
G2 Series Mark II
Cooled CCD Cameras
User’s Guide

Version 1.1
Modified on July 27th, 2018
All information furnished by Moravian Instruments is believed to be
accurate. Moravian Instruments reserves the right to change any
information contained herein without notice.
G2 cameras are not authorized for and should not be used within Life
Support Systems without the specific written consent of the Moravian
Instruments. Product warranty is limited to repair or replacement of
defective components and does not cover injury or property or other
consequential damages.
Copyright © 2000-2018, Moravian Instruments
Moravian Instruments
Masarykova 1148
763 02 Zlín
Czech Republic
phone: +420 577 107 171
web: http://www.gxccd.com/
e-mail: info@gxccd.com

Table of Contents
Introduction .................................................................................................. 5
G2 Camera Overview .................................................................................... 8
CCD Detectors and Camera Electronics ...................................................... 12
CCD sensor .............................................................................................. 15
Model G2-0400 ................................................................................... 16
Model G2-1600 ................................................................................... 16
Model G2-3200 ................................................................................... 16
Model G2-8300 ................................................................................... 16
Model G2-2000 ................................................................................... 17
Model G2-4000 ................................................................................... 17
Camera Electronics .................................................................................. 17
Model G2-0400 ................................................................................... 18
Model G2-1600 ................................................................................... 19
Model G2-3200 ................................................................................... 19
Model G2-8300 ................................................................................... 19
Model G2-2000 ................................................................................... 19
Model G2-4000 ................................................................................... 19
Cooling and power supply ........................................................................... 21
Power supply ........................................................................................... 22
Mechanical Specifications ........................................................................... 24
Camera with Internal Filter Wheel .......................................................... 25
Camera with “XS” External Filter Wheel ................................................. 27
Camera without filter wheel ................................................................... 28
Optional accessories ................................................................................... 30
Telescope adapters ................................................................................. 30

Off-Axis Guider Adapter (OAG) ............................................................... 30
Attaching camera head to telescope mount ........................................... 31
Camera head color variants .................................................................... 32
Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter .................................................................. 33
Adjusting of the telescope adapter ............................................................. 34
Camera Maintenance .................................................................................. 37
Desiccant exchange ................................................................................. 37
Exchanging the silica-gel...................................................................... 38
Changing Filters ....................................................................................... 39
Opening the camera head ................................................................... 39
Changing the Whole Filter Wheel ........................................................... 40
Changing the Telescope Adapter ............................................................ 41
Power Supply Fuse .................................................................................. 42

5
Introduction
Thank you for choosing the Moravian Instruments camera. The cooled G2
series Mark II CCD cameras were developed for imaging under extremely
low-light conditions in astronomy, microscopy and similar areas.
Design of this series inherits from earlier G2 Mark I cameras but brings
some significant enhancements. G2 cameras employ precise electronics
providing uniform frames and extremely low read noise limited only by
CCD detector itself.
Modular mechanical construction allows various camera variants to be
combined with rich set of accessories, including telescope adapters, offaxis guider adapters, internal or external filter wheels, Ethernet adapters,
guiding cameras etc.
Rich software and driver support allows usage of G2 camera without
necessity to invest into any 3rd party software package thanks to included
free SIPS software package. However, ASCOM (for Windows) and INDI (for
Linux) drivers, shipped with the camera, provide the way to integrate G2
camera with vast variety of camera control programs.
The G2 cameras are designed to work in cooperation with a host Personal
Computer (PC). As opposite to digital still cameras, which are operated
independently on the computer, the scientific slow-scan, cooled cameras
usually require computer for operation control, image download,
processing and storage etc. To operate the camera, you need a computer
which:
1. Is compatible with a PC standard and runs modern 32 or 64-bit
Windows operating system.
2. Is compatible with a PC standard and runs 32 or 64-bit Linux
operating system.
Drivers for 32-bit and 64-bit Linux systems are provided, but the
SIPS camera control and image processing software, supplied
with the camera, requires Windows operating system.

6
3. Support for x64 based Apple Macintosh computers is also
included.
Only certain software packages are currently supported on Mac.
G2 cameras require at last one free USB 2.0 port to communicate with a
host PC.
A simple and cheap device called “USB hub” can expand number of
available USB port. Typical USB hub occupies one computer USB port
and offers four or seven additional USB ports. Make sure the USB hub
is USB 2.0 high-speed compatible.
Alternatively, it is possible to use the “Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter”
device. This device can connect up to four Gx cameras of any type (not only
G2, but also G0, G1, G3 and G4) and offers 1 Gbps and 10/100 Mbps
Ethernet interface for direct connection to the host PC. Because the PC
then uses TCP/IP protocol to communicate with the cameras, it is possible
to insert WiFi adapter or other networking device to the communication
path.
Please note while the USB standard allows usage of cable no longer
than approx. 5 meters, the TCP/IP communication protocol used to
connect the camera over the Ethernet adapter is routable, so the
distance between camera setup and the host PC is virtually unlimited.
The G2 cameras need an external power supply to operate. It is not
possible to run the camera from the power lines provided by the USB
cable, which is common for webcams or very simple imagers. G2 cameras
integrate highly efficient CCD chip cooling, shutter and possibly filter
wheel, so their power requirements significantly exceed USB line power
capabilities. On the other side separate power source eliminates problems
with voltage drop on long USB cables or with drawing of laptop batteries
etc.
Also note the camera must be connected to some optical system (e.g. the
telescope) to capture images. The camera is designed for long exposures,
necessary to acquire the light from faint objects. If you plan to use the

7
camera with the telescope, make sure the whole telescope/mount setup is
capable to track the target object smoothly during long exposures.

8
G2 Camera Overview
G2 camera head is designed to be easily used with a set of accessories to
fulfil various observing needs. Camera head itself is manufactured in two
different variants:
Camera with Internal filter wheel.
Camera with control port for External filter wheel. This model
allows attachment of several variants of external filter wheels
with various number of filter positions and sizes.
Figure 1: G2 Camera Mark II without filter wheel (left), with Internal filter wheel
(middle) and with attached External filter wheel (right)
G2 camera model with Internal filter wheel accepts two sizes of filters:
Filter wheel with 5 positions for unmounted D31 mm filters or
filters in 1.25” threaded cells.
Filter wheel with 6 positions for unmounted D26 mm (or 1”)
filters.
There are two sizes of the External filter wheels, each capable to accept
two sizes of filters, available for the G2 cameras:
Extra small “XS” size wheel for 8 unmounted filters D31 mm or
filters in 1.25” threaded cells.

9
Extra small “XS” size wheel for 7 unmounted filters D36 mm.
Small “S” size wheel for 12 unmounted filters D31 mm or filters in
1.25” threaded cells.
Small “S” size wheel for 10 unmounted filters D36 mm.
Because G2 series of cameras can work with various sensors, not all
filter wheel/filter variants can be used with every detector. For
instance, G2-8300 camera works with CCD measuring 22.7 mm
diagonally. Depending on the used optics f/ratio, 1” or even 1.25”
filters can cause more or less significant vignetting when combined
with such sensor.
Please note the camera head is designed to either accept Internal filter
wheel or to be able to connect to the External filter wheel, but not both. If
the Internal filter wheel variant is used, External filter wheel cannot be
attached.

10
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of G2 camera system components

11
Components of G2 Camera system include:
1. G2 camera head with Internal Filter Wheel (5 or 6 positions)
2. G2 camera head capable to control External Filter Wheel
3. External Filter Wheel “XS” size (7 or 8 positions)
4. External Filter Wheel “S” size (10 or 12 positions)
5. G0 guider camera
6. G1 guider camera
G0 and G1 cameras are completely independent devices with
their own USB connection to the host PC. They can be used
either on G2 OAG or on standalone guiding telescope.
Both G0 and G1 camera can share the Gx Camera Ethernet
Adapter with up to 3 other Gx cameras to be accessed over
network.
7. Off-Axis Guider with M48×0.75 thread
8. Off-Axis Guider with M42×0.75 thread (T2)
9. Thick adapter base, compensating EFW thickness to achieve
proper back focal distance for cameras without filter wheel
10. 1.75” dovetail rail for G2 camera head
11. Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter (x86 CPU)
12. Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter (ARM CPU)
Camera Ethernet Adapter allows connection of up to 4 Gx
cameras of any type on the one side and 1 Gbps Ethernet on the
other side. This adapter allows access to connected Gx cameras
using routable TCP/IP protocol over unlimited distance.
13. 5-positions internal filter wheel for 1.25”/D31 mm filters
14. 8-positions external filter wheel “XS” for 1.25”/D31 mm filters
15. 7-positions external filter wheel “XS” for D36 mm filters
16. 12-positions external filter wheel “S” for 1.25”/D31 mm filters
17. 10-positions external filter wheel “S” for D36 mm filters
18. 7-positions external filter wheel “S” for 2”/D50 mm filters
19. M42×0.75 (T-thread) or M48×0.75 threaded adapters, 55 mm BFD
20. Canon EOS bayonet lens adapter
21. Nikon bayonet lens adapter

12
CCD Detectors and Camera Electronics
G2 Mark II series of CCD cameras are manufactured with two kinds of CCD
detectors:
G2 cameras with OnSemi KAF Full Frame (FF) CCD architecture.
Almost all Full Frame CCD detector area is exposed to light. This is
why these detectors provide very high quantum efficiency. FF CCD
detectors, intended for research applications, are not equipped
with so-called Anti Blooming Gate (ABG – a gate, which prohibits
blooming of the charge to neighboring pixels when image is overexposed) to ensure linear response to light through the whole
dynamic range. FF CCD detectors used for astrophotography are
equipped with ABG to eliminate disrupting blooming streaks
within field of view.
Cameras with Full Frame, non-ABG detectors are suitable for
scientific applications, where linear response is necessary for
photometric applications in astronomy, microscopy etc. High
quantum efficiency could be used also for narrow-band imaging,
where overexposure is a rare exception, and for imaging of small
objects without a bright star in the field of view.
Figure 3: “Full Frame” CCD schematic diagram

13
G2 cameras with OnSemi KAI Interline Transfer (IT) architecture.
There is a shielded column of pixels just beside each column of
active pixels on these detectors. The shielded columns are called
Vertical registers. One pulse moves charge from exposed pixels to
shielded pixels on the end of each exposure. The the charge is
moved from vertical registers to horizontal register and digitized
in the same way like in the case of Full Frame detectors. This
mechanism is also known as “electronic shuttering” because it
allows very short exposures and also digitization of the image
without mechanically shielding of the detector from incoming
light.
Also, G2 cameras with IT CCDs are equipped with mechanical
shutter, because electronic shutter does not allow dark-frame
exposures, necessary for proper image calibration etc.
The price for electronic shutter if lower quantum efficiency
(sensitivity) of IT detectors compared to FF ones. Also, all IT
detectors are equipped with ABG, so they can acquire images of
very bright objects without charge blooming to neighboring pixels.
Figure 4: “Interline Transfer” CCD schematic diagram

14
G2 camera Mark II models with Full Frame CCD detectors:
Model G2-0400 G2-1600 G2-3200 G2-8300
CCD sensor KAF-0402ME KAF-1603ME KAF-3200ME KAF-8300
Resolution 768 × 512 1536 × 1024 2184 × 1472 3358 × 2536
Pixel size 9 × 9 μm 9 × 9 μm 6.8 × 6.8 μm 5.4 × 5.4 μm
Sensor size 6.9 × 4.6 13.8 × 9.2 14.9 × 10.0 18.1 × 13.7
ABG No No No Yes
Color mask No No No No*
* G2-8300 camera is available in the G2-8300C version with color CCD
detector (with Bayer mask), capable of single-shot color images.
G2 camera models with Interline Transfer CCD detectors:
Model G2-2000 G2-2000C G2-4000 G2-4000C
CCD sensor KAI-2020 KAI-2020 KAI-4022 KAI-4022
Resolution 1604 × 1204 1604 × 1204 2056 × 2062 2056 × 2062
Pixel size 7.4 × 7.4 μm 7.4 × 7.4 μm 7.4 × 7.4 μm 7.4 × 7.4 μm
Sensor size 11.9 × 8.9 11.9 × 8.9 15.2 × 15.2 15.2 × 15.2
ABG Yes Yes Yes Yes
Color mask No Yes No Yes
Cameras with “C” suffix contain CCD detector covered with so-called Bayer
mask. Color filters of three basic colors (red, green, blue) cover all pixels, so
every pixel detects only light of particular color.
These cameras are able to acquire color image in single exposure, without
the necessity to change color filters. On the other side color mask brings
lower sensitivity and limits the capability to perform exposures using
narrow-band filters etc.
Because each pixel is covered by one of three basic color filters, it is
necessary to compute (interpolate) remaining two colors for each pixel,

15
which of course limits resolution of color image. Imaging using color
detectors is described in the “Color images” chapter.
CCD sensor
Quantum efficiency (sensitivity) of CCD detectors used in G2 cameras
depends on the particular camera model.
Figure 5: Quantum efficiency of OnSemi CCD detectors used in G2 cameras
Inherent dark current of these detectors is quite low compared to other
CCD detectors, suitable for scientific applications, which results into very
good signal/noise ratio.
Figure 6: Dark current of some OnSemi CCD detectors, used in G2 cameras

16
Model G2-0400
G2-0400 model uses 0.4 MPx CCD OnSemi KAF-0402ME.
Resolution 768 × 512 pixels
Pixel size 9 × 9 μm
Imaging area 6.9 × 4.6 mm
Full well capacity Approx. 100 000 e
-
Output node capacity Approx. 220 000 eDark current 1 e-/s/pixel at 0°C
Dark signal doubling 6.3 °C
Model G2-1600
G2-1600 model uses 1.6 MPx CCD OnSemi KAF-1603ME.
Resolution 1536 × 1024 pixels
Pixel size 9 × 9 μm
Imaging area 13.8 × 9.2 mm
Full well capacity Approx. 100 000 e
-
Output node capacity Approx. 220 000 eDark current 1 e-/s/pixel at 0°C
Dark signal doubling 6.3 °C
Model G2-3200
G2-3200 model uses 3.2 MPx CCD OnSemi KAF-3200ME.
Resolution 2184 × 1472 pixels
Pixel size 6.8 × 6.8 μm
Imaging area 14.9 × 10.0 mm
Full well capacity Approx. 55 000 e
-
Output node capacity Approx. 110 000 eDark current 0.8 e-/s/pixel at 0°C
Dark signal doubling 6.0 °C
Model G2-8300
G2-8300 model uses 8 MPx CCD OnSemi KAF-8300.
Resolution 3358 × 2536 pixels
Pixel size 5.4 × 5.4 μm
Imaging area 18.1 × 13.7 mm
Full well capacity Approx. 25 000 e
-

17
Output node capacity Approx. 55 000 eDark current 0.15 e-/s/pixel at 0°C
Dark signal doubling 5.8 °C
KAF-8300 CCD detector with color (Bayer) mask can be used in the G28300C camera.
Model G2-2000
G2-2000 model uses 2 MPx CCD MPx OnSemi KAI-2020.
Resolution 1604 × 1204 pixels
Pixel size 7.4 × 7.4 μm
Imaging area 11.9 × 8.9 mm
Full well capacity Approx. 40 000 e
-
Output node capacity Approx. 80 000 eDark current 0.3 e-/s/pixel at 0°C
Dark signal doubling 7.0 °C
KAI-2020 CCD detector with color (Bayer) mask can be used in the G22000C camera.
Model G2-4000
G2-4000 model uses 4 MPx CCD MPx OnSemi KAI-4022.
Resolution 2056 × 2062 pixels
Pixel size 7.4 × 7.4 μm
Imaging area 15.2 × 15.2 mm
Full well capacity Approx. 40 000 e
-
Output node capacity Approx. 80 000 eDark current 0.3 e-/s/pixel at 0°C
Dark signal doubling 7.0 °C
KAI-4022 CCD detector with color (Bayer) mask can be used in the G24000C camera.
Camera Electronics
16-bit A/D converter with correlated double sampling ensures high
dynamic range and CCD chip-limited readout noise. Fast USB interface
ensures image download time within seconds.

18
Maximum length of single USB cable is approx. 5 m. This length can be
extended to 10 m or 15 m by using single USB hub or active USB extender
cable. Up to 5 hubs or active extenders can be used in one connection.
Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter device allows connection of up to four Gx
cameras of any type through Ethernet interface and TCP/IP network.
Because TCP/IP protocol can be routed, the distance between camera and
host PC can be virtually unlimited.
ADC resolution 16 bits
Sampling method Correlated double sampling
Read modes Preview
Low-noise
Horizontal binning 1 to 4 pixels
Vertical binning 1 to 4 pixels
Sub-frame readout Arbitrary sub-frame
Computer interface USB 2.0 high-speed
USB 1.1 full-speed compatible
Binning can be combined independently on both axes.
Image download time and system read noise depends on the CCD chip
used in particular camera model as well as on the camera read mode.
Preview read mode provides system read noise approx. 1 or 2 e-
above CCD chip read noise.
Low Noise read mode is somewhat slower, but ensures system
read noise roughly equal to the manufacturer-specified chip read
noise.
Model G2-0400
Gain 1.5 e-/ADU (1×1 binning)
2.0 e-/ADU (other binnings)
System read noise 13 e- RMS (Low noise)
15 e- RMS (Preview)
Download time 0.25 s (Low noise)
0.16 s (Preview)

19
Model G2-1600
Gain 1.5 e-/ADU (1×1 binning)
2.0 e-/ADU (other binnings)
System read noise 13 e- RMS (Low noise)
15 e- RMS (Preview)
Download time 0.95 s (Low noise)
0.67 s (Preview)
Model G2-3200
Gain 0.8 e-/ADU (1×1 binning)
1.3 e-/ADU (other binnings)
System read noise 7 e- RMS (Low noise)
9 e- RMS (Preview)
Download time 1.95 s (Low noise)
1.39 s (Preview)
Model G2-8300
Gain 0.4 e-/ADU (1×1 binning)
0.8 e-/ADU (other binnings)
System read noise 8 e- RMS (Low noise)
9 e- RMS (Preview)
Download time 4.95 s (Low noise)
3.48 s (Preview)
Model G2-2000
Gain 0.5 e-/ADU (1×1 binning)
0.8 e-/ADU (other binnings)
System read noise 7 e- RMS (Low noise)
9 e- RMS (Preview)
Download time 1.06 s (Low noise)
0.73 s (Preview)
Model G2-4000
Gain 0.5 e-/ADU (1×1 binning)
0.8 e-/ADU (other binnings)
System read noise 7 e- RMS (Low noise)
9 e- RMS (Preview)

20
Download time 2.30 s (Low noise)
1.56 s (Preview)
Stated read noise is measured on particular CCD sensor, evaluated
during camera design. Actual read noise of different sensors varies
within sensor manufacturing batch and also among various
manufacturing batches. The camera read noise is determined by the
sensor itself and the camera manufacturer cannot affect it.

21
Cooling and power supply
Regulated thermoelectric cooling is capable to cool the CCD chip up to
50 °C below ambient temperature. The Peltier hot side is cooled by fan.
The CCD chip temperature is regulated with ±0.1 °C precision. High
temperature drop and precision regulation ensure very low dark current
for long exposures and allow proper image calibration.
The camera head contains two temperature sensors – the first sensor
measures directly the temperature of the CCD chip. The second one
measures the temperature inside the camera shell.
Figure 7: Back side of the G2 Mark II camera head contains vents for a fan, cooling
Peltir hot side
The cooling performance depends on the environmental conditions and
also on the power supply. If the power supply voltage drops below 12 V,
the maximum temperature drop is lower.

22
CCD chip cooling Thermoelectric (Peltier modules)
Maximal cooling ΔT >50 °C below ambient
Regulated cooling ΔT 48 °C below ambient (85% cooling)
Regulation precision ±0.1 °C
Hot side cooling Forced air cooling (fan)
Maximum temperature difference between CCD and ambient air may
be reached when the cooling runs at 100% power. However,
temperature cannot be regulated in such case, camera has no room
for lowering the CCD temperature when the ambient temperature
rises. Typical temperature drop can be achieved with cooling running
at approx. 85% power, which provides enough room for regulation.
Power supply
The 12 V DC power supply enables camera operation from arbitrary power
source including batteries, wall adapters etc. Universal 100-240 V AC/5060 Hz, 60 W “brick” adapter is supplied with the camera. Although the
camera power consumption does not exceed 55 W, the 60 W power supply
ensures noise-free operation.
Warning:
The power connector on the camera head uses center-plus pin.
Although all modern power supplies use this configuration, always
make sure the polarity is correct if you use own power source.
Camera head supply 12 V DC
Camera head power consumption 15 W without cooling
40 W maximum cooling
Power connector 5.5/2.5 mm, center +
Adapter input voltage 100-240 V AC/50-60 Hz
Adapter output voltage 12 V DC/5 A
Adapter maximum power 60 W

23
Power consumption is measured on the AC side of the supplied 12 V
AC/DC power supply. Camera consumes less energy from 12 V power
supply than state here.
The camera contains its own power supplies inside, so it can be
powered by unregulated 12 V DC power source – the input voltage can
be anywhere between 10 and 14 V. However, some parameters (like
cooling efficiency) can degrade if the supply drops below 12 V.
G2 camera measures its input voltage and provides it to the control
software. Input voltage is displayed in the Cooling tab of the CCD
Camera control tool in the SIPS. This feature is important especially if
you power the camera from batteries.
Figure 8: 12 V DC/5 A power supply adapter for G2 camera

24
Mechanical Specifications
Compact and robust camera head measures only 114×114×65 mm (approx.
4.5×4.5×2.6 inches). The head is CNC-machined from high-quality
aluminum and black anodized. The head itself contains USB-B (device)
connector and 12 V DC power plug. Integrated mechanical shutter allows
streak-free image readout, as well as automatic dark frame exposures,
which are necessary for unattended, robotic setups.
Camera head with integrated Internal filter wheel is 77.5 mm thick. Filter
wheel offers 5 positions for standard 1.25-inch threaded filter cells. A
variant of filter wheel with 6 positions for unmounted D26 mm filters is
also available.
Internal mechanical shutter Yes, blade shutter
Shortest exposure time 0.1 s
Longest exposure time Limited by chip saturation only
Internal filter wheel 5 positions for 1.25” threaded cells or
for D31 mm unmounted filters
6 positions for D26 mm unmounted
filters
Head dimensions 114×114×77.5 mm (Internal filter wheel)
114×114×65 mm (without filter wheel)
Back focal distance 33.5 mm (base of adjustable adapters)
Camera head weight 1.15 kg (with Internal filter wheel)
1.00 kg (without filter wheel)
1.70 kg (with “XS” External filter wheel)
1.95 kg (with “S” External filter wheel)
Filter wheel with 6 positions can cause vignetting (shielding of the
detector corners) if large CCD detector is used.
Back focus distance is measured from the sensor to the base on which
adjustable adapters are mounted. Various adapters then provide back
focal distance specific for the particular adapter type (e.g. M48
threaded adapter back focal distance is 55 mm).

25
Stated back focal distance already calculates with glass permanently
placed in the optical path (e.g. optical window covering the CCD cold
chamber).
When the adjustable adapter base, intended for camera with Internal
Filter Wheel, is mounted on camera without filter wheel, the resulting
back focal distance is only 21 mm.
Camera with Internal Filter Wheel
Figure 9: G2 camera head front view dimensions
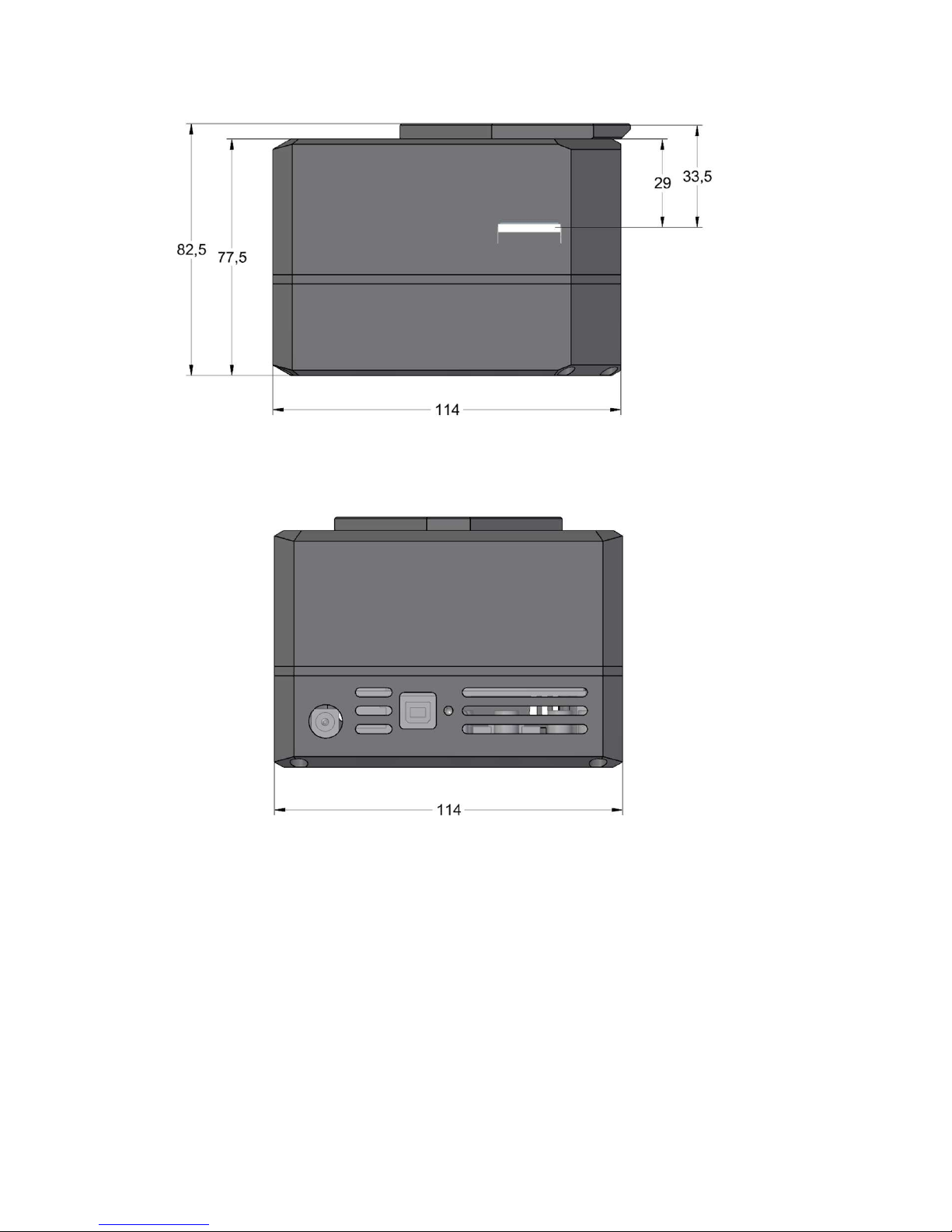
26
Figure 10: G2 camera head with Internal Filter Wheel side view dimensions
Figure 11: G2 camera head bottom view dimensions
27
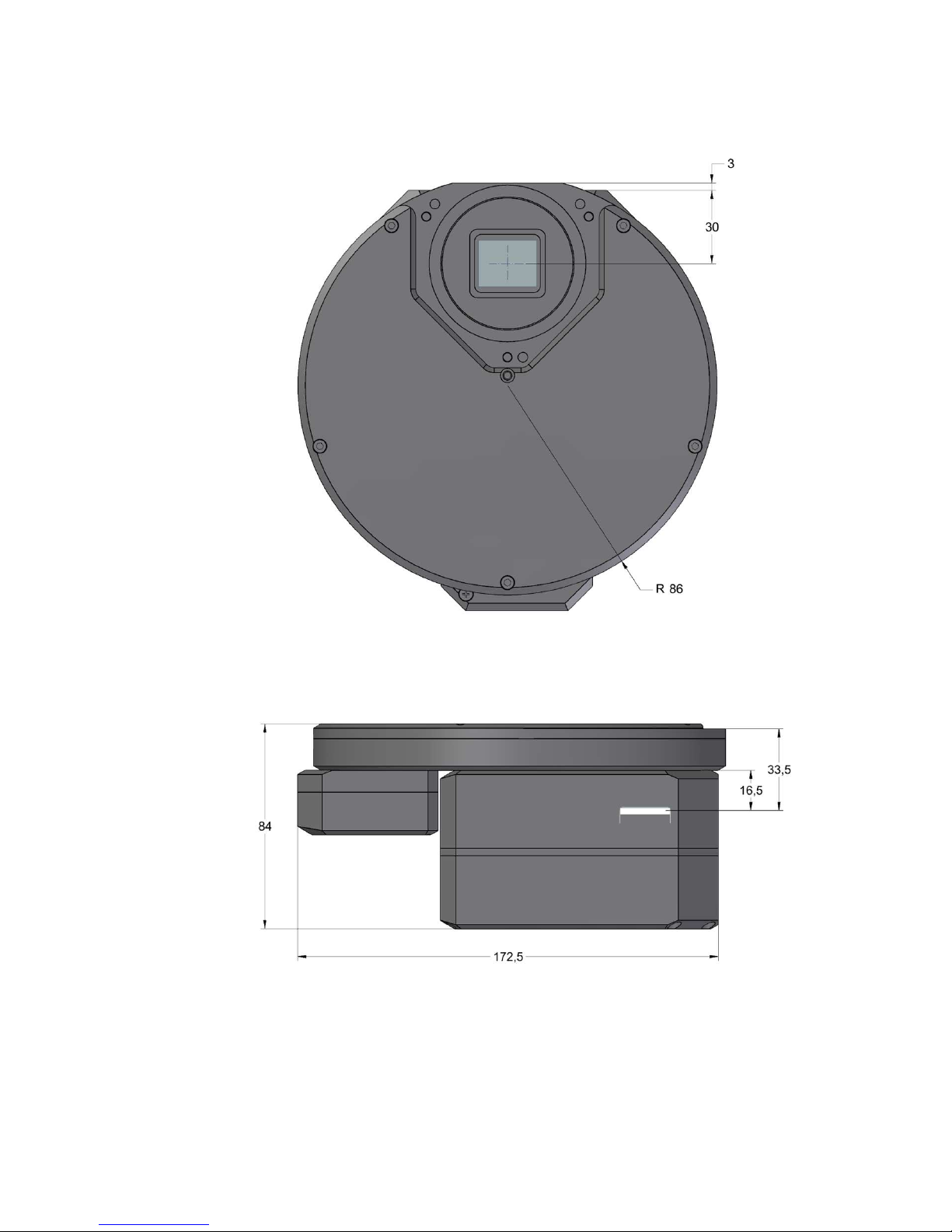
Camera with “XS” External Filter Wheel
Figure 12: G2 camera head with External filter wheel front view dimensions
Figure 13: G2 camera head with External filter wheel side view dimensions

28
Figure 14: G2 camera head with External filter wheel bottom view dimensions
The “S” sized External Filter Wheel diameter is greater (see External Filter
Wheel User's Guide), but the back focal distance of all external filter
wheels is identical.
Camera without filter wheel
If the camera model, intended for usage with External filter wheel, is used
without filter wheel at all, two types of adjustable adapter bases can be
used.
When a “thin” adapter base, intended for camera with Internal filter
wheel, is used, the back focal distance is only 21 mm.
Figure 15: Camera without filter wheel with "thin" adapter base
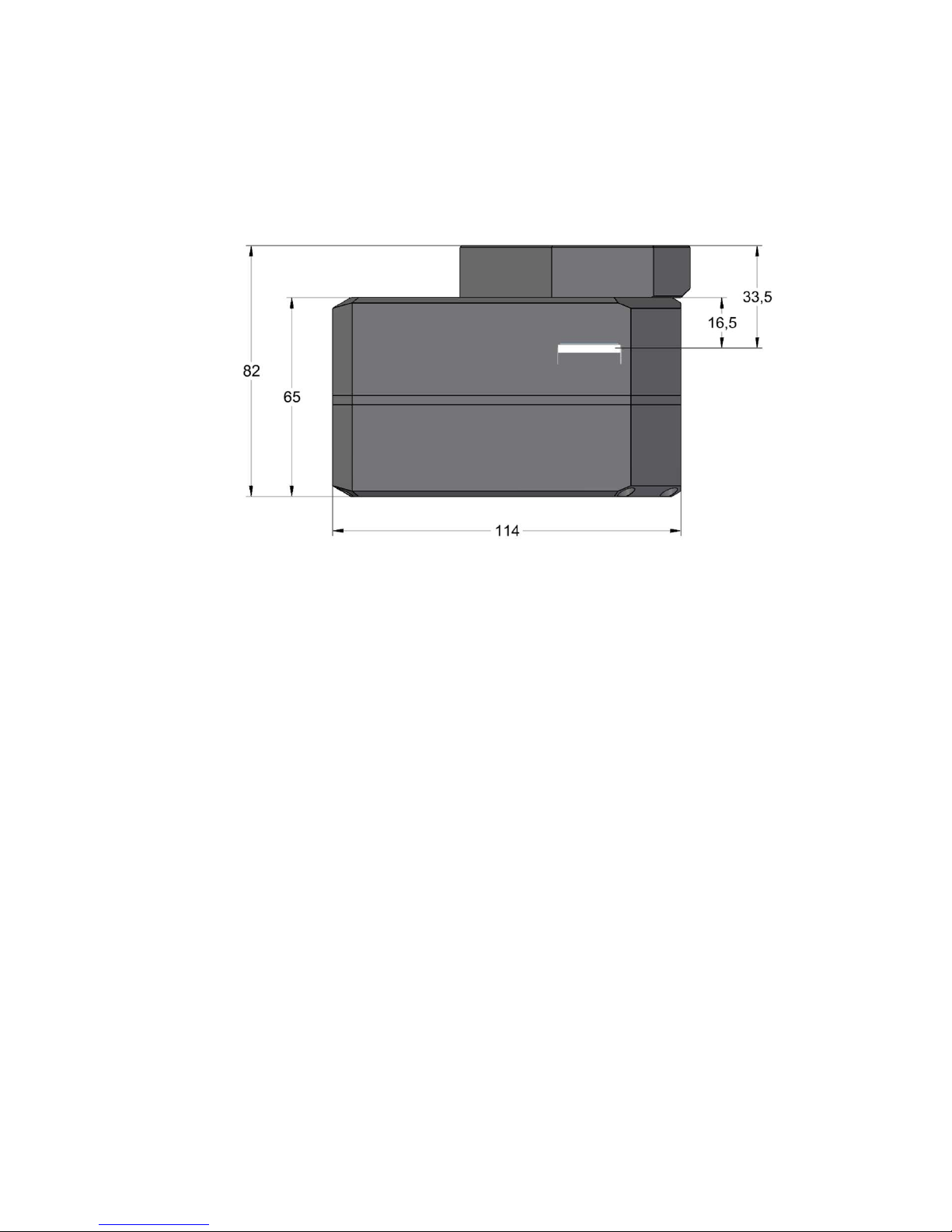
29
“Thick” adapter base has the same thickness like the External filter wheel.
This means all adapters, attached to this thick base, keep the same
33.5 mm back focal distance like the camera with External filter wheel
attached or camera with Internal filter wheel and “thin” adapter base.
Figure 16: Camera without filter wheel with "thick" adapter base
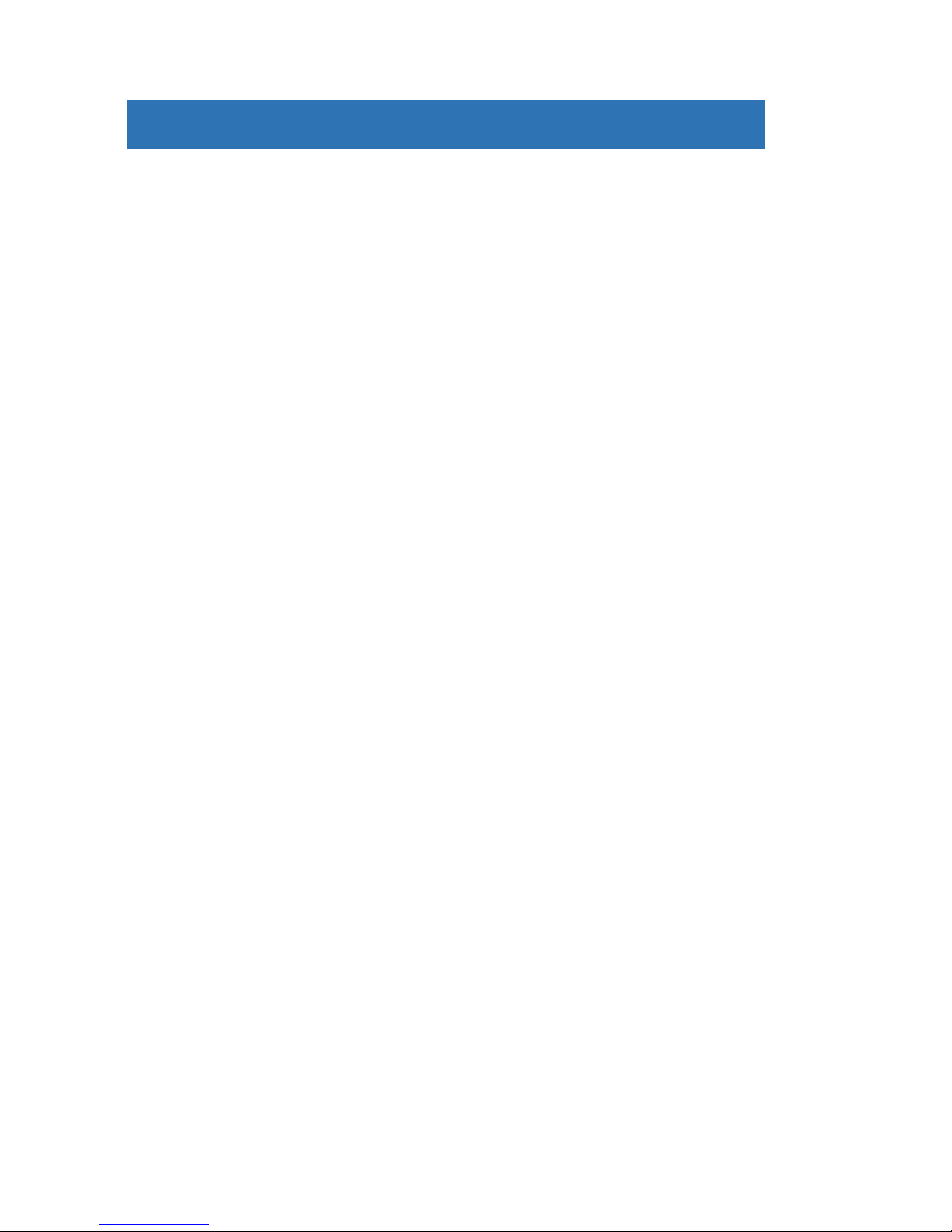
30
Optional accessories
Various accessories are offered with G2 Mark II cameras to enhance
functionality and help camera integration into imaging setups.
Telescope adapters
Various telescope and lens adapters for the G2 Mark II cameras are
offered. Users can choose any adapter according to their needs and other
adapters can be ordered separately.
2-inch barrel – adapter for standard 2" focusers.
T-thread short – M42×0.75 inner thread adapter.
T-thread with 55 mm BFD – M42×0.75 inner thread adapter,
preserves 55 mm back focal distance.
M48×0.75 short – adapter with inner thread M48×0.75.
M48×0.75 with 55 mm BFD – adapter with inner thread
M48×0.75, preserves 55 mm back focal distance.
Canon EOS bayonet – standard Canon EOS lens adapter,
preserves 44 mm back focal distance.
Nikon F bayonet – standard Nikon F lens adapter, preserves
46.5 mm back focal distance.
Mark II adapters are attached either directly to the External filter wheel
front plate or to the adjustable adapter base mounted on the camera
head.
Off-Axis Guider Adapter (OAG)
G2 camera can be optionally equipped with Off-Axis Guider Adapter. This
adapter contains flat mirror, tilted by 45° to the optical axis. This mirror
reflects part of the incoming light into guider camera port. The mirror is
located far enough from the optical axis not to block light coming to the
main camera sensor, so the optics must be capable to create large enough
field of view to illuminate the tilted mirror.
G2-OAG is manufactured in two variants, one with M42×0.75 thread (Tthread) and another with M48×0.75 thread. Both variants are designed to
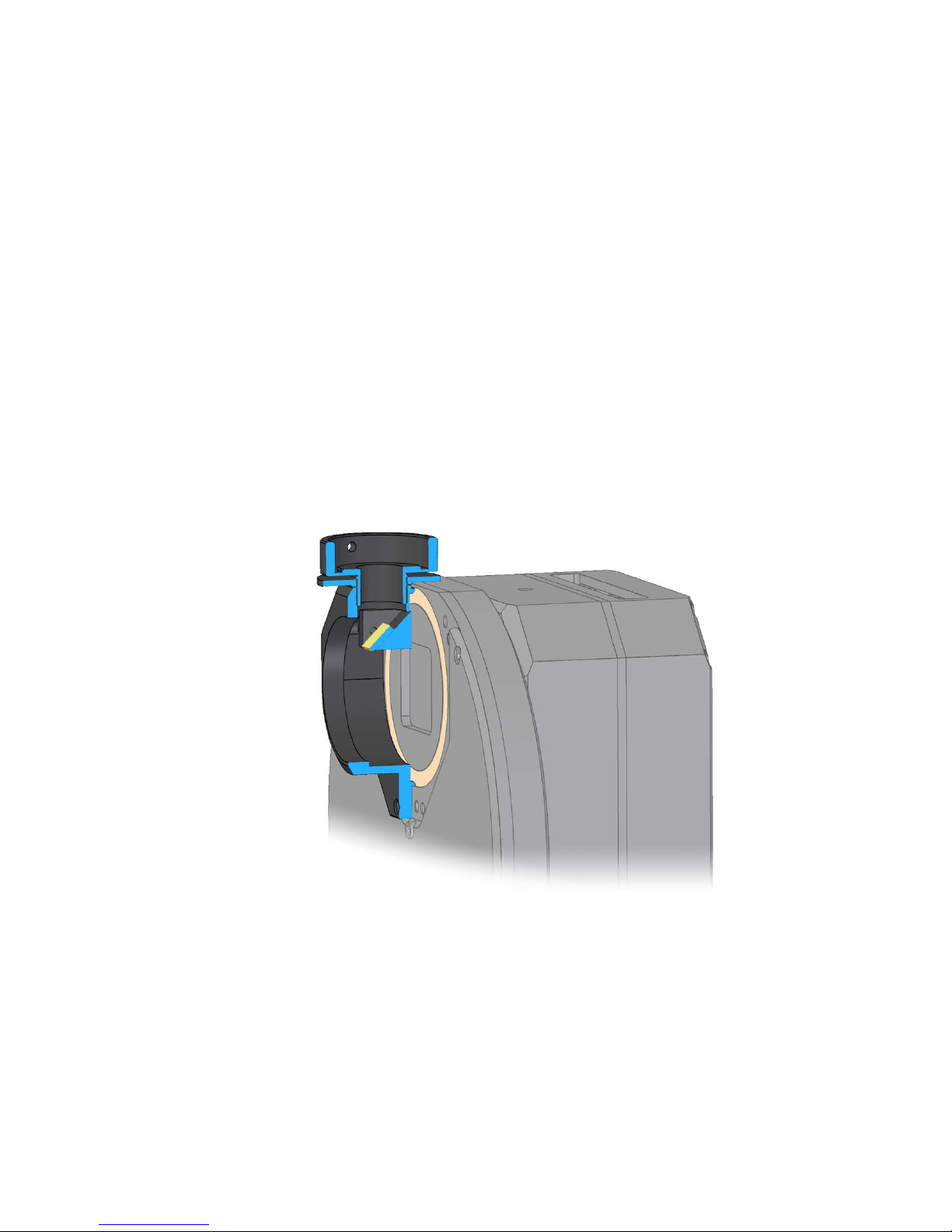
31
be compatible with external filter wheels and to preserve 55 mm distance
from the sensor.
If the OAG has to be used on camera with internal filter wheel, the OAG is
mounted to adapter base like any other adapter. Resulting Back focal
distance remains the same.
If the OAG is used on camera without filter wheel, thicker adapter base
must be used to keep the Back focal distance and to allow the guiding
camera to reach focus.
OAG guider port is compatible with G0 and G1 cameras. It is necessary to
replace the CS/1.25” adapter with short, 10 mm variant in the case of G1
cameras. Because G1 cameras follow CS-mount standard, (BFD 12.5 mm),
any camera following this standard with 10 mm long 1.25” adapter should
work properly with the G2-OAG.
Figure 17: G2-OAG sectional rendering illustrating reflecting mirror
Attaching camera head to telescope mount
G2 camera heads are equipped with “tripod” thread (0.25”) on the top
side. This thread can be used to attach 1.75 inch “dovetail bar” (Vixen
standard). It is then possible to attach the camera head, e.g. equipped with

32
photographic lens, directly to various telescope mounts supporting this
standard.
Figure 18: 1.75" bar for standard telescope mounts
Camera head color variants
Camera head is available in several color variants of the center plate. Visit
manufacturer's web pages for current offering.
Figure 19: G2 Mark II camera color variants

33
Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter
Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter allows connection of up to 4 Gx cameras of
any type on the one side and 1 Gbps Ethernet on the other side. This
adapter allows access to connected Gx cameras using routable TCP/IP
protocol over practically unlimited distance.
Figure 20: The Gx Camera Ethernet Adapter with two connected cameras

34
Adjusting of the telescope adapter
All telescope/lens adapters of the G2 Mark II series of cameras can be
slightly tilted. This feature is introduced to compensate for possible
misalignments in perpendicularity of the telescope optical axis and sensor
plane.
Figure 21: Releasing of the “pushing” screw
The Mark II camera telescope adapters are attached using three “pulling”
screws. As the adapter tilt is adjustable, another three “pushing” screws
are intended to fix the adapter after some pulling screw is released to
adjust the tilt.
Warning:
Both pulling and pushing screws, used on the G2 camera adapter, are
fine-pitch M4×0.5 thread screws, not standard M4 thread ones. Always

35
use only screws supplied with the adapter, using of normal M4 screws
damages the adapter.
Because the necessity to adjust two screws (one pushing, one pulling) at
once is inconvenient, the adapter tilting mechanism is also equipped with
ring-shaped spring, which pushes the adapter out of the camera body. This
means the pushing screws can be released and still slight releasing of the
pulling screw means the distance between the adapter and the camera
body increases. The spring is designed to be strong enough to push the
camera head from the adapter (fixed on the telescope) regardless of the
camera orientation.
When all three pulling screws are fully tightened, releasing of just one
or two of these screws does not allow adapter to move, or at last only
very slightly thanks to deformation of the adapter body. If the adapter
has to be adjusted, it is necessary to slightly release all three pulling
screws, which makes room for tilt adjustment.
Figure 22: Adjusting of the "pulling" screw

36
Only after the proper tilt is reached, the pushing screws should be slightly
tightened to fix the adapter in the desired angle relative to camera head.
This ensures long-time stability of the adjusted adapter.
Adjustable telescope/lens adapters are attached slightly differently
depending if the adapter is attached directly to the camera head (e.g.
when camera is equipped with internal filter wheel) or to the External filter
wheel case.
G2 Mark II adapters are not mounted directly on the camera
head. Instead a tilting adapter base, holding the circular spring, is
always used.
If the External filter wheel is used, the adapted base is not
necessary, as the Mark II External filter wheel front plate is
already designed to hold the spring and it also contains threads to
fix respective adapters.
Figure 23: Mark II External filter wheels are already designed to for adjustable
telescope adapters

37
Camera Maintenance
The G2 camera is a precision optical and mechanical instrument, so it
should be handled with care. Camera should be protected from moisture
and dust. Always cover the telescope adapter when the camera is removed
from the telescope or put the whole camera into protective plastic bag.
Desiccant exchange
The G2 camera cooling is designed to be resistant to humidity inside the
CCD chamber. When the temperature decreases, the copper cold finger
crosses freezing point earlier than the CCD chip itself, so the water vapor
inside the CCD chamber freezes on the cold finger surface first. Although
this mechanism works very reliably in majority of cases, it has some
limitations, especially when the humidity level inside the CCD chamber is
high or the chip is cooled to very low temperatures.
This is why a cylindrical container, filled with silica-gel desiccant, is placed
inside the camera head. This cylindrical chamber is connected with the
insulated cooled CCD chamber itself.
Warning:
High level of moisture inside the CCD cold chamber can cause camera
malfunction or even damage to the CCD sensor. Even if the frost does
not create on the detector when the CCD is cooled below freezing
point, the moisture can be still present. It is necessary to keep the CCD
chamber interior dry by the regular exchange of the silica-gel
desiccant. The frequency of necessary silica-gel exchanges depends on
the camera usage. If the camera is used regularly, it is necessary to dry
the CCD chamber every few months.
It is possible dry the wet silica-gel by baking it in the oven (not the
microwave one!) to dry it again. Dry the silica-gel for at last one or two
hours at temperature between 120 and 140 °C.
The silica-gel used in G2 cameras changes its color according to amount of
absorbed water – it is bright yellow or orange when it is dry and turns to
transparent without any color hue when it becomes wet. It is

38
recommended to shorten replacement interval if the silica-gel is
completely transparent upon replacement. If it is still yellow-orange, it is
possible to prolong the replacement interval.
Figure 24: Silica-gel container is accessible from the camera back side
Exchanging the silica-gel
G2 Mark II cameras employ the same desiccant container like the larger G3
and G4 cameras. The whole container can be unscrewed, so it is possible to
exchange silica-gel without the necessity to remove the camera from the
telescope.
Silica-gel is held inside the container with a perforated cap. This cap is also
screwed into the container body, so it is easy to exchange the silica-gel
inside the container after it is worn out or damaged e.g. by too high
temperature etc.
The container itself does not contain any sealing (the sealing remains
attached to the CCD cold chamber inside the camera head), it consists of
aluminum parts only. So, it is possible to heat the whole container to

39
desired temperature without risking of the temperature-induced sealing
damage.
This design also allows usage of some optional parts:
Threaded hermetic cap, which allows sealing of the dried
container when it is not immediately attached to the camera
head.
Alternate (somewhat longer) desiccant container, modified to be
able to be screw in and tightened (as well as released and
screwed out) without any tool.
The sealing cap as well as the tool-less container are not supplied with
the camera, they are supplied only as optional accessory.
Figure 25: Optional cap, standard container and the tool-less variant of the
container
Changing Filters
It is necessary to open the camera head to change filters or the whole filter
wheel. To open the head, unscrew the six bolts holding camera head
together.
Opening the camera head
The blade shutter rotates 180° between individual snapshots. Camera
cover could be opened only when the shutter is fully closed (covers the

40
CCD). If for instance the camera is unplugged from power adapter while
exposing, the shutter remains open. Camera cannot be opened in such
case.
Warning:
Shutter can be damaged while removing the camera cover if not in
proper position.
After removing the screws carefully turn the camera head by the telescope
adapter upward. Gently pull the front part of the case. Notice there are
two cables, connecting the filter wheel motor and the filter position optical
bar, plugged into the electronics board. It is not necessary to unplug these
cables to change filters, but if you unplug them, take care to connect them
again in the proper orientation!
Figure 26: Filters can be exchanged after removing of the camera front cover
Changing the Whole Filter Wheel
The whole filter wheel can be changed at once. It is necessary to remove
the front part of the camera case the same way as in the case of changing
filters. The filter wheel can be removed when you unscrew the bolt on the
center of the front part of camera case. Take care not to damage the
horseshoe-shaped optical bar when replacing the filter wheel.

41
Changing the Telescope Adapter
All adapters of the Mark II cameras are attached using three “pulling”
screws. As the adapter tilt is adjustable, another three “pushing” screws
are intended to fix the adapter in place.
If the adapter has to be replaced for another one, it is necessary to
unscrew the three pulling screws. The adapter then can be removed and
replaced with another one.
Warning:
Both pulling and pushing screws, used on the G2 camera adapter, are
fine-pitch M4×0.5 thread screws, not standard M4 thread ones. Always
use only screws supplied with the adapter, using of normal M4 screws
damages the adapter.
Always make sure to carefully locate the ring-shaped spring prior to
attaching the adapter.
Figure 27: Removing of the adjustable telescope adapter

42
Power Supply Fuse
The power supply inside the camera is protected against connecting of
inverted-polarity power plug or against connecting of too-high DC voltage
(above 15 V) by a fuse. If such event happens and the cooling fans on the
back side of the camera do not work when the camera is connected to
proper power supply, return the camera to the service center for repair.
 Loading...
Loading...