MOTOROLA MC74LCX652DTR2, MC74LCX652DWR2 Datasheet

SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
1
REV 1
Motorola, Inc. 1997
3/97
&-&$*! *$
(%) #, ( !#)* (
(%) #, ( #*" +$ %$
#*" &$ (%* %'+*) % +*'+*)
** &%%, (*#%!
The MC74LCX652 is a high performance, non–inverting octal
transceiver/registered transceiver operating from a 2.7 to 3.6V supply.
High impedance TTL compatible inputs significantly reduce current
loading to input drivers while TTL compatible outputs offer improved
switching noise performance. A VI specification of 5.5V allows
MC74LCX652 inputs to be safely driven from 5V devices. The
MC74LCX652 is suitable for memory address driving and all TTL level
bus oriented transceiver applications.
Data on the A or B bus will be clocked into the registers as the
appropriate clock pin goes from a LOW–to–HIGH logic level. Two Output
Enable pins (OEBA
, OEAB) are provided to control the transceiver
outputs. In the transceiver mode, data present at the high impedance port
may be stored in either the A or the B register or in both. The select
controls (SBA, SAB) can multiplex stored and real–time (transparent
mode) data. In the isolation mode (both outputs disabled), A data may be
stored in the B register or B data may be stored in the A register. When in
the real–time mode, it is possible to store data without using the internal
registers by simultaneously enabling OEAB and OEBA
. In this
configuration, each output reinforces its input (data retention is not
guaranteed in this mode).
• Designed for 2.7 to 3.6V V
CC
Operation
• 5V T olerant — Interface Capability With 5V TTL Logic
• Supports Live Insertion and Withdrawal
• I
OFF
Specification Guarantees High Impedance When VCC = 0V
• LVTTL Compatible
• LVCMOS Compatible
• 24mA Balanced Output Sink and Source Capability
• Near Zero Static Supply Current in All Three Logic States (10µA)
Substantially Reduces System Power Requirements
• Latchup Performance Exceeds 500mA
• ESD Performance: Human Body Model >2000V; Machine Model >200V
Figure 1. 24–Lead Pinout (Top View)
2324 22 21 20 19 18
21 34567
V
CC
17
8
16
9
15
10
CBA SBA OEBA B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5
CAB SAB OEAB A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6
14
11
13
12
B6 B7
A7 GND
LOW–VOLTAGE CMOS
OCTAL TRANSCEIVER/
REGISTERED TRANSCEIVER
WITH DUAL ENABLE
PIN NAMES
Function
Side A Inputs/Outputs
Side B Inputs/Outputs
Clock Pulse Inputs
Select Control Inputs
Output Enable Inputs
Pins
A0–A7
B0–B7
CAB, CBA
SAB, SBA
OEBA
, OEAB
DW SUFFIX
24–LEAD PLASTIC SOIC PACKAGE
CASE 751E–04
DT SUFFIX
24–LEAD PLASTIC TSSOP PACKAGE
CASE 948H–01
SD SUFFIX
24–LEAD PLASTIC SSOP PACKAGE
CASE 940D–03
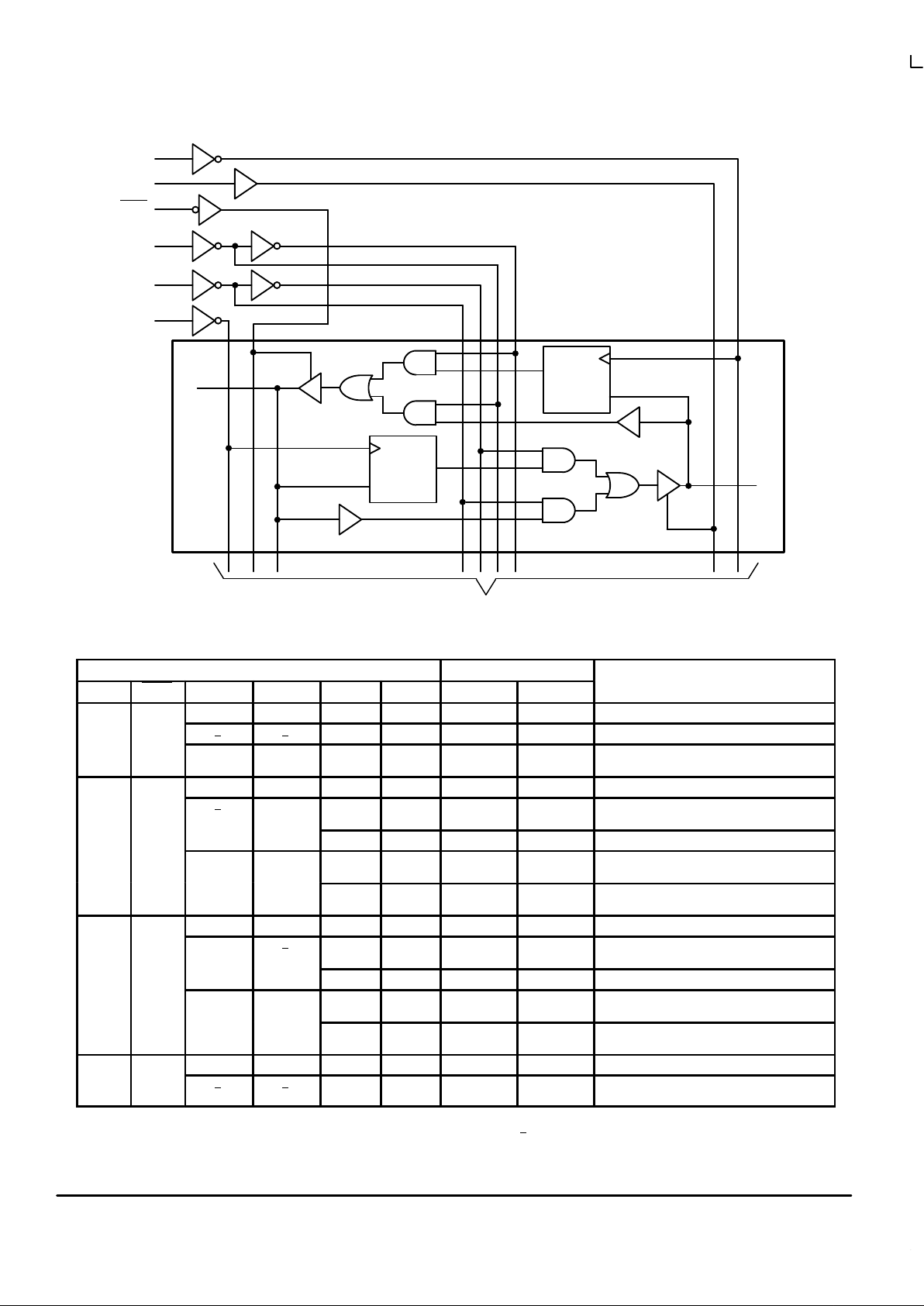
Figure 2. Logic Diagram
C
D
Q
OEBA
OEAB
CBA
SBA
SAB
CAB
C
D
Q
A0
B0
1 of 8 Channels
To 7 Other Channels
1
3
21
22
2
23
MC74LCX652
MOTOROLA LCX DATA
BR1339 — REV 3
2
FUNCTION TABLE
Inputs
Data Ports
OEAB OEBA CAB CBA SAB SBA An Bn
O
perating Mode
L H Input Input
↑ ↑ X X X X Isolation, Hold Storage
↑ ↑ X X l
h
l
h
Store A and/or B Data
H H Input Output
↑ X* L X L
H
L
H
Real Time A Data to B Bus
H X X QA Stored A Data to B Bus
↑ X* L X l
h
L
H
Real Time A Data to B Bus; Store A Data
H X L
H
QA
QA
Clock A Data to B Bus; Store A Data
L L Output Input
X* ↑ X L L
H
L
H
Real Time B Data to A Bus
X H QB X Stored B Data to A Bus
X* ↑ X L L
H
l
h
Real Time B Data to A Bus; Store B Data
X H QB
QB
L
H
Clock B Data to A Bus; Store B Data
H L Output Output
↑ ↑ H H QB QA Stored A Data to B Bus,
Stored B Data to A Bus
H = High Voltage Level; h = High Voltage Level One Setup Time Prior to the Low–to–High Clock Transition; L = Low Voltage Level; l = Low Voltage Level One Setup
Time Prior to the Low–to–High Clock T ransition; X = Don’t Care; ↑ = Low–to–High Clock Transition; ↑
= NOT Low–to–High Clock Transition; QA = A input storage register;
QB = B input storage register; * = The clocks are not internally gated with either the Output Enables or the Source Inputs. Therefore, data at the A or B ports may be
clocked into the storage registers, at any time. For ICC reasons, Do Not Float Inputs.
MC74LCX652
LCX DATA
BR1339 — REV 3
3 MOTOROLA
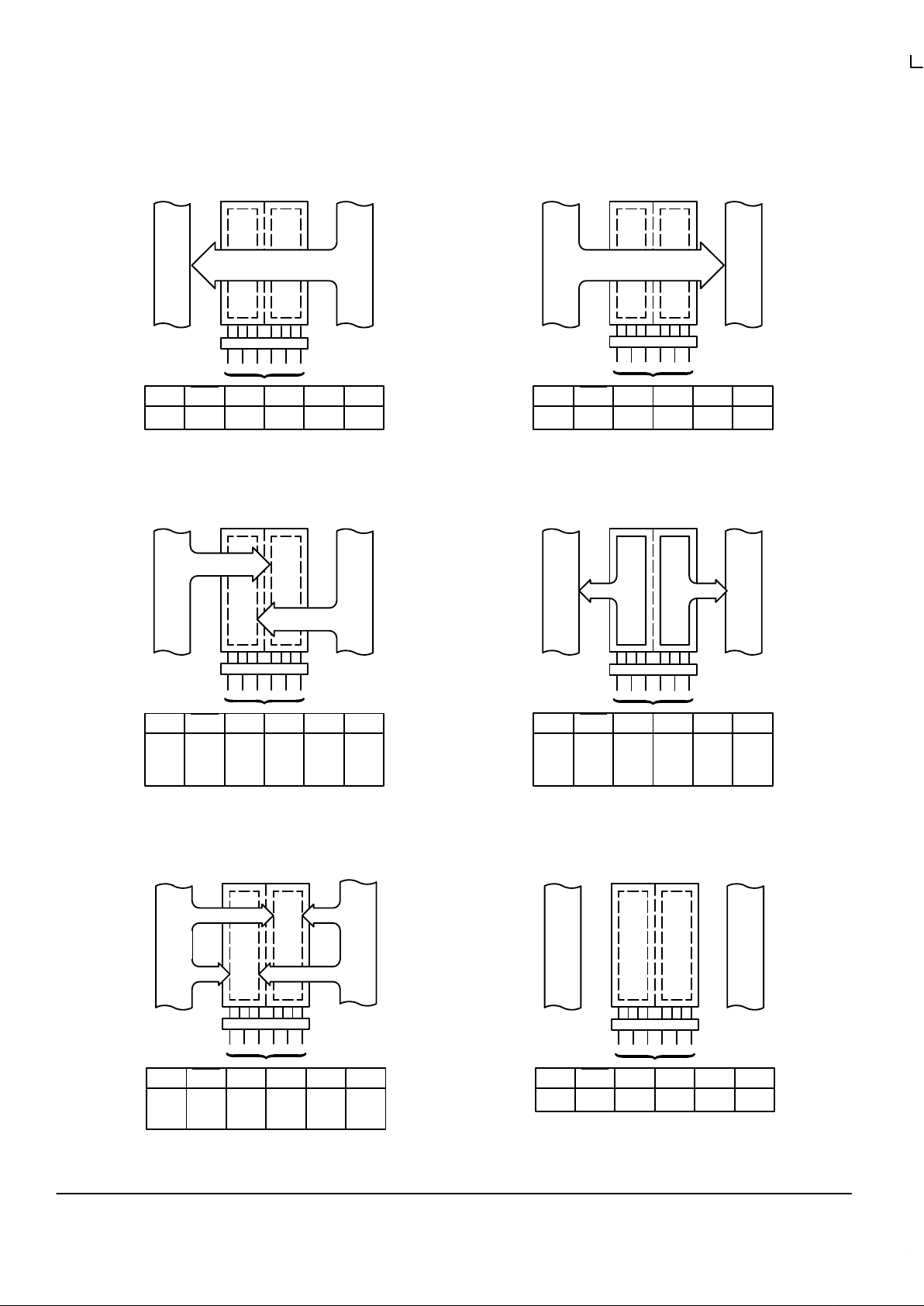
Figure 3. Bus Applications
BUS A
BUS B
OEABLOEBA
L
CABXCBAXSABXSBA
L
Real Time Transfer – Bus B to
Bus A
BUS A
BUS B
OEABHOEBA
H
CABXCBAXSABLSBA
X
Real Time Transfer – Bus A to
Bus B
BUS B
OEAB
X
L
L
OEBA
H
X
H
CAB
↑
X
↑
CBA
X
↑
↑
SAB
X
X
X
SBA
X
X
X
Store Data from Bus A, Bus B or
Bus A and Bus B
BUS A
BUS B
OEAB
H
L
H
OEBA
H
L
L
CAB
H or L
X
H or L
CBA
X
H or L
H or L
SAB
H
X
H
SBA
X
H
H
Transfer A Stored Data to Bus B
or B Stored Data to Bus A or
Both at the Same Time
BUS A
OEAB
H
L
OEBA
H
L
CAB
↑
↑
CBA
↑
↑
SAB
L
X
SBA
X
L
Store Bus A in Both Registers or
Store Bus B in Both Registers
BUS A
BUS B
OEABLOEBA
H
CAB
H or L
CBA
H or L
SABXSBA
X
Isolation
BUS A
BUS B
 Loading...
Loading...