Page 1

C185
- Combined Display Logger
USER MANUAL
Page 2

MoTeC C185 User Manual
Copyright © 2014 – MoTeC Pty Ltd
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
While every effort is taken to ensure correctness, no responsibility will be taken for the
consequences of any inaccuracies or omissions in this manual.
V 2.0, June 2014
Page 3

C185 User Manual MoTeC
Contents
Introduction .............................................................................. 1
Features ................................................................................................ 1
System Overview .................................................................................. 3
Typical Devices Used With C185 ............................................... 4
Installation ................................................................................ 8
Mounting and Wiring ............................................................................. 8
Connecting Devices .............................................................................. 9
Inputs .......................................................................................... 9
Outputs ..................................................................................... 11
Communications ....................................................................... 11
Connecting Devices Examples ................................................ 13
Software Installation ........................................................................... 14
C185 Dash Manager Software ................................................. 14
i2 Data Analysis Software ........................................................ 14
Telemetry Monitor Software ..................................................... 15
Connecting the C185 to a PC .................................................. 15
Configuration ......................................................................... 16
Configuration File ............................................................................... 16
Channels ............................................................................................. 17
Channel Properties ................................................................... 19
Selecting Channels .................................................................. 20
Connections ........................................................................................ 22
Configuring Inputs .................................................................... 22
Configuring Outputs ................................................................. 22
Configuring Communications ................................................... 22
Calculations ........................................................................................ 23
Special Calculations ................................................................. 23
General Purpose Calculations ................................................. 23
Functions ............................................................................................ 24
Data Logging ............................................................................ 24
Display ...................................................................................... 28
Page 4

MoTeC C185 User Manual
Other Functions ........................................................................ 36
Operation ................................................................................ 37
Retrieving the Logged Data ..................................................... 37
Sending and Retrieving Configuration Files ............................. 37
Zeroing Sensors ....................................................................... 37
Checking Operation .................................................................. 38
Configuration Versions and Updating ...................................... 38
Upgrading C185 ....................................................................... 39
Password Protection ................................................................ 39
Other Online Activities .............................................................. 39
Appendices ............................................................................ 41
Specifications ...................................................................................... 41
C185 Upgrades................................................................................... 43
Characteristics .................................................................................... 44
Input Characteristics ................................................................. 44
Output Characteristics .............................................................. 49
Pin List by Pin Number ....................................................................... 50
Pin List by Function ............................................................................ 53
Mounting Dimensions ......................................................................... 57
Wiring .................................................................................................. 58
Connector ................................................................................. 58
Wire Specification ..................................................................... 58
PC Connection ......................................................................... 59
CAN Bus Wiring Requirements ................................................ 60
C185 to ECU wiring (RS232) ................................................... 61
Update Rate Summary ....................................................................... 63
Command line..................................................................................... 64
CAN Bus Bandwidth Limit .................................................................. 66
Comms Error Codes ........................................................................... 67
PC Connection - IP Address ............................................................... 70
Windows Keyboard Shortcuts ............................................................ 74
Glossary .............................................................................................. 78
Page 5

Page 6

MoTeC Introduction 1
Introduction
The C185 comes standard as a combined full colour display, powe rful control
device and fully programmable data logger with 250 MB memory (500
optional). The anti-reflective, high contrast display is clear and vibrant in direct
sunlight. Displayed channels and labels are configurable on supplied layouts;
software for fully configurable custom layouts available early 2014. The C185
acquires data from devices such as an ECU and displays data channels,
warning alarms, lap times, fuel calculations, maths functions and much more.
Features
The C185 comes with a range of features as standard and several options
available as upgrades to customise and grow your system. These additional
features are activated through a simple password acquired from MoTeC, at
any time when you need it. See C185 Upgrades
General
• High resolution 125 mm (5" approx) colour LCD display, with brightness
for sunlight readability
• 10 full colour (RGB) LEDs; colour, function and intensity are fully
programmable
• Suitable for bikes, cars, marine and industrial applications
• Compact, durable and reliable unit
• Supports wideband Lambda from PLMs or LTCs, using Bosch LSU or NTK
UEGO 5 wire sensors
• Straightforward control for lights, fans, pumps and PID controlled devices
• Easily integrates with MoTeC CAN based products such as ECUs and
expanders. Full I/O expansion available with use of E888, E816, VIM and
SVIM expanders.
Logging and Analysis
• Internal data logging, 250 MB standard or 500 MB optional.
• Fast download via Ethernet
• Accommodating over 300 channels derived from a mixture of analogue
and digital inputs, RS232 and CAN data channels
• Configurable to use sensors from some existing engine management
systems
• Data analysis with i2 Standard or optional i2 Pro software
Page 7

2 Introduction MoTeC
• Telemetry (T2) and remote logging options
Display
• Colour TFT LCD, anti-reflective
• 12 customisable layout options
• Customisable measurement units and warnings
• Configurable dial, sweep or bar graph can display any channel with
optional peak, hold and shift markers
• 48 user-defined alarms, e.g. Low Oil Pressure, Low Fuel, Fast Lap
• Programmable overrides - particularly useful for showing values such as
lap times
• Three programmable modes or 'pages' with customisable labels ensure
the driver is shown only the most relevant information at any given time
• Adjustable backlight
Software
• Windows-based software designed for setup and management of the
display and data logging system
• The user can generate a configuration file offline and then send the
completed configuration to the C185
• Calculations including lap times, lap gain/loss, speed and distance, fuel
prediction
• Monitor active channels—view all channels live
• Sensor zeroing
• Details editor including event, venue and vehicle details
• Extensive Help screens
• Latest software version is available free of charge from
www.motec.com/downloads
Page 8

3 MoTeC Introduction
Compatibility
• MoTeC ECUs: M4*, M48*, M8*, M400, M600, M800, M880, M1
• MoTeC Accessories: VIM, SVIM, E888, E816, SLM, PLM, LTC, BR2,
PDM, GPS, VCS, Telemetry etc.
• Many non-MoTeC devices
*For some ECUs, an additional cable/adaptor may be required in
Required Accessories
Refer to Connecting the C185 to a PC
• Standard Ethernet cable
• Any one of the following Ethernet to Autosport connections
o #62206 C185 loom
o #61131 Ethernet cable unterminated, 2 meter
o #61132 Ethernet to Autosport pins cable, 1.8 m
System Overview
The C185 offers extensive possibilities to integrate with ECUs, peripheral
devices and accessories to form a complete solution that powers, controls,
logs, monitors and communicates virtually any automotive parameter.
The picture shows just one example. For a tailored solution to your application
contact your dealer or check out the website.
Page 9

4 Introduction MoTeC
Typical Devices Used With C185
ECUs
The C185 can be connected to most MoTeC ECUs and some other
manufacturers' models either via CAN or RS232. This avoids duplication of
sensors and allows the C185 to display and log many ECU parameters.
The typical update rate is about 20 times per second for RS232 and 50 times
per second for CAN.
Sensors
The C185 inputs can be connected to a wide variety of sensors. Different
types of sensors are available to suit different types of measurements, for
example: temperature, pressure, movement etc.
Sensors convert a physical measurement (e.g. pressure) into an electrical
signal (e.g. volts).
Different types of sensors generate different types of electrical signals. For
example most temperature sensors convert the temperature into a variable
resistance which may be measured by an Analogue Temperature input,
however most wheel speed sensors generate a variable frequency signal
which must be connected to either a Digital input or a Speed input.
Expanders
VIM / SVIM
The VIM is a compact and versatile input expander module with 24
analogue inputs of various types including high speed, high resolution and
differential types. The VIM also has two digital inputs with programmable
trigger levels.
Several VIMs may be connected to the C185 providing more than 300
sensor inputs. The VIM supports many different types of sensors including
unamplified thermocouples and strain gauges.
The Synchronous Versatile Input Module (SVIM) is a compact expander
that works the C185 to facilitate the synchronised logging of high speed,
high resolution inputs. Multiple SVIMs are synchronised so that every
SVIM in the vehicle samples its high resolution AV inputs at the same
instant in time.
SVIMs are versatile in nature and can be located close to sensors,
reducing the weight and complexity of wiring. When used in multiples, up
to 200 sensor inputs are available. The SVIM supports many different
types of sensors, including unamplified thermocouples and strain gauges.
Page 10

MoTeC Introduction 5
E888/E816
The C185 supports two E888 or E816 Expanders allowing expansion of
the number of inputs and outputs.
The E888 has 8 x 10 bit thermocouple inputs, 8 x 10 bit voltage inputs, 4
digital inputs, 2 switch inputs and 8 outputs.
The E816 has 16 x 10 bit voltage inputs, 4 digital inputs, 2 switch inputs
and 8 outputs.
Note: The E888 / E816 inputs have lower resolution than the VIM/SVIM
inputs and have slower update rates.
Accessories
BR2
A BR2 Beacon Receiver may be connected to the C185, which allows the
C185 to calculate lap times for display and to provide lap information for
the data logging analysis software.
SLM
The SLM Shift Light Module can be used for shift lights, warnings and
other driver alerts.
It comprises 8 LEDs that can be programmed to display any colour.
GPS
The C185 supports many GPS (Global Positioning System) devices
allowing the C185 to record speed, generate lap times and measure
position information.
This information can be used in the i2 data analysis software to create
track maps, and plot and compare driven lines.
Telemetry
The C185 supports transmission of data via a telemetry radio to a remote
location such as a pit garage. This allows monitoring of the current vehicle
condition, position on the track, lap times, fuel remaining, laps remaining
etc.
The telemetry system provides three major functions:
1. Real time data that is transmitted continuously and can be shown on
graphs, gauges and other displays.
2. End of lap data which shows summary information at the end of a lap
such as lap time, maximum temperatures etc.
3. Telemetry analysis which exports the real time data to the i2 analysis
software at the end of each lap or on demand which allows normal
Page 11

6 Introduction MoTeC
analysis of the data including maths calculations, while the vehicle is still
on the track.
Other telemetry features include: warning alarms, position of multiple
vehicles on a track map, broadcast data via DDE (Dynamic Data
Exchange) or via IP (Internet Protocol).
Note: The Telemetry option is required for the basic functionality. The
Remote Logging option is required in addition to the Telemetry option for
the Telemetry Analysis function.
High Definition Video
MoTeC brings true high definition to motorsport with its new HD Video
Capture System. The HD-VCS provides superior quality video and
numerous features designed specifically for the racing environment.
Features include:
• Genuine High Definition with 1080p @ 30 frames per second
• Automatic Start/Stop, eliminating the possibility of drivers forgetting to
turn it on
• 12 V power direct from the vehicle - no batteries to recharge
• Live gauges
• Over 5 hours of recording at 1080p
• Records to removable storage up to 32 GB
• Video can be played directly from the card
• Automatic CAN Synchronisation with data in i2 (available late 2013)
• Compact, lightweight recording unit
automatically recorded on the video
Lambda Measurement
PLM
The PLM Professional Lambda Meter measures the air fuel ratio over a
wide range of mixtures with fast response time. It is compatible with Bosch
LSU and NTK UEGO Lambda sensors and displays the Lambda readings
via the integrated display.
LTC/LTCD
The LTC Lambda to CAN modules provide accurate Lambda
measurements even when the exhaust gas temperature changes rapidly.
They are compatible with the Bosch LSU 4.9 Lambda sensor and transmit
Lambda readings via the CAN bus.
Page 12

MoTeC 7 Introduction Remote Displays
A remote display device may be connected to the C185 to allow display of any
value that the C185 calculates, such as lap times and warning alarm
messages.
The C185 supports D153, D175 displays which are connected via CAN.
PDMs
Power Distribution Modules are designed to replace conventional relays,
fuses and circuit breakers by providing electronically switched power to the
various electrical systems in the vehicle. This simplifies wiring and switch
requirements, while increasing reliability.
Full diagnostic information, including output currents and error status can be
transmitted via CAN to the C185.
Several models are available to suit vehicles with different complexity ranging
from 15 to 32 outputs and 12 to 23 inputs.
Other Devices
Many other devices can be connected to the C185. Contact your dealer for
advice.
Page 13
8 Installation MoTeC
Installation
Mounting and Wiring
C185 has three threaded mounting posts. For further detail see Mounting
Dimensions.
Mounting Tips
• Avoid twisting the case: use washers between the unit and the mounting
panel to ensure that the unit is mounted only at the mounting points and
do not over tighten the mounting screws.
• Vibration isolation may be desirable if the vehicle vibrates severely.
• Mount so that the connector may be easily accessed.
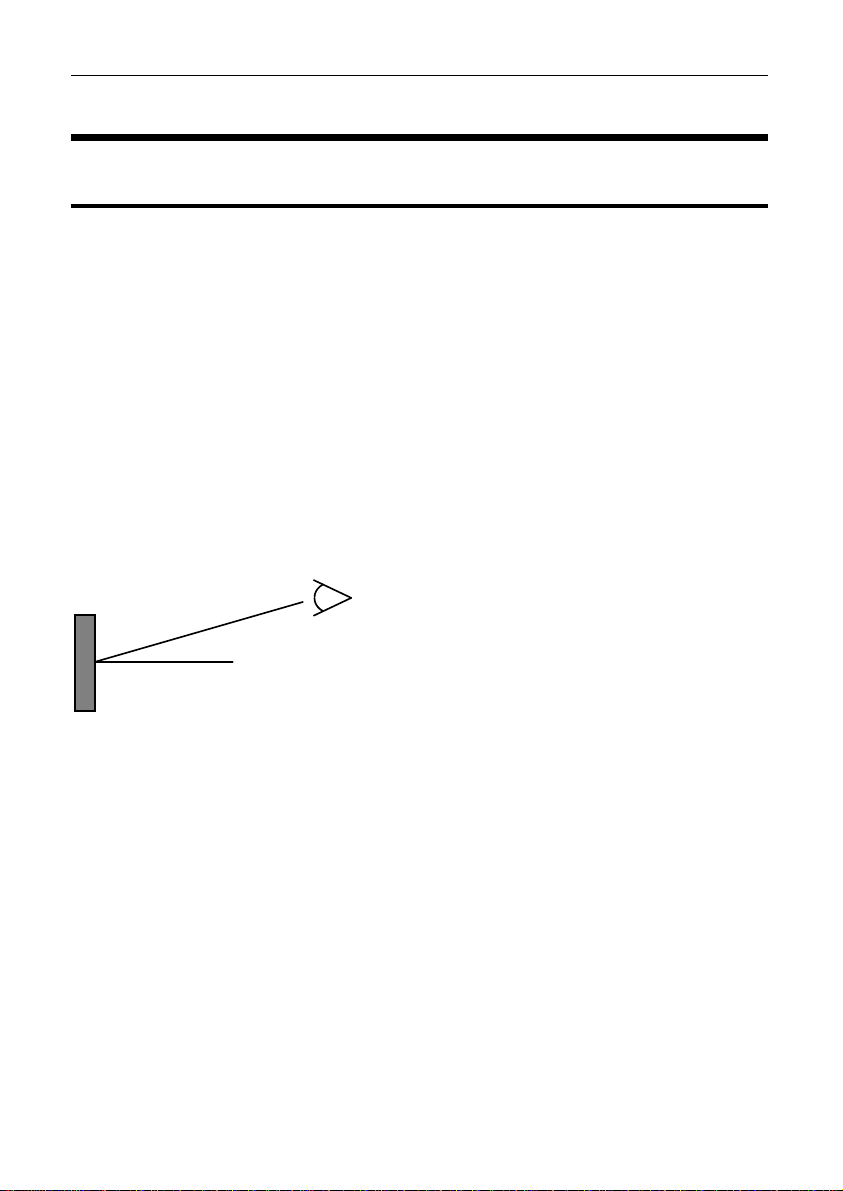
• Orientation: for best contrast, the display should be viewed at an angle of
approximately 20 degrees, However the C185 will give good contrast
between 0 and 40 degrees. Display reflections should also be considered
when determining the mounting angle.
20°
The C185 uses a 79 pin Autosport connector. See Connector and Pin List by
Pin Number for full details.
Wiring Tips
• To ensure that the connector is sealed, plug unused holes with filler plugs.
A heat shrink boot may also be used if desired.
• Use 22# Tefzel wire (Mil Spec M22759/16-22) (5 A max at 100 °C)
• Tefzel wire is difficult to strip unless the correct stripping tool is used.
• Be careful not to nick the wires as this may result in wire failure or poor
crimping.
• Some sensor connectors may not be available with 22# terminals, in which
case doubling the wire over gives the equivalent of an 18# wire. This is
suitable for many of the common sensor terminals.
Page 14

MoTeC Installation 9
• Use the correct crimping tool for all contacts to ensure a reliable
connection.
• Power the C185 via a separate switch and a 5 ampere fuse, to ensure the
PC can communicate with the C185 without the need to power the rest of
the vehicle.
• The C185 ground must have a direct connection to the vehicle battery.
• C185 is connected to other devices via the CAN bus. Refer to CAN Bus
Wiring Requirements for details.
Connecting Devices
Inputs
Input Types
A range of sensors is available to suit different types of measurement, e.g.
temperatures, pressures, speed. Each type of measurement generates a
different electrical signal that requires a suitable input type.
Each sensor needs to be connected to the type of input designed to suit that
type of sensor.
MoTeC devices have the following input types available:
• Analogue Voltage Inputs
• Analogue Temperature Inputs
• Switch Inputs
• Digital Inputs
• Wheel Speed Inputs
Note: Some inputs require a device upgrade to make them available
In addition to sensors connected to the inputs, the C185 has internal sensors
available for battery voltage, 3-axis G force and device temperature.
Analogue Voltage Inputs
Analogue Voltage inputs are normally used to measure the signals from
analogue voltage type sensors, i.e. sensors with variable voltage outputs,
such as:
o Rotary or linear potentiometers
o Signal conditioned 3 wire pressure sensors
o Thermocouple amplifiers
o Accelerometers
Page 15

10 Installation MoTeC
These inputs can also be used to measure two wire variable resistance
sensors if an external pull-up resistor is connected from the input to the 5
V sensor supply.
Additionally, on/off switch signals may be connected, which may also
require an external pull-up resistor.
Analogue Temp Inputs
Analogue Temperature inputs are identical to Analogue Voltage inputs,
except that they contain a 1000 ohm resistor which is connected internally
from the input pin to the 5 V sensor supply. This allows the Analogue
Temperature inputs to be used with two wire variable resistance se nsors
such as:
o Two wire thermistor temperature sensors
o Two wire variable resistance pressure sensors
Some voltage output sensors can also be used if they can drive the 1000
ohm resistor without causing an error in their reading (e.g. MoTeC
Thermocouple Amplifier).
Additionally, on/off switch signals may be connected.
Switch Inputs
Switch inputs are generally used for the external switches required to
operate the display. These inputs have a 4700 ohm resistor connected
internally from the input pin to the 5 V sensor supply so that a switch can
be simply connected between the input pin and 0 V.
They can also be connected to a brake switch or other switch.
Digital Inputs
Digital Inputs are identical to Switch Inputs except that they include the
following additional measurement methods:
o Frequency: The frequency of the input signal is measured
o Period: The time between successive pulses is measured
o Pulse width: The low time of the pulse is measured
o Count: Counts the number of pulses
o Beacon: For connection of a lap beacon
Speed Inputs
Speed Inputs are identical to Digital Inputs except that they can also be
configured to suit Variable Reluctance (Magnetic) sensors e.g. so me
wheel speed sensors. Because the amplitude of the signal from these
Page 16

MoTeC Installation 11
sensors varies with speed of rotation, variable trigger levels are required,
which must vary with the frequency of the input signal.
The Speed Inputs can also be used with Hall Effect type wheel speed
sensors.
The Pulse Width measurement method measures the high time of the
pulse rather than the low time as measured by the Digital Inputs.
Input Specifications
For full specifications refer to Input Characteristics.
Expanders
If additional sensors are required, input expanders can be used e.g. E888,
E816, VIM, SVIM. Sensors can be connected to the expander inputs and
communicate via either RS232 or CAN. See Configuring Communications.
Outputs
Auxiliary Outputs are used to control various vehicle functions e.g.
o Gear Change Lights
o Warning Lights
o Thermatic Fan
o Gear Box Oil Pump
Note: Devices that consume more than the maximum current (e.g. motors)
should be driven via a relay or PDM.
Output Specifications
Full specifications can be found in Output Characteristics.
Expanders
If additional outputs are required, output expanders can be used e.g.E888,
PDM. Expander outputs can perform the same tasks as the device outputs
and can be driven by communication via either RS232 or CAN. See
Configuring Communications.
Communications
Communications are used to send and receive data from one device to
another. There are two communication protocols; RS232 and CAN. Generally
older devices use RS232 and newer devices use CAN.
Page 17

12 Installation MoTeC
CAN (Controller Area Network) Communications
This protocol enables communication between all devices connected to the
same bus. The CAN bus allows communicating at high speeds. The C185 has
two independent CAN communications ports that can be connected to other
devices with a compatible CAN port. The bus speed for each interface can be
set independently.
Typical devices communicating over CAN:
o 'Hundred series' ECU: M400, M600, M800, M880
o Shift Light Module: SLM
o Lambda meters: LTC, PLM
o Expanders and input modules: E888/E816, VIM
o Displays: SDL
o Beacon receiver: BR2
These devices communicate at 1 Mbit/sec, so any other devices connected
on the CAN bus must also communicate at 1 Mbit/sec. If a device
communicates at another speed, it should be wired to the other CAN bus, and
the speed of that CAN bus must be set to match the speed of the device.
RS232 Serial Communications
This is a one to one protocol, communicating from one device to one other
device. Typical devices communicating over RS232:
o M4, M48 ECUs
o Radio telemetry device
o Global positioning system: GPS
Note: The C185 can communicate with devices for which it has the
appropriate communications protocol defined. For other devices, users can
define their own custom communication settings.
Page 18
MoTeC Installation 13
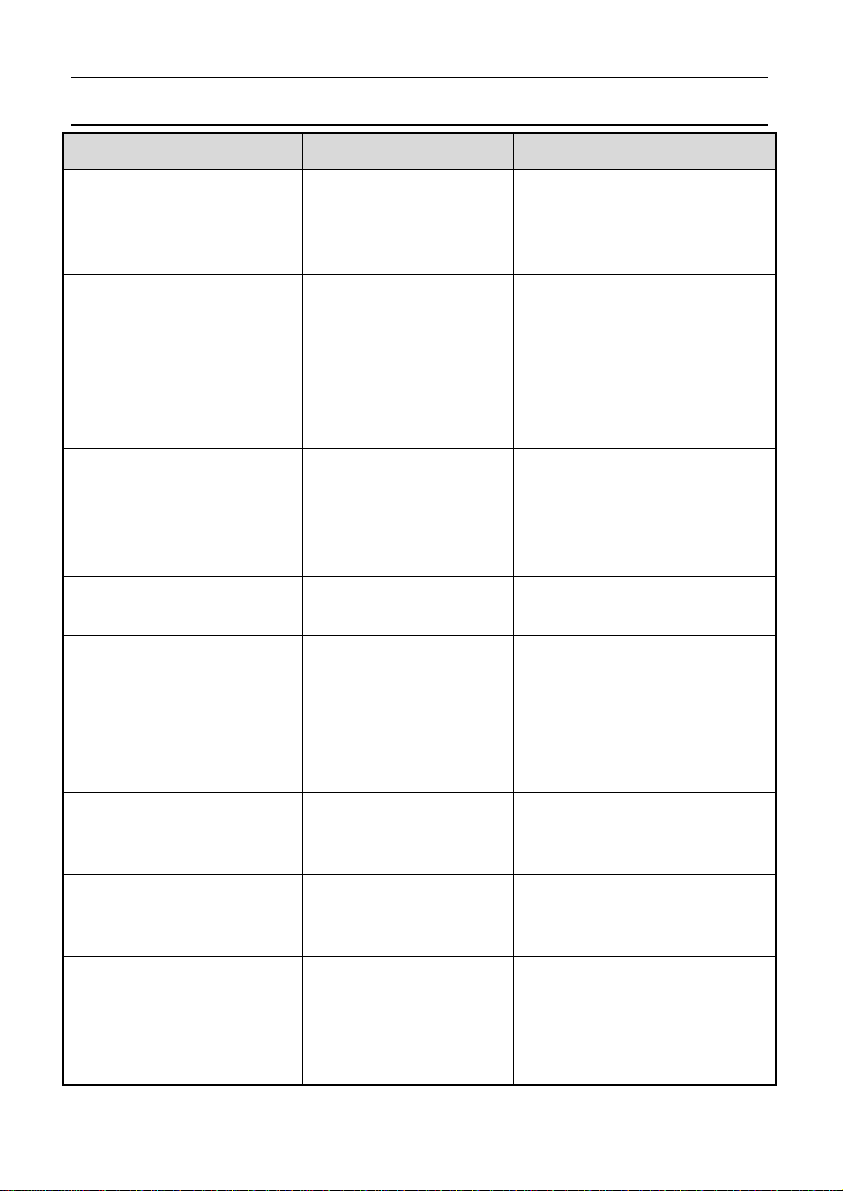
Connecting Devices Examples
Device
Sensors
External Buttons for:
- Display mode
- Display next line (and
optional previous line)
- Alarm acknowledge
- Lap number reset
- etc.
External LED Lights
SLM Shift Light Module
K-type Thermocouples
Connect via Remarks
Inputs:
The appropriate
input type depends
on the sensor type
Inputs:
Switch input
Alternatively Digital
or Analogue Voltage
inputs can be used
Outputs:
Auxiliary output
Communications:
CAN
Inputs:
Analogue Voltage or
Analogue
Temperature input
Communications:
CAN
MoTeC supplies
datasheets with wiring
details for all sensors via
the website
Wire between C185 input
and C185 0V.
If wired to an Analogue
Voltage input connect an
external pull-up resistor
between the input pin and
the 5 V sensor supply.
Wire between one of the
Auxiliary Outputs and
battery positive and
include a current limiting
resistor
Connect via TCA
Connect via E888 or
VIM/SVIM
ECU M4, M48, M8
ECU 'hundred series':
(M400, M600, M800,
M880), M1
Telemetry
Communications:
RS232
Communications:
CAN
Communications:
RS232
Uses the Telemetry
feature of the ECU to send
data to the C185
Ensure the ECU and C185
are connected on the
same CAN bus
Wiring is dependent on the
particular telemetry
system; refer to the wiring
details supplied with the
telemetry system
Page 19
14 Installation MoTeC
Software Installation
C185 Dash Manager Software
C185 Dash Manager software is used for configuration, testing, retrieving the
logged data, and for general management of the C185.
C185 Dash Manager supports configuration of the following connected
devices: VIM, SVIM, E888/E816, SLM.
PC Requirements
C185 Dash Manager runs under Windows XP or Vista operating systems. The
minimum recommended PC specification is a Pentium 90 with 16MB RAM
and an Ethernet port
Installing C185 Dash Manager Software
• Go to the MoTeC website at www.motec.com and navigate to
software/latestreleases/C185 Dash Manager software
OR Locate C185 Dash Manager software on the MoTeC Resource Disc
• Save the selected file in your preferred location (for example desktop)
• When downloading is finished, double click on the file and select run
• Follow the instructions on the InstallShield Wizard
• To start the program after installation, click the C185 Manager icon on the
desktop or click Start > All Programs > MoTeC > C185 > C185 Dash
Manager
Updating C185 Dash Manager Software
• Software updates are available to give access to the latest features.
Download the latest software version from the website and follow the
software installation instructions to update to the new version.
• To update the associated firmware in the device select Upgrade Dash
Version from the Online menu. See Configuration Versions and Updating.
i2 Data Analysis Software
i2 data analysis software is used to analyse the logged data that has been
recorded by the C185. Any number and combination of graphs, gauges and
reports can be analysed simultaneously. The i2 environment can be
customised to specific user requirements.
There are two levels of analysis functionality available; i2 Pro and
i2 Standard.
Page 20

MoTeC 15 Installation
i2 Standard is included, while i2 Pro requires the optional Pro Analysis
upgrade. See C185 Upgrades.
i2 Pro provides advanced mathematics, multiple overlay laps, and unlimited
components, workbooks and worksheets.
Telemetry Monitor Software
The Telemetry Monitor software is used to monitor the optional telemetry link
and allows viewing of live data in various graphical formats such as chart s,
bar graphs and dial gauges. It can also show the vehicle's current track
position on a track map and compare the current vehicle data to reference
data.
Telemetry Monitor software requires the optional Telemetry upgrade. See
C185 Upgrades.
Connecting the C185 to a PC
The C185 connects to the Ethernet port on the PC. This requires a connector
for the standard Ethernet cable in the loom.
The C185 loom #61213 incorporates this connector. Alternatively the
connector can be wired into an existing loom using the unterminated Ethernet
cable (#61131) or the Ethernet to Autosport pins cable (#61132).
All options are used in conjunction with a standard Ethernet cable.
Connection details are described in Wiring.
PC Communications Setup
To enable PC communications a connection must be setup in the C185 Dash
Manager to match the C185 serial number.
• On the Tools menu click Connection Set t ings an d then click Add
• Click OK to choose IP (Ethernet). This is the only available connection
type
• Enter the C185 serial number
If the PC needs to communicate with more than one C185, repeat the steps.
Only one connection can be active at a time. To switch to a different C185
select the appropriate connection and click Make Active.
Network Connection
Optionally, the C185 can be connected to a network. This allows for any
PC on the network to communicate with the C185.
For more information on IP addresses see PC Connection - IP Address.
Page 21
16 Configuration MoTeC
Configuration
All aspects of the C185 can be configured including, which sensor is
connected to which input, the calibration of each sensor, what to display and
where to display it, what to log and how fast to log it, tacho range, warning
alarms, multi stage shift lights, etc.
The configuration is stored in a configuration file on the PC. When starting
C185 Dash Manager the menu items related to changing the configuration are
unavailable. To make them available, load a configuration file either by
opening an existing file or by creating a new one.
All changes to the C185 configuration are performed ‘Offline’, i.e. without the
PC communicating with the C185. The changes are saved in the configuration
file on the PC. The file must be sent to the C185 before the changes take
effect. See Operation.
Tip: When using a laptop in and around a car, it is often not practical to use a
mouse to navigate through the program. Using the keyboard to select options
is easier. An overview is given in Windows Keyboard Shortcuts.
Configuration File
From the File menu the following option are available:
• New creates a new configuration based on a predefined template.
• Open selects an existing file.
Right-click the configuration file to Rename, Delete, Send to a disk etc.
• Save after a new configuration has been defined, it should be saved with
a meaningful name.
• Save as can be used to create a copy of an existing configuration file by
giving it a new name.
• Edit Details allows for entering event, venue and vehicle details to be
stored with the configuration file.
• Check Channels verifies that all channels are correctly generated.
• Edit Configuration Comments allows for other comments to be stored with
the configuration file.
• View Configuration Summary gives a quick overview of the configuration
file.
• Convert Logging Image allows users to manually convert a log file for use
in i2.
• Exit exits the program.
Page 22

MoTeC Configuration 17
Tip: The most recently used files appear at the bottom of the File menu. This
is often the easiest way to open an existing file.
Backups
Whenever a file is saved, the previous content of the file is saved in the Save
Backups directory. The total number of files is limited to 100.
Channels
Channels are used to convey information between the various systems of the
C185. For example an input pin may feed a channel called ‘Fuel Pressure’.
This channel may then be used by another system, such as the Display
System or Data Logging systems.
The C185 channel scheme allows complete flexibility in channel usage, as
any available channel can be used by any other function, i.e. any channel can
be logged, displayed, used in conditions, used in alarms, used as an input to
the user definable tables, etc.
All systems within the C185 that generate values must feed one of the
channels.
Pre-defined Channels
MoTeC has defined an extensive list of channels.
General Purpose Channels
Since the use of all channels cannot be predetermined, a number of general
purpose channels have been included for occasions when a suitable
predefined channel is not available.
These general purpose channels may be required when measuring an
uncommon value, or when a general purpose function needs to generate a
special output channel. For example, a 3D table may generate an output
channel to control a valve of some sort, in which case a general purpose
channel may be used and named appropriately.
Page 23
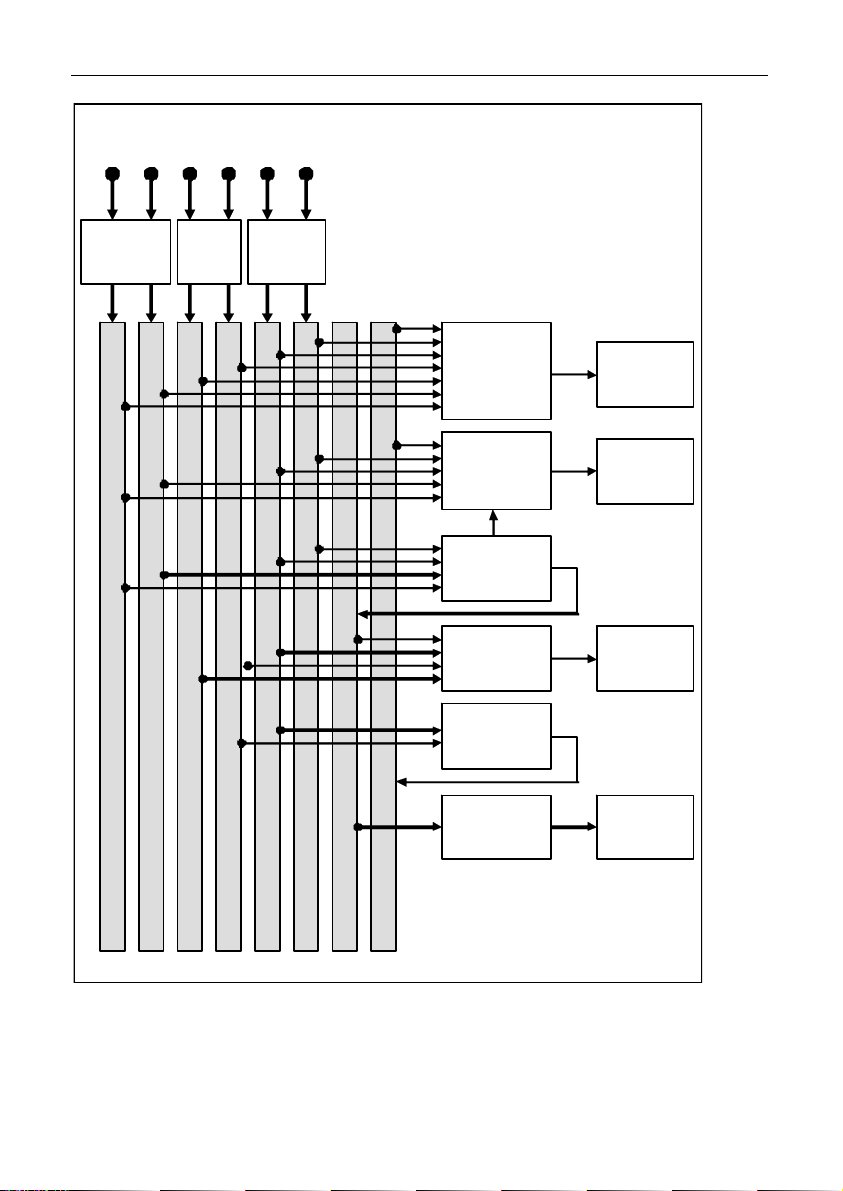
18 Configuration MoTeC
Cha nnel Co nnecti on Example
Sensors
Analogue
Inputs
Speed
Inputs
ECU
CAN
Comms
Data
Logging
System
Display
System
Alarm
System
RS232
Comms
Gear
Detection
Loggi ng
Memory
LCD
Display
Telemetry
Auxiliary
Outputs
Fuel Pressure
Oil Pressure
Wheel Speed Front
Wheel Speed Rear
Engine R PM
larm Warning Light
Engine Tem perature
Gear
Warning
Light
Channels
Page 24

MoTeC Configuration 19
Channel Properties
Each channel has defined properties, some of which may be modified by the
user. Predefining these properties makes the channels easy to use
throughout the rest of the software.
• Properties that may be modified by the user
o Name
The channel names (and abbreviations) may be changed if necessary.
However name changes should be limited to name preferences rather
than redefining the purpose of the channel, except for the general
purpose channels which may be renamed to suit the current use.
o Abbreviation
o Units (e.g. degrees Celsius, degrees Fahrenheit)
The units for a channel can be selected from a predefined list, for
example the Engine Temperature channel may have units of degrees
Celsius, Fahrenheit or Kelvin. Conversion between units is
automatically handled by the software.
Note: The units are used for display purposes only. This means that
the units can be changed at any time without affecting the calibration of
the channel.
• Fixed properties
o Measurement type (e.g. Temperature)
Defining the measurement type allows the channels to be displayed in
any unit suitable for that type, with automatic conversion between the
units. For example all temperature channels can be displayed in
degrees Celsius, Fahrenheit or Kelvin.
o Resolution
The resolution of all channels is fixed, for example the resolution of the
Engine Temperature channel is fixed at 0.1 °C.
Fixed channel resolutions ensure that the unit conversion system
works properly and that channel comparisons can be performed
correctly.
o Suitable logging rates
o Suitable display filtering
o Minimum and maximum range
Page 25
20 Configuration MoTeC
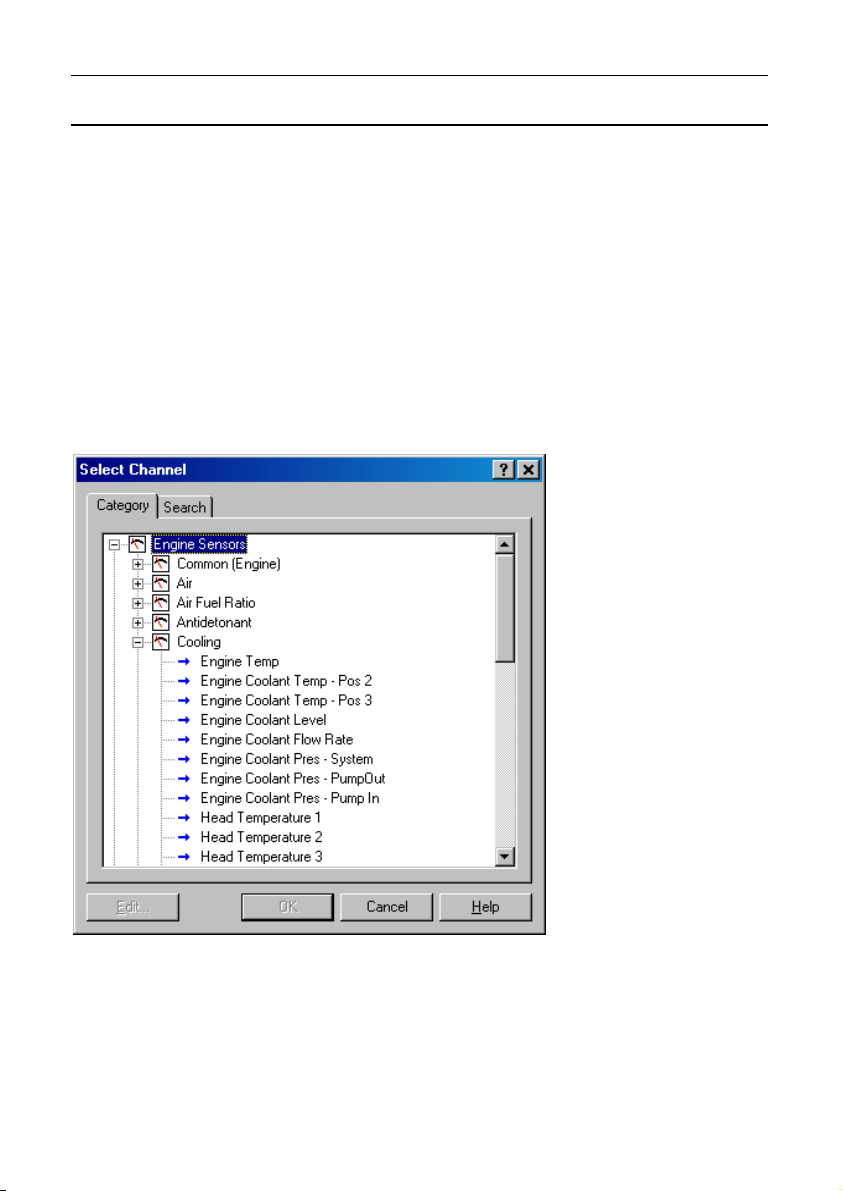
Selecting Channels
There are two methods of selecting channels, either the Category Method or
the Search Method.
Category Method
This method divides all the channels into categories and sub categories, so
that the list can be narrowed down to a small list of channels. For example,
the ‘Engine Sensors / Cooling’ category shows a list of channels asso ciated
with the cooling system of the engine.
When selecting a channel from the complete list of channels, it is usually
easiest to use the category selection method, for example when assigning a
channel to an input pin.
Tip: To expand a category click on the plus sign (+) next to the category
name.
Page 26
MoTeC 21 Configuration
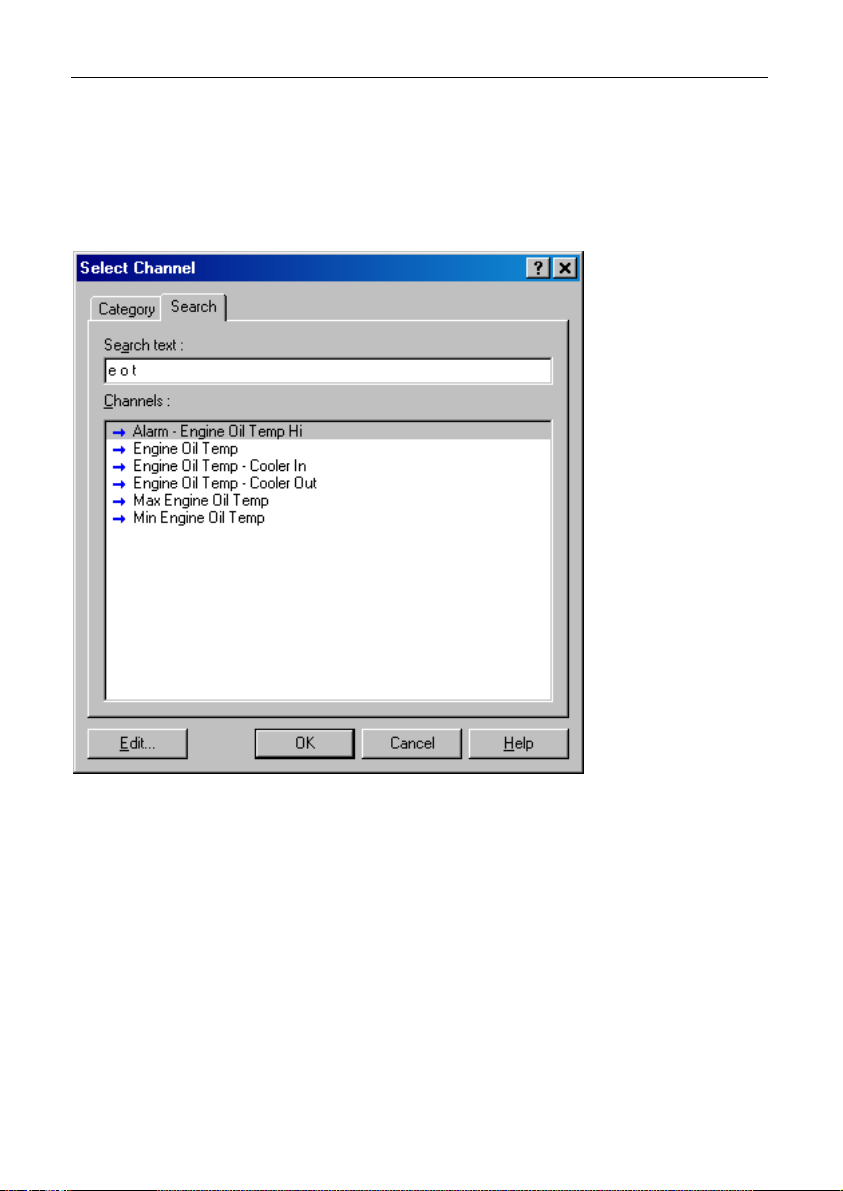
Search Method
This method lists all channels in alphabetical order and allows a channel to be
found either by typing the first few letters of any word in the channel name, or
by scrolling through the list.
Note: The words may be typed out of order so that ‘Engine Oil Temp’ could
be found by typing "temp eng oil" or "oil t eng" or "e o t”
T
his method is most useful when selecting a channel from the available
channels. For example, if ‘Engine Temperature’ has been assigned to an
input pin, it can be easily located in the Search list, since this list normally
contains 50 to 100 items.
only
Page 27

22 Configuration MoTeC
Connections
Configuring Inputs
• On the Connections menu, click Devices
• Select the device (e.g. C185) and then click the Input pins tab
This will list all inputs available for this product
Note: Some inputs require the 52 I/O Upgrade to make them available.
See C185 Upgrades
• Select the input and click Channel (or double click the input)
• Assign a measurement channel to the input and click OK
The channel needs to be calibrated using one of two options
• Select Load Cal if a pre-defined calibration is available
OR
• Double-click the input to enter a calibration
Other tasks:
• Change Cal – to change the calibration
• Spd Levels – only for speed inputs
• Settings – to set default
Configuring Outputs
• On the Connections menu, click Devices
• Select device (e.g. C185) and then click the Output Pins tab to list all
outputs available for this product
Note: Some outputs require 52 I/O Upgrade to make them available. See
C185 Upgrades.
• Select the output and click Change (or doubleclick the output)
• Select a mode to make appropriate settings available
• Follow the directions on the screen and when all settings are done click
OK
Configuring Communications
• On the Connections menu, click Communications
• Select an available communications section (CAN or RS232)
• Click Select and choose one of the available communications templates
Page 28

MoTeC Configuration 23 Comms Templates
Communication templates are available for most connected MoTeC devices.
When MoTeC releases new products, new communication templates will also
be released. These will be incorporated in the latest software versions. See
Updating C185 Dash Manager Software on how to update to a new software
version to make the latest communication templates available.
Calculations
The C185 has special and user definable general purpose cal culations
available. They are set up from the Calculations menu.
Special Calculations
• Lap Time and Number click on the tabs to set up Lap Time, Lap Speed,
Running Lap Time, Split Lap Times, Lap Number, Laps Remaining
• Speed and Distance click on the tabs to set up Ground Speed, Drive
Speed, Wheel Slip, Lap Distance, Trip Distance, Odometer
• Lap Gain / Loss to set up a continuous indication how far behind or ahead
the vehicle is compared to a reference lap
• Gear Detection to set up Current Gear
• Fuel Prediction click on the tabs to set up Fuel Used, Fuel Usage, Fuel
Remaining, Laps Remaining, Fuel Used per Lap
• Running Min / Max to set up Minimum Corner Speed, Maximum Straight
Speed and other Min/Max values
General Purpose Calculations
• Tables to set up 2D and 3D Lookup Tables
• Timers to set up General Purpose Timers
• User Conditions to activate items such as a Thermatic Fan or Gearbox Oil
Pump
• Channel Maths to perform basic calculations on channels
• Advanced Maths to perform advanced calculations
• Bit Combine to set up a bit mask
• PID Control to set up the p
For details refer to C185 Dash Manager online help.
roportional,integralandderivativegain control
Page 29

24 Configuration MoTeC
Functions
Data Logging
Data logging allows sensor readings and calculated values to be stored in the
C185 memory for later analysis using the i2 Data Analysis software.
To configure logging
• On the Functions menu, click Logging
• Select the relevant tabs to set up the logging parameters
Refer to C185 Dash Manager online help for additional information.
Power
The C185 power can be turned off at any time without losing the logged data,
because it uses FLASH memory that does not require an internal battery to
keep it alive.
Logging Memory
The C185 comes with 250 MB memory as standard. The Data Logging
upgrade will increase this to 500 MB. See C185 Upgrades.
Start and Stop Logging Conditions
To avoid logging unnecessary data, logging can be started and stopped by
user definable conditions.
For example logging might start when the vehicle exceeds 50 km/h, and stop
when the engine RPM is below 500 RPM for 10 seconds.
C185 provides the normal logging type; this will continuously log data to
memory whenever the Start Condition is true and the Stop Condition is false.
Memory Usage
When the logging memory is full the C185 may be configured to either stop
logging, or to overwrite the oldest data, which ensures that the most recent
data is always available. This is referred to as cyclic logging.
For most applications it is recommended that cyclic logging is used.
Logging Time
The maximum logging time is dependent on the logging memory size, the
number of items logged and the rate at which they are logged. The
configuration software will report the total available logging time.
Page 30

MoTeC Configuration 25 Logging Setup Files
The logging list can be saved and loaded from a file. This allows multiple
logging setups to be used.
Logging Rate
The logging rate sets how often each channel is logged and can be set
individually for each channel. The C185 can store values at up to 1000 times
per second.
The rate at which the values are logged must be fast enough to record all
variations in the reading. If the value is logged too slowly, the readings can be
totally meaningless. For example, suspension position may need to be logged
at 200 times per second or more.
However, if a value is logged faster than necessary it will not improve the
accuracy of the logged data. It will just reduce the total logging time available.
For example, the engine temperature only needs to be logged at once per
second.
CAN Bus Bandwidth Limit
High logging rates also increase the amount of data that is being received
from the measurement devices, which increases the amount of data on the
CAN bus. This can lead to exceeding the CAN bus bandwidth limit. See
CAN Bus Bandwidth Limit.
Note: The C185 Manager will warn if the bandwidth is likely to be
exceeded.
Maximum Logging Rate
The maximum logging rate is limited to the update rate of the particular
channel. This varies significantly depending on the source of the channel.
For example, some VIM inputs update at 5000 Hz, whereas some
communications devices may only update at 50 Hz. Also some internal
calculations may be limited to 100 Hz.
Update Rate
Each input is measured at a maximum rate which is dependent on the
capabilities of the measuring device and may also vary between inputs on that
device. For example the VIM has some inputs that update at 500 Hz and
others that update as fast as 5000 Hz. See Update Rate Summary.
Anti-Alias Filter
If a channel is logged at a rate slower than its specified update rate then an
optional anti-alias filter can be applied.
Page 31

26 Configuration MoTeC
The anti-alias filter is used to average out any variations in the signal between
logged values. This ensures that unrepresentative values are not logged.
The anti-alias filter is implemented by averaging the channel values between
logging events. For example, if a channel has an update rate of 1000 Hz and
it is logged at 100 Hz then the preceding 10 samples will be averaged each
time it is logged.
The anti-alias filter is normally turned on by default when a channel is added
to the logging list, but may be turned off if required. For normal purposes it is
recommended that the anti-alias filter is left turned on.
Note: For some channels the anti-alias filter cannot be turned on because the
averaging performed by the filter would cause incorrect values. This is the
case for on/off channels and channels where the bit values have a particular
meaning, for example error group channels.
Real Time Value (VIM/SVIM, ADL2, SDL)
For channels that come from a VIM, SVIM an ADL2 or an SDL the logging
anti-alias filter also affects the real-time value of the channel. This is the
value that all other parts of the system see, such as the various
calculations.
Note: The anti-alias filter is limited to 50 Hz for real time values even if the
channel is logged at a lower rate. For example, a channel logged at 10 Hz
will be filtered and updated at 10 Hz in the logging and 50 Hz for the real
time value.
Note: Channels that are not logged are updated at 50 Hz.
Real Time Value (For devices other than VIM, SVIM, ADL2, SDL)
The real time value from other devices and from internal calculations is not
anti-aliased at the logging rate, however the value can be anti-aliased in
the logging.
Phase Shift
The anti-alias filter will cause a phase shift (time delay) of half the logging
rate. For example, a channel logged at 100 Hz is logged every 10
milliseconds, so it is delayed by 5 milliseconds.
For most purposes this time delay is not an issue.
Channels logged at the same rate are delayed by the same amount, which
negates this effect when comparing these channels.
This applies to all channels whether they are generated internally from a
calculation or whether they are generated externally from devices such as
a VIM or a display device.
Page 32

MoTeC Configuration 27 Track Map Sensor Requirements
In order for the i2 Data Analysis software to plot a track map the following
sensors are required and must be logged.
• Lateral G force (internal sensor)
• Wheel Speed
• Lap Beacon (the ‘Beacon’ Channel must be logged)
• Optionally Longitudinal G force (internal sensor)
A Longitudinal G force sensor should be used if the vehicle has only one
wheel speed sensor. This allows the analysis software to eliminate wheel
lockups which is essential when creating or using a track map.
Page 33

28 Configuration MoTeC
Display
The C185 display is a high contrast, high brightness colour LCD display.
The displayed channels and labels are configured on a display style that can
be chosen from a list of predefined styles. Alternatively, a custom display may
be created using the separately purchased Display Creator software. See
Display Creator DBC File Setup.
To configure the display
1. On the Functions menu, click Display
2. Select the required mode (Race, Practice, Warmup) by selecting the
relevant tab.
3. Select the required display style.
4. Set the labels and channels you want to display for each of the
numeric displays. To do this double click on the relevant display, or:
a. Select the display.
b. Select the Change button.
Page 34

29 MoTeC Configuration
Display Modes (Pages)
The display has three display modes; the default names are Race, Practice
and Warmup. The mode is changed by pressing the button assigned to this
function.
The mode names can be changed to suit your individual needs; this is done
by double-clicking on the Page Label field.
Race Page
The Race display is normally used to display minimal information, e.g. RPM,
Lap Time, Fuel Remaining or Laps Remaining.
Practice Page
The Practice display is normally used to display basic information, plus
information to help the driver improve lap times, e.g. Lap Time, Lap
Gain/Loss, Maximum Straight Speed, Minimum Corner Speed or Corner Exit
Speed.
Warm-up Page
The Warm-up display is normally used to display important engine sensor
readings during engine warm-up, e.g. RPM, Battery Voltage, Engine
Temperature, Oil Pressure, Oil Temperature and Fuel Pressure.
Gain / Loss Bar
The Gain / Loss bar can be configured to graphically represent the current
value of the Lap Gain/Loss Running channel. If not configured the Gain / Loss
Bar does not display.
Example Bar / Loss Bar
This bar can be customised to suit a user's preference. For example:
• Setting the scale and the time units.
• Customise the labels at either end of the bar (in the example above, Left
and Right is used, another example is +2 and -2, where 2 is the scaling
value).
• Invert colours, that is - red or green on either side.
• Specify the negative to the left or right.
Page 35

30 Configuration MoTeC
Dial or Bar Graph (depending on style chosen)
Example dial
Example sweep bar
Example linear bar
The dial or bar graph has a user definable range and is typically used as a
tacho, however it can be used to display any other value.
A fully programmable shift point can be displayed, which can also be gear
dependent.
Page 36

31 MoTeC Configuration
Top Displays
The three numeric displays shown above can be programmed to display any
channel value.
The numeric displays can show any channel value plus up to two override
values. Override values display each time their value is updated. This is
useful for values that are updated periodically. The override values are shown
for a programmable period of time. For example, a numeric display could
normally show the Running Lap Time (which is continuously updating), then
be overwritten by the Lap Time for 10 seconds each time the Lap Time is
updated.
The label above each of the numeric displays can be changed to suit the
channel assigned.
Page 37

32 Configuration MoTeC
Centre Display
The centre display is normally used to display the current gear but can be
used for other purposes.
Bottom Display
Page 38

33 MoTeC Configuration
At the bottom, up to 20 lines can be accommodated, with each line containing
up to 3 channel values at a time.
The label above each value can be changed to suit the channel assigned.
The 20 lines can be scrolled up or down using external buttons.
Similar to the top numeric displays, the bottom display can show up to four
override values.
Four Line Style
Where the four line style is chosen, it shows four lines of values at a time, with
up to three values per line.
The 20 lines can be scrolled up or down, 4 lines at a time, using external
buttons.
Alarms
Any alarms generated are displayed at the bottom of the display. The active
alarm message displays across the complete row, overriding all other values
until the alarm is acknowledged. To draw the driver's attention to the display,
it is recommended to activate a warning light.
The message can be defined as required and can include the current sensor
reading or the sensor reading when the alarm was triggered.
The alarms remain active until they are acknowledged, either by a driver
activated switch or automatically after a defined period of time.
Page 39

34 Configuration MoTeC
The warning alarm limits are fully programmable and may include up to 6
comparisons to ensure that the alarms are only activated at the correct time.
For example, an engine temperature alarm may activate at 95 °C if the ground
speed has been above 50 km/h for 30 seconds. The speed comparison
avoids the alarm showing during a pit stop due to heat soak. Additionally
another comparison could be set at a higher temperature to cover all other
situations.
The comparison values can be automatically incremented or (decremented)
when an alarm occurs. For example the engine temperature alarm may be set
at 95 °C with and increment of 5 °C, so the second time the alarm activates at
100 °C. A limit may be set on the number of times the comparison value is
allowed to increment. An alarm may return to its original value after a period
of time, in case the alarm condition was temporary.
The alarms can be dependent on the current display Mode (for example
Warm-up, Practice or Race).
Display Formatting
Units
All display units can be changed to suit the driver preferences, for example,
show temperatures in Fahrenheit rather than in Celsius.
Note: This is independent of the units used for other purposes.
Decimal Places
The number of decimal places can be reduced for display purposes, for
example the engine temperature is measured to 0.1 °C but is better displayed
with no decimal places.
Display Creator DBC File Setup
When using Display Creator, communications and channels need to be set
up. To automate this, a DBC file is created when the Dash Manager
configuration is saved. This file can then be imported into Display Creator.
The Display Creator Channels and Display Creator Settings tabs are used to
set the definitions for creation of the DBC file. This file is then imported into
DisplayCreator to automate the communications and channels setup.
Display Creator Channels tab
This tab is used to select the channels to include in the DBC file. The DBC file
is created when the configuration is saved.
The DBC file is imported by Display Creator to automate the setup of
communications and channels.
Note: Channels selected in the Display Creator Setting tab must also be
selected in this list for them to be included in the DBC file.
Page 40

MoTeC Configuration 35
Display Creator Settings tab
This tab is used to define page display behaviour.
Note: The channels selected on this tab must also be included in the Display
Creator Channels list for them to be included in the DBC file for import to
Display Creator.
Number of Pages
Specifies the number of pages defined in the applicable Display Creator
configuration.
Preserve Page
If ticked and the device is power cycled, the last page that was displayed for
at least five second before the power cycle occurred will display.
If not ticked and the device is power cycled, the default page will display.
Page Channels
Specifies the channels used to set page up, down and reset values.
Page up is the next page in numeric sequence, default channel is Display
Page Up Button.
Page down is the previous page in numeric sequence, default channel is
Display Page Down Button.
Page reset returns the display to the default page, default channel is Display
Page Reset Button.
Output Channels
This is used to select the output channel, which is the channel that controls
the page displayed, default channel is Display Page.
Note: For page control to function, this channel should be included in the
Display Creator Channels list so that it is included in the DBC file for import to
Display Creator.
For example, if the output channel value is 3 (that is page 3 is displayed), it is
increased to 4 via the Display Page Button Up channel and decreased to 2 via
the Display Page Down Button channel.
Page 41

36 MoTeC Configuration
Other Functions
The C185 can perform many other functions accessible from the Functions
menu including the following:
• Shift Lights – to configure the shift point values for use with the Shift
Lights.
• Shift Light Module – to configure the C185 10 stage shift lights as well as
an additional MoTeC's SLM-C or SLM.
• Telemetry to set up telemetry channels
• Tell-tales Setup to store minimum or maximum values
• Engine Log Setup to set up four separate engine logs with separate
conditions
• Diagnostics Log Setup to set up conditions and channels for the
diagnostics log
• Preserved Channels to set up the conditions when to preserve channel s
Refer to C185 Dash Manager online help for additional information.
Page 42

MoTeC Operation 37
Operation
To perform any of the activities in the Online menu, the PC needs to
communicate to the C185.
Note: All other menu items perform offline activities.
Retrieving the Logged Data
• On the Online menu, click Get Logged Data
A personal computer is used to unload the logged data from the C185. The
logged data is then stored on the computer hard disk.
After each unload the user has the option to clear the logging memory.
The unload may be interrupted part way through if necessary by
disconnecting the computer. The partial unload will contain the most recently
logged data and will be stored on the computer hard disk. In this case the
C185 logging memory is not cleared and logging will continue as normal at
the end of the existing data. Next time the logged data is unloaded both the
new data and the previously partly unloaded data will be retrieved.
Sending and Retrieving Configuration Files
• On the Online menu, click Send Configuration to se nd the currently open
configuration file
When a configuration file is sent to the C185 the existing C185 data is
retrieved and stored in the From Dash Backups directory to use in case the
data in the C185 needs to be restored. The maximum number of files is 10.
• On the Online menu, click Get Configuration to retrieve the current
configuration file
This is normally not necessary unless the original file is not available on the
PC.
Zeroing Sensors
Some sensors require regular zeroing, for example Steering Angle,
Suspension Position, Ride Heights, G Force Sensors & Throttle Position.
C185 Dash Manager provides a feature for easy zeroing of all these sensors.
Page 43

38 Operation MoTeC
Checking Operation
Monitor Channels
• On the Online menu, click Monitor Chan nels
• To show any channel on an oscilloscope style screen, click Utilities and
then Oscilloscope
The currently active channels can be monitored to check the operation of all
functions and measurements.
Simulate
• On the Online menu, click Simulate
The Simulate feature allows most input channels to be manually changed so
that the C185 operation can be checked under abnormal conditions, e.g. High
Engine Temp. This is extremely useful for checking that the C185 is working
as expected.
Test
• On the Online menu click the approp riate test
A number of tests are provided to check the operation of the C185, such as
the Display Test.
Configuration Versions and Updating
• On the Online menu, click Upgrade Dash Version
The software inside the C185 (firmware) can be updated by the user at any
time to take advantage of the latest features.
Matching Versions
The firmware version must match the version of the C185 Dash Manager
software on the PC in order to communicate. C185 Dash Manager will show a
warning if the versions do not match.
Tip:
To check the version of C185 Dash Manager, click About MoTeC C185 Dash
Manager on the Help menu.
The firmware version is displayed on the bottom line of the display for 2
seconds when the C185 is powering up.
Matching Configuration File
The configuration file must also match the software and firmware versions
used. The display will show a warning if the file does not match.
Page 44

MoTeC Operation 39
Configuration files can be updated by choosing the option to automatically
update the configuration file while updating the software (firmware). It can
also be done manually by upgrading the configuration file and sending it to
C185:
• On the File menu, click Open
• In the Files of type box select the ne w version file extension.
The file will be converted to the new version format and saved with the
same file name but with the new version file extension.
Note: The old file is not changed.
• On the Online menu, click Send Configuration to se nd the configuration
file to the C185
Upgrading C185
• On the Online menu, click Enable Dash Options
Several options are available as upgrades to customise and grow your
system.
The currently enabled options can be listed and new options can be activated
through a password acquired from MoTeC.
Password Protection
• On the Online menu, click Set Access Passwords
Several C185 capabilities can be protected from unauthorised access by
using the password protection.
Other Online Activities
Many other activities are accessible from the Online menu including the
following:
• Set Reference Lap to send a reference lap to the C185 used in the lap
gain/loss system. See Calculations.
• View to view:
o configuration settings e.g. Tell-tales, Engine Log
o GPS Beacon Definitions
o saved details e.g. Running Totals
o Device Halt Counts
• Retrieve to retrieve Tell-tales and Engine Log
• Communication to list the current Connections Settings
• Miscellaneous
Page 45

40 MoTeC Operation
o Erase Logged Data without unloading
o Serial Number to view the Serial and Hardware Number.
The Serial Number is required when ordering upgrade passwords.
The Hardware Number is for MoTeC internal use.
o Change Display Mode to switch between Race, Warm-up and Race
mode
Refer to C185 Dash Manager online help for additional information.
Page 46

MoTeC Appendices 41
Appendices
Specifications
Specifications listed as optional are available as upgrades to customise and
grow your system. These additional features are activated through a simple
password acquired from MoTeC, at any time when you need it. An overview
of the upgrades can be found in C185 Upgrades.
Logging
• 250 MB standard logging memory (500 MB optional)
• Logging rates up to 1000 samples per second
• Fast Ethernet download
Display
• Type: Colour TFT LCD, anti-reflective
• Resolution: 800 x 480, anti-aliased graphics
• Layouts: selectable fixed layouts, user programmable layouts available in
future releases
• 48 user-defined, scrollable message lines with programmable overrides
• 3 programmable modes with customisable labels
Inputs
• 10 (20 with I/O upgrade*) analogue voltage inputs:
- 4 (8*) x 0 to 5.46 V, 1.33 mV resolution
- 6 (12*) x 0 to 15.0 V, 3.66 mV resolution
• 4 (8 with I/O upgrade) analogue temperature inputs
- 0 to 15 V, 3.66 mV resolution
• 4 x Digital inputs
• 4 x Speed inputs with voltage measuring capability
• 2 x Switched inputs
• Compatible with VIM/SVIM input expanders
Outputs
• 6 x PWM, digital or switched outputs (8 optional)
• 1.0 Amp max, current limited and thermal overload protected
• Compatible with up to 2 E888/E816 input/output expanders
Page 47

42 Appendices MoTeC
Internal Sensors
• 3 axis G sensor
• Dash temperature sensor
• Sensor supply voltage
• Battery voltage
Communications
• 4 configurable CAN buses, with individually programmable CAN bus
speeds. One can be used as RS232 Receive. Only 2 of the CAN buses
support VIM/SVIM Expanders
o Maximum data range 1 Mbit/sec
o Recommended terminating impedance 100 ohm
• 2 dedicated RS232 ports
Physical
• Size: 134.5 x 103.9 x 20.2 mm excluding connector
• Weight 410 g
• 1 x 79 pin Autosport connector
Power Supply
• Operating voltage: 6 to 32 volt DC
• Operating current: 0.5 ampere typical (excluding sensor currents)
• Reverse Battery protection
• Battery Transient protection
Operating Temperature
• Internal Temperature Range: –20 to 70 °C (above 60 °C maximum
backlight brightness progressively reduced)
• Ambient Temperature Range: –20 to 55 °C
Sensor Supply Current
• 5 V Sensor supply: 0.25 ampere maximum
• 8 V Sensor supply: 0.25 ampere maximum
Page 48

MoTeC Appendices 43
C185 Upgrades
Several options are available as upgrades to customise and grow your
system. These additional features are activated through a password acquired
from MoTeC, at any time when you need it.
For the C185 Dash Logger the following upgrades are available:
Data Logging
Increases the internal logging memory to 500 MB. (Standard 250 MB memory
available)
Pro Analysis
Provides access to advanced i2 Pro data analysis software with multiple
graph overlays, X-Y plots, advanced maths functions, synchronised video
(automatic alignment), and flexible layouts to accommodate virtually any user
preference.
T2 Telemetry
Enables transmission of live data from the vehicle to the pit where it can be
viewed in real time using the MoTeC Telemetry Monitor software. Requires
radio modems or other means of transmission.
The upgrade allows use of the older Telemetry Monitor or T2 Telemetry.
Remote Logging
Enables conversion of telemetry data into a log file to use with i2 analysis
software. Requires the Telemetry upgrade.
I/O
Provides additional input/output functionality consisting of:
• 10 extra analogue voltage inputs
• 4 extra analogue temperature inputs
• Advanced Functions, which provides:
- Advanced Maths
- Channel Maths
- 16 x 2D Tables (instead of 4)
- 16 x 3D Tables (instead of 4)
- 50 User Conditions (instead of 20)
Page 49

44 Appendices MoTeC
Characteristics
Input Characteristics
Analogue Voltage Inputs
Suitable for: Potentiometers
Voltage output sensors
Variable resistance sensors with pull-up
resistor
Measure Voltage
Range:
Input Resistance: 100k ohms to 0 V
Resolution:
Measurement
Methods:
Update Rate: 1000 times/second
Filter: 240 Hz 1st order
Calibration Accuracy: Gain 0.05% max (Ratiometric method)
Inputs 1—4 and 11—14: 0 to 5.46 V
All other Inputs: 0 to 15.0 V
Note: Voltages outside this range may affect
the readings on other inputs.
Inputs 1—4 and 11—14: 1.33 mV
All other Inputs: 3.66 mV
Ratiometric
Absolute
Variable Resistance Off/On
Gain 0.15% max (Absolute method)
Offset ± 6 mV max
Linearity ± 6 mV max
Temperature Stability 60 ppm/°C max
Calibration Schedule 12 months
Page 50

MoTeC Appendices 45 Analogue Temp Inputs
Suitable for: 2 wire variable resistance sensors some voltage
output sensors
Measure Voltage Range: 0 to 15.0 V
Note: Voltages outside this range may affect the
readings on other inputs.
Input Resistance: 1000 ohms p ull-up to 5 V sensor supply
+100 k to 0 V
Resolution: 3.66 mV
Measurement Methods: Ratiometric
Absolute
Variable Resistance
Off/On
Update Rate: 1000 times / second
Filter: 290 Hz 1st order
Calibration Accuracy:
Gain: 0.05% max (Ratiometric method)
Gain: 0.15% max (Absolute method)
Offset: ± 6 mV max
Linearity: ± 6 mV max
Temperature Stability: 60 ppm/°C max
Calibration Schedule: 12 months
Switch Inputs
Suitable for: Switch to 0 V
Off/On Voltage signal
Pull-up Resistor: 2200 ohms to 3.3 V
Voltage Range: 0 to 15 V
Positive Trigger Threshold: 2.4 V max
Negative Threshold: 0.6 V min
Hysteresis: 0.4 V Min
Measurement Methods: Off/On only
Filter Time Constant: 22 usec
Page 51

46 Appendices MoTeC
Digital Inputs
Suitable for: Switch to 0 V
Logic signal and open collector device (e.g. Hall
Switch)
Pull-up Resistor: 2200 ohms to 3.3 V
Voltage Range: 0 to 15 V
Positive Trigger Threshold: 2.4 V max
Negative Threshold: 0.6 V min
Hyst eresis: 0.4 V min
Update Rate: 100 times / second
Filter Time Constant: 22 usec
Measurement Methods:
Frequency
Resolution 0.1 Hz
Maximum Frequency 3200 Hz
Rising Edge Triggered
Period 1 usec
Measures period between rising edges
Resolution 1 usec
Maximum 32 msec
Period 100 usec
Measures period between rising edges
Resolution 100 usec
Maximum 3.2 sec
Pulse Width 1 usec
Measures pulse low time
Resolution 1 usec
Maximum 32 msec
Pulse Width 100 usec
Measures pulse low time
Resolution 100 usec
Maximum 3.2 sec
Page 52

MoTeC Appendices 47 Speed Inputs
Hall mode
Suitable for: Switch to 0 V
Pull-up Resistor 2200 ohms to 2.7 V
Voltage Range 0 to 15V
Trigger Threshold Selectable between -1.33 V and 4.68 V
Magnetic mode
Suitable for: Two wire magnetic sensor (variable reluctance
Input Resistance 100k ohms to ground (no pull-up)
Voltage Range -80 V to +80 V
Programmable trigger
levels
For both modes
A 2200 ohm pull-up resistor connected to 2.7 V.
Logic signal
Open collector device (e.g. Hall Switch)
The pull-up resistor is disengaged and the
trigger levels can be varied depending on the
input frequency.
sensor)
-1.33 V to 4.68 V
Update Rate: 100 times / second
Filter Time Constant 25 usec
Hysteresis 0.17 V min
Measurement Methods:
Frequency
Resolution 0.1 Hz
Maximum Frequency 3200 Hz
Falling Edge Triggered
Period 1 usec
Measures period between falling edges
Resolution 1 usec
Maximum 32 msec
Page 53

48 Appendices MoTeC
Period 100 usec
Measures period between falling edges
Resolution 100 usec
Maximum 3.2 sec
Pulse Width 1 usec
Measures pulse high time
Resolution 1 usec
Maximum 32 msec
Pulse Width 100 usec
Measures pulse high time
Resolution 100 usec
Maximum 3.2 sec
Page 54

MoTeC Appendices 49 Analogue Input Sampling
4 times oversampling is scheduled with samples taken every 250 usec,
providing measurements every 1 msec.
The following inputs are sampled at 250 usec, with microsecond offsets as
shown in the table:
Offsets
0.0 usec AT1 AV1 AV15
+9.3 usec AT2 AV2 AV16
+20.9 usec AT3 AV3 AV17
+30.1 usec AT4 AV4 AV18
+39.4 usec AT5 AV5 AV19
+51.0 usec AT6 AV6 AV20
+60.3 usec AT7 AV7 AV21
+71.9 usec AT8 AV8 AV22
+81.1 usec N/A AV9 AV23
+90.4 usec 8VSEN AV10 AV24
+102.0 usec 5VSEN AV11 INT TEMP
+111.3 usec ACCELX AV12 SPD1
+122.9 usec ACCELY AV13 SPD2
+132.1 usec ACCELZ AV14 SPD3
+141.4 usec N/A BAT VOLTS SPD4
0.0 usec +1.5 usec +3.1 usec
Output Characteristics
Output Type: Open Collector (Drives to ground) with weak pull-up
(10 kΩ) to battery positive
Current: 1.0 A max, current limited & thermal overload protected
Output Clamp: 40 V Flyback Clamp (no clamp diode to supply).
Page 55

50 Appendices MoTeC
Pin List by Pin Number
Pin Name Function
1 AV15 Analogue Voltage Input 15
2 AV16 Analogue Voltage Input 16
3 AV17 Analogue Voltage Input 17
4 AV18 Analogue Voltage Input 18
5 AV19 Analogue Voltage Input 19
6 0V Sensor 0 V
7 BAT- Battery Negative
8 BAT+ Battery Positive
9 AUX1 Auxiliary Output 1
10 AUX2 Auxiliary Output 2
11 AUX3 Auxiliary Output 3
12 AUX4 Auxiliary Output 4
13 AUX5 Auxiliary Output 5
14 AUX6 Auxiliary Output 6
15 RS232-2 TX RS232-2 Transmit Output
16 RS232-2 RX RS232-2 Receive Input
17 0V Sensor 0 V
18 5V Sensor 5 V
19 AV7 Analogue Voltage Input 7
20 AV8 Analogue Voltage Input 8
21 AV9 Analogue Voltage Input 9
22 AV10 Analogue Voltage Input 10
23 AV11 Analogue Voltage Input 11
24 AV12 Analogue Voltage Input 12
25 AV13 Analogue Voltage Input 13
Page 56

MoTeC Appendices 51
Pin Name Function
26 AV14 Analogue Voltage Input 14
27 0V Sensor 0 V
28 5V Sensor 5 V
29 Reserved
30 Reserved
31 Reserved
32 Reserved
33 0V Sensor 0 V
34 AT1 Analogue Temp Input 1
35 AT2 Analogue Temp Input 2
36 AT3 Analogue Temp Input 3
37 AT4 Analogue Temp Input 4
38 AT5 Analogue Temp Input 5
39 AT6 Analogue Temp Input 6
40 0V Sensor 0 V
41 AT7 Analogue Temp Input 7
42 AT8 Analogue Temp Input 8
43 0V Sensor 0 V
44 5V Sensor 5 V
45 AV1 Analogue Voltage Input 1
46 AV2 Analogue Voltage Input 2
47 AV3 Analogue Voltage Input 3
48 AV4 Analogue Voltage Input 4
49 AV5 Analogue Voltage Input 5
50 AV6 Analogue Voltage Input 6
51 0V Sensor 0 V
52 DIG1 Digital Input 1
Page 57

52 Appendices MoTeC
Pin Name Function
53 DIG2 Digital Input 2
54 DIG3 Digital Input 3
55 DIG4 Digital Input 4
56 0V Sensor 0 V
57 SW1 Switch Input 1
58 SW2 Switch Input 2
59 CAN4L CAN 4 Low
60 CAN4H CAN 4 High
61 0V Sensor 0 V
62 8V Sensor 8 V
63 SPD1 Speed Input 1
64 SPD2 Speed Input 2
65 SPD3 Speed Input 3
66 SPD4 Speed Input 4
67 E-TX+ Ethernet Transmit +
68
E-TX– Ethernet Transmit –
69 AV20 Analogue Voltage Input 20
70 RS232-1 TX RS232 Transmit Output
71 CAN3L CAN 3 Low
72 CAN3H CAN 3 High
73 CAN1L CAN 1 Low
74 CAN1H CAN 1 High
75 CAN2L CAN 2 Low / RS232 Ground Input
76 CAN2H CAN 2 High / RS232 Receive Input
77 E-RX+ Ethernet Receive +
78
E-RX– Ethernet Receive –
79 RS232-1 RX RS232 Receive Input
Page 58

MoTeC Appendices 53
Pin List by Function
Pin Name Function
Battery Power
7 BAT- Battery Negative
8 BAT+ Battery Positive
Analogue Voltage Inputs
45 AV1 Analogue Voltage Input 1
46 AV2 Analogue Voltage Input 2
47 AV3 Analogue Voltage Input 3
48 AV4 Analogue Voltage Input 4
49 AV5 Analogue Voltage Input 5
50 AV6 Analogue Voltage Input 6
19 AV7 Analogue Voltage Input 7
20 AV8 Analogue Voltage Input 8
21 AV9 Analogue Voltage Input 9
22 AV10 Analogue Voltage Input 10
23 AV11 Analogue Voltage Input 11
24 AV12 Analogue Voltage Input 12
25 AV13 Analogue Voltage Input 13
26 AV14 Analogue Voltage Input 14
1 AV15 Analogue Voltage Input 15
2 AV16 Analogue Voltage Input 16
3 AV17 Analogue Voltage Input 17
4 AV18 Analogue Voltage Input 18
5 AV19 Analogue Voltage Input 19
69 AV20 Analogue Voltage Input 20
Page 59

54 Appendices MoTeC
Pin Name Function
Analogue Temp Inputs
34 AT1 Analogue Temp Input 1
35 AT2 Analogue Temp Input 2
36 AT3 Analogue Temp Input 3
37 AT4 Analogue Temp Input 4
38 AT5 Analogue Temp Input 5
39 AT6 Analogue Temp Input 6
41 AT7 Analogue Temp Input 7
42 AT8 Analogue Temp Input 8
Switch Inputs
57 SW1 Switch Input 1
58 SW2 Switch Input 2
Digital Inputs
52 DIG1 Digital Input 1
53 DIG2 Digital Input 2
54 DIG3 Digital Input 3
55 DIG4 Digital Input 4
Speed Inputs
63 SPD1 Speed Input 1
64 SPD2 Speed Input 2
65 SPD3 Speed Input 3
66 SPD4 Speed Input 4
Auxiliary Outputs
9 AUX1 Auxiliary Output 1
Page 60

MoTeC Appendices 55
Pin Name Function
10 AUX2 Auxiliary Output 2
11 AUX3 Auxiliary Output 3
12 AUX4 Auxiliary Output 4
13 AUX5 Auxiliary Output 5
14 AUX6 Auxiliary Output 6
8 V Sensor
62 8V Sensor 8 V
5 V Sensor
18 5V Sensor 5 V
28 5V Sensor 5 V
44 5V Sensor 5 V
0 V Sensor
6 0V Sensor 0 V
17 0V Sensor 0 V
27 0V Sensor 0 V
33 0V Sensor 0 V
40 0V Sensor 0 V
43 0V Sensor 0 V
51 0V Sensor 0 V
56 0V Sensor 0 V
61 0V Sensor 0 V
CAN Interface
73 CAN1L CAN 1 Low
74 CAN1H CAN 1 High
75 CAN2L CAN 2 Low / RS232 Ground Input
Page 61

56 Appendices MoTeC
Pin Name Function
76 CAN2H CAN 2 High / RS232 Receive Input
71 CAN3L CAN 3 Low
72 CAN3H CAN 3 High
59 CAN4L CAN 4 Low
60 CAN4H CAN 4 High
Ethernet
68 E-TX- Ethernet Transmit -
67
78 E-RX- Ethernet Receive -
77
E-TX+ Ethernet Transmit +
E-RX+ Ethernet Receive +
RS232
70 RS232-1 TX RS232 Transmit Output
79 RS232-1 RX RS232 Receive Input
15 RS232-2 TX RS232-2 Transmit Output
16 RS232-2 RX RS232-2 Receive Input
Reserved
29
30
31
32
Page 62

MoTeC Appendices 57
Mounting Dimensions
C185
Note:
• All dimensions in [mm]
• Ensure product is not stressed when mounted
• Dimensions indicate actual product size, allow for clearance when
mounting
Page 63

58 Appendices MoTeC
Wiring
Connector
C185 connector
Mating connector
79 pin Autosport connector
#68086
Wire Specification
Wire
Wire to suit C185 connector: 22# Tefzel, Mil Spec : M22759/16-22
M22759/16 Wire Ratings (for various wire gauges)
Insulation Material: Tefzel
Conductor: Tin Plated Copper
Voltage Rating: 600 V
Maximum Temperature: 150 °C
Wire Gauge
[AWG]
22 0.38 5 0.045 14
20 0.61 6 0.028 8.5
18 0.96 9 0.018 5.5
16 1.2 12 0.014 4.3
Cross
Sectional Area
[mm2]
Max Current
at 100 °C
Ambient [A]
Resistance
[ohm / m])
Resistance
[ohm / 1000 ft]
14 1.9 18 0.009 2.7
12 3.0 24 0.006 1.8
Crimp Tool
Crimp Tool: M22520/2-01
Positioner for Crimp Tool: M22520/2-07
Crimp Contacts are type 22D (needed to set the crimp tool correctly)
Wire Stripping Tool
Recommended: Ideal Industries 45-2133 stripping tool with LB1195 wire stop
Page 64

MoTeC Appendices 59
PC Connection
Ethernet Wiring Schematic:
ADL3 / C185
Pin Function Pin Function
77
78 Ethernet RX – 2 Ethernet TX –
67 Ethernet TX + 3 Ethernet RX +
68 Ethernet TX – 6 Ethernet RX –
Ethernet RX + 1 Ethernet TX +
Ethernet Connector pin
Pin numbering
Plug Socket
Wire
CAT5 UTP Ethernet cable
Cable
An Ethernet RJ45 socket, connecting to a standard Ethernet cable, is
provided on:
• #62207 C185 loom incorporating
• #61131 Ethernet cable, unterminated, 2 meter
• #61132 Ethernet to Autosport pins cable, 1.8 m
Page 65

60 Appendices MoTeC
R
CAN Bus Wiring Requirements
• The CAN bus should consist of a twisted pair trunk with 100R (0.25 watt)
terminating resistors at each end.
o If the CAN bus is less than 2 meter (7 ft) long, a single termination
resistor may be used.
• The preferred cable for the trunk is 100R data cable.
• The maximum length of the bus is 16 meter (50 ft)
• CAN devices (such as MoTeC Dash Loggers, ECUs etc) may be
connected to the trunk with up to 500 mm (20 in) of twisted wire.
100R T er m inati ng
Resistors at each
end of the CAN Bus
These wires must be twisted
Minimum one twist per 50 mm (2 in)
CAN-HI
CAN-LO
100R
CAN-LO
CAN-HI
CAN
Device
<< CAN Bus >>
500 mm
max
CAN-HI
CAN
Device
CAN-LO
CAN-LO
CAN-HI
CAN
Device
500mm max
100
Page 66

MoTeC Appendices 61
C185 to ECU wiring (RS232)
The following details the methods for connecting the C185 to the various
MoTeC ECUs via RS232. In all cases this is done using the serial data stream
generated by the Telemetry function of each ECU.
In the case of the M800, M880 and M4e the C185 may be directly wired to the
ECU because these ECUs use RS232 interface levels. On the M48, M4 (pre
M4e) and the M8, a Computer Interface Module (CIM) or a PCI cable is
required to convert the signals to RS232.
M800 / M880
Note:
• The data to the C185 will be interrupted while a PC is connected (DOS
software only)
• The 9 pin connector is not used if using the Windows Calibration software.
• Data may be sent to the C185 via the CAN bus as an alternative to the
serial connection.
M4e
Note:
• Older M4 ECUs require a different connection method
• The data to the C185 will be interrupted while a PC is connected.
M48, M4 (pre M4e) and M8
The M48 & M8 and M4 (pre M4e) require the use of a CIM module or a PCI
Cable to convert the logic level signals used by these ECUs into RS232
levels.
Page 67

62 Appendices MoTeC
Using a CIM Module
Refer to the CIM module drawing for full wiring details.
Note: The data to the C185 will be interrupted while a PC is connected.
Page 68

MoTeC Appendices 63
Update Rate Summary
Device Input Type Maximum Update
Rate (per second)
C185 Analogue Voltage Inputs 1000
C185 Analogue Temperature Inputs 1000
C185 Digital Inputs and Speed Inputs 100
C185 RS232 and CAN Communications 50 max *
C185 CAN comms fast receive 1000
ACL RS232 Communications 200 *
ACL General CAN communications 200 *
VIM AV Fast Inputs 5000
VIM AV Differential Voltage Inputs 1000
VIM AV High Resolution Inputs 500
VIM AV Special Inputs 2000
VIM Speed Inputs 100
ADL2/SDL Analogue Voltage Inputs 1 to 4
(ADL2/SDL) and 11 to 14 (ADL2)
ADL2/SDL Other Analogue Voltage Inputs 500
ADL2/SDL Analogue Temperature Inputs 500
ADL2/SDL Lambda Inputs 100
ADL2/SDL Digital & Speed Inputs 100
SDL Internal G Sensors 100
E888 Thermocouple Inputs
(First Device / Second Device)
E888/816 Analogue Voltage & Digital Inputs
(First Device / Second Device)
* RS232 & General CAN Communications update rate depends on how
frequently the data is sent from the device. Typically the update rate from an
M4, M48, M8 or M800 ECU is about 20 times per second using RS232 and
about 50 times per second for the M800 using CAN.
1000
100 / 50
200 / 50
Page 69

64 Appendices MoTeC
Command line
Usage:
dash.exe -c[connection] -d -x -l -e -t -s [config file name]
[config file name]
(Optional)
Fully qualified path to the configuration file.
(eg "c:\motec\dash\config\bathurst.d30")
Note: the path must included the file extension (eg .d30)
Options :
Each of the following options can be given as "/[character]" or "-[character]".
They are shown here as "-[character]".
-c[Connection Name]
(Optional)
Select a preconfigured connection by name as configured in the dash
connections dialog.
(eg -c"Primary CAN Connection").
Note: There must not be a space between the c and the connection name.
-d
(Optional)
Causes the debug console to be displayed.
Only available for debug builds.
-x
(Optional)
Causes the app to terminate when one the following tasks has been
performed.
Page 70

MoTeC Appendices 65 Tasks :
One or more of the following may be specified.
-l
(Optional)
Perform a “Get Logged Data” operation.
-e
(Optional)
Perform a “Get Engine Log” operation.
-t
(Optional)
Perform a “Get Tell-tale Values” operation.
-p
(Optional)
Perform a “Print Summary” operation.
Note: The configuration file must be specified using a fully qualified path
including the file extension.
(e.g. -p "c:\motec\dash\config\bathurst.d30")
Note: There must be a space between -p and configuration file name.
-s
(Optional)
Perform a “Send Configuration” operation.
Note: The configuration file must be specified using a fully qualified path
including the file extension.
(e.g. -s "c:\motec\dash\config\bathurst.d30")
Note: There must be a space between -s and configuration file name.
-u
(Optional)
Perform an “Upgrade Dash Version” operation.
Page 71

66 Appendices MoTeC
CAN Bus Bandwidth Limit
The total available CAN bandwidth available on a single CAN bus is
1 Mbit/sec.
The bandwidth used by the total of all devices on a particular CAN bus must
not exceed approximately 90% of this value (900000 bits/second)
If the total bandwidth required exceeds this specification then some devices
should be connected to the second CAN bus.
Note: C185 Dash Manager will warn if the bandwidth is likely to be exceeded.
VIM
Approximate Bandwidth = Total Measurement Rate (samples/sec) x 30 (bits
per sample)
Note: The Measurement Rate for each input is equal to the logging rate for
that input or 50 Hz, whichever is higher.
Example Calculation
4 channels at 2000 Hz
20 channels at 500 Hz
40 channels at 20 Hz (Occupies 50 Hz)
Calculation:
Total Measurement Rate = 4 x 2000 + 20 x 500 + 40 x 50 =
20000 (samples/sec)
Approximate Bandwidth = 20000 x 30 = 600000 (bits/sec)
E888/E816
Device on first CAN Address
Bandwidth = 145000 (bits/sec)
Device on second CAN Address
Bandwidth = 55000 (bits/sec)
Other Devices
BR2, SLM , PLM Negligible
SDL, ADL2, MDD, M800 ECU TBD
Page 72

MoTeC Appendices 67
Comms Error Codes
The "Comms CAN x Diagnostic" and "Comms RS232 Diagnostic" channels
seen can be used to diagnose communications problems.
Multiple errors are shown by error codes added together. For exa mple: A
RS232 error of 9 = parity + overrun.
The error values have the following definitions:
RS232 Errors
Errors generated by RS232 communications.
1 PARITY Parity bit incorrect. The comms parity setup is
wrong, or there is electrical interference
causing errors in the data.
2 FRAMING Not seeing the stop bit. The baud rate or stop
bit setup is wrong or there is electrical
interference causing errors in the data.
4 NOISE Glitch in the data. Electrical interference is
causing glitches in the signal. (C185 does not
generate this error)
8 OVERRUN A byte was received before the previous byte
was read indicating that the processor was too
busy to read the message.
512 NO DATA A valid message header was not found - either
there is a wiring fault or comms is setup
incorrectly.
1024 CHECKSUM A valid message header was found, but the
checksum was wrong. If seen in combination
with other errors there is electrical noise. If only
checksum errors occur there may be a
software incompatibility between the C185 and
the other device.
2048 WRONG DATA Could not decode the protocol.
General CAN Errors
Errors generated by general CAN communications.
2 FRAMING Only generated when used with an
E888/E816 expander. Inconsistent message
length.
Page 73

68 Appendices MoTeC
8 OVERRUN Receive or transmit overrun error. In the
receive case a byte was received before the
previous byte was read indicating that the
processor is too busy to read the message.
In the transmit case the transmit buffer is full
which could happen if the CAN bus is too
busy.
256 BAD CONFIG The device configuration is not valid (eg
overlapping CAN addresses)
512 NO DATA A valid message header was not found -
either there is a wiring fault or comms is
setup incorrectly, (problem could be at either
end). E.g.: transmit and receive CAN IDs do
not match.
1024 CHECKSUM Only generated wh en used with an Async
Expander. See RS232 errors
2048 WRONG DATA Only generated when used with an Async
Expander or E888/E816 Expander. Async
Expander: Could not decode the protocol.
E888/E816: Compound ID incorrect.
4096 BUS WARNING More than 96 errors have occurred on the
CAN bus. Check wiring and termination
resistors. The CAN bus may still be
operational.
8192 BUS OFF More than 255 errors have occurred on the
CAN bus. CAN communications is
suspended when this error occurs. Check
wiring, termination resistors and the CAN
baud rate. Also check that CAN HI and CAN
LO are correct (not swapped).
16384 CAN TRANSMIT CAN bus transmit warning
"VIMCOM" Errors
Errors generated by "VIMCOM" devices (VIM, ADL2, SDL).
Note: VIM COM devices are connected via CAN.
C185 Errors
These errors are generated by the C185 communications system.
2 FRAMING Incorrect number of samples received.
Page 74

MoTeC Appendices 69
256 BAD CONFIG Configuration mismatch between C185
and device. Resend the configuration.
512 NO DATA VIMCOM packets have not been found.
Either there is a wiring fault or C185
Connections is setup incorrectly.
2048 WRONG DATA VIMCOM packet has bad length.
4096 BUS WARNING More than 96 errors have occurred on
the CAN bus. Check wiring and
termination resistors. The CAN bus may
still be operational.
8192 BUS OFF More than 255 errors have occurred on
the CAN bus. CAN communications is
suspended when this error occurs.
Check wiring, termination resistors and
the CAN baud rate. Also check that CAN
HI and CAN LO are correct (not
swapped).
VIMCOM Device Errors.
These error codes are sent once by the VIMCOM device on resuming data
transmission and therefore indicate why data was previously not being
transmitted.
4097 STARTUP Device has restarted (normally due to
power up) Data is not sent until sync is
achieved.
4098 HALT Data not sent due to deliberate halt. For
example configuration or firmware being
sent.
4099 OVERRUN Data not sent due to transmit buffer
overrun (possibly due to CAN bus too
busy)
4100 SYNC TIMEOUT Data not sent due to C185 sync
message timeout (sync not received
from C185)
4101 CAN ERROR Data not sent due to error on CAN bus
4102 SYNC
EXCEEDED
Data not sent due to excessive sync
error (synchronisation too far out)
Page 75

70 Appendices MoTeC
PC Connection - IP Address
Basic Direct Connection (Automatic IP Address)
The simplest way to connect the C185 to a PC is directly to an Ethernet port
on the PC and using the default network settings (automatically obtain an IP
address)
This method can take up to 60 seconds to connect on Windows XP. On
Windows Vista it takes approximately 8 seconds. This delay will occur every
time the Ethernet cable is connected to the C185 or the C185 is power cycled.
The advantage of this method is that the PC can be connected to a network
when it is not connected to the C185 without having to change any settings on
the PC (assuming the network is configured to obtain an IP address
automatically)
When the C185 is connected to the PC, a network connection icon will appear
in the Windows taskbar tray. To check that connection is in progress, place
the cursor over this icon. It will show “Acquiring Network Address”. Once the
connection is established the message will show "Limited or No Connectivity".
This is normal when using this method and means that Windows h as
automatically assigned an IP Address to the PC.
To check if the PC is configured to obtain an IP address automatically:
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel
2. Double click on Network Connections
3. Double click on the connection that is to be used to connect to the
C185, usually this is called Local Area Connection
4. Click Properties
5. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) from the list
6. Click Properties
7. Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is selected
Page 76

MoTeC Appendices 71
Fast Direct Connection (Fixed IP Address)
If the Basic Direct Connection method takes too long to connect, a more
advanced setup can be used to reduce connection times to around 3
seconds.
Notes:
• Please be aware that changing the PC's network settings can make
connections to other devices on the network stop working.
• Only change the PC network settings if the PC does not need to be
connected to a network or to a device such as a cable or ADSL modem via
the same Ethernet port.
• If the PC has a second Ethernet port that is not used to connect to a
network then this can be used without affecting the network.
• On some PCs an unused Ethernet port may be available if the PC always
connects to the network via a wireless connection.
Page 77

72 Appendices MoTeC
To configure the PC with a fixed IP address:
1. Click Start | Settings | Control Panel
2. Double click on Network Connections
3. Double click on the connection that is used to connect to the C185,
usually Local Area Connection
4. Click Properties
5. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) from the list
6. Click Properties
7. Select Use the following IP address
8. Enter the IP address and Subnet mask shown below.
Network Connection
The C185 can also be connected to a network rather than directly to a single
PC. This allows any PC on the network to communicate with the C185.
The connection time to the C185 will be less than 3 seconds (if the C185 is
already powered and running)
Note: The PC network settings should not be changed.
Page 78

MoTeC Appendices 73 Network Switches and Cables
The C185 must be connected to the network via a network switch.
All MoTeC's PC connection cables (see PC Connection) are Ethernet
crossover cables, that allow direct connection to a PC and are compatible with
network switches that support auto cable sensing (sometimes called “AutoMDI/MDI-X” or “Universal Cable Recognition”)
If the network switch does not support crossover cables MoTeC recommends
upgrading the network switch rather than having two types of cables, which
may cause confusion.
Page 79

74 Appendices MoTeC
Windows Keyboard Shortcuts
When using a laptop in and around a car, it is often not practical to use a
mouse to navigate through the program.
Using the keyboard to select options is easier.
Main Menu
To access the main menu, press ALT + the key for the underlined letter in the
menu, followed by the underlined letter of the item in the drop down menu.
E.g. ALT + F, N for F
Alternatively press and release ALT, select the desired menu item using the
arrow keys, press ENTER to activate it.
Closing a Window
Press ENTER for OK or Close (only when the OK or Close button has a bold
line around it)
Press ESC to Cancel or Close
ile New.
Getting Help
• Press F1 to get help on the current window or item
• Press ALT + H if the screen has a Help button
• Select Help from the Main Menu to access the main help system.
Page 80

MoTeC Appendices 75 Selecting an Item in a Window
To access the various items in a window, press ALT + the key for the
underlined letter of the item of interest, e.g. to select the ‘F
press ALT + F
Alternatively use the TAB key to move through the dialog box (use SHIFT +
TAB to move backwards). The selected control is usually indicated by a
dotted line around it, or by highlighting the text or item selected within the
control.
lash Light’ item
Using the Selected Item
The method of using the selected item (or control) depends on the type of
control. The common controls are detailed below:
Command Button
Command buttons are generally used to show another screen or perform a
particular function.
Press ALT + the key for the underlined letter (S
navigate to the command button. To select, press ENTER or SPACEBAR.
Check Box
A check box is used to tick on or off a particular option.
Press ALT + the key for the underlined letter (F
navigate to the Check Box. To select, press SPACEBAR.
), or use the TAB key to
), or use the TAB key to
Page 81

76 Appendices MoTeC
Group Box
The Group box is used to select an item from a group of options.
Press ALT + the key for the underlined letter (F,
key to navigate to the Group box. To select, use the arrow keys.
Text Box
A text box is used to enter a value or text.
Press ALT + the key for the underlined letter (M
navigate to the Text box, type in the new value or text. Use the
BACKSPACE or DELETE to remove unwanted characters.
List Box
A or D), or use the TAB
) or use the TAB key to
A list is used to select from a number of options.
Press ALT + the key for the underlined letter (M
navigate to the List Box. To select, use the arrow keys.
Drop-down List Box
A Drop-down list box is used to select from a number of items, but only the
selected item is shown until a new item needs to be selected.
) or use the TAB key to
Page 82

MoTeC Appendices 77
Press ALT + the key for the underlined letter (L) or use the TAB key to
navigate to the Drop down List Box. To select the desired item, use the
arrow keys, and press ENTER to close the list.
Tabs
Tabs are used to select the different tab pages of a screen.
To select the next tab, press CTRL + TAB. To select the previous tab,
press CTRL + SHIFT +TAB.
Tree Structure
A Tree Structure is used to select items from a hierarchical list
The UP ARROW key moves the cursor up (selects the item above)
The DOWN ARROW key moves the cursor down (selects the item below)
The RIGHT ARROW key expands; expandable branches indicated by a
plus sign (+)
The LEFT ARROW key collapses; collapsible branches indicated by a
minus sign (-)
Page 83

78 Appendices MoTeC
Glossary
MoTeC Devices
ACL Advanced Central Logger
ADL2 Advanced Dash Logger - second generation
C185 Colour Display Loger
BR2 Beacon Receiver
BTX Beacon Transmitter
CIM Computer Interface Module
CLS Central Logging System
DBW4 Drive By Wire expander
E816 Input/Output Expander
E888 Input/Output Expander
i2 MoTeC data analysis software
i2 Pro MoTeC data analysis software, professional version
IEX Ignition EXpander
LTC Lambda to CAN module
LTCD Lambda to CAN Dual module
M1 Latest ECU for modern engines
M2R ECU dedicated to run 2 rotor engines
M4 ECU for engines with up to 4 cylinders or up to 2 rotors
M400 ECU for modern engines with up to 4 cylinders or up to 2 rotors
M48 ECU for engines with up to 8 cylinders and 2 rotors
M600 ECU for modern engines with up to 6 cylinders or up to 3 rotors
M800 ECU for modern engines with up to 12 cylinders or up to 4
rotors
M800 Plug-In ECU for direct replacement of a factory ECU
M880 ECU for modern engines with up to 12 cylinders or up to 4
rotors
MDC Mitsubishi Diff Controller
MDD Mini Digital Display
MLS ECU dedicated to run Chevrolet LS1 and Lexus/Toyota V8s
PCI cable PC Interface cable
PDM15 Power Distribution Module with 15 outputs
Page 84

MoTeC 79 Appendices
PDM16 Power Distribution Module with 16 outputs
PDM30 Power Distribution Module with 30 outputs
PDM32 Power Distribution Module with 32 outputs
PLM Professional Lambda Meter
RTC Real Time Clock
SDC Subaru Diff Controller
SDL Sport Dash Logger
SGA Strain Gauge Amplifier
SLM Shift Light Module
SUU Software Update Unit
TCM Traction Control Module
VIM Versatile Input Module
Other
Calibration The process of converting an electrical value into a physical
CAN Controller Area Network - communication protocol
CDI Capacitive Discharge Ignition
ECU Engine Control Unit
GPS Global Positioning System
MAF Mass Air Flow
MAP Manifold Absolute Pressure
PID Proportional, Integral and Derivative gain
PWM Pulse Width Modulated.
RPM Revolutions Per Minute
RS232 Recommended Standard 232, communication protocol
RX Receive
TDC Top Dead Centre
TX Transmit
value e.g. Volts into kilometres per hour
Page 85

80 Notes
 Loading...
Loading...