MOTOROLA MC33077D, MC33077DR2, MC33077P Datasheet

The MC33077 is a precision high quality, high frequency, low noise
monolithic dual operational amplifier employing innovative bipolar design
techniques. Precision matching coupled with a unique analog resistor trim
technique is used to obtain low input offset voltages. Dual–doublet frequency
compensation techniques are used to enhance the gain bandwidth product
of the amplifier. In addition, the MC33077 of fers low input noise voltage, low
temperature coefficient of input offset voltage, high slew rate, high AC and
DC open loop voltage gain and low supply current drain. The all NPN
transistor output stage exhibits no deadband cross–over distortion, large
output voltage swing, excellent phase and gain margins, low open loop
output impedance and symmetrical source and sink AC frequency
performance.
The MC33077 is tested over the automotive temperature range and is
available in plastic DIP and SO–8 packages (P and D suffixes).
• Low Voltage Noise: 4.4 nV/ Hz
• Low Input Offset V oltage: 0.2 mV
• Low TC of Input Offset V oltage: 2.0 µV/°C
• High Gain Bandwidth Product: 37 MHz @ 100 kHz
• High AC Voltage Gain: 370 @ 100 kHz
High AC Voltage Gain: 1850 @ 20 kHz
• Unity Gain Stable: with Capacitance Loads to 500 pF
• High Slew Rate: 1 1 V/µs
• Low Total Harmonic Distortion: 0.007%
• Large Output Voltage Swing: +14 V to –14.7 V
• High DC Open Loop Voltage Gain: 400 k (112 dB)
• High Common Mode Rejection: 107 dB
• Low Power Supply Drain Current: 3.5 mA
• Dual Supply Operation: ±2.5 V to ±18 V
Ǹ
@ 1.0 kHz
Order this document by MC33077/D
DUAL, LOW NOISE
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
SEMICONDUCTOR
TECHNICAL DATA
8
1
P SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 626
8
1
D SUFFIX
PLASTIC PACKAGE
CASE 751
(SO–8)
Representative Schematic Diagram (Each Amplifier)
R1 R6 R8 R11 R16
J
1
Q1
Q1
C1
Bias Network
Neg
Q2
Q4
D
1
Q5
R2
R3
Q6
R5
R4 R7
Q8
C2
D2
C3
PosQ7 Q9
D3
Q11
R9
Z1
Q12
Q10
R10 R12
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
C6
Q13
Q14
D4
R13
R14
D5
Q16
R15
Q17
D6
R17 R18
D7
C7
C8
Q19
Q20
V
Q21
V
R19
Q22
R20
V
PIN CONNECTIONS
CC
out
Output 1
Inputs 1
1
–
2
4
V
EE
+
3
(Dual, Top View)
1
–
2
+
ORDERING INFORMATION
Operating
Device
MC33077D
MC33077P
EE
Motorola, Inc. 1996 Rev 0
Temperature Range
TA = – 40° to +85°C
8V
CC
7
Output 2
6
5
Package
SO–8
Plastic DIP
Inputs 2
1
MC33077
MAXIMUM RATINGS
Rating Symbol Value Unit
Supply Voltage (VCC to VEE) V
Input Differential Voltage Range V
Input Voltage Range V
Output Short Circuit Duration (Note 2) t
Maximum Junction Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
Maximum Power Dissipation P
NOTES: 1. Either or both input voltages should not exceed VCC or VEE (See Applications Information).
2.Power dissipation must be considered to ensure maximum junction temperature (TJ) is not
exceeded (See power dissipation performance characteristic, Figure 1).
S
IDR
IR
SC
J
stg
D
+36 V
(Note 1) V
(Note 1) V
Indefinite sec
+150 °C
–60 to +150 °C
(Note 2) mW
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (V
Characteristics Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Input Offset Voltage (RS = 10 Ω, VCM = 0 V, VO = 0 V)
TA = +25°C
TA = –40° to +85°C
Average Temperature Coefficient of Input Offset Voltage
RS = 10 Ω, VCM = 0 V, VO = 0 V, TA = –40° to +85°C
Input Bias Current (VCM = 0 V, VO = 0 V)
TA = +25°C
TA = –40° to +85°C
Input Offset Current (VCM = 0 V, VO = 0 V)
TA = +25°C
TA = –40° to +85°C
Common Mode Input Voltage Range (∆VIO ,= 5.0 mV, VO = 0 V) V
Large Signal Voltage Gain (VO = ±1.0 V , RL = 2.0 kΩ)
TA = +25°C
TA = –40° to +85°C
Output Voltage Swing (VID = ±1.0 V)
RL = 2.0 kΩ
RL = 2.0 kΩ
RL = 10 kΩ
RL = 10 kΩ
Common Mode Rejection (Vin = ±13 V) CMR 85 107 — dB
Power Supply Rejection (Note 3)
VCC/VEE = +15 V/ –15 V to +5.0 V/ –5.0 V
Output Short Circuit Current (VID = ±1.0 V , Output to Ground)
Source
Sink
Power Supply Current (VO = 0 V, All Amplifiers)
TA = +25°C
TA = –40° to +85°C
NOTE: 3. Measured with VCC and VEE simultaneously varied.
= +15 V, VEE = –15 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
CC
|VIO|
∆VIO/∆T — 2.0 — µV/°C
I
IB
I
IO
ICR
A
VOL
V
O+
V
O–
V
O+
V
O–
PSR 80 90 — dB
I
SC
I
D
±13.5 ±14 — V
150 k
125 k
+13.0
+13.4
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
+10
–20
—
—
0.13
—
280
—
15
—
400 k
—
+13.6
–14.1
+14.0
–14.7
+26
–33
3.5
—
1.0
1.5
1000
1200
180
240
—
—
—
–13.5
—
–14.3
+60
+60
4.5
4.8
mV
nA
nA
V/V
V
mA
mA
2
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
MC33077
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (V
Characteristics Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
Slew Rate (Vin = –10 V to +10 V, RL = 2.0 kΩ, CL = 100 pF, AV = +1.0) SR 8.0 11 — V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product (f = 100 kHz) GBW 25 37 — MHz
AC Voltage Gain (RL = 2.0 kΩ, VO = 0 V)
f = 100 kHz
f = 20 kHz
Unity Gain Frequency (Open Loop) f
Gain Margin (RL = 2.0 kΩ, CL = 10 pF) A
Phase Margin (RL = 2.0 kΩ, CL = 10 pF) ∅
Channel Separation (f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz, RL = 2.0 kΩ, VO = 10 Vpp) CS — –120 — dB
Power Bandwidth (VO = 27
Distortion (RL = 2.0 kΩ)
AV = +1.0, f = 20 Hz to 20 kHz
VO = 3.0 V
AV = 2000, f = 20 kHz
VO = 2.0 V
VO = 10 V
AV = 4000, f = 100 kHz
VO = 2.0 V
VO = 10 V
Open Loop Output Impedance (VO = 0 V, f = fU) |ZO| — 36 — Ω
Differential Input Resistance (VCM = 0 V) R
Differential Input Capacitance (VCM = 0 V) C
Equivalent Input Noise Voltage (RS = 100 Ω)
f = 10 Hz
f = 1.0 kHz
Equivalent Input Noise Current (f = 1.0 kHz)
f = 10 Hz
f = 1.0 kHz
rms
pp
pp
pp
pp
, RL = 2.0 kΩ, THD ≤ 1%) BW
p–p
= +15 V, VEE = –15 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.)
CC
A
VO
U
m
m
p
THD
in
in
e
n
i
n
—
—
— 7.5 — MHz
— 10 — dB
— 55 —
— 200 — kHz
—
—
—
—
—
— 270 — kΩ
— 15 — pF
—
—
—
—
370
1850
0.007
0.215
0.242
0.3.19
0.316
6.7
4.4
1.3
0.6
—
—
Degrees
—
—
—
—
—
nV/ Hz√
—
—
pA/ Hz√
—
—
V/V
%
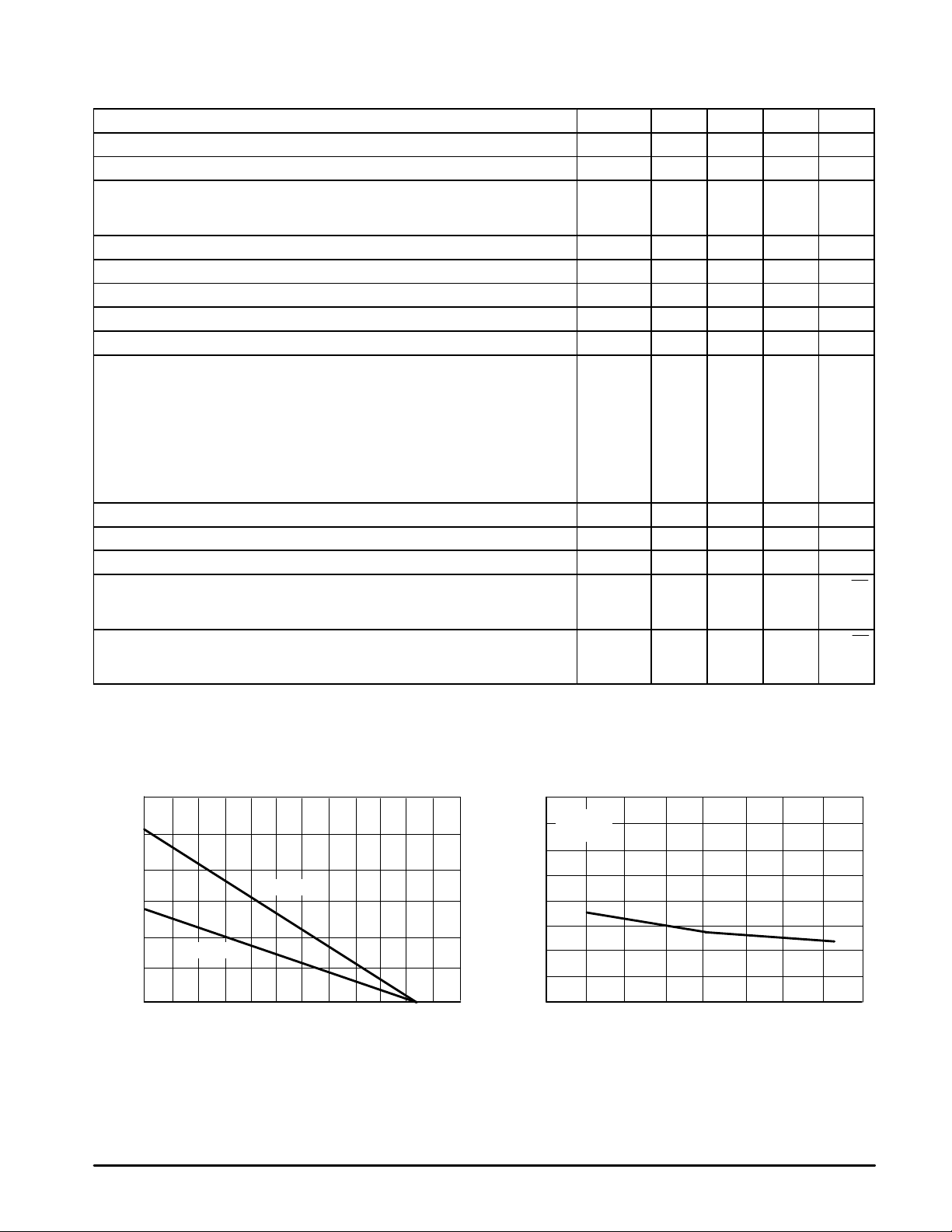
Figure 1. Maximum Power Dissipation
versus T emperature
2400
2000
1600
1200
800
, MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION (mW)
400
0
D(MAX)
P
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
MC33077D
MC33077P
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
Figure 2. Input Bias Current
versus Supply V oltage
800
VCM = 0 V
°
C
TA = 25
600
400
200
, INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)I
IB
0
0 2.5 5.0 7.5 10 12.5 15 17.5 20
VCC, |VEE|, SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
3
MC33077
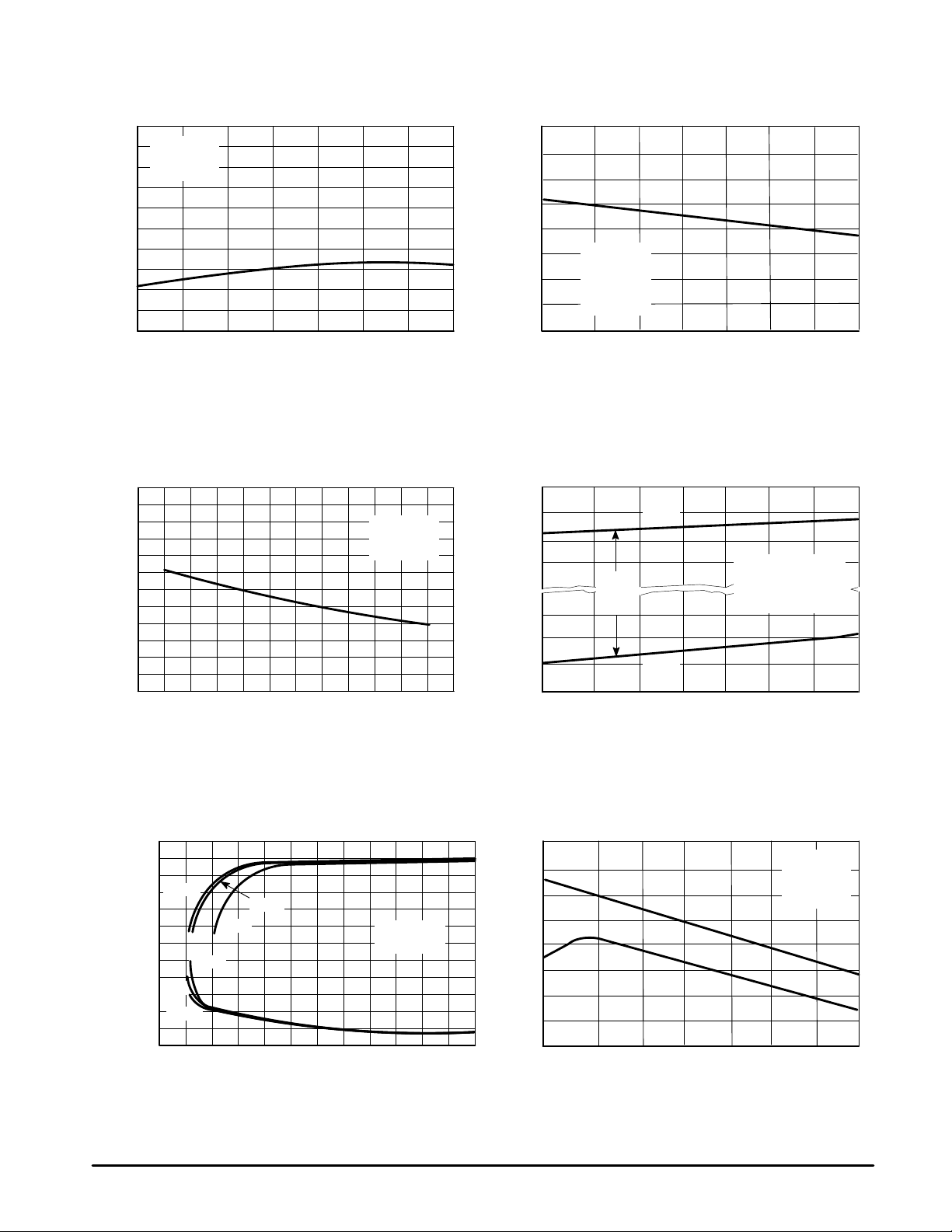
Figure 3. Input Bias Current
versus T emperature
1000
VCC = +15 V
VEE = –15 V
800
VCM = 0 V
600
400
, INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)I
200
IB
0
–55 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125 –55 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 5. Input Bias Current versus
1.0
0.5
0
–0.5
IO
V , INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE (mV)
–1.0
Figure 6. Input Common Mode V oltage Range
Common Mode V oltage
600
500
400
300
200
, INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)I
IB
100
0
–15 –10 –5.0 0 5.0 10 15
VCM, COMMON MODE VOLTAGE (V)
VCC = +15 V
VEE = –15 V
TA = 25
°
C
VCC 0.0
VCC –0.5
VCC –1.0
VCC –1.5
VEE +1.5
VEE +1.0
VEE +0.5
, INPUT COMMON MODE VOT AGE RANGE (V)
VEE +0.0
–55 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125
ICR
V
Figure 4. Input Offset Voltage
versus T emperature
VCC = +15 V
VEE = –15 V
Ω
RS = 10
VCM = 0 V
AV = +1.0
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
versus T emperature
+V
CM
VCC = +3.0 V to +15 V
Input
Voltage
Range
–V
CM
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
VEE = –3.0 V to –15 V
∆
VIO = 5.0 mV
VO = 0 V
sat
V , OUTPUT SATURA TION VOLTAGE (V)
4
Figure 7. Output Saturation Voltage versus
Load Resistance to Ground
VCC 0
VCC –2
–55°C
VCC –4
125°C
VEE +4
VEE +2
VEE 0
°
C
25
–55
°
C
0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 –55 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125
25°C
125°C
RL, LOAD RESISTANCE T O GROUND (kΩ)
VCC = +15 V
VEE = –15 V
SC
|I |, OUTPUT SHOR T CIRCUIT CURRENT (mA)
50
40
30
20
10
Figure 8. Output Short Circuit Current
versus T emperature
Sink
Source
TA, AMBIENT TEMPERATURE (°C)
MOTOROLA ANALOG IC DEVICE DATA
VCC = +15 V
VEE = –15 V
±
1.0 V
VID =
Ω
RL < 100
 Loading...
Loading...