Mosel Vitelic V54C365324V-8, V54C365324V-6, V54C365324V-7, V54C365324V-55, V54C365324V-5 Datasheet
...
MOSEL VITELIC
1
V54C365324V
200/183/166/143 MHz 3.3 VOLT
ULTRA HIGH PERFORMANCE
2M X 32 SDRAM 4 BANKS X 512Kbit X 32
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
PRELIMINARY
V54C365324V -5 -55 -6 -7 -8 Unit
Clock Frequency (tCK) 200 183 166 143 125 MHz
CAS
Latency 33333clocks
CycleTime(t
CK
)55.5678ns
Access Time (t
AC
)55.5666ns
Features
■ JEDEC Standard 3.3V Po w er Supply
■ The V54C365324V is ideally suited for high
performance graphi c s peripheral applications
■ Single Pulsed RAS
Interface
■ Programmable CAS Latency: 2, 3
■ All Inputs are sampled atthe positive going edge
of clock
■ Programmable Wrap Sequence: Sequential or
Interleave
■ Programmable Burst Length: 1, 2, 4, 8 and Full
Page for Sequential and 1, 2, 4, 8 for Interleave
■ DQM 0-3 for B yte Masking
■ Auto & Self Refresh
■ 2K Refresh Cycles/32 m s
■ Burst Read with Single Write Operation
Description
The V54C365324V is a 67,108, 864 bits synchronous high data rate DRA M organized as 4 x
524,288 words by 32 bits. The device is designed to
comply with JEDEC standards set for synchronous
DRAM products, both electrically and mechanically.
Synchronous design allows precise cycle control
with the system clock. The CAS latency, burst
length and burst sequence must be programm ed
into device prior to access operation.
2
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365324V
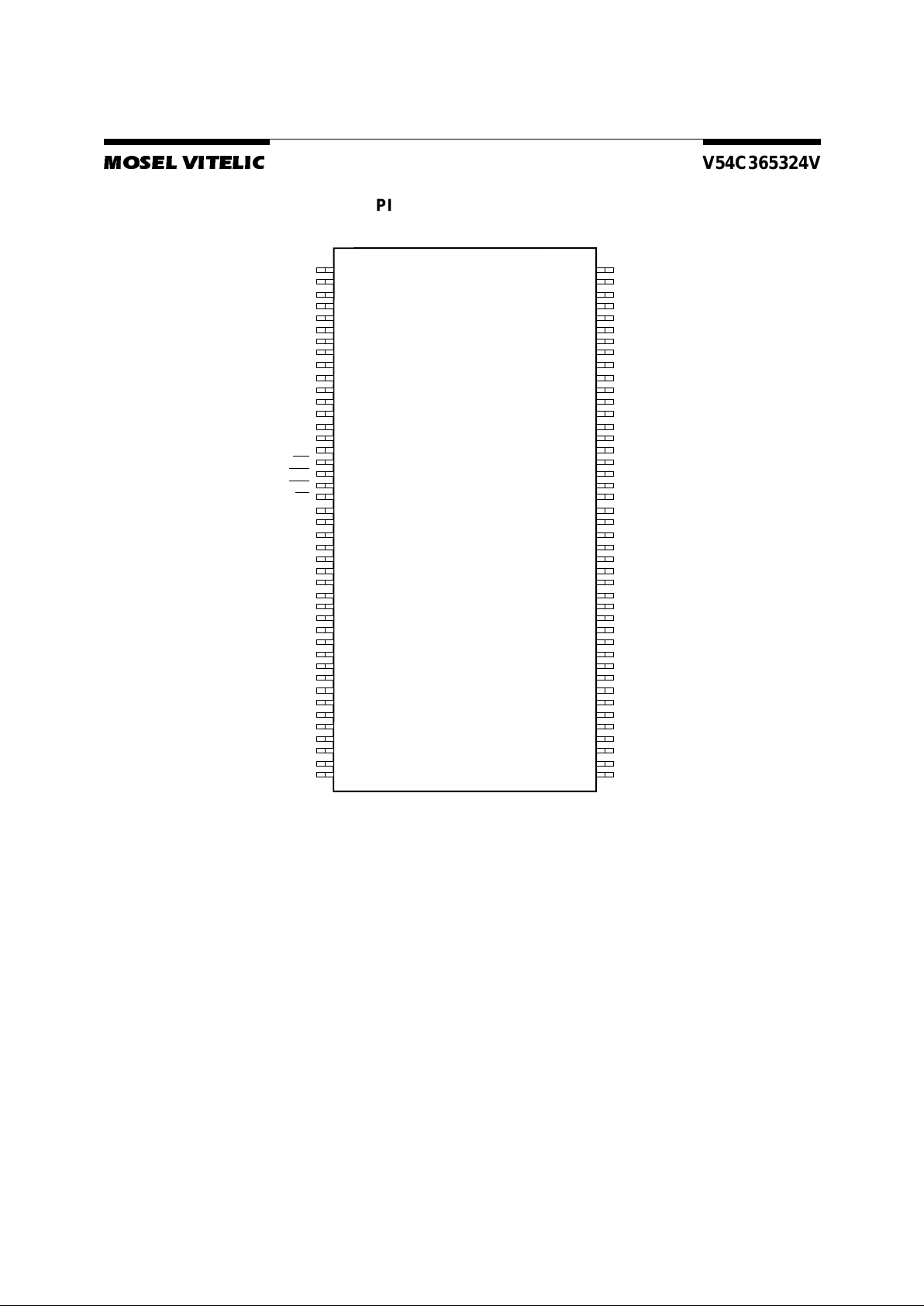
PIN CO NFIGURATION
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
V
DD
DQ
0
V
DDQ
DQ
1
DQ
2
V
SSQ
DQ
3
DQ
4
V
DDQ
DQ
5
DQ
6
V
SSQ
DQ
7
NC
V
DD
DQM
0
WE
CAS
RAS
CS
NC
BA0
BA1
A
10
/AP
A
0
A
1
A
2
DQM
2
V
DD
NC
DQ
16
V
SSQ
DQ
17
DQ
18
V
DDQ
DQ
19
DQ
20
V
SSQ
DQ
21
DQ
22
V
DDQ
DQ
23
V
DD
V
SS
DQ
15
V
SSQ
DQ
14
DQ
13
V
DDQ
DQ
12
DQ
11
V
SSQ
DQ
10
DQ
9
V
DDQ
DQ
8
NC
V
SS
DQM
1
NC
NC
CLK
CKE
A9
A8
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
DQM
3
V
SS
NC
DQ
31
V
DDQ
DQ
30
DQ29
V
SSQ
DQ
28
DQ
27
V
DDQ
DQ
26
DQ
25
V
SSQ
DQ
24
V
SS
86 Pin TSOP (II)
(400mil x 875mil)
(0.5mm Pin pitch)
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365324V
3
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
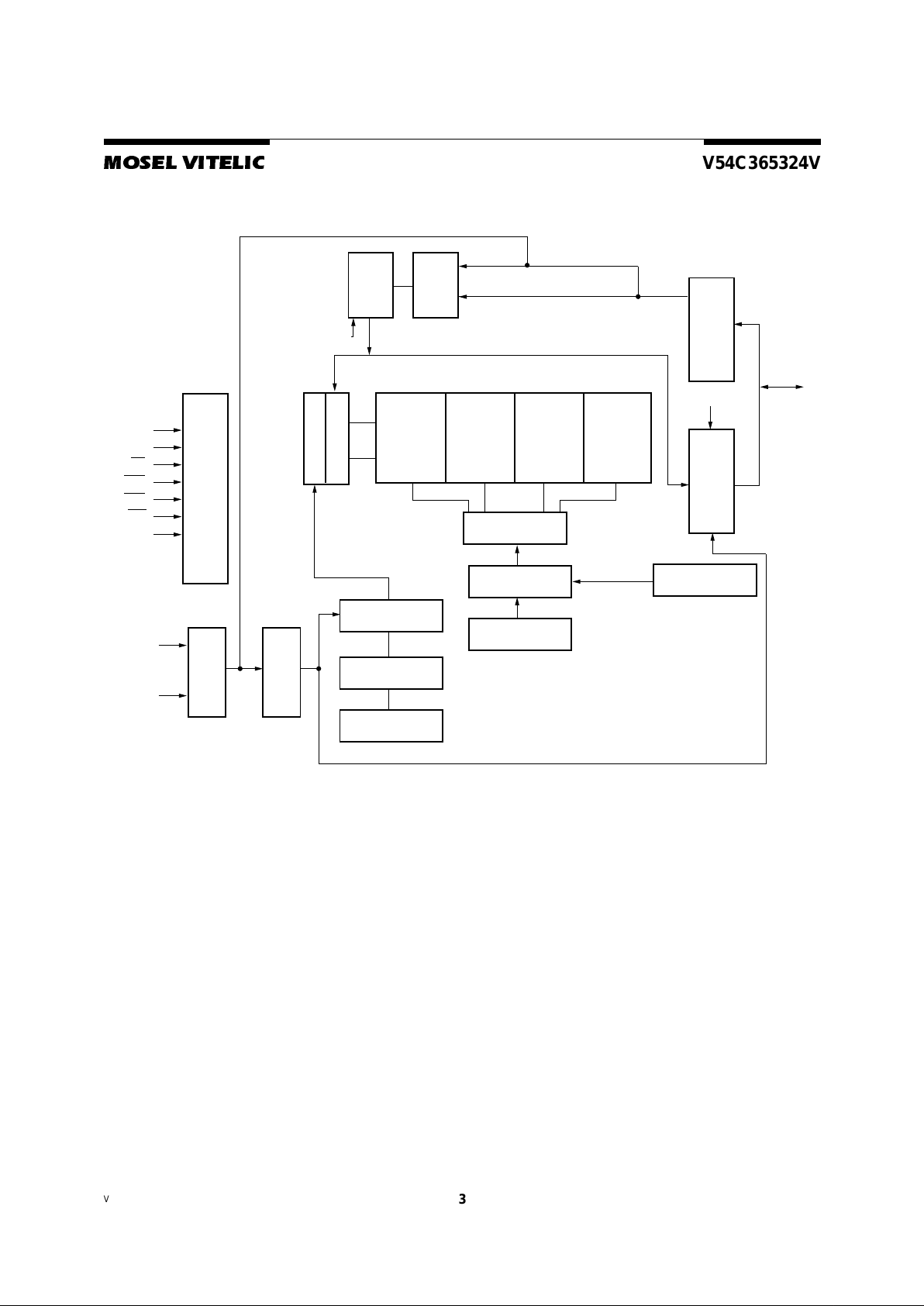
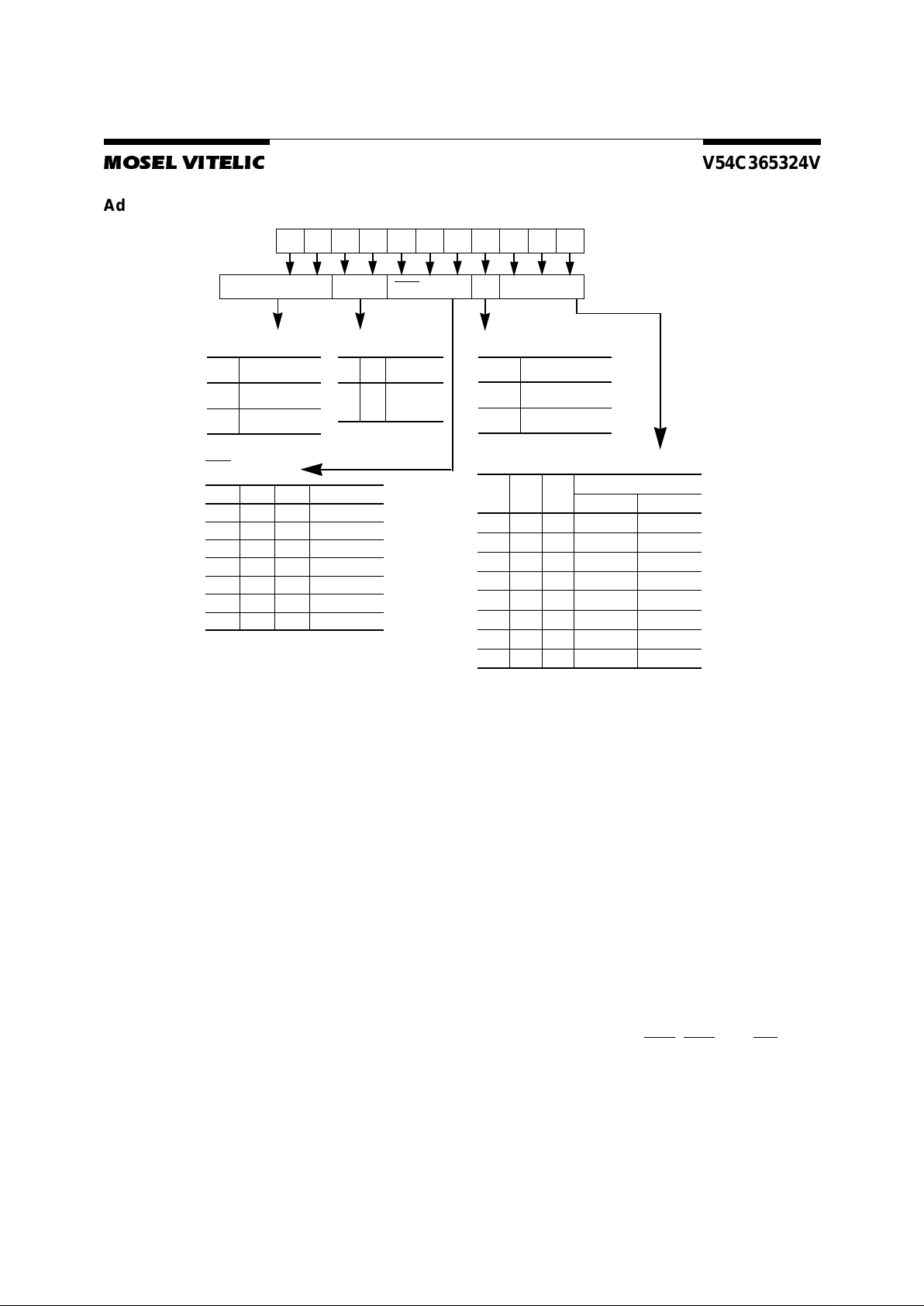
Block Diagram
CLK
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
DQMi
CLK
Address
A0-A
7
Column Address
Buffer
Row Address
Buffer
Refresh
Counter
Latency &
Burst Length
Output
Buffer
Input
Buffer
Programming
Register
Column Decoder
Sense Amplifier
Timing
Register
Column Address
Counter
Row
Decoder
Bank0
512K x 32
MUX
Write
Control
Logic
DQMi
DQMi
DQ
0
-DQ
31
Column Addresses
A
0-A10
, BA0, BA1
Row Addresses
Bank1
512K x 32
Bank2
512K x 32
Bank3
512K x 32
4
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365324V
Signal Pin Description
Pin Name Input Function
CLK Clock Input Systemclock input.Activeonthepositiverising edgeto sampleallinputs
CKE Clock Enable Activates the CLK signal when high and deactivatesthe CLK when low.
CKE low initiates the power down mode, suspend mode, or the self refresh mode
CS
Chip Select Disables or enablesdeviceoperation by maskingor enablingall inputs
except CLK, CKE and DQMi
RAS
Row Address Strobe Latchesrow addresseson the positive edge of CLK withRAS low. En-
ables row access & precharge
CAS
Column Address Strobe Latches column addresses on the positive edge of CLK with CAS low.
Enablescolumnaccess
WE
WriteEnable Enableswriteoperation
A
0-A10
Address During a bank activate command, A0-A10defines the row address.
During a read or write command, A
0-A7
defines the column address. In
addition to the column addressA
10
isused to invokeautoprechargeBA
define the bank to be precharged. A
10
islow, autoprechargeis disabled
during a precharge cycle, If A
10
ishigh,allbankwill beprecharged,if A
10
is low, the BA0, BA1 is used to decide which bank to precharge
BA
0
,BA
1
Bank Select Selectswhichbank to activate.
DQ
0
-DQ
31
Data Input/Output Data inputs/output are multiplexed on the same pins
DQMi Data Input/Output Mask Makes data output Hi-Z. Blocks data input when DQM is active
VDD/VSS Power Supply/Ground Power Supply. +3.3V ± 0.3V/ground
VDDQ/VSSQ Data Output Power/Ground Provides isolatedpower/groundto DQs for improvednoise immunity
NC No Connection
5
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365324V
Address Input for Mode Set (Mode Re gister Operation)
Power O n and Initialization
The default power on state of the mode register is
supplier specific and may be undefined. The
following power on and i nitialization sequence
guarantees the device is preconditioned to each
users specific needs. Like a conv ent ional DRAM,
the Synchronous DRAM must be powered up and
initialized in a predefined manner. During power on,
all VCC and VCCQ pins mus t be b uilt up
simultaneously to t he specified voltage when the
input signals are held in the “NOP” state. The power
on voltage must not exceed VCC+0.3V on any of
the input pins or VCC supplies. The CLK signal
must be st arted at the same time. After power on,
an initial pause of 200 µs is required followed by a
precharge of both banks using the precharge
command. To prevent data content ion on the DQ
bus during poweron, it is requiredthat the DQM and
CKE pins be held high during the i nitial pause
period. Once all banks hav e been precharged, the
Mode Register S et Command mus t be issued to
initialize the Mode Register. A minimum of eight
Auto Refresh cycles (CBR) are also required.These
may be done before or after programming the Mode
Register. Failure to follow these steps may lead to
unpredictable start-up modes.
Programming the Mode Register
The Mode register designates the operation
mode at the read or write cycle. This register is divided into 4 fields. A Burst Length Field to set the
length of the burst, an Addressing Selection bit to
program the column access sequen ce in a burst cycle (interleaved or sequential), a CAS LatencyField
to set the access time at clock cycle and a Operation mode field to differentiate between normal operation (Burst read and burst Write) and a special
Burst Read and S ingle Write m ode. The mode set
operation must be done before any activate command after the initial power up. Any content of the
mode register can be altered by re-executing the
mode set command. All banks must be in precharged state and CKE must be high at least one
clock before t he mode s et operation. After t he mode
register is set, a Standby or NOP command is
required. Lo w signals of RAS
,CAS, and WE at the
positive edge of the clock activate the mode set
operation. A ddres s input data at this timing defines
parameters to be set as shown inthe previous table.
A3A4 A2 A1 A0
A9
A8 A7 A6 A5
Address Bus (Ax)
BT Burst LengthCAS Latency
Mode Register
CAS Latency
A6 A5 A4 Latency
000 Reserve
001 Reserve
010 2
011 3
101 Reserve
110 Reserve
111 Reserve
Burst Length
A2 A1 A0
Length
Sequential Interleave
000 1 1
001 2 2
010 4 4
011 8 8
1 0 0 Reserve Reserve
1 0 1 Reserve Reserve
1 1 0 Reserve Reserve
1 1 1 Full Page Reserve
Burst Type
A3 Type
0 Sequential
1 Interleave
Test Mode
A8 A7 Mode
00
Mode Reg
Set
Test
Mode
Write Burst Length
Write Burst Length
A9 Length
0Burst
1 Single Bit
A10

6
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365324V
Read and Write Operation
When RAS is low and both CAS and WE are high
at the positive edge of the clock, a RAS cycle starts.
According to address data, a word line of the selected bank is act ivated and all of sense amplifiers associated to the wo rdline are set. A CAS
cycle is
triggered by setting RAS
high and CAS low at a
clock timing after a nec es s ary delay, t
RCD
,fromthe
RAS
timing. W E is used to define either a read
(WE
=H)orawrite(WE= L) at this stage.
SDRAM provides a wide variety of fast ac c ess
modes. In a single CAS cycle, serial data read or
write operations are allowed at up to a 200 MHz
data rate. The numbers of serial data bits are the
burst length program medat the mode s et operation,
i.e., one of 1, 2, 4, 8 and full page. Column addres ses are segment ed by the burst length and serial
data accesses are done within this boundary. The
first column address to be ac c es s ed is supplied at
the CAS timing and the subseq uent addresses are
generated automatically by the programmed burst
length and its sequence. For example, in a burst
length of 8 with interleave sequence, if the first address is ‘2’, then the rest of the burst sequence is 3,
0, 1, 6, 7, 4, and 5.
Full page burst operati on is only possible using
the sequential burst type and page le ngth is a func tion of the I/O organisation and column addressing.
Full page burst operation do not self terminate once
the burst length has been reached. In other words,
unlike burst l ength of 2, 3 or 8, full page burst continues until it is terminated us ing another command.
Similar t o the page mode of co nventional
DRAM’s, burst read or write accesses on any column address a re possible once the RAS cycle
latches the sense amplifiers. The maximu m t
RAS
or
therefresh interval time limits the number of random
column accesses . A new burs t access can be done
even before the previous burst ends. The interrupt
operation a t every c lock cycles is supported. When
the previous burs t is interrupted, the remaining addresses are overridden by the new addres s with t he
full burst length. An interrupt which acc ompanies
with an operation change from a read to a write is
possible by exploiting DQM to avoid bus contention.
When two or more banks are activated
sequentially, interleaved bank read or write
operations are possibl e. With the programmed
burst length, al ternate access and precharge
operations on two or more banks can realize fast
serial data access modes among many different
pages. Once two or more bank s are activated,
column to column interleave operation can be done
between different pages.
Refresh Mode
SDRAM has two refresh modes, Aut o Refresh
and S elfRefres h. Auto Refresh is similar to the CA S
-before-RAS refresh of conventional DRAMs. All of
banks must be p rech arged before applying any refresh m ode. A n on-chip address counter increments
the wordand the bank addresses and no bank information is required for both refresh modes.
Burst Length and Sequence:
Burst
Length
Starting Address
(A2 A1 A0)
Sequential Burst Addressing
(decimal)
Interleave Bur st Addressing
(decimal)
2 xx0
xx1
0, 1
1, 0
0, 1
1, 0
4x00
x01
x10
x11
0, 1, 2, 3
1, 2, 3, 0
2, 3, 0, 1
3, 0, 1, 2
0, 1, 2, 3
1, 0, 3, 2
2, 3, 0, 1
3, 2, 1, 0
8 000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0
2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1
3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2
4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4
6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5
7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1 0 3 2 5 4 7 6
2 3 0 1 6 7 4 5
3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4
4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
5 4 7 6 1 0 3 2
6 7 4 5 2 3 0 1
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Full
Page
nnn Cn, Cn+1, Cn+2,..... not supported

7
V54C365324V Rev. 1.2 August 2001
MOSEL VITELIC
V54C365324V
The chip enters the Auto Refresh mode, when
RAS
and CAS are held low and CKE and WE are
held high at a clock timing. The mode restores w ord
line after the refresh and no external precharge
command is necess ary. A minimum tRC time is required between two automatic refreshes in a burst
refresh mode. The same rule applies to any access
command after the automatic refresh operation.
The chip has an on-chip timer and the Self Refresh mode is available. It enters the mode when
RAS
,CAS, and CKE are low and WE is high at a
clock timing. A ll of external control signals including
the clock are disabled. Returning CKE to high enables the clock and initiates the refresh exit operation. After the exit command, at least one t
RC
delay
is required prior to any access command.
DQM Function
DQM has two functions for data I/O read and
write operations. During reads, when it turns to
“high” at a clock timing, data outputs are disabled
and become high im pedanc e after two clock delay
(DQM Data Disable Latency t
DQZ
). It also provides
a d ata mask function for writes. When DQM is activated, the writeoperation at the next clock is prohibited(DQMWriteMaskLatencyt
DQW
= zero clocks).
DQM is used for device selection, byte selection
and bus control in a mem ory system. DQM0 controls DQ0 t o DQ7, DQM1 controls DQ8 to DQ15,
DQM2 controls DQ16 to DQ23, DQM 3 controls
DQ24 to DQ31.
Suspend Mode
Duringn ormal access mode, CKE isheld high enabling the clock. When CKE is low, it freezes the internal clock and extends data read and write
operations. One clock delay is required for mode
entry and exit (Clock Suspend L atency t
CSL
).
Power Down
In order to reduce standby power c onsumption, a
power down mode is available. All bank s must be
precharged and the neces s ary Precharge delay
(trp) must occur before the SDRAM c an enter the
Power Down mode. Once the Power Down mode is
initiated by holding CKE low, all of the receiver circuits except CLK and CKE are gated off. The P ower
Down mode does not perform any refresh operations, therefore the device can’t remain in Power
Down mode longer th an the Refresh period (tref) of
the device. Exit f r om this mode is performed by taking CKE “high”. One clock delay is required for
mode ent ry and exit.
Auto Precharge
Two methods are available t o precharge
SDRAMs. In an automatic precharge mode, the
CAS tim ing accepts one extra address, A8, to dete rmine whether the chip restores or not after the operation. If A8 is hi gh when a Read Command is
issued, the Read with Auto-Precharge function is
initiated. The SDRAM automatically enters the precharge operation one clock before the last data out
for CAS
latencies2, two clocks for CAS latencies 3.
If A8 is high when a Write Command is issued, the
Write with Auto-Precharge funct ion is initiated.
The SDRAM aut omatically ent ers the precharge operation a time delay equal to t
WR
(Write recovery
time) after the last data in.
Precharge Command
There is also a s eparate precharge command
available. When RAS
and WE are low and CAS is
high at a clock t im ing, it triggers the precharge operation. With A 8 being low, the BA is used select
bank to precharge. The precharge command can be
imposed one clock before the last data out for CAS
latency = 2, two clocks bef ore the last data out for
CAS latency = 3. Writes require a time delay twr
from the last data out to apply the precharge command.
Burst Termination
Once a burst read or write operation has been initiated, there are several methods in which to terminate the burst operation prematurely. These
methods include using another Read or Write Command to interrupt an existing burst operation, u se a
Precharge Command to interrupt a burst cycle and
close the active bank, or using the Burs t Stop Command to terminate the existing bu rst operation but
leave the bank open for future Read or Write Commands to the sam e page of the active bank. When
interrupting a burst with another Read or Write
Command care must be taken to avoid I/O contention. The Burst Stop Command, however, has the
fewest restrictions making it the easiest method to
use w hen terminating a burst operation before ithas
been completed. If a Burs t Stop command is issued
during a burst write operation, then any residual
data from the burst write cycle will be ignored. Data
that is presented on the I/O pins before the Burst
Stop C omm and is registe red will be written to the
memory.
 Loading...
Loading...