Motan OPTIMUS MT, C15SPV 24MEFM, MAXOPTIMUS C17 SPV 31 MEF Technical Instructions

KÖBER LTD DUMBRAVA ROSIE - VADURI BRANCH OFFICE
Branch Office:Vaduri, No. 280, Alexandru cel Bun, Neamt District, Postal Code 617511, Romania
Phone : +40.233.24.17.46, 233.24.19.33, Fax : +40.233.24.19.29
E-mail : , www.motan.rooffice.vaduri@kober.ro
TECHNICAL INSTRUCTIONS
FOR INSTALLATION/ USAGE/ MAINTENANCE
Köber LTD
Vaduri Branch Office
1798
OPTIMUS MT
C15SPV 24MEFM

CONTENTS
General presentationof the wall hung gasboiler
Connection for evacuation of theflue gases ...............................................................
Operating mode
.................................................................................
..........................................................
....................................................
General description of the wallhung gas boiler ...........................................................
Description of the boilers types..................................................................................
Symbols ....................................................................................................................
General instructions concerning the safetyof the wall hung gas boiler ........................
Technical characteristics...........................................................................................
Functional and constructive characteristics ..............................................................
Constitutive elements of wall hung gas boiler.............................................................
The heat generator ...................................................................................................
The exhaust gases/water heat exchanger.................................................................
The heating and domestic hotwater circuits Hydrauliccircuits ..................................
The command and control system ............................................................................
The external shell ......................................................................................................
The hydraulic characteristic of circulationpump .........................................................
Mounting/installation instructions ..............................................................................
The location of the unit...............................................................................................
The central heating ...................................................................................................
The gas supply ..........................................................................................................
The electric power supply .........................................................................................
Instructions for the final user(beneficiary) ..................................................................
Operating instructions ..............................................................................................
The control panel .......................................................................................................
The LCD display board inthe user module .................................................................
The LCD display in theuser module ................................................
The pressure checking ..............................................................................................
Additional facilities that may beobtained by ...............................................................
Handing over to the beneficiary.................................................................................
Recommendations for the yearly checking ...............................................................
Marking, documents, packing, storage, transport, quality and warranty conditions .....
Marking ......................................................................................................................
Documents ................................................................................................................
Packing ......................................................................................................................
Storage .....................................................................................................................
Shipment ...................................................................................................................
Quality and warranty conditions .................................................................................
Responsibilities during the warranty period ...............................................................
Malfunctions which refer to themanufacturer's responsibility ....................................
Malfunctions which refer to theresponsibility of the utilities provider ...........................
Malfunctions for which the manufactureris not responsible .......................................
List and plans necessary formounting and putting into service ...................................
Plan 1 ........................................................................................................................
Plan 2 .........................................................................................................................
Plan 3 .........................................................................................................................
Plan 4 .........................................................................................................................
Plan 5 .........................................................................................................................
The domestic hot water module, The heating module, Antifrost function, Auto-checking
and safety functions, The boiler shutting down in safety conditions .....................................
The functioning of the heating unit
Other functions concerning the safety ofthe boiler
Pg
Pg
Pg.
Pg
Pg 4
Pg 5
Pg 5
Pg 6
Pg 6
Pg 7
Pg 7
Pg 8
Pg 8
Pg 9
Pg 10
Pg 10
Pg 10
Pg 11
Pg 11
Pg 12
Pg 13
Pg 13
Pg 13
Pg 13
Pg 13
Pg 15
Pg 16
Pg 17
Pg 17
Pg 18
Pg 19
Pg 19
Pg 20
Pg 20
Pg 20
Pg 20
Pg 20
Pg 20
Pg 20
Pg 21
Pg 21
Pg 22
Pg 22
Pg 23
Pg 23
Pg 24
Pg 25
Pg 26
Pg 27
. 3
. 3
3
. 3
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
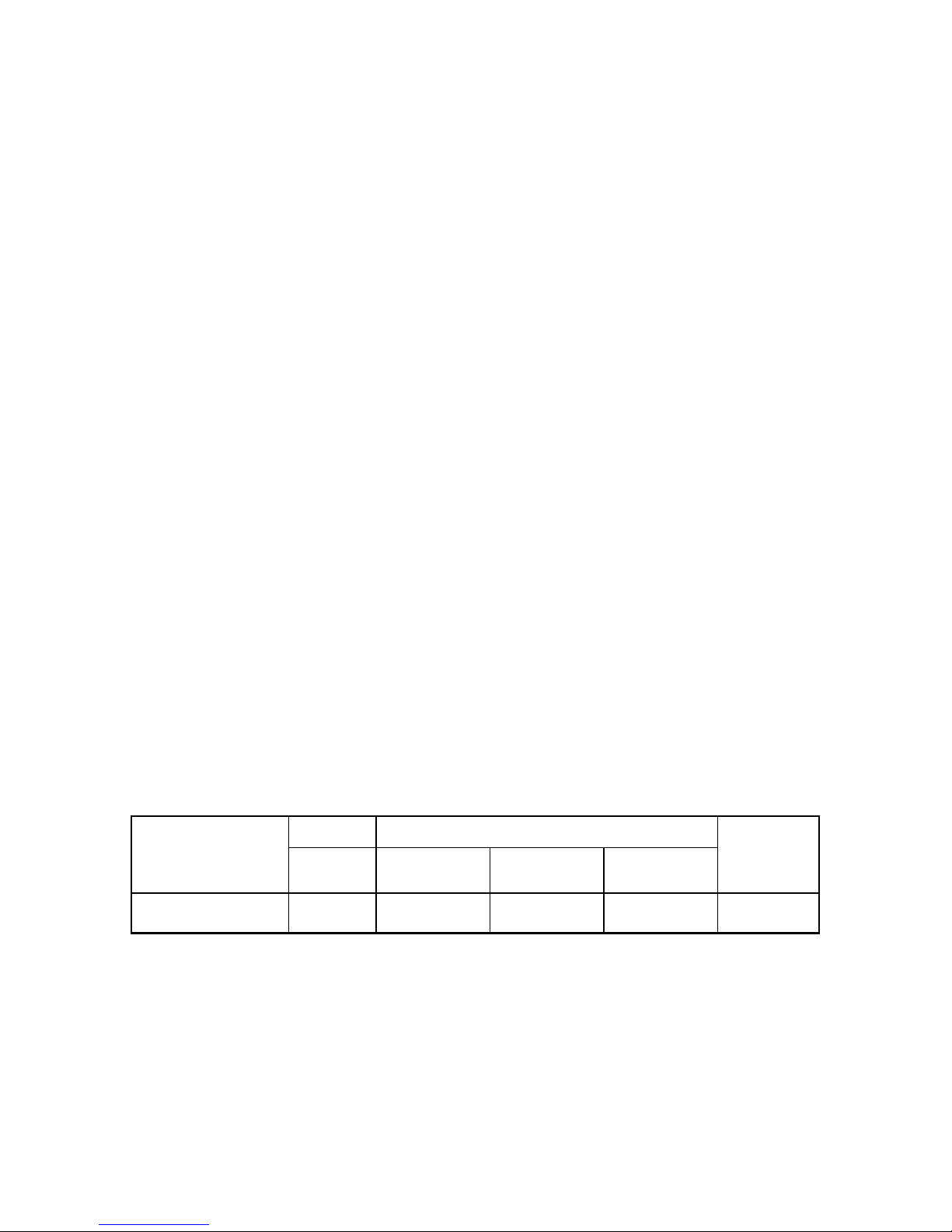
INTRODUCTION TO THE BOILER
General description of the boiler
The wall hung gas boiler is a fuel gas-consuming appliance which has the role of
turning the fuel gas power into thermal energy through burning.
This appliance runs unsupervised due to its protection and control systems.
The boiler is made of many parts that we are going to describe in the following
chapters.
The gas enters inside the boiler through the gas feeding circuit made ofa coupling
and a reducing valve which will be set at 20 mbar for G20 A(L) and A(H) subgroups.
The reducing valve will be set at 37 mbar for LPG (propane subgroups and propanebutane mixtures). Thus it gets into the gas valve which has the role of controlling the
gas discharge at the outlet to the burner.
The ignition achieves by flame activating by an ignition electrode, by means of
an ignition transformer.
During the combustion, the flame sensing is made by an ionization sensor.
The boiler type with forced draft is provided with a fan which evacuates the
exhaust gases. In the initiation phase, this evacuates an air volume to provide an
unexplosive ignition. The explosive ignition may occur due to a gas storage from the
non-operating period.
The combustion chamber, as a plate parallelotope, interior ceramics fibre-lined,
is designed to allow the transfer to the exchanger with less heat leakages.
In case of the CH circuit of the two heat exchangers type, the heat resulted from
fuel gas ignition is taken over by the monothermal heat exchanger and sent to the
thermal agent (water) which is delivered by the circulating pump through the heating
installation. In case of on the DHW circuit, a water discharge is detected by the
flowmeter, the 3- way gas valve is energized. The 3- way gas valve achieves the
transition from the central heating circuit on the short circuit through the plate heat
exchanger (the main plate heat exchanger) and the heat transfer is realized by means
of this to the DHW circuit (the secondary plate heat exchanger).
The scavenging is realized by means of the fan.
The running protection andcontrol are performed electronically. The boiler setting
is made from the control board (see the chapter concerning this subject).
DESCRIPTION OF THE BOILER
3
BOILER
TYPE
C15 SPV 24 MEFM
Useful power
Accessories
[kcal/h] The fan The pump
The
expansion
vessel
DHW
instant
production
20670
X X X X
SYMBOLS
S- with instant production of DHW (without cumulation)
P- with pump
V-with closed expansion vessel
24-the maximum power output in kW
M- the burner is supplied by a continuous modulating valve
E- the ignition and the control of the flame are electronically-made
F-the forced scavenging
M-monothermal
OPTIMUS MT

C 15 SPV 24 MEFM
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS CONCERNING THE BOILER SAFETY
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
This manual is part of the product and it has tobe given to the user.
Read this manual carefully and keep it carefully for a further application by the user and by the
mounting and installing authorized personnel.
The installation, the putting into service, the service-repair operations and a periodical
technical checking are performed only by authorized personnel in accordance with the regulations
in force. All the indications of this manual must be respected; any exception may cause damages
and the producer isn`t responsible forthese.
In case of a defective running of the device, shut it down and call up immediately one of the
breakdown services units.
To guarantee the boiler efficiency and its correct running it is recommendable that the boiler be
checked yearly by the qualified personnel,complying with the manufacturer`s conditions.
If the device is sold or given, make sure it is delivered with its technical handbook in order to be
consulted by the new user/ installer.
In case of some components damaging there will be used only the original components. You
must have the manufacturer`s acceptance to use some components from another company, you
must obtain the writtenacceptanceof the producer sothat you may use those components.
This boiler will be used properly. Any other usewill be considered unsuitable.
There is excluded any contractual or extra-contractual responsibility of the producer for the
damages caused by the installing or usage errors and by thenon-observance of his instructions.
The maximum limit of the water hardness inlet is of maximum 5ºF (French degrees) on the
DHW circuit, equal to 50 mg CaCO2 or an equivalent quantity of other salts as Ca and Mg. It is
compulsory to install asoftener filter onthe domestic water circuit, a mechanical impurities filter (Y
filter) on the CH installation return and a pressure controller onthe gas supply circuit.
It is recommendable to use these boilers types presented in this manual to heat areas of 150
mp (at a mediumheight of 2,5 m of the heat volume).
Unsubmitting to these technical manual regulations as to the warranty certificate leads to
warranty loss.
4
RESETMOD

Name
Type OPTIMUS MT - C 15 SPV 24 MEFM
Forced
Sealed
92,7%
93,7%
10 - 23,7 kw
10,9 - 25,49 kw
20 mbar
35 mbar
30 - 37 mbar
230 VAC, 50 Hz
160 W
40 kg
1 L
1,1- 2,6 Nm /h
0,4 - 1,07 kg/h
Draft
Combustion chamber
Efficiency at maximum load
Efficiency at minimum load
Useful power (min/ max)
Burner nominal load (min/ max)
Gas pressure
NG on coupling ( behind the reducer)
NG on maximum admitted output
LPG
Power-supply
Power consumption
Weight
Heat exchanger output
-
0,5 ºi 3 bar
40 - 80°C
3/4"
1/2"
3/4"
275
415
700
850
7 L
Central heating
Minimum and maximum admitted pressure
Temperature on the heating circuit
Connections - inlet outlet central heating
- inlet outlet DHW
- gas supply
Dimensions - depth (mm)
- Width (mm)
- Height (mm)
- With mounted elbow (mm)
Expansion vessel with membrane
NG consumption (8500 kcal/ Nm3)
At useful power (max/ min)
LPG consumption (20425 kcal/ kg)
At maximum output
3
5
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
CONSTRUCTIVE AND FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS
30 - 60°C
13,5 l/min
9,7 l/min
7,5l/min
DHW temperature range
Flow values
Ät °C=25
Ät °C=35
Ät °C=45
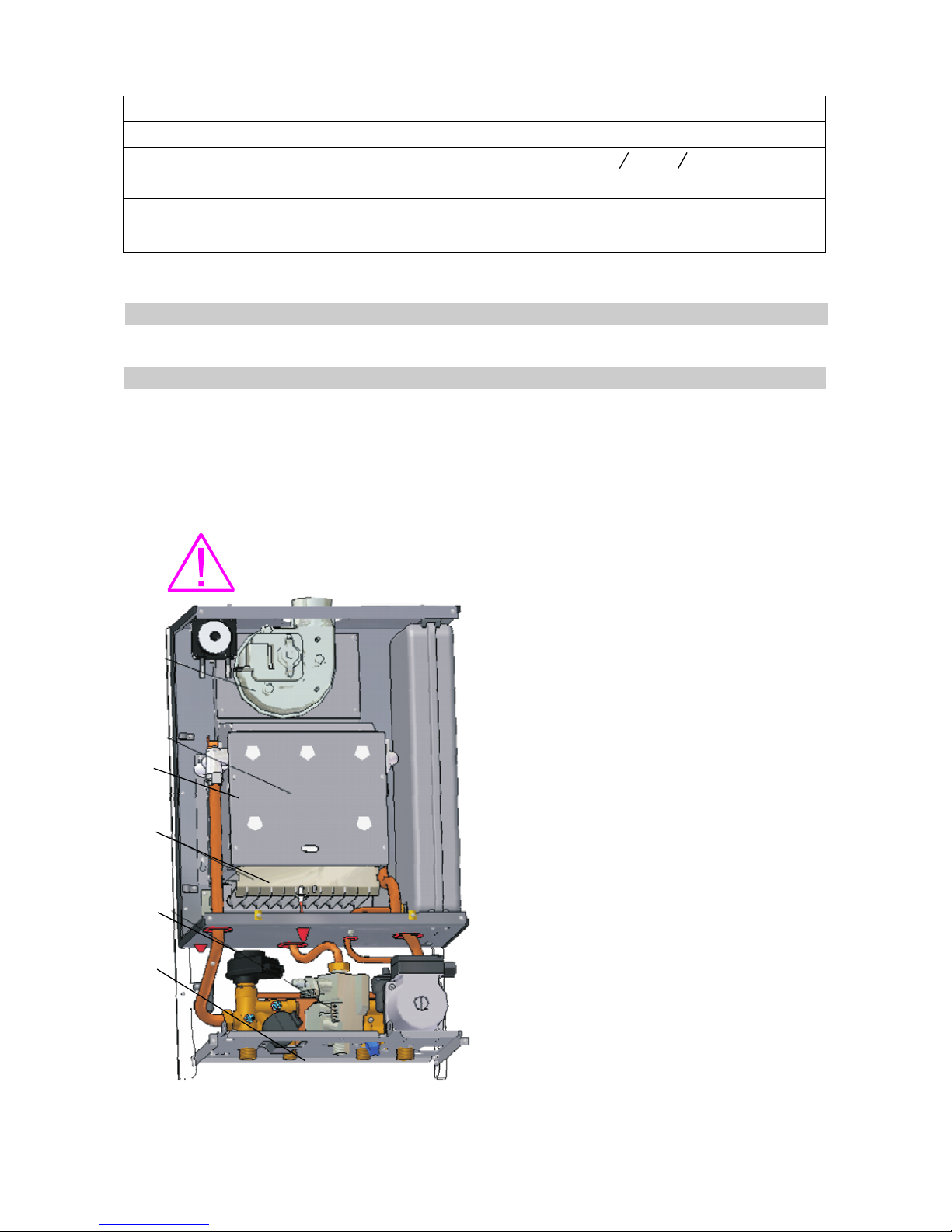
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS OF THE BOILER
The heat generator
It is designed to supply the necessary heat for the heating exchange withthe heating and DHW
circuits. It is made of the following elements:
The gas feeding circuit will be performed through a reducing valve which will set the inlet
pressure at 20-25 mbar NG,respectively 30-37 mbar for LPG.
It is compulsory to mount a pressure controller on the gas
feeding circuit.
1. The gas valve
2. The burner
is designed to allow a
continuous modulation of combustion,
supplying the minimum, medium and
maximum gas pressures required by the
boiler running at the minimum, medium and
maximum load. The connector between the
gas valve and the burner is the copper pipe
(14x1).
is stainless-made, forced or
atmospherics, with 11 cannularinclines and it
runs with fuel gas (NG or LPG). The burner
output is set in a modulated systemby means
of a gas modulating valve so that it supply a
maximum useful power of 23,7 kW.
3. The combustion chamber is design to
allow the heat transfer to the heat exchanger
with less heat leakages. We chose a simple
constructive solution as a rectangular piping
of 170 mm between the burner and the heat
exchanger. To reduce the heat leakages, the
piping walls are isolated indoor with heat
insulating material (ceramics fibres).
4
3
2
1
Domestic cold water pressure
Exhaust gases temperature at rated output
Burned gases connection ( input- output)
Burned gases connection length
Orientative values
Maximum water content in the installation
Maximum surface of the precinct
0,2 - 8 bar
142,4°C
O 100 / O 60
Max 3 m
150 l
150 m²
6

7
4
The boiler is provided with afan for scavenging.
The flue system and the air supply (for the boiler with forced draft) is made of two concentric
pipes connected to the outside of the room where the boileris mounted.
is monothermal, the domestic water is
heated through the plate heat exchanger.
From the power pointof viewthe rated output is of 24kW and the efficiency over 93%.
-
The fan
The exhaust gases/ water heat exchanger
The exhaust gases/ water heat exchanger
The heating and DHW circuits - Hydraulic circuits
- DHW circuit is with plateheat exchanger.
5
7
They are designed to allow thethermal
transfer to the external heating
and DHW installations.
- the loading circuit of the installation is
made of the valve and the copper pipe
connected to the domestic cold water
supply line;
- the relief valve of the circuit is designed
to reduce the pressure from the heating
circuit and to open at 3 bars full
pressure;
- the ventilation circuit of the installation
is made of an air-release valve which
allows the air discharge from the heating
circuit, mounted on the circulating pump
shell;
- The heating agent recirculating pump (7)
is designed to supply the output
necessary for the heating agent recycling
through the heating circuit;
- Expansion vessel is designed to allow
the expansion processes from the heat
installation, preventing from hydraulics
overstraining or damaging. This has a
capacity of 7 litres.
- The automatic by-pass circuit is made of
a copper pipe of 14x1 mm fixed between
the heating circuit turn and return and a
safety valve set to open at 0,3 bar to
allow the heat carrier recycling through
the heat exchanger and pump, in case of
some pressure differences,
between the external heat installation
turn and return at over 0,3 bar.
The heating circuit
8
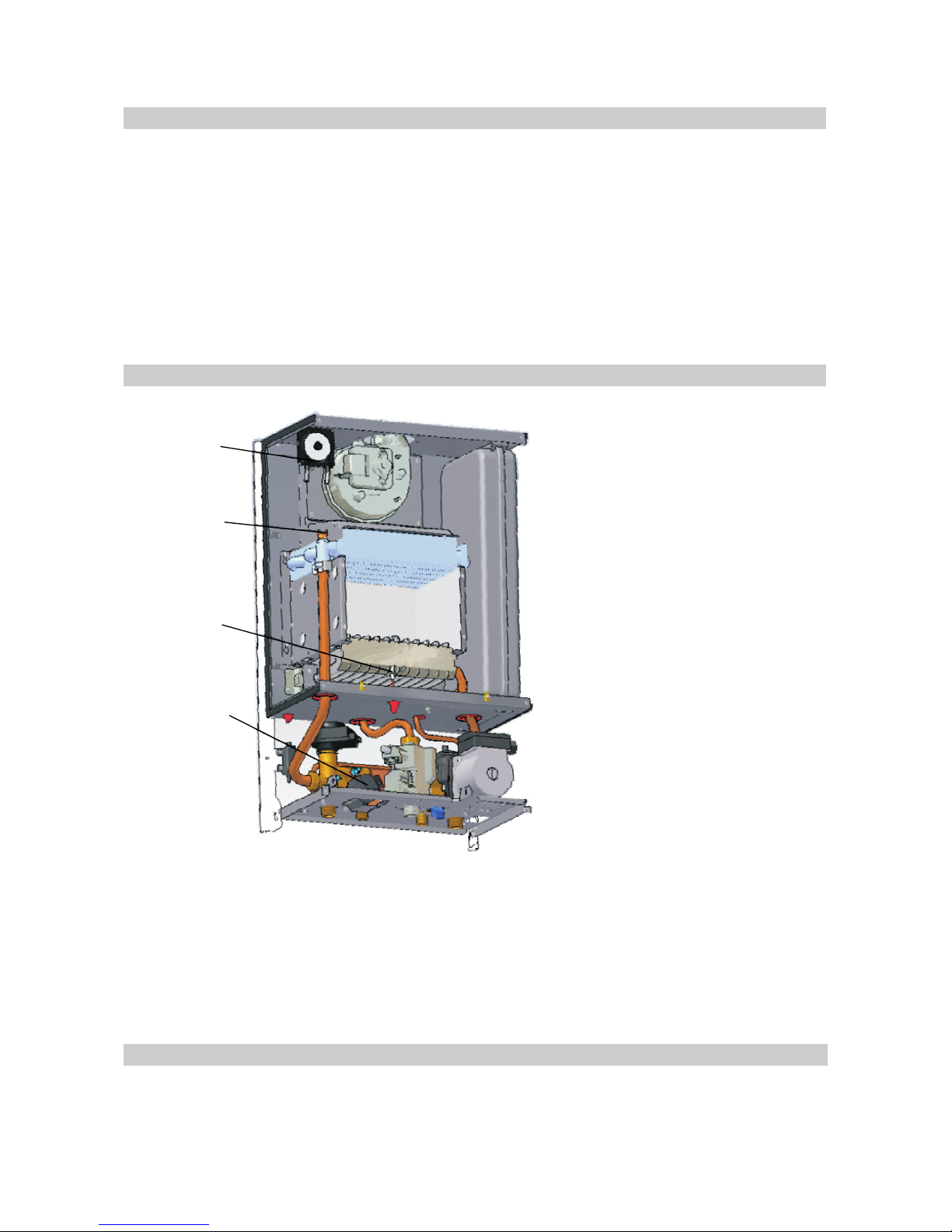
The command and control system of the boiler running performs:
The command and controlsystem is madeof thefollowing components:
- the ignition and the protection when the flame is extinguished, provided by the electronic
ignition;
- the protection when the gas is switched off, provided by electro-valve;
- the water pressure signalling in the boiler, provided by minimum pressure sensor;
- the temperature signalling on the heating and DHW circuits, provided by the electronic board
functions;
- the setting of the heating cycle following the instructions of the temperature control switch;
- the safety of the boiler against excessive temperature, provided by the safety thermostat at
overpressure, through the safety valve and at water leakages through the minimum pressure
switch from the circuit;
- protection against draft deficiency, by the fan derangement or the exhaust piping blockage of
the exhaust gases, provided by the combustion pressure switch .
- the electronic board
-
- heating circuit temperature
sensor
- DHW temperature sensor
- Flowmeter
- Ignition/ ionization electrode
as a
controller of the boiler running
(see the attached drawing).
the measuring and pilot cells
of the functional parameters for the
boiler
which sends the
temperature signal to the electronic
control block of the heating circuit.
which sends the temperature signal
to the electronic control block of the
DHW circuit.
as a detector of
the DHW consumption which sends
the DHW circuit running command
to the electronic control block.
(8) with double role, of combustion
flame activation and sensing.
- Air pressure switch (9)
- Temperature sensors
- Temperature switch (10)
- Programmer ambient sensor
- Water pressure sensor
The external shell
as a detector and controller of the exhaust gases, which
determines the heating and DHW circuits running.
as reading the temperature on the heating circuit (the electronic
board display).
as a detector and controller of the maximum temperature on the
heating circuit which sends the non-running command of the heating circuit in case a maximum
admitted temperature is exceeded.
as setting the ambient temperature from a room (optional).
as a detector of the minimum pressure on the heating circuit.
It has a parallelepipedal shape. It is detachable and electrostatically painted.
The shell covers the pressurized combustion chamber and the enclosed installations.
9
10
8
11
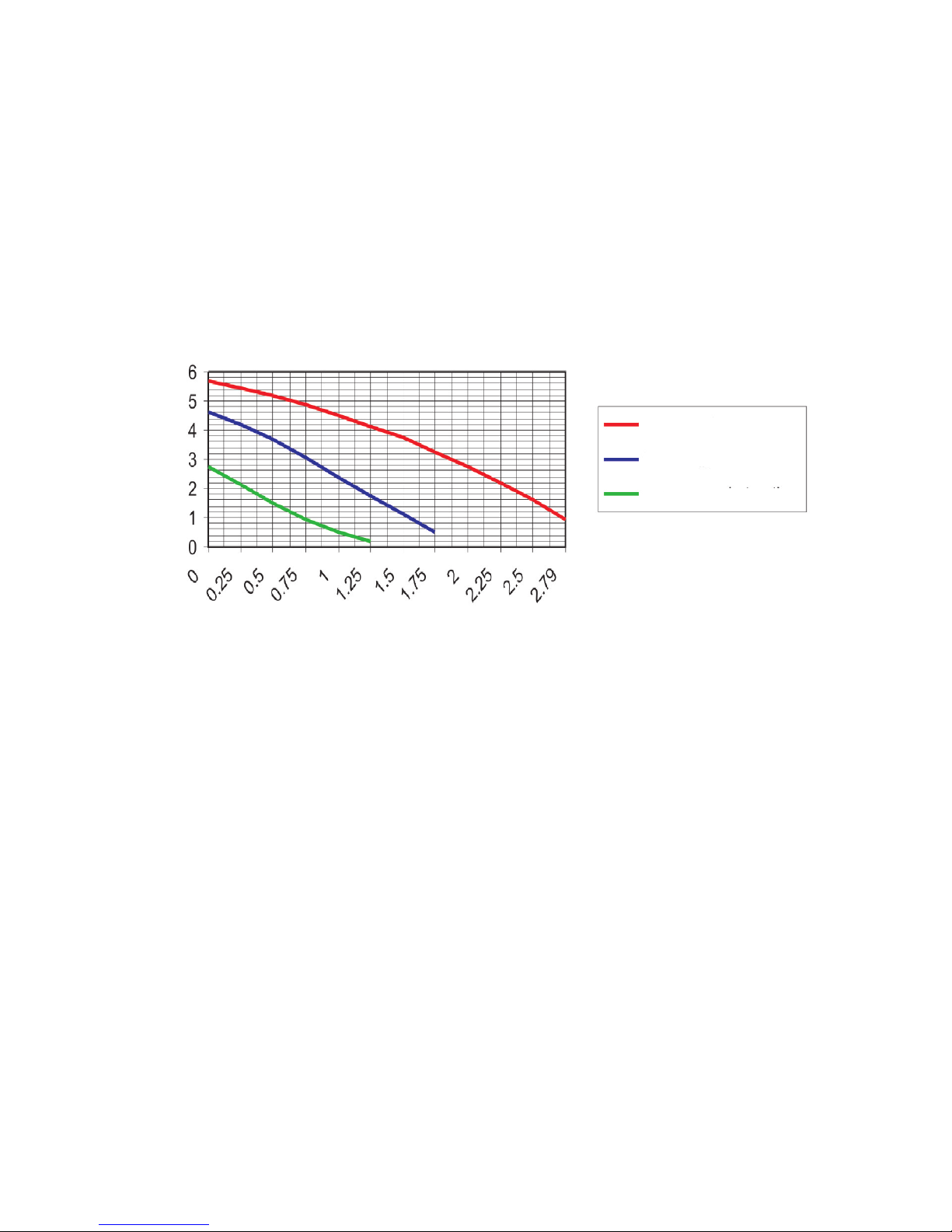
For designing the central heating installation we must be aware of the hydraulic features of the
pump.
9
The hydraulic characteristic of the pump
Pressure pump P[mca]
Pump output Q[mc/h]
the third stage of
the speed
the second stage
of the speed
the first stage of
the speed
 Loading...
Loading...