Mosel Vitelic V54C365804VDL Datasheet
MOSEL VITELIC
1
V54C365804VD(L)
HIGH PERFORMANCE 143/133/125 MHz
3.3 VOLT 8M X 8 SYNCHRONOUS DRAM
4BANKSX2MbitX8
V54C365804VD(L) Rev.0.9 September 2001
PRELIMINARY
7758PC8
System Frequency (f
CK
) 143MHz 133MHz 125 MHz 125 MHz
Clock Cycle Time (t
CK3
) 7 ns 7.5 ns 8 ns 8 ns
Clock Access Time (t
AC3
)CASLatency = 3 5.4 ns 5.4 ns 6 ns 7 ns
Clock Access Time (t
AC2
) CAS Latency = 2 5.5 ns 6ns 6 ns 7 ns
Features
■ 4 banks x 2Mbit x 8 organization
■ High speed data transfer rates up to 143 MHz
■ Full Synchronous Dynamic RAM, with all signals
referenced to clock rising edge
■ Single Pulsed RAS
Interface
■ Data Mask for Read/Write Control
■ Four Banks controlled by BA0 & BA1
■ Programmable CAS
Latency: 2, 3
■ Programmable Wrap Sequenc e: Sequential
or Interleave
■ Programmable B urs t Length:
1, 2, 4, 8 and full page for Sequential Type
1, 2, 4, 8 for Interleave Type
■ Multiple Burst Read with Single Write O perat ion
■ Automatic and Controlled Precharge Command
■ Random Column Address every CLK (1-N Rule)
■ Suspend Mode and Power Down M ode
■ Auto Refresh and Self Refresh
■ Refresh Interval: 4096 cycles /64 ms
■ Available in 54 Pin 400 m il TSOP-II
■ LVTTL Interface
■ Single +3.3 V ±0.3 V Power Supply
Description
The V54C365804VD(L) is a four bank Synchronous DRAM organized as 4 banks x 2Mbit x 8. The
V54C365804VD(L) achieves high speed data transfer rates up to 143 MHz by employing a chip architecture that prefetches multiple bits and then
synchronizes the output data to a system clock
All of the control, address, data input and output
circuits are synchronized with the positive edge of
an externally supplied clock.
Operating the four memory banks in an interleaved fashion allows random access operation to
occur at h igher rate than is possible with standard
DRAMs. A s equential and gapless data rate of up to
143 MHz is possible depending on burst length,
CAS
latency and speed grade of the device.
Device Usage Chart
Operating
Temperature
Range
Package Outline Access Time (ns) Power
Temperature
MarkT 7 75 8PC 8 Std. L
0°Cto70°C • •••••• Blank
2
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
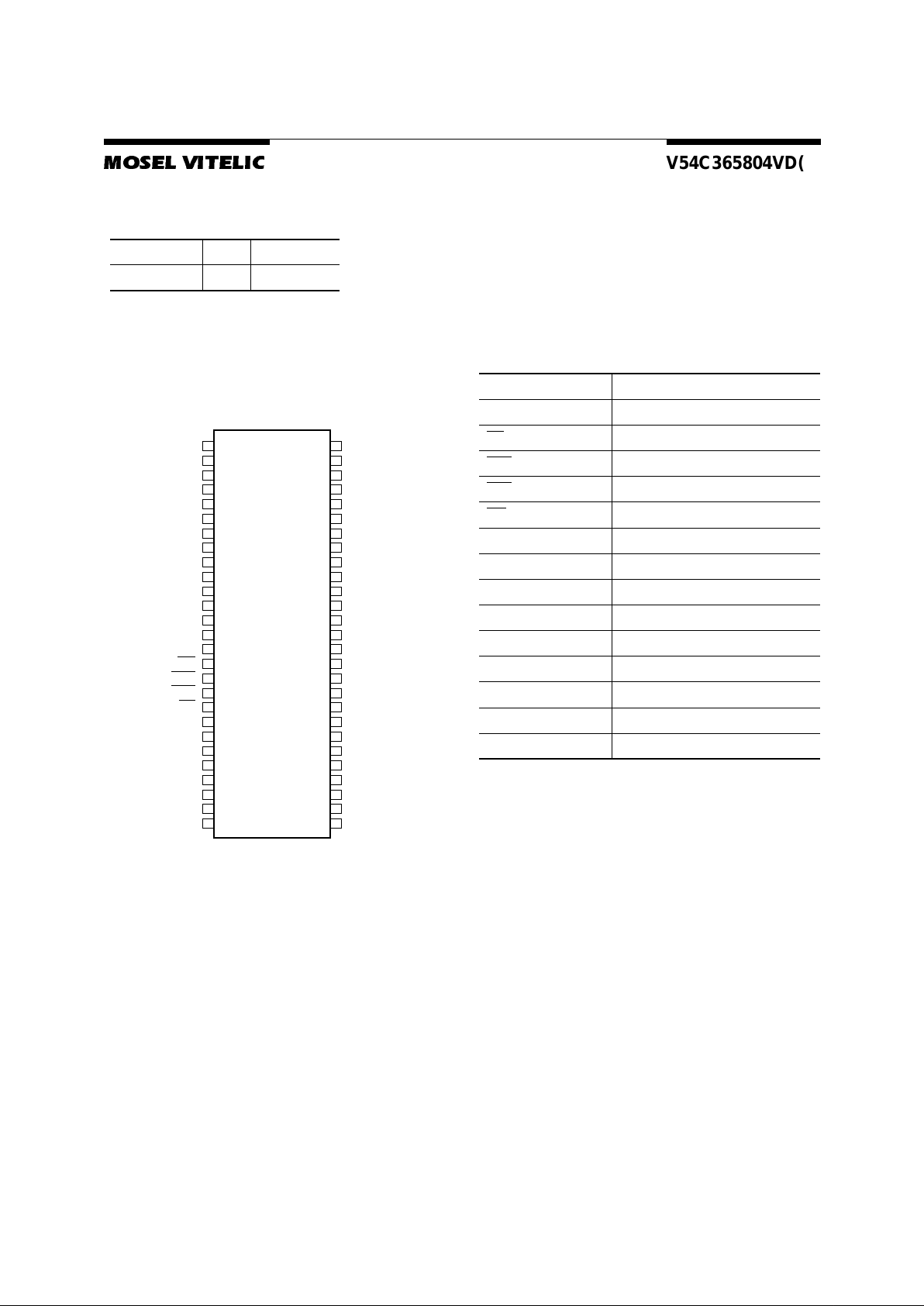
54 Pin Plastic TSOP-II
PIN CONFIGURATION
Top View
Pin Names
V
CC
I/O
1
V
CCQ
NC
I/O
2
V
SSQ
NC
I/O
3
V
CCQ
NC
I/O
4
V
SSQ
NC
V
CC
NC
WE
CAS
RAS
CS
BA0
BA1
A
10
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
V
CC
V
SS
I/O
8
V
SSQ
NC
I/O
7
V
CCQ
NC
I/O
6
V
SSQ
NC
I/O
5
V
CCQ
NC
V
SS
NC
DQM
CLK
CKE
NC
A
11
A
9
A
8
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
365804VA 01
CLK Clock Input
CKE Clock Enable
CS
Chip Select
RAS
Row Ad dress Strobe
CAS
ColumnAddressStrobe
WE
Write Enable
A
0–A11
AddressInputs
BA0, BA1 Bank Select
I/O
1
–I/O
8
Data Input/Output
DQM Data Mask
V
CC
Power(+3.3V)
V
SS
Ground
V
CCQ
Powerfor I/O’s(+3.3V)
V
SSQ
Ground for I/O’s
NC Not connected
Description Pkg. Pin Count
TSOP-II T 54
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
3
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
Capacitance*
TA=0to70°C, VCC=3.3V± 0.3 V, f = 1 Mhz
*Note:Capacitance is sampled and not 100% tested.
Symbol Parameter
Max. Unit
C
I1
Input Capacitance (A0 to A11) 5 pF
C
I2
Input Capacitance
RAS
,CAS,WE,CS, CLK, CKE, DQM
5pF
C
IO
Output Capacitance(I/O) 6.5 pF
C
CLK
Input Capacitance (CLK) 4 pF
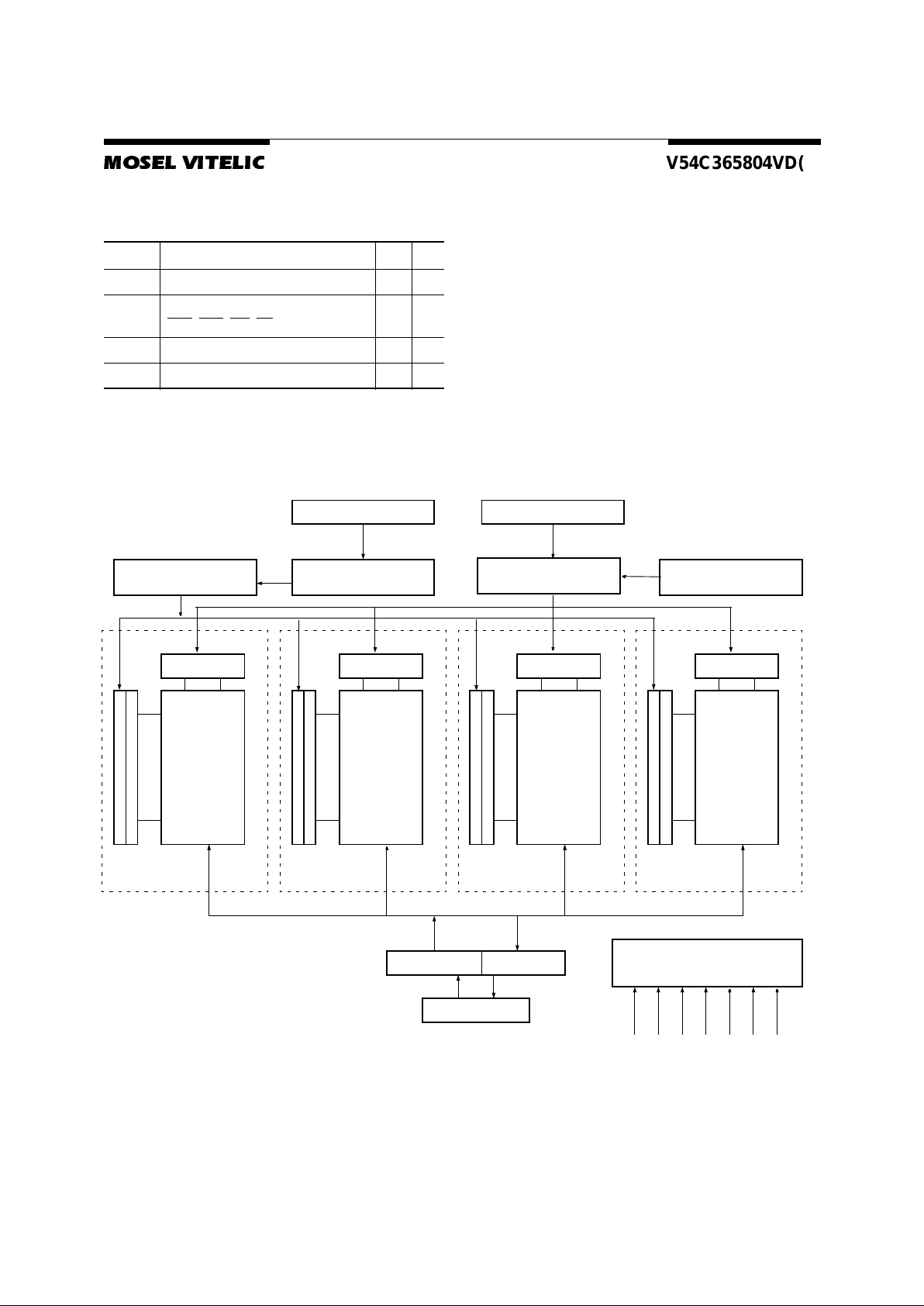
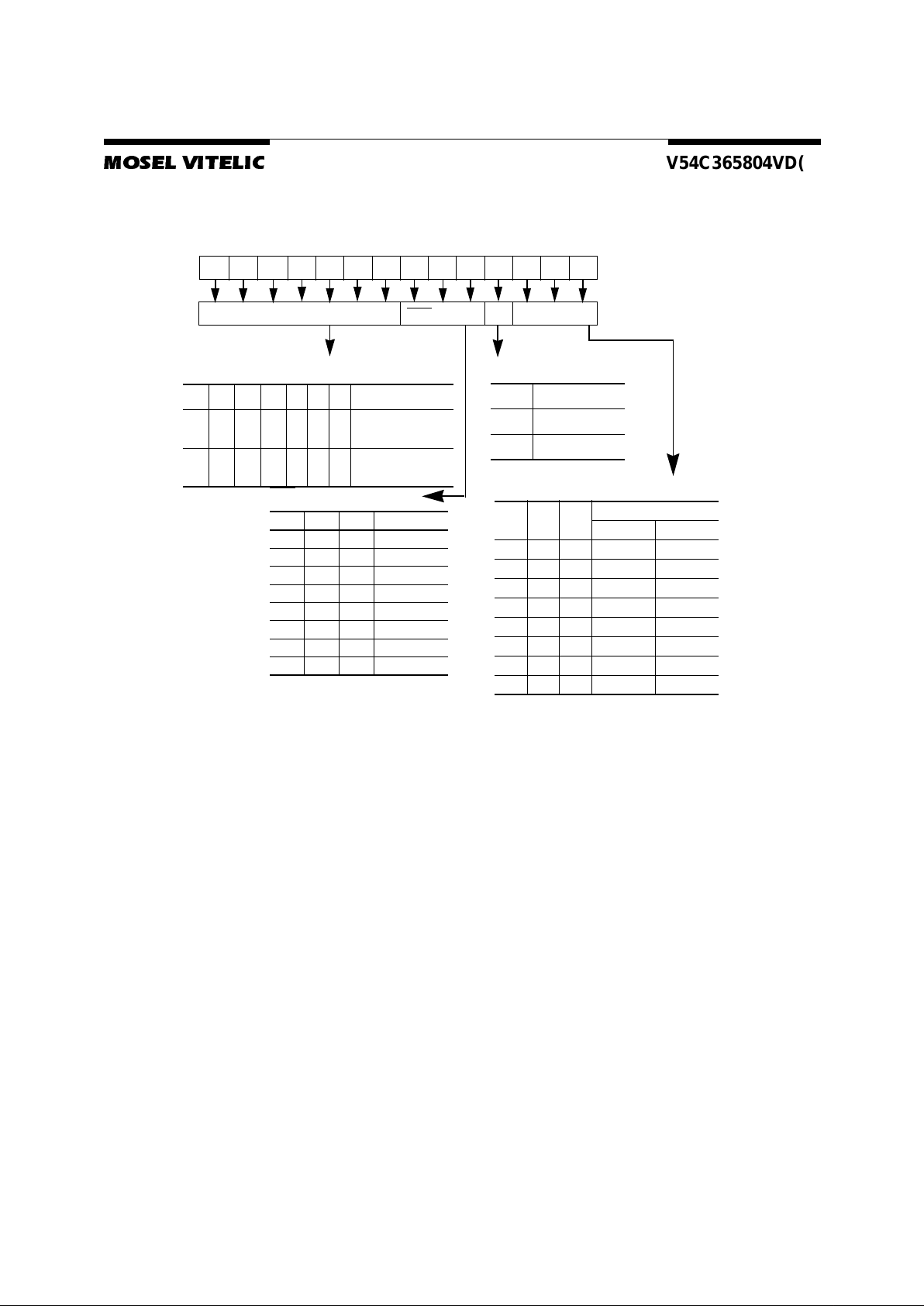
Block Diagram
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 0
4096 x 512
x8bit
Column decoder
Sense amplifier & I(O) bus
Row decoder
Memoryarray
Bank 1
4096 x 512
x8bit
Column decoder
Sense amplifier & I(O) bus
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 2
4096 x 512
x8bit
Column decoder
Sense amplifier & I(O) bus
Row decoder
Memory array
Bank 3
4096 x 512
x8bit
Column decoder
Sense amplifier & I(O) bus
Inputbuffer Output buffer
I/O1-I/O
8
Columnaddress
counter
Columnaddress
buffer
Row address
buffer
RefreshCounter
A0 - A11,BA0, BA1A0 - A8, AP, BA0, BA1
Control logic & timing generator
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
DQM
Row Addresses
Column Addresses
4
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
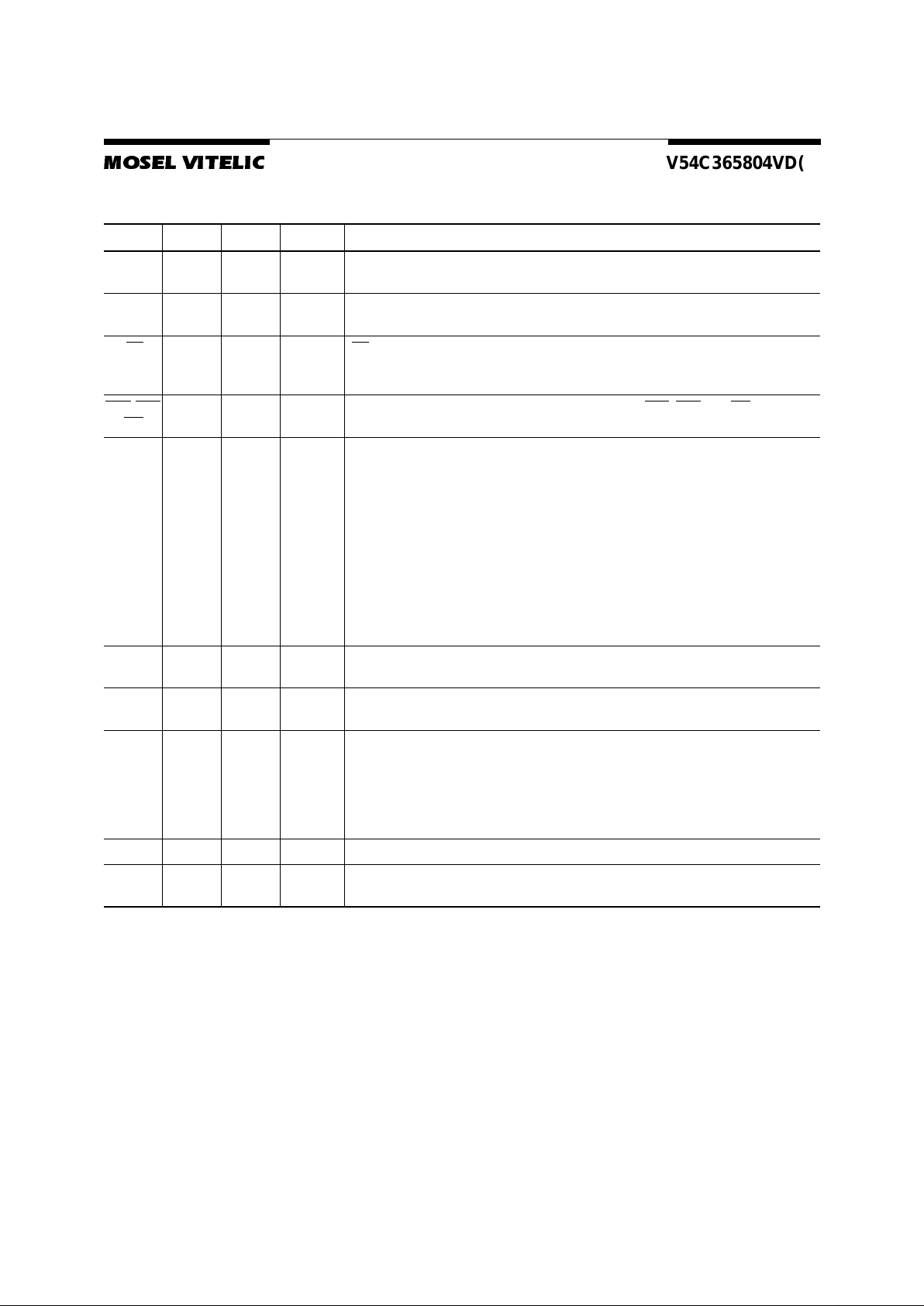
Signal Pin Description
Pin Type Signal Polarity Function
CLK Input Pulse Positive
Edge
The system clock input.A ll of the SDRAM inputs are sampled on the rising edge of the
clock.
CKE Input Level ActiveHigh Activatest he CLK signalwhen high and deactivates the CLK signal when low, thereby
initiates eitherthePower Downmode,Suspend mode, or the Self Refreshmode.
CS
Input Pulse Active Low CS enablesthecommand decoderwhen low and disables the commanddecoder when
high. When the command decoder is disabled, new commands are ignored but previous
operations continue.
RAS
,CASWEInput Pulse Active Low When sampled at the positiverising edge of the clock, CAS,RAS,andWEdefinethe
command to be executed by the SDRAM.
A0 - A11 Input Level — Duringa Bank Activatecommandcycle,A0-A11 defines the row address (RA0-RA11)
when sampledat the rising clock edge.
Duringa Read or Write commandcycle, A0-An defines the column address(CA0-CAn)
when sampledat the rising clock edge.CAn dependsfrom the SDRAM organization:
8M x 8 SDRAM CA0–CA8 (Page Length = 512 bits)
In additiontothe column address, A10(=AP) is used to invoke autoprechargeoperation
at the end of the burst read or write cycle. If A10 is high,autoprechargeis selected and
BA0, BA1 defines the bank to be precharged. If A10 is low, autoprecharge is disabled.
Duringa Prechargecommand cycle,A10(=AP)isusedin conjunction withBA0and BA1
to control which bank(s) to precharge. If A10 is high, all four banks will BA0 and BA1 are
used to define whichbankto precharge.
BA0,
BA1
Input Level — Selects which bank is to be active.
DQx Input
Output
Level — Data Input/Outputpins operate in the same manner as on conventionalDRAMs.
DQM Input Pulse Active High The Data Input/Output mask places the DQ buffers in a high impedance state when sam-
pledhigh. In Read mode, DQM hasa latencyof two clock cyclesand controls theoutput
buffers likean output enable.In Writemode, DQM has alatencyofzeroand operatesas
a word mask by allowing input data to be written if it is low but blocks the write operation
if DQM is high.
One DQM input is present in x4 and x8 DRAMs.
VCC, VSS Supply Power and ground for the input buffersand the core logic.
VCCQ
VSSQ
Supply ——Isolated power supply and ground for the output buffers to provide improved noise
immunity.
5
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Operation Definition
All of SDRAM operations are defined by s ta tes of control signals CS,RAS,CAS,WE,andDQMatthe
positive edge of the clock. Th e following list shows the thruth table for the operation commands.
Notes:
1. V = Valid , x = Don’t Care, L = Low Level, H = High Level
2. CKEn signalis input levelwhen commandsare provided,CKEn-1 signal is input level one clock before the commands
are provided.
3. Theseare stateof bank designated by BS0, BS1 signals.
4. Devicestate is Full Page Burst operation
5. PowerDownMode can not entry in the burstcycle.When this commandassertin the burst mode cycle device is clock
suspendmode.
Operation
Device
State
CKE
n-1
CKE
nCSRAS CAS WE DQM
A0-9,
A11 A10
BS0
BS1
Row Activate Idle
3
HXLLHHXVVV
Read Active
3
HXLHLHXVLV
Read w/Autoprecharge Active
3
HXLHLHXVHV
Write Active
3
HXLHLLXVLV
Write with Autoprecharge Active
3
HXLHLLXVHV
RowPrecharge Any HXLLHLXXL V
Precharge All Any H X L L H L X X H X
ModeRegisterSet Idle HXLLLLXVVV
No Operation Any H X L H H H X X X X
Device Deselect Any H X H X X X X X X X
Auto Refresh Idle H H L L L H X X X X
Self Refresh Entry Idle H L L L L H X X X X
Self Refresh Exit Idle
(Self Refr.) L H
HXXX
XXXX
LHHX
Power Down Entry Idle
Active
5
HL
HXXX
XXXX
LHHX
Power Down Exit Any
(Power
Down)
LH
HXXX
XXXX
LHHL
Data Write/OutputEnable Active H X X X X X L X X X
Data Write/OutputDisable Active H X X X X X H X X X
6
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Power On and Initialization
The default power on state of the mode register is
supplier specific and may be und efi ned. The
following power on and initialization sequence
guarantees the device is preconditioned to each
users specific needs. Like a conventional DRAM,
the Synchronous DRAM must be powered up and
initialized in a predefined manner. During power on,
all VCC and VCCQ p ins must be built up
simultaneously to the specified voltage when the
input signals are hel d in the “NOP” state. The power
on voltage must not exceed VCC+0.3V on any of
the input pins or VCC supplies. The CLK signal
must be started at the same time. After power on,
an initial pause of 200 µs is required followed by a
precharge of both banks using t he precharge
command. To prevent data contention on the DQ
bus du ring power on, it is required that the DQMand
CKE pins be held high during the initial paus e
period. Once all banks have been precharged, the
Mode Register Set Command must be issued to
initialize the Mode Register. A m ini mum of eight
Auto Refresh cycles (CB R ) are also required .These
may be done before or after programm ing the Mo de
Register. Failure to fo llow t hes e steps may lead to
unpredictable s tart-up modes.
Programming the Mode Register
The Mode register d es ignates the operation
mode at the read or write cycle. This register is divided into 4 fields. A Burst Lengt h Field t o set the
length of the burst, an Addres s ing Selection bit to
program the column access sequence in a burst cycle (interleaved or sequ ential), a CAS LatencyField
to set the access time at clock cycle and a Operation mode field to d ifferentiate between normal operation (B urs t read and burst Write) and a special
Burst Read and Single Write mode. The mode set
operation must be done bef ore a ny act ivate command after t he initial power up. Any content of the
mode reg ister can be altered by re-executing the
mode set command. All banks must be in precharged s ta te and CKE mus t be high at least o ne
clock before the mode set operation. After the mode
register is set, a Standby or NOP com mand is required. Low signals of RAS
,CAS, and WE at the
positive edge of the clock activate the mode set operation. Addres s input data at this timing defines parameters to be set as shown in the prev ious table.
Read and Write Operation
When RA S is low and bot h C AS and WE are high
at the positive edge of the clock, a RAS cycle starts.
According to address data, a word line of the selected bank is activated and all of sense amplifiers associated t o the wordline are set. A CAS
cycle is
triggered by setting RAS
high a nd CAS low at a
clock timing after a nec es sa ry delay, t
RCD
,fromthe
RAS
timing. WE is used to define either a read
(WE
=H)orawrite(WE= L) at th is stage.
SDRAM provides a wide variety of fast access
modes. In a single CAS cycle, serial data read or
write operations are allowed at up to a 143 MHz
data rate. The numbers of serial data bits are the
burstlength programmed at the mode set operation,
i.e., one of 1, 2, 4, 8 and full page. Colu mn addresses are segmented by the burst length and serial
data accesses are done within this boundary. The
first column addres s to be ac ce ssed is supplied at
the CAS timing and the subsequent addresses are
generated automatically by t he programmed burst
length and its sequence. For example, in a burst
length of 8 with interleave sequence, if the first address is ‘2’, then t he rest of the burst s equenc e is 3,
0, 1, 6, 7, 4, and 5.
Full page burst operation is only possible using
the sequential burst type and page length is a function of the I/O organisation and column addressing.
Full page burst operation do not self terminate once
the burst leng th has been reached. In other words,
unlike burst length of 2, 3 or 8, full page burst continues until it is term inated us ing another command.
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
7
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
Address Input for Mode Set (Mode Register Operation)
Similar to the page m ode of conventional
DRAM’s, burst read or write accesses on any column address are possible once the RAS cycle
latches the sense amplifiers. The ma ximum t
RAS
or
therefresh interval time limits the number of random
column accesses. A new burst access can be done
even before the prev ious burst ends. The interrupt
operation at every clock cycles is supported. When
the previous burst is interrupt ed, the remain ing addresses are overridden by the new address with the
full burst length. An interrupt which accompanies
with an o peration change from a read to a write is
possible by exploi ting DQM to avoid bus contention.
When two or more banks are activated
sequentially, interleaved bank read or write
operations are possible. With the programmed
burst length, alternate access and precharge
operations on two or m ore banks can realize fast
serial data access modes among many different
pages. Once t wo or more banks are activated,
column to column interleave operation can be done
between di fferent pages.
A11
A3A4 A2 A1 A0
A10 A9
A8 A7 A6 A5
Address Bus (Ax)
BT Burst LengthCAS Latency
Mode Register
CAS Latency
A6 A5 A4 Latency
0 0 0 Reserve
0 0 1 Reserve
010 2
011 3
100 4
1 0 1 Reserve
1 1 0 Reserve
1 1 1 Reserve
Burst Length
A2 A1 A0
Length
Sequential Interleave
000 1 1
001 2 2
010 4 4
011 8 8
1 0 0 Reserve Reserve
1 0 1 Reserve Reserve
1 1 0 Reserve Reserve
111FullPageReserve
Burst Type
A3 T y pe
0 Sequential
1 Interleave
Operation Mode
BA1 BA0 A11 A10 A9 A8 A7 Mode
0000000
Burst Read/Burst
Write
0000100
Burst Read/Single
Write
Operation Mode
BA0BA1
8
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Burst Length and S equence:
Refresh Mode
SDRAM has two refresh modes, Auto Refresh
and Self Refresh. Auto Refresh is similar to the CAS
-before-RAS refresh of conventional DRAMs. All of
banks must be precharged before applying any refresh mode.An on-chip address count er increments
the word and the bank addresses and no bank information is required for both refresh modes.
The chip enters t he Auto Ref r es h mode, w hen
RAS
and CAS are held low and CKE and WE are
held high at a clock timing. The mode restores word
line after the refresh and no external precharge
command is ne ce ssary. A minimum tRC time is required between two automatic refreshes in a burst
refresh mode. The same rule applies to any access
command after the automatic refresh operation.
The chip has an on-chip timer and the Self Refresh mode is avail able. It enters the mode when
RAS
,CAS, and CKE are low and WE is high at a
clock timing. All of ex ternal control signals inclu ding
the clock are disa bled. Returning CKE to high enables the c lock and initiates t he refres h exit operation. After the exit command, at least one t
RC
delay
is required prior to any access command.
DQM Function
DQM has two functions for data I/O read and
write operations. During reads, when it turns to
“high” at a clock timing, data outputs are disabled
and become high impedance after two clock delay
(DQM Data Disable Latency t
DQZ
). It also provides
a data mask function for writes. When DQM is act ivated, th e write operation atthe next c lock is prohibited (DQM Write Mask Latency t
DQW
= zero clocks).
Suspend Mode
Duringnormal access mode, CKE is heldhigh enabling the clock. W hen CKE is low, it freezes the internal clock and extends data read and write
operations. O ne clock delay is required f or mode
entry and exit (Clock Suspend Latency t
CSL
).
Power Down
In order to reduc e standby power consumption, a
power down mode is available. All banks must be
precharged and the necessary Precharge delay
(trp) must occur before the SDRAM can enter the
Power Down mode. Once the Power Down mode is
initiated by holding CKE low, all of the receiver circuits except CLK and CKE are gated off. The Power
Down mode does not perform any refresh operations, therefore the device can’t remain in Power
Down mode longer than the R efresh period (tref) of
the device. Exit from this mode is p erformed by taking CKE “high”. One clock delay is required for
mode entry and exit.
Auto Precharge
Two methods are available to p re ch arge
SDRAMs. In an automatic prec harge mode, the
CAS timing accepts one extra address, CA 10, to
determine whether the chip restores or not after the
Burst
Length
Starting Address
(A2 A1 A0)
Sequential Burst Addressing
(decimal)
Interleave Bur st Addressing
(decimal)
2 xx0
xx1
0, 1
1, 0
0, 1
1, 0
4x00
x01
x10
x11
0, 1, 2, 3
1, 2, 3, 0
2, 3, 0, 1
3, 0, 1, 2
0, 1, 2, 3
1, 0, 3, 2
2, 3, 0, 1
3, 2, 1, 0
8 000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1
3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2
4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4
6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5
7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 0 3 2 5 4 7 6
2 3 0 1 6 7 4 5
3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4
4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
5 4 7 6 1 0 3 2
6 7 4 5 2 3 0 1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Full
Page
nnn Cn, Cn+1, Cn+2,..... not supported
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
9
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
operation. If CA10 is high when a Read Command
is issued, the Read with Auto-Precharge function
is initiated. The SDRAM automatically ent ers the
precharge operation one clock before the last data
out for CAS
latencies 2, two clocks for CAS latencies 3 and three clocks for CAS latencies 4. If
CAS10 is high when a Write Command is issued,
the Write with Auto-Precharge function is initiated. The SDRAM auto maticall y enters the precharge
operation a time delay equal to t
WR
(Write recovery
time) after the last data in.
Precharge Command
There is also a separate precharge command
available. When RA S
and WE are low and CAS is
high at a clock timing, it triggers the precharge operation. Three address bits, BA0, BA1 and A1 0 are
used to define banks as shown in the following list.
The precharge comm and can be imposed one clock
before the last da ta out for CAS latency = 2, two
clocks before the last data out for CAS latency = 3
and three clocks before the last data out for CAS latency= 4. Writes require a time delay twr from the
last data out to apply the precharge command.
Bank S elect ion by Address Bits:
Burst Termination
Once a burst read or write operation has been initiated, there are several methods in which to terminate the burst operation prematurely. These
methods include using another Read or Write Command to interrupt an existing burst operation, use a
Precharge Command to interrupt a burst cycle and
close the active bank , or using the Burst Stop Command to terminate the existing burst operation but
leave the bank open for future Read or Write Commands to the s ame page of the act ive bank. When
interrupting a burst with another Read or Write
Command care must be taken to avoid I/O contention. The Burst Stop Command, however, has the
fewest restrictions mak ing it the easiest method to
use when terminating a burst operat ion before it ha s
been completed. If a Burst Stop command is issued
during a burst write operation, then any residual
data from the burst write cycle will be ignored. Data
that is presented on t he I/O pins before the Burst
Stop Command is registered will be written to t he
memory.
A10 BA0 BA1
0 0 0 Bank 0
0 0 1 Bank 1
0 1 0 Bank 2
0 1 1 Bank 3
1XX allBanks
10
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Operating temperature range ..................0 to 70 °C
Storage temperat ure range ...............-55 to 150 °C
Input/output voltage..................-0.3 to (V
CC
+0.3)V
Power supply voltage ..........................-0.3 to 4.6 V
Power dissipation .............................................1 W
Data out current (short circuit)......................50 mA
*Note: Stresses above thoselistedunder “Absolute Maximum
Ratings” may cause permanent damage of the device.
Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Recommended O peration and Characteristics for LV-TTL
TA=0to70°C; VSS=0V;VCC,V
CCQ
=3.3V± 0.3 V
Note:
1. All voltages are referenced to V
SS
.
2. V
IH
may overshootto VCC+ 2.0 V for pulse width of < 4ns with 3.3V.VILmay undershoot to -2.0 V for pulse width < 4.0 ns with
3.3V.Pulsewidthmeasured at 50% points with amplitudemeasured peak to DC reference.
Parameter Symbol
Limit Values
Unit Note smin. max.
Inputhighvoltage V
IH
2.0 Vcc+0.3 V 1, 2
Input low voltage V
IL
– 0.3 0.8 V 1, 2
Output highvoltage (I
OUT
= – 2.0 mA) V
OH
2.4 – V
Output low voltage (I
OUT
=2.0mA) V
OL
– 0.4 V
Input leakagecurrent, any input
(0 V < V
IN
< 3.6 V, all other inputs = 0 V)
I
I(L)
– 55µA
Output leakage current
(DQ is disabled,0 V < V
OUT<VCC
)
I
O(L)
– 55µA
11
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Operating Currents (T
A
=0to70°C, VCC=3.3V± 0.3V)
(Recommended Operating Conditions unless otherwise noted)
Notes:
7. Theseparametersdepend on the cyclerate andthesevalues are measured by the cycle rate under the minimumvalue of t
CK
and
t
RC
. Input signals are changedone time duringtCK.
8. These parameter depend on output loading. Specified values are obtained with output open.
Symbol Parameter & Test Condition
Max.
Unit Note-7 -75 -8PC -8
ICC1 Operating Current
t
RC=tRCMIN.,tRC=tCKMIN
.
Active-precharge command
cycling,
without Burst Operation
1 bank operation 150 140 130 130 mA 7
ICC2P Precharge StandbyCurrent
in Power Down Mode
CS
=VIH,CKE≤ V
IL(max)
tCK=min. 2222mA7
ICC2PS t
CK
=Infinity 1111mA7
ICC2N Precharge Standby Current
in Non-Power Down M ode
CS
=VIH,CKE≥ V
IL(max)
tCK=min. 45403535mA
ICC2NS t
CK
=Infinity 5555mA
ICC3 No Operating Current
t
CK
=min,CS=V
IH(min)
bank ; active state ( 4 banks)
CKE ≥ V
IH(MIN.)
55 50 45 45 mA
ICC3P CKE <
V
IL(MAX.)
(Powerdown mode)
8888mA
ICC4 Burst Operating Curren t
t
CK
=min
Read/Write command cycling
120 120 110 110 mA 7,8
ICC5 Auto Refresh Current
t
CK
=min
AutoRefreshcommand cycling
150 140 130 130 mA 7
ICC6 Self RefreshCurrent
SelfRefresh Mode, CKE=<0.2V
1111mA
L-version 500 500 500 500 µA
12
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
AC Cha racteristics
1,2, 3
TA=0to70°C; VSS=0V;VDD=3.3V±0.3V,tT=1ns
# Symbol Parameter
Limit Values
Unit Note
-7 -75
-8PC
-8
Min. Max . Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
Clock and Clock Enable
1tCKClock Cycle Time
CAS
Latency = 3
CAS
Latency = 2
7
10––
7.510–
–
8
10
–
–812––
s
ns
ns
2t
CK
ClockFrequency
CAS
Latency = 3
CAS
Latency = 2
––143
100––
133
100––
125
100––
12583MHz
MHz
3t
AC
Access Time from Clock
CAS
Latency = 3
CAS
Latency = 2
–_5.4
5.5–_
5.46–
_
6
6
–
_
7
7
ns
ns
2, 4
4t
CH
ClockHigh Pulse Width 2.5 – 2.5 – 3 – 3 – ns
5t
CL
ClockLow PulseWidth 2.5 – 2.5 – 3 – 3 – ns
6t
T
TransitionTim 0.3 1.2 0.3 1.2 0.5 10 0.5 10 ns
Setup and Hold Times
7tISInputSetupTime 1.5 – 1.5 – 2 – 2.5 – ns 5
8t
IH
Input Hold Time 0.8 – 0.8 – 1 – 1 – ns 5
9t
CKS
CKE Setup Time 1.5 – 1.5 – 2 – 2.5 – ns 5
10 t
CKH
CKE Hold Time 0.8 – 0.8 – 1 – 1 – ns 5
11 t
RSC
Mode Register Set-up Time 14 – 15 – 16 – 16 – ns
12 t
SB
Power Down Mode Entry Time 0 7 0 7.5 0 8 0 8 ns
Common Parameters
13 t
RCD
Row to Column Delay Time 20 – 20 – 20 – 24 – ns 6
14 t
RP
Row PrechargeTime 20 – 20 – 20 – 24 – ns 6
15 t
RAS
Row Active Time 42 100K 45 100K 45 100k 48 100k ns 6
16 t
RC
Row Cycle Time 60 – 60 – 60 – 72 – ns 6
17 t
RRD
Activate(a) to Activate(b) Command
Period
14 – 15 – 16 – 20 – ns 6
18 t
CCD
CAS(a) to CAS(b) Command Period 1 – 1 – 1 – 1 – CLK
Refresh Cycle
19 t
REF
RefreshPeriod (4096 cycles) — 64 — 64 — 64 — 64 ms
20 t
SREX
Self Refresh Exit Time 10 10 10 12 ns
13
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Read Cycle
21 t
OH
Data OutH old Time 2.7 – 2.7 – 3 – 3 – ns 2
22 t
LZ
Data Out to Low Impedance Time 1 – 1 – 0 – 0 – ns
23 t
HZ
Data Out to High Impedance Time – 5.4 – 5.4 3 8 3 8 ns 7
24 t
DQZ
DQM Data Out Disable Latency – 2 – 2 – 2 – 2CLK
Write Cycle
25 t
WR
WriteRecovery Time 2 – 2 – 2 – 2 – CLK
26 t
DQW
DQM Write Mask Latency 0 – 0 – 0 –––CLK
# Symbol Parameter
Limit Values
Unit Note
-7 -75
-8PC
-8
Min. Max . Min. Max. Min. Max . Min. Max.
AC Cha racteristics (Cont’d)
14
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
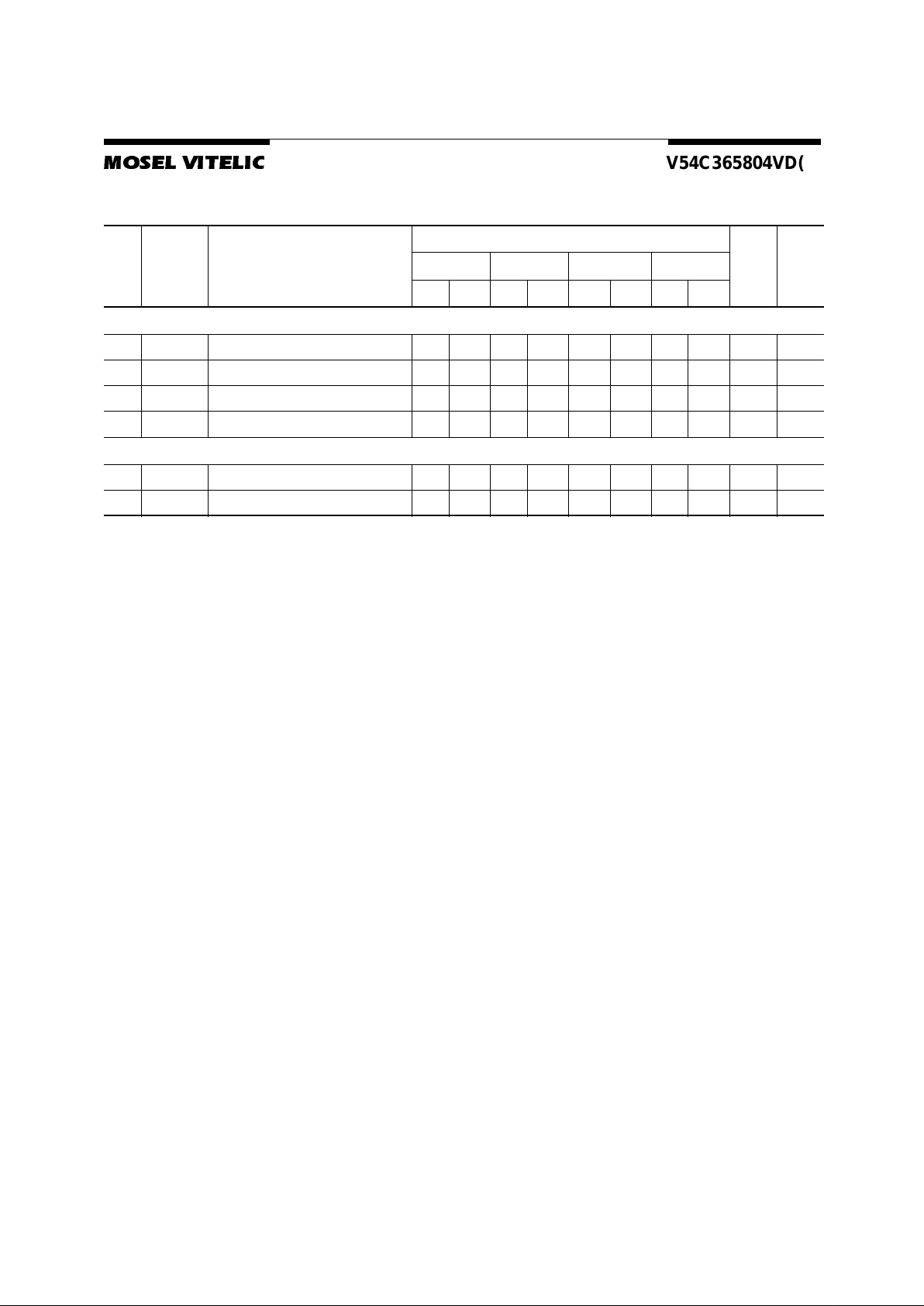
Notes for AC Parameters:
1. For pr oper power-up see the operation section of this data sheet.
2. AC timing testshaveV
IL
= 0.8V andVIH= 2.0Vwith the timingreferencedto the 1.4 V crossoverpoint. The transition
timeismeasuredbetweenV
IH
and VIL.AllACmeasurementsassume tT= 1nswith the AC output loadcircuitshown
in Figure 1.
4. If clock rising time is longer than 1 ns, a time (t
T
/2 – 0.5) ns has to be added to this parameter.
5. If t
T
is longer than 1 ns, a time (tT– 1) ns has to be added to this parameter.
6. These parameter account for the number of clock cycle and depend on the operating frequency of the clock, as
follows:
the number of clock cycle = specified value of timing period (counted in fractions as a whole number)
Self Refresh Exit is a synchronous operation and begins on the 2nd positive clock edge after CKE returns high.
Self Refresh Exit is not complete until a time period equal to tRC is satisfied once the Self Refresh Exit command
is registered.
7. Referenced to the time which the output achieves the open circuit condition,not to output voltage levels
1.4V
1.4V
tCS tCH
tAC
tAC
tLZ
tOH
tHZ
CLK
COMMAND
OUTPUT
50 pF
I/O
Z=50Ohm
+1.4V
50 Ohm
VIH
VIL
t
T
Figure1.
tCK

15
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
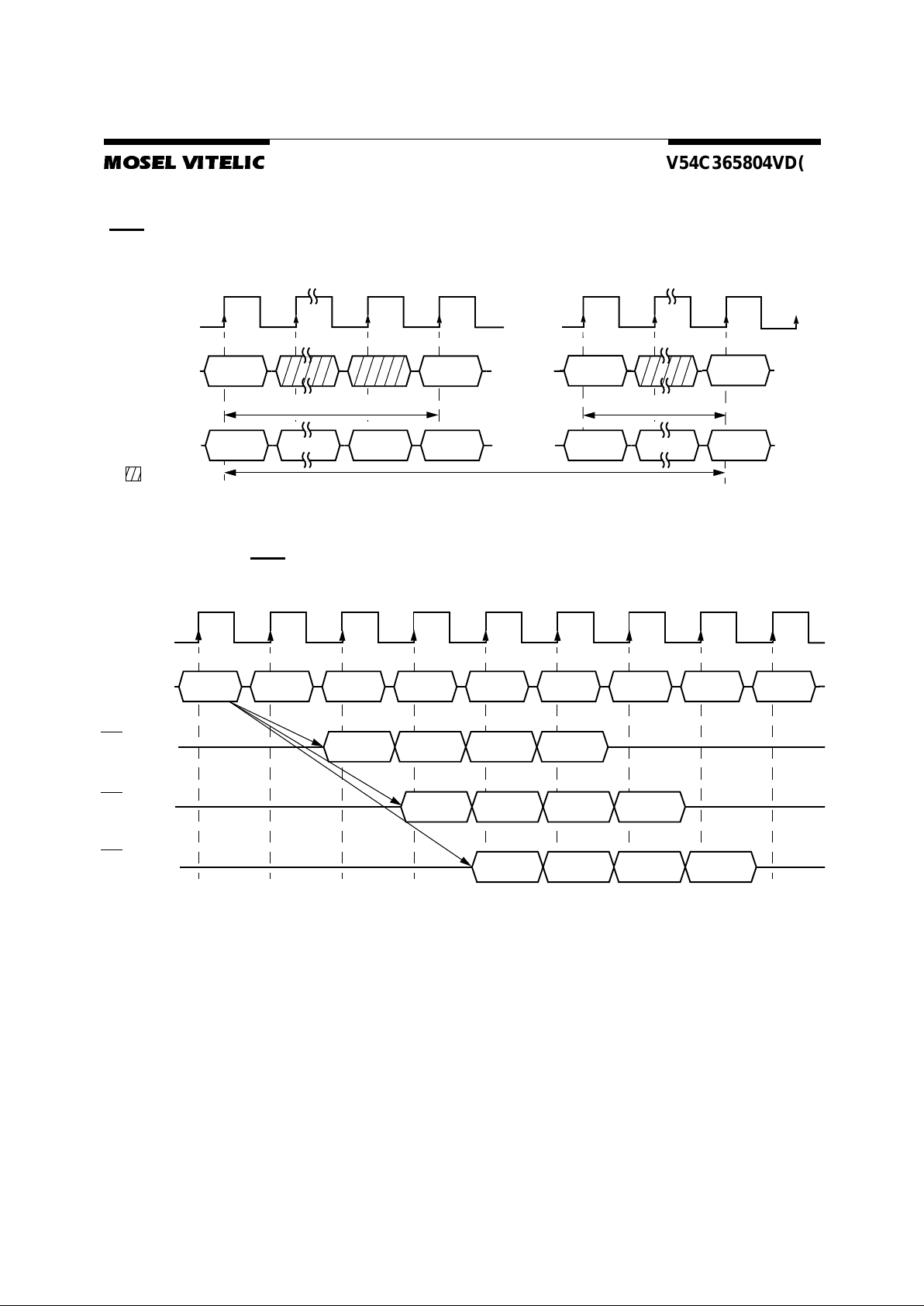
Timing Diagrams
1. Bank Activate Command Cycle
2. Burst Read Operation
3. Read Interrupted by a Read
4. Read to Write Interval
4.1ReadtoWriteInterval
4.2 Minimum Read t o Write Interval
4.3 Non-Minimum Read to Write Interva l
5. Burst Write Operati on
6. Write and Read Interrupt
6.1 Write Interrupted by a Write
6.2 Write Interrupted by Read
7. Burst Write & Read with A ut o-Prechar ge
7.1 Burst Write with Auto-Precharge
7.2 Burst Read with Auto-Precharge
8. Burst Termination
8.1 Termination of a Full Page Burst Write Operation
8.2 Termination of a Full Page Burst Write Operation
9. AC- Parameters
9.1 AC Parameters for a Write Timing
9.2 AC Parameters for a R ead Timing
10. Mo de Register Set
11. Power on Sequence and A ut o Refresh ( CB R)
12. Clock Suspension (using CKE)
12.1 Clock Suspension Du r ing Burst Read CAS
Latency = 2
12. 2 Clock Suspension During Burs t Read CAS
Latency = 3
12. 3 Clock Suspension During Burs t Write CA S
Latency = 2
12. 4 Clock Suspension During Burs t Write CA S
Latency = 3
13. Power Down Mode and Clock Suspend
14. Self Refresh (Entry and Exit)
15. Auto Refresh (CBR)

16
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
Timing Diagrams (Cont’d)
16. Random Column Read ( Page within same Ban k)
16.1 CAS
Latency = 2
16.2 CAS
Latency = 3
17. Random Column Write ( Page within same Bank)
17.1 CAS
Latency = 2
17.2 CAS
Latency = 3
18. Random Row Read ( Interleaving Banks ) with Prech arge
18.1 CAS
Latency = 2
18.2 CAS
Latency = 3
19. Random Row Write ( Interleaving Banks) with Precharge
19.1 CAS
Latency = 2
19.2 CAS
Latency = 3
20. Full Page Rea d Cycle
20.1 CAS
Latency = 2
20.2 CAS
Latency = 3
21. Full Page Write Cycle
21.1 CAS
Latency = 2
21.2 CAS
Latency = 3
22. Precharge Termination of a B urst
22.1 CAS
Latency = 2
22.2 CAS
Latency = 3
17
V54C365804VD(L) Rev. 0.9 September 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365804VD(L)
1. Bank Activate Command Cy cle
(CAS
latency = 3)
2. Burst Read Operation
(Burst Length = 4, CAS
latency = 2, 3, 4)
ADDRESS
CLK
T0 TT1 T TTT
COMMAND
NOP NOP NOP
Bank A
Row Addr.
Bank A
Activate
Write A
with Auto
Bank A
Col. Addr.
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
Bank B
Activate
Bank A
Row Addr.
Bank A
Activate
t
RCD
: “H” or “L”
t
RC
Precharge
t
RRD
Bank B
Row Addr.
COMMAND
READ A
NOP NOP NOP NOP NOP NOP NOP
DOUT A
0
CAS latency = 2
t
CK3,
I/O’s
CAS latency = 3
t
CK4,
I/O’s
CAS latency = 4
DOUT A
1
DOUT A2DOUT A
3
NOP
CLK
T0 T2T1 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8
t
CK2,
I/O’s
DOUT A
0
DOUT A
1
DOUT A
2
DOUT A
3
DOUT A
0
DOUT A1DOUT A
2
DOUT A
3
 Loading...
Loading...