Page 1

Programmer’s
Programmer’s
Manual
Monarch
6017
Manual
HandiPrint
Printer
TC6017PM Rev. AC 06/02 ©2001 Monarch Marking Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 2
Each product and program carries a respective written warranty, the only warranty on which the customer can
rely. Monarch reserves the right to make changes in the product, the programs, and their availability at any
time and without notice. Although Monarch has made every effort to provide complete and accurate
information in this manual, Monarch shall not be liable for any omissions or inaccuracies. Any update will be
incorporated in a later edition of this manual.
©2000 Monarch Marking Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form by any means, without
the prior written permission of Monarch Marking Systems, Inc.
WARNING
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
CANADIAN D.O.C. WARNING
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise
emissions from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of
the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques dépassant
les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de la classe A prescrites dans
le Réglement sur le brouillage radioélectrique édicte par le ministère des
Communications du Canada.
Trademarks
Paxar
Monarch
SYMBOL
is a trademark of Paxar Corporation.
,
6017, and HandiPrint are trademarks of Monarch Marking Systems, Inc.
,
SPT, and PPT are trademarks of Symbol Technologies, Inc.
Monarch Marking Systems
170 Monarch Lane
Miamisburg, Ohio 45342
Page 3

Table of Contents i
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction................................................................................................1-1
Duty Cycle ...............................................................................................1-1
Conventions Used in this Manual ...............................................................1-2
Creating and Printing Formats ....................................................................2-1
Overview..................................................................................................2-1
Creating Text Fields..................................................................................2-1
Selecting Character Sets.......................................................................2-2
Formatting Text ....................................................................................2-2
Creating Graphic Fields.............................................................................2-3
Using Data Stream Graphics..................................................................2-4
Using Flash Memory Graphics................................................................2-5
Creating Bar Code Fields ..........................................................................2-7
Specifying Particular Bar Codes.............................................................2-8
Positioning Fields ................................................................................... 2-10
Configuring the Printer...............................................................................3-1
Selecting the Operating Mode....................................................................3-1
Setting the Print Contrast ..........................................................................3-1
Setting the Power Mode ............................................................................3-2
Checking the Battery Voltage.....................................................................3-2
Using the Power-Off Timer ........................................................................3-3
Supply Control Commands.........................................................................3-5
Printer Responses ................................................................................3-6
Checking Version Information ....................................................................3-6
Communicating with the Handheld..............................................................3-7
Miscellaneous Control Characters ..............................................................3-8
Page 4

ii Table of Contents
Modifying Resident Fonts ...........................................................................4-1
Font Sizes................................................................................................4-1
Defining New Characters...........................................................................4-2
Selecting Character Sets...........................................................................4-3
Loading New Characters............................................................................4-4
Saving Modified Fonts...............................................................................4-4
Using the Magnetic Card Reader .................................................................5-1
Error Messages ....................................................................................5-3
Using the Bar Code Scanner .......................................................................6-1
Sample Application.................................................................................... A-1
Application Code ......................................................................................A-1
Page 5
Introduction 1-1
INTRODUCTION
The Monarch® 6017™ HandiPrint™ printer works with application
programs written for the SYMBOL® SPT® 1700 or PPT® 2700 handheld
computers (“handheld”). The handheld/printer combination is suitable for
retail printing applications.
The printer control language contains commands to
♦ create and print formats.
♦ configure the printer.
♦ enable the use of certain printer features.
The application writes a data stream of commands (in the printer's control
language) to the printer. It writes these commands either directly or through
the Symbol Application Programming Interface (API). For information about
the API, refer to Symbol's Web site (www.symbol.com
).
This manual describes the printer's control language.
Duty Cycle
The HandiPrint 6017 printer is designed to print up to 1000 inches per day.
The average print rate is 1 inch every 10 seconds at a text character print
density of 25% (i.e., one character printed out of every four positions). Bar
codes and graphics are more dense (print with more dots) than text and may
need a lower duty cycle. If the duty cycle is exceeded, the printer may not print
1
all of the information that was sent to it.
Page 6
1-2 Introduction
Conventions Used in this Manual
Following are the conventions used in the syntax descriptions of each
command.
Symbol Description
- Separates items in the command sequence.
< > Indicates a variable with a single-byte value.
' ' Indicates the value is a literal. Enter the value as it appears or
use the ASCII hex values for the same characters.
( ) Indicates a variable of any length.
# # Indicates a variable of an exact length.
ESC Indicates the beginning of a command sequence. Enter 1B hex
for this item.
CR-LFNAK
Indicates the end of a response from the printer. In the
response, it is represented as 0D 0A 15 hex.
These conventions make it easier for you to read the commands' syntax
descriptions. They are not part of the data streams. For example,
ESC-'F1' may be the syntax description, but the application substitutes 1B
for
ESC. Also, - and ' (and other such characters described here) are not
part of the data stream.
The printer ignores commands with syntax errors.
Page 7
Creating and Printing Formats 2-1
CREATING AND PRINTING
FORMATS
A format is the design of what your application prints. It consists of fields
placed at various locations on the format. Fields can contain text, graphics,
and bar codes.
This chapter describes how to create a format.
Overview
To create a format:
1. Draw a rough sketch of how you want the format to look. For example,
a graphic may appear at the top, followed by the name of your
organization, followed by a list of items purchased. Your format could
be organized any number of ways.
There are .157-inch no-print zones on the left and right
sides of the format, and a .7-inch no-print zone at the
top of the format.
2. Code the commands to implement your format design, as described in
this chapter.
3. Add any commands to the data stream related to how the printer
performs. For example, at the data stream's beginning, enter the
command to initialize the printer (
18 hex).
4. Embed the data stream in the application and test what you have
written.
Creating Text Fields
Text fields can contain letters, numbers, and symbols. To specify text for
the format, write the text directly to the printer. There is no special
command to use. There are, however, commands/control characters to
select a character set to use and to format the text.
2
Page 8
2-2 Creating and Printing Formats
Selecting Character Sets
The printer can use the ANSI or ASCII character sets. These character sets
are preloaded in the printer. ANSI characters are the default.
You can modify character sets/fonts resident in the
printer. See “Modifying Resident Fonts.”
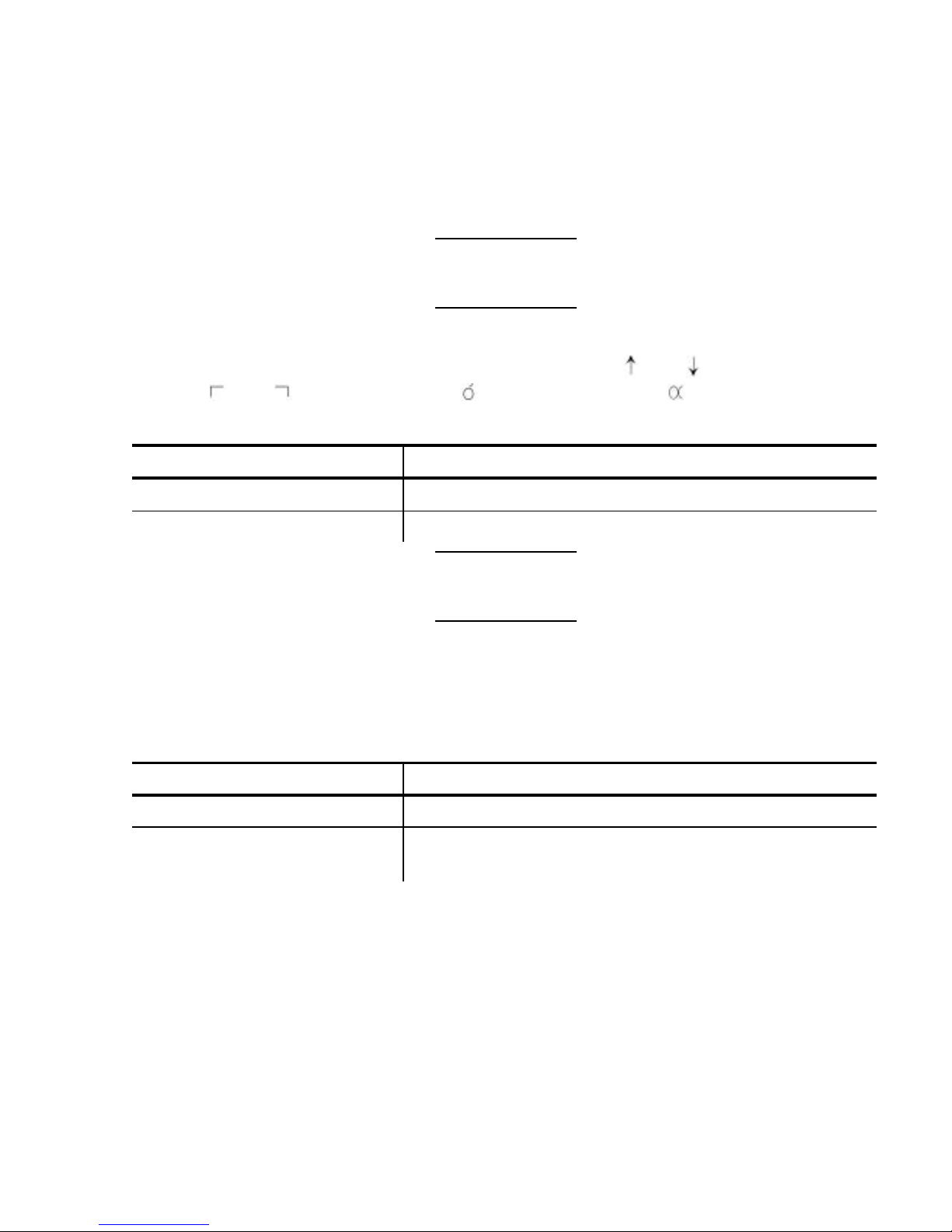
Character Exceptions
Both character sets have missing characters. The
and characters
replace and , respectively; the character replaces .
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'F1' Selects ANSI characters.
ESC-'F2' Selects ASCII characters.
F1 and F2 are two-character strings, not the familiar
notation for function keys 1 and 2.
Formatting Text
For the text on your format, you can choose the font, its size, spacing, and
style (normal or bold).
Command Summary
Command Description
1C hex (Extend) Prints characters twice as high as normal.
1D hex (Extendoff) Stops printing characters twice as high as
normal.
Page 9

Creating and Printing Formats 2-3
Command Description
ESC-'k'-<font> Selects a font. Standard Bold is the default.
<font> 0 Large Rotated (90 degrees clockwise)
1 Large Normal
2 Standard Bold
3 Standard Normal
4 Reduced Bold
5 Reduced Normal
ESC-'U'-<mode> Turns bold printing on or off.
<mode> 0 Turn off bold printing.
1 Turn on bold printing.
ESC-'a'-<space> Specifies the amount the space for the printer
to leave between lines of text.
<space> 0-10 The amount of space (in increments of
.125 mm). The default is 3 (.375 mm).
Example: ESC-a2 Sets the space between text lines to .25 mm.
Creating Graphic Fields
The printer can print bitmap graphics from
♦ data streams
♦ flash memory.
You use the same commands for both methods. However, if you use a data
stream, you must recreate the graphic every time you want to print it. If you
put the graphic in flash memory, you create it only once, and then retrieve it
when you want to print it.
Page 10
2-4 Creating and Printing Formats
Using Data Stream Graphics
You print data stream graphics one line at a time. To create a line, you
specify bits to turn off or on. Bits turned off represent white space, and bits
turned on represent part of the graphic. There is a .125 mm gap between
consecutive lines.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'V'-01 hex-00 hex#data#
Prints a graphic line.
#data# 72 hex bytes, indicating the dots to turn on or
off. For example, if a specified byte is FF, all
the dots are on. If it is 01, only one dot is on,
and the other 7 are off.
If you accidentally specify less than 72 bytes,
the printer does not print the graphic. If you
specify more than 72 bytes, a fatal exception
occurs.
You do not directly specify the bits turned on or off.
You specify the bits in groups of eight by using hex
values.
Example
This line of code prints a solid horizontal line of dots.
ESC-V-1-0FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
FFFF
Page 11

Creating and Printing Formats 2-5
Using Flash Memory Graphics
You can also use a graphic previously stored in flash memory. You are
limited to one graphic stored in memory at a time. Saving a graphic to flash
memory when there is already one there overwrites the previous one.
To store a graphic in flash memory:
1. Remove the printer’s battery and wait several seconds.
2. Re-insert the battery and enter Download Mode immediately (see
below). It takes two commands to make the transition to Download
Mode. Design the application so that it waits to send the second
command until the printer responds to the first command by returning a
‘?‘ character.
3. Transmit the graphic one line at a time, using a graphic created as
described in “Using Data Stream Graphics.”
4. Save the graphic to flash memory (see below). When it receives the
command, the printer returns a ‘D‘ character, and begins the save.
When the save is complete, the printer transmits an ‘!’ character, and
then an ‘X’ character every 500 milliseconds.
5. Remove the printer’s battery and wait several seconds before replacing
it.
Page 12
2-6 Creating and Printing Formats
Command Summary
Commands Description
ESC-'DL' Step 1 of entering Download Mode. After
processing this command, the printer returns a
‘?’ character.
ESC-'LG0' Step 2 of entering Download Mode. Any
character not accepted as part of this
command is sent back the handheld.
ESC-'LG'-FF hex Saves the graphic. After receiving this
command, the printer returns a ‘D’ character,
and then saves the graphic.
When finished, the printer sends an ‘!’
character, then it sends an ‘X’ character every
500 milliseconds.
ESC-'Lg0' Prints the graphic stored in flash memory.
ESC-'V'-<low>-<high>#data#
Prints a number of graphic lines.
<low> and <high> The hex digits (listed backward) of a number
indicating how many lines to print. For
example, to print 10 lines,
<low> is A, and
<high> is 0.
#data# 72 hex bytes, indicating the dots to turn on or
off. For example, if a specified byte is FF, all
the dots are on. If it is 01, only one dot is on,
and the other 7 are off.
If you accidentally specify less than 72 bytes,
the printer does not print the graphic. If you
specify more than 72 bytes, a fatal exception
occurs.
Note that you are not directly specifying the bits turned
on or off. You are specifying the bits in groups of eight
by using two digit hex values.
Page 13
Creating and Printing Formats 2-7
Creating Bar Code Fields
The printer can print the following bar codes, with or without humanreadable data.
♦ Code 39
♦ Codabar
♦ Interleaved 2 of 5
♦ Code 128 (UCC/EAN-128)
♦ UPC/EAN/JAN
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'z'-<bctype><length>-<height>-
<data>
Prints a bar code without human-readable
data.
ESC-'Z'-<bctype><length>-<height><data>
Prints a bar code with human-readable data.
<bctype> The type of bar code to print (values are the
ASCII representation, not hex).
'1' Code 39
'2' Code 128 (UCC/EAN-128)
'3' Interleaved 2 of 5
'4' UPC/EAN/JAN
'5' Codabar
<length> The data length, specified in hex. This value
is dependent on the bar code you choose with
<bctype>. See “Specifying Particular Bar
Codes.”
Page 14
2-8 Creating and Printing Formats
Command Description
<height> The bar code height, specified in hex, in
increments of .125 mm. <height> can be no
smaller than 14. For example, 14 = 2.5 mm,
15 = 2.625 mm, etc.
For UPC/EAN/JAN bar codes, the height you
specify includes a 1.25 mm drop bar pattern
after the bar code.
(data) The data for the bar code. It must equal
<length>. See “Specifying Particular Bar
Codes” for data restrictions, which vary by bar
code.
Specifying Particular Bar Codes
Values for the <length> and <data> parameters depend on the type of bar
code you choose with
<bctype>.
Bar Code
<length> <data>
Code 39 9 (maximum) 0-9, A-Z, -, (space), $,
/, +, and %
Interleaved 2 of 5 24 (maximum) Pairs of numeric
characters (0-9)
UPC/EAN/JAN UPCA: 12
UPCE: 7
EAN/JAN-8: 8
EAN/JAN-13: 13
These lengths are fixed
and all include a check
digit.
0-9
Codabar 20 (maximum) plus start
and stop characters.
The printer adds the
stop character
automatically.
Data: 0-9, $, -, :, /, .,
and +.
Start: a (the default),
b, c, or d.
Page 15

Creating and Printing Formats 2-9
Code 128 (UCC/EAN-128) Details
For Code 128 (UCC/EAN-128) bar codes,
<length> can be a maximum of
18 (with alphanumeric/control code data) or 36 (if you use subset C and
numeric pairs).
The first character of
<data> must specify the subset to use: A, B, or C
(listed as
87, 88, and 89 hex, respectively). The rest of the data can be all
256 ASCII characters by using a combination of the subsets. The data must
appear as numeric pairs corresponding to the hex values for the ASCII
character in question.
Each subset enables the bar code to contain different characters. Subset A
uses
20-3F hex and 40-7F hex (read by a bar code reader as 00-7F hex),
subset B uses
20-7F hex, and subset C uses 30-39 hex.
The following table explains how to switch from one subset to another.
Character Subset A Subset B Subset C
80 hex Function 3 Function 3
81 hex Function 2 Function 2
82 hex* Shift Shift
83 hex Switch to Subset C Switch to Subset C
84 hex Switch to Subset B Function 4 Switch to Subset B
85 hex Function 4 Switch to Subset A Switch to Subset A
86 hex Function 1 Function 1 Function 1
* A temporary, one character shift to another subset.
The following table describes the purpose of each function.
Function
Number
Purpose
1 Uses reserved Code 128 characters (UCC/EAN128).
2 Appends data (subsets A and B only).
3 Initializes a bar code reader.
4 Extends characters. For example, 'a' (97 decimal) is
changed to '
β' (225 decimal) by adding 128 to it. This
function is unavailable in subset C.
Page 16

2-10 Creating and Printing Formats
Positioning Fields
The following commands/control characters move the supply through the
printer to position the fields on the format. The application can also write
spaces to the printer before it prints text to position a field.
There are .157-inch no-print zones on the image area’s
right and left sides and a .7-inch no-print zone at the
top.
Command Summary
Command Description
D hex (CR) Advances to the beginning of the next line.
C hex (FF) Advances 10 lines.
14 hex (Norm)/F hex (SI) Sets the printer to 48-column mode.
E hex (SO) Sets the printer to 24-column mode.
B hex (VT) Advances 5 lines.
9 hex (HT) Tabs to the next position or the beginning of
the next line.
A hex (LF) Advances to the beginning of the next line.
ESC-'J'-<num> Performs a specified number of line feeds.
<num> 1-FF The number of line feeds, specified in
hex. The default is 1 (.125 mm).
Page 17

Configuring the Printer 3-1
CONFIGURING THE PRINTER
There are several commands for configuring the printer. You can include
these commands at any place in a data stream. This chapter describes
these commands.
Selecting the Operating Mode
The printer works in either online or buffer mode. In online mode, the
printer prints characters as soon as they are received. In buffer mode, the
printer receives and stores characters, and then prints them upon receipt of
an EOT control character (
4 hex).
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'P#' Selects online mode.
ESC-'P$' Selects buffer mode.
Setting the Print Contrast
You can increase or decrease the print contrast for lighter or darker print.
This setting affects the print speed (the higher the contrast, the lower the
speed and vice versa). The print contrast also depends on the battery
voltage.
We recommend designing your
applications so the user can adjust
the print contrast.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'P'-<value> Sets the print contrast.
<value> 0-9 0 is the highest contrast and 9 is the
lowest contrast. The default is 5.
3
Page 18

3-2 Configuring the Printer
Setting the Power Mode
The printer can operate in five different power modes, each using a different
number of printhead sections, which are groups of dots on the printhead.
The mode selected also affects the print speed (the more printhead sections
used, the faster the printer speed and vice versa).
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'P'-<value> Sets the power mode.
<value> The number of printhead sections to use,
specified in hex.
1 Use one printhead section.
2 Use two printhead sections.
3 Use three printhead sections.
6 Use six printhead sections.
7 Default. Dynamically choose the
number of printhead sections to use (1,
2, 3, or 6), depending on what is
printed.
Checking the Battery Voltage
The following commands/control characters involve the printer's battery.
We recommend designing your
applications so the user can check
the printer's battery voltage.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'P^' Prints the battery voltage.
ESC-'P!' Requests the battery voltage from the printer.
Page 19

Configuring the Printer 3-3
Command Description
16 hex (Ctrl-V) Requests the print buffer and battery statuses.
The printer responds with:
ESC-'B'-#pbchars#-CR-LF-ESC-'V'-#volts#CR-LF-ESC-'M'-#card#-CR-LF-NAK
#pbchars# The number of characters
currently in the print buffer,
shown as four ASCII hex digits,
which are “OR’d” with 30 hex.
#volts# Four ASCII decimal digits. The
first three are the battery
voltage (form x.x).
The fourth character categorizes
the voltage listed to give it a
reference. Values are 1-4,
where 1 is high and 4 is low.
#card# Four ASCII hex digits (which are
“OR’d” with 30 hex) representing
the time left before the printer
enters sleep mode.
Using the Power-Off Timer
The printer has a power-off timer to conserve battery life. After a specified
period of inactivity occurs, the printer goes into sleep mode. This feature is
similar to the Auto-Off feature on your handheld.
The printer returns to normal mode when it starts receiving commands
again, but the countdown re-starts after every character received.
Before powering down, the printer transmits Auxon then Xoff.
Page 20

3-4 Configuring the Printer
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'M'-<digit1><digit2>-'0'-CR
Sets the power-off timer’s inactivity period.
<digit1> and <digit2>
0-9 The first and second digits,
respectively, of the number of seconds
to set the inactivity period to. To
disable the timer, set both parameters
to 0.
Example:
ESC-M560-CR
Sets the inactivity period to 56 seconds.
ESC-'C' Sets the inactivity period to the default (20
seconds).
Be careful when using sleep mode
with buffer mode. If there is data
in the print buffer when the printer
goes into sleep mode, you lose
the data.
Page 21

Configuring the Printer 3-5
Supply Control Commands
The commands in this section control how the printer uses black-mark
supplies.
Be aware of the features of your supplies (distance between black marks,
existence of any preprinted text, etc.) as you code these commands. For
example, you may have to code the black mark search command multiple
times if the marks are farther apart than the maximum search allows.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'QJ'-<lines> Moves the printer backward in .125mm line
increments.
<lines> 00 hex –
FF hex
The number of lines to move.
ESC-'QQ'-<lines> Specifies the number of .125mm lines to
continue printing after failing to detect a black
mark.
<lines> 00 hex –
FF hex
The number of lines to print. The
default is 28 hex.
ESC-'QF'-<max> Searches for a black mark, advancing in
.25mm line increments.
<max> 00 hex –
FF hex
The maximum number of lines to
move.
ESC-'QB'-<max> Searches for a black mark, moving backward
in .25mm line increments.
<max> 00 hex –
FF hex
The maximum number of lines to
move.
Page 22

3-6 Configuring the Printer
Printer Responses
The printer responds to the two black mark search commands, with either of
the following sequences.
Command Description
ESC-'Q'-3F hex-3F hex#high#-#low#
Black mark found.
ESC-'Q'-30 hex-30 hex#high#-#low#
Black mark not found.
#high# 30 hex –
3F hex
The left digit of the hex number
representing the number of lines
moved to find the black mark.
#low# 30 hex –
3F hex
The right digit of the hex number
representing the number of lines
moved to find the black mark.
Checking Version Information
Your application can check the versions of both the printer’s hardware and
firmware.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'P(' Requests the firmware version. The printer
responds with:
ESC-'('-#version#-CR-LF-NAK
#version# Four ASCII characters
representing the firmware
version.
ESC-'P)' Requests the hardware version. The printer
responds with:
ESC-')'-'099'-<version>-CR-LF-NAK
<version> An ASCII character representing
the hardware version.
Page 23

Configuring the Printer 3-7
Communicating with the Handheld
The printer and handheld cannot communicate unless they use these
communication parameter values:
♦ Baud Rate - 19200
♦ Stop Bits - 1
♦ Parity - None
♦ Data Bits - 8
♦ Flow Control – RTS/CTS
The following control characters are related to communications between the
printer and the handheld.
Command Summary
Command Description
12 hex (Auxon) Sent by the printer to indicate the printer is
online (transmitted upon initial power up, a
paper reload, or clearing of a paper jam).
15 hex (Auxoff) Sent by the printer just before a power down
or when the supplies run out.
11 hex (Xon) Sent by either device to indicate it is ready to
receive data.
13 hex (Xoff) Sent by the receiving device to indicate the
transmission must end.
Page 24

3-8 Configuring the Printer
Miscellaneous Control Characters
Command Summary
Command Description
18 hex (Cancel) Re-initializes the printer. We recommend you
begin all data streams with this command.
8 hex (BS) Removes the last character entered in the
print buffer.
4 hex (EOT) Sent by the printer to indicate the buffer is
empty and the printer is idle.
Page 25

Modifying Resident Fonts 4-1
MODIFYING RESIDENT FONTS
You can modify the printer’s resident fonts by redefining the characters.
To modify a font, perform the tasks in the following sections (in the order
the sections are listed).
Each time you modify a font, it replaces the current font
definition. The only way to return to the default font is
to reload the original definition.
Font Sizes
Before you start, take note of the maximum size of characters in the font you
want to use.
Number Name Character
Size (w x h)
0 Large Rotated
(90 degrees clockwise)
14 x 16
1 Large Normal 16 x 21
2 Standard Bold 12 x 21
3 Standard Normal 10 x 21
4 Reduced Bold 9 x 21
5 Reduced Normal 8 x 21
4
Page 26

4-2 Modifying Resident Fonts
Defining New Characters
You must define each new character separately, performing the following
procedure for each one.
1. Define the character in a matrix. The matrix size depends on the font
you use (see “Font Sizes”). Think of the matrix as a bitmap showing
the character’s design. Following is an example.
Left Byte Right Byte
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Leave at least one column blank to the character’s right
so character strings do not run together.
2. Translate each line into two bit sequences (left byte/right byte), where
an empty square is 0, and a filled-in square is a 1. For example, the
second line from the top is 00000000 01000000.
3. Convert each bit sequence into two hex characters. For example, the
second line from the top is 00 40.
The Next Step
You have now defined the new character you want to create. The next step
is to select the character set to load it in.
Page 27

Modifying Resident Fonts 4-3
Selecting Character Sets
Before selecting a character set, remove the printer’s battery and wait
several seconds. Then, replace the battery and immediately use one of
these commands to select the character set to modify.
When it receives either of these commands, the printer copies the character
set to memory, then sends a ‘?’ character to the handheld.
The printer returns any characters not accepted as part of this command.
Do Not send any commands to the printer between
turning it on and selecting the character set.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'DA0' Selects characters from the ASCII character
set (33-127).
ESC-'DX'-<charfont> Selects characters and fonts from the
Extended ASCII or ANSI character set (128-
255).
<charfont> 0 Extended ASCII characters – Large
Rotated, Large Normal, and Standard
Bold fonts.
1 Extended ASCII characters – Standard
Normal, Reduced Bold, and Reduced
Normal fonts.
2 ANSI characters –Large Rotated, Large
Normal, and Standard Bold fonts.
3 ANSI characters –Standard Normal,
Reduced Bold, and Reduced Normal
fonts.
The Next Step
You have now selected the character set you are modifying. The next step
is to load the character into the set.
Page 28

4-4 Modifying Resident Fonts
Loading New Characters
This step allows you to load the new characters at a particular position in
the set.
Command Summary
Command Description
<ESC>-'D'-<font><code>-<matrix>
Loads a character at a particular position.
<font> The font to save the character in.
Value ASCII Fonts Extended ASCII
and ANSI Fonts
0 Large Normal
Standard Bold
Large Normal
Standard Bold
Standard Normal
1 Standard Normal Large Rotated
Reduced Bold
Reduced Normal
2 Reduced Bold
Reduced Normal
<code> The hex character code for the new character:
21 hex – 7F hex (ASCII) or 80 hex – FF hex
(Extended ASCII and ANSI).
#matrix# The hex data from the matrix describing the
new character (see “Defining New
Characters”).
The Next Step
You have now modified the character set. The next step is to save the font.
Saving Modified Fonts
To save the modified font into flash memory, use ESC-'D'-FF hex. When the
fonts have been saved, the printer sends a ‘!’ character to the handheld.
Then, it sends an ‘X’ character every 500 milliseconds.
Next, remove the battery and wait several seconds before replacing it.
Page 29

Using the Magnetic Card Reader 5-1
USING THE MAGNETIC CARD
READER
Optional. Your printer may have a magnetic card reader, which reads
up to three tracks of magnetically encoded data from cards conforming to
the ANSI/ISO 7810 and 7811 standards. After reading the data, the printer
returns the information to the handheld.
Before preparing the reader for a swipe, the handheld wakes the printer up
by sending a few characters to it. The printer responds with XON to indicate
the reader is ready.
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'M'-#timer#<tracks>-CR
Prepares the reader for a magnetic card
swipe. The reader’s LED turns on when the
printer receives this command, indicating it is
waiting for the operator to swipe the card. On
a successful swipe, the LED goes out.
#timer# Sets the reader’s timer. If the operator does
not swipe the card through the reader before
the timer runs out, an error occurs. Values
are 00-99 (seconds). 00 disables the timer.
<tracks> The combination of tracks to read.
1 Track 1 only.
2 Track 2 only.
3 Track 3 only.
4 Tracks 1 and 2 together.
5 Tracks 2 and 3 together.
6 Tracks 1, 2, and 3 together.
5
Page 30

5-2 Using the Magnetic Card Reader
Command Description
The reader responds to the read command
with:
#trck#-(data)-'?'-CR-LF-NAK
#trck# Track indicator. Values are %/1/
(track 1), ;/2/ (track 2), and +/3/
(track3).
(data) The data read from the card. This
field can be empty. If an error
occurs, this field contains an E
character and the error message text
(see ”Error Messages”).
2 hex (Ctrl-B) Requests the print buffer and card reader
statuses. The printer responds with:
ESC-'B'-#pb#-CR-LF-ESC-'M'-#sleep#- CR- LFNAK
#pb# The number of characters currently
in the print buffer, shown as four
hex digits, which are “OR’d” with
30 hex.
#sleep# Four ASCII hex digits (which are
“OR’d” with 30 hex) representing
the time left before the printer
enters sleep mode.
ESC-'C' Cancels the reading process.
Page 31

Using the Magnetic Card Reader 5-3
Error Messages
Following is the format of the data returned when an error occurs with the
magnetic card reader. When an error occurs, the reader’s LED blinks once.
Syntax Description
'%'-'E,'-#error#-','-(text)CR-LF
Indicates an error occurred.
#error#,(text) Error number and corresponding text.
05 Timeout Expired.
07 Invalid Track Number.
08 Unsupported Track Selected.
09 Cancel Request.
Considerations
♦ We recommend designing your applications so the user can manually
enter data when the reader cannot read a card.
♦ Keep the value for the timer long enough to allow the swipe, but small
enough to not allow multiple swipes. If multiple swipes are done (with
different cards) and each uses different tracks to store data, the data
sent back to the handheld will be a mixture from the two cards.
Page 32

5-4 Using the Magnetic Card Reader
Page 33

Using the Bar Code Scanner 6-1
USING THE BAR CODE SCANNER
The operator can use the handheld’s scanner indirectly from buttons on
the printer. This functionality must be built into the application.
The printer does not do the scanning. It communicates with the handheld,
indicating the operator is pressing the printer’s scanner buttons, and the
handheld should activate the scanner.
The application must integrate these commands with the commands running
the scanner. For example, using the API commands, the application must
enable the scanner and define the connection to the printer buttons before
performing the scan.
The interaction between the printer and handheld goes as follows:
1. The application defines the data the handheld expects from the printer
to indicate the printer’s button(s) are being pressed.
2. When the operator presses the printer button(s), the printer
automatically sends the data indicating the buttons are being pressed.
3. When the operator releases the printer button(s), the printer
automatically sends the data indicating the buttons have been released.
4. The handheld disables the printer’s scanner buttons.
6
Page 34

6-2 Using the Bar Code Scanner
Command Summary
Command Description
ESC-'Y'-(on)-(onstring)(off)-(offstring)
Defines what data the handheld expects from
the printer to indicate the printer buttons are
being pressed, and when they are not.
(on) The number of characters in (onstring).
(onstring) The data indicating the buttons are being
pressed.
(off) The number of characters in (offstring).
(offstring) The data indicating the buttons have been
released.
Example
ESC-'Y'-'2'-'ON'-'3'-'OFF'
Specifies to enable/disable the scanner
buttons with the words ON and OFF.
ESC-'Y00' Disables the printer’s scanner buttons.
Page 35

Sample Application A-1
SAMPLE APPLICATION
This appendix describes a sample application that prints the following
sales receipt.
Application Code
The printer’s data stream is integrated with the commands that make up the
handheld’s application. For example, the application must define and
initialize variables, open the serial port and allocate memory before it sends
the data stream to the printer.
A
Page 36

A-2 Sample Application
Dim ESC 'Declare variables
Dim CR
Dim CmdString
Dim Buffer
Dim BufferSize
Dim iSerialPort
Dim iReturn
Dim CRLF
Dim LF
Dim NAK
Dim Byte
Dim String
ESC = Chr(27) 'Initialize variables
CR = Chr(13)
CRLF = Chr(13) & Chr(10)
LF = Chr(10)
NAK = Chr(21)
Byte = ""
String=""
LPrint(Chr(24)) 'Reinitialize Printer
LPrint(ESC & "P#") 'Online Mode
LPrint(ESC & "F1") 'ASCII Chars
LPrint(ESC & "k3") 'Font 3
LPrint(ESC & "A0") 'Zero space between lines
Page 37

Sample Application A-3
'Set up data stream
CmdString = ESC & "P#" & CRLF & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & " Paxar/Monarch" & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & " 170 Monarch Ln." & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & " Miamisburg, OH 45342" & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & " Phone: (937) 865-2123" & CRLF & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & " SALES RECEIPT" & CRLF & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & "Description Qty. Total" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "1.Monarch 9490 5 3495" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "2.Monarch 9403 4 995" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "3.Monarch 6035 3 4995" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "4.Monarch 6030 2 2995" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "5.Monarch 9450 1 995" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & " -----" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & " Total 13475" & CRLF & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & "AMEX 37xvz55xx315001" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "Exp. Date 10/01" & CRLF & CRLF & CRLF
CmdString = CmdString & ESC & "z1" & Char(6) & Chr(64) & "123456"
CmdString = CmdString & LF & Chr(12)
CmdString = CmdString & "" & LF
CmdString = CmdString & "" & LF
'Allocate the port
iSerialPort = SerialPortAllocate()
iReturn = SerialPortOpenText(iSerialPort, 0, 19200, CRLF, CRLF)
iReturn = SerialPortConfigure(iSerialPort,19200,8,"None",1,"Hardware")
BufferSize = 512 + 32 'Allocate buffer
Buffer = MemoryAllocate(BufferSize)
iReturn = SerialPortSetBuffer(iSerialPort, Buffer, BufferSize)
'Send data stream
iReturn = SerialPortWriteString(iSerialPort, CmdString)
While Byte <> NAK 'Wait for response
Byte = SerialPortReadString(iSerialPort, 1)
if Byte = NAK then exit while
String = String & Byte
Wend
MsgBox(String)
Page 38

A-4 Sample Application
Buffer = MemoryFree(Buffer) 'Deallocate the port
iReturn = SerialPortClose(iSerialPort)
iReturn = SerialPortFree(iSerialPort)
LPrint(Chr(12)) 'Form feed
MsgBox("Done") 'Finish up
If ClosePort() = false then
MsgBox("Close Failed")
EndIf
Page 39

Index-1
INDEX
A
application, sample, A-1
B
bar code
fields, creating, 2-7
scanner, using, 6-1
specifying particular, 2-8
types available, 2-8
battery voltage, checking, 3-2
black mark supplies, 3-5
buffer mode, 3-1
C
character
defining new, 4-2
exceptions, 2-2
loading new, 4-4
sets, selecting (creating text fields),
2-2
sets, selecting (font modification), 4-3
checking
battery voltage, 3-2
print buffer status, 3-3
version information,3- 6
Codabar bar codes, 2-8
Code 128 (UCC/EAN-128 bar codes, 2-9
Code 39 bar codes, 2-8
commands
bar code field creation, 2-7
bar code scanner, 6-2
battery voltage checking, 3-2
character set selection, 2-2, 4-3
data stream graphic, 2-4
field positioning, 2-10
flash memory graphic, 2-6
formatting text, 2-2
handheld communication, 3-7
loading new characters, 4-4
magnetic card reader, 5-1
miscellaneous control characters, 3-8
operating mode selection, 3-1
power mode setting, 3-2
power-off timer, 3-4
print contrast setting, 3-1
supply control, 3-5
version information checking, 3-6
communicating with handheld, 3-7
communication parameters, 3-7
configuring printer, 3-1
contrast, print, 3-1
control characters, miscellaneous, 3-8
control of supplies, 3-5
conventions in manual, 1-2
Page 40

Index-2
creating
bar code fields, 2-7
formats, 2-1
graphic fields, 2-3
text fields, 2-1
D
data stream graphics, 2-4
defining new characters, 4-2
duty cycle, 1-1
E
errors, magnetic card reader, 5-3
exceptions, character, 2-2
F
fields
bar code, 2-7
definition, 2-1
graphic, 2-3
positioning, 2-10
text, 2-1
firmware version, 3-6
flash memory graphics, 2-5
fonts
modified, 4-4
resident, 4-1
sizes, 4-1
formats
definition, 2-1
printing and creating, 2-1
formatting text, 2-2
G
graphics
data stream, 2-4
fields, 2-3
flash memory, 2-5
H
handheld, communicating with, 3-7
hardware version, 3-6
I
initialization of printer, 3-8
Interleaved 2 of 5 bar codes, 2-8
introduction, 1-1
L
loading new characters, 4-4
M
magnetic card reader
errors, 5-3
using, 5-1
manual, conventions in, 1-2
Page 41

Index-3
mode
buffer, 3-1
online, 3-1
operating, 3-1
power, 3-2
modifying resident fonts, 4-1
O
online mode, 3-1
operating mode, selecting, 3-1
P
positioning fields, 2-10
power mode, setting, 3-2
power-off timer, using, 3-3
print buffer status, checking, 3-3
print contrast, setting, 3-1
printer
configuring, 3-1
initialization, 3-8
supply control responses, 3-6
printing formats, 2-1
R
resident fonts, modifying, 4-1
responses (supply control), 3-6
S
sample application, A-1
saving modified fonts, 4-4
scanner, bar code, 6-1
selecting
character sets (creating text fields),
2-2
character sets (font modification), 4-3
operating mode, 3-1
setting
power mode, 3-2
print contrast, 3-1
sizes of fonts, 4-1
status, print buffer, 3-3
supplies, black mark, 3-5
T
text
fields, creating, 2-1
formatting, 2-2
timer, power-off, 3-3
U
UPC/EAN/JAN bar codes, 2-8
using
bar code scanner, 6-1
data stream graphics, 2-4
flash memory graphics, 2-5
magnetic card reader, 5-1
power-off timer, 3-3
V
version information, checking, 3-6
voltage, battery, 3-2
Page 42

Index-4
Page 43

Page 44

For supplies, service, or assistance call toll free:
1-800-543-6650 (In the U.S.A.)
1-800-263-4650 (In Canada)
www.monarch.com
 Loading...
Loading...