Morrell SW-MNG-24GE2GSFP User Manual

SW-MNG-24GE2GSFP
24-Port 10/100/1000Mbps + 2-Port Gigabit SFP
Managed Ethernet Switch
User Manual
Version 1.1 | 10/22/2016

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Product Introduction ..................................................................... 4
1.1 Product Overview .................................................................................. 4
1.2 Features ................................................................................................ 4
1.3 External Component Description .......................................................... 5
1.3.1 Front Panel ................................................................................................ 5
1.3.2 Rear Panel ................................................................................................. 6
1.4 Package Contents ................................................................................. 7
Chapter 2 Installing and Connecting the Switch .......................................... 8
2.1 Installation ............................................................................................. 8
2.1.1 Desktop Installation .................................................................................... 8
2.1.2 Rack-mountable Installation in 19-inch Cabinet ......................................... 9
2.1.3 Power on the Switch .................................................................................. 9
2.2 Connect Computer (NIC) to the Switch ............................................... 10
Chapter 3 How to Login the Switch ............................................................. 11
3.1 Switch to End Node ............................................................................. 11
3.2 How to Login the Switch ...................................................................... 11
Chapter 4 Switch Configuration ................................................................... 13
4.1 Quickly setting ..................................................................................... 13
4.2 PORT ................................................................................................... 16
4.2.1 Basic config ............................................................................................. 16
4.2.2 Port aggregation ...................................................................................... 17
4.2.3 Port mirroring ........................................................................................... 19
4.2.4 Port rate-limit ........................................................................................... 20
4.2.5 Storm control ............................................................................................ 21
4.2.6 Port isolation ............................................................................................ 22
4.3 VLAN ................................................................................................... 23
4.3.1 VLAN config ............................................................................................. 24
4.3.2 Trunk-port setting ..................................................................................... 25
4.3.3 Hybrid-port setting ................................................................................... 26
4.4 Fault/Safety ......................................................................................... 27
4.4.1 Anti attack ................................................................................................ 28
4.4.1.1 Anti DHCP attack .................................................................................................. 28
4.4.1.2 Anti DOS ............................................................................................................... 30
4.4.1.3 IPsource guard ..................................................................................................... 31
4.4.1.4 Anti three bind ....................................................................................................... 32
4.4.2 Channel detection .................................................................................... 34
4.4.2.1 Ping testing ........................................................................................................... 34
1

4.4.2.2 Tracert testing ....................................................................................................... 35
4.4.2.3 Cable testing ......................................................................................................... 36
4.4.3 ACL .......................................................................................................... 37
4.5 MSTP ................................................................................................... 39
4.5.1 MSTP region ............................................................................................ 39
4.5.2 MSTP bridge ............................................................................................ 40
4.6 DHCP relay .......................................................................................... 43
4.6.1 DHCP relay .............................................................................................. 43
4.6.2 0ption82 ................................................................................................... 44
4.7 QoS ...................................................................................................... 46
4.7.1 Remark .................................................................................................... 46
4.7.2 Queue config ........................................................................................... 48
4.7.3 Mapping the queue .................................................................................. 49
4.7.3.1 Service class queue mapping .............................................................................. 49
4.7.3.2 Differential service class mapping ........................................................................ 50
4.7.3.3 Port to service class mapping .............................................................................. 51
4.8 Address table ....................................................................................... 52
4.8.1 Mac add and delete ................................................................................. 53
4.8.2 Mac study and laging ............................................................................... 54
4.8.3 Mac address filtering ................................................................................ 55
4.9 Snmp config ......................................................................................... 56
4.9.1 Snmp config ............................................................................................. 56
4.9.1.1 Snmp config .......................................................................................................... 5 6
4.9.1.2 Community config ................................................................................................. 57
4.9.1.3 View config ........................................................................................................... 58
4.9.1.4 Group config ......................................................................................................... 5 9
4.9.1.5 User config ............................................................................................................ 60
4.9.1.6 Trap ....................................................................................................................... 61
4.9.2 Rmon config ............................................................................................. 62
4.9.2.1 Statistics group ..................................................................................................... 6 2
4.9.2.2 History group ........................................................................................................ 6 3
4.9.2.3 Event group .......................................................................................................... 6 4
4.9.2.4 Alarm group .......................................................................................................... 6 5
4.10 SYSTEM ............................................................................................ 66
4.10.1 System config ........................................................................................ 67
4.10.1.1 System settings .................................................................................................. 67
4.10.1.2 System restart ..................................................................................................... 69
4.10.1.3 Password change ............................................................................................... 70
4.10.1.4 SSH login ............................................................................................................ 71
4.10.1.5 Telnet login .......................................................................................................... 72
4.10.1.6 System log .......................................................................................................... 7 2
4.10.2 System upgrade ..................................................................................... 74
4.10.3 Config management ............................................................................... 75
4.10.3.1 Current configuration .......................................................................................... 75
2

4.10.3.2 Configuration backup.......................................................................................... 77
4.10.3.3 Restore factory configuration ............................................................................. 78
4.10.4 Config save ............................................................................................ 79
4.10.5 Administrator privileges .......................................................................... 80
4.10.6 Info collect .............................................................................................. 80
Appendix: Technical Specifications ............................................................ 82
3

Chapter 1 Product Introduction
Congratulations on your purchasing of the Web Smart Ethernet Switch. Before you install
and use this product,please read this manual carefully for full exploiting the functions of
this product.
1.1 Product Overview
The Web Smart Ethernet Switch provides the seamless network connection. This device
integrates 1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet, 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and 10Mbps Ethernet
network capabilities in a highly flexible package. With 24-10/100/1000Mbps
Auto-Negotiation RJ45 ports, all ports support Auto MDI/MDIX function. The Switch with a
low-cost, easy-to-use, high per-formance upgrade your old network to a 1000Mbps
Gigabit network. It is essential to helping solve network bottlenecks that frequently
develop as more advanced computer users and newer applications continue to demand
greater network resources.
The switch is easy to install and use. It requires no configuration and installation. It is a
great selection for office network.
1.2 Features
Comply with IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u, IEEE802.3ab, IEEE802.3x, IEEE802.3z,
EEE802.3ad standards
Supports IEEE802.3x flow control for Full-duplex Mode and back pressure for
Half-duplex Mode
Supports MAC address auto-learning and auto-aging
Store and forward mode operates
Support SNMP/RMON/TELENT
Supports IEEE802.1Q VLAN,4K VLAN Table
Support IEEE802.1p Priority Queues
Support ACL Function, 1.5K-entry ALC table
Support Storm Control
Support QoS、Port Mirroring、Link Aggregation Protocol
LED indicators for monitoring power, link/activity
Web-based Management Support
Internal power adapter supply
4

1.3 External Component Description
1.3.1 Front Panel
The front panel of the Switch consists of 24 x 10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports,2 x SFP
ports,1 x Console port, 1 x Reset button and a series of LED indicators as shown as
below.
Figure 1 - Front Panel
10/100/1000Mbps RJ-45 ports (1~24):
Designed to connect to the device with a bandwidth of 10Mbps, 100Mbps or 1000Mbps.
Each has a corresponding 10/100/1000Mbps LED.
SFP ports (SFP1, SFP2):
Designed to install the SFP module and connect to the device with a bandwidth of
1000Mbps. Each has a corresponding 1000Mbps LED.
Console port (Console):
Designed to connect with the serial port of a computer or terminal for monitoring and
configuring the Switch.
Reset button (Reset):
Keep the device powered on and press down the button for about 5 seconds. The system
restores the factory default settings.
LED indicators:
The LED Indicators will allow you to monitor, diagnose and troubleshoot any potential
problem with the Switch, connection or attached devices.
Figure 2 - LED Indicators
5
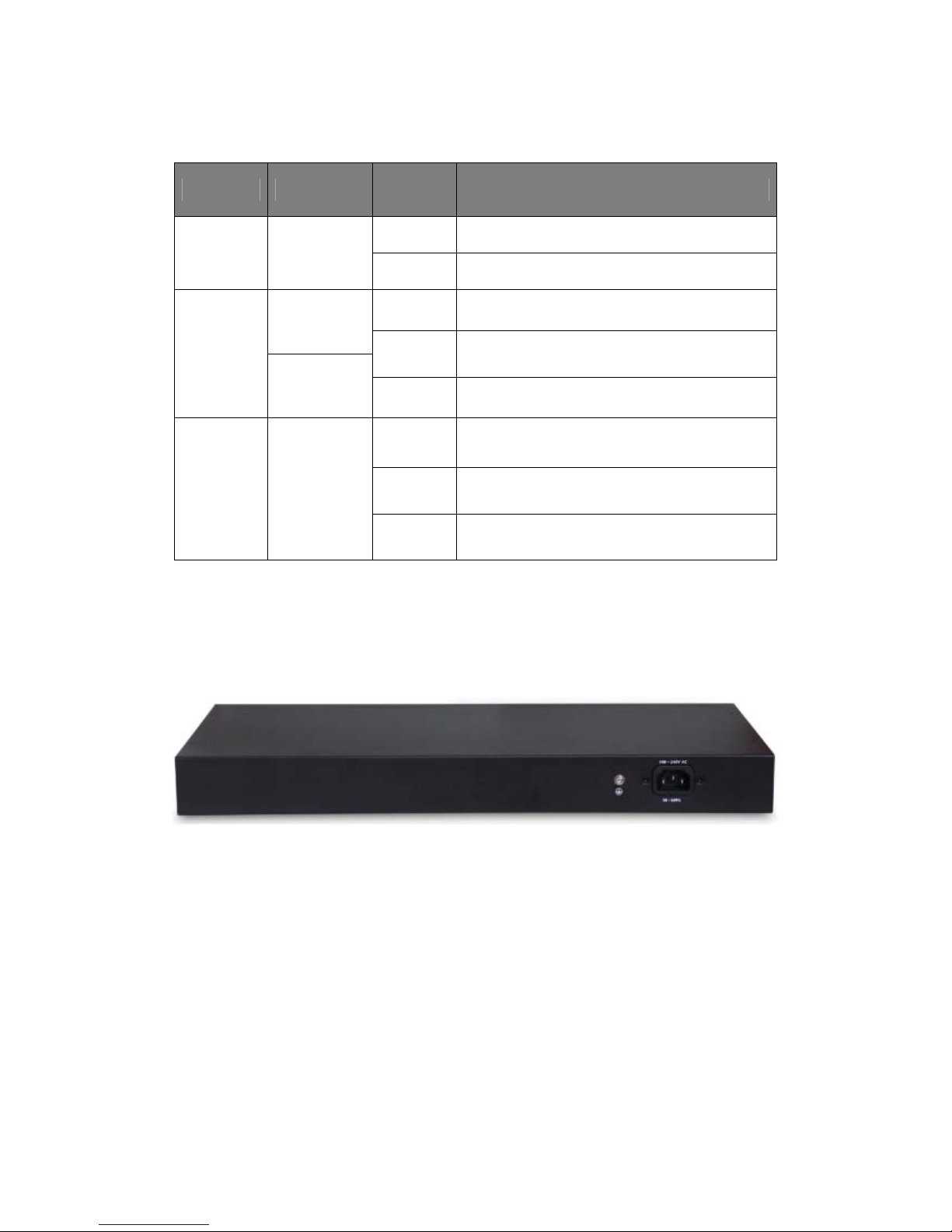
The following chart shows the LED indicators of the Switch along with explanation of each
indicator.
LED COLOR STATUS STATUS DESCRIPTION
On Power On
Power Red
Off Power Off
On A device is connected to the port
Off A device is disconnected to the port
Flashing Sending or receiving data
On A device is connected to the port
Off A device is disconnected to the port
Flashing Sending or receiving data
LNK/ACT/
Speed
(1~24)
SFP1
SFP2
10/100Mbps:
Amber
1000Mbps:
Green
Green
1.3.2 Rear Panel
The rear panel of the Switch contains AC power connector and one marker shown as
below.
AC Power Connector:
Power is supplied through an external AC power adapter. It
50~60Hz.
Grounding Terminal:
The Switch already comes with Lightning Protection Mechanism. You can also ground
the Switch through the PE (Protecting Earth) cable of AC cord or with Ground Cable.
Figure 3 - Rear Panel
6
supports AC 100~240V,

1.4 Package Contents
Before installing the Switch, make sure that the following the "packing list" listed OK. If any
part is lost and damaged, please contact your local agent immediately. In addition, make
sure that you have the tools install switches and cables by your hands.
One Web Smart Ethernet Switch
Four rubber feet, two mounting ears and eights screws
One AC power cord
One User Manual
7
Chapter 2 Installing and Connecting the Switch
This part describes how to install your Web Smart Ethernet Switch and make connections
to it. Please read the following topics and perform the procedures in the order being
presented.
2.1 Installation
Please follow the following instructions in avoid of incorrect installation causing device
damage and security threat.
Put the Switch on stable place or desktop in case of falling damage.
Make sure the Switch works in the proper AC input range and matches the voltage
labeled on the Switch.
To keep the Switch free from lightning, do not open the Switch’s shell even in power
failure.
Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and adequate ventilation around
the Switch.
Make sure the cabinet to enough back up the weight of the Switch and its
accessories.
2.1.1 Desktop Installation
Sometimes users are not equipped with the 19-inch standard cabinet. So when installing
the Switch on a desktop, please attach these cushioning rubber feet provided on the
bottom at each corner of the Switch in case of the external vibration. Allow adequate
space for ventilation between the device and the objects around it.
Figure 4 - Desktop Installation
8
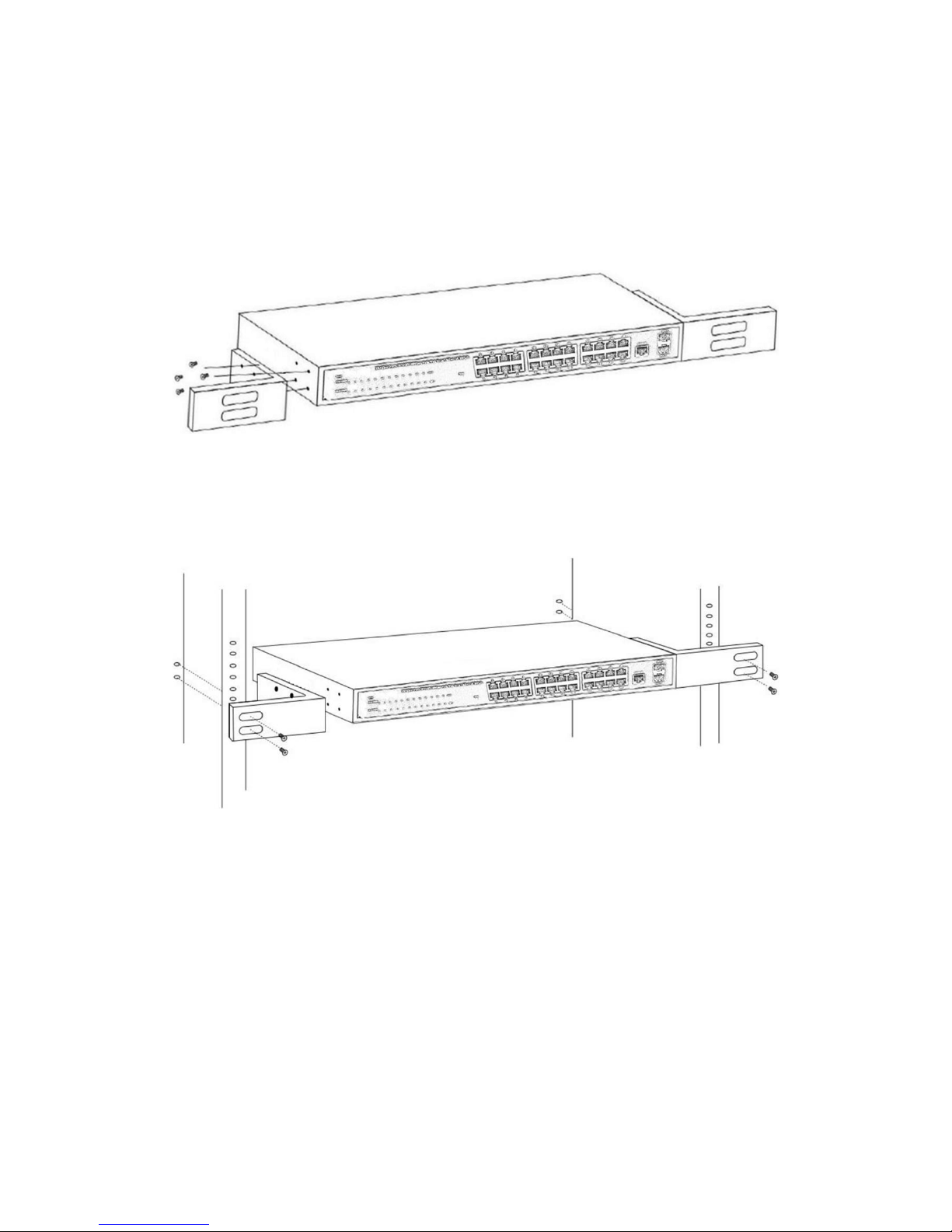
2.1.2 Rack-mountable Installation in 19-inch Cabinet
The Switch can be mounted in an EIA standard-sized, 19-inch rack, which can be placed
in a wiring closet with other equipment. To install the Switch, please follow these steps:
a. attach the mounting brackets on the Switch’s side panels (one on each side) and
secure them with the screws provided.
Figure 5 - Bracket Installation
b. use the screws provided with the equipment rack to mount the Switch on the rack and
tighten it.
2.1.3 Power on the Switch
The Switch is powered on by the AC 100-240V 50/60Hz internal high-performance power
supply. Please follow the next tips to connect:
AC Electrical Outlet:
It is recommended to use single-phase three-wire receptacle with neutral outlet or
multifunctional computer professional receptacle. Please make sure to connect the metal
ground connector to the grounding source on the outlet.
AC Power Cord Connection:
Connect the AC power connector in the back panel of the Switch to external receptacle
Figure 6 - Rack Installation
9

with the included power cord, and check the power indicator is ON or not. When it is ON, it
indicates the power connection is OK.
2.2 Connect Computer (NIC) to the Switch
Please insert the NIC into the computer, after installing network card driver, please
connect one end of the twisted pair to RJ-45 jack of your computer, the other end will be
connected to any RJ-45 port of the Switch, the distance between Switch and computer is
around 100 meters. Once the connection is OK and the devices are power on normally,
the LINK/ACT/Speed status indicator lights corresponding ports of the Switch.
10
Chapter 3 How to Login the Switch
3.1 Switch to End Node
Use standard Cat.5/5e Ethernet cable (UTP/STP) to connect the Switch to end nodes as
described below. Switch ports will automatically adjust to the characteristics(MDI/MDI-X,
speed, duplex) of the device to which is connected.
Please refer to the LED Indicator Specification. The LNK/ACT/Speed LEDs for each port
lights on when the link is available.
3.2 How to Login the Switch
As the Switch provides Web-based management login, you can configure your computer’s
IP address manually to log on to the Switch. The default settings of the Switch are shown
below.
Parameter Default Value
Default IP address 192.168.2.1
Default Username admin
Default Password admin
You can log on to the configuration window of the Switch through following steps:
1. Connect the Switch with the computer NIC interface.
2. Power on the Switch.
3. Check whether the IP address of the computer is within this network segment:
192.168.2.xxx (“xxx” ranges 2~254), for example, 192.168.2.100.
4. Open the browser, and enter http://192.168.2.1 and then press “Enter”. The Switch
login window appears,
the following picture:
11
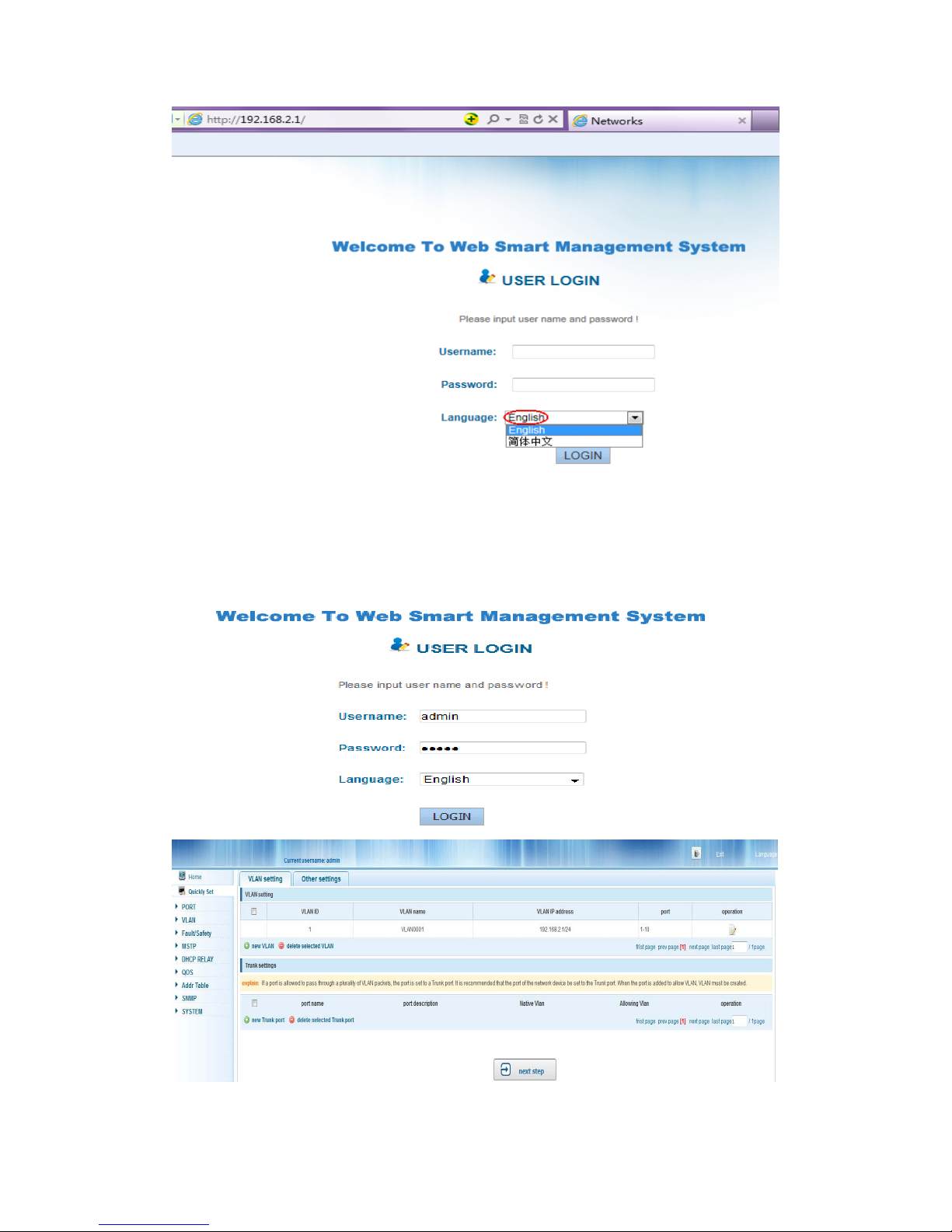
Figure 7- Login Windows
5. Switching language to english .Enter the Username and Password (The factory
default Username is admin and Password is admin), and then click “login” to log in to the
Switch configuration window as below.
12
Chapter 4 Switch Configuration
The Web Smart Ethernet Switch Managed switch software provides rich layer 2
functionality for switches in your networks. This chapter describes how to use Web-based
management interface(Web UI) to this switch configure managed switch software
features.
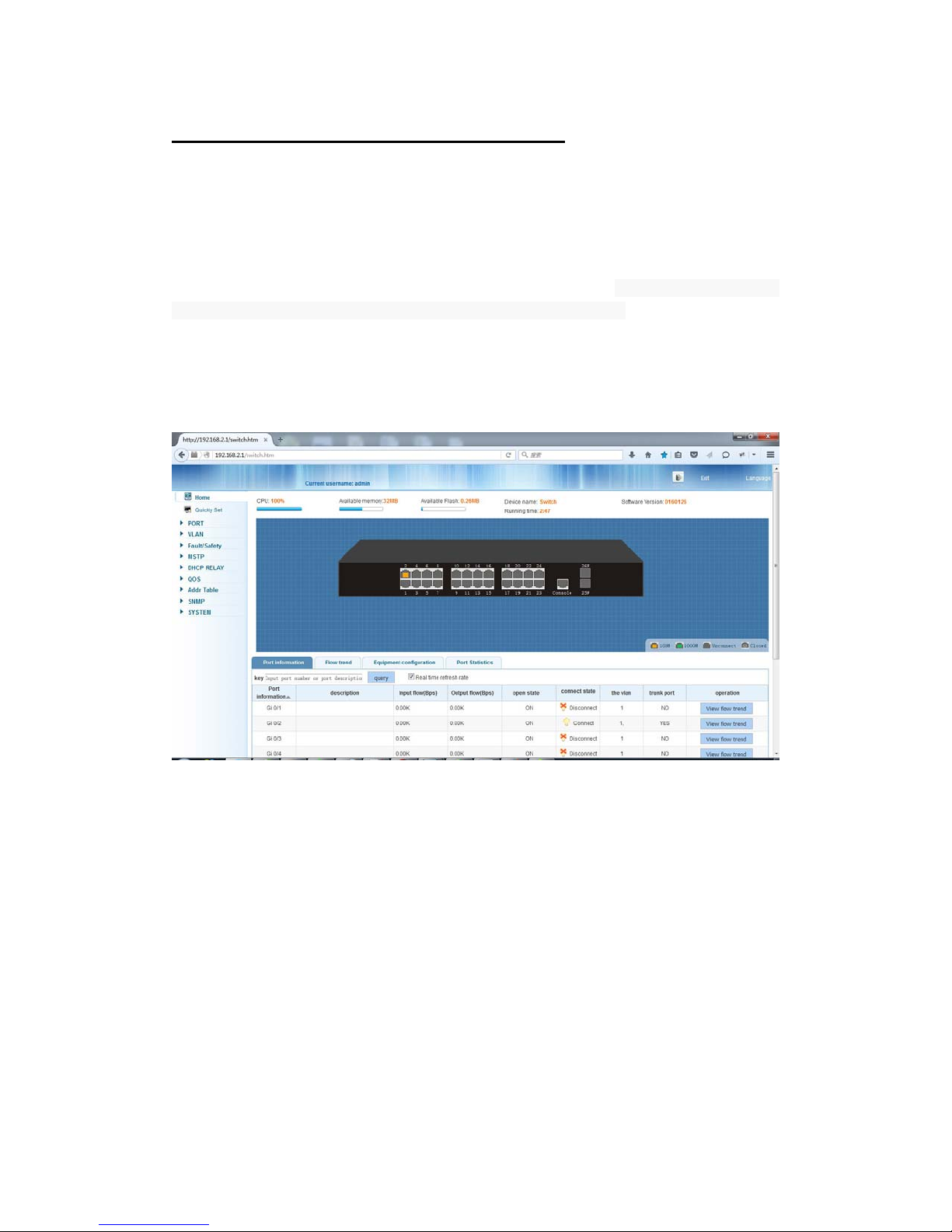
In the Web UI, the left column shows the configuration menu. Above you can see the
information for switch system, such as memory, software version.The middle shows the
switch’s current link status. Green squares indicate the port link is up, while black squares
indicate the port link is down. Below the switch panel, you can find a common toolbar to
provide useful functions for users. The rest of the screen area displays the configuration
settings.
4.1 Quickly setting
In the navigation bar to select “quickly setting”, can create a VLAN in this module, add
the port in the VLAN ,set the basic information and modify the switch login password. the
following picture:
13
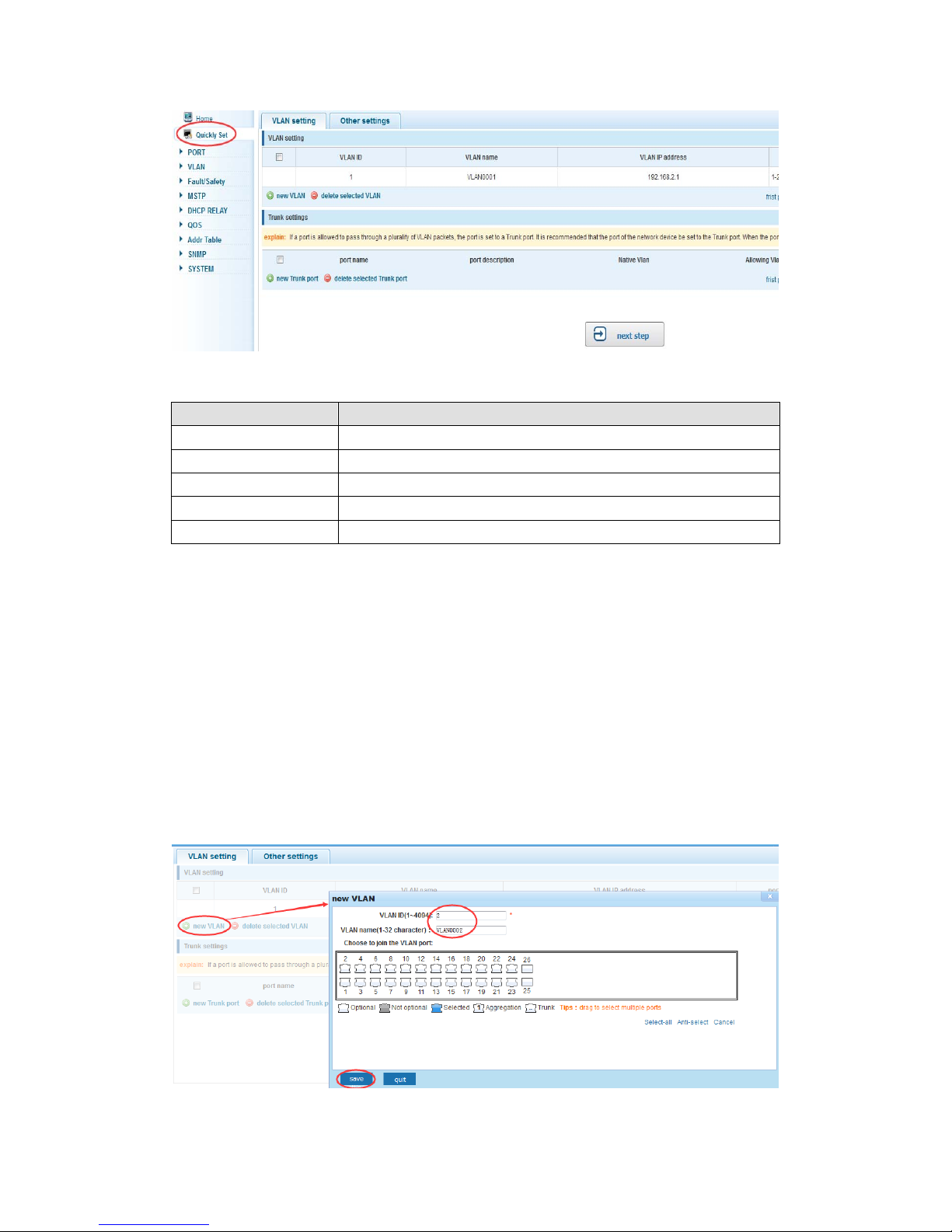
【parameter description】
parameter description
VLAN ID VLAN number,24GE default VLAN 1
VLAN name VLAN mark
Manage IP Manage the IP address of the VLAN
device name Switch name
Manage VLAN Switches management in use of the VLAN
【instructions】
Native VLAN: as a Trunk, the mouth will belong to a Native VLAN. The so-called Native
VLAN, is refers to UNTAG send or receive a message on the interface, is considered
belongs to the VLAN. Obviously, the interface of the default VLAN ID (PVID) in the IEEE
802.1 Q VLAN ID is the Native VLAN. At the same time, send belong to Native VLAN
frame on the Trunk, must adopt UNTAG way.
Allowed VLAN list: a Trunk can transport the equipment support by default all the VLAN
traffic (1-4094). But, also can by setting the permission VLAN Trunk at the mouth of the list
to limit the flow of some VLAN can't through the Trunk.
【Configuration example】
1) VLAN setting:such as create VLAN 2 ,Sets the port 8 to Trunk ,Native VLAN 2
14
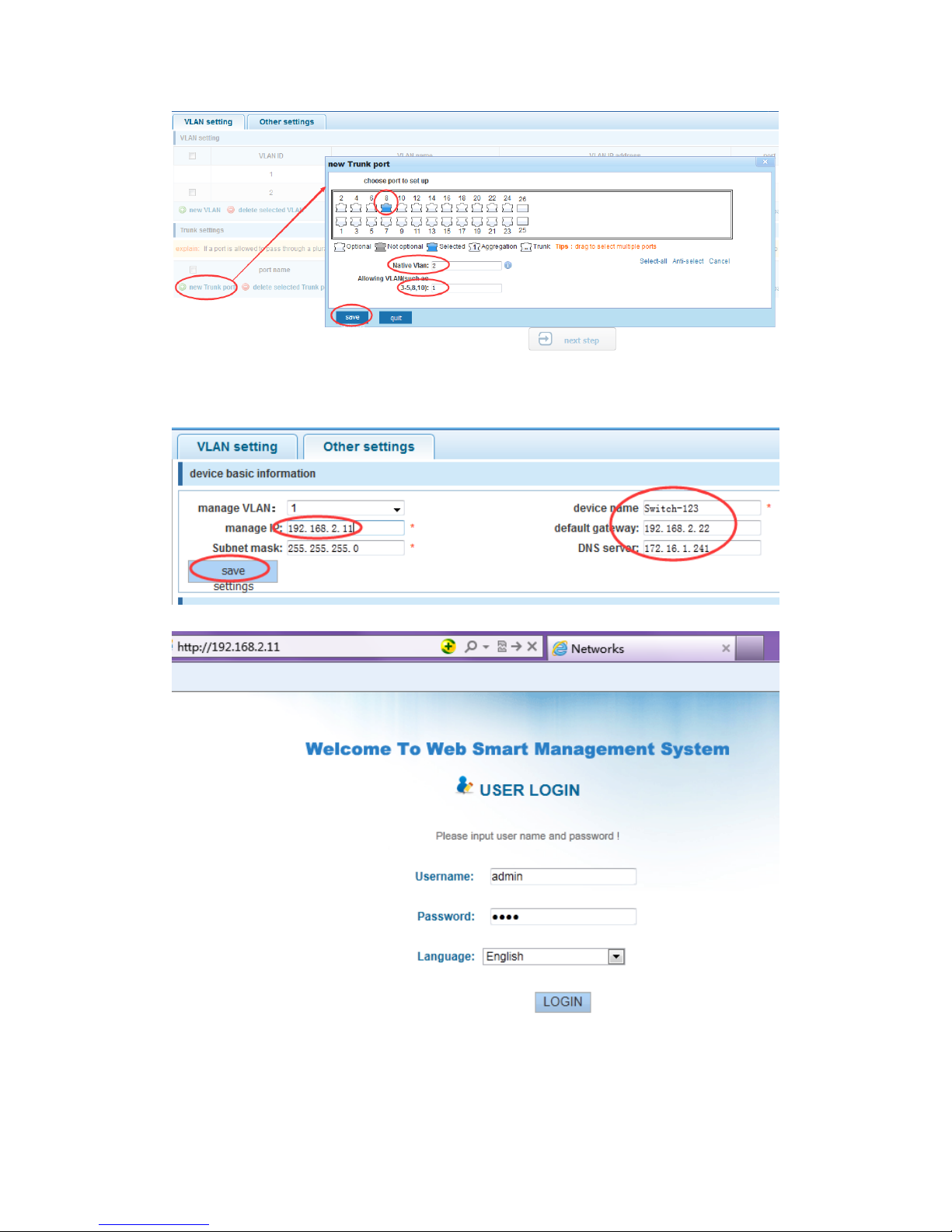
2) click“next step” button ,into other settings,such as : manage ip address set as
192.168.2.11,device name set as switch-123,default gateway with the dns server set as
172.16.1.241
Use 192.168.2.11 to log in, set a new password for 1234
15
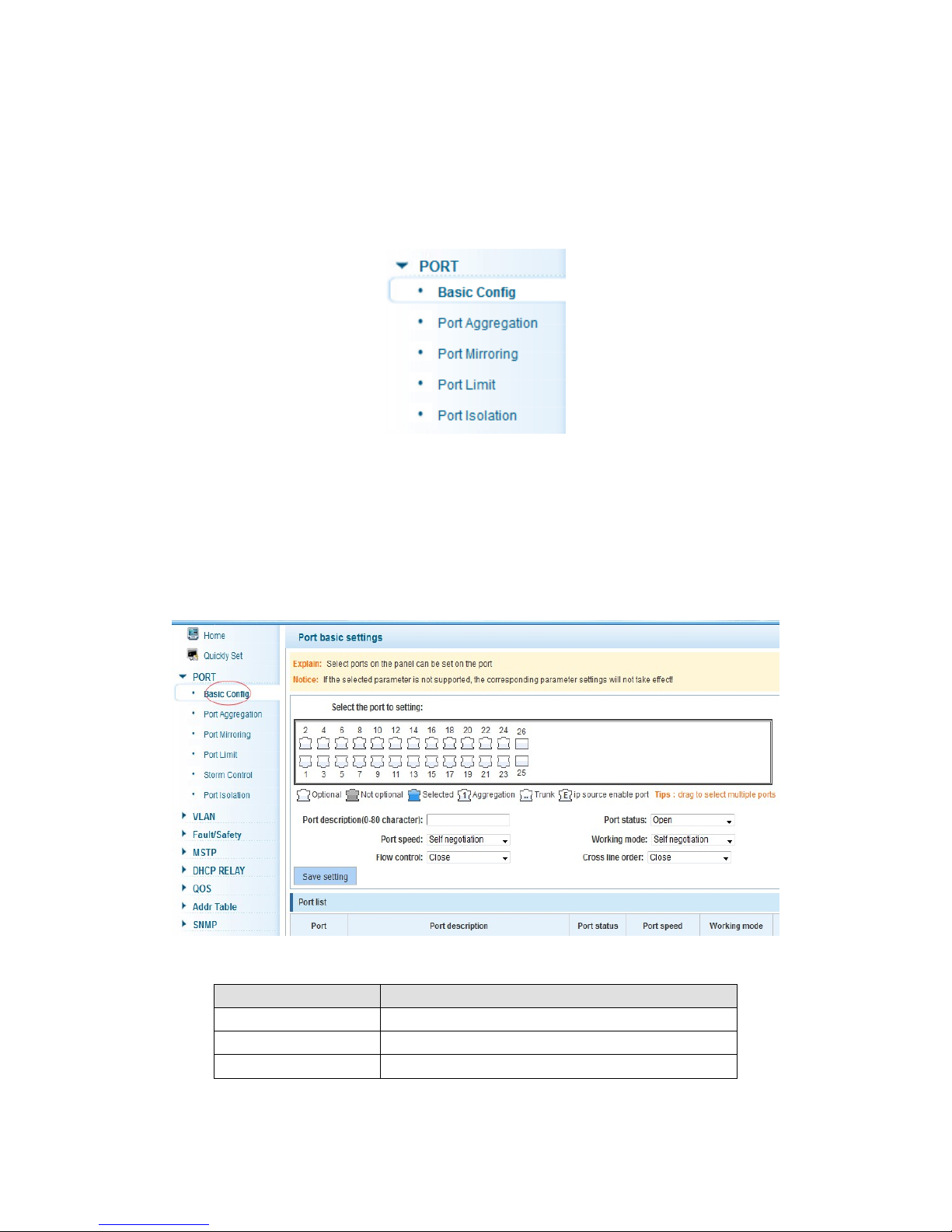
4.2 PORT
In the navigation bar to select “PORT”,You may conduct basic config, port aggregation,
port mirroring , port limit and port isolation.
4.2.1 Basic config
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>basic config”,For panel port to port described ,
port speed, port status, working mode, flow control, cross line order configuration, the
following picture:
【parameter description】
parameter description
port Select the current configuration port number
port status Choose whether to close link port
flow control Whether open flow control
16
Can choose the following kinds:
Aggregation
port speed
working mode
port described The port is described
Cross line sequence Whether open intersection line sequence
10 M
100 M
1000 M
Can choose the following kinds:
Self negotiated
10 M
100 M
1000 M
【instructions】
Open flow control should be negotiated will close, negotiated close is to set port speed
rate and working mode; Set the port rate more than actual rate of port, the port will be
up.
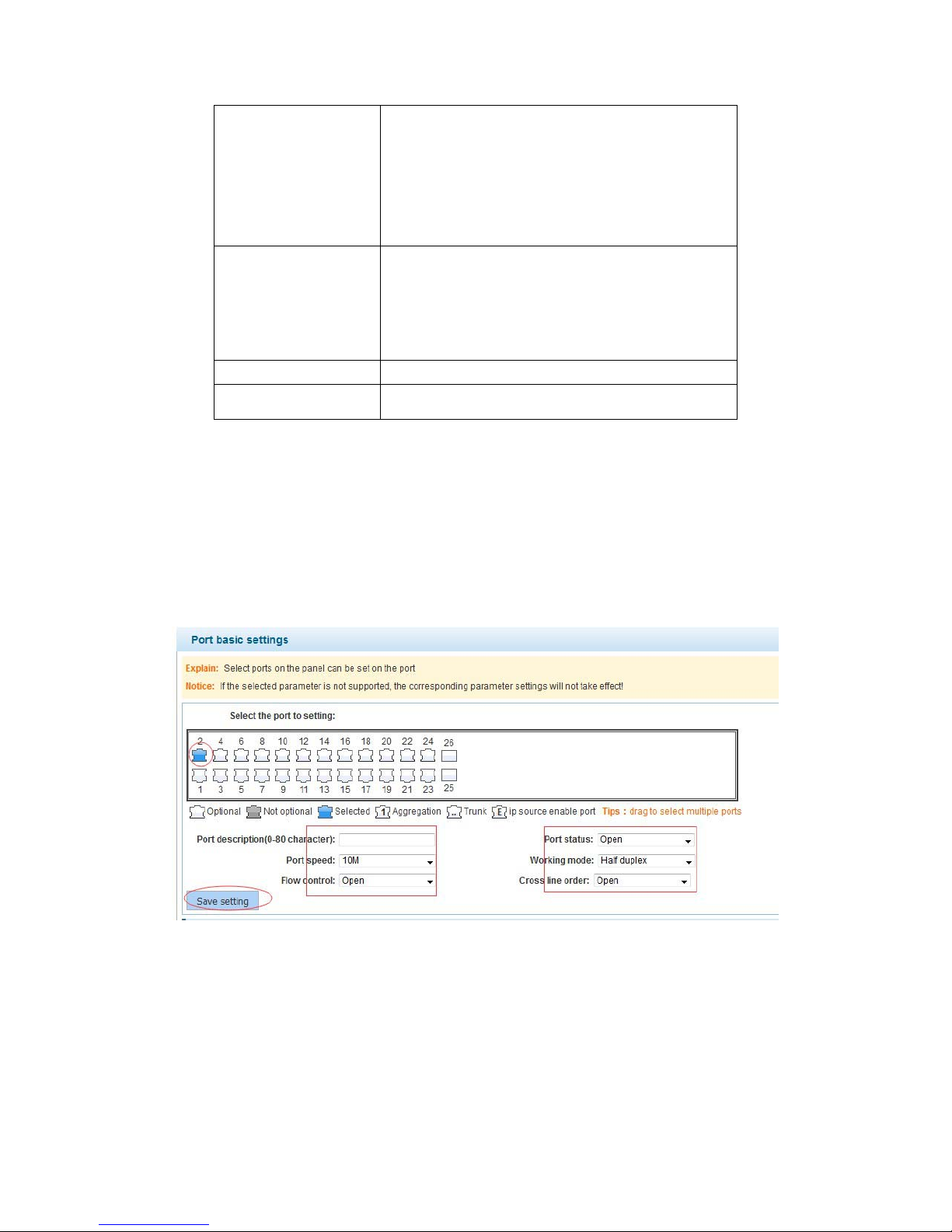
【Configuration example】
Such as:The port is set to 10 M, half duplex, open flow control and cross line sequence
and port state
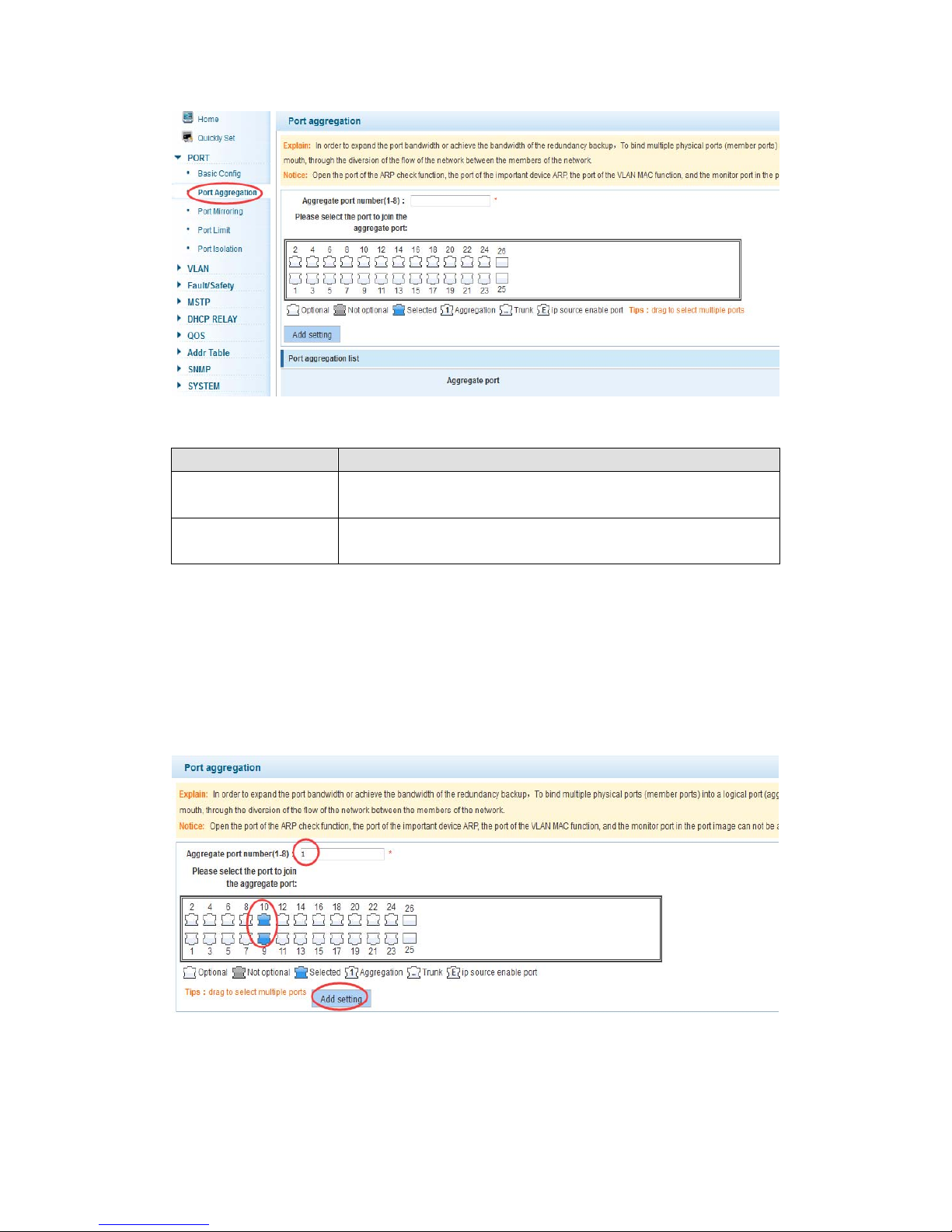
4.2.2 Port aggregation
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>port aggregation”,In order to expand the port
bandwidth or achieve the bandwidth of the redundancy backup,the following picture:
17
【parameter description】
parameter description
26GE switch can be set up eight link trunk group, group_1 to
Aggregation port
Member port
group_8
For each of the members of the group and add your own port,
and with members of other groups
【instructions】
Open the port of the ARP check function, the port of the important device ARP, the port of
the VLAN MAC function, and the monitor port in the port image can not be added!
【Configuration example】
Such as: set the port 9, 10, for aggregation port 1, lets this aggregation port 1 connected
to other switch aggregation port 1 to build switch links .
18
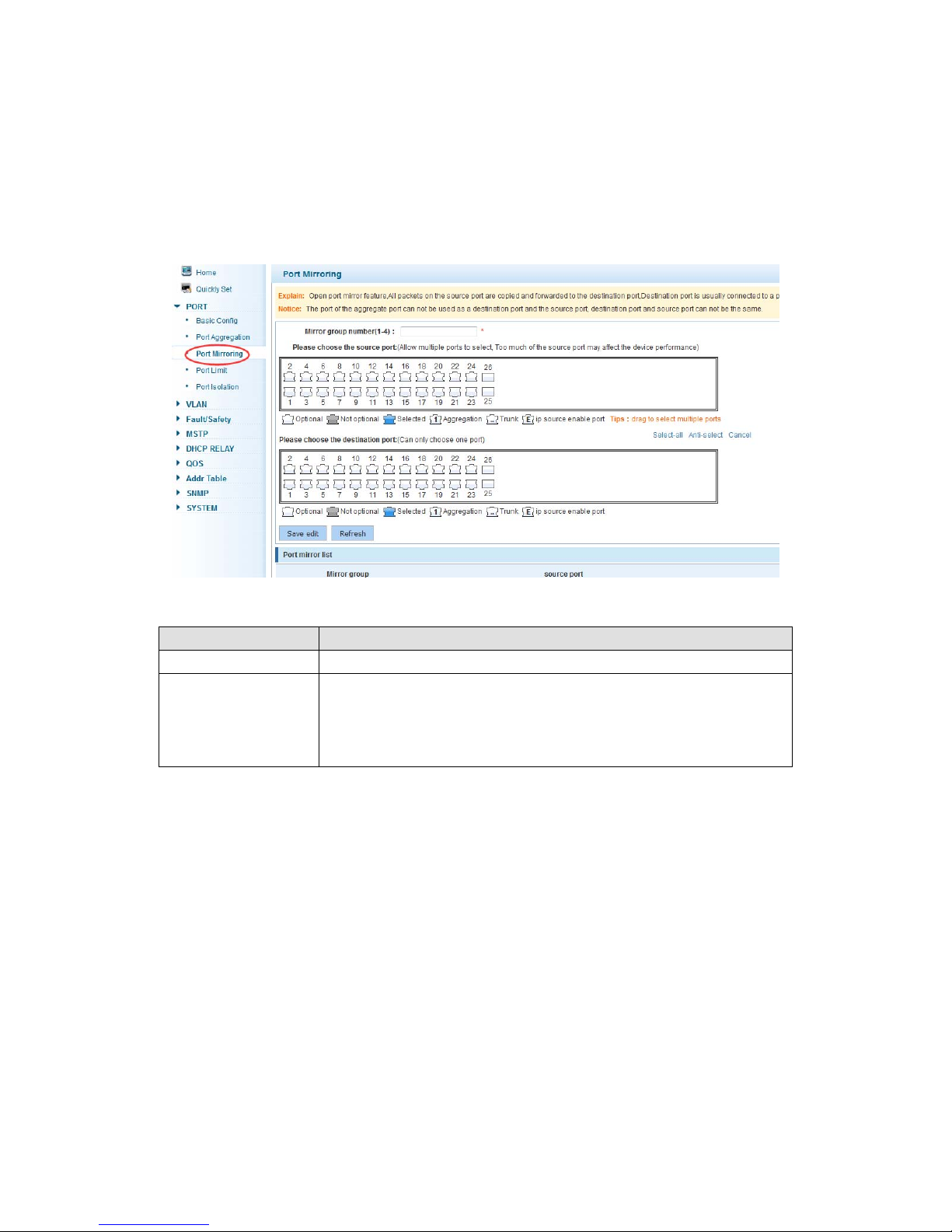
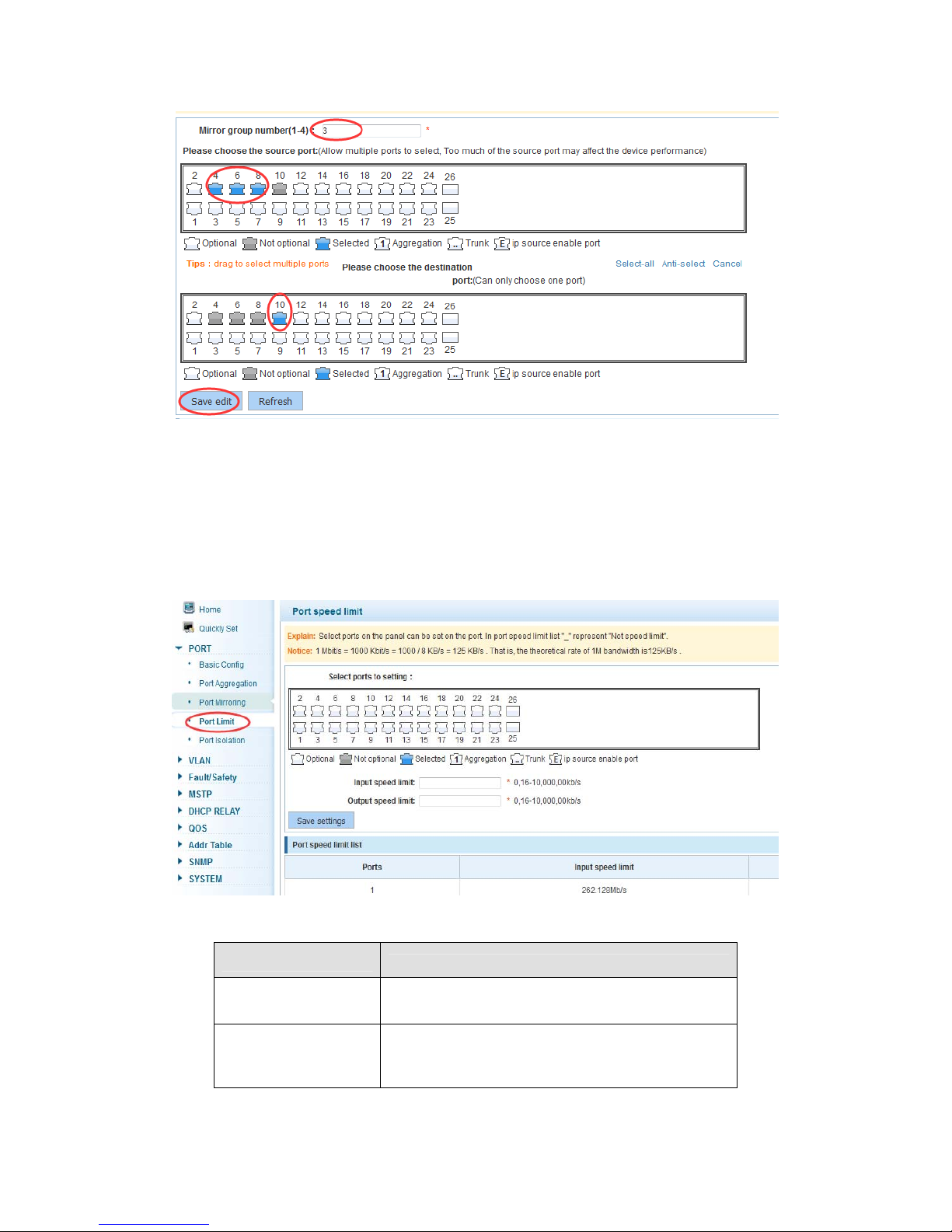
4.2.3 Port mirroring
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>port mirroring”,Open port mirror feature,All
packets on the source port are copied and forwarded to the destination port,Destination
port is usually connected to a packet analyzer to analyze the source port,Multiple ports
can be mirrored to a destination port,the following picture:
【parameter description】
parameter description
Source port To monitor the port in and out of flow
Destination port
Mirror group
【instructions】
The port of the aggregate port can not be used as a destination port and the source port,
destination port and source port can not be the same.
【Configuration example】
Such as: set a mirror group for port 10 regulatory port 4, 6, 8 on and out flow conditions
Set destination port,All packets on the source port are copied and
forwarded to the destination port
Range :1-4
19
4.2.4 Port rate-limit
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>port rate-limit ”,
To port output, input speed limit,the following picture:
【parameter description】
parameter
Input speed limit
description
Set port input speed
Output speed limit
Set port output speed
20
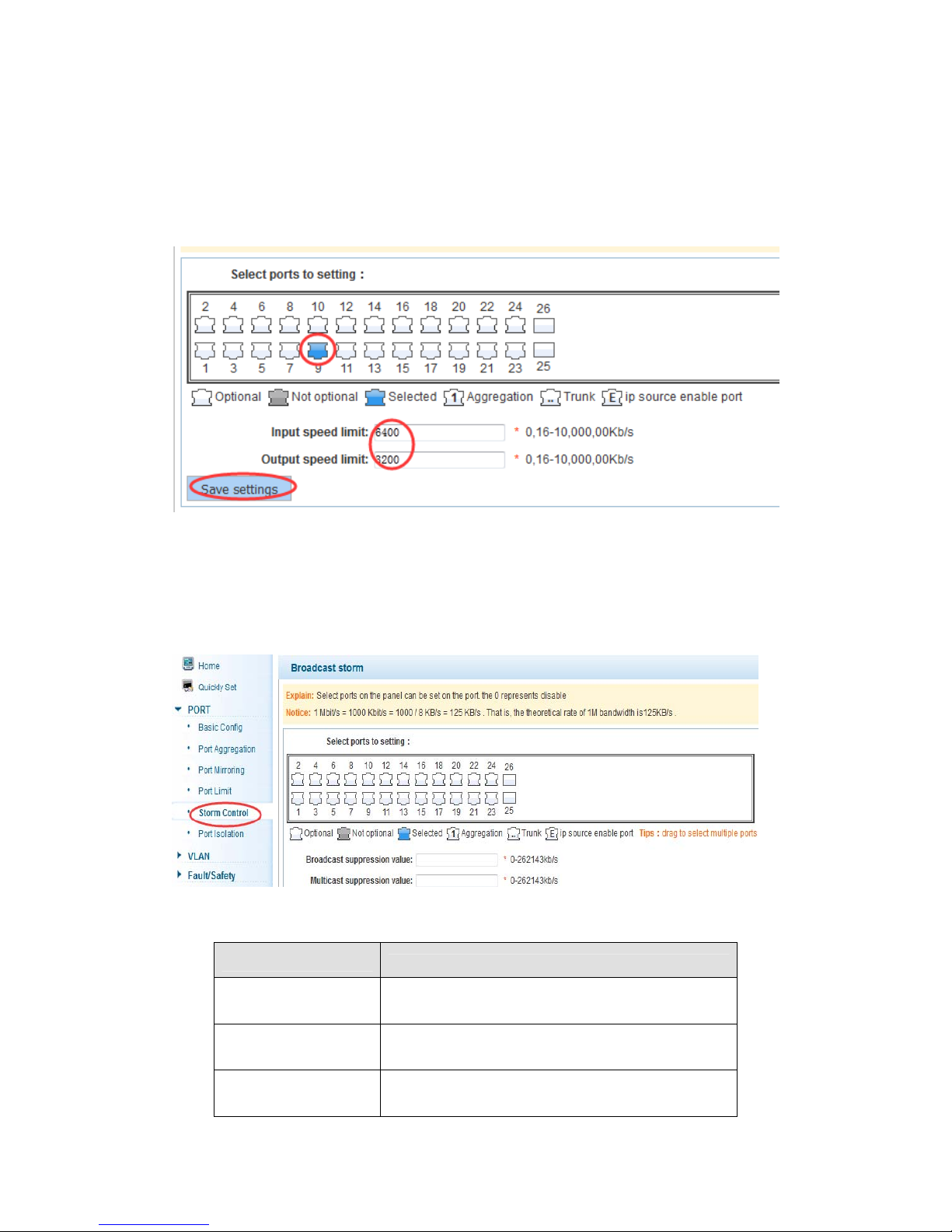
【instructions】
1 Mbit/s = 1000 Kbit/s = 1000 / 8 KB/s = 125 KB/s . That is, the theoretical rate of 1M
bandwidth is125KB/s .
【Configuration example】
Such as: the port 9 input rate is set to 6400 KB/s, the output rate is set to 3200 KB/s
4.2.5 Storm control
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>Storm control”,
To port storm control config,the following ficture:
【parameter description】
parameter
Broadcast
suppression value
Multicast suppression
value
Unicast suppression
value
description
Storm suppression value of the broadcast packets
Storm suppression value of the multicast packets
Storm suppression value of the unicast packets
21
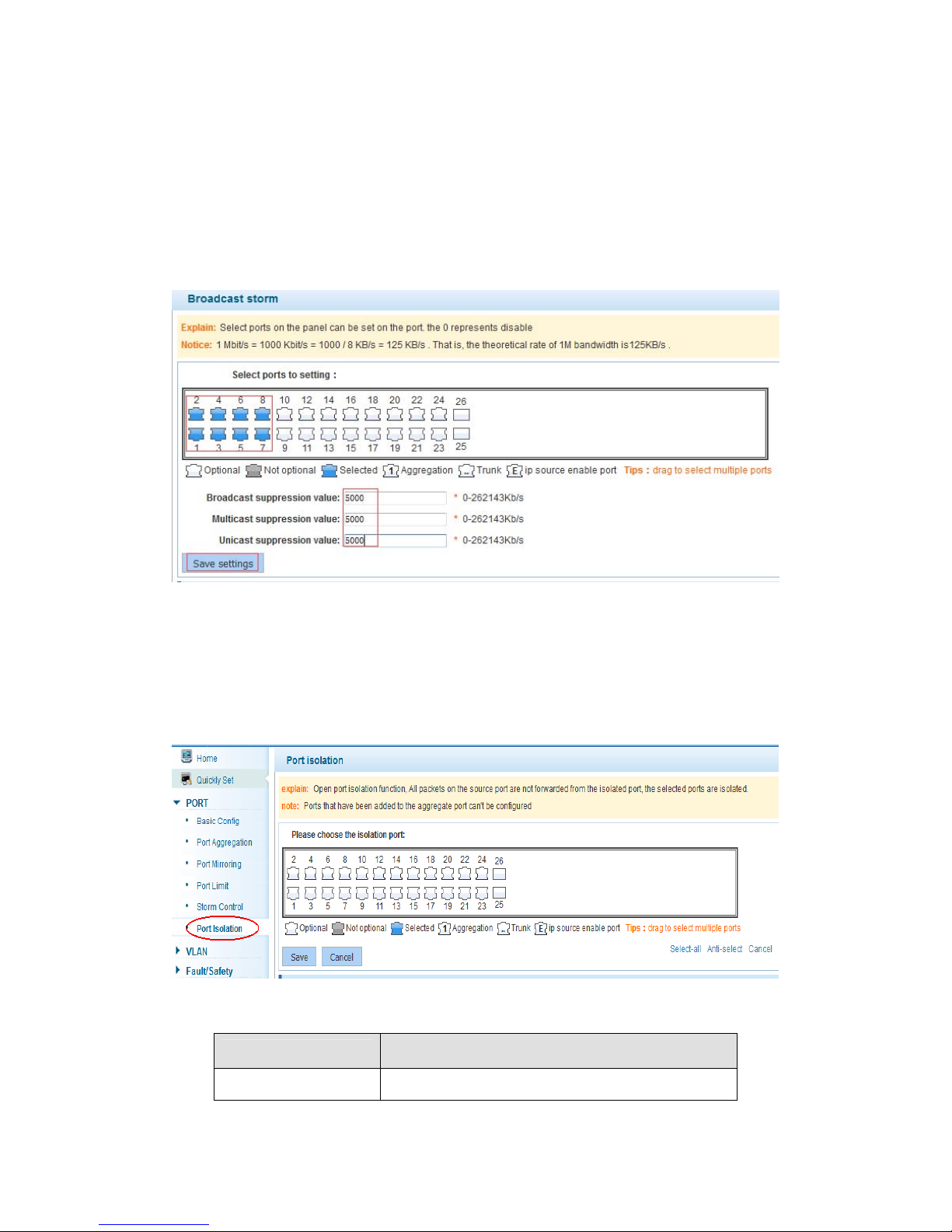
【instructions】
1 Mbit/s = 1000 Kbit/s = 1000 / 8 KB/s = 125 KB/s . That is, the theoretical rate of 1M
bandwidth is125KB/s .
【Configuration example】
Such as: should be forwarded to the port 1-8 of all kinds of packet forwarding rate is 5000
KB/s
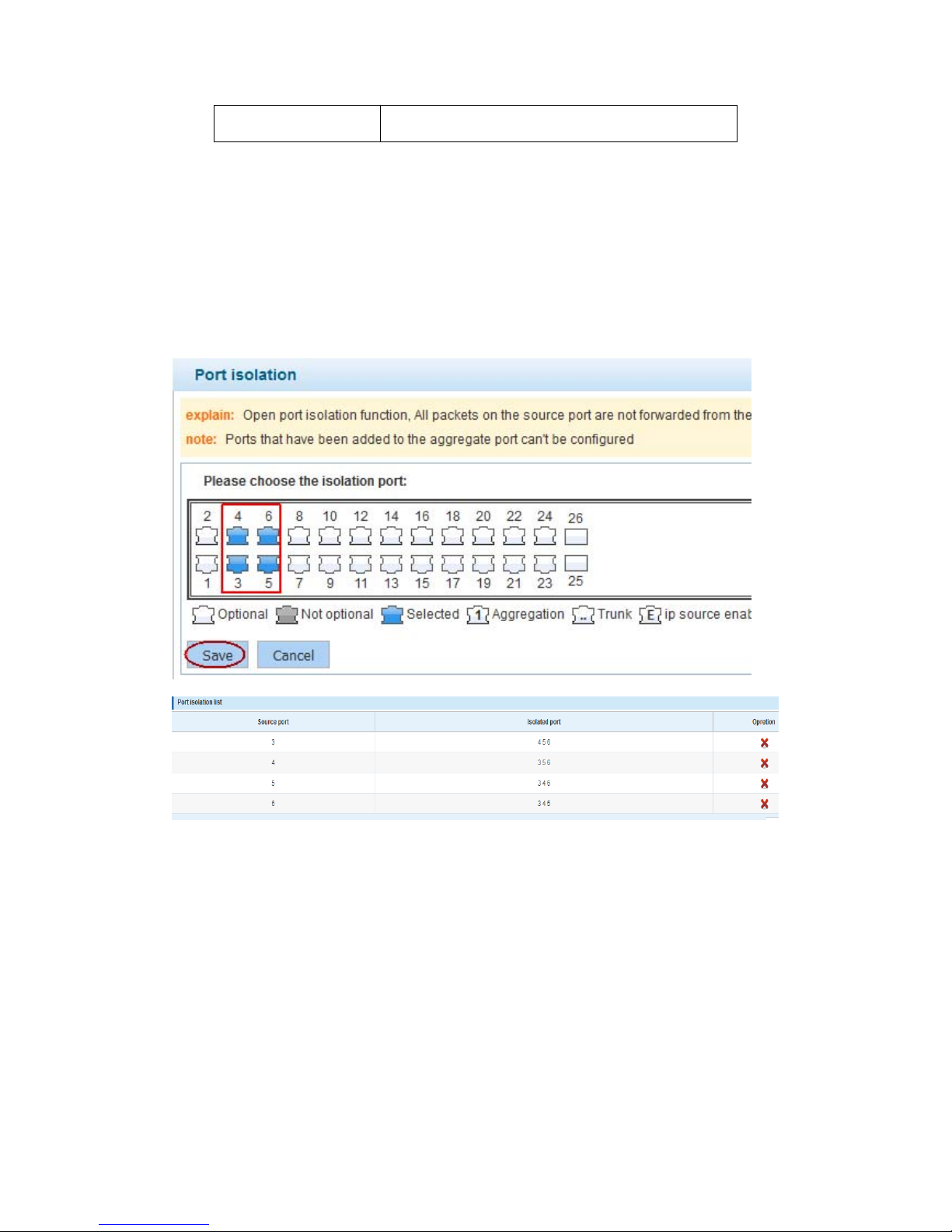
4.2.6 Port isolation
In the navigation bar to select “PORT>port isolation ”,
ports are isolated.the following picture:
【parameter description】
parameter
Source port Choose a port, to configure the isolated port
description
22
Isolated port
Port will be isolated
【instructions】
Open port isolation function, All packets on the source port are not forwarded from the
isolated port, the selected ports are isolated.
Ports that have been added to the aggregate port aren't also capable of being a
destination port and source port, destination port and source port cannot be the same
【Configuration example】
Such as: the port 3, 4, 5, and 6 ports are isolated
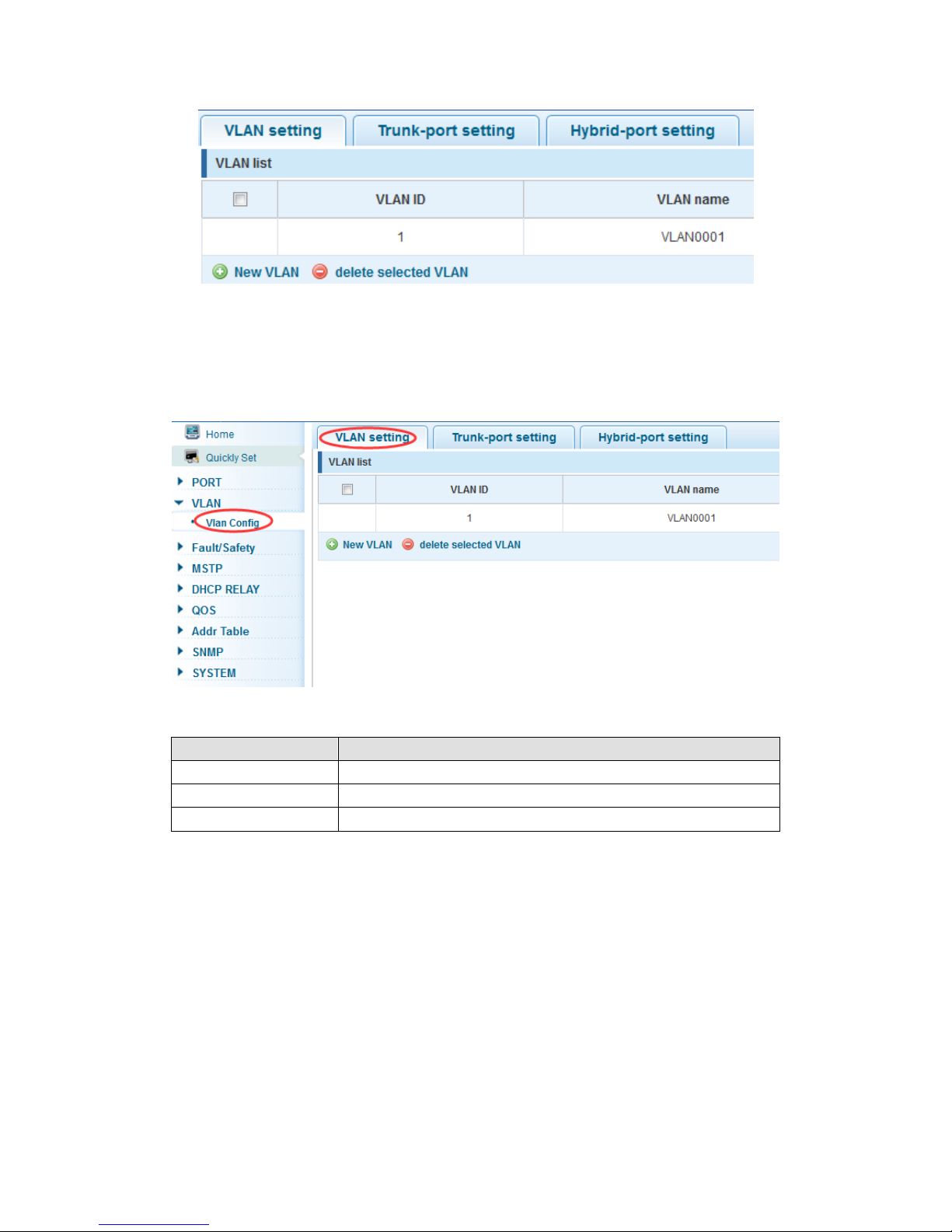
4.3 VLAN
In the navigation bar to select“VLAN”,You can manage the VLAN config, Trunk
Settings and Hybrid Settings ,the following picture:
23
4.3.1 VLAN config
In the navigation bar to select“VLAN config”,Vlans can be created and set the port to the
VLAN (port default state for the access mode) ,the following picture:
【parameter description】
parameter description
VLAN ID VLAN number,24GE default VLAN 1
VLAN name VLAN mark
VLAN IP address Manage switch ip address
【instructions】
Management VLAN, the default VLAN cannot be deleted. Add ports to access port, port
access mode can only be a member of the VLAN.
【Configuration example】
Such as: connect switches pc1, pc2 couldn't ping each other, will be one of the PC
connection port belongs to a VLAN 2
24
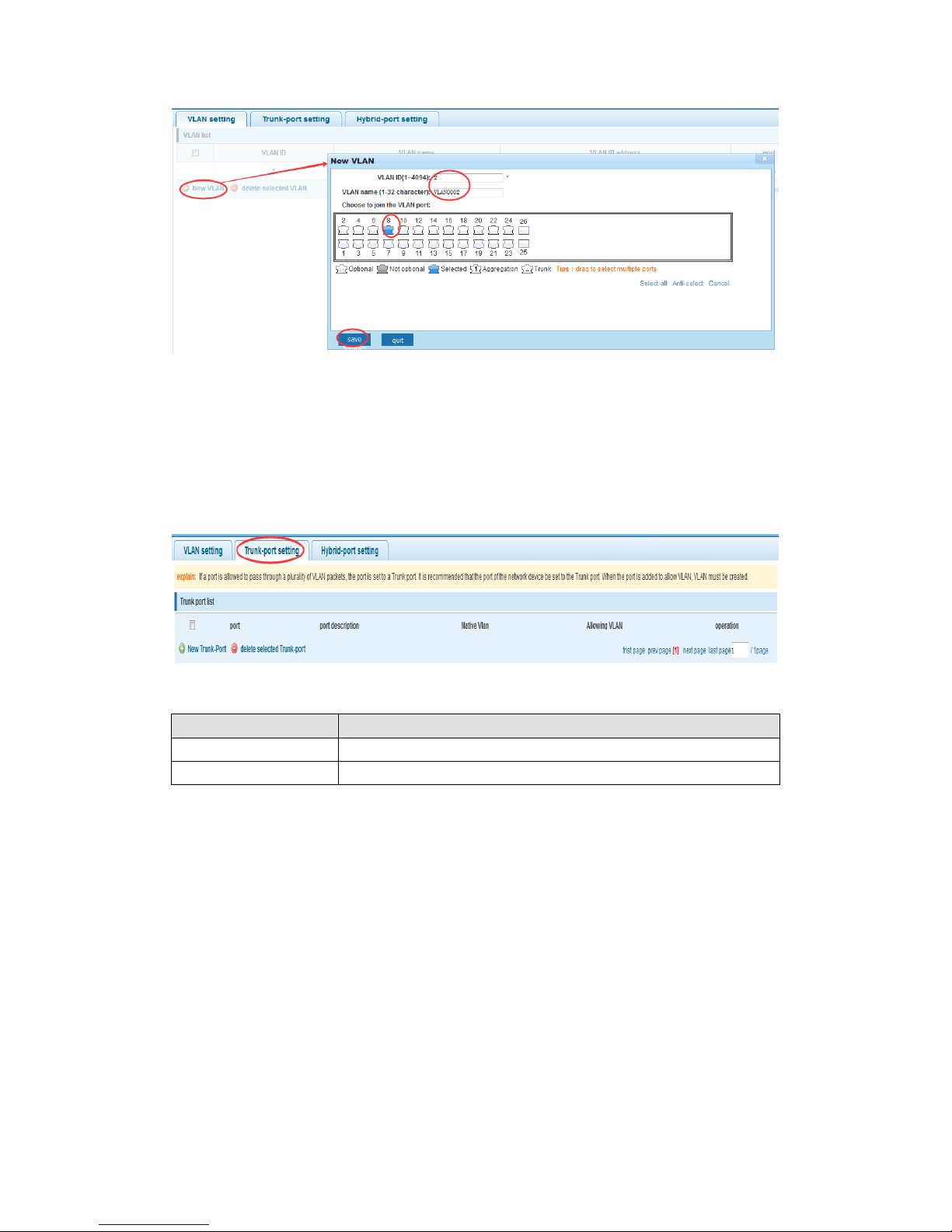
4.3.2 Trunk-port setting
In the navigation bar to select“VLAN config>trunk-port setting”,can set port to Trunk
port,the following picture:
【parameter description】
parameter description
Native VLAN Only set one
Allowing vlan Can set up multiple
【instructions】
Native VLAN: as a Trunk, the mouth will belong to a Native VLAN. The so-called Native
VLAN, is refers to UNTAG send or receive a message on the interface, is considered
belongs to the VLAN. Obviously, the interface of the default VLAN ID (PVID) in the IEEE
802.1 Q VLAN ID is the Native VLAN. At the same time, send belong to Native VLAN
frame on the Trunk, must adopt UNTAG way.
Allowed VLAN list: a Trunk can transport the equipment support by default all the VLAN
traffic (1-4094). But, also can by setting the permission VLAN Trunk at the mouth of the list
to limit the flow of some VLAN can't through the Trunk.
【Configuration example】
Such as:PVID=VLAN2
PC1:192.168.2.122,port 8, access VLAN2
PC2:192.168.2.123,port 9, Trunk allowed VLAN 1-2
25
 Loading...
Loading...