Page 1

E365 Trouble Shooting
Service Manual
Compal Communications, Inc.
1
Page 2
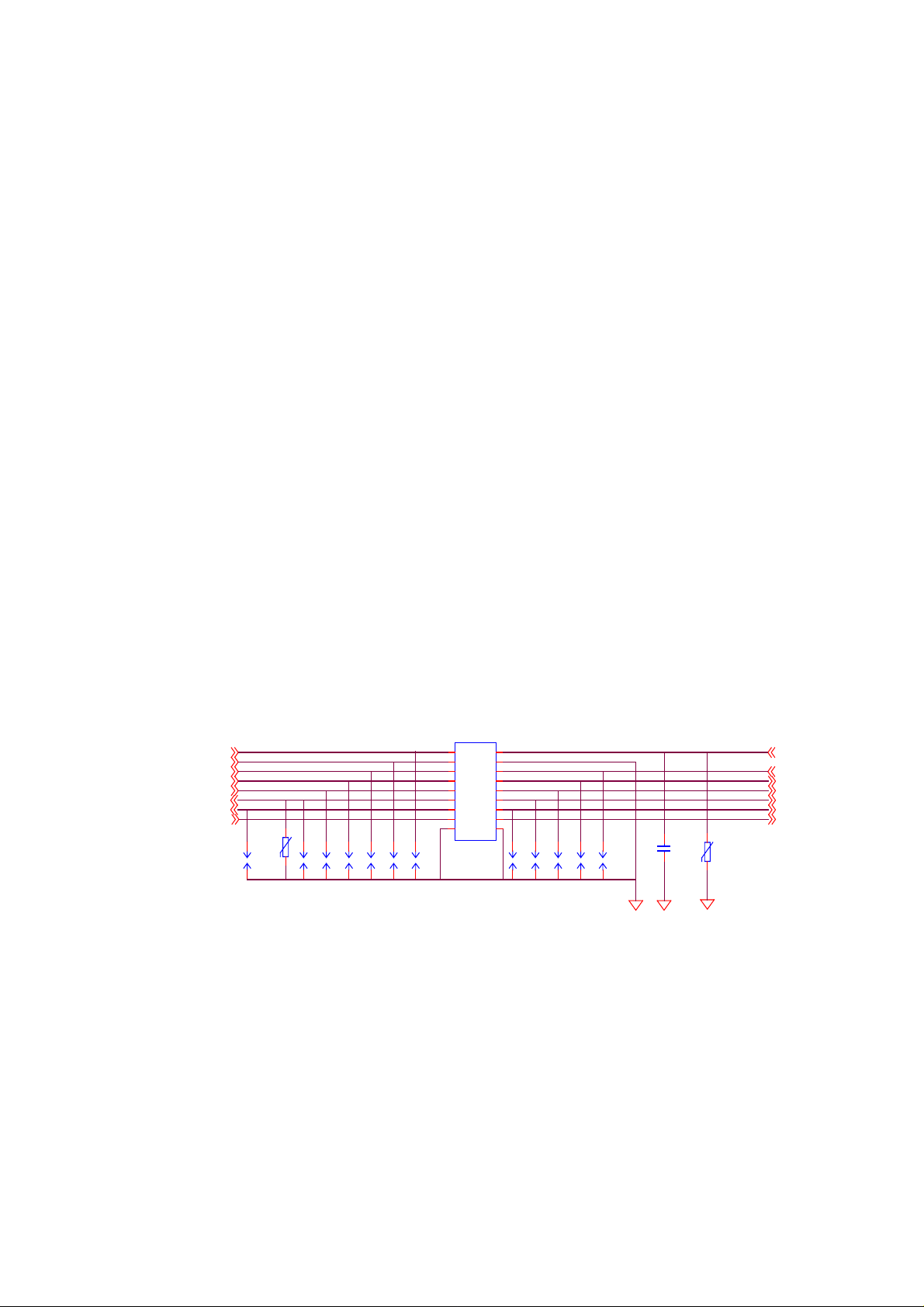
Baseband Descriptions
△
1. The mobile phone can’t boot after inserting the battery?
•STEP1. Check the energy of battery greater than 3.8v.(>3.8v)
a. to charge the battery. b. change the battery.
•STEP2. Check the battery connector
a. recombination. b.change the battery connector
•STEP3. Check the BTB connector between M/B and MMI
a. recombination
•STEP4. Check the MMI whether in normal
a. recombination
•STEP5. Check the software in correct
a. Re D/L
2. The mobile phone turn off automatically after turn on?
•STEP 1.Check battery if voltage enough greater than(>3.8v)
a. recombination b. Change battery
•STEP 2.Check ADC(3.4v) is correct
a. Re-adjustment ADC(3.4v)
•STEP 3.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B.
STEP3.1check J2.Row4 and GND maybe short.
STEP3.2.check J2 Pwon and GND maybe short.
BTB_CON
COL0
COL1
COL2
COL3
COL4
PWON
ROW0
VDDS-MIF_2.8V
varistor 5.5V 0402
GAP3
S
VR16
GAP4
S
GAP5
S
GAP7SGAP9
GAP6
S
GAP8
S
1
18
2
17
3
16
4
15
J2
5
14
6
13
7
12
11
8
10
9
GAP14
GAP12
GAP10
S
S
GAP11
S
GAP13
S
S
S
DGND
C46
22pF 0402
DGND
VR3
varistor 5.5V 0402
DGND
3. The screen display can’t search SIM card when insert SIM after turn on.
•STEP 1.Check the SIM card whether to louse.
a. Change SIM card.
•STEP 2.Check the SIM connecter.
VBAT
LEDKEYN
ROW4
ROW3
ROW2
ROW1
LIGHTSENSER_EN
a. Change SIM connector.
•STEP 3.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B.
a. if change SIM connector isn’t ok,then change a new IOTA.
2
Page 3
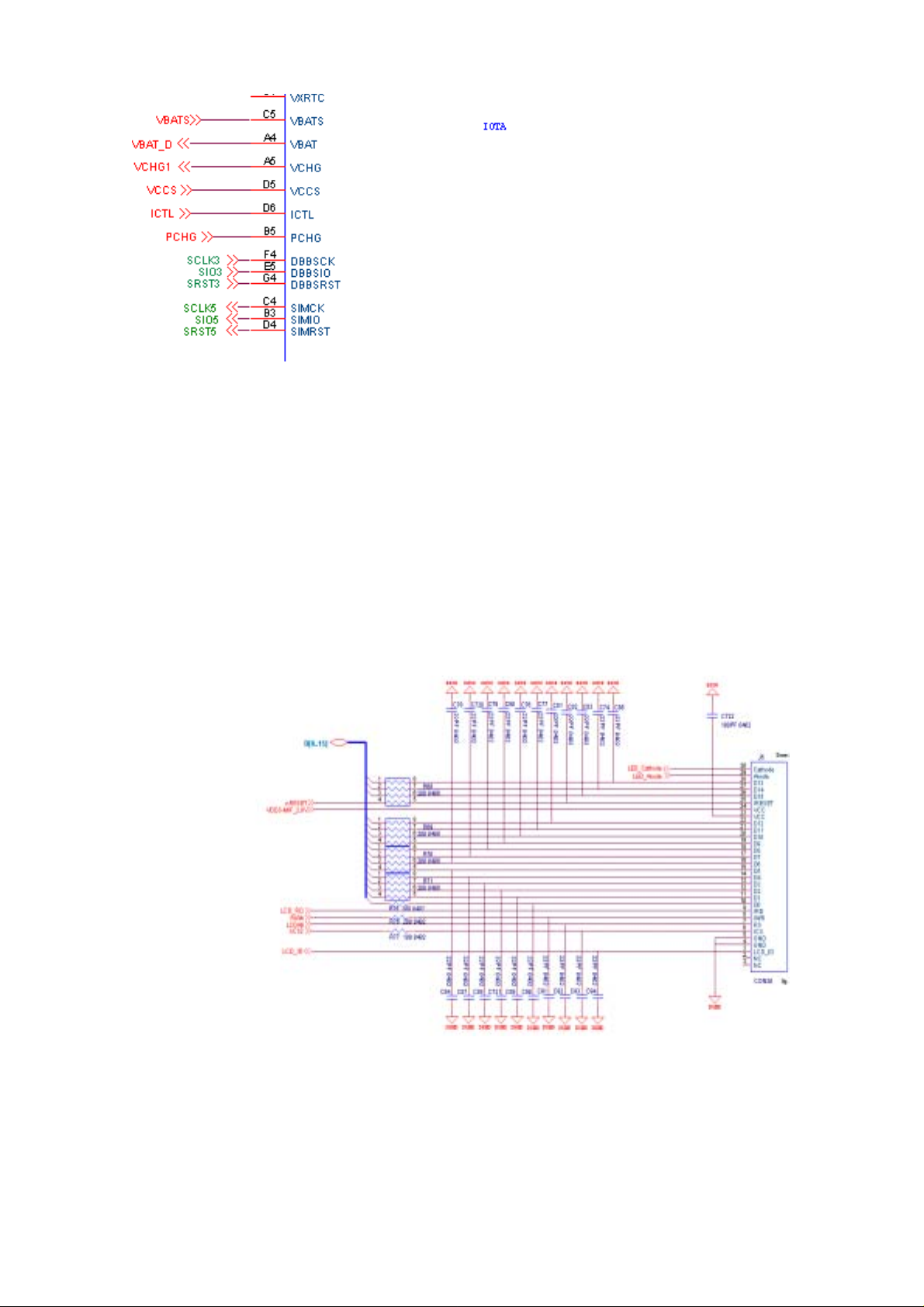
5. No display on LCD after turn on?
•STEP 1.Check the connector of LCD and FPC
a. recombination
•STEP 2.Check the LCD whether to louse
a. Change LCD
•STEP 3.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B.
STEP 3.1.checkVDDS-MIF_2.8V =2.8V (if VRMEM<2.7V, the LCD will not
work)
STEP 3.2. check J6 every PIN’s impedance, then you can find one of them
has problem
6. Has not LCM backlight :
•STEP 1. Check SET is correct
a. To set up LCD light bright mode.
•STEP 2. Check LCD and M/B whether to connect
a. Recombination.
•STEP 3. Check LCD failure
3
Page 4
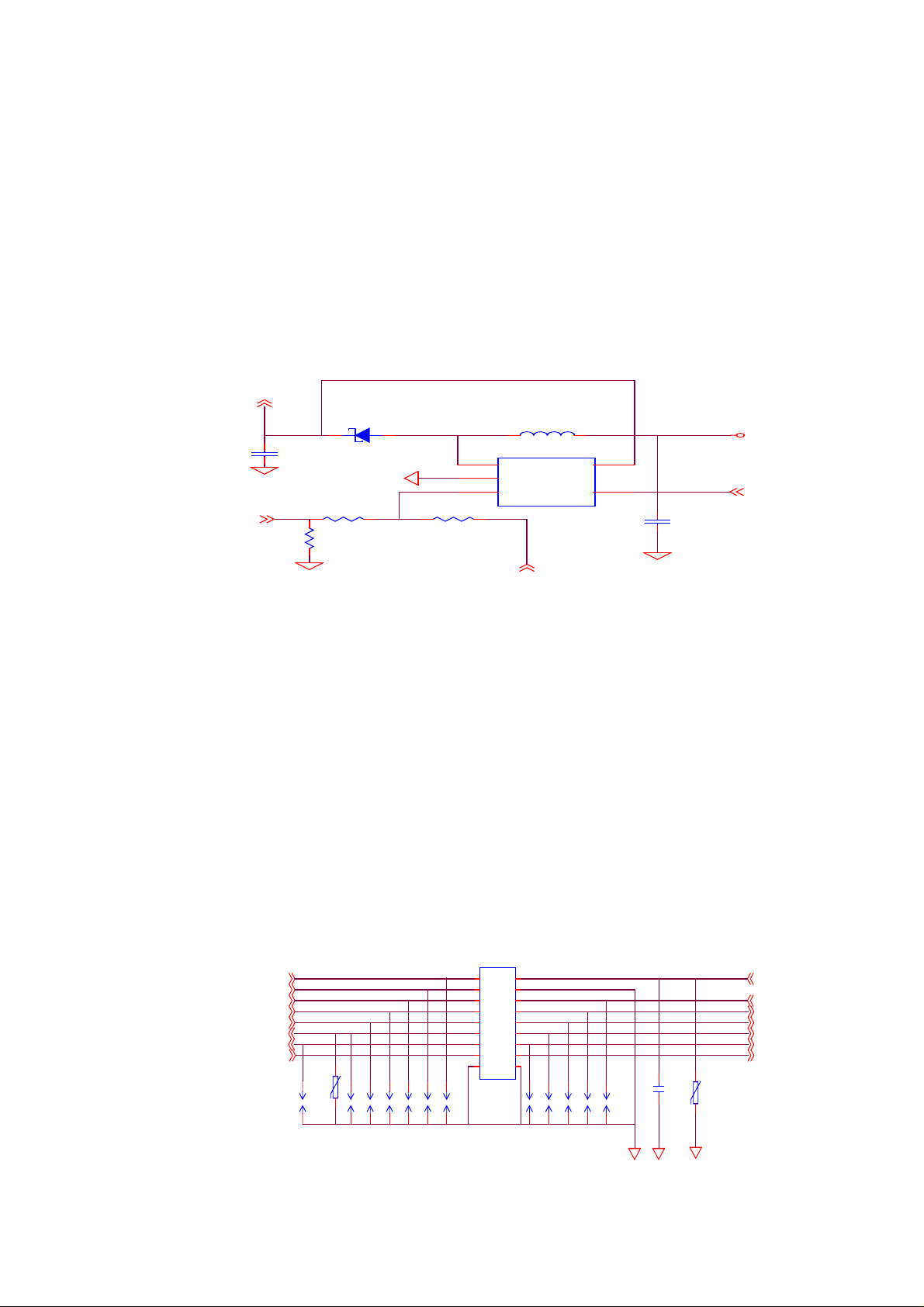
a. Change LCD.
•STEP 4.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B
STEP 1.Check U11 is slant.
STEP 2. when you press the keypad ,measure U11.4=2.7V
STEP 3. if RR1 have about 0.4V,then change U11.
STEP 4.if U11.4 < 2.7V,then change a new G2.
STEP 5.if step1 to step4 is ok, then check U6.3 about 10V
STEP 6.if U11.1<8V ,then change a new U11 or FL1、D6.
.
LED_Anode
0.22uF 0603
LED_Cathode
D6
CC1
DGND
RR1
56 0402
RB551V-30
R36
0 0402
DGND
23
DGND
R40
0 0402 NM
1
2
3
VDDS-MIF_2.8V
U11
SW
GND
FB
22uH
MP1523
FL1
5
BIAS
4
EN
CC2
1uF 0603
DGND
7. Has not Keypad Backlight ?
•STEP 1 Check the BTB connector between M/B and MMI
a. Recombination
•STEP 2.Check MMI whether to have problem
a. Change MMI
•STEP 3.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B.
VBAT
LEDLCM_EN
STEP3.1.use meter to check J2 every PIN impedance, then you can find
one of them has
problem.
BTB_CON
COL0
COL1
COL2
COL3
COL4
PWON
ROW0
VDDS-MIF_2.8V
varistor 5.5V 0402
GAP3
S
VR16
GAP4
S
GAP5
S
GAP7SGAP9
GAP6
S
GAP8
S
1
18
2
17
3
16
4
15
J2
5
14
6
13
7
12
11
8
10
9
GAP10
S
S
GAP11
S
S
GAP13
S
S
DGND
22pF 0402
DGND
GAP14
GAP12
C46
varistor 5.5V 0402
DGND
VR3
Step3.2 LEDKEY_EN= 1.4 ~ 2.8V, BQ3.pin3 = 1V DC
4
VBAT
LEDKEYN
ROW4
ROW3
ROW2
ROW1
LIGHTSENSER_EN
Page 5
E
LEDB
R64 0 0402 NM
LEDK
KeyLed_En
R65 1.5K 0402
C73
33nF 0402
R67
1K 0402
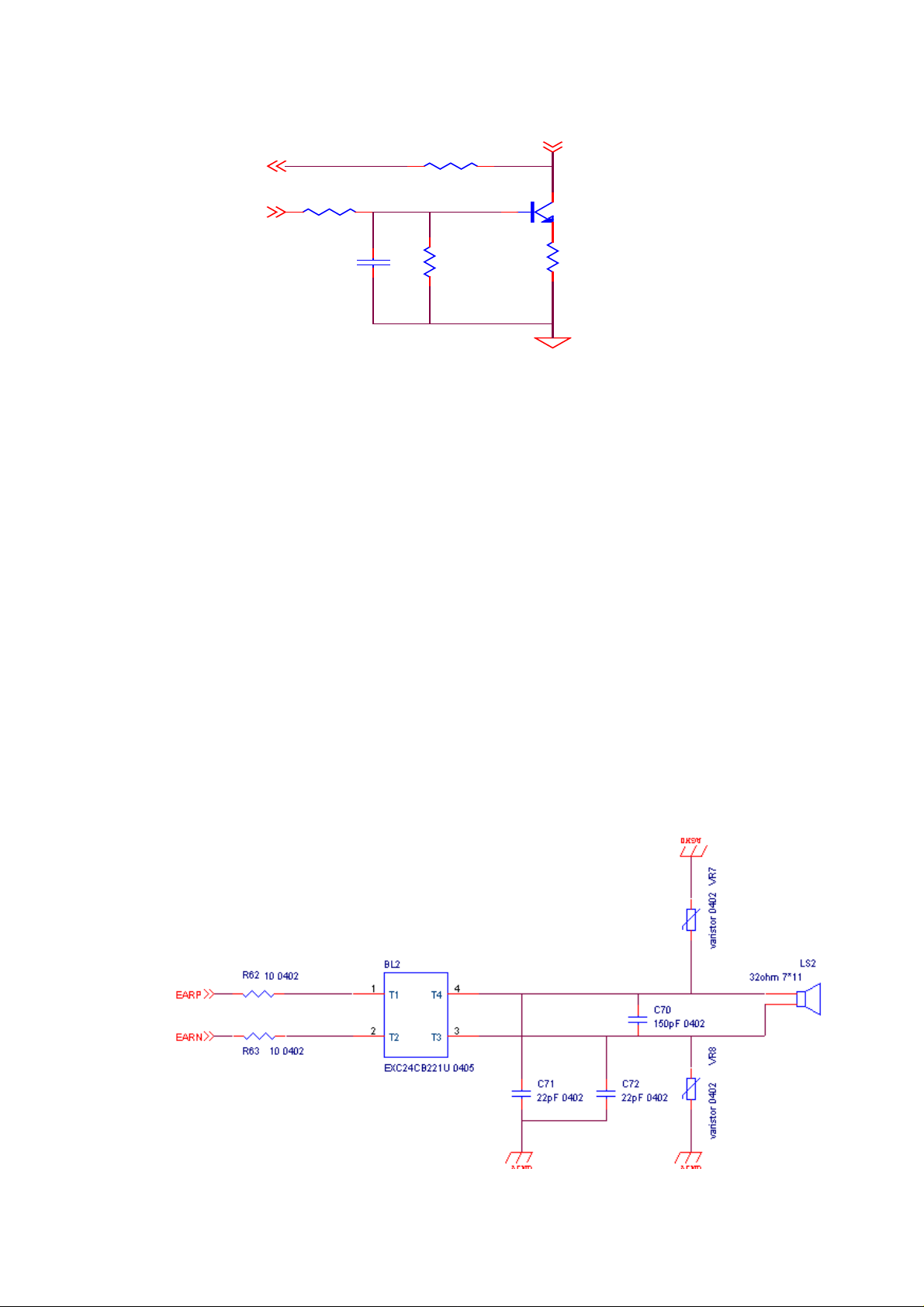
8. Receiver has no key tone or sound.
•STEP 1.Check SET is correct
a. set up to key tone mode.
•STEP 2.Check Receiver pin is that slanting or sag
a. To adjust the Receiver pin.
•STEP 3.Check Receiver whether in normal
a. Change Receiver.
•STEP 4.Check M/B pad is that oxidation or dirty
a. Use a eraser to clean the pad.
2
DGND
2SC5585 EMT3
1 3
R66
4.7 0402
BQ3
•STEP 5.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B
STEP 5.1.check every part impedance (R62、R63、C70、C71,C72、VR7、
VR8).
STEP 5.2.if every part is ok, then change a new IOTA.
5
Page 6
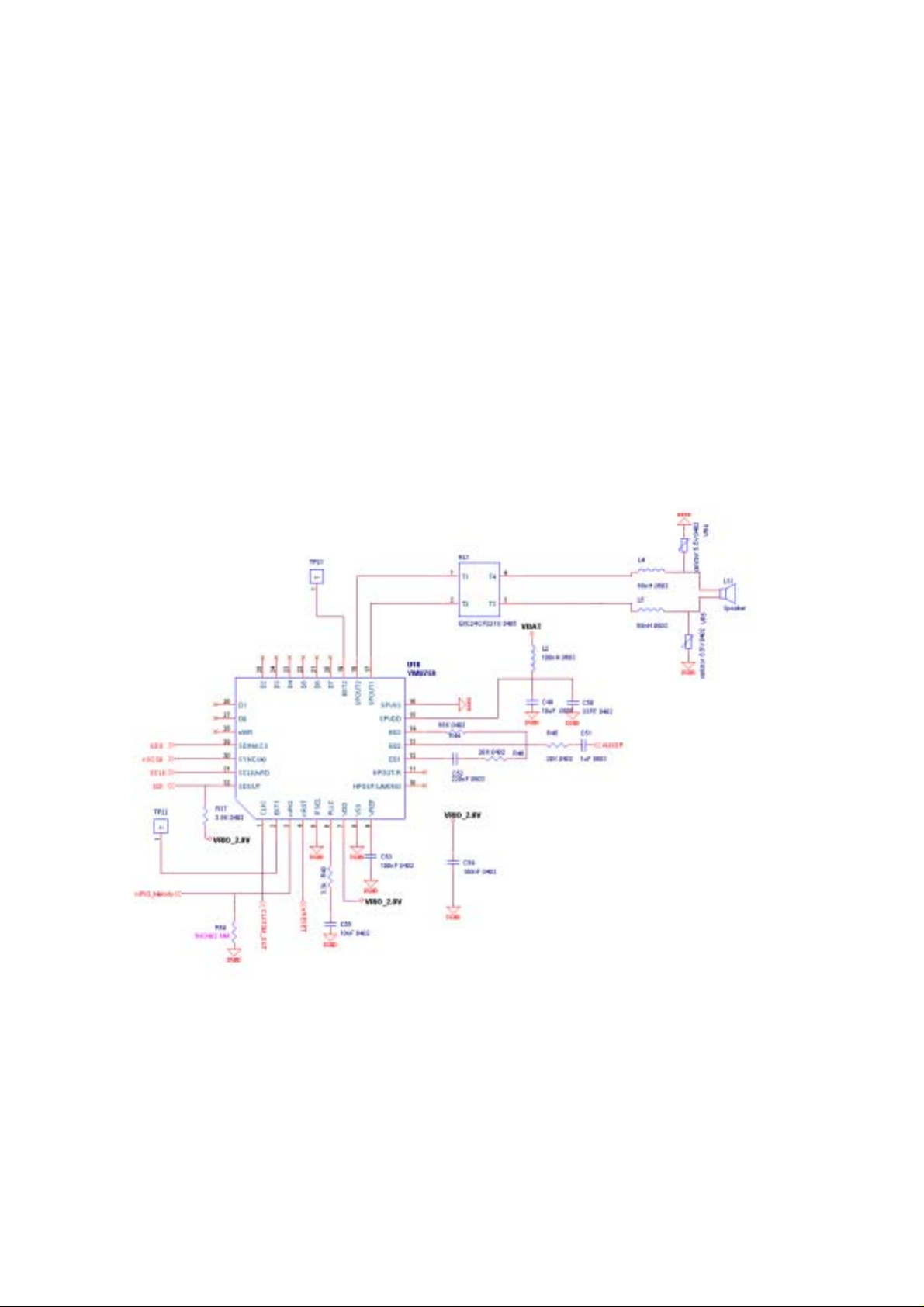
9. No ring tone
•STEP 1.Check SET is correct
a. Set up to ring mode.
•STEP 2.Check speaker hold has screwed
a. lock up a screw.
•STEP 3.Check speaker failure?
a. Change Speaker.
•STEP 4.Check speaker Connector damage?
a. Changed Speaker Connector.
•STEP 5.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B.
STEP5.1.check MELODY “Pin17、Pin18” impedance.
STEP5.2.if step1 is ok, measure L2, C49, C50, R45, R46,
R44,C51,C52,R37,C53,C54,C55,R48 impedance. Then
you can find one of them has problem.
10. Can not charging:
•STEP 1.Check if you use the right adaptor
a. Change right adaptor.
•STEP 2.Check I/O Connector failure?
a. Change I/O Connector.
•STEP 3.Check I/O Connector Pin1&Pin2 solder creak?
a. I/O Connector Pin1&Pin2 re-soldering.
6
Page 7
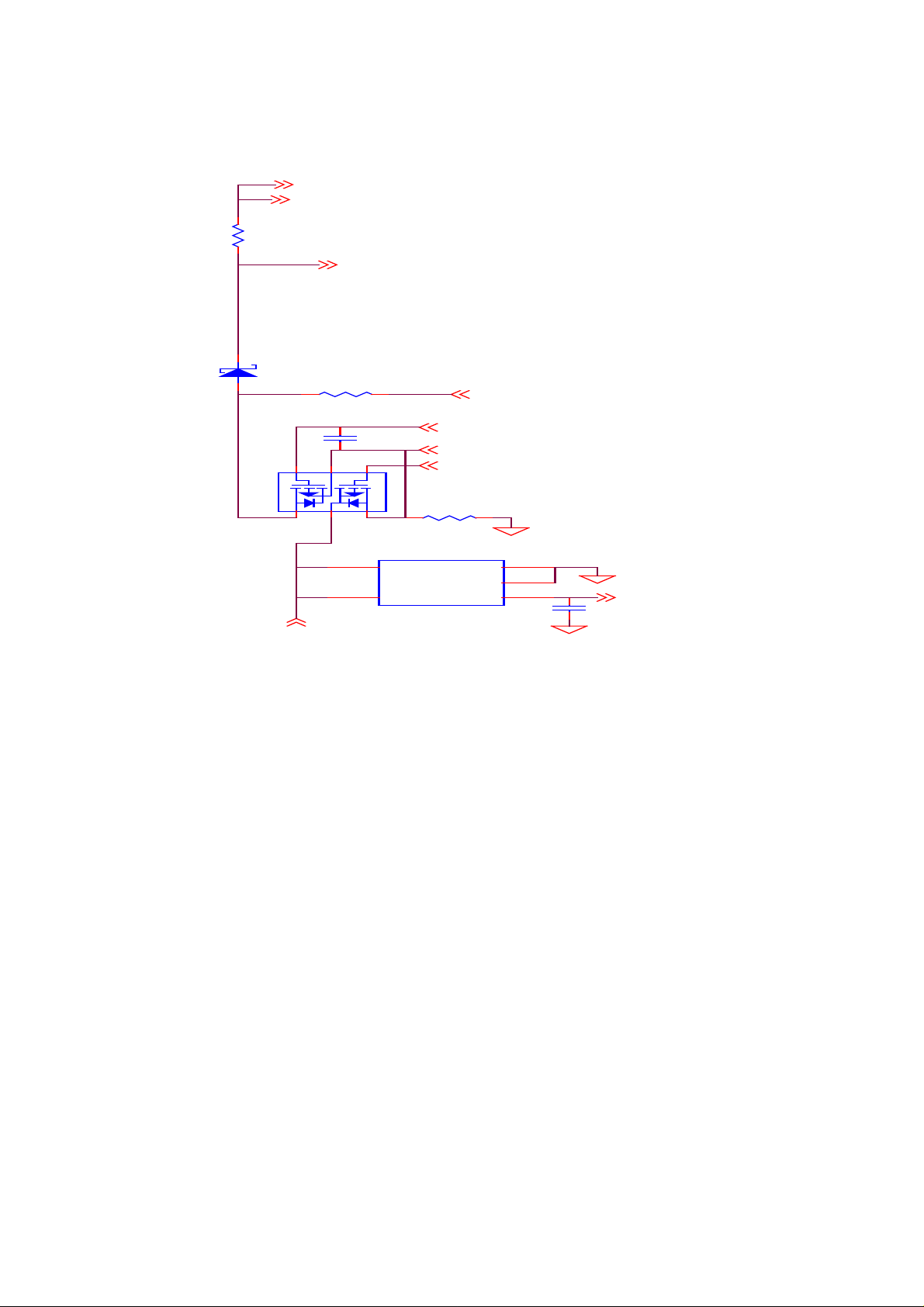
•STEP 4.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B. STEP 4.1.if U2.4 <5.8v,then change a new U2.
STEP 4.2.if step1 is ok, then change a new IOTA.
VBAT
VBATS
R1
0.15 0805 1%
VCCS
D2
RB160M-30
2 3
68 0805 1% NM
3
4
VCHG
R5
C10
22nF 0402
2
1
FDC6506P
5
6
U3
4
IN
5
VCC
NCP345
U2
ICTL
VCHG1
nCHG
CNTRL
GND
R15
OUT
PCHG
100K 0402
DGND
3
2
1
DGND
DGND
1uF 0603
nCHG
C21
11. Key has not function
•STEP 1. Check the BTB connector between M/B and MMI is well?
a. Recombination.
•STEP 2. Check MMI whether to have problem
a. Change MMI.
•STEP 3.Check MMI Pad whether to oxidize and dirty
a. Use a eraser to clean the pad.
•STEP 4. .IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could
be caused by M/B.
STEP 4.1.check BTB connector is short.
STEP 4.2.if not short, then change a new G2
7
Page 8
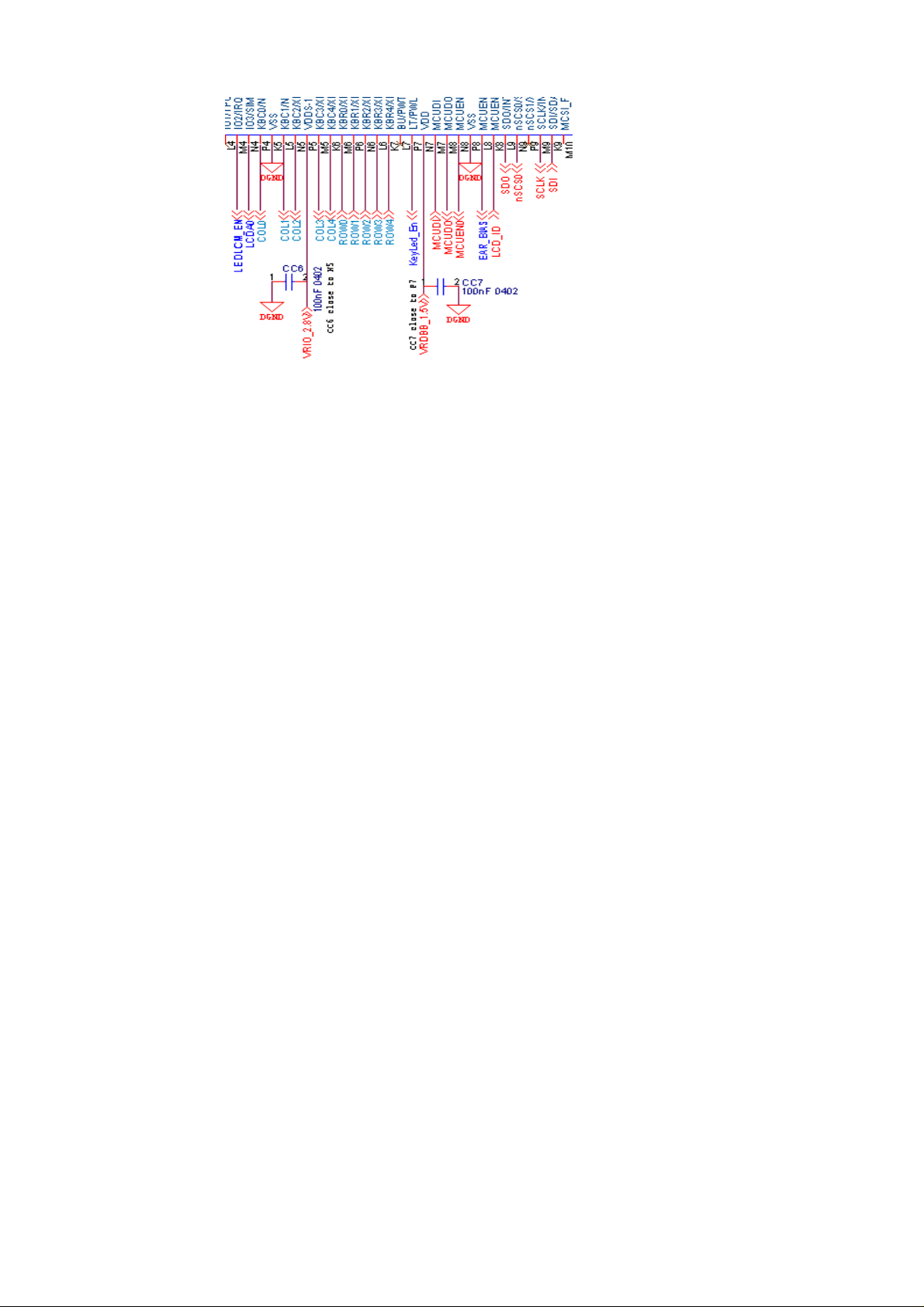
12. Has not vibration or vibrator can not stop.
•STEP 1.Check SET is correct
a. Set up to vibrate mode.
•STEP 2.Check Vibrator Pin is that slanting and sag
a. To adjust the Vibrator Pin.
•STEP 3. Check Vibrator failure?
a. Change Vibrator.
•STEP 4. Check M/B pad is that oxidation or dirty
a. Use a eraser to clean the pad.
•STEP 5.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
caused by M/B.
STEP 5.1.check F1 ,BQ1 ,R42, R43, D4 maybe slant.
STEP 5.2.check the voltage of BQ1.3 > 3.4V.
STEP 5.3.measure R42, R43 impedance is ok.
STEP 5.4.if step1 to step3 is ok, then change new BQ1
STEP 5.5.if above mention all in normal, then change a new IOTA.
8
Page 9

VBAT
F1
1
SGM20F1E104-2A 2012
I/O1
4
G
DGND DGND
3
G
I/O2
2
No. G3240010
DAC
1 2
R42
33 0402
DGND
R43
10K 0402
1SS400 SC79
2
1 3
D4
2 1
DGND
BQ1
2SC5592 SC59
0.95mm
M1
MOTOR 4.0*8.8-1.5V-KHN4NZ1D
3930408801W
13. Micphone can not work:
•STEP 1.Check MIC failure?
a. Change MIC.
•STEP 2.Check M/B pad is that oxidation or dirty
a. Use a eraser to clean the pad.
•STEP 3.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could
be caused by M/B.
STEP 3.1.check EF2 is slant.
STEP 3.2.check C65、C66、C67、R59、R61、C68、C69、R58、R60 impedance.
STEP 3.3.if above mention all in normal, then change a new IOTA.
MICIP
MICIN
MICBIAS
AGND
C65 100nF 0402
C66
R58
330 0402
C68
10uF 0805
R60
330 0402
100nF 0402
R59
1K 0402
C69
100nF 0402
R61
1K 0402
EMIF01-10005W5 SOT323-5L
EF2
5
O1
4
O2
GND
1
I1
2
3
I2
AGND
C67
100pF 0402
1
MIC+
2
MIC-
OBG-13SA 42-C2
14. No sound on earphone?
•STEP 1.Check use Earphone is failure?
a. Change right Earphone.
•STEP 2. Check Earphone Jack is failure?
a. Change Earphone Jack.
•STEP 3.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could be
MIC1
9
Page 10

caused by M/B.
STEP 3.1.if the earphone has no sound, check the soldering of SPACE R51.
STEP 3.2.if step1 is ok, then check EF1、L3、C57 soldering.
STEP 3.3.if above mention all in normal, then change a new SPACE IOTA
15. Has big Leakage current :
If leakage current > 100mA , battery on for a long time , we can touch the surface
of component , If the component heat more than other , It may be fail .
If leakage current <100mA , replace component.
16. Can not record Time
•STEP 1.Check RTC battery whether powerful or failure
a. Change RTC battery.
•STEP 2.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could
be caused by M/B.
STEP 2.1.if TP24 <> 32.768K,then change a new U2.
STEP 2.2.if change a new U2 isn’t ok ,then change a new G2.
17. Can not Download
•STEP 1.Check Download Tool SET
10
Page 11

a. Reset.
•STEP 2.Check use right Data cable or failure
a. Change Data cable.
•STEP 3.Check I/O Connector failure
a. Change I/O Connector.
•STEP 4.Check I/O Connector Pin3-Pin16 solder creak
a. I/O Connector Pin3-Pin16 re-soldering.
•STEP 5.IF above-mentioned are all in normal condition then the problem could
be caused by M/B.
STEP5.1.if TP4<>13M,then change a new 13M.
STEP5.2. if TP24=32.768k,then change a new flash.
STEP5.3.if TP24<>32.768k,then change G2.
STEP5.4.if TP24<>32.768k,then pull out G2.measure IOTA’s 5 modules
voltage whether in normal.
STEP5.5.if IOTA is ok, then change a new G2. Space final, you can download
software.
TP4(13M) TP24(32K)
18 DSC no function
STEP 1..Check the connector of DSC and FPC
11
Page 12

a. recombination
STEP 2.Check the DSC whether to louse
a. Change DSC
STEP 3 . check the DSC’s LDO whether have output voltage.
STEP3.1 If the COMS_EN <2.5V, then change the G2
STEP3.2 If the LDO (U13) has no voltage output, then change U13
D25V
L6
100nH 0402
RR26
L8
100nH 0402
C97
2.2uF/6V
L7
100nH 0402
VBAT
COMS_EN
C99
RR9
100K 0402 nm
DGND
C700
100nF 0402
10nF 0402
DGND
2.5V FOR OV7645FB
U13
1
Vin
VOUT2.5
2
EN1
VOUT3.0
3
EN2
4
BYP
NC5GND
MIC2211-2.5/3.3BML
NC
NC
RR26
1SS400 SC-79(W99685)
DD25V
10
9
8
7
6
D33V
C98
1uF/6V
DGND
0 0603
DGND
AVDDP
S25V
AVSSP
STEP 4. CLK13M_DSC have no 13MHz
a. Change the inverter U18.
D33V
RR14
10
C723
5
100pF
0402
DGND
CLK13M_DSC
10%
50V
NPO
4
U18
NC
VCC
IN
OUT
GND
TC7SHU04FU
SC70-5
RR15
1M
1
2
3
DGND
C724
CLK13M_OUT
100pF
X7R
0402
10%
50V
STEP5. check the U12.E10 have no 13MHz
a. change the U12
12
Page 13

#02#.
STEP6 move the CMOS sensor , then power on the handset and press
If it can’t get the firmware version such as 1.08 . the U12’s data
bus or control bus could have some trouble
a. change the U12
19. light sensor no function
step 1. check the VDDS-MIF-2.8V whether have 2.8V.
a. Check the BTB connector between M/B and MMI
step 2. check the LIGHTSENSER_EN whether have variably voltage
a. please change Q1 or R1.
VDDS-MIF_2.8V
R1
10k
Q1
Photo-Transistor
DGND
C6
?nF 0402 NM
DGND
LIGHTSENSER_EN
Step 3 check the LIGHTSENSER_EN have variably voltage
13
Page 14

a. please change the IOTA.
14
Page 15

△ Radio Frequency Descriptions
E365 RF Block Diagram :
The Aero transceiver consists of the Si4200 GSM transceiver, Si4201 universal
baseband interface, and Si4133T dual RF synthesizer. The highly integrated
solution eliminates the IF SAW filter, low noise amplifiers (LNAs) for three bands,
transmit and RF voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) modules, and more than 60
other discrete components found in conventional designs.
The receive section uses a digital low-IF architecture which avoids the difficulties
associated with directconversion while delivering lower solution cost and reduced
complexity. The universal baseband interface is compatible with any supplier’s
baseband subsystem.
The transmit section is a complete up conversion path from the baseband
subsystem to the power amplifier, and uses an offset phase locked loop (PLL) with
a fully integrated transmit VCO. The frequency synthesizer uses Silicon
Laboratories’ proven technology, which includes integrated RF and IF VCOs,
varactors and loopfilters.
15
Page 16

Receiver Block Diagram :
The Aero transceiver uses a low-IF receiver architecture that allows for the on-chip
integration of the channel selection filters. The Si4200 integrates three
differential-input LNAs. The LNA inputs are matched to the 200 Ohm balanced
output SAW filters through external LC matching networks.
A quadrature image-rejeject mixer downconverts the RF signal to a 100kHz
intermediate frequency (IF) with the RFLO from the Si4133T frequency
synthesizer. The mixer output is amplified with an analog programmable gain
amplifier (PGA). The quadrature IF signal is digitized with high resolution A/D
converters (ADCs).
The Si4201 downconverts the ADC output to baseband with a digital 100kHz
quadrature LO signal. Digital decimation and IIR filters perform channel selection
to remove blocking and reference interference signals. After channel selection, the
digital output is scaled with a digital PGA. DACs drive a differential analog signal
onto the RXIP, RXIN, RXQP and RXQN pins.
16
Page 17

Transmitter Block Diagram :
The transmit (TX) section consists of an I/Q baseband upconverter, an offset
phase-locked loop (OPLL) and two 50 Ohm output buffers that can drive external
poweramplifiers (PA).
A quadrature mixer upconverts the differential in-phase (TXIP, TXIN) and
quadrature (TXQP, TXQN) signals with the IFLO to generate a SSB IF signal
which is filtered and used as the reference input to the OPLL. The Si4133
generates the IFLO frequency between 766MHz and 896 MHz. The IFLO is
divided by two to generate the quadrature LO signals for the quadrature
modulator, resulting in an IF between 383 and 448MHz.
The OPLL consists of a feedback mixer, a phase detector, a loop filter, and a fully
integrated TXVCO. The TXVCO is centered between the DCS1800 and PCS1900
bands, and its output is divided by two for the GSM 850 and E-GSM 900 bands.
The Si4133T generates the RFLO frequency between 1272 and 1483 MHz.
Low-pass filters before the OPLL phase detector reduce the harmonic content of
the quadrature modulator and feedback mixer outputs.
17
Page 18

Frequency Plan of Aero
For Tx and Rx intermediate frequency plan
Tx intermediate frequency
Band IF frequency (MHz) Channel LO frequency (MHz)
E-GSM
399*2 975~1023 (890+0.2*(ARFCN-1024))+IF/2
399*2 0~24 (890+0.2*ARFCN)+IF/2
395*2 25~49 (890+0.2*ARFCN)+ IF/2
399*2 50~124 (890+0.2* ARFCN)+ IF/2
DCS 383*2 512~885 (1710.2+0.2*( ARFCN -512))-IF/2
E-GSM : fLO=fRF + fIF/2
DCS/PCS : fLO=fRF - fIF/2
Rx intermediate frequency 100kHz
Band Channel LO frequency (MHz)
975~1023 ((935+0.2*(ARFCN-1024))-0.1)*2 E-GSM
0~124 ((935+0.2*ARFCN)-0.1)*2
DCS 512~885 (1805.2+0.2*(ARFCN-512))-0.1
E-GSM: f
/2 =fRF – 0.1 DCS / PCS: fLO =fRF – 0.1
LO
Tx (Low, Mid, High channel)
Band IF frequency(MHz) LO frequency (MHz) Channel
399*2 1279.2 975
E-GSM
399*2 1301.4 62
399*2 1313.8 124
DCS
383*2 1327.2 512
383*2 1364.6 699
383*2 1401.8 885
Rx (Low, Mid, High channel)
Band LO frequency (MHz) Channel
E-GSM
1850.2 975
1894.6 62
1919.4 124
DCS
1805.1 512
1842.5 699
1879.7 885
18
Page 19

RX : GSM900
1. Set HP8960 or HP8922 : Operating mode : Test mode , Test function :
BCH+TCH
2. Ch 62 : 947.4MHz , cell power : -60dBm
3. Press RX_900(62)
Signal 2
Signal 1
4. RX 900 signal 1 : Use probe to touch U101 pin 8 (freq = 947.4MHz)
5. RX 900 signal 2 : Use probe to touch U101 pin 10 (freq = 947.4MHz)
Signal 3
6. RX 900 signal 3 : Use probe to touch F101 pin 4/6 (freq = 947.4MHz)
19
Page 20

Signal 4
7. RX 900 signal 4 : Use oscilloscope probe to touch RXQP, RXQN, RXIP,
RXIN from U203 pin 2~5 and you can find that ( For Example : The RXIP
signal )
20
Page 21

RX : DCS1800
1. Set HP8960 or HP8922 : Operating mode : Test mode , Test function :
BCH+TCH
2. Ch 699 : 1842.6MHz , cell power : -60dBm
3. Press RX_1800(699)
Signal 2
4. RX 1800 signal 1 : Use probe to touch U101 pin 8 (freq = 1842.6MHz)
5. RX 1800 signal 2 : Use probe to touch U101 pin 1 (freq = 1842.6MHz)
Signal 1
Signal 3
6. RX 1800 signal 3 : Use probe to touch F102 pin 4/6 (freq = 1842.6MHz)
21
Page 22

TX : GSM900
1. Set HP8960 or HP8922 : Operating mode : Test mode , Test function :
BCH+TCH
2. Ch 62 : 902.4MHz , cell power : -60dBm , MS_TX_level : 5
3. Press TX_900(62)
Signal 2
Signal 1
4. TX 900 signal 1 : Use probe to touch U301 pin 23/24 (freq = 1301.4MHz)
5. TX 900 signal 2 : Use probe to touch U301 pin 26/27 (freq = 798MHz)
( If signal 1 and 2 are OK, synthesizer and tranceiver are OK
If there are not then we have to check the inductor (L302 or L301) value
and solder)
22
Page 23

Signal 3
6. TX 900 signal 3 : Use oscilloscope probe to touch R205/6/7/8 pin 4/3 and you
can find that ( For Example : The TXIP signal )
23
Page 24

Signal 4Signal 5
7. TX 900 signal 4 : Use probe to touch R402 pin 2 (frequency 902.4MHz)
8. TX 900 signal 5 : Use probe to touch R402 pin 1 (frequency 902.4MHz)
(If signal 4 and 5 are OK, TXVCO is OK.)
Signal 6
9. TX 900 signal 6 : Use oscilloscope probe to touch R401 and we can find that
24
Page 25

Signal 7
10. TX 900 signal 7 : If 8960 or 8922 could show output power, PA is OK. If
8960 or 8922 show Freq_error, Peak_phase_error, RMS_phase_error are
inside the standard, Tx is OK.
TX : DCS1800
1. Set HP8960 or HP8922 : Operating mode : Test mode , Test function :
BCH+TCH
2. Ch 699 : 1747.6MHz , cell power : -60dBm , MS_TX_level : 0
3. Press TX_1800(699)
Signal 2
Signal 1
4. TX 1800 signal 1 : Use probe to touch U301 pin 23/24 (freq = 1364.6MHz)
5. TX 1800 signal 2 : Use probe to touch U301 pin 26/27 (freq = 766MHz)
( If signal 1 and 2 are OK, synthesizer and tranceiver are OK
25
Page 26

If there are not then we have to check the inductor (L302 or L301) value and
solder)
Signal 3
6. TX 1800 signal 3 : Use oscilloscope probe to touch R205/6/7/8 pin 4 (3) and
the result is similar to the GSM TXIQ.
Signal 4
Signal 5
26
Page 27

7. TX 1800 signal 4 : Use probe to touch R403 pin 2 (frequency 1747.6MHz)
8. TX 1800 signal 5 : Use probe to touch R403 pin 1 (frequency 1747.6MHz)
(If signal 4 and 5 are OK, TXVCO is OK.)
Signal 6
9. TX 1800 signal 6 : Use oscilloscope probe to touch R401 and the diagram is
similar to GSM APC.
10. TX 1800 signal 7 : If 8960 or 8922 could show output power, PA is OK. If
8960 or 8922 show Freq_error, Peak_phase_error, RMS_phase_error are
inside the standard, Tx is OK.
27
Signal 7
 Loading...
Loading...