
Installation
Start-Up
Maintenance
Parts
Warranty
MODCON500 / 700 / 850
VWH Models*
Mod Con
Volume Water Heaters
*“VWH” Denotes Hot Water Supply Boiler
“LP” Denotes Propane Gas Operation
“HL” Denotes Installed High and Low Gas Pressure
Switches
“WL” Denotes Installed High Temperature Water Limit
This Manual For Use With Boilers Manufactured After
August 13, 2013
Heat Exchanger Bears the ASME “H” Stamp
This manual must only be used by a qualied installer / service technician. Read all instructions in this manual before
installing. Perform steps in the given order. Failure to do so could result in substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, or maintenance could void product warranty and cause
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
HTP reserves the right to make product changes or updates without notice and will not be held liable for typographical
errors in literature.
The surfaces of these products contacted by potable (consumable) water contain less than 0.25% lead by weight as
required by the Safe Drinking Water Act, Section 1417.
NOTE TO CONSUMER: PLEASE KEEP ALL INSTRUCTIONS FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
272 Duchaine Blvd. New Bedford, MA 02745 www.htproducts.com
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

2
IF THE INFORMATION IN THIS MANUAL IS NOT FOLLOWED EXACTLY, A FIRE OR EXPLOSION MAY RESULT, CAUSING
PROPERTY DAMAGE, PERSONAL INJURY, OR LOSS OF LIFE. DO NOT STORE GASOLINE OR OTHER FLAMMABLE
VAPORS AND LIQUIDS IN THE VICINITY OF THIS OR ANY OTHER APPLIANCE.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
• Do not try to light any appliance.
• Do not touch any electrical switch.
• Do not use any phone in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor’s phone. Follow the gas supplier’s instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the re department. Installation and service must be provided by a qualied
installer, service agency, or the gas supplier.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

The following dened terms are used throughout this manual
to bring attention to the presence of hazards of various risk
levels or to important product information.
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in serious personal injury or
death.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in personal injury or death.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, may result in moderate or minor personal
injury.
CAUTION used without the safety alert symbol indicates
a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in property damage.
NOTICE is used to address practices not related to personal
injury.
Foreword
This manual is intended to be used in conjunction with other
literature provided with the boiler. This includes all related
control information. It is important that this manual, all other
documents included in this system, and additional publications
including the Code for the Installation of Heat Producing
Appliances and National Fuel Gas Code - ANSI Z223.1 (latest
versions), be reviewed
in their entirety before
beginning any work.
Installation should be
made in accordance
with the regulations
of the Authority
Having Jurisdiction,
local code authorities,
and utility companies
which pertain to this
type of water heating
equipment.
Authority Having
Jurisdiction (AHJ) – The
AHJ may be a federal,
state, local government,
or individual such as a
re chief, re marshal,
chief of a re prevention
bureau, labor
department or health
department, building
ocial or electrical
inspector, or others
3
having statutory authority. In some circumstances, the property
owner or his/her agent assumes the role, and at government
installations, the commanding ocer or departmental ocial
may be the AHJ.
NOTE: HTP, Inc. reserves the right to modify product technical
specications and components without prior notice.
For the Installer
This boiler must be installed by qualied and licensed personnel.
The installer should be guided by the instructions furnished with
the boiler, and by local codes and utility company requirements.
In the absence of local codes, preference should be given to the
National Fuel Gas Code - ANSI Z223.1, latest version.
Installations Must Comply With:
Local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws, regulations,
and ordinances.
The latest version of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1,
from American Gas Association Laboratories, 8501 East Pleasant
Valley Road, Cleveland, OH 44131.
In Canada - CGA No. B149 (latest version), from Canadian Gas
Association Laboratories, 55 Scarsdale Road, Don Mills, Ontario,
Canada M3B 2R3. Also, Canadian Electrical Code, C 22.1, from
Canadian Standards Association, 5060 Spectrum Way, Suite
100, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada L4W 5N6.
Code for the Installation of Heat Producing Appliances (latest
version) from American Insurance Association, 85 John Street,
New York, NY 11038.
The latest version of the National Electrical Code, NFPA No. 70.
NOTE: The gas manifold and controls met safe lighting and
other performance criteria when undergoing tests specied in
ANSI Z21.13 - latest edition.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
4
The CSD-1 ASME Code, Section CW-400 requires that hot
water heating and supply boilers have a) a UL 353 temperature
control device, b) at least one (1) temperature-actuated control
to shut o the fuel supply when system water reaches a preset
operating temperature, c) a high temperature limit control that
prevents the water temperature from exceeding the maximum
allowable temperature by causing a safety shutdown and
lockout, and d) its own sensing element and operating switch.
The temperature control system integrated into the 926
control provided with this heating appliance complies with
the requirements of CSD-1 Section CW-400 as a temperature
operation control. The control monitors the temperature
dierence between the inlet and the outlet sensor, which is
aected by boiler water ow. If this temperature dierence
exceeds 55°F (typically because of low water ow or very low
heat load), the control will reduce the maximum fan speed.
If the temperature dierence exceeds 60°F, the control will
eectively sense there is little or no water ow or heat load and
shut the boiler down. The controller will restart automatically
once the temperature dierence has dropped below 55°F and
the minimum o time (anti-cycle time) has expired. In addition,
if the control senses that the outlet water temperature has
reached 210°F, the boiler is put into a hard lockout and requires
manual reset to restart.
Table of Contents
Part 1 - General Safety Information 5
A. Improper Combustion 5
B. Gas 5
C. When Servicing the Water Heating System 5
D. Boiler Water 6
E. Freeze Protection 6
F. High Elevation Installations 6
G. Water Temperature Adjustment 6
Part 2 - Before You Start 7
A. What’s in the Box 8
B. How the Boiler Operates 8
C. Optional Equipment 8
Part 3 - Prepare the Boiler 9
A. Locating the Boiler 9
B. Flooring 10
C. Leveling 10
D. Clearances for Service Access 10
E. Residential Garage and Closet Installations 11
F. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe 11
1. Direct Vent of Exhaust and Intake 12
2. Indoor Combustion Air in Conned or Unconned Space 12
G. Prevent Combustion Air Contamination 12
H. Removing a Boiler from a Common Vent System 12
I. Water Chemistry Requirements* 13
Part 4 - Piping 14
A. General Plumbing Information 15
B. Relief Valve 15
C. Backow Preventer 15
D. Potable Expansion Tank 15
E. Circulators 16
F. Scalding 16
G. High Velocity Circulator Pump 16
H. Water Chemistry 18
J. Applications 19
Part 5 - Venting and Condensate Removal 22
A. General 22
B. Approved Materials for Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe 23
C. Additional Requirements for Installation in Canada 23
D. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe Location 24
E. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe Sizing 25
F. Longer Vent Runs 25
G. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe Installation 25
H. Applications 26
1. Direct Vent Installation of Exhaust and Intake 26
2. Room and Indoor Combustion Ventilation Requirements
29
I. Condensate Removal System 30
Part 6 - Wiring 31
A. Installation Must Comply With 31
B. Field Wiring Terminations 31
C. Field Wiring 31
D. Line Voltage Wiring for Standard Boiler 32
E. Alarm Connections 32
F. Low Voltage Connections for Standard Boiler 33
G. Tank Sensor or Mechanical Control 33
H. System / Pipe Sensor 33
I. Optional 0-10 Volt Building Control Signal 33
J. Optional High Gas Pressure Switch 33
K. Optional Low Gas Pressure Switch 33
L. Flow Switch 33
M. Wiring of Cascade System Communication Bus 33
N. Cascade Master Pump and Sensor Wiring 34
O. Cascade Follower Pump and Sensor Wiring 34
Part 7 - Gas Connections 37
A. Gas Piping 37
B. Gas Table 38
C. Check Inlet Gas Pressure 38
D. Boiler Gas Valve 39
Part 8 - Start-Up Preparation 40
A. Check / Control Water Chemistry 40
B. Check for Gas Leaks 40
C. Condensate Removal 40
D. Final Checks Before Starting Boiler 40
E. Setting Up a Single Boiler 40
F. Setting Up a Cascaded System 41
G. Lockout Condition 41
H. Cascade System Programming 41
Part 9 - Start-Up Procedure 42
A. Control Overview 42
B. Navigation of the Display 42
C. Operating Instructions 43
D. Programming Boiler Settings 43
E. Programming the System Setting 44
F. System Setting Program Navigation 44
G. Resetting the Maintenance Schedule 46
Part 10 - Start-Up Procedures for the Installer 46
A. Boiler Control Status Menu 46
B. Cascade Menu 47
C. Boiler Test Mode 48
Part 11 - Troubleshooting 49
A. Boiler Error and Fault Codes 49
B. Boiler Error 49
C. Boiler Fault 49
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

D. User Interface Display 50
Part 12 - Maintenance 55
A. Procedures 55
B. Combustion Chamber Coil Cleaning Instructions 55
C. Cleaning Water Side of Heat Exchanger 56
Part 13 - Installation Checklist 61
Part 14 - Maintenance Report 61
Limited Warranty 65
Maintenance Notes 67
Customer Installation Record Form 68
5
This boiler has been designed to heat potable water ONLY.
Using this boiler to heat non-potable uid WILL VOID product
warranty, and could result in property damage, personal injury,
or death.
Altering any HTP, Inc. boiler with parts not manufactured by
HTP, Inc. WILL INSTANTLY VOID the boiler warranty and could
result in property damage, personal injury, or death.
Part 1 - General Safety Information
This boiler is approved for indoor installations only and is not
intended for use as a pool heater. Clearance to combustible
materials: 0” top, bottom, sides, and back. Left side has
all boiler mechanical connections. Boiler must have room
for service: 24” front is minimum recommended service
clearance. (A combustible door or removable panel is
acceptable front clearance.) This boiler has been approved for
closet installation and installation on combustible ooring. Do
not install directly on carpeting. Install the boiler in a location
where temperature and pressure relief valve discharge or a
leak will not result in damage to the surrounding area. If such
a location is not available, install an auxiliary catch pan. Use
only Category IV vent systems.
Installer - Read all instructions in this manual before installing.
Perform steps in the given order.
User - This manual is for use only by a qualied heating
installer / service technician. Have this boiler serviced /
inspected annually by a qualied service technician.
FAILURE TO ADHERE TO THE GUIDELINES ON THIS PAGE
CAN RESULT IN SUBSTANTIAL PROPERTY DAMAGE,
SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH.
NOTE: If the boiler is exposed to the following, do not
operate. Immediately call a qualied service technician.
1. Fire
2. Damage
3. Water
Failure to follow this information could result in property
damage, severe personal injury, or death.
DO NOT USE THIS BOILER IF ANY PART HAS BEEN
SUBMERGED IN WATER. Immediately call a qualied
service technician. The boiler MUST BE replaced if it has been
submerged. Attempting to operate a boiler that has been
submerged could create numerous harmful conditions, such
as a potential gas leakage causing a re and/or explosion, or
the release of mold, bacteria, or other harmful particulates
into the air. Operating a previously submerged boiler could
result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
NOTE: Boiler damage due to ood or submersion is
considered an Act of God, and IS NOT covered under product
warranty.
NOTE: Obey all local codes. Obtain all applicable permits
before installing the boiler.
NOTE: Install all system components and piping in such a
manner that does not reduce the performance of any re
rated assembly.
Do not use this boiler for anything other than its intended
purpose (as described in this manual). Doing so could result in
property damage and WILL VOID product warranty.
High heat sources (sources generating heat 100oF / 37oC or
greater, such as stove pipes, space heaters, etc.) may damage
plastic components of the boiler as well as plastic vent pipe
materials. Such damages ARE NOT covered by warranty. It is
recommended to keep a minimum clearance of 8” from high
heat sources. Observe heat source manufacturer instructions,
as well as local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws,
regulations and ordinances when installing this boiler and
related components near high heat sources.
Due to low water content of the boiler, improperly sizing the
boiler in regard to potable water heating load will result in
excessive boiler cycling and accelerated component failure.
HTP DOES NOT warrant failures caused by improperly sized
boiler applications. DO NOT oversize the boiler to the system.
Modular boiler installations greatly reduce the likelihood of
boiler oversizing.
A. Improper Combustion
Do not obstruct the ow of combustion and ventilating air.
Adequate air is necessary for safe operation. Failure to keep the
exhaust vent and combustion air intake clear of ice, snow, or
other debris could result in property damage, serious personal
injury, or death.
B. Gas
Should overheating or gas supply fail to shut o, turn o the
manual gas control valve to the boiler.
C. When Servicing the Water Heating System
Be sure to disconnect electrical power before opening boiler
cabinet or performing service. Failure to do so could result in
electrical shock, property damage, serious personal injury, or
death.
To avoid electric shock, disconnect electrical supply before
performing maintenance.
NOTE: When inquiring about service or troubleshooting,
reference the model and serial numbers from the boiler rating
label.
To avoid severe burns, allow boiler and associated equipment to
cool before servicing.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
6
D. Boiler Water
Do not use petroleum-based cleaning or sealing compounds in
a water heating system. Gaskets and seals in the system may be
damaged. This can result in substantial property damage.
Do not use “homemade cures” or “patent medicines”. Damage
to the boiler, substantial property damage, and/or serious
personal injury may result.
E. Freeze Protection
NOTE: Consider piping and installation when determining boiler
location.
Failure of the boiler due to freeze related damage IS NOT
covered by product warranty.
NEVER use any toxic chemical, including automotive, standard
glycol antifreeze, or ethylene glycol made for hydronic (nonpotable) systems. These chemicals can attack gaskets and seals
in water systems, are poisonous if consumed, and can cause
personal injury or death.
UNCRATING THE BOILER - Any claims for damage or
shortage in shipment must be led immediately against the
transportation company by the consignee.
F. High Elevation Installations
Natural gas at high elevation might contain less heating value
than typical 1,000 BTU/cu ft and therefore can cause improper
air / gas mix leading to improper combustion. For natural gas
installations above 3,000 ft, call your gas provider to determine
the heating value of the supplied natural gas.
G. Water Temperature Adjustment
If the boiler is going to have a set temperature above 120oF, you
must use an ASSE 1017 rated mixing valve to avoid severe burns
or death from scalding temperatures.
Households with small children, disabled, or elderly persons
may require a 120oF or lower temperature setting to prevent
severe personal injury or death due to scalding.
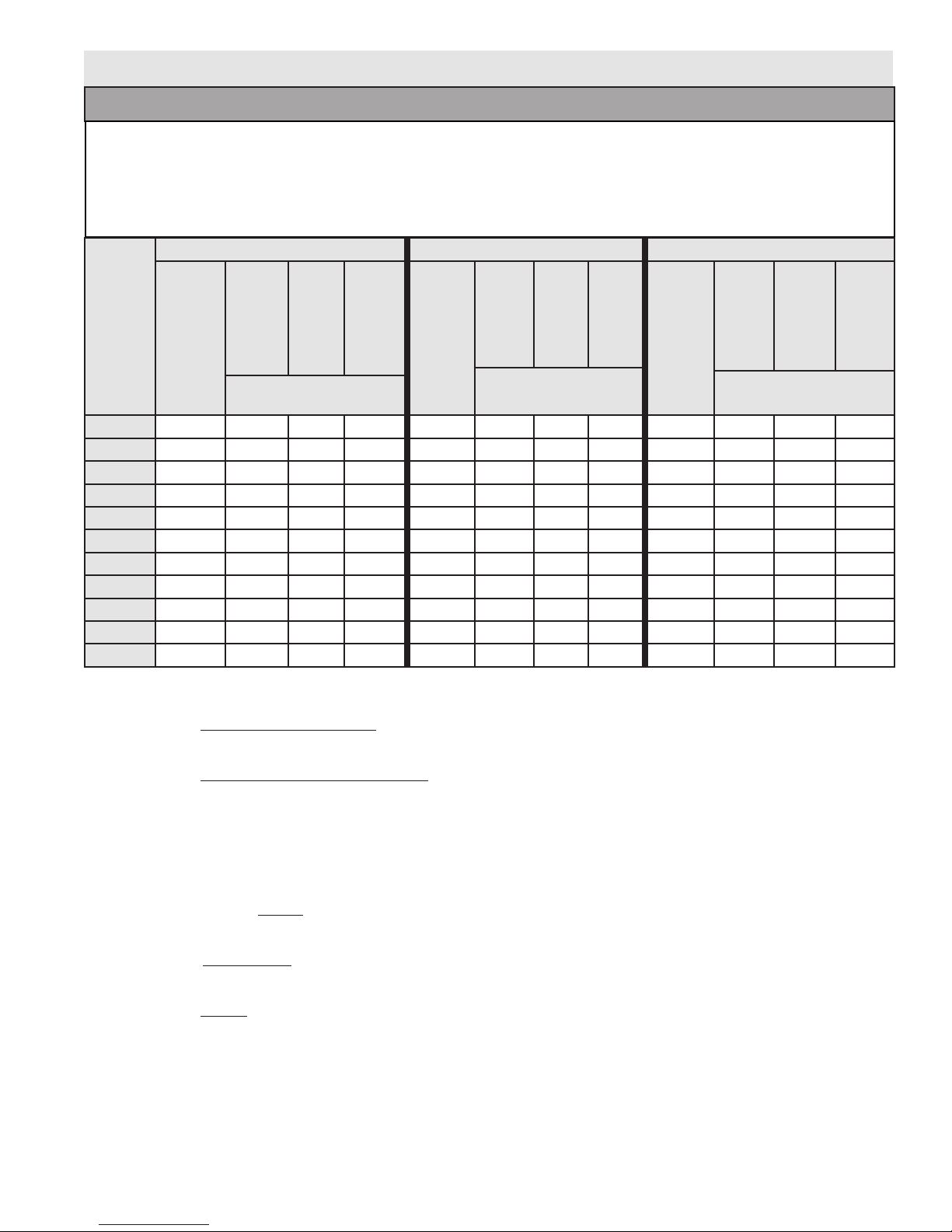
Approximate Time / Temperature Relationships in Scalds
o
120
F More than 5 minutes
o
F 1 1/2 to 2 minutes
125
o
F About 30 seconds
130
o
F About 10 seconds
135
o
F Less than 5 seconds
140
o
F Less than 3 seconds
145
o
F About 1 1/2 seconds
150
o
F About 1 second
155
Table 1 - Approximate Time / Temperature Relationships in Scalds
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
Part 2 - Before You Start
CAUTION
VWH units must be connected to a storage tank. You must not have a direct connection of the potable water system into the heat
exchanger. This could cause ow issues, short cycling, and an increase of mineral build-up in the unit. This system is designed
to have incoming potable water ow through the storage tank rst, then through the heat exchanger. Failure to connect the
VWH boiler to a storage tank of the minimum size requirements (119 gallons for a single 500VWH; 175 gallons for a single
700/850VWH) will result in property damage and/or premature boiler failure. Damages resulting from incorrect installation or
from use of products not approved by HTP, Inc. ARE NOT covered by warranty.
500VWH 700VWH 850VWH
First
Hour
∆T
(Delta T)
o
(
F)
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
Table 2 - VWH Ratings with Storage Tanks - NOTE: Gallons Per Hour Does Not Take a Storage Tank into Account
Min Tank Size (Gal.) = Required Flow (GPM) X 10
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Gallons
Per Hour
1414 859 883 894 1980 1206 1217 1260 2404 1449 1459 1502
1131 872 902 915 1584 1225 1238 1292 1923 1467 1481 1534
943 884 920 937 1320 1244 1260 1324 1602 1486 1502 1566
808 897 939 958 1131 1262 1281 1356 1374 1505 1524 1599
707 910 958 979 990 1281 1303 1388 1202 1524 1545 1631
628 923 977 1001 880 1300 1324 1420 1068 1542 1566 1663
566 935 995 1022 792 1319 1345 1453 961 1561 1588 1695
514 948 1014 1044 720 1337 1367 1485 874 1580 1609 1727
471 961 1033 1065 660 1356 1388 1517 801 1599 1631 1759
435 974 1052 1087 609 1375 1410 1549 740 1617 1652 1791
404 986 1070 1108 566 1394 1431 1581 687 1636 1674 1824
Rating
119
Gallon
Tank
Contact HTP for Available
First
Hour
Rating
175
Gallon
Tank
Storage Tanks
First
Hour
Rating
200
Gallon
Tank
Gallons
Per Hour
First
Hour
Rating
119
Gallon
Tank
Contact HTP for Available
First
Hour
Rating
175
Gallon
Tank
Storage Tanks
First
Hour
Rating
200
Gallon
Tank
Gallons
Per Hour
First
Hour
Rating
175
Gallon
Tank
Contact HTP for Available
First
Hour
Rating
200
Gallon
Tank
Storage Tanks
First
Hour
Rating
300
Gallon
Tank
7
Mixing Factor (Mf) = VWH Outlet Temp - Inlet Temp
70
First Hour Rating = Total VWH Output X VWH Eciency + .75 X Total Storage X M
[ (VWH Outlet Temp - Inlet Temp) X 8.31
Example:
2 500VWH Boilers - Total Output = 1,000,000 BTU @ 94% Eciency
VWH Outlet Temp = 140oF - Inlet Temp = 40oF
2 Storage Tanks (119 Gallons Each) =Total Storage = 238 Gallons
Mixing Factor (Mf) = 140 - 40
70
First Hour Rating = 1,000,000 X .94 + .75 X 238 X 1.43
[(140 - 40) X 8.31
First Hour Rating = 940,000 + 179 X 1.43
[ 831
First Hour Rating = [1,131 + 179] X 1.43
First Hour Rating = 1,310 X 1.43
First Hour Rating = 1,873 Gallons
= 1.43
]
]
]
f
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

8
A. What’s in the Box
Remove all sides of the shipping crate of the boiler.
Components included with the boiler:
• Temperature and Pressure Gauge
• Pressure Relief Valve
• Three (3) Stainless Steel Screens
• Supply and Return Thermistors
• Wiring Harness
• Flow Switch and Fitting
• System/Pipe Sensor
• Installation Manual and Warranty
• User’s Information Manual
• CSD-1 Form
• H-3 Data Sheet
B. How the Boiler Operates
VWH® condensing technology intelligently delivers large
amounts of hot water while maximizing eciency. Outlined
below are the features of the system and how they operate:
Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger
The highly ecient stainless steel heat exchanger is designed to
use the cold water return from the storage tank and extract the
last bit of heat before it is exhausted.
Modulating Combustion System
The combustion system modulates the output of the burner
during operation to match system demand and achieve the
control set point while in operation. The set point can change by
internal or external signals to enhance the overall performance
of the system.
Control
The integrated control system monitors the system and
regulates fan speed to control boiler output. This allows the
boiler to deliver only the amount of heat energy required and
nothing more.
The control can regulate the output of multiple boilers through
its cascade system function. The cascade system is capable of
connecting up to eight boilers together in such a way that they
function as one boiler system. This allows for greater turn down
ratios and provides systematic control of the multiple boilers in
an installation to minimize downtime and maximize eciency.
The cascade system works by establishing one boiler as the
master and the other connected boilers as followers. The
master boiler requires a sensor to provide feedback on set point
temperature in order to adjust heating input from the connected
boilers. Each cascaded boiler will have its own pump to provide
maximum ow and control heat exchanger ow rate.
Text Display and Operational LED Light Indicators
The display allows the user to change system parameters and
monitor system outputs.
Gas Valve
Senses suction from the blower, allowing gas to ow only if
powered and combustion air is owing.
Integrated Venturi (500 Models) or Swirl Plate (700/850
Models)
Controls air and gas ow into the burner.
Burner
The high grade stainless steel burner uses premixed air and gas
to provide a wide range of ring rates.
Spark Ignition
The burner is ignited by applying high voltage through the
system spark electrode. The spark from the electrode ignites
mixed gas o of the burner.
Supply Water Temperature Sensor
This sensor monitors the boiler outlet water temperature
(System Supply). The control adjusts boiler ring rate so the
supply temperature will match the boiler set point.
Return Water Temperature Sensor
This sensor monitors boiler return water temperature (System
Return).
Temperature and Pressure Gauge
Allows the user to monitor system temperature and pressure.
Electrical eld connections with terminal strips
The electrical cover allows easy access to the clearly marked
line voltage and low voltage terminal strips to facilitate wiring
the boiler.
Condensate Collection System
This boiler is a high eciency appliance and will produce
condensate. The condensate collection system has a oat
switch which monitors condensate level and prevents
condensate from backing up into the combustion system.
Inside the collection system is a built in trap which seals
the combustion system from the connected drain. This
condensate should be neutralized to avoid damage to the
drainage system or piping.
Flow Protection
The supplied ow switch is designed to protect the boiler
during low ow conditions. The boiler control also monitors
ow through the heat exchanger by monitoring the return
and supply sensors and will shut down the burner before
overheating occurs.
System Pipe Sensor
This sensor is designed to be used in a cascade system. When
placed on the supply line feeding the storage tank, the system
pipe sensor measures the temperature of return water and
communicates with the control system to modulate the ring
rate of the connected boilers.
NOTE: When using a system sensor, pipe insulation must be
wrapped around it to improve temperature measurement
accuracy and increase overall system eciency.
0-10 Volt Input
Allows the installer to connect a BMS (Building Management
System) to control the boiler.
Indirect Tank Sensor (optional)
Monitors storage tank temperature.
C. Optional Equipment
Optional equipment available from HTP (and Part #):
• Indirect Tank Sensor (7250P-325)
• 4” Stainless Steel Vent Termination Kit (V2000)
• 6” Stainless Steel Vent Termination Kit (V3000)
• High and Low Gas Pressure Switch Kit with Manual
Reset (7350P-600)
• UL 353 Compliant Low Water Cut-O Interface Kit with
Manual Reset (7350P-601)
• Alarm System (to monitor any failure) (7350P-602)
• PC Connection Kit (7250P-320)
• Condensate Neutralizer (7350P-611)
• Caster Kit (7350p-604)
• Glass-Lined Storage Tanks (GL-119, GL-175)
• Stainless Steel Storage Tank (SSU-119CB)
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
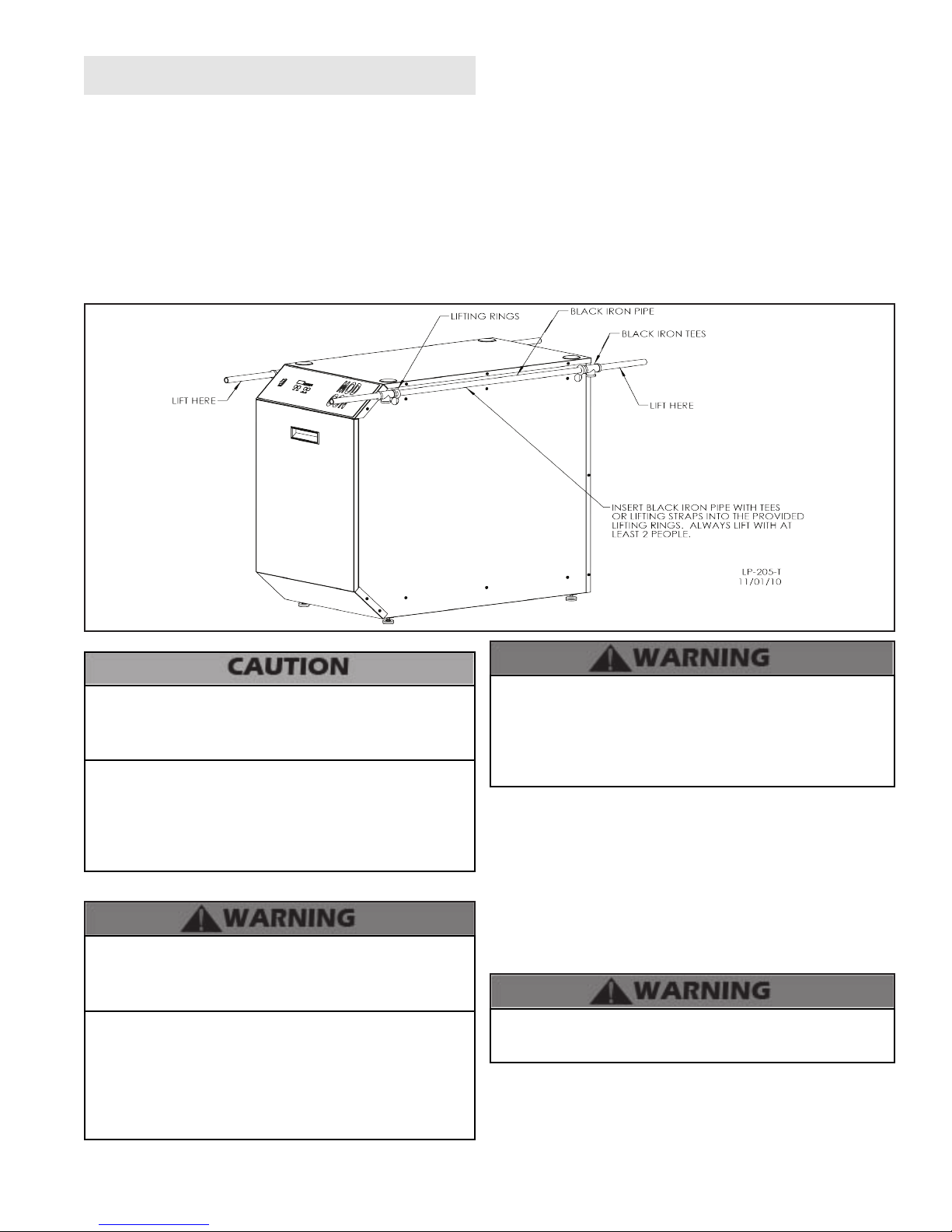
Part 3 - Prepare the Boiler
Remove all sides of the shipping crate to allow the boiler to
be moved into its installation location. Pick the boiler up by
the lifting rings to avoid damage to the boiler enclosure. Use
either solid 3/4” diameter black iron pipe or lifting straps to lift
the boiler o its shipping crate. The boiler is heavy. At least
two individuals are needed to properly handle the boiler. The
boiler is also equipped with leveling feet that can be used
to level the boiler properly on an uneven location surface. If
surface ooring is rough, take care when moving the boiler
into position, as catching the leveling feet could damage the
boiler.
1. Installation Area (Mechanical Room) Operating Conditions
• Ensure ambient temperatures are higher than 32
o
F / 0oC
and lower than 104oF / 40oC
• Prevent the air from becoming contaminated by the
products, places, and conditions listed in this manual
• Avoid continuously high levels of humidity
• Never close existing ventilation openings
• Ensure a minimum 1” clearance around hot water and
exhaust vent pipes
• NOTE: To prevent condensing in the fan, it is recommended
to avoid prolonged exposure to temperatures below 45
9
o
F
Figure 1 - Lifting the Boiler
COLD WEATHER HANDLING - If the boiler has been stored in
a very cold location (BELOW 0oF) before installation, handle
with care until the components come to room temperature.
Failure to do so could result in damage to the boiler.
Carefully consider installation when determining boiler
location. Please read the entire manual before attempting
installation. Failure to properly take factors such as boiler
venting, piping, condensate removal, and wiring into account
before installation could result in wasted time, money, and
possible property damage and personal injury.
A. Locating the Boiler
This boiler is certied for indoor use only. DO NOT INSTALL
OUTDOORS. Outdoor installations ARE NOT covered by
warranty. Failure to install the boiler indoors could result in
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Incorrect ambient conditions can lead to damage to the
heating system and put safe operation at risk. Ensure that
the installation location adheres to the information included
in this manual. Failure to do so could result in property
damage, serious personal injury, or death. Failure of boiler
or components due to incorrect operating conditions IS NOT
covered by product warranty.
This boiler has a condensate disposal system that may freeze
if exposed to sustained temperatures below 32oF. Precautions
should be taken to protect the condensate trap and drain lines
from sustained freezing conditions. Failure to take precautions
could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or
death.
2. Check for nearby connections to:
• System water piping
• Venting connections
• Gas supply piping
• Electrical power
• Condensate drain
3. Check area around boiler. Remove any combustible materials,
gasoline, and other ammable liquids.
Failure to keep the boiler area clear and free of combustible
materials, liquids, and vapors can result in substantial property
damage, severe personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
10
The service life of the boiler’s exposed metallic surfaces, such
as the casing, as well as internal surfaces, such as the heat
exchanger, are directly inuenced by proximity to damp and
salty marine environments. In such areas higher concentration
levels of chlorides from sea spray coupled with relative humidity
can lead to degradation of boiler components. In these
environments, boilers must not be installed using direct vent
systems which draw outdoor air for combustion. Such boilers
must be installed using room air for combustion. Indoor air
will have a much lower relative humidity, and hence potential
corrosion will be minimized.
High heat sources (generating heat 100oF / 37oC or greater,
such as boiler ue pipes, space heaters, etc.) may damage
plastic components of the boiler as well as plastic vent pipe
materials. Such damages ARE NOT covered by warranty. It is
recommended to keep a minimum clearance of 8” from high
heat sources. Observe heat source manufacturer instructions,
as well as local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws,
regulations, and ordinances when installing this boiler and
related components near high heat sources.
Locate the boiler where any leakage from the relief valve,
related piping, tank, or connections will not result in damage
to surrounding areas or lower oors of the building. The boiler
should be located near a oor drain or installed in a drain pan.
Leakage damages ARE NOT covered by warranty.
Failure of the boiler or components due to incorrect operating
conditions IS NOT covered by product warranty.
4. Gas control system components must be protected from
dripping water during operation and service.
5. If the boiler is to replace an existing boiler, check for and
correct any existing system problems, such as:
• System leaks
• Location that could cause the system and boiler to freeze
and leak
• Incorrectly sized expansion tank
6. Clean and ush system when reinstalling a boiler.
NOTE: When installing in a zero clearance location, it may
not be possible to read or view some product labeling. It is
recommended to make note of the boiler model and serial
number.
Assure that the oor and structure of the installation location
are sucient to support the full installed weight of the
boiler, including water content of the heat exchanger and
related piping. Failure to ensure the oor and structure of the
installation location are structurally sound before installation
of the boiler can result in structural failure, substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
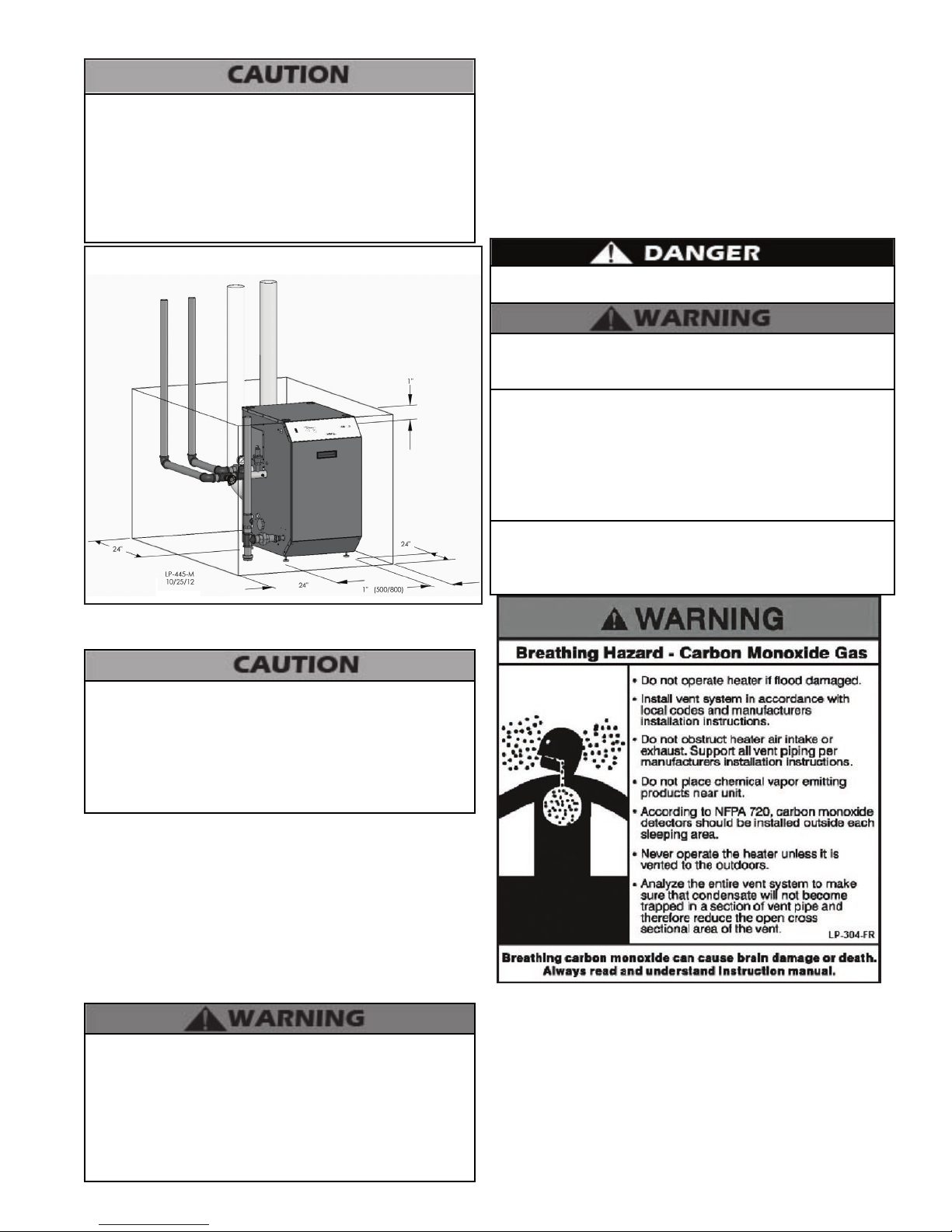
C. Leveling
In order for the condensate to properly ow out of the
collection system, the area where you locate the boiler must
be level. Location must also fully support the weight of the
lled boiler.
Figure 2 - Correct and Incorrect Leveling
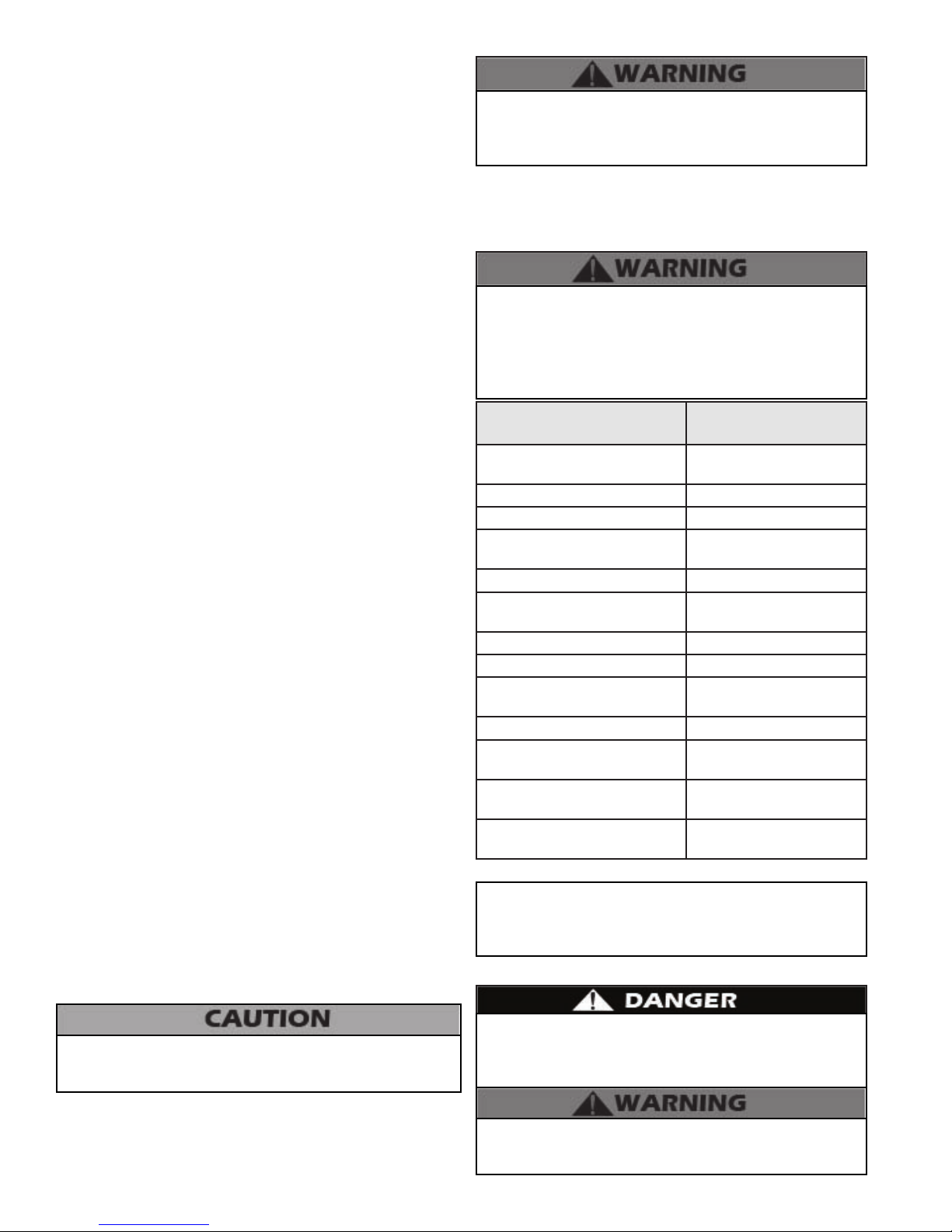
D. Clearances for Service Access
NOTE: If you do not provide the minimum clearances shown
in Figure 3 it might not be possible to service the boiler without
removing it from the space.
NOTE: A combustible door or removable panel is acceptable
front clearance.
Use extreme care not to drop the boiler or cause bodily injury
while lifting the boiler.
Gas conversion should be performed BEFORE the boiler is
installed. Carefully follow the gas conversion instructions when
performing the conversion.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in property
damage, severe personal injury, or death.
B. Flooring
This boiler is approved for installation on combustible ooring,
but must never be installed on carpeting. Installing this boiler on
carpeting could result in re, property damage, severe personal
injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
The space must be provided with combustion / ventilation air
openings correctly sized for all other appliances located in the
same space as the boiler. The boiler cover must be securely
fastened to prevent the boiler from drawing air from the
boiler room. This is particularly important if the boiler is in a
room with other appliances. Failure to comply with the above
warnings could result in substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
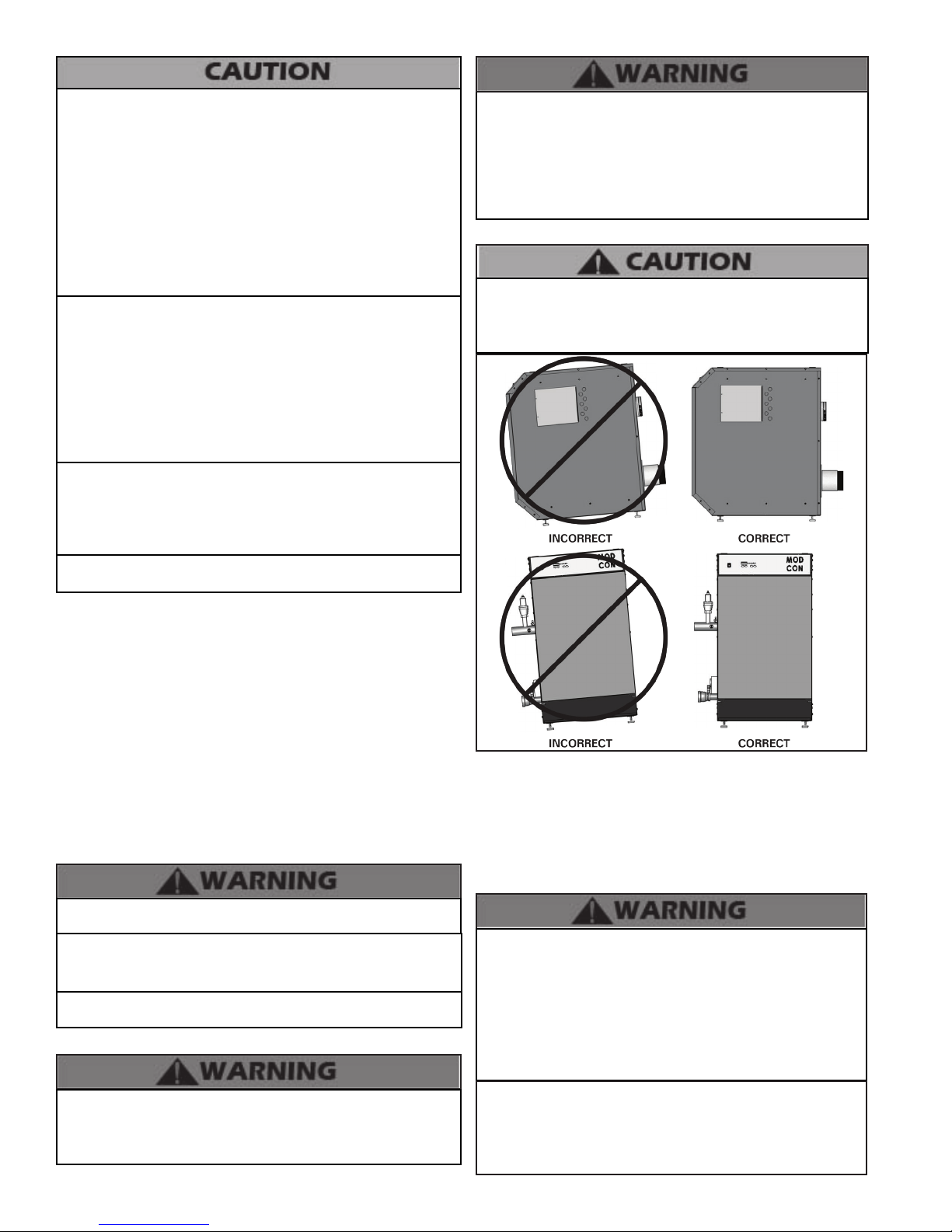
This boiler must be installed upright in the vertical position
as described in this manual. DO NOT attempt to install this
boiler in any other orientation. Doing so will result in improper
boiler operation and property damage, and could result in
serious personal injury or death.
All boilers eventually leak. It is recommended to install a
catch pan beneath the boiler. This catch pan should be sized
with a maximum depth of 2”, and a minimum diameter 2”
greater than the diameter of the boiler. The catch pan should
empty into an open drain line. This drain line should be 3/4”
ID minimum, piped to an open drain. Failure to follow these
instructions could result in property damage. Such damages
ARE NOT covered by product warranty.
11
F. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe
The boiler is rated ANSI Z21.13 Category IV (pressurized vent,
likely to form condensate in the vent) and requires a special vent
system designed for pressurized venting.
NOTE: The venting options described here (and further
detailed in the Venting section, this manual) are the lone
venting options approved for this boiler. Failure to vent the
boiler in accordance with the provided venting instructions
will void the warranty.
Failure to vent the boiler properly will result in serious personal
injury or death.
Do not attempt to vent this boiler by any means other than
those described in this manual. Doing so will void the warranty
and may result in severe personal injury or death.
Vents must be properly supported. Boiler exhaust and intake
connections are not designed to carry heavy weight. Vent
support brackets must be within 1’ of the boiler and the balance
at 4’ intervals. Boiler must be readily accessible for visual
inspection for rst 3’ from the boiler. Failure to properly support
vents could result in property damage, severe personal injury,
or death.
The exhaust discharged by this boiler may be very hot. Avoid
touching or other direct contact with the exhaust gases of the
vent termination assembly. Doing so could result in severe
personal injury or death.
Figure 3 - Recommended Service Clearances
E. Residential Garage and Closet Installations
Check with your local Authority Having Jurisdiction for
requirements when installing the boiler in a garage or
closet. Please read the entire manual before attempting
installation. Failure to properly take factors such as venting,
piping, condensate removal, and wiring into account before
installation could result in wasted time, money, and possible
property damage and personal injury.
Precautions
If the boiler is located in a residential garage, per ANSI Z223.1:
• Install the boiler burner and ignition devices a minimum of 18” above the oor of the garage. This will
ensure the burner and ignition devices are well o the
oor.
• When raising the boiler ensure the entire bottom and
fully lled weight of the boiler are fully supported.
• Locate or protect the boiler so it cannot be damaged
by a moving vehicle.
The space must be provided with correctly sized combustion/
ventilation air openings for all other appliances located in the
space with the boiler. For power venting installations using
room air for combustion, refer to the venting section, this
manual, for descriptions of conned and unconned spaces.
Do not install the boiler in an attic. Failure to comply with
these warnings could result in substantial property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
12
1. Direct Vent of Exhaust and Intake
If installing a direct vent option, combustion air must be drawn
from the outdoors directly into the boiler intake and exhaust
must terminate outdoors. There are three basic direct vent
options detailed in this manual: 1. Side Wall Venting, 2. Roof
Venting, and 3. Unbalanced Venting.
Be sure to locate the boiler such that the exhaust vent and
intake piping can be routed through the building and properly
terminated. Dierent vent terminals can be used to simplify and
eliminate multiple penetrations in the building structure (see
Optional Equipment in Venting Section). The exhaust vent and
intake piping lengths, routing, and termination methods must
all comply with the methods and limits given in the Venting
Section, this manual.
When installing a combustion air intake from outdoors, care
must be taken to utilize uncontaminated combustion air. To
prevent combustion air contamination, see Table 3.
2. Indoor Combustion Air in Conned or Unconned Space
This boiler requires fresh, uncontaminated air for safe operation
and must be installed in a mechanical room where there is
adequate combustion and ventilating air. NOTE: To prevent
combustion air contamination, see Table 3.
Combustion air from the indoor space can be used if the space
has adequate area or when air is provided through a duct or
louver to supply sucient combustion air based on the boiler
input. Never obstruct the supply of combustion air to the boiler.
If the boiler is installed in areas where indoor air is contaminated
(see Table 3) it is imperative that the boiler be installed as direct
vent so that all combustion air is taken directly from the outdoors
into the boiler intake connection.
Unconned space is space with volume greater than 50 cubic
feet per 1,000 BTU/hr (4.8 cubic meters per kW) of the total
input rating of all fuel-burning appliances installed in that space.
Rooms connected directly to this space through openings not
furnished with doors are considered part of the space. See
Venting Section for details.
Conned space is space with volume less than 50 cubic feet per
1,000 BTU/hr (4.8 cubic meters per kW) of the total input rating
of all fuel-burning appliances installed in that space. Rooms
connected directly to this space through openings not furnished
with doors are considered part of the space.
When drawing combustion air from inside a conventionally
constructed building to a conned space, such space should be
provided with two permanent openings: one located 6” (15 cm)
below the space ceiling, the other 6” (15cm) above the space
oor. Each opening should have a free area of one square inch
2
per 1,000 BTU/hr (22cm
/kW) of the total input of all appliances
in the space, but not less than 100 square inches (645cm2).
If the conned space is within a building of tight construction, air
for combustion must be obtained from the outdoors as outlined
in the Venting section of this manual.
Failure to provide an adequate supply of fresh combustion
air can cause poisonous ue gases to enter the living space,
resulting in severe personal injury or death. To prevent
combustion air contamination, see Table 3.
G. Prevent Combustion Air Contamination
Install intake air piping for the boiler as described in the
Venting Section, this manual. Do not terminate exhaust in
locations that can allow contamination of intake air.
Ensure that the intake air will not contain any of the
contaminants in Table 3. Contaminated air will damage the
boiler, resulting in possible substantial property damage,
severe personal injury, or death. For example, do not pipe
intake air near a swimming pool or laundry facilities. These
areas always contain contaminants.
Products to Avoid
Spray cans containing
uorocarbons
Permanent wave solutions Swimming pools
Chlorinated waxes / cleaners Metal fabrication plants
Chlorine-based swimming pool
chemicals
Calcium chloride used for thawing Refrigeration repair shops
Sodium chloride used for water
softening
Refrigerant leaks Auto body shops
Paint or varnish removers Plastic manufacturing plants
Hydrochloric or Muriatic acid
Cements and glues New building construction
Antistatic fabric softeners used in
clothes dryers
Chlorine-type bleaches, laundry
detergents, and cleaning solvents
Adhesives used to fasten building
products
Table 3 - Products and Areas Likely to Have Contaminants
Areas Likely to Have
Contaminants
Dry cleaning / laundry areas
and establishments
Beauty shops
Photo processing plants
Furniture renishing areas
and establishments
Remodeling areas
Garages and workshops
NOTE: DAMAGE TO THE BOILER CAUSED BY EXPOSURE
TO CORROSIVE VAPORS IS NOT COVERED BY
WARRANTY. (Refer to the limited warranty for complete
terms and conditions.)
H. Removing a Boiler from a Common Vent System
When drawing combustion air from the outside into the
mechanical room, care must be taken to provide adequate
freeze protection.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
Do not install the boiler into a common vent with any other
appliance. This will cause ue gas spillage or appliance
malfunction, resulting in possible substantial property
damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Failure to follow all instructions can result in ue gas spillage
and carbon monoxide emissions, causing severe personal
injury or death.

13
When removing an existing boiler, follow the steps below.
1. Seal any unused openings in the common venting system.
2. Visually inspect the venting system for proper size and
horizontal pitch to determine if there is blockage, leakage,
corrosion, or other deciencies that could cause an unsafe
condition.
3. If practical, close all building doors, windows, and doors
between the space in which the boiler remains connected to
the common venting system and other spaces in the building.
Turn on clothes dryers and any appliances not connected to
the common venting system. Turn on any exhaust fans, such
as range hoods and bathroom exhausts, at maximum speed.
Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close all replace
dampers.
4. Place in operation the appliance being inspected. Follow the
lighting instructions. Adjust the thermostat so the appliance
will operate continuously.
5. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening after 5
minutes of main burner operation. Use the ame of a match
or candle or smoke from a cigarette.
6. After it has been determined that each appliance remaining
connected to the common venting system properly vents
when tested as outlined, return doors, windows, exhaust fans,
replace dampers, and any other gas burning appliances to
their previous condition of use.
7. Any improper operation of the common venting system
should be corrected to conform to the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1. When resizing any portion of the common
venting system, the system should approach the minimum
size as determined using the appropriate tables in Appendix
G of ANSI Z223.1.
I. Water Chemistry Requirements*
Chemical imbalance of the water supply may aect eciency and
cause severe damage to the boiler and associated equipment.
HTP recommends having water quality professionally analyzed
to determine whether it is necessary to install a water softener.
It is important that the water chemistry on both the domestic
hot water and central heating sides are checked before
installing the boiler, as water quality will aect the reliability of
the system. In addition, operating temperatures above 140oF
will cause the boiler to operate continuously, accelerating the
build-up of lime scale and possibly shortening the service life of
the boiler. Failure of a boiler due to lime scale build-up, low pH,
or other chemical imbalance IS NOT covered by the warranty.
• Sodium less than 20 mGL
• Water pH between 6.0 and 8.0
• Maintain water pH between 6.0 and 8.0. Check with
litmus paper or have it chemically analyzed by water
treatment company.
• If the pH diers from above, consult local water
treatment for treatment needed.
• Hardness less than 7 grains
• Consult local water treatment companies for unusually
hard water areas (above 7 grains hardness).
• Chlorine concentration less than 100 ppm
• Using chlorinated fresh water should be acceptable as
levels are typically less than 5 ppm.
• Do not connect the boiler to directly heat swimming
pool or spa water.
• Do not ll boiler or operate with water containing
chlorine in excess of 100 ppm.
*NOTE: It is recommended to clean the heat exchanger at
least once a year to prevent lime scale buildup. To clean the
heat exchanger, follow the maintenance procedure in this
manual.
Hardness: Less than 7 grains
Chloride levels: Less than 100 ppm
pH levels: 6 - 8
TDS: Less than 2000 ppm
Sodium: Less than 20 mGL
Figure 4 - CO Warning Label
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
14
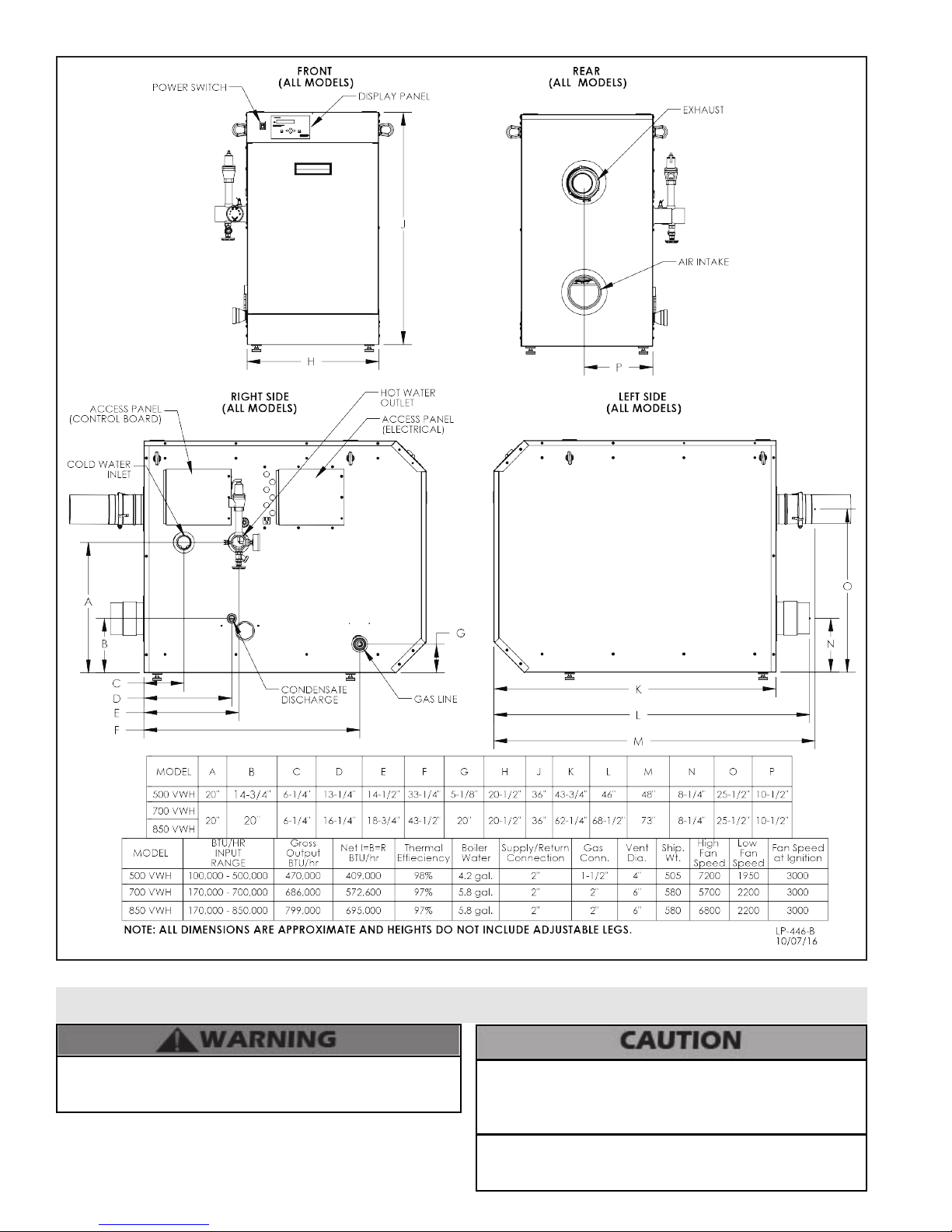
Figure 5 - Boiler Dimensions - NOTE: All Dimensions Are Approximate - VWH in Model Number Denotes Volume Water Heater Model
Part 4 - Piping
Failure to follow the instructions in this section WILL VOID the
warranty and may result in property damage, severe personal
injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
Dielectric unions or galvanized steel ttings must not be used
in a system with this boiler. Doing so WILL VOID the warranty.
Use only copper, brass, or stainless steel ttings. Teon thread
sealant must be used on all connections.
DO NOT pipe this boiler with black iron, galvanized steel,
steel, or lead pipe. Doing so will result in premature product
failure and property damage, and WILL VOID the warranty.

15
Plumbing of this product should only be done by a qualied,
licensed plumber in accordance with all local plumbing codes.
The boiler is designed to be connected to a storage tank to supply
domestic hot water. HTP oers 119 and 175 gallon size storage
tanks in either stainless steel or glass-lined construction. These
storage tanks will be directly connected to the boiler supply and
return connection.
VWH units must be connected to a storage tank. Failure to
connect the VWH boiler to a storage tank of the minimum size
requirements (119 gallons for a single 500VWH; 175 gallons
for a single 700/850VWH) will result in property damage and/
or premature boiler failure. Damages resulting from incorrect
installation or from use of products not approved by HTP, Inc.
ARE NOT covered by warranty.
A. General Plumbing Information
The building piping system must meet or exceed the the piping
requirements in this manual.
The control module uses temperature sensors to provide both
high limit protection and modulating temperature control. The
control module also provides low water protection by sensing
the water level in the heat exchanger. Some codes/jurisdictions
may require additional external controls..
Use two wrenches when tightening water piping at boiler. Use
one wrench to prevent the boiler return or supply line from
turning. Failure to prevent piping connections from turning
could cause damage to boiler components.
NOTE: The addition of a high temperature limiting device is
important if the boiler is to be connected to a domestic hot
water system.
Connect the cold water supply to both the storage bottom
port and the supply side of the boiler (shown in Applications,
this manual). It is important that you install a ow check on
the supply line of the boiler BEFORE connecting the feed line
to the storage tank. This allows the cold feed to ow through
the storage tank rst. It is recommended that you install shut
o valves on the cold feed line for future ease of service. If there
is a back ow preventer or any type of no return valve in the
system, then you must install an additional tee for a suitable
potable hot water expansion tank. Connect the storage tank
return line to the return connection located on the boiler (shown
in Applications, this manual). Then connect the storage tank hot
water outlet to the hot water plumbing lines.
B. Relief Valve
Connect discharge piping to a safe disposal location following
the guidelines below.
To avoid water damage or scalding due to relief valve operation:
• Discharge line must be connected to relief valve outlet
and run to a safe place of disposal. Terminate the
discharge line in a manner that will prevent possibility of
severe burns or property damage should the relief valve
discharge.
• Discharge line must be as short as possible and the same
size as the valve discharge connection throughout its
entire length.
• Discharge line must pitch downward from the valve
and terminate at least 6” above the oor drain, making
discharge clearly visible.
• The discharge line shall terminate plain, not threaded,
with a material serviceable for temperatures of 375oF
or greater.
• Do not pipe discharge to any location where freezing
could occur.
• No valve may be installed between the relief valve and
boiler or in the discharge line. Do not plug or place any
obstruction in the discharge line.
• Test the operation of the relief valve after lling and
pressurizing the system by lifting the lever. Make sure
the valve discharges freely. If the valve fails to operate
correctly, immediately replace with a new properly
rated relief valve.
• Test T&P valve at least once annually to ensure the
waterway is clear. If valve does not operate, turn the
boiler “o” and call a plumber immediately.
• Take care whenever operating relief valve to avoid
scalding injury or property damage.
FAILURE TO COMPLY WITH THE ABOVE GUIDELINES
COULD RESULT IN FAILURE OF RELIEF VALVE OPERATION,
RESULTING IN POSSIBILITY OF SUBSTANTIAL PROPERTY
DAMAGE, SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH.
Do not thread a cap or plug into the relief valve or relief
valve line under any circumstances! Explosion and property
damage, serious injury, or death may result.
RE-INSPECTION OF T&P RELIEF VALVES: T&P valves
should be inspected AT LEAST ONCE EVERY THREE
YEARS, and replaced if necessary, by a licensed plumbing
contractor or qualied service technician to ensure that the
product has not been aected by corrosive water conditions
and to ensure that the valve and discharge line have not been
altered or tampered with illegally. Certain naturally occuring
conditions may corrode the valve and its components over
time, rendering the valve inoperative. Such conditions can
only be detected if the valve and its components are physically
removed and inspected. Do not attempt to conduct an
inspection on your own. Contact your plumbing contractor
for a re-inspection to assure continued safety.
FAILURE TO RE-INSPECT THE T&P VALVE AS DIRECTED
COULD RESULT IN UNSAFE TEMPERATURE AND/OR
PRESSURE BUILD-UP WHICH CAN RESULT IN PROPERTY
DAMAGE, SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH.
C. Backow Preventer
Use a backow preventer specically designed for boiler
installations. This valve should be installed on the cold water
ll supply line per local codes.
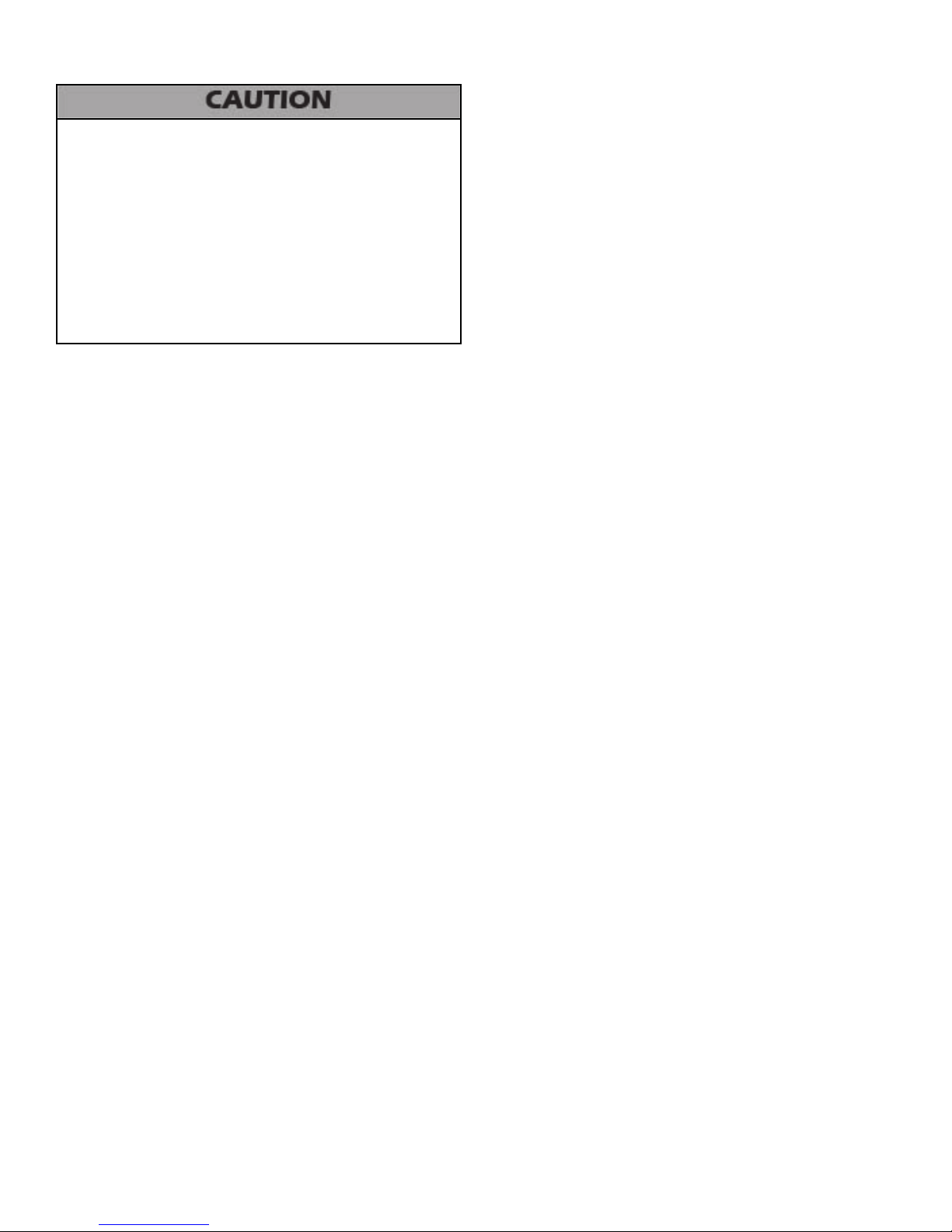
D. Potable Expansion Tank
A potable hot water expansion tank is required to oset
heated water expansion. In most city plumbing systems, the
water meter has a no return or back ow device built into
the system to prevent back owing of water into city mains.
Some local codes require back ow preventers on all incoming
water supplies. The hot water expansion tank must be listed
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
16
for potable water use. The expansion tank should be located on
the cold inlet piping close to the boiler.
Expansion Tank and Make-Up Water
1. Ensure that the expansion tank is sized to correctly handle
boiler and system water volume and temperature.
Expansion tanks must be sized according to total system
volume. This includes all length of pipe, all xtures, boilers, etc.
Failure to properly size for system expansion could result in
wasted time, money, possible property damage, serious injury,
or death.
Undersized expansion tanks cause system water to be lost from
the relief valve, causing make-up water to be added. Eventual
boiler failure can result due to excessive make-up water
addition. SUCH FAILURE IS NOT COVERED BY WARRANTY.
DO NOT install automatic air vents on closed type expansion
tank systems. Air must remain in the system and return to the
tank to provide an air cushion. An automatic air vent would
cause air to leave the system, resulting in improper operation
of the expansion tank.
The expansion tank must be suitable for hot potable water
systems.
Expansion Tank Sizing*
VWH Model Heat Exchanger Volume (Gallons)
500 4.2
700/850 5.8
Table 5 - *Add Required Storage Tank Gallon Size to Heat Exchanger
Volume - 119 and 175 Gallon Tanks Available
2. The expansion tank must be located as shown in Applications,
this manual, or following recognized design methods. See
expansion tank manufacturer’s instructions for details.
E. Circulators
Every VWH system requires special attention to circulator size
to overcome pressure drop through the boiler and its related
piping. All circulators installed on the VWH system must be
designed for potable water installations. Boiler pressure drop is
detailed in this manual.
Water temperature above 140oF requires the circulator to run
continuously. Water hardness must be between 5 and 7 grains.
Hardness above 7 grains will damage the heat exchanger and
shorten the service life of the boiler.
DO NOT use the boiler circulator in any location other than
the ones shown in this manual. The boiler circulator location is
selected to ensure adequate ow through the boiler. Failure to
comply with this caution could result in unreliable performance
and nuisance shutdowns from insucient ow.
F. Scalding
This boiler can deliver scalding water at any faucet in the system.
Be careful whenever using hot water to avoid scalding injury.
Certain appliances such as dishwashers and automatic clothes
washers may require increased water temperatures. By setting
the thermostat on this boiler to obtain the increased water
temperature required by these appliances you may create the
potential for scald injury.
To protect against
injury, install a mixing
valve in the water
system. This valve
will reduce point
of use discharge
temperatures by
mixing cold and hot
water in branch supply
lines. Such valves
are available from
your local plumbing
supplier.
Table 4 details the
relationship of water
temperature and
time with regard to
scald injury and may
be used as a guide in
determining the safest
water temperature for your applications.
The risk of scalding increases when raising tank temperature.
Use a water tempering or mixing valve when raising tank
temperature to lessen the chance of scalds. Consult codes
for conformance. Failure to install a temperature limiting
or mixing valve and follow these instructions could result in
property damage, severe personal injury, or death due to
scalds.
Approximate Time / Temperature Relationships in Scalds
o
120
F More than 5 minutes
o
F 1 1/2 to 2 minutes
125
o
F About 30 seconds
130
o
F About 10 seconds
135
o
F Less than 5 seconds
140
o
F Less than 3 seconds
145
o
F About 1 1/2 seconds
150
o
F About 1 second
155
Table 4 - Approximate Time / Temperature Relationships in Scalds
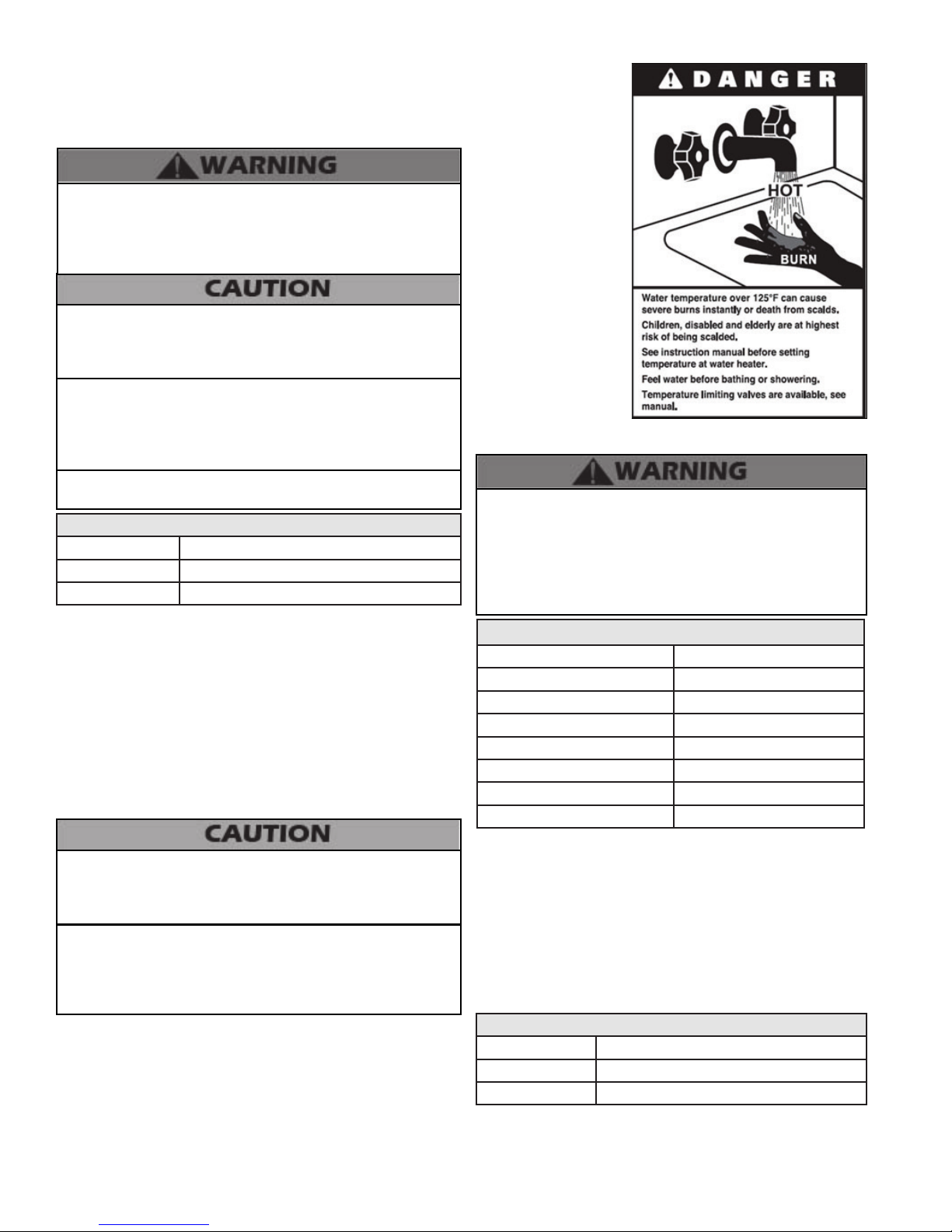
G. High Velocity Circulator Pump
Every VWH system requires special attention to pump size in
order to overcome pressure drop through the boiler and its
related piping. All circulators installed on the VWH system
must be designed for a potable water system.
In addition, the heat exchanger has a minimum total water
volume that must be taken into account when sizing the
circulator. Minimum ow rates are listed in the table below.
Minimum Boiler Flow Rates
VWH Model Minimum Flow (GPM)
500 33
700/850 54
Table 6 - Minimum Flow Rates
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
17
500 Model 700/850 Models
Table 7 - Heat Exchanger Pressure Drop
The chart below represents various system design temperature rise through the boiler along with respective ows and friction
loss. This is provided to aid in circulator selection.
System Temperature Rise Chart
20°Δt 25°Δt 30°Δt
Model Friction Ft Flow Rate (GPM) Friction Ft Flow Rate (GPM) Friction Ft Flow Rate (GPM)
500 19’ 50 11’ 40 8’ 33
700/850 35’ 85 26’ 65 18’ 54
Table 8 - Temperature Rise, Friction Feet, and Flow Rate
Table 9 - Multiple Boiler Manifold Piping
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
18
H. Water Chemistry
Chemical imbalance of the water supply may aect eciency and
cause severe damage to the boiler and associated equipment.
HTP recommends having water quality professionally analyzed
to determine whether it is necessary to install a water softener.
It is important that the water chemistry on both the domestic
hot water and central heating sides are checked before
installing the boiler, as water quality will aect the reliability of
the system. In addition, operating temperatures above 140oF
will cause the boiler to operate continuously, accelerating the
build-up of lime scale and possibly shortening the service life of
the boiler. Failure of a boiler due to lime scale build-up, low pH,
or other chemical imbalance IS NOT covered by the warranty.
Water Hardness
Water hardness is mainly due to the presence of calcium and
magnesium salts dissolved in the water. The concentration of
these salts is expressed in mg/L, ppm or grains per gallon, as a
measure of relative hardness of water. Grains per gallon is the
common reference measurement used in the U.S. water heater
industry. Hardness expressed as mg/L or ppm may be divided
by 17.1 to convert to grains per gallon. Water may be classied
as very soft, slightly hard, moderately hard, or hard based on
its hardness number. The minerals in the water precipitate out
when the water is heated and cause accelerated lime and scale
accumulation on a heat transfer surface.
If the hardness of the water exceeds the maximum level of 7
grains per gallon, water should be softened to a hardness level
no lower than 5 grains per gallon. Water softened as low as 0 to 1
grain per gallon may be under-saturated with respect to calcium
carbonate, resulting in water that is aggressive and corrosive.
pH of Water
pH is a measure of relative acidity, neutrality or alkalinity.
Dissolved minerals and gases aect water pH. The pH scale
ranges from 0 to 14. Water with a pH of 7.0 is considered neutral.
Water with a pH lower than 7 is considered acidic. Water pH
higher than 7 is considered alkaline. A neutral pH (around 7)
is desirable for most potable water applications. Corrosion
damage and boiler failures resulting from water pH levels of
lower than 6 or higher than 8 ARE NOT covered by the warranty.
The ideal pH range for water used in a storage tank or a water
heater system is 7.2 to 7.8.
Total Dissolved Solids
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is a measurement of all minerals
and solids dissolved in a water sample. The concentration of
total dissolved solids is usually expressed in parts per million
(ppm).
Water with a high TDS concentration will greatly accelerate lime
and scale formation in the hot water system. Most high TDS
concentrations precipitate out of the water when heated. This
can generate a scale accumulation on the heat transfer surface
that will greatly reduce the service life of a boiler. This scale
accumulation can also impede the ability of the heat exchanger
to transfer heat into the water. A heat exchanger damaged or
blocked by lime/scale accumulation must be replaced.
The manufacturer of the boiler has no control of water quality,
especially TDS levels in your system. Total dissolved solids in
excess of 2,000 ppm will accelerate lime and scale formation
in the heat exchanger. Heat exchanger failure due to total
dissolved solids in excess of 2,000 ppm is a non-warrantable
condition. Failure of a boiler due to lime scale build up on the
heating surface IS NOT covered by the warranty.
Hardness: Less than 7 grains
Chloride levels: Less than 100 ppm
pH levels: 6-8
TDS: Less than 2000 ppm
Sodium: Less than 20 mGL
*NOTE: It is recommended you clean heat exchanger at
least once a year to prevent lime scale buildup. Follow the
maintenance procedure in the Maintenance Section of this
manual to clean the heat exchanger
Piping components
Water heating system piping
System piping MUST be sized per technical pipe requirements
listed in this manual. Reducing pipe size can restrict ow rate
through the boiler, causing inadvertent short cycling and poor
system performance.
Check valves
Field supplied. Check valves are recommended for installation
as shown in Piping Details.
Boiler isolation valves
Field supplied. Full port ball valves are required. Failure to
use full port ball valves could result in a restricted ow rate
through the boiler.
Anti-scald mixing valve
Field supplied. A thermostatic mixing valve is recommended
when storing domestic hot water above 115°F.
Unions
Field supplied: Recommended for unit serviceability. DO NOT
USE DIELECTRIC UNIONS!
ONLY BRASS, COPPER, OR STAINLESS STEEL.
Pressure relief valve
Factory supplied on VWH. The pressure relief valve is sized
to ASME specications. Storage tank may require additional
relief valves depending on local codes.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
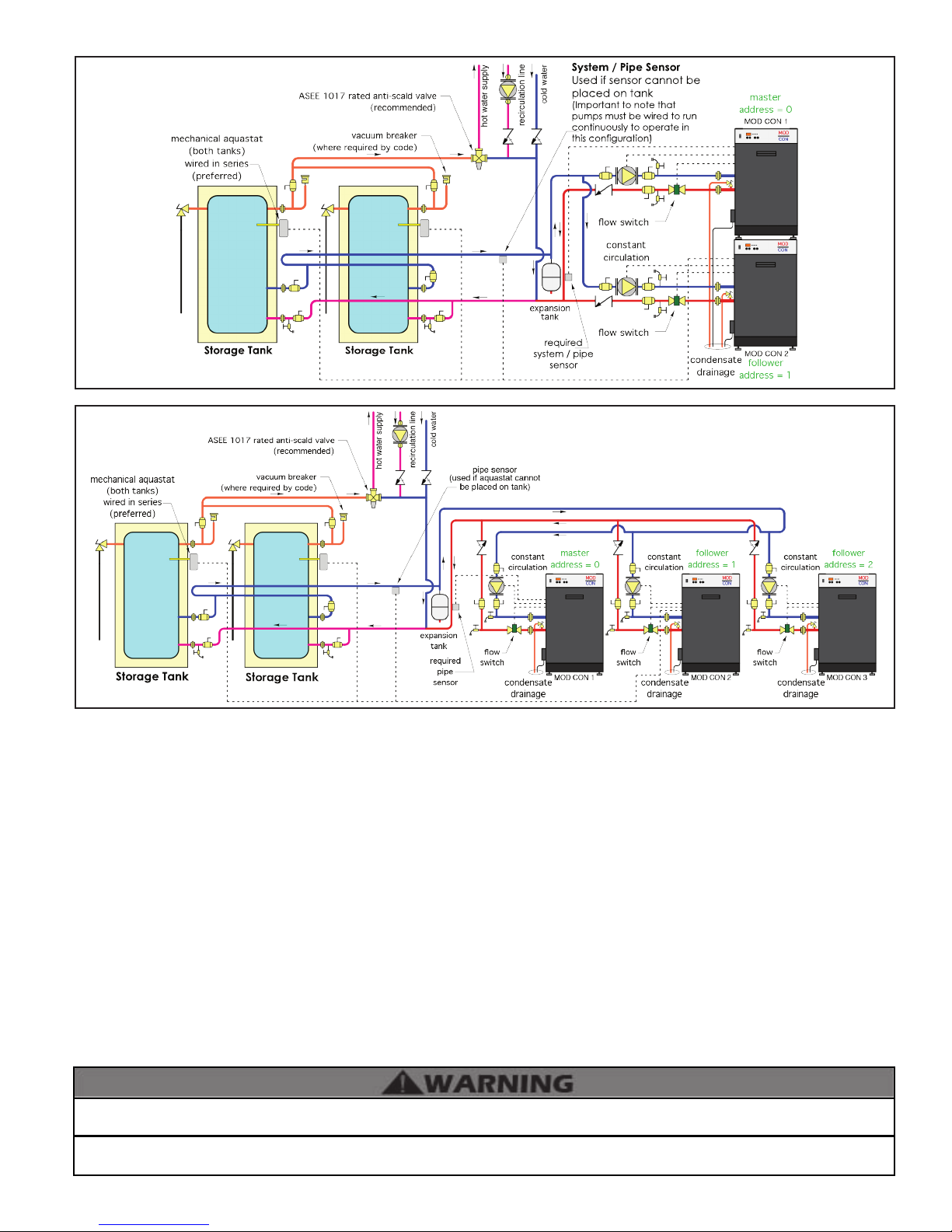
Storage Tank
System / Pipe Sensor
Used if sensor cannot be placed at tank
(Important to note that pumps must be wired
to run continuously to operate in this configuration)
Indirect /
Tank
Sensor
Preferred
Location
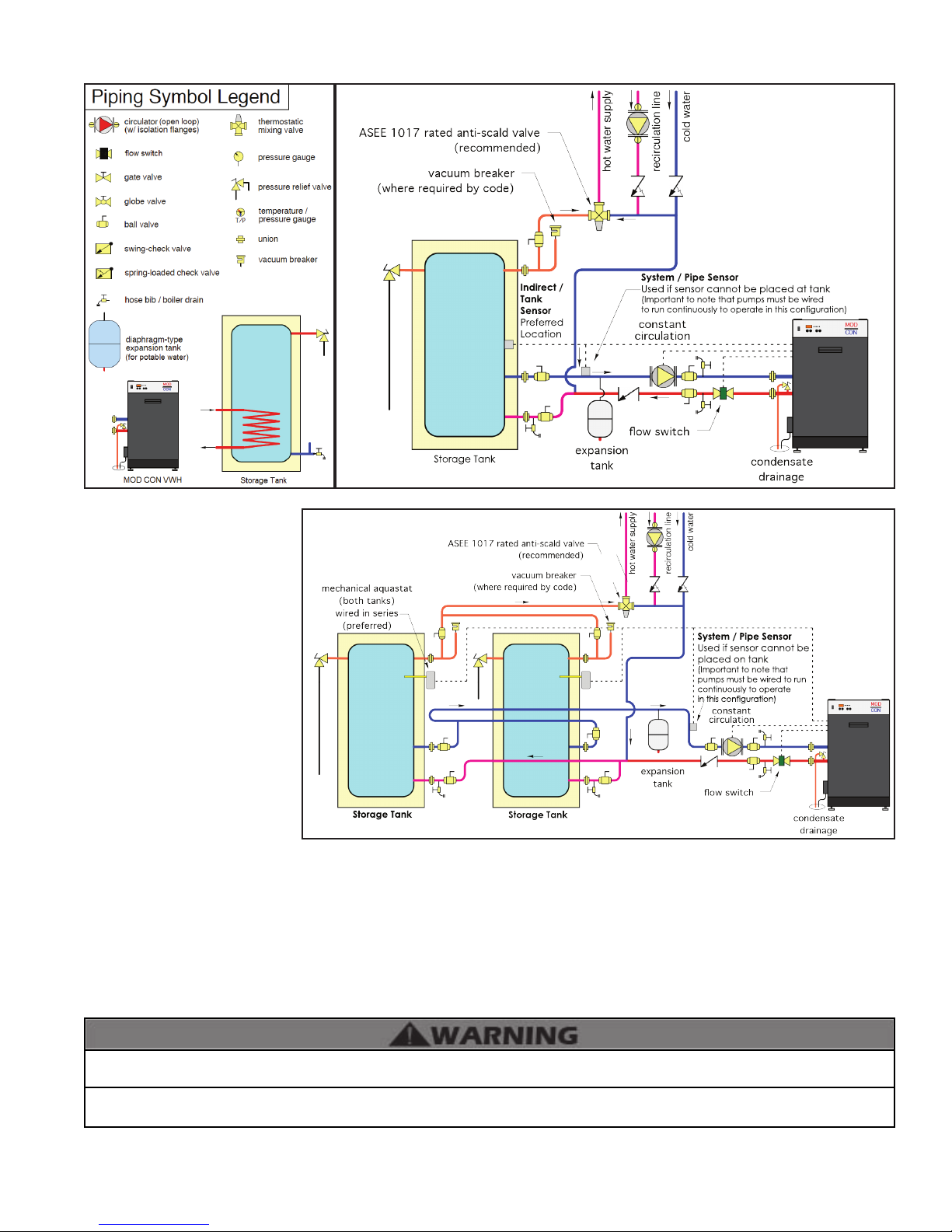
I. Applications
System / Pipe Sensor
Used if sensor cannot be
placed on tank
(Important to note that
pumps must be wired to run
continuously to operate
in this configuration)
in this configuration)
Storage Tank
19
Figure 6 - Piping Legend Figure 7 - VWH Boiler with Storage Tank
FIGURE NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to show
system piping concept only.
Installer
is responsible for all equipment &
detailing required by local codes.
2. Boiler circulator must be rated for
open loop application. Do not use
cast-iron circulators.
3. Boiler circulator(s) operate
continuously.
4. The minimum pipe size for
connecting a storage tank is 1 1/2”.
5. The minimum pipe size for
connecting a boiler is 2”. When
sizing and installing a multiple boiler
system, see Multiple Boiler Manifold
Piping Chart, this manual.
6. All pumps are shown with isolation
anges or full port ball valves for
isolation. The alternative is standard
anges with full port ball valves and a
Figure 8 - VWH Boiler with Two Storage Tanks
separate ow check valve.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators and check valves.
8. Install vacuum relief valve in accordance with local code requirements.
9. Multiple boilers and storage tanks shall be installed with reverse return piping (as shown).
10. Expansion tank must be rated for use with potable water.
11. Use either indirect/tank sensor or system/pipe sensor mounted on common return to the boiler.
12. Aquastat or system/pipe sensor connects to DHW sensor input on boiler.
13. The minimum storage tank size for a 500VWH is 119 gallons. The minimum storage tank size for a 700/850VWH is 175 gallons.
An ASSE 1017 thermostatic mixing valve is recommended on all tanks if the hot water temperature leaving the tank is above
119oF. Failure to do so could result in substantial property damage, serious injury, or death.
The piping will not support the weight of the circulators. Refer to the circulator manufacturer’s instructions to properly support
the circulator. Failure to comply with these instructions could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

20
Storage Tank
System / Pipe Sensor
Used if sensor cannot be place on tank
(Important to note that pumps must be wired to
run continuously to operate in this configuration)
Required
System /
Pipe
Sensor
System / Pipe Sensor
Used if sensor cannot be placed on tank
(Important to note that pumps must be wired to
run continuously to operate in this configuration)
Storage Tank
FIGURE NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to show
system piping concept only.
Installer is responsible for all
equipment & detailing required by
local codes.
2. Boiler circulator must be rated for
open loop application. Do not use
cast-iron circulators.
3. Boiler circulator(s) operate
continuously.
4. The minimum pipe size for
connecting a storage tank is 1 1/2”.
5. The minimum pipe size for
connecting a boiler is 2”. When
sizing and installing a multiple
boiler system, see Multiple Boiler
Manifold Piping Chart, this manual.
6. All pumps are shown with
isolation anges or full port ball
valves for isolation. The alternative
is standard anges with full port ball
valves and a separate ow check
valve.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters
of straight pipe upstream of all
circulators and check valves.
8. Install vacuum relief valve
in accordance with local code
requirements.
9. Multiple boilers and storage
tanks shall be installed with reverse
return piping (as shown).
10. Expansion tank must be rated
for use with potable water.
11. Use either indirect/tank sensor
or system/pipe sensor mounted on
common return to the boiler.
12. Wire the tank or system/pipe
sensor to the DHW sensor terminals
input on the follower boiler
addressed as #1.
13. Wire the tank or system / pipe
sensor connected to the DHW
sensor terminals on the follower
boiler addressed as #1.
14. The system / pipe sensor must
be placed on common piping to the
tank as close to the tank as possible.
15. The system / pipe sensor is wired
to the system sensor terminals on
the master boiler.
16. The minimum storage tank size for a 500VWH is 119 gallons. The minimum storage tank size for a 700/850VWH is 175 gallons.
Figure 9 - Two VWH Boilers with Storage Tank
Figure 10 - Two Stacked VWH Boilers with Storage Tank
An ASSE 1017 thermostatic mixing valve is recommended on all tanks if the hot water temperature leaving the tank is above
119oF. Failure to do so could result in substantial property damage, serious injury, or death.
The piping will not support the weight of the circulators. Refer to the circulator manufacturer’s instructions to properly support
the circulator. Failure to comply with these instructions could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
required
system / pipe
sensor
System / Pipe Sensor
Used if sensor cannot be
placed on tank
(Important to note that
pumps must be wired to run
continuously to operate in
this configuration)
this configuration)
Storage Tank
Figure 11 - Two Stacked VWH Boilers with Two Storage Tanks
Storage Tank
21
Figure 12 - Three VWH Boilers with Two Storage Tanks
FIGURE NOTES:
1. This drawing is meant to show system piping concept only.
2. Boiler circulator must be rated for open loop application. Do not use cast-iron circulators.
3. Boiler circulator(s) operate continuously.
4. The minimum pipe size for connecting a storage tank is 1 1/2”.
5. The minimum pipe size for connecting a boiler is 2”. When sizing and installing a multiple boiler system, see Multiple Boiler Manifold Piping
Chart, this manual.
6. All pumps are shown with isolation anges or full port ball valves for isolation. The alternative is standard anges with full port ball valves and
a separate ow check valve.
7. Install a minimum of 12 diameters of straight pipe upstream of all circulators and check valves.
8. Install vacuum relief valve in accordance with local code requirements.
9. Multiple boilers and storage tanks shall be installed with reverse return piping (as shown).
10. Expansion tank must be rated for use with potable water.
11. Use either indirect/tank sensor or system/pipe sensor mounted on common return to the boiler.
12. Wire the tank or system/pipe sensor to the DHW sensor terminals input on the follower boiler addressed as #1.
13. Wire the tank or system / pipe sensor connected to the DHW sensor terminals on the follower boiler addressed as #1.
14. The system / pipe sensor must be placed on common piping to the tank as close to the tank as possible.
15. The system / pipe sensor is wired to the system sensor terminals on the master boiler.
16. The minimum storage tank size for a 500VWH is 119 gallons. The minimum storage tank size for a 700/850VWH is 175 gallons.
An ASSE 1017 thermostatic mixing valve is recommended on all tanks if the hot water temperature leaving the tank is above
119oF. Failure to do so could result in substantial property damage, serious injury, or death.
The piping will not support the weight of the circulators. Refer to the circulator manufacturer’s instructions to properly support the
circulator. Failure to comply with these instructions could result in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Installer is responsible for all equipment & detailing required by local codes.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

22
Part 5 - Venting and Condensate Removal
The boiler must be vented as detailed in this section. Ensure
exhaust vent and intake piping complies with these instructions
regarding vent system. Inspect nished exhaust vent and intake
piping thoroughly to ensure all joints are well secured, airtight,
and comply with all applicable code requirements, as well as the
instructions provided in this manual. Failure to properly install
the vent system will result in severe personal injury or death.
A. General
This boiler is certied as a “Category IV” appliance and requires
a special venting system. The vent system will operate with
a positive pressure in the pipe. Exhaust gases must be piped
directly outdoors using the vent materials and rules outlined
in these instructions. Do not connect vent connectors
serving appliances vented by natural draft into any portion of
mechanical draft systems operating under positive pressure.
Follow the venting instructions carefully. Failure to do so will
result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury,
or death.
1. Installation should be made in accordance with the regulations
of the Authority Having Jurisdiction, local code authorities, and
utility companies which pertain to this type of water heating
equipment.
2. Install the venting system in accordance with these
instructions and with the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/
NFPA 54, CAN/CGA B149, and / or applicable provisions of local
building codes.
3. This boiler must be vented with materials, components, and
systems listed and approved for Category IV appliances.
Exhaust and intake are to be piped separately. This boiler cannot
share a common exhaust or intake with multiple appliances.
Failure to follow these instructions will result in substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
NOTE: To avoid contamination often contained in indoor air, it
is best to pipe all intake combustion air directly to the outdoors.
NOTE: If exhaust vent pipe system passes through an unheated
space such as an alcove or attic, the space must be heated.
Improper seating of vent pipe gaskets can cause eventual
gasket failure and exhaust gas leakage. Ensure the exhaust vent
pipe is properly beveled and seated before insertion into the
ue adapter. Failure to do so could result in property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
Due to the extreme ammability of most glues, cements,
solvents, and primers used to join plastic exhaust vent and
intake pipes, explosive solvent vapors must be cleared from
all vent piping before start-up. Avoid using excess cement or
primer, as this may pool in the vent pipes. Vent assemblies
should be allowed to cure for a period of at least 8 hours before
powering a connected appliance. Failure to follow these
instructions will result in substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death. It is the installers’ responsibility to
understand the hazards associated with explosive solvents
and take the necessary precautions to avoid these risks.
DO NOT insulate the rst 3 feet of the exhaust vent. CPVC,
Polypropylene, or Stainless Steel pipe material MUST be
used for the rst 3 feet of the vent run if the exhaust vent is
insulated or passes through an enclosed space greater than
6”, such as a wall. The balance of the vent run can be installed
with standard Schedule 40 PVC pipe. Failure to comply with
this warning could result in property damage, severe personal
injury, or death.
Exhaust vent adaptors are not designed as load-bearing
devices, and must not be used to support exhaust vent piping.
All vent pipes must be properly connected, supported, and
the exhaust vent must be pitched a minimum of 1/4” per foot
back to the boiler to allow drainage of condensate. Failure
to properly support vent piping and follow the information
in this statement could result in product damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

B. Approved Materials for Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe
Item Material
United States Canada
PVC Schedule 40/80 ANSI / ASTM D1785
PVC-DWV* ANSI / ASTM D2665
Exhaust Vent or Intake
Pipe and Fittings
CPVC Schedule 40/80 ANSI / ASTM F441
Polypropylene UL-1738 or ULC-S636
Stainless Steel AL29-4C Certied for Category IV and Direct Vent Appliance Venting
Pipe Cement
PVC ANSI / ASTM D2564
CPVC ANSI / ASTM F493
Pipe Primer PVC / CPVC ASTM F656
• The exhaust and intake components installed with this boiler must be used for near boiler piping BEFORE transitioning to
the approved materials listed above. DO NOT REMOVE these installed components. Doing so WILL VOID boiler warranty.
• PVC / CPVC pipe and ttings of the same diameter are considered interchangeable.
• DO NOT use Foam Core Pipe in any portion of the exhaust piping from this boiler.
• DO NOT connect PVC / CPVC to PP without an approved vent connector.
• When installing AL29-4C vent piping, install a PVC-to-stainless adapter at the boiler vent connection, and at the
termination when using a PVC termination kit. DO NOT mix AL29-4C piping from dierent manufacturers unless using
adapters specically designed for the purpose by the manufacturer.
• A double wall vent may be used when using stainless steel vent material in a freezing climate.
• *PVC-DWV may be used for air intake applications ONLY.
• Contact the venting material manufacturer if there is any question about the applicability of the proposed venting
material.
Failure to follow these directions will result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Table 10 - Approved Materials for Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe
Standards for Installation In:
PVC, CPVC, and PP Venting Must
be ULC-S636 Certied. IPEX is
an approved manufacturer in
Canada.
IPEX System 636 Cements and
Primers
23
DO NOT mix components from dierent venting systems
without proper adapters. The vent system could fail, causing
leakage of ue products into the living space. Use only the
approved pipe and tting materials, and primer and cement
specically designed for the material used, as listed in the
above table. Failure to do so could result in property damage,
serious injury, or death.
High heat sources (generating heat 100oF / 37oC or greater,
such as boiler ue pipes, space heaters, etc.) may damage
plastic components of the boiler as well as plastic vent pipe
materials. Such damages ARE NOT covered by warranty. It is
recommended to keep a minimum clearance of 8” from high
heat sources. Observe heat source manufacturer instructions,
as well as local, state, provincial, and national codes, laws,
regulations, and ordinances when installing this boiler and
related components near high heat sources.
NOTE: The use of double-wall vent or insulated material for
the combustion air intake pipe is recommended in cold climates to prevent the condensation of airborne moisture in
the incoming combustion air.
C. Additional Requirements for Installation in Canada
1. Installations must be made with a vent pipe system certied
to ULC-S636. IPEX is an approved vent manufacturer in Canada
supplying vent material listed to ULC-S636. Additionally,
you may use AL29-4C stainless steel venting to comply with
Canadian requirements.
2. The rst three (3) feet of vent pipe from the boiler ue
outlet must be readily accessible for visual inspection. 3.
The components of the certied vent system must not be
interchanged with other vent systems or unlisted pipe / ttings.
Cellular foam core piping may be used on air inlet piping only.
You must not use “B” vent in an exhaust application. “B” vent
is for intake applications ONLY. Using “B” vent in an exhaust
application will result in serious injury or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

24
E I
Area Where Terminal Is Not Permitted
Intake Pipe Terminal
Exhaust Vent Terminal
D. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe Location
Figure 13 - Exit Terminals for Direct Vent Systems - ANSI Z223.1 / NFPA 54 for US and CAN/CSA B149.1 for Canada
DETERMINE EXHAUST VENT AND INTAKE PIPE LOCATION –
NOTES:
INSTALLATIONS IN THE UNITED STATES
A. Provide a minimum of 1 foot clearance from the bottom of the
exhaust vent and intake pipe above the expected snow accumulation
level. Snow removal may be necessary to maintain clearance.
B. Provide a minimum of 1 foot distance from exhaust vent termination
to any door, operable window, or gravity intake into any building.
C. Provide a minimum of 1 foot distance from exhaust vent termination
to any permanently closed door or window.
D. Provide a minimum of 4 feet vertical clearance from the exhaust
vent to all roof overhangs.
E. Locating exhaust vent termination near roof overhangs will result in
the formation of icicles in freezing weather, and could result in blockage
of the exhaust vent. To prevent icicles from forming, maintain 4 feet
vertical clearance from the exhaust vent to all roof overhangs.
F. Provide 4 feet clearance from the outside corner of vertical walls,
chimneys, etc., as well as horizontal corners created by roof overhangs.
G. Provide 6 feet clearance from the inside corner of vertical walls,
chimneys, etc., as well as horizontal corners created by roof overhangs.
H. Provide 4 feet clearance from center line within a height of 15 feet
above electrical meters, gas meters, gas regulators, relief equipment,
exhaust fans and inlets.
I. Provide 4 feet horizontal clearance from electrical meters, gas
meters, gas regulators, relief equipment, exhaust fans and inlets. In
no case shall the exit terminal be above or below the aforementioned
equipment unless the 4 foot horizontal distance is maintained.
J. This boiler vent system shall terminate at least 3 feet (0.9 m) above
any forced air intake located within 10 ft (3 m).
NOTE: This does not apply to the combustion air intake of a direct-vent
appliance.
K. When venting with a two pipe system, maximum distance between
exhaust vent and intake pipe is 6 feet (1.8 m). Minimum d i s t a n c e
between exhaust vent and intake pipe on single direct vented appliance
is 10” (0.255 m) center-to-center. Minimum distance between exhaust
vents and intake pipes on multiple boilers is 10” (0.255 m) center-tocenter.
L. When adjacent to a public walkway, locate exit terminal at least 7
feet above grade.
In addition:
• Total length of vent piping shall not exceed the limits specied
in this manual.
• The vent piping for this direct vented appliance is approved
for zero clearance to combustible construction.
• The ue products coming from the exhaust vent will create a
large plume when the boiler is in operation. Avoid venting in
areas that will aect neighboring buildings or be considered
objectionable.
• DO NOT locate exhaust vent or intake pipe in a parking area
where machinery may damage the pipe.
• DO NOT locate the exhaust vent or intake pipe terminals
under a porch, balcony, or veranda.
• Avoid terminating exhaust vents near shrubs, air conditioners,
or other objects that will obstruct the exhaust stream.
• DO NOT vent over a public walkway. Condensate could drip
or freeze and create a nuisance or hazard.
• NOTE: Due to potential moisture build-up, sidewall venting
may not be the preferred venting option. Carefully consider
venting installation and location to save time and cost.
INSTALLATIONS IN CANADA
NOTE: Canadian installation must comply with the CAN/CSA B149.1
code and applicable local codes and supersede the restrictions for
the United States outlined in this section.
It is required to insert exhaust and intake screens into the vent
terminations to prevent blockage caused by debris or birds.
Failure to keep terminations clear could result in property
damage, severe personal injury, or death.
The building owner is responsible for keeping the exhaust
and intake terminations free of snow, ice, or other potential
blockages, as well as scheduling routing maintenance. Failure
to keep the vent piping terminations clear and properly
maintain the boiler could result in property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
For each oor containing bedroom(s), a carbon monoxide
detector and alarm shall be placed in the living area outside
the bedrooms, as well as in the room that houses the boiler.
Detectors and alarms shall comply with NFPA 720 (latest
edition). Failure to comply with these requirements could
result in product damage, severe personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

25
E. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe Sizing
1. The exhaust vent and intake pipe size is 4” for the 500 model
and 6” for the 700/850 models.
2. The maximum total equivalent length of exhaust vent and
intake pipe should not exceed 200 feet.
a. The equivalent length of elbows, tees, and other ttings
are listed in the Friction Loss Table.
Friction Loss Equivalent in Piping and Fittings
Fittings or Piping
90 Degree Elbow* 3’ 3’ 3’
45 Degree Elbow 1’ 1’ 1’
Coupling 0’ 0’ 0’
Air Inlet Tee 0’ 0’ 0’
Straight Pipe 1’ 1’ 1’
V Series Vent Kit 1’ 1’ 1’
AL20 4c Vent Terminal 1’ 1’ 1’
Table 11 - *Friction loss for long radius elbow is 1 foot less. NOTE:
Consult Polypropylene venting instructions for friction loss and
pressure drop equivalents.
Equivalent Feet
4” 6” 8”
b. For example: If the exhaust vent is 4” in diameter, has
two 90o elbows, and 10 feet of PVC pipe we will calculate:
Exhaust Vent Equivalent Length = (2x3) + 10 = 16 feet.
Further, if the 4” intake pipe has two 90o elbows, one 45o
elbow, and 10 feet of PVC pipe, the following calculation
applies:
Intake Pipe Equivalent Length = (2x3) + 1 + 10 = 17 feet.
The total equivalent length is 33 feet, well below the
maximum of 200 feet.
c. Eort should be made to keep a minimum dierence in
equivalent length between the exhaust vent and intake
pipe.
3. The minimum total equivalent length is 16 feet.
Do not exceed the maximum lengths for vent pipes. Excessive
length could result in boiler shutdown and property damage.
Failure to provide a minimum total vent length of 16
equivalent feet could result in property damage and improper
product operation.
F. Longer Vent Runs
The maximum total equivalent length can be extended
by increasing the diameter of both the exhaust vent and
intake pipes equally. However, the transitions should begin
a minimum of 16 equivalent feet from the boiler. Transitions
should always be made in vertical sections of pipe to prevent
the condensate from pooling in the vent pipe.
The maximum equivalent length for increased diameter vent
pipes is 275 ft, which includes 16 ft from with boiler with a
transition total of 259 ft upsize piping for longer vent runs.
Figure 14 - Extended Vent Runs
Standard
Vent Connection and
Maximum Total
Equivalent Length
4” (200’) 6” x 4” 6” (275’)
6” (200’) 8” x 6” 8” (275’)
Table 12 - Vent Run Transition
Reducing
Coupling
Increased Vent Size
and Maximum Total
Equivalent Length
Total maximum equivalent length of increased diameter exhaust
vent and intake pipe must not exceed the lengths dened in this
manual. Failure to keep the total equivalent length below the
maximum lengths determined in this manual will result in faulty
boiler operation, substantial property damage, serious personal
injury, or death.
G. Exhaust Vent and Intake Pipe Installation
All joints of positive pressure vent systems must be sealed
completely to prevent leakage of ue products into the living
space. Failure to do so could result in property damage, serious
injury, or death.
1. Use only solid PVC, CPVC, or stainless steel pipe or a
Polypropylene vent system approved for use with Category IV
appliances.
FOAM CORE PIPING IS NOT APPROVED FOR EXHAUST VENT
APPLICATIONS. Foam core piping may be used on air inlet
piping only.
2. Remove all burrs and debris from joints and ttings.
3. When using PVC or CPVC pipe, all joints must be properly
cleaned, primed, and cemented. Use only cement and primer
approved for use with the pipe material. Cement must conform
to ASTM D2564 for PVC and ASTM F493 for CPVC pipe. NOTE:
DO NOT CEMENT POLYPROPYLENE PIPE.
4. Ensure the vent is located where it will not be exposed to
prevailing winds.
5. In all roof venting applications, exhaust discharge must point
away from the pitch of the roof.
6. If the exhaust vent is to be terminated in a walled o area
(such as a roof with a parapet wall), ensure the exhaust vent
terminates a minimum of 10’ from nearest wall and extends level
with or above the top of the wall. This will ensure ue gas does
does not get trapped and possibly recirculated into the intake air
pipe, which could contaminate the combustion air.
7. To prevent water leakage, install adequate roof ashing where
the pipe enters the roof.
8. Do not locate vent over public walkways, driveways, or
parking lots. Condensate could drip and freeze, resulting in a slip
hazard or damage to vehicles and machinery.
9. Due to potential moisture build-up, sidewall venting may not
be the preferred venting option. To save time and cost, carefully
consider venting installation and location.
10. Horizontal lengths of exhaust vent must slope back towards
the boiler not less than ¼” per foot to allow condensate to drain
from the vent pipe.
11. The exhaust vent must terminate where vapors cannot make
accidental contact with people or pets, or damage shrubs or
plants.
12. In vacant chimney applications, install and seal a rain cap
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

26
Two Pipe Roof Venting with
Intake (Elbow) and
Exhaust (Coupling)
over existing chimney openings.
13. All piping must be fully supported. Use pipe hangers at a
minimum of 4 foot intervals to prevent sagging of the pipe
where condensate may form.
14. Do not use the boiler to support any piping.
15. Ensure the outdoor exhaust vent termination is screened to
prevent blockage caused by debris or birds.
16. Ensure the outdoor intake pipe termination is screened to
prevent blockage caused by debris or birds.
H. Applications
1. Direct Vent Installation of Exhaust and Intake
If installing a direct vent option, combustion air must be drawn
from the outdoors directly into the boiler intake, and exhaust
must terminate outside. There are three basic direct vent
options detailed in this manual: 1. Side Wall Venting, 2. Roof
Venting, and 3. Unbalanced Venting.
Be sure to locate the boiler such that the exhaust vent and
intake pipe can be routed through the building and properly
terminated. Dierent vent terminals can be used to simplify and
eliminate multiple penetrations in the building structure (see
Optional Equipment in Venting Section). The exhaust vent and
intake pipe lengths, routing and termination methods must all
comply with the methods and limits given in the Venting section
of this manual.
When installing a combustion air intake from outdoors, care
must be taken to utilize uncontaminated combustion air. NOTE:
To prevent combustion air contamination, see Table 3.
Two Pipe Sidewall Venting
with Intake (Elbow) and
Coupling (Exhaust)
Insert Intake/Exhaust
EXHAUST
Screen into Coupling
12" MIN.
EXTERIOR WALL
1" MIN.
Take extra precaution to adequately support the weight of vent
pipes terminating through the roof. Failure to properly support
roof terminated piping could result in property damage, serious
injury, or death.
MAINTAIN 12" MINIMUM
CLEARANCE ABOVE HIGHEST
ANTICIPATED SNOW LEVEL
OR GRADE, WHICHEVER IS
GREATER (TYP)
LP-505-A
06/23/15
Figure 15 - Two Pipe Roof and Sidewall Venting
INTAKE
Insert Intake/Exhaust Screen
into Open End of Elbow
NOTE: These drawings are meant to demonstrate system
venting only. The installer is responsible for all equipment and
detailing required by local codes.
All vent pipes must be glued, properly supported, and the
exhaust pitched a minimum of 1/4” per foot back to the
boiler to allow drainage of condensate. When placing support
brackets on vent piping, the rst bracket must be within 1 foot
of the boiler and the balance of 4 foot intervals on the vent
pipe. Venting must be readily accessible for visual inspection
from the rst three feet from the boiler.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

Sidewall Venting
with Kit
Figure 16 - Venting with Optional Kits (NOT INCLUDED WITH THE
SIDE VIEW
FRONT VIEW
Intake
Exhaust
FRONT VIEW
SIDE VIEW
LP-325-PP
03/03/11
BOILER)
NOTE: These drawings are meant to demonstrate system
venting only. The installer is responsible for all equipment and
detailing required by local codes.
All vent pipes must be glued, properly supported, and the
exhaust pitched a minimum of 1/4” per foot back to the boiler
to allow drainage of condensate. When placing support
brackets on vent piping, the rst bracket must be within 1 foot
of the boiler and the balance of 4 foot intervals on the vent
pipe. Venting must be readily accessible for visual inspection
from the rst three feet from the boiler.
27
Figure 17 - Horizontal (Snorkel) Venting
NOTES:
A. For every 1” of overhang, the exhaust vent must be located 1” vertical
below overhang (overhang means top of building structure and not two
adjacent walls [corner of building]).
B. Typical installations require 12” minimum separation between
bottom of exhaust outlet and top of air intake.
C. Maintain 12” minimum clearance above highest anticipated snow
level or grade (whichever is greater).
D. Minimum 12” between vents when installing multiple vents.
E. 12” minimum beyond air intake.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

28
Figure 18 - Unbalanced Venting - Roof Exhaust and Sidewall Intake
NOTE: These drawings are meant to demonstrate system
venting only. The installer is responsible for all equipment and
detailing required by local codes.
All vent pipes must be glued, properly supported, and the
exhaust pitched a minimum of 1/4” per foot back to the boiler to
allow drainage of condensate. When placing support brackets
on vent piping, the rst bracket must be within 1 foot of the
boiler and the balance of 4 foot intervals on the vent pipe.
Venting must be readily accessible for visual inspection from
the rst three feet from the boiler.
An unbalanced vent system can be installed ONLY when the
exhaust is in the vertical position. Failure to do so could result in
serious personal injury or death.
Take extra precaution to adequately support the weight of vent
pipes terminating through the roof. Failure to properly support
roof terminated vent piping could result in property damage,
serious personal injury, or death due to ue gas leakage.
Figure 19 - Roof and Sidewall Venting with Stainless Steel
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

2. Room and Indoor Combustion Ventilation Requirements
When using an indoor combustion air installation, the
mechanical room MUST be provided with properly sized
openings, and/or be of sucient volume to assure adequate
combustion air and proper ventilation for all gas red appliances
in the mechanical room to assure adequate combustion air and
proper ventilation. The requirements shown here are for the
boiler only. Additional gas red appliances in the mechanical
room will require an increase in the net free area and/or
volume to supply adequate combustion air for all appliances.
This must be done in accordance with the National Fuel Gas
Code, NFPA 54 / ANSI Z223.1.
This boiler can be vented using mechanical room air only for
combustion. No combustion air openings are needed when
the boiler is installed in a space with a volume NO LESS than 50
cubic feet per 1,000 BTU/hr of all installed gas red appliances
and the building MUST NOT BE of “Tight Construction”.
TIGHT CONSTRUCTION: A building with less than .4 ACH
(air changes per hour). For buildings of “Tight Construction”,
provide air openings into the building from the outside.
Indoor and outdoor combustion air may be combined by
applying a ratio of available volume to required volume times
the required outdoor air opening(s) size(s). This must be done
in accordance with the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54 /
ANSI Z223.1.
1. If air is taken directly from outside the building with no duct,
provide two permanent openings to the mechanical room
each with a net free area of one square inch per 4000 BTU/hr
input. See Figure 20.
2. If combustion and ventilation air is taken from the outdoors
using a duct to deliver the air to the mechanical room, each of
the two openings should be sized based on a minimum free
area of one square inch per 2000 BTU/hr input. See Figure 21.
3. If air is taken from another interior space combined with the
mechanical room:
a. Two spaces on same story: Each of the two openings
specied should have a net free area of one square inch for
each 1000 BTU/hr input, but not less than 100 square inches.
b. Two spaces on dierent stories: One or more openings
should have a net free area of two square inches per 1000
BTU/hr.
See Figure 22 for reference.
4. If a single combustion air opening is provided to bring
combustion air in directly from the outdoors, the opening
must be sized based on a minimum free area of one square
inch per 3000 BTU/hr. This opening must be located within 12”
of the top of the enclosure. See Figure 23.
Combustion air requirements are based on the latest edition
of the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54 / ANSI Z223.1, CGA
Standard CAN/CSA B149.1 in Canada. Check all local code
requirements for combustion air.
All dimensions based on net free area in square inches. Metal
louvers or screens reduce the free area of a combustion air
opening a minimum of approximately 25%. Check with louver
manufacturers for exact net free area of louvers.
Where two openings are provided, one must be within 12”
of the ceiling, and one must be within 12”of the oor of the
mechanical room. Each opening must have a net free area as
specied in Table 13. Single openings shall commence within
12” of the ceiling. The minimum dimension of air openings
should not be less than 3”.
29
Figure 20 - Combustion Air from Outdoors
Figure 21 - Combustion Air through Ductwork
Figure 22 - Combustion Air from Indoors
Figure 23 - Combustion Air from Outdoors - Single Opening
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

30
Under no circumstances should the mechanical room ever
be under negative pressure. Particular care should be taken
where exhaust fans, attic fans, clothes dryers, compressors, air
handling units, etc., may take away air from the unit. Failure
to follow these instructions could result in property damage or
personal injury.
Combustion air supply must be completely free of any
ammable vapors that may ignite, or chemical fumes which may
be corrosive to the boiler. See Table 3 for a list of combustion
air contaminants. These chemicals, when burned, form acids
which quickly attack the stainless steel heat exchanger, headers,
ue connectors, and the vent system. The result is improper
combustion and premature boiler failure. Such failure IS NOT
covered under warranty.
EXHAUST FANS: Any fan or appliance which exhausts air from
the mechanical room may deplete the combustion air supply
and/or cause a downdraft in the venting system. Spillage of ue
products from the venting system into an occupied living space
can cause a very hazardous condition that must be corrected
immediately.
Minimum Recommended Combustion Air Supply to
Mechanical Room
Figure 20 Figure 21
*Outside Air from 2
Openings Directly
Model
500
700
850
Model
500
700
850
Table 13 - Indoor Combustion Air Sizing
The above requirements are for the boiler only; additional gas red
appliances in the mechanical room will require an increase in the net
free area and/or volume to supply adequate combustion air for all
appliances.
No combustion air openings are needed when the boiler is installed in
a space with a volume NO LESS than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 BTU/hr
of all installed gas red appliances. Buildings MUST NOT be of *”Tight
Construction”.
1
Outside air openings shall communicate with the outdoors.
2
Combined interior space must be 50 cubic feet per 1,000 BTU/hr input.
Buildings MUST NOT be of *”Tight Construction”.
from Outdoors
Top
Opening,
2
in
125 125 250 250
175 175 350 350
215 215 425 425
Inside Air from 2 Ducts Delivered
from Interior Space
Same Story
Top
Opening,
2
in
500 500 1000 170
700 700 1400 235
850 850 1700 285
1
Bottom
Opening,
2
in
Figure 22 Figure 23
Bottom
Opening,
2
in
*Outside Air from 2
Ducts Delivered from
Outdoors
Top
Opening,
2
in
2
Dierent
Stories
Top
Opening,
2
in
1
Bottom
Opening,
2
in
*Outside
Air from 1
Opening
Directly
from
Outdoors,
2 1
in
I. Condensate Removal System
NOTE: Check with your local gas company to determine if
combustion condensate disposal is permitted in your area. In
the state of Massachusetts, condensate must be neutralized
before entering a drain.
This boiler is a high eciency appliance, and therefore
produces condensate: a by-product of the combustion
process. A condensate collection system with an internal
oat switch monitors condensate level to prevent it from
backing up into the combustion system. There is a ¾” socket
connection provided to connect the outlet of the collection
system to a drain or condensate pump.
Condensate from the boiler is slightly acidic with a pH of 3.2 -
4.5. To avoid long term damage to the drainage system and to
meet local code requirements, HTP recommends neutralizing
condensate with a Condensate Neutralizer Kit (Part # 7350P-
611). The neutralizer kit connects to the drain system and
contains limestone chips that neutralize the pH level of the
condensate. The neutralizer kit should be checked annually
and the limestone chips replenished if necessary. When
replacing the limestone chips, take care to ensure chips are no
smaller than ½” to avoid blockage in condensate piping (refer
to gure below for piping of the condensate neutralizer.)
Figure 24 - Condensate Piping
NOTES:
1. Condensate line must be pitched at least ¼” per foot to
properly drain. If this cannot be done, or a very long length
of condensate hose is used, increase the condensate line
to a minimum of 1” ID and place a tee in the line after the
condensate neutralizer to properly reduce vacuum lock in the
drain line.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

2. PVC or CPVC pipe should be the only material used for
condensate line. Steel, brass, copper, and other metals will be
subject to corrosion or deterioration.
3. A frozen condensate line could result in a blocked vent
condition. It is very important to protect the condensate
line from freezing temperatures or any type of blockage.
In installations that may encounter sustained freezing
conditions, the use of heat tape is recommended to avoid
freezing of the condensate line. It is also recommended to bush
up the condensate line size to 1” and terminate condensate
discharge as close to the unit as possible. Longer condensate
runs are more prone to freezing. Damages due to frozen or
blocked condensate lines ARE NOT covered by warranty.
4. Support of the condensate line may be necessary to avoid
blockage of the condensate ow.
5. To allow proper drainage on longer horizontal condensate
runs, tubing size may need to increase to 1” and a second line
vent may be required.
NOTE: To clean out condensate trap, see Maintenance
section.
The condensate line must remain unobstructed. If allowed
to freeze in the line or obstructed in any other manner,
condensate can exit from the boiler tee, resulting in potential
water damage to property. When installing a condensate
pump, select one approved for use with condensing boilers
and furnaces. The condensate pump should have an overow
switch to prevent property damage from spillage. Condensate
from the boiler will be slightly acidic (pH from 3.2 to 4.5).
Install a neutralizing lter if required by local codes.
Is is very important that condensate piping be no smaller
than 3/4”. Use a tee at the condensate connection with a
branch vertically up and open to the atmosphere to prevent a
vacuum that could obstruct the ow of condensate from the
boiler. To prevent sagging and maintain pitch, condensate
piping should be supported with pipe supports.
When installing a condensate pump, select one approved for
use with condensing boilers and furnaces. The pump should
have an overow switch to prevent property damage from
condensate spillage.
Power to the optional condensate pump is continuous. When
the boiler is powered o the condensate pump will remain on.
It is important to remember to turn o the condensate pump
when powering down the boiler. Failure to do so could result
in property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Part 6 - Wiring
To avoid electrical shock, turn o all power to the boiler prior
to opening an electrical box within the unit. Ensure the power
remains o while any wiring connections are being made.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in component
or product failure, serious injury, or death. Such product
failure IS NOT covered by warranty.
Jumping out control circuits or components WILL VOID
product warranty and can result in property damage, personal
injury, or death.
31
It is of extreme importance that this unit be properly grounded. It
is very important that the building system ground is inspected by
a qualied electrician prior to making this connection. Electrical
power must only be turned on when the boiler is completely
lled with cold water. Failure to follow these instructions could
result in component or product failure, serious injury, or death.
Electrical Shock Hazard - Turn o electrical power supply at
service entrance panel before making any electrical connections.
Failure to follow do do so could result in serious injury, or death.
Label all wires prior to disconnecting them when servicing
the boiler. Wiring errors can cause improper and dangerous
operation. Failure to follow these instructions may result in
property damage or personal injury.
Wiring must be NEC Class 1. If original wiring supplied with the
boiler must be replaced, use only TEW 105 oC wire or equivalent.
Boiler must be electrically grounded as required by the National
Electrical Code, ANSI/NFPA 70 - Latest Edition.
A. Installation Must Comply With
1. National Electrical Code and any other national, state,
provincial, or local codes or regulations.
2. In Canada, CSA C22.1, Canadian Electrical Code Part 1, and
any local codes.
B. Field Wiring
Terminations
All connections made
to the boiler in the
eld are done inside
the electrical junction
box located on the
left side of the unit.
Multiple knockout
locations are available
to route eld wires
into and out of the
electrical junction
box.
Figure 25 - Knockout Locations
C. Field Wiring
Check water chemistry section for acceptable levels. If water
chemistry is acceptable, pumps may be wired directly to pump
terminals. If water chemistry levels are too high, you must
wire pumps to line voltage to run continuously to prevent lime
buildup.
Pumps
The Mod Con VWH application requires a circulator pump
for each boiler. Circulator pumps can be wired directly to the
controller as shown in Figure 26 or wired directly to line voltage
for continuous operation. Only wire the circulator pump to the
controller if a tank sensor or mechanical control can be mounted
to the storage tank, otherwise circulator pumps must be wired
to run continuously.
The circulator pump wired to the boiler control will have a default
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

32
program of a 5 minute post purge to provide stabilization and
post cleaning of the heat exchanger. The boiler control is capable
of supplying 120 volts at up to 3 amps to run the circulator pump.
If using a larger circulator pump requiring more than 3 amps or
higher voltage, an external motor starter, sized appropriately
for the pump motor, must be used. This starter should have a
120 VAC coil. If a starter with a 120 VAC coil is used, it can be
wired directly to the appropriate pump terminals as shown in
Figure 26.
Tank and Sensor Connections
When the Mod Con VWH is used in a single tank installation, it
is recommended to use a sensor (7250P-325) placed in a well
in the storage tank for best temperature control. If multiple
tanks are used in the installation, it is recommended to put a
mechanical aquastat in each tank and wire them in series to
provide temperature control of the tanks. (See Applications
for reference.) The control in the Mod Con VWH will read
either the temperature of the tank sensor or the status of
the aquastats, and cause the boiler to run until the water
temperature of the tank(s) meets the desired set point.
If a sensor or aquastat cannot be placed directly in the tank,
then one sensor should be used on the pipe carrying water
from the tank(s) to the boiler. To minimize temperature
loss in the piping, this sensor should be placed as close
to the tank(s) as possible. The use of a pipe sensor will be
somewhat less accurate than using a sensor in the tank, and
has the disadvantage of requiring the boiler pump(s) to run
continuously so the sensor is always measuring the tank
water temperature.
In a multiple Mod Con VWH installation, where the boilers are
connected for cascade operation, a system sensor is needed
in addition to the tank or pipe sensor described above. The
system sensor is mounted on the common pipe to the tank(s)
from the boilers as close to the tank(s) as possible. The
purpose of this sensor is to serve as feedback to the control
and provide it with the aggregate temperature of all ring
boilers. The master boiler control will then re the boilers in
cascade sequence to maintain the water temperature in this
pipe and provide correct tank heating.
The electrical junction box has separate, clearly marked
terminal strips for line voltage and low voltage wiring. Special
jacks are provided for trouble-free cascade system wiring
using standard CAT3 or CAT5 patch cables.
used to operate the pump. If the starter is equipped with a 120
volt coil, the coil connections may be connected directly to
the terminals marked BOILER HOT and BOILER NEUT. Refer
to Figure 29 for a representative drawing of this conguration.
If a motor starter is used, it should be selected, installed,
and wired in compliance with all local electrical codes and
requirements. In the absence of such codes or requirements,
the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70) should be followed.
D. Line Voltage Wiring for Standard Boiler
NOTE: A termination plug is included in the CAT 3 / CAT 5 Bus
Connection Point, labeled J3 in Figure 26. DO NOT REMOVE
THIS PLUG! Doing so will aect boiler operation and void
warranty.
1. Connect the incoming power wiring to the line voltage
terminal strip in the electrical junction box at terminals 120V,
Neutral, Ground (shown in Figure 26).
2. A line voltage fused disconnect switch may be required,
externally mounted and connected according to local codes that
may apply.
3. If the pump used for the boiler operates at 120 volts and less
than 3 amps is required, it may be connected directly to the
terminals marked BOILER HOT, BOILER NEUT, and BOILER
GRD. If the pump operates at a voltage other than 120 volts and/
or requires more than 3 amps, an external motor starter must be
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
Figure 26 - VWH Control Wiring
E. Alarm Connections
The control includes a dry contact alarm output. This is an SPDT
circuit, rated at 5 amps at 120 volts. This contact can be used to
activate an alarm light or bell or notify a building management
system if the boiler goes into a lockout condition. The circuit
between the ALARM COM and NC terminals is closed during
normal operation and the circuit between ALARM COM
and NO is open during normal operation. The connections
depicted in Figure 26 show two 120 volt lights connected to

33
the alarm terminals. One light will be on when the boiler is in
normal mode and the other light will be on when the boiler is
in lockout mode.
F. Low Voltage Connections for Standard Boiler
1. All low voltage cables should enter the electrical junction
box through the provided knock out holes as shown in Figure
25.
2. Connect all low voltage eld devices to the low voltage
terminal strip located in the electrical junction box.
G. Tank Sensor or Mechanical Control
Connect the tank sensor or mechanical controls to the TANK
SENSOR terminals (10, 11) of the low voltage terminal strip as
shown in Figure 26. The control will automatically determine
which type of sensor is connected and operate accordingly.
Failure to use the correct sensor may result in tank
temperature being either above or below set point, and
could result in decreased performance, substantial property
damage, or heightened risk of injury or death due to scalds.
Caution should be used to ensure neither of these terminals
becomes connected to ground.
NOTE: If sensor wires are located in an area with sources of
potential electromagnetic interference (EMI), the sensor
wires should be shielded, or the wires routed in a grounded
metal conduit. If using shielded cable, the shielding should be
connected to the common ground of the boiler.
H. System / Pipe Sensor
The system/pipe sensor
can be used to control
the temperature
of the storage tank
when a tank sensor
or mechanical control
cannot be mounted.
The system/pipe sensor
would be wired into the
terminals of the low
voltage terminal strip
as shown on Figure
26. It is important
to note that when a
system/pipe sensor is
used, the circulating
pump must be wired to
operate continuously;
otherwise the boiler
will short cycle.
The system/pipe sensor
can also be used in a cascade system when the sensor is placed
on the supply line of multiple boilers that feed the storage
tank. This will control the temperature and modulate the
ring rate of the connected boilers. The system/pipe sensor
would then be wired into the master boiler terminals on the
low voltage strip as shown on Figure 29.
I. Optional 0-10 Volt Building Control Signal
1. A signal from a building management system may be
connected to the boiler to enable remote control. This signal
should be a 0-10 volt positive-going DC signal. When this input
is enabled using the installer menu, a building control system
can be used to control the set point temperature of the boiler.
The control interprets the 0-10 volt signal as follows; when the
signal is between 0 and 1.5 volts, the boiler will be in standby
mode, not ring. When the signal rises above 1.5 volts, the boiler
will ignite. As the signal continues to rise towards its maximum
of 10 volts, the boiler will increase in set point temperature. See
Part 10 for details on the setting of function 16.
2. Connect a building management system or other auxiliary
control signal to the terminals marked 16, 0-10 VOLT + and
17, 0-10 VOLT – in the electrical junction box (shown in Figure
26). Caution should be used to ensure that the 0-10 VOLT +
connection does not become connected to ground.
J. Optional High Gas Pressure Switch
1. If an optional high gas pressure switch is used, it should be
installed on the outlet side of the gas valve. This is normally
closed and will open if the pressure goes above 1.5” w.c. on the
outlet side.
2. Locate the two pigtails hanging from the electrical box inside
of the boiler cabinet. Remove and discard the jumper plug from
one of the unused pigtails.
3. Connect the high gas pressure switch to the pigtail that you
removed the jumper plug from.
K. Optional Low Gas Pressure Switch
1. If an optional low gas pressure switch is used, it should be
installed on the inlet side of the gas valve. This is normally closed
and will open if the pressure goes below 1” w.c. on the inlet side.
2. Locate the two pigtails hanging from the electrical box inside
of the boiler cabinet. Remove and discard the jumper plug from
one of the unused pigtails.
3. Connect the low gas pressure switch to the pigtail that you
removed the jumper plug from.
L. Flow Switch
This VWH boiler requires the use of a ow switch. The ow switch
kit comes packaged with detailed installation instructions which
should be read and followed to ensure a functional system.
M. Wiring of Cascade System Communication Bus
1. A Cascade Bus Termination Plug has been installed on the
customer connection board of this boiler. The purpose of this
plug is to stabilize communication between multiple boilers and
reduce electrical “noise”. See Figures 27 and 28 for Cascade Bus
Termination Plug installation detail.
NOTE: It is important that the termination plug in multiple
boilers (cascaded units) be installed as depicted in Figure 28.
Leave the plug installed in the J3 port on the Master boiler.
Remove the plug on intermediate Follower boilers. Move the
plug to the J4 port on the nal Follower boiler.
2. Use standard CAT3 or CAT5 computer network patch cables
to connect the communication bus between each of the boilers.
These cables are readily available at any oce supply, computer,
electronic, department or discount home supply store in varying
lengths. If you possess the skills you can also construct custom
length cables.
3. It is recommended to use the shortest length cable that will
reach between the boilers and create a neat installation. Do not
run unprotected cables across the oor where they may become
wet or damaged. Avoid running communication cables parallel
and close to or against high voltage (120 volt or greater) wiring.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

34
HTP recommends that the maximum length of communication
bus cables not exceed 200 feet.
4. Route the communication cables through one of the
knockouts in the cabinet.
5. Connect the boilers in a daisy chain conguration as shown
below. It is best to wire the boilers using the shortest wire
runs rather than trying to wire them in the order that they are
addressed. The communication bus jacks on the customer
connection panel are interchangeable so you can use either one
or both in any order to connect the cable.
If you have connected the boilers to each other properly, there
will be no open communication connection ports.
Figure 27 - Wiring Cascade System
O. Cascade Follower Pump and Sensor Wiring
1. Connect the boiler pump to the terminals labeled 1 (HOT), 2
(NEUT), and 3 (GND).
2. An alarm bell or light can be connected to the alarm contacts
of the follower boiler. The normally closed alarm contact may
be used to turn a device o if the boiler goes into lockout
mode. The alarm contacts are rated 5 amps at 120 VAC.
To connect an alarm device, connect the power for the device
to the ALARM COM terminal. Connect the alarm device hot
wire to the ALARM NO terminal. Connect the neutral or return
of the alarm device to the neutral or return of the power for
the alarm device.
To connect a device that
should be powered o
during a boiler lockout
condition, follow the same
instructions as above
except use the ALARM NC
terminal rather than the
ALARM NC terminal.
Note that in a cascade
system the alarm output
of the boiler addressed as
#1 will also be active if the
master boiler has a lockout
condition. The alarm
output of boilers addressed
as 2-7 will only activate an
alarm if a lockout condition
occurs on that specic
boiler.
Figure 28 - Cascade Termination Plug Detail
N. Cascade Master Pump and Sensor Wiring
1. Place the cascade master overlay sticker onto the eld
connection board of the boiler designated as the cascade master.
2. If it is desired to have the boiler control the boiler pump,
connect the boiler pump to the BOILER HOT, BOILER NEUT,
and BOILER GND terminals.
3. Connect the system sensor to the terminals marked SYS
SENSOR.
4. Do not connect anything to the OUTDOOR SENS or
THERMOSTAT terminals.
5. If 0-10 volt positive going DC signal input is used, connect to
marked terminals.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

35
Figure 29 - Cascade Master and Follower Wiring
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

36
N
**** DHW TANK
G H
120 VAC
LINE
OUTDOOR
TT TERMINALS
0-10 VOLT
RS485 BUS
RS485 BUS
X4-5
X4-6
X4-15
X4-16
X5-3
X5-4
X4-8
X4-9
ALARM
***
DHW
PUMP
***
BOILER
PUMP
+
-
CR1
9
8
7
CR1
120V J7-1
F3
GND
NEUT
2
5
CR1
120V
F2
F1
B A
JUMPER IN 'B' POSITION
FOR ALL MODCON UNITS
MAN RESET
HIGH WATER
TEMP
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
J3-3
J3-4
J3-5
J4-3
J4-4
J4-4
RELAY
4
6
1
3
BLOWER
MOTOR
GAS VALVE
J7-3
J6-1
J8-3
J6-3
J8-4
J8-1
J6-2
J6-4
J6-5
J6-6
J5-1
J5-2
J5-3
J5-4
J5-5
J5-10
J5-9
J5-8
J5-7
J5-6
SUPPLY
RETURN
POWER
SWITCH
CONDENSATE
RECEPTICAL
AUTO RESET
HIGH WATER
TEMP
DETAIL "A"
LOW WATER LEVEL APPLICATION FOR STANDARD BOILER ONLY ( NOT FOR VWH )
*
FLOW SWITCH FOR VWH APPLICATION ( OPTIONAL FOR STANDARD BOILER APPLICATION )
**
MAX 3 AMPS/120 VAC. USE CONTACTOR IN PLACE OF PUMP FOR GREATER DRAW.
***
FOR DOUBLE STACK UNITS - SUPPLY MANIFOLD SYSTEM SENSOR BOTTOM BOILER
****
X5-7
X5-5
X5-8
X4-2
X4-14
X4-10
X8-8
X4-3
X8-3
X8-6
X4-1
X4-11
X4-13
X8-1
X4-12
X8-2
X4-7
X4-17
X6-2
X6-1
X6-4
926
CONTROL
WIRING CONNECTION DIAGRAM
500, 700, and 850 MODELS
ORANGE
SPARK CABLE TO SPARK ELECTRODE
FLAME RECTIFICATION
24VAC <12VA
GAS VALVE
CONDENSATE
FULL
FLAPPER
VALVE
LOW WATER
LEVEL
FLUE
BVPS
ECO
PROBE
*
REAR FRONT
THERMAL
FUSE
BLOWER
MOTOR
FLOW SWITCH
TEMP LIMIT
SWITCH
*
*
HIGH GAS
PRESSURE
OPTIONAL
X-2
TEXT DISPLAY
X6-5
X4-5
X4-6
X4-15
X4-16
X5-3
X5-4
SEE DETAIL "A" FOR 120V GAS
VALVE WIRING APPLICATION
X4-8
X4-9
X8-4
X8-10
X8-9
X4-19
X4-20
X4-18
X4-4
X8-7
X8-5
RIBBON CABLE
LOW GAS
PRESSURE
UL353
LWCO
Figure 30 - Internal Connection Diagram
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

Part 7 - Gas Connections
Failure to follow all precautions could result in re, explosion,
severe injury, or death.
It is very important that you are connected to the type of
gas noted on the rating plate. “LP” for liqueed petroleum,
propane gas, or “NG” for natural or city gas. Do not do a gas
conversion without an approved gas conversion kit. Prior to
turning the gas on, all gas connections must be approved by
the local gas supplier or utility, in addition to the governing
authority.
A gas conversion kit comes with 500 model boilers ONLY.
Field conversions ARE NOT ALLOWED on the 700/850
models. A properly calibrated combustion analyzer must be
used to verify proper combustion. Failure to follow the above
instructions could result in property damage, serious injury,
or death.
The gas supply shall have a maximum inlet pressure of less
than 14” w.c. (3.5 kPa), and a minimum of 3.5” w.c. (.87 kPa).
The entire piping system, gas meter and regulator must be
sized properly to prevent pressure drop greater than 0.5” (.12
kPa) as stated in the National Fuel Gas Code. This information
is listed on the rating label.
37
designed to structurally support a large amount of weight.
5. Purge all gas lines thoroughly to avoid start up issues with air
in the lines.
6. Sealing compound must be approved for gas connections.
Care must be taken when applying compound to prevent
blockage or obstruction of gas ow which may aect the
operation of the unit.
Support gas supply piping with hangers, not by the boiler or its
accessories. The boiler gas valve and blower will not support the
weight of the piping. Make sure the gas piping is protected from
physical damage and freezing, where required. Failure to follow
these instructions could result in gas leakage, and result in re,
explosion, property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
Do not use Teon tape on gas line pipe thread. Use a pipe
compound rated for use with natural and propane gases. Apply
sparingly on male pipe ends, leaving the two end threads bare
and ow unobstructed. Failure to follow these instructions could
result in gas leakage or blockage, and result in re, explosion,
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
UL recognized fuel gas detectors are recommended in
all enclosed propane and natural gas applications where
there is a potential for an explosive mixture of fuel gas to
accumulate. The installation of these detectors should
be made in accordance with the detector manufacturer’s
recommendations, and/or local laws. Failure to install fuel gas
detectors in these applications could result in re, explosion,
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
The gas connection on the boiler is 1 1/2” for the 500 model
and 2” for the 700/850 models. It is mandatory that this tting
is used for connection to a eld fabricated drip leg as shown
in the illustration per the National Fuel Gas Code. You must
ensure that the entire gas line to the connection at the boiler
is no smaller than the unit supplied connection.
Once all inspections have been performed, the piping must
be leak tested. If the leak test requirement is a higher test
pressure than the maximum inlet pressure, you must isolate
the boiler from the gas line. In order to do this, shut the gas
o using factory and eld-installed gas cocks. This will prevent
high pressure. Failure to do so may damage the gas valve. In
the event the gas valve is exposed to a pressure greater than
½ PSI, 14” w.c. (3.5 kPa), the gas valve must be replaced.
Never use an open ame (match, lighter, etc.) to check gas
connections.
A. Gas Piping
1. Run the gas supply line in accordance with all applicable
codes.
2. Locate and install manual shuto valves in accordance with
state and local requirements.
3. In Canada, the Manual Shuto must be identied by the
installing contractor.
4. It is important to support gas piping as the unit is not
Figure 31 - Gas Connection
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

38
Never use an open ame (match or lighter) to check for gas
leaks. Use a soapy solution to test connection. Failure to use
a soapy solution test or check gas connection for leaks can
result in substantial property damage, severe personal injury,
or death.
Use two wrenches when tightening gas piping at the boiler: One
to prevent the boiler gas line from turning. Failure to prevent
the boiler gas connection from turning could result in damage
to the gas line components, substantial property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
CSA or UL listed exible gas connections can be used when
installing the boiler. Flexible gas connections have dierent
capacities and must be sized correctly for the connected boiler
ring rates. Consult with the ex line supplier to assure the
line size is adequate for the job. Follow local codes for proper
installation and service requirements.
B. Gas Table
Refer to Table 14 to size the supply piping to minimize pressure
drop between the meter or regulator and unit. Maximum
capacity of pipe in cubic feet of gas per hour for gas pressures of
.5 w.c. or less and a pressure drop of .3 inch w.c.
C. Check Inlet Gas Pressure
The gas valve is equipped with an inlet gas pressure tap that can
be used to measure the gas pressure to the unit. To check gas
pressure, perform the steps listed below:
1. IMPORTANT! Before you connect to the inlet pressure, shut
o the gas and electrical power to unit.
2. Loosen the pressure tap with a small screwdriver. Refer to
Figures 32 and 33 for location.
3. Each unit is equipped with a needle valve that will accept a
5/16 ID hose to connect to a digital manometer or liquid gauge
to measure incoming pressure from 0-35” w.c.
4. Turn on the gas and power up the unit.
5. Put the unit into manual test mode (details on test mode in
Part 10). In test mode, monitor pressure to assure it does not
drop below 1 inch from its idle reading. If gas pressure is out of
range or pressure drop is excessive, contact the gas utility, gas
supplier, qualied installer, or service agency to determine
correct action that is needed to provide proper gas pressure
to the unit. If Gas Pressure is within normal range proceed to
Step 6.
6. Exit test mode, then turn power o and shut o gas supply
at the manual gas valve before disconnecting the hose from
the gas monitoring device. Tighten screw on the pressure tap
and turn gas on. Check for leaks with soapy solution. Bubbles
will appear on the pipe to indicate a leak is present.
Ensure the pressure tap screw is properly tightened to prevent
gas leaks. Failure to do so could cause substantial property
damage, severe personal injury, or death.
The gas piping must be sized for the proper ow and length
of pipe to avoid pressure drop. The gas meter and regulator
must be properly sized for the total gas load. If you experience
a pressure drop greater than 1” w.c. (.87 kPa), the meter,
regulator or gas line may be undersized or in need of service.
You can attach a manometer to the incoming gas drip leg after
removing the cap. The gas pressure must remain between 3.5”
(.87 kPa) and 14” (3.5 kPa) during stand-by (static) mode and
while in operating (dynamic) mode.
If an in-line regulator is used, it must be a minimum of 10 feet
from the boiler. It is very important that the gas line is properly
purged by the gas supplier or utility. Failure to properly purge
the lines, or improper line sizing, will result in ignition failure.
This problem is especially noticeable in NEW LP installations
and empty tank situations. This situation can also occur when
a utility company shuts o service to an area to provide
maintenance to their lines. This gas valve must not be replaced
with a conventional gas valve under any circumstances.
DO NOT adjust or attempt to measure gas valve outlet
pressure. The gas valve is factory-set for the correct outlet
pressure and requires no eld adjustment. Attempts by the
installer to adjust or measure the gas valve outlet pressure
could result in damage to the valve and cause substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
(0.6 Specic gravity gas; 0.5” WC pressure drop)
*Schedule 40 iron pipe size in nominal inches
Cubic Ft. Hr. 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
Model 1 Boiler 2 Boilers 3 Boilers 4 Boilers 5 Boilers 6 Boilers 7 Boilers 8 Boilers
500 @ 100’ of
Pipe
500 @ 250’ of
Pipe
1 1/2” 2” 2 1/2” 3” 3” 3” 4” 4”
2” 2 1/2” 3” 3” 4” 4” 4” 4”
Cubic Ft. Hr. 700/850 1400/1700 2100/2550 2800/3400 3500/4250 4200/5100 4900/5950 5600/6800
Model 1 Boiler 2 Boilers 3 Boilers 4 Boilers 5 Boilers 6 Boilers 7 Boilers 8 Boilers
700/850 @
100’ of Pipe
700/850 @ 250’
of Pipe
Table 14 - Gas Supply Piping Size Chart for Boilers
2” 2 1/2” 3” 4” 4” 4” 4” 5”
2 1/2” 3” 4” 4” 5” 5” 5” 5”
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
Natural Gas Supply Piping Capacity Chart

D. Boiler Gas Valve
Figure 32 - 500 Model Gas Valve
39
Do not do a gas conversion on this boiler
without an ocially approved conversion
kit and instructions supplied by HTP. Failure
to use a conversion kit when converting
the boiler to re on Natural or Propane gas
will result in extremely dangerous burner
operation, leading to re, explosion, severe
personal injury, or death.
Strain on the gas valve and ttings may result
in vibration, premature component failure
and gas leakage, and result in re, explosion,
property damage, severe personal injury, or
death.
Adjustments to the throttle screw or
oset may only be made by a qualied gas
technician using a calibrated combustion
analyzer capable of measuring CO2 and CO.
Failure to follow this instruction could result
in re, explosion, property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
Ensure that the high gas pressure regulator is
as least 6 – 10 feet upstream of the appliance.
Failure to do so could result in substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or
death.
Figure 33 - 700/850 Models Gas Valve
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

40
Part 8 - Start-Up Preparation
A. Check / Control Water Chemistry
Chemical imbalance of your water can cause severe damage
to your boiler and associated equipment, and may also
aect eciency. You may have to have your water quality
professionally analyzed to determine whether you need to
install a water softener. It is important that the water chemistry
on both the domestic hot water and central heating sides are
checked before installing the boiler, as water quality will aect
the reliability of the system. Outlined below are those water
quality parameters which need to be met in order for the
system to operate eciently for many years. Failure of a heat
exchanger due to lime scale build-up on the heating surface,
low pH or other imbalance IS NOT covered by the warranty.
To assure extended service life, it is recommended to test water
quality prior to installation. Listed below are some guidelines.
Do not use petroleum-based cleaning or sealing compounds in
the boiler system. Damage to elastomer seals and gaskets in the
system could occur, resulting in substantial property damage.
Sodium less than 20 mGL
Water pH between 6.0 and 8.0
1. Maintain boiler water pH between 6.0 and 8.0. Check with
litmus paper or have it chemically analyzed by a water treatment
company.
2. If the pH diers from above, consult local water treatment
company for treatment needed.
Hardness less than 7 grains
Consult local water treatment companies for unusually hard
water areas (above 7 grains hardness).
Chlorine concentration less than 100 ppm
1. Using chlorinated fresh water should be acceptable since
drinking water chlorine levels are typically less than 5 ppm.
2. Do not connect the boiler to directly heat a swimming pool or
spa water.
3. Do not ll boiler or operate with water containing chlorine in
excess of 100 ppm.
Hardness: Less than 7 grains
Chloride Levels: Less than 100 ppm
pH Levels: 6-8
TDS: Less than 2000 ppm
Sodium: Less than 20 mGL
B. Check for Gas Leaks
Before starting the boiler, and during initial operation, smell
near the oor and around the boiler for gas odorant or any
unusual odor. Remove boiler front door and smell interior of
boiler enclosure. Do not proceed with startup if there is any
indication of a gas leak. Repair any leaks at once.
PROPANE BOILERS ONLY – The propane supplier mixes an
odorant with the propane to make its presence detectable. In
some instances the odorant can fade, and the gas may no longer
have an odor. Before startup (and periodically thereafter), have
the propane supplier verify the correct odorant level in the gas.
C. Condensate Removal
1. The boiler is a high eciency condensing boiler. Therefore,
the unit has a condensate drain. Condensate uid is nothing
more than water vapor, derived from combustion products,
similar to that produced by an automobile when it is initially
started.
Condensation is slightly acidic (typically with a pH of 3 to 5)
and must be piped with the correct materials. Never pipe the
condensate using steel, copper, brass or other materials that
will be subject to corrosion. Plastic PVC or CPVC pipe are the
only approved materials.
A condensate neutralizer, if required by local authorities,
can be made up of lime crystals, marble or phosphate chips
that will neutralize the condensate. This may be done by the
installer or you may purchase a condensate neutralizer from
HTP (7350P-611).
2. The boiler is equipped with a ¾ female socket weld tting
connection that must be piped to a local drain. It is very
important that the condensate line is sloped downward away
from the boiler to a suitable inside drain. If the condensate
outlet on the appliance is lower than the drain, you must use a
condensate removal pump, available from HTP (554200). This
pump is equipped with two leads that can be connected to an
alarm or another type of warning device to alert the user of
a condensate overow, which, if not corrected, could cause
property damage.
3. If a long horizontal run is used, it may be necessary to create
a vent in the horizontal run to prevent a vacuum lock in the
condensate line.
4. Do not expose the condensate to freezing temperatures.
5. It is very important you support the condensation line to
assure proper drainage.
D. Final Checks Before Starting Boiler
1. Read Startup Procedures within this manual for proper
steps to start boiler. (See Startup Report to record steps for
future reference.)
2. Verify the boiler and system are full of water and all system
components are correctly set for operation.
Ensure the boiler is full of water before ring the burner.
Failure to do so will damage the boiler. Such damage IS NOT
covered by warranty, and could result in property damage,
severe personal injury, or death.
3. Fill condensate trap with water.
4. Verify electrical connections are correct and securely
attached.
5. Inspect exhaust vent and intake piping for signs of
deterioration from corrosion, physical damage or sagging.
Verify exhaust vent and intake piping are intact and correctly
installed per Venting Section and local codes.
E. Setting Up a Single Boiler
When power is applied to the boiler, the control rst
completes a power-up systems check. During this time the
combustion fan may run. The display will initially show the
current boiler outlet temperature. If a fault is detected during
the power-up test, the control will display the appropriate
fault code. Otherwise, the display will continue to show the
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

41
boiler outlet temperature and stand-by, waiting for a demand
for hot water. If the temperature of the tank sensor falls below
the tank set point minus the tank dierential temperature, a
demand for hot water is generated by the control.
When a demand for hot water is received, the control begins
the following demand sequence. The boiler rst turns on the
pump (if it is not wired to run continuously). Once the pump is
running, the control will display LOW WATER FLOW and wait
for the water ow in the system to increase to an acceptable
level determined by the ow switch on the outside of the
boiler. (NOTE: This step may happen very rapidly. If ow is
adequate, LOW WATER FLOW may never display.)
Once ow through the boiler is adequate, the control will
measure the supply temperature. If it is below the set point
temperature minus the ignition dierential set point, the
control will ignite the burner. After the burner is lit, the
control modulates the ring rate to control the supply water
temperature at the set point temperature plus the supply
oset temperature (installer #4) above the tank set point
temperature. When the tank temperature is equal to the
tank set point temperature, the control will extinguish the
burner and run the combustion fan to purge gasses from the
combustion chamber. In addition, the pump will run for a
pump post purge interval. The control will then be in standby,
waiting to process the next demand for heat.
During this process, the control will extinguish the burner
if it senses a dangerous or unsafe condition. If the control
determines that a dangerous or unsafe condition has occurred,
the control may lock out the boiler and prevent it from igniting
until a maintenance person diagnoses the problem, repairs
it, and resets the control. In the event that the control goes
into lockout, it will show a diagnostic code on the display,
illuminate the LED fault indicator, and close the alarm relay
contacts to aid in recognition of the condition, diagnosis, and
repair.
F. Setting Up a Cascaded System
If the boiler is part of a cascaded system the operation is
somewhat dierent. The control of each boiler in a cascaded
system completes its own power up system check as described
above. One of the boilers in the cascade system is designated
as the master boiler. After the master boiler completes its
power up sequence, it checks the communication bus to see if
any other boilers are present. If other boilers are present, the
master control determines these follower boiler addresses.
The master boiler control will recheck the bus every few
seconds as long as it is powered up to update the status of the
connected boilers. The control in the master boiler processes
all heat demands and dictates which of the follower boilers
should light and what ring rate the followers should try to
achieve.
When the master boiler receives a demand for heat, it
determines which boiler is rst in the ring sequence and
sends that boiler a command to begin a demand sequence.
That boiler will then begin a demand sequence as described
above. Once the boiler ignites, the master boiler control will
increase the ring rate command to that boiler until the system
sensor temperature is at the tank set point temperature plus
the supply oset temperature (installer #4), or that boiler is
at high ring rate. If the command from the master boiler
control gets to the high ring rate of the follower boiler,
but the system sensor is below the required temperature, the
master boiler control will then tell the next boiler in the ring
sequence to begin its demand sequence. The master boiler
control will then begin to ramp up the ring rate command of
that boiler. This process will continue while there is a demand
until all boilers in the cascade system are at high re or the
desired temperature of the system sensor is reached. If the
system sensor temperature reaches tank set point and installer
#4 before all boilers are at high re, the master control will
modulate the cascade command signal to maintain the system
sensor at tank set point and installer #4 until the demand is
complete. When the tank temperature is equal to the set point
temperature, the demand is complete, and the master boiler
control will extinguish all boilers that may be lit. If the demand
decreases, the ring rate command and amount of boilers lit will
decrease exactly opposite as described above.
Whenever the master boiler control needs to re a follower
boiler, it sends a ring rate command to that boiler. The
follower boiler will respond to the command until its supply
sensor temperature gets to be 5
o
F above the tank set point
temperature plus the supply oset temperature (installer #4),
at which point the individual boiler will modulate on its own so
as not to overheat. As a result, it is not uncommon to see the
cascade output at maximum but individual boilers ring at less
than their maximum ring rate.
G. Lockout Condition
If any boilers, including the master boiler in the cascade system,
are in a lockout condition, the master control will recognize the
lockout condition and skip over the boiler in the ring sequence.
Each boiler in the cascade system is responsible for its own
safety functions. So, if any individual boiler control senses an
unsafe condition, it will extinguish the burner and, if necessary,
go to a lockout condition. In this way, every boiler in the system
has its individual safety controls intact and operational, even if
the ring of the boiler is under control of the master boiler.
In the event that the system sensor fails, all boilers in the
system will ignite simultaneously when there is a demand, and
each boiler will individually regulate ring rates to maintain
the master set point temperature (tank set point + installer
#4) at the individual supply sensors built into the boiler. If this
should happen, the master boiler will display an E03 fault code,
indicating that the supply sensor has failed.
H. Cascade System Programming
1. If the boiler is used alone, skip this section.
2. Programming the Master Boiler:
a. Make sure there is no demand for heat being supplied to
the boiler.
b. Apply power to the boiler.
c. Enter the system setting program navigation following
instructions in Part 10 of this manual.
d. Verify that cascade address function 15 is set to 0. This
makes the master boiler address 0. NOTE: The Master Boiler
MUST be addressed as 0. This establishes the unit as the
master in a cascaded system.
e. Change Cascade Mode function 23 from VISION3 to ALL
926 if cascaded system IS NOT common vented. If cascade
system IS common vented, set Function 23 to the total
number of boilers in the system (4 BOILERS for a four boiler
system, 6 BOILERS for a six boiler system, etc.)
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

42
f. Exit the installer menu.
NOTE: The temperature set point of the master must match
the follower boiler set point in order for the system to operate
properly.
3. Programming Follower Boilers:
NOTE: READ THE NOTES BELOW BEFORE PROGRAMMING
FOLLOWER BOILERS
• The boiler addressed as 1 will share its alarm output with
the master boiler.
• It is recommended but not necessary to address boilers in
the order that they are wired.
• No two boilers can have the same address.
• It is not required to use all consecutive address numbers.
• Maximum amount of boilers in a cascaded system is eight
(8).
a. Make sure there is no demand for heat being supplied to
the master boiler
b. Apply power to the follower boiler you are working on.
c. Enter system settings following instructions in Part 10 of
this manual
d. Set cascade address parameter 15 to 1 for the rst follower,
2 for the second follower, etc. depending which boiler you
are programming based on the above notes. This establishes
the boiler as a follower in a cascaded system and enables
data to be transferred as needed for the system to function
at full capability.
NOTE: ONLY select number 8 if using a Vision 3 panel for
cascade operations instead of a master boiler.
e. Change “CASCADE MODE” Function 23 to “ALL 926”
if the cascade system is not to be common vented. If the
cascade system IS to be common vented, set Function 23 to
COMMON FLUE.
f. Exit the installer menu.
NOTE: The temperature set point of the follower must match
the master boiler set point in order for the system to operate
properly.
Part 9 - Start-Up Procedure
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY READ BEFORE OPERATING
1. This boiler does not have a pilot. It is equipped with an
ignition device which automatically lights the burner. Do not
try to light the burner by hand.
2. BEFORE OPERATING: Smell all around the boiler area for
gas. Be sure to smell next to the oor because some gas is
heavier than air and will settle on the oor.
3. WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS
• Do not try to light any boiler.
• Do not touch any electric switch, do not use any phone
in your building.
• Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor’s
phone. Follow the gas suppliers’ instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the re
department.
• Turn o the gas shuto valve (located outside the
boiler) so that the handle is crosswise to the gas pipe.
If the handle will not turn by hand, don’t try to force
or repair it, call a qualied service technician. Force or
attempted repair may result in a re or explosion.
4. Do not use this boiler if any part has been under water.
Immediately call a qualied service technician to inspect the
boiler and to replace any part of the control system and any
gas control that has been damaged.
5. The boiler shall be installed so the gas ignition system
components are protected from water (dripping, spraying,
rain, etc.) during boiler operation and service (circulator
replacement, condensate trap, control replacement, etc.)
Failure to follow these instructions could result in property
damage, serious personal injury, or death.
If you discover any evidence of a gas leak, shut down the
boiler at once. Find the leak source with a bubble test and
repair immediately. Do not start the boiler again until the
leak is repaired. Failure to comply could result in substantial
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
A. Control Overview
The control is one of the primary safety devices of the boiler.
It monitors the safety sensors of the boiler to assure safe and
ecient operation.
The control has many features associated with system design.
This section addresses programming features, including
Boiler Settings / System Settings / Maintenance Settings and
System Diagnostics, to help in customizing your control. It
is important to fully understand control capabilities before
customization, as its factory defaults may already t your
system design and not require any adjustment at all.
B. Navigation of the Display
The display includes a two line backlit LCD readout to provide
informative messages about the operation of the boiler. Many
operating parameters can be viewed and adjusted by using
the six buttons on the display. The function of each button is
described below.
RESET – The RESET button has two functions.
– Resets any lockout error code
– Returns the user to the default display screen.

43
ENTER – The ENTER key is used to access parameter
programming mode. To access this mode, hold down the
ENTER key for more than 4 seconds. The readout will change
to:
ENTER MENU CODE
000
One of the zeroes will be blinking. Use the ^ v arrow keys to
change the blinking digit to the correct value. Use the < >
arrow keys to select the next digit to change and again use the
^ v keys to change the value. Repeat until the correct code is
entered. Press the ENTER key to accept the code entered. If
the code is correct, the readout will change to the appropriate
screen. If the programming code is not accepted, the readout
will continue to display as shown above.
ENTER is also used to enable a function for editing. After the
user navigates to the desired function, the user holds down
ENTER for one second. When ENTER is released, the function
value will begin to blink. The function can now be changed
using the ^ v keys. After the new value is displayed, the user
then presses ENTER for 1 second to lock the new value of the
function. The value will then stop blinking.
LEFT AND RIGHT ARROW KEYS – < > are used to navigate
between the default display, status display, analog and
cascade displays if they are enabled. The < > keys are also used
in programming modes to change between programmable
functions. It is recommended you use the Menu Maps in
the back of this manual and the detailed menu instructions
printed in this section to help in menu navigation.
UP AND DOWN ARROW KEYS – ^ v are used to navigate
between the various functions displayed in the menu. After
the function is enabled for editing by pushing the ENTER
key, the ^ v keys are used to adjust the function upward or
downward to the desired value.
C. Operating Instructions
Before operating the unit, it is important to remove the cover
and verify that the gas line and water lines are connected to
boiler and fully purged. If you smell gas, STOP; Follow the
safety instructions listed in the rst part of this section. If you
do not smell gas, follow the next steps.
1. Turn down the thermostats before applying power to the
boiler. If 0–10 volt or other inputs are used, make sure that
they are set so there is no call for heat while programming.
2. Turn on the power to the boiler or boilers if a cascade system
used.
3. Next, check the boiler settings. Adjustment and factory
defaults are outlined within this section. If a cascade system
is used, it is important that all the boilers have the same boiler
settings.
4. Next, check the system settings. Adjustments and factory
defaults are outlined within this section. If a cascade system
is used, it is important that the Master Boiler is programmed
with the correct system settings.
5. Create a demand on the boiler or boilers if a cascade system
is used. The user can monitor system functions when the
boilers are operational.
6. If the boilers fail to start, refer to the troubleshooting
section in the back of this manual.
D. Programming Boiler Settings
Boiler Setting Program Access
Note: Programming the boiler control is not possible when the
boiler is ring. Make sure any input which can create a demand
on the boiler, such as the tank thermostat, is turned o, so the
boiler will remain idle to allow programming.
Screen Description
To access the boiler setting program,
ENTER MENU CODE
000
ENTER MENU CODE
600
Table 15 - Boiler Setting Access
Boiler Setting Program Navigation
Once the code is conrmed, the user can start to set the Boiler
Settings. Use the arrow keys on the display to navigate through
the Boiler Settings. A blinking setting indicates the setting can
be changed. To change a setting, press ENTER. Boiler settings
can be increased by pressing ^ and decreased by pressing v on
the display. When done, press ENTER. The setting will stop
blinking and the user can move on to next setting. Press RESET
to exit programming and store settings. Listed below are the
boiler settings that can be programmed into the control.
Screen Description
IGNITION DIFF SET
o
F
7
TANK SETPOINT
o
F
120
TANK DIFF SETPOINT
o
F
7
TEMP DISPLAY C OR F
o
F
Table 16 - Boiler Setting Program Navigation
Clock Settings
(NOTE: The clock will reset if the boiler is powered o for more
than a week.)
Screen Description
CLOCK MODE (12/24)
08/28/2009 Fr 9:42A
CLOCK HOUR
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
CLOCK MINUTE
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
press and hold ENTER for 4 seconds
until the display shows the screen at
left.
Use the arrow keys to log in the Boiler
Menu Access Code - 600. Press ENTER
to conrm the code and access the
Boiler Setting Program navigation
menu.
Allows the user to adjust the ignition
dierential set point from 1oF to 36oF
(Factory Default 7oF). Degrees below
set point must be equal to or below
tank dierentials.
Adjusts the tank set point from 59oF to
180oF (Factory Default 120oF).
Adjusts the tank dierential set point
o
from 1
7
demand starts.
F to 18oF (Factory Default
o
F). Degrees below set point where
Adjusts the temperature
measurement in F = Fahrenheit to
C = Celsius (Default is Fahrenheit).
Changes the clock from 12 hour mode
(8:45 PM) to 24 hour mode (20:45). To
change to 24 hour mode, press ENTER.
The letter (A or P) after the time will
blink. Press the up or down arrow key
once and the letter will disappear.
Press ENTER to save the new setting.
Allows the user to adjust the hour
setting.
Adjusts the minute setting.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

44
Screen Description
CLOCK DAY OF WEEK
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
CLOCK DATE MODE
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
CLOCK YEAR
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
CLOCK MONTH
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
CLOCK DATE
08/28/2009 Fr 10:01A
Table 17 - Clock Setting Screens
Adjusts the day of the week.
Allows the user to switch to European
date format (2009/08/28) from US
format (08/28/2009).
Adjusts the year setting.
Adjusts the month setting.
The clock is set.
NOTE: The internal clock does not adjust for daylight savings
time and requires manual adjustment.
E. Programming the System Setting
System Setting Program Access
Note: Programming the boiler control is not possible when the
boiler is ring. Make sure any input which can create a demand
on the boiler, such as the tank thermostat, is turned o, so the
boiler will remain idle to allow programming.
Screen Description
To access the boiler setting program,
ENTER MENU CODE
000
ENTER MENU CODE
925
Table 18 - System Setting Access
press and hold ENTER for 4 seconds
until the display shows the screen at
left.
Use the arrow keys to log in the Boiler
Menu Access Code - 925. Press ENTER
to conrm the code and access the
Boiler Setting Program navigation
menu.
F. System Setting Program Navigation
Once the System Menu Access Code is conrmed, the user can
begin to set the system setting menu. Use the < > keys on the
display to navigate through the System Settings. To change a
setting, press ENTER. System settings can be increased by
pressing ^ and decreased by pressing v on the display. When
done, press ENTER. The setting will stop blinking and you can
move on to next setting. Press RESET to exit programming and
store settings. Listed below are the boiler settings that can be
programmed into the control.
Screen Description
Function 1 Factory Program Mode
This indicates that the control is
MODE
VWH MODE 1
Function 3 DHW Tank Max Temp
DHW TANK MAX TEMP
o
F 3
180
congured correctly for a volume
water heater. Do not change this
setting.
This is the maximum temperature
that can be selected in boiler settings
for the DHW tank. Factory Default is
180oF. (Range: 95oF to 180oF)
Screen Description
Function 4 Burner O Dierential
This is the amount of degrees
above tank set point that the
BURNER OFF DIFF
o
F 4
20
Function 6 VWH Post Pump Time
VWH POST PUMP TIME
0 MINUTES 6
Function 7 Warm Weather Shuto
WARM WEATHER OFF
o
F 7
68
Function 8 Min Outdoor Temp
MIN OUTDOOR TEMP
o
F 8
5
Function 9 Max Supply Temp
MAX SUPPLY TEMP
o
F 9
190
Function 10 Max Outdoor Temp
MAX OUTDOOR TEMP
o
F 10
68
Function 11 Min Supply Temp
MIN SUPPLY TEMP
o
F 11
95
Function 12 Min Boiler Temp
MIN BOILER TEMP
o
F 12
68
Function 13 CH Post Pump Time
CH POST PUMP TIME
0 MINUTES 13
Function 14 DHW Priority
DHW PRIORITY
30 MINUTES 14
Function 15 Cascade Address
CASCADE ADDRESS
0 15
Function 16 Optional Inputs
OPTIONAL INPUT
RETURN SEN 16
burner will maintain its outlet
water temperature while there is a
demand for heat. Factory Default is
20oF. (Range: 1oF to 45oF)
The boiler pump has the ability to
post purge energy from the boiler
to the tank after the set point has
been achieved. Please note that
running the pump for a time greater
than 5 minutes may cause tank
energy to be released back to the
heat exchanger. Factory Default of 0
Minutes. (Range: 0 – 10 minutes)
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Not applicable on this product.
Bus addressing boilers (maximum
boilers allowed 8 in a cascade
system). Master Boiler address is 0
and Following Boilers are addressed
1 thru 7. Default: 0 (Range: 0 – 8).
NOTE: ONLY USE ADDRESS 8 if
using a Vision 3 panel.
Allows the user to select optional
inputs to control or monitor the
system. Default: RETURN (Range:
O / Booster Board / 0-10 Volt / DHW
Sensor / Return Sen).
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

45
Screen Description
Function 17 0-10 Volt Function
Control boiler modulation through
0-10 VOLT FUNCTION
TEMPERATURE 17
temperature control. Factory
Default = Temperature (Temperature
only on VWH).
Function 18 Step Modulation Mode
STEP MODULATE MODE
ON 18
Not applicable on this product.
Function 19 Boiler DHW Temp
BOILER SUPPLY DHW
o
F 19
180
Not applicable on this product.
Function 20 Water Safety Input
The user can select various water
WATER SAFETY INPUT
WATER PRESSURE 20
safety inputs used in the boiler
system. Default: Flow Switch
(Range: None / Low Water Cut O /
Flow Switch / Water Pressure).
Function 21 Error Outdoor Sensor
ERROR OUTD SENSOR
OFF 21
Not applicable on this product.
Function 22 Adjust Boiler Output %
ADJ HEATER OUTPUT
100% 22
Adjusts the boiler output down
from 100% to 50%. Factory Default:
100%. (Range: 100% – 50%)
Function 23 Cascade Mode
Allows the user to select cascade
mode. Select VISION 3 if boiler
is operating alone or using an
older Vision 3 control panel for
cascade operation. Select ALL 926
to establish a cascaded system
WITHOUT common vent. In
cascaded systems WITH a common
vent, select the number of cascaded
CASCADE MODE
VISION 3 23
boilers in the system on the cascade
master (2 BOILERS in a two boiler
system, 6 BOILERS in a six boiler
system, etc.) On cascade followers
in a common vent system, select
COMMON FLUE to establish a
cascaded system WITH common
vent. Factory Default: VISION 3
(Range: VISION 3 / ALL 926 / 2 – 8
BOILERS [on cascade master ONLY]
/ COMMON FLUE [on cascade
followers ONLY]).
Function 24 Cascade Rotation
Sets the amount of hours before
the rst boiler in the cascade ring
CASCADE ROTATION
48 HOURS 24
rotation will be changed. NOTE: If
this is set to 0, the ring order of the
boilers will not rotate. Default: 48
hours (Range: 0 – 240 hours).
Function 25 Cascade DHW Mode
NOT USED
NOT USED 25
Not applicable on this product.
Screen Description
Function 26 System Freeze Protection
NOTE: This parameter is only
present if the boiler is a cascade
master. Allows the user to set the
SYS FREEZE PROT
PROTECT OFF 26
freeze protection when a system
pump is used. Factory Default: OFF.
Selection of temperature activates
freeze protection. (Range: OFF,
o
F – 104oF).
-40
Function 27 Error System Sensor
Sets the control to display an error
message if the system sensor is
ERROR SYSTEM SENS
ON 27
open or shorted. NOTE: This error
does not stop the boiler (or boilers)
from running. Factory Default: ON
(Range: ON / OFF).
Function 28 Freeze Protection
FREEZE PROTECTION
ON 28
Allows the user to set freeze
protection on the boiler. Factory
Default: ON (Range: ON / OFF).
Function 29 DHW Modulation Mode
DHW MODULATE MODE
NORMAL MOD 29
Not applicable on this product.
Function 30 Extra Boiler Mode
Allows for a non HTP boiler to
be controlled when the cascade
EXTRA BOILER MODE
OFF 30
output has risen above the percent
of the cascade ring rate set in this
parameter. Factory Default: O
(Range: 50% - 100%).
Function 31 System Sensor Mode
Suppresses the ‘NO FOLLOWER’
SYSTEM SENSOR MODE
OFF 31
display message if the boiler is used
as a cascade master boiler with no
follower boilers connected. Factory
Default: OFF (Range: ON / OFF).
Function 32 Service Schedule
Selects a service date or time based
on the boiler run hours to program
SERVICE SCHEDULE
OFF 32
the boiler maintenance schedule.
Factory Default: OFF (Range: Date
or Run Hours). NOTE: Without
setting this function, Functions
33/34/35/36 will not display.
Function 37 Modbus Mode
Enables Modbus Mode on the
appliance. Factory Default: OFF
(Range: OFF, ON, AUTO). NOTE:
Turning Modbus Mode “ON” will open
a number of additional parameters
to customize Modbus installation.
MODBUS MODE
OFF 37
See Modbus Instructions (lp-372) for
details. NOTE: Turning this Mode
“ON” without a connected and
powered Modbus communication
adapter (p/n 7350P-629) will result
in improper appliance operation.
Service calls associated with this
ARE NOT covered by warranty.
Table 19 - System Setting Program Navigation
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

46
NOTE: For the following functions, you must have your
maintenance function turned on.
To change these functions, press ENTER. The left most digit will
begin to blink. Use the ^ or v arrows to change the digit. Use
the < > arrow keys to switch between digits. When you’ve made
your selection, press ENTER again.
Screen Description
Function 33 Year
SERVICE SCHEDULE
YEAR 00/00/2000 33
SERVICE SCHEDULE
10000’s
Function 34 Month
SERVICE SCHEDULE
MONTH 00 /00/2000 34
SERVICE SCHEDULE
10000’s 00
Function 35 Day
SERVICE SCHEDULE
DAY 00/00/2000 35
SERVICE SCHEDULE
10000’s 0000
Function 36 Telephone
TELEPHONE #
000 000 0000 36
Table 20 - Maintenance Reminder Function Screens
000000 33
0000 34
00 35
Allows the user to set the year of the
next service reminder.
Hours
Allows the user to set the left two digits
of the amount of run hours before next
service reminder.
If the date function was selected, this
function programs the month. If you
selected the run hour function, you
will need to program 10,000 hours, if
required.
Hours
Allows the user to set the middle two
digits of the amount of run hours
before next service reminder.
Sets the day of next service reminder.
Hours
Sets the two right digits of the amount
of run hours for the next service
reminder.
Allows the user to input a telephone
number that will display when
maintenance is required.
G. Resetting the Maintenance Schedule
When the system control ashes MAINTENANCE REQUIRED,
it is advisable that you call for service. After the service is
performed, reset the schedule for the next required service by
using the following steps.
Press ENTER on the display for 3 seconds. The Menu code
will appear as 000. This does not change. Press ENTER again.
SERVICE SCHEDULE RESET will be displayed. Using the > key
scroll to the selection of year or hours. Press ENTER to reset the
selected Service Schedule. To change a setting, press ENTER.
Press the ^ and v keys to make adjustments. Press ENTER when
reset is complete.
Part 10 - Start-Up Procedures for the Installer
Screen Description
SUPPLY SEN 180
RETURN SEN 150oF
Press v once.
NA NA
SUPPLY SEN 122
Press v once.
0-10 SIGNL ON
*
Press v once.
CAS SET 190
SYSTEM 112oF
Press v once.
TANK SET 120
RET / TANK OFF
Press v once.
NA 11
FLUE 95
Press v once.
FLAME 0.0uA
FAN SPEED 3497 RPM
Press v once.
0-10 V 0.0V
*
Press v once.
o
o
o
o
o
o
This is the rst screen that appears
after pressing >, and shows the
actual temperatures measured
F
by the supply and return sensors.
NOTE: If the boiler is congured to
use a 0 – 10 volt input, the return
sensor is disabled and the second
line of the display will be blank.
The actual temperature measured
by the supply sensor is displayed on
F
the bottom.
Shows if 0-10 volt is enabled.
This screen appears only when the
boiler is set as a Master Boiler.
This screen displays the cascade set
point (maximum 190
line. The system sensor reading is
F
on the second line. The control will
cascade the boilers up to this set
point depending on demand.
Displays the current tank
temperature set point on the top line.
The actual temperature measured
by the tank or return sensor (HTP
7250P-325) is displayed on the
F
bottom line. If a mechanical aquastat
is used in place of the recommended
sensor, the second line will display
‘OFF’ in place of the temperature
if the aquastat measures close to
its set temperature, or ‘ON’ if the
aquastat temperature is too low.
The second line displays the current
F
F
boiler ue temperature.
This screen displays boiler ame
current on the top line. The second
line displays boiler fan speed.
The top line displays the voltage on
the optional input. This voltage is
only relevant if an external 0-10 volt
signal is being used to control the
boiler.
o
F) on the top
A. Boiler Control Status Menu
The boiler control also has the ability to review system status.
To access the status screens, press >. Once the rst value is
displayed, press ^ and v to scroll through additional information.
At any point press RESET to exit the status screens.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

47
This display shows the status of
the communication bus between
multiple boilers. If in a single boiler
conguration, the display will
BUS COMM NO CONN
Press v once.
POWER ON 0H
CH ON 0H
Press v once.
VWH ON 0H
GOOD IGNIT 1X
Press v once.
SYS CH ON 0H
SYS VWH ON 0H
Table 21 - Boiler Control Status Menu Screens
show ‘NO CONN’. In a multiple
boiler conguration, if this is the
Master Boiler and other boilers are
connected to the communication
bus and powered, this screen will
show the address of each boiler
connected to the bus.
The top line indicates the amount of
hours the boiler has been powered
over its life. The second line is not
applicable.
The top line indicates the hours the
burner has been on for hot water
demand over the boiler’s life. The
second line indicates how many
times the burner has successfully
ignited over the boiler’s life.
The top line is not applicable. The
second line registers system pump
hours on the cascade master ONLY.
The next ten screens display the last ten boiler lockout faults.
Press v to scroll through the faults from most recent to oldest.
Screen Description
This screen displays the most recent
boiler control lockout fault. The
FAULT HISTORY 1
07/27/2009 Mo 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 2
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 3
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
top line will alternate between the
words ‘FAULT HISTORY’ and the
fault code encountered. The bottom
line displays the date and time the
fault occurred.
This screen displays the second
oldest boiler control lockout fault.
The top line will alternate between
the words ‘FAULT HISTORY’ and
the actual fault encountered. The
bottom line will display the date and
time that the fault occurred.
This screen displays the third oldest
boiler control lockout fault. The top
line will alternate between the words
‘FAULT HISTORY’ and the actual
fault encountered. The bottom line
will display the date and time that
the fault occurred.
This screen displays the fourth
oldest boiler control lockout fault.
FAULT HISTORY 4
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 5
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 6
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 7
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 8
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Press v once.
FAULT HISTORY 9
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
FAU LT HISTO RY 10
08/28/2009 Fr 5:19A
Table 22 - Boiler Fault Screens
The top line will alternate between
the words ‘FAULT HISTORY’ and
the actual fault encountered. The
bottom line will display the date and
time that the fault occurred.
This screen displays the fth oldest
boiler control lockout fault. The top
line will alternate between the words
‘FAULT HISTORY’ and the actual
fault encountered. The bottom line
will display the date and time that
the fault occurred.
This screen displays the sixth oldest
boiler control lockout fault. The top
line will alternate between the words
‘FAULT HISTORY’ and the actual
fault encountered. The bottom line
will display the date and time that
the fault occurred.
This screen displays the seventh
oldest boiler control lockout fault.
The top line will alternate between
the words ‘FAULT HISTORY’ and
the actual fault encountered. The
bottom line will display the date and
time that the fault occurred.
This screen displays the eighth
oldest boiler control lockout fault.
The top line will alternate between
the words ‘FAULT HISTORY’ and
the actual fault encountered. The
bottom line will display the date and
time that the fault occurred.
This screen displays the ninth oldest
boiler control lockout fault. The top
line will alternate between the words
‘FAULT HISTORY’ and the actual
fault encountered. The bottom line
will display the date and time that
the fault occurred.
This screen displays the tenth oldest
boiler control lockout fault. The top
line will alternate between the words
‘FAULT HISTORY’ and the actual
fault encountered. The bottom line
will display the date and time that
the fault occurred.
B. Cascade Menu
This menu is accessed by pressing < at the default menu or >
at the status menu.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

48
Screen Description
CASCADE MASTER READY
SYS PUMP OFF
CASCADE NO FOLLOWER
SYS PUMP OFF
CASCADE NO SENSOR
SYS PUMP OFF
CASCADE VWH 0123 567
SYS PUMP ON 12:47P
Press v once.
This screen displays when the boiler
is congured as a Cascade Master
and the system is ready to accept
a demand for heat. The second line
indicates the cascade system pump
output status. This screen alternates
with the default screen every 5
seconds or can be accessed by
pressing the
screen.
This screen displays when the boiler
is congured as a Master Boiler and
there are no connected follower
boilers, or the follower boilers are not
powered. The second line indicates
cascade system pump output status.
This screen alternates with the
default screen every 5 seconds or
can be accessed by pressing the
key from the default screen.
This screen displays when the boiler
is congured as a Master Boiler and
there is no system temperature
sensor connected or the system
sensor is defective. The cascade
system will still function in this
situation with reduced eciency.
All boilers will run simultaneously
rather than in a staged fashion.
The second line indicates cascade
system pump output status. This
screen will alternate with the default
screen every 5 seconds or can be
accessed by pressing the
the default screen.
This screen displays information
about cascade status. The VWH in
the center of the top line shows that
cascade demand is coming from
the tank sensor or thermostat. You
may also see 0-10 if the demand
is from a 0-10 volt input. The
following numbers show which
boiler addresses are currently
communicating to the master.
If a boiler address is not used or
communicating, the number will
not display. In the example to
the left, boiler address #4 is not
communicating. When a boiler in the
system is ring, its address number
will alternate with a ‘.’ to signify it
is ring. The bottom line shows the
status of the system pump output
contacts.
< key from the default
< key from
This screen displays overall cascade
power output. The range of this
value is the number of boilers
CASCADE PWR 100%
PRESE NT 01 2345 67
Press v once.
CASCADE SYST 118
CAS CADE SET 1 90oF
Press v once.
<
BOILER 0 100%
BOILER 1 56%
Press v once.
BOILER 2 0%
BOILER 3 0%
Press v once.
BOILER 4 0%
BOILER 5 0%
Press v once.
BOILER 6 0%
BOILER 7 0%
Table 23 - Cascade Menu
communicating with the Master x
100. For example, if 8 boilers are
connected and ring, the maximum
cascade power is 800%. The second
line shows which boiler addresses
are communicating with the Master.
This screen displays current system
o
F
temperature sensor reading on the
top line and the cascade system
temperature setting on the bottom.
This screen displays the current
cascade power demand output
on a per connected boiler basis
for boilers addressed as 0 and 1.
In the example, boiler 0 is being
commanded to re at 100% and
boiler 1 at 56%. If this were a 2 boiler
system, the ‘CASCADE PWR’ screen
above would read 156%.
This screen displays the current
cascade power demand output on a
per connected boiler basis for boilers
addressed as 2 and 3.
This screen displays the current
cascade power demand output on a
per connected boiler basis for boilers
addressed as 4 and 5.
This screen displays the current
cascade power demand output on a
per connected boiler basis for boilers
addressed as 6 and 7.
C. Boiler Test Mode
This function is intended to simplify gas adjustment. The
following tables include recommended combustion settings
by fuel type and boiler fan speeds. Automatic modulation does
not take place while the controller is in Test Mode. However,
the boilers will modulate down if the program set point is
reached while running in Test Mode. It is recommended to
enter Test Mode with the largest load possible to create such a
heat demand that Test Mode will not be interrupted. To enter
Test Mode press ^ and ENTER simultaneously.
NOTE: The boiler will automatically exit Test Mode after 20
minutes of operation.
To leave Test Mode press ^ and v simultaneously.
SERVICE RUN 3400 RPM
PUMP ON 4:49P
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

Combustion Settings on All Models
Fan Speed
Carbon
Monoxide
(CO) PPM
Carbon
Dioxide
(CO2) %
Table 24 - Combustion Settings - All Models
Model Ignition Min Max
500
700
850 6800
Table 25 - Fan Speeds
Natural Gas (NG) Propane (LP)
Low Ignition High Low Ignition High
5-50 35-100
8-10 8 1/2-10 1/2 9-10 1/2 9 1/2-11
3000
<150 5-50 35-100 <150
Fan Speeds
1950 7200
2200
5700
Part 11 - Troubleshooting
A. Boiler Error and Fault Codes
If any of the sensors detect an abnormal condition, or an
internal component fails during the operation of the boiler,
the display may show an error message and error code. This
message and code may be the result of a temporary condition,
in which case the display will revert to its normal readout
when the condition is corrected, or it may be a condition that
the controller has evaluated as not safe to restart the boiler. In
this case, the boiler control will be locked out, the red FAULT
light will be lit, and the message “LOCKOUT” will be displayed
on the readout in the lower line.
The boiler will not start until a qualied technician has repaired
the boiler and pressed the RESET button for more than 1
second. If there is an error message displayed on the readout,
and the message “LOCKOUT” is not displayed and the FAULT
light is not lit, then the message is the result of a temporary
condition and will disappear when the problem corrects itself.
IMPORTANT NOTE: If you see error messages on your display
readout, call a technician immediately, since the message
may indicate a more serious problem will occur soon.
49
When servicing or replacing components that are in direct
contact with boiler water, be certain that:
• There is no pressure in the boiler. (Pull the release on the
relief valve. Do not depend on the pressure gauge reading.
• The boiler water is not hot.
• The electrical power is disconnected.
• The gas is shut o.
Failure to make these checks could result in substantial property
damage, serious personal injury, or death.
DO NOT USE THIS APPLIANCE IF ANY PART HAS BEEN
SUBMERGED IN WATER. Immediately call a qualied service
technician. The appliance MUST BE replaced if it has been
submerged. Attempting to operate an appliance that has been
submerged could create numerous harmful conditions, such as
a potential gas leakage causing a re and/or explosion, or the
release of mold, bacteria, or other harmful particulates into the
air. Operating a previously submerged appliance could result in
property damage, severe personal injury, or death.
NOTE: Appliance damage due to ood or submersion is
considered an Act of God, and IS NOT covered under product
warranty.
If overheating occurs or the gas supply fails to shut o, do not
turn o electrical power to the circulating pump. This may
aggravate the problem and increase the likelihood of boiler
damage. Instead, shut o the gas supply to the boiler at the gas
service valve. Failure to do so may result in property damage,
personal injury, or death.
Label all wires prior to disconnecting them when servicing
the boiler. Wiring errors can cause improper and dangerous
operation. Failure to follow these instructions may result in
property damage or personal injury.
NOTE: If system return temperatures are maintained below the
dew point, condensation will form on the inside of the boiler
cabinet and cause some internal sheet metal components to
rust.
B. Boiler Error
The controller will display an error code and message when
an error condition occurs. These error codes, descriptions, and
recommended corrective actions are described in Section D.
C. Boiler Fault
1. The controller will illuminate the red “FAULT” indication
light and display a fault code and message when a fault
condition occurs. The alarm output will also activate. Most
fault conditions cause the CH pump to run in an attempt to
cool the boiler.
2. Note the displayed fault code and refer to Section D for an
explanation of the message along with several suggestions for
corrective actions.
3. Press RESET to clear the fault and resume operation. Be
sure to observe the operation of the unit for a period of time
to assure correct operation and no reoccurrence of fault
message.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

50
D. User Interface Display
Cascade Control Fault Codes
Screen Description Possible Remedy
Disconnect the system sensor from the wiring and
E03 indicates a problem with the system
sensor circuit. The circuit could be open or
shorted. Possible reasons for this error are:
There is no system sensor connected to the
Master Boiler.
SYS SUPPLY SENSOR
PUMP OFF E03
TEMPER BLOCKING
PUMP ON TT
HIGH FLUE PRESS FLU
PUMP ON
WARNING: Do not use jumper to remedy an FLU error. Faulty switch MUST be replaced. Failure to follow this instruction could result in
serious personal injury or death.
24 VOLT LOW LOU
PUMP ON
WATER HIGH TEMP F00
PUMP ON
The system sensor is faulty.
There is a short circuit in the system sensor
wiring; possibly from a staple placed through
the wire, or damage to the wire causing both
conductors to touch.
The system sensor wiring is open due to
defect or damage.
TT indicates there is a demand for heat on
the boiler, the pump is powered on, and the
supply sensor temperature is too high for
the boiler to ignite. This occurs because the
water temperature measured by the supply
sensor is higher than the tank temperature –
ignition di setting.
FLU indicates excessive ue pressure. This
code resets automatically after the high
pressure condition is resolved. The second
line indicates pump status.
LOU indicates the 24 volt power supply on
the control is damaged or overloaded. This
code resets automatically if it is the result
of an overload and the overload condition
is removed. The second line indicates the
status of the pump. Note that while 24 volt
power is low, the pump output will be on.
F00 indicates the water in the boiler has
overheated. The boiler will not restart until it
cools suciently and a technician determines
and repairs the cause of overheating and
pushes RESET on the display. This is a serious
safety issue as indicated by the illuminated
red light and the word LOCKOUT ashing
on the display. During this lockout fault, the
pump will be on in an eort to cool the boiler
down.
measure it’s resistance. Compare the measured resistance
to the table in this manual to see if it corresponds to the
temperature of the sensor. If the resistance does not
agree with the sensor, replace the sensor. If the sensor
is OK, disconnect the sensor wiring from both the boiler
and the sensor and check continuity using an ohmmeter.
Repair or replace as necessary.
If this error is present, the boilers in the cascaded group
will run and ignite simultaneously when there is a heat
demand. Each boiler will modulate to maintain set
point temperature on its own supply sensor. This code
automatically resets when repair is complete. This code
will not display if system setting function ERROR SYSTEM
SENS is set to OFF.
This message will stay present until the water temperature
measured by the supply sensor is less than the tank
temperature – ignition di setting.
1. Assure the ue is not blocked.
2. Check the switch wiring by applying a jumper in place
of the switch. If the code clears with the jumper in place,
REPLACE the ue switch and connect the wires to the
new switch BEFORE running boiler.
1. Check line voltage. It must be between 100 and 128
volts.
2. If available, connect a PC and use HTP service software
to check the 24v supply display in the lower left corner of
the screen. The number displayed here must be greater
than 128 and should be no greater than 250. Use this as a
troubleshooting guide as you follow the steps below.
3. Remove the 10 pin Molex connector from the customer
connection board. If the message clears the problem is
with external sensor wiring. Examine the external sensor
wiring for shorts to the ground, repairing as necessary. If
the message is still present and the boiler is so equipped,
disconnect the UL 353 low water cut-o to see if the
message clears. Replace the faulty part. Check the low
voltage wire harness in boiler for shorts to ground.
4. If a message only occurs when the burner tries to light,
check the gas valve for excessive current draw.
5. If a message is present when the low voltage harness is
disconnected from the 926 control board, replace the 926
control board.
1. Check circulator pump operation.
2. If the circulator pump is running, ensure there is water
in the system and that the water is moving through the
system as intended. Ensure that all correct ball valves and
or zone valves are open or closed as intended.
3. Observe the temperature/pressure gauge. If the water
is not too hot and this message is displayed, check the
wiring to the water ECO sensor and repair if necessary. If
the wiring is ok and this code is still present and the water
is not excessively hot, replace the ECO sensor.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

Screen Description Possible Remedy
FLUE TEMP/WAT LV F01
PUMP ON
SUPPLY SENSOR F02
PUMP ON
RETURN SENSOR F03
PUMP ON
FLUE SENSOR F04
PUMP ON
This code indicates that one of the safety
interlock switches present in the unit has
tripped. There are several interlock switches
that could possibly trip and cause this error.
The following four switches are installed and
are standard equipment in all boilers.
1. Flue ECO – Trips if the ue temperature
is excessive. This switch has to be manually
reset.
2. Boiler module thermal fuse – Trips if there
is excessive heat on the rear of the heat
exchanger.
3. Boiler module front temperature switch Trips if there is excessive heat on the front of
the heat exchanger.
4. Blocked vent pressure switch (BVPS) – This
switch trips if there is excessive pressure in
the ue and automatically resets.
The following switches are optional
equipment that may be installed on the
VWH. These devices have indicator lights on
them showing of they are tripped.
1. High gas pressure switch – This switch
trips if there is excessive gas pressure on
the outlet side of the gas valve and must be
manually reset.
2. Low gas pressure switch – This switch trips
if there is low gas pressure on the inlet side
of the gas valve and must be manually reset.
3. UL 353 Low Water Cuto – This device trips
if the water level in the boiler is low and must
be manually reset.
F02 indicates the supply temperature sensor
of the boiler has failed. The boiler will not
restart until a technician replaces the sensor
and pushes RESET on the display. This is
a serious safety issue as indicated by the
illuminated red light and the word LOCKOUT
ashing on the display. During this lockout
fault, the pump will be on.
F03 indicates the return temperature sensor
of the boiler has failed. The boiler will not
restart until a technician replaces the sensor
and pushes RESET on the display. This is
a serious safety issue as indicated by the
illuminated red light and the word LOCKOUT
ashing on the display. During this lockout
fault, the pump will be on.
F04 indicates that the ue temperature
sensor of the boiler has failed. The boiler will
not restart until a technician replaces the
sensor and pushes RESET on the display. This
is a serious safety issue as indicated by the
illuminated red light and the word LOCKOUT
ashing on the display. During this lockout
fault, the pump will be on.
1. Check to see if the boiler with the F01 code displayed
has any of the optional switches installed.
2. If so, check to see if the indicator light on any of the
devices is showing that they are tripped.
3. If an indicator light is illuminated, investigate the source
of the error for that particular switch.
4. If there are no optional switches or none of the indicator
lights is illuminated on the optional switches then use an
ohmmeter to test each of the standard switches one at a
time. Turn the power o to the boiler and disconnect the
switch to be tested from the boiler to determine which
one has tripped.
When you nd the tripped switch investigate the cause
of the fault based on the purpose of the switch. NOTE:
The common reasons for the temperature switches to trip
are a) low water ow through the boiler, or b) poor heat
transfer from the water to the load.
5. If no switches are tripped, push RESET on the boiler.
If the boiler tries to ignite or ignites and only runs for a
short time and the F01 code returns, investigate the ue
for blockage.
1. Check the electrical connection to the thermistor on
the outlet manifold. Verify 5 VDC by checking the Molex
connector. If there is no 5 VDC, check the harness. If
harness is OK, replace the control. Verify thermistor
values by referencing chart in this manual.
2. Replace thermistor if necessary.
NOTE: The boiler will reset automatically once the fault
is corrected.
1. Check circulator pump operation.
2. Ensure adequate ow through the boiler by accessing
the status menu and determining there is less than a 50
o
rise from the return thermistor to the supply thermistor.
3. Troubleshoot thermistor by following the steps in F02.
Inspect the ue sensor for physical damage or corrosion
and replace it if necessary. Check the electrical connection
to the ue sensor and repair as necessary. Measure the
resistance of the sensor and refer to the sensor resistance
table in this manual. The temperature on the chart should
be close to the temperature in the ue. If not, replace the
ue sensor.
51
F
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

52
Screen Description Possible Remedy
SUPPLY TEMP HIGH F05
PUMP ON
RETURN TEMP HIGH F06
PUMP ON
NO FLAME ON IGN F09
PUMP ON
F05 indicates the boiler supply temperature
is excessive. When accompanied by the
red FAULT light and LOCKOUT ashing on
the display, this code indicates the supply
sensor temperature has exceeded 230
o
F and
a serious safety issue exists. The boiler will
not restart until a technician determines and
repairs the cause of excessive temperature
and pushes RESET on the display.
If the FAULT light is not illuminated and
this message is displayed, the supply temperature of the boiler is at or above 210
The message will clear automatically when
the temperature drops below 194
o
F. During
o
F.
the time that this fault is displayed, the pump
will be on.
This display indicates that the boiler
return temperature is excessive. When
accompanied by the red FAULT light and
LOCKOUT ashing on the display, this code
indicates that the return sensor temperature
has exceeded 230
o
F and a serious safety
issue exists. The boiler will not restart until a
technician determines and repairs the cause
of excessive temperature and pushes RESET
on the display.
If the red FAULT light is not illuminated and
this message is displayed, then the return
temperature of the boiler is at or above
210oF. The message will clear automatically
when the temperature drops below 194oF.
During the time that this message or lockout
fault is displayed, the pump will be on.
The boiler tried to ignite four times during
one heat call and failed. This is a serious
safety issue as indicated by the illuminated
red light and the word LOCKOUT ashing on
the display. The boiler will not restart until a
technician determines and repairs the cause
of ignition failure and pushes RESET on the
display. During this lockout fault, the pump
will remain on.
1. Check circulator pump operation.
2. Ensure adequate ow through the boiler by accessing
the status menu and determining there is less than a 50°F
rise from the return thermistor to the supply thermistor.
3. Check the direction of ow o the boiler circulator. (See
Piping Details in this manual.)
4. Troubleshoot the thermistor by following steps in F02.
1. Check circulator pump operation.
2. Ensure adequate ow through the boiler by accessing
the status menu and determining there is less than a 50°F
rise from the return thermistor to the supply thermistor.
3. Check the direction of ow on boiler circulator. (See
Piping Details in this manual.)
4. Troubleshoot thermistor by following steps in F02.
1. Watch the igniter through the observation window.
2. If there is no spark, check the spark electrode for the
proper .196” (5.0 mm ± 1mm) gap. See below.
3. Remove any corrosion from the spark electrode and
ame rectier probe.
4. If there is a spark but no ame, check the gas supply to
the boiler.
5. If there is a ame, check the ame sensor.
6. Check any ue blockage or condensate blocks.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

The ame was lost 3 times while the boiler
was ring during 1 demand call. This is a
serious safety issue as indicated by the
FLAME LOSS F10
PUMP ON
FALSE FLAME SIG F11
PUMP ON
FAN SPEED ERROR F13
PUMP ON
FLAP CLOSED F15 Flapper valve physically stuck closed.
FLAP OPEN F16 Flapper valve physically stuck open.
CONDENSATE FULL F20
PUMP OFF
illuminated red light and the word LOCKOUT
ashing on the display. The boiler will not
restart until a technician determines and
repairs the cause of ame loss and pushes
RESET on the display. During this lockout
fault, the pump will be on.
There is ame when the control is not telling
the boiler to run. This is a serious safety issue
as indicated by the illuminated red light and
the word LOCKOUT ashing on the display.
The boiler will not restart until a technician
determines and repairs the cause and pushes
RESET on the display. During this lockout
fault, the pump will be on.
The fan is not running at the speed
determined by the control. Fan speed has
been more than 30% faster or slower than
the commanded speed for more than 10
seconds. This is a serious safety issue as
indicated by the illuminated red light and
the word LOCKOUT ashing on the display
.This boiler will not restart until a technician
determines and repairs the cause and pushes
RESET on the display. During this lockout
fault, the pump will be on.
The condensate trap is full. This is a serious
safety issue as indicated by the illuminated
red light and the word LOCKOUT ashing on
the display. The boiler will not restart until a
technician determines and repairs the cause
and pushes RESET on the display. During this
lockout fault, the pump will be o.
53
1. Monitor gas pressure to the unit while in operation.
2. Assure the ame is stable when lit.
3. Check if the display readout changes from “GAS VALVE
ON” to “RUN” within a few seconds of boiler ignites.
4. Check the FLAME signal on the display. It should be
above 1.0 when the boiler is ring.
5. If the signal reads less than 1 microampere, clean the
ame rectier and spark probe.
6. If the problem persists and the ‘FLAME” signal is still
less than 1.0, replace the ame probe and spark igniter
probe.
7. The ame signal should be steady after the boiler has
been ring for 1 minute and is normally at 5.0 to 9.0. If the
ame signal is not steady, disassemble the burner door
and check the burner and its sealing gaskets.
1. Look into window. If there is ame, turn the gas o to
the unit at the service valve and replace the gas valve.
2. If the ame signal on the status menu is greater than
1.0 when the burner is not lit, replace the spark ignitor and
the ame rectication probe.
3. If the ame signal is not present after turning o the gas
supply, check the gas valve electrical connection.
4. Check for condensate backup. Repair condensate
system as necessary. If condensate has partially lled
the combustion chamber, the refractory wall may be
damaged and should be replaced.
5. Turn the gas on at the service valve after corrective
action is taken.
6. If the refractory wall falls against the rectier probe, it
may conduct the signal to ground, giving a false reading.
1. Check the combustion fan wiring.
2. Measure DC voltage from the red fan wire to ground
while it is connected to the fan. It should be between 24
and 40 volts. If it is lower than 24 volts, check for excessive
external loads connected to the boiler sensor terminals
3. Disconnect the 5 pin plug from the fan and check the
voltage on the red wire again. If it is now between 24-40
volts, replace the fan. If it is still below 24 volts replace the
boiler control board.
1. Check ue system for obstructions.
2. Check proper communication between boilers.
3. Check operation of apper valve.
4. Check wiring between valve and controller.
5. Replace valve-apper.
1. Check ue system for obstructions.
2. Check proper communication between boilers.
3. Check operation of apper valve.
4. Check wiring between valve and controller.
5. Replace valve-apper.
1. Check condensate lines for obstructions.
2. Check oat switch in condensate reservoir.
3. Check wiring from condensate reservoir to 926 control
and repair as necessary.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

54
Screen Description Possible Remedy
There was an error while programming
the control and the memory is corrupt. The
boiler control will not function in this state
and the pump will be o as indicated on
the bottom line. This error only occurs if a
PROGRAM ERROR F31
PUMP OFF
CONTROL PROGRAMED PP
LOW WATER FLOW FL
PUMP ON
The following blocking codes will block operation until the control determines the situation safe for boiler operation.
FLUE TEMP HIGH E07
PUMP OFF TIME
COMMON FLUE BLOCK
E16
LINE VOLTAGE E19
PUMP OFF
Table 26 - Boiler Error and Fault Codes
technician is programming the control and
the programming function fails. The only way
to recover from this error is to reprogram the
control. If this error occurs at any time other
than when a technician is servicing the boiler,
the control has failed and must be replaced
by a qualied technician.
The control has been programmed by a
technician or the factory. After programming,
the control is left in a locked out mode.
FL indicates there is low water ow in the
boiler. FL only displays on VWH products.
This code automatically resets when water
ow is high enough for the boiler to run
safely. The second line indicates pump status.
The pump should always be on when this
code is displayed. When there is a demand,
the control will start the pump, wait for the
ow switch to indicate ow then try to ignite
the boiler. This display occurs after the pump
is energized for several seconds and the ow
is still too low.
E07 indicates the ue sensor temperature
is excessive and above 210
displayed the boiler will not respond to a
demand for heat. When the ue temperature
decreases below 194oF, the display will return
to normal and allow the boiler to respond to
a heat demand. The bottom line indicates the
status of the pump. The pump will remain o
when this error is displayed.
Common ue blocking or apper valve
feedback failure.
E19 indicates the line voltage frequency is
out of range. This could happen if the boiler
is being powered from a small gasoline
powered generator that is overloaded or not
functioning correctly.
o
F. When E07 is
The control must be reprogrammed. If programming
does not solve the problem, the control must be replaced.
Press RESET for at least 1 second to use the control.
1. Check to see if boiler pump is functioning. Repair as
necessary.
2. Be sure water is owing in the system. Check for valves
that should be open, plugged lter screens, etc.
3. Check the ow switch and wiring. Repair as necessary.
Check the ue for obstructions and any sign of damage,
especially signs of excessive heat. Repair as necessary.
Run the boiler and check the ue temperature with an
external thermometer. If the ue temperature on the
thermometer does not agree with the ue temperature
displayed in the status menu, inspect the wiring to
the ue temperature sensor in the boiler and repair as
necessary. If the wiring is intact replace the ue sensor. If
the ue temperature is excessive on the status menu and
the test thermometer reads the same, check and adjust
combustion controls on the boiler. If the problem persists,
inspect the target wall in the combustion chamber and
replace it if cracked or damaged.
1. Ensure boiler is properly programmed.
2. Check ue system for obstructions.
3. Check proper communication between boilers.
4. Check operation of apper valve.
5. Check wiring between valve and controller.
6. Replace valve-apper.
Inspect power wiring to the boiler and repair as necessary.
If connected to line voltage, notify the power company.
If connected to an alternate power source such as
a generator or inverter, make sure the line voltage
frequency supplied by the device is 60 Hz.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

55
Part 12 - Maintenance
A. Procedures
Periodic maintenance should be performed once a year by a
qualied service technician to assure that all the equipment
is operating safely and eciently. The owner should make
necessary arrangements with a qualied heating contractor
for periodic maintenance of the boiler. The installer must also
inform the owner that a lack of proper care and maintenance
of the boiler may result in a hazardous condition.
BEFORE EACH HEATING SEASON a trained and qualied
service technician should perform the inspections as per the
boiler inspection and maintenance schedule in this manual.
Failure to do so could result in death or serious injury.
The combustion chamber insulation in this product contains
ceramic ber material. Ceramic bers can be converted
to cristobalite in very high temperature applications. The
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has
concluded, “Crystalline silica inhaled in the form of quartz
or cristobalite from occupational sources is carcinogenic to
humans (Group 1).”
• Avoid breathing dust and contact with skin and eyes.
• Use a NIOSH certied dust respirator (N95). This type
of respirator is based on the OSHA requirements for
cristobalite at the time this document was written. Other
types of respirators may be needed depending on job
site conditions. Current NIOSH recommendations can
be found on the NIOSH website: http://www.cdc.gov/
niosh/homepage.html. NIOSH approved respirators,
manufacturers, and phone numbers are also listed on
this website.
• Wear long-sleeved, loose tting clothing, gloves, and eye
protection.
• Apply enough water to the combustion chamber lining
to prevent dust.
• Wash potentially contaminated clothes separately from
other clothing. Rinse clothes washer thoroughly.
NIOSH stated First Aid.
• Eye: Irrigate immediately.
• Breathing: Fresh air.
B. Combustion Chamber Coil Cleaning Instructions
*Before beginning this procedure, have on hand the following
items:
• a nylon, stainless steel, or brass brush (not steel)
• gloves and eye protection
1. Shut down the boiler by using the following steps:
a. Close the gas valve. Shut down the unit, and wait for it to
be cool to the touch.
b. Disconnect the condensate piping from the outside
connection, (not from the boiler side), so ow from
condensate reservoir can be observed.
c. Disconnect electrical connections from the gas valve,
spark electrode, ame rectication probe, and combustion
blower.
d. Remove the four (4) screws on the aluminum ¾” NPT
connector on the right side of the gas valve.
e. Disconnect the wiring connected to the combustion
Supply Temperature Sensor
(7250P-324)
Outdoor Sensor
(7250P-319)
Outside
Temperature
o
F)
(
-22 171800 32 32550
-13 129800 41 25340
-4 98930 50 19870
5 76020 59 15700
14 58880 68 12490
23 45950 77 10000
32 36130 86 8059
41 28600 95 6535
50 22800 104 5330
59 18300 113 4372
68 14770 122 3605
77 12000 131 2989
86 9804 140 2490
95 8054 149 2084
104 6652 158 1753
113 5522 167 1481
Table 27 - Sensor Temperature Resistance
Resistance
(ohms)
High / Low
Temp Sensor
Temp. (oF)
Boiler Sensor
(7250P-667)
Indirect Sensor
(7350P-325)
Resistance
(Ohms)
176 1256
185 1070
194 915
202 786
212 667
blower motor.
f. Remove the six (6) 10MM nuts from the burner plate
assembly.
g. Pull the entire burner plate assembly with blower still
attached towards you, while removing or pushing aside any
wiring to allow removal of the assembly.
2. Spray the coils liberally with a spray bottle lled with clear
tap water. Conne the spray to the area being cleaned. Avoid
getting the ceramic target wall wet. If the condensate system is
blocked, use a vacuum to clear it.
3. Scrub coils of any buildup with a nylon, stainless steel, or brass
brush. Do not use a steel brush. Vacuum the debris from the
coils.
4. Spray the coils again with clear tap water. Conne the spray
to the area being cleaned. Flush the combustion chamber with
fresh water until it runs clear from the condensate reservoir. At
this point, the boiler should be ready to be reassembled.
a. Inspect gaskets.
b. Reinstall the burner assembly
c. Replace and tighten the six (6) 10MM nuts to the burner
plate using staggered tightening sequence. (See detail.)
d. Reconnect all wiring connections
e. Inspect the gas valve. Ensure the O-ring is in place.
f. Replace the four (4) screws on the aluminum connector on
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

56
the gas valve. Turn the gas back on. (IMPORTANT: CHECK
FOR GAS LEAKS!)
g. Turn boiler power back on and create a heat demand. When
boiler is lit observe condensate ow from the boiler. Be sure
the boiler is operating properly.
h. Reconnect the condensate piping to the outside condensate
connection.
Do not use solvents to clean any of the burner components.
The components could be damaged, resulting in unreliable or
unsafe boiler operation, substantial property damage, severe
personal injury, or death.
Figure 34 - Heat Exchanger Detail
C. Cleaning Water Side of Heat Exchanger
1. Make sure power is turned o to the boiler. Run water through
the hot water system to
ensure it is below room
temperature.
2. Close isolation valves
on the return and supply
connections to the
boilers as shown in the
piping diagrams in this
manual. Slowly open the
ball valves and release
pressure into a bucket.
Once pressure is released,
connect a hose to the
water line to ush the
boiler. Scale removing
solution may be used, but
must be approved for use
with stainless steel and
FDA approved for use in a
potable water system.
3. Thoroughly ush the heat exchanger before commissioning
the unit back in service.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

57
Figure 35 - 500 Model Combustion System Replacement Parts
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

58
Figure 36 - 700/850 Models Combustion System Replacement Parts
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

18
59
19
11
12
20
21
10
22
7
3
6
7
5
4
2
1
6
16
9
8
3
17
13
15
MOD CON
MOD CON
ITEM
ITEM
500VWH
500VWH
1 7500P-033 7500P-033 ECO HIGH LIMIT SENSOR(W/O-RING)
1 7500P-033 7500P-033 ECO HIGH LIMIT SENSOR(W/O-RING)
2 7500P-100 7500P-100 O-RING-ECO HIGH LIMIT SENSOR
2 7500P-100 7500P-100 O-RING-ECO HIGH LIMIT SENSOR
3 7450P-280 7450P-280 SENSOR, NTC
3 7450P-280 7450P-280 SENSOR, NTC
4 7500P-002 7500P-002 ECO SWITCH-190 DEGREES
4 7500P-002 7500P-002 ECO SWITCH-190 DEGREES
5 7350P-004 7350P-004 2" INLET /NIPPLE (w/O-RING)
5 7350P-004 7350P-004 2" INLET /NIPPLE (w/O-RING)
6 7350P-072 7350P-072 O-RING- INLET/OUTLET NIPPLE
6 7350P-072 7350P-072 O-RING- INLET/OUTLET NIPPLE
7 7350P-015 7350P-015 2" INLET NIPPLE CLIP
7 7350P-015 7350P-015 2" INLET NIPPLE CLIP
8 7350P-002 7350P-002 2" OUTLET NIPPLE (w/O-RING)
8 7350P-002 7350P-002 2" OUTLET NIPPLE (w/O-RING)
9 SN1018 SN1018 3/4"NPT X 3" NIPPLE - BRASS
9 SN1018 SN1018 3/4"NPT X 3" NIPPLE - BRASS
10 7350P-065 7350P-065 150# RELIEF VALVE=3/4" NPT
10 7350P-065 7350P-065 150# RELIEF VALVE=3/4" NPT
11 7350P-219 7350P-220 VENT ADAPTER
11 7350P-219 7350P-220 VENT ADAPTER
12 7250P-739 7250P-739 FLUE ECO SWITCH - 160 DEGREES
12 7250P-739 7250P-739 FLUE ECO SWITCH - 160 DEGREES
13 7350P-613 7350P-613 CONDENSATE COLLECTOR ASSEMBLY
13 7350P-613 7350P-613 CONDENSATE COLLECTOR ASSEMBLY
14 7350P-167 7350P-167 CONDENSATE OVERFLOW SWITCH
14 7350P-167 7350P-167 CONDENSATE OVERFLOW SWITCH
15 7350P-113 7350P-113 2" PVC PLUG
15 7350P-113 7350P-113 2" PVC PLUG
16 7350P-277 7350P-277 DRAIN VALVE
16 7350P-277 7350P-277 DRAIN VALVE
17 7250P-499 7250P-499 TEMP/PRESSURE GAUGE
17 7250P-499 7250P-499 TEMP/PRESSURE GAUGE
18 7250P-160 7250P-160 PRESSURE SWITCH
18 7250P-160 7250P-160 PRESSURE SWITCH
19 7000P-805 7000P-805 PLASTIC TUBING 3/16 ID X 5/16 OD X 12"
19 7000P-805 7000P-805 PLASTIC TUBING 3/16 ID X 5/16 OD X 12"
20 7250P-154 7250P-154 S.S. BARBED FITTING 1/4 HOSE X 10-32
20 7250P-154 7250P-154 S.S. BARBED FITTING 1/4 HOSE X 10-32
21 7250P-152 7250P-152 O-RING, SILICONE 2-007 - BARBED FITTING
21 7250P-152 7250P-152 O-RING, SILICONE 2-007 - BARBED FITTING
22 7350P-605 7350P-605 FLOW SWITCH KIT FOR MOD CON VWH
22 7350P-605 7350P-605 FLOW SWITCH KIT FOR MOD CON VWH
MOD CON
MOD CON
700 VWH
700 VWH
MOD CON
MOD CON
850VWH
850VWH
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
Figure 37 - Water Side Replacement Parts - All Models
14
LP-446-A
07/28/16
07/28/16
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

60
Figure 38 - Cabinet Replacement Parts - All Models
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

Part 13 - Installation Checklist
Light O Activities Date Completed:
Check all piping and gas connections.
Verify all are tight.
1. Fill the Heating System
2. Check Gas Pipe
3. Check Combustion
4. Check Electrical
Connections
5. Verify System Operation
6. Record Ionization
Current
7. Storage Tank
8. Mixing Valve
9. Convert the Boiler
(500 Model ONLY)
Notes:
Pressurize system. PSI
Add water to prime condensate cup.
Verify near boiler piping is properly
supported.
Leak test using locally approved methods
(consult jurisdictional code book).
Check incoming gas pressure (3.5 to 14”
WC).
Check the “drop” on light o (less than 1”
WC).
Check and adjust (if necessary) carbon
dioxide content.
Check and adjust (if necessary) carbon
monoxide content.
Ensure all electrical connections of line
voltage (pumps, etc.) and low voltage
circuits (system sensor, outdoor sensor,
etc.) are properly wired.
Turn up thermostat to verify wiring
connections.
Check uA reading at d7 on the status
menu (see Start-Up section, this manual).
Verify safety and operation of the storage
tank. Record settings.
Ensure thermostatic mixing valve is
properly supported and installed.
If necessary, convert the boiler to the
proper fuel type.
Locate the stickers in the appropriate
locations on the boiler.
Verify combustion settings after gas
conversion - Carbon Dioxide.
Verify combustion settings after gas
conversion - Carbon Monoxide.
Mail in conversion registration.
Static WC
%CO2 High Fire %CO2 Low Fire
ppm CO High Fire ppm CO Low Fire
uA High Fire uA Low Fire
DHW Setpoint DHW Dierential
%CO2 High Fire %CO2 Low Fire
ppm CO High Fire ppm CO Low Fire
61
Dynamic WC
Table 28 - Installation Checklist
Part 14 - Maintenance Report
In unusually dirty or dusty conditions, care must be taken to
keep boiler cabinet door in place at all times. Failure to do so
VOIDS the warranty.
Allowing the boiler to operate with a dirty combustion
chamber will hurt operation. Failure to clean the heat
exchanger as needed by the installation location could result
in boiler failure, property damage, personal injury, or death.
Such product failures ARE NOT covered under warranty.
The boiler requires minimal periodic maintenance under normal
conditions. However, in unusually dirty or dusty conditions,
periodic vacuuming of the cover to maintain visibility of the
display and indicators is recommended.
Periodic maintenance should be performed once a year by a
qualied service technician to assure that all the equipment
is operating safely and eciently. The owner should make
necessary arrangements with a qualied heating contractor for
periodic maintenance of the boiler. Installer must also inform
the owner that the lack of proper care and maintenance of the
boiler may result in a hazardous condition.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

62
Inspection Activities Date Last Completed
Piping 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
Near boiler piping
Vent
System 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
Visual Do a full visual inspection of all system components.
Functional Test all functions of the system (Heat, Safeties).
Temperatures
Electrical
Connections Check wire connections. Make sure connections are tight.
Smoke and CO
Detector
Circuit Breakers Check to see that the circuit breaker is clearly labeled. Exercise circuit
Switch and Plug Verify ON/OFF switch and convenience plug are both functional.
Chamber / Burner 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
Combustion
Chamber
Spark Electrode Clean. Set gap at 1/4” Clean probe with plumbers cloth to remove
Combination Ignitor
and Flame Probe
Condensate 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
Neutralizer Check condensate neutralizer. Replace if necessary.
Condensate Pipe Disconnect condensate pipe. Clean out dirt. Fill with water to level
Gas 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
Pressure Measure incoming gas pressure (3.5 to 14” WC).
Pressure Drop Measure drop in pressure on light o (no more than 1” WC).
Check Gas Pipe for
Leaks
Combustion 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
CO / CO2 Levels Check CO and CO2 levels in exhaust. See Start-Up Procedures for
Safeties 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
ECO (Energy Cut
Out)
Flow Switch Activate heating call and monitor system to ensure ow switch and
Sensors Check wiring. Verify through ohms reading.
Final Inspection 1st Year 2nd Year 3rd Year 4th Year*
Check List Verify that you have completed entire check list. WARNING: FAILURE
Homeowner Review what you have done with the homeowner.
Table 29 - *Continue annual maintenance beyond the 4th year as required.
Check boiler and system piping for any sign of leakage; make sure
pipes are properly supported.
Check condition of all vent pipes and joints. Ensure the vent piping
terminations are free of obstructions and blockages.
Verify safe settings on boiler or anti-scald valve.
Verify programmed temperature settings.
Verify devices are installed and working properly. Change batteries if
necessary.
breaker.
Check burner tube and combustion chamber coils. Clean according
to maintenance section of manual. Vacuum combustion chamber.
Replace any gaskets that show signs of damage.
oxides.
Check ionization in uA (d7 in Status Menu in Start-Up Procedures).
Record high re and low re. Clean probe with plumbers cloth to
remove oxides.
of outlet and reinstall. (NOTE: Verify the ow of condensate, making
sure that the hose is properly connected during nal inspection.)
Check gas piping. Test for leaks and signs of aging. Make sure all pipes
are properly supported.
ranges. Record at high and low re.
Check continuity on ue and water ECO. Replace if corroded.
pump are operating correctly.
TO DO SO COULD RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

ADDITIONAL INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
ANSI/UL 2034 listed and IAS certified.
FOR THE COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS
In the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, the installer or service agent shall be a plumber or
gas fitter licensed by the Commonwealth.
When installed in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts or where applicable state codes
may apply; the unit shall be installed with a CO detector per the requirements listed below.
5.08: Modifications to NFPA-54, Chapter 10
(1) Revise NFPA-54 section 10.5.4.2 by adding a second exception as follows:
Existing chimneys shall be permitted to have their use continued when a gas conversion
burner is installed, and shall be equipped with a manually reset device that will
automatically shut off the gas to the burner in the event of a sustained back-draft.
(2) Revise 10.8.3 by adding the following additional requirements:
63
(a) For all side wall horizontally vented gas fueled equipment installed in every dwelling,
building or structure used in whole or in part for residential purposes, including those owned
or operated by the Commonwealth and where the side wall exhaust vent termination is less
than seven (7) feet above finished grade in the area of the venting, including but not limited
to decks and porches, the following requirements shall be satisfied:
1. INSTALLATION OF CARBON MONOXIDE DETECTORS. At the time of installation of the side
wall horizontal vented gas fueled equipment, the installing plumber or gasfitter shall observe
that a hard wired carbon monoxide detector with an alarm and battery back-up is installed
on the floor level where the gas equipment is to be installed. In addition, the installing
plumber or gasfitter shall observe that a battery operated or hard wired carbon monoxide
detector with an alarm is installed on each additional level of the dwelling, building or
structure served by the side wall horizontal vented gas fueled equipment. It shall be the
responsibility of the property owner to secure the service of qualified licensed professionals
for the installation of hard wired carbon monoxide detectors
a. In the event that the side wall horizontally vented gas fueled equipment is installed
in a crawl space or an attic, the hard wired carbon monoxide detector with alarm
and battery back-up may be installed on the next adjacent floor level.
b. In the event that the requirements of this subdivision cannot be met at the time of
completion of installation, the owner shall have a period of thirty (30) days to comply
with the above requirements; provided, however, that during said thirty (30) day
period, a battery operated carbon monoxide detector with an alarm shall be
installed.
2. APPROVED CARBON MONOXIDE DETECTORS. Each carbon monoxide detector as
required in accordance with the above provisions shall comply with NFPA 720 and be
LP-172
REV. 02/16/06
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

64
3. SIGNAGE. A metal or plastic identification plate shall be permanently mounted to the
exterior of the building at a minimum height of eight (8) feet above grade directly in line with
the exhaust vent terminal for the horizontally vented gas fueled heating appliance or
equipment. The sign shall read, in print size no less than one-half (1/2) inch in size, “GAS VENT
DIRECTLY BELOW, KEEP CLEAR OF ALL OBSTRUCTIONS”.
4. INSPECTION. The state or local gas inspector of the side wall horizontally vented gas
fueled equipment shall not approve the installation unless, upon inspection, the inspector
observes carbon monoxide detectors and signage installed in accordance with the
provisions of 248 CMR 5.08 (2)(a) 1 through 4.
(b) EXEMPTIONS: the following equipment is exempt from 248 CMR 5.08 (2)(a) 1 through 4:
1. The equipment listed in Chapter 10 entitled “Equipment Not Required to be
Vented” in the most current edition of NFPA 54 as adopted by the Board; and
2. Product Approved side wall horizontally vented gas fueled equipment installed in a
room or structure separate from the dwelling, building or structure used in whole or in
part for residential purposes.
(c) MANUFACTURER REQUIREMENTS – GAS EQUIPMENT VENTING SYSTEM PROVIDED. When
the manufacturer of Product Approved side wall horizontally vented gas equipment
provides a venting system design or venting system components with the equipment, the
instructions provided by the manufacturer for installation of the equipment and the venting
system shall include:
1. Detailed instructions for the installation of the venting system design or the venting
system components; and
2. A complete parts list for the venting system design or venting system.
(d) MANUFACTURER REQUIREMENTS – GAS EQUIPMENT VENTING SYSTEM NOT PROVIDED.
When the manufacturer of a Product Approved side wall horizontally vented gas fueled
equipment does not provide the parts for venting the flue gases, but identifies “special
venting systems”, the following requirements shall be satisfied by the manufacturer:
1. The referenced “special venting system” instructions shall be included with the
appliance or equipment installation instructions; and
2. The “special venting systems” shall be Product Approved by the Board, and the
instructions for that system shall include a parts list and detailed installation instructions.
(e) A copy of all installation instructions for all Product Approval side wall horizontally vented
gas fueled equipment, all venting instructions, all parts lists for venting instructions, and/or all
venting design instructions shall remain with the appliance or equipment at the completion
of the installation.
LP-172
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
REV. 02/16/06

65
VWH
Limited Warranty
Five year warranty to assure your complete satisfaction.
HTP warrants each VWH to be free from defects in material
and workmanship according to the following terms, conditions
and time periods. UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED THESE
WARRANTIES COMMENCE ON THE DATE OF INSTALLATION.
COVERAGE
A. During the rst year after the date of installation, HTP warrants
that it will repair or replace, at its option, any defective or
malfunctioning component of the VWH that is found to have
failed due to manufacturer’s defect. Replacement parts will be
warranted for ninety (90) days.
B. During the rst through fth year after the date of installation,
HTP warrants that it will repair or replace, at its option, any
defective VWH that is found to have failed due to manufacturer’s
defect. No other component of the VWH will be replaced during
this period (with exception to the blower motor, which will have
a limited warranty of 3 years).
C. Should a defect or malfunction result in a leakage of water
within the above-stated warranty periods due to defective
material or workmanship, malfunction or failure to comply with
the above warranty, with such defects or malfunctioning having
been veried by an authorized HTP representative, then HTP will
replace the defective or malfunctioning VWH with a replacement
VWH of the nearest comparable model available at the time
of replacement. The replacement VWH will be warranted for
the unexpired portion of the applicable warranty period of the
original VWH.
D. If government regulations, industry certication, or similar
standards require the replacement VWH or part(s) to have features
not found in the defective VWH or part(s), you will be charged
the difference in price represented by those required features.
If you pay the price difference for those required features and/
or to upgrade the size and/or other features available on a new
replacement VWH or part(s), you will also receive a complete new
limited warranty for that replacement VWH or part(s).
E. In the event of a leakage of water of a replacement VWH due
to defective material or workmanship, malfunction, or failure to
comply with the above warranty, HTP reserves the right to refund
to the original purchaser the published wholesale price available
at the date of manufacture of the original VWH.
F. If, at the time of a request for service the purchaser cannot
provide a copy of the original sales receipt or the warranty card
registration, the warranty period for the VWH shall then be
deemed to have commenced thirty (30) days after the date of
manufacture of the VWH and NOT the date of installation of the
VWH.
G. It is expressly agreed between HTP and the original consumer
purchaser that repair, replacement, or refund are the exclusive
remedies of the original consumer purchaser.
OWNER’S RESPONSIBILITIES
The owner or installer must:
1. To avoid the exclusion list in this warranty, it is recommended
that the VWH be maintained in accordance to the maintenance
procedure listed in the installation manual. Preventive
maintenance can help to avoid any unnecessary breakdown of
your appliance and keep your appliance running at its optimum
efciency.
2. All related heating components must be maintained in good
operating condition.
3. All lines must be checked to conrm that all condensate drains
properly from the unit.
4. Operate the VWH at pressures not exceeding the working
pressure shown on the rating plate.
5. Use the VWH in a system with a properly sized and installed
thermal expansion tank.
6. Make provisions so if the VWH or any component part or
connection thereto should leak, the resulting ow of water will
not cause damage to the area in which it is installed.
WARRANTY EXCLUSIONS
HTP does not warrant:
1. All labor charges incurred by any person in connection with the
examination or replacement of parts claimed by the purchaser to
be defective.
2. Any failed components of the heat system not manufactured
by HTP as part of the VWH.
3. VWHs repaired or altered without prior written approval of
HTP so as to affect adversely their reliability.
4. Any damages, defects or malfunctions resulting from improper
maintenance, misuse, abuse, accident, negligence, freezing and
the like.
5. Any damage or failure resulting from hard water scale buildup
on the tank heat exchanger tubes.
6. Any damage or failure resulting from contaminated air,
including, but not limited to, sheetrock particles, plasterboard
particles, dirt or dust, being introduced into the VWH or its
components including, but not limited to, the outside tubes of
the heat exchanger.
7. Damages, malfunctions, or failures resulting from failure to
install the VWH in accordance with applicable building codes/
ordinances or good plumbing and electrical trade practices.
8. Damages, malfunctions, or failures resulting from improper
installation, failure to operate the VWH at pressures not
exceeding the working pressure shown on the rating plate, or
failure to maintain and operate the VWH in accordance with the
manufacturer’s printed instructions.
9. Damages, malfunctions, or failures caused by operating the
water heater with modied, altered, or unapproved parts.
10. Failure to operate the VWH in a system with a properly sized
and installed thermal expansion tank.
11. Failures or performance problems caused by improper sizing
of the water heater, expansion device, or piping.
12. Any damage or failure resulting from improper water
chemistry. WATER CHEMISTRY REQUIREMENTS – Sodium less
than 20mGL. Water pH between 6.0 and 8.0. Hardness less than 7
grains. Chlorine concentration less than 100 ppm.
13. Any damages, malfunctions, or failures resulting from the use
of dielectric unions.
14. Components of the VWH that are not defective, but must be
replaced during the warranty period as a result of reasonable
wear and tear.
15. Components of the VWH that are subject to warranties, if
any, given by their manufacturers, HTP does not adopt these
warranties.
16. Malfunctions resulting from, or repairs necessitated by, ood,
re, wind, or lightning, or uses of the VWH for purposes other
than that for which it was designed.
17. Any unit purchased from an unauthorized dealer or any
online retailer.
18. Units installed outside the fty states (and the District of
Columbia) of the United States of America and Canada.
PROCEDURES FOR WARRANTY SERVICE REQUESTS
Any claim for warranty assistance must be made promptly.
Determine if the VWH is “in-warranty” (that is, within the
applicable warranty period) by reviewing a copy of the original
sales receipt. You must present a copy of the original sales receipt
for a warranty service request.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

66
If your VWH is “in-warranty”, contact the retailer from whom the
VWH was purchased (or the installer) for assistance. Be prepared
to provide the retailer or installer with a copy of your original
receipt, complete model and serial numbers, and the date of
installation of your VWH, in addition to explanation of your
problem.
Warranty coverage is subject to validation of “in-warranty”
coverage by HTP claims department personnel. All alleged
defective or malfunctioning parts must be returned to HTP
via the local distribution channels where original purchase
was made. NOTE: Any parts or VWHs returned to HTP for
warranty analysis will become the property of HTP and will
not be returned, even if credit is denied.
If all warranty conditions are satised, HTP will provide
replacement parts to the retailer.
If you have questions about the coverage of this warranty, please
contact HTP at the address or phone number stated below:
HTP
272 Duchaine Blvd.
New Bedford, MA. 02745
Attention: Warranty Service Department
(800) 323-9651
SERVICE, LABOR AND SHIPPING COSTS
This warranty does not extend to shipping charges, delivery
expenses, or administrative fees incurred by the purchaser in
repairing or replacing the VWH. This warranty does not extend
to labor costs beyond the coverage specied in this warranty
document.
HTP reserves the right to change specications or discontinue
models without notice.
LIMITATIONS OF YOUR HTP WARRANTY AND REMEDIES
THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND
ARE GIVEN AND ACCEPTED IN LIEU OF ANY AND ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
WITHOUT LIMITATION THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE AND ANY OBLIGATION, LIABILITY, RIGHT, CLAIM
OR REMEDY IN CONTRACT OR TORT, WHETHER OR NOT
ARISING FROM HTP’S NEGLIGENCE, ACTUAL OR IMPUTED.
THE REMEDIES OF THE PURCHASER SHALL BE LIMITED TO
THOSE PROVIDED HEREIN TO THE EXCLUSION OF ANY
OTHER REMEDIES INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION,
INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, SAID
INCIDENTAL AND CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROPERTY DAMAGE, LOST PROFIT
OR DAMAGES ALLEGED TO HAVE BEEN CAUSED BY ANY
FAILURE OF HTP TO MEET ANY OBLIGATION UNDER THIS
AGREEMENT INCLUDING THE OBLIGATION TO REPAIR AND
REPLACE SET FORTH ABOVE. NO AGREEMENT VARYING OR
EXTENDING THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES, REMEDIES OR
THIS LIMITATION WILL BE BINDING UPON HTP. UNLESS IN
WRITING AND SIGNED BY A DULY AUTHORIZED OFFICER
OF HTP. THE WARRANTIES STATED HEREIN ARE NOT
TRANSFERABLE AND SHALL BE FOR THE BENEFIT OF THE
ORIGINAL PURCHASER OF A VWH ONLY.
NO OTHER WARRANTIES
Your HTP warranty gives you specic legal rights, and you
may also have other rights that vary from state to state. Some
states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages so this limitation or exclusion may not
apply to you.
These are the only written warranties applicable to the VWH
manufactured and sold by HTP. HTP neither assumes nor
authorizes anyone to assume for it any other obligation or
liability in connection with said VWHs.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

Maintenance Notes
67
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16

68
Customer Installation Record Form
The following form should be completed by the installer for you to keep as a record of the installation in case of a warranty
claim. After reading the important notes at the bottom of the page, please also sign this document.
Customer’s Name
Date of Installation
Installation Address
Product Name / Serial Number(s)
Comments
Installer’s Code / Name
Installers Phone Number
Signed by Installer
Signed by Customer
Installation Notes
IMPORTANT
Customer: Please only sign after the installer has fully reviewed the installation, safety, proper operation, and maintenance of the
system. If the system has any problems please call the installer. If you are unable to make contact, please call your sales representative.
Distributor / Dealer: Please insert contact details.
LP-446-r4 Rev. 10.12.16
 Loading...
Loading...