INSTALLATION AND SERVICE MANUAL
gas-fired indoor separated combustion duct furnaces
WARNING
1. Improper installation, adjustment, alteration,
service or maintenance can cause property
damage, injury or death, and could cause
exposure to substances which have been
determined by various state agencies to
cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Read the installation,
operating and maintenance instructions
thoroughly before installing or servicing this
equipment.
2. Installing, starting up and servicing heating,
ventilation and air conditioning equipment
poses significant hazards and requires
specialized knowledge of Modine products
and training in performing those services.
Failure to have any service properly
performed by, or making any modification to
Modine equipment without the use of,
qualified service personnel could result in
serious injury to person and property,
including death. Therefore, only qualified
service personnel should work on any
Modine products.
AIR 5-593.10
5H0768550003
May, 2017
model IFS
Approved for use in California by the CEC.
FOR YOUR SAFETY
IF YOU SMELL GAS:
1. Open windows.
2. Don’t touch electrical switches.
3. Extinguish any open flame.
4. Immediately call your gas supplier.
FOR YOUR SAFETY
The use and storage of gasoline or other
flammable vapors and liquids in open
containers in the vicinity of this appliance is
hazardous.
Inspection on Arrival
1. Inspect unit upon arrival. In case of damage, report it
immediately to transportation company and your local
factory sales representative.
2.
Check rating plate on unit to verify that power supply meets
available electric power at the point of installation.
3. Inspect unit upon arrival for conformance with description of
product ordered (including specifications where applicable).
CAUTION
To prevent premature heat exchanger failure
do not locate ANY gas-fired units in areas
where chlorinated, halogenated, or acid
vapors are present in the atmosphere.
PLEASE BE SURE TO LEAVE IT WITH THE OWNER WHEN YOU LEAVE THE JOB.
THIS MANUAL IS THE PROPERTY OF THE OWNER.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS / TABLE OF CONTENTS
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS
THE INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE INSTRUCTIONS
IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE FOLLOWED TO PROVIDE SAFE,
EFFICIENT AND TROUBLE-FREE OPERATION. IN ADDITION,
PARTICULAR CARE MUST BE EXERCISED REGARDING
THE SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS LISTED BELOW. FAILURE
TO PROPERLY ADDRESS THESE CRITICAL AREAS COULD
RESULT IN PROPERTY DAMAGE OR LOSS, PERSONAL
INJURY, OR DEATH. THESE INSTRUCTIONS ARE SUBJECT
TO ANY MORE RESTRICTIVE LOCAL OR NATIONAL CODES.
HAZARD INTENSITY LEVELS
1. DANGER: Indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, WILL result in death or serious injury.
2. WARNING: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, COULD result in death or serious injury.
3. CAUTION: Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, MAY result in minor or moderate injury.
4. IMPORTANT: Indicates a situation which, if not avoided,
MAY result in a potential safety concern.
DANGER
Appliances must not be installed where they may be exposed
to a potentially explosive or flammable atmosphere.
WARNING
1. This gas fired heating equipment must be vented - do not
operate unvented.
2. A built-in power exhauster is provided - additional external
power exhausters are not required or permitted.
3. If you are replacing an existing heater, it may be
necessary to resize the venting systems. Improperly
sized venting systems can result in vent gas leakage or
the formation of condensate. Refer to the National Fuel
Gas Code ANSI Z223.1 or CSA B149.1 latest edition.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in injury or
death.
4. Under no circumstances should two sections of double
wall vent pipe be joined together within one horizontal
vent system due to the inability to verify complete seal of
inner pipes.
5. All field gas piping must be pressure/leak tested prior to
operation. Never use an open flame. Use a soap solution or
equivalent for testing.
6. Gas pressure to appliance controls must never exceed 14"
W.C. (1/2 psi).
7. Disconnect power supply before making wiring connections
to prevent electrical shock and equipment damage.
8. All appliances must be wired strictly in accordance with
wiring diagram furnished with the appliance. Any wiring
different from the wiring diagram could result in a hazard
to persons and property.
9. Any original factory wiring that requires replacement must
be replaced with wiring material having a temperature
rating of at least 105°C.
10. To reduce the opportunity for condensation, the minimum
sea level input to the appliance, as indicated on the serial
plate, must not be less than 5% below the rated input, or
5% below the minimum rated input of dual rated units.
11. Ensure that the supply voltage to the appliance, as
indicated on the serial plate, is not 5% greater than the
rated voltage.
12. When servicing or repairing this equipment, use only
factory-approved service replacement parts. A complete
replacement parts list may be obtained by contacting
Modine Manufacturing Company. Refer to the rating plate
on the appliance for complete appliance model number,
serial number, and company address. Any substitution of
parts or controls not approved by the factory will be at the
owner's risk.
CAUTION
1. Installation must conform with local building codes or in the
absence of local codes, with Part 7, Venting of Equipment,
of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 (NFPA 54) latest edition. In Canada installation must be in accordance
with CSA B149.1.
2. Purging of air from gas supply line should be performed as
described in ANSI Z223.1 - latest edition “National Fuel
Gas Code”, or in Canada in CAN/CGA-B149 codes.
3. Do not attempt to reuse any mechanical or electrical
controller which has been wet. Replace defective controller.
4. Ensure that the supply voltage to the appliance is not 5%
less than the rated voltage.
1. To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, do not locate
NY gas-fired appliances in areas where corrosive vapors
(i.e. chlorinated, halogenated or acid) are present in the
atmosphere.
2. To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, the input to
the appliance, as indicated on the serial plate, must not
exceed the rated input by more than 5%.
3. To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, observe heat
exchanger tubes by looking at the heat exchanger through
field installed access openings in connecting ductwork.
If the tubes become red while blower and duct furnace are
in operation, additional baffles must be inserted between
blower and duct furnace to assure uniform air flow across
the heat exchanger.
4. To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, with all control
systems, a blower starting mechanism must be provided so
that the blower is running or energized within 45 seconds of
the gas control operation.
5. Start-up and adjustment procedures should be performed by
a qualified service agency.
6. To check most of the Possible Remedies in the
troubleshooting guide listed in Table 24.1, refer to the
applicable sections of the manual.
Table of Contents
Inspection on Arrival .................................................................... 1
Special Precautions ..................................................................... 2
SI (Metric) Conversion Factors .................................................... 3
Unit Location................................................................................ 3
Location Recommendations................................................. 3
Combustible Material and Service Clearances .................... 3
Unit Suspension .......................................................................... 3
Installation ................................................................................... 4
Direction of Airflow ...............................................................4
Duct Installation and Airflow Distribution .............................. 4
Venting ................................................................................. 5
Gas Connections................................................................ 10
Considerations for Elevation .............................................. 11
Electrical Connections........................................................ 12
Start-Up Procedure.................................................................... 12
Pilot Burner and Main Burner Adjustment .......................... 13
Air Shutter Adjustment .......................................................14
Control Operating Sequence.............................................. 14
Variable Air Movement Applications ................................... 15
Gas Control Options........................................................... 16
Performance .............................................................................. 18
Air Temperature and External Static Pressure Limits ......... 18
Pressure Drop Curves........................................................ 18
Dimensionals ............................................................................. 19
Maintenance .............................................................................. 22
Manifold Assembly Removal .............................................. 23
Burner and Pilot Assembly Removal .................................. 23
Service & Troubleshooting....................................................24-25
Replacement Parts Ordering ..................................................... 26
Model Identification.................................................................... 27
Commercial Warranty ...................................................Back Page
IMPORTANT
2
AIR 5-593.9
SI (METRIC) CONVERSION FACTORS / UNIT LOCATION
SI (METRIC) CONVERSION FACTORS
Table 3.1
To Convert Multiply By To Obtain
"W.C. 0.24 kPa
psig 6.893 kPa
°F (°F-32) x 0.555 °C
inches 25.4 mm
feet 0.305 meters
CFM 0.028 m3/min
To Convert Multiply By To Obtain
CFH 1.699 m3/min
Btu/ft3 0.0374 mJ/m
pound 0.453 kg
Btu/hr 0.000293 kW/hr
gallons 3.785 liters
psig 27.7 "W.C.
UNIT LOCATION
DANGER
Appliances must not be installed where they may be exposed
to a potentially explosive or flammable atmosphere.
IMPORTANT
To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, do not locate
ANY gas-fired appliances in areas where corrosive vapors (i.e.
chlorinated, halogenated or acid) are present in the atmosphere.
Location Recommendations
1. When locating the furnace, consider general space and
heating requirements, availability of gas and electrical
supply, and proximity to vent locations.
2. Unit must be installed on the positive pressure side of the
circulating blower.
3. Be sure the structural support at the unit location site is
adequate to support the weight of the unit. For proper
operation the unit must be installed in a level horizontal
position.
4. Do not install units in locations where the flue products can
be drawn into the adjacent building openings such
as windows, fresh air intakes, etc.
5. Be sure that the minimum clearances to combustible
materials and recommended service clearances are
maintained. Units are designed for installation on noncombustible surfaces with the minimum clearances shown
in Figure 3.1 and Table 3.2.
6. Units installed downstream of refrigeration systems, or
exposed to inlet air temperatures of 40°F or less, may
experience condensation. Therefore, provisions should
be made for disposal of condensate. Means have been
provided in the bottom pan of the unit to accommodate a
condensate drain line connection flange.
7. When locating units, it is important to consider that the
combustion air and exhaust vent piping must be connected
to the outside atmosphere, vent terminals should be located
adjacent to one another. The maximum equivalent lengths
are listed in Table 6.1 on page 6.
8. In garages or other sections of aircraft hangars such as
offices and shops that communicate with areas used for
servicing or storage, keep the bottom of the unit at least 7'
above the floor unless the unit is properly guarded to provide
user protection from moving parts. In parking garages, the
unit must be installed in accordance with the standard for
parking structures ANSI/NFPA 88A, and in repair garages
the standard for repair garages NFPA #88B. In Canada,
installation of unit heaters in airplane hangars must be in
accordance with the requirements of the enforcing authority,
and in public garages in accordance with the current CAN/
CGA-B149 codes.
9. Do not install units in locations where gas ignition system is
exposed to water spray, rain, or dripping water.
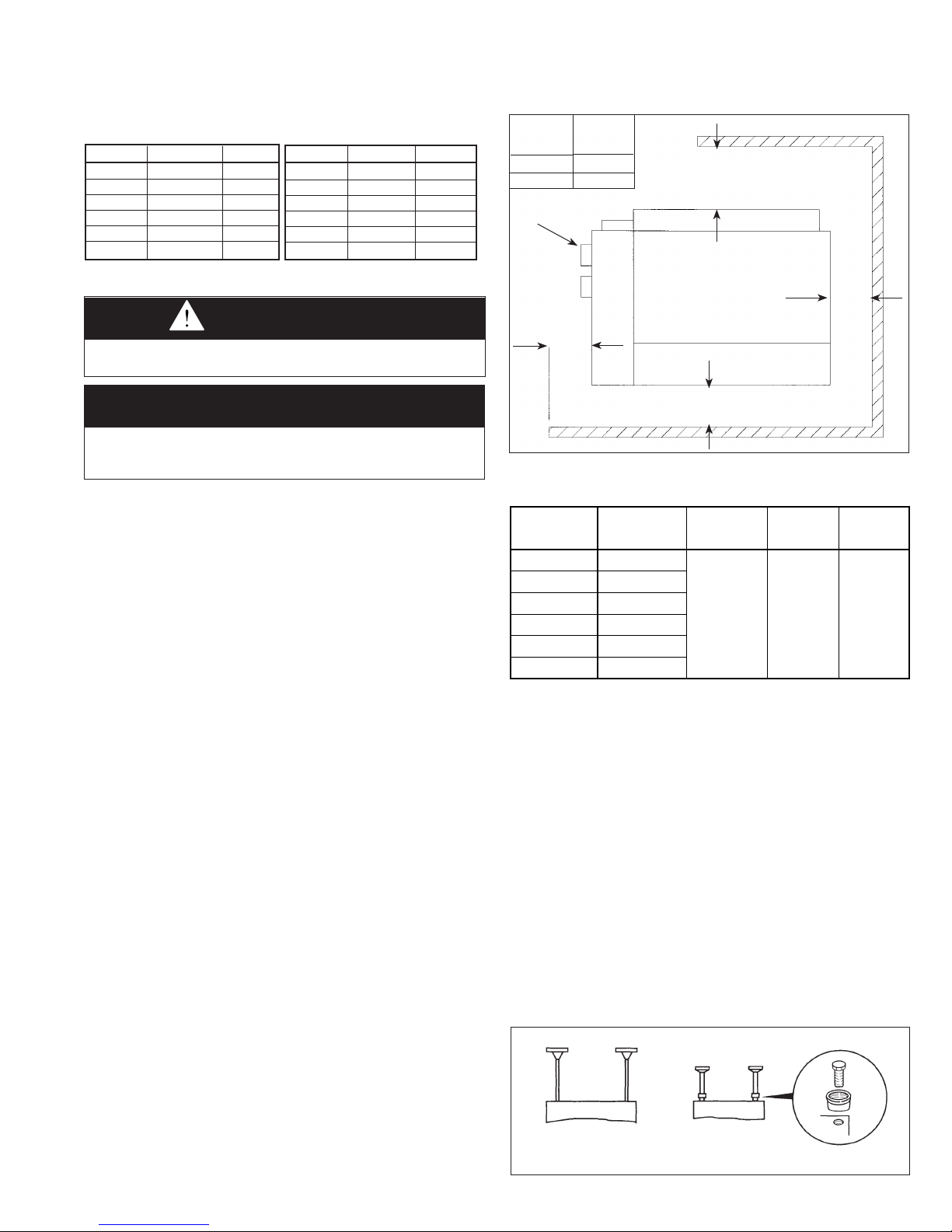
Figure 3.1 - Combustible Material and Service Clearances
Size
(A)
75 thru 175 1"
3
200 thru 400 2"
j A 3'' minimum clearance to combustible material is required from the vent collar.
Table 3.2 - Recommended Service Clearances
UNIT SUSPENSION
Be sure the means of suspension is adequate to support the
weight of the unit (see Dimensional Data for unit weights).
For proper operation, the unit must be installed in a level
horizontal position. Combustible material and service
clearances as specified in Figure 3.1 and Table 3.2 must be
strictly maintained.
1. Four 1/2" - 13NC tapped holes in top of furnace are
2. NOTE: A pipe hanger adapter kit, shown in Figure 3.2, is
Figure 3.2 - Suspension Methods
AIR 5-593.9
Access
Model
Side
TOP = 3"
j
NON-ACCESS
ACCESS
SIDE = A
Model Size
75 18"
100/125 20"
150/175 25"
200/225 27"
250/300 30"
350/400 41"
Access Side
BOTTOM = 1"
(A)
SIDE = 0
Non-Access
Side (B)
6" 10" 0"
Top
(C)
Bottom
(D)
provided to accept ceiling hangers. To assure that flames
are directed into the center of the heat exchanger tubes,
the furnace must be supported in a vertical position. Use a
spirit level to ensure that unit is suspended correctly.
available as an accessory from the factory. One kit consists
of two drilled 3/4" IPS pipe caps and two 1/2 - 13 x 1-3/4"
capscrews to facilitate threaded pipe suspension. Two kits
are required for mounting all duct furnace models.
C
(Threaded Rod)
(Pipe Adapter Kit)
3
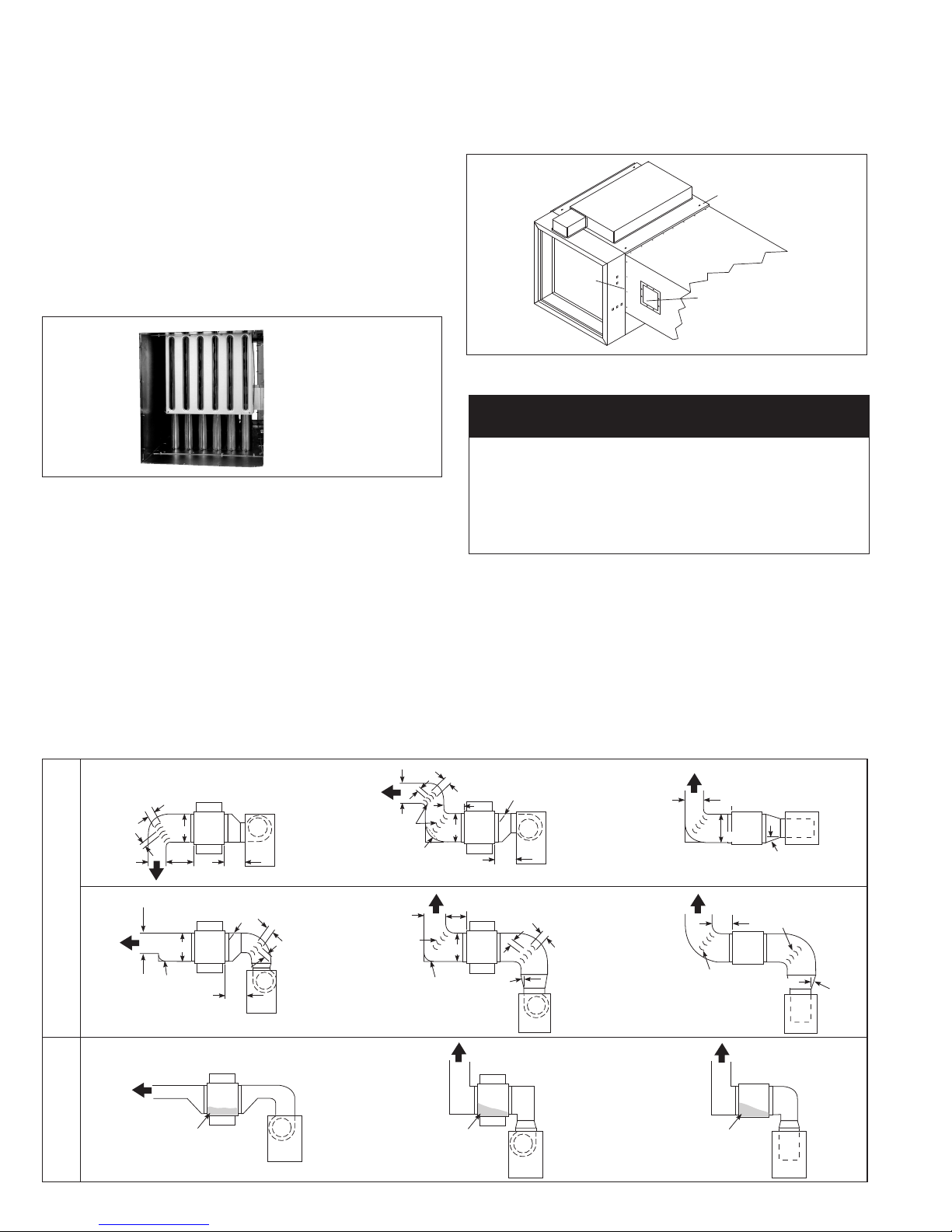
INSTALLATION
Straight
Ductwork
Duct Furnace
Ductwork
Access
Panel
Mounting Holes
Direction of Airflow
Select proper direction of airflow. For models in which the 10th
digit of the model number is an “L” for Low Temperature Rise,
the airflow direction is fully reversible without modification to the
duct furnace. See Airflow Reversal Note.
If the unit is provided with an air distribution baffle (models in
which the 10th digit of the model number is an “H” for High
Temperature Rise), the air baffle must face the air inlet direction
as shown in Figure 4.1. If it is necessary to reverse the airflow
direction, remove the four screws securing the air distribution
baffle, reverse the air distribution baffle to the air inlet side and
replace the screws. See Airflow Reversal Note.
Figure 4.1 - Air Distribution Baffle Location
Baffle location
shown on entering
air side of duct
furnace.
Airflow Reversal Note: If factory installed discharge air options
(thermostat, freeze protection, etc.) were provided, these
options would have to be relocated to the discharge air side of
the duct furnace.
Duct Installation (refer to Figure 4.2)
1. The furnace is designed to accept straight ductwork.
All connections between the ductwork and the furnace
MUST be airtight to prevent air leakage. Seams with
cracks in ductwork should be caulked and/or taped and
be of permanent type.
2. Provide removable access panels on both the upstream
and downstream sides of the ductwork. These openings
should be large enough to view smoke or reflect light inside
the casing to indicate leaks in the heat exchanger and to
check for hot spots on heat exchangers due to poor air
distribution or lack of sufficient air (CFM).
Figure 4.2 - Duct Connections
Airflow Distribution
IMPORTANT
To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, observe heat
exchanger tubes by looking at the heat exchanger through
field installed access openings in connecting ductwork. If
the tubes become red while blower and duct furnace are in
operation, additional baffles must be inserted between blower
and duct furnace to assure uniform air flow across the heat
exchanger.
1. Provide uniform air distribution over the heat exchanger.
Use turning vanes where required (see Figure 4.3) to obtain
uniform air distribution. Avoid installing as in “G”, “H” & “J” of
Figure 4.3.
2. A bottom, horizontal discharge type blower should be
installed at least 12" from the furnace (See “A”, Figure 4.3).
3. A top, horizontal discharge type blower should be installed
at least 24" from the furnace (See “B”, Figure 4.3). Provide
air baffle at top of duct to deflect air down to the bottom of
heat exchanger.
Figure 4.3 - Typical Duct & Airflow Installation
Turning
Vanes
3" Min.
3" Max.
B
B
RECOMMENDED INSTALLATIONS
INSTALLATIONS
NOT RECOMMENDED
4
4
A
SIDE
A
12"
Min.
A
12"
Min.
Air
Baffle
SIDE
24"
Min.
G H J
SIDE
3" Max.
Turning
Vanes
Turning
Vanes
B
Baffle
3" Max.
B
BaffleBaffle
B
SIDE
SIDE
15° Max.
SIDE
Baffle
24"
Min.
Turning
Vanes
3" Max.
Air
Dimensions “B” should never be less than 1/2 of “A”.
3" Min.
Turning
Vanes
3" Min.
12"
Min.
A
12"
Min.
A
No AirNo Air No Air
AIR 5-593.9
B
12"
Min.
12"
Min.
Turning
Vanes
C
TOP
A
15° Max.
FED
Turning
Vanes
TOP
15° Max.
TOP
INSTALLATION - VENTING
W ARNING
1. Gas fired heating equipment must be vented - do not
operate unvented.
2. A built-in power exhauster is provided - additional external
power exhausters are not required or permitted.
3. If you are replacing an existing heater, it may be
necessary to resize the venting systems. Improperly sized
venting systems can result in vent gas leakage or the
formation of condensate. Refer to the National Fuel Gas
Code ANSI Z223.1 or CSA B149.1 latest edition. Failure
to follow these instructions can result in serious injury or
death.
4. Under no circumstances should two sections of double
wall vent pipe be joined together within one horizontal
vent system due to the inability to verify complete seal of
inner pipes.
CAUTION
Installation must conform with local building codes or in the
absence of local codes, with Part 7, Venting of Equipment, of
the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 (NFPA 54) - latest
edition. In Canada installation must be in accordance with
CSA B149.1.
A3. All heaters come with factory installed vent and combustion
air adapters for attaching the pipe to the heater. The pipe
diameters are 4" for model sizes 75-175 and 6" for model
sizes 200-400. All units are classified as Category III
vented appliances, which defined by ANSI is positive
pressure, non-condensing, and requires the vent system to
be gastight. Attach the vent pipe to the adapter with 3
corrosion resistant screws. (Drill pilot holes through the vent
pipe and adapter prior to screwing in place). Vent pipe must
not be smaller than the connector size. Category III vent
systems listed by a nationally recognized agency and
matching the diameters specified may be used. Different
brands of vent materials may not be intermixed.
A4. Limit the total equivalent vent pipe length to a minimum of
5' and a maximum as shown in Table 5.1, making the vent
system as straight as possible. Total equivalent vent pipe
length must include elbows. The equivalent length of a 4"
elbow is 5' and for a 6" elbow is 7'.
Table 5.1 - Individual Total Equivalent Lengths for
Combustion Air and Exhaust Vent Pipes
Model Size Minimum (ft) Maximum (ft)
75 5 48
100, 125, 150, 175 5 55
200, 225 5 70
250, 300 5 63
350, 400 5 70
Model IFS duct furnaces must be vented with the proper
passageway as described in these instructions to convey flue
gases from the unit or the vent connector to the outside
atmosphere. The heaters must also have a separate
combustion air intake pipe to bring in fresh air for combustion
from the outside atmosphere.
The venting instructions are organized in sections, based on
installation type. The sections are identified as follows:
Section Installation Instructions by Vent System Type
A General Instructions for ALL installations
B VERTICAL 2-PIPE vent systems j
C HORIZONTAL 2-PIPE vent systems j
vent systems j
j The differences between Vertical and Horizontal vent systems in 2-Pipe or
HORIZONTAL AND VERTICAL CONCENTRIC
D
Concentric Vent congurations will be identied in “Section A - General
Instructions – All Units”.
Section A - General Instructions - All Units
A1. If the heater being installed is replacing existing equipment
and using the existing vent system from that equipment,
inspect the venting system for proper size and horizontal
pitch, as required in the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI
Z223.1 or CSA B149.1 Installation Code-latest edition and
these instructions. Determine that there is no blockage or
restriction, leakage, corrosion and other deficiencies, which
could cause an unsafe condition.
A2. The combustion air and vent pipes should be galvanized
steel or other suitable corrosion resistant material. Follow
the National Fuel Gas Code for minimum thickness of vent
material. The minimum thickness for connectors varies
depending on the pipe diameter. Do not vent unit with PVC
or other forms of plastic venting material.
A5. A minimum of 12" straight pipe is recommended from the
flue outlet before turns in the vent pipe.
A6. Horizontal sections of vent and combustion air pipes are to
be installed with a minimum downward slope from the
appliance of 1/4 inch per foot and suspended securely
from overhead structures at points not greater than 3'
apart.
A7. Fasten individual lengths of vent together with at least
three corrosion resistant sheet metal screws.
A8. Keep single wall vent pipe at least 6" from combustible
materials. For double wall vent pipe, follow the vent pipe
manufacturer’s clearances to combustibles. The minimum
distance from combustible materials is based on the
combustible material surface not exceeding 160°F.
Clearance from the vent pipe (or the top of the unit) may
be required to be greater than 6" if heat damage other
than fire could result (such as material distortion or
discoloration).
A9. Avoid venting through unheated space when possible.
When venting does pass through an unheated space or if
the unit is installed in an environment that promotes
condensation, insulate runs greater than 5' to minimize
condensation. Inspect for leakage prior to insulating and
use insulation that is noncombustible with a rating of not
less than 400°F. Install a tee fitting at the low point of the
vent system and provide a drip leg with a clean out cap as
shown in Figure 7.1.
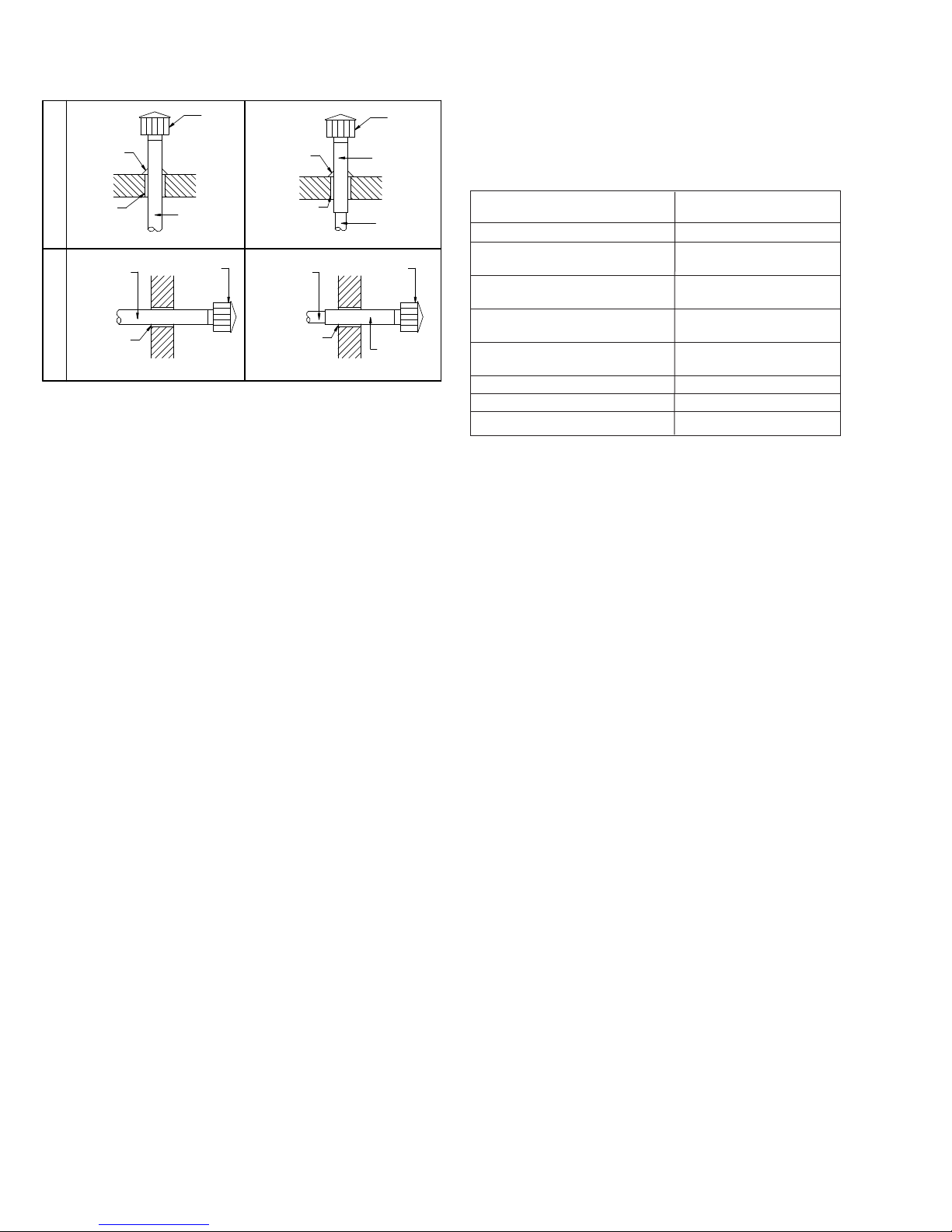
A10. When the vent passes through a combustible INTERIOR
wall or floor, a metal thimble 4" greater than the vent
diameter is necessary. If there is 6' or more of vent pipe in
the open space between the appliance and where the vent
pipe passes through the wall or floor, the thimble need only
be 2" greater than the diameter of the vent pipe. If a
thimble is not used, all combustible material must be cut
away to provide 6" of clearance. Where authorities have
jurisdiction type B vent may be used for the last section of
vent pipe to maintain clearance to combustibles while
passing through wall or floor. See Figure 6.1. Any material
used to close the opening must be noncombustible.
AIR 5-593.9
5
INSTALLATION - VENTING
Figure 6.1 - Venting Through Combustible Roof or Wall
LISTED
CAP
FLASHING
LISTED
Vertical Venting
THIMBLE
SINGLE WALL
Horizontal Venting
ROOF
PIPE
LISTED
THIMBLE
SINGLE WALL
PIPE
MODINE
SPECIFIED
CAP
ROOF
FLASHING
CLEARANCE
SPECIFIED BY
TYPE B VENT
MANUFACTURER
SINGLE WALL
PIPE
CLEARANCE
SPECIFIED BY
TYPE B VENT
MANUFACTURER
j See Instruction A12 for attaching single wall pipe to double wall pipe
A11. All seams and joints of un-gasketed single wall pipe must
be sealed with metallic tape (3M aluminum foil tapes 433
or 363 are acceptable) or silastic suitable for temperatures
up to 400°F. Wrap the tape two full turns around the vent
pipe. One continuous section of double wall vent pipe may
be used within the vent system. Refer to instruction A12 in
“Section A – General Instructions – All Units” for attaching
double wall pipe to single wall pipe.
A12. The following are General Instructions for Double Wall
(Type B) Terminal Pipe Installation. Under no
circumstances should two sections of double wall vent
pipe be joined together within one horizontal vent system
due to the inability to verify complete seal of inner pipes.
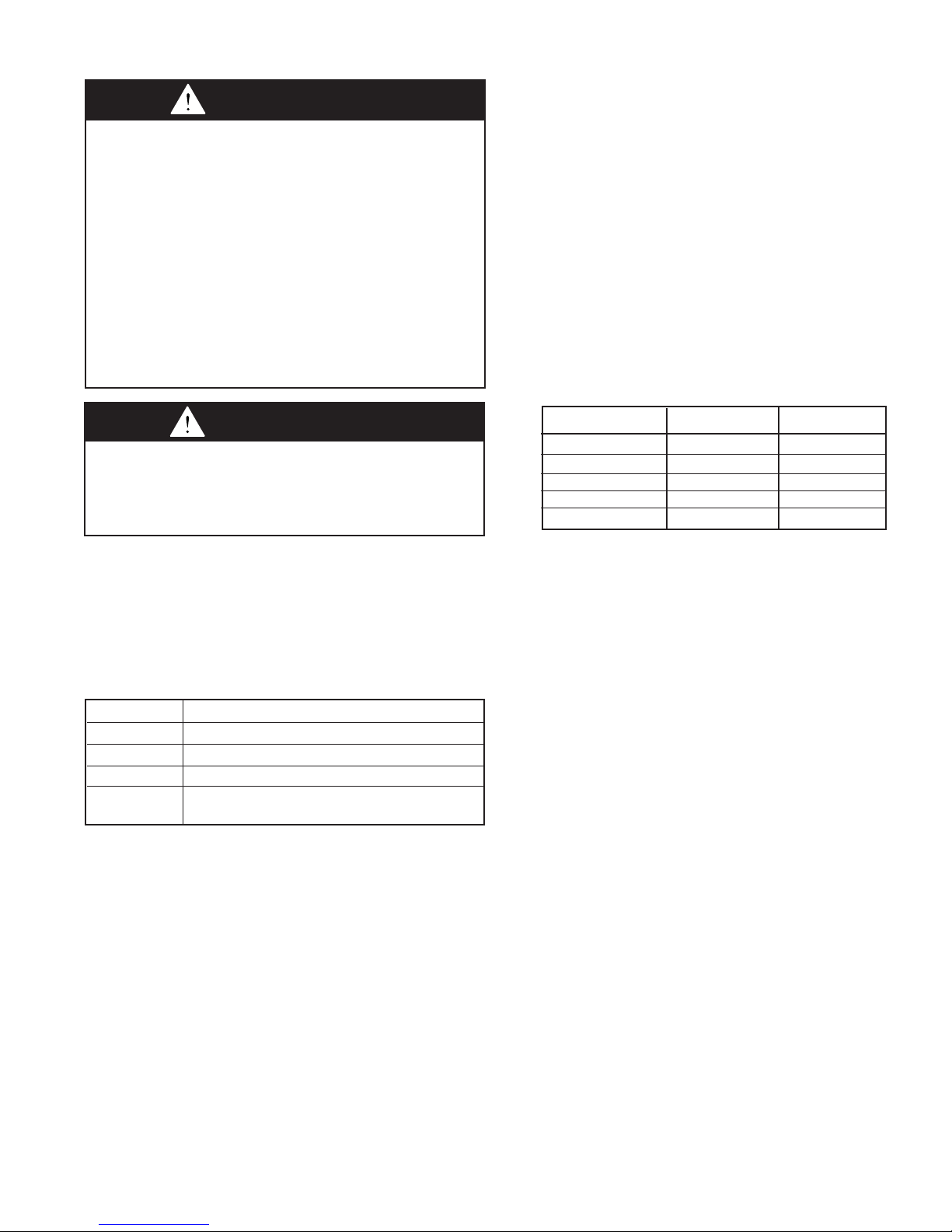
How to attach a single wall vent terminal to double
wall (type B) vent pipe:
1. Look for the “flow” arrow on the vent pipe.
2. Slide the vent terminal inside the exhaust end of the
double wall vent pipe.
3. Drill (3) holes through the pipe and the vent terminal.
Using 3/4" long sheet metal screws, attach the cap to
the pipe. Do not over tighten.
How to connect a single wall vent system to double
wall (type B) vent pipe:
1. Slide the single wall pipe inside the inner wall of the
double wall pipe.
2. Drill (3) holes through both walls of the single and
double wall vent pipes. Using 3/4" sheet metal screws,
attach the two pieces of pipe. Do not over tighten.
3. The gap between the single and double wall pipe must
be sealed but it is not necessary to fill the full volume of
the annular area. To seal, run a large bead of 400°F
silastic around the gap.
A13 Do NOT vent this appliance into a masonry chimney.
A14. Do NOT use dampers or other devices in the vent or
combustion air pipes.
A15.
The venting system must be exclusive to a single
appliance, and no other appliance is allowed to be vented
into it.
A16. Precautions must be taken to prevent degradation of
building materials by flue products.
A17. Single wall vent pipe must not pass through any
unoccupied attic, inside wall, concealed space, or floor.
A18. Uninsulated single wall vent pipe must not be used
outdoors for venting appliances in regions where the 99%
winter design temperature is below 32°F.
6
LISTED
CAP
DOUBLE WALL
PIPE
SINGLE WALL
PIPE
MODINE
SPECIFIED
CAP
DOUBLE WALL
PIPE
A19. Long runs of horizontal or vertical combustion air pipes
A20. Vent termination clearances must be maintained:
Table 6.1 - Vent Termination Clearances
j Do not terminate the vent directly above a gas meter or regulator.
k The vent must be at least 6" higher than anticipated snow depth.
A21. Vertical combustion air pipes should be fitted with a tee
A22. In addition to following these General Instructions, specific
Vertical Vent System Determination
• Vertical vent systems terminate vertically (up) (an
• Determine the venting configuration as follows:
> For two building penetrations through the wall or roof
> For a single larger building penetration through the
> For all other cases, proceed to the next section for
Horizontal Vent System Determination
• Horizontal vent systems terminate horizontally
(sideways) (an example is shown in Figure 8.1).
• Determine the venting configuration as follows:
> For two building penetrations through the wall or roof
> For a single larger building penetration through the
AIR 5-593.9
may require insulation in very cold climates to prevent the
buildup of condensation on the outside of the pipe where
the pipe passes through conditioned spaces.
Minimum Clearances for
Forced air inlet within 10 feet 3 feet above
Combustion air inlet of another
appliance
Door, window, gravity air inlet, 4 feet horizontal and below
or any building opening 1 foot above
Electric meter, gas meter, gas 4 feet horizontal (U.S.)
regulator, and relief equipment j 6 feet horizontal (Canada)
Gas regulator
6 feet horizontal (Canada)
Adjoining building or parapet wall 6 feet all directions
Adjacent public walkways 7 feet all directions
Grade (ground level) 3 feet above k
Structure
Vent Terminal Location
6 feet all directions
3 feet horizontal (U.S.)
j
with a drip leg and a clean out cap to prevent against the
possibility of any moisture in the combustion air pipe from
entering the unit. The drip leg should be inspected and
cleaned out periodically during the heating season.
instructions for Vertical and Horizontal vent systems in
2-Pipe or Concentric Vent configurations must also be
followed. The following outlines the differences:
example is shown in Figure 7.1).
(one for the combustion air inlet pipe and one for the
vent pipe), proceed to “Section B - Vertical 2-Pipe
Venting”.
wall or roof, through which both the combustion air
inlet and vent pipes will pass, proceed to “Section D Horizontal and Vertical Concentric Venting”.
Horizontal Vent System Determination.
(one for the combustion air inlet pipe and one for the
vent pipe), proceed to “Section C - Horizontal 2-Pipe
Venting”.
wall or roof, through which both the combustion air
inlet and vent pipes will pass, proceed to “Section D Horizontal and Vertical Concentric Venting”.
INSTALLATION - VENTING
Section B - Vertical 2-Pipe Vent System
Installation
B1. This section applies to vertically vented 2-pipe (one
combustion air inlet pipe and one vent pipe) vent systems
and is in addition to “Section A - General Instructions - All
Units”.
B2. Vertical vent systems terminate vertically (up).
B3. It is recommended to install a tee with drip leg and clean
out cap as shown in Figures 7.1 or 7.2.
B4. The combustion air and vent pipes must be terminated with
(2) Gary Steel Model 1092 caps.
B5. Vertical vents must terminate a minimum horizontal and
vertical distance from roof lines and adjacent walls or
obstructions. These minimum distances are outlined in
Figure 7.1 and Table 7.1 or Figure 7.2.
B6. The vent must terminate at least 1 foot above and 16
inches horizontally from the combustion air inlet.
B7. Once venting is complete, proceed section titled “Installation
- Gas Connections”.
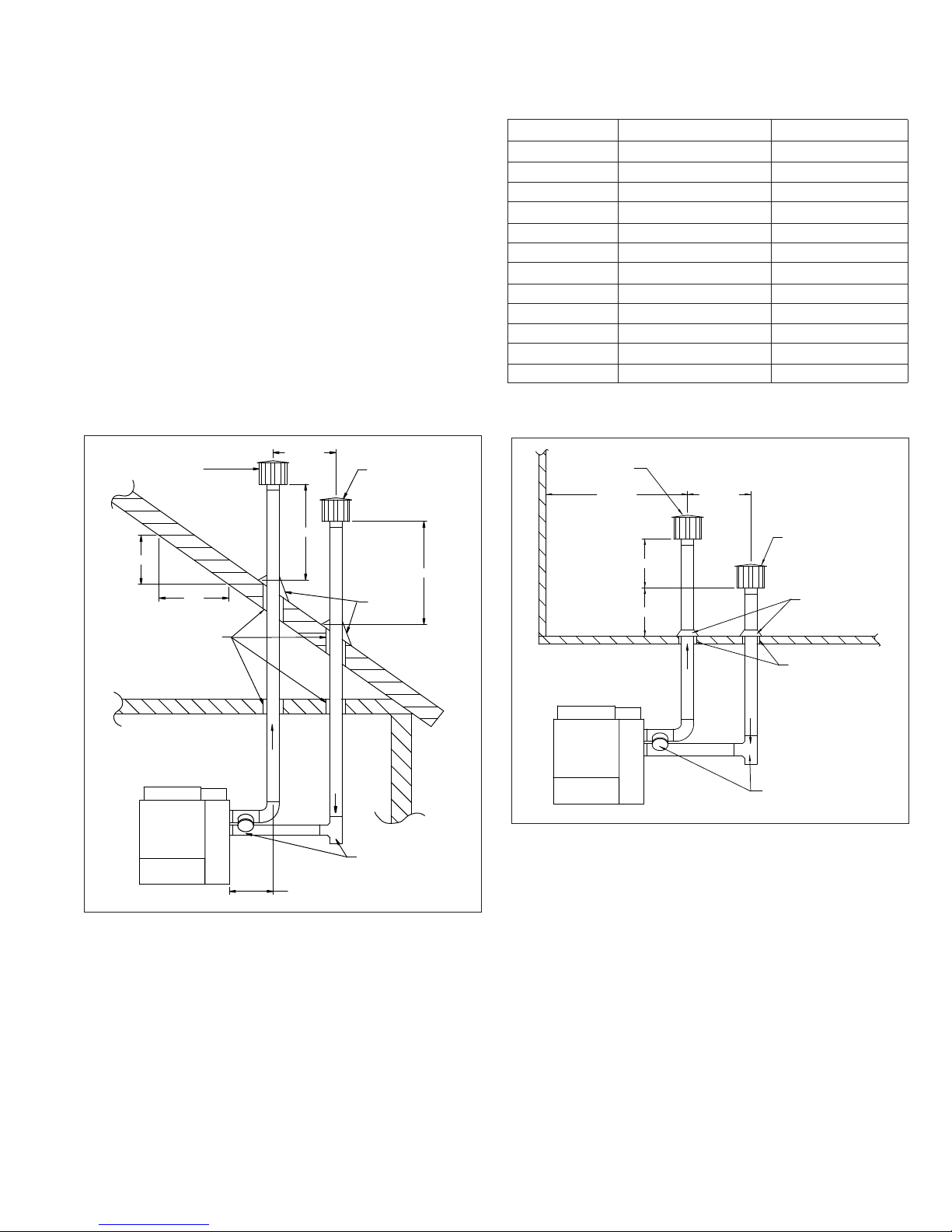
Figure 7.1 - Vertical Venting - 2 Pipes Sloped Roof
16" MIN.
LISTED VENT
TERMINAL
X"
12"
ROOF PITCH = X/12
USE LISTED THIMBLE
THROUGH CEILING
AND ROOF
"H" MIN. *
LISTED AIR
INLET TERMINAL
SEE TABLE 8.1
FOR "H"
DIMENSION
"H" MIN. *
ROOF
FLASHING
* SIZE TO EXPECTED
SNOW DEPTH.
Table 7.1 - Minimum Height from Roof to Lowest
Discharge Opening
Rise X (in) Roof Pitch Min Height H (ft) j
0-6 Flat to 6/12 1.00
6-7 6/12 to 7/12 1.25
7-8 7/12 to 8/12 1.50
8-9 8/12 to 9/12 2.00
9-10 9/12 to 10/12 2.50
10-11 10/12 to 11/12 3.25
11-12 11/12 to 12/12 4.00
12-14 12/12 to 14/12 5.00
14-16 14/12 to 16/12 6.00
16-18 16/12 to 18/12 7.00
18-20 18/12 to 20/12 7.50
20-21 20/12 to 21/12 8.00
j Size according to expected snow depth.
Figure 7.2 - Vertical Venting - 2 Pipes Flat Roof
LISTED VENT
TERMINAL
24" MIN.
TO WALL OR
ADJOINING BUILIDING
12" MIN.
12" MIN. *
* SIZE TO EXPECTED
SNOW DEPTH.
16" MIN.
LISTED AIR
INLET TERMINAL
ROOF FLASING
USE LISTED THIMBLE
THROUGH ROOF
EXHAUST
12" MIN.
RECOMMENDED
COMBUSTION AIR
TEE WITH DRIP LEG
AND CLEANOUT CAP
EXHAUST
COMBUSTION AIR
TEE WITH DRIP LEG
AND CLEANOUT CAP
Section C - Horizontal 2-Pipe Vent System
Installation
C1. This section applies to horizontally vented 2-pipe vent
systems (one combustion air inlet pipe and one vent pipe)
and is in addition to “Section A - General Instructions - All
Units”.
C2. Horizontal vent systems terminate horizontally (sideways).
C3. All horizontal vents must be terminated with a Gary Steel
1092 vent cap. The cap must terminate a minimum
distance from the external wall, as summarized in
Figure 8.1.
C4. The termination of horizontally vented system must extend
12 inches beyond the exterior surface of an exterior wall.
C5. The combustion air pipe must be a minimum of 16 inches
below the vent pipe, and 24 inches from the exterior wall.
C6. Construct the vent system as shown in Figure 8.1.
AIR 5-593.9
7
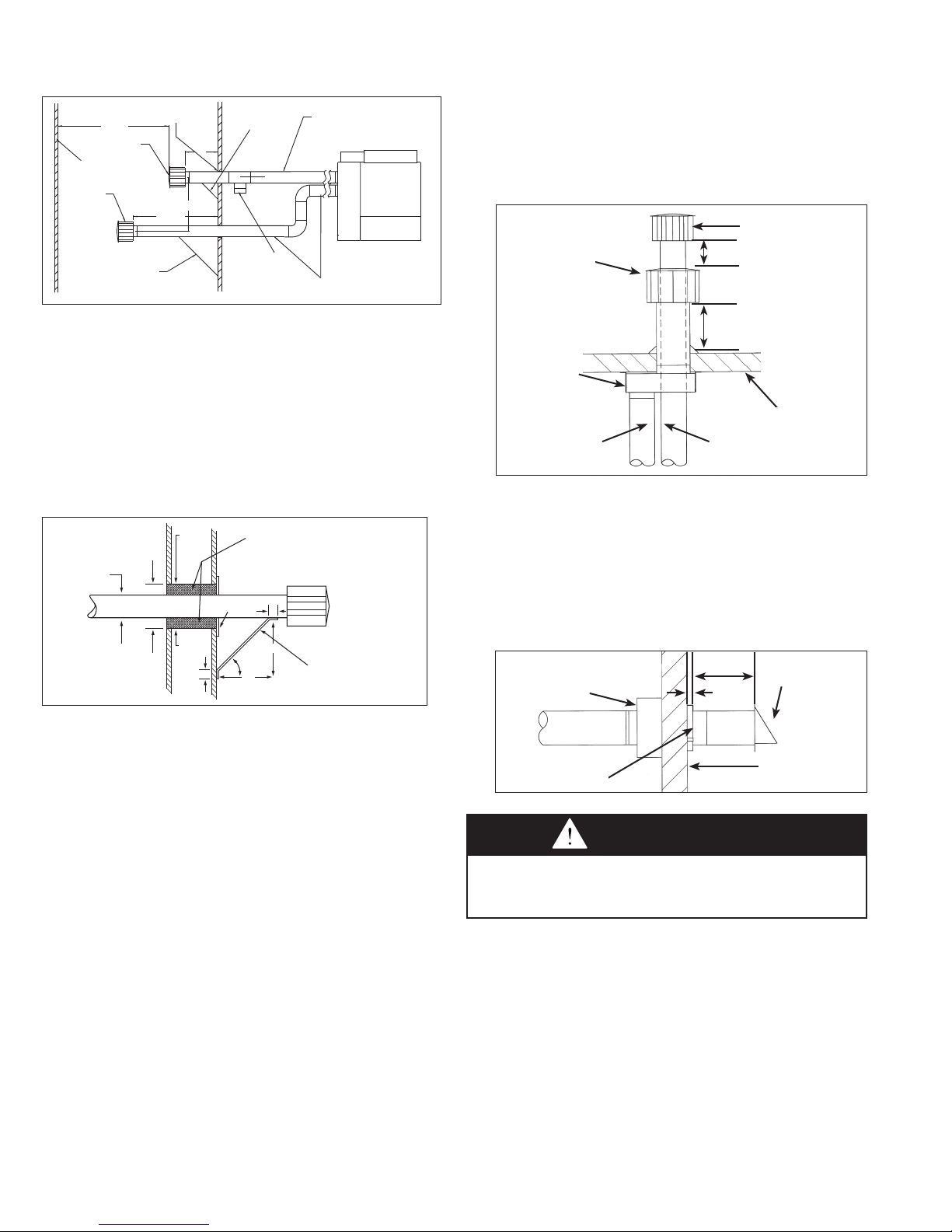
INSTALLATION - VENTING
COMBUSTION AIR
EXHAUST
24'' MIN.
24'' MIN.
12''
16'' MIN.
SUPPORT BRACKET
(See Fig. 9.2 for detail)
SUPPORT BRACKET
(See Fig. 9.2 for detail)
TERMINAL
TERMINAL
ADJACENT
BUILDING
TEE WITH DRIP
LEG AND
CLEANOUT CAP
AT LOW POINT
OF VENT SYSTEM
PITCH VENT PIPE DOWNWARD
FROM APPLIANCE 1/4" PER FOOT
PITCH COMBUSTION AIR
PIPE DOWNWARD FROM
APPLIANCE 1/4" PER FOOT
MUST USE THIMBLE
THROUGH WALL
Figure 8.1 - Horizontal 2-Pipe Venting
C7. When horizontal vents pass through a combustible wall (up
to 8 inches thick), the vent passage must be constructed
and insulated as shown in Figure 8.2.
C8. The vent must be supported as shown in Figure 8.2.
C9. When condensation may be a problem, the vent system
shall not terminate over public walkways or over an area
where condensate or vapor could create a nuisance or
hazard or could be detrimental to the operation of
regulators, relief openings, or other equipment.
Figure 8.2 - Exhaust Vent Construction Through
Combustible Walls and Support Bracket
METAL FACE
PLATE
45
1"
FIBER GLASS
INSULATION
MIN. 2"
1"
9"
9"
VENT TERMINATION
SUPPORT BRACKET
(where required)
(Make from 1" x 1" steel angle)
VENT PIPE
DIAMETER
2" MIN.
2" MIN.
METAL
SLEEVE
METAL
SLEEVE
For Vertically Vented Units (Refer to Figure 8.3):
j Concentric adapter assembly (same for horizontal and
vertical kits)
k Standard Gary Steel 1092 vent termination
l Specially designed inlet terminal (part #5H75154)
Figure 8.3 - Vertical Concentric Vent Kit Components
Outlet Vent
Combustion Air
Inlet Terminal
Concentric
Vent Adapter
Box
Combustion Air Exhaust
6" Min.
12" Min.*
Termination Cap
* Size according
to expected
snow depth.
Building
Roof / Ceiling
For Horizontally Vented Units (Refer to Figure 8.4):
j Concentric adapter assembly (same for horizontal and
vertical kits)
k Special vent termination cap (part #5H75150)
l Special inlet air guard
Figure 8.4 - Horizontal Concentric Vent Kit
Components
Concentric
Vent Adapter
Box
14" Min.
1" Min.
Outlet Vent
Termination Cap
C10. Maintain a 1/4" per foot downward slope away from the
heater and place a drip leg with clean out near the exit of
the vent as shown in Figure 8.1, or allow the condensate
to drip out the end.
C11. For a vent termination located under an eave, the
distance of the overhang must not exceed 24". The
clearance to combustibles above the exterior vent must
be maintained at a minimum of 12". Consult the National
Fuel Gas Code for additional requirements for eaves that
have ventilation openings.
C12. Once venting is complete, proceed section titled
“Installation - Gas Connections”.
Section D - Concentric Vent System
Installation
D1. This section applies to both horizontally and vertically
vented concentric vent systems as defined in “Section A –
General Instructions – All Units”, and is in addition to the
instructions in that section.
D2. When utilizing the concentric vent option, it should have
been predetermined whether the appliance will be
horizontally or vertically vented. Before proceeding, verify
that the concentric vent kit received contains the correct
components for the installation:
8
The concentric vent adapter box must be installed inside of
the structure or building. Do not install this box on the exterior
of a building or structure.
D3. Once the kit contents have been verified as correct for the
D4. The adapter box is to be mounted on the interior side of the
AIR 5-593.9
Combustion Air
Intake Guard
Building Side Wall
CAUTION
direction of venting, the concentric vent adapter box is to be
installed. Determine the location of the box. Be sure to
maintain all clearances as listed in these instructions.
building. It must not be mounted outside the building. The
adapter box has integral mounting holes for ease of
installation. When horizontal venting multiple units, the
minimum spacing between any sides of the adapter boxes
must be 18" and boxes must not overlap in the vertical
plane (above or below). When condensation may be a
problem, the vent system shall not terminate over public
walkways or over an area where condensate or vapor could
create a nuisance or hazard or could be detrimental to the
operation of regulators, relief openings, or other equipment.
INSTALLATION - VENTING
D5. The adapter box can be mounted flush to the wall (for
horizontal kits) or to the ceiling (for vertical kits). The box
can also be offset from the wall or ceiling by using field
supplied brackets. When mounting the box, consider
serviceability and access to the vent and combustion air
pipes. If the box is to be mounted using field supplied
brackets, these brackets must be strong enough to rigidly
secure the box to the wall or ceiling, and should be made
from corrosion resistant material.
D6. Determine the length of the vent pipe and combustion air
inlet pipe for the selected location. THE VENT PIPE WILL
PASS THROUGH THE CONCENTRIC VENT BOX. THE
LAST SECTION OF VENT PIPE IS A CONTINUOUS
LENGTH OF DOUBLE WALL “B” VENT. See section A12
for attaching and terminating double wall pipe. Begin with
pipe lengths on the concentric pipe side of the adapter box
referring to Figure 9.1. These pipes will extend through
the building wall or roof as well as any added length for
the thickness of the wall and the offset from any field
installed brackets.
For Vertical Concentric Vent Kits
(refer to Figure 8.3):
• The bottom of the combustion air intake pipe must
terminate above the snow line, or at least 12 inches
above the roof, whichever distance is greater.
• The bottom of the vent cap must terminate at least 6
inches above the top of the combustion air intake cap.
For Horizontal Concentric Vent Kits
(refer to Figure 8.4):
• The combustion air intake pipe must terminate at least
1 inch from the wall to prevent water from running down
the wall and into the pipe.
• The back of the vent cap must terminate at least 14
inches from the combustion air intake pipe.
D7. Cut the concentric side vent and combustion air pipes to
the proper length as determined in the previous step. Note
that the vent pipe diameter is 4" and the combustion air
intake pipe diameter is 6" for model sizes 75-175, and 6”
and 8” respectively for model sizes 200-400. The pipes
must be single wall galvanized or stainless steel material,
except for the last section of vent pipe, which must be one
continuous length of double wall B-vent extended through
the concentric vent box and combustion air inlet pipe on
the concentric side of the box.
D8. Allow the concentric side vent pipe to pass through the
concentric vent adapter box, as shown in Figure 9.1.
Attach the double wall vent pipe to the single wall vent
pipe that goes to the unit. Be sure to seal the joint and
the open area around the double wall vent. Seal all joints
and seams using sealant suitable for temperatures up to
400°F.
D9. Slide the combustion air pipe over the vent pipe and
attach to the air inlet of the concentric adapter box, as
shown in Figure 9.1, using at least 3 corrosion resistant
sheet metal screws. Seal the joint and seam using sealant
suitable for temperatures up to 400°F.
D10. Place this assembly (the adapter box, vent pipe and
combustion air pipe) through the wall or roof and verify
that the distance requirements as defined in Step D7 are
met. Securely attach the assembly building.
D11. From outside the building, caulk the gap between the
combustion air intake pipe and the building penetration.
D12. Attach the combustion air intake and vent pipe
terminations as follows:
Figure 9.1 - Adapter Box with Combustion Air Intake
Pipe Attached
Outlet Vent
Pipe Extended
Through Box
A
Combustion Air
Pipe Attached
4.57”
B
Model Sizes A B
75-175 13.33" 18.84"
200-400 17.00" 15.27"
For Vertical Concentric Vent Kits
(refer to Figure 8.3):
• Slide the combustion air cap down over the vent pipe
and fasten it to the combustion air pipe with at least 3
corrosion resistant sheet metal screws.
• Attach the vent cap to the vent pipe using at least 3
corrosion resistant sheet metal screws. Refer to
instruction A12 for connecting terminal to double wall
pipe.
• Caulk the gap between the combustion air cap and the
vent pipe with silicone sealant, or other appropriate
sealants suitable for metal to metal contact and for
temperatures up to 400° F.
For Horizontal Concentric Vent Kits
(refer to Figure 8.4):
• Attach the combustion air intake guard using corrosion
resistant screws at the end of the combustion air intake
pipe to prevent animals and debris from entering.
• Attach the vent cap to the vent pipe using at least 3
corrosion resistant sheet metal screws.
D13. Install vent pipe and combustion air pipe between unit
heater and concentric vent adapter box as outlined in
“Section A – General Instructions – All Units”.
D14. Once venting is complete, proceed to the section titled
“Installation - Gas Connections”.
AIR 5-593.9
9

INSTALLATION
GAS
SUPPLY LINE
GAS
SUPPLY LINE
GROUND
JOINT
UNION
W/ BRASS
SEAT
MANUAL GAS
SHUT-OFF VALVE
3"
MIN.
SEDIMENT
TRAP
PLUGGED
1/8" NPT TEST
GAGE CONNECTION
TO
CONTROLS
Gas Connections
WARNING
1. All field gas piping must be pressure/leak tested prior to
operation. Never use an open flame. Use a soap solution or
equivalent for testing.
2. Gas pressure to appliance controls must never exceed 14"
W.C. (1/2 psi).
3. To reduce the opportunity for condensation, the minimum
sea level input to the appliance, as indicated on the serial
plate, must not be less than 5% below the rated input, or 5%
below the minimumm rated input of dual rated units.
CAUTION
Purging of air from gas supply line should be performed as
described in ANSI Z223.1 - latest edition “National Fuel Gas
Code”, or in Canada in CAN/CGA-B149 codes.
IMPORTANT
To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, the input to the
appliance, as indicated on the serial plate, must not exceed
the rated input by more than 5%.
1. Installation of piping must conform with local building codes,
or in the absence of local codes, with the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1 (NFPA 54) - Latest Edition. In Canada,
installation must be in accordance with CAN/CGA-B149.1 for
natural gas units and CAN/CGA-B149.2 for propane units.
2. Piping to units should conform with local and national
requirements for type and volume of gas handled, and
pressure drop allowed in the line. Refer to Table 10.1 to
determine the cubic feet per hour (cfh) for the type of gas
and size of unit to be installed. Using this cfh value and the
length of pipe necessary, determine the pipe diameter from
Table 11.2. Where several units are served by the same
main, the total capacity, cfh and length of main must be
considered. Avoid pipe sizes smaller than 1/2". Table 10.1
allows for a 0.3" W.C. pressure drop in the supply pressure
from the building main to the unit. The inlet pressure to the
unit must be 6-7" W.C. for natural gas and 11-14" W.C. for
propane gas. When sizing the inlet gas pipe diameter, make
sure that the unit supply pressure can be met after the 0.3"
W.C. has been subtracted. If the 0.3" W.C. pressure drop is
too high, refer to the Gas Engineer’s Handbook for other gas
pipe capacities.
3. The gas piping to the unit can enter the unit from the side of
the unit or from below. Install a ground joint union with brass
seat and a manual shut-off valve external of the unit casing,
and adjacent to the unit for emergency shut-off and easy
servicing of controls, including a 1/8" NPT plugged tapping
accessible for test gauge connection (See Figure 10.1).
4. Provide a sediment trap before each unit in the line where
low spots cannot be avoided. (See Figure 10.1).
5. When Pressure/Leak testing, pressures above 14" W.C.
(1/2 psi), close the field installed shut-off valve, disconnect
the appliance and its combination gas control from the gas
supply line, and plug the supply line before testing. When
testing pressures 14" W.C. (1/2 psi) or below, close the
manual shut-off valve on the appliance before testing.
10
Figure 10.1 - Recommended Sediment Trap/Manual Shutoff Valve Installation - Side or Bottom Gas Connection
j Manual shut-off valve is in the “OFF” position when handle is perpendicular to pipe.
Table 10.1 - Burner Orifice Sizing and Gas Consumption
Model
j Based on natural gas properties of 1040 Btu/Cu. Ft. and specific gravity of 0.60.
k Based on propane gas properties of 2500 Btu/Cu. Ft. and specific gravity of 1.53.
Table 10.2 - Gas Pipe Capacities (Cu. Ft. per Hour) j
j Capacities in Cubic Feet per Hour through Schedule 40 pipe with maximum
k For Pipe Capacity with Propane Gas, divide Natural gas capacity by 1.6. Example:
AIR 5-593.9
Gas Type
Size
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
300
350
400
Pipe
Length
(feet)
10 132 278 520 1050 1600 3050
20 92 190 350 730 1100 2100
30 73 152 285 590 890 1650
40 63 130 245 500 760 1450
50 56 115 215 440 670 1270
60 50 105 195 400 610 1150
70 46 96 180 370 560 1050
80 43 90 170 350 530 990
90 40 84 160 320 490 930
100 38 79 150 305 460 870
125 34 72 130 275 410 780
150 31 64 120 250 380 710
0.3" W.C. pressure drop with up to 14" W.C. gas pressure. Specific gravity is 0.60
for Natural gas and 1.50 for Propane gas.
What is the Propane gas pipe capacity for 60 feet of 1-1/4" pipe? The Natural gas
capacity is 400 CFH. Divide by 1.6 to get 250 CFH for Propane gas.
Cfh 72.1 30.0
Orice Drill Size 20 39
Cfh 96.1 40.0
Orice Drill Size 30 45
Cfh 120.2 50.0
Orice Drill Size 25 42
Cfh 144.2 60.0
Orice Drill Size 30 45
Cfh 168.3 70.0
Orice Drill Size 27 43
Cfh 192.3 80.0
Orice Drill Size 23 42
Cfh 216.3 90.0
Orice Drill Size 20 39
Cfh 240.4 100.0
Orice Drill Size 25 42
Cfh 288.7 120.0
Orice Drill Size 20 39
Cfh 336.5 140.0
Orice Drill Size 27 43
Cfh 384.6 160.0
Orice Drill Size 23 42
1/2” 3/4” 1” 1-1/4” 1-1/2” 2”
Natural
j
Natural Gas k
Propane
k
Orice Qty
1
2
2
3
3
3
3
4
4
6
6

INSTALLATION
Considerations for Elevation
The standard rating for Model IFS is certified for elevations up to
2,000 feet above sea level. Operation at elevations above 2,000
feet requires ratings be reduced 4% for each 1000 feet above
sea level per ANSI Z223.1. The exception is for units in Canada,
CSA requires that ratings be reduced 10% for elevations
between 2,001 and 4,500 feet. The following instructions are for
units that will be installed over 2,000 feet elevation. If this does
not apply, you may skip ahead to the Electrical Connections
section on page 12.
Manifold Pressure Adjustment
The unit manifold pressure is factory set for operation at
elevations up to 2000 feet as follows:
• For Natural Gas units, 3.5" W.C. based on a gas heating value
of 1,050 BTU/ft3.
• For Propane Gas units, 10.0" W.C. based on a gas heating
value of 2,500 BTU/ft3.
For higher elevations, some utility companies may derate the
BTU content (heating value) of the gas provided at altitude to a
lower value to allow certain heating appliances to be used with
no manifold pressure adjustments. For this reason it is necessary
that the supplying utility be contacted for detailed information
about the gas type and BTU content (heating value) before
operating any heater. Table 11.1 shows the standard derated
heating values of natural and propane gases at various
elevations.
Table 11.1 Gas Heating Values at Altitude (Btu/ft3) jkln
Altitude (ft) Natural Gas Propane
0-2,000 1,050 2,500
2,001-3,000
3,001-4,000
4,001-4,500
4,501-5,000 856 2,038
5,001-6,000 822 1,957
6,001-7,000 789 1,879
7,001-8,000 757 1,803
8,001-9,000 727 1,731
9,001-10,000 698 1,662
j Values shown are for 3.5" W.C. manifold pressure for Natural Gas and 10.0"
W.C. for Propane Gas. If the local utility supplies gas with a different Btu/ft3
value, use Equation 11.1 to calculate the required manifold pressure.
k Gas heating values shown are derated 4% per 1,000' of elevation (10%
between 2,000' and 4,500' elevation in Canada) in accordance with ANSI
Z223.1 and CSA-B149, respectively.
l 945 Btu/ft3 for Canada
m 2,250 Btu/ft3 for Canada
n When installed at altitudes above 2,000', a pressure switch may need to be
changed. Refer to Table 11.2 to determine if a switch change is required.
If the utility is supplying gas with heating values SAME as shown
in Table 11.1, the manifold pressure should remain set to 3.5"
W.C. for natural gas and 10.0" W.C. for propane gas and you
may proceed to the section on this page titled “Selection of the
Proper High Altitude Kit”.
If the utility is supplying gas with heating values DIFFERENT
than shown in Table 11.1, use Equation 11.1 to determine the
appropriate manifold pressure for the elevation and gas heating
value being supplied. Note what that value is, as it will be
needed later for Start-Up. Proceed to the section on this page
titled “Selection of the Proper High Altitude Kit”.
929 l 2,212 m
892 l 2,123 m
874 l 20,80 m
Equation 11.1 - Manifold Pressure for Gas Heating
Values Different Than Shown in Table 11.1
Where:
MP
BTU
BTU
MPSL = Manifold Pressure (" W.C.), at Sea Level
NOTE: For units equipped with two-stage or modulating gas
controls, only the high fire manifold pressure needs to be
adjusted. No adjustments to the low fire manifold pressure are
necessary on these units.
= Manifold Pressure (" W.C.) at installed
ELEV
TBL
ACT
elevation
= BTU/ft3 content of gas from Table 11.1
= BTU/ft3 content of gas obtained from the
utility company
(use 3.5" W.C. for natural gas and
10.0" W.C. for propane)
Selection of the Proper High Altitude Kit
All units installed at elevations greater than 2000 feet above sea
level require a kit, in addition to potential manifold pressure
adjustment outlined in the previous step. To determine the proper
kit to use, refer to Table 11.2. For more information, refer to the
latest revision of Modine Bulletin 75-530.
Table 11.2 - High Altitude Kit Selection Table jkl
Item Code by Elevation Above Sea Level (ft)
Model
j Applies to both installations in the U.S. and Canada.
k Applies to both natural and propane gas.
l All kits include a High Altitude Conversion Label and Installation Instructions.
Additionally, all kits except 67248 include a Pressure Switch to replace the
standard switch.
If a unit is to be installed at higher elevations AND converted from
natural gas to propane gas operation, a propane conversion kit
must be used in conjunction with the manifold pressure
adjustment and high altitude kit listed above. For the Selection
and Installation Instructions for propane conversion kits, please
see the latest revision of Modine Bulletin 75-511.
2,001-
Size
2,500
75 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248
100 67248 67248 67248 67248 77785 77785 68406
125 67248 77786 77786 77786 77785 77785 68406
150 77787 77786 77786 77786 77785 77785 68406
175 77786 77786 68408 68408 68408 68410 68410
200 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248
225 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248
250 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248
300 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248 67248
350 67248 67248 67248 77786 77785 77785 68406
400 77786 77786 77785 77785 77785 68410 68410
2,501-
4,500
4,501-
5,000
5,001-
5,500
5,501-
6,500
6,501-
7,000
7,001-
7,500
AIR 5-593.9
11

INSTALLATION / START-UP PROCEDURE
Electrical Connections START-UP PROCEDURE
WARNING
1. Disconnect power supply before making wiring
connections to prevent electrical shock and equipment
damage.
2. All appliances must be wired strictly in accordance with
wiring diagram furnished with the appliance. Any wiring
different from the wiring diagram could result in a hazard
to persons and property.
3. Any original factory wiring that requires replacement must
be replaced with wiring material having a temperature
rating of at least 105°C.
4. Ensure that the supply voltage to the appliance, as
indicated on the serial plate, is not 5% greater than rated
voltage.
CAUTION
Ensure that the supply voltage to the appliance, as indicated
on the serial plate, is not 5% less than rated voltage.
1. Installation of wiring must conform with local building
codes, or in the absence of local codes, with the National
Electric Code ANSI/NFPA 70 - Latest Edition. Unit must
be electrically grounded in conformance to this code.
In Canada, wiring must comply with CSA C22.1, Part 1,
Electrical Code.
2. All duct furnaces are provided with a wiring diagram located
on the inside door of the electrical junction box. Refer to
this wiring diagram for all wiring connections. For factory
installed options and field installed accessory wiring, refer
to Set A and Set B on the provided wiring diagram.
3. The power supply to the duct furnace should be protected
with a fused disconnect switch.
4. Refer to the unit serial plate (see Figure 26.1) for the amp
draw of the duct furnace. Size the disconnect switch to
cover the amp draw of the unit. For 460V and 575V units
(Digit 14=F or G) a step down transformer is required.
Units with Digit 15=1 require a 250VA transformer, units
with Digit 15=2 require a 500VA transformer, and units with
Digit 15=3 or 4 require a 1000VA transformer
5. Refer to the unit dimensional drawing on page 18 for the
electrical knockout locations.
IMPORTANT
Start-up and adjustment procedures should be performed by a
qualified service agency.
1. Turn off power to the unit at the disconnect switch. Check
that fuses or circuit breakers are in place and sized correctly.
Turn all hand gas valves to the “OFF” position.
2. Check that the supply voltage matches the unit supply
voltage listed on the serial plate. Verify that all wiring is
secure and properly protected. Trace circuits to insure that
the unit has been wired according to the wiring diagram.
3. Check that all electrical and gas connections to the unit are
sealed to prevent air leakage.
4. Check to insure that the venting system is installed and free
from obstructions.
5. Check to see that there are no obstructions to the intake and
discharge of the duct furnace.
6. Perform a visual inspection of the unit to make sure no
damage has occurred during installation.
7. Turn on power to the unit at the disconnect switch. Check to
insure that the voltage between terminals 1 and 2 is 24V.
8. Check the thermostat, ignition control, gas valve, power
exhauster motor, and supply fan blower motor for electrical
operation. If these do not function, recheck the wiring
diagram. Check to insure that none of the Gas Control
Options & Accessories (see page 16) have tripped.
9. Recheck the gas supply pressure at the field installed
manual-shut-off valve. The inlet pressure should be 6"-7"
W.C. on natural gas or 11"-14" W.C. on propane. If inlet
pressure is too high, install an additional pressure regulator
upstream of the combination gas control.
10. Open the field installed manual gas shut-off valve.
11. Open the manual main gas valve on the combination gas
control. Call for heat with the thermostat and allow the
pilot to light. On a call for heat the power exhauster relay
will energize the power exhauster motor. Once the power
exhauster motor reaches full speed, the differential pressure
switch will close before the pilot can light. If the pilot does
not light, purge the pilot line. If air purging is required,
disconnect the pilot line at outlet of pilot valve. In no case
should line be purged into heat exchanger. Check the pilot
flame length (See Pilot Burner Adjustment).
12. Once the pilot has been established, check to make sure
that the main gas valve opens. Check the manifold gas
pressure (See Main Burner Adjustment) and flame length
(See Air Shutter Adjustment) while the circulating air blower
is operating.
13. Check to insure that gas controls sequence properly
(See Control Operating Sequence). Verify if the unit has
any additional control devices and set according to the
instructions in the Gas Controls Options.
14. Once proper operation of the duct furnace has been verified,
remove any jumper wires that were required for testing.
15. Close the electrical compartment door.
16. Replace all exterior panels.
12
AIR 5-593.9

START-UP PROCEDURE
Pilot Burner Adjustment
The pilot burner is orificed to burn properly with an inlet
pressure of 6-7" W.C. on natural gas and 11-14" W.C. on
propane gas, but final adjustment must be made after
installation. If the pilot flame is too long or large, it is possible
that it may cause soot and/or impinge on the heat exchanger
causing failure. If the pilot flame is shorter than shown, it may
cause poor ignition and result in the controls not opening the
combination gas control. A short flame can be caused by a
dirty pilot orifice. Pilot flame condition should be observed
periodically to assure trouble-free operation.
To Adjust the Pilot Flame
1. Create a call for heat from the thermostat.
2. Remove the cap from the pilot adjustment screw. For
location, see the combination gas control literature supplied
with unit.
3. Adjust the pilot length by turning the screw in or out
to achieve a soft steady flame 3/4" to 1" long and
encompassing 3/8"-1/2" of the tip of the thermocouple or
flame sensing rod (See Figure 13.1).
4. Replace the cap from the pilot adjustment screw.
Figure 13.1 - Correct Pilot Flame
3/4" to 1"
Main Burner Adjustment
The gas pressure regulator (integral to the combination gas
control) is adjusted at the factory for average gas conditions.
It is important that gas be supplied to the duct furnace in
accordance with the input rating on the serial plate. Actual
input should be checked and necessary adjustments made
after the duct furnace is installed. Over-firing, a result of too
high an input, reduces the life of the appliance and increases
maintenance. Under no circumstances should the input exceed
that shown on the serial plate.
Measuring the manifold pressure is done at the tee in the
manifold (See Figure 13.2).
To Adjust the Manifold Pressure
1. Move the field installed manual shut-off valve to the “OFF”
position.
2. Remove the 1/8" pipe plug in the pipe tee and attach a water
manometer of “U” tube type which is at least 12" high.
3. Move the field installed manual gas shut-off valve to the “ON”
position.
4. Create a high fire call for heat from the thermostat.
5. Determine the correct high fire manifold pressure. For natural
gas 3.5” W.C., for propane gas 10” W.C. Adjust the main
gas pressure regulator spring to achieve the proper manifold
pressure (for location, see the combination gas control
literature supplied with unit).
6. If the unit has Electronic Modulation gas controls (determine
from the Model Identification Digit 12), the low fire gas
pressure needs to be adjusted. Using Figure 13.3 for item
number locations, this is accomplished as follows:
a. Disconnect power.
b. Remove all wires from duct furnace terminal “43” and
remove cover plate (2).
c. Turn on power at the disconnect switch.
d. Remove the maximum adjustment screw (4), spring (5),
and plunger (8). A small magnet is useful for this purpose.
CAUTION - The plunger is a precision part. Handle
carefully to avoid marring or picking up grease
and dirt. Do not lubricate.
e. Using minimum adjusting screw (9), adjust low fire
manifold pressure to 0.56" W.C. for natural gas and
1.6" W.C. for propane gas.
f. Replace plunger and spring retainer, spring, and
maximum adjusting screw in proper order.
g. Using maximum adjustment screw (4), adjust high fire
manifold pressure to 3.5" W.C. for natural gas and 10"
W.C. for propane gas.
h. Disconnect power.
i. Replace cover plate (2) and re-install all wires from
duct furnace terminal “43”.
7. After adjustment, move the field installed manual shut-off
valve to the “OFF” position and replace the 1/8" pipe plug.
8. After the plug is in place, move the field installed manual
shut-off valve to the “ON” position and recheck pipe plugs for
gas leaks with soap solution.
Figure 13.3 - Maxitrol Modulating Valve Adjustments
Figure 13.2 - Manifold Pressure Test Point
MANIFOLD TEE
AIR 5-593.9
1. TOP HOUSING
2. COVER PLATE
3. SEAL GASKET
4. MAXIMUM ADJUSTMENT SCREW
5. MAXIMUM ADJUSTMENT SPRING
6. SOLENOID
7. MINIMUM ADJUSTMENT SPRING
8. PLUNGER
9. MINIMUM ADJUSTMENT SCREW
10. MINIMUM ADJUSTMENT SCREW STOP
13

START-UP PROCEDURE
Air Shutter Adjustment
Proper operation provides a soft blue flame with a well-defined
inner core. A lack of primary air will reveal soft yellow-tipped
flames. Excess primary air produces short, well-defined flames
with a tendency to lift off the burner ports. For both natural
and propane gas, the air shutters can be adjusted to control
the burner flame height. The air shutters can be accessed by
reaching behind the manifold tee shown in Figure 23.1. The
larger models may require the removal of the manifold (see
Manifold Assembly Removal).
Natural Gas Flame Control
Control of burner flames on duct furnaces utilizing natural gas
is achieved by resetting the primary air shutters (See Figure
23.1) to either increase or decrease primary combustion air.
Prior to flame adjustment, operate duct furnace for about fifteen
minutes. The main burner flame can be viewed after loosening
and pushing aside the gas designation disc on the side of the
burner box.
To increase primary air, loosen the air shutter set screws and
move the air shutters closer to the manifold until the yellowtipped flames disappear. (See Figure 23.1 for air shutter and
heat exchanger support locations.) To decrease primary air,
move the air shutters away from the manifolds until flames
no longer lift from burner ports, but being careful not to cause
yellow tipping. Retighten set screws after adjustment.
Propane Gas Flame Control
An optimum flame will show a slight yellow tip. Prior to flame
adjustment, operate furnace for at least fifteen minutes. Loosen
air shutter set screws and move the air shutters away from the
manifold to reduce the primary air until the yellow flame tips
appear. Then increase the primary air until yellow tips diminish
and a clean blue flame with a well defined inner cone appears.
IMPORTANT
To prevent premature heat exchanger failure, with all control
systems, a blower starting mechanism must be provided so
that the blower is running or energized within 45 seconds of
the gas control operation.
Control Operating Sequence
Duct furnaces are supplied with intermittent pilot systems with
continuous retry, which both the main burner and pilot burner
are turned off 100% when the thermostat is satisfied. On a call
for heat, the system will attempt to light the pilot for 70 seconds.
If the pilot is not sensed for any reason, the ignition control will
wait for approximately six minutes with the combination gas
control closed and no spark. After six minutes, the cycle will
begin again. After three cycles, some ignition controllers lockout
for approximately one hour before the cycle begins again. This
will continue indefinitely until the pilot flame is sensed or power
is interrupted to the system.
Note: Gas Control Options (see page 16) could change the
listed sequence of operation based on their function.
The descriptions given are for the basic duct furnace.
Single Furnace Controls
Staged Control (Digit 12=1 or 2):
These units utilize a single- or two-stage combination gas valve,
an ignition control, and a low voltage thermostat.
Electronic Modulating Control (Digit 12=4, 7, or 8):
These units utilize a single-stage combination gas valve, an
electronic modulating gas valve, a modulating amplifier, an
ignition control, and one of the following:
• Modulating room thermostat
• Modulating duct thermostat with remote temperature set point
adjuster
• Building Management System (BMS) signal by others (an
inverted signal where 0 VDC or 4 mA is high fire and 10 VDC
or 20 mA is low fire).
14
The control operating sequence for all units is as follows:
1. The thermostat calls for heat. For BMS controlled units, the
BMS closes a heat enable contact at the unit.
2. The power exhauster relay is energized starting the power
exhauster motor. Once the motor has reached full speed, the
differential pressure switch closes. The power exhauster prepurge time delay relay then closes after 20 to 40 seconds and
energizes the gas control circuit.
3. The pilot valve opens and the spark igniter sparks in an
attempt to light the pilot. (If the unit was not provided with a
time delay relay, the blower starts).
4. Once the pilot is lit, the flame sensor proves the pilot and
stops the spark igniter from sparking.
5. The main gas valve is opened and the main burner is
controlled as follows:
a. Single-Stage Units: The main burner is lit to 100% full fire.
b. Two-Stage Units: The main burner is lit to 50% fire. If
the temperature at the thermostat continues to fall, the
thermostat will call for high stage heat and the main burner
is lit to 100% full fire.
c. Modulating Thermostat (Room or Duct): The main
gas valve is opened 100% and the burner firing rate is
modulated between 40% and 100% full fire. A resistance
AIR 5-593.9

START-UP PROCEDURE
signal (8000 to 12000 ohms) in the thermostat is converted
by the modulating amplifier to an inverted DC voltage
(0VDC for high fire to 12 VDC for low fire). The output
voltage is applied to the modulating gas valve to control
the gas flow to the main burner. The modulating valve is
modulated open or closed based on the voltage from the
amplifier (less gas flow required = higher voltage, more gas
flow required = lower voltage).
Note: When modulating duct sensing is utilized, a room
override thermostat can be added. When the room override
calls for heat, the burner modulates to full fire operation
until the room override is satisfied. The unit then reverts
back to duct sensing control. When equipped with both,
either the duct sensor or the room override thermostat can
call for heat.
d. BMS Signal: The main gas valve is opened 100% and the
burner firing rate is modulated between 40% and 100% full
fire. A BMS 0-10VDC or 4-20mA signal (inverted, such that
0 VDC or 4 mA is high fire and 10 VDC or 20 mA is low fire)
is converted by the signal conditioner/modulating amplifier
into an inverted DC voltage (0VDC for high fire to 12 VDC
for low fire). The output voltage is applied to the modulating
gas valve to control the gas flow to the main burner. The
signal conditioner can accept a 0-10 VDC signal when all
the dip switches are in the “OFF” position and 4-20 mA
signal when all the dip switches are in the “ON” position.
The modulating valve is modulated open or closed based
on the voltage from the amplifier (less gas flow required =
higher voltage, more gas flow required = lower voltage),
which correlates to the control signal from the BMS.
Note: For further information regarding the operation of
any of the electronic modulating system options above,
consult the literature provided with the unit.
6. If the unit was provided with a time delay relay, the blower
starts after 30 to 45 seconds.
7. The unit continues to operate until the thermostat is satisfied,
Once satisfied:
a. Single-Stage Units: Both the main and pilot valves close
100%.
b. Two-Stage Units: Once the high stage of the thermostat
is satisfied, the main valve closes to 50% fire. The unit
continues to operate until the low stage thermostat is
satisfied, at which time both the main and pilot valves close
100%.
c. Electronic Modulation Units: The unit continues to
operate in this manner until the thermostat is satisfied or
the BMS heat enable contact opens. Power is then cut to
both the main and pilot valves, closing them 100% and
stopping gas flow to the main and pilot burners.
8. If the unit was not provided with a time delay relay, the blower
stops immediately. If the unit was provided with a time delay
relay, the blower stops after 30 to 45 seconds.
Multiple Furnace Controls
Staged Control (Digit 12=1 or 2):
For control of multiple staged units, each furnace would be
individually controlled. Refer to the section for Single Furnace
Controls, Staged Control (Digit 12=1 or 2).
Electronic Modulating Control (Digit 12=4):
Electronic modulation control of multiple furnaces with model
nomenclature Digit 12=4 is not available. Refer to the section
below for Electronic Modulating Control (Digit 12 = 5 and 6).
Electronic Modulating Control (Digit 12=7, or 8):
For control of multiple electronic modulation units for BMS
control, each furnace would be individually controlled. Refer to
the section for Single Furnace Controls, Electronic Modulation
Control (Digit 12=7 or 8).
Electronic Modulating Control (Digit 12=5 and 6):
These units are the same as Electronic Modulating Gas Controls
– Single Furnace (Digit 12=4) except the Master unit (Digit
12=5) features a modulating amplifier capable of driving multiple
modulating gas valves for systems with a Master and up to three
Slave units (Digit 12=6). Slave units do not have a modulating
amplifier. The units would be controlled by one of the following:
• Modulating room thermostat
• Modulating duct thermostat with remote temperature set point
adjuster
The sequence of operation for Electronic Modulating Gas
Controls - Master/Slave is the same as Electronic Modulating
Gas Controls - Single Furnace. The modulating amplifier sends
an equal voltage signal to all of the modulating gas valves so
that they modulate at the same percentage, between 40% and
100% full fire.
Variable Air Movement Applications
When the air mover supplied by others can provide variable air
movement (i.e. variable frequency drive units), the allowable
minimum CFM of the duct furnace can be 66% of the minimum
listed CFM in Table 18.1 if the unit is applied as follows:
1. The unit is provided with 2-stage or electronic modulating gas
controls (See Model Identification).
2. The unit is provided with a discharge air controller.
3. The system does not include a room thermostat.
The discharge air thermostat will prevent the unit from firing
above the allowable 100°F rise when the unit is at or above the
minimum CFM by monitoring the discharge air and going to low
fire. A room thermostat, because it is located remote from the
unit, could cause the unit to over-fire.
AIR 5-593.9
15

START-UP PROCEDURE
6
7
2
3
5
4
1
POWER
EXHAUSTER
MOTOR
IGNITION
CONTROLER
POWER
EXHAUSTER
RELAY
OPTIONAL
CONTROL
RELAY
SUPPLY
POWER
TERMINAL
STRIP
CONTROL
TRANSFORMER
LOW VOLTAGE
TERMINAL
STRIP
Gas Control Options
The unit must be reviewed to determine if any of the listed gas
control options were supplied.
j Time Delay Relay
The Time Delay Relay is factory installed in the duct furnace
electrical junction box. The standard duct furnace is provided
for instantaneous fan operation. On a call for heat, the blower is
energized at the same time as the gas controls. The optional time
delay relay allows the gas controls to operate for approximately 30
seconds before the blower starts. This allows the heat exchanger
a warm up period so that the initial delivered air coming out of the
ductwork is not cool. The time delay relay also keeps the motor
running for approximately 30 seconds after the call for heat has
been satisfied to remove the residual heat from the heat exchanger.
k Low Gas Pressure Switch
The low gas pressure switch is factory installed in the duct furnace
above the gas train. The switch monitors the gas pressure
upstream of all the gas controls and shuts off the electric supply
to the ignition controller and combination gas valve if low gas
pressure is experienced. This will shut off all gas flow to the burner.
The switch has an automatic reset so that if the gas pressure
is interrupted and then is returned, the switch will automatically
allow the unit to operate when gas conditions are returned to the
allowable range of the pressure switch. The pressure switch range
is 2" to 14" W.C. and should be set to insure that the minimum
inlet gas pressure is available (6" W.C. for natural gas, 11" W.C. for
propane gas).
l High Gas Pressure Switch
The high gas pressure switch is factory installed in the duct
furnace above the gas train. The switch monitors the gas
pressure downstream of all the gas controls and shuts off
the electric supply to the ignition controller and combination
gas valve if high gas pressure is experienced right before the
manifold. This will shut off all gas flow to the burner. The switch
has a manual reset so that if the gas pressure is too high, a
service person must check the unit to make sure that none of
the gas controls have been damaged by the high gas pressure
and then reset the switch to allow the unit to operate when gas
conditions are returned to the allowable range of the pressure
switch. The pressure switch range is 2" to 16" W.C. and should
be set to insure that the maximum manifold gas pressure is not
exceeded (3.5" W.C. for natural gas, 10" W.C. for propane gas).
o Air Flow Proving Switch
The air flow proving switch is factory installed in the duct
furnace electrical junction box. The air flow proving switch
monitors the pressure differential between the duct furnace
and the atmosphere. The purpose of the air flow proving switch
is to cut power to the gas controls if a positive pressure is not
measured by the switch. This could be caused by a lack of air
movement through the heat exchanger.
NOTE: The air flow proving switch will prevent any heat
exchanger warm-up (the unit should not be equipped
with a time delay relay) because the gas controls can
not be energized until air flow is proven.
Setting the Air Flow Proving Switch
The range of the air flow proving switch is adjustable between 0.17"
to 5.0" W.C.
1. Set the thermostat so that there is a call for heat. This should
start the blower and then the burner ignition sequence.
2. Turn the set screw of the pressure switch clockwise until it stops.
This will set the pressure at 5.0" W.C.
3. Turn the screw counter-clockwise until the gas controls light and
then one additional full turn (This is approximately 0.25'' W.C.).
This will allow for dirty filters or any other slight static pressure
increases in the system.
p Manual Reset High Limit
The manual reset high limit switch is factory installed in place
of the standard automatic reset high limit switch located in the
duct furnace electrical junction box. In case of a failure of the
blower motor, blockage of the inlet air, etc., the manual reset
switch prevents the unit from cycling on the high limit. If the
limit temperature is exceeded, a service person must inspect
the unit for the cause of the high discharge temperature, take
corrective action, and then reset the switch.
Figure 16.1 - Location of Gas Control Options
m Supply Air Fire Stat
The fire stat is factory installed in the duct furnace electrical junction
box with the sensor in the discharge air stream. In case of elevated
temperatures in the supply air, the manual reset switch shuts
down the entire unit. If the limit temperature is exceeded, a service
person must inspect the unit for the cause of the high discharge
temperature, take corrective action, and then reset the switch.
n Timed Freeze Protection
The timed freeze protection system is factory installed in the
duct furnace electrical junction box with the sensor (30°-75°F
adjustable) factory installed in discharge air stream. On initial
start-up, the timed delay in the system allows the unit to go
through the normal ignition sequence. The timed delay is a
manual reset switch and adjustable for 1-10 minutes. In the
event that the unit fails to fire after this period, the discharge air
sensor will sense the cold air and will shut down the entire unit.
16
AIR 5-593.9

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
AIR 5-593.9
17

PERFORMANCE
202,500
202,500
162,000
162,000162,000
2,308 CFM
2,308 CFM
5,769 CFM
Table 18.1 - Air Temperature Rise jkl
Model
Size
Input
(Btu/Hr)
Output
(Btu/Hr)
20 m 40 m 50 m
75 75,000 60,750 2,813 1,406 1,125 938 865 804 750 703 662 625 592 563
100 100,000 81,000 3,750 1,875 1,500 1,250 1,154 1,071 1,000 938 882 833 789 750
125 125,000 101,250 4,688 2,344 1,875 1,563 1,442 1,339 1,250 1,172 1,103 1,042 987 938
150 150,000 121,500 5,625 2,813 2,250 1,875 1,731 1,607 1,500 1,406 1,324 1,250 1,184 1,125
175 175,000 141,750 6,563 3,281 2,625 2,188 2,019 1,875 1,750 1,641 1,544 1,458 1,382 1,313
200 200,000 162,000 7,500 3,750 3,000 2,500 2,308 2,143 2,000 1,875 1,765 1,667 1,579 1,500
225 225,000 182,250 8,438 4,219 3,375 2,813 2,596 2,411 2,250 2,109 1,985 1,875 1,776 1,688
250 250,000 202,500 9,375 4,688 3,750 3,125 2,885 2,679 2,500 2,344 2,206 2,083 1,974 1,875
300 300,000 243,000 11,250 5,625 4,500 3,750 3,462 3,214 3,000 2,813 2,647 2,500 2,368 2,250
350 350,000 283,500
400 400,000 324,000
j Ratings are shown for elevations up to 2000 feet. For higher elevations, refer to section "Considerations for Elevation" on page 11.
k Minimum Air Temperature Rise is 20°F and Maximum Air Temperature Rise is 100°F. The Maximum Discharge Air Temperature is 150°F.
l High air temperature rise units include an air distribution baffle and restrictor change when compared to the low air temperature rise units. Field conversion of a high air temperature
rise to a low air temperature rise unit (or the opposite) requires a factory supplied conversion kit.
m The certified range of the High Temperature Rise Duct Furnaces is 20°-100°F but it is recommended that they be used from 60°-100°F to reduce the system pressure drop.
n For Variable Air Movement Applications, see page 15.
o The maximum CFM for the 350 and 400 sizes is 11,111CFM for high air temperature rise units (Digit 10=H) based on the maximum unit pressure drop.
13,125 o
15,000 o
6,563 5,250 4,375 4,038 3,750 3,500 3,281 3,088 2,917 2,763 2,625
7,500 6,000 5,000 4,615 4,286 4,000 3,750 3,529 3,333 3,158 3,000
Air Temperature Rise Through Unit (°F)
60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
Figure 18.1 - Recommended Unit Configurations
j All duct furnaces are designed for a maximum allowable static pressure of 3.0" W.C. on the heat exchanger.
j
Figure 18.2 - Low Air Temperature Rise Duct
Furnace Pressure Drop vs. CFM Curves
1.4
Caution:
Do not exceed the CFM ranges
1.2
indicated in Table 18.1
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
PRESSURE DROP (D P " W.C.)
0.2
0.0
75
1000
2000
100/125
3000
150/175
4000
5000
200/225
6000
7000
CFM
8000
250/300
9000
10000
350/400
11000
12000
13000
14000
15000
Figure 18.3 - High Air Temperature Rise Duct
Furnace Pressure Drop vs. CFM Curves
3.0
2.8
Caution:
Do not exceed the CFM ranges
2.6
indicated in Table 18.1
2.4
2.2
2.0
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.2
1.0
PRESSURE DROP (D P " W.C.)
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0.0
1000
75
2000
150/175
100/125
3000
4000
5000
6000
CFM
200/225
7000
250/300
8000
9000
350/400
10000
11000
12000
18
AIR 5-593.9

DIMENSIONS
END VIEW
SIDE VIEW
1.06" SIDE GAS
CONNECTION
KNOCK-OUT
1.06" BOTTOM GAS
CONNECTION
KNOCK-OUT
1.06" BOTTOM GAS
CONNECTION
KNOCK-OUT
ELECTRICAL
CONNECTIONS
(BOTH SIDES)
20.00
13.32
MOUNTING HOLES
26.63
33.40
35.40
1.00
4.24
7.30
M
L
COMBUSTION
AIR INLET
K
EXHAUST
OUTLET
2.00
1.93
G
F
E
D
A
.72B -- MOUNTING HOLES
C8.66
8.26
6.38
H
AIR TUNNEL
WIDTH
J
AIR TUNNEL
HEIGHT
9.06
J
AIR TUNNEL
HEIGHT
Figure 19.1 - Unit Dimensions (all dimensions in inches)
Table 19.1 - Indoor Separated Combustion Duct Furnace Dimensions (All dimensions in inches)
Model Size
Dimensions 75 100/125 150/175 200/225 250/300 350/400
A 23.74 26.24 30.50 32.60 35.60 47.14
B 13.98 16.48 20.74 22.85 25.85 37.39
C 12.58 15.08 19.34 21.45 24.48 36.00
D 33.04 33.04 33.04 37.04 37.04 37.04
E 28.61 28.61 28.61 32.61 32.61 32.61
F 23.08 23.08 23.08 26.43 26.43 26.43
G 18.19 18.19 18.19 19.21 19.21 19.21
H 15.12 17.62 21.88 23.99 26.99 38.53
J 18.90 18.90 18.90 22.90 22.90 22.90
K j 3.86 3.86 3.86 5.86 5.86 5.86
L j 4.17 4.17 4.17 6.18 6.18 6.18
M 10.26 10.26 10.26 9.60 9.60 9.60
Gas Connection Pipe Size 1/2" 1/2" 1/2" 1/2" 3/4" 3/4"
Approx. Unit Shipping 226# 250# 273# 325# 385# 454#
Weight Unit Net 151# 170# 188# 230# 275# 329#
j Nominal vent pipe size is 4" (Models 75-175) and 6" (Models 200-400). Exhaust pipe installed over collar. Combustion air pipe installed inside collar.
AIR 5-593.9
19

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
20
AIR 5-593.9

THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
AIR 5-593.9
21

MAINTENANCE
WARNING
1. Installing, starting up and servicing heating, ventilation and
air conditioning equipment poses significant hazards and
requires specialized knowledge of Modine products and
training in performing those services. Failure to have any
service properly performed by, or making any modification
to Modine equipment without the use of, qualified service
personnel could result in serious injury to person and
property, including death. Therefore, only qualified service
personnel should work on any Modine products.
2. When servicing or repairing this equipment, use only
factory-approved service replacement parts. A complete
replacement parts list may be obtained by contacting
Modine Manufacturing Company. Refer to the rating plate
on the appliance for complete appliance model number,
serial number, and company address. Any substitution of
parts or controls not approved by the factory will be at the
owner’s risk.
Duct Furnace
When providing annual maintenance for the duct furnace, keep
the unit free from dust, dirt, grease and foreign matter. Pay
particular attention to:
1. The combustion air and exhaust vent piping.
2. The burner ports and pilot burner orifices (avoid the use of
hard, sharp instruments capable of damaging surfaces for
cleaning these ports). To check the burner port and pilot
burner orifice, see Burner and Pilot Assembly Removal.
3. The air shutters and main burner orifices (avoid the use of
hard, sharp instruments capable of damaging surfaces for
cleaning these orifices). To check the air shutters and main
burner orifices, see for Manifold Assembly Removal.
The heat exchanger should be checked annually for cracks
and discoloration of the tubes. If a crack is detected, the heat
exchanger should be replaced before the unit is put back into
service. If the tubes are dark gray, airflow across the heat
exchanger should be checked to insure that a blockage has not
occurred or the blower is operating properly.
CAUTION
Do not attempt to reuse any mechanical or electrical controller
which has been wet. Replace defective controller.
IMPORTANT
To check most of the Possible Remedies in the troubleshooting
guide listed in Table 24.1, refer to the applicable sections of
the manual.
All heating equipment should be serviced before each heating
season to assure proper operations. The following items may
be required to have more frequent service schedule based on
the environment in which the unit is installed, and the frequency
of the equipment operation.
Before any service, BE SURE TO TURN OFF GAS AT THE
MANUAL SHUT-OFF VALVE AHEAD OF THE COMBINATION
GAS CONTROL AND TURN OFF ALL ELECTRIC POWER TO
THE HEATER AND AIR MOVING SYSTEM.
Blower Assembly
The blower assembly includes the bearings, drive sheaves and
belts.
Blower bearings should be checked and lubricated based on
the blower manufacturer’s recommendations. Bearings should
also be checked for any unusual wear and replaced if needed.
Drive sheaves should be checked at the same time the bearings
are inspected. Check to make sure the sheaves are in alignment
and are securely fastened to the blower and motor shafts.
Belt tension should be rechecked shortly after the unit has been
installed to check for belt stretching. After the initial start-up,
monthly checks are recommended.
Electrical Wiring
The electrical wiring should be checked annually for loose
connections or deteriorated insulation.
Gas Piping & Controls
The gas valves and piping should be checked annually for
general cleanliness and tightness.
The gas controls should be checked to insure that the unit is
operating properly.
Manifold Assembly Removal
To remove the manifold (refer to Figure 23.1)
1. Shut off gas and electric supply.
2. Remove the burner side access panel.
3. Disconnect gas manifold at ground union joint.
4. Remove the two screws holding the manifold to the heat
exchanger support.
5. Slide the manifold through the manifold bracket.
6. Clean the orifices and adjust the air shutters as necessary.
7. Follow steps 3-6 in reverse order to install the manifold
assembly.
8. Turn on the electric and gas supply.
9. Check the ground union joint for leaks with a soap solution.
Tighten if necessary.
10. Install the burner side access panel.
Filters
If the unit is supplied with a dirty filter switch and light, clean or
replace the filters any time the dirty filter light comes on.
Units which do not have a dirty filter warning light should have
the filters checked monthly. Clean or replace if necessary. In
dirty atmospheres, filter maintenance may be required more
often.
22
AIR 5-593.9

MAINTENANCE
Figure 23.2 - Burner and Pilot Assembly RemovalFigure 23.1 - Manifold Assembly Removal
ELECTRICAL
JUNCTION
BURNER SIDE
ACCESS PANEL
BOX
HEAT EXCHANGER
SUPPORT
SERIAL PLATE ON
OUTSIDE OF DOOR
(NOT SHOWN)
GROUND
UNION
JOINT
MANIFOLD
Burner and Pilot Assembly Removal
To remove the burner (refer to Figure 23.2)
1. Shut off gas and electric supply.
2. Remove the burner side access panel.
3. Disconnect the pilot supply line from the gas valve.
4. Disconnect the ignition cable from the ignition controller
(located in the electrical junction box). Feed the cable
through the bushing in the bottom of the electrical junction
box.
5. Remove the screws holding the burner side access panel.
Attached to the panel are the burner retaining pins that
align the burner.
6. Slide the burner assembly out. The pilot is attached to the
burner assembly.
7. Examine the burner and pilot assembly for cleanliness
and/or obstructions as necessary (see Duct Furnace for
cleaning instructions).
8. Replace the burner assembly in reverse order. In replacing
the burner, be certain that the rear burner slots are located
properly on the burner retaining pins. Do not force the
burner side access panel, it will not fit if the burner is not
properly aligned.
9. Reconnect the ignition cable and pilot gas supply line.
10. Install the burner side access panel.
11. Turn on the electric and gas supply.
PILOT
ASSEMBLY
IGNITION
CABLE
PILOT
SUPPLY
LINE
AIR SHUTTERS
(NOT SHOWN)
ARE LOCATED
ON THE
ORIFICES
AIR 5-593.9
23

SERVICE & TROUBLESHOOTING
Table 24.1 - Troubleshooting
Trouble Possible Cause Possible Remedy
Power Exhauster Motor will not start
Pilot does not light
1. Power supply is off.
2. No 24V power to thermostat.
3. Thermostat malfunction.
4. Defective power exhauster relay.
5. Defective power exhauster motor.
1. Main gas is off.
2. Power supply is off.
3. Air in gas line.
4. Dirt in pilot orifice.
5. Gas pressure out of proper range.
6. Pilot valve does not open.
a. Defective ignition controller.
b. Defective gas valve.
7. No Spark at ignitor.
a. Loose wire connections.
b. Pilot sensor is grounded.
c. Defective ignition controller.
8. Safety device has cut power.
1. Turn on main power.
2. Check control transformer.
3. Check/replace thermostat.
4. Replace power exhauster relay.
5. Replace power exhauster motor.
1. Open manual gas valve.
2. Turn on main power.
3. Purge gas line.
4. Check for plugged pilot orifice and clean
with compressed air if necessary.
5. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
Minimum for Natural Gas - 6" W.C.
Minimum for Propane Gas - 11" W.C.
6. Check wiring for 24 volts to valve.
a. Replace ignition controller.
b. Replace gas valve.
7.
a. Check all ignition controller wiring.
b. Replace sensor if cracked or worn
c. Replace ignition controller.
8. Check all safety devices (High limit, air
flow proving switch, differential pressure
switch, gas pressure switches, etc.)
Determine and correct problem. Reset
if necessary.
Main burners do not light (Pilot is lit)
Lifting Flames (See Figure 25.1)
Yellow Tipping
(With propane gas, some yellow tipping is
always present.)
Flashback
Floating Flames (See Figure 25.2)
Flame Rollout (See Figure 25.3)
1. Defective valve.
2. Loose wiring.
3. Defective pilot sensor
4. Defective ignition controller.
5. Improper thermostat wiring.
1. Too much primary air.
2. Main pressure set too high.
3. Orifice too large.
1. Insufficient primary air.
2. Dirty orifice.
3. Misaligned orifice.
1. Too much primary air.
2. Main pressure set too high.
3. Orifice too large
1. Insufficient primary air.
2. Main pressure set too high.
3. Orifice too large.
4. Blocked vent.
1. Main pressure set too high.
2. Orifice too large.
3. Blocked vent.
1. Replace valve.
2. Check wiring to gas valve.
3. Replace pilot sensor.
4. Replace ignition controller.
5. Verify wiring compared to wiring diagram.
1. Reduce primary air.
2. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
3. Check orifice size with those listed on
the serial plate.
1. Increase primary air.
2. Check orifices and clean with
compressed air if necessary.
3. Check manifold, replace if necessary.
1. Reduce primary air.
2. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
3. Check orifice size with those listed on
the serial plate.
1. Increase primary air.
2. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
3. Check orifice size with those listed on
the serial plate.
4. Clean/correct venting system.
1. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
2. Check orifice size with those listed on
the serial plate.
3. Clean/correct venting system.
24
AIR 5-593.9

SERVICE & TROUBLESHOOTING
Trouble Possible Cause Possible Remedy
Not Enough Heat
Too Much Heat
1. Unit cycling on high limit. j
a. Obstructions/leaks in duct system.
b. Main pressure set too high.
c. Blower motor not energized.
d. Loose belt
e. Blower speed too low.
f. Blocked/damaged venting system.
g. Air distribution baffle removed (high
temperature rise units only).
h. Defective high limit switch.
2. Main pressure set too low.
3. Too much outside air.
4. Thermostat malfunction.
5. Gas controls wired incorrectly.
6. Unit undersized.
1. Thermostat malfunction.
2. Gas controls do not shut-off.
a. Gas controls wired incorrectly.
b. Short circuit.
3. Main gas pressure set too high.
4. Defective gas valve.
1.
a. Clean/correct duct system.
b. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
c. Check/correct to insure blower motor
operates within 45 seconds of when
- gas controls are energized.
d. Adjust belt tension.
e. Check/correct blower drive settings for
proper rpm.
f. Check/correct venting system.
g. Replace air distribution baffle.
h. Replace high limit switch.
2. Adjust main gas pressure.
Minimum for Natural Gas — 6" W.C.
Minimum for Propane Gas — 11" W.C.
3. Adjust outside air damper to decrease
outside air percentage (if possible).
4. Check/replace thermostat.
5. Check unit wiring against the wiring
diagram.
6. Check design conditions. If unit is
undersized, an additional unit(s) or other
heat source must be added.
1. Check/replace thermostat.
2.
a. Check unit wiring against the wiring
diagram.
b. Check for loose or worn wires.
3. Adjust to a maximum of 14" W.C.
4. Replace gas valve.
j Automatic Reset High Limit
The duct furnace comes standard with an automatic reset high
limit switch that will shut-off the gas should the discharge air
temperature become excessive. See Figure 16.1, indicator p for
the location of either the standard automatic or optional manual
reset high limit switch. The switch should operate only when
something is seriously wrong with the unit operation. Anytime
the switch operates, correct the difficulty immediately or serious
damage may result. If the switch cuts off the gas supply during
normal operation, refer to the “Not Enough Heat” section of
Service & Troubleshooting.
Figure 25.1 - Lifting Flame Condition
Figure 25.2
Floating Flame Condition
Figure 25.3
Flame Rollout Appearance
AIR 5-593.9
25

REPLACEMENT PARTS ORDERING
Ordering
When servicing, repairing or replacing parts on these units, locate the serial plate of the unit and always give the complete Model
Number and Serial Number from the serial plate. The serial plate is located on the door of the electrical control box. The factory part
number for some common replacement parts are listed on the sample serial plate (See Figure 26.1). For a complete description of
the model number, see Model Identification.
Figure 26.1
26
AIR 5-593.9

MODEL IDENTIFICATION
Indoor Separated Combustion Duct Furnace Model Nomenclature
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
PT UC V MBH HE DS AS ATR GT GV SS SV TR
1 - Product Type (PT)
I - Duct Furnace - Indoor
2 - Unit Configuration (UC)
F - Furnace
3 - Venting (V)
S - Separated Combustion
4,5,6 - Furnace Input Rating (MBH)
75 - 75,000 Btu/Hr Input
100 - 100,000 Btu/Hr Input
125 - 125,000 Btu/Hr Input
150 - 150,000 Btu/Hr Input
175 - 175,000 Btu/Hr Input
7 - Heat Exchanger/Burner/Drip Pan Material (HE)
A - Aluminized Steel
S - 409 Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger/Burner
T - 409 Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger/Burner/Drip Pan
8 - Development Sequence (DS)
F - Single Stage M - 2-stage or Modulating
9 - Access Side (AS)
R - Right Hand L - Left hand
10 - Air Temperature Rise (ATR)
H - High 20°-100°F L - Low 20°-60°
200 - 200,000 Btu/Hr Input
225 - 225,000 Btu/Hr Input
250 - 250,000 Btu/Hr Input
300 - 300,000 Btu/Hr Input
350 - 350,000 Btu/Hr Input
400 - 400,000 Btu/Hr Input
11 - Gas Type (GT)
N - Natural with ignition controller
P - Propane with ignition controller
12 - Gas Valve (GV)
1 - Single Stage 5 - Electronic Modulation Master
2 - Two Stage 6 - Electronic Modulation Slave
4 - Electronic Modulation 7 - Electronic Modulation 0-10 Vdc External Input
8 - Electronic Modulation 4-20 mA External Input
13 - Additional Safety Switches (SS)
0 - No Additional Switches 2 - High Gas Pressure Switch
1 - Low Gas Pressure Switch 3 - High & Low Gas Pressure Switch
14 - Supply Voltage (SV)
A - 115/60/1 D - 208/60/3
B - 208/60/1 E - 230/60/3
C - 230/60/1 F - 460/60/3
G - 575/60/3
15 - Transformer (TR)
1 - 40 VA 3 - 150 VA
2 - 75 VA 4 - 250 VA
0 - None
Figure 27.1 - Serial Number Designations
S 09 17 09 36 10 0123 10000
SERIAL NUMBER PREFIX
<blank> if standard
"S" if Special Product Order
SERIES IDENTITY NUMBER
CONTROL SUPPLIER
01-Robertshaw 09-White Rodgers
05-Honeywell 17-United Technologies
08-Fenwal
GAS VALVE SUPPLIER
01-Robertshaw 09-White Rodgers
05-Honeywell
SPO NUMBER
<blank> if standard
##### if Special Product Order
SEQUENTIAL NUMBER
Varies - 0000 TO 9999
Each unit in a week has a
unique number
YEAR
PRODUCED
WEEK
PRODUCED
AIR 5-593.9
27

COMMERCIAL WARRANTY
Seller warrants its products to be free from defects in material and
workmanship, EXCLUSIVE, HOWEVER, of failures attributable to the use
of materials substituted under emergency conditions for materials normally
employed. This warranty covers replacement of any parts furnished from the
factory of Seller, but does not cover labor of any kind and materials not
furnished by Seller, or any charges for any such labor or materials, whether
such labor, materials or charges thereon are due to replacement of parts,
adjustments, repairs, or any other work done. This warranty does not apply to
any equipment which shall have been repaired or altered outside the factory of
Seller in any way so as, in the judgment of Seller, to affect its stability, nor
which has been subjected to misuse, negligence, or operating conditions in
excess of those for which such equipment was designed. This warranty does
not cover the effects of physical or chemical properties of water or steam or
other liquids or gases used in the equipment.
BUYER AGREES THAT SELLER’S WARRANTY OF ITS PRODUCTS TO BE
FREE FROM DEFECT IN MATERIAL AND WORKMANSHIP, AS LIMITED
HEREIN, SHALL BE IN LIEU OF AND EXCLUSIVE OF ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WHETHER ARISING
FROM LAW, COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE OF TRADE, OR OTHERWISE,
THERE ARE NO OTHER WARRANTIES, INCLUDING WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR PURPOSE, WHICH EXTEND
BEYOND THE PRODUCT DESCRIPTION CONFIRMED BY BUYER AND
SELLER AS OF THE DATE OF FINAL AGREEMENT.
This warranty is void if the input to the product exceeds the rated input as
indicated on the product serial plate by more than 5% on gas-fired and oil-fired
units, or if the product in the judgment of SELLER has been installed in a
corrosive atmosphere, or subjected to corrosive fluids or gases, been subjected
to misuse, negligence, accident, excessive thermal shock, excessive humidity,
physical damage, impact, abrasion, unauthorized alterations, or operation
contrary to SELLER’S printed instructions, or if the serial number has been
altered, defaced or removed.
BUYER AGREES THAT IN NO EVENT WILL SELLER BE LIABLE FOR
COSTS OF PROCESSING, LOST PROFITS, INJURY TO GOODWILL, OR
ANY OTHER CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES OF ANY KIND
RESULTING FROM THE ORDER OR USE OF ITS PRODUCT, WHETHER
ARISING FROM BREACH OF WARRANTY, NONCONFORMITY TO
ORDERED SPECIFICATIONS, DELAY IN DELIVERY, OR ANY LOSS
SUSTAINED BY THE BUYER.
BUYER’S REMEDY FOR BREACH OF WARRANTY, EXCLUSIVE OF ALL
OTHER REMEDIES PROVIDED BY LAW, IS LIMITED TO REPAIR OR
REPLACEMENT AT THE FACTORY OF SELLER, ANY COMPONENT WHICH
SHALL, WITHIN THE APPLICABLE WARRANTY PERIOD DEFINED HEREIN
AND UPON PRIOR WRITTEN APPROVAL, BE RETURNED TO SELLER
WITH TRANSPORTATION CHARGES PREPAID AND WHICH THE
EXAMINATION OF SELLER SHALL DISCLOSE TO HAVE BEEN DEFECTIVE;
EXCEPT THAT WHEN THE PRODUCT IS TO BE USED BY BUYER AS A
COMPONENT PART OF EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURED BY BUYER,
BUYER’S REMEDY FOR BREACH, AS LIMITED HEREIN, SHALL BE
LIMITED TO ONE YEAR FROM DATE OF SHIPMENT FROM SELLER. FOR
GAS-FIRED PRODUCTS INSTALLED IN HIGH HUMIDITY APPLICATIONS
AND UTILIZING STAINLESS STEEL HEAT EXCHANGERS, BUYER’S
REMEDY FOR BREACH, AS LIMITED HEREIN, SHALL BE LIMITED TO
TEN YEARS FROM DATE OF SHIPMENT FROM SELLER.
These warranties are issued only to the original owner-user and cannot be
transferred or assigned. No provision is made in these warranties for any
labor allowance or field labor participation. Seller will not honor any expenses
incurred in its behalf with regard to repairs to any of Seller’s products. No
credit shall be issued for any defective part returned without proper written
authorization (including, but not limited to, model number, serial number,
date of failure, etc.) and freight prepaid.
OPTIONAL SUPPLEMENTAL WARRANTY
Provided a supplemental warranty has been purchased, Seller extends the
warranty herein for an additional four (4) years on certain compressors.
Provided a supplemental warranty has been purchased, Seller extends the
warranty herein for an additional four (4) years or nine (9) years on certain
heat exchangers.
EXCLUSION OF CONSUMABLES & CONDITIONS BEYOND SELLER’S
CONTROL
This warranty shall not be applicable to any of the following items: refrigerant
gas, belts, filters, fuses and other items consumed or worn out by normal wear
and tear or conditions beyond Seller’s control, including (without limitation as
to generality) polluted or contaminated or foreign matter contained in the air or
water utilized for heat exchanger (condenser) cooling or if the failure of the part
is caused by improper air or water supply, or improper or incorrect sizing of
power supply.
Component
Applicable Models
Heat Exchangers
Gas-Fired Units except MPR Models
Heat Exchangers
Low Intensity Infrared Units , Gas Heat option on
MPR models
Compressors
Condensing Units for Cassettes
Burners
Low Intensity Infrared Units
Compressors
MPR Models
Other
Components excluding Heat Exchangers,
Coils, Condensers, Burners, Sheet Metal
Heat Exchangers/Coils
Indoor and Outdoor Duct Furnaces and
System Units, Steam/Hot Water Units,
Oil-Fired Units, Electric Units, Cassettes,
Vertical Unit Ventilators, Geothermal Units
Compressors
Vertical Unit Ventilators, Geothermal Units
Burners
High Intensity Infrared Units
Sheet Metal Parts
All Products
TEN YEARS FROM DATE OF FIRST BENEFICIAL USE BY BUYER OR ANY OTHER USER, WITHIN
TEN YEARS FROM DATE OF RESALE BY BUYER OR ANY OTHER USER, WITHIN TEN YEARS
FROM DATE OF RESALE BY BUYER IN ANY UNCHANGED CONDITION, OR WITHIN ONE
HUNDRED TWENTY-SIX MONTHS FROM DATE OF SHIPMENT FROM SELLER, WHICHEVER
OCCURS FIRST
FIVE YEARS FROM DATE OF FIRST BENEFICIAL USE BY BUYER OR ANY OTHER USER, WITHIN
FIVE YEARS FROM DATE OF RESALE BY BUYER OR ANY OTHER USER, WITHIN FIVE YEARS
FROM DATE OF RESALE BY BUYER IN ANY UNCHANGED CONDITION, OR WITHIN SIXTY-SIX
MONTHS FROM DATE OF SHIPMENT FROM SELLER, WHICHEVER OCCURS FIRST
TWO YEARS FROM DATE OF FIRST BENEFICIAL USE BY BUYER OR ANY OTHER USER, WITHIN
TWO YEARS FROM DATE OF RESALE BY BUYER IN ANY UNCHANGED CONDITION, OR WITHIN
THIRTY MONTHS FROM DATE OF SHIPMENT FROM SELLER, WHICHEVER OCCURS FIRST
ONE YEAR FROM DATE OF FIRST BENEFICIAL USE BY BUYER OR ANY OTHER USER, WITHIN
ONE YEAR FROM DATE OF RESALE BY BUYER IN ANY UNCHANGED CONDITION, OR WITHIN
EIGHTEEN MONTHS FROM DATE OF SHIPMENT FROM SELLER, WHICHEVER OCCURS FIRST
“APPLICABLE WARRANTY PERIOD”
As Modine Manufacturing Company has a continuous product improvement program, it reserves the right to change design and specifications without notice.
© Modine Manufacturing Company 2017
Modine Manufacturing Company
1500 DeKoven Avenue
Racine, WI 53403
Phone: 1.866.823.1631 (toll free)
www.modinehvac.com/schoolsystems
 Loading...
Loading...