Page 1
Hardware and Engineering
DF5-...
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
1st published 2001, edition 09/01
© Moeller GmbH, Bonn
Author: Holger Friedrich, Jörg Randermann
Editor: Michael Kämper
Translator: David Long
All brand and product names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of the owner concerned.
All rights reserved, including those of the translation.
No part of this manual may be reproduced in any form
(printed, photocopy, microfilm or any otherprocess) or processed,
duplicated or distributed by means of electronic systems without
written permission of Moeller GmbH, Bonn.
Subject to alterations without notice.
Page 2

Warning!
Dangerous electrical voltage!
Before commencing the installation
• Disconnect the power supply of the device.
• Ensure that devices cannot be accidentally restarted.
• Verify isolation from the supply.
• Earth and short circuit.
• Cover or enclose neighbouring units that are live.
• Follow the engineering instructions (AWA) of the
device concerned.
• Only suitably qualified personnel in accordance with
EN 50 110-1/-2 (VDE 0105 Part 100) may work on this
device/system.
• Before installation and before touching the device ensure
that you are free of electrostatic charge.
• The functional earth (FE) must be connected to the protective
earth (PE) or to the potential equalisation. The system installer
is responsible for implementing this connection.
• Connecting cables and signal lines should be installed so
that inductive or capacitive interference do not impair the
automation functions.
• Install automation devices and related operating elements in
such a way that they are well protected against unintentional
operation.
• Suitable safety hardware and software measures should be
implemented for the I/O interface so that a line or wire
breakage on the signal side does not result in undefined
states in the automation devices.
• Ensure a reliable electrical isolation of the low voltage for the
24 volt supply. Only use power supply units complying with
IEC 60 364-4-41 (VDE 0100 Part 410) or HD 384.4.41 S2.
• Deviations of the mains voltage from the rated value must
not exceed the tolerance limits given in the specifications,
otherwise this may cause malfunction and dangerous
operation.
• Devices that are designed for mounting in housings or control
cabinets must only be operated and controlled after they have
been installed with the housing closed. Desktop or portable
units must only be operated and controlled in enclosed
housings.
• Measures should be taken to ensure the proper restart of
programs interrupted after a voltage dip or failure. This should
not cause dangerous operating states even for a short time.
If necessary, emergency-stop devices should be implemented.
• Wherever faults in the automation system may cause
damage to persons or property, external measures must be
implemented to ensure a safe operating state in the event of
a fault or malfunction (for example, by means of separate limit
switches, mechanical interlocks etc.).
• According to their degree of protection frequency inverters may
feature during operation live, bright metal, or possibly moving,
rotating parts or hot surfaces.
• The impermissible removal of the necessary covers, improper
installation or incorrect operation of motor or frequency
inverter may cause the failure of the device and may lead to
serious injury or damage.
• The relevant national regulations apply to all work carried on
live frequency inverters.
• The electrical installation must be carried out in accordance
with the relevant regulations (e. g. with regard to cable cross
sections, fuses, PE).
• All work relating to transport, installation, commissioning and
maintenance must only be carried out by qualified personnel.
(IEC 60 364 and HD 384 and national work safety regulations).
• Installations fitted with frequency inverters must be provided
with additional monitoring and protective devices in
accordance with the relevant safety regulations etc.
Modifications to the frequency inverters using the operating
software are permitted.
• Emergency stop devices complying with IEC/EN 60 204-1 must
be effective in all operating modes of the automation devices.
Unlatching the emergency-stop devices must not cause restart.
Moeller GmbH
Safety instructions
I
Page 3

• All shrouds and doors must be kept closed during operation.
• In order to reduce hazards to persons or equipment, the user
must include in the machine design measures that restrict the
consequences of a malfunction or failure of the drive
(increased motor speed or sudden standstill of motor).
These measures include:
– Other independent devices for monitoring safety-related
variables (speed, travel, end positions etc.).
– Electrical or non-electrical system related measures
(interlocks or mechanical interlocks).
– Live parts or cable connections of the frequency inverter
must not be touched after it has been disconnected from the
power supply due to the charge in capacitors. Appropriate
warning signs must be provided.
II
Page 4
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Contents
About this Manual 5
Abbreviations and symbols 5
1 About DF5 series frequency inverters 7
System overview 7
Type code 8
Inspecting the items supplied 9
Layout of the DF5 10
– Frequency inverter characteristics 11
Selection criteria 11
Intended use 12
Service and guarantee 12
2 Engineering 13
Features of the DF5 13
Connection to the mains 14
– Electrical grid types 14
– Mains voltage, Mains frequency 14
– Interaction with compensation devices 15
– Fuses and cable cross-sections 15
– Protection of persons and domestic animals
with residual-current protective devices 15
– Mains contactor 16
– Current peaks 16
– Mains choke 16
– Line filter, Radio interference filter 16
EMC guidelines 17
– EMC interference class 17
3 Installation 19
DF5 Installation 19
– Mounting position 19
– Installation dimensions 20
– DF5 attachment 21
EMC compliance 22
– EMC compliant installation 22
– Radio interference filter usage 22
– EMC measures in the control panel 23
– Grounding 24
– Screening 24
Electrical connection 26
– Connecting the power section 28
– Connecting the signalling relay 36
– Connecting the control signal terminals 38
1
Page 5

Contents
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
4 DF5 Operation 43
Initial startup 43
LCD keypad 44
Operation with LCD keypad 44
– Menu overview 44
– Changing display and basic parameters 45
– Changing the parameters of the extended
parameter groups 46
Display after the supply voltage is applied 47
Operational warning message 48
5 Programming the control signal terminals 49
Overview 49
Frequency display FM 52
– Analog frequency display 52
– Digital frequency display 53
Programmable digital inputs 1 to 5 54
Start/Stop 55
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4 selection 56
– Current setpoint value AT (4 to 20 mA) 58
– Second time ramp 2CH 59
– Controller inhibit and coasting of the
motor FRS (free run stop) 60
– External fault message EXT 61
– Restart inhibit USP 62
– Reset: RST 63
–Jog mode (JOG) 64
– PTC thermistor input: PTC 65
– Software protection SFT 66
Programmable digital outputs 11 and 12 67
Frequency value messages FA1/FA2 68
– RUN operational 70
– Overload message OL 71
– PID controller deviation message OD 72
– Error message AL 73
Signalling relay terminals K11, K12, K14 74
2
Page 6

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Contents
6 Setting Parameters 75
Setting the display parameters 75
Basic functions 76
– Input/display frequency value 76
– Acceleration time 1 76
– Deceleration time 1 77
– Direction of rotation 77
Setting the frequency and start command parameters 78
– Definition of frequency setpoint value 78
– Start command 78
– Base frequency 79
– Maximum end frequency 79
Analog setpoint value matching 80
Voltage/frequency characteristics and boost 81
DC braking (DC-Break) 82
Operating frequency range 83
PID controller 84
– The PID closed-loop control 84
– Structure and parameters of the PID controller 87
– Example for setting K
and T
p
i
92
– Application examples 93
Automatic voltage regulation (AVR) 95
Time ramps 96
Automatic restart after a fault 97
Electronic motor protection 98
Current limit 99
Parameter protection 100
Magnetizing current 100
Other functions 101
– Carrier frequency 101
– Initialization 101
– Country version 101
– Frequency factor for display via PNU d07 101
– Inhibit of the OFF key 102
– Motor restart after cancellation of the FRS signal 102
– Display when a remote operating unit is used 102
7 Messages 103
Fault messages 103
Other messages 104
8 Fault correction 105
3
Page 7
Contents
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Appendix 107
Technical Data 107
Dimensions and weights 111
Cables and fuses 112
Mains contactors 113
Radio interference filter 115
Mains choke 116
Connection examples 117
– Operation through an external potentiometer 117
– Operation through an analog setpoint value 117
– Operation with fixed frequencies 118
Abbreviations of parameters and functions 119
Standard form for user defined parameter settings 120
®
UL
Caution, Warnings and Instructions 125
– Preparation for Wiring 125
– Determination of Wire and Fuse Sizes 125
– Terminal Dimensions and Tightening Torque 126
Index 127
4
Page 8
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
About this Manual
This manual describes the frequency inverters of the DF5 series.
This manual contains special information which is required for
engineering, installation and operation of the DF5 series frequency
inverters. The features, parameters and functions are described in
detail and illustrated by the use of examples for the most important applications. All the details stated relate to the hardware and
software versions specified.
Abbreviations and symbols
Abbreviations and symbols with the following meanings are
described in this manual:
EMC: Electro Magnetic Compatibility
ESD: Electro static discharge
(Electro Static Discharge)
HF: High Frequency
IGBT: Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
PES: PE – connection (earth) of the screen (cable)
PNU: Parameter Number
WE: Factory default setting
All measurements are in millimeters unless otherwise stated.
In some of the illustrations, the enclosure of the frequency inverter
as well as other safety relevant parts may be omitted for the
purpose of improved visualization. However, the frequency
inverter must always be operated in the enclosure with all necessary safety relevant parts and components.
Read the manual carefully before you install and operate the
frequency inverter. We assume that you have a good knowledge
of engineering fundamentals and that you are familiar with the
electrical systems and the principles which apply, and are able to
read, understand and apply information contained in technical
drawings.
X indicates instructions to be followed
Makes you aware of interesting tips and additional
h
information
Caution!
warns about the possibility of minor material damage.
Warning!
warns about the possibility of major material damage and
minor injury.
Warning!
warns about the possibility of major material damage and
severe injury or death.
In order to improve the readability, the title of the chapter is indicated on the top of the left-hand page and the current section is
indicated on the top of the right-hand page. Pages where chapters
commence and blank pages at the end of the chapter are an
exception.
5
Page 9

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
6
Page 10
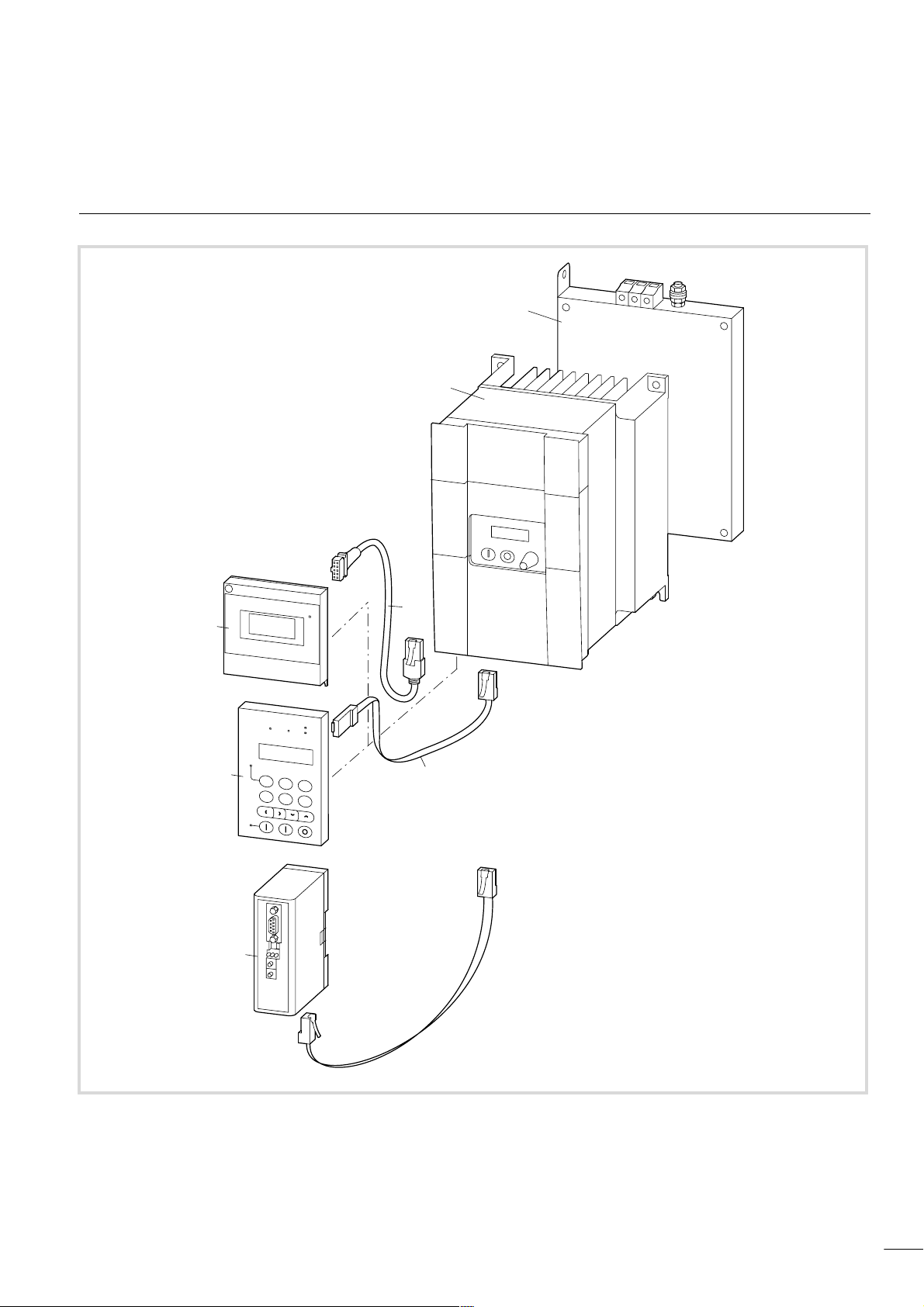
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
1 About DF5 series frequency inverters
System overview
a
b
g
f
c
d
e
Figure 1: System overview
a DF5 series frequency inverters-...
b DE5-LZ... RFI filter
c DE5-CBL-...-ICL connection cable
d DEX-CBL-...-ICS connection cable
e DE5-NET-DP interface module for PROFIBUS-DP
f DEX-DEY-10 external keypad
g DE5-KEY-RO3 external display module
7
Page 11
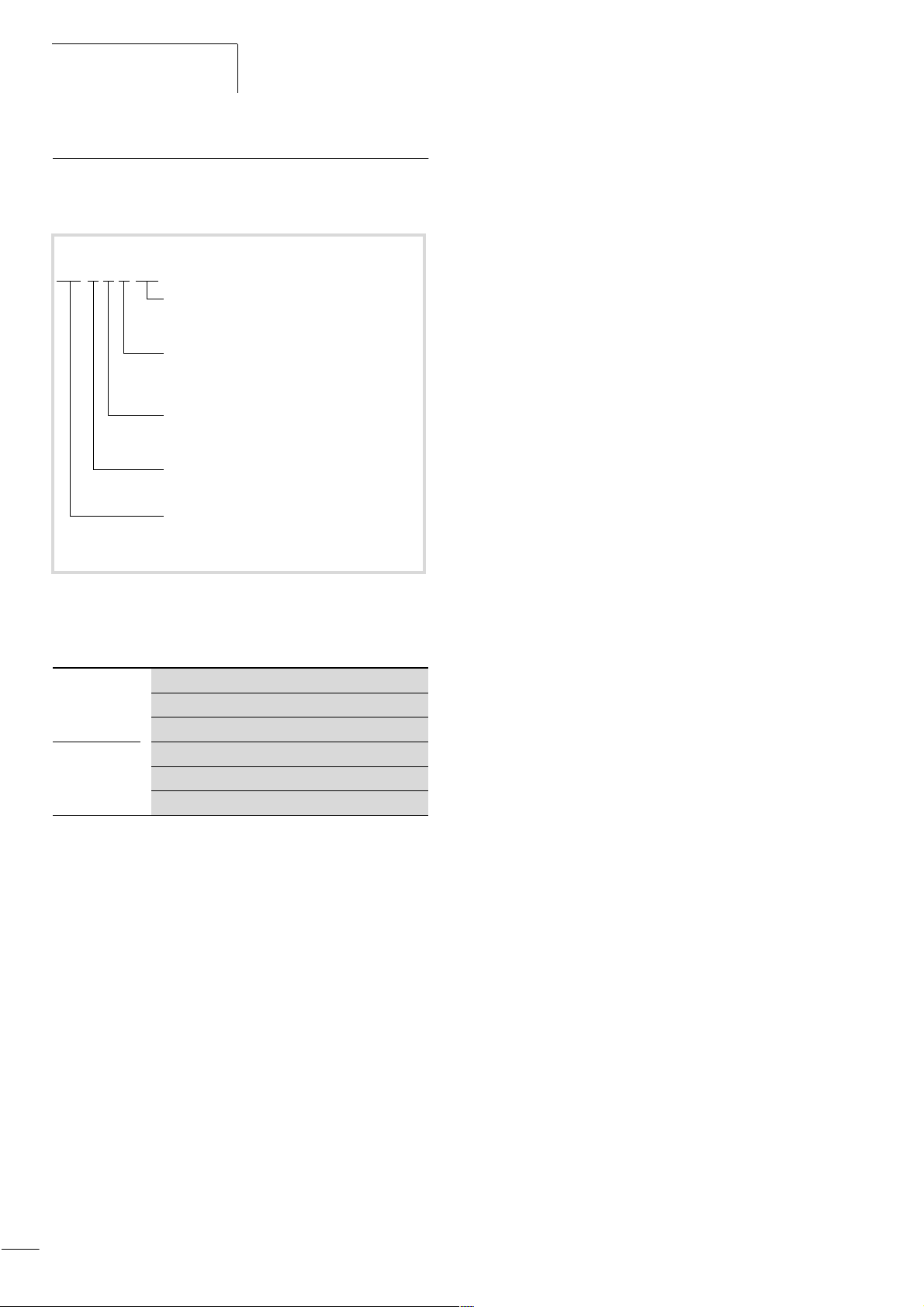
About DF5 series frequency
inverters
Type code
Type code and type designation of the DF5 series frequency
inverter:
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
DF5-xxx-yyy
Motor rating code
Incoming supply: EU rated voltage (230 V/400 V)
Version and model number
0 = basic version
1 = system devices
2 = voltage code suffix
Supply connection, voltage code (EU rated value)
2 = 230 V (180 V – 0 % to 252 V + 0 %)
4 = 400 V (342 V – 0 % to 506 V + 0 %)
Supply connection, phase code
1 = single-phase
3 = three-phase
Family name:
Drives Frequency Inverter, Generation 5
Figure 2: Type code DF5 series frequency inverters
Examples:
DF5-322-075
DF5-340-5K5
Frequency inverters of the DF5 series
Single-phase or three-phase supply: 230 V
Assigned motor rating: 0.75 kW at 230 V
Frequency inverters of the DF5 series
Three-phase mains supply voltage: 400 V
Assigned motor rating: 5.5 kW at 400 V
8
Page 12
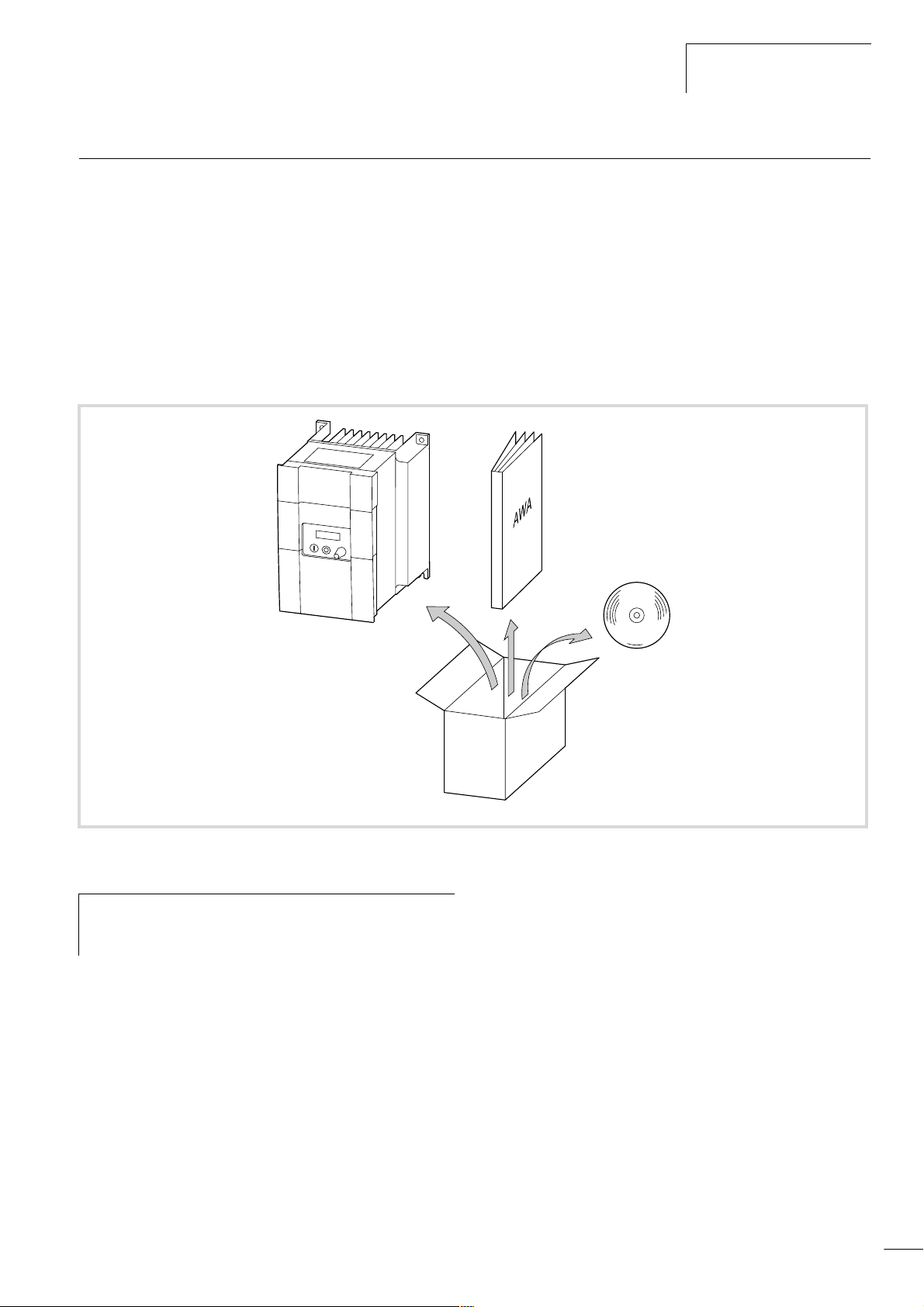
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Inspecting the items supplied
Inspecting the items supplied
Frequency inverters of the DF5 series frequency inverters are carefully packed before delivery. The device may be transported only in
its original packaging with a suitable transport system (see weight
details). Observe the instructions and the warnings on the side of
the packaging. This also applies after the device is removed from
the package.
Open the packaging with suitable tools and inspect the contents
immediately after delivery to ensure that they are complete and
undamaged. The package must contain the following items:
• a DF5 series frequency inverter,
• the installation instructions AWA8230-1935,
• a CD with:
– this manual in PDF format as well as in further languages
– the parameter definition software;
the requirements are: A PC with Windows 95, 98, ME, 2000,
NT and the DEX-CBL-2M0-PC connection cable
Figure 3: Equipment supplied
Using the nameplate attached to the frequency inverter,
h
check to ensure that the frequency inverter is the type
which you have ordered.
9
Page 13

About DF5 series frequency
inverters
Layout of the DF5
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
m e
Figure 4: Designations of the DF5
a Front cover, can be opened without tools
b Integrated keypad
c Terminal shroud
d Front cover flap with keypad
e Signalling relay terminals
f Heat sink
g Optional radio interference filter
e
j
k
l
cab
i
h
h Power terminals
i Screw for opening the front enclosure
j Control signal terminals
k Enclosure
l Earth connection (PE)
m Interface connection
e
d
f
g
10
Page 14
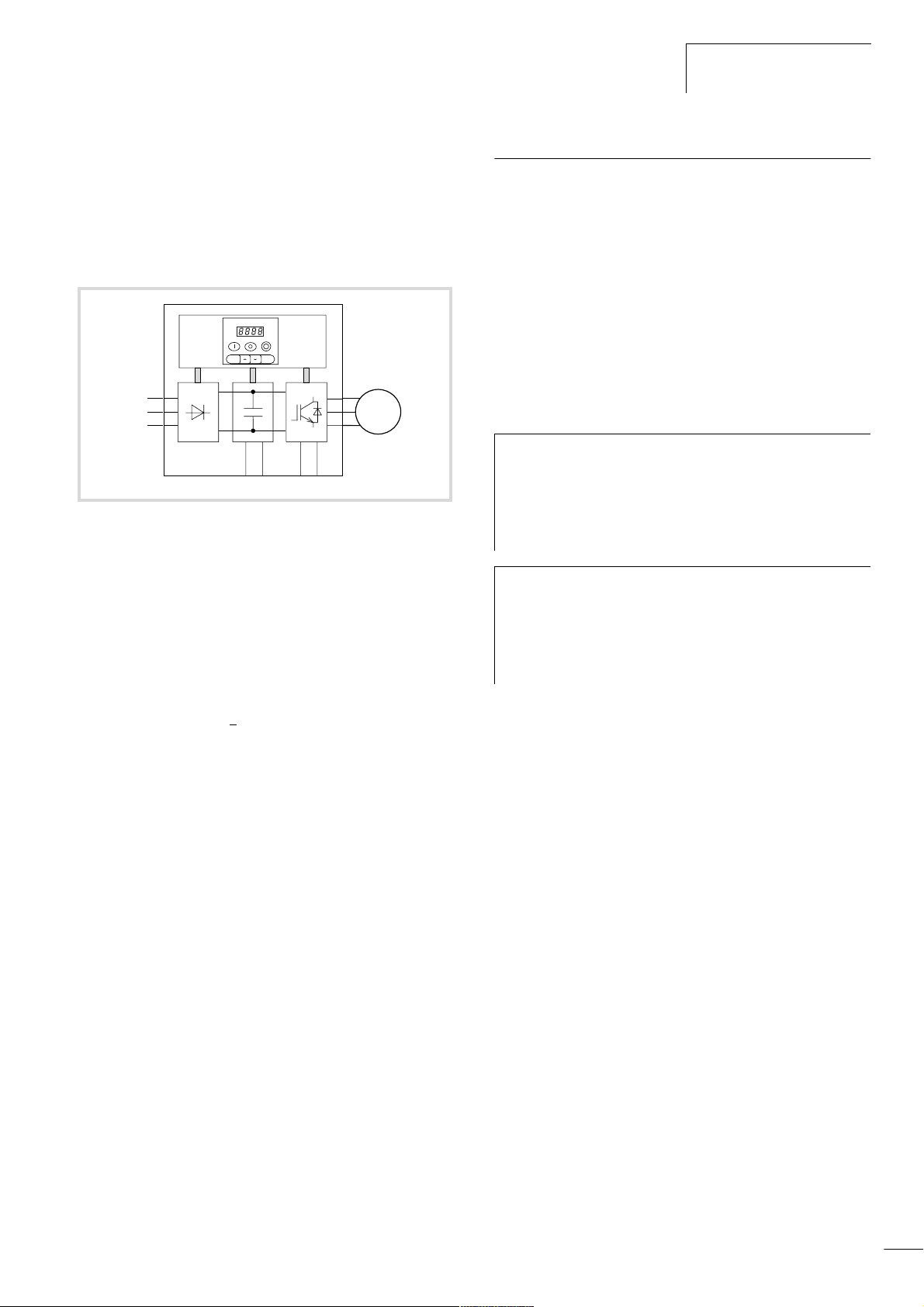
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Selection criteria
Frequency inverter characteristics
The DF5 series convert the voltage and frequency of an existing
three-phase supply to a DC voltage and use this voltage to generate a three-phase supply with adjustable voltage and frequency.
This variable three-phase supply allows stepless variability of
three-phase asynchronous motors.
f
h
a
bc d
Figure 5: Functional diagram of the frequency inverter
a Supply via an interference suppressor
Mains voltage U
-322 1/3 AC 230 V, 50/60 Hz
DF5
-340 3 AC 400 V, 50/60 Hz
DF5
b The bridge rectifiers convert the AC voltage of the electrical supply to
a DC voltage.
c The DC link contains a charging resistor, smoothing capacitor and
switched-mode power supply unit. It enables coupling of the DC bus
voltage and the DC current supply:
DC bus voltage (U
d IGBT power inverter:
The power inverter converts the DC voltage of the DC link to a variable
three-phase alternating voltage with variable frequency.
e Output voltage (U
three-phase, variable AC voltage, 0 to 100 % of the input voltage
)
(U
LN
Output frequency (f
Variable frequency, 0.5 to 360 Hz
Output rated current (I
1.8 to 22.5 A with about 1.5 times the starting current for 60 s, with
a switching frequency of 5 kHz and with an ambient temperature of
40 °C
Motor connection, assigned shaft output (P
0.18 to 2.2 kW at 230 V
0.37 to 7.5 kW at 400 V
f Programmable control section with keypad and interface.
(EU-rated voltage):
LN
) = W2 x mains voltage (ULN)
ZK
), motor connection:
2
):
2
):
2N
2
M
3
˜
e
):
Selection criteria
The frequency inverter is selected to suit the rated motor current.
The output rated current of the frequency inverter must however,
be greater than or equal to the rated motor current.
The following drive data is assumed to be known:
• type of motor (three-phase asynchronous motor),
• mains voltage = supply voltage of the motor (e.g. 3 ~ 400 V),
• rated motor current (guide value, dependent on the circuit type
and the supply voltage),
• load torque (quadratic, constant, with 1.5-times the starting
torque),
• ambient temperature (maximum temperature 40 °C).
With the parallel connection of multiple motors to the
h
output of a frequency inverter, the motor currents are
subject to vector addition, i.e. the active in-phase current
and reactive current components are added separately.
Select the frequency inverter rating to ensure that the
total current can be supplied by the frequency inverter.
If a motor switches during operation on the output of a
h
frequency inverter, the motor draws a multiple of its rated
current. Select the rating of the frequency inverter to
ensure that the starting current plus the sum of the
currents of the running motors does not exceed the rated
output current of the frequency inverter.
The rated output current of the frequency inverter can be found in
the technical data in the Appendix from Page 107.
11
Page 15

About DF5 series frequency
inverters
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Intended use
The DF5 series frequency inverters are not domestic appliances.
They are designed only for industrial use as system components.
The DF5 series frequency inverters are electrical apparatus for
controlling variable speed drives with three-phase motors. They
are designed for installation in machines or for use in combination
with other components within a machine or system.
After installation in a machine, the frequency inverters must not be
taken into operation until the associated machine has been
confirmed to comply with the safety requirements of Machinery
Safety Directive (MSD) 89/392/EEC and meets the requirements of
EN 60204. The user of the equipment is responsible for ensuring
that the machine use complies with the relevant EU Directives.
The CE-mark attached to the DF5 series frequency inverters
confirm that, when used in a typical drive configuration, the
apparatus complies with the European Low Voltage Directive
(LVD) and the EMC Directives (Directive 73/23/EEC, as amended
by 93/68/EEC and Directive 89/336/EEC, as amended by 93/68/
EEC).
Frequency inverters of the DF5 series are suitable for use in public
and non-public networks in the described system configuration.
Depending on their location of use, external filtering may be
necessary.
Service and guarantee
In the unlikely event that you have a problem with your Moeller
frequency inverter, please contact your local sales office.
Please have the following data and information concerning the to
hand:
• exact frequency inverter type designation (a nameplate)
• date of purchase
• exact description of the problem which has occurred with the
frequency inverter.
If some of the information printed on the nameplate is not legible,
please state only the information which is clearly legible.
Information concerning the guarantee can be found in the Moeller
General Terms and Conditions of Sale.
Connection to IT networks (networks without a ground potential
reference point) is not permitted as the devices internal filter capacitors connect the network to the ground potential (enclosure). On
earth free networks, this can lead to dangerous situations or
damage to the device (isolation monitoring required).
On the output of the frequency inverter (terminals U, V, W) you
may not:
• connect a voltage or capacitive loads (e.g. phase compensation
capacitor),
• connect multiple frequency inverters in parallel,
• make a direct connection to the input (bypass).
Observe the technical data and terminal requirements. Refer to the
equipment nameplate or label and the documentation for more
details.
Any other usage constitutes improper use.
12
Page 16
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
2 Engineering
This chapter describes the ”Features of the DF5” as well as guidelines and regulations concerning the following subjects:
• Connection to the mains
• EMC guidelines
Features of the DF5
Ambient temperatures
Operation
Storage Ta = –25 to +70 °C
Transport
Permissible ambient influences
Resistance to vibration Vibrations and shaking: maximum 5.9 m/s2 (0.6 g) at 10 to 55 Hz
Pollution degree
Packaging
Climatic conditions
Installation altitude
Mounting position
Free surrounding areas
Electrical data
Emitted interference IEC/EN 61800-3 (EN 55011 group 1, class B)
Noise immunity
Insulation resistance
Leakage current to PE
Degree of protection
Protection against direct contact
Protective isolation against switching circuitry
Protective measures
Control/regulation
Modulation method Pulse width modulation (PWM), V/f-predetermined control (linear,quadratic)
Switching frequency
Torque
Output frequency
Relay
1)
Range 0.5 to 360 Hz
Frequency resolution
Error limit at 25 °C g10 °C
Changeover contact • AC 250 V, 2.5 A (resistive load)
Ta = –10 to +40 °C with rated current Ie without derating,
up to +50 °C with reduced carrier frequency of 2 kHz and reduced output current to 80 % I
Ta = –25 to +70 °C
VDE 0110 Part 2, pollution degree 2
Dust proof packaging (DIN 4180)
Class 3K3 according to EN 50178 (non-condensing, average relative humidity 20 to 90 %)
Up to 1000 m above sea level
Vertically suspended
100 mm above and below device
IEC/EN 61800-3, industrial environment
Overvoltage category III according to VDE 0110
Greater than 3.5 mA according to EN 50178
IP20
Finger and back-of-hand proof (VBG 4)
Safe isolation from the mains. Double basic isolation according to EN 50178
Overcurrent, earth fault, overvoltage, undervoltage, overload, overtemperature, electronic motor
protection: I
5 kHz (WE), can be selected between 0.5 and 16 kHz
At start 1.5 x MN for 60 s with assigned motor rating, every 600 s
0.1 Hz, at digital setpoint, maximum frequency/1000 with analog setpoint
Digital setpoint definition g0.01 % of the maximum frequency
Analog setpoint definition g0.2 % of the maximum frequency
• AC 250 V, 0.2 A (inductive load, cos v = 0.4)
• AC 100 V, minimum 10 mA
• DC 30 V, 3 A (resistive load)
• DC 30 V, 0.7 A (inductive load, cos v = 0.4)
• DC 5 V, minimum 100 mA
2
t monitoring and PTC input (thermistor or temperature contacts)
e
13
Page 17
Engineering
Internal voltages
Control 24 V DC, maximum 30 mA
Setpoint value definition
Analog and digital actuation
Analog inputs • 1 input, 0 to 10 V, input impedance 10 kO
Digital inputs/outputs
Monitor output
Keypad (integrated)
Operation 6 function keys for control and parameter definition of the DF5
Display
Potentiometer
1) If the frequency inverter is to be installed in a control panel, enclosure or similar installation, the prevalent ambient temperature within these enclosures or control panels is considered to be the ambient temperature T
remains within permissible limits.
10 V DC, maximum 10 mA
• 1 input, 4 to 20 mA, load impedance 250 O
5 Freely programmable inputs
2 Outputs, open collector (maximum 27 V DC, 50 mA)
1 output for frequency or current, 10 V, maximum 1 mA
Four character 7 segment display and seven LEDs (status messages)
Setpoint definition (0 to 270°)
. The use of fans should be considered to ensure that the ambient temperature
a
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Connection to the mains
The DF5 series frequency inverters can be used without limitation
with every type of electrical grid (Electrical grids according to
IEC 364
-3).
Electrical grid types
Electrical grids with a direct earthing point (TT/TN
-systems):
• Operation of the frequency inverters of the DF5 series with TT
-systems is possible without limitation. Adhere to the rated
TN
data of the DF5 series frequency inverters.
If many frequency inverters with a single-phase supply are
h
connected to the mains, the symmetric distribution on all
three mains poles should be considered as well as the
loading of the common neutral pole (mains r.m.s current).
If necessary, the cross-section of the neutral pole must be
increased, if it conducts the total current of all singlephase devices.
Grids with isolated centre point (IT
-systems):
• Operation of the frequency inverters of the DF5 series with
IT
-systems is only conditionally possible. A prerequisite is a
suitable device (isolation monitoring), which monitors earth
faults and isolates the frequency inverter from the mains.
Caution!
With an earth fault in an IT
-system, the capacitors of the
frequency inverter which are switched to earth are subject
to a very high voltage. Therefore, safe operation of the
frequency inverter cannot be guaranteed. The situation
can be remedied with an additional isolating transformer
with an earthed centre point on its secondary, which is
then used to supply the input of the frequency inverter.
This constitutes an individual TN-system for the frequency
-/
inverter.
Mains voltage, Mains frequency
The rated data for the frequency inverters of the DF5 take the
European and American standard voltages into account:
• 230 V, 50 Hz (EU) and 240 V, 60 Hz (USA) with DF5-322,
• 400 V, 50 Hz (EU) und 460 V, 60 Hz (USA) with the DF5-340
The permitted mains voltage range is:
• 230/240 V: 180 V – 0% to 252V+0%
• 400/460 V: 342 V – 0% to 506V+0%
The permissible frequency range is 47 Hz – 0% to 63Hz+0%.
The device assignment of the motor rating to the mains voltage is
listed in Section ”Technical Data”, Page 107 in the Appendix.
14
Page 18
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Connection to the mains
Interaction with compensation devices
The DF5 series frequency inverters only accept a minimal fundamental reactive power from the AC voltage supply. Compensation
is therefore unnecessary.
Caution!
Operation of the frequency inverters of the DF5 series on
the mains with p.f. correction equipment is only permitted
when this equipment is dampened with chokes.
Fuses and cable cross-sections
When the devices are connected to the mains, the fuses and cable
cross-sections which are required are dependent on the rating of
the frequency inverter and the operation mode of the drive.
Caution!
The voltage drop under load conditions should be considered when selecting the cable cross-section. Compliance
to further standards (e.g. VDE 0113, VDE 0289) is the
responsibility of the user.
The recommended fuses and the assignment of the DF5 series
frequency inverters are listed in Section ”Cables and fuses”,
Page 112 in the Appendix.
The national and regional standards (e.g. VDE 0113, EN 60204)
must be observed and the necessary approvals (e.g. UL) at the site
of installation must be fulfilled.
When the device is operated in a UL
-approved fuses, fuse bases and cables can be used.
UL
-approved system, only
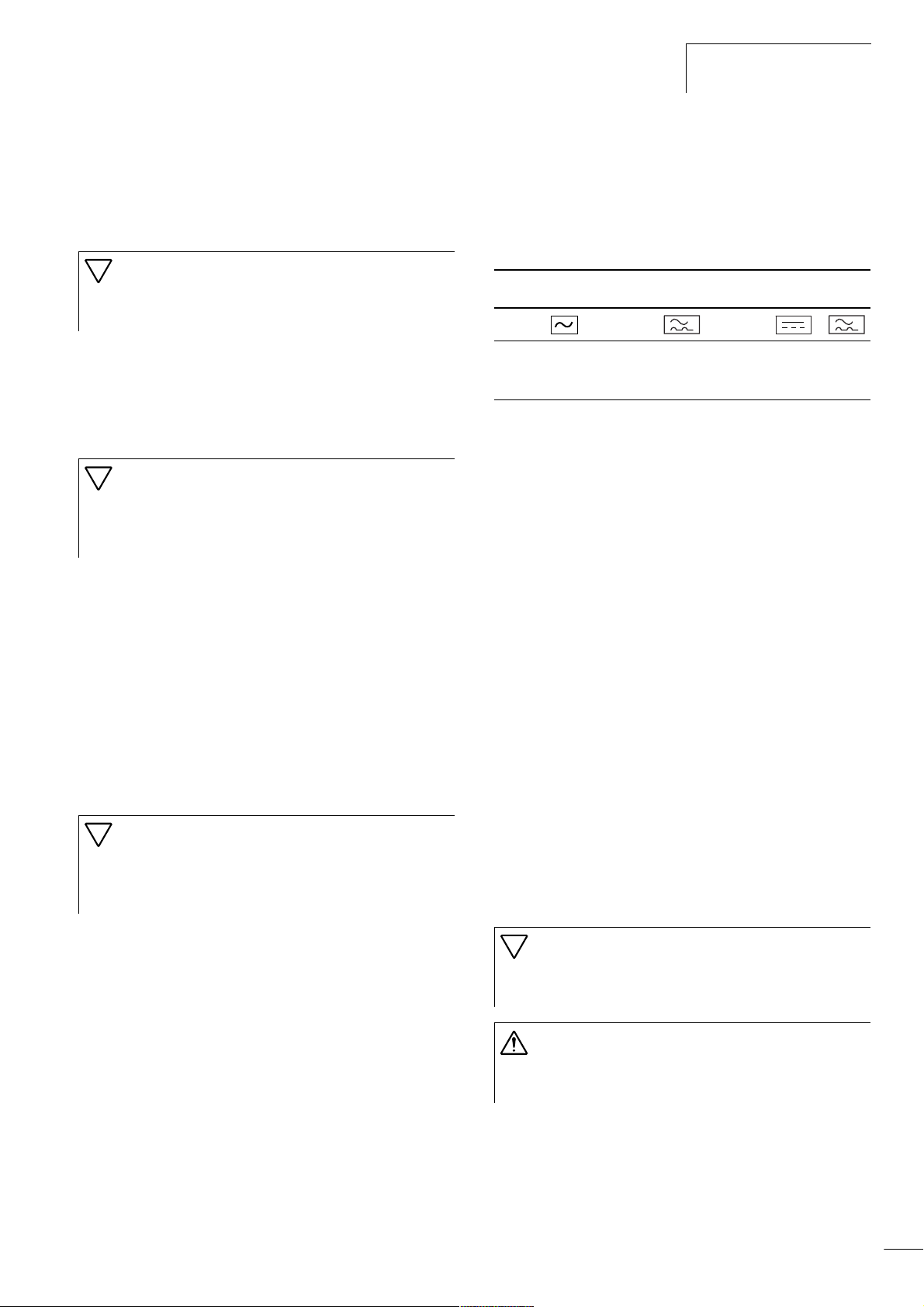
Protection of persons and domestic animals with residualcurrent protective devices
Residual-current circuit-breakers RCCB (according to VDE 0100,
also referred to as ELCBs). Universal current sensitive ELCBs according to EN 50178 and IEC 755.
Identification on the residual-current circuit-breakers
Logo
Type alternating
current sensitive
(RCCB, Type AC)
pulse current
sensitive
(RCCB, Type A)
universal current
sensitive
(RCCB, Type B)
The frequency inverter is internally equipped with a mains rectifier.
With a short circuit to an exposed conductive part, a fault DC
current can block the trip of the alternating current sensitive or
pulse current sensitive residual-current circuit-breaker and thus
eliminate the protective function. We therefore recommend the
use of:
•“Pulse current sensitive residual-current circuit-breakers” with
a rated current f 30 mA with frequency inverters with a singlephase supply ( .
•”Universal current sensitive residual-current circuit-breakers”
with a rated current f 300 mA with frequency inverters with a
single-phase supply on frequency inverters with three-phase
supply .
The fault current recommended values of the DF5 series frequency
inverters and the assigned radio interference filter are listed in
Section ”Radio interference filter”, Page 115 in the Appendix.
The leakage currents to ground (according to EN 50178) are
greater than 3.5 mA. The PE terminal and the enclosure must be
connected to the earth-current circuit.
Caution!
The prescribed minimum cross-sections of PE-conductors
(EN 50178, VDE 0160) must be observed. Select the
cross-section of the PE
-conductor as least as large as the
terminal capacity of the power terminals.
Spurios tripping of a residual-current circuit-breaker can be
activated by the following:
• by capacitive compensation currents of the cable screens,
particularly with long screened motor cables,
• by simultaneous connection of multiple frequency inverters to
the mains supply,
• with the use of additional chokes and filters (radio interference
filter, line filter).
Caution!
Residual-current circuit-breakers may only be installed on
the primary side between the incoming supply and the
frequency inverter.
Warning!
Only use cables, residual-current circuit-breakers and
contactors which have a suitable rating. Otherwise there
is a danger of fire.
15
Page 19
Engineering
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Mains contactor
The mains contactor is connected to the mains side input cables
L1, L2, L3 (type dependant). It allows the operational switch on
and off of the DF5 series frequency inverters from the mains supply
as well as shutdown during a fault.
Mains contactors and the assignment with the DF5 series
frequency inverters are listed in Section ”Mains contactors”,
Page 113 in the Appendix.
Current peaks
In the following cases, a relatively high peak current can occur on
the primary side of the frequency inverter (i.e. on the supply
voltage side), which under certain conditions, can destroy the
input rectifier of the frequency inverter:
• Imbalance of the voltage supply greater than 3 %.
• The maximum power output of the supply point must be at least
10 times greater than the maximum frequency inverter rating
(approx 500 kVA).
• If sudden voltage dips in the supply voltage are to be expected,
e.g. :
– a number of frequency inverters are operated on a common
supply voltage.
– a Thyristor system and a frequency inverter or operated on a
common supply voltage.
– power factor correction devices are switched on or off.
In the cases mentioned, a mains choke with approx. 3 % voltage
drop at rated operation should be installed.
Mains choke
The mains choke (also referred to as a commutating choke or line
reactor) is connected to the mains side input cables L1, L2, L3 (type
dependent). It reduces the harmonics and leads to a reduction of
the apparent mains current by up to 30 %.
A mains choke also limits current peaks which occur, caused by
potential dips (e.g. caused by p.f. correction equipment or earth
faults) or switching operations on the mains.
The mains choke increases the lifespan of the DC link capacitors
and consequently the lifespan of the frequency inverter. Its use is
also recommended:
• with a single-phase supply (DF5-322),
• with derating (temperatures above +40 °C, sites of installation
which are more than 1000 m above sea level),
• with parallel operation of multiple frequency inverters on a
single mains supply point,
• with DC link coupling of multiple frequency inverters
(interconnected operation).
Mains chokes and the assignment to DF5 series frequency inverters are listed in Section ”Mains choke”, Page 116 in the
Appendix.
Line filter, Radio interference filter
Line filters are a combination of mains chokes and radio interference filters in a single enclosure. They reduce the current harmonics and dampen high frequency radio interference levels.
Radio interference filters only dampen high frequency radio interference levels.
16
Caution!
When line filters or radio interference filters are used, the
leakage current to earth increases. Observe this point
when residual-current circuit-breakers are used.
Page 20

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
EMC guidelines
EMC guidelines
The limit values for emitted interference and immunity with variable speed drives are described in the IEC/EN 61800
-3 product
standard.
When operating the frequency inverters of the DF5 series in coun-
tries which are part of the European Union (EU), the EMC guideline
89/336/EEC must be observed. The following conditions described
must be observed in order to comply with this guideline:
Supply voltage (mains voltage) for the frequency inverter:
• voltage fluctuation g10 % or less
• voltage imbalance g3% or less
• frequency variation g4 % or less
If the above mentioned conditions are not fulfilled, the respective
mains choke must be installed (a Section ”Mains choke” in the
Appendix, Page 116).
EMC interference class
When installation is completed according to the Section ”Installa-
tion”, described in ”EMC guidelines” Page 17 and with the use of
a radio interference filter, the frequency inverters of the DF5 series
comply to the following standards:
• Emitted interference:
IEC/EN 61800-3 (EN 55011 group 1, class B)
• Noise immunity:
EN 61800-3, industrial environment
Noise immunity
DF5 series frequency inverters conform with the requirements of
the EC/EN 61800
-3 EMC-product standard for industrial use
(second environment), and the higher interference immunity
values in domestic environments (first environment) with the
assigned radio interference filters.
A domestic environment can be understood to be a connection
point (transformer feeder) to which domestic households are also
connected.
The EMC
-guideline for an industrial system requires electromag-
netic compatibility with the environment as a whole. The product
standard examines a typical drive system in principle as a complete
system, i.e. the combination of frequency inverter, cables and
motor.
Emitted interference and radio interference suppression
DF5 series frequency inverters conform with the requirements of
the EC/EN 61800
-3 EMC-product standard for domestic use (first
environment), and therefore also with the higher interference
immunity values in industrial environments (second environment)
with the assigned radio interference filters.
Ensure compliance to the limit values with the following points:
• reduction of performance related interference with line filters
and/or radio interference filters including mains chokes.
• reduction of the electromagnetic emission interference by
screening motor cables and signal cables.
• compliance with installation guidelines (EMC compliant
installation).
With frequency inverters, performance related and emitted interference increase with the switching frequency. The frequency of
occurrence of performance related interference also increase with
longer motor cables. When the respective radio interference filter
is used, the EN 61800-3 standard is complied to as follows:
Conformity
General Limited
First environment
(Public power grid)
Second environment (Industrial)
1) This is a product with limited conformity according to IEC/
EN 61800-3. This product can cause radio frequency interference in
domestic environments. In this case, it is necessary that the user
undertakes the required protection measures.
Up to 10 m motor cable
lengths with 16 kHz
(maximum switching
frequency)
Up to 20 m motor cable
lengths with maximum
5 kHz switching frequency
Up to 50 m Up to 50 m
Up to 50 m
1)
17
Page 21

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
18
Page 22
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
3 Installation
The DF5 series frequency inverters should be installed in a control
panel or in a metal enclosure (e.g. IP54).
During installation or assembly operations on the
h
frequency inverter, all ventilation slots and openings
should be covered to ensure that foreign bodies and
objects do not penetrate the device.
DF5 Installation
The DF5 series frequency inverters must be installed vertically on a
non-flammable base.
Mounting position
F 30˚
F 30˚
Figure 6: Mounting position
F 30˚
F 30˚
19
Page 23
Installation
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Installation dimensions
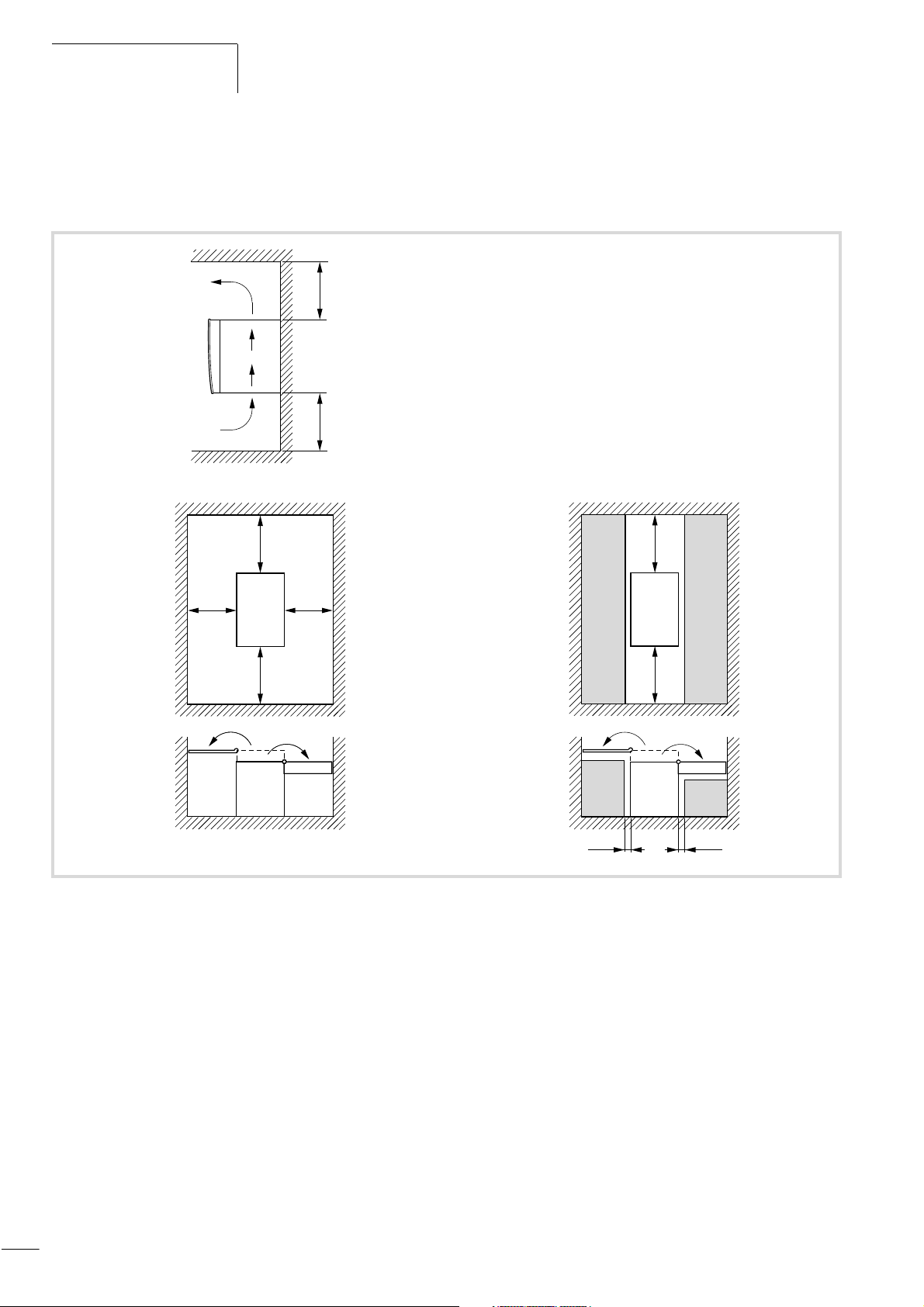
A free space of 100 mm minimum is required above and below the
device (thermal air circulation).
f 100f 100
f 100f 100
f 80
f 120
Please ensure that the front cover of the enclosure can always be
opened and closed without impediment to ensure that the control
terminals can be connected.
f 100
Figure 7: Installation dimensions
Dimensions and weights of the DF5 can be found in the Appendix
Section ”Dimensions and weights” from Page 111.
f 100
f 10f 10
20
Page 24
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
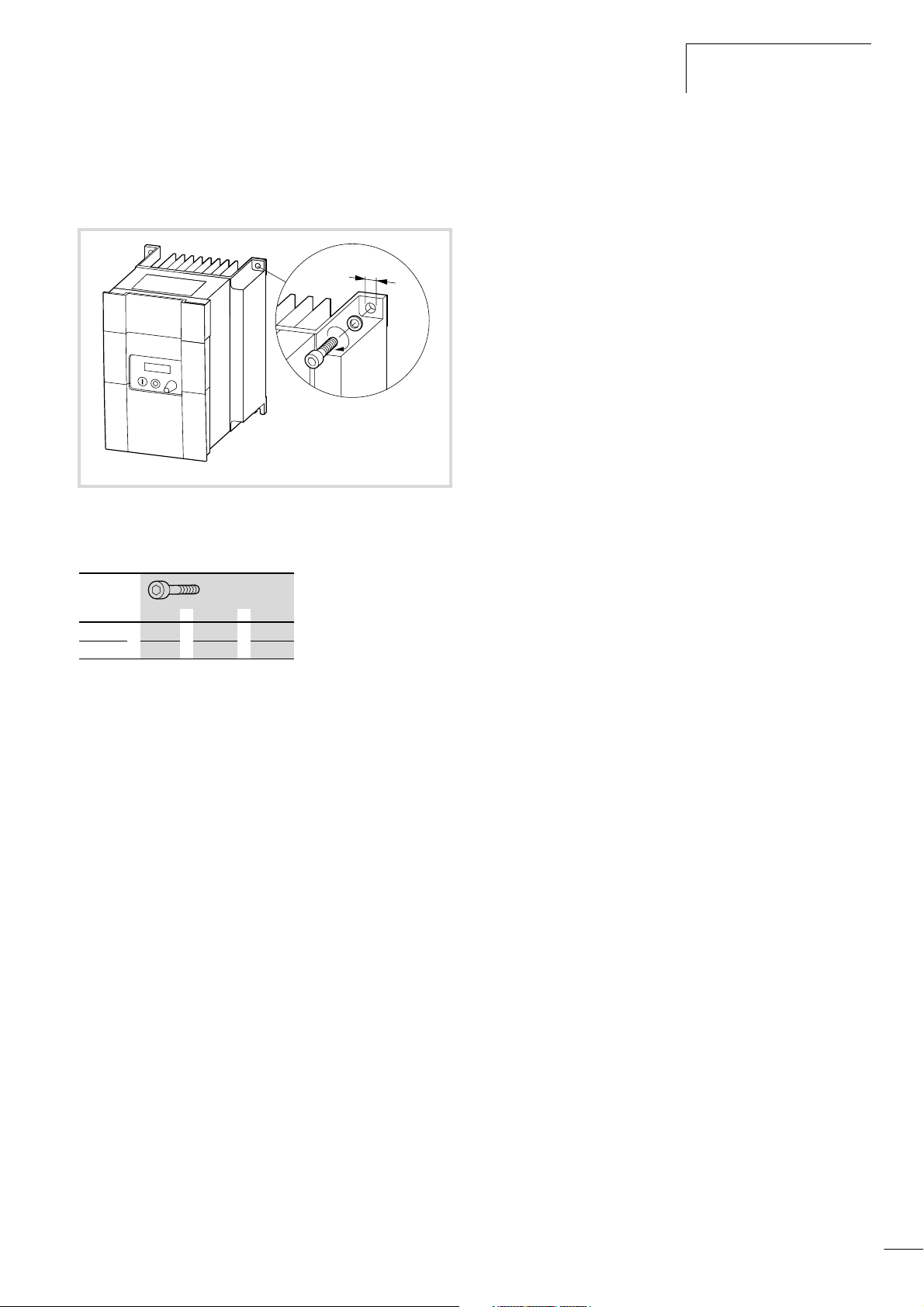
DF5 attachment
Install the DF5 series frequency inverter according to Fig. 8 and
tighten the screws with the following torques (a Table 1):
o
DF5 Installation
Figure 8: DF5 attachment
Table 1: Tightening torque's of the attachment screws
o
[mm]
5 M4 3 Nm 26 lbin
7
M6 4 Nm 35 lbin
21
Page 25
Installation
EMC compliance
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
EMC compliant installation
The frequency inverter operates with fast electronic switching
devices e.g. transistors (IGBT). For this reason, radio interference
can occur on the output of the frequency inverter, which may
effect other electronic devices located in the direct vicinity such as
radio receivers or measurement instruments. In order to offer
protection against this radio frequency interference (RFI), the
devices should be screened and installed as far away as possible
from the frequency inverters.
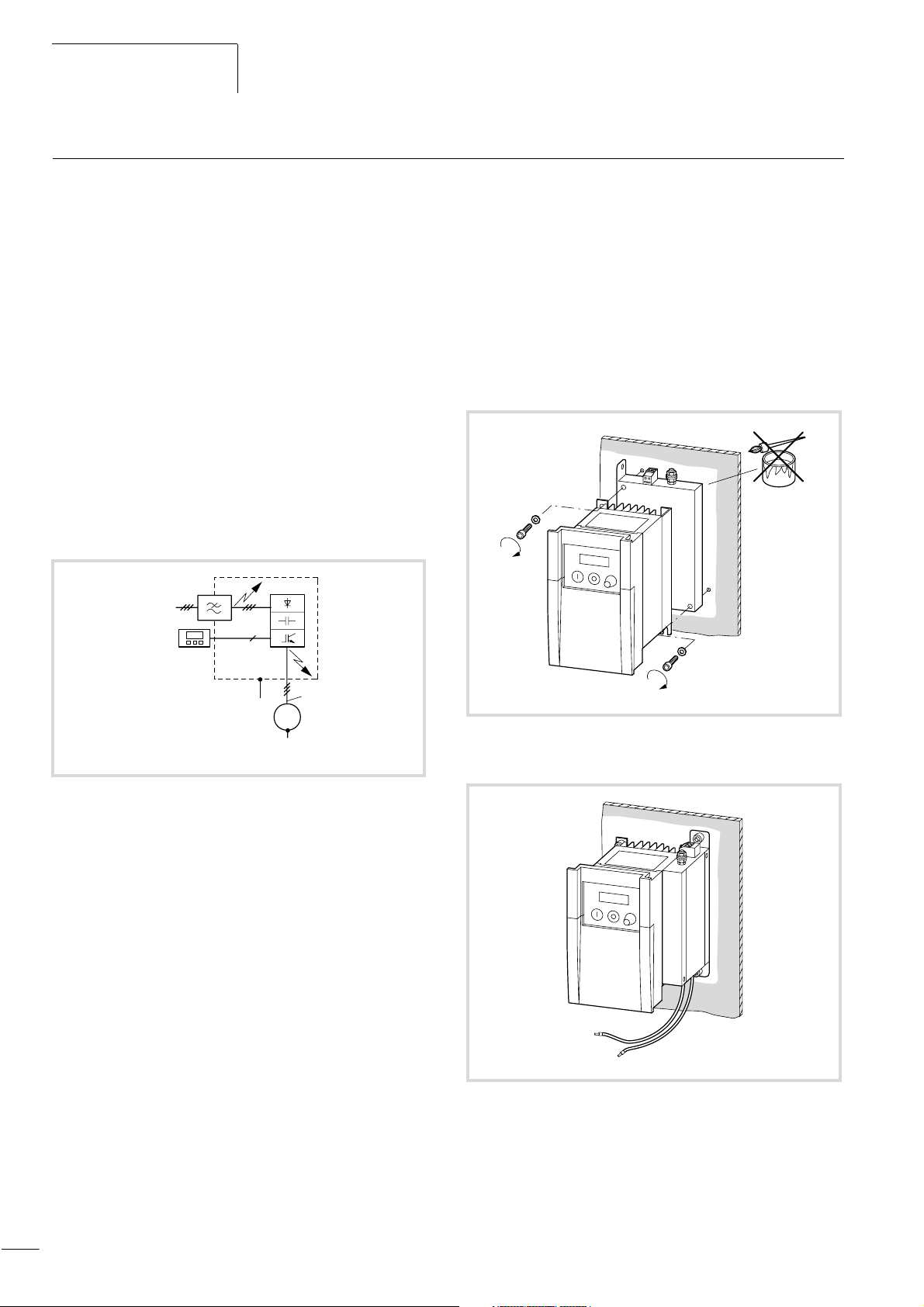
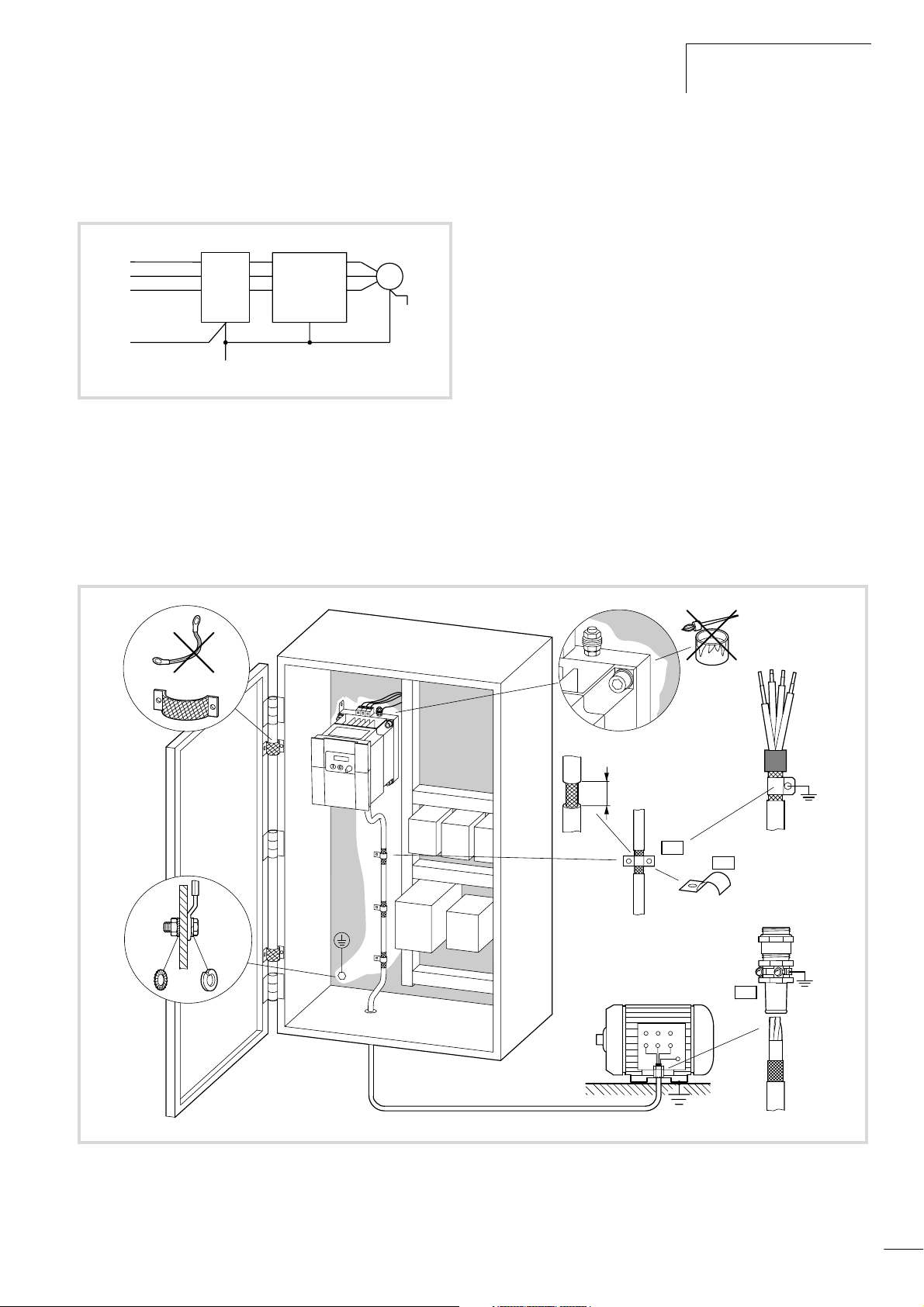
We recommend the following measures for EMC compliant installation:
• installation of the frequency inverter in a metallic, electrically
conducting enclosure with a good connection to earth.
• installation of a radio interference filter on the input of the
frequency inverter in its direct vicinity
• screened motor cables (short cable lengths).
Z1
Uh
G1
6
Radio interference filter usage
The RFI filter should be installed in the direct vicinity of the
frequency inverter. The connection cable between the frequency
inverter and filter should be as short as possible. Screened cables
are required if the length exceeds 30 cm.
The radio interference filters assigned for the DE5-LZ... series
(a Section ”Radio interference filter” in the Appendix,
Page 115) enable the installation below (foot-print) or on the side
(book-type) of the DF5 series frequency inverters.
3h
a
M
E
E
Figure 9: DF5 and radio interference filter in a sealed enclosure
Z1: RFI filter
G1:frequency inverter
a Screened motor cable
X Ground the metallic enclosure via a cable which should be as
short as possible (a Fig. 9).
Figure 10: foot-print-Aufbau
Figure 11: Seitlicher Anbau
22
Radio interference filters produce leakage currents which can be
significantly larger than the rated values in the event of a fault
(phase failure, load unbalance). The filters must be earthed before
use in order to avoid dangerous voltages. As the leakage currents
Page 26
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
EMC compliance
are high frequency interference sources, the earthing measures
must be undertaken with low resistance's on surfaces which as
large as possible.
Z1 G1
R2
L1
L2
L3
PE
L1
L2
L3
L/L1
S2
L2
T2
N/L3
e
U
V
W
3h
M
E
E
Figure 12: Earthing measures
Z1: EMC filter
G1:frequency inverter
With leakage currents f 3.5 mA, the VDE 0160 and EN 60335
stipulate that either:
• the protective conductor must have a cross-section f 10 mm
• the protective conductor is monitored to ensure continuity or
• an additional protective conductor is also installed.
For the frequency inverters of the DF5 series use the assigned filter
DE5-LZ....
EMC measures in the control panel
To ensure EMC-compliant setup, connect all metallic components
of the devices and of the control cabinet with each other using a
large cross-section conductor with good HF conducting properties.
Do not make connections to painted surfaces (Eloxal, yellow chromated). If there is no alternative, use contact and scraper washers
to ensure contact with the base metal. Connect mounting plates
to each other, and the cabinet doors with the cabinet using
contacts with large surface areas and short HF wires.
An overview or all EMC measures can be seen in the following
figure.
2
,
PE
Figure 13: EMC-compliant setup
15
PES
W2
U2
V2
U1
W1
V1
PES
PES
PE
23
Page 27
Installation
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Fit additional RFI filters or mains filters and frequency inverters as
closely as possible to each other and on a single metal plate
(mounting plate).
Lay cables in the control cabinet as near as possible to the ground
potential. Cables that hang freely act as antennae.
To prevent transfer of electromagnetic energy, lay interferencesuppressed cables (e.g. mains supply before the filter) and signal
lines as far away as possible (at least 10 cm) from HF-conducting
cables (e.g. mains supply cable after a filter, motor power cable).
This applies especially where cables are routed in parallel. Never
use the same cable duct for interference-suppressed and HF
cables. Where unavoidable, cables should always cross over at
right angles to each other.
Never lay control or signal cables in the same duct as power
cables. Analog signal cables (measured values, setpoints and
correction values) must be screened.
Z1G1 Gn Zn
M1
3h
Grounding
Connect the ground plate (mounting plate) with the protective
earth using a short cable. To achieve the best results, all conducting components (frequency inverter, mains filter, motor filter,
mains choke) should be connected by an HF wire, and the protective conductor should be laid in a star configuration from a central
earthing point. This produces the best results.
Ensure that the earthing measures have been correctly implemented (a Fig. 14). No other device which has to be earthed
should be connected to the earthing terminal of the frequency
inverter. If more than one frequency inverter is to be used, the earthing cables should not form a closed loop.
Mn
M
PE
M
3h
PE
Figure 14: Star-type point to point earthing
PE
Screening
Unscreened cables behave like antennae, i.e. they act as transmitters and receivers. To ensure EMC-compliant connection, screen
all interference-emitting cables (frequency inverter/motor output)
and interference-sensitive cables (analog setpoint and measured
value cables).
The effectiveness of the cable screen depends on a good screen
connection and a low screen impedance. Use only screens with
tinned or nickel plated copper braiding, braided steel screens are
unsuitable. The screen braid must have an overlap ratio of at least
85 percent and an overlap angle of 90°.
PE PE
e
a
e
Figure 15: Sample motor cable
a CU screen braid
b PVC outer sheath
c Strands (CU-strands)
d PVC core insulation
3 x black, 1 x green/yellow
e Textile braid and PVC inner material
b
c
d
24
Page 28
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
EMC compliance
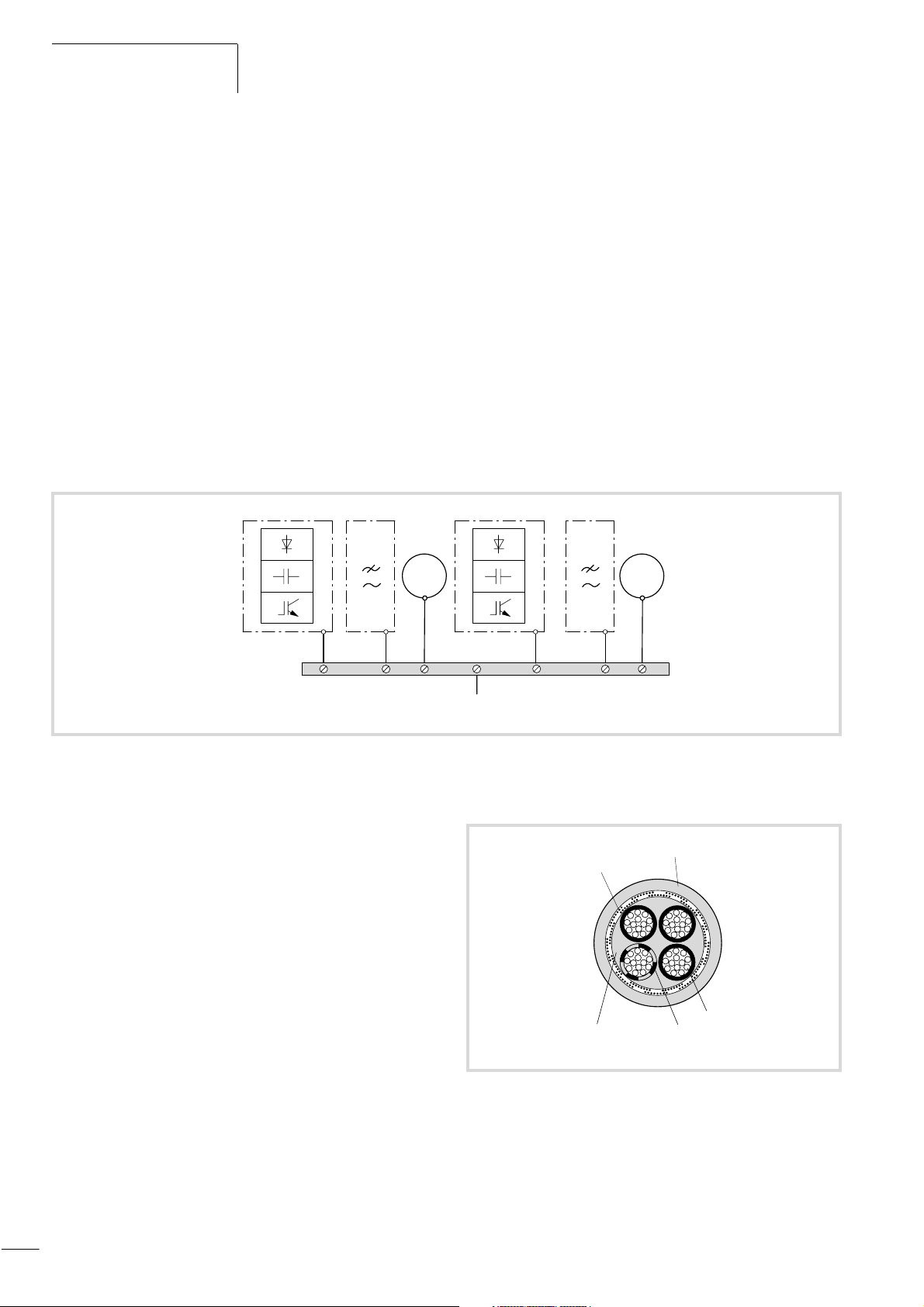
The screened cable between frequency inverter and motor should
be as short as possible. Connect the screen to earth at both ends
of the cable using a large contact surface connection.
Lay the cables for the supply voltage separately from the signal
cables and control cables.
Never unravel the screening or use pigtails to make a connection.
Figure 16: Inadmissible screen grounding (pigtails)
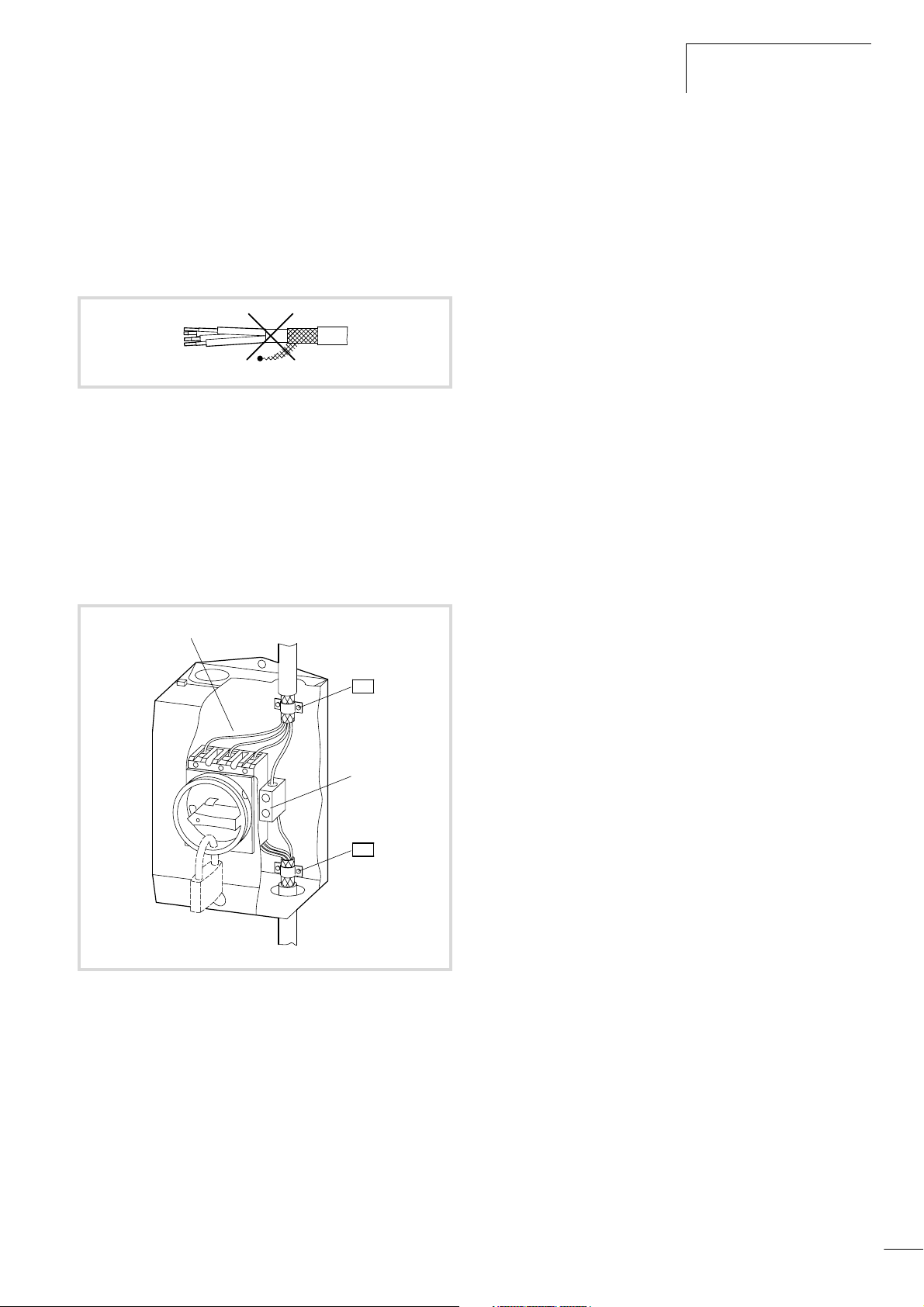
If contactors, maintenance switches, motor protection relays,
motor reactors, filters or terminals are installed in the motor
cabling, interrupt the screen near these components and connect
it to the mounting plate (PES) using a large contact surface
connection. The free, unscreened connecting cables should not be
longer then about 100 mm.
Example: Maintenance switch
In an EMC-compliant control cabinet (metal-enclosed, damped to
about 10 dB), the motor cables do not need to be screened
provided that the frequency inverter and motor cables are spatially
separated from each other and arranged in a separate partition
from the other control system components. The motor cable screening must then be connected via a large surface area connection
at the control cabinet (PES).
The control cable and signal (analog setpoint and measured value)
cable screens must be connected only at one cable end. Connect
the screen to ground using a large-area contact surface; ensure
that the connection has a low impedance. Digital signal cable
screens must be connected at both cable ends with large-surface,
low-resistance connections.
a
PES
b
PES
Figure 17: Maintenance switch, e.g. T… in an enclosure
a Metal plate
b Insulated PE-terminal
25
Page 29

Installation
Electrical connection
In this section, you will find information for connection of the
motor and the supply voltage to the power terminals, and the
signal cables to the control terminals and signalling relay.
Warning!
The wiring stages may only commence after the frequency
inverters have been correctly installed and attached.
Otherwise, there is a danger of electrical shock or injury.
Warning!
Wiring may only be carried out under no voltage
conditions.
Warning!
Only use cables, residual-current circuit-breakers and
contactors which have a suitable rating. Otherwise there
is a danger of fire.
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
An overview of the connections can be found in the following
illustration.
26
Page 30
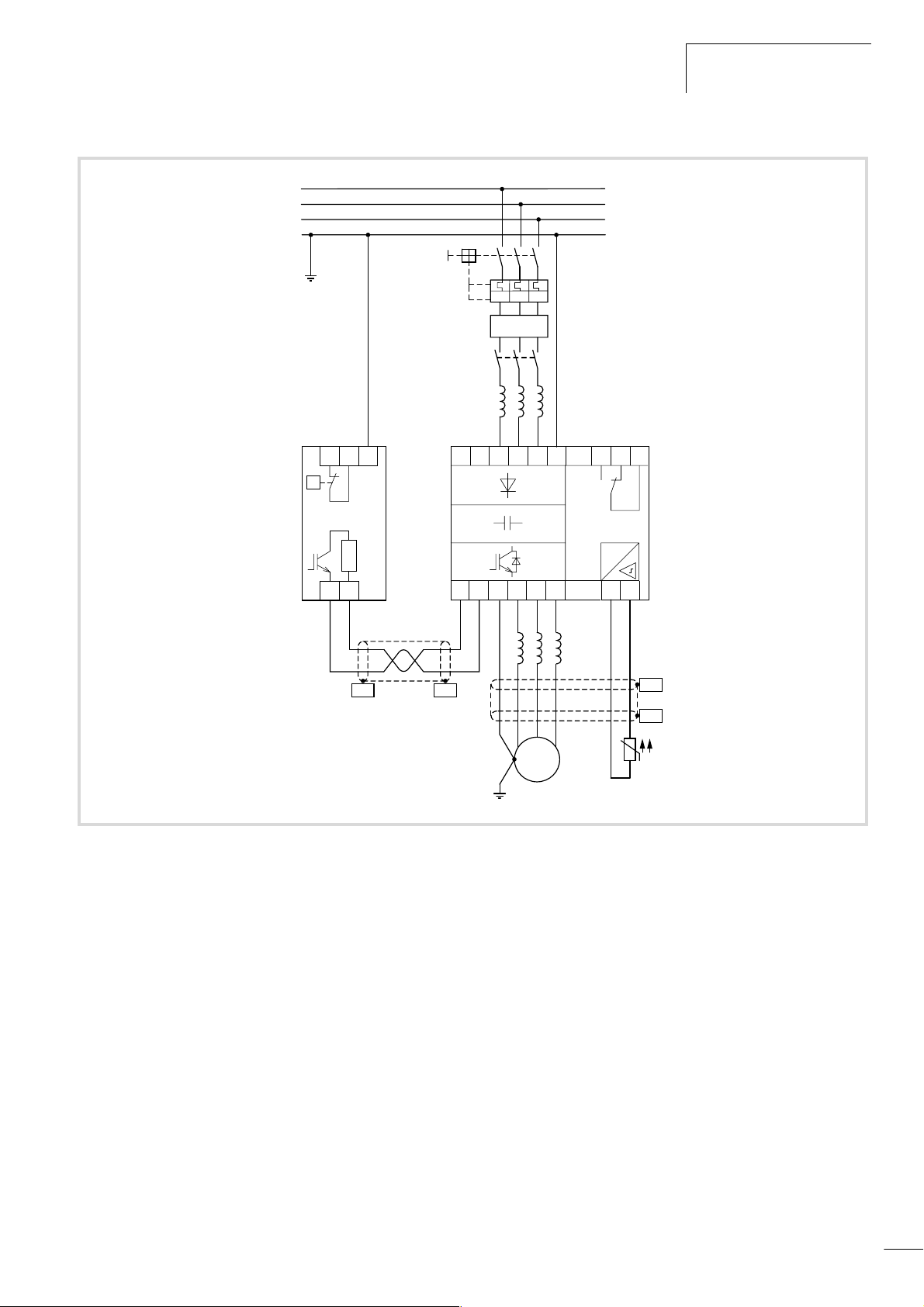
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
a
L1
L2
L3
PE
Electrical connection
3 h 400 V, 50/60 Hz
b
I > I > I >
j
T1 T2 PE
i
DE4-BM4...
–UG
+UG
PES
c
d
e
f
PES
DC+ DC–
i
L1 L2
PE
FI
U
L3 PE
VW
M
3
˜
K14 K12 K11
#
L5
g
PES
h
PES
i
Figure 18: Power connection, example with 400 V
a Network configuration, mains voltage, mains frequency
interaction with p.f. compensation systems
b Fuses and cable cross-sections
c Protection of persons and domestic animals with residual-current
protective devices
d Mains contactor
e Mains choke, radio interference filter, line filter
f Mounting, installation
power connection
EMC measures
example of circuits
g Motor filter
dv/dt filter
sinusoidal filter
h Motor cables, cable length
i Motor connection
parallel operation of multiple motors on an single frequency inverter
j Braking resistors, braking units
DC link coupling
DC supply
27
Page 31

Installation
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Connecting the power section
The flap on the front enclosure must be opened in order to connect
the cables to the supply voltage and signal relay terminals.
Complete the following steps with the tools stated and
h
without the use of force.
Open the front cover and the front of the enclosure
X First of all open the front cover
1
X Loosen the screw
I
MIN
PRG
MAX
ENTER
2
1
POWER
RUN
PRG
I
PRG
Hz
A
MIN
MAX
ENTER
Figure 19: Opening the front cover
2
Figure 20: Loosen the screw
28
Page 32

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
X Flap open the front cover and remove the terminal shroud. Power terminal arrangement
The arrangement of the power terminals can be seen in the
following figure.
4
a
L+
DC+ DC–
Electrical connection
3
a
Figure 21: Open the front cover and remove the terminal shroud
a Power terminals
Table 2: Description of the power terminals
Terminal
designation
L, L1, L2, L3, N Supply voltage (mains
U, V, W Frequency inverter
L+, DC+
DC+, DC–
e, PE
Function Description
• Single-phase mains voltage: Connection to L and N
voltage)
• Three-phase mains voltage: Connection to L1, L2, L3
Connection of a three-phase motor
output
External DC choke Normally, the terminals L+ and DC+ are assigned with a
jumper. If a d.c.-link choke is used, the jumper must be
removed.
DC link These terminals are used for the connection of an optional
braking resistor as well as for DC linking and DC feed of
multiple frequency inverters.
Earthing Enclosure earthing (prevents the presence of dangerous
voltages on the enclosure with a malfunction)
L/L1 L2 U V WN/L3
L1 L2 L3
M
3 h
Figure 22: Arrangement of the power terminals
a Internal connection. Remove if a d.c.-link choke is used.
N/L3L2L/L1 U V W
M
3 h
29
Page 33

Installation
Power terminal connection Laying the cables
Warning!
The supply voltage must suit the frequency inverter which
is selected (a Section ”Appendix”, Page 107):
• DF5-322: Single-phase or three-phase: 230 V
(180 to 264 V g 0%)
• DF5-340: three-phase 400 V (342 to 506 V g 0%)
Lay the cables for the power section separately from the signal
cables and control cables.
The motor cables which are to be connected must be screened.
The maximum cable length must not exceed 50 m. With larger
cable lengths, a motor choke is required for dv/dt-limitation
If the cable leading from the frequency inverter to motor is longer
than approx. 10 m, it is possible that the available thermal relays
Warning!
The mains voltage may not be connected for any reason
to the output terminals U, V and W. Danger of electrical
(bimetallic relays) will malfunction due to high frequency harmonics. Install a motor filter on the output of the frequency inverter
in this case.
shock or fire.
Warning!
Warning!
Each phase of the supply voltage for the frequency
inverter must be protected by a fuse (danger of fire).
Do not connect cables to the terminals in the power
section which are not designated. These terminals are
partially without function (dangerous voltages) or are
reserved for DF5 internal purposes.
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Warning!
Ensure that all power cables are correctly tightened on the
Tightening torques and conductor cross-sections
power section.
Warning!
The frequency inverter must be earthed. Danger of
electrical shock or fire.
Table 3: Tightening torque's and conductor cross-sections for the power terminals
L, L1, L2, L3, N
L+, DC+, DC–
U, V, W, PE
DF5- mm
322-018
322-037
322-055
340-037
340-075
340-1K5
340-2K2
322-075
322-1K1
340-3K0
340-4K0
322-1K5
322-2K2
340-5K5
340-7K5
2
AWG mm mm Nm
1.5 16 6 to 8 7.1 M3.5
1.5 16 8 to 10 9 M4 1.2 to 1.3 1
2.5 14 8 to 10 9 M4 1.2 to 1.3 1
4 12 12 to 14 13 M5 2 to 2.2 2
X Screw on the cables tightly according to Table 3.
M4 (PE)
Warning!
Tighten the screws on the terminals correctly
(a Table 3), so that they do not come loose
unintentionally.
0.8 to 0.9 1
30
Page 34

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
e
PES
PE
Figure 23: Cable connection to the power terminals
Connecting the supply voltage
X Connect the supply voltage to the power terminals:
– Single-phase supply voltage: L, N and PE
– Three-phase supply voltage: L1, L2, L3 and PE
Electrical connection
31
Page 35

Installation
Connecting the motor cable
X Connect the motor cable to the U, V, W and PE terminals:
L1
L
N
PE
F1
PE PE
L2
L3
PE
Q1
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
F1, Q1 =
h
III
K1M
L1
Z1
DF5-322...
1 h 230 V, 50/60 Hz
G1
K1M
V2U2
L1 L2 L3
W1V1U1
PE
W2
PE
PE
1
PE
2
N
L
PE
N
L
PE
L1
Z1
L1 L2 L3
DF5-322...
3 h 230 V, 50/60 Hz
DF5-340...
3 h 400 V, 50/60 Hz
W
DC+
DC–L+U
V
PE
PES
PES
X1
PES
PES
PE
M1
M
3 ~
Figure 24: Power terminal connection example
F1, Q1:Line protection
K1M: Mains contactor
L1: Mains choke
Z1: RFI filter
Observe the electrical connection data (rating data) on
h
the rating label (nameplate) of the motor.
The stator winding of the motor can be connected as a star or delta
configuration in accordance with the rating data on the nameplate.
32
e
Page 36

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Electrical connection
U1 V1 W1
W2 U2 V2
Figure 25: Connection types
/ 400 V230
0,75S1
kW
rpm
1410 50 Hz
Figure 26:
Frequency inverter
Mains voltage Single-phase
Mains current
Motor circuit
Motor current
Motor voltage
Example of a motor nameplate
DF5322--075 DF5340--075
230 V
9 A 3.3 A
Delta Star
4 A 2.3 A
3 AC 0 to 230 V 3 AC 0 to 400 V
Warning!
If motors whose insulation is not suitable for operation
with frequency inverters are used, the motor may be
destroyed.
U1 V1 W1
W2 U2 V2
4.0 / 2.3
ϕ
cos
3-phase 400 V
0.67
U1 V1 W1
W2 U2 V2
FWD
Figure 27: Direction of rotation, change of rotation direction
U1 V1 W1
W2 U2 V2
REV
You reverse the direction of rotation of the motor shaft with
frequency inverter operation on the DF5 by:
A
• exchanging two of the phases connected to the motor.
• triggering terminal 1 (FWD = clockwise) or
2 (REV = anticlockwise).
• applying a control command via the interface or fieldbus interface connection.
The speed of a three-phase motor is determined by the number of
pole pairs and the frequency. The output frequency of the DF5
series frequency inverter can be varied infinitely in the range from
0.5 to 360 Hz.
Connection of pole-changing three-phase motors (Dahlander
changing pole motors), rotor-fed three-phase commutator shunt
motors (slipring rotor) or reluctance motors, synchronous motors
and servo motors is possible, when they are approved for use with
frequency inverters by the motor manufacturer.
Warning!
The operation of a motor with speeds higher than the
rated speed (nameplate) can cause mechanical damage to
the motor (bearings, unbalance) and the machinery to
which it is connected and can lead to dangerous operating conditions!
If you use a motor filter or a sinusoidal filter here, the rate of
voltage rise can be limited to values of approx. 500 V/ms
(DIN VDE 0530, IEC 2566).
In the factory default setting, frequency inverters of the DF5 series
have a clockwise rotating field. Rotation of the motor shaft to the
right is achieved by connecting the motor and frequency inverter
terminals as follows:
Motor DF5
U1
V1
W1
U
V
W
Caution!
Uninterrupted operation in the lower frequency range
(less than approx. 25 Hz) can lead to thermal damage
(overheating) with self-ventilated motors. Possible
counter-measures include: Over-dimensioning or external
cooling independant of motor speed.
Observe the manufacturers recommendations for operation of the motor.
33
Page 37

Installation
Parallel connection of motors on a frequency inverter
The DF5 series frequency inverters can control multiple motors
connected in parallel. If differing motor speeds are required, they
must be selected via the number of pole pairs and/or the gear
transmission ratio.
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
K1M
F1
M1
Figure 28: Parallel connection of multiple motors
U1 V1 W1
M
3
˜
K2M
F2
M2
Caution!
If a frequency inverter controls a number of motors in
parallel, the contactors for the individual motors must be
designed for AC
-3 operation. You may not use the mains
contactors from the table in the Appendix Section ”Mains
contactors”, Page 113. These mains contactors are only
designed for the mains (primary) currents of the frequency
inverter. If they are used in the motor circuit, the contacts
could weld.
The load resistance on the output of the frequency inverter is
reduced by parallel connection of the motors. The total stator
inductivity is reduced and the leakage capacitance increases. As a
result, the current distortion is larger when compared to operation
with a single motor load. In order to reduce the current distortion,
chokes or sinusoidal filters can be used on the frequency inverter
output.
The current consumption of all the connected motors may
h
not exceed the rated output current I
of the frequency
2N
inverter.
It is not possible to use electronic motor protection when
h
operating the frequency inverter with a number of
connected motors. You must however, protect each motor
with Thermistors and/or overload relays.
K3M
U1 V1 W1
M
3
˜
F3
M3
U1 V1 W1
M
3
˜
If motors with large differences in output power (e.g. 0.37 kW and
2.2 kW) are connected in parallel to the output of a frequency
inverter, problems can occur during the start phase and at low
speeds. It is possible, that motors with a low motor rating are
unable to develop the required torque. This is due to the relatively
high ohmic resistance's in the stators of these motors. They require
a higher voltage during the start phase and at low speeds.
Motor cable
Only screened motor cables may be used for EMC related compatability. The length of the motor cable and the associated use of
further components has an influence on the operating mode and
the operational behaviour. With parallel operation (multiple
motors connected to the frequency inverter output) the resulting
cable lengths l
l
= SlM x Wn
res
SlM: Sum of all motor cable lengths
: Number of motor circuits
n
M
With long motor cables, the leakage currents can cause
h
must be calculated:
res
M
the “earth fault” fault indication due to parasitic cable
capacities. In this case, motor filters must be used.
Keep the motor cables as short as possible as it will positively
influence the drive behaviour.
34
Page 38

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Electrical connection
Motor filters, dv/dt-filters, sinusoidal filters
Motor filters (chokes) compensate for capacitive currents with
long motor cables and with grouped drives (multiple connection of
parallel drives to a single inverter).
The use of motor filters is recommended (observe the manufacturers instructions):
• with grouped drives
• with the operation of three-phase current asynchronous motors
with maximum frequencies greater than 200 Hz,
• with the operation of reluctance motors or permanently-excited
synchronous motors with maximum frequencies greater than
120 Hz.
With dv/dt filters, the voltage on the motor terminals are limited
to values less than 500 V/ms. They should be applied with motors
with unknown or insufficient withstand voltage for the insulation.
Caution!
During the engineering phase, the voltage drop associated with motor filters and dv/dt filters must be considered as it can be up to 4 % of the frequency inverter
output voltage.
When sinusoidal filters are used, the motors are supplied with
voltage and current which is almost sinusoidal.
Bypass operation
If you want to have the option of operating the motor with the
frequency inverter or directly from the mains supply, the incoming
supplies must be locked mechanically:
Caution!
Switch-over between the frequency inverter and the
mains supply must be undertaken in a no voltage state.
Warning!
The frequency inverter outputs (U, V, W) may not be
connected to the mains voltage (destruction of the device,
danger of fire).
L2
L3
L1
Q1
>
I>I>I
K1M
L1 L2 L3
Caution!
During the engineering phase, it is necessary to consider
that the sinusoidal filter on the output voltage and the
switching frequency of the frequency inverter must be
adapted to suit each other.
The voltage drop on the sinusoidal filter can be up to
15 % of the frequency inverter output voltage.
G1
S1
M1
Figure 29: Bypass motor control
UVW
M
3h
35
Page 39

Installation
Connecting the signalling relay
The following figure indicates the position of the signalling relay.
a
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Figure 30: Connecting the signalling relay
a Signalling relay terminals
When connecting the signalling relay, support the open
h
enclosure front.
Table 4: Description of the signalling relay terminals
Terminal designation
K11 Default settings:
K12
K14
Table 5: Signalling relay conductor cross-sections and tightening torques
Description
• Operating signal: K11-K14 closed.
• Fault message or power supply off:
K11-K12 closed
Characteristics of the relay contacts:
• Maximum 250 V AC/2.5 A (resistive) or 0.2 A (inductive, power factor = 0.4);
Minimum 100 V AC/10 mA
• Maximum 30 V DC/3.0 A (resistive) or 0.7 A (inductive, power factor = 0.4);
Minimum 5 V DC/100 mA
K12K11 K14
2
mm
n
1 x 0.14 to 1.5 6 6 to 16 0.4 x 2.5 0.5 to 0.6
0.14 to 0.75 6 – 0.4 x 2.5 0.5 to 0.6
2 x
36
mm AWG mm Nm
M3
Page 40

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
X Fit the terminal shroud to the enclosure again and close the
enclosure front.
1
2
Electrical connection
PES
Figure 31: Close the power section
PE
37
Page 41

Installation
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Connecting the control signal terminals
The following figure shows the arrangement of the individual
control signal terminals.
L54321P24
h O OI L FM CM2 12 11
Figure 32: Location of the control signal terminals
Function of the control signal terminals
ESD measures
Discharge yourself on an earthed surface before touching
the frequency inverter and its accessories.
This prevents damage to the devices through electrostatic
discharge.
Table 6: Meaning of the control signal terminals
No. Function Level Default setting Technical data, description
L Common reference
potential
5 Digital input
4 Digital input
3 Digital input
2 Digital input
1 Digital input
P24 Control voltage output
h Setpoint voltage output
OAnalog input
OI Analog input
L Common reference
potential
FM Analog output
0 V – Reference potential for the internal voltage sources
P24 and H
HIGH = +12 to +27 V
LOW = 0 to +3 V
+24 V – Supply voltage for actuation of digital inputs 1 to 5.
+10 V – Supply voltage for external setpoint potentiometer.
0 to +10 V Frequency setpoint value
4 to 20 mA Frequency setpoint value
0V – Reference potential for the internal voltage source
0 to +10 V Frequency actual value
Reset PNP logic, configurable, Ri=33kO
Reference potential: Terminal L
FF2 (FF3) = fixed frequency 2
(3)
FF1 (FF3) = fixed frequency 1
(3)
REV = anticlockwise rotation
FWD = clockwise rotation
(0 to 50 Hz)
(0 to 50 Hz)
(0 to 50 Hz)
PNP logic, configurable, Ri=5kO
Reference potential: Terminal L
Load carrying capacity: 30 mA
Reference potential: Terminal L
Load carrying capacity: 10 mA
Reference potential: Terminal L
Ri = 10 kO
Reference potential: Terminal L
RB = 250 O
Output: Terminal L
P24 and H
Configurable, monitored DC voltage; 10 V corres-
ponds to set final frequency (50 Hz).
Accuracy: g5 % from final value
Load carrying capacity: 1 mA
Reference potential: Terminal L
38
Page 42

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Electrical connection
No. Function
CM2 External control voltage
Level Default setting Technical data, description
Up to 27 V – Connection: Reference potential (0 V) of the
input
12 Transistor output
11 Transistor output
Up to 27 V = CM2 RUN (operation) Configurable, open collector
Frequency setpoint reached
Control signal terminal wiring
Wire the control signal terminals to suit their application. For a
description of how to change the functions of the control signal
terminals, see Section ”Programming the control signal terminals”
from Page 49 .
Caution!
Never connect terminal P24 with terminals L, H, OI or FM.
external voltage source for the transistor outputs,
terminals 11 and 12.
Load carrying capacity: Up to 100 mA
(sum of terminals 11 + 12)
Load carrying capacity: Up to 50 mA
Caution!
Never connect terminal H with terminal L.
Use twisted or screened cables for connecting to the control signal
terminals. Earth the screen on one side with a large contact area
near the frequency inverter. The cable length should not exceed
20 m. For longer cables, use a suitable signal amplifier.
The following figure shows a sample protective circuit for the
control signal terminals
1
2
H O
F 20 m
L
4K7
R1 REV FWD
Figure 33: Control terminal connection (factory setting)
2 1
M
P24
15
PES
PE
PES
M
ZB4-102-KS1
3
Cu 2.5 mm
M4
2
39
Page 43

Installation
When connecting a relay to one of the digital outputs 11 or 12,
connect a free-wheel diode in parallel with the relay, so that the
self-induction voltage generated when the relay is switched off
cannot destroy the digital outputs.
CM2 1211
+ 24 V
100 mA
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
ba
Figure 34: Relay with free-wheel diode
Use relays that switch reliably at 24 V H and a current of
h
about 3 mA.
Lay the control and signal cables separately from the
h
mains and motor cables.
f 100
Figure 35: Crossover of signal and power cables
a Power cable: L1, L2, L3 or L and N, U, V, W, L+, DC+, DC–
b Signal cables: H, O, OI, L, FM, 1 to 5, 11 and 12, CM2, P24
40
Page 44

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Example for the protective circuit of the digital inputs when the
internal P24 supply voltage is used, or when a separate external
24 V power supply is used:
Electrical connection
+24 V
+24 V
24 V
+24 V
Q..
Q..
Q..
Q..
Q..
0 V
24 V
Q..
Q..
Q..
Q..
Q..
P24
5
4
3
2
1
L
+24 V
DF5
5
4
3
2
1
Figure 36: Triggering of the digital inputs
0 V
L
DF5
41
Page 45

Installation
Caution!
Before commissioning, remove the covering on the upper
ventilation slots and openings, as the frequency inverter
will otherwise overheat a Fig. 37.
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Figure 37: Removing the upper cover
42
Page 46

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
4 DF5 Operation
This section describes how to commission the DF5 series frequency
inverters and deals with issues that need to be observed during its
operation.
Initial startup
Observe the following points before you take the frequency
inverter into operation:
• Ensure that the power cables L and N or L1, L2 and L3 as well
as the frequency inverter outputs U, V and W are correctly
connected.
• The control lines must be connected correctly.
• The earth terminal must be connected correctly.
• Only the terminals marked as earthing terminals must be
earthed.
• The frequency inverter must be installed vertically on a nonflammable surface (e.g. a metal surface).
• Remove any residue from wiring operations – such as pieces of
wire – and all tools from the vicinity of the frequency inverter.
• Make sure that the cables connected to the output terminals are
not short-circuited or connected to earth.
• Ensure that all terminal screws have been tightened sufficiently.
• Make sure that the frequency inverter and the motor are correct
for the mains voltage.
• The configured maximum frequency must match the maximum
operating frequency of the connected motor.
• Never operate the frequency inverter with opened power
section covers. The front enclosure must be closed and secured
with the screw provided.
The control signal terminals are wired as follows.
OH
F 20 m
4K7
Figure 38: Connecting control signal terminals (default settings)
X Switch on the supply voltage.
2L
1 P24
PES
S2
S1
M
M
FWD
REVR1
The POWER and Hz LEDs light up (keypad). The display should
indicate 0.0.
X Close switch S1 (FWD = clockwise rotation).
X With potentiometer R1, you can set the frequency and therefore
the motor speed.
The motor turns clockwise and the display indicates the set
frequency.
X Open switch S1.
Caution!
Do not carry out h.v. tests. Built-in overvoltage filters are
fitted between the mains voltage terminals and earth,
which could be destroyed.
Sparkover voltage and insulation resistance tests (megger
h
tests) have been carried out by the manufacturer.
The motor speed is reduced to zero (Display: 0.0).
X Close switch S2 (REV = anticlockwise rotation).
X With potentiometer R1, you can set the frequency and therefore
the motor speed.
The motor turns anticlockwise and the display indicates the set
frequency.
X Open switch S2.
The motor speed is reduced to zero (Display: 0.0).
If both switches S1 and S2 are closed, the motor will not start. The
motor speed reduces to zero during operation if you close both
switches.
43
Page 47

DF5 Operation
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Caution!
Check the following points during or after the “initial
operation” so that damage to the motor does not occur:
• Was the direction of rotation correct?
• Has a fault occurred during acceleration or
deceleration?
• Was the frequency display correct?
• Did any unusual motor noises or vibrations occur?
If a fault has occurred due to overcurrent or overvoltage, increase
the acceleration or deceleration time (a Section ”Acceleration
time 1”, Page 76 and Section ”Deceleration time 1” Page 77).
By default, the ON key and the potentiometer on the keypad
(a Fig. 39 and a Table 7) have no functions assigned to
them. For details about activating these operator controls, see
Section ”Setting the frequency and start command parameters”,
Page 78.
LCD keypad
The following illustration shows the LCD keypad of the DF5.
b
c
POWER
MIN
Hz
d
A
e
MAX
ENTER
a
k
j
i
RUN
PRG
PRG
Table 7: Explanation of the operating and indication elements
Number Name Explanation
a RUN LED LED lights up in RUN mode, if the
frequency inverter is ready for operation
or operational.
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j On key and
k
7 segment
display
POWER LED LED is lit when the frequency inverter
Hz or A LED Indication in b: output frequency (Hz)
Potentiometer and LED
ENTER key The key is used for saving entered or
ENTER
Arrow keys Selecting functions, changing numeric
PRG key For selecting and exiting the program-
PRG
OFF key Stop the running motor and acknow-
LED
PRG LED LED is lit during parameterization.
Display for frequency, motor current,
error messages, etc.
has power.
or output current (A)
Frequency setpoint setting
LED is lit when the potentiometer is
activated.
changed parameters.
values
Increase
Reduce
ming mode.
ledge a fault message. Active by
default, also for actuation through
terminals.
Starts the motor in the specified direction (not active by default).
hgf
Figure 39: Keypad view
For an explanation of the elements, see Table 7.
44
Operation with LCD keypad
The functions of the DF5 are organized in parameter groups. The
following sections describe how to set the parameter values and
how the setting menu is structured.
For a detailed description of the parameters, see Section ”Setting
Parameters”, Page 75.
Menu overview
The following figure shows the sequence in which the parameters
appear on the display. Table 8 provides a brief description of the
parameters.
Page 48

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PRG
PRG
PRG
PRG
a
Operation with LCD keypad
Table 8: Explanation of the parameters
Display Explanation
Display
parameter
d 01 Output frequency display
d 02
d 03
d 04
d 05
d 06
d 07
d 08
d 09
Basic
parameters
F 01 Frequency setpoint adjustment
F 02
F 03
F 04
Extended parameter groups
A -- Extended functions group A
b --
C --
Output current display
Direction of rotation display
PID feedback display
Digital inputs 1 to 5 status
Status of digital outputs 11 and 12
Scaled output frequency
Display of last alarm
Display of second and third to last alarm
Set acceleration time 1
Set deceleration time 1
Direction of rotation adjustment
Extended functions, group B
Extended functions, group C
Figure 40: Menu structure of the DF5 keypad
a The display is dependant on the display parameter
(PNU d01 to d09) from which you return.
For a detailed explanation of the parameters, see Section ”Setting
Parameters”, Page 75.
Changing display and basic parameters
Press the PRG key to switch from display or RUN mode to
programming mode. The PRG lamp lights up in this mode.
You can access the individual parameters or parameter groups
with the UP and DOWN arrow keys (a Fig. 40).
To access the programming mode, press the PRG key. You can
modify the parameter values with the arrow keys.
Exceptions are the display parameters PNU d01 to d09. These
parameters have no values. After you have selected a display parameter with the arrow keys, you can return to the display mode with
the PRG key. The display reflects the selected display parameter
(a Section ”Setting the display parameters”, Page 75).
Parameter values can be accepted with the ENTER key or rejected
with the PRG key.
By pressing the PRG key in the range of the display parameters
PNU d01 to d09, you return to the display mode.
45
Page 49

DF5 Operation
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Example for changing acceleration time 1: PNU F02
The frequency inverter is in the display mode and the RUN lamp is
lit.
X Press the PRG key.
The frequency inverter changes to the programming mode, the
PRG lamp lights up and d01 or the most recently modified para-
meter appears on the display.
X Press the DOWN key six times until F02 appears on the
display.
X Press the PRG key.
The set acceleration time 1 in seconds appears on the display (WE
= 10.0).
X The set value is changed with the UP and DOWN arrow keys.
There are now two possibilities:
X Accept the displayed value by pressing the ENTER key.
X Reject the displayed value by pressing the PRG key.
The display responds with F02.
X Press the DOWN key six times until d01 appears on the
display.
X Press the PRG key.
The frequency inverter changes over to the display mode and
displays the set frequency.
Changing the parameters of the extended parameter groups
The following example illustrates how to change PNU A03 of the
extended parameter group A. You can change the parameter
values of groups B and C exactly as described in the example. For
a detailed description of the extended parameter groups, see from
Section ”Setting the frequency and start command parameters”,
Page 78.
An example of how to change the base frequency PNU A03
X Press the PRG key to change over to the programing mode.
The most recently modified parameter appears on the display and
the PRG lamp lights up.
X Press the UP or DOWN key until the extended parameter group
A-- appears on the display.
X Press the PRG key.
The display indicates A01.
X Press the UP key twice until A03 appears on the display.
X Press the PRG key.
The value set under PNU A03 (WE = 50.0) appears.
X You can change the value with the UP and DOWN arrow keys.
There are now two possibilities:
X Accept the displayed value by pressing the ENTER key.
X Reject the displayed value by pressing the PRG key.
a
PRG PRG
b
6 x
Figure 41: Change acceleration time 1
a Display dependent on the selected display parameter PNU d01 to
d09
b Display of the most recently changed parameter
PRG
F02 = 9.9
ENTER
PRG
F02 = 10.0
The display indicates A03.
X Press the PRG key.
The display indicates A--.
X Press the DOWN key three times until d01 appears.
X Press the PRG key.
46
Page 50

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The frequency inverter changes over to the display mode and
displays the current frequency.
Display after the supply voltage is applied
a
PRG
PRG PRG
b
3 x
PRG
Figure 42: Change the base frequency (example with default setting)
a Display dependent on the selected display parameter PNU d01 to d09
b Display of the most recently changed parameter
Display after the supply voltage is applied
After the supply voltage is switched on, the last screen which was
visible before switch off will reappear (not, however, within the
extended parameter groups).
PRG
A03 = 49.9
ENTER
PRG
A03 = 50.0
47
Page 51

DF5 Operation
Operational warning message
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Warning!
If the supply voltage recovers after a brief failure, the
motor may restart automatically if a start signal is still
present. If personnel are endangered as a result, an
external circuit must be provided which excludes a restart
after voltage recovery.
Warning!
If the frequency inverter has been configured so that the
stop command is not issued via the OFF key on the LCD
keypad, pressing the OFF key will not switch off the
motor. A separate Emergency-Stop switch must be
provided in the case.
Warning!
Maintenance and inspection of the frequency inverter
may only be undertaken at least 5 minutes after the
supply voltage has been switched off. Failure to observe
this point can result in electric shock as a result of the high
voltages involved.
Warning!
Never pull on the cable to unplug connectors (e.g. for
fan or circuit boards).
Warning!
If a malfunction is responded to by a reset, the motor
will start automatically if a start signal is applied at the
same time. To avoid the risk of serious or fatal injury to
personnel, you must ensure that the start signal is not
present before acknowledging an error message with a
reset.
Warning!
When the supply voltage for the frequency inverter is
applied when the start signal is active, the motor will
start immediately. Make sure that the start signal is not
active before the supply voltage is switched on.
Warning!
Cables or plug connectors may not be connected or
disconnected during operation when the supply voltage is
switched on.
Caution!
To prevent a risk of serious or fatal injury to personnel,
never interrupt the operation of the motor by opening the
contactors installed on the primary or secondary side.
The ON key is functional only if the corresponding para-
h
meters of the frequency inverter have been configured
accordingly (a Section ”Setting the frequency and start
command parameters”, Page 78).
Before operating motors at frequencies above the stan-
h
dard 50 or 60 Hz, contact their manufacturers to verify
that the motors are suitable for operation at higher
frequencies. The motors could otherwise incur damage.
48
Page 52

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
5 Programming the control signal terminals
This section describes how to assign various functions to the
control signal terminals.
Overview
Table 9 provides an overview of the control signal terminals and a
brief description of the functions which you can assign to the
programmable digital inputs and outputs. For a detailed description of the individual functions, see from Page 52.
Table 9: Function description
1)
Name Value
Digital inputs 1 to 5 Parameter definition under PNU C01 to C05
FWD 00 Clockwise
Function Description
REV
(start/stop)
FWD
f
P2412
M
REV 01 Anticlockwise
(start/stop)
FF1 02 Programmable fixed
FF2 03
frequencies 1 to 4
FF3 04
FF4 05
JOG 06 Jog mode
2CH 09 Second time ramp
FRS 11 Controller inhibit (free
run stop)
M
FWD
REV
FWD input closed: motor starts up in a clockwise direction.
FWD input open: motor coasts to a stop (clockwise rotation).
REV input: same case for anticlockwise rotation as with FWD
FWD and REV inputs closed simultaneously: motor coasts to a stop.
Example: Four fixed frequencies
f
f
s
f
3
f
2
f
1
f
s
FF1
FF2
FWD
fs=0 to f
For four fixed frequency stages (three programmable fixed frequencies and a setpoint value), two
fixed frequency inputs (3 = FF1 and 4 = FF2) are required (2
max
2
= 4).
RST
FF2
FF1
REV
FWD
P241234LOH5
The jogging mode, which is activated by switching on the JOG input, is used, for example, for
setting up a machine in manual mode. When a start signal is received, the frequency programmed
under PNU A38 is applied to the motor. Under PNU A39, you can select one of three different
operating modes for stopping the motor.
Activates the second acceleration and deceleration with PNU A92 and PNU A93 respectively
When FRS is switched on, the motor is immediately switched off and coasts to a stop.
49
Page 53

Programming the control
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
signal terminals
1)
Name Value
Function Description
EXT 12 External fault When the EXT input is switched on, the fault signal activates PNU E12 and the motor switches off.
The fault signal can be acknowledged, for example, with the RST input.
USP 13 Restart inhibit
When the USP input is switched on, the restart inhibit is active. This prevents a motor restart when
the voltage recovers after a mains failure while a start signal is present.
SFT 15 Parameter protection
Switching on the SFT input to activate the parameter protection prevents loss of the entered parameters by inhibiting write operations to these parameters.
AT 16 Setpoint input OI (4 to
When the AT input is switched on, only the setpoint value input OI (4 to 20 mA) is processed.
20 mA) active
RST 18 Reset
To acknowledge an error message, switch on the RST input. If a reset is initiated during operation,
the motor will coast to a stop. The RST input is a make (NO) contact; it cannot be programmed as
a break contact (NC).
PTC 19 Connection for a PTC
thermistor
P24 – +24 V H for digital
You can only program digital input 5 with PNU C05 as an input for a PTC thermistor. Use terminal
L as the reference potential.
24 V H potential for digital inputs 1 to 5
inputs
Frequency setpoint definition
h – +10 V setpoint voltage
for external potentiometer
Setpoint value can be set with
potentiometer:
LOIOH
Setpoint value through voltage
input:
LOIO
Setpoint value through
current input:
LOI
O – Analog input for
frequency setpoint
(0 to +10 V)
PES
PES
+
–
PES
+
–
OI – Analog input for
frequency setpoint
(4 to 20 mA)
L – 0 V reference potential
for setpoint inputs
R: 1 to 10 kO 0 to 10 V H
Input impedance: 10 kO
The OI input for a setpoint value from 4 to 20 mA is only used when the digital input configured
as the AT input is closed.
4 to 20 mA H
Load resistor: 250 O
analog output
FM – Frequency monitor The frequency can be output via a connected analog or digital measurement device via this input.
As an option, the motor current can be displayed.
L – 0V
0 V reference potential for the FM output
50
Page 54

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
1)
Name Value
Function Description
Digital outputs 11 and 12 Parameter definition under PNU C21 and C22
FA1 01 Signal when frequency is
f
s
reached or exceeded
f
2
f
1
Overview
Connection of a signal
relay to digital output 11
or 12:
12CM2
24 V
50 mA
FA1
FA2
Transistor output
(open collector)
fs = setpoint frequency
FA2 02 If a digital signal is configured as FA1, a signal is issued as long as
(maximum 27 V H,
50 mA)
the setpoint value is achieved. If a digital signal is configured as FA2,
a signal is output as long as the frequencies defined under PNU C42
and PNU C43 are exceeded.
RUN 00 RUN signal
OL 03 Signal on overload
The RUN signal is output during operation of the motor.
The OL signal is output when the overload alarm threshold
(adjustable under PNU C41) is exceeded.
OD 04 Signal on PID control
deviation
AL 05 Signal (alarm) on fault
CM2 – 0V
The OD signal is output when the PID control deviation set under
PNU C44 is exceeded.
The AL signal is issued when a fault occurs.
0 V reference potential for the programmable digital outputs 11 and 12. These transistor outputs
(open collector) are controlled through optocouplers, whose reference potential is CM2. CM2 is
isolated L.
Signalling relay
K11 – Signalling relay contacts During normal, healthy operation, terminals K11-K14 are closed. If a malfunction occurs or the
K12
K14
supply voltage is switched off, the terminals K11-K12 are closed.
Maximum permissible values:
• 250 V ~; maximum load 2.5 A (purely resistive) or 0.2 A (with a power factor of 0.4)
• 30 V H; maximum load 3.0 A (purely resistive) or 0.7 A (with a power factor of 0.4)
• Minimum values necessary: 100 V ~ with a load of 10 mA or 5 V H with a load of 100 mA
1) To activate the function, enter this value in the corresponding parameter.
51
Page 55

Programming the control
signal terminals
Frequency display FM
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The FM terminal provides the output frequency or the motor
current as a frequency signal.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
C23 Display via FM
– 00 Indication of the output frequency (analog 0 to 10 V H signal) 00
output
Value Function WE
01 Indication of motor current (analog 0 to 10 V H signal; 100 % rated
current corresponds to 5 V H)
02 Display of the output frequency (digital impulse signal)
Analog frequency display
The signal output (PNU C23 = 00 or 01) is a square-wave, with a
constant period of oscillation. Its pulse width is proportional to the
current frequency value (0 to 10 V correspond to 0 Hz to the end
frequency).
FML
–
0 – 10 V
1 mA
+
Analog frequency meter
0 to 10 V
1mA
t
T
t/T = variable
T = 4 ms (constant)
10 V
The selection between the frequency display and display of the
motor current is made under PNU C23.
Signal compensation takes place in PNU b81. The signal accuracy
after compensation is g5%.
If for example, a higher level of smoothing of the FM signal is
required for a motor current display, an external low-pass filter
circuit is required. The accuracy is approx. g20 %.
FML
33 kO
82 kO
+
1 mF
–
0 – 10 V
1 mA
+
Figure 43: Connection of an analog frequency meter
PNU Name Adjustable in
Value Function WE
RUN mode
b81 Adjustment
j 0 to 255 The analog signal issued on the FM terminal (frequency actual value or
value for
analog signal
on FM terminal
Figure 44: Example for a low-pass circuit
80
output current) can be adjusted here. The impulse signal (digital
frequency actual value) cannot be compensated.
52
Page 56

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Digital frequency display
The frequency of this signal (PNU C23 = 02) changes proportionally to the output frequency. The pulse duty factor remains
constant at about 50 %.
Frequency display FM
FML
–
f
+
Digital frequency meter T = 1/(output frequency x factor)
T
10 V
Figure 45: Digital frequency meter connection
The signal frequency results from the product of the current output
frequency and an adjustable factor at PNU b86.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
b86 Frequency
j 0.1 to 99.9 The product of the value displayed under PNU d01 and this factor is
factor
Value Function WE
displayed at PNU d07. This value is also available at the FM terminal.
1.0
53
Page 57

Programming the control
signal terminals
Programmable digital inputs 1 to 5
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
You can assign various functions to terminals 1 to 5. Depending
on your requirements, these terminals can be configured as
follows:
• clockwise start signal (FWD),
• anticlockwise start signal (REV),
• selection inputs for various fixed frequencies (FF1 to FF4),
• reset input (RST),
• etc.
The terminal function for each of the programmable digital inputs
1 to 5 occurs via PNU C01 to C05, i.e. you use PNU C01 to specify
the function of digital input 1, PNU C02 to specify the function of
digital input 2, etc. You cannot, however, assign the same function
to two inputs.
Programmable digital inputs 1 to 5 are configured as make
contacts by default. If, therefore, the function of an input terminal
is to be activated, the corresponding input must be closed (i.e. the
input terminal is connected to terminal P24). Conversely, to deactivate the input terminal, the input must be opened.
Caution!
If an EEPROM error occurs (fault message E08), all
parameters must be checked to ensure that they are
correct (particularly the RST input).
Table 10: Digital inputs 1 to 5
PNU Terminal Adjustable in
RUN mode
C01 1 – a Table 11 00
C02 2
C03 3
C04 4
C05 5
Value WE
01
02
03
18
A detailed description of the input functions can be found on the
pages listed in Table 11.
Tabelle 11: Functions of the digital inputs
Value Function Description a Page
00 FWD Start/stop clockwise 55
01 REV
02 FF1
03 FF2
04 FF3
05 FF4
06 JOG
09 2CH
11 FRS
12 EXT
13 USP
15 SFT
16 AT
18 RST
19 PTC
Start/stop anticlockwise 55
First fixed frequency input 56
Second fixed frequency input
Third fixed frequency input
Fourth fixed frequency input
Jog mode 64
Second acceleration and
deceleration time
Motor shutdown and free
run stop
External fault 61
Restart inhibit 62
Parameter protection 66
Setpoint input through current 58
Reset 63
PTC thermistor input
(digital input 5 only)
59
60
65
If required, the digital inputs can be configured as break (NC)
contacts. For this purpose, under PNU C11 to C15 (corresponding
to digital inputs 1 to 5), 01 is to be input. An exception exists only
for inputs which you configure as RST (reset) or as PTC (PTC thermistor input). These inputs can only be operated as make (NO)
contacts.
Caution!
If you reconfigure digital inputs configured as FWD or REV
as break contacts (the default setting is as a make
contact), the motor starts immediately. They should only
be reconfigured as break contacts when it is absolutely
essential.
54
Table 12: Configuring digital inputs as break contacts
PNU TerminalValueAdjustable in
RUN mode
C11 1 00 or 01– 00: Make
C12 2
C13 3
C14 4
C15 5
Function WE
contact
01: Break
contact
00
Page 58

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Start/Stop
Start/Stop
Clockwise rotation FWD
If you activate a digital input which has been configured as a FWD
input, the motor starts to run in a clockwise direction. If you deactivate the input, the motor coasts to a stop.
If the FWD and the REV inputs are activated simultaneously, the
motor coasts to a stop.
FWD
P241
Figure 46: Digital input 1 configured as FWD „Start/Stop clockwise
rotation“
Anticlockwise operation: REV
If you activate a digital input which has been configured as an REV
input, the motor starts to run in an anticlockwise direction. If you
deactivate the input, the motor coasts to a stop.
REV
P2413
Issue start command
By default, the start command is issued through the inputs configured as FWD or REV. If however, the start command is currently
issued via the ON key on the keypad, set under PNU A02 the value
01 (start command via FWD/REV input) (a Section ”Start
command”, Page 78).
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as FWD by setting the
corresponding PNU (C01 to C05) to 00.
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as REV by setting the
corresponding PNU (C01 to C05) to 01.
Warning!
If the supply voltage for the frequency inverter is applied
when the start signal is activated, the motor will start
immediately. Make sure, therefore, that the start signal is
not active before the supply voltage is switched on.
Warning!
If the FWD/REV input is opened (inactive state if FWD/REV
is configured as a make contact) and then it is reconfigured as a break contact, it must be noted that the motor
will start immediately after the reconfiguration.
Figure 47: Digital input 2 configured as REV “Start/Stop
anticlockwise”
55
Page 59

Programming the control
signal terminals
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4 selection
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
With the digital inputs configured as FF1 to FF4 you can select up
to 16 user-definable fixed frequencies (including frequency
setpoints), depending on which of the inputs is active or inactive
(a Table 13). It is not necessary to use all the fixed frequency
selection inputs at the same time. Using only three inputs, for
example, allows you to choose between eight fixed frequencies;
with two fixed frequency selection inputs, four fixed frequencies
are available for selection.
The fixed frequencies have a higher priority than all other setpoint
values and can be accessed at any time through inputs FF1 to FF4
without needing to be enabled separately. Jog mode, to which the
highest priority is assigned, is the only operation with a higher
priority than the fixed frequencies.
Table 13: Fixed frequencies
Fixed
frequency
stage
0 = f
s
f
1
f
2
f
3
f
4
f
5
f
6
f
7
f
8
f
9
f
10
f
11
f
12
f
13
f
14
f
15
0 = input deactivated
1 = input activated
PNU Input
FF4 FF3 FF2 FF1
Frequency
0 0 0 0
setpoint
value
a21 0 0 0 1
a22 0 0 1 0
a23 0 0 1 1
a24 0 1 0 0
a25 0 1 0 1
a26 0 1 1 0
a27 0 1 1 1
a28 1 0 0 0
a29 1 0 0 1
a30 1 0 1 0
a31 1 0 1 1
a32 1 1 0 0
a33 1 1 0 1
a34 1 1 1 0
a35 1 1 1 1
f
FF1
FF2
FF3
FWD
3
f
5
f
2
f
1
f
7
f
6
f
4
f
s
Figure 49: Function chart of “Fixed frequency“ control FF1 to FF3
X Program one or more of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as FF1 to FF4,
by entering the values 02 (FF1) to 05 (FF4) under the corresponding PNU (C01 to C05).
The fixed frequencies can be programmed in two ways:
• input of the fixed frequencies under PNU A21 to A35,
• input of the fixed frequencies under PNU F01.
With PNU F01, it is possible to modify the parameter even though
the parameter protection PNU b31 is set (a Page 66).
Input of the fixed frequencies under PNU A21 to 35
X Goto PNU A21 and press the PRG key.
X Use the arrow keys to enter the fixed frequency and confirm
with the ENTER key.
X Repeat these steps for PNU A22 to A35 to suit your required
frequencies.
Input of the fixed frequency under PNU F01
For frequency input under PNU F01, the value 02 must be set
beforehand in PNU A01.
X To select a fixed frequency stage, activate the digital inputs as
listed in Table 13.
X Goto PNU F01.
FF4
FF3
FF2
FF1
4
P24123
Figure 48: Digital inputs 1 to 4 configured as FF1 to FF4
(fixed frequency)
56
The current frequency appears on the display.
X Use the arrow keys to enter the fixed frequency and confirm
with the ENTER key.
The entered value is saved in the parameter which you have
selected with the digital inputs (a Table 13).
X Repeat these steps for your additional fixed frequencies.
Page 60

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4
selection
Specifying frequency setpoints
The frequency setpoint value can be assigned in one of three ways,
dependent on PNU A01:
• via the installed potentiometer on the keypad,
PNU A01 = 00;
Table 14: Fixed frequency parameters
PNU Name
A01 Defined
frequency
setpoint
A20 Frequency
setpoint value
A21 Fixed
A22
A23
...
A35
F01 Display/input
frequency
of frequency
value
Adjustable in
RUN mode
– 00 Definition with the potentiometer on the keypad 01
j 0.5 to 360 Hz You can input a frequency setpoint value. You must input 02 under
Value Function WE
01 Definition via analog input O (0 to 10 V) or OI (4 to 20 mA)
02 Definition under PNU F01 and/or PNU A20
PNU A01 for this purpose.
You can assign a frequency to each of the 15 fixed frequency parameters
from PNU A21 to A35.
Display of the current frequency setpoint value or the current fixed
frequency.
Modified values are saved with the ENTER key according to the selection
of the digital inputs configured as FF1 to FF4.
Resolution g0.1 Hz
• via analog input O (0 to 10 V) or OI (4 to 20 mA),
PNU A01 = 01 (WE);
• via PNU F01 or PNU A20, PNU A01 = 02.
Selecting fixed frequencies
X The set fixed frequency values are selected by activating the
respective digital inputs (a Table 13).
0.0
If one or more of the fixed frequencies exceeds 50 Hz, you
h
must first increase the end frequency accordingly with
PNU A (04 (a Section ”Maximum end frequency”,
Page 79).
Fixed frequency stage 0 (none of the inputs FF1 to FF4 are
h
activated) corresponds to the frequency setpoint value.
Depending on the configuration PNU A01 it is possible to
implement via the integrated potentiometer, the setpoint
input values O or OI, or via PNU F01 and PNU A20.
57
Page 61

Programming the control
signal terminals
Current setpoint value AT (4 to 20 mA)
When the digital input which has been configured as AT is active,
the setpoint value is defined by the current flow (4 to 20 mA) on
terminal OI. If however the AT input is inactive, the setpoint value
is defined by the voltage present (0 to 10 V) at terminal O.
AT
P245
Figure 50: Digital input 5 configured as AT (setpoint value via
current)
Under PNU A01, enter the type of frequency setpoint definition.
With a default setting of 01, the voltage 0 to 10 V present on
terminal O or the current of 4 to 20 mA flowing into terminal OI is
interpreted as the setpoint value. Depending on whether the AT
input is active or not. If it has not yet been correctly configured, set
the parameter to 01.
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as AT, by inputting the
value 16 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05) to 16.
58
Page 62

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Second time ramp 2CH
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4
selection
If the digital input which has been configured as 2CH is active, the
motor will be accelerated or braked with the second acceleration
or deceleration time. If the 2CH input is again deactivated, a changeover to the first acceleration/deceleration time takes place.
2CH
FWD
P2413
Figure 51: Digital input 3 configured as the “second time ramp” 2CH
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
Value Function WE
FWD/REV
2CH
a
b
f
O
Figure 52: Function chart for 2CH (second acceleration time)
: output frequency
f
o
a First acceleration time
b Second acceleration time
X Set under PNU A92 and PNU A93, the required value for the
second acceleration and delay time.
X Then set under PNU A94, the value 00 so that the changeover
to the second acceleration and delay time via the 2CH input is
enabled (this is the default setting).
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as 2CH, by setting the
value 09 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05).
A92 Second accele-
ration time
A93 Second decele-
ration time
A94 Changeover
from the first to
the second
time ramp
If you set PNU A94 to 01, the changeover to the second
h
j 0.1 to 3 000 s Setting times for the second acceleration and deceleration time
– 00 Changeover to the second time ramp if an active signal is present on a
01 Changeover to the second time ramp when the frequencies entered under
acceleration or deceleration time can take place automatically at the frequency set under PNU A95 or A96
(a Section ”Time ramps”, Page 96).
The value for the first acceleration and deceleration time
h
is defined in PNU F01 and F02 (a Section ”Acceleration
time 1”, Page 76).
15
0.1 to 999.9 s; resolution: 0.1 s
1000 to 3000 s; resolution: 1 s
00
2CH digital input.
PNU A95 and/or A96 are achieved
59
Page 63

Programming the control
signal terminals
Controller inhibit and coasting of the motor FRS
(free run stop)
If you activate the digital input configured as FRS, the motor is
switched off and coasts to a stop (for example if an EmergencyStop is made). If you deactivate the FRS input, then, depending on
the converter’s configuration, frequency output is either synchro-
nized to the current speed of the coasting motor or restarts at
0Hz.
FWD/REV
FRS
n
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
a
M
c
t
b
w
FRS
FWD
P2434
Figure 53: Configuration of digital input 3 as “controller inhibit” FRS
(free run stop) and 4 as FWD (start/stop clockwise
rotation)
PNU Name Adjustable in
Value Function WE
RUN mode
b03 Delay time
– 0.3 to 100 s Here, set a time which is to expire before an automatic restart is initiated
until restart
b88 Motor restart
after removal
of the FRS
– 00 0 Hz restart after deactivation of the FRS input 00
01 Synchronization of the motor to the current motor speed after the delay
signal
Figure 54: Function chart “control inhibit and free run stop” FRS
:motor speed
n
M
: delay time (setting under PNU b03)
t
w
a Motor coasts to a stop
b Synchronization to the current motor speed
c Restart from 0 Hz
X Set under PNU b88, if the motor is to restart with 0 Hz after
deactivation of the FRS input, or if a synchrinization to the
current motor speed after a waiting time (PNU b03) is to occur.
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as FRS, by inputting the
value 11 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05).
after a fault signal. This time can also be used in conjunction with the FRS
function. During the delay, the following message appears on the LED
display:
time entered under PNU b03.
1.0
60
Page 64

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
External fault message EXT
If the digital input configured as EXT is activated, the fault
message E12 is initiated (e.g. an input used for the bimetal
contacts). The fault message remains active even if the EXT input
is deactivated again and must be acknowledged with a reset.
A reset can be carried out with:
• the RST input or
• the OFF key.
• Alternatively, the supply voltage can be switched off and on
again.
EXT
FWD
P2413
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4
selection
Figure 55: Digital input 1 configured as FWD “start/stop clockwise
rotation” and digital input 3 as EXT “external fault”
FWD/REV
EXT
a
n
M
RST
K14
Figure 56: Function chart for EXT (external fault message)
: motor speed
n
M
K14: signalling relay contact K14
a Motor coasts to a stop
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as EXT, by inputting the
value 12 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05).
Warning!
After a reset, the motor restarts immediately if a start
command (FWD or REV) is present.
61
Page 65

Programming the control
signal terminals
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Restart inhibit USP
If the digital input configured as USP is activated, the restart
inhibit is also activated. This prevents restart of the motor, when
the voltage recovers after a mains fault if a simultaneous start
command (active signal on FWD or REV) is present. Fault message
E13 is issued. By pressing the OFF key or by an active signal on the
RST input, E13 is erased. Alternatively, the start command can be
revoked.
USP
FWD
P2413
Figure 57: Digital input 1 configured as FWD (start/stop clockwise
rotation) and digital input 3 as USP (restart inhibit).
U
N
FWD/REV
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as USP, by inputting the
value 13 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05).
Warning!
If the restart inhibit has activated (fault message E13) and
this fault message is acknowledged with a reset
command when the start command (input FWD or REV
active) is still active, it is important to note that the motor
will start to run immediately.
If you issue a start signal within three seconds of reestab-
h
lishing the power supply and the restart inhibit is active,
the restart inhibit is also triggered and issues fault
message E13. When the restart inhibit is used, you should
therefore wait for at least 3 seconds before issuing a start
command to the frequency inverter.
The restart inhibit can still be executed, after an undervol-
h
tage fault message (E09) when a reset command is issued
via the RST input.
USP
K14
f
O
E13
Figure 58: Function chart for USP (restart inhibit)
:supply voltage
U
N
K14: signalling relay contact K14
: output frequency
f
o
a Revoke start command (alarm no longer present)
b Start command
a
b
62
Page 66

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Reset: RST
A fault message can be acknowledged by activating and subsequently deactivating (i.e. resetting) the digital input configured as
RST.
RST
P244
Figure 59: Digital input 4 configured as RST (reset)
f 12 ms
RST
K14
~ 30 ms
Figure 60: Function chart for RST (reset)
K14: signalling relay contact K14
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4
selection
Warning!
If a malfunction is responded to by a reset, the motor will
start immediately if a start signal is applied simultaneously. To avoid the risk of serious or fatal injury to
personnel, you must ensure that the start signal is not
present before acknowledging an error message with a
reset.
When a fault condition has occurred, the OFF key on the
h
keypad acts as a RESET key, and can be used instead of
the RST input to reset the fault.
If the RST input is active for more than 4 seconds, it can
h
cause a false trip.
The RST input is always a make (NO) contact and cannot
h
be programmed as a break contact (NC).
Alternatively, you can acknowledge a fault message by
h
briefly switching the supply voltage off and on again.
If a reset is initiated during operation, the motor will coast
h
to a stop.
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as RST, by inputting the
value 18 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05).
63
Page 67

Programming the control
signal terminals
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Jog mode (JOG)
When the digital input configured as JOG is activated, the motor
can be operated in jog mode. This mode is used, e.g. for manual
setting actions on machinery by issuing a start command on the
FWD or REV input with a relatively low frequency without applying
an acceleration ramp to the motor.
JOG
FWD
P2413
Figure 61: Digital input 1 configured as FWD (start/stop clockwise
rotation) and 3 as JOG (jog mode).
JOG
FWD/REV
a
n
M
a
X Input under PNU A38 the frequency which is to be applied to
the motor when jog mode is active.
Make sure that the frequency is not too high, as it is applied
directly to the motor without an acceleration ramp. This could
cause a fault message to occur. Set a frequency below about 5 Hz.
X As the start command in jog mode is to be set via the FWD or
REV input, set under PNU A02 the value 01.
X Under PNU A39, you determine how the motor is to be braked.
X Program one of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as JOG, set the value
06 under the respective PNU (C01 to C05).
Caution!
Make sure that the motor has stopped before using jog
mode.
Figure 62: Function chart for JOG (jog mode)
n
:motor speed
M
a Depending on the setting of PNU A39
00: free run (coast)
01: deceleration ramp
02: DC braking
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A02 Start command – 01 The start command for starting the motor is issued by the digital inputs
A38 Frequency in
jog mode
A39 Type of motor
stop in jog
mode
Jog mode cannot be applied if the value set for the jog
h
j 0.5 to 9.99 Hz The frequency to be applied to the motor in jog mode. 1.0
– 00 Stop command on: the motor coasts to halt 00
Value Function WE
configured as FWD or REV.
02 The start command for starting the motor is issued by the ON key on the
keypad.
01 Stop command on: the motor is braked to standstill using a deceleration
ramp
02 Stop command on: the motor is braked to standstill using DC braking
mode frequency under PNU A38 is less than the start
frequency set under PNU b82 (a Section ”RUN operational”, Page 70)
01
64
Jog mode can only be activated when the frequency
h
inverter is in the Stop state.
Page 68

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PTC thermistor input: PTC
If programmable digital input 5 is configured as PTC, the motor
temperature can be monitored with a thermistor with a positive
temperature coefficient (PTC) connected to terminals 5 and L. If
the resistance of the thermistor rises above 3000 O (g10 %), the
motor is stopped and fault message E35 is displayed.
PTC
5L
i
Figure 63: Digital input 5 configured as PTC (thermistor input)
X Program digital input 5 as PTC by setting PNU C05 to 19.
Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4
selection
The PTC thermistor can be connected only to digital input
h
5, not to digital inputs 1 to 4 .
If digital input 5 is configured as PTC, but no thermistor is
h
connected, fault message E35 is displayed.
The PTC input is always a make contact; it cannot be
h
configured as a break contact.
65
Page 69

Programming the control
signal terminals
Software protection SFT
If you activate the digital input configured as SFT, the configured
parameters cannot be overwritten unintentionally.
SFT
FWD
P2413
Figure 64: Digital input 3 configured as “Software protection” SFT
X First of all set under PNU b31 if the software protection should
also apply for the frequency setting under PNU F01.
X Then, program one or more of the digital inputs 1 to 5 as SFT,
set the value 15 under PNU (C01 to C05).
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
b31 Software
dependent
parameter
protection
There is however, an alternative method of software
h
– 00 Software protection through SFT input; all functions inhibited 01
Value Function WE
01 Software protection through SFT input; input via PNU F01 possible
02 Software protection without SFT input; all functions inhibited
03 Software protection without SFT input; input via PNU F01 possible
protection available which does not require an SFT input.
For this purpose, set under PNU b31 the value 02 or 03,
depending on whether or not the software protection
should also apply for the frequency setting made with
PNU F01.
66
Page 70

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Programmable digital outputs 11 and 12
Programmable digital outputs
11 and 12
The programmable digital outputs 11 and 12 are open collector
transistor outputs (a Fig. 65), to which e.g. relays can be
connected. These outputs can both be utilized for various functions, for example to signal when a determined frequency setpoint
is reached or when a fault occurs.
11, 12
– +
CM2
24 V
F 27 V H, 50 mA
Figure 65: Digital output
Transistor output: maximum 27 V H, 50 mA
The terminal function for each of the programmable digital inputs
11 and 12 is implemented via PNU C21 and C22, i.e. with
PNU C21 the function for digital output 11 is determined and with
PNU C22 the function for digital output 12 is determined.
Table 15: Digital outputs 11 and 12
PNU Terminal
Adjustable in
RUN mode
Value WE
Programmable digital inputs 11 and 12 are by default configured
as break (NC) contacts. If, therefore, you activate the function of
an output terminal, the corresponding input opens; if you deactivate it, the output closes.
If required, the digital inputs can be configured as make (NO)
contacts. To do this, enter 00 under PNU C31 and C32 (corresponding to digital output 11 and 12) for this purpose.
Table 17: Configuration of digital outputs as make contacts
PNU TerminalValueAdjustable in
RUN mode
C31 11 00 or 01– 00: Make
C32 12
Function WE
01
contact
01: Break
contact
C21 11 – a Table 16 01
C22 12
00
A detailed description of the output functions can be found on the
pages listed in Table 16.
Table 16: Functions of the digital outputs
Value Function
00 RUN Signal during operation of the
01 FA1
02 FA2
03 OL
04 OD
05 AL
Description a Page
70
motor
Frequency setpoint reached 68
Frequency exceeded
Overload 71
PID control deviation
exceeded
Fault 73
72
67
Page 71

Programming the control
signal terminals
Frequency value messages FA1/FA2
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The digital output configured as FA1 will be activated as soon as
the setpoint frequency is achieved.
The digital output configured as FA2 is activated as long as the
frequencies set under PNU C42 and C43 are exceeded.
To ensure a certain level of hysterysis, the FA1 and FA2 signals are
activated 0.5 Hz before the frequency setpoint value or the
frequency value set under PNU C42 is achieved and deactivated
1.5 Hz after the frequency setpoint value or the frequency value
set under PNU C43 is achieved.
f
O
0.5 Hz
FA1
PNU F01
60 ms
Figure 66: Function chart for FA1 (frequency achieved)
f
: output frequency
o
F01: setpoint value
As the digital outputs 11 and 12 are configured as break contacts, FA1
is active with “0”.
0.5 Hz
1.5 Hz
PNU F01
60 ms
1.5 Hz
f
O
PNU C42
PNU C43
FA2
0.5 Hz
60 ms
1.5 Hz
Figure 68: Function chart for FA2 “frequency exceeded”
: output frequency
f
o
As the digital outputs 11 and 12 are configured as break contacts, FA2
is active with “0”.
X If you want to configure a programmable output as FA2, you
must set the frequency under PNU C42, at which the FA2 signal
is to be generated in the acceleration phase.
X With PNU C43, you set the respective frequency which is to
remain active until the FA2 signal is deactivated during deceleration.
X Program one of the digital outputs 11 or 12 as an FA1 or FA2
output by setting under PNU C21 or C22, the value 01 for FA1
or 02 for FA2.
The transition of an FA1 or FA2 signal from the inactive to
h
the active state takes place with a delay of about 60 ms.
FA1/FA2
1112CM2
24 V
50 mA
Figure 67: Digital output 11 configured as FA1/FA2 (frequency
achieved/exceeded)
68
Page 72

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Frequency value messages
FA1/FA2
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
C42 Frequency from
– 0 to 360 Hz The digital output (11 or 12)
which FA2
becomes active
during acceleration
C43 Frequency at
which FA2
becomes inactive
during deceleration
Value Function WE
f
PNU C42
PNU C43
configured as FA2 becomes
active when the frequency
0.0
entered here is exceeded
during acceleration.
FA2
The digital output (11 or 12) configured as FA2 remains active as long
as the actual frequency remains higher than the frequency entered
during deceleration (a also the illustration for PNU C42).
69
Page 73

Programming the control
signal terminals
RUN operational
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The digital output configured as RUN remains activated as long as
a frequency not equal to 0 Hz is present, i.e. as long as the motor
is driven in a clockwise or anticlockwise direction.
RUN
1112CM2
24 V
50 mA
Figure 69: Digital output 11 configured as RUN “operational”
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
b82 Increased start
– 0.5 to 9.9 Hz An increase in the start frequency leads to a corresponding reduction in
frequency
Value Function WE
the acceleration and deceleration times (for example to overcome high
frictional resistance). If the frequencies are too high, fault message E02
may be issued. With the set start frequency, the motor starts without a
ramp function.
FWD/REV
a
f
O
RUN
Figure 70: Function chart for RUN “operational”
: output frequency
f
o
a At PNU b82 set start frequency
As the digital outputs 11 and 12 are configured as break contacts, RUN
is active with “0”.
X Program one of the digital inputs 11 or 12 as a RUN output by
a
setting the value 00 under PNU C21 or C22.
0.5
70
Page 74

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Overload message OL
The digital output configured as OL is activated when a freely
selectable motor current is exceeded. The OL output is active as
long as the motor current is higher than this threshold.
OL
1112CM2
24 V
50 mA
Frequency value messages
FA1/FA2
I
M
OL
PNU C41
Figure 71: Digital output 11 configured as an OL “overload
message”
PNU Name Adjustable in
Value Function WE
RUN mode
C41 Overload alarm
– 0 to 2 x I
threshold
1) Frequency inverter’s rated current
Figure 72: Function chart for OL “Overload message”
As the digital outputs 11 and 12 are configured as break contacts, OL
is active with “0”.
X If you want to configure a programmable digital output as OL,
you must set the current under PNU C41, at which the OL signal
activates when it has been exceeded.
X Then, program one or more of the digital outputs 11 or 12 as
the OL output, by setting the value 03 under PNU C21 or C22.
1)
e
The current value entered here determines when the OL overload signal should be activated.
1)
I
e
71
Page 75

Programming the control
signal terminals
PID controller deviation message OD
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The digital output configured as OD is activated when a user definable PID deviation (actual value versus setpoint value) is
exceeded. The OD output remains active as long as this differential
is exceeded.
OD
1112CM2
24 V
50 mA
Figure 73: Digital output 11 configured as OD “PID deviation”
a
Figure 74: Function chart for OD “PID deviation”
a Setpoint
b Actual value
As the digital outputs 11 and 12 are configured as break contacts, OD
is active with “0”.
X If you want to configure a programmable output as OD, you
b
PNU C44
PNU C44
OD
must set the threshold under PNU C44 at which the OD signal
should be activated.
X Then, program one or more of the digital outputs 11 or 12 as
the OD output, by setting the value 04 under PNU C21 or C22 .
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
C44 PID regulator
deviation
– 0 to 100% If the deviation between the setpoint and actual value exceeds the
Value Function WE
3.0
value entered here when the PID controller is active, the OD signal
activates.
72
Page 76

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Error message AL
The digital output configured as AL activates when a fault has
occurred.
AL
1112CM2
24 V
50 mA
Figure 75: Digital output 11 configured as AL (fault occurrence)
X Program one of the digital inputs 11 or 12 as the AL output, by
setting the value 05 under PNU C21 or C22.
When the AL output is configured as a break contact (default
setting), remember that there is a delay from the time the supply
voltage is switched on until the AL output is closed, and a fault
message relating to the AL output therefore appears for a short
time after the supply is switched on.
Frequency value messages
FA1/FA2
Please note that the programmable digital outputs (including the
one configured as AL) are open collector types and therefore have
different electrical characteristics than the signalling relay outputs
(terminals K11, K12 and K14). In particular, the maximum voltage
and current carrying capacity ratings are significantly lower than
those of the relay outputs.
After the frequency inverter supply voltage has been switched off,
the AL output remains active until the DC bus voltage has dropped
below a certain level. This time depends, among other factors, on
the load applied to the inverter.
The delay from the time a fault occurs until the AL output is activated is about 300 ms.
73
Page 77

Programming the control
signal terminals
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Signalling relay terminals K11, K12, K14
If a fault occurs, the signalling relay (changeover) is triggered. The
switching conditions can be programmed as required.
Table 18: Default setting of the signalling relay
Default setting of the signalling relay Reconfigured signalling relay terminals (PNU C33 = 00)
Fault or DF5 switched off Operating message Fault message Operating message or DF5
switched off
K12K11 K14
K12K11 K14 K12K11 K14
K12K11 K14
Voltage Operating
status
On Normal Open Closed On Normal Closed Open
On Fault Closed Open On Fault Open Closed
Off – Closed Open Off – Closed Open
X Use the above table to configure contacts K11–K12 or K11–K14
K11–K12 K11–K14 Voltage Operating
status
K11–K12 K11–K14
as make or break contacts under PNU C33.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
C33 Signalling relay
output
– 00 K11-K14 close with a fault message 01
After a fault has occurred, the associated fault message is retained
even after the voltage supply is switched off. The fault message
can be displayed again after the voltage has been switched back
on. However, the inverter is reset when the device is switched off,
i.e. the fault message will not be signalled on the terminals of the
Value Function WE
01 K11-K14 close when the supply voltage is applied
When the signalling relay output is configured as a break contact
(default setting), it is important to remember that there is a delay
from the time the supply voltage is switched on until the AL output
is closed, and that a fault message for the AL output therefore
appears for a short time after the supply is switched on.
signalling relay after the inverter is switched back on.
If however, the fault signalling is to be retained even after
h
the inverter is switched back on, a latching (self maintaining) relay should be used.
74
Page 78

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
6 Setting Parameters
The parameters listed in this section can be set using the keypad.
The adjustment and setting possibilities listed below are themati-
cally arranged according to their function. This provides a clear
overview of all parameters assigned to a particular functional area
(e.g. Section ”DC braking (DC-Break)”, PNU A51 to A55).
Setting the display parameters
In this section, you will see which parameters can be set using the
display on the keypad.
PNU Name Function
d01 Output frequency in Hz Output frequency display from 0.5 to 360 Hz. The “Hz” lamp on the keypad lights up.
d02
d03
d04
d05
d06
d07
d08
d09 Older fault messages (fault
Motor current in A Display of the output current from 0.01 to 999.9 A. The “A” lamp on the keypad lights up.
Direction of rotation Display:
F for clockwise rotation (forward),
•
r for anticlockwise rotation (reverse),
•
0 for stop
•
Actual value x factor Only with active PID closed loop control. The factor is set under PNU A75 and can have a value from
0.01 to 99.99; the default setting is 1.0.
Status of digital inputs 1 to 5 Example: Digital inputs 1, 3 and 5 are activated. The digital inputs 2 and 4 are
deactivated.
54321
Digital outputs 11 and 12 and
fault message output
K14 12 11
Output frequency x factor The display of the product of the factor (PNU b86) and the output frequency in the range 0.01 to
99990.
Examples:
• Display
•
•
•
Last alarm indication Display of the most recent fault message and (after the PRG key is pressed) the output frequency,
motor current and DC bus voltage at the time the fault occurred. If a fault message is not available,
the display shows
Display of the second from last and (after the PRG key is pressed) third from last fault message. If
message register)
neither the second last or third last fault message has been stored, the display shows
11.11 corresponds to 11.11,
111.1 corresponds to 111.1,
1111. corresponds to 1111,
1111 corresponds to 11110.
Example: The digital output 11 and the signal output K14 are activated. Digital
output 12 is deactivated.
---
---
75
Page 79

Setting Parameters
Basic functions
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Input/display frequency value
PNU F01 displays the current frequency setpoint value or the
current fixed frequency. You can change the frequencies with the
arrow keys and save the settings in accordance with the setting of
PNU A01 and the fixed frequency stages FF1 to FF4 (digital inputs)
(a Section “Fixed frequency FF1 to FF4 selection”, Page 56).
With PNU F01, you can change parameters even when the parameter protection PNU b31 has been set (a Page 66).
Display/input frequency setpoint value
If you have not activated any fixed frequencies, PNU F01 displays
the frequency setpoint value.
The frequency setpoint value can be assigned in one of three ways,
depending on PNU A01:
• via the installed potentiometer on the keypad, PNU A01 = 00;
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
F01 Input/indication
of frequency
setpoint value
j 0.5 to 360 Hz Resolution g0.1 Hz
Value Function WE
• via analog input O (0 to 10 V) or OI (4 to 20 mA),
PNU A01 = 01 (default setting);
• via PNU F01 or PNU A20, PNU A01 = 02.
If you specify the frequency setpoint value with PNU A20
(a Page 78), you can enter a new value under PNU F01. This is
automatically saved under PNU A20:
X Change the current value with the arrow keys.
X Save the modified value with the ENTER key.
The saved value is automatically written to PNU A20.
Displaying/entering fixed frequencies
If you have activated the fixed frequencies via the functions FF1 to
FF4 of the digital inputs, PNU F01 displays the selected fixed
frequencies.
For information about changing the fixed frequencies, see
Section“Input of the fixed frequency under PNU F01”, Page 56.
0.0
The setpoint can be defined using various methods:
• With PNU F01 or A20: Enter the value 02 under PNU A01.
• With the potentiometer on the keypad: Enter the value 00 under
PNU A01.
• With a 0 to 10 V voltage signal or a 4 to 20 mA current signal at input
terminals O or OI: Enter the value 01 under PNU A01.
• With the digital inputs configured as FF1 to FF4. After selection of the
required fixed frequency stage using FF1 to FF4, the frequency for the
respective stage can be entered.
The display of the setpoint value is independent of which method was
used to set the setpoint value.
Acceleration time 1
Acceleration time 1 defines the time in which the motor reaches its
end frequency after a start command is issued.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
F02 Acceleration
time 1
76
j 0.1 to 3 000 s Resolution of 0.1 s at an input of 0.1 to 999.9
Value Function WE
10.0
Resolution of 1 s at an input of 1000 to 3000
Page 80

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Deceleration time 1
Deceleration time 1 defines the time in which the motor brakes to
0 Hz after a stop command.
Basic functions
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
F03 Deceleration
time 1
j 0.1 to 3 000 s Resolution of 0.1 s at an input of 0.1 to 999.9
Value Function WE
Direction of rotation
The direction of rotation defines the direction in which the motor
turns after a start command is issued.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
F04 Direction of
rotation
– 00 The motor runs in a clockwise direction. 00
Value Function WE
01 The motor runs in an anticlockwise direction.
10.0
Resolution of 1 s at an input of 1000 to 3000
77
Page 81

Setting Parameters
Setting the frequency and start command parameters
This section describes the methods for adjusting and setting the
start command and basic frequency-related parameters.
Definition of frequency setpoint value
With PNU A01, you set how the frequency setpoint value is to be
defined:
• Via the potentiometer on the keypad
• Via analog input O (0 to 10 V) or OI (4 to 20 mA)
• Definition under PNU F01 and/or PNU A20
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A01 Defined
frequency
setpoint
A20 Frequency
setpoint value
F01 Display/input
of frequency
value
– 00 Definition with the potentiometer on the keypad 01
j 0.5 to 360 Hz You can input a frequency setpoint value. You must assign 02 under
j Display of the current frequency setpoint value or the current fixed
Value Function WE
01 Definition via analog input O (0 to 10 V) or OI (4 to 20 mA)
02 Definition under PNU F01 and/or PNU A20
PNU A01 for this purpose.
frequency.
Modified values are saved with the ENTER key according to the selection
of the digital inputs configured as FF1 to FF4 (a Section ”Fixed
frequency FF1 to FF4 selection”, Page 56).
Resolution g0.1 Hz
Start command
With PNU A02, you define whether the start command is issued
using the ON key of the keypad or through the digital inputs configured as FWD and REV.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
Value Function WE
0.0
A02 Start command – 01 The start command for starting the motor is issued by the digital inputs
configured as FWD or REV.
02 The start command for starting the motor is issued by the ON key on the
keypad.
78
01
Page 82

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Base frequency
The base frequency is the frequency at which the output voltage
has its maximum value.
Setting the frequency and start
command parameters
PNU Name Adjustable in
Value WE
RUN mode
A03 Base frequency – 50 to 360 Hz 50
Maximum end frequency
If you want to set another frequency range with a constant voltage
that lies beyond the base frequency set under PNU A03, this
frequency is set with PNU A04. The maximum end frequency may
not be smaller than the base frequency.
100
U
[%]
0
f
1
f
2
f
[Hz]
Figure 76: Maximum end frequency
f
: base frequency
1
: maximum end frequency
f
2
PNU Name
Adjustable in
RUN mode
A04 Maximum end
– 50 to 360 Hz 50
frequency
Value WE
79
Page 83

Setting Parameters
Analog setpoint value matching
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The external setpoint signal can be specifically matched with parameters PNU A11 to A16, which are described below. A configurable voltage or current setpoint range can be assigned to a configurable frequency range.
Furthermore, analog setpoint signal filtering can be adjusted using
PNU A16.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A11 Frequency with
– 0 to 360 Hz Here, the frequency that corresponds to the minimum voltage setpoint
minimum
setpoint value
A12 Frequency with
maximum
setpoint value
A13 Minimum
setpoint value
A14 Maximum
setpoint value
A15 Conditions for
start frequency
A16 Analog input
filter time
constant
Value Function WE
0 to 360 Hz Here, the frequency that corresponds to the maximum voltage setpoint
0 to 100 % The minimum setpoint value entered here relates to the maximum
0 to 100 % The maximum setpoint value entered here relates to the maximum
Determines the behaviour at setpoint values below the minimum setpoint value. 01
00 The frequency defined under PNU A11 is applied to the motor.
01 A frequency of 0 Hz is applied to the motor.
To reduce the inverter’s response time to setpoint changes at the O or OI terminal, and
thereby determine the degree to which analog signal harmonics are filtered, you can enter
a value between 1 and 8 here.
1 Minimal filtering effect/fast response to setpoint value changes
....
8 Maximum filtering effect/slow response to setpoint value changes
f
[Hz]
PNU A12
PNU A15 = 00
PNU A11
PNU A13 PNU A14
0 V
4 mA 20 mA
PNU A15 = 01
Figure 77: Setpoint value matching
x: Voltage or current setpoint signal on analog input O or OI
value under PNU A13 is set.
value under PNU A14 is set.
possible voltage or current setpoint (10 V or 20 mA).
possible voltage or current setpoint (10 V or 20 mA).
10 V
0.0
0.0
0
100
8
80
Page 84

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Voltage/frequency characteristics and boost
Voltage/frequency
characteristics and boost
The boost with the V/f characteristic has the effect of boosting the
voltage (and consequently boosting the torque) in the lower
frequency range. The manual boost raises the voltage in the
frequency range from the start frequency (standard setting 0.5 Hz)
to half the base frequency (25 Hz with the standard setting of
50 Hz) in every operating stage (acceleration, normal operation,
deceleration), independently of the motor load. With automatic
boost, in contrast, the voltage is boosted according to the motor
load. A voltage boost may cause a fault message and trip due to
the higher currents involved.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
Value Function WE
U
[%]
100
PNU A42 = 50
0
5.0
PNU A43 = 10 %
Figure 78: Boost characteristics
Parameter settings:
A41 = 00
A42 = 50
A43 = 10.0
A44 = 00
A45 = 100
25.0
50.0
[Hz]
f
A41 Boost characteristics – 00 Manual boost 00
01 Automatic boost
A42 Manual boost
j 0 to 99 % Setting the voltage boost level with manual boost. 11
percentage
A43 Maximum boost at 1 %
of the base frequency
A44 Voltage/frequency
characteristic
j 0 to 50 % Setting the frequency with the highest voltage boost as a percen-
tage of the base frequency.
– You can select a quadratic or a V/f
[%]
U
100
0
b
a
characteristic for accelerating or
decelerating the motor.
f
10.0
00
a Linear
b Quadratic
00 Linear V/f characteristic (constant torque).
01 Quadratic V/f characteristic (reduced torque)
A45 Output voltage
j 50 to 100 %
of the input
voltage
[%]
U
100
50
0
The output voltage can
be set to 50 to 100 % of
the input voltage.
f
100
81
Page 85

Setting Parameters
DC braking (DC-Break)
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
To activate DC braking, apply a stop signal (PNU A51 to A55). By
applying a pulsed DC voltage to the motor stator, a braking torque
is induced in the rotor and acts against the rotation of the motor.
With DC braking, a high level of stopping and positioning accuracy
can be achieved.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A51 DC braking active/
inactive
A52 DC braking starting
frequency
A53 DC braking waiting
time
A54 DC braking torque
A55 DC braking duration
– 00 DC braking is not used (is inactive) 00
Value Function WE
01 DC braking is used (is active)
0.5 to 10 Hz DC braking is active if the frequency is less than the frequency
0.0 to 5 s When the frequency set with PNU A52 is reached, the motor
0 to 100 % Adjustment range for the level of braking torque. 0
0.0 to 60 s The time during which DC braking is active. 0.0
Caution!
DC braking results in additional heating of the motor. You
should therefore configure the braking torque (PNU A54)
as low and the braking duration (PNU A55) as short as
possible.
0.5
entered here.
0.0
coasts for the time duration entered here before DC braking is
activated.
82
Page 86

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Operating frequency range
Operating frequency range
The frequency range which is determined by the values configured
under PNU b82 (start frequency) and PNU A04 (end frequency)
can be limited by PNU A61 and A62 (a Fig. 79). As soon as the
frequency inverter receives a start command, it applies the
frequency set under PNU A62.
f
[Hz]
PNU A04
PNU A61
PNU A62
PNU b82
0
Figure 79: Upper frequency limit (PNU A61) and lower frequency
limit (PNU A62)
10
U
[V]
To avoid resonance within the drive system, it is possible to
program three frequency jumps under PNU A63 to A68. In the
example (a Fig. 80 ), the first frequency jump (PNU A63) is
defined as 15 Hz, the second (PNU A65) as 25 Hz and the third
(PNU A67) as 35 Hz. In the example, the frequency jump widths
(adjustable under PNU A64, A66 and A68) are set to 1 Hz.
f
[Hz]
35
25
15
0
t
15 Hz
<
>
<
>
0.5 Hz
0.5 Hz
PNU A64
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A61 Maximum operating
– 0.5 to 360 Hz This function can be deactivated by entering 0.0 0.0
frequency
A62 Minimum operating
frequency
A63 First frequency jump
A64 First jump width
A65 Second frequency jump
A66 Second jump width
A67 Third frequency jump
A68 Third jump width
Figure 80: Frequency jumps
Value Function WE
0.5 to 360 Hz 0.0
0.1 to 360 Hz 0.0
0.1 to 10 Hz 0.5
0.1 to 360 Hz 0.0
0.1 to 10 Hz 0.5
0.1 to 360 Hz 0.0
0.1 to 10 Hz 0.5
83
Page 87

Setting Parameters
PID controller
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
The DF5 series frequency inverter is a PID controller. This can be
used, for example, for flow and throughput controllers with fans
and pumps. PID control has the following features:
• The setpoint value can be issued via the frequency inverter
keypad or via an external digital signal (fixed frequencies).
Sixteen different setpoint values are possible. In addition, the
setpoint can be defined with an analog input signal (0 to 10 V
or 4 to 20 mA).
• With the DF5, you can implement the actual value signal feedback through an analog input voltage (of up to 10 V) or an
analog input current (up to 20 mA).
• The permissible range for the actual value signal feedback can
be specifically matched (e.g. 0 to 5 V, 4 to 20 mA, or other
ranges).
G1
a
+
w
–
P
+
I
D
+
+
d
b
• With the aid of a scale adjustment, you can match the setpoint
signal and/or the actual value signal to the actual physical
quantities (such as air or water flow, temperature, etc.) and
represent them on the display.
The PID closed-loop control
“P” stands for Proportional, “I” stands for Integral and “D”
stands for Differential. In control engineering, the combination of
these three terms is termed PID closed-loop control, PID regulation
or PID control. PID closed-loop control is used in numerous types
of application, e.g. for controlling air and water flow or for controlling pressure and temperature. The output frequency of the
inverter is controlled by a PID control algorithm to ensure that the
deviation between the setpoint and actual value is as small as
possible. The following figure shows a block diagram representation of a PID closed loop control:
c
M
~
3
x
P1
B1
Figure 81: PID closed-loop control block diagram
G1:frequency inverter DF5
w: Setpoint value
x: Actual value
P1: Controlled variable
B1: Measured value converter
PID closed loop control is only possible after the type of
h
setpoint value and actual value used have been defined.
a System deviation
b Converter
c Fans, pumps or similar devices
d Frequency setpoint value
84
Page 88

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PID controller
The example in the following figure shows a fan control:
G1
w
0... +10 V H ; 4 – 20 mA
x
B1
a
M
~
3
Figure 82: Example of a fan control
G1:DF5 series frequency inverters
w: Setpoint value
x: Actual value
P1: Controlled variable
B1: Measured value converter
a Fan
P1
P: Proportional component
This component ensures that the output frequency and the system
deviation are subject to a proportional relationship. Using
PNU A72, the so-called proportional gain (K
), expressed in %,
p
can be defined.
The following figure illustrates the relationship between system
deviation and output frequency. A large value for K
results in a
p
quick reaction to a change of the system deviation. If, however, K
is too large, the system becomes unstable.
[%]
f
100
Kp = 2
75
50
Kp = 1
Kp = 0.75
Kp = 0.5
I: Integral component
This component results in a correction of the output frequency by
integration of the system deviation. In the case of purely proportional control, a large system deviation causes a large change in the
output frequency. It follows, then, that if the system deviation is
very small, the change in the output frequency is also very small.
The problem is that the system deviation cannot be completely
eliminated. Hence the need for an integral component.
The integral component causes a continuous adding up of the
system deviation so that the deviation can be reduced to zero. The
reciprocal value of the integration gain is the integration time
=1/Ki.
T
i
With the DF5 series frequency inverters, set the integration time
(T
). The value may be between 0.5 s and 150 s. To disable the
i
integral component, enter 0.0.
D: Differential component
This component causes a differentiation of the system deviation.
As pure proportional control uses the current value of the system
deviation and pure integral control values from previous actions, a
certain delay in the control process always occurs. The D component compensates for this behaviour.
Differential control corrects the output frequency using the rate of
change of the system deviation. The output frequency can therefore be compensated very quickly.
K
can be set between 0 and 100 s.
d
The PID controller
A PID controller combines the P, I and D components described in
the previous sections. In order to achieve the optimum control
characteristics, each of the three PID parameters must be set.
p
frequency is guaranteed by the proportional component; the inte-
Uniform control behaviour without large steps in the output
gral component minimizes the existing system deviation the
steady-state and the differential component ensures a quick
response to a rapidly changing actual value signal.
As differential control is based on a differentiation of the system
deviation, it is very sensitive and also responds to unwanted
signals, such as interference, which can result in system instability.
Differential control is normally not required for flow, pressure and
temperature control.
25
Figure 83: Proportional gain K
x: System deviation
p
Kp = 0.25
0.2 F Kp F 0.5
10050 75250
x [%]
The maximum output frequency in the above figure is defined as
100 %. K
can be set between 0.2 and 5.0 under PNU A72.
p
85
Page 89

Setting Parameters
Setting the PID parameters
Values for the PID parameters must be chosen depending on the
application. and the system’s control characteristics. To ensure
correct PID closed loop control, the following points should be
observed:
• Stable steady-state behaviour,
• Fast reaction
• Small system deviation in the steady state.
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
w
a
t
Parameters K
range. As a general rule, increasing one of the parameters K
(= reduction of T
, Ti and Kd must be set within the stable operating
p
, Ki
p
) and Kd results in a system with a faster
i
response. A very large increase however, causes system instability,
as the returned actual value increases and decreases continuously
as if subject to oscillation. In the worst case, divergent behaviour
will be the result (a Fig. 84 to Fig. 87):
w
a
t
Figure 84: Divergent behaviour
w: Setpoint value
a Output signal
w
a
t
Figure 85: Oscillation, dampened
w: Setpoint value
a Output signal
Figure 86: Good regulation behaviour
w: Setpoint value
a Output signal
w
a
t
Figure 87: Slow regulation, large static system deviation
w: Setpoint value
a Output signal
The following table provides guidelines for setting each
parameter.
Table 19: Setting the controller regulation times
Setpoint
change
Setpoint and
actual value
After increase
of K
p
Causes a slow reaction: Increase proportional
component (K
Causes a fast but
unstable reaction
Differ greatly: Reduce integral
Approach each other
after oscillation:
The reaction is still slow: Increase D component
The reaction is still
unstable:
Set a lower P
component
component (T
Set a higher I
component
)
(K
d
Set a lower D
component
)
p
)
i
86
Page 90

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PID controller
Structure and parameters of the PID controller
PID controller active/inactive
DF5 frequency inverters can operate in one of the following two
control modes:
• Frequency control active (i.e. PID closed loop control inactive)
• PID closed loop control active
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A71 PID control active/inac-
– 00 PID closed loop control is not used (inactive) 00
tive
Value Function WE
01 PID closed loop control is used (active)
Frequency control is the standard method of control used by many
frequency inverters. A setpoint value is defined by a control unit
(keypad) as an analog voltage or current signal, or via a 4 bit wide
digital command applied to the control signal terminals.
With PID closed loop control, the inverter’s output frequency is
controlled by a control algorithm to ensure that the deviation
between the setpoint and actual value is kept at zero.
You can switch between both modes with PNU A71 (PID control
active/inactive).
Parameter
The following figure illustrates which parameters are effective in
different areas of the PID block diagram. The stated parameters
(e.g. PNU A72) correspond to those on the integrated frequency
inverter keypad:
PNU A75
PNU F01
w
a
b
(PNU A76)
Figure 88: PID closed loop control parameters
w: Setpoint value
x: Actual value
: output frequency
f
o
PNU A75
PNU A12
PNU A11
0
PNU A01
-1
PNU A13
PNU A14
P: PNU A72
I: PNU A73
–
x
D: PNU A74
PNU A75 PNU d04
++
+
f
+
O
a Frequency definition with keypad, fixed frequency
b Analog definition with potentiometer, analog inputs, current or
voltage
87
Page 91

Setting Parameters
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PNU Function Adjustable in
RUN mode
A01 Defined
frequency
setpoint
A11 Frequency with
minimum
setpoint value
A12 Frequency with
maximum
setpoint value
A13 Minimum
setpoint value
A14 Maximum
setpoint value
d04 Actual value x
factor
F01 Input/display
frequency value
A72 P component of
the PID controller
A73 I component of
the PID controller
A74 D component of
the PID controller
A75 Setpoint factor of
the PID controller
A76 Input actual
value signal for
PID controller
– 00 Definition with the potentiometer on the keypad 01
– 0 to 360 Hz Here, the frequency that corresponds to the minimum voltage setpoint
– 0 to 360 Hz Here, the frequency that corresponds to the maximum voltage setpoint
– 0 to 100 % The minimum setpoint value entered here relates to the maximum
– 0 to 100 % The maximum setpoint value entered here relates to the maximum
j – Only with active PID closed loop control. The factor is set under
j 0.5 to 360 Hz Resolution g0.1 Hz
j 0.2 to 5.0 Adjustment range of the proportional component of the PID closed loop
j 0.0 to 150 s Adjustment time Ti of the integral component of the PID closed loop
j 0.0 to 100 s Adjustment time Td of the differential component of the PID closed loop
– 0.01 to 99.99 The display of the frequency setpoint or actual value can be multiplied
– 00 Actual value signal present on analog input OI (4 to 20 mA) 00
Value Function WE
01 Definition via analog input O (0 to 10 V) or OI (4 to 20 mA)
02 Definition under PNU F01 and/or PNU A20
0.0
value under PNU A13 is set.
0.0
value under PNU A14 is set.
0
possible voltage or current setpoint (10 V or 20 mA).
100
possible voltage or current setpoint (10 V or 20 mA).
–
PNU A75, from 0.01 to 99.99; default setting = 1.0.
0.0
The setpoint can be defined using various methods:
• With PNU F01 or A20: Enter the value 02 under PNU A01.
• With the potentiometer on the keypad: Enter the value 00 under
PNU A01.
• With a 0 to 10 V voltage signal or a 4 to 20 mA current signal at input
terminals O or OI: Enter the value 01 under PNU A01.
• With the digital inputs configured as FF1 to FF4. After selection of the
required fixed frequency stage using FF1 to FF4, the frequency for the
respective stage can be entered.
The display of the setpoint value is independent of which method was
used to set the setpoint value.
1.0
control
1.0
control
0.0
control
1.00
by a factor, so that process related quantities (e.g. flow or similar) can
be displayed instead of the frequency.
01 Actual value signal present on analog input O (0 to 10 V)
Internal regulator-based calculations
All calculations within the PID algorithm are carried out in percentages, so that different physical units can be used, such as
• Pressure (N/m
• Flow rate (m
2
),
3
/min),
• Temperature (°C), etc.
The setpoint and returned actual values can, for example, also be
compared as percentages.
88
A useful scaling function (PNU A75) is also available. When these
parameters are used, you can define the setpoint directly as the
required physical quantity and/or display setpoint and actual
values as physical quantities suitable for the process.
Additionally, analog signal matching (PNU A11 to A14) is available, with which a range based on the actual value feedback can
be defined. The following graphs illustrate the mode of operation
of this function.
Page 92

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PID controller
Setpoint definition
There are three ways of entering the setpoints:
• Keypad
• Digital control signal terminal input (4 bit)
• Analog input (terminals O-L or OI-L)
If the digital setpoints are defined through the control signal terminals, define the required setpoint value in PNU A21 to A35. The
setting procedure is similar to the one which is used in frequency
regulation mode (i.e. with a deactivated PID controller) for setting
the respective fixed frequencies (a Section ”Fixed frequency FF1
to FF4 selection”, Page 56).
f
100
[%]
0
PNU A13 = 20 %
PNU A14 = 100 %
10 V2 V
20 mA4 mA
100 %20 %
f
100
[%]
0
PNU A13 = 0 %
PNU A14 = 50 %
Actual value feedback and actual value signal matching
You can specify the actual value signal as follows:
• With an analog voltage on control signal terminal O
(maximum 10 V)
• With an analog current on control signal terminal OI
(maximum 20 mA)
One of the two methods mentioned is selected via PNU A76.
To adapt the operation of the PID controller to the respective appli-
cation, the actual value feedback signal can also be matched as
shown in Figure 89:
f
100
[%]
10 V5 V
20 mA10 mA
100 %50 %
0
PNU A13 = 25 %
PNU A14 = 75 %
7.5 V
15 mA
75 %
10 V2.5 V
20 mA5 mA
100 %25 %
f
100
[%]
25
0
PNU A13 = 20 %
PNU A14 = 100 %
PNU A11 = 25 %
PNU A12 = 100 %
10 V2 V
20 mA4 mA
100 %20 %
f
100
[%]
75
0
PNU A13 = 0 %
PNU A14 = 50 %
PNU A11 = 0 %
PNU A12 = 75 %
Figure 89: Analog actual value signal matching
As evident from the graphs, the setpoint value must be within the
valid range on the vertical axis if you have set functions PNU A11
and A12 to a value not equal to 0. Because there is no feedback
signal, stable control cannot otherwise be guaranteed. This means
that the frequency inverter will either
• output the maximum frequency,
• go to stop mode,
• or output a lower limit frequency.
f
100
[%]
75
25
10 V5 V
20 mA10 mA
100 %50 %
0
7.5 V
15 mA
75 %
10 V2.5 V
20 mA5 mA
100 %25 %
PNU A13 = 25 %
PNU A14 = 75 %
PNU A11 = 25 %
PNU A12 = 75 %
89
Page 93

Setting Parameters
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Scaling adjustment
Scaling adjustment and scaling allow the setpoint and actual value
to be displayed and the setpoint value to be entered directly in the
correct physical unit. For this purpose, 100 % of the returned
actual value is taken as a basis. By default, inputs and displays are
based on 0 to 100 %.
Example: In the first diagram in Figure 89, 20 mA of the feedback
signal correspond to 100 % of the PID internal factor. If for
example the current flow is 60 m
20 mA, the parameter is set to 0.6 with PNU A75 (= 60/100). With
PNU d04, the process corrected value can be displayed and the
setpoint value can be entered directly as a process corrected
quantity.
G1
a
B1
P1
w [%]
PNU F01
0 – 60m
3
w [%]
PNU F01
= 0 – 100 %
M
~
3
Factory default setting PNU A75 = 0.6
x
4 – 20 mA
PNU d01
= 0 – 100 %
Figure 90: Example for scaling adjustment
w: Setpoint value
x: Returned actual value
a Fan
/min
G1
3
/min with a feedback signal of
x
4 – 20 mA
PNU d01
3
/min
0 – 60m
M
~
3
B1
P1
a
Summary of the relevant parameters
With the DF5 series frequency inverters, the same parameters are
used for both the frequency control mode and the PID mode. The
designations of the respective parameter only relate to the
frequency control mode, however, as this mode is used in most
cases. When the PID mode is used, some of the parameters have
other designations.
The following table contains an explanation of these parameters
in conjunction with the frequency control mode as well as the PID
mode:
PNU Meaning of the parameters when used in
Frequency control mode PID mode
d04 – Display of the returned actual value
F01
A01
A11
A12
A13
A14
A21 to A35
Displays of the output frequency Display of the setpoint value
Defined frequency setpoint Defined setpoint
Frequency with minimum setpoint value (Units: Hz) Feedback percentage actual value for lower acceptance
threshold (units: %)
Frequency with maximum setpoint value (Units: Hz) Feedback percentage actual value for upper acceptance
threshold (Units: %)
Minimum setpoint value (Units: Hz) Lower acceptance threshold for the voltage or current on the
actual value input (Units: %)
Maximum setpoint value (Units: Hz) Upper acceptance threshold for the voltage or current at the
actual value input (Unit: %)
Fixed frequencies 1 to 15 Digital adjustable setpoint values 1 to 15
90
Page 94

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PID controller
PNU
A71 – PID control active/inactive
A72
A73
A74
A75
A76
Settings in the frequency control mode
Before you use the PID mode, you must configure the parameters
in frequency control mode. Observe the following two points:
Acceleration and deceleration ramp
The output frequency calculated by the PID algorithm is not immediately available on the frequency inverter output, as the output
frequency is affected by the set acceleration and deceleration
times. Even when, for example, a large D component is defined,
the current output frequency is significantly influenced by the
acceleration and deceleration time, and this causes unstable regulation.
To achieve stable behaviour in each PID closed loop control range,
Meaning of the parameters when used in
Frequency control mode PID mode
P component of the PID controller
I component of the PID controller
D component of the PID controller
Setpoint factor of the PID controller
Input actual value signal for PID controller
After every acceleration and deceleration ramp parameter change,
parameters PNU A72, A73 and A74 must be rematched.
Frequency jumps/range
Frequency jumps must be defined to meet the following requirement: A change to the feedback actual value signal must not occur
during execution of a frequency jump. If a stable operating point
exists within a frequency jump range, operation between both end
values of this range occurs.
Configuration of setpoint value and actual value
In PID mode, you must first of all specify how the setpoint is to be
defined and where the actual value is to be supplied. The following
table provides the required settings:
the acceleration and deceleration times should be set as low as
possible.
Actual value input Setpoint value definition
Integrated keypad Digital via control
terminals
(fixed frequencies)
Analog voltage
(O-L: 0 to 10 V)
Analog current
(OI–L: 4 to 20 mA)
PNU A01 = 02
PNU A76 = 01
PNU A01 = 02
PNU A76 = 00
PNU A01 = 02
PNU A76 = 01
PNU A01 = 02
PNU A76 = 00
It is not impossible to enter the setpoint value and the actual value
through the same analog input terminal.
Please note that the frequency inverter brakes and stops according
to the set deceleration ramp as soon as a stop command is issued
during PID operation.
Scaling
Please set the scaling to the process-corrected physical quantity as
required by your application, i.e. to flow, pressure, temperature,
etc. For a detailed description, see Section ”Scaling adjustment”,
Page 90.
Setpoint adjustment via digital inputs
The following points must be observed when setting the setpoint
via digital inputs (4 bit):
Integrated
potentiometer
PNU A01 = 00
PNU A76 = 01
PNU A01 = 00
PNU A76 = 00
Analog voltage on
O-L
– PNU A01 = 01
PNU A01 = 01
PNU A76 = 00
Analog current
on OI-L
PNU A76 = 01
–
Assignment of the digital inputs
The DF5 series have five programmable digital inputs. Assign the
functions FF1 to FF4 to four of the inputs. Use PNU C01 to C05 for
this purpose, corresponding to the inputs 1 to 5 of the frequency
inverter.
Adjustment of the setpoint values
First of all, select the required number of different setpoints (up to
16) from the following table. Under PNU A21 (corresponds to the
first setpoint) to A35 (corresponds to 15th setpoint), enter the
required setpoint. PNU A20 and F01 correspond to setpoint 0.
If the setpoints are to be scaled, note that the setpoints
h
must be entered as process-corrected quantity values in
accordance with this scaling.
91
Page 95

Setting Parameters
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
.
No. FF4 FF3 FF2 FF1 Setpoint number (PNU)
1 0 0 0 0 Setpoint value 0
(PNU A20 or F 01)
0 0 0 1 Setpoint value 1 (PNU A21)
2
0 0 1 0 Setpoint value 2 (PNU A22)
3
0 0 1 1 Setpoint value 3 (PNU A23)
4
5
0 1 0 0 Setpoint value 4 (PNU A24)
0 1 0 1 Setpoint value 5 (PNU A25)
6
0 1 1 0 Setpoint value 6 (PNU A26)
7
8
0 1 1 1 Setpoint value 7 (PNU A27)
1 0 0 0 Setpoint value 8 (PNU A28)
9
1 0 0 1 Setpoint value 9 (PNU A29)
10
1 0 1 0 Setpoint value 10 (PNU A30)
11
1 0 1 1 Setpoint value 11 (PNU A31)
12
1 1 0 0 Setpoint value 12 (PNU A32)
13
1 1 0 1 Setpoint value 13 (PNU A33)
14
15
1 1 1 0 Setpoint value 14 (PNU A34)
1 1 1 1 Setpoint value 15 (PNU A35)
16
1: On
0: Off
If, for example, you only require up to four different setpoint
values, only FF1 and FF2 need to be used; for five to eight different
setpoint values, only FF1 to FF3 are required.
Activating PID mode
X Set PNU A71 to 01.
You can make this setting at the very start, before making all other
settings.
Example for setting K
and Ti
p
As for the parameter changes, check the output frequency or the
feedback actual value signal with an oscilloscope (a Fig. 84 to
Fig. 87, Page 86).
Use two different setpoint values and switch between them using
the digital control signal terminals.
The output should then always exhibit a stable behaviour.
Adjustment of the P component
Begin by setting only the P component, but not the I component
and the D component.
X First of all, set a small P component via PNU A72 and check the
result.
X If necessary, slowly increase this value until an acceptable
output behaviour has been achieved.
Alternatively, set a very large P component and observe the behaviour of the output signal. If the behaviour is unstable, set a lower
value and observe the result. Repeat this process.
If the behaviour is unstable, reduce the P component.
The P component is correct when the system deviation reaches a
static state within acceptable limits.
Setting the integral component and matching K
First of all, define a very small integral component in PNU A73.
X
X Set the P component a little lower.
p
If the system deviation does not decrease, reduce the integral
component a little. If the performance becomes unstable as a
result, reduce the P component.
X Repeat this process until you have found the correct parameter
settings.
Note about the automatic voltage regulation (AVR)
function
If you have set the AVR function (PNU A81) to 02, whereby the
automatic voltage regulation function with an active PID closed
loop control is deactivated only during deceleration of the motor,
the motor may, depending on the application, start to “knock”. In
such cases, the motor accelerates and decelerates repeatedly and
smooth running of the motor is not guaranteed. In this case, set
the AVR function to 01 (OFF).
92
Page 96

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
PID controller
Application examples
This section contains some setting examples for practical
applications.
G1
w
x
4 – 20 mA
B1
a
M
~
3
Figure 91: Examples for flow control
w: Setpoint value, 4 Bit digital
3
x: feedback actual value (500 m
/min at 20 mA)
B1: Measured value converter
P1: Flow sensor
a Pump
P1
Flow control
The example shown in the figure below has the setpoint values
3
/min and 300 m3/min:
150 m
500 m3/min
100
3
60
/min
300 m
3
150 m
/min
30
5.8 mA
29 %
10.6 mA
53 %
20 mA
100 %
4 mA0
20 %
PNU
Meaning in PID control mode Value Notes
F01 Setpoint 150 Direct input of “150 m3/min”, as the scaling
factor has been set
A01
A11
Frequency setpoint definition 02 Keypad
Feedback percentage actual value for lower acceptance threshold
0 0%
(Units: %)
A12
Feedback percentage actual value for upper acceptance threshold
100 100 %
(Units: %)
A13
Lower acceptance threshold for voltage or current on the actual value
20 20 %
input (in %)
A14
Upper acceptance threshold for voltage or current on the actual value
100 100 %
input (in %)
A21
A71
A72
A73
A74
A75
A76
Digitally adjustable setpoint value 1 300 300 m3/min
PID control active/inactive 01 PID mode active
P component of the PID controller – Application dependent
I component of the PID controller –
D component of the PID controller –
Setpoint factor of the PID controller 5.0 100 % at 500 m3/min
Input actual value signal for PID controller 00 Feedback from OI–L terminal
93
Page 97

Setting Parameters
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Temperature control
With the flow control in the previous example, the frequency
inverter’s output frequency increases if the feedback signal is less
than the setpoint and falls if the feedback signal is greater than the
setpoint. With temperature control, the opposite behaviour must
G1
B1
w
x
0... +10 V H
P1
a
M
~
3
Figure 92: Example for temperature control
w: Setpoint value, 4 Bit digital
x: Feedback actual value (50 °C at 10 V)
B1: Measured value converter
P1: Temperature sensor
a Fan
be implemented: if the temperature is above the setpoint, the
inverter must increase its output frequency to increase the speed
of the connected fan.
The following figure contains an example for temperature control
with the two setpoints 20 and 30 °C:
50 °C
100%
60%
30 °C
40%
20 °C
0
4 V
40 %
6 V
60 %
10 V
100 %
PNU
Meaning in PID control mode Value Notes
F01 Setpoint 20 Direct input of “20 °C”, as the scaling
factor has been set
A01
A11
Frequency setpoint definition 02 Keypad
Feedback percentage actual value for lower acceptance threshold
100 100 %
(Units: %)
A12
Feedback percentage actual value for upper acceptance threshold
0 0%
(Units: %)
A13
Lower acceptance threshold for voltage or current on the actual value
0 0%
input (in %)
A14
Upper acceptance threshold for voltage or current on the actual value
100 100 %
input (in %)
A21
A71
A72
A73
A74
A75
A76
Digitally adjustable setpoint value 1 30 30 °C
PID control active/inactive 01 PID mode active
P component of the PID controller – Application dependent
I component of the PID controller –
D component of the PID controller –
Setpoint factor of the PID controller 0.5 100 % at 50 °C
Input actual value signal for PID controller 01 Feedback from O-L terminal
94
Page 98

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Automatic voltage regulation (AVR)
Automatic voltage regulation
(AVR)
The AVR function stabilizes the motor voltage if there are fluctuations on the DC bus voltage. These deviations result from, for
example:
• Unstable mains supplies or
• DC bus voltage dips or peaks caused by short acceleration and
deceleration times.
A stable motor voltage provides a high level of torque, particularly
during acceleration.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A81 Characteristic of the
AVR function
A82 Motor voltage for AVR
function
– 00 AVR function active during entire operation. 02
– 200, 220, 230,
Value Function WE
01 AVR function is not active.
02 AVR function active during operation except for deceleration
240, 380, 400,
415, 440, 460
If the mains voltage is higher than the rated motor voltage, enter
the mains voltage under PNU A82 and reduce the output voltage
in PNU A45 to the rated motor voltage.
Regenerative motor operation (without AVR function) results in a
rise in the DC bus voltage in the deceleration phase (particularly
with very short deceleration times), which also leads to a corresponding rise in the motor voltage. The increase in the motor
voltage causes an increase in the braking torque. For this reason,
you can deactivate the AVR function for deceleration under
PNU A81.
The settings depend on the device series used:
• 200 V series: 200, 220, 230, 240 V
• 400 V series: 380, 400, 415, 440, 460 V
230/
400
Example: With 440 V mains voltage and 400 V rated motor
voltage, enter 440 under PNU A82 and 91 %
(= 400/440 x 100 %) under PNU A45.
95
Page 99

Setting Parameters
Time ramps
09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
During operation, you can switch over from the time ramps configured under PNU F02 and F03 to those configured under PNU A92
and A93. This can be done either by applying an external signal to
input 2CH at any time or when the frequencies configured under
PNU A95 and A96 are reached.
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
A92 Second accelera-
j 0.1 to 3 000 s Setting times for the second acceleration and deceleration time
tion time
A93 Second decelera-
tion time
A94 Changeover from
– 00 Changeover to the second time ramp if an active signal is present on
the first to the
second time ramp
A95 Acceleration time
– 0.0 to 360.0 Hz Here, set a frequency at which the changeover from the first to the
changeover
frequency
A96 Deceleration time
– 0.0 to 360.0 Hz Here, set a frequency at which the changeover from the first to the
changeover
frequency
A97 Acceleration
– Here, you can set a linear or an S-curve acceleration characteristic for motor acceleration
characteristic
Value Function WE
01 Changeover to the second time ramp when the frequencies entered
(first and second time ramp):
f
f
t
1
PNU A95
Figure 93: Time ramps
: acceleration time 1
t
1
: acceleration time 2
t
2
0.1 to 999.9 s; resolution: 0.1 s
1000 to 3000 s; resolution: 1 s
a 2CH digital input.
under PNU A95 and/or A96 are achieved
second acceleration time is to occur.
second deceleration time is to occur.
2CH/PNU A95
t
2
t
15
00
0.0
0.0
00
A98 Deceleration
96
characteristic
00
01
t
00 Linear acceleration of the motor from the first to the second time
ramp
01 S-curve characteristic for acceleration of the motor from the first to
the second time ramp
– 00 Linear deceleration of the motor from the second to the first time
ramp
01 S-curve characteristic for deceleration of the motor from the second
to the first time ramp
00
Page 100

09/01 AWB8230-1412GB
Automatic restart after a fault
Automatic restart after a fault
With the default settings, each malfunction triggers a fault
message. An automatic restart is possible after the following fault
Warning!
When a fault has occurred, this function initiates an automatic restart of the frequency inverter if a start command
is present after the set waiting time has expired. Ensure
an automatic restart does not present a danger for
personnel.
messages have occurred:
• Overcurrent (PNU E01 to E04, up to four restart attempts within
10 minutes before a fault message is issued)
• Overvoltage (PNU E07 and E15, up to three restart attempts
within 10 minutes before a fault message is issued)
• Undervoltage (PNU E09, up to 16 restart attempts within 10
minutes, then a fault message is issued)
PNU Name Adjustable in
RUN mode
b01 Restart mode – 00 The above fault messages are displayed when the associated fault occurs
b02 Permissible
power failure
duration
b03 Delay time
until restart
– 0.3 to 25 s Here, you set a time duration during which the undervoltage condition is
– 0.3 to 100 s Here, set a time which is to expire before an automatic restart is initiated
Value Function WE
(restart is not activated).
01 A restart at the start frequency after the time set under PNU b03 has
elapsed.
02 After the time set under PNU b03 has elapsed, the inverter synchronizes
to the current motor rotation speed and the motor accelerates for the set
acceleration time.
03 After the time set under PNU b03 has elapsed, the inverter synchronizes
to the current motor rotation speed and the motor brakes for the set deceleration time. A fault message is then displayed.
met without the corresponding fault message in PNU E09 being initiated.
after a fault signal. This time can be used in conjunction with the FRS function. During the delay, the following message appears on the LED display:
00
1.0
1.0
97
 Loading...
Loading...