAM
❏ SCSI bus interface with DMA
❏ Four serial ports with EIA-232-D interface
❏ Centronics (parallel) printer port
❏ Ethernet transceiver interface with DMA
❏ 187Bug debug monitor firmware
2-1
Page 26
Board Level Hardware Description
2
Onboard Memory Mezzanine Module
The MVME187 onboard DRAM mezzanine boards are available in
different sizes and with programmable parity protection or Error
Checking and Correction (ECC) protection.
❏ The main board and a single mezzanine board together take
one slot.
❏ Motorola software supports mixed parity and ECC memory
boards on the same main board.
❏ Mezzanine board sizes are 4, 8, 16, or 32 MB (parity), or 4, 8,
16, 32, 64, or 128 MB (ECC);
Ð Two mezzanine boards may be stacked to provide 256MB
of onboard RAM (ECC) or 64 MB (parity). The stacked
configuration requires two VMEbus slots.
❏ The DRAM is four-way interleaved to efficiently support
cache burst cycles.
❏ The parity mezzanines are only supported on 25 MHz main
boards.
A functional description of the Onboard DRAM starts on page 2-15.
SCSI Mass Storage Interface
The MVME187 provides for mass storage subsystems through the
industry-standard SCSI bus. These subsystems may include
❏ Hard and floppy disk drives
❏ Streaming tape drives
❏ Other mass storage devices.
A functional description of the SCSI Interface starts on page 2-22.
2-2
Page 27
General Description
Serial Ports
The serial ports support standard baud rates of 110 to 38.4K baud.
Serial
Port
1 Minimum Asynchronous RXD, CTS, TXD, and RTS
2
and 3 Full Asynchronous RXD, CTS, DCD, TXD, RTS,
4 Full Both RXD, CTS, DCD, TXD, RTS,
Function
Synchronous/
Asynchronous
Signals Bit Rates
and DTR
and DTR
All four serial ports use EIA-232-D drivers and receivers located on
the main board, and all the signal lines are routed to the I/O
connector.
A functional description of the Serial Port Interface starts on page
2-18.
Parallel (Printer) Port
2
Synchronous up
to 64 k bits per
second
The 8-bit bidirectional parallel port may be used as a Centronicscompatible parallel printer port or as a general parallel I/O port.
A functional description of the Parallel Port Interface starts on page
2-20.
Ethernet T ransceiver Interface
The Ethernet transceiver interface is located on the MVME187, and
the industry standard connector is located on the MVME712X
transition module.
A functional description of the Ethernet Interface starts on page
2-21.
2-3
Page 28
Board Level Hardware Description
2
187Bug Firmware
The MVME187Bug debug monitor firmware (187Bug) is provided
in two of the four EPROM sockets on the MVME187.
It provides:
❏ Over 50 debug commands
❏ Up/down load commands
❏ Disk bootstrap load commands
❏ A full set of onboard diagnostics
❏ A one-line assembler/disassembler
The 187Bug user interface accepts commands from the system
console terminal.
187Bug can also operate in a System Mode, which includes choices
from a service menu.
Features
2-4
❏ M88000 Microprocessor (one MC88100 MPU and two
MC88200 or MC88204 CMMUs)
❏ 4/8/16/32/64MB of 32-bit DRAM with parity or
4/8/16/32/64/128/256MB of 32-bit DRAM with ECC
protection
❏ Four 44-pin PLCC ROM sockets (organized as two banks of
32 bits)
❏ 128KB Static RAM (with optional battery backup as a factory
build special request)
❏ Status LEDs for FAIL, STAT, RUN, SCON, LAN, +12V (LAN
power),
❏ 8K by 8 static RAM and time of day clock with battery backup
SCSI, and VME.
Page 29

Features
❏ RESET and ABORT switches
❏ Four 32-bit tick timers for periodic interrupts
❏ Watchdog timer
❏ Eight software interrupts
❏ I/O
Ð SCSI Bus interface with DMA
Ð Four serial ports with EIA-232-D buffers with DMA
Ð Centronics printer port
Ð Ethernet transceiver interface with DMA
❏ VMEbus interface
Ð VMEbus system controller functions
Ð VMEbus interface to local bus (A24/A32, D8/D16/D32
and D8/D16/D32/D64BLT) (BLT = Block Transfer)
Ð Local bus to VMEbus interface (A16/A24/A32,
D8/D16/D32)
Ð VMEbus interrupter
Ð VMEbus interrupt handler
Ð Global CSR for interprocessor communications
Ð DMA for fast local memory - VMEbus transfers
(A16/A24/A32, D16/D32 and D16/D32/D64BLT)
2
2-5
Page 30
Board Level Hardware Description
2
Specifications
Table 2-1. MVME187 General Specifications
Characteristics SpeciÞcations
Power requirements
(with all four EPROM sockets
populated and excluding
external LAN transceiver)
Operating temperature 0û to 55û C at point of entry of forced air
Storage temperature -40û to +85û C
Relative humidity 5% to 90% (non-condensing)
Physical
dimensions
Double-high
VMEboard
PC board with
mezzanine
module only
PC board with
connectors and
front panel
+5 Vdc (+/-5%) 3.5 A (typical), 4.5 A (maximum)
(at 25 MHz, with 32MB parity DRAM)
5.0 A (typical), 6.5 A (maximum)
(at 33 MHz, with 128MB ECC DRAM)
+12 Vdc (+/-5%) 100 mA (maximum)
(1.0 A (maximum) with offboard LAN
transceiver)
-12 Vdc (+/- 5%) 100 mA (maximum)
(approximately 490 LFM)
Height 9.187 inches (233.35 mm)
Depth 6.299 inches (160.00 mm)
Thickness 0.662 inches (16.77 mm)
Height 10.309 inches (261.85 mm)
Depth 7.4 inches (188 mm)
Thickness 0.80 inches (20.32 mm)
Conformance to Requirements
These boards are designed to conform to the requirements of the
following specifications:
❏ VMEbus Specification (IEEE 1014-87)
❏ EIA-232-D Serial Interface Specification, EIA
❏ SCSI Specification
2-6
Page 31

Board Level Overview
Board Level Overview
M88000
DRAM EPROM
VMEchip2
82596CA
LAN
ETHERNET
VMEbus
Figure 2-1. MVME187 General Block Diagram
53C710
SCSI
MK48T08
BBRAM
& CLOCK
CD2401
SCC
SERIAL IO
2
PRINTER
PORT
PCCchip2
128KB
STATIC
RAM
bd069 9211
Connectors
Adapters
The MVME187 has two 96-position DIN connectors: P1 and P2.
❏ P1 rows A, B, C, and P2 row B provide the VMEbus
interconnection.
❏ P2 rows A and C provide the connection to the SCSI bus,
serial ports, Ethernet, and printer.
I/O on the MVME187 is connected to the VMEbus P2 connector.
The main board is connected to the transition modules through a P2
adapter board and cables.
2-7
Page 32

Board Level Hardware Description
2
Transition Modules
MVME712X transition modules provide configuration headers and
provide industry standard connectors for the I/O devices. Refer to
Figure 3-3 on page 3-22.
❏ The MVME187 supports the transition modules MVME712-
12, MVME712-13, MVME712M, MVME712A, MVME712AM,
and MVME712B (referred to in this manual as MVME712X,
unless separately specified).
Transition modules and adapter boards are covered in
MVME712M, Transition Module and P2 Adapter Board User's Manual,
and MVME712A, MVME712-12, MVME712-13, MVME712A,
MVME712AM, and MVME712B Transition Modules and LCP2
Adapter Board User's Manual.
ASICs
The MVME187 board features several Application Specific
Integrated Circuits (ASICs) including:
❏ VMEchip2
2-8
❏ PCCchip2
❏ MEMC040
❏ MCECC
All programmable registers in the MVME187 that reside in ASICs
are covered in the Single Board Computers Programmer's Reference
Guide.
Page 33

Board Level Overview
VMEchip2 ASIC
Provides the VMEbus interface. The VMEchip2 includes:
2
❏ Two tick timers
❏ Watchdog timer
❏ Programmable map decoders for the master and slave
interfaces, and a VMEbus to/from local bus DMA controller
❏ VMEbus to/from local bus non-DMA programmed access
interface
❏ VMEbus interrupter
❏ VMEbus system controller
❏ VMEbus interrupt handler
❏ VMEbus requester
Table 2-2. Bus Transfers
Transfer type Can be...
Processor-to-VMEbus D8, D16, or D32
PCCchip2 ASIC
The PCCchip2 ASIC provides two tick timers and the interface to
the:
VMEchip2 DMA to the
VMEbus
❏ LAN chip
❏ SCSI chip
❏ Serial port chip
❏ Printer port
❏ BBRAM
D16, D32, D16/BLT,
D32/BLT, or D64/MBLT
2-9
Page 34

Board Level Hardware Description
2
MEMC040 Memory Controller ASIC
The MEMC040 memory controller ASIC provides the
programmable interface for the parity-protected DRAM mezzanine
board.
MCECC Memory Controller ASIC
The MCECC memory controller ASIC provides the programmable
interface for the ECC-protected DRAM mezzanine board.
Functional Description
The major functional blocks of the MVME187 covered in this
section are:
❏ Front panel switches and LED indicators
❏ Data bus structure
❏ M88000 MPU
❏ EPROM
2-10
❏ SRAM
❏ Onboard DRAM
❏ Battery backed up RAM and clock
❏ VMEbus interface
❏ I/O interfaces
❏ Local resources
Page 35

Functional Description
Front Panel Switches and LEDs
There are two switches and eight LEDs on the boardÕs front panel
(refer to Table 2-3, Table 2-4, and Figure 3-1 on page 3-6).
Table 2-3. Front Panel Switches
Switch
Name
RESET
ABORT
LED
Name
FAIL
STAT
RUN
SCON
LAN
+12V
SCSI
VME
The RESET switch resets all onboard devices and drives SYSRESET* if the
board is system controller. The RESET switch may be disabled by software.
When enabled by software, the ABORT switch generates an interrupt at a userprogrammable level. It is normally used to abort program execution and
return to the debugger.
Table 2-4. Front Panel LEDs
Color Description
Red The FAIL LED lights when the BRDFAIL signal line is active.
Yellow The STAT LED is controlled by software on the MVME187.
Green
Green
Green The LAN LED lights when the LAN chip is local bus master.
Green
Green The SCSI LED lights when the SCSI chip is local bus master.
Green
The RUN LED lights when the local bus TIP* signal line is low. This
indicates one of the local bus masters is executing a local bus cycle.
The SCON LED lights when the MVME187 is the VMEbus system
controller.
The +12V LED lights when +12V power is available to the Ethernet
transceiver interface.
The VME LED lights when the board is using the VMEbus (VMEbus
AS* is asserted by the VMEchip2) or when the board is accessed by
the VMEbus (VMEchip2 is the local bus master).
Description
2
2-11
Page 36

Board Level Hardware Description
2
Data Bus Structure
The local data bus on theMVME187 is a 32-bit synchronous bus
based on the MC68040 bus, and supports burst transfers and
snooping.
Local Bus Arbitration
The various local bus master and slave devices use the local bus to
communicate.
The local bus is arbitrated by priority type arbiter and the priority
of the local bus masters from highest to lowest is:
1. 82596CA LAN (highest)
2. CD2401 serial (through the PCCchip2)
3. 53C710 SCSI
4. VMEbus
5. MPU (lowest)
In general, any master can access any slave; however, not all
combinations pass the Òcommon sense test.Ó Refer to the Single
Board Computers Programmer's Reference Guide and to the user's
guide for each device to determine its port size, data bus
connection, and any restrictions that apply when accessing the
device.
M88000 MPU
The MVME187 is based on the M88000 family and uses one
MC88100 MPU and two MC88200 or MC88204 CMMUs.
One CMMU is used for the data cache and one is used for the
instruction cache.
More information is available in the MC88100 and MC88200 user's
manuals and the MC88204 data sheet.
2-12
Page 37

Functional Description
EPROM
Four 44-pin PLCC/CLCC EPROM sockets for 27C102JK or
27C202JK type EPROMs. They are:
❏ Organized in two 32-bit wide banks supporting 8-, 16-, and
32-bit read accesses
❏ Controlled by the VMEchip2
❏ Mapped to local bus address 0 following a local bus reset
Ð This allows the MC88100 to start executing code at address
0 following a reset.
Programmable EPROM Features
❏ Map decoder
❏ Access time
❏ When accessible at address 0
Static RAM
The MVME187 includes 128KB of 32-bit wide 100 ns static RAM
(SRAM), which:
2
❏ Supports 8-, 16-, and 32-bit wide accesses.
❏ Allows debugger operation and execution of limited
diagnostics without the DRAM mezzanine.
❏ Is controlled by the VMEchip2; the access time is
programmable.
2-13
Page 38

Board Level Hardware Description
2
Optional SRAM Battery Backup
SRAM battery backup is optionally available on the MVME187, but
only as a factory build and only by special request. (Contact your local
Motorola sales office for details). The battery backup function,
provided by a Dallas DS1210S nonvolatile controller chip and a
RAYOVAC FB1225 battery, supports primary and secondary
power sources.
The onboard power source is a RAYOVAC FB1225 battery which
has two BR1225-type lithium cells and is socketed for easy removal
and replacement. A small capacitor is provided to allow the battery
to be quickly replaced without data loss (i.e., the battery must be
replaced within 30 seconds).
If your MVME187 is equipped with SRAM battery backup, when
the main board power fails, the DS1210S selects the source with the
highest voltage.
If one source should fail, the DS1210S switches to the redundant
source.
Each time the board is powered, the DS1210S checks power sources,
allowing software to provide an early warning to avoid data loss:
2-14
❏ If the voltage of the backup sources is less than two volts, the
second memory access cycle is blocked.
❏ Because the DS1210S may block the second access, the
software should do at least two accesses before relying on the
data.
With the optional battery backup, the MVME187 provides jumpers
(see Optional SRAM Backup Power Source Select Header J6 on page
3-11) that allow either power source of the DS1210S to be connected
to the VMEbus
+5 V STDBY pin or to one cell of the onboard battery.
The power leads from the battery are exposed on the solder side of
the board, therefore the board should not be placed on a conductive
surface or stored in a conductive bag unless the battery is removed.
Page 39

Functional Description
!
Caution
Lithium batteries incorporate inflammable materials
such as lithium and organic solvents. If lithium batteries
are mistreated or handled incorrectly, they may burst
open and ignite, possibly resulting in injury and/or fire.
When dealing with lithium batteries, carefully follow the
precautions listed below in order to prevent accidents.
❏ Do not short circuit.
❏ Do not disassemble, deform, or apply excessive pressure.
❏ Do not heat or incinerate.
❏ Do not apply solder directly.
❏ Do not use different models.
❏ Do not charge.
❏ Always check proper polarity.
To remove the battery from the module, carefully pull the battery
from the socket. (Data will be lost if a new battery is not installed
within 30 seconds.)
Before installing a new battery, ensure that the battery pins are
clean. Note the battery polarity and press the battery into the
socket.
2
Onboard DRAM
The MVME187 onboard DRAM is located on a mezzanine board.
The mezzanine boards are available in different sizes and with
parity protection or ECC protection.
Note Parity mezzanines are only supported on 25 MHz main
boards.
2-15
Page 40

Board Level Hardware Description
2
boards on the same main board.
The DRAM is four-way interleaved to efficiently support cache
burst cycles.
Onboard DRAM mezzanines are available in these configurations:
Motorola software does support mixed parity and ECC memory
❏ 4, 8, 16, or 32MB with parity protection
❏ 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 MB with ECC protection
Stacking Mezzanines
Two mezzanine boards may be stacked to provide up to 256MB of
onboard RAM (ECC).
❏ The MVME187 board and a single mezzanine board together
take one slot.
❏ The stacked configuration requires two VMEboard slots.
DRAM Programming Considerations
❏ The DRAM map decoder can be programmed to
accommodate different base address(es) and sizes of
mezzanine boards.
2-16
❏ Onboard DRAM is disabled by a local bus reset and must be
programmed before the DRAM can be accessed.
❏ Most DRAM devices require some number of access cycles
before the DRAMs are fully operational.
Ð Normally this requirement is met by the onboard refresh
circuitry and normal DRAM installation. However,
software should insure a minimum of 10 initialization
cycles are performed to each bank of RAM.
Refer to the MEMC040 or the MCECC in the Single Board Computers
Programmer's Reference Guide for detailed programming
information.
Page 41

Functional Description
Battery Backed Up RAM and Clock
The MK48T08 RAM and clock chip is a 28-pin package that
provides
❏ A time-of-day clock
❏ An oscillator
❏ A crystal
❏ Power fail detection
❏ Memory write protection
❏ 8KB of RAM
❏ A battery
The clock provides
❏ Seconds, minutes, hours, day, date, month, and year in BCD
24-hour format
❏ Automatic corrections for 28-, 29- (leap year), and 30-day
months
2
No interrupts are generated by the clock.
The MK48T08 is an 8 bit device; however, the interface provided by
the PCCchip2 supports 8-, 16-, and 32-bit accesses to the MK48T08.
Refer to the MK48T08 data sheet for detailed programming
information.
2-17
Page 42

Board Level Hardware Description
2
VMEbus Interface
The VMEchip2 provides:
❏ Local bus to VMEbus interface
❏ VMEbus to local bus interface
❏ Local-VMEbus DMA controller functions
❏ VMEbus system controller functions
I/O Interfaces
The MVME187 provides onboard I/O for many system
applications.
❏ The I/O functions include:
Ð Serial ports
Ð Printer port
Ð Ethernet transceiver interface
Ð SCSI mass storage interface
❏ An external I/O transition board such as the MVME712X
should be used to convert the I/O connector pinout to
industry-standard connectors.
❏ The configuration headers are located on the MVME187 and
The I/O on the MVME187 is connected to the VMEbus P2
connector. The MVME712X transition module is connected to the
MVME187 through cables and a P2 adapter board.
Serial Port Interface
The CD2401 serial controller chip (SCC) implements the four serial
ports. The serial ports support the standard baud rates (110 to 38.4K
baud). The four serial ports are different functionally because of the
limited number of pins on the P2 I/O connector.
2-18
the MVME712X transition board.
Page 43

Functional Description
All four serial ports use EIA-232-D drivers and receivers located on
the MVME187, and all the signal lines are routed to the I/O
connector.
❏ Serial port 1 is a minimum function asynchronous port. It
uses RXD, CTS, TXD, and RTS.
❏ Serial ports 2 and 3 are full function asynchronous ports.
They use RXD, CTS, DCD, TXD, RTS, and DTR.
❏ Serial port 4 is a full function asynchronous or synchronous
port. It can operate at synchronous bit rates up to 64 k bits per
second. It uses RXD, CTS, DCD, TXD, RTS, and DTR. It also
interfaces to the synchronous clock signal lines.
Serial Interface Programming Considerations
❏ The MVME187 board hardware ties the DTR signal from the
CD2401 to the pin labeled RTS at connector P2. Likewise, RTS
from the CD2401 is tied to DTR on P2. Therefore, when
programming the CD2401, assert DTR when you want RTS,
and RTS when you want DTR.
❏ The interface provided by the PCCchip2 allows the 16-bit
CD2401 to appear at contiguous addresses.
2
❏ Accesses to the CD2401 must be 8 or 16 bits: 32-bit accesses
are not permitted.
❏ The CD2401 supports DMA operations to local memory.
❏ Because the CD2401 does not support a retry operation
necessary to break VMEbus lockup conditions, the CD2401
DMA controllers should not be programmed to access the
VMEbus.
❏ The hardware does not restrict the CD2401 to onboard
DRAM.
Refer to the CD2401 data sheet for detailed programming
information.
2-19
Page 44

Board Level Hardware Description
2
Parallel Port Interface
The PCCchip2 provides an 8-bit bidirectional parallel port. This
port may be used as a Centronics-compatible parallel printer port
or as a general parallel I/O port.
All eight bits of the port must be either inputs or outputs (no
individual bit selection).
In addition to the 8 bits of data, there are two control pins and five
status pins.
When used as a parallel printer port, these pins function as follows:
Status Pins Printer Acknowledge (ACK*)
Printer Fault (FAULT*)
Printer Busy (BSY)
Printer Select (SELECT)
Printer Paper Error (PE)
Control Pins Printer Strobe (STROBE*)
Input Prime (INP*)
2-20
Each of the status pins can generate an interrupt to the MPU in any
of the following programmable conditions:
❏ High level
❏ Low level
❏ High-to-low transition
❏ Low-to-high transition
Page 45

Functional Description
The PCCchip2 provides an auto-strobe feature similar to that of the
MVME147 PCC.
Ethernet Interface
The 82596CA implements the Ethernet transceiver interface. The
82596CA accesses local RAM using DMA operations to perform its
normal functions.
The Ethernet transceiver interface is located on the MVME187, and
the industry standard connector is located on the MVME712X
transition module.
Every MVME187 is assigned an Ethernet Station Address. The
address is $08003E2xxxxx where xxxxx is the unique 5-nibble
number assigned to the board (i.e., every MVME187 has a different
value for xxxxx).
2
❏ In auto-strobe mode, after a write to the Printer Data Register,
the PCCchip2 automatically asserts the STROBE* pin for a
selected time specified by the Printer Fast Strobe control bit.
❏ In manual mode, the Printer Strobe control bit directly
controls the state of the STROBE* pin.
Each module has the Ethernet Station Address displayed on a label
attached to the VMEbus P2 connector. In addition, the six bytes
including the Ethernet address are stored in the configuration area
of the BBRAM. That is, 08003E2xxxxx is stored in the BBRAM.
❏ At an address of $FFFC1F2C, the upper four bytes (08003E2x)
can be read.
❏ At an address of $FFFC1F30, the lower two bytes (xxxx) can
be read.
The MVME187 debugger has the capability to retrieve or set the
Ethernet address.
If the data in the BBRAM is lost, the user should use the number on
the VMEbus P2 connector label to restore it.
2-21
Page 46

Board Level Hardware Description
2
Buffer Overruns
Because the 82596CA has small internal buffers and the VMEbus
has an undefined latency period, buffer overrun may occur if the
DMA is programmed to access the VMEbus. Therefore, the
82596CA should not be programmed to access the VMEbus.
Support functions for the 82596CA are provided by the PCCchip2.
Refer to the 82596CA user's guide for detailed programming
information.
SCSI Interface
The MVME187 provides for mass storage subsystems through the
industry-standard SCSI bus. These subsystems may include hard
and floppy disk drives, streaming tape drives, and other mass
storage devices.
The SCSI interface is implemented using the NCR 53C710 SCSI I/O
controller.
Support functions for the 53C710 are provided by the PCCchip2.
Refer to the 53C710 user's guide for detailed programming
information.
2-22
SCSI Termination
Because this board has no provision for SCSI termination, you must
ensure that the SCSI bus is terminated properly.
❏ If the SCSI bus ends at the P2 Adapter, termination resistors
must be installed on the R1, R2, and R3 sockets using three 8pin SIP resistors. Note: +5V power to the SCSI bus TERM
power line and termination resistors is provided through a
fuse located on the P2 transition board.
❏ If there are additional SCSI mass storage devices in your
system, make sure that terminators are installed on the last
device in the SCSI chain.
Page 47

Functional Description
Local Resources
The MVME187 includes many resources for the local processor.
These include tick timers, software programmable hardware
interrupts, watchdog timer, and local bus timeout.
Programmable Tick Timer s
Four 32-bit programmable tick timers with 1 µs resolution are
provided, two in the VMEchip2 and two in the PCCchip2. The tick
timers can be programmed to generate periodic interrupts to the
processor.
Watchdog Timer
A watchdog timer function is provided in the VMEchip2. When the
watchdog timer is enabled, it must be reset by software within the
programmed time or it times out. The watchdog timer can be
programmed to generate a SYSRESET signal, local reset signal, or
board fail signal if it times out.
Software-Programmable Hardware Interrupts
Eight software-programmable hardware interrupts are provided
by the VMEchip2. These interrupts allow software to create a
hardware interrupt.
2
Local Bus Timeout
The MVME187 provides a timeout function for the local bus. When
the timer is enabled and a local bus access times out, a Transfer
Error Acknowledge (TEA) signal is sent to the local bus master. The
timeout value is selectable by software for 8 µsec, 64 µsec, 256 µsec,
or infinite. The local bus timer does not operate during VMEbus
bound cycles. VMEbus bound cycles are timed by the VMEbus
access timer and the VMEbus global timer.
2-23
Page 48

Board Level Hardware Description
2
Memory Maps
There are two points of view for memory maps:
1. Local bus memory map Ð the mapping of all resources as viewed by local bus
masters
2. VMEbus memory map Ð the mapping of onboard resources as viewed by VMEbus
Masters
Local Bus Memory Map
The local bus memory map is split into different address spaces by
the transfer type (TT) signals. The local resources respond to the
normal access and interrupt acknowledge codes.
Normal Address Range Devices
The memory map of devices that respond to the normal address
range is shown in the following tables. The normal address range is
defined by the Transfer Type (TT) signals on the local bus.
2-24
❏ On the MVME187, Transfer Types 0 and 1 define the normal
address range.
Table 2-5 on page 2-25 is the entire map from $00000000 to
$FFFFFFFF. Many areas of the map are user-programmable, and
suggested uses are shown in the table.
❏ The cache inhibit function is programmable in the MMUs.
❏ The onboard I/O space must be marked cache inhibit and
serialized in its page table.
Table 2-6 on page 2-26 further defines the map for the local I/O
devices.
Page 49

Memory Maps
Table 2-5. Local Bus Memory Map
Address
Range
$00000000 DRAMSIZE
DRAMSIZE
- $FF7FFFFF
$FF800000 -
$FFBFFFFF
$FFC00000 -
$FFDFFFFF
$FFE00000 -
$FFE1FFFF
$FFE20000 -
$FFEFFFFF
$FFF00000 -
$FFFEFFFF
$FFFF0000 -
$FFFFFFFF
Devices Accessed Port Size Size
User programmable
(onboard DRAM)
User programmable
(VMEbus)
ROM D32 4MB N 1
Reserved -- 2MB -- 5
SRAM D32 128KB N --
SRAM (repeated) D32 896KB N --
Local I/O devices
(refer to next table)
User programmable
(VMEbus A16)
D32 DRAMSIZE N 1, 2
D32/D16 3GB ? 3, 4
D32-D8 1MB Y 3
D32/D16 64KB ? 2, 4
Software
Cache
Inhibit
Notes
Notes
1. Onboard EPROM appears at $00000000 - $003FFFFF following a local bus
reset. The EPROM appears at 0 until the ROM0 bit is cleared in the
VMEchip2. The ROM0 bit is located at address $FFF40030 bit 20. The
EPROM must be disabled at 0 before the DRAM is enabled. The VMEchip2
and DRAM map decoders are disabled by a local bus reset.
2. This area is user-programmable. The suggested use is shown in the table.
The DRAM decoder is programmed in the MEMC040 or MCECC chip, and
the local-to-VMEbus decoders are programmed in the VMEchip2.
3. Size is approximate.
4. Cache inhibit depends on devices in area mapped.
5. This area is not decoded. If these locations are accessed and the local bus
timer is enabled, the cycle times out and is terminated by a TEA signal.
2
2-25
Page 50

Board Level Hardware Description
2
local bus Main Memory Map.
Table 2-6. Local I/O Devices Memory Map
Address Range Devices Accessed Port Size Size Notes
$FFF00000 - $FFF3FFFF Reserved -- 256KB 4 $FFF40000 - $FFF400FF VMEchip2 (LCSR) D32 256B 1,3 $FFF40100 - $FFF401FF VMEchip2 (GCSR) D32-D8 256B 1,3 $FFF40200 - $FFF40FFF Reserved -- 3.5KB 4,6 $FFF41000 - $FFF41FFF Reserved -- 4KB 4 $FFF42000 - $FFF42FFF PCCchip2 D32-D8 4KB 1 $FFF43000 - $FFF430FF MEMC040/MCECC #1 D8 256B 1 $FFF43100 - $FFF431FF MEMC040/MCECC #2 D8 256B 1
The following table focuses on the Local I/O Devices portion of the
$FFF43200 - $FFF43FFF MEMC040s/MCECCs
(repeated)
$FFF44000 - $FFF44FFF reserved -- 4KB 4
$FFF45000 - $FFF451FF CD2401 (Serial Comm.
Cont.) $FFF45200 - $FFF45DFF Reserved -- 3KB 6,8 $FFF45E00 - $FFF45FFF Reserved -- 512B 8 $FFF46000 - $FFF46FFF 82596CA (LAN) D32 4KB 1,7 $FFF47000 - $FFF47FFF 53C710 (SCSI) D32/D8 4KB 1 $FFF48000 - $FFF4FFFF Reserved -- 32KB 4 $FFF50000 - $FFF6FFFF Reserved -- 128KB 4 $FFF70000 - $FFF76FFF Reserved -- 28KB 5 $FFF77000 - $FFF77FFF CODE CMMU D32 4KB 1 $FFF78000 - $FFF7EFFF Reserved -- 28KB 5 $FFF7F000 - $FFF7FFFF DATA CMMU D32 4KB 1 $FFF80000 - $FFF9FFFF Reserved -- 128KB 5 $FFFA0000 - $FFFBFFFF Reserved -- 128KB 4 $FFFC0000 - $FFFCFFFF MK48T08 (BBRAM,
TOD Clock) $FFFD0000 - $FFFDFFFF Reserved -- 64KB 4 $FFFE0007 IACK LEVEL 1 D8 1 byte 2
-- 3.5KB 1,6
D16-D8 512B 1
D32-D8 64KB 1
2-26
Page 51

Memory Maps
Table 2-6. Local I/O Devices Memory Map (Continued)
Address Range Devices Accessed Port Size Size Notes
$FFFE000B IACK LEVEL 2 D8 1 byte 2 $FFFE000F IACK LEVEL 3 D8 1 byte 2 $FFFE0013 IACK LEVEL 4 D8 1 byte 2 $FFFE0017 IACK LEVEL 5 D8 1 byte 2 $FFFE001B IACK LEVEL 6 D8 1 byte 2 $FFFE001F IACK LEVEL 7 D8 1 byte 2 $FFFE0020 - $FFFEFFFF IACK LEVELS
(repeated)
-- 64KB 2,6
Notes
1. For a complete description of the register bits, refer to the Single Board
Computers Programmer's Reference Guide or to the data sheet for the specific
chip.
2. Byte reads should be used to read the interrupt vector. These locations do
not respond when an interrupt is not pending. If the local bus timer is
enabled, the access times out and is terminated by a TEA signal.
3. Writes to the LCSR in the VMEchip2 must be 32 bits. LCSR writes of 8 or 16
bits terminate with a TEA signal. Writes to the GCSR may be 8, 16 or 32 bits.
Reads to the LCSR and GCSR may be 8, 16 or 32 bits.
4. This area does not return an acknowledge signal. If the local bus timer is
enabled, the access times out and is terminated by a TEA signal.
5. This area does return an acknowledge signal.
6. Size is approximate.
7. Port commands to the 82596CA must be written as two 16-bit writes: upper
word first and lower word second.
8. The CD2401 appears repeatedly from $FFF45200 to $FFF45FFF. If the local
bus timer is enabled, the access times out and is terminated by a TEA signal.
2
2-27
Page 52

Board Level Hardware Description
2
VMEbus Memory Map
This section describes the mapping of local resources as viewed by
VMEbus masters. Default addresses for the slave, master, and
GCSR address decoders are provided by the ENV command. Refer
to Appendix A.
VMEbus Accesses to the Local Bus
The VMEchip2 includes a user-programmable map decoder for the
VMEbus to local bus interface. The map decoder allows you to
program the starting and ending address and the modifiers the
MVME187 responds to.
VMEbus Short I/O Memory Map
The VMEchip2 includes a user-programmable map decoder for the
GCSR. The GCSR map decoder allows you to program the starting
address of the GCSR in the VMEbus short I/O space.
2-28
Page 53

3Hard ware Preparation and
This Chapter Covers
This chapter provides instructions on:
❏ Unpacking the equipment
❏ Preparing the hardware
❏ Installing the MVME187 RISC Single Board Computer
Note that hardware preparation instructions for the MVME712X
transition module are provided in separate userÕs manuals for each
model. Refer to the userÕs manual you received with your
MVME712X.
Unpacking the Equipment
Installation
3
!
Caution
Note If the shipping carton is damaged upon receipt, request
that the carrier's agent be present during unpacking
and inspection of the equipment.
Unpack the equipment from the shipping carton. Refer to the
packing list and verify that all items are present. Save the packing
material for storing and reshipping of the equipment.
Avoid touching areas of integrated circuitry; static
discharge can damage circuits.
3-1
Page 54

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Overview of Startup Procedure
The following list identifies the things you will need to do before
3
you can use this board, and where to find the information you need
to perform each step. Be sure to read this chapter and all Caution
notes, and have the related documentation with you before you
begin.
Table 3-1. Startup Overview
Stage What you will need to do... Refer to...
1 Prepare the MVME187. Preparing the
Hardware
Ensure that EPROM devices are properly
installed in their sockets.
ConÞgure adapters and MVME712X
transition modules.
Install/remove jumpers on headers. Jumper Settings 3-7
2 Prepare the chassis. Preparing the
Turn power off to chassis and peripherals. The userÕs
Disconnect AC power cable.
Remove chassis cover.
Remove Þller panels from card slots.
3 Install your MVME187 in the chassis. Installing the
Remove IACK and BG jumpers from
backplane.
Checking the
187Bug EPROMs
The userÕs manual you
received with your
MVME712X module
MVME187 for
Installation
manual you
received with
your chassis
Hardware
On
page...
3-5
3-7
3-14
3-15
3-16
3-2
Slide the module into the chassis and
fasten it securely.
Page 55

Overview of Startup Procedure
Table 3-1. Startup Overview (Continued)
Stage What you will need to do... Refer to...
4 Install adapter boards and transition modules. Transition
Modules and
Adapter Boards
Overview
Installing
Transition
Modules and
Adapter Boards
Set jumpers on the transition module(s). The userÕs manual you
Connect and install the MVME712X
transition module.
Connect and install the P2 adapter board.
5 Connect peripherals. Connecting
Connect and install any optional SCSI
device cables.
Connect a console terminal to the
MVME712X.
received with your
MVME712X
Peripherals
You may also wish to
obtain the Single Board
Computer SCSI Software
UserÕs Manual
On
page...
3
3-17
3-20
3-20
Connect any other optional devices or
equipment you will be using, such as
serial or parallel printers, host computers,
etc.
6 Complete the installation. The userÕs
Reassemble chassis.
Reconnect AC power.
EIA-232-D
Interconnections
Port Numbers 5-7
Disk/Tape
Controller Data
manual you
received with
your chassis
E-1
B-1
3-24
3-3
Page 56

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Table 3-1. Startup Overview (Continued)
Stage What you will need to do... Refer to...
On
page...
3
7 Start up the system. Starting the
System
Power up the system. Front Panel
Switches and
LEDs
Initialize the real-time clock. Initializing the
Real-Time Clock
Note that the debugger prompt appears. Powering Up the
System
Starting Up
187Bug
You may also wish to
obtain the Debugging
Package for Motorola 88K
RISC CPUs UserÕs Manual
and the 187Bug
Diagnostics UserÕs Manual
Examine and/or change environmental
parameters.
Examining
and/or Changing
Environmental
Parameters
3-24
2-11
3-25
3-25
4-6
3-25
3-4
Setting
Environment to
Bug/Operating
System
Program the PCCchip2 and VMEchip2. Memory Maps 2-24
Troubleshoot the system. Troubleshooting
Solve any startup problems
the MVME187:
Solving Startup
Problems
A-3
D-1
Page 57

Preparing the Hardware
This section covers:
❏ Modifying hardware configurations before installation
❏ Checking the 187Bug EPROMs
❏ Factory jumper settings
❏ Preparing your MVME187
❏ Preparing the system chassis
Modifying Configuration before Installation
To select the desired configuration and ensure proper operation of
the MVME187, certain option modifications may be necessary
before installation.
The location of the switches, jumper headers, connectors, and LED
indicators on the MVME187 is illustrated in Figure 3-1.
Preparing the Hardware
3
Option Modification
The MVME187 has provisions for option modification via:
❏ Software control for most options
❏ Jumper settings on headers for some options
❏ Bit settings in control registers after installation for most
other options
Ð Control registers are described in the Single Board
Computer Programmer's Reference Guide as listed in Related
Documentation in Chapter 1 of this manual.
3-5
Page 58

Hardware Preparation and Installation
MVME
187
2
3
STATFAIL
RUN SCON
+12V
LAN
SCSI VME
1
DS1
J1
DS2
16
15
1
F1
DS3
2
DS4
19
20
J3
29
39
40
6
28
1
XU1
18
17
7
J2
(OPTIONAL)
1
2
65
29
39
40
6
28
1
XU2
18
17
7
J6
29
39
40
1
6
28
XU3
SKT
18
17
7
COMPONENTS ARE REMOVED FOR CLARITY
1
2
29
39
40
6
28
1
XU4
SKT
18
17
7
A1B1C1
P1
A32
B32
C32
ABORT
RESET
PRIMARY SIDE
S1 S2
60
59
J4
2
1
60
59
MEZZANINE BOARD
J5
2
1
J7 J8
C32
11
33
1380 9404
Figure 3-1. MVME187 Switches, Headers, Connectors, Fuses, and LEDs
F2
A1B1C1
P2
A32
B32
3-6
Page 59

Checking the 187Bug EPROMs
Be sure that the two factory installed 128K x 16 187Bug EPROMs are
in the proper sockets.
EPROM Location
❏ Odd-numbered label (such as B01): EPROM in socket XU1
(for Least Significant Half-Words)
❏ Even-numbered label (such as B02): EPROM in XU2 (for Most
Significant Half-Words)
EPROM Orientation
Be sure that physical chip orientation is correct:
❏ The flatted corner of each EPROM aligns with the
corresponding portion of the EPROM socket on the
MVME187.
Preparing the Hardware
3
User-programmed EPROMs
There are two spare EPROM sockets, XU3 and XU4, available to
carry user-programmed EPROMs.
Jumper Settings
The MVME187 has been factory tested and is shipped with the
factory jumper settings described on the following pages. The
MVME187 operates with its required and factory-installed Debug
Monitor, 187Bug, with these factory jumper settings.
3-7
Page 60

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Optional Jumper Settings
Most of the optional functions on your board can be changed
through software control or bit settings in control registers. If your
3
installation requires it, however, you may change jumper settings
on the following headers:
❏ Jumper pins 9 through 16 on header J1 are general purpose
software readable jumpers open to your application.
❏ Header J2 enables/disables the MVME187 as system
controller.
❏ Optional header J6 selects the SRAM backup power source
(this is only available as an optional factory build special
request).
❏ Headers J7 and J8 select serial port 4 to drive or receive
TRXC4 and RTXC4 clock signals.
General Purpose Software Readable Header J1
3-8
Each MVME187 may be configured with readable jumpers. They
can be read as a register (at $FFF40088) in the VMEchip2 LCSR. The
bit values are read as a one when the jumper is off, and as a zero
when the jumper is on
Reserved/DeÞned Bits
Jumpers on header J1 affect 187Bug operation as listed in Table 3-2.
The factory (default) configuration is with all eight jumpers
installed (see Table 3-3).
The MVME187BUG reserves/defines the four lower order bits
(GPI3 to GPI0). Table 3-2 describes the bits reserved/defined by the
debugger:
Page 61

Table 3-2. J1 Bit Descriptions
Bit J1 Pins Description
Preparing the Hardware
Bit #0 (GPI0) 1-2 When this bit is a one (high), it instructs the debugger to use
local Static RAM for its work page (i.e., variables, stack, vector
tables, etc.). This bit will be high when jumper is removed.
Bit #1 (GPI1) 3-4 When this bit is a one (high), it instructs the debugger to use
the default setup/operation parameters in ROM versus the
user setup/operation parameters in NVRAM. This is the same
as depressing the RESET and ABORT switches at the same
time. This feature can be used in the event the user setup is
corrupted or does not meet a sanity check. Refer to the ENV
command (Appendix A) for the ROM defaults. This bit will be
high when jumper is removed.
Bit #2 (GPI2) 5-6 Reserved for future use.
Bit #3 (GPI3) 7-8 Reserved for future use.
Bit #4 (GPI4) 9-10 Open to your application.
Bit #5 (GPI5) 11-12 Open to your application.
Bit #6 (GPI6) 13-14 Open to your application.
Bit #7 (GPI7) 15-16 Open to your application.
Table 3-3. Factory Settings for J1 General Purpose Readable Jumpers
3
Header
Number
J1
Header
Description
General
purpose
software
readable
jumpers
ConÞguration Jumpers
GPI0 - GPI3:
GPI7
GPI6
GPI5
GPI4
GPI3
Reserved
GPI4 - GPI7:
15
7
User-deÞnable
(Factory
16
8
conÞguration)
GPI2
GPI1
GPI0
1
2
3-9
Page 62

Hardware Preparation and Installation
J2
1 2
System Controller Header J2
The MVME187 can be VMEbus system controller. The system
controller function is enabled by installing a jumper on header J2
3
(see Table 3-4). When the MVME187 is system controller, the SCON
LED is turned on.
Table 3-4. Settings for J2 System Controller Header
Header
Number
J2
Header
Description
System
controller
header
ConÞguration Jumpers
System
controller
(Factory
conÞguration)
J2
Not system
controller
1
2
3-10
Page 63

Preparing the Hardware
Optional SRAM Backup Power Source Select Header J6
Header J6 is an optional header used to select the SRAM backup
power source on the MVME187, if the optional battery is present.
(The battery backup for SRAM is optionally available, but only as a
factory build and only by special request.)
If your system is equipped with the optional battery
!
Caution
Serial Port 4 Clock Configuration Select Headers J7 and J8
backup, do not remove the jumpers from J6. This will
disable the SRAM. If your board contains optional
header J6, but the optional battery is removed, jumpers
must be installed between pins 1 and 3 and pins 2 and 4
for the factory configuration as shown in Table 3-5.
Serial port 4 can be configured to use clock signals provided by the
TRXC4 and RTXC4 signal lines.
Headers J7 and J8 on the MVME187 configure serial port 4 to drive
or receive TRXC4 and RTXC4, respectively (see Table 3-6).
3
❏ Factory configuration sets port 4 to receive both signals.
❏ The alternative configuration sets port 4 to drive both signals
The remaining configuration of the clock lines is accomplished
using the Serial Port 4 Clock Configuration Select header on the
MVME712M transition module. Refer to the MVME712M
Transition Module and P2 Adapter Board User's Manual for
configuration of that header.
3-11
Page 64

Hardware Preparation and Installation
J6
2
6
4
1
5
3
J6
1
5
2
6
3
4
Table 3-5. Settings for Optional J6 SRAM Backup Power Source
Select Header
3
Header
Number
Header
Description
ConÞguration Jumpers
Primary source
VMEbus
+5V STBY
Secondary source
VMEbus +5V STBY
J6
1
3
5
2
4
6
(Factory
conÞguration)
J6
1
3
5
2
4
6
J6
Primary source
optional battery
Secondary source
optional battery
SRAM backup
power source
select header
Primary source
VMEbus +5V STBY
Secondary source
optional battery
Primary source
optional battery
Secondary source
VMEbus +5V STBY
3-12
Page 65

Preparing the Hardware
J7
J7
Table 3-6. Settings for J7 and J8 Serial Port 4 Clock Configuration
Select Headers
Header
Number
J7
J8
Header
Description
Serial Port 4
clock
conÞguration
select headers
ConÞguration Jumpers
Receive TRXC4
(Factory
conÞguration)
Drive TRXC4
Receive RTXC4
(Factory
conÞguration)
1
2
3
1
2
3
J8
1
2
3
J8
1
Drive RTXC4
2
3
3
3-13
Page 66

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Preparing the MVME187 for Installation
Refer to the setup procedures in the manuals for your particular
3
Step Action
1 Install/remove jumpers on headers according to the Jumper Settings in this
2 ConÞgure adapters and transition modules according to the MVME712X
chassis or system for additional details concerning the installation
of the MVME187 into a VME chassis.
Table 3-7. MVME187 Preparation Procedure
chapter and as required for your particular application.
❏ Jumpers on header J1 affect 187Bug operation as listed in Jumper
Settings. The default condition is with all eight jumpers installed
❏ A jumper installed/removed on header J2 enables/disables the
system controller function of the MVME187.
❏ Install jumpers on headers J7 and J8 to configure serial port 4 to
use clock signals provided by the TRXC4 and RTXC4 signal lines.
transition module
user's manuals.
3 Ensure that EPROM devices are properly installed in their sockets.
❏ Factory configuration is with two EPROMs installed for the
MVME187Bug debug monitor, in sockets XU1 and XU2.
3-14
Page 67

Preparing the System Chassis
Now that the MVME187 module is ready for installation, prepare
the system chassis and determine slot assignments (for peripherals,
transition modules, etc.) as follows:
Preparing the Hardware
3
Inserting or removing modules while power is applied
!
could result in damage to module components.
Caution
Dangerous voltages, capable of causing death, are
!
Warning
present in this equipment. Use extreme caution when
handling, testing, and adjusting.
Table 3-8. Chassis Preparation/Slot Selection Procedure
Step Action
1 Turn all power OFF to chassis and peripherals.
2 Disconnect AC power cable from source.
3 Remove chassis cover as shown in the user's manual for your
particular chassis or system.
4 Remove the Þller panel(s) from the appropriate card slot(s) at the front
and rear of the chassis (if the chassis has a rear card cage).
If the MVME187 is conÞgured as
system controller:
It must be installed in the
left-most card slot (slot 1) to
correctly initiate the bus-grant
daisy-chain and to have proper
operation of the IACK-daisy-chain
driver.
If it is not conÞgured as system
controller:
It may be installed in any doubleheight unused card slot.
3-15
Page 68

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Installing the Hardware
This section covers
3
Installing the MVME187 in the Chassis
Step Action
❏ Installation of the MVME187 into a VME chassis
❏ Overview and installation of transition modules and adapter
boards
❏ Connection of peripheral equipment such as console
terminals, optional SCSI drives, and serial or parallel printers
Note that if the MVME187 is to be used as system controller, it must
installed in the left-most card slot (slot 1), otherwise it may be installed in
any unused double-height card slot.
Table 3-9. MVME187 Installation Procedure
1 Remove IACK and BG jumpers from backplane for the card slot that the
MVME187 is to be installed in.
2 Carefully slide the MVME187 into the card slot in the front of the chassis.
❏ The MVME187 requires power from both P1 and P2. Be sure the
module is seated properly into the P1 and P2 connectors on the
backplane.
❏ Do not damage or bend connector pins.
❏ Fasten the MVME187 in the chassis with screws provided,
making good contact with the transverse mounting rails to
minimize RFI emissions.
3-16
Page 69

Installing the Hardware
Transition Modules and Adapter Boards Overview
The MVME187 supports the MVME712-12, MVME712-13,
MVME712M, MVME712A, MVME712AM, and MVME712B
transition modules (referred to in this manual as MVME712X,
unless separately specified).
Note Other modules in the system may have to be moved to
allow space for the MVME712M which has a doublewide front panel.
MVME712X transition modules provide configuration headers and
industry-standard connectors for internal and external I/O devices.
The I/O on the MVME187 is connected to the VMEbus P2
connector.
❏ The MVME712X transition module is connected to the
MVME187 through cables and a P2 adapter board as shown
in Figure 3-2 on page 3-18.
3
Note Some cable(s) are not provided with the MVME712X
module(s), and therefore must be made or provided by
the user. (Motorola recommends using shielded cables
for all connections to peripherals to minimize
radiation.)
3-17
Page 70

Hardware Preparation and Installation
MVME712X
TERMINATOR
MVME187
3
P1
LC P2
ADAPTER
J2
P2
P2
J3
J2, P2, OR J11
ENCLOSURE BOUNDARY
3-18
1859 9609
Figure 3-2. Typical Internal SCSI and Serial Port Connections
Page 71

Equipment Connections
Some connection diagrams are in the Single Board Computer
Programmer's Reference Guide.
The MVME712X transition modules and P2 adapter boards connect
peripheral equipment to the MVME187 as shown in Table 3-10.
Table 3-10. Peripheral Connections
Equipment Type Connect Through...
Installing the Hardware
3
Console terminals, host computer
systems, modems, or serial printers
Parallel printers Centronics printer port on the
Optional internal modems (see the
userÕs manual for your transition
module for details)
Internal SCSI drives Adapter board and transition module
External SCSI drives SCSI interface connector on the
Ethernet connections Ethernet port on the transition module
EIA-232-D serial ports on the
transition module
transition module
Optional modem port, replacing serial
port 2 on the transition module
transition module
3-19
Page 72

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Installing Transition Modules and Adapter Boards
Table 3-11. Transition Module and Adapter Board Installation Overview
3
Stage What you will need to do... Refer to...
1 Set jumpers on the transition
module(s) and install SCSI
terminators (if needed) on the P2
adapter board.
2 Connect and install the MVME712X
transition module in the front or the
rear of the chassis
3 Connect and install
❏ The P2 adapter board at the
.
P2 connector on the
backplane at the MVME187
slot.
❏ SCSI cable(s) from the P2
adapter board to the
MVME712X transition
module and internal SCSI
devices.
Connecting Peripherals
The MVME187 mates with (optional) terminals or other peripherals
at the EIA-232-D serial ports (marked SERIAL PORTS 1, 2, 3, and 4
on the MVME712X transition module), parallel port, SCSI ports,
and LAN Ethernet port, as shown in Figure 3-3 on page 3-22.
Module Preparation in the userÕs
manual for your transition module
and adapter board, and
SCSI Bus Termination on page 3-29
Installation Instructions in the userÕs
manual for your transition module
and adapter board
Installation Instructions in the userÕs
manual for your transition module
and adapter board
Module Preparation in the userÕs
manual for your transition module
and adapter board, and SCSI Bus
Termination on page 3-29
3-20
Note Some cable(s) are not provided with the MVME712X
module(s), and therefore are made or provided by the
user. (Motorola recommends using shielded cables for
all connections to peripherals to minimize radiation.)
Page 73

Installing the Hardware
Table 3-12. Peripheral Connection Procedures
Step Action... Refer to...
1 Connect and install any optional SCSI device
cables from J3 on the P2 Adapter to internal
devices and/or the MVME712B or MVME712M to
external SCSI devices (typical conÞgurations
shown in Figure 3-2 on page 3-18 and Figure 3-3 on
The Single Board
Computer Programmer's
Reference Guide for some
possible connection
diagrams
page 3-22).
2 Connect the terminal to be used as the 187Bug system console to the default
debug EIA-232-D port at serial port 1 on the MVME712X transition module.
3 Set up the terminal as follows:
❏ eight bits per character
❏ one stop bit per character
❏ parity disabled (no parity)
❏ baud rate 9600 baud (default baud rate of MVME187 ports at
powerup)
After power-up, the baud rate of the debug port can be reconÞgured by using
the Port Format (PF) command of the 187Bug debugger.
4 Connect devices such as a host computer system and/or a serial printer to the
other EIA-232-D port connectors with the appropriate cables and conÞguration.
After power-up, these ports can be reconÞgured by programming the
MVME187 CD2401 Serial Controller Chip (SCC), or by using the 187Bug PF
command.
3
Set up the device serial ports as described in Step
3.
After powerup, the baud rate of the port can be
reconÞgured by using the Port Format (PF)
command of the 187Bug debugger.
5 Connect a parallel device, such as a printer, to the
printer port on the MVME712X transition module.
(You may also use a module such as the MVME335
for a parallel port connection.)
ConÞguring a Port under
the PF (Port Format)
command in the
Debugging Package for
88K RISC CPUs UserÕs
Manual
The Single Board
Computer Programmer's
Reference Guide for some
possible connection
diagrams
3-21
Page 74

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Note In order for high-baud rate serial communication
between 187Bug and the terminal to work, the terminal
must do some form of handshaking. If the terminal
3
being used does not do hardware handshaking via the
CTS line, then it must do XON/XOFF handshaking. If
you get garbled messages and missing characters, you
should check the terminal to make sure XON/XOFF
handshaking is enabled. Refer to Configuring a Port
under the PF (Port Format) command in the Debugging
Package for 88K RISC CPUs UserÕs Manual.
MVME712B
MVME712X
J1
J3
J4
J5
J15
J12
J2
J7
J10
J11
P2 ADAPTER
J2
J3
MVME187
P1
3-22
P2
P2
ENCLOSURE BOUNDARY
Figure 3-3. Using MVME712A/AM and MVME712B
Page 75

MVME
712A/12/13
CONSOLE TTY01
Installing the Hardware
MVME
SERIAL PORT 1 SERIAL PORT 2 SERIAL PORT 3 SERIAL PORT 4
712B
3
MVME
712A
(MVME712M
similar)
Optional Modem
Port
PRINTER
To J10 on
Transition Module
To J2 on
Adapter Board
ETHERNET
MVME
712B
(if used)
SCSI INTERFACE
Figure 3-4. Typical Transition Module Peripheral Port Connectors
3-23
Page 76

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Completing the Installation
Table 3-13. Installation Completion Procedure
3
Step Action...
1 Reassemble the chassis.
2 Reconnect the AC power.
Starting the System
After completing the preparation and installation procedures, you
are ready to start up your system.
Table 3-14. System Startup Overview
Stage What you will need to do... Refer to...
1 Power up the system and note that the
debugger prompt appears.
2 Initialize the real-time clock. Page 3-25.
3 Examine and/or change
environmental parameters.
4 Program the PCCchip2 and
VMEchip2.
Page 3-25; Starting Up 187Bug on page
4-6; and the MVME187Bug Debugging
Package User's Manual.
Page 3-25 and ConÞgure and
Environment Commands on page A-1.
System Considerations on page 3-27,
Memory Maps
on page 2-8, and the Single Board
Computer Programmer's Reference
Guide.
on page 2-24, ASICs
3-24
Page 77

Installing the Hardware
Powering Up the System
The following table shows what takes place when you turn
equipment power ON (depending on whether 187Bug is in Board
Mode or in System Mode):
If 187Bug is in...
Board Mode 187Bug executes some self-checks and displays the debugger prompt
187-Bug>
3
System Mode The system performs a
selftest and tries to
autoboot.
If the conÞdence test fails, the test aborts
when the Þrst fault occurs. If possible, an
appropriate message is displayed, and
control then returns to the menu (refer to
Chapter 4, Debugger General
Information, and Chapter 5, Using the
187Bug Debugger for ENV and MENU
commands).
Initializing the Real-Time Clock
The onboard real-time clock (RTC) is backed up with a selfcontained battery. Before shipment of this board, the clock of the
RTC device was stopped to preserve battery life.
The boardÕs ÒSelftestsÓ (ST) and operating systems require the clock
of the RTC to be operating. Table 3-15 shows the steps required to
initialize the RTC, depending on the mode.
Examining and/or Changing Environmental Parameters
Use the 187BugÕs ENV command to verify the NVRAM (BBRAM)
parameters, and optionally use ENV to make changes to the
Environmental parameters. Refer to Appendix A for the
Environment parameters.
3-25
Page 78

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Table 3-15. RTC Initialization Procedure
Step Action
3
1 Allow 187Bug to boot up normally. Stop the auto-boot sequence by
2 At the 187-Bug> prompt, enter
TIME to display the current date and
time of day.
3 At the
set the time and date. Use the following command line structure:
SET [<MMddyyhhmm>]|[<+/-CAL>;C]
For example:
187-Bug>SET 0522961037 <Return>
WED May 22 10:37:00.00 1996
187-Bug>
Where the arguments are: MM=month, dd=day of the month, yy=year,
hh=hour in ÒmilitaryÓ (24 hour) time, and mm=minutes.
Board Mode System Mode
pressing the <BREAK> key. (If the
system has already started and failed
a conÞdence test in system mode, you
should be in the debugger menu).
Select (3) from the debugger menu to
get the debugger prompt.
187-Bug> prompt, use the SET command to initialize the RTC and to
Programming the PCCchip2 and VMEchip2
See System Considerations below, and refer to Memory Maps on
page 2-24, and the Single Board Computer Programmer's Reference
Guide for details of your particular system environment.
3-26
Page 79

System Considerations
Backplane Power Connections
The MVME187 needs to draw power from both P1 and P2 of the
VMEbus backplane. P2 is also used for the upper 16 bits of data for
32-bit transfers, and for the upper 8 address lines for extended
addressing mode. The MVME187 may not operate properly
without its main board connected to P1 and P2 of the VMEbus
backplane.
Memory Address Ranges
Whether the MVME187 operates as a VMEbus master or as a
VMEbus slave, it is configured for 32 bits of address and for 32 bits
of data (A32/D32). However, it handles A16 or A24 devices in
certain address ranges. D8 and/or D16 devices in the system must
be handled by the MC88100 software. Refer to the memory maps in
the Single Board Computer Programmer's Reference Guide as listed in
Related Documentation in Chapter 1.
System Considerations
3
DRAM Addressing
The MVME187 contains shared onboard DRAM whose base
address is software-selectable. Both the onboard processor and
offboard VMEbus devices see this local DRAM at base physical
address $00000000, as programmed by the MVME187Bug
firmware. This may be changed, by software, to any other base
address. Refer to the Single Board Computer Programmer's Reference
Guide for details.
Global Bus Timeout
If the MVME187 tries to access offboard resources in a non-existent
location, and is not system controller, and if the system does not
have a global bus timeout, the MVME187 waits forever for the
VMEbus cycle to complete. This would cause the system to hang
up.
3-27
Page 80

Hardware Preparation and Installation
Multiple Module Cage Configuration
Multiple MVME187s may be configured into a single VME card
cage. In general, hardware multiprocessor features are supported.
3
GCSR Location Monitor Register
Other MPUs on the VMEbus can interrupt, disable, communicate
with and determine the operational status of the RISC processor(s).
One register of the GCSR set includes four bits which function as
location monitors to allow one MVME187 processor to broadcast a
signal to other MVME187 processors, if any. All eight GCSR
registers are accessible from any local processor as well as from the
VMEbus.
Ethernet LAN (+12 Vdc) Fuse
The MVME187 provides +12 Vdc power to the Ethernet LAN
transceiver interface through a 1-amp fuse (F2) located on the
MVME187. The +12V LED lights when +12 Vdc is available. The
fuse is socketed and is located adjacent to diode CR1 near
connector P1. If the Ethernet transceiver fails to operate, check the
fuse. When using the MVME712M transition module, the yellow
LED (DS1) on the MVME712M front panel lights when LAN power
is available, indicating that the fuse is good.
3-28
Page 81

SCSI Bus Termination
❏ The MVME187 provides SCSI terminator power through a 1-
amp fuse (F1) located on the P2 adapter board. The fuse is
socketed. If the fuse is blown, the SCSI devices may not
operate or may function erratically.
❏ When the P2 adapter board is used with an MVME712M and
the SCSI bus is connected to the MVME712M, the green LED
(DS2) on the MVME712M front panel lights when there is
SCSI terminator power. If the LED flickers during SCSI bus
operation, the fuse should be checked.
❏ Because this board has no provision for SCSI termination,
you must ensure that the SCSI bus is terminated properly. If
you use a P2 Adapter, the adapter has sockets (R1, R2, R3) for
terminating the SCSI lines using three 8-pin SIP resistor
networks.
Storage and the Real-Time Clock
For storage of this product, be sure the RTC is put into the
power save mode. This will extend the life of the battery
contained in this part. To put the part into the power save
mode, use the PS command of the debugger. For example:
187-Bug>ps <Return>
(Clock is in Battery Save mode)
187-Bug>
System Considerations
3
3-29
Page 82

Hardware Preparation and Installation
3
3-30
Page 83

4Debugger General
Information
This Chapter Covers
❏ An introduction to the MVME187Bug firmware package
❏ Booting and restarting 187Bug
❏ Disk input/output support capabilities
❏ Network support capabilities
Introduction to MVME187Bug
This section covers:
❏ Overview of M88000 firmware
❏ Description of 187Bug
❏ Comparison with M68000-based firmware
4
❏ 187Bug implementation
❏ Memory requirements
Overview of M88000 Firmware
The firmware for the M88000-based (88K) series of board and
system level products has a common genealogy, deriving from the
BUG firmware currently used on all Motorola M68000-based CPU
modules. The M88000 firmware family provides a high degree of
functionality and user friendliness, and yet stresses portability and
ease of maintenance. This member of the M88000 firmware family
is implemented on the MVME187 RISC Single Board Computer,
and is known as the MVME187Bug, or just 187Bug.
4-1
Page 84

Debugger General Information
Description of 187Bug
The 187Bug package is a powerful evaluation and debugging tool
for systems built around the MVME187 RISC-based
microcomputers.
4
187Bug consists of three parts:
❏ The ÒdebuggerÓ or Ò187BugÒ; a command-driven user-
interactive software debugger, described in Chapter 5
❏ A command-driven diagnostic package for the MVME187
hardware
❏ A user interface which accepts commands from the system
console terminal
Command Facilities
Facilities are available for loading and executing user programs
under complete operator control for system evaluation.
187Bug includes commands for these tasks:
❏ Display and modification of memory
❏ Breakpoint and tracing capabilities
❏ A powerful assembler/disassembler useful for patching
programs
❏ A self-test at powerup feature which verifies the integrity of
the system
Trap #496 Routines
Various 187Bug routines that handle I/O, data conversion, and
string functions are available to user programs through the TRAP
#496 handler. The TRAP #496 handler is accessible through any of
the trap exception commands TB0, TB1, TBND, and TCND, with
trap vector #496.
4-2
Page 85

Debugger or Diagnostic Directories
When using 187Bug, you operate out of either the debugger
directory or the diagnostic directory.
Introduction to MVME187Bug
If you are in...
The debugger directory 187-Bug> All of the debugger
The diagnostic directory 187-Diag> All of the diagnostic
You may switch between directories by using the Switch
Directories (SD) command.
You may examine the commands in the current directory by using
the Help (HE) command.
Keyboard Control
Because 187Bug is command-driven, it performs its various
operations in response to user commands entered at the keyboard.
When you enter a command, 187Bug executes the command and
the prompt reappears. However, if you enter a command that
causes execution of user target code (e.g., "GO"), then control may
or may not return to 187Bug, depending on the outcome of the user
program.
With the
prompt...
You have available...
4
commands
commands as well as all
of the debugger
commands
4-3
Page 86

Debugger General Information
Comparison with M68000-Based Firmware
If you have used one or more of Motorola's other debugging
packages, you will find the RISC 187Bug very similar, after making
due allowances for the architectural differences between the
M68000 and M88000 CPU architectures. These differences are
4
primarily reflected as follows:
❏ Instruction mnemonics and addressing modes of the
assembler/disassembler differ somewhat in 187Bug.
❏ 187Bug uses registers instead of the stack for the passing of
arguments to or from the TRAP #496 handler.
❏ The interactive commands in 187Bug are more consistent. For
example, delimiters between commands and arguments may
now be commas or spaces interchangeably.
187Bug Implementation
MVME187Bug is written largely in the ÒCÓ programming
language, providing benefits of portability and maintainability.
Where necessary, assembler has been used in the form of separately
compiled modules containing only assembler code; no mixed
language modules are used.
4-4
Physically, 187Bug is contained in two of the four 44-pin
PLCC/CLCC EPROMs, providing 512KB (128K words) of storage.
Both EPROMs are necessary regardless of how much space is
actually occupied by the firmware, because of the 32-bit wordoriented M88000 memory bus architecture.
The executable code is checksummed at every power-on or reset
firmware entry, and the result (which includes a pre-calculated
checksum contained in the EPROMs), is tested for an expected zero.
Thus, users are cautioned against modification of the EPROMs
unless re-checksum precautions are taken.
Page 87

Memory Requirements
The program portion of 187Bug is approximately 512KB of code,
consisting of download, debugger, and diagnostic packages and
contained entirely in EPROM. The EPROM sockets on the
MVME187 are mapped starting at location $FF800000.
Booting and Restarting 187Bug
187Bug requires a minimum of 64KB of contiguous read/write
memory to operate.
The ENV command controls where this block of memory is located.
Regardless of where the onboard RAM is located, the first 64KB is
used for 187Bug stack and static variable space and the rest is
reserved as user space.
Whenever the MVME187 is reset, the target IP is initialized to the
address corresponding to the beginning of the user space, and the
target stack pointers are initialized to addresses within the user
space, with the target Pseudo Stack Pointer (R31) set to the top of
the user space.
At power up or reset, all 8KB of memory at addresses $FFE0C000
through $FFE0DFFF is completely changed by the 187Bug initial
stack.
Booting and Restarting 187Bug
This section covers the following tasks:
❏ Starting up 187Bug
4
❏ Autoboot
❏ ROMboot
❏ Network boot
❏ Restarting the system
4-5
Page 88

Debugger General Information
Starting Up 187Bug
1. Verify that the MVME187 is properly installed and operating
as described in Table 3-1 on page 3-2.
2. Power up the system. 187Bug executes some self-checks and
4
displays the debugger prompt
Board Mode). However, if the ENV command (Appendix A)
has put 187Bug in System Mode, the system performs a
selftest and tries to autoboot. Refer to the ENV and MENU
commands listed in Table 5-1.
If the confidence test fails, the test is aborted when the first
fault is encountered. If possible, an appropriate message is
displayed, and control then returns to the menu.
187-Bug> (if 187Bug is in
Autoboot
Autoboot is a software routine that is contained in the 187Bug
EPROMs to provide an independent mechanism for booting an
operating system.
Autoboot Sequence
1. The autoboot routine automatically scans for controllers and
2. If a valid bootable device is found, a boot from that device is
3. At powerup, Autoboot is enabled, and if the drive and
4-6
devices in a specified sequence until a valid bootable device
containing a boot media is found or the list is exhausted.
started.
The controller scanning sequence goes from the lowest
controller Logical Unit Number (LUN) detected to the
highest LUN detected. (Controllers, devices, and their LUNs
are listed in Appendix B).
controller numbers encountered are valid, the system console
displays the following message:
"Autoboot in progress... To abort hit <BREAK>"
Page 89

ROMboot
Booting and Restarting 187Bug
4. Following this message there is a delay to allow you an
opportunity to abort the Autoboot process if you wish. To
gain control without Autoboot, you can press the
or the software
5. Then the actual I/O begins: the program pointed to within
the volume ID of the media specified is loaded into RAM and
control passed to it.
Autoboot is controlled by parameters contained in the ENV
command. These parameters allow the selection of specific boot
devices and files, and allow programming of the Boot delay. Refer
to the ENV command in Appendix A for more details.
There are two spare EPROM sockets, XU3 and XU4, available to
carry user-programmed EPROMs. Therefore, you do not have to
reprogram the 187Bug EPROMs in order to implement the
ROMboot feature.
ABORT or RESET switches.
BREAK key
4
One use of ROMboot might be resetting SYSFAIL* on an
unintelligent controller module. The NORB command disables the
function.
ROMboot Sequence
1. ROMboot is configured/enabled and executed at powerup
2. If ROMboot code is installed, a user-written routine is given
(optionally also at reset) in one of two ways:
a. By the Environment (ENV) command (refer to
Appendix A)
b. By the RB command assuming there is valid code in the
EPROMs (or optionally elsewhere on the module or
VMEbus) to support it.
control (if the routine meets the format requirements).
4-7
Page 90

Debugger General Information
For a user's ROMboot module to gain control through the
ROMboot linkage, four requirements must be met:
Requirement... Optionally, with the ENV command...
Power must have just been
4
applied.
Your routine must be located
within the MVME187 ROM
memory map.
The ASCII string ÒBOOTÓ must be located within the speciÞed memory range.
Your routine must pass a checksum test, which ensures that this routine was really
intended to receive control at powerup.
Change this to respond to any reset.
Change this to any other portion of the onboard
memory, or even offboard VMEbus memory.
For complete details on how to use ROMboot, refer to the
Debugging Package for Motorola 88K RISC CPUs User's Manual.
Network Boot
Network Auto Boot is a software routine contained in the 187Bug
EPROMs that provides a mechanism for booting an operating
system using a network (local Ethernet interface) as the boot device.
Network Boot Sequence
1. The Network Auto Boot routine automatically scans for
controllers and devices in a specified sequence until a valid
bootable device containing a boot media is found or the list is
exhausted.
4-8
2. If a valid bootable device is found, a boot from that device is
started.
The controller scanning sequence goes from the lowest
controller Logical Unit Number (LUN) detected to the
highest LUN detected. (Refer to Appendix C for default
LUNs.)
Page 91

3. At powerup, Network Boot is enabled, and providing the
drive and controller numbers encountered are valid, the
following message is displayed on the system console:
"Network Boot in progress... To abort hit <BREAK>"
Following this message there is a delay to allow you to abort
the Network Boot process if you wish. To gain control
without Network Boot, you can press the
software
4. Then the actual I/O begins: the program pointed to within
the volume ID of the media specified is loaded into RAM and
control passed to it.
Network Auto Boot is controlled by parameters contained in the
NIOT and ENV commands. These parameters allow the selection
of specific boot devices, systems, and files, and allow programming
of the Boot delay. Refer to the ENV command in Appendix A.
Restarting the System
Booting and Restarting 187Bug
ABORT or RESET switches.
BREAK key or the
4
You can initialize the system to a known state in three different
ways: reset, abort, and break. Each has characteristics which make
it more appropriate than the others in certain situations.
The debugger has a special feature which can be used in the event
your setup/operation parameters are corrupted or do not meet a
sanity check. This feature:
❏ Is activated by pressing the RESET and ABORT switches at the
same time, and releasing the
RESET switch before the ABORT
switch.
❏ Instructs 187Bug to use the default setup/operation
parameters in ROM instead of your setup/operation
parameters in NVRAM.
Refer to the ENV command (Appendix A) for the ROM defaults.
4-9
Page 92

Debugger General Information
Reset
Pressing and releasing the MVME187 front panel
RESET switch
initiates a system reset.
Reset must be used if the processor ever halts, or if the 187Bug
environment is ever lost (vector table is destroyed, stack corrupted,
4
etc.).
❏ COLD and WARM reset modes are available.
❏ By default, 187Bug is in COLD mode.
During COLD reset:
1. A total system initialization takes place, as if the MVME187
had just been powered up.
2. All static variables (including disk device and controller
parameters) are restored to their default states.
3. The breakpoint table and offset registers are cleared.
4. The target registers are invalidated.
5. Input and output character queues are cleared.
6. Onboard devices (timer, serial ports, etc.) are reset, and
Abort
4-10
7. The first two serial ports are reconfigured to their default
state.
During WARM reset:
1. The 187Bug variables and tables are preserved, as well as the
target state registers and breakpoints.
Abort is invoked by pressing and releasing the
ABORT switch on the
MVME187 front panel.
Abort should be used to regain control if the program gets caught
in a loop, etc.
Page 93

Booting and Restarting 187Bug
Whenever abort is invoked while running target code (a user
program), a ÒsnapshotÓ of the processor state is captured and
stored in the target registers. For this reason, abort is most
appropriate when terminating a user program that is being
debugged. The target IP, register contents, etc., help to pinpoint the
malfunction.
Abort Sequence
4
Break
Pressing and releasing the
ABORT switch does the following:
1. Generates a local board condition which may interrupt the
processor if enabled.
2. Displays the target registers on the screen, reflecting the
machine state at the time the
ABORT switch was pressed.
3. Removes any breakpoints installed in the user code and
keeps the breakpoint table intact.
4. Returns control to the debugger.
A ÒBreakÓ is generated by pressing and releasing the
BREAK key on
the console terminal keyboard.
❏ Break does not generate an interrupt.
❏ The only time break is recognized is when characters are sent
or received by the console port.
Many times it may be desirable to terminate a debugger command
prior to its completion; for example, during the display of a large
block of memory. Break allows you to terminate the command.
4-11
Page 94

Debugger General Information
Break Sequence
1. Removes any breakpoints in your code and keeps the
breakpoint table intact.
2. Takes a snapshot of the machine state if the function was
entered using SYSCALL. This machine state is then accessible
4
to you for diagnostic purposes.
SYSFAIL* Assertion/Negation
Upon a reset/powerup condition the debugger asserts the VMEbus
SYSFAIL* line (refer to the VMEbus specification). SYSFAIL* stays
asserted if any of the following has occurred:
❏ Confidence test failure
❏ NVRAM checksum error
❏ NVRAM low battery condition
❏ Local memory configuration status
❏ Self test (if System Mode) has completed with error
❏ MPU clock speed calculation failure
After debugger initialization is done and none of the above
situations have occurred, the SYSFAIL* line is negated. This
indicates to the user or VMEbus masters the state of the debugger.
In a multi-computer configuration, other VMEbus masters could
view the pertinent control and status registers to determine which
CPU is asserting SYSFAIL*. SYSFAIL* assertion/negation is also
affected by the ENV command. Refer to Appendix A.
MPU Clock Speed Calculation
The clock speed of the microprocessor is calculated and checked
against a user definable parameter contained in NVRAM (refer to
the CNFG command in Appendix A). If the check fails, a warning
message is displayed.
4-12
Page 95

Disk I/O Support
187Bug can initiate disk input/output by communicating with
intelligent disk controller modules over the VMEbus.
This section covers:
Disk I/O Support
❏ Blocks Versus Sectors
❏ Device Probe Function
❏ Disk I/O via 187Bug Commands
❏ Disk I/O via 187Bug System Calls
❏ Default 187Bug Controller and Device Parameters
❏ Disk I/O Error Codes
Disk Support Facilities
Disk support facilities built into 187Bug consist of the following:
❏ Command-level disk operations
❏ Disk I/O system calls (only via one of the TRAP #496
instructions) for use by user programs
❏ Defined data structures for disk parameters
Parameter T ables
Parameters such as the address where the module is mapped and
the type and number of devices attached to the controller module
are kept in tables by 187Bug. Default values for these parameters
are assigned at powerup and cold-start reset, but may be altered as
described in the section on default parameters, later in this chapter.
4
Supported Controllers
Appendix B contains a list of the controllers presently supported, as
well as a list of the default configurations for each controller.
4-13
Page 96

Debugger General Information
Blocks V ersus Sectors
The logical block defines the unit of information for disk devices. A
disk is viewed by 187Bug as a storage area divided into logical
blocks. By default, the logical block size is set to 256 bytes for every
block device in the system. The block size can be changed on a per
4
device basis with the IOT command.
The sector defines the unit of information for the media itself, as
viewed by the controller. The sector size varies for different
controllers, and the value for a specific device can be displayed and
changed with the IOT command.
When a disk transfer is requested, the start and size of the transfer
is specified in blocks. 187Bug translates this into an equivalent
sector specification, which is then passed on to the controller to
initiate the transfer. If the conversion from blocks to sectors yields
a fractional sector count, an error is returned and no data is
transferred.
Device Probe Function
A device probe with entry into the device descriptor table is done
whenever a specified device is accessed; i.e., when system calls
.DSKRD, .DSKWR, .DSKCFIG, .DSKFMT, and .DSKCTRL, and
debugger commands BH, BO, IOC, IOP, IOT, MAR, and MAW
are used.
The device probe mechanism utilizes the SCSI commands "Inquiry"
and "Mode Sense". If the specified controller is non-SCSI, the probe
simply returns a status of "device present and unknown". The
device probe makes an entry into the device descriptor table with
the pertinent data. After an entry has been made, the next time a
probe is done it simply returns with "device present" status (pointer
to the device descriptor).
4-14
Page 97

Disk I/O via 187Bug Commands
These following 187Bug commands are provided for disk I/O.
Detailed instructions for their use are found in the Debugging
Package for Motorola 88K RISC CPUs User's Manual. When a
command is issued to a particular controller LUN and device LUN,
these LUNs are remembered by 187Bug so that the next disk
command defaults to use the same controller and device.
IOI (Input/Output Inquiry)
This command is used to probe the system for all possible
CLUN/DLUN combinations and display inquiry data for devices
which support it. The device descriptor table only has space for 16
device descriptors; with the IOI command, you can view the table
and clear it if necessary.
IOP (Physical I/O to Disk)
IOP allows you to read or write blocks of data, or to format the
specified device in a certain way. IOP creates a command packet
from the arguments you have specified, and then invokes the
proper system call function to carry out the operation.
Disk I/O Support
4
IOT (I/O Teach)
IOT allows you to change any configurable parameters and
attributes of the device. In addition, it allows you to see the
controllers available in the system.
IOC (I/O Control)
IOC allows you to send command packets as defined by the
particular controller directly. IOC can also be used to look at the
resultant device packet after using the IOP command.
BO (Bootstrap Operating System)
BO reads an operating system or control program from the
specified device into memory, and then transfers control to it.
4-15
Page 98

Debugger General Information
BH (Bootstrap and Halt)
BH reads an operating system or control program from a specified
device into memory, and then returns control to 187Bug. It is used
as a debugging tool.
4
Disk I/O via 187Bug System Calls
All operations that actually access the disk are done directly or
indirectly by 187Bug TRAP #496 system calls. (The command-level
disk operations provide a convenient way of using these system
calls without writing and executing a program.)
The following system calls are provided to allow user programs to
do disk I/O:
.DSKRD Disk read. System call to read blocks from a disk into
memory.
.DSKWR Disk write. System call to write blocks from memory onto a
disk.
.DSKCFIG Disk conÞgure. This function allows you to change the
conÞguration of the speciÞed device.
.DSKFMT Disk format. This function allows you to send a format
command to the speciÞed device.
.DSKCTRL Disk control. This function is used to implement any
special device control functions that cannot be
accommodated easily with any of the other disk functions.
Refer to the Debugging Package for Motorola 88K RISC CPUs User's
Manual for information on using these and other system calls.
Controller Command Packets
To perform a disk operation, 187Bug must eventually present a
particular disk controller module with a controller command
packet which has been especially prepared for that type of
controller module. (This is accomplished in the respective
controller driver module.)
4-16
Page 99

Disk I/O Support
A command packet for one type of controller module usually does
not have the same format as a command packet for a different type
of module. The system call facilities which do disk I/O accept a
generalized (controller-independent) packet format as an
argument, and translate it into a controller-specific packet, which is
then sent to the specified device.
Refer to the system call descriptions in the Debugging Package for
Motorola 88K RISC CPUs User's Manual for details on the format and
construction of these standardized "user" packets.
The packets which a controller module expects to be given vary
from controller to controller. The disk driver module for the
particular hardware module (board) must take the standardized
packet given to a trap function and create a new packet which is
specifically tailored for the disk drive controller it is sent to. Refer
to documentation on the particular controller module for the
format of its packets, and for using the IOC command.
Default 187Bug Controller and Device Parameters
4
187Bug initializes the parameter tables for a default configuration
of controllers and devices (refer to Appendix B). If the system needs
to be configured differently than this default configuration (for
example, to use a 70MB Winchester drive where the default is a
40MB Winchester drive), then these tables must be changed.
4-17
Page 100

Debugger General Information
There are three ways to change the parameter tables:
Using...
Command
BO or BH
4
Command
IOT
The
source
code
When you invoke one of
these commands...
The conÞguration area of
the disk is read and the
parameters
corresponding to that
device are rewritten
according to the
parameter information
contained in the
conÞguration area.
You can use this
command to reconÞgure
the parameter table
manually for any
controller and/or device
that is different from the
default.
In the source code, you
may change the
permanent conÞguration
Þles and rebuild 187Bug
so that it has different
defaults.
Change
status is...
Temporary The default parameter
Temporary The default parameter
Permanent until changed again.
If a cold-start reset occurs...
information is written back
into the tables.
information is written back
into the tables.
Disk I/O Error Codes
187Bug returns an error code if an attempted disk operation is
unsuccessful.
4-18
 Loading...
Loading...