4-157
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
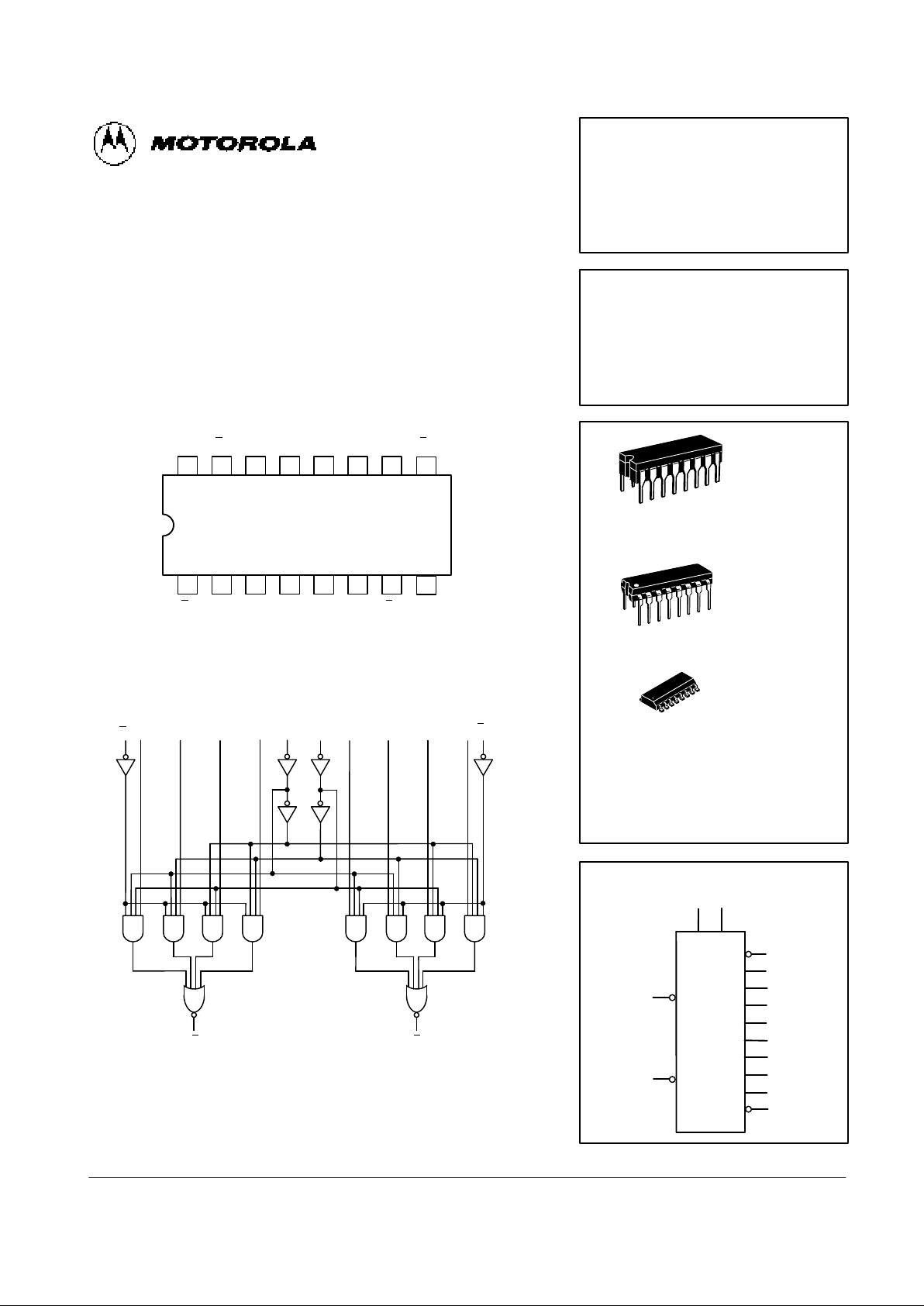
DUAL 4-INPUT MULTIPLEXER
The MC54/74F352 is a very high speed dual 4-input multiplexer with common Select inputs and individual Enable inputs for each section. It can select
two bits of data from four sources. The two buffered outputs present data in
the inverted (complementary) form. The F352 is the functional equivalent of
the F153 except with inverted outputs.
• Inverted Version of the F153
• Separate Enables for Each Multiplexer
• Input Clamp Diode Limits High-Speed Termination Effects
CONNECTION DIAGRAM (TOP VIEW)
1516 14 13 12 11 10
21 3 4 5 6 7
V
CC
9
8
E
bS0I3bI2bI1bI0bZb
E
aS1I3aI2aI1aI0aZa
GND
LOGIC DIAGRAM
Ea
I
0aI1aI2aI3aS1S0I0bI1bI2bI3b
E
b
Z
a
Z
b
MC54/74F352
DUAL 4-INPUT
MULTIPLEXER
FAST SCHOTTKY TTL
J SUFFIX
CERAMIC
CASE 620-09
N SUFFIX
PLASTIC
CASE 648-08
16
1
16
1
ORDERING INFORMATION
MC54FXXXJ Ceramic
MC74FXXXN Plastic
MC74FXXXD SOIC
16
1
D SUFFIX
SOIC
CASE 751B-03
LOGIC SYMBOL
2 14
1
6
5
4
3
10
11
12
13
15
9
7
Z
a
Z
b
S
1
S
0
E
a
I
0a
I
1a
I
2a
I
3a
I
0b
I
1b
I
2b
I
3b
E
b
VCC = PIN 14
GND = PIN 7
4-158
FAST AND LS TTL DATA
MC54/74F352
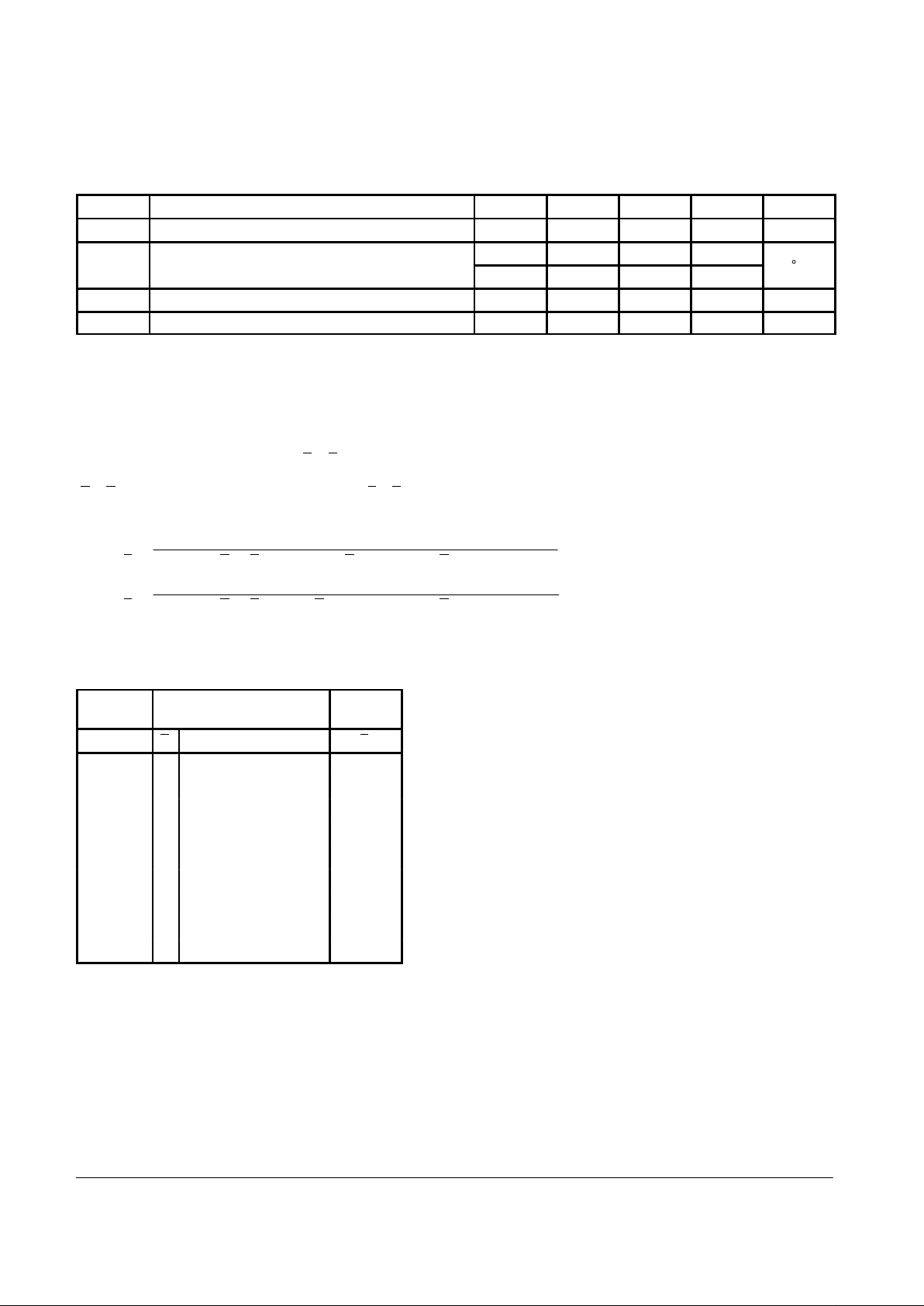
GUARANTEED OPERATING RANGES
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
V
CC
Supply Voltage 54, 74 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
T
A
Operating Ambient Temperature Range
54 - 55 25 125
A
74 0 25 70
°C
I
OH
Output Current — High 54, 74 –1.0 mA
I
OL
Output Current — Low 54, 74 20 mA
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The F352 is a dual 4-input multiplexer. It selects two bits of
data from up to four sources under the control of the common
Select inputs (S0, S1).The two 4-input multiplexer circuits
have individual active-LOW Enables(E
a
, Eb) which can be
used to strobe the outputs independently . When the Enables
(E
a
, Eb) are HIGH, the corresponding outputs (Za, Zb) are
forced HIGH.
The logic equations for the outputs are shown below:
The F352 can be used to move data from a group of registers to a common output bus. The particular register from
which the data came would be determined by the state of the
Select inputs. A less obvious application is as a function generator. The F352 can generate two functions of three variables. This is useful for implementing highly irregular random
logic.
Z
a
=Ea • (I0a • S1 • S0 + I1a • S1 • S0 + I2a • S1 • S0 + I3a • S1 • S0)
Z
b
=Eb • (I0b • S1 • S0 + I1b • S1 • S0 + I2b • S1 • S0 + I3b • S1 • S0)
FUNCTION TABLE
Select
Inputs
Inputs (a or b) Output
S0S
1
E I
0
I1I2I
3
Z
X X H X X X X H
L L L L X X X H
L L L H X X X L
H L L X L X X H
H L L X H X X L
L H L X X L X H
L H L X X H X L
H H L X X X L H
H H L X X X H L
H = HIGH Voltage Level
L = LOW Voltage Level
X = Don’t Care
 Loading...
Loading...