
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
1
REV 4
Motorola, Inc. 1997
2/97
The MPC950/951 are 3.3V compatible, PLL based clock driver
devices targeted for high performance clock tree designs. With output
frequencies of up to 180MHz and output skews of 375ps the MPC950 is
ideal for the most demanding clock tree designs. The devices employ a
fully differential PLL design to minimize cycle–to–cycle and long term
jitter. This parameter is of significant importance when the clock driver is
providing the reference clock for PLL’ s on board today’s microprocessors
and ASiC’s. The devices offer 9 low skew outputs, the outputs are
configurable to support the clocking needs of the various high
performance microprocessors.
• Fully Integrated PLL
• Oscillator or Crystal Reference Input
• Output Frequency up to 180MHz
• Outputs Disable in High Impedance
• Compatible with PowerPC, Intel and High Performance RISC
Microprocessors
• TQFP Packaging
• Output Frequency Configurable
• ±100ps Typical Cycle–to–Cycle Jitter
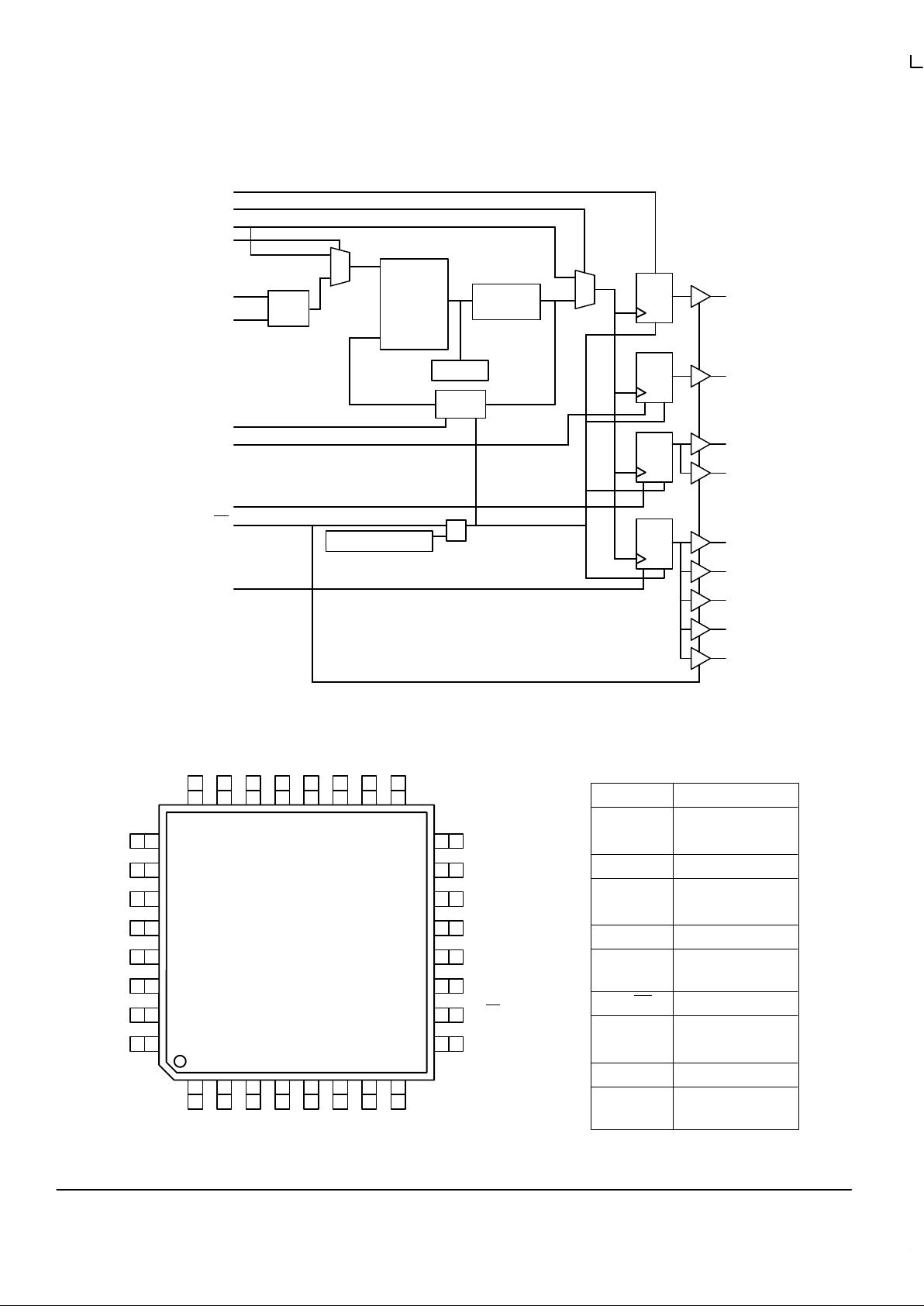
Two selectable feedback division ratios are available on the MPC950
to provide input reference clock flexibility. The FBSEL pin will choose
between a divide by 8 or a divide by 16 of the VCO frequency to be
compared with the input reference to the MPC950. The internal VCO is
running at either 2x or 4x the high speed output, depending on
configuration, so that the input reference will be either one half, one fourth
or one eighth the high speed output.
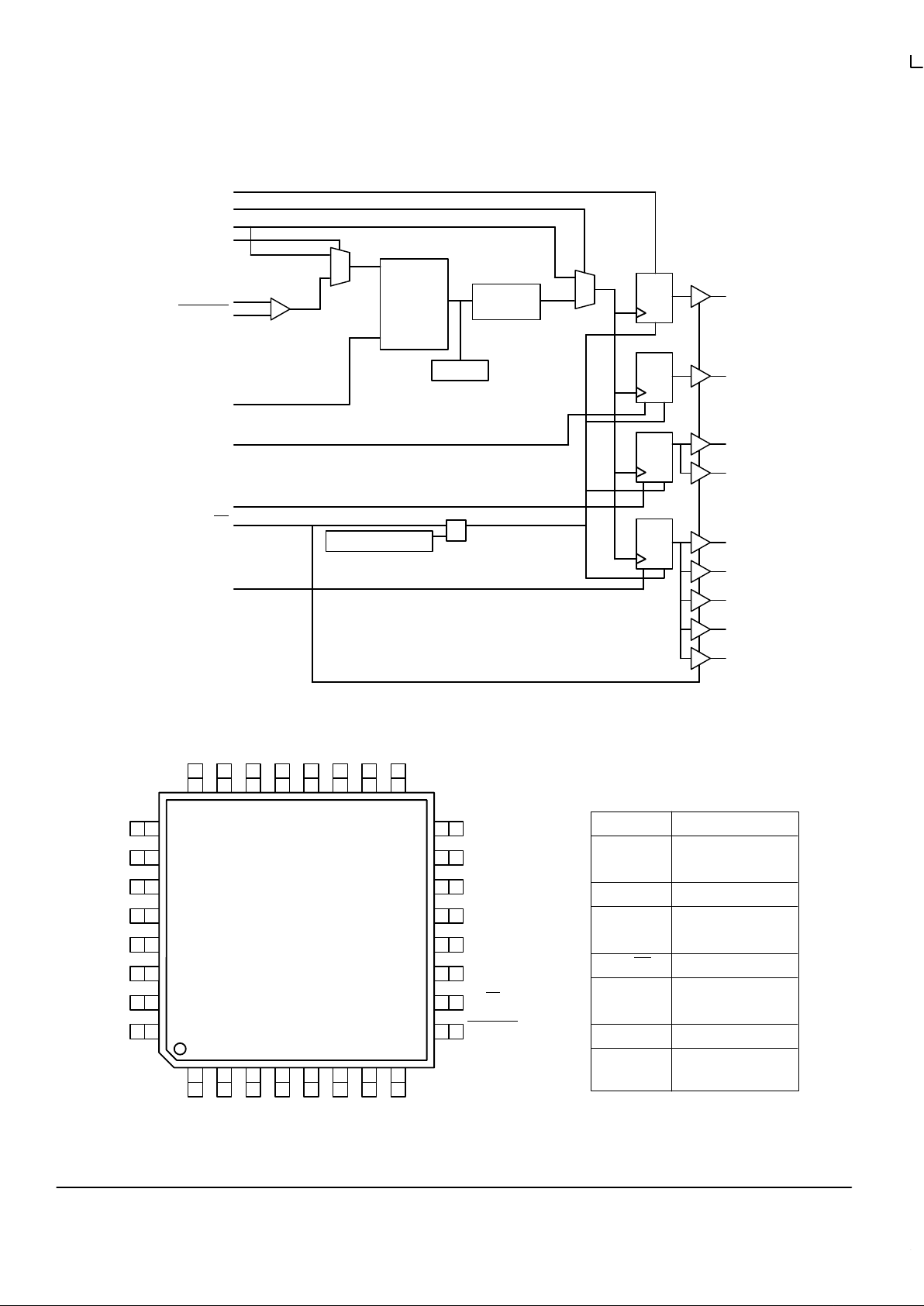
The MPC951 replaces the crystal oscillator and internal feedback of the MPC950 with a differential PECL reference input and
an external feedback input. These features allow for the MPC951 to be used as a zero delay, low skew fanout buf fer. In addition,
the external feedback allows for a wider variety of input–to–output frequency relationships. The MPC951 REF_SEL pin allows for
the selection of an alternate LVCMOS input clock to be used as a test clock or to provide the reference for the PLL from an
LVCMOS source.
The MPC950 provides an external test clock input for scan clock distribution or system diagnostics. In addition the REF_SEL
pin allows the user to select between a crystal input to an on–board oscillator for the reference or to chose a TTL level oscillator
input directly. The on–board crystal oscillator requires no external components beyond a series resonant crystal.
Both the MPC950 and MPC951 are fully 3.3V compatible and require no external loop filter components. All inputs accept
LVCMOS or LVTTL compatible levels while the outputs provide LVCMOS levels with the capability to drive terminated 50Ω
transmission lines. Select inputs do not have internal pull–up/pull–down resistors and thus must be set externally. If the
PECL_CLK inputs are not used, they can be left open. For series terminated 50Ω lines, each of the MPC950/951 outputs can
drive two traces giving the device an effective fanout of 1:18. The device is packaged in a 7x7mm 32–lead TQFP package to
provide the optimum combination of board density and performance.
PowerPC is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation. Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
LOW VOLTAGE
PLL CLOCK DRIVER
FA SUFFIX
32–LEAD TQFP PACKAGE
CASE 873A–02
MPC950 MPC951
MOTOROLA TIMING SOLUTIONS
BR1333 — Rev 6
2
MPC950 LOGIC DIAGRAM
÷2/÷
4
Qa
VCO
200–480MHz
PHASE
DETECTOR
LPF
÷8/÷
16
MR/OE
xtal
OSC
fselc
fselb
FBsel
xtal2
xtal1
Tclk
÷4/÷
8
Qb
÷4/÷
8
Qc0
÷4/÷
8
Qd0
Qc1
Qd1
Qd2
Qd3
Qd4
fseld
Ref_Sel
PLL_En
fsela
POWER–ON RESET
(Pull Down)
MR/OE
GNDO
Qb
VCCO
Qa
GNDO
TCLK
PLL_En
Ref_Sel
Qd2
VCCO
Qd3
GNDO
Qd4
VCCO
xtal2
Qc0
VCCO
Qc1
GNDO
Qd0
VCCO
Qd1
GNDO
VCCA
FBsel
fsela
fselb
fselc
fseld
GNDI
xtal1
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
12345678
24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
16
MPC950
FUNCTION TABLES
Ref_Sel Function
1
0
TCLK
XTAL_OSC
PLL_En Function
1
0
PLL Enabled
PLL Bypass
FBsel Function
1
0
÷8
÷16
MR/OE Function
1
0
Outputs Disabled
Outputs Enabled
fseln Function
1
0
Qa = ÷4; Qb:d = ÷8
Qa = ÷2; Qb:d = ÷4
MPC950 MPC951
TIMING SOLUTIONS
BR1333 — Rev 6
3 MOTOROLA
MPC951 LOGIC DIAGRAM
÷2/÷
4
Qa
VCO
200–550MHz
PHASE
DETECTOR
LPF
MR/OE
fselc
fselb
PECL_CLK
PECL_CLK
Tclk
÷4/÷
8
Qb
÷4/÷
8
Qc0
÷4/÷
8
Qd0
Qc1
Qd1
Qd2
Qd3
Qd4
fseld
Ref_Sel
PLL_En
fsela
POWER–ON RESET
Ext_FB
(Pull Up)
(Pull Down)
MR/OE
PECL_CLK
GNDO
Qb
VCCO
Qa
GNDO
TCLK
PLL_En
Ref_Sel
Qd2
VCCO
Qd3
GNDO
Qd4
VCCO
Qc0
VCCO
Qc1
GNDO
Qd0
VCCO
Qd1
GNDO
VCCA
Ext_FB
fsela
fselb
fselc
fseld
GNDI
PECL_CLK
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
12345678
24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
16
MPC951
FUNCTION TABLES
Ref_Sel Function
1
0
TCLK
PECL_CLK
PLL_En Function
1
0
PLL Enabled
PLL Bypass
MR/OE Function
1
0
Outputs Disabled
Outputs Enabled
fseln Function
1
0
Qa = ÷4; Qb:d = ÷8
Qa = ÷2; Qb:d = ÷4
MPC950 MPC951
MOTOROLA TIMING SOLUTIONS
BR1333 — Rev 6
4
FUNCTION TABLE – MPC950/951
INPUTS OUTPUTS TOTALS
fsela fselb fselc fseld Qa(1) Qb(1) Qc(2) Qd(5) Total 2x Total x T otal x/2
0 0 0 0 2x x x x 1 8 0
0 0 0 1 2x x x x/2 1 3 5
0 0 1 0 2x x x/2 x 1 6 2
0 0 1 1 2x x x/2 x/2 1 1 7
0 1 0 0 2x x/2 x x 1 7 1
0 1 0 1 2x x/2 x x/2 1 2 6
0 1 1 0 2x x/2 x/2 x 1 3 5
0 1 1 1 2x x/2 x/2 x/2 1 0 8
1 0 0 0 x x x x 0 9 0
1 0 0 1 x x x x/2 0 4 5
1 0 1 0 x x x/2 x 0 7 2
1 0 1 1 x x x/2 x/2 0 2 7
1 1 0 0 x x/2 x x 0 8 1
1 1 0 1 x x/2 x x/2 0 3 6
1 1 1 0 x x/2 x/2 x 0 6 3
1 1 1 1 x x/2 x/2 x/2 0 1 8
NOTE: x = f
VCO
/4; 200MHz < f
VCO
< 480MHz.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
V
CC
Supply Voltage –0.3 4.6 V
V
I
Input Voltage –0.3 VDD + 0.3 V
I
IN
Input Current ±20 mA
T
Stor
Storage Temperature Range –40 125 °C
* Absolute maximum continuous ratings are those values beyond which damage to the device may occur. Exposure to these conditions or
conditions beyond those indicated may adversely affect device reliability. Functional operation under absolute–maximum–rated conditions is
not implied.
DC CHARACTERISTICS (TA = 0° to 70°C, VCC = 3.3V ±5%)
Symbol Characteristic Min Typ Max Unit Condition
V
IH
Input HIGH Voltage LVCMOS Inputs 2.0 3.6 V
V
IL
Input LOW Voltage LVCMOS Inputs 0.8 V
V
PP
Peak–to–Peak Input Voltage PECL_CLK 300 1000 mV
V
CMR
Common Mode Range PECL_CLK VCC–2.0 VCC–0.6 mV Note 1.
V
OH
Output HIGH Voltage 2.4 V IOH = –40mA, Note 2.
V
OL
Output LOW Voltage 0.5 V IOL = 40mA, Note 2.
I
IN
Input Current ±120 µA
C
IN
Input Capacitance 4 pF
C
pd
Power Dissipation Capacitance 25 pF Per Output
I
CC
Maximum Quiescent Supply Current 90 115 mA All VCC Pins
I
CCPLL
Maximum PLL Supply Current 15 20 mA VCCA Pin Only
1. V
CMR
is the difference from the most positive side of the differential input signal. Normal operation is obtained when the “HIGH” input is within
the V
CMR
range and the input swing lies within the VPP specification.
2. The MPC950/951 outputs can drive series or parallel terminated 50Ω (or 50Ω to VCC/2) transmission lines on the incident edge (see Applications
Info section).
 Loading...
Loading...