Motic BA310 Pol Instruction Manual

BA310 Pol
Polarizing Microscope
Instructions Manual
WWW.MOTIC.COM
MOTIC INCORPORATION LTD.

We are constantly endeavouring to improve our instruments and to adapt them to the requirements of
modern research techniques and testing methods. This involves modification to the mechanical
structure and optical design of our instruments.
Therefore, all descriptions and illustrations in this instruction manual, including all specifications are
subject to change without notice.
Although every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of this instruction manual, if you note any
points that are unclear or inaccurate, please contact Motic agency or our Technical Service directly.
0

Introduction
Polarizing microscopes are used in the study of thin sections of minerals and rocks as well as other
anisotropic materials (fibers, plastics, etc.). The optical system is similar to that of modern compound
microscopes.
The most distinctive features of a polarizing microscope are the rotatable stage, polarizer and analyzer,
Bertrand lens system as well as mica plate, gypsum plate and quartz wedge. This special equipment
allows the evaluation of properties and characteristics of materials that cannot be measured by other
microscope methods.
1

Table of contents
1. Nomenclature 5
2. Setting Up The Instrument 9
3. Assembling the microscope 10
3.1 Verifying input voltage 10
3.2 Halogen lamp 11
3.3 Specimen clip 11
3.4 Attachable mechanical stage (optional) 11
3.5 Objectives 11
3.6 Condenser 11
3.7 Intermediate tube 12
3.8 Analyser slider 12
3.9 Compensators 12
3.10 Eyepiece tube 12
3.11 Eyepieces 12
3.12 Filters 13
3.13 Power cord 13
3.14 Epi-illuminator
4. Microscopy 14
Manipulation of each component
4.1 Coarse and fine focusing 14
A. Coarse focus torque adjustment 14
B. Coarse focus lock 14
4.2 Stage upper limit stop adjustment 15
4.3 Beam split slider 15
4.4 Interpupillary distance adjustment 15
4.5 Diopter adjustment 16
4.6 Centering the condenser 16
4.7 Use of aperture diaphragm 17
4.8 Use of field diaphragm 17
4.9 Brightness and contrast adjustment 18
4.10 Orientation of polarizer and analyzer 18
4.11 Focusing and centering the bertrand lens 19
2

4.12 Compensators 20
A. 1/4λ-plate 20
B. 1λ-plate 20
C. Quartz Wedge 20
4.13 Centering the Objectives 21
4.14 Epi-illuminator
5. Photomicrographic procedure 22
6. Terminology 23
7. Troubleshooting table 25
8. Care and maintenance 27
9. Warning labels 29
3
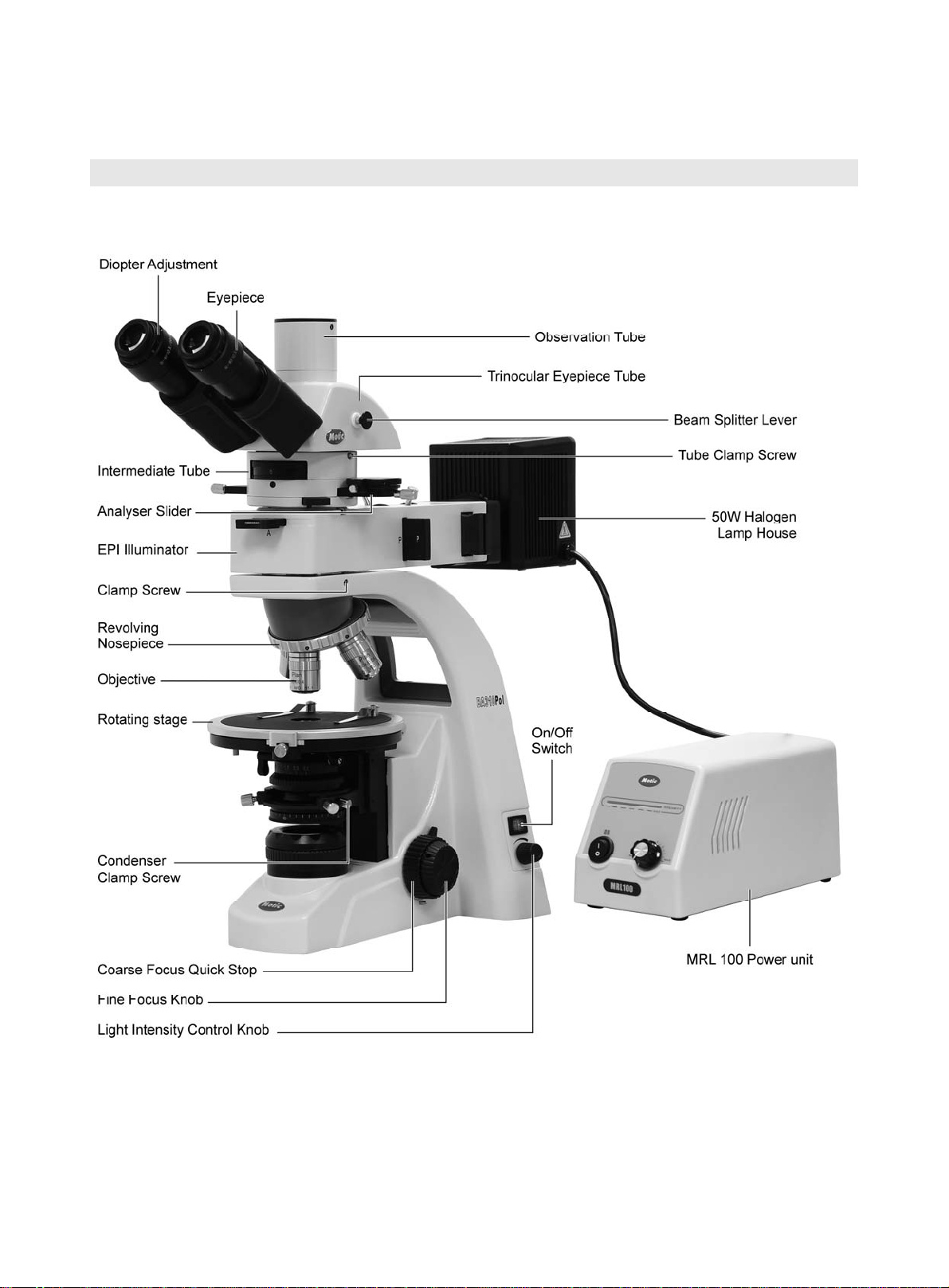
1 . Nomenclature
BA310 EPI-Pol
4
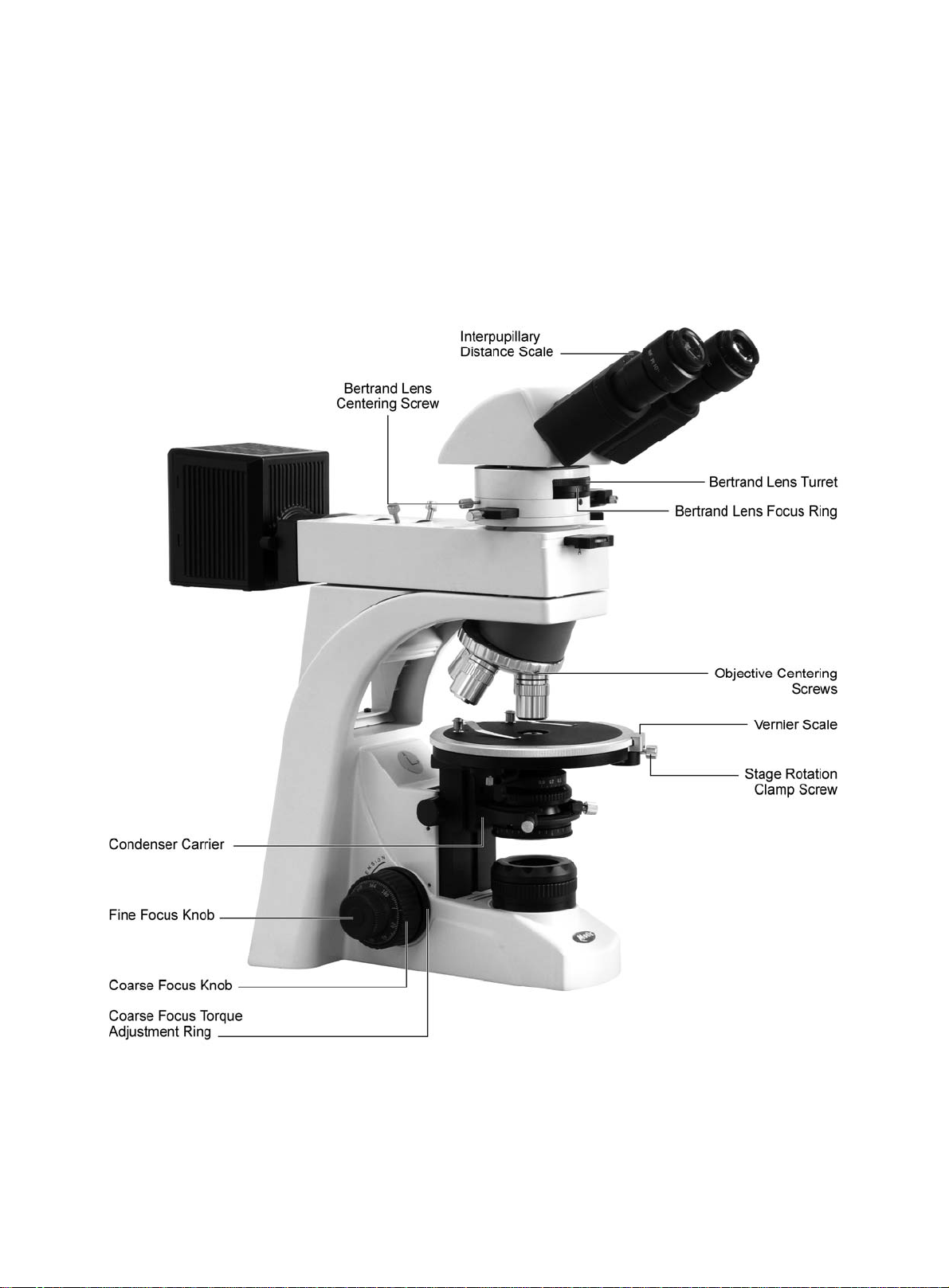
BA310 EPI-Pol
5
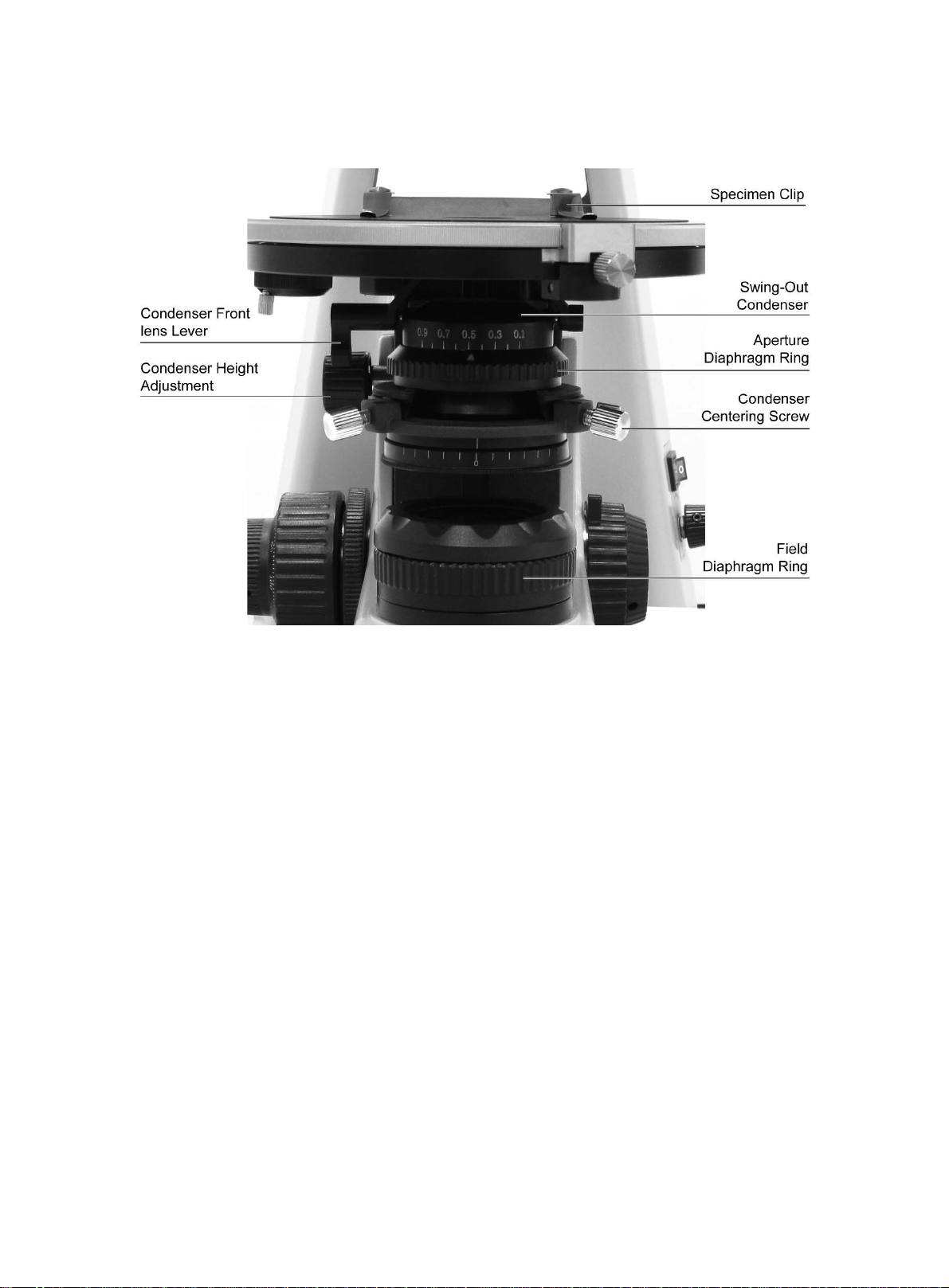
6

2. Setting up the Instrument
Avoid placing the instrument in locations exposed to direct sunlight, dust, vibration, high temperature,
high humidity and where it is difficult to unplug the power supply cord.
Operating environment
Indoor use
Altitude: Max 2000 meters
Ambient temperature: 15°C to 35°C
Maximum relative humidity: 75% for temperature up to 31ºC decreasing linearly to 50% relative
humidity at 40ºC
Supply voltage fluctuations: Not to exceed ±10% of the normal voltage
Pollution degree: 2 (in according with IEC60664)
Installation / Overvoltage category: 2 (in according with IEC60664)
Air Pressure of 75kPa to 106kPa
Avoid frost, dew, percolating water, and rain
7
 Loading...
Loading...