Page 1

Yasnac MRC Controller
January 20, 1995
MAN
ArcWorld 6000
Operator's Manual
Part Number 132340-7
TEL: 513-847-6200 FAX: 513-847-6277
24-HOUR SERVICE HOTLINE: 513-847-3200
The information contained within this document is the proprietary property of Motoman, Inc., and
may not be copied, reproduced or transmitted to other parties without the expressed written
MOTO
805 Liberty Lane
West Carrollton, OH 45449
authorization of Motoman, Inc.
Page 2

All Rights Reserved
Because we are constantly improving our products, we reserve the right to change specifications without
notice. YASNAC and MOTOMAN are registered trademarks of YASKAWA Electric Manufacturing.
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Page
1.0 INTRODUCTION............................................................................................ 1
1.1 ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT............................................................... 1
1.2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW.......................................................................... 1
1.2.1 System Layout..................................................................... 3
1.2.2 Optional Equipment.............................................................. 3
1.3 REFERENCE TO OTHER DOCUMENTATION ................................... 4
1.4 CUSTOMER SERVICE INFORMATION ............................................. 4
2.0 SAFETY.......................................................................................................... 5
2.1 STANDARD CONVENTIONS............................................................. 6
2.2 GENERAL SAFEGUARDING TIPS..................................................... 7
2.3 MECHANICAL SAFETY DEVICES ...................................................... 7
2.4 INSTALLATION SAFETY.................................................................... 8
2.5 PROGRAMMING SAFETY ................................................................ 8
2.6 OPERATION SAFETY ........................................................................ 9
2.7 MAINTENANCE SAFETY................................................................. 10
3.0 DESCRIPTION OF EQUIPMENT................................................................. 11
3.1 K-SERIES ROBOT DESCRIPTION.................................................. 11
3.2 MRC CONTROLLER........................................................................ 11
3.2.1 Servo Power..................................................................... 12
3.2.2 Mode Select...................................................................... 13
3.2.3 Cycle Select...................................................................... 13
3.2.4 Emergency Stop................................................................ 13
3.2.5 Alarm / Error.................................................................... 13
3.2.6 Hold.................................................................................. 13
3.2.7 Start................................................................................. 13
3.2.8 Playback Box Sub-Panel.................................................... 13
3.3 PROGRAMMING PENDANT.......................................................... 14
3.3.1 Display.............................................................................. 15
3.3.2 Robot Speed Indicators...................................................... 15
3.3.3 Emergency Stop................................................................ 15
3.3.4 Keypad.............................................................................. 15
3.3.5 Servo Power..................................................................... 15
Page 4

3.4 MRM2-SERIES POSITIONER......................................................... 15
3.4.1 Part / Fixture Rating......................................................... 16
3.4.2 Swing Diameter................................................................. 16
3.4.3 Temperature Operating Range........................................... 16
Page 5

3.4.4 Humidity............................................................................ 16
3.4.5 Shock Rating..................................................................... 16
3.4.6 Sweep Speed ..................................................................... 17
3.4.7 Servo Head Stock Speed.................................................... 17
3.4.8 Air Requirements.............................................................. 17
3.4.9 Electrical Requirements..................................................... 17
3.4.10 Welding Current Rating..................................................... 17
3.4.11 Locking Pins...................................................................... 17
3.4.12 Arc Shield......................................................................... 18
3.5 OP-STATION.................................................................................. 18
3.5.1 Emergency Stop................................................................ 18
3.5.2 Hold.................................................................................. 18
3.5.3 Cycle Start....................................................................... 19
3.5.4 Station Ready.................................................................... 19
3.5.5 Alarm............................................................................... 19
3.5.6 Servo On.......................................................................... 19
3.5.7 Positioner Auto / Manual................................................... 19
3.5.8 Master Job Start .............................................................. 19
3.5.9 Operator Station Enable / Disable...................................... 19
3.5.10 Reset................................................................................ 20
3.6 WELDING POWER SOURCE........................................................... 20
3.6.1 Main Power...................................................................... 20
3.6.2 Volt / Amp Settings............................................................ 20
3.6.3 Terminal Connectors......................................................... 20
3.6.4 Local / Remote Operation................................................... 20
3.6.5 Feeder Control Receptacles............................................... 21
3.6.6 Circuit Breakers............................................................... 22
3.6.7 AC Receptacles................................................................. 22
3.7 WELDING EQUIPMENT.................................................................. 22
3.7.1 PWF4 Wire Feeder............................................................ 22
3.7.2 Universal Welding Interface (UWI)................................... 22
3.7.3 MIG Torch....................................................................... 22
3.7.4 RAM Breakaway Mount.................................................... 23
3.8 SAFETY EQUIPMENT ..................................................................... 23
3.8.1 Arc Screens...................................................................... 23
3.8.2 Fencing............................................................................. 23
3.8.3 Interlocks......................................................................... 24
3.8.4 Safety Mats...................................................................... 24
3.8.5 Emergency Stops............................................................... 24
4.0 OPERATION................................................................................................ 25
4.1 OPERATION................................................................................... 25
Page 6

4.1.1 Start Up........................................................................... 25
4.1.2 Loading / Unloading Procedures......................................... 26
4.1.3 Fault Recovery.................................................................. 26
Page 7

4.1.4 E-STOP Recovery............................................................. 26
4.1.5 Shock Sensor Recovery..................................................... 27
4.1.6 Shut Down........................................................................ 29
4.2 ALARMS AND ERRORS.................................................................. 29
4.2.1 Error Messages................................................................ 29
4.2.2 Minor Alarms................................................................... 29
4.2.3 Major Alarms................................................................... 30
4.3 PROGRAMMING............................................................................ 30
4.3.1 Cube Assignment............................................................... 30
4.3.2 Sweeping Positioner to Side A............................................ 31
4.3.3 Sweeping Positioner to Side B............................................ 31
4.3.4 Rotating Headstock........................................................... 32
4.3.5 Programming.................................................................... 32
4.3.6 I/O Assignment................................................................. 34
4.4 SAMPLE JOBS................................................................................ 35
4.4.1 Master Job (No Group Axes)............................................ 35
4.4.2 Sweep to A Job (R1 + S1).................................................. 36
4.4.3 Sweep to B Job................................................................. 38
4.4.4 Weld Side A Job (Multiple Weld Jobs)................................ 39
4.4.5 Weld Side A Job (Single Weld Job)..................................... 39
4.4.6 Weld Side B Job................................................................ 40
4.4.7 Clean Job (R1 Job)............................................................ 41
5.0 MAINTENANCE ........................................................................................... 42
5.1 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE............................................................ 42
5.2 SPARE PARTS LIST......................................................................... 43
5.3 FUSE AND CIRCUIT BREAKER PROTECTION............................... 44
APPX. A RISK ASSESSMENT.......................................................................... A-1
APPX. B SYSTEM OUTLINE ............................................................................ B-1
APPX. C ELECTRICAL DRAWINGS.................................................................. C-1
APPX. D MECHANICAL DRAWINGS.............................................................. D-1
INDEX ......................................................................................................... Index 1
Page 8

LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
Figure 1-1 System Layout...................................................................................... 2
Figure 3-1 MRC Controller................................................................................. 12
Figure 3-2 MRC Playback Box............................................................................ 12
Figure 3-3 Programming Pendant........................................................................ 14
Figure 3-4 Operator Control Panel (Op-Station)................................................. 18
Figure 3-5 Excel-Arc Controls............................................................................ 21
Figure 4-1 Shock Sensor Override...................................................................... 28
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 5-1 Periodic Maintenance.......................................................................... 42
Table 5-2 Spare Parts........................................................................................ 43
Table 5-3 Excel-Arc 6045 CV Fuses and Circuit Breakers.................................. 44
Table 5-4 MRC Cabinet Fuses and Circuit Breakers............................................ 44
Table 5-5 Universal Welding Interface (UWI) Fuses and Circuit Breakers........... 46
Table 5-6 COMARC III Fuses and Circuit Breakers............................................ 46
Page 9

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 1 MOTOMAN
1.0 INTRODUCTION
The ArcWorld 6000 is part of the ArcWorld family of standardized arc welding
solutions. It is a fully integrated welding system, and is supported from wire to
weld by Motoman, Inc.
The ArcWorld 6000 features a Motoman arc welding robot and MRC controller
with menu-driven arc welding application software, complete welding package,
180˚ reciprocating positioner, operator interface, and total safety environment.
1.1 ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT
This manual provides operation instructions for the ArcWorld 6000 system. In
addition to this introduction, the manual includes the following sections:
• Section 2: Safety
• Section 3: Description of Equipment
• Section 4: Operation
• Section 5: Maintenance
• Appendices
The Safety Section of the manual provides information regarding the safe use and
operation of the ArcWorld 6000 system.
Section 3 of this manual provides a detailed description of the major components of
the ArcWorld system. This section includes a table of component specifications.
The Operation Section of the manual provides instructions to operate the ArcWorld
system. In this section, we describe the various operator controls and indicators.
We also provide procedures for start-up, loading, normal operation, fault recovery,
and shut-down. Finally, the section contains a number of sample robot programs.
In the Maintenance Section, you will find a table listing periodic maintenance
requirements for the ArcWorld 6000 cell. This section includes detailed
instructions to perform specific maintenance tasks. It also includes a list of
recommended spare parts.
Appendix A is a Risk Assessment document. The remaining appendices to this
manual contain a full set of reference drawings.
1.2 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The ArcWorld 6000 provides a complete arc welding solution in a standardized
configuration. The system is designed around a Motoman arc welding robot and
includes a complete welding package. A dual ferris-wheel positioner allows an
Page 10
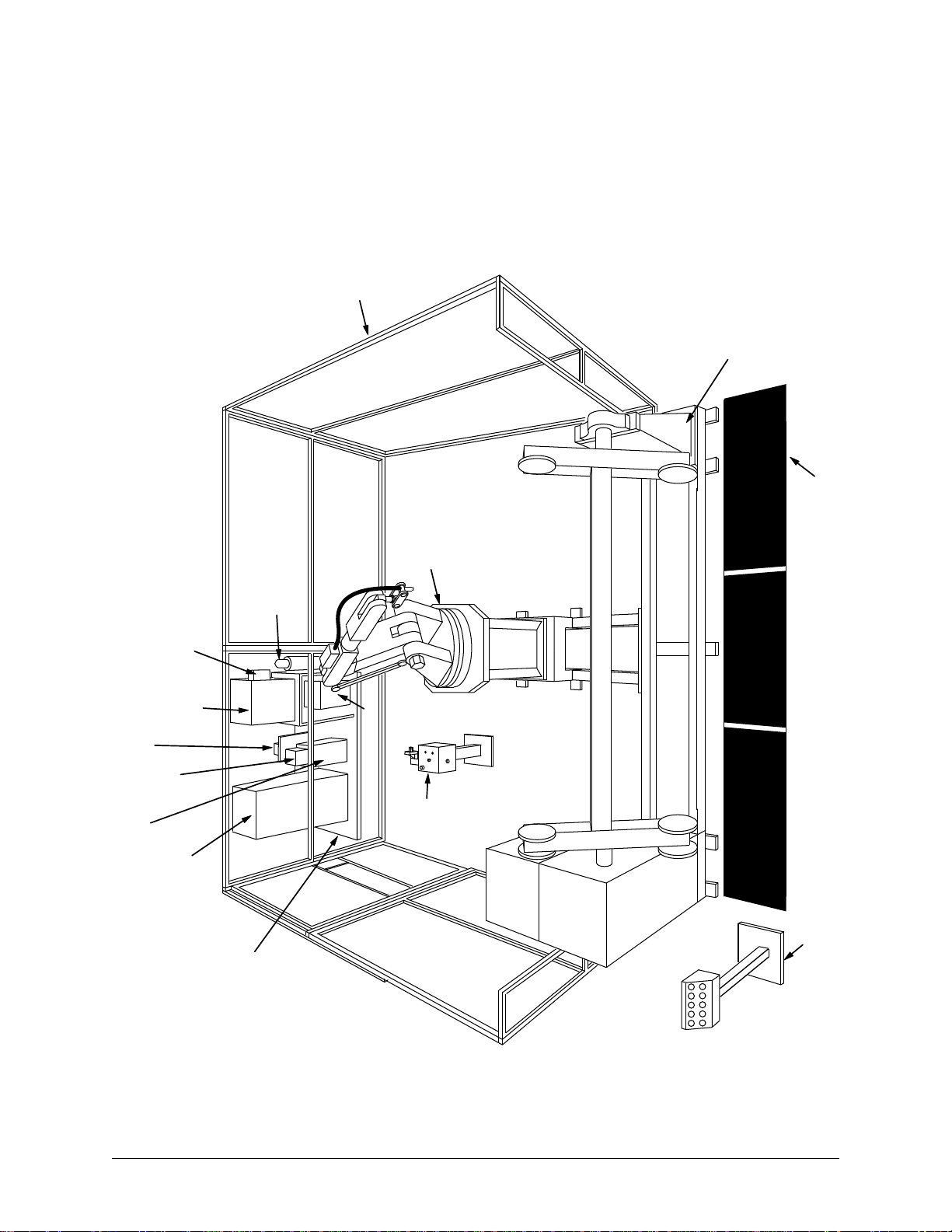
ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 2 MOTOMAN
operator to prepare and set up parts on one side while the robots weld on the other
side. The cell provides a full complement of safety features designed to protect
both personnel and equipment.
Assembled
Fence
Robot
Auxiliary
Equipment
Common Base
Operator
Station
Positioner
Gas Bottle
(customer supplied)
Safety Mats
MRC
Cabinet
Water
Circulator
Disconnect
Disconnect
Transformer
Com-Arc
Welding
Power
Source
Torch
Tender
Page 11

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 3 MOTOMAN
Figure 1-1 System Layout
Page 12

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 4 MOTOMAN
1.2.1 System Layout
The illustration in Figure 1-1 shows the system layout for the ArcWorld 6000 cell.
The ArcWorld 6000 includes the following major components:
• Motoman robot manipulator and MRC controller
• MRM2 series dual ferris-wheel positioner
• Master operator station
• Welding equipment, including the following:
• Excel-Arc welding power source
• Torch (water-cooled or air-cooled)
• Wire feeder
• Welding interface
• Torch breakaway
• Safety equipment, including the following:
• Safety fencing with arc curtains
• Interlocked safety mats
• Interlocked cell door
• Positioner arc screen
The MRC controller and welding power source share a common base. Additional
auxiliary components, such as the COMARC unit and water circulator, can be
located on this base as well. The robotic cell is fully enclosed by safety fencing and
an interlocking door. Safety mats prevent positioner cycling while anyone stands in
front of the positioner. All operator controls, including those on the MRC and
welding power supply, are accessible from outside of the robotic enclosure.
1.2.2 Optional Equipment
The following optional equipment is available for use with the ArcWorld 6000:
• Torch tender
• Wire cutter
• COMARC III
• Heavy duty positioners
• Stationary tables
Page 13

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 5 MOTOMAN
1.3 REFERENCE TO OTHER DOCUMENTATION
For additional information refer to the following:
• Motoman K10 MRC Manipulator Manual (Part Number 132330-7)
• Motoman K6 MRC Manipulator Manual (Part Number 132330-4)
• Motoman MRC Operator's Manual for Arc Welding (Part Number 132332-1)
• Motoman MRC User Functions Manual (Part Number 132331-1)
• Motoman ArcWorld 6000 Installation Manual (Part Number 132341-7)
• Motoman RM2-250SE2 Manual (Part Number TT-503.8)
• Motoman RM2-500SE2 Manual (Part Number TT-504.2)
• Additional vendor's manuals
1.4 CUSTOMER SERVICE INFORMATION
If you are in need of technical assistance, contact the Motoman service staff at
(513) 847-3200. Have the following information ready before you call:
• Robot Type (K3, K6, K10, etc.)
• Robot Serial Number (located on the back side of the robot arm)
• Application Type (palletizing, welding, handling, etc.)
• Robot Sales Order Number (located on back side of robot and MRC controller)
Page 14

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 6 MOTOMAN
2.0 SAFETY
It is the purchaser's responsibility to ensure that all local, county, state, and national
codes, regulations, rules, or laws relating to safety and safe operating conditions for
each installation are met and followed.
We suggest that you obtain and review a copy of the ANSI/RIA National Safety
Standard for Industrial Robots and Robot Systems. This information can be
obtained from the Robotic Industries Association by requesting ANSI/RIA
R15.06. The address is as follows:
Robotic Industries Association
900 Victors Way
P.O. Box 3724
Ann Arbor, Michigan 48106
TEL: 313/994-6088
FAX: 313/994-3338
Ultimately, the best safeguard is trained personnel. The user is responsible for
providing personnel who are adequately trained to operate, program, and maintain
the robot cell. The robot must not be operated by personnel who have not
been trained!
We recommend that all personnel who intend to operate, program, repair, or use
the robot system be trained in an approved Motoman training course and become
familiar with the proper operation of the system.
This safety section addresses the following:
• Standard Conventions (see Section 2.1)
• General Cautions and Warnings (see Section 2.2)
• Mechanical Safety Devices (see Section 2.3)
• Installation Safety (see Section 2.4)
• Programming Safety (see Section 2.5)
• Operation Safety (see Section 2.6)
• Maintenance Safety (see Section 2.7)
Page 15

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 7 MOTOMAN
2.1 STANDARD CONVENTIONS
This manual includes information essential to the safety of personnel and
equipment. As you read through this manual, be alert to the four signal words:
• DANGER
• WARNING
• CAUTION
• NOTE
Pay particular attention to the information provided under these headings which are
defined below (in descending order of severity).
➪
DANGER!
Information appearing under the DANGER caption concerns the
protection of personnel from the immediate and imminent
hazards that, if not avoided, will result in immediate, serious
personal injury or loss of life in addition to equipment damage.
➪
WARNING!
Information appearing under the WARNING caption concerns the
protection of personnel and equipment from potential hazards
that can result in personal injury or loss of life in addition to
equipment damage.
➪
CAUTION!
Information appearing under the CAUTION caption concerns the
protection of equipment, software, and data from hazards that
can result in minor personal injury or equipment damage.
NOTE: Information appearing in a NOTE caption provides additional information which is helpful in
understanding the item being explained.
Page 16

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 8 MOTOMAN
2.2 GENERAL SAFEGUARDING TIPS
All operators, programmers, plant and tooling engineers, maintenance
personnel, supervisors, and anyone working near the robot must become
familiar with the operation of this equipment. All personnel involved with the
operation of the equipment must understand potential dangers of operation.
General safeguarding tips are as follows:
• Improper operation can damage the equipment. Only trained personnel familiar
with the operation of this robot, the operator's manuals, the system equipment,
and options and accessories should be permitted to operate this robot system.
• Do not enter the robot cell while it is in operation. Place the robot in
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) mode and ensure that all motion has stopped before
entering the cell.
• Improper connections can damage the robot. All connections must be made
within the standard voltage and current ratings of the robot I/O (Inputs and
Outputs).
• The robot must be placed in Emergency Stop (E-Stop) mode whenever it is not
in use.
2.3 MECHANICAL SAFETY DEVICES
The safe operation of the robot, positioner, auxiliary equipment, and system is
ultimately the user's responsibility. The conditions under which the equipment will
be operated safely should be reviewed by the user. The user must be aware of the
various national codes, RIA safety recommendations, and other local codes that
may pertain to the installation and use of industrial equipment. Additional safety
measures for personnel and equipment may be required depending on system
installation, operation, and/or location. The following safety measures are available:
• Safety fences and barriers
• Light curtains
• Door interlocks
• Safety mats
• Floor markings
• Warning lights
Check all safety equipment frequently for proper operation. Repair or replace any
non-functioning safety equipment immediately.
Page 17

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 9 MOTOMAN
2.4 INSTALLATION SAFETY
Safe installation is essential for protection of people and equipment. The user must
be aware of the various national codes, RIA safety recommendations, and other
local codes that may pertain to the installation and use of industrial equipment.
Additional safety measures for personnel and equipment may be required
depending on system installation, operation, and/or location. The following
suggestions are intended to supplement, but not replace, existing federal, local, and
state laws and regulations.
• Ensure that only trained personnel familiar with the operation of this robot, the
operator's manuals, the system equipment, and options and accessories are
permitted to operate this robot system.
• Identify the work envelope of each robot with floor markings, signs, and
barriers.
• Position all controllers outside the robot work envelope.
• Whenever possible, install safety fences to protect against unauthorized entry
into the work envelope.
• Eliminate areas where personnel might get trapped between a moving robot and
other equipment (pinch points).
• Provide sufficient room inside the workcell to permit safe teaching and
maintenance procedures.
2.5 PROGRAMMING SAFETY
All operators, programmers, plant and tooling engineers, maintenance personnel,
supervisors, and anyone working near the robot must become familiar with the
operation of this equipment. All personnel involved with the operation of the
equipment must understand potential dangers of operation. General safeguarding
tips are as follows:
• Any modifications to ladder nodes, parts 1 and 2 of the controller PLC can
cause severe personal injury or death, as well as damage to the robot! Do not
make any modifications to the ladder. Making any changes without the written
permission of Motoman will VOID YOUR WARRANTY!
• Some operations require standard passwords and some require special
passwords. Special passwords are for Motoman use only. YOUR
WARRANTY WILL BE VOID if you use these special passwords.
• Back up all programs and jobs onto a floppy disk whenever program changes
are made. To avoid loss of information, programs, or jobs, a backup must
always be made before any service procedures are done and before any changes
are made to options, accessories, or equipment.
• The concurrent I/O (Input and Output) function allows the customer to modify
the internal ladder inputs and outputs for maximum robot performance. Great
Page 18

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 10 MOTOMAN
care must be taken when making these modifications. Double-check all
modifications under every mode of robot operation to ensure that you have not
created hazards or dangerous situations that may damage the robot or other
parts of the system.
• Improper operation can damage the equipment. Only trained personnel familiar
with the operation, manuals, electrical design, and equipment interconnections
of this robot should be permitted to operate the system.
• Inspect the robot and work envelope to ensure no potentially hazardous
conditions exist. Be sure the area is clean and free of water, oil, debris, etc.
• Ensure that all safeguards are in place.
• Check the E-STOP button on the teach pendant for proper operation before
programming.
• Keep the teach pendant with you when you enter the workcell.
• Ensure that only the person holding the teach pendant enters the workcell.
• Test any new or modified program at low speed for at least one full cycle.
2.6 OPERATION SAFETY
All operators, programmers, plant and tooling engineers, maintenance personnel,
supervisors, and anyone working near the robot must become familiar with the
operation of this equipment. All personnel involved with the operation of the
equipment must understand potential dangers of operation. General safeguarding
tips are as follows:
• Check all safety equipment for proper operation. Repair or replace any nonfunctioning safety equipment immediately.
• Inspect the robot and work envelope to ensure no potentially hazardous
conditions exist. Be sure the area is clean and free of water, oil, debris, etc.
• Ensure that all safeguards are in place.
• Improper operation can damage the equipment. Only trained personnel familiar
with the operation, manuals, electrical design, and equipment interconnections
of this robot should be permitted to operate the system.
• Do not enter the robot cell while it is in operation. Place the robot in
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) mode and ensure that all motion has stopped before
entering the cell.
• The robot must be placed in Emergency Stop (E-Stop) mode whenever it is not
in use.
• This equipment has multiple sources of electrical supply. Electrical
interconnections are made between the controller, external servo box, and other
equipment. Disconnect and lockout/tagout all electrical circuits before making
any modifications or connections.
• All modifications made to the controller will change the way the robot operates
and can cause severe personal injury or death, as well as damage the robot.
Page 19

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 11 MOTOMAN
This includes controller parameters; ladder nodes, parts 1 and 2; and I/O (Input
and Output) modifications. Check and test all changes at slow speed.
Page 20

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 12 MOTOMAN
2.7 MAINTENANCE SAFETY
All operators, programmers, plant and tooling engineers, maintenance personnel,
supervisors, and anyone working near the robot must become familiar with the
operation of this equipment. All personnel involved with the operation of the
equipment must understand potential dangers of operation. General safeguarding
tips are as follows:
• Do not perform any maintenance procedures before reading and understanding
the proper procedures in the appropriate manual.
• Check all safety equipment for proper operation. Repair or replace any nonfunctioning safety equipment immediately.
• Improper operation can damage the equipment. Only trained personnel familiar
with the operation, manuals, electrical design, and equipment interconnections
of this robot should be permitted to operate the system.
• Back up all your programs and jobs onto a floppy disk whenever program
changes are made. A backup must always be made before any servicing or
changes are made to options, accessories, or equipment to avoid loss of
information, programs, or jobs.
• Do not enter the robot cell while it is in operation. Place the robot in
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) mode and ensure that all motion has stopped before
entering the cell.
• The robot must be placed in Emergency Stop (E-Stop) mode whenever it is not
in use.
• Ensure all safeguards are in place.
• Use proper replacement parts.
• This equipment has multiple sources of electrical supply. Electrical
interconnections are made between the controller, external servo box, and other
equipment. Disconnect and lockout/tagout all electrical circuits before making
any modifications or connections.
• All modifications made to the controller will change the way the robot operates
and can cause severe personal injury or death, as well as damage the robot.
This includes controller parameters; ladder nodes, parts 1 and 2; and I/O (Input
and Output) modifications. Check and test all changes at slow speed.
• Improper connections can damage the robot. All connections must be made
within the standard voltage and current ratings of the robot I/O (Inputs and
Outputs).
Page 21

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 13 MOTOMAN
3.0 DESCRIPTION OF EQUIPMENT
3.1 K-SERIES ROBOT DESCRIPTION
The standard ArcWorld 6000 uses either a Motoman K6 or K10 robot
manipulator. The Motoman K6 and K10 robots and YASNAC MRC Controller
represent state-of-the-art technology in robotics today. The six-axis K6 robots have
a payload of 6 kg (13.2 lbs). They feature a 1,322 mm (52.01 in.) reach and have a
relative positioning accuracy of ± 0.1 mm (0.004 in.). The six-axis K10 robots
have a payload of 10 kg (22 lbs). They feature a 1,555 mm (61.2 in.) reach and
have a relative positioning accuracy of ± 0.1 mm (0.004 in.).
Each robot can reach below its own base as well as behind itself. These robots can
also be mounted in floor, wall, or ceiling configurations with few hardware
modifications. The Motoman K-Series robots have been constructed for ease of
maintenance, utilizing brushless AC servo motors with absolute positioning
encoders. All motors are readily accessible. A combination of capacitance and
lithium batteries in both the robot encoder assemblies and in the Motoman
YASNAC MRC controller protects program position data for up to one year. The
replacement life for the lithium battery is approximately three years.
3.2 MRC CONTROLLER
The MRC controller (Figure 3-1) coordinates the operation of the ArcWorld
system. It provides the following control functions:
• User interface
• Main logic functions
• Input / output control
• Servo control
• Numeric processing
• Variable data memory
• Program and constant data memory
• Analog welding command functions
• Welding interface
• Power distribution
The MRC controls the movement of the manipulators, processes input and output
signals, controls the operation of the welding power supply, and provides the
signals to operate the welding system. It maintains variable data and performs the
numeric processing to convert to and from different coordinate systems.
Page 22
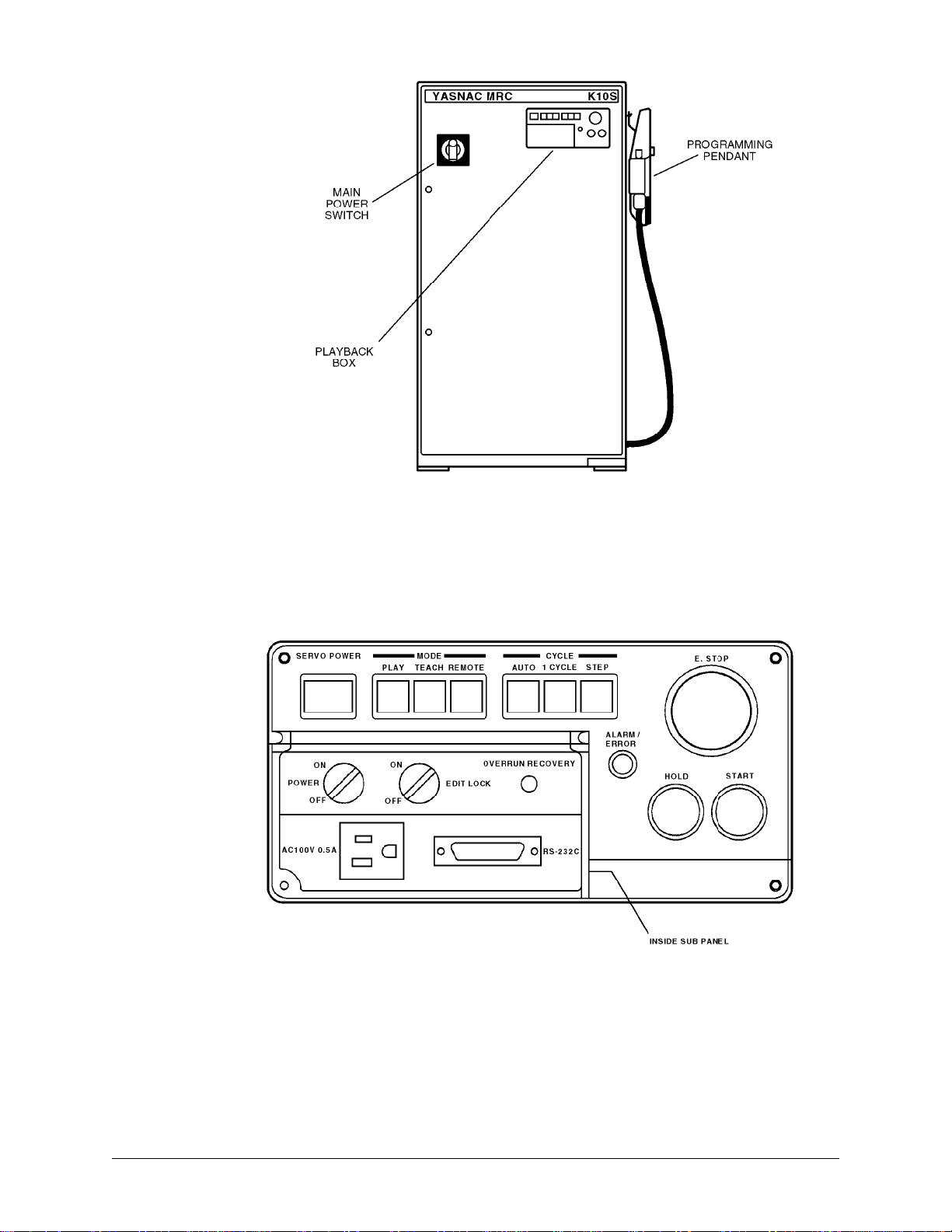
ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 14 MOTOMAN
Figure 3-1 MRC Controller
The playback box (Figure 3-2) on the MRC has the primary system controls. The
following paragraphs describe the MRC controls.
Figure 3-2 MRC Playback Box
3.2.1 Servo Power
The SERVO POWER pushbutton switch turns on the robot servo power. An
indicator lamp in the switch lights when servo power is on.
Page 23

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 15 MOTOMAN
3.2.2 Mode Select
The Mode Select pushbutton switches (PLAY, TEACH, and REMOTE) set the
robot's mode of operation. Indicator lamps in the Mode Select switches light to
show the current mode of operation. Refer to your MRC Operator's Manual for
more information.
3.2.3 Cycle Select
The Cycle Select pushbutton switches (AUTO, 1-CYCLE, and STEP) set the
operating method for playback operations. Indicator lamps in the Cycle Select
switches light to show the selected playback method. Refer to your MRC
Operator's Manual for more information.
3.2.4 Emergency Stop
The E. STOP button is connected to the system emergency stop circuit.
Interrupting the E-Stop circuit causes the robot to go into the E-Stop condition.
Pressing the E. STOP pushbutton immediately turns off servo power.
3.2.5 Alarm / Error
The ALARM / ERROR indicator lights whenever an alarm or error condition
occurs. After you reset the alarm or error condition, the indicator lamp goes off.
3.2.6 Hold
The HOLD button is a normally closed, momentarily actuated switch. Pressing the
HOLD button stops the operation of the manipulator. The Hold state is active only
while the switch is held down. The indicator lamp lights whenever the robot is in a
Hold state. Refer to your MRC Operator's Manual for more information.
3.2.7 Start
Pressing the START button causes the manipulator playback operation to start.
The indicator lamp lights during playback.
3.2.8 Playback Box Sub-Panel
The playback box has an inside sub-panel that contains additional user controls.
Refer to your MRC Operator's Manual for more information.
Page 24
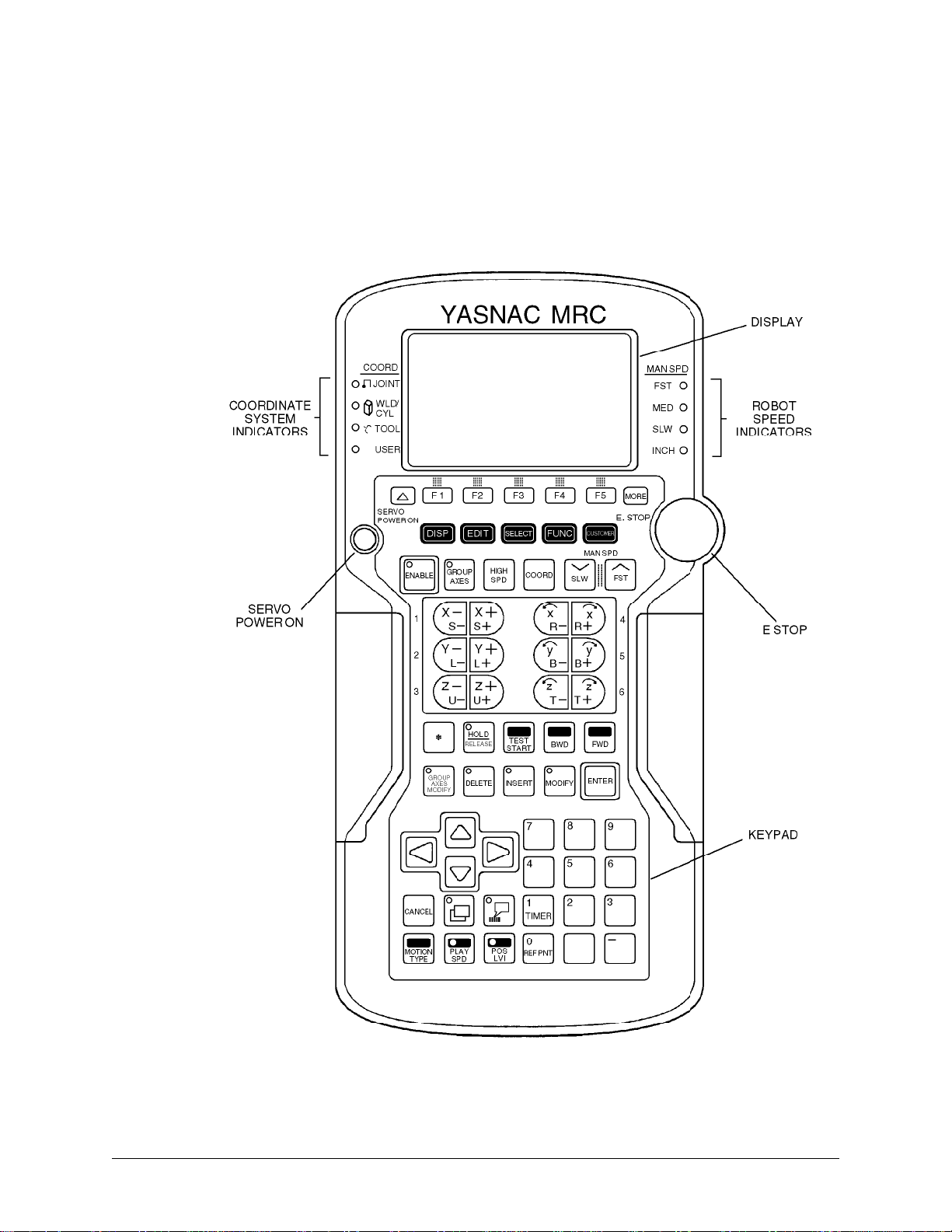
ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 16 MOTOMAN
3.3 PROGRAMMING PENDANT
A programming pendant (Figure 3-3) provides the primary user interface with the
system. The pendant has a 12-line LCD display and keypad. The system uses the
INFORM II robot language and a menu driven interface to simplify operator
interaction with the robot. By using the pendant, the operator can teach robot
motion, and perform programming, editing, maintenance, and diagnostic functions.
Figure 3-3 Programming Pendant
Page 25

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 17 MOTOMAN
3.3.1 Display
The programming pendant has a 12-line LCD display. The display provides status
information, system messages and prompts, and a graphic work area. Refer to
your MRC Operator's Manual for more information.
3.3.2 Robot Speed Indicators
The MAN SPD indicators light to show the selected robot manipulator speed.
3.3.3 Emergency Stop
The E. STOP button is connected to the system emergency stop circuit.
Interrupting the E-Stop circuit causes the robot to go into the E-Stop condition.
Pressing the E. STOP pushbutton immediately turns off servo power.
3.3.4 Keypad
The user keypad on the programming pendant serves as an input device. The keys
are grouped into different functional sections to simplify operator use. For more
information, refer to your MRC Operator's Manual.
3.3.5 Servo Power
The SERVO POWER pushbutton switch turns on the robot servo power. An
indicator lamp in the switch lights when servo power is on.
3.3.6 Coordinate System Indicators
The COORD indicators light to show the currently active coordinate system.
3.4 MRM2-SERIES POSITIONER
The ArcWorld 6000 cell uses one of two different reciprocating positioners: the
MRM2-550 or the MRM2-1100. The MRM2-Series positioners are AC servo
controlled by the master robot to provide coordinated motion while welding or
between welds. The standard distance between the headstock and tailstock
faceplates on the MRM2-550 positioner is 2.6 meters (approximately 102"). The
standard distance between the headstock and tailstock faceplates on the MRM21100 positioner is 3.0 meters (approximately 118").
The load side of the positioner is fixed for loading and unloading parts. The
patented servo motor design of this ferris-wheel type positioner is used to sweep
the positioner workstations into and out of the robot envelope.
Page 26

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 18 MOTOMAN
A fixture frame is typically mounted between the headstock and tailstock faceplates.
Fixtures are either mounted on or integrated to these frames for positioning and
clamping of production parts. Pneumatic and electrical signals can be run to the
fixtures if required. Depending on part size(s) and weight(s), single, multiple, or a
combination of parts can be mounted to the fixture frame to provide a highly
flexible system.
3.4.1 Part / Fixture Rating
The combined weight of the part(s) and fixture(s) on each side of the MRM2-550
reciprocating positioner is 550 pounds (1100 pounds total). The maximum offset
load for the MRM2-550 is 375 pounds. The positioner will not sweep if the load
on one side is more than 375 pounds heavier than the load on the other side.
The combined weight of the part(s) and fixture(s) on each side of the MRM2-1100
reciprocating positioner is 1100 pounds (2200 pounds total). The maximum offset
load for the MRM2-1100 is 639 pounds. The positioner will not sweep if the load
on one side is more than 639 pounds heavier than the load on the other side.
3.4.2 Swing Diameter
The maximum swing diameter for a part on the MRM2-550 positioner is 0.98
meters (approximately 37.4"). The maximum swing diameter for a part on the
MRM2-1100 positioner is 1.1 meters (approximately 43.3").
3.4.3 Temperature Operating Range
40 - 110˚ Fahrenheit.
3.4.4 Humidity
Non-condensing 10 - 90% relative humidity.
NOTE: In high humidity areas, the tooling plate may rust or corrode. Surface protection should be
used.
3.4.5 Shock Rating
Less than 0.5 G.
Page 27

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 19 MOTOMAN
3.4.6 Sweep Speed
Torque Time
MRM2-550 1000 N.m 4 sec
MRM2-1100 2000 N.m 5 sec
3.4.7 Servo Head Stock Speed
Torque Speed
MRM2-550 1050 N.m 0 - 16.8 rpm
MRM2-1100 1050 N.m 0 - 16.8 rpm
3.4.8 Air Requirements
80 psi minimum.
3.4.9 Electrical Requirements
The MRC controller supplies the electrical power required to operate the 180˚
reciprocating positioners. These requirements consists of a 24 VDC interface
circuit, and a 208 VAC, 6.2 amp circuit for the MRM2-550 motor and drive, or a
208 VAC, 9.0 amp circuit for the MRM2-1100 motor and drive.
3.4.10 Welding Current Rating
The MRM2 positioners have a welding current capacity of 700 amperes at 100%
duty cycle. The welding ground system consists of a spring loaded copper brush
that contacts a large ring mounted behind the surface of the faceplate. The ground
cable to the welding power source is connected to the ground stud located on the
right side of the positioner base when facing the back of the ArcWorld 6000 cell.
3.4.11 Locking Pins
The MRM2-1100 positioner has sweep lock drive pins and fixture locking pins for
positioner Side A and Side B. There are two of each on the MRM2-1100. The
sweep lock pins keep the sweep axis from turning while the servo advances and
withdraws. The fixture locking pins are spring loaded, so when the servo
withdraws, the pins engage. This keeps the headstock from turning when the servo
motor retracts.
Page 28

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 20 MOTOMAN
3.4.12 Arc Shield
The MRM2 positioners are provided with a sheet metal screen for arc radiation
protection between the operator loading zone and the welding zone. Do not operate
this equipment unless the arc shield is in place.
3.5 OP-STATION
The operator control station (Figure 3-4) includes a NEMA enclosure on a standalone pedestal. The following paragraphs describe each of the Op-station controls.
ALARM
RESET
ROBOT HOLD
MASTER JOB
START
MOTOMAN
STATION READY
POSITIONER
AUTO/MAN
SERVO ON
ESTOP
OPERATOR STATION
ENABLE/DISABLE
WARNING!
CYCLE START
CYCLE START
3.5.1 Emergency Stop
Figure 3-4 Operator Control Panel (Op-Station)
The operator station E-STOP, the robot E-STOP, the air pressure switch, the
sliding door interlocks, and the ArcWorld 6000 safety mats are connected in series
in the Emergency Stop circuit. If the E-Stop circuit is interrupted, the robots and
the MRM2 positioner go into the E-Stop condition. The operator station E-STOP
light comes on when the E-STOP button is pressed. In the E-Stop condition,
power to the positioner interface is removed. This stops the positioner sweep.
Page 29

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 21 MOTOMAN
3.5.2 Hold
The operator station HOLD button is a normally closed pushbutton and is
connected to the MRC to cause the robots to go into the Hold condition when the
button is pressed.
3.5.3 Cycle Start
The palm buttons in the operator station use an anti tie-down technique for robot
input. The anti tie-down timer is set for 10 seconds. Holding the palm buttons
down for more than 10 seconds, causes the timer to time out and prevents the input
from reaching the robot. The CYCLE START buttons are connected to robot Input
#1.
3.5.4 Station Ready
The STATION READY lamp is interlocked with the robot CUBE #1 output. The
robot Output #1 turns on the STATION READY lamp.
3.5.5 Alarm
The ALARM lamp is connected to the robot Alarm Occurrence output. The
ALARM lamp turns on when one of the robots encounters a major or minor alarm
condition. The ALARM lamp also lights when the positioner is not reset.
3.5.6 Servo On
The SERVO ON pushbutton is connected to the robot Servo On input. The robot
servo motors will turn on when the SERVO ON pushbutton is pressed and an EStop condition does not exist.
3.5.7 Positioner Auto / Manual
The POSITIONER AUTO / MANUAL selector switch is used to select Automatic
or Manual Mode for the MRM2 positioner. The selector switch is connected to
robot Input #2. When the selector switch is in the Automatic position, the robots
process the part after the positioner sweeps. In Manual Mode, the robot does not
process the part after the positioner sweeps. This function is dependent on the
structure of the master job.
3.5.8 Master Job Start
The MASTER JOB START pushbutton is connected to the robot external start
input. The robot will start the current active job when pressed if the robot is in Play
Mode and the servo motors are on.
Page 30

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 22 MOTOMAN
3.5.9 Operator Station Enable / Disable
The OPERATOR STATION ENABLE / DISABLE selector switch is used to
transfer primary control of the ArcWorld cell from the MRC to the Op-Station.
The REMOTE MODE button on the MRC playback box lights when the opstation is enabled. Most programming pendant functions are disabled.
3.5.10 Reset
The RESET pushbutton is connected to the robot alarm reset input. Any alarm or
error condition will be cleared when this button is pressed. In addition, the RESET
pushbutton and the RIGHT CYCLE START pushbuttons are interlocked and,
when pressed simultaneously, enable the MRM2 positioner if the robot servo
motors are on. The positioner needs to be enabled at initial power up, or after an
emergency stop or shock sensor condition.
3.6 WELDING POWER SOURCE
The Excel-Arc power source (Figure 3-5) is a constant voltage transformer-rectifier
type welding machine. It provides volt-current characteristic curves that are
essentially flat. This power source can be used with most MIG applications from
thin sheet metal to heavy gauge plate.
3.6.1 Main Power
The Input Power Switch (7) turns on the main power to the Excel-Arc unit. The
main power must be on before any other section of the power source can operate.
The pilot light (1) illuminates when main power is on.
3.6.2 Volt / Amp Settings
The Welding Voltage / Amperes Control (2) adjusts the welding output and open
circuit voltage. The Volt / Amp Meter and Switch (3) display either DC voltage or
DC current depending on the position of the switch. Refer to your Excel-Arc
manual for additional information.
3.6.3 Terminal Connectors
The two terminals on the front of the Excel-Arc power source serve as connection
points for the welding leads. The Positive Terminal (4) connects positive welding
lead (to the wire feeder). The Negative Terminal (5) connects to the negative
welding lead (to the positioner).
Page 31

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 23 MOTOMAN
3.6.4 Local / Remote Operation
The Local / Remote Output Control Selector Switch (6) sets the mode of operation
for the power source. For ArcWorld applications this switch should be set to
REMOTE. Refer to your Excel-Arc manual for additional information.
Figure 3-5 Excel-Arc Controls
Page 32

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 24 MOTOMAN
3.6.5 Feeder Control Receptacles
The Feeder Control Receptacle Panel (8) located in the back of the power source
provides connectors for use with remote voltage control applications. For
ArcWorld applications, the MRC connects to the 19-pin connector.
3.6.6 Circuit Breakers
The Excel-Arc power source uses two 10 amp circuit breakers (9 and 10). One
circuit breaker protects the 24 volt circuit, the other protects the 115 volt circuit.
3.6.7 AC Receptacles
The Excel-Arc unit has two standard 115 V AC Receptacles (11). These provide
auxiliary power at a maximum current of 10 amps. For applications using the
water-cooled torch, the water circulator plugs into one of these receptacles.
3.7 WELDING EQUIPMENT
In addition to the Excel-Arc power sources, the ArcWorld 6000 system provides a
complete complement of arc welding equipment. In its standard configuration, the
ArcWorld system includes the following:
• PWF-600 wire feeder
• UWI welding interface
• Either an air cooled or water cooled MIG torch
• Torch breakaway mount
3.7.1 PWF4 Wire Feeder
The PWF4 wire feeder mounts on the robot arm. This 4-roll wire feeder provides
reliable wire feeding at rates up to 750 IPM. An integral gas valve provides fast
gas response time. The PWF4 feeder has an inch forward button to help simplify
set-up and reduce change-over time. The PWF4 wire feeder uses interchangeable
feed rolls to accommodate different types and sizes of wire.
3.7.2 Universal Welding Interface (UWI)
The UWI interface provides microprocessor control to the wire feeder and power
source. It scales the signals from the MRC to the appropriate levels required for
control of the welding components. It also provides isolation of the power source
analog signals.
Page 33

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 25 MOTOMAN
3.7.3 MIG Torch
The ArcWorld 6000 uses either an air-cooled or water-cooled robotic/automatic
MIG torch. These are heavy-duty torches designed for quick replacement while
requiring minimum robot reprogramming. The MIG torch mounts on the end of
the robot wrist. For applications that use the water-cooled torch, the ArcWorld
6000 includes a suitable water circulator kit.
3.7.4 RAM Breakaway Mount
A Motoman RAM torch breakaway mount protects the robot, workpiece, fixture,
and positioner. It provides multi-directional impact detection, including Z-axis
collisions. The torch breakaway causes the robot to stop immediately upon impact.
Keyed joints assure accurate re-alignment of components.
3.8 SAFETY EQUIPMENT
The ArcWorld 6000 system incorporates a host of safety equipment. When all
standard safety precautions are taken, the safety equipment helps to ensure safe
operation of the robotic cell. The ANSI/RIA R15.06 Robot Safety Standard
stipulates the user is responsible for safeguarding.
Users are responsible for
determining whether the provided safeguards are adequate for plant
conditions. Users must also ensure that safeguards are maintained in
working order.
The ArcWorld 6000 safety features include the following:
• Arc screens
• Safety fencing
• Dual interlocking cell door
• Interlocked safety mats
• Emergency stop (E-STOP) buttons
3.8.1 Arc Screens
Two separate arc screens are used on the ArcWorld 6000. The first is a metal arc
screen on the turntable positioner. This screen blocks arc radiation and sparks from
the welding operation. The material used to cover the safety fencing of the entire
robotic cell acts as the second arc screen. This material reduces the amount of ultraviolet radiation that escapes from the robotic cell.
Page 34

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 26 MOTOMAN
➪
WARNING!
Although this screen blocks dangerous arc radiation, you should
not look directly at the arc during operation without protective
eyewear!
3.8.2 Fencing
The safety fencing provided with the ArcWorld 6000 encloses the entire robotic
cell. It forms a physical barrier to prevent entry into the robot envelope.
3.8.3 Interlocks
Dual safety interlocks on the cell entrance door prevent entry into the cell during
operation. The interlocks consist of a pull plug and magnetic door switch.
Opening the cell door with the robot in Play causes an E-Stop and shuts down the
entire system.
3.8.4 Safety Mats
The safety mat provided with the ArcWorld 6000 helps prevent serious injury to
anyone entering the positioner area during the sweeping process. If a person steps
on this mat when the positioner is in motion, an E-Stop occurs causing the entire
system to shut down.
3.8.5 Emergency Stops
In addition to the interlocking devices described above, the ArcWorld 6000 has
strategically placed emergency stops (E-STOPS). These are operator actuated
devices that, when activated, immediately cause the system to shut down. The
following is a list of their locations:
• The MRC control panel has one E-STOP button.
• The MRC programming pendant has one E-STOP button.
• The positioner operator station has one E-STOP button.
In addition, the following conditions also cause an emergency stop:
• Opening the cell door while the robot is in Play mode.
• Stepping on the safety mat while the positioner is sweeping.
• Loss of air system pressure.
• Activating the shock sensor.
Page 35

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 27 MOTOMAN
4.0 OPERATION
This section provides operation instructions for the ArcWorld 6000 system.
Operation procedures include the following:
• System start up
• Part set up
• Normal operation
• Fault recovery
• System shut down
We have included several sample programs. The listed programs demonstrate the
proper format and instruction sequences for different operations. You can use
these programs as guidelines when creating programs for your specific
applications.
4.1 OPERATION
The ArcWorld 6000 is a fully integrated robotic MIG welding cell. The robot
welds on one side of the 180˚ reciprocating positioner, while the operator loads
parts on the opposite side. Once the robot is finished with its process, it return to
the safe position. The operator can then initiate the positioner sweep enabling the
robot to start welding on the next part.
The safety door interlocks prevent anyone from entering the cell while the robot is
in Play Mode. If anyone steps on the safety mats in front of the part loading area
during the positioner sweep, an E-Stop occurs.
4.1.1 Start Up
To start up the ArcWorld 6000 from a power off condition, proceed as follows:
1. Turn on the MRC disconnect.
2. Turn on the power source disconnect.
3. Set the INPUT POWER switch on the welding power source to ON. The pilot
light should glow.
4. Set the Main Power switch on the MRC to ON.
5. Open the regulator valve on the welding gas supply.
6. Make sure that the enclosure door is closed and the safety plug is connected.
7. Press the TEACH MODE button on the MRC playback box. The indicator
lamp in the switch should light.
Page 36

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 28 MOTOMAN
8. Press the SERVO POWER button on the MRC playback box. The indicator
lamp in the switch should light.
9. Press the RESET button and the right CYCLE START button on the operator
station at the same time to initialize the positioner. The ALARM lamp goes off.
10. Use the programming pendant to move the robot to the starting position
(CUBE 1 position).
11. Call up the master job.
12. Press the PLAY MODE button on the MRC playback box, and then press the
AUTO CYCLE button. The indicator lamps in the switches should light.
13. Set the OPERATOR STATION ENABLE / DISABLE switch to the
ENABLE position.
14. Press the MASTER JOB START button on the operator station.
15. Wait for the STATION READY indicator to light.
The ArcWorld 6000 Cell is now ready for operation.
4.1.2 Loading / Unloading Procedures
The following is the typical sequence of operations for the ArcWorld 6000 Cell
after startup:
1. Load production parts on the fixtures located on the operator side of the MRM2
positioner.
2. Step off the safety mats and wait for the STATION READY indicator to light.
3. Press both CYCLE START palm buttons on the operator station to sweep the
positioner. This places the unwelded parts in the robot work envelope.
4. After the positioner sweeps, the robot begins the welding sequence on the parts.
Coordinated motion capabilities allow programming to rotate the parts on the
positioner, and weld or move the robot between welds at the same time.
5. Unload the welded parts from the fixture on the operator side.
6. Repeat Steps 1 through 5 to continue production.
4.1.3 Fault Recovery
Under varying conditions an alarm or error can occur. Clearing an alarm or error
condition may require different operator intervention depending on the nature of the
alarm or error. In some cases, simply resetting the robot and restarting the
operation is sufficient. In other instances, you must first remedy the condition
causing the alarm or error. Refer to paragraph 4.2, Alarms and Errors.
4.1.4 E-STOP Recovery
An E-Stop can occur under one of the following conditions:
Page 37

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 29 MOTOMAN
• Pressing the E-STOP button on the operator station, the programming pendant,
or the MRC terminal.
• Opening the sliding door on the robot enclosure or removing the safety plug
when the robot is not in Teach Mode.
• Stepping on the safety mat when the MRM2 positioner is sweeping.
• Activation of the shock sensor, indicating a robot crash.
• Loss of air system pressure.
To restart the ArcWorld 6000 Cell after an E-Stop condition occurs, follow the
procedure below.
1. To clear the E-Stop condition, do any of the following actions that apply:
• Release the E-STOP button on the operator station, the programming
pendant, or the MRC playback box.
• Close the sliding door and connect the safety plug.
• Step off the safety mat.
• Clear the Shock Sensor condition (refer to paragraph 4.1.5).
• Restore operating air pressure.
2. Press the SERVO ON button on the operator station.
➪
CAUTION!
Make sure the robots are in a clear position to continue motion.
A crash may occur if the robots cannot clear the part or fixtures
when they resume motion.
3. Press the RESET button and the right CYCLE START button on the operator
station to initialize the system.
4. Press the MASTER JOB START button on the operator station.
The ArcWorld 6000 Cell will continue its operation.
4.1.5 Shock Sensor Recovery
The ArcWorld welding package includes a RAM breakaway torch mount. This
mount is designed to protect the torch from damage in case of a crash. A slight
deflection of the torch activates a SHOCK SENSOR error. A more severe crash
separates the torch mount from the robot arm. The SHOCK SENSOR error is
factory set to an E-Stop condition.
To override the shock sensor, do the following:
1. Disconnect the shock sensor plug from the connector at the front of the wire
feeder (see Figure 4-1).
Page 38

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 30 MOTOMAN
2. Connect the shock sensor jumper (Motoman P/N 132601-1) to the connector at
the front of the wire feeder.
3. Press the RESET and right CYCLE START buttons on the operator's station at
the same time.
4. Use the programming pendant to operate the manipulator out of the impact
position.
5. Re-attach the sections of the torch breakaway mount if the impact caused them
to separate.
Feeder
Housing
Shock Sensor
Cord
Torch
Assembly
Breakaway
Shock
Sensor Plug
Shock Sensor
Jumper
Figure 4-1 Shock Sensor Override
To resume operation after clearing the Shock Sensor condition, proceed as follows:
1. Disconnect the shock sensor jumper from the connector at the front of the wire
feeder (see Figure 4-1).
➪
CAUTION!
You must remove the shock sensor jumper during normal
operation. Failure to do so can result in equipment damage.
2. Connect the shock sensor plug to the connector at the front of the wire feeder.
3. Close the interlocked enclosure doors.
4. Press the SERVO ON button on the MRC or programming pendant.
Page 39

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 31 MOTOMAN
5. Press the RESET and right CYCLE START buttons on the operator's station at
the same time. This initializes the positioner.
➪
CAUTION!
You may need to move the robot to recover from a crash. To avoid
another crash, make sure that the robot has a clear path to the
next step.
6. Press the MASTER JOB START button.
4.1.6 Shut Down
Use the following procedure to shut down the ArcWorld 6000 Cell after operation
is complete:
1. Make sure the robot is in the starting position (CUBE 1 position).
2. To turn off the robot servo motors, press the E-STOP button on either the
operator station, programming pendant, or MRC playback box.
3. Press the TEACH MODE button on the MRC playback box.
4. Set the MRC Main Power switch to the OFF position.
5. Turn off the MRC disconnect.
6. Set the INPUT POWER switch on the welding power source to the OFF
position.
7. Turn off the power source disconnect.
8. Close the regulator valve on the welding gas supply.
The ArcWorld 6000 Cell is now shut down.
4.2 ALARMS AND ERRORS
Alarms and errors will cause the program to stop. There are three levels of alarms
and errors: Error Messages, Minor Alarms, and Major Alarms.
For more detailed information about alarm recovery, refer to your Motoman MRC
Manipulator Manual.
4.2.1 Error Messages
These are simple errors such as pressing the START button when the robot is not
in Play mode, or enabling the programming pendant without the servo power being
live.
Page 40

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 32 MOTOMAN
Errors like these are cleared by pressing the CANCEL or ENABLE button on the
programming pendant.
4.2.2 Minor Alarms
Minor alarms are usually programming errors. Minor alarms might occur if a
circle has been programmed with fewer than three circular points, etc.
These alarms are cleared by pressing one of the following:
• RELEASE soft key on the programming pendant
• RESET button on the operator's station
• ENABLE button on the programming pendant twice
4.2.3 Major Alarms
Major alarms are hardware failures. Major alarms might occur because of a servo
tracking error or an abnormal speed associated with crashes.
To clear these alarms, you must turn off the controller and then turn it on again.
4.3 PROGRAMMING
The MRM2 positioner with its programmable axis offers a high degree of
programming flexibility. The robot can be programmed to weld a part with the
headstock stationary, or the robot and headstock can move simultaneously to weld
a part while turning.
You can program the robots independently (R1 job), the station axis independently
(S1 job), or robot and station axis together (R1 + S1). You must select the axis
combination when teaching the job initially. We recommend programming the
robot and station axis together (R1 + S1 jobs) to reduce the risk of interference.
➭
WARNING!
The positioner axis operates as another robot axis and has the
potential of hazardous motion.
➭
CAUTION
If the robot is working on a part and the headstock is not turning,
DO NOT assume that the headstock will not turn. The robot is
Page 41

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 33 MOTOMAN
executing programmed steps which could index the headstock at
any time.
NOTE: The ArcWorld 6000 robot S-axis is restricted by hard stops on the robot base and internal soft
stops. Do not change.
4.3.1 Cube Assignment
The system uses the Cube #1 Output as an interlock for sweeping. This is a
software zone around the tool center point (TCP). It should be defined with the
robot clear of the positioner sweep motion. The Cube #1 Output can be viewed in
diagnostics under Specified Outputs. To assign the K6 or K10 robot manipulator
position to Cube #1, refer to your MRC User Functions and Operator's Manuals.
Page 42

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 34 MOTOMAN
4.3.2 Sweeping Positioner to Side A
NOTE: Before sweeping, make sure the weight of parts and fixturing is approximately equal on Sides
A and B of the positioner. (Refer to paragraph 3.4.1.)
NOTE: Before sweeping at first power up, make sure the correct job has been loaded.
To sweep the Motoman MRM2 positioner to Side A:
1. Press the SERVO ON button on the operator station.
2. Make sure that the robot is in Cube #1 with the headstock in sweep position
(marks on headstock lined up, refer to your positioner manual).
3. Press the PLAY MODE button on the MRC playback box. The indicator lamp
in the switch should light.
4. If this is the first power up, or an E-Stop recovery, press the RESET button
and right CYCLE START button.
5. Press the MASTER JOB START button.
6. Press the CYCLE START palm buttons. The drive unit disengages the
headstock and engages the sweep axis.
7. The sweep axis locking pin retracts and the MRC moves the external sweep
axis (S1) 180˚ to align Side A.
8. The sweep locking pin engages.
9. The drive unit engages Side A.
When the positioner sweeps into position at Side A, the drive unit engages the
headstock. IN #9 turns off. Side B faces towards the operator, and IN #10, FIX. B
LOCK ON, turns on.
4.3.3 Sweeping Positioner to Side B
To sweep the Motoman MRM2 positioner to Side B:
1. Press the SERVO ON button on the operator station.
2. Make sure that the robots are in Cube #1 with the headstock in sweep position
(marks on headstock lined up, refer to your positioner manual).
3. Press the PLAY MODE button on the MRC playback box. The indicator lamp
in the switch should light.
4. If this is the first power up, or an E-Stop recovery, press the RESET button
and right CYCLE START button.
5. Press the MASTER JOB START button.
6. Press the CYCLE START palm buttons. The drive unit disengages the
headstock and engages the sweep axis.
Page 43

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 35 MOTOMAN
7. The sweep axis locking pin retracts and the MRC moves the external sweep
axis (S1) 180˚ to align Side B.
8. The sweep locking pin engages.
9. The drive unit engages Side B.
When the positioner sweeps into position at Side B, the drive unit engages the
headstock. IN #10 turns off. Side A faces towards the operator, and IN #9, FIX.
A LOCK ON, turns on.
4.3.4 Rotating Headstock
To rotate the Motoman MRM2 headstock:
1. Enable the programming pendant.
2. Press the GROUP AXES key and make sure the key LED lights.
3. Press the X+ or X- keys to move the headstock. Jog speed is set on the
programming pendant.
NOTE: The GROUP AXES key must be turned off to move the robots with the motion keys.
4.3.5 Programming
You can program three types of moves:
• Rotation of the positioner during air cut moves.
• Robot motion with positioner stationary.
• Rotation of the positioner during welding.
The job you create may consist of a combination of the above. The first two types
of moves assume a robot plus station group axis specification (R1 + S1). The last
type of move is called station synchronous and should be programmed with a
station plus robot group axis specification (S1 + R1).
Rotating the Positioner During Air Cut Moves
1. Teach the robot to the desired position.
2. Rotate the positioner to the desired position.
a. Press the GROUP AXES button on the programming pendant so LED is
on.
b. Press MAN SPEED button to select the desired axis speed while teaching.
c. Press the first set of motion keys, +X or -X, to move the axis in the desired
direction.
3. Record the step after designating the motion type and playback speed.
Page 44

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 36 MOTOMAN
4. Check the path with the STEP FWD/BWD keys. The position for the robot or
positioner may have to be altered to prevent torch interference.
➭
WARNING!
The positioner axis operates as another robot axis and has the
potential for hazardous motion.
NOTE: The GROUP AXES button must be turned off to move the robot.
NOTE: Normally, air cut moves are taught at Joint moves. The speed for Joint moves is specified as a
percentage of maximum speed (VJ=.01 - VJ=100.00). The axis which takes the longest time
to complete the programmed motion automatically determines the speed of the system. This
might be a wrist axis, a major robot axis, or the positioner axis. Cycle times can be reduced by
changing wrist orientation, robot position, and headstock position simultaneously between
program points rather than making the moves independently. Setting the speed at 100.00 will
normally establish the quickest time between steps.
Robot Motion with the Positioner Stationary
1. Program the robot position without moving the positioner axis.
2. Set motion type and speeds in the normal fashion.
Rotation of the Positioner During Welding
The MRC controller can coordinate motion with the external axis. This requires
calibration of the headstock and robot at the time of installation. Jobs programmed
for coordinated motion must be taught as S1 + R1 jobs.
Move instructions for coordinated motion are registered using the following
format:
Coordinated
motion instruction
SMOVL=138 Slave side
(manipulator with torch)
MOVL Master side
(positioner with workpiece)
In coordinated motion instructions, an "S" prefixes the instruction to the slave side.
Page 45

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 37 MOTOMAN
Converting Programs from Side A to Side B
The positioner uses the external axis to sweep the positioner in addition to driving
the headstock. This results in the external axis position being 180˚ offset from the
other side. This offset amount can be determined from the difference in the
external axis pulse counts at the two sweep positions. Software can be used to
modify the position of the external axis in a job copied to run on the opposite side.
1. Determine the pulse count difference of the external axis between Side A and
Side B.
2. Set the pulse count offset amount into an EX variable.
3. Make a copy of the original job. Designate the proper side in the original and
copied job name.
4. Use the Modify Position (MODPOS) function to change the position of the
external axis in the program.
5. Step through the new program to verify the path.
4.3.6 I/O Assignment
The ArcWorld 6000 positioner and ArcWorld operator station use the following
Motoman MRC user and dedicated inputs and outputs:
MRC User Inputs
IN#1 Cycle Start interlocked with Cube #1
IN#2 Auto/Manual Selector Switch
IN#9 Fixture A Lock On
IN#10 Fixture B Lock On
IN#11 Servo Drive Return
IN#12 Servo Drive Forward
IN#13 In Position (on MRM2-550 only)
IN#13 Sweep Lock On (on MRM2-1100 only)
IN#14 Sweep Lock Off (on MRM2-1100 only)
MRC User Outputs
OUT#1 Station Ready interlocked with Cube #1
OUT#4 Wire Cutter (optional)
OUT#9 Withdraw Servo
OUT#10 Advance Servo
Page 46

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 38 MOTOMAN
OUT#11 Sweep Lock On (on MRM2-1100 only)
OUT#12 Sweep Lock Off (on MRM2-1100 only)
In order to sweep the positioner, the robot must be in Cube #1, and OUT#1 of the
master robot must be ON to enable the operator station.
Page 47

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 39 MOTOMAN
MRC Dedicated Inputs
• External Emergency Stop
• External Over Travel
• External Servo On
• External Hold
• Anti-Tie Down
• External Start
• Alarm Reset
MRC Dedicated Outputs
• Servo On
• Alarm Occurrence
• Teach Mode
• Cube #1
For more information on the Motoman MRC User and Dedicated I/O, refer to the
MRC Controller I/O Structure Manual and MRC Dedicated I/O Guidelines
Manual.
4.4 SAMPLE JOBS
The following jobs are shown as examples only. Your system may have other
features and / or options requiring program changes. Double-check your system
before running these jobs. Lines that begin with an apostrophe (') are comments
added for clarification only and do not appear in the actual program listing.
4.4.1 Master Job (No Group Axes)
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 CALL JOB:SWEEPTOA IF IN#(09)=ON
002 TIMER T=0.20
003 CALL JOB:SWEEPTOB IF IN#(10)=ON
004 END
Page 48

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 40 MOTOMAN
4.4.2 Sweep to A Job (R1 + S1)
Lines 009 through 011, and lines 013 and 014 in the job listing below apply to the
systems using an MRM2-1100 positioner only.
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 001 MOVJ P050 EX052 VJ=25.00
'Program position with robot at safe position in Cube #1 and
headstock in sweep orientation.
002 DOUT OT#(1) ON
'Turn on Station Ready lamp on operator station.
003 WAIT IN#(01)=ON
'Wait for Cycle Start palm buttons.
004 WAIT IN#(09)=ON
'Verify that locking pin on Side A is engaged.
005 DOUT OT#(10) OFF
Turn off ADVANCE SERVO.
006 DOUT OT#(09) ON
'Turn on WITHDRAW SERVO to retract drive unit.
007 WAIT IN#(11)=ON
'Wait for SERVO DRIVE RTN input indicating the drive
unit is fully retracted.
008 WAIT IN#(10)=ON
'Wait for FIX B LOCK ON input to verify that the locking
pin has engaged the headstock.
009 DOUT OT#(11) OFF
'Turn off SWEEP LOCK ON output.
010 DOUT OT#(12) ON
'Turn on SWEEP LOCK OFF output to retract the locking
pin from the sweep axis.
011 WAIT IN#(14)=ON
'Wait for SWEEP LOCK OFF input to verify the sweep
locking pin has been retracted.
012 002 MOVJ P050 EX051 VJ=25.00 CONT
'The robot moves the external axis only, until Side A lines
up with the drive unit and the sweep locking pins.
013 DOUT OT#(12) OFF
Page 49

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 41 MOTOMAN
'Turns off the SWEEP LOCK OFF output.
014 DOUT OT#(11) ON
'Turns on the SWEEP LOCK ON output. This is necessary
to keep the sweep axis from turning.
015 WAIT IN#(13)=ON
'Wait for SWEEP LOCK ON input to verify that pin is
engaged.
016 DOUT OT#(09) OFF
'Turn off WITHDRAW SERVO output.
017 DOUT OT#(10) ON
'Turn on ADVANCE SERVO output to send the drive unit
forward to engage the headstock.
018 WAIT IN#(12)=ON
'Wait for SERVO DRIVE FORWARD input to verify the
drive unit is fully forward.
019 WAIT IN#(09)=OFF
'Wait for FIX A LOCK ON input to go off and verify that
the headstock locking pins have been retracted.
020 DOUT OT#(1) OFF
'Turn off the STATION READY lamp.
021 JUMP JOB:A-JOBS IF IN#(02)=ON
'Jump to the job for side A. It is important to use a job
Jump and not a Call instruction. Use Input #2 as a jump
condition. The job will execute only if the operator station
selector switch is set to AUTO.
022 RET
023 END
NOTE: The sweep positions are programmed in position variables. They are factory set and should not
require editing. Care should be taken not to use these variables in other programs. You can
edit position variables from the file display.
Page 50

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 42 MOTOMAN
4.4.3 Sweep to B Job
Lines 008 through 010, and lines 013 and 014 in the job listing below apply to the
systems using an MRM2-1100 positioner only.
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 001 MOVJ P050 EX051 VJ=25.00
002 DOUT OT#(1) ON
003 WAIT IN#(01)=ON
004 WAIT IN#(10)=ON
005 DOUT OT#(10) OFF
006 DOUT OT#(09) ON
007 WAIT IN#(11)=ON
008 DOUT OT#(11) OFF
009 DOUT OT#(12) ON
010 WAIT IN#(14)=ON
011 WAIT IN#(09)=ON
012 002 MOVJ P050 EX051 VJ=25.00
013 DOUT OT#(12) OFF
014 DOUT OT#(11) ON
015 WAIT IN#(13)=ON
016 DOUT OT#(09) OFF
017 DOUT OT#(10) ON
018 WAIT IN#(12)=ON
019 WAIT IN#(10)=OFF
020 DOUT OT#(1) OFF
021 CALL JOB:B-JOBS IF IN#(02)=ON
022 RET
023 END
Page 51

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 43 MOTOMAN
4.4.4 Weld Side A Job (Multiple Weld Jobs)
➪
CAUTION!
Do not attempt to run programs from Side B on Side A.
The headstock position for jobs on Side B will be 180˚ off from programs on Side
A. Refer to paragraph 4.3.5, Programming, for information on converting a Side B
job to a Side A job.
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 001 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
002 CALL JOB:WELD1-A
003 CALL JOB:WELD2-A
004 CALL JOB:WELD3-A
005 CALL JOB:CLEAN IF B00=6
006 002 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
007 RET
008 END
4.4.5 Weld Side A Job (Single Weld Job)
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 001 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
002 002 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
003 003 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
004 004 MOVC V=93.0 CONT
005 ASF #1
006 005 MOVC V=12.7 CONT
007 006 MOVC V=12.7 CONT
008 007 MOVC V=12.7 CONT
009 AEF #1
010 008 MOVJ VJ=50.00 CONT
011 009 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
Page 52

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 44 MOTOMAN
012 INC B00
013 RET
014 END
4.4.6 Weld Side B Job
➪
CAUTION!
Do not attempt to run programs from Side B on Side A.
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 001 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
002 CALL JOB:WELD1-B
003 CALL JOB:WELD2-B
004 CALL JOB:WELD3-B
005 CALL JOB:CLEAN IF B00=6
006 002 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
007 RET
008 END
Page 53

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 45 MOTOMAN
4.4.7 Clean Job (R1 Job)
Line Step Function
000 000 NOP
001 001 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
002 002 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
003 003 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
004 004 MOVL V=187.0 CONT
005 TIMER T=1.50
006 005 MOVL V=187.0 CONT
007 006 MOVL V=187.0 CONT
008 007 MOVL V=187.0 CONT
009 TIMER T=1.00
010 008 MOVL V=187.0 CONT
011 009 MOVL V=166.7 CONT NWAIT
012 PULSE OT#(63 T=0.50
013 010 MOVL V=187.0 CONT
014 PULSE OT#(13 T=0.50
015 011 MOVL V=46.0 CONT
016 012 MOVJ VJ=100.00 CONT
017 SET B00=0
018 RET
019 END
➪
CAUTION!
Robot will operate independently of the external axis. Be sure
the robot points are clear of the positioner and fixture.
NOTE: This program will operate on Side A or Side B because there are no external axis positions
NOTE: Steps 11 through 15 are for the optional wire cutter.
Page 54

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 46 MOTOMAN
5.0 MAINTENANCE
5.1 PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
For periodic maintenance procedures and schedules for the K6 robot, the K10
robot, and the MRC controller, refer to your K6 MRC Manipulator Manual or K10
MRC Manipulator Manual.
For additional maintenance information regarding the reciprocating positioners,
refer to your positioner manual.
For maintenance information regarding the welding power source, refer to your
Excel-Arc Owner's Manual.
Table 5-1 provides a list of periodic maintenance to be performed on the ArcWorld
6000 cell. Keep in mind that the maintenance intervals given serve as guidelines
only, you should adjust the frequency of maintenance to suit your specific work
conditions.
➪
CAUTION!
Use only the anti-freeze provided by Motoman. Automotive antifreeze contains stop-leak additives that will clog the small
torch water-cooling ports, and damage the gaskets in the water
circulator pump.
Table 5-1 Periodic Maintenance
Frequency Component Procedure
Regularly MRM2-550 servo
headstock RV drive
unit
Check for proper grease levels and
quality. Use Epinoc APO grease
(Motoman P/N 132434-1) as
required.
Daily Water circulator
(water-cooled torch
application only)
Check the fluid in the water
circulator. Add fluid as required.
Use the approved antifreeze
(Motoman P/N 131224-1) and
distilled water.
Daily Air system water
trap on the front of
MRM2 positioner
Check water trap and empty if
required.
Page 55

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 47 MOTOMAN
Table 5-1 Periodic Maintenance (Continued)
Frequency Component Procedure
Monthly MRM2 weld
grounds
Lubricate with Burndy Penetrox E
conductive copper lubricant (part
no. PEN-E-8).
500 operating hrs MRM2 drive pins
and locking pins
Spray the drive and locking pins
with a molycote BR2 grease or
equivalent.
1000 operating hrs MRM2 positioner
gears
Lubricate with Shell 1029 or
equivalent.
20,000 operating hrs MRM2-550 servo
headstock RV drive
Change the grease in the drive unit.
Use Epinoc APO grease
(Motoman P/N 132434-1).
20,000 operating hrs MRM2-1100 servo
headstock Cyclo
drive unit
Change the grease in the drive unit.
Use Shell Alvania RA.
5.2 SPARE PARTS LIST
Table 5-2 Spare Parts
Description Part No.
AW 6000 safety mat kit 130157-5
Positioner interface 4-pole relay, 24 VDC 470108-5
Positioner interface fuse, 2 A 250 V 400647-3
Positioner interface fuse, 1/2 A 250 V 130293-2
Valve, 2-way (FESTO) JMVH-51/8 B
Page 56

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 48 MOTOMAN
5.3 FUSE AND CIRCUIT BREAKER PROTECTION
Tables 5-3 through 5-7 give the locations of fuses and circuit breakers that are
significant to the operation of the total system. In most cases, MRC spare fuses are
placed in the accessory bag with the MRC.
➪
WARNING!
Replace fuses with the same type and rating. Replacement of
fuses with higher amperage rating or lower voltage will damage
the robot controller and/or auxiliary equipment necessitating
costly replacement.
Abbreviations:
CB – designates circuit breaker
F, FU or 101FU – designates fuse
Table 5-3 Excel-Arc 6045 CV Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Device
Designator Rating Part Number Location Purpose
CB1 10A
115V
203627-7 Upper rear panel Protect 115V circuit
CB2 10A 24V 203627-7 Upper rear panel Protect 24V circuit
F1 .5 A W-11166-11 On contactor box Protect contactor
circuit
Table 5-4 MRC Cabinet Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Device
Designator Rating Part Number Location Purpose
CB
(1MCCB)
50 A
30 A
NF50-SS
NF30-SS
Upper left front
K10
Upper left front
K6
Main circuit breaker
for incoming 200 V
AC, 3 phase for
MRC cabinet
Page 57

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 49 MOTOMAN
CB (1SV) 15 A
20 A
Under PC servo
board (K10)
Lower servo
pack edge (K6)
Protects input for
servo pack 1SV for
S axis
Table 5-4 MRC Cabinet Fuses and Circuit Breakers (Continued)
Device
Designator Rating Part Number Location Purpose
CB (2SV) 15 A
20 A
Under PC servo
board (K10)
Lower servo
pack edge (K6)
Protects input for
servo pack 2SV for
L axis
CB 15 A Under PC servo
board
Protects input for
servo pack 3SV for
U axis
CB 10 A Under PC servo
board
Protects input for
servo pack 4SV for
R axis
CB 10 A Under PC servo
board
Protects input for
servo pack 5SV for
B axis
CB 10 A Under PC servo
board
Protects input for
servo pack 6SV for
T axis
FU1 5 A GDL-5 MTU-01 Protects CPT10199
transformer, brake,
and fan circuits
FU2 5 A GDL-5 MTU-01 Protects CPT10199
transformer, brake,
and fan circuits
FU4 4 A GP-40 MTU-01 Protects robot brake
circuits
FU5 4 A GP-40 MTU-01 Protects robot brake
circuits
1FU 1 A GDL-1 Top/left/rear Protects the four fan
circuits of the MRC
Page 58

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 50 MOTOMAN
2FU 1 A GDL-1 Top/left/rear Protects the control
transformer and fan
(above computer
rack) in the MRC
3FU 1 A GDL-1 Top/left/rear Protects the control
transformer and fan
(above computer
rack) in the MRC
Table 5-4 MRC Cabinet Fuses and Circuit Breakers (Continued)
Device
Designator Rating Part Number Location Purpose
4FU 1 A GDL-1 Top/left/rear Protects the 100 V
AC supply to the
AC receptacle for the
floppy disk
controller power
FU1 3 A SM1101 MBB-02 External voltage
protection - 24V
FU2 3 A SM1101 MBB-02 External voltage
protection - 24V
Table 5-5 Universal Welding Interface (UWI) Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Device
Designator Rating Part Number Location Purpose
F1 8A 250V On KXA motor
speed control
Limits damage from
shorts or component
breakdowns in DC
power supply
module
FU1 4A 250V Wickman
19374K-4A
On interface
board
Protects 115V circuit
FU2 .25A
125V
Wickman
19303K250A
On interface
board
Protects shock
sensor circuit
FU3 .5A 125V Wickman
19303K500A
On interface
board
Protects 24V circuit
Page 59

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Page 51 MOTOMAN
Table 5-6 COMARC III Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Device
Designator Rating Part Number Location Purpose
Fuse 1A 250V TD-1 Front of
COMARC box
Protect 200V circuit
Page 60

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Appx. A MOTOMAN
APPX. A RISK ASSESSMENT
Page 61

Risk Assessment Page 1 MOTOMAN
ArcWorld 6000
MOTOMAN Risk Assessment
ArcWorld 6000 System
Application: Arc Welding Robot Type: K6 or K10
Customer: Varies Plant Loc.: Varies
See cell layout
This document was prepared to explain the rationale behind the safeguarding of
MOTOMAN's ArcWorld 6000 robot cell.
It is the User's responsibility to
review this document and verify that the safeguards are adequate for their
plant conditions. This review should include the current revision of ANSI/RIA
R15.06 American National Standard for Industrial Robot Systems - Safety
Requirements. The User must also ensure that safeguards are used and maintained.
SAFEGUARDING PERSONNEL
Safeguarding Plant Personnel
• Barrier around robot work envelope.
• Interlocked gate for access to cell.
• Curtain around cell blocks ultra-violet radiation from arc.
• Serious hazards are identified by warning labels.
Safeguarding Operator
• Interlocked gates stop robot motion if opened in PLAY mode.
• Dual sensors on interlocked gates make safeguards difficult for operator to
defeat.
• Emergency Stop button on operator station.
• Two station positioner keeps operator out of robot work envelope.
• Extended length safety mats are interlocked to stop positioner motion when
activated. Requires reset at operator station to restart.
• Robot program will wait for Cycle Start buttons before sweeping positioner.
Page 62

Risk Assessment Page 2 MOTOMAN
ArcWorld 6000
• Cycle Start has dual palm buttons, anti-tie down, positioned for two hand
operation.
Safeguarding Teacher
• Interlocked gate: Active in PLAY mode; Inactive in TEACH mode.
• Clearance of 24" between robot and fencing.
• Emergency Stop button on programming pendant.
• S-axis motion restricted by hardstops.
• TEACH LOCK prevents operation from controller while programming
pendant is enabled.
• Sweeping of positioner from pendant requires deliberate action.
• Continuous stepping is at reduced speed.
Safeguarding Maintenance Personnel
• Robot controls are outside barrier.
• Positioner controls are inside cell, but do not require robot drive power to
troubleshoot.
• Electrical energy sources equipped with lockout/tagout.
• Programming pendant displays I/O status and other diagnostic functions.
SOURCES OF HAZARDS
Unauthorized Access
• Interlocked barrier.
• Dual interlocks, difficult to defeat by operator.
Human Errors in Judgment
• Safety mat interlocked with positioner.
• Dual palm cycle start.
• Emergency Stops on operator station, robot controller, and programming
pendant.
Control Errors
• Most Safety features independent of program logic.
Page 63

Risk Assessment Page 3 MOTOMAN
ArcWorld 6000
• Program must have instructions to wait for palm buttons to sweep.
Page 64

Risk Assessment Page 4 MOTOMAN
ArcWorld 6000
Mechanical / Electrical Failures
• Safety mat supplied with fail-safe circuit.
• Redundant door interlocks.
• Interlocks designed to fail-safe.
• Robot has sophisticated control loop designed to remove drive power in case of
positioning error.
Environmental
• Sheet metal partition and UV curtain to help prevent eye damage from ultra-
violet radiation.
• UV curtain helps contain welding sparks.
NOTE: Fume ventilation may be required depending on application and plant conditions. (To be
determined and provided by USER.)
NOTE: Care must be used when handling and securing compressed and combustible gasses. (User
supplied.)
Installation Defects
• Safeguards will place the robot in Emergency Stop unless they are correctly
connected.
• Safety fence is self supporting when fully erected (fencing should be lagged).
• Equipment is shipped on bases to ease installation and provide a secure
mounting surface (robot base needs to be leveled and lagged).
Power System Failure or
Inadvertent Power Initiation
• Easy recovery from power failure.
• Different levels of power up; primary power on, controller power on, servo
power on, and robot start. Difficult to inadvertently start.
EQUIPMENT PROTECTION
Page 65

Risk Assessment Page 5 MOTOMAN
ArcWorld 6000
Human Errors
• Torch breakaway protects robot and torch in the case of a torch crash.
• Cube interlock requires the robot to be in a "safe" position before the positioner
can index.
Power Faults
• Isolation transformer and circuit breaker protect robot from power surges.
• Robot "remembers" its position and place in program at power down.
• Data has battery backup and can be saved on optional floppy disk drive.
WHAT-IF CONSIDERATIONS
What if personnel reach over safety mat and pinch an arm on moving parts?
Extended length mats are provided to help prevent inadvertent access to moving
parts.
What if there is a hazard not covered by a warning label?
Labels are provided on positioner, robot, power source, feeder, transformer, and
robot controller. Persons working on equipment should have adequate training to
identify hazards.
Page 66

ArcWorld 1000 Operator's Manual Appx. B MOTOMAN
APPX. B SYSTEM OUTLINE
This section contains the following outline drawings:
Drawing Number Title Sheet Number
131929 Cell Layout Sheet 1 of 19
131929 Main Bill of Material Sheet 2 of 19
131929 Cell Layout Sheet 17 of 19
131929 Cell Layout Sheet 18 of 19
131929 Cell Layout Sheet 19 of 19
Page 67

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Appx. C MOTOMAN
APPX. C ELECTRICAL DRAWINGS
This section contains the following electrical drawings:
Drawing Number Title Sheet Number
131929 Power Distribution Sheet 3 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MRY01 Board Sheet 4 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MEW01 Board Sheet 5 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MI004 Board Sheet 6 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MI004 Board Sheet 7 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MI003 Board Sheet 8 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MI003 Board Sheet 9 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MI003 Board Sheet 10 of 19
131929 MRC I/O, MI003 Board Sheet 11 of 19
131929 Cable Layout Sheet 12 of 19
131929 Ladder Diagram Sheet 13 of 19
131929 Ladder Diagram Sheet 14 of 19
131929 Ladder Diagram Sheet 15 of 19
131929 Ladder Diagram Sheet 16 of 19
131093 MSV01 to Servopack Sheet 1 of 1
131982 MRC to EXSB Sheet 1 of 1
131438 2.2KW Power Cable Sheet 1 of 1
131437 EXSB to Positioner Sheet 1 of 1
131094 MRC to Positioner Sheet 1 of 1
131413 Encoder Pigtail Cable Sheet 1 of 1
132366 Bill of Materials Sheet 1 of 2
132366 Circuit Diagram Sheet 2 of 2
130161 Connection/Schematic Diagram Sheet 6 of 7
Page 68

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Appx. D MOTOMAN
APPX. D MECHANICAL DRAWINGS
This section contains the following mechanical drawings:
Drawing Number Title Sheet Number
130930 AC Servo Drive Sheet 1 of 1
130102 MRC ArcWorld Sheet 2 of 2
130157 Safety Mat Sheet 5
130161 Station, Operator Sheet 1 of 7
130161 Station, Operator Sheet 2 of 7
Page 69

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 1 MOTOMAN
INDEX
A
About This Document, 1
AC Receptacles, 22
Air Requirements, 17
Alarm / Error, 13
Alarm, 19
Alarms and Errors, 29
Arc Screens, 23
Arc Shield, 18
C
Circuit Breakers, 22
Clean Job (R1 Job), 41
Coordinate System Indicators, 15
Cube Assignment, 30
Customer Service Information, 4
Cycle Select, 13
Cycle Start, 19
D
Description of Equipment, 11
Display, 15
Page 70

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 2 MOTOMAN
Page 71

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 3 MOTOMAN
E
E-Stop Recovery, 26
Electrical Requirements, 17
Emergency Stop, 13, 15, 18
Emergency Stops, 24
Error Messages, 29
Excel-Arc Controls, 21
F
Fault Recovery, 26
Feeder Control Receptacles, 21
Fencing, 23
Fuse and Circuit breaker Protection, 44
G
General Safeguarding Tips, 7
H
Hold, 13, 18
Humidity, 16
I
I/O Assignment, 34
Page 72

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 4 MOTOMAN
Installation Safety, 8
Interlocks, 24
Introduction, 1
K
K-Series Robot Description, 11
Keypad, 15
L
Loading / Unloading Procedures, 26
Local / Remote Operation, 20
Locking Pins, 17
M
Main Power, 20
Maintenance, 42
Maintenance Safety, 10
Major Alarms, 30
Master Job (No Group Axes), 35
Master Job Start, 19
Mechanical Safety Devices, 7
MIG Torch, 22
Minor Alarms, 29
Mode Select, 13
MRC Controller, 11, 12
Page 73

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 5 MOTOMAN
MRC Playback Box, 12
MRM2-Series Positioner, 15
Page 74

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 6 MOTOMAN
O
Op-Station, 18
Operation, 25
Operation Safety, 9
Operator Control Panel (Op-Station), 18
Operator Station Enable / Disable, 19
Optional Equipment, 3
P
Part / Fixture Rating, 16
Periodic Maintenance, 42
Playback Box Sub-Panel, 13
Positioner Auto / Manual, 19
Programming, 30, 32
Programming Pendant, 14
Programming Safety, 8
PWF4 Wire Feeder, 22
R
RAM Breakaway Mount, 23
Reference to Other Documentation, 4
Reset, 20
Robot Speed Indicators, 15
Rotating Headstock, 32
Page 75

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 7 MOTOMAN
Page 76

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 8 MOTOMAN
S
Safety, 5
Safety Equipment, 23
Safety Mats, 24
Sample Jobs, 35
Servo Head Stock Speed, 17
Servo On, 19
Servo Power, 12, 15
Shock Rating, 16
Shock Sensor Override, 28
Shock Sensor Recovery, 27
Shut Down, 29
Spare Part List, 43
Standard Conventions, 6
Start, 13
Start Up, 25
Station Ready, 19
Sweep Speed, 17
Sweep to A Job (R1 + S1), 36
Sweep to B Job, 38
Sweeping Positioner to Side A, 31
Sweeping Positioner to Side B, 31
Swing Diameter, 16
System Layout, 2, 3
System Overview, 1
Page 77

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 9 MOTOMAN
Page 78

ArcWorld 6000 Operator's Manual Index 10 MOTOMAN
T
Temperature Operating Range, 16
Terminal Connectors, 20
U
Universal Welding Interface (UWI), 22
V
Volt / Amp Settings, 20
W
Weld Side A Job (Multiple Weld Jobs), 39
Weld Side A Job (Single Weld Job), 39
Weld Side B Job, 40
Welding Current Rating, 17
Welding Equipment, 22
Welding Power Source, 20
 Loading...
Loading...